Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO

Your ultimate guide to questionnaires and how to design a good one
The written questionnaire is the heart and soul of any survey research project. Whether you conduct your survey using an online questionnaire, in person, by email or over the phone, the way you design your questionnaire plays a critical role in shaping the quality of the data and insights that you’ll get from your target audience. Keep reading to get actionable tips.
What is a questionnaire?
A questionnaire is a research tool consisting of a set of questions or other ‘prompts’ to collect data from a set of respondents.
When used in most research, a questionnaire will consist of a number of types of questions (primarily open-ended and closed) in order to gain both quantitative data that can be analyzed to draw conclusions, and qualitative data to provide longer, more specific explanations.
A research questionnaire is often mistaken for a survey - and many people use the term questionnaire and survey, interchangeably.
But that’s incorrect.
Which is what we talk about next.
Get started with our free survey maker with 50+ templates
Survey vs. questionnaire – what’s the difference?
Before we go too much further, let’s consider the differences between surveys and questionnaires.
These two terms are often used interchangeably, but there is an important difference between them.
Survey definition
A survey is the process of collecting data from a set of respondents and using it to gather insights.
Survey research can be conducted using a questionnaire, but won’t always involve one.
Questionnaire definition
A questionnaire is the list of questions you circulate to your target audience.
In other words, the survey is the task you’re carrying out, and the questionnaire is the instrument you’re using to do it.
By itself, a questionnaire doesn’t achieve much.
It’s when you put it into action as part of a survey that you start to get results.
Advantages vs disadvantages of using a questionnaire
While a questionnaire is a popular method to gather data for market research or other studies, there are a few disadvantages to using this method (although there are plenty of advantages to using a questionnaire too).
Let’s have a look at some of the advantages and disadvantages of using a questionnaire for collecting data.
Advantages of using a questionnaire
1. questionnaires are relatively cheap.
Depending on the complexity of your study, using a questionnaire can be cost effective compared to other methods.
You simply need to write your survey questionnaire, and send it out and then process the responses.
You can set up an online questionnaire relatively easily, or simply carry out market research on the street if that’s the best method.
2. You can get and analyze results quickly
Again depending on the size of your survey you can get results back from a questionnaire quickly, often within 24 hours of putting the questionnaire live.
It also means you can start to analyze responses quickly too.
3. They’re easily scalable
You can easily send an online questionnaire to anyone in the world and with the right software you can quickly identify your target audience and your questionnaire to them.
4. Questionnaires are easy to analyze
If your questionnaire design has been done properly, it’s quick and easy to analyze results from questionnaires once responses start to come back.
This is particularly useful with large scale market research projects.
Because all respondents are answering the same questions, it’s simple to identify trends.
5. You can use the results to make accurate decisions
As a research instrument, a questionnaire is ideal for commercial research because the data you get back is from your target audience (or ideal customers) and the information you get back on their thoughts, preferences or behaviors allows you to make business decisions.
6. A questionnaire can cover any topic
One of the biggest advantages of using questionnaires when conducting research is (because you can adapt them using different types and styles of open ended questions and closed ended questions) they can be used to gather data on almost any topic.
There are many types of questionnaires you can design to gather both quantitative data and qualitative data - so they’re a useful tool for all kinds of data analysis.
Disadvantages of using a questionnaire
1. respondents could lie.
This is by far the biggest risk with a questionnaire, especially when dealing with sensitive topics.
Rather than give their actual opinion, a respondent might feel pressured to give the answer they deem more socially acceptable, which doesn’t give you accurate results.
2. Respondents might not answer every question
There are all kinds of reasons respondents might not answer every question, from questionnaire length, they might not understand what’s being asked, or they simply might not want to answer it.
If you get questionnaires back without complete responses it could negatively affect your research data and provide an inaccurate picture.
3. They might interpret what’s being asked incorrectly
This is a particular problem when running a survey across geographical boundaries and often comes down to the design of the survey questionnaire.
If your questions aren’t written in a very clear way, the respondent might misunderstand what’s being asked and provide an answer that doesn’t reflect what they actually think.
Again this can negatively affect your research data.
4. You could introduce bias
The whole point of producing a questionnaire is to gather accurate data from which decisions can be made or conclusions drawn.
But the data collected can be heavily impacted if the researchers accidentally introduce bias into the questions.
This can be easily done if the researcher is trying to prove a certain hypothesis with their questionnaire, and unwittingly write questions that push people towards giving a certain answer.
In these cases respondents’ answers won’t accurately reflect what is really happening and stop you gathering more accurate data.
5. Respondents could get survey fatigue
One issue you can run into when sending out a questionnaire, particularly if you send them out regularly to the same survey sample, is that your respondents could start to suffer from survey fatigue.
In these circumstances, rather than thinking about the response options in the questionnaire and providing accurate answers, respondents could start to just tick boxes to get through the questionnaire quickly.
Again, this won’t give you an accurate data set.
Questionnaire design: How to do it
It’s essential to carefully craft a questionnaire to reduce survey error and optimize your data . The best way to think about the questionnaire is with the end result in mind.
How do you do that?
Start with questions, like:
- What is my research purpose ?
- What data do I need?
- How am I going to analyze that data?
- What questions are needed to best suit these variables?
Once you have a clear idea of the purpose of your survey, you’ll be in a better position to create an effective questionnaire.
Here are a few steps to help you get into the right mindset.
1. Keep the respondent front and center
A survey is the process of collecting information from people, so it needs to be designed around human beings first and foremost.
In his post about survey design theory, David Vannette, PhD, from the Qualtrics Methodology Lab explains the correlation between the way a survey is designed and the quality of data that is extracted.
“To begin designing an effective survey, take a step back and try to understand what goes on in your respondents’ heads when they are taking your survey.
This step is critical to making sure that your questionnaire makes it as likely as possible that the response process follows that expected path.”
From writing the questions to designing the survey flow, the respondent’s point of view should always be front and center in your mind during a questionnaire design.
2. How to write survey questions
Your questionnaire should only be as long as it needs to be, and every question needs to deliver value.
That means your questions must each have an individual purpose and produce the best possible data for that purpose, all while supporting the overall goal of the survey.
A question must also must be phrased in a way that is easy for all your respondents to understand, and does not produce false results.
To do this, remember the following principles:
Get into the respondent's head
The process for a respondent answering a survey question looks like this:
- The respondent reads the question and determines what information they need to answer it.
- They search their memory for that information.
- They make judgments about that information.
- They translate that judgment into one of the answer options you’ve provided. This is the process of taking the data they have and matching that information with the question that’s asked.
When wording questions, make sure the question means the same thing to all respondents. Words should have one meaning, few syllables, and the sentences should have few words.
Only use the words needed to ask your question and not a word more .
Note that it’s important that the respondent understands the intent behind your question.
If they don’t, they may answer a different question and the data can be skewed.
Some contextual help text, either in the introduction to the questionnaire or before the question itself, can help make sure the respondent understands your goals and the scope of your research.
Use mutually exclusive responses
Be sure to make your response categories mutually exclusive.
Consider the question:
What is your age?
Respondents that are 31 years old have two options, as do respondents that are 40 and 55. As a result, it is impossible to predict which category they will choose.
This can distort results and frustrate respondents. It can be easily avoided by making responses mutually exclusive.
The following question is much better:
This question is clear and will give us better results.
Ask specific questions
Nonspecific questions can confuse respondents and influence results.
Do you like orange juice?
- Like very much
- Neither like nor dislike
- Dislike very much
This question is very unclear. Is it asking about taste, texture, price, or the nutritional content? Different respondents will read this question differently.
A specific question will get more specific answers that are actionable.
How much do you like the current price of orange juice?
This question is more specific and will get better results.
If you need to collect responses about more than one aspect of a subject, you can include multiple questions on it. (Do you like the taste of orange juice? Do you like the nutritional content of orange juice? etc.)
Use a variety of question types
If all of your questionnaire, survey or poll questions are structured the same way (e.g. yes/no or multiple choice) the respondents are likely to become bored and tune out. That could mean they pay less attention to how they’re answering or even give up altogether.
Instead, mix up the question types to keep the experience interesting and varied. It’s a good idea to include questions that yield both qualitative and quantitative data.
For example, an open-ended questionnaire item such as “describe your attitude to life” will provide qualitative data – a form of information that’s rich, unstructured and unpredictable. The respondent will tell you in their own words what they think and feel.
A quantitative / close-ended questionnaire item, such as “Which word describes your attitude to life? a) practical b) philosophical” gives you a much more structured answer, but the answers will be less rich and detailed.
Open-ended questions take more thought and effort to answer, so use them sparingly. They also require a different kind of treatment once your survey is in the analysis stage.
3. Pre-test your questionnaire
Always pre-test a questionnaire before sending it out to respondents. This will help catch any errors you might have missed. You could ask a colleague, friend, or an expert to take the survey and give feedback. If possible, ask a few cognitive questions like, “how did you get to that response?” and “what were you thinking about when you answered that question?” Figure out what was easy for the responder and where there is potential for confusion. You can then re-word where necessary to make the experience as frictionless as possible.
If your resources allow, you could also consider using a focus group to test out your survey. Having multiple respondents road-test the questionnaire will give you a better understanding of its strengths and weaknesses. Match the focus group to your target respondents as closely as possible, for example in terms of age, background, gender, and level of education.
Note: Don't forget to make your survey as accessible as possible for increased response rates.
Questionnaire examples and templates
There are free questionnaire templates and example questions available for all kinds of surveys and market research, many of them online. But they’re not all created equal and you should use critical judgement when selecting one. After all, the questionnaire examples may be free but the time and energy you’ll spend carrying out a survey are not.
If you’re using online questionnaire templates as the basis for your own, make sure it has been developed by professionals and is specific to the type of research you’re doing to ensure higher completion rates. As we’ve explored here, using the wrong kinds of questions can result in skewed or messy data, and could even prompt respondents to abandon the questionnaire without finishing or give thoughtless answers.
You’ll find a full library of downloadable survey templates in the Qualtrics Marketplace , covering many different types of research from employee engagement to post-event feedback . All are fully customizable and have been developed by Qualtrics experts.
Qualtrics // Experience Management
Qualtrics, the leader and creator of the experience management category, is a cloud-native software platform that empowers organizations to deliver exceptional experiences and build deep relationships with their customers and employees.
With insights from Qualtrics, organizations can identify and resolve the greatest friction points in their business, retain and engage top talent, and bring the right products and services to market. Nearly 20,000 organizations around the world use Qualtrics’ advanced AI to listen, understand, and take action. Qualtrics uses its vast universe of experience data to form the largest database of human sentiment in the world. Qualtrics is co-headquartered in Provo, Utah and Seattle.
Related Articles
December 20, 2023
Top market research analyst skills for 2024
November 7, 2023
Brand Experience
The 4 market research trends redefining insights in 2024
September 14, 2023
How BMG and Loop use data to make critical decisions
August 21, 2023
Designing for safety: Making user consent and trust an organizational asset
June 27, 2023
The fresh insights people: Scaling research at Woolworths Group
June 20, 2023
Bank less, delight more: How Bankwest built an engine room for customer obsession
June 16, 2023
How Qualtrics Helps Three Local Governments Drive Better Outcomes Through Data Insights
April 1, 2023
Academic Experience
How to write great survey questions (with examples)
Stay up to date with the latest xm thought leadership, tips and news., request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Writing Survey Questions
Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions. Creating good measures involves both writing good questions and organizing them to form the questionnaire.
Questionnaire design is a multistage process that requires attention to many details at once. Designing the questionnaire is complicated because surveys can ask about topics in varying degrees of detail, questions can be asked in different ways, and questions asked earlier in a survey may influence how people respond to later questions. Researchers are also often interested in measuring change over time and therefore must be attentive to how opinions or behaviors have been measured in prior surveys.
Surveyors may conduct pilot tests or focus groups in the early stages of questionnaire development in order to better understand how people think about an issue or comprehend a question. Pretesting a survey is an essential step in the questionnaire design process to evaluate how people respond to the overall questionnaire and specific questions, especially when questions are being introduced for the first time.
For many years, surveyors approached questionnaire design as an art, but substantial research over the past forty years has demonstrated that there is a lot of science involved in crafting a good survey questionnaire. Here, we discuss the pitfalls and best practices of designing questionnaires.
Question development
There are several steps involved in developing a survey questionnaire. The first is identifying what topics will be covered in the survey. For Pew Research Center surveys, this involves thinking about what is happening in our nation and the world and what will be relevant to the public, policymakers and the media. We also track opinion on a variety of issues over time so we often ensure that we update these trends on a regular basis to better understand whether people’s opinions are changing.
At Pew Research Center, questionnaire development is a collaborative and iterative process where staff meet to discuss drafts of the questionnaire several times over the course of its development. We frequently test new survey questions ahead of time through qualitative research methods such as focus groups , cognitive interviews, pretesting (often using an online, opt-in sample ), or a combination of these approaches. Researchers use insights from this testing to refine questions before they are asked in a production survey, such as on the ATP.
Measuring change over time
Many surveyors want to track changes over time in people’s attitudes, opinions and behaviors. To measure change, questions are asked at two or more points in time. A cross-sectional design surveys different people in the same population at multiple points in time. A panel, such as the ATP, surveys the same people over time. However, it is common for the set of people in survey panels to change over time as new panelists are added and some prior panelists drop out. Many of the questions in Pew Research Center surveys have been asked in prior polls. Asking the same questions at different points in time allows us to report on changes in the overall views of the general public (or a subset of the public, such as registered voters, men or Black Americans), or what we call “trending the data”.
When measuring change over time, it is important to use the same question wording and to be sensitive to where the question is asked in the questionnaire to maintain a similar context as when the question was asked previously (see question wording and question order for further information). All of our survey reports include a topline questionnaire that provides the exact question wording and sequencing, along with results from the current survey and previous surveys in which we asked the question.
The Center’s transition from conducting U.S. surveys by live telephone interviewing to an online panel (around 2014 to 2020) complicated some opinion trends, but not others. Opinion trends that ask about sensitive topics (e.g., personal finances or attending religious services ) or that elicited volunteered answers (e.g., “neither” or “don’t know”) over the phone tended to show larger differences than other trends when shifting from phone polls to the online ATP. The Center adopted several strategies for coping with changes to data trends that may be related to this change in methodology. If there is evidence suggesting that a change in a trend stems from switching from phone to online measurement, Center reports flag that possibility for readers to try to head off confusion or erroneous conclusions.
Open- and closed-ended questions
One of the most significant decisions that can affect how people answer questions is whether the question is posed as an open-ended question, where respondents provide a response in their own words, or a closed-ended question, where they are asked to choose from a list of answer choices.
For example, in a poll conducted after the 2008 presidential election, people responded very differently to two versions of the question: “What one issue mattered most to you in deciding how you voted for president?” One was closed-ended and the other open-ended. In the closed-ended version, respondents were provided five options and could volunteer an option not on the list.
When explicitly offered the economy as a response, more than half of respondents (58%) chose this answer; only 35% of those who responded to the open-ended version volunteered the economy. Moreover, among those asked the closed-ended version, fewer than one-in-ten (8%) provided a response other than the five they were read. By contrast, fully 43% of those asked the open-ended version provided a response not listed in the closed-ended version of the question. All of the other issues were chosen at least slightly more often when explicitly offered in the closed-ended version than in the open-ended version. (Also see “High Marks for the Campaign, a High Bar for Obama” for more information.)
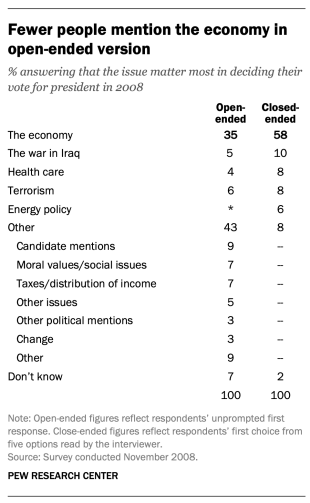
Researchers will sometimes conduct a pilot study using open-ended questions to discover which answers are most common. They will then develop closed-ended questions based off that pilot study that include the most common responses as answer choices. In this way, the questions may better reflect what the public is thinking, how they view a particular issue, or bring certain issues to light that the researchers may not have been aware of.
When asking closed-ended questions, the choice of options provided, how each option is described, the number of response options offered, and the order in which options are read can all influence how people respond. One example of the impact of how categories are defined can be found in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in January 2002. When half of the sample was asked whether it was “more important for President Bush to focus on domestic policy or foreign policy,” 52% chose domestic policy while only 34% said foreign policy. When the category “foreign policy” was narrowed to a specific aspect – “the war on terrorism” – far more people chose it; only 33% chose domestic policy while 52% chose the war on terrorism.
In most circumstances, the number of answer choices should be kept to a relatively small number – just four or perhaps five at most – especially in telephone surveys. Psychological research indicates that people have a hard time keeping more than this number of choices in mind at one time. When the question is asking about an objective fact and/or demographics, such as the religious affiliation of the respondent, more categories can be used. In fact, they are encouraged to ensure inclusivity. For example, Pew Research Center’s standard religion questions include more than 12 different categories, beginning with the most common affiliations (Protestant and Catholic). Most respondents have no trouble with this question because they can expect to see their religious group within that list in a self-administered survey.
In addition to the number and choice of response options offered, the order of answer categories can influence how people respond to closed-ended questions. Research suggests that in telephone surveys respondents more frequently choose items heard later in a list (a “recency effect”), and in self-administered surveys, they tend to choose items at the top of the list (a “primacy” effect).
Because of concerns about the effects of category order on responses to closed-ended questions, many sets of response options in Pew Research Center’s surveys are programmed to be randomized to ensure that the options are not asked in the same order for each respondent. Rotating or randomizing means that questions or items in a list are not asked in the same order to each respondent. Answers to questions are sometimes affected by questions that precede them. By presenting questions in a different order to each respondent, we ensure that each question gets asked in the same context as every other question the same number of times (e.g., first, last or any position in between). This does not eliminate the potential impact of previous questions on the current question, but it does ensure that this bias is spread randomly across all of the questions or items in the list. For instance, in the example discussed above about what issue mattered most in people’s vote, the order of the five issues in the closed-ended version of the question was randomized so that no one issue appeared early or late in the list for all respondents. Randomization of response items does not eliminate order effects, but it does ensure that this type of bias is spread randomly.
Questions with ordinal response categories – those with an underlying order (e.g., excellent, good, only fair, poor OR very favorable, mostly favorable, mostly unfavorable, very unfavorable) – are generally not randomized because the order of the categories conveys important information to help respondents answer the question. Generally, these types of scales should be presented in order so respondents can easily place their responses along the continuum, but the order can be reversed for some respondents. For example, in one of Pew Research Center’s questions about abortion, half of the sample is asked whether abortion should be “legal in all cases, legal in most cases, illegal in most cases, illegal in all cases,” while the other half of the sample is asked the same question with the response categories read in reverse order, starting with “illegal in all cases.” Again, reversing the order does not eliminate the recency effect but distributes it randomly across the population.
Question wording
The choice of words and phrases in a question is critical in expressing the meaning and intent of the question to the respondent and ensuring that all respondents interpret the question the same way. Even small wording differences can substantially affect the answers people provide.
[View more Methods 101 Videos ]
An example of a wording difference that had a significant impact on responses comes from a January 2003 Pew Research Center survey. When people were asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule,” 68% said they favored military action while 25% said they opposed military action. However, when asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule even if it meant that U.S. forces might suffer thousands of casualties, ” responses were dramatically different; only 43% said they favored military action, while 48% said they opposed it. The introduction of U.S. casualties altered the context of the question and influenced whether people favored or opposed military action in Iraq.
There has been a substantial amount of research to gauge the impact of different ways of asking questions and how to minimize differences in the way respondents interpret what is being asked. The issues related to question wording are more numerous than can be treated adequately in this short space, but below are a few of the important things to consider:
First, it is important to ask questions that are clear and specific and that each respondent will be able to answer. If a question is open-ended, it should be evident to respondents that they can answer in their own words and what type of response they should provide (an issue or problem, a month, number of days, etc.). Closed-ended questions should include all reasonable responses (i.e., the list of options is exhaustive) and the response categories should not overlap (i.e., response options should be mutually exclusive). Further, it is important to discern when it is best to use forced-choice close-ended questions (often denoted with a radio button in online surveys) versus “select-all-that-apply” lists (or check-all boxes). A 2019 Center study found that forced-choice questions tend to yield more accurate responses, especially for sensitive questions. Based on that research, the Center generally avoids using select-all-that-apply questions.
It is also important to ask only one question at a time. Questions that ask respondents to evaluate more than one concept (known as double-barreled questions) – such as “How much confidence do you have in President Obama to handle domestic and foreign policy?” – are difficult for respondents to answer and often lead to responses that are difficult to interpret. In this example, it would be more effective to ask two separate questions, one about domestic policy and another about foreign policy.
In general, questions that use simple and concrete language are more easily understood by respondents. It is especially important to consider the education level of the survey population when thinking about how easy it will be for respondents to interpret and answer a question. Double negatives (e.g., do you favor or oppose not allowing gays and lesbians to legally marry) or unfamiliar abbreviations or jargon (e.g., ANWR instead of Arctic National Wildlife Refuge) can result in respondent confusion and should be avoided.
Similarly, it is important to consider whether certain words may be viewed as biased or potentially offensive to some respondents, as well as the emotional reaction that some words may provoke. For example, in a 2005 Pew Research Center survey, 51% of respondents said they favored “making it legal for doctors to give terminally ill patients the means to end their lives,” but only 44% said they favored “making it legal for doctors to assist terminally ill patients in committing suicide.” Although both versions of the question are asking about the same thing, the reaction of respondents was different. In another example, respondents have reacted differently to questions using the word “welfare” as opposed to the more generic “assistance to the poor.” Several experiments have shown that there is much greater public support for expanding “assistance to the poor” than for expanding “welfare.”
We often write two versions of a question and ask half of the survey sample one version of the question and the other half the second version. Thus, we say we have two forms of the questionnaire. Respondents are assigned randomly to receive either form, so we can assume that the two groups of respondents are essentially identical. On questions where two versions are used, significant differences in the answers between the two forms tell us that the difference is a result of the way we worded the two versions.

One of the most common formats used in survey questions is the “agree-disagree” format. In this type of question, respondents are asked whether they agree or disagree with a particular statement. Research has shown that, compared with the better educated and better informed, less educated and less informed respondents have a greater tendency to agree with such statements. This is sometimes called an “acquiescence bias” (since some kinds of respondents are more likely to acquiesce to the assertion than are others). This behavior is even more pronounced when there’s an interviewer present, rather than when the survey is self-administered. A better practice is to offer respondents a choice between alternative statements. A Pew Research Center experiment with one of its routinely asked values questions illustrates the difference that question format can make. Not only does the forced choice format yield a very different result overall from the agree-disagree format, but the pattern of answers between respondents with more or less formal education also tends to be very different.
One other challenge in developing questionnaires is what is called “social desirability bias.” People have a natural tendency to want to be accepted and liked, and this may lead people to provide inaccurate answers to questions that deal with sensitive subjects. Research has shown that respondents understate alcohol and drug use, tax evasion and racial bias. They also may overstate church attendance, charitable contributions and the likelihood that they will vote in an election. Researchers attempt to account for this potential bias in crafting questions about these topics. For instance, when Pew Research Center surveys ask about past voting behavior, it is important to note that circumstances may have prevented the respondent from voting: “In the 2012 presidential election between Barack Obama and Mitt Romney, did things come up that kept you from voting, or did you happen to vote?” The choice of response options can also make it easier for people to be honest. For example, a question about church attendance might include three of six response options that indicate infrequent attendance. Research has also shown that social desirability bias can be greater when an interviewer is present (e.g., telephone and face-to-face surveys) than when respondents complete the survey themselves (e.g., paper and web surveys).
Lastly, because slight modifications in question wording can affect responses, identical question wording should be used when the intention is to compare results to those from earlier surveys. Similarly, because question wording and responses can vary based on the mode used to survey respondents, researchers should carefully evaluate the likely effects on trend measurements if a different survey mode will be used to assess change in opinion over time.
Question order
Once the survey questions are developed, particular attention should be paid to how they are ordered in the questionnaire. Surveyors must be attentive to how questions early in a questionnaire may have unintended effects on how respondents answer subsequent questions. Researchers have demonstrated that the order in which questions are asked can influence how people respond; earlier questions can unintentionally provide context for the questions that follow (these effects are called “order effects”).
One kind of order effect can be seen in responses to open-ended questions. Pew Research Center surveys generally ask open-ended questions about national problems, opinions about leaders and similar topics near the beginning of the questionnaire. If closed-ended questions that relate to the topic are placed before the open-ended question, respondents are much more likely to mention concepts or considerations raised in those earlier questions when responding to the open-ended question.
For closed-ended opinion questions, there are two main types of order effects: contrast effects ( where the order results in greater differences in responses), and assimilation effects (where responses are more similar as a result of their order).
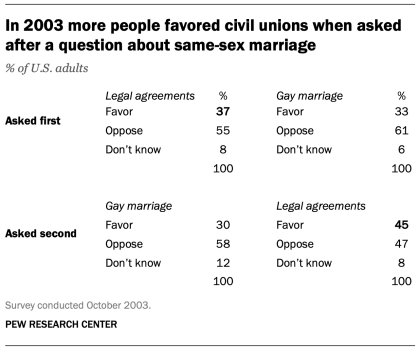
An example of a contrast effect can be seen in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in October 2003, a dozen years before same-sex marriage was legalized in the U.S. That poll found that people were more likely to favor allowing gays and lesbians to enter into legal agreements that give them the same rights as married couples when this question was asked after one about whether they favored or opposed allowing gays and lesbians to marry (45% favored legal agreements when asked after the marriage question, but 37% favored legal agreements without the immediate preceding context of a question about same-sex marriage). Responses to the question about same-sex marriage, meanwhile, were not significantly affected by its placement before or after the legal agreements question.
Another experiment embedded in a December 2008 Pew Research Center poll also resulted in a contrast effect. When people were asked “All in all, are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the way things are going in this country today?” immediately after having been asked “Do you approve or disapprove of the way George W. Bush is handling his job as president?”; 88% said they were dissatisfied, compared with only 78% without the context of the prior question.
Responses to presidential approval remained relatively unchanged whether national satisfaction was asked before or after it. A similar finding occurred in December 2004 when both satisfaction and presidential approval were much higher (57% were dissatisfied when Bush approval was asked first vs. 51% when general satisfaction was asked first).
Several studies also have shown that asking a more specific question before a more general question (e.g., asking about happiness with one’s marriage before asking about one’s overall happiness) can result in a contrast effect. Although some exceptions have been found, people tend to avoid redundancy by excluding the more specific question from the general rating.
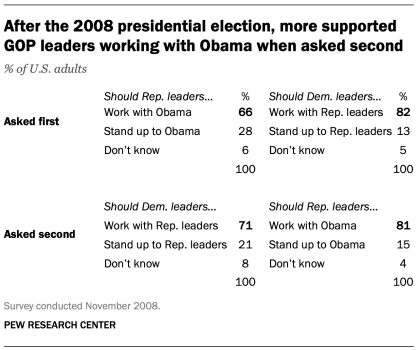
Assimilation effects occur when responses to two questions are more consistent or closer together because of their placement in the questionnaire. We found an example of an assimilation effect in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in November 2008 when we asked whether Republican leaders should work with Obama or stand up to him on important issues and whether Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders or stand up to them on important issues. People were more likely to say that Republican leaders should work with Obama when the question was preceded by the one asking what Democratic leaders should do in working with Republican leaders (81% vs. 66%). However, when people were first asked about Republican leaders working with Obama, fewer said that Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders (71% vs. 82%).
The order questions are asked is of particular importance when tracking trends over time. As a result, care should be taken to ensure that the context is similar each time a question is asked. Modifying the context of the question could call into question any observed changes over time (see measuring change over time for more information).
A questionnaire, like a conversation, should be grouped by topic and unfold in a logical order. It is often helpful to begin the survey with simple questions that respondents will find interesting and engaging. Throughout the survey, an effort should be made to keep the survey interesting and not overburden respondents with several difficult questions right after one another. Demographic questions such as income, education or age should not be asked near the beginning of a survey unless they are needed to determine eligibility for the survey or for routing respondents through particular sections of the questionnaire. Even then, it is best to precede such items with more interesting and engaging questions. One virtue of survey panels like the ATP is that demographic questions usually only need to be asked once a year, not in each survey.
U.S. Surveys
Other research methods.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
- Privacy Policy

Home » Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples
Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples
Table of Contents

Questionnaire
Definition:
A Questionnaire is a research tool or survey instrument that consists of a set of questions or prompts designed to gather information from individuals or groups of people.
It is a standardized way of collecting data from a large number of people by asking them a series of questions related to a specific topic or research objective. The questions may be open-ended or closed-ended, and the responses can be quantitative or qualitative. Questionnaires are widely used in research, marketing, social sciences, healthcare, and many other fields to collect data and insights from a target population.
History of Questionnaire
The history of questionnaires can be traced back to the ancient Greeks, who used questionnaires as a means of assessing public opinion. However, the modern history of questionnaires began in the late 19th century with the rise of social surveys.
The first social survey was conducted in the United States in 1874 by Francis A. Walker, who used a questionnaire to collect data on labor conditions. In the early 20th century, questionnaires became a popular tool for conducting social research, particularly in the fields of sociology and psychology.
One of the most influential figures in the development of the questionnaire was the psychologist Raymond Cattell, who in the 1940s and 1950s developed the personality questionnaire, a standardized instrument for measuring personality traits. Cattell’s work helped establish the questionnaire as a key tool in personality research.
In the 1960s and 1970s, the use of questionnaires expanded into other fields, including market research, public opinion polling, and health surveys. With the rise of computer technology, questionnaires became easier and more cost-effective to administer, leading to their widespread use in research and business settings.
Today, questionnaires are used in a wide range of settings, including academic research, business, healthcare, and government. They continue to evolve as a research tool, with advances in computer technology and data analysis techniques making it easier to collect and analyze data from large numbers of participants.
Types of Questionnaire
Types of Questionnaires are as follows:
Structured Questionnaire
This type of questionnaire has a fixed format with predetermined questions that the respondent must answer. The questions are usually closed-ended, which means that the respondent must select a response from a list of options.
Unstructured Questionnaire
An unstructured questionnaire does not have a fixed format or predetermined questions. Instead, the interviewer or researcher can ask open-ended questions to the respondent and let them provide their own answers.
Open-ended Questionnaire
An open-ended questionnaire allows the respondent to answer the question in their own words, without any pre-determined response options. The questions usually start with phrases like “how,” “why,” or “what,” and encourage the respondent to provide more detailed and personalized answers.
Close-ended Questionnaire
In a closed-ended questionnaire, the respondent is given a set of predetermined response options to choose from. This type of questionnaire is easier to analyze and summarize, but may not provide as much insight into the respondent’s opinions or attitudes.
Mixed Questionnaire
A mixed questionnaire is a combination of open-ended and closed-ended questions. This type of questionnaire allows for more flexibility in terms of the questions that can be asked, and can provide both quantitative and qualitative data.
Pictorial Questionnaire:
In a pictorial questionnaire, instead of using words to ask questions, the questions are presented in the form of pictures, diagrams or images. This can be particularly useful for respondents who have low literacy skills, or for situations where language barriers exist. Pictorial questionnaires can also be useful in cross-cultural research where respondents may come from different language backgrounds.
Types of Questions in Questionnaire
The types of Questions in Questionnaire are as follows:
Multiple Choice Questions
These questions have several options for participants to choose from. They are useful for getting quantitative data and can be used to collect demographic information.
- a. Red b . Blue c. Green d . Yellow
Rating Scale Questions
These questions ask participants to rate something on a scale (e.g. from 1 to 10). They are useful for measuring attitudes and opinions.
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely are you to recommend this product to a friend?
Open-Ended Questions
These questions allow participants to answer in their own words and provide more in-depth and detailed responses. They are useful for getting qualitative data.
- What do you think are the biggest challenges facing your community?
Likert Scale Questions
These questions ask participants to rate how much they agree or disagree with a statement. They are useful for measuring attitudes and opinions.
How strongly do you agree or disagree with the following statement:
“I enjoy exercising regularly.”
- a . Strongly Agree
- c . Neither Agree nor Disagree
- d . Disagree
- e . Strongly Disagree
Demographic Questions
These questions ask about the participant’s personal information such as age, gender, ethnicity, education level, etc. They are useful for segmenting the data and analyzing results by demographic groups.
- What is your age?
Yes/No Questions
These questions only have two options: Yes or No. They are useful for getting simple, straightforward answers to a specific question.
Have you ever traveled outside of your home country?
Ranking Questions
These questions ask participants to rank several items in order of preference or importance. They are useful for measuring priorities or preferences.
Please rank the following factors in order of importance when choosing a restaurant:
- a. Quality of Food
- c. Ambiance
- d. Location
Matrix Questions
These questions present a matrix or grid of options that participants can choose from. They are useful for getting data on multiple variables at once.
Dichotomous Questions
These questions present two options that are opposite or contradictory. They are useful for measuring binary or polarized attitudes.
Do you support the death penalty?
How to Make a Questionnaire
Step-by-Step Guide for Making a Questionnaire:
- Define your research objectives: Before you start creating questions, you need to define the purpose of your questionnaire and what you hope to achieve from the data you collect.
- Choose the appropriate question types: Based on your research objectives, choose the appropriate question types to collect the data you need. Refer to the types of questions mentioned earlier for guidance.
- Develop questions: Develop clear and concise questions that are easy for participants to understand. Avoid leading or biased questions that might influence the responses.
- Organize questions: Organize questions in a logical and coherent order, starting with demographic questions followed by general questions, and ending with specific or sensitive questions.
- Pilot the questionnaire : Test your questionnaire on a small group of participants to identify any flaws or issues with the questions or the format.
- Refine the questionnaire : Based on feedback from the pilot, refine and revise the questionnaire as necessary to ensure that it is valid and reliable.
- Distribute the questionnaire: Distribute the questionnaire to your target audience using a method that is appropriate for your research objectives, such as online surveys, email, or paper surveys.
- Collect and analyze data: Collect the completed questionnaires and analyze the data using appropriate statistical methods. Draw conclusions from the data and use them to inform decision-making or further research.
- Report findings: Present your findings in a clear and concise report, including a summary of the research objectives, methodology, key findings, and recommendations.
Questionnaire Administration Modes
There are several modes of questionnaire administration. The choice of mode depends on the research objectives, sample size, and available resources. Some common modes of administration include:
- Self-administered paper questionnaires: Participants complete the questionnaire on paper, either in person or by mail. This mode is relatively low cost and easy to administer, but it may result in lower response rates and greater potential for errors in data entry.
- Online questionnaires: Participants complete the questionnaire on a website or through email. This mode is convenient for both researchers and participants, as it allows for fast and easy data collection. However, it may be subject to issues such as low response rates, lack of internet access, and potential for fraudulent responses.
- Telephone surveys: Trained interviewers administer the questionnaire over the phone. This mode allows for a large sample size and can result in higher response rates, but it is also more expensive and time-consuming than other modes.
- Face-to-face interviews : Trained interviewers administer the questionnaire in person. This mode allows for a high degree of control over the survey environment and can result in higher response rates, but it is also more expensive and time-consuming than other modes.
- Mixed-mode surveys: Researchers use a combination of two or more modes to administer the questionnaire, such as using online questionnaires for initial screening and following up with telephone interviews for more detailed information. This mode can help overcome some of the limitations of individual modes, but it requires careful planning and coordination.
Example of Questionnaire
Title of the Survey: Customer Satisfaction Survey
Introduction:
We appreciate your business and would like to ensure that we are meeting your needs. Please take a few minutes to complete this survey so that we can better understand your experience with our products and services. Your feedback is important to us and will help us improve our offerings.
Instructions:
Please read each question carefully and select the response that best reflects your experience. If you have any additional comments or suggestions, please feel free to include them in the space provided at the end of the survey.
1. How satisfied are you with our product quality?
- Very satisfied
- Somewhat satisfied
- Somewhat dissatisfied
- Very dissatisfied
2. How satisfied are you with our customer service?
3. How satisfied are you with the price of our products?
4. How likely are you to recommend our products to others?
- Very likely
- Somewhat likely
- Somewhat unlikely
- Very unlikely
5. How easy was it to find the information you were looking for on our website?
- Somewhat easy
- Somewhat difficult
- Very difficult
6. How satisfied are you with the overall experience of using our products and services?
7. Is there anything that you would like to see us improve upon or change in the future?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Conclusion:
Thank you for taking the time to complete this survey. Your feedback is valuable to us and will help us improve our products and services. If you have any further comments or concerns, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Applications of Questionnaire
Some common applications of questionnaires include:
- Research : Questionnaires are commonly used in research to gather information from participants about their attitudes, opinions, behaviors, and experiences. This information can then be analyzed and used to draw conclusions and make inferences.
- Healthcare : In healthcare, questionnaires can be used to gather information about patients’ medical history, symptoms, and lifestyle habits. This information can help healthcare professionals diagnose and treat medical conditions more effectively.
- Marketing : Questionnaires are commonly used in marketing to gather information about consumers’ preferences, buying habits, and opinions on products and services. This information can help businesses develop and market products more effectively.
- Human Resources: Questionnaires are used in human resources to gather information from job applicants, employees, and managers about job satisfaction, performance, and workplace culture. This information can help organizations improve their hiring practices, employee retention, and organizational culture.
- Education : Questionnaires are used in education to gather information from students, teachers, and parents about their perceptions of the educational experience. This information can help educators identify areas for improvement and develop more effective teaching strategies.
Purpose of Questionnaire
Some common purposes of questionnaires include:
- To collect information on attitudes, opinions, and beliefs: Questionnaires can be used to gather information on people’s attitudes, opinions, and beliefs on a particular topic. For example, a questionnaire can be used to gather information on people’s opinions about a particular political issue.
- To collect demographic information: Questionnaires can be used to collect demographic information such as age, gender, income, education level, and occupation. This information can be used to analyze trends and patterns in the data.
- To measure behaviors or experiences: Questionnaires can be used to gather information on behaviors or experiences such as health-related behaviors or experiences, job satisfaction, or customer satisfaction.
- To evaluate programs or interventions: Questionnaires can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions by gathering information on participants’ experiences, opinions, and behaviors.
- To gather information for research: Questionnaires can be used to gather data for research purposes on a variety of topics.
When to use Questionnaire
Here are some situations when questionnaires might be used:
- When you want to collect data from a large number of people: Questionnaires are useful when you want to collect data from a large number of people. They can be distributed to a wide audience and can be completed at the respondent’s convenience.
- When you want to collect data on specific topics: Questionnaires are useful when you want to collect data on specific topics or research questions. They can be designed to ask specific questions and can be used to gather quantitative data that can be analyzed statistically.
- When you want to compare responses across groups: Questionnaires are useful when you want to compare responses across different groups of people. For example, you might want to compare responses from men and women, or from people of different ages or educational backgrounds.
- When you want to collect data anonymously: Questionnaires can be useful when you want to collect data anonymously. Respondents can complete the questionnaire without fear of judgment or repercussions, which can lead to more honest and accurate responses.
- When you want to save time and resources: Questionnaires can be more efficient and cost-effective than other methods of data collection such as interviews or focus groups. They can be completed quickly and easily, and can be analyzed using software to save time and resources.
Characteristics of Questionnaire
Here are some of the characteristics of questionnaires:
- Standardization : Questionnaires are standardized tools that ask the same questions in the same order to all respondents. This ensures that all respondents are answering the same questions and that the responses can be compared and analyzed.
- Objectivity : Questionnaires are designed to be objective, meaning that they do not contain leading questions or bias that could influence the respondent’s answers.
- Predefined responses: Questionnaires typically provide predefined response options for the respondents to choose from, which helps to standardize the responses and make them easier to analyze.
- Quantitative data: Questionnaires are designed to collect quantitative data, meaning that they provide numerical or categorical data that can be analyzed using statistical methods.
- Convenience : Questionnaires are convenient for both the researcher and the respondents. They can be distributed and completed at the respondent’s convenience and can be easily administered to a large number of people.
- Anonymity : Questionnaires can be anonymous, which can encourage respondents to answer more honestly and provide more accurate data.
- Reliability : Questionnaires are designed to be reliable, meaning that they produce consistent results when administered multiple times to the same group of people.
- Validity : Questionnaires are designed to be valid, meaning that they measure what they are intended to measure and are not influenced by other factors.
Advantage of Questionnaire
Some Advantage of Questionnaire are as follows:
- Standardization: Questionnaires allow researchers to ask the same questions to all participants in a standardized manner. This helps ensure consistency in the data collected and eliminates potential bias that might arise if questions were asked differently to different participants.
- Efficiency: Questionnaires can be administered to a large number of people at once, making them an efficient way to collect data from a large sample.
- Anonymity: Participants can remain anonymous when completing a questionnaire, which may make them more likely to answer honestly and openly.
- Cost-effective: Questionnaires can be relatively inexpensive to administer compared to other research methods, such as interviews or focus groups.
- Objectivity: Because questionnaires are typically designed to collect quantitative data, they can be analyzed objectively without the influence of the researcher’s subjective interpretation.
- Flexibility: Questionnaires can be adapted to a wide range of research questions and can be used in various settings, including online surveys, mail surveys, or in-person interviews.
Limitations of Questionnaire
Limitations of Questionnaire are as follows:
- Limited depth: Questionnaires are typically designed to collect quantitative data, which may not provide a complete understanding of the topic being studied. Questionnaires may miss important details and nuances that could be captured through other research methods, such as interviews or observations.
- R esponse bias: Participants may not always answer questions truthfully or accurately, either because they do not remember or because they want to present themselves in a particular way. This can lead to response bias, which can affect the validity and reliability of the data collected.
- Limited flexibility: While questionnaires can be adapted to a wide range of research questions, they may not be suitable for all types of research. For example, they may not be appropriate for studying complex phenomena or for exploring participants’ experiences and perceptions in-depth.
- Limited context: Questionnaires typically do not provide a rich contextual understanding of the topic being studied. They may not capture the broader social, cultural, or historical factors that may influence participants’ responses.
- Limited control : Researchers may not have control over how participants complete the questionnaire, which can lead to variations in response quality or consistency.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples

How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings
As a staple in data collection, questionnaires help uncover robust and reliable findings that can transform industries, shape policies, and revolutionize understanding. Whether you are exploring societal trends or delving into scientific phenomena, the effectiveness of your research questionnaire can make or break your findings.
In this article, we aim to understand the core purpose of questionnaires, exploring how they serve as essential tools for gathering systematic data, both qualitative and quantitative, from diverse respondents. Read on as we explore the key elements that make up a winning questionnaire, the art of framing questions which are both compelling and rigorous, and the careful balance between simplicity and depth.
Table of Contents
The Role of Questionnaires in Research
So, what is a questionnaire? A questionnaire is a structured set of questions designed to collect information, opinions, attitudes, or behaviors from respondents. It is one of the most commonly used data collection methods in research. Moreover, questionnaires can be used in various research fields, including social sciences, market research, healthcare, education, and psychology. Their adaptability makes them suitable for investigating diverse research questions.
Questionnaire and survey are two terms often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings in the context of research. A survey refers to the broader process of data collection that may involve various methods. A survey can encompass different data collection techniques, such as interviews , focus groups, observations, and yes, questionnaires.
Pros and Cons of Using Questionnaires in Research:
While questionnaires offer numerous advantages in research, they also come with some disadvantages that researchers must be aware of and address appropriately. Careful questionnaire design, validation, and consideration of potential biases can help mitigate these disadvantages and enhance the effectiveness of using questionnaires as a data collection method.

Structured vs Unstructured Questionnaires
Structured questionnaire:.
A structured questionnaire consists of questions with predefined response options. Respondents are presented with a fixed set of choices and are required to select from those options. The questions in a structured questionnaire are designed to elicit specific and quantifiable responses. Structured questionnaires are particularly useful for collecting quantitative data and are often employed in surveys and studies where standardized and comparable data are necessary.
Advantages of Structured Questionnaires:
- Easy to analyze and interpret: The fixed response options facilitate straightforward data analysis and comparison across respondents.
- Efficient for large-scale data collection: Structured questionnaires are time-efficient, allowing researchers to collect data from a large number of respondents.
- Reduces response bias: The predefined response options minimize potential response bias and maintain consistency in data collection.
Limitations of Structured Questionnaires:
- Lack of depth: Structured questionnaires may not capture in-depth insights or nuances as respondents are limited to pre-defined response choices. Hence, they may not reveal the reasons behind respondents’ choices, limiting the understanding of their perspectives.
- Limited flexibility: The fixed response options may not cover all potential responses, therefore, potentially restricting respondents’ answers.
Unstructured Questionnaire:
An unstructured questionnaire consists of questions that allow respondents to provide detailed and unrestricted responses. Unlike structured questionnaires, there are no predefined response options, giving respondents the freedom to express their thoughts in their own words. Furthermore, unstructured questionnaires are valuable for collecting qualitative data and obtaining in-depth insights into respondents’ experiences, opinions, or feelings.
Advantages of Unstructured Questionnaires:
- Rich qualitative data: Unstructured questionnaires yield detailed and comprehensive qualitative data, providing valuable and novel insights into respondents’ perspectives.
- Flexibility in responses: Respondents have the freedom to express themselves in their own words. Hence, allowing for a wide range of responses.
Limitations of Unstructured Questionnaires:
- Time-consuming analysis: Analyzing open-ended responses can be time-consuming, since, each response requires careful reading and interpretation.
- Subjectivity in interpretation: The analysis of open-ended responses may be subjective, as researchers interpret and categorize responses based on their judgment.
- May require smaller sample size: Due to the depth of responses, researchers may need a smaller sample size for comprehensive analysis, making generalizations more challenging.
Types of Questions in a Questionnaire
In a questionnaire, researchers typically use the following most common types of questions to gather a variety of information from respondents:
1. Open-Ended Questions:
These questions allow respondents to provide detailed and unrestricted responses in their own words. Open-ended questions are valuable for gathering qualitative data and in-depth insights.
Example: What suggestions do you have for improving our product?
2. Multiple-Choice Questions
Respondents choose one answer from a list of provided options. This type of question is suitable for gathering categorical data or preferences.
Example: Which of the following social media/academic networking platforms do you use to promote your research?
- ResearchGate
- Academia.edu
3. Dichotomous Questions
Respondents choose between two options, typically “yes” or “no”, “true” or “false”, or “agree” or “disagree”.
Example: Have you ever published in open access journals before?
4. Scaling Questions
These questions, also known as rating scale questions, use a predefined scale that allows respondents to rate or rank their level of agreement, satisfaction, importance, or other subjective assessments. These scales help researchers quantify subjective data and make comparisons across respondents.
There are several types of scaling techniques used in scaling questions:
i. Likert Scale:
The Likert scale is one of the most common scaling techniques. It presents respondents with a series of statements and asks them to rate their level of agreement or disagreement using a range of options, typically from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree”.For example: Please indicate your level of agreement with the statement: “The content presented in the webinar was relevant and aligned with the advertised topic.”
- Strongly Agree
- Strongly Disagree
ii. Semantic Differential Scale:
The semantic differential scale measures respondents’ perceptions or attitudes towards an item using opposite adjectives or bipolar words. Respondents rate the item on a scale between the two opposites. For example:
- Easy —— Difficult
- Satisfied —— Unsatisfied
- Very likely —— Very unlikely
iii. Numerical Rating Scale:
This scale requires respondents to provide a numerical rating on a predefined scale. It can be a simple 1 to 5 or 1 to 10 scale, where higher numbers indicate higher agreement, satisfaction, or importance.
iv. Ranking Questions:
Respondents rank items in order of preference or importance. Ranking questions help identify preferences or priorities.
Example: Please rank the following features of our app in order of importance (1 = Most Important, 5 = Least Important):
- User Interface
- Functionality
- Customer Support
By using a mix of question types, researchers can gather both quantitative and qualitative data, providing a comprehensive understanding of the research topic and enabling meaningful analysis and interpretation of the results. The choice of question types depends on the research objectives , the desired depth of information, and the data analysis requirements.
Methods of Administering Questionnaires
There are several methods for administering questionnaires, and the choice of method depends on factors such as the target population, research objectives , convenience, and resources available. Here are some common methods of administering questionnaires:

Each method has its advantages and limitations. Online surveys offer convenience and a large reach, but they may be limited to individuals with internet access. Face-to-face interviews allow for in-depth responses but can be time-consuming and costly. Telephone surveys have broad reach but may be limited by declining response rates. Researchers should choose the method that best suits their research objectives, target population, and available resources to ensure successful data collection.
How to Design a Questionnaire
Designing a good questionnaire is crucial for gathering accurate and meaningful data that aligns with your research objectives. Here are essential steps and tips to create a well-designed questionnaire:
1. Define Your Research Objectives : Clearly outline the purpose and specific information you aim to gather through the questionnaire.
2. Identify Your Target Audience : Understand respondents’ characteristics and tailor the questionnaire accordingly.
3. Develop the Questions :
- Write Clear and Concise Questions
- Avoid Leading or Biasing Questions
- Sequence Questions Logically
- Group Related Questions
- Include Demographic Questions
4. Provide Well-defined Response Options : Offer exhaustive response choices for closed-ended questions.
5. Consider Skip Logic and Branching : Customize the questionnaire based on previous answers.
6. Pilot Test the Questionnaire : Identify and address issues through a pilot study .
7. Seek Expert Feedback : Validate the questionnaire with subject matter experts.
8. Obtain Ethical Approval : Comply with ethical guidelines , obtain consent, and ensure confidentiality before administering the questionnaire.
9. Administer the Questionnaire : Choose the right mode and provide clear instructions.
10. Test the Survey Platform : Ensure compatibility and usability for online surveys.
By following these steps and paying attention to questionnaire design principles, you can create a well-structured and effective questionnaire that gathers reliable data and helps you achieve your research objectives.
Characteristics of a Good Questionnaire
A good questionnaire possesses several essential elements that contribute to its effectiveness. Furthermore, these characteristics ensure that the questionnaire is well-designed, easy to understand, and capable of providing valuable insights. Here are some key characteristics of a good questionnaire:
1. Clarity and Simplicity : Questions should be clear, concise, and unambiguous. Avoid using complex language or technical terms that may confuse respondents. Simple and straightforward questions ensure that respondents interpret them consistently.
2. Relevance and Focus : Each question should directly relate to the research objectives and contribute to answering the research questions. Consequently, avoid including extraneous or irrelevant questions that could lead to data clutter.
3. Mix of Question Types : Utilize a mix of question types, including open-ended, Likert scale, and multiple-choice questions. This variety allows for both qualitative and quantitative data collections .
4. Validity and Reliability : Ensure the questionnaire measures what it intends to measure (validity) and produces consistent results upon repeated administration (reliability). Validation should be conducted through expert review and previous research.
5. Appropriate Length : Keep the questionnaire’s length appropriate and manageable to avoid respondent fatigue or dropouts. Long questionnaires may result in incomplete or rushed responses.
6. Clear Instructions : Include clear instructions at the beginning of the questionnaire to guide respondents on how to complete it. Explain any technical terms, formats, or concepts if necessary.
7. User-Friendly Format : Design the questionnaire to be visually appealing and user-friendly. Use consistent formatting, adequate spacing, and a logical page layout.
8. Data Validation and Cleaning : Incorporate validation checks to ensure data accuracy and reliability. Consider mechanisms to detect and correct inconsistent or missing responses during data cleaning.
By incorporating these characteristics, researchers can create a questionnaire that maximizes data quality, minimizes response bias, and provides valuable insights for their research.
In the pursuit of advancing research and gaining meaningful insights, investing time and effort into designing effective questionnaires is a crucial step. A well-designed questionnaire is more than a mere set of questions; it is a masterpiece of precision and ingenuity. Each question plays a vital role in shaping the narrative of our research, guiding us through the labyrinth of data to meaningful conclusions. Indeed, a well-designed questionnaire serves as a powerful tool for unlocking valuable insights and generating robust findings that impact society positively.
Have you ever designed a research questionnaire? Reflect on your experience and share your insights with researchers globally through Enago Academy’s Open Blogging Platform . Join our diverse community of 1000K+ researchers and authors to exchange ideas, strategies, and best practices, and together, let’s shape the future of data collection and maximize the impact of questionnaires in the ever-evolving landscape of research.
Frequently Asked Questions
A research questionnaire is a structured tool used to gather data from participants in a systematic manner. It consists of a series of carefully crafted questions designed to collect specific information related to a research study.
Questionnaires play a pivotal role in both quantitative and qualitative research, enabling researchers to collect insights, opinions, attitudes, or behaviors from respondents. This aids in hypothesis testing, understanding, and informed decision-making, ensuring consistency, efficiency, and facilitating comparisons.
Questionnaires are a versatile tool employed in various research designs to gather data efficiently and comprehensively. They find extensive use in both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies, making them a fundamental component of research across disciplines. Some research designs that commonly utilize questionnaires include: a) Cross-Sectional Studies b) Longitudinal Studies c) Descriptive Research d) Correlational Studies e) Causal-Comparative Studies f) Experimental Research g) Survey Research h) Case Studies i) Exploratory Research
A survey is a comprehensive data collection method that can include various techniques like interviews and observations. A questionnaire is a specific set of structured questions within a survey designed to gather standardized responses. While a survey is a broader approach, a questionnaire is a focused tool for collecting specific data.
The choice of questionnaire type depends on the research objectives, the type of data required, and the preferences of respondents. Some common types include: • Structured Questionnaires: These questionnaires consist of predefined, closed-ended questions with fixed response options. They are easy to analyze and suitable for quantitative research. • Semi-Structured Questionnaires: These questionnaires combine closed-ended questions with open-ended ones. They offer more flexibility for respondents to provide detailed explanations. • Unstructured Questionnaires: These questionnaires contain open-ended questions only, allowing respondents to express their thoughts and opinions freely. They are commonly used in qualitative research.
Following these steps ensures effective questionnaire administration for reliable data collection: • Choose a Method: Decide on online, face-to-face, mail, or phone administration. • Online Surveys: Use platforms like SurveyMonkey • Pilot Test: Test on a small group before full deployment • Clear Instructions: Provide concise guidelines • Follow-Up: Send reminders if needed
Thank you, Riya. This is quite helpful. As discussed, response bias is one of the disadvantages in the use of questionnaires. One way to help limit this can be to use scenario based questions. These type of questions may help the respondents to be more reflective and active in the process.
Thank you, Dear Riya. This is quite helpful.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
![a research questionnaire sample What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Questionnaire: The ultimate guide, advantages & examples

What is a Questionnaire?
A questionnaire is a research instrument that consists of a set of questions or other types of prompts that aims to collect information from a respondent. A research questionnaire is typically a mix of close-ended questions and open-ended questions .
Open-ended, long-form questions offer the respondent the ability to elaborate on their thoughts. Research questionnaires were developed in 1838 by the Statistical Society of London.
LEARN ABOUT: Candidate Experience Survey
The data collected from a data collection questionnaire can be both qualitative as well as quantitative in nature. A questionnaire may or may not be delivered in the form of a survey , but a survey always consists of a questionnaire.
LEARN ABOUT: Testimonial Questions
Advantages of a good questionnaire design
- With a survey questionnaire, you can gather a lot of data in less time.
- There is less chance of any bias(like selection bias ) creeping if you have a standard set of questions to be used for your target audience. You can apply logic to questions based on the respondents’ answers, but the questionnaire will remain standard for a group of respondents that fall in the same segment.
- Surveying online survey software is quick and cost-effective. It offers you a rich set of features to design, distribute, and analyze the response data.
- It can be customized to reflect your brand voice. Thus, it can be used to reinforce your brand image.
- The responses can be compared with the historical data and understand the shift in respondents’ choices and experiences.
- Respondents can answer the questionnaire without revealing their identity. Also, many survey software complies with significant data security and privacy regulations.
LEARN ABOUT: Structured Questionnaire

Characteristics of a good questionnaire
Your survey design depends on the type of information you need to collect from respondents. Qualitative questionnaires are used when there is a need to collect exploratory information to help prove or disprove a hypothesis. Quantitative questionnaires are used to validate or test a previously generated hypothesis. However, most questionnaires follow some essential characteristics:
- Uniformity: Questionnaires are very useful to collect demographic information, personal opinions, facts, or attitudes from respondents. One of the most significant attributes of a research form is uniform design and standardization. Every respondent sees the same questions. This helps in data collection and statistical analysis of this data. For example, the retail store evaluation questionnaire template contains questions for evaluating retail store experiences. Questions relate to purchase value, range of options for product selections, and quality of merchandise. These questions are uniform for all customers.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
- Exploratory: It should be exploratory to collect qualitative data. There is no restriction on questions that can be in your questionnaire. For example, you use a data collection questionnaire and send it to the female of the household to understand her spending and saving habits relative to the household income. Open-ended questions give you more insight and allow the respondents to explain their practices. A very structured question list could limit the data collection.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
- Question Sequence: It typically follows a structured flow of questions to increase the number of responses. This sequence of questions is screening questions , warm-up questions, transition questions, skip questions, challenging questions, and classification questions. For example, our motivation and buying experience questionnaire template covers initial demographic questions and then asks for time spent in sections of the store and the rationale behind purchases.
Types & Definitions
As we explored before, questionnaires can be either structured or free-flowing. Let’s take a closer look at what that entails for your surveys.
- Structured Questionnaires: Structured questionnaires collect quantitative data . The questionnaire is planned and designed to gather precise information. It also initiates a formal inquiry, supplements data, checks previously accumulated data, and helps validate any prior hypothesis.
- Unstructured Questionnaires: Unstructured questionnaires collect qualitative data . They use a basic structure and some branching questions but nothing that limits the responses of a respondent. The questions are more open-ended to collect specific data from participants.
Types of questions in a questionnaire
You can use multiple question types in a questionnaire. Using various question types can help increase responses to your research questionnaire as they tend to keep participants more engaged. The best customer satisfaction survey templates are the most commonly used for better insights and decision-making.
Some of the widely used types of questions are:
- Open-Ended Questions: Open-ended questions help collect qualitative data in a questionnaire where the respondent can answer in a free form with little to no restrictions.
- Dichotomous Questions: The dichotomous question is generally a “yes/no” close-ended question . This question is usually used in case of the need for necessary validation. It is the most natural form of a questionnaire.
- Multiple-Choice Questions: Multiple-choice questions are a close-ended question type in which a respondent has to select one (single-select multiple-choice question) or many (multi-select multiple choice question) responses from a given list of options. The multiple-choice question consists of an incomplete stem (question), right answer or answers, incorrect answers, close alternatives, and distractors. Of course, not all multiple-choice questions have all of the answer types. For example, you probably won’t have the wrong or right answers if you’re looking for customer opinion.
- Scaling Questions: These questions are based on the principles of the four measurement scales – nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio . A few of the question types that utilize these scales’ fundamental properties are rank order questions , Likert scale questions , semantic differential scale questions , and Stapel scale questions .
LEARN ABOUT: System Usability Scale
- Pictorial Questions: This question type is easy to use and encourages respondents to answer. It works similarly to a multiple-choice question. Respondents are asked a question, and the answer choices are images. This helps respondents choose an answer quickly without over-thinking their answers, giving you more accurate data.
Types of Questionnaires
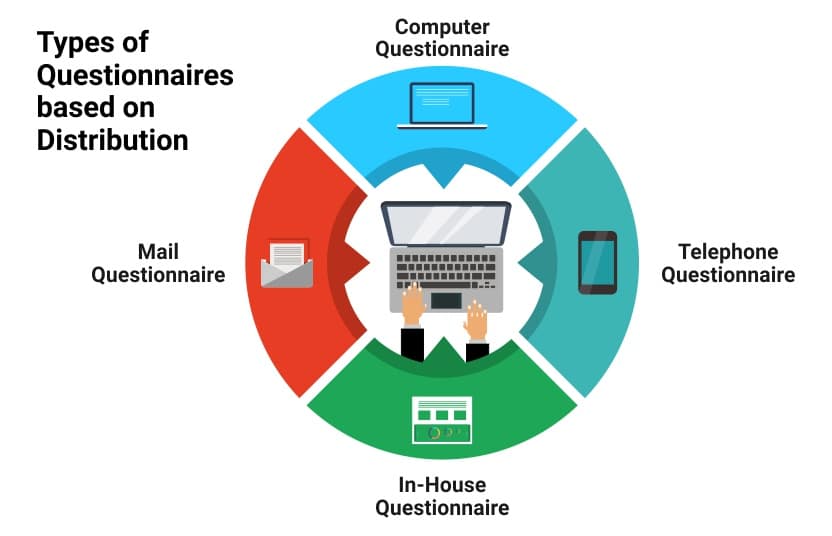
Questionnaires can be administered or distributed in the following forms:
- Online Questionnaire : In this type, respondents are sent the questionnaire via email or other online mediums. This method is generally cost-effective and time-efficient. Respondents can also answer at leisure. Without the pressure to respond immediately, responses may be more accurate. The disadvantage, however, is that respondents can easily ignore these questionnaires. Read more about online surveys .
- Telephone Questionnaire: A researcher makes a phone call to a respondent to collect responses directly. Responses are quick once you have a respondent on the phone. However, a lot of times, the respondents hesitate to give out much information over the phone. It is also an expensive way of conducting research. You’re usually not able to collect as many responses as other types of questionnaires, so your sample may not represent the broader population.
- In-House Questionnaire: This type is used by a researcher who visits the respondent’s home or workplace. The advantage of this method is that the respondent is in a comfortable and natural environment, and in-depth data can be collected. The disadvantage, though, is that it is expensive and slow to conduct.
LEARN ABOUT: Survey Sample Sizes
- Mail Questionnaire: These are starting to be obsolete but are still being used in some market research studies. This method involves a researcher sending a physical data collection questionnaire request to a respondent that can be filled in and sent back. The advantage of this method is that respondents can complete this on their own time to answer truthfully and entirely. The disadvantage is that this method is expensive and time-consuming. There is also a high risk of not collecting enough responses to make actionable insights from the data.
How to design a Questionnaire
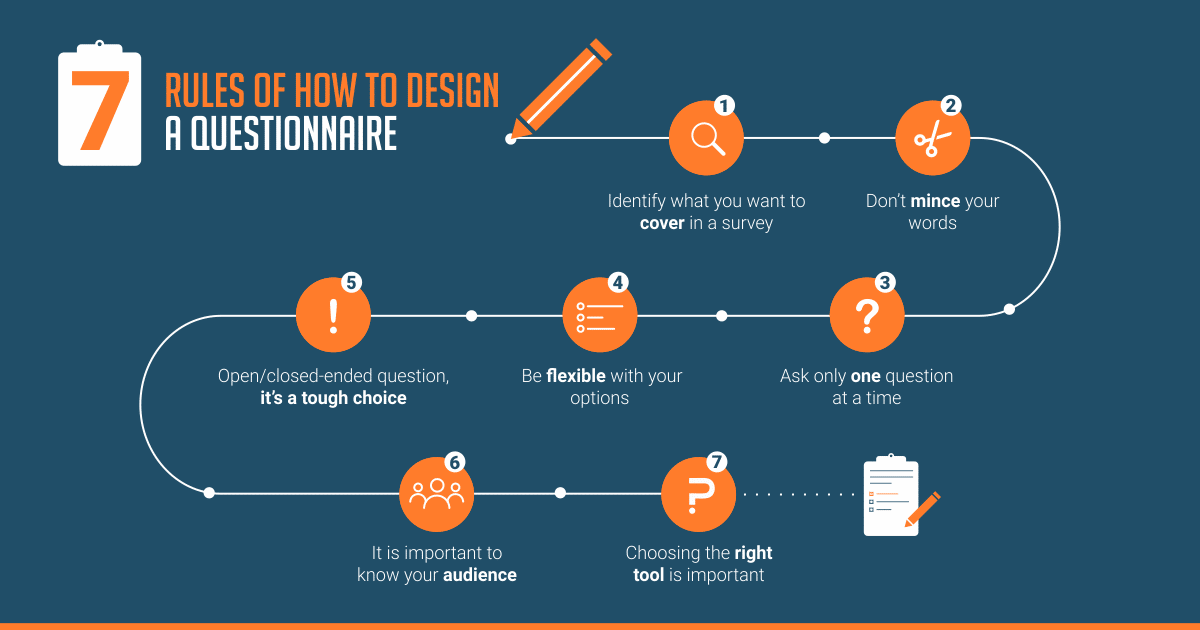
Questionnaire design is a multistep process that requires attention to detail at every step.
Researchers are always hoping that the responses received for a survey questionnaire yield useable data. If the questionnaire is too complicated, there is a fair chance that the respondent might get confused and will drop out or answer inaccurately.
LEARN ABOUT: Easy Test Maker
As a survey creator , you may want to pre-test the survey by administering it to a focus group during development. You can try out a few different questionnaire designs to determine which resonates best with your target audience. Pre-testing is a good practice as the survey creator can comprehend the initial stages if there are any changes required in the survey .
Steps Involved in Questionnaire Design
1. identify the scope of your research:.
Think about what your questionnaire is going to include before you start designing the look of it. The clarity of the topic is of utmost importance as this is the primary step in creating the questionnaire. Once you are clear on the purpose of the questionnaire, you can begin the design process.
LEARN ABOUT: Social Communication Questionnaire
2. Keep it simple:
The words or phrases you use while writing the questionnaire must be easy to understand. If the questions are unclear, the respondents may simply choose any answer and skew the data you collect.
3. Ask only one question at a time:
At times, a researcher may be tempted to add two similar questions. This might seem like an excellent way to consolidate answers to related issues, but it can confuse your respondents or lead to inaccurate data. If any of your questions contain the word “and,” take another look. This question likely has two parts, which can affect the quality of your data.
4. Be flexible with your options:
While designing, the survey creator needs to be flexible in terms of “option choice” for the respondents. Sometimes the respondents may not necessarily want to choose from the answer options provided by the survey creator. An “other” option often helps keep respondents engaged in the survey.
5. The open-ended or closed-ended question is a tough choice:
The survey creator might end up in a situation where they need to make distinct choices between open or close-ended questions. The question type should be carefully chosen as it defines the tone and importance of asking the question in the first place.
If the questionnaire requires the respondents to elaborate on their thoughts, an open-ended q u estion is the best choice. If the surveyor wants a specific response, then close-ended questions should be their primary choice. The key to asking closed-ended questions is to generate data that is easy to analyze and spot trends.
6. It is essential to know your audience:
A researcher should know their target audience. For example, if the target audience speaks mostly Spanish, sending the questionnaire in any other language would lower the response rate and accuracy of data. Something that may seem clear to you may be confusing to your respondents. Use simple language and terminology that your respondents will understand, and avoid technical jargon and industry-specific language that might confuse your respondents.
For efficient market research, researchers need a representative sample collected using one of the many sampling techniques , such as a sample questionnaire. It is imperative to plan and define these target respondents based on the demographics required.
7. Choosing the right tool is essential:
QuestionPro is a simple yet advanced survey software platform that the surveyors can use to create a questionnaire or choose from the already existing 300+ questionnaire templates.
Always save personal questions for last. Sensitive questions may cause respondents to drop off before completing. If these questions are at the end, the respondent has had time to become more comfortable with the interview and are more likely to answer personal or demographic questions.
Differences between a Questionnaire and a Survey
Read more: Difference between a survey and a questionnaire
Questionnaire Examples
The best way to understand how questionnaires work is to see the types of questionnaires available. Some examples of a questionnaire are:
USE THIS FREE TEMPLATE
The above survey questions are typically easy to use, understand, and execute. Additionally, the standardized answers of a survey questionnaire instead of a person-to-person conversation make it easier to compile useable data.
The most significant limitation of a data collection questionnaire is that respondents need to read all of the questions and respond to them. For example, you send an invitation through email asking respondents to complete the questions on social media. If a target respondent doesn’t have the right social media profiles, they can’t answer your questions.
Learn More: 350+ Free Survey Examples and Templates
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 8 Data Trends to Understand the Future of Data
May 30, 2024

Top 12 Interactive Presentation Software to Engage Your User
May 29, 2024

Trend Report: Guide for Market Dynamics & Strategic Analysis

Cannabis Industry Business Intelligence: Impact on Research
May 28, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Creating a Questionnaire
Create the perfect questionnaire and collect actionable data using our online guide!

Table of Contents
- How to Create
Questionnaire Types
- Collecting Responses
- Analyzing Results
- Getting Started
What is a Questionnaire?
Definition: A questionnaire is a convenient way to collect feedback. A questionnaire can be used to measure customer satisfaction, capture employee feedback, or even conduct product research. Responses can be collected via email, web link, QR code, or using a survey panel.
The term "survey" and "questionnaire" are commonly used interchangeably. A questionnaire refers to the questions used to collect feedback (the form itself). A survey relates to the entire research process, including summarizing and analyzing questionnaire data.
Getting Started + Tips
How to make a questionnaire: Keep questions short and focused on one topic at a time. Use multiple-choice questions to fit answers into a specific category. Use an open-ended question to capture comments. A Likert scale or MaxDiff question can be used for market research. Collect responses for your questionnaire using an email collector, an anonymous link, or even a QR code.
The following 6 tips will help you create the perfect questionnaire:
1) Use 10 Questions or Less
The shorter you keep your survey, the higher your completion rates. Longer questionnaires usually tend to have a high drop-off percentage. Keeping your surveys to 10 questions or fewer forces you to draft a study that only includes important questions; you should remove trivial questions during the draft process.
2) One Idea Per Question
Make sure each question only covers one topic. Try to include only one topic at a time. For example, in an employee survey, you would not want to ask, "Do you feel satisfied with your compensation and career advancement?". Instead, you would like to separate "compensation" and "career advancement" into two questions or use a Likert scale , putting each question on a separate row.
3) Group Similar Questions Together
Suppose the survey is more than ten questions; similar questions should be grouped on separate pages. If you don't want to use more than one page, add extra spacing between groups of the question; extra white space can increase the increase the readability of your questionnaire.
4) Use Skip/Display Logic
If you have questions that only apply to certain people, consider using skip or display logic to show those questions conditionally. This will help reduce the length of your survey and boost response rates.
If you have questions that only apply to certain people, consider using skip or display logic to show those questions conditionally. This will help reduce the length of your survey and boost response rates. For example, if you asked, "Are you currently looking for new employment opportunities?". If the answer were "yes," a follow-up question would ask, "Why?"
5) Use Research Questions Like MaxDiff
Research questions are an excellent tool for customer or product questionnaires. Instead of asking multiple questions on which features are essential or what price is desirable, question types like MaxDiff and Conjoint will provide you with high-quality, actionable data that can be used for feature prioritization and product pricing. In addition, these question types will reduce the length of your questionnaire.
6) Keep the Audience in Mind
An employee questionnaire should use an anonymous link to collect responses; this will help boost trust and increase honest answers. If doing a customer study, consider adding custom data to the weblink to help identify responses. A survey panel and current customers can lend fresh perspectives for general market research.
Questionnaire Templates
Adding customer surveys to your Google review strategy will add additional data points to improve customer satisfaction. In addition, surveys are a valuable tool to identify ways to improve, establish internal benchmarks, and conduct pricing and product research to improve your company's products.
While there are numerous types of questionnaires (or survey types), these are the five most common general categories:
1) Customer Satisfaction
Capturing customer feedback is one of the most common uses of questionnaires. A good customer satisfaction survey will always revolve around a Net Promoter Score question. When the Net Promoter Score question results are tallied, one number from -100 is 100 is displayed. This number is ideal for benchmarks. Net Promoter provides quick and actionable feedback when combined with an open-ended text question.
2) Customer Effort
Measuring how easily customers can complete a purchase or take a specific action is crucial for the customer experience strategy. A customer effort score question is a rating scale from 1 to 7 (disagree to agree). Results for this question are averaged; the higher the score, the easier it is for your customers to complete tasks.
3) Employee Satisfaction & Engagement
Employee satisfaction and engagement are often used interchangeably but measure different things. Both types of surveys often use opinion scales to ask questions.
Employee satisfaction measures how satisfied employees are with their job and work environment. Standard measures of employee satisfaction include salary, benefits, and co-worker relationships.
Employee engagement relates to the emotional commitment employees have to an organization. It goes beyond simple satisfaction. Standard measures of engagement include belief in the company mission, opportunities for career growth, and being inspired to perform at a high level.
4) Employee Exit Interviews
When employees leave for new opportunities, sending a questionnaire is a great way to understand why that employee is leaving. The feedback obtained here can be used to improve the workplace and reduce employee turnover.
5) Product Research
MaxDiff is used to identify what is most important to your audience. For example, if building a new mobile application, asking a group of users what they think is least and most important will help guide product strategy; your team should only focus on the important areas.
For pricing a new product, Van Westendorp will give you a range of prices the market is willing to expect. You could price your product too high or too low without a question like this, reducing your market penetration.
Collecting Responses For Your Questionnaire
There are a few different ways to collect feedback for questionnaires. Depending on your needs, each one could have an advantage.
With email distribution, you would upload a list of email addresses, and the platform would automatically place a link to your questionnaire inside the email body. One advantage is sending email reminders to respondents who still need to complete your survey. In addition, the email links are unique for each respondent, so you can track email open and click rates. As a result, email surveys are ideal for customer research.
A web link is a convenient way to collect feedback at your convenience. You can place a web link on social media, your website, or even inside your CRM email program (instead of an email collector with a unique link to each person). Custom data can be included in the link, such as store location. This custom data can be used to segment and filter results.
Anonymous Link
When you want to protect your respondents' identities, you use an anonymous link . Anonymous inks do not store respondent information, IP address, or email address. Because of this, anonymous survey links are perfect for employee surveys.
QR code Surveys
QR code surveys can be placed on paper receipts, product packaging, or flyers. In addition, QR codes are a great way to collect feedback after or during an event or even during in-person focus groups.
Survey Panels
If you're conducting market research and need access to a customer base, using a survey panel will get you the responses required. A good survey panel will allow you to target specific demographics, job titles, or interest levels (such as car enthusiasts). When using survey panels, you'll want to double-check and clean your data for low-quality responses. People who speed through your survey or mark the first answer for all questions should be removed.
How to Analyze Questionnaire Data
When analyzing the data from a questionnaire, consider a few advanced techniques like the ones below. These techniques will give you better insights than just simple graphs and charts.
Creating a segment or a cross-tabulation is the easiest way to dive deeper into your results. For example, if you conducted an employee satisfaction survey, the overall scores for the company could be high. But that might only tell part of the story. For example, if your company has multiple departments, you should create a cross-tabulation for each department. You might notice that there is one department with low scores. or one department with high scores.
If your company conducted its first Net Promoter Score survey and the results were -10, that score would be your benchmark. Each subsequent customer survey you run should be compared against that initial number to improve it each time.
TURF Analysis
This is an advanced research technique but very valuable. TURF analysis analysis stands for "Total Unduplicated Reach and Frequency" and is used to find the combination of items that would provide the highest reach level. For example, suppose you ask, "Which of the following flavor of ice cream would you buy?" If you run a TURF analysis on the results, you could find the top 3 or 4 combinations of flavors that would result in the highest sales.
Unsure Where to Start?
Creating a questionnaire can be a challenging process. However, these three suggestions can help you with the perfect questionnaire strategy.
1) Talk With Your Team
Some departments might want to conduct pricing research and do simple Net Promoter Score surveys. Having your organization aligned on strategy will simplify the process and eliminate any possibility of re-work. An aligned strategy will also mean a shorter study with fewer overlapping questions.
2) Start with a Template
A pre-made template will show you how to format and word questions. Next, try multiple templates to understand the various question types.
3) Look at Competitor Surveys
You might notice competitors asking specific questions - this would be a sign that those questions provide valuable metrics. If you can incorporate the great things your competition does while making it more efficient for respondents, your questionnaire campaigns will have a greater chance of success.
Get Started Now
We have you covered on anything from customer surveys, employee surveys, to market research. Get started and create your first survey for free.

Research Questionnaire
Questionnaire generator.

When a researcher creates a research paper using the scientific method they will need to use a gathering method that is adjacent to the research topic. This means that the researcher will use a quantitative research method for a quantitive topic and a qualitative method for a qualitative one. The research questionnaire is one of the quantitative data-gathering methods a researcher can use in their research paper.
1. Market Research Questionnaire Template Example
- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
Size: 38 KB
2. Market Research Questionnaire Example

Size: 94 KB
3. Research Questionnaire Example

4. Sample Market Research Questionnaire
Size: 35 KB
5. Research Survey Questionnaire

Size: 42 KB
6. Research Survey Questionnaire Construction

Size: 80 KB
7. Research Questionnaire Survey of Consumers

Size: 39 KB
8. Guide to the Design of Research Questionnaires

Size: 77 KB
9. Planning Survey Research Questionnaires

Size: 85 KB
10. Climate Change Survey Questionnaires
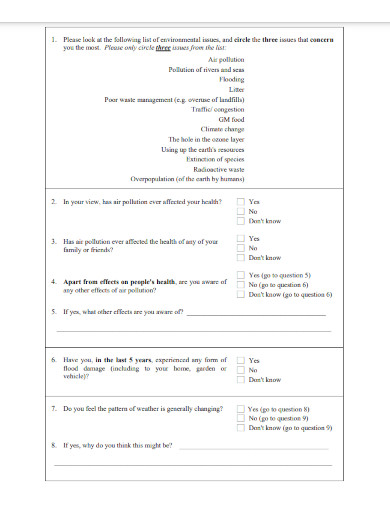
Size: 41 KB
11. Survey Questionnaire Design

Size: 96 KB
12. Developing Questionnaires for Educational Research

Size: 81 KB
13. Graudate Research Student Questionnaires

14. Sample Research Survey Questionnaires

Size: 46 KB
15. Market Research Questionnaire Example

16. Research Survey Questionnaire Example
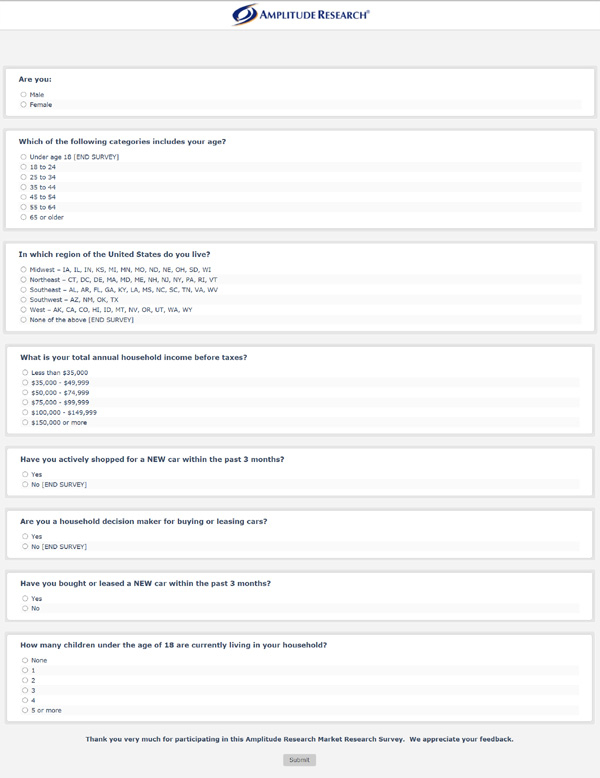
17. Product X Research Study Questionnaire Example

What Is a Research Questionnaire?
A research questionnaire is a physical or digital questionnaire that researchers use to obtain quantitative data. The research questionnaire is a more in-depth version of a survey as its questions often delve deeper than survey questions .
How to Write a Research Questionnaire
A well-made research questionnaire can effectively and efficiently gather data from the population. Creating a good research questionnaire does not require that many writing skills , soft skills , or hard skills , it just requires the person to properly understand the data set they are looking for.
Step 1: Select a Topic or Theme for the Research Questionnaire
Begin by choosing a topic or theme for the research questionnaire as this will provide much-needed context for the research questionnaire. Not only that but the topic will also dictate the tone of the questions in the questionnaire.
Step 2: Obtain or Use a Research Questionnaire Outline
You may opt to use a research questionnaire outline or outline format for your research questionnaire. This outline will provide you with a structure you can use to easily make your research questionnaire.
Step 3: Create your Research Questionnaire
Start by creating questions that will help provide you with the necessary data to prove or disprove your research question. You may conduct brainstorming sessions to formulate the questions for your research questionnaire.
Step 4: Edit and Have Someone Proofread the Questionnaire
After you have created and completed the research questionnaire, you must edit the contents of the questionnaire. Not only that but it is wise to have someone proofread the contents of your questionnaire before deploying the questionnaire.
How does a research questionnaire help businesses?
A successful business or company utilizes research questionnaires to not only obtain data from their customers but also to gather data about the performance and quality of the employees in the business. The research questionnaire provides the business or company with actionable data, which they can use to improve the product, service, or commodity to obtain more customers.
Do I need to provide a consent form when I ask someone to answer the research questionnaire?
Yes, consent is very important as without this the data you have gathered from your questionnaires or surveys are useless. Therefore it is important to provide a consent form with your research questionnaire when you are asking a participant to answer the document.
What type of answers are allowed in the research questionnaire?
Research questionnaires can host a multitude of types of questions each with its specific way of answering. A questionnaire can use multiple-choice questions, open-ended questions, and closed questions. Just be sure to properly pace the questions as having too many different types of answering styles can demotivate or distract the target audience, which might lead to errors.
A research questionnaire is a data-gathering document people can use to obtain information and data from a specific group of people. Well-made and crafted research questionnaires will provide much-needed information one can use to answer a specific research question.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a fun quiz to find out which historical figure you're most like in your study habits
Design a survey to discover students' favorite school subjects and why they love them.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Perspect Clin Res
- v.14(3); Jul-Sep 2023
- PMC10405529
Designing and validating a research questionnaire - Part 1
Priya ranganathan.
Department of Anaesthesiology, Tata Memorial Centre, Homi Bhabha National Institute, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
Carlo Caduff
1 Department of Global Health and Social Medicine, King’s College London, London, United Kingdom
Questionnaires are often used as part of research studies to collect data from participants. However, the information obtained through a questionnaire is dependent on how it has been designed, used, and validated. In this article, we look at the types of research questionnaires, their applications and limitations, and how a new questionnaire is developed.
INTRODUCTION
In research studies, questionnaires are commonly used as data collection tools, either as the only source of information or in combination with other techniques in mixed-method studies. However, the quality and accuracy of data collected using a questionnaire depend on how it is designed, used, and validated. In this two-part series, we discuss how to design (part 1) and how to use and validate (part 2) a research questionnaire. It is important to emphasize that questionnaires seek to gather information from other people and therefore entail a social relationship between those who are doing the research and those who are being researched. This social relationship comes with an obligation to learn from others , an obligation that goes beyond the purely instrumental rationality of gathering data. In that sense, we underscore that any research method is not simply a tool but a situation, a relationship, a negotiation, and an encounter. This points to both ethical questions (what is the relationship between the researcher and the researched?) and epistemological ones (what are the conditions under which we can know something?).
At the start of any kind of research project, it is crucial to select the right methodological approach. What is the research question, what is the research object, and what can a questionnaire realistically achieve? Not every research question and not every research object are suitable to the questionnaire as a method. Questionnaires can only provide certain kinds of empirical evidence and it is thus important to be aware of the limitations that are inherent in any kind of methodology.
WHAT IS A RESEARCH QUESTIONNAIRE?
A research questionnaire can be defined as a data collection tool consisting of a series of questions or items that are used to collect information from respondents and thus learn about their knowledge, opinions, attitudes, beliefs, and behavior and informed by a positivist philosophy of the natural sciences that consider methods mainly as a set of rules for the production of knowledge; questionnaires are frequently used instrumentally as a standardized and standardizing tool to ask a set of questions to participants. Outside of such a positivist philosophy, questionnaires can be seen as an encounter between the researcher and the researched, where knowledge is not simply gathered but negotiated through a distinct form of communication that is the questionnaire.
STRENGTHS AND LIMITATIONS OF QUESTIONNAIRES
A questionnaire may not always be the most appropriate way of engaging with research participants and generating knowledge that is needed for a research study. Questionnaires have advantages that have made them very popular, especially in quantitative studies driven by a positivist philosophy: they are a low-cost method for the rapid collection of large amounts of data, even from a wide sample. They are practical, can be standardized, and allow comparison between groups and locations. However, it is important to remember that a questionnaire only captures the information that the method itself (as the structured relationship between the researcher and the researched) allows for and that the respondents are willing to provide. For example, a questionnaire on diet captures what the respondents say they eat and not what they are eating. The problem of social desirability emerges precisely because the research process itself involves a social relationship. This means that respondents may often provide socially acceptable and idealized answers, particularly in relation to sensitive questions, for example, alcohol consumption, drug use, and sexual practices. Questionnaires are most useful for studies investigating knowledge, beliefs, values, self-understandings, and self-perceptions that reflect broader social, cultural, and political norms that may well diverge from actual practices.
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONNAIRES
Research questionnaires may be classified in several ways:
Depending on mode of administration
Research questionnaires may be self-administered (by the research participant) or researcher administered. Self-administered (also known as self-reported or self-completed) questionnaires are designed to be completed by respondents without assistance from a researcher. Self-reported questionnaires may be administered to participants directly during hospital or clinic visits, mailed through the post or E-mail, or accessed through websites. This technique allows respondents to answer at their own pace and simplifies research costs and logistics. The anonymity offered by self-reporting may facilitate more accurate answers. However, the disadvantages are that there may be misinterpretations of questions and low response rates. Significantly, relevant context information is missing to make sense of the answers provided. Researcher-reported (or interviewer-reported) questionnaires may be administered face-to-face or through remote techniques such as telephone or videoconference and are associated with higher response rates. They allow the researcher to have a better understanding of how the data are collected and how answers are negotiated, but are more resource intensive and require more training from the researchers.
The choice between self-administered and researcher-administered questionnaires depends on various factors such as the characteristics of the target audience (e.g., literacy and comprehension level and ability to use technology), costs involved, and the need for confidentiality/privacy.
Depending on the format of the questions
Research questionnaires can have structured or semi-structured formats. Semi-structured questionnaires allow respondents to answer more freely and on their terms, with no restrictions on their responses. They allow for unusual or surprising responses and are useful to explore and discover a range of answers to determine common themes. Typically, the analysis of responses to open-ended questions is more complex and requires coding and analysis. In contrast, structured questionnaires provide a predefined set of responses for the participant to choose from. The use of standard items makes the questionnaire easier to complete and allows quick aggregation, quantification, and analysis of the data. However, structured questionnaires can be restrictive if the scope of responses is limited and may miss potential answers. They also may suggest answers that respondents may not have considered before. Respondents may be forced to fit their answers into the predetermined format and may not be able to express personal views and say what they really want to say or think. In general, this type of questionnaire can turn the research process into a mechanical, anonymous survey with little incentive for participants to feel engaged, understood, and taken seriously.
STRUCTURED QUESTIONS: FORMATS
Some examples of close-ended questions include:
e.g., Please indicate your marital status:
- Prefer not to say.
e.g., Describe your areas of work (circle or tick all that apply):
- Clinical service
- Administration
- Strongly agree
- Strongly disagree.
- Numerical scales: Please rate your current pain on a scale of 1–10 where 1 is no pain and 10 is the worst imaginable pain
- Symbolic scales: For example, the Wong-Baker FACES scale to rate pain in older children
- Ranking: Rank the following cities as per the quality of public health care, where 1 is the best and 5 is the worst.
A matrix questionnaire consists of a series of rows with items to be answered with a series of columns providing the same answer options. This is an efficient way of getting the respondent to provide answers to multiple questions. The EORTC QLQ-C30 is an example of a matrix questionnaire.[ 1 ]
For a more detailed review of the types of research questions, readers are referred to a paper by Boynton and Greenhalgh.[ 2 ]
USING PRE-EXISTING QUESTIONNAIRES VERSUS DEVELOPING A NEW QUESTIONNAIRE
Before developing a questionnaire for a research study, a researcher can check whether there are any preexisting-validated questionnaires that might be adapted and used for the study. The use of validated questionnaires saves time and resources needed to design a new questionnaire and allows comparability between studies.
However, certain aspects need to be kept in mind: is the population/context/purpose for which the original questionnaire was designed similar to the new study? Is cross-cultural adaptation required? Are there any permission needed to use the questionnaire? In many situations, the development of a new questionnaire may be more appropriate given that any research project entails both methodological and epistemological questions: what is the object of knowledge and what are the conditions under which it can be known? It is important to understand that the standardizing nature of questionnaires contributes to the standardization of objects of knowledge. Thus, the seeming similarity in the object of study across diverse locations may be an artifact of the method. Whatever method one uses, it will always operate as the ground on which the object of study is known.
DESIGNING A NEW RESEARCH QUESTIONNAIRE
Once the researcher has decided to design a new questionnaire, several steps should be considered:
Gathering content
It creates a conceptual framework to identify all relevant areas for which the questionnaire will be used to collect information. This may require a scoping review of the published literature, appraising other questionnaires on similar topics, or the use of focus groups to identify common themes.
Create a list of questions
Questions need to be carefully formulated with attention to language and wording to avoid ambiguity and misinterpretation. Table 1 lists a few examples of poorlyworded questions that could have been phrased in a more appropriate manner. Other important aspects to be noted are:
Examples of poorly phrased questions in a research questionnaire
- Provide a brief introduction to the research study along with instructions on how to complete the questionnaire
- Allow respondents to indicate levels of intensity in their replies, so that they are not forced into “yes” or “no” answers where intensity of feeling may be more appropriate
- Collect specific and detailed data wherever possible – this can be coded into categories. For example, age can be captured in years and later classified as <18 years, 18–45 years, 46 years, and above. The reverse is not possible
- Avoid technical terms, slang, and abbreviations. Tailor the reading level to the expected education level of respondents
- The format of the questionnaire should be attractive with different sections for various subtopics. The font should be large and easy to read, especially if the questionnaire is targeted at the elderly
- Question sequence: questions should be arranged from general to specific, from easy to difficult, from facts to opinions, and sensitive topics should be introduced later in the questionnaire.[ 3 ] Usually, demographic details are captured initially followed by questions on other aspects
- Use contingency questions: these are questions which need to be answered only by a subgroup of the respondents who provide a particular answer to a previous question. This ensures that participants only respond to relevant sections of the questionnaire, for example, Do you smoke? If yes, then how long have you been smoking? If not, then please go to the next section.
TESTING A QUESTIONNAIRE
A questionnaire needs to be valid and reliable, and therefore, any new questionnaire needs to be pilot tested in a small sample of respondents who are representative of the larger population. In addition to validity and reliability, pilot testing provides information on the time taken to complete the questionnaire and whether any questions are confusing or misleading and need to be rephrased. Validity indicates that the questionnaire measures what it claims to measure – this means taking into consideration the limitations that come with any questionnaire-based study. Reliability means that the questionnaire yields consistent responses when administered repeatedly even by different researchers, and any variations in the results are due to actual differences between participants and not because of problems with the interpretation of the questions or their responses. In the next article in this series, we will discuss methods to determine the reliability and validity of a questionnaire.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
20+ SAMPLE Research Questionnaires Templates in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages
Research questionnaires templates | ms word | google docs | apple pages, 20+ sample research questionnaires templates, what is a research questionnaire, types of research questionnaires, how to make an effective research questionnaire, research questionnaire vs. research survey, the dos and don’ts of a research questionnaire.
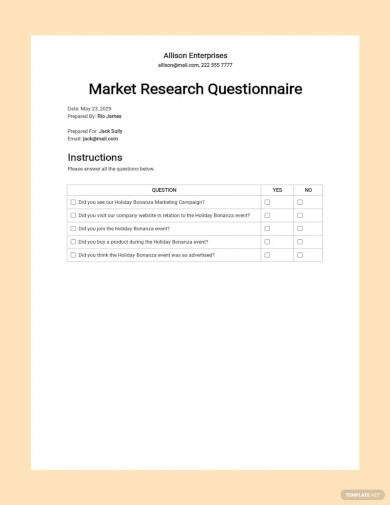

Market Research Questionnaire Template

Veterans Health Care Survey Questionnaire

Basic Market Survey Questionnaire
Market Research Questionnaires Format

Research Protocol Survey

Clinical Study PI Questionnaire

Human Study Questionnaire

Research Interest Questionnaire

Research Financial Disclosure Questionnaire
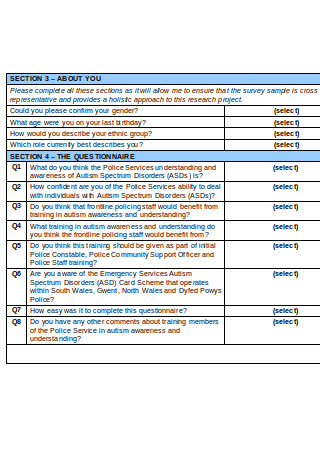
Research Project Questionnaire

Questionnaire for Legal Practitioners

Sample Research Questionnaire

Research Survey Questionnaires
Research Standard Questionnaires

Auto Compensation Research Questionnaire

Orientation Research Questionnaire
Research Questionnaire Format
Social Research Questionnaire

Social Survey Questionnaire

Research into Questionnaire Design
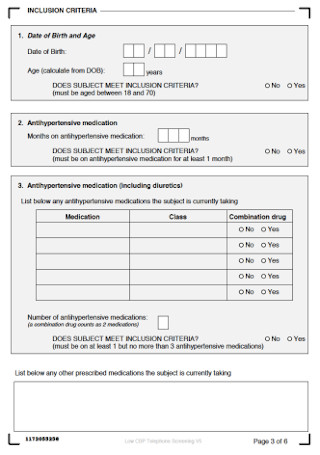
Questionnaires in Clinical Research
1. open-ended questionnaires, 2. closed-ended questionnaires, 3. mixed questionnaires, 4. pictorial questionnaires, step 1: identify the goals of your research questionnaire , step 2: define your target respondents, step 3: create questions , step 4: choose an appropriate question type , step 5: design the sequence and layout of the questions.
- The instrument used for data collection
- Is a tool that is distributed
- May contain open- or closed-ended questions
- Collects information on a topic
- Process of gathering and analyzing data
- Is an activity that is conducted
- Mainly comprised of closed-ended questions
- Aims to draw data for statistical analysis
Dont’s
Share this post on your network, file formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 51+ sample food questionnaire templates in pdf | ms word | google docs | apple pages.

A food questionnaire can be used for a lot of purposes by a variety of businesses in the food service, hospitality, catering, and restaurant industry. Developing a food questionnaire is…
42+ SAMPLE Audit Questionnaire Templates in PDF | MS Word

Whether you come from a startup business to a long-time respected company, any work contains inevitable problems. Indeed, every success, even the smallest ones, deserves to be celebrated. But…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
Research survey examples, templates, and types
Research surveys help base your next important decision on data. With our survey research templates and questions, gather valuable data easily and improve your business.
Get started
What are the benefits of survey research?
Providing data that can be relied on. Whether conducting market research or preparing a new product launch, research surveys supply the precise information needed to succeed. Avoid the confusion of conflicting opinions with data analysis that provides a clear picture of what people think.
At SurveyPlanet, we’re committed to making survey research easy to conduct. With our templates, have access to questions that will deliver the data you need.
The wide variety of research survey templates available is how to get useful data quickly—which makes developing more powerful solutions easier. Survey research can provide data you can rely on.
The wide variety of survey templates available helps develop the correct solution. At SurveyPlanet, we're committed to making research surveys easy to conduct and with our templates, we deliver on that promise.
What are research questionnaires?
They are a tool that returns insight about any topic. Just asking friends, family, and coworkers about a new product is not the best approach. Why? To put it simply, they're not a representative sample and may have biases.
What is needed is the opinions of your target audience. At the end of the day, it is their opinion that matters most. This requires a large enough sample to produce statistically significant data. That's where online surveys can play an important role.
Types of research surveys
Research questionnaires are a great tool to gain insights about all kinds of things (and not just business purposes). These surveys play an important role in extracting valuable insights from diverse populations. When thoughtfully designed, they become powerful instruments for informed decision-making and the advancement of knowledge across various domains.
Let's dive deeper into the types of surveys and where to apply them to get the best results.
Market research survey
Most businesses fail because their management believes their products and services are great—while the market thinks otherwise. To sell anything, the opinions of the people doing the buying need to be understood. Market research surveys offer insights about where a business stands with potential customers—and thus its potential market share—long before resources are dedicated to trying to make a product work in the marketplace.
Learn more about market research surveys.
Media consumption research survey
This type of survey explores how different people consume media content. It provides answers about what they view, how often they do so, and what kind of media they prefer. With a media consumption survey, learn everything about people's viewing and reading habits.
Reading preferences research survey
Ever wondered how, why, and what people enjoy reading? With a reading preferences research survey, such information can be discovered. By further analyzing the data, learn what different groups of people read (and the similarities and differences between different groups).
Product research survey
When launching a new product, understanding its target audience is crucial. This type of survey is a great tool that provides valuable feedback and insight that can be incorporated into a successful product launch.
Learn more about product research surveys.
Brand surveys
These help ascertain how customers feel about a brand. People buy from those they connect with; therefore, ask about their experiences and occasionally check in with them to see if they trust your brand.
Learn more about brand surveys.
Path-to-purchase research surveys
A path-to-purchase research survey investigates the steps consumers take from initial product awareness to final purchase. It typically includes questions about the decision-making process, product research, and factors influencing the ultimate purchasing decision. Such surveys can be conducted through various methods, but the best is via online surveys. The results of path-to-purchase surveys help businesses and marketers understand their target audience and develop effective marketing strategies.
Marketing research surveys
These help a company stand out from competitors and tailor marketing messages that better resonate with a target audience. Market research surveys are another type of research that is crucial when launching a new product or service.
Learn more about marketing research surveys.
Academic research surveys
These surveys are instrumental in improving knowledge about a specific subject. Consolidated results can be used to improve the efficiency of decision-making. Reliability is produced using methodologies and tools like questionnaires, surveys, interviews, and structured online forms.
Learn more about academic surveys.
Types of research methods
The three main types of research methods are exploratory, descriptive, and causal research.
Exploratory research
Exploratory research is conducted when a researcher seeks to explore a new subject or phenomenon with limited or no prior understanding. The primary goal of exploratory research is to gain insights, generate ideas, and form initial hypotheses for more in-depth investigation. This type of research is often the first step in the research process and is particularly useful when the topic is not well-defined or when there is a lack of existing knowledge. Researchers often use open-ended questions and qualitative methods to gather data, allowing them to adapt their approach as they learn more about the topic.
Descriptive research
Descriptive research aims to provide an accurate and detailed portrayal of a specific phenomenon or group. Unlike exploratory research, which seeks to generate insights and hypotheses, descriptive research is focused on describing the characteristics, behaviors, or conditions of a subject without manipulating variables.
Causal research
Causal research, also known as explanatory or experimental research, seeks to establish a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more variables. The primary goal of causal research is to determine whether a change in one variable causes a change in another variable. Unlike descriptive research, which focuses on describing relationships and characteristics, causal research involves manipulating one or more independent variables to observe their impact on dependent variables.
The research survey application
Research methods are designed to produce the best information from a group of research subjects (aka, the focus group). Such methods are used in many types of research and studies. They are methodologies that can be used for research study and data collection.
Depending on the kind of research and research methodology being carried out, different types of research survey questions are used, including multiple choice questions , Likert , scale questions , open-ended questions , demographic questions , and even image choice questions .
There are many survey applications that can collect data from many customers quickly and easily—a great way to get information about products, services, customer experiences, and marketing efforts.
Why you should use research questionnaires
The power of research questionnaires lies in their ease of use and cost-effectiveness. They provide answers to the most vital questions. What are the main benefits of these surveys?
- You don't have to wonder WHO, WHAT, and WHY because this type of analysis provides answers to those—and many other—questions.
- With a complete understanding of what's important in a research project, the best inquiries can be incorporated into survey questions.
- Get an unbiased opinion from a target audience and use it to your advantage.
- Collect data that matters and have it at your fingertips at all times.
Advantages and disadvantages of survey research
People use these surveys because they have many advantages compared to other research tools. What are the main advantages?
- Cost-effective.
- Collect data from many respondents.
- Quantifiable results.
- Convenient.
- The most practical solution for gathering data.
- Fast and reliable.
- Easily comparable results.
- Allows for the exploration of any topic.
While such advantages make it a no-brainer to use research questionnaires, it's always good to know their disadvantages:
- Biased responses.
- Cultural differences in understanding questions.
- Analyzing and understanding responses can be difficult.
- Some people won't read the questions before answering.
- Survey fatigue.
However, when these issues are understood, mitigation strategies can be activated. Every research method has flaws, but we firmly believe their benefits outweigh their disadvantages.
To execute a research campaign, the creation of a survey is one of the first steps. This includes designing questions or using a premade template. Below are some of the best research survey examples, templates, and tips for designing these surveys.
20 research survey examples and templates
Specific survey questions for research depend on your goals. A research questionnaire can be conducted about any topic or interest. Here are some of the best questions and ranking prompts:
- How often do you purchase books without actually reading them?
- What is your favorite foreign language film?
- During an average day, how many times do you check the news?
- Who is your favorite football player of all time? Why?
- Have you ever used any of the following travel websites to plan a vacation?
- Do you currently use a similar or competing product?
- On a scale of 1 to 5, how satisfied are you with the product?
- What is your single favorite feature of our product?
- When our product becomes available, are you likely to use it instead of a similar or competing product?
- What improvements would you suggest for our service?
- Please rank the following features in order of importance.
- How often do you consume fruits and vegetables in a typical week?
- How many days per week do you engage in physical activity?
- Do you prefer traditional classroom learning or online learning?
- How many hours a week do you spend studying for your courses?
- What are your career aspirations upon completing your education?
- Please rate our website's user interface from poor to excellent.
- In what ways can we better support you as a customer?
- Please rank the following factors in order of importance when choosing a new car.
- Order the following smartphone features based on your preference.
Of course, you get demographic information like:
- Employment status
- Marital status
- Household income
No matter the research topic, this demographic information will lead to better data-driven conclusions. Interested in knowing more about demographic survey questions? Check out our blog post explaining the advantages of gathering demographic information and how to do it appropriately.
Sign up for SurveyPlanet for free. Conduct your first survey to explore what people think. And don't worry about questions because we have some amazing templates to get you started.
Sign up now
Free unlimited surveys, questions and responses.
28 Questionnaire Examples, Questions, & Templates to Survey Your Clients
Published: May 15, 2023
The adage "the customer is always right" has received some pushback in recent years, but when it comes to conducting surveys , the phrase is worth a deeper look. In the past, representatives were tasked with solving client problems as they happened. Now, they have to be proactive by solving problems before they come up.

Salesforce found that 63% of customers expect companies to anticipate their needs before they ask for help. But how can a customer service team recognize these customer needs in advance and effectively solve them on a day-to-day basis?
![a research questionnaire sample → Free Download: 5 Customer Survey Templates [Access Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/9d36416b-3b0d-470c-a707-269296bb8683.png)
A customer questionnaire is a tried-and-true method for collecting survey data to inform your customer service strategy . By hearing directly from the customer, you'll capture first-hand data about how well your service team meets their needs. In this article, you'll get free questionnaire templates and best practices on how to administer them for the most honest responses.
Table of Contents:
Questionnaire Definition
Survey vs. questionnaire, questionnaire templates.
- Questionnaire Examples
Questionnaire Design
Survey question examples.
- Examples of Good Survey Questions
How to Make a Questionnaire
A questionnaire is a research tool used to conduct surveys. It includes specific questions with the goal to understand a topic from the respondents' point of view. Questionnaires typically have closed-ended, open-ended, short-form, and long-form questions.
The questions should always stay as unbiased as possible. For instance, it's unwise to ask for feedback on a specific product or service that’s still in the ideation phase. To complete the questionnaire, the customer would have to imagine how they might experience the product or service rather than sharing their opinion about their actual experience with it.
Ask broad questions about the kinds of qualities and features your customers enjoy in your products or services and incorporate that feedback into new offerings your team is developing.
What makes a good questionnaire?
Define the goal, make it short and simple, use a mix of question types, proofread carefully, keep it consistent.
A good questionnaire should find what you need versus what you want. It should be valuable and give you a chance to understand the respondent’s point of view.
Make the purpose of your questionnaire clear. While it's tempting to ask a range of questions simultaneously, you'll get more valuable results if you stay specific to a set topic.
According to HubSpot research , 47% of those surveyed say their top reason for abandoning a survey is the time it takes to complete.
So, questionnaires should be concise and easy to finish. If you're looking for a respondent’s experience with your business, focus on the most important questions.
.webp)
5 Free Customer Satisfaction Survey Templates
Easily measure customer satisfaction and begin to improve your customer experience.
- Net Promoter Score
- Customer Effort Score
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
5 Customer Survey Templates
Featured resource.
Your questionnaire should include a combination of question types, like open-ended, long-form, or short-ended questions.
Open-ended questions give users a chance to share their own answers. But closed-ended questions are more efficient and easy to quantify, with specific answer choices.
If you're not sure which question types are best, read here for more survey question examples .
While it's important to check spelling and grammar, there are two other things you'll want to check for a great questionnaire.
First, edit for clarity. Jargon, technical terms, and brand-specific language can be confusing for respondents. Next, check for leading questions. These questions can produce biased results that will be less useful to your team.
Consistency makes it easier for respondents to quickly complete your questionnaire. This is because it makes the questions less confusing. It can also reduce bias.
Being consistent is also helpful for analyzing questionnaire data because it makes it easier to compare results. With this in mind, keep response scales, question types, and formatting consistent.
In-Depth Interviews vs. Questionnaire
Questionnaires can be a more feasible and efficient research method than in-depth interviews. They are a lot cheaper to conduct. That’s because in-depth interviews can require you to compensate the interviewees for their time and give accommodations and travel reimbursement.
Questionnaires also save time for both parties. Customers can quickly complete them on their own time, and employees of your company don't have to spend time conducting the interviews. They can capture a larger audience than in-depth interviews, making them much more cost-effective.
It would be impossible for a large company to interview tens of thousands of customers in person. The same company could potentially get feedback from its entire customer base using an online questionnaire.
When considering your current products and services (as well as ideas for new products and services), it's essential to get the feedback of existing and potential customers. They are the ones who have a say in purchasing decisions.
A questionnaire is a tool that’s used to conduct a survey. A survey is the process of gathering, sampling, analyzing, and interpreting data from a group of people.
The confusion between these terms most likely stems from the fact that questionnaires and data analysis were treated as very separate processes before the Internet became popular. Questionnaires used to be completed on paper, and data analysis occurred later as a separate process. Nowadays, these processes are typically combined since online survey tools allow questionnaire responses to be analyzed and aggregated all in one step.
But questionnaires can still be used for reasons other than data analysis. Job applications and medical history forms are examples of questionnaires that have no intention of being statistically analyzed. The key difference between questionnaires and surveys is that they can exist together or separately.
Below are some of the best free questionnaire templates you can download to gather data that informs your next product or service offering.
What makes a good survey question?
Have a goal in mind, draft clear and distinct answers and questions, ask one question at a time, check for bias and sensitivity, include follow-up questions.
To make a good survey question, you have to choose the right type of questions to use. Include concise, clear, and appropriate questions with answer choices that won’t confuse the respondent and will clearly offer data on their experience.
Good survey questions can give a business good data to examine. Here are some more tips to follow as you draft your survey questions.
To make a good survey, consider what you are trying to learn from it. Understanding why you need to do a survey will help you create clear and concise questions that you need to ask to meet your goal. The more your questions focus on one or two objectives, the better your data will be.
You have a goal in mind for your survey. Now you have to write the questions and answers depending on the form you’re using.
For instance, if you’re using ranks or multiple-choice in your survey, be clear. Here are examples of good and poor multiple-choice answers:
Poor Survey Question and Answer Example
California:
- Contains the tallest mountain in the United States.
- Has an eagle on its state flag.
- Is the second-largest state in terms of area.
- Was the location of the Gold Rush of 1849.
Good Survey Question and Answer Example
What is the main reason so many people moved to California in 1849?
- California's land was fertile, plentiful, and inexpensive.
- The discovery of gold in central California.
- The East was preparing for a civil war.
- They wanted to establish religious settlements.
In the poor example, the question may confuse the respondent because it's not clear what is being asked or how the answers relate to the question. The survey didn’t fully explain the question, and the options are also confusing.
In the good example above, the question and answer choices are clear and easy to understand.
Always make sure answers and questions are clear and distinct to create a good experience for the respondent. This will offer your team the best outcomes from your survey.
It's surprisingly easy to combine multiple questions into one. They even have a name — they’re called "double-barreled" questions. But a good survey asks one question at a time.
For example, a survey question could read, "What is your favorite sneaker and clothing apparel brand?" This is bad because you’re asking two questions at once.
By asking two questions simultaneously, you may confuse your respondents and get unclear answers. Instead, each question should focus on getting specific pieces of information.
For example, ask, "What is your favorite sneaker brand?" then, "What is your favorite clothing apparel brand?" By separating the questions, you allow your respondents to give separate and precise answers.
Biased questions can lead a respondent toward a specific response. They can also be vague or unclear. Sensitive questions such as age, religion, or marital status can be helpful for demographics. These questions can also be uncomfortable for people to answer.
There are a few ways to create a positive experience with your survey questions.
First, think about question placement. Sensitive questions that appear in context with other survey questions can help people understand why you are asking. This can make them feel more comfortable responding.
Next, check your survey for leading questions, assumptions, and double-barreled questions. You want to make sure that your survey is neutral and free of bias.
Asking more than one survey question about an area of interest can make a survey easier to understand and complete. It also helps you collect more in-depth insights from your respondents.
1. Free HubSpot Questionnaire Template
HubSpot offers a variety of free customer surveys and questionnaire templates to analyze and measure customer experience. Choose from five templates: net promoter score, customer satisfaction, customer effort, open-ended questions, and long-form customer surveys.
2. Client Questionnaire Template
It's a good idea to gauge your clients' experiences with your business to uncover opportunities to improve your offerings. That will, in turn, better suit their lifestyles. You don't have to wait for an entire year to pass before polling your customer base about their experience either. A simple client questionnaire, like the one below, can be administered as a micro survey several times throughout the year. These types of quick survey questions work well to retarget your existing customers through social media polls and paid interactive ads.
1. How much time do you spend using [product or service]?
- Less than a minute
- About 1 - 2 minutes
- Between 2 and 5 minutes
- More than 5 minutes
2. In the last month, what has been your biggest pain point?
- Finding enough time for important tasks
- Delegating work
- Having enough to do
3. What's your biggest priority right now?
- Finding a faster way to work
- Problem-solving
- Staff development

3. Website Questionnaire Template
Whether you just launched a brand new website or you're gathering data points to inform a redesign, you'll find customer feedback to be essential in both processes. A website questionnaire template will come in handy to collect this information using an unbiased method.
1. How many times have you visited [website] in the past month?
- More than once
2. What is the primary reason for your visit to [website]?
- To make a purchase
- To find more information before making a purchase in-store
- To contact customer service
3. Are you able to find what you're looking for on the website homepage?
4. Customer Satisfaction Questionnaire Template
If you've never surveyed your customers and are looking for a template to get started, this one includes some basic customer satisfaction questions. These will apply to just about any customer your business serves.
1. How likely are you to recommend us to family, friends, or colleagues?
- Extremely unlikely
- Somewhat unlikely
- Somewhat likely
- Extremely likely
2. How satisfied were you with your experience?
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10
3. Rank the following items in terms of their priority to your purchasing process.
- Helpful staff
- Quality of product
- Price of product
- Ease of purchase
- Proximity of store
- Online accessibility
- Current need
- Appearance of product
4. Who did you purchase these products for?
- Family member
- On behalf of a business
5. Please rate our staff on the following terms:
- Friendly __ __ __ __ __ Hostile
- Helpful __ __ __ __ __ Useless
- Knowledgeable __ __ __ __ __ Inexperienced
- Professional __ __ __ __ __ Inappropriate
6. Would you purchase from our company again?
7. How can we improve your experience for the future?
________________________________.
5. Customer Effort Score Questionnaire Template
The following template gives an example of a brief customer effort score (CES) questionnaire. This free template works well for new customers to measure their initial reaction to your business.
1. What was the ease of your experience with our company?
- Extremely difficult
- Somewhat difficult
- Somewhat easy
- Extremely easy
2. The company did everything it could to make my process as easy as possible.
- Strongly disagree
- Somewhat disagree
- Somewhat agree
- Strongly agree
3. On a scale of 1 to 10 (1 being "extremely quickly" and 10 being "extremely slowly"), how fast were you able to solve your problem?
4. How much effort did you have to put forth while working with our company?
- Much more than expected
- Somewhat more than expected
- As much as expected
- Somewhat less than expected
- Much less than expected
6. Demographic Questionnaire Template
Here's a template for surveying customers to learn more about their demographic background. You could substantiate the analysis of this questionnaire by corroborating the data with other information from your web analytics, internal customer data, and industry data.
1. How would you describe your employment status?
- Employed full-time
- Employed part-time
- Freelance/contract employee
- Self-employed
2. How many employees work at your company?
3. How would you classify your role?
- Individual Contributor
4. How would you classify your industry?
- Technology/software
- Hospitality/dining
- Entertainment
Below, we have curated a list of questionnaire examples that do a great job of gathering valuable qualitative and quantitative data.
4 Questionnaire Examples
1. customer satisfaction questions.
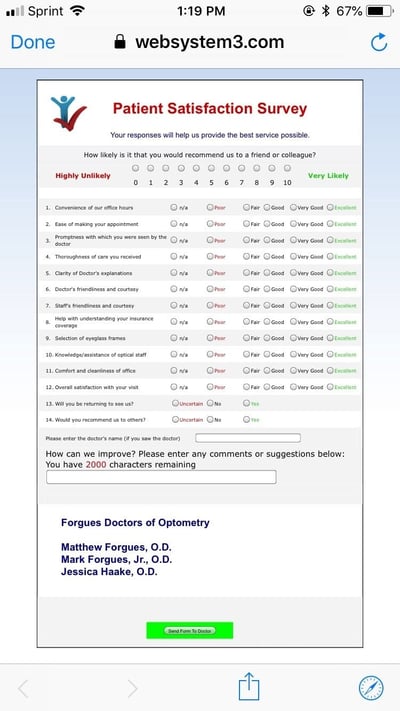
Learn more about HubSpot's Customer Survey software.
Multiple-Choice
Multiple-choice questions offer respondents several answers to choose from. This is a popular choice of questionnaire format since it's simple for people to fill out and for companies to analyze.
Multiple-choice questions can be in single-answer form (respondents can only choose one response) or multiple-answer form (respondents can choose as many responses as necessary).
Multiple-choice survey question examples : "Which of the following social media platforms do you use most often?"
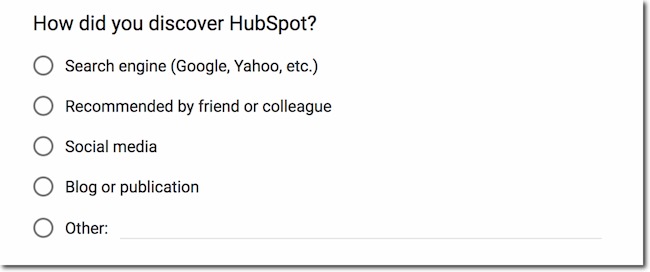
Image Source
Rating Scale
Rating scale questions offer a scale of numbers and ask respondents to rate topics based on the sentiments assigned to that scale. This is effective when assessing customer satisfaction.
Rating scale survey question examples : "Rate your level of satisfaction with the customer service you received today on a scale of 1-10."
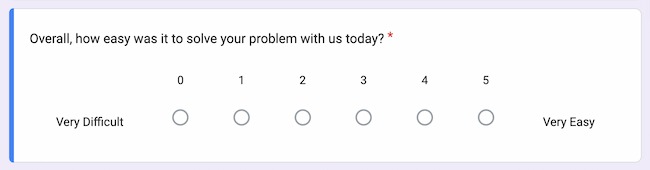
Yes or no survey questions are a type of dichotomous question. These are questions that only offer two possible responses. They’re useful because they’re quick to answer and can help with customer segmentation.
Yes or no survey questions example : "Have you ever used HubSpot before?"
Likert Scale
Likert scale questions assess whether a respondent agrees with the statement, as well as the extent to which they agree or disagree.
These questions typically offer five or seven responses, with sentiments ranging from items such as "strongly disagree" to "strongly agree." Check out this post to learn more about the Likert scale .
Likert scale survey question examples : “How satisfied are you with the service from [brand]?”

Open-ended questions ask a broader question or offer a chance to elaborate on a response to a close-ended question. They're accompanied by a text box that leaves room for respondents to write freely. This is particularly important when asking customers to expand on an experience or recommendation.
Open-ended survey question examples : "What are your personal goals for using HubSpot? Please describe."
Matrix Table
A matrix table is usually a group of multiple-choice questions grouped in a table. Choices for these survey questions are usually organized in a scale. This makes it easier to understand the relationships between different survey responses.
Matrix table survey question examples : "Rate your level of agreement with the following statements about HubSpot on a scale of 1-5."
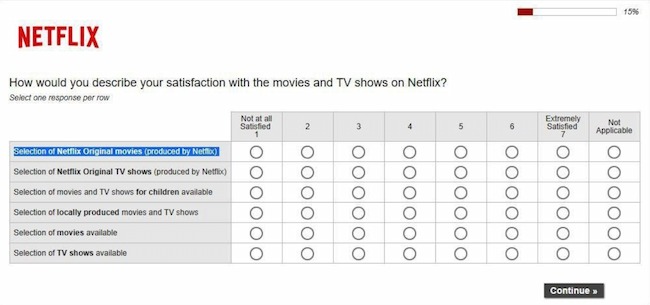
Rank Order Scaling
These questions ask respondents to rank a set of terms by order of preference or importance. This is useful for understanding customer priorities.
Rank order scaling examples : "Rank the following factors in order of importance when choosing a new job."
Semantic Differential Scale
This scale features pairs of opposite adjectives that respondents use for rating, usually for a feature or experience. This type of question makes it easier to understand customer attitudes and beliefs.
Semantic differential scale question examples : "Rate your overall impression of this brand as friendly vs. unfriendly, innovative vs. traditional, and boring vs. exciting."
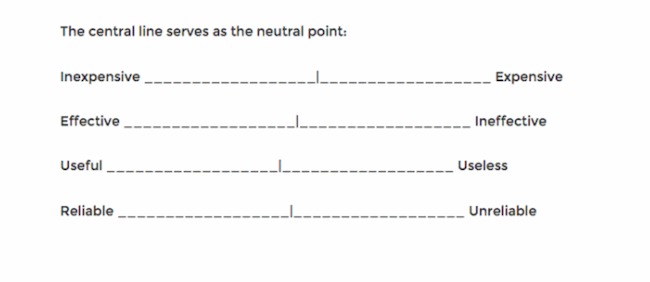
Side-By-Side Matrix
This matrix table format includes two sets of questions horizontally for easy comparison. This format can help with customer gap analysis.
Side-by-side matrix question examples : "Rate your level of satisfaction with HubSpot's customer support compared to its ease of use."
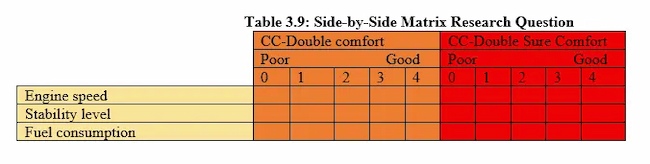
Stapel Scale
The Stapel rating scale offers a single adjective or idea for rating. It uses a numerical scale with a zero point in the middle. This survey question type helps with in-depth analysis.
Stapel scale survey question examples : "Rate your overall experience with this product as +5 (excellent) to -5 (terrible)."
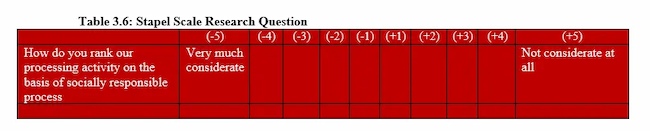
Constant Sum Survey Questions
In this question format, people distribute points to different choices based on the perceived importance of each point. This kind of question is often used in market research and can help your team better understand customer choices .
Constant sum survey question examples : "What is your budget for the following marketing expenses: Paid campaigns, Events, Freelancers, Agencies, Research."
Image Choice
This survey question type shows several images. Then, it asks the respondent to choose the image that best matches their response to the question. These questions are useful for understanding your customers’ design preferences.
Image choice survey questions example : "Which of these three images best represents your brand voice?"

Choice Model
This survey question offers a hypothetical scenario, then the respondent must choose from the presented options. It's a useful type of question when you are refining a product or strategy.
Choice model survey questions example : "Which of these three deals would be most appealing to you?"
Click Map Questions
Click map questions offer an image click on specific areas of the image in response to a question. This question uses data visualization to learn about customer preferences for design and user experience.
Click map question examples : "Click on the section of the website where you would expect to find pricing information."

Data Upload
This survey question example asks the respondent to upload a file or document in response to a question. This type of survey question can help your team collect data and context that might be tough to collect otherwise.
Data upload question examples : "Please upload a screenshot of the error you encountered during your purchase."
Benchmarkable Questions
This question type asks a respondent to compare their answers to a group or benchmark. These questions can be useful if you're trying to compare buyer personas or other customer groups.
Benchmarkable survey questions example : "Compare your company's marketing budget to other companies in your industry."
Good Survey Questions
- What is your favorite product?
- Why did you purchase this product?
- How satisfied are you with [product]?
- Would you recommend [product] to a friend?
- Would you recommend [company name] to a friend?
- If you could change one thing about [product], what would it be?
- Which other options were you considering before [product or company name]?
- Did [product] help you accomplish your goal?
- How would you feel if we did not offer this product, feature, or service?
- What would you miss the most if you couldn't use your favorite product from us?
- What is one word that best describes your experience using our product?
- What's the primary reason for canceling your account?
- How satisfied are you with our customer support?
- Did we answer all of your questions and concerns?
- How can we be more helpful?
- What additional features would you like to see in this product?
- Are we meeting your expectations?
- How satisfied are you with your experience?
1. "What is your favorite product?"
This question is a great starter for your survey. Most companies want to know what their most popular products are, and this question cuts right to the point.
It's important to note that this question gives you the customer's perspective, not empirical evidence. You should compare the results to your inventory to see if your customers' answers match your actual sales. You may be surprised to find your customers' "favorite" product isn't the highest-selling one.
2. "Why did you purchase this product?"
Once you know their favorite product, you need to understand why they like it so much. The qualitative data will help your marketing and sales teams attract and engage customers. They'll know which features to advertise most and can seek out new leads similar to your existing customers.
3. "How satisfied are you with [product]?"
When you have a product that isn't selling, you can ask this question to see why customers are unhappy with it. If the reviews are poor, you'll know that the product needs reworking, and you can send it back to product management for improvement. Or, if these results are positive, they may have something to do with your marketing or sales techniques. You can then gather more info during the questionnaire and restrategize your campaigns based on your findings.
4. "Would you recommend [product] to a friend?"
This is a classic survey question used with most NPS® surveys. It asks the customer if they would recommend your product to one of their peers. This is extremely important because most people trust customer referrals more than traditional advertising. So, if your customers are willing to recommend your products, you'll have an easier time acquiring new leads.
5. "Would you recommend [company name] to a friend?"
Similar to the question above, this one asks the customer to consider your business as a whole and not just your product. This gives you insight into your brand's reputation and shows how customers feel about your company's actions. Even if you have an excellent product, your brand's reputation may be the cause of customer churn . Your marketing team should pay close attention to this question to see how they can improve the customer experience .
6. "If you could change one thing about [product], what would it be?"
This is a good question to ask your most loyal customers or ones that have recently churned. For loyal customers, you want to keep adding value to their experience. Asking how your product can improve helps your development team find flaws and increases your chances of retaining a valuable customer segment.
For customers that have recently churned, this question gives insight into how you can retain future users that are unhappy with your product or service. By giving these customers a space to voice their criticisms, you can either reach out and offer solutions or relay feedback for consideration.
7. "Which other options were you considering before [product or company name]?"
If you're operating in a competitive industry, customers will have more than one choice when considering your brand. And if you sell variations of your product or produce new models periodically, customers may prefer one version over another.
For this question, you should offer answers to choose from in a multiple-selection format. This will limit the types of responses you'll receive and help you get the exact information you need.
8. "Did [product] help you accomplish your goal?"
The purpose of any product or service is to help customers reach a goal. So, you should be direct and ask them if your company steered them toward success. After all, customer success is an excellent retention tool. If customers are succeeding with your product, they're more likely to stay loyal to your brand.
9. "How would you feel if we did not offer this product, feature, or service?"
Thinking about discontinuing a product? This question can help you decide whether or not a specific product, service, or feature will be missed if you were to remove it.
Even if you know that a product or service isn't worth offering, it's important to ask this question anyway because there may be a certain aspect of the product that your customers like. They'll be delighted if you can integrate that feature into a new product or service.
10. "If you couldn't use your favorite product from us, what would you miss the most about it?"
This question pairs well with the one above because it frames the customer's favorite product from a different point of view. Instead of describing why they love a particular product, the customer can explain what they'd be missing if they didn't have it at all. This type of question uncovers "fear of loss," which can be a very different motivating factor than "hope for gain."
11. "What word best describes your experience using our product?"
Your marketing team will love this question. A single word or a short phrase can easily sum up your customers’ emotions when they experience your company, product, or brand. Those emotions can be translated into relatable marketing campaigns that use your customers’ exact language.
If the responses reveal negative emotions, it's likely that your entire customer service team can relate to that pain point. Rather than calling it "a bug in the system," you can describe the problem as a "frustrating roadblock" to keep their experience at the forefront of the solution.
12. "What's the primary reason for canceling your account?"
Finding out why customers are unhappy with your product or service is key to decreasing your churn rate . If you don't understand why people leave your brand, it's hard to make effective changes to prevent future turnover. Or worse, you might alter your product or service in a way that increases your churn rate, causing you to lose customers who were once loyal supporters.
13. "How satisfied are you with our customer support?"
It's worth asking customers how happy they are with your support or service team. After all, an excellent product doesn't always guarantee that customers will stay loyal to your brand. Research shows that one in six customers will leave a brand they love after just one poor service experience.
14. "Did we answer all of your questions and concerns?"
This is a good question to ask after a service experience. It shows how thorough your support team is and whether they're prioritizing speed too much over quality. If customers still have questions and concerns after a service interaction, your support team is focusing too much on closing tickets and not enough on meeting customer needs .
15. "How can we be more helpful?"
Sometimes it's easier to be direct and simply ask customers what else you can do to help them. This shows a genuine interest in your buyers' goals which helps your brand foster meaningful relationships with its customer base. The more you can show that you sincerely care about your customers' problems, the more they'll open up to you and be honest about how you can help them.
16. What additional features would you like to see in this product?
With this question, your team can get inspiration for the company's next product launch. Think of the responses as a wish list from your customers. You can discover what features are most valuable to them and whether they already exist within a competitor's product.
Incorporating every feature suggestion is nearly impossible, but it's a convenient way to build a backlog of ideas that can inspire future product releases.
17. "Are we meeting your expectations?"
This is a really important question to ask because customers won't always tell you when they're unhappy with your service. Not every customer will ask to speak with a manager when they're unhappy with your business. In fact, most will quietly move on to a competitor rather than broadcast their unhappiness to your company. To prevent this type of customer churn, you need to be proactive and ask customers if your brand is meeting their expectations.
18. "How satisfied are you with your experience?"
This question asks the customer to summarize their experience with your business. It gives you a snapshot of how the customer is feeling in that moment and their perception of your brand. Asking this question at the right stage in the customer's journey can tell you a lot about what your company is doing well and where you can stand to improve.
Next, let's dig into some tips for creating your own questionnaire.
Start with templates as a foundation. Know your question types. Keep it brief when possible. Choose a simple visual design. Use a clear research process. Create questions with straightforward, unbiased language. Make sure every question is important. Ask one question at a time. Order your questions logically. Consider your target audience. Test your questionnaire.
1. Use questionnaire templates.
Rather than build a questionnaire from scratch, consider using questionnaire templates to get started. HubSpot's collection of customer-facing questionnaire templates can help you quickly build and send a questionnaire to your clients and analyze the results right on Google Drive.
Vrnda LeValley , customer training manager at HubSpot, recommends starting with an alignment question like, "Does this class meet your expectations?" because it gives more context to any positive or negative scores that follow. She continues, "If it didn't meet expectations, then there will potentially be negative responses across the board (as well as the reverse)."
3. Keep it brief, when possible.
Most questionnaires don't need to be longer than a page. For routine customer satisfaction surveys, it's unnecessary to ask 50 slightly varied questions about a customer's experience when those questions could be combined into 10 solid questions.
The shorter your questionnaire is, the more likely a customer will complete it. Plus a shorter questionnaire means less data for your team to collect and analyze. Based on the feedback, it will be a lot easier for you to get the information you need to make the necessary changes in your organization and products.
4. Choose a simple visual design.
There's no need to make your questionnaire a stunning work of art. As long as it's clear and concise, it will be attractive to customers. When asking questions that are important to furthering your company, it's best to keep things simple. Select a font that’s common and easy to read, like Helvetica or Arial. Use a text size that customers of all abilities can navigate.
A questionnaire is most effective when all the questions are visible on a single screen. The layout is important. If a questionnaire is even remotely difficult to navigate, your response rate could suffer. Make sure that buttons and checkboxes are easy to click and that questions are visible on both computer and mobile screens.
5. Use a clear research process.
Before planning questions for your questionnaire, you'll need to have a definite direction for it. A questionnaire is only effective if the results answer an overarching research question. After all, the research process is an important part of the survey, and a questionnaire is a tool that's used within the process.
In your research process, you should first come up with a research question. What are you trying to find out? What's the point of this questionnaire? Keep this in mind throughout the process.
After coming up with a research question, it's a good idea to have a hypothesis. What do you predict the results will be for your questionnaire? This can be structured in a simple "If … then …" format. A structured experiment — yes, your questionnaire is a type of experiment — will confirm that you're only collecting and analyzing data necessary to answer your research question. Then, you can move forward with your survey .
6. Create questions with straightforward, unbiased language.
When crafting your questions, it's important to structure them to get the point across. You don't want any confusion for your customers because this may influence their answers. Instead, use clear language. Don't use unnecessary jargon, and use simple terms in favor of longer-winded ones.
You may risk the reliability of your data if you try to combine two questions. Rather than asking, "How was your experience shopping with us, and would you recommend us to others?" separate it into two separate questions. Customers will be clear on your question and choose a response most appropriate for each one.
You should always keep the language in your questions unbiased. You never want to sway customers one way or another because this will cause your data to be skewed. Instead of asking, "Some might say that we create the best software products in the world. Would you agree or disagree?" it may be better to ask, "How would you rate our software products on a scale of 1 to 10?" This removes any bias and confirms that all the responses are valid.
7. Ask only the most important questions.
When creating your questionnaire, keep in mind that time is one of the most valuable commodities for customers. Most aren't going to sit through a 50-question survey, especially when they're being asked about products or services they didn't use. Even if they do complete it, most of these will be half-hearted responses from fatigued customers who simply want to be finished with it.
If your questionnaire has five or 55 questions, make sure each has a specific purpose. Individually, they should be aimed at collecting certain pieces of information that reveal new insights into different aspects of your business. If your questions are irrelevant or seem out of place, your customers will be easily derailed by the survey. And, once the customer has lost interest, it'll be difficult to regain their focus.
8. Ask one question at a time.
Since every question has a purpose, ask them one at a time. This lets the customer focus and encourages them to share a thoughtful response. This is particularly important for open-ended questions where customers need to describe an experience or opinion.
By grouping questions together, you risk overwhelming busy customers who don't have time for a long survey. They may think you're asking them too much, or they might see your questionnaire as a daunting task. You want your survey to appear as painless as possible. Keeping your questions separated will make it more user-friendly.
9. Order your questions logically.
A good questionnaire is like a good book. The beginning questions should lay the framework, the middle ones should cut to the core issues, and the final questions should tie up all loose ends. This flow keeps customers engaged throughout the entire survey.
When creating your questionnaire, start with the most basic questions about demographics. You can use this information to segment your customer base and create different buyer personas.
Next, add in your product and services questions. These are the ones that offer insights into common customer roadblocks and where you can improve your business's offerings. Questions like these guide your product development and marketing teams looking for new ways to enhance the customer experience.
Finally, you should conclude your questionnaire with open-ended questions to understand the customer journey. These questions let customers voice their opinions and point out specific experiences they've had with your brand.
10. Consider your target audience.
Whenever you collect customer feedback, you need to keep in mind the goals and needs of your target audience. After all, the participants in this questionnaire are your active customers. Your questions should be geared toward the interests and experiences they've already had with your company.
You can even create multiple surveys that target different buyer personas. For example, if you have a subscription-based pricing model, you can personalize your questionnaire for each type of subscription your company offers.
11. Test your questionnaire.
Once your questionnaire is complete, it's important to test it. If you don't, you may end up asking the wrong questions and collecting irrelevant or inaccurate information. Start by giving your employees the questionnaire to test, then send it to small groups of customers and analyze the results. If you're gathering the data you're looking for, then you should release the questionnaire to all of your customers.
How Questionnaires Can Benefit Your Customer Service Strategy
Whether you have one customer or 1000 customers, their opinions matter when it comes to the success of your business. Their satisfaction with your offerings can reveal how well or how poorly your customer service strategy and business are meeting their needs. A questionnaire is one of the most powerful, cost-effective tools to uncover what your customers think about your business. When analyzed properly, it can inform your product and service launches.
Use the free questionnaire templates, examples, and best practices in this guide to conduct your next customer feedback survey.
Now that you know the slight difference between a survey and a questionnaire, it’s time to put it into practice with your products or services. Remember, a good survey and questionnaire always start with a purpose. But, a great survey and questionnaire give data that you can use to help companies increase the way customers respond to their products or services because of the questions.
Net Promoter, Net Promoter System, Net Promoter Score, NPS, and the NPS-related emoticons are registered trademarks of Bain & Company, Inc., Fred Reichheld, and Satmetrix Systems, Inc.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in July 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

Nonresponse Bias: What to Avoid When Creating Surveys

How to Make a Survey with a QR Code

50 Catchy Referral Slogans & How to Write Your Own
![a research questionnaire sample How Automated Phone Surveys Work [+Tips and Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/phone-survey.webp)
How Automated Phone Surveys Work [+Tips and Examples]

Online Panels: What They Are & How to Use Them Effectively

The Complete Guide to Survey Logic (+Expert Tips)

Focus Group vs. Survey: Which One Should You Use?
![a research questionnaire sample Leading Questions: What They Are & Why They Matter [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/leading-questions-hero.webp)
Leading Questions: What They Are & Why They Matter [+ Examples]

What are Survey Sample Sizes & How to Find Your Sample Size

24 Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Survey Questions to Ask Your Employees
5 free templates for learning more about your customers and respondents.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples
Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 10 October 2022.
A questionnaire is a list of questions or items used to gather data from respondents about their attitudes, experiences, or opinions. Questionnaires can be used to collect quantitative and/or qualitative information.
Questionnaires are commonly used in market research as well as in the social and health sciences. For example, a company may ask for feedback about a recent customer service experience, or psychology researchers may investigate health risk perceptions using questionnaires.
Table of contents
Questionnaires vs surveys, questionnaire methods, open-ended vs closed-ended questions, question wording, question order, step-by-step guide to design, frequently asked questions about questionnaire design.
A survey is a research method where you collect and analyse data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.
Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives, placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
But designing a questionnaire is only one component of survey research. Survey research also involves defining the population you’re interested in, choosing an appropriate sampling method , administering questionnaires, data cleaning and analysis, and interpretation.
Sampling is important in survey research because you’ll often aim to generalise your results to the population. Gather data from a sample that represents the range of views in the population for externally valid results. There will always be some differences between the population and the sample, but minimising these will help you avoid sampling bias .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Questionnaires can be self-administered or researcher-administered . Self-administered questionnaires are more common because they are easy to implement and inexpensive, but researcher-administered questionnaires allow deeper insights.
Self-administered questionnaires
Self-administered questionnaires can be delivered online or in paper-and-pen formats, in person or by post. All questions are standardised so that all respondents receive the same questions with identical wording.
Self-administered questionnaires can be:
- Cost-effective
- Easy to administer for small and large groups
- Anonymous and suitable for sensitive topics
But they may also be:
- Unsuitable for people with limited literacy or verbal skills
- Susceptible to a nonreponse bias (most people invited may not complete the questionnaire)
- Biased towards people who volunteer because impersonal survey requests often go ignored
Researcher-administered questionnaires
Researcher-administered questionnaires are interviews that take place by phone, in person, or online between researchers and respondents.
Researcher-administered questionnaires can:
- Help you ensure the respondents are representative of your target audience
- Allow clarifications of ambiguous or unclear questions and answers
- Have high response rates because it’s harder to refuse an interview when personal attention is given to respondents
But researcher-administered questionnaires can be limiting in terms of resources. They are:
- Costly and time-consuming to perform
- More difficult to analyse if you have qualitative responses
- Likely to contain experimenter bias or demand characteristics
- Likely to encourage social desirability bias in responses because of a lack of anonymity
Your questionnaire can include open-ended or closed-ended questions, or a combination of both.
Using closed-ended questions limits your responses, while open-ended questions enable a broad range of answers. You’ll need to balance these considerations with your available time and resources.
Closed-ended questions
Closed-ended, or restricted-choice, questions offer respondents a fixed set of choices to select from. Closed-ended questions are best for collecting data on categorical or quantitative variables.
Categorical variables can be nominal or ordinal. Quantitative variables can be interval or ratio. Understanding the type of variable and level of measurement means you can perform appropriate statistical analyses for generalisable results.
Examples of closed-ended questions for different variables
Nominal variables include categories that can’t be ranked, such as race or ethnicity. This includes binary or dichotomous categories.
It’s best to include categories that cover all possible answers and are mutually exclusive. There should be no overlap between response items.
In binary or dichotomous questions, you’ll give respondents only two options to choose from.
White Black or African American American Indian or Alaska Native Asian Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander
Ordinal variables include categories that can be ranked. Consider how wide or narrow a range you’ll include in your response items, and their relevance to your respondents.
Likert-type questions collect ordinal data using rating scales with five or seven points.
When you have four or more Likert-type questions, you can treat the composite data as quantitative data on an interval scale . Intelligence tests, psychological scales, and personality inventories use multiple Likert-type questions to collect interval data.
With interval or ratio data, you can apply strong statistical hypothesis tests to address your research aims.
Pros and cons of closed-ended questions
Well-designed closed-ended questions are easy to understand and can be answered quickly. However, you might still miss important answers that are relevant to respondents. An incomplete set of response items may force some respondents to pick the closest alternative to their true answer. These types of questions may also miss out on valuable detail.
To solve these problems, you can make questions partially closed-ended, and include an open-ended option where respondents can fill in their own answer.
Open-ended questions
Open-ended, or long-form, questions allow respondents to give answers in their own words. Because there are no restrictions on their choices, respondents can answer in ways that researchers may not have otherwise considered. For example, respondents may want to answer ‘multiracial’ for the question on race rather than selecting from a restricted list.
- How do you feel about open science?
- How would you describe your personality?
- In your opinion, what is the biggest obstacle to productivity in remote work?
Open-ended questions have a few downsides.
They require more time and effort from respondents, which may deter them from completing the questionnaire.
For researchers, understanding and summarising responses to these questions can take a lot of time and resources. You’ll need to develop a systematic coding scheme to categorise answers, and you may also need to involve other researchers in data analysis for high reliability .
Question wording can influence your respondents’ answers, especially if the language is unclear, ambiguous, or biased. Good questions need to be understood by all respondents in the same way ( reliable ) and measure exactly what you’re interested in ( valid ).
Use clear language
You should design questions with your target audience in mind. Consider their familiarity with your questionnaire topics and language and tailor your questions to them.
For readability and clarity, avoid jargon or overly complex language. Don’t use double negatives because they can be harder to understand.
Use balanced framing
Respondents often answer in different ways depending on the question framing. Positive frames are interpreted as more neutral than negative frames and may encourage more socially desirable answers.
Use a mix of both positive and negative frames to avoid bias , and ensure that your question wording is balanced wherever possible.
Unbalanced questions focus on only one side of an argument. Respondents may be less likely to oppose the question if it is framed in a particular direction. It’s best practice to provide a counterargument within the question as well.
Avoid leading questions
Leading questions guide respondents towards answering in specific ways, even if that’s not how they truly feel, by explicitly or implicitly providing them with extra information.
It’s best to keep your questions short and specific to your topic of interest.
- The average daily work commute in the US takes 54.2 minutes and costs $29 per day. Since 2020, working from home has saved many employees time and money. Do you favour flexible work-from-home policies even after it’s safe to return to offices?
- Experts agree that a well-balanced diet provides sufficient vitamins and minerals, and multivitamins and supplements are not necessary or effective. Do you agree or disagree that multivitamins are helpful for balanced nutrition?
Keep your questions focused
Ask about only one idea at a time and avoid double-barrelled questions. Double-barrelled questions ask about more than one item at a time, which can confuse respondents.
This question could be difficult to answer for respondents who feel strongly about the right to clean drinking water but not high-speed internet. They might only answer about the topic they feel passionate about or provide a neutral answer instead – but neither of these options capture their true answers.
Instead, you should ask two separate questions to gauge respondents’ opinions.
Strongly Agree Agree Undecided Disagree Strongly Disagree
Do you agree or disagree that the government should be responsible for providing high-speed internet to everyone?
You can organise the questions logically, with a clear progression from simple to complex. Alternatively, you can randomise the question order between respondents.
Logical flow
Using a logical flow to your question order means starting with simple questions, such as behavioural or opinion questions, and ending with more complex, sensitive, or controversial questions.
The question order that you use can significantly affect the responses by priming them in specific directions. Question order effects, or context effects, occur when earlier questions influence the responses to later questions, reducing the validity of your questionnaire.
While demographic questions are usually unaffected by order effects, questions about opinions and attitudes are more susceptible to them.
- How knowledgeable are you about Joe Biden’s executive orders in his first 100 days?
- Are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the way Joe Biden is managing the economy?
- Do you approve or disapprove of the way Joe Biden is handling his job as president?
It’s important to minimise order effects because they can be a source of systematic error or bias in your study.
Randomisation
Randomisation involves presenting individual respondents with the same questionnaire but with different question orders.
When you use randomisation, order effects will be minimised in your dataset. But a randomised order may also make it harder for respondents to process your questionnaire. Some questions may need more cognitive effort, while others are easier to answer, so a random order could require more time or mental capacity for respondents to switch between questions.
Follow this step-by-step guide to design your questionnaire.
Step 1: Define your goals and objectives
The first step of designing a questionnaire is determining your aims.
- What topics or experiences are you studying?
- What specifically do you want to find out?
- Is a self-report questionnaire an appropriate tool for investigating this topic?
Once you’ve specified your research aims, you can operationalise your variables of interest into questionnaire items. Operationalising concepts means turning them from abstract ideas into concrete measurements. Every question needs to address a defined need and have a clear purpose.
Step 2: Use questions that are suitable for your sample
Create appropriate questions by taking the perspective of your respondents. Consider their language proficiency and available time and energy when designing your questionnaire.
- Are the respondents familiar with the language and terms used in your questions?
- Would any of the questions insult, confuse, or embarrass them?
- Do the response items for any closed-ended questions capture all possible answers?
- Are the response items mutually exclusive?
- Do the respondents have time to respond to open-ended questions?
Consider all possible options for responses to closed-ended questions. From a respondent’s perspective, a lack of response options reflecting their point of view or true answer may make them feel alienated or excluded. In turn, they’ll become disengaged or inattentive to the rest of the questionnaire.
Step 3: Decide on your questionnaire length and question order
Once you have your questions, make sure that the length and order of your questions are appropriate for your sample.
If respondents are not being incentivised or compensated, keep your questionnaire short and easy to answer. Otherwise, your sample may be biased with only highly motivated respondents completing the questionnaire.
Decide on your question order based on your aims and resources. Use a logical flow if your respondents have limited time or if you cannot randomise questions. Randomising questions helps you avoid bias, but it can take more complex statistical analysis to interpret your data.
Step 4: Pretest your questionnaire
When you have a complete list of questions, you’ll need to pretest it to make sure what you’re asking is always clear and unambiguous. Pretesting helps you catch any errors or points of confusion before performing your study.
Ask friends, classmates, or members of your target audience to complete your questionnaire using the same method you’ll use for your research. Find out if any questions were particularly difficult to answer or if the directions were unclear or inconsistent, and make changes as necessary.
If you have the resources, running a pilot study will help you test the validity and reliability of your questionnaire. A pilot study is a practice run of the full study, and it includes sampling, data collection , and analysis.
You can find out whether your procedures are unfeasible or susceptible to bias and make changes in time, but you can’t test a hypothesis with this type of study because it’s usually statistically underpowered .
A questionnaire is a data collection tool or instrument, while a survey is an overarching research method that involves collecting and analysing data from people using questionnaires.
Closed-ended, or restricted-choice, questions offer respondents a fixed set of choices to select from. These questions are easier to answer quickly.
Open-ended or long-form questions allow respondents to answer in their own words. Because there are no restrictions on their choices, respondents can answer in ways that researchers may not have otherwise considered.
A Likert scale is a rating scale that quantitatively assesses opinions, attitudes, or behaviours. It is made up of four or more questions that measure a single attitude or trait when response scores are combined.
To use a Likert scale in a survey , you present participants with Likert-type questions or statements, and a continuum of items, usually with five or seven possible responses, to capture their degree of agreement.
You can organise the questions logically, with a clear progression from simple to complex, or randomly between respondents. A logical flow helps respondents process the questionnaire easier and quicker, but it may lead to bias. Randomisation can minimise the bias from order effects.
Questionnaires can be self-administered or researcher-administered.
Researcher-administered questionnaires are interviews that take place by phone, in person, or online between researchers and respondents. You can gain deeper insights by clarifying questions for respondents or asking follow-up questions.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2022, October 10). Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 31 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/questionnaire-design/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, doing survey research | a step-by-step guide & examples, what is a likert scale | guide & examples, reliability vs validity in research | differences, types & examples.
- Open access
- Published: 26 May 2024
The sense of coherence scale: psychometric properties in a representative sample of the Czech adult population
- Martin Tušl 1 ,
- Ivana Šípová 2 ,
- Martin Máčel 2 ,
- Kristýna Cetkovská 2 &
- Georg F. Bauer 1
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 293 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
279 Accesses
Metrics details
Sense of coherence (SOC) is a personal resource that reflects the extent to which one perceives the world as comprehensible, manageable, and meaningful. Decades of empirical research consistently show that SOC is an important protective resource for health and well-being. Despite the extensive use of the 13-item measure of SOC, there remains uncertainty regarding its factorial structure. Additionally, a valid and reliable Czech version of the scale is lacking. Therefore, the present study aims to examine the psychometric properties of the SOC-13 scale in a representative sample of Czech adults.
An online survey was completed by 498 Czech adults (18–86 years old) between November 2021 and December 2021. We used confirmatory factor analysis to examine the factorial structure of the scale. Further, we examined the variations in SOC based on age and gender, and we tested the criterion validity of the scale using the short form of the Mental Health Continuum (MHC) scale and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) scale as mental health outcomes.
SOC-13 showed an acceptable one- and three-factor fit only with specified residual covariance between items 2 and 3. We tested alternative short versions by systematically removing poorly performing items. The fit significantly improved for all shorter versions with SOC-9 having the best psychometric properties with a clear one-factorialstructure. We found that SOC increases with age and males score higher than females. SOC showed a moderately strong positive correlation with MHC, and a moderately strong negative correlation with GAD. These findings were similar for all tested versions supporting the criterion validity of the SOC scale.
Our findings suggest that shortened versions of the SOC-13 scale have better psychometric properties than the original 13-item version in the Czech adult population. Particularly, SOC-9 emerges as a viable alternative, showing comparable reliability and validity as the 13-item version and a clear one-factorial structure in our sample.
Peer Review reports
Sense of coherence (SOC) was introduced by the sociologist Aaron Antonovsky as the main pillar of his salutogenic theory, which explains how individuals cope with stressors and stay healthy even in case of adverse life situations [ 1 ]. SOC is a personal resource defined as a global orientation to life determining the degree to which one perceives life as comprehensible, manageable, and meaningful [ 2 ]. A strong SOC enables individuals to cope with stressors and manage tension, thus moving to the ease-end of the ease/disease continuum [ 2 , 3 ]. A person’s strength of SOC can be measured with the Orientation to Life Questionnaire commonly referred to as the SOC scale [ 4 ]. The original version is composed of 29 items (SOC-29) and Antonovsky recommended 13 items for the short version of the scale (SOC-13). To date, both versions of the scale have been used across diverse populations in at least 51 languages and 51 countries [ 5 ]. Studies have consistently shown that SOC correlates strongly with different health and well-being outcomes [ 6 , 7 ] and quality of life measures [ 8 ]. In the context of the recent COVID-19 pandemic, SOC has been identified as the most important protective resource in relation to mental health [ 9 ]. Regarding individual differences, SOC has been shown to strengthen over the life course [ 10 ], males usually score higher than females [ 11 ], and some studies indicate that SOC increases with the level of education [ 12 ]. However, despite the extensive evidence on the criterion validity of the scale, there is still a lack of clarity about its underlying factor structure and dimensionality.
The SOC scale was conceptualized as unidimensional suggesting that SOC in its totality, as a global orientation, influences the movement along the ease/dis-ease continuum [ 2 ]. However, the structure of the scale is rather multidimensional as each item is composed of multiple elements. Antonovsky developed the scale according to the facet theory [ 13 , 14 ] which assumes that social phenomena are best understood when they are seen as multidimensional. Facet theory involves the construction of a mapping sentence which consists of the facets and the sentence linking the facets together [ 15 ]. The SOC scale is composed of five facets: (i) the response mode (comprehensibility, manageability, meaningfulness); (ii) the modality of stimulus (instrumental, cognitive, affective), (iii) its source (internal, external, both), (iv) the nature of the demand it poses (concrete, diffuse, affective), (v) and its time reference (past, present, future). For example, item 3 “Has it happened that people whom you counted on disappointed you?” is a manageability item that can be described with the mapping sentence as follows: "Respondent X responds to an instrumental stimulus (“counted on”), which originated from the external environment (“people”), and which poses a diffuse demand (“disappointed”) being in the past (“has it happened”)." Although each item can be categorized along the SOC component comprehensibility, manageability, or meaningfulness, the items also share elements from the other four facets with items within the same, but also within the other SOC components (see 2, Chap. 4 for details). As Antonovsky states [ 2 , p. 87]: “The SOC facet pulls the items apart; the other facets push them together.”
Thus, the multi-facet nature of the scale can create difficulties in identifying the three theorized SOC components using statistical methods such as factor analysis. In fact, both the unidimensional and the three-dimensional SOC-13 rarely yield an acceptable fit without specifying residual covariance between single items (see 5 for an overview). This has been further exemplified in a recent study which examined the dimensionality of SOC-13 using a network perspective. The authors were unable to identify a clear structure and concluded that SOC is composed of multiple elements that are deeply linked and not necessarily distinct [ 16 ]. As a result, several researchers have suggested modified [ 17 ] or abbreviated versions of the scale, such as SOC-12 [ 18 , 19 ], SOC-11 [ 20 , 21 , 22 ], or SOC-9 [ 23 ], which have empirically shown a better factorial structure. This prompts the general question, whether an alternative short version should be preferred over the 13-item version. In fact, looking into the original literature [ 2 ], it is not clear why Antonovsky chose specifically these 13 items from the 29-item scale. We will address this question with the Czech version of the SOC-13 scale.
Salutogenesis in the Czech Republic
Salutogenesis and the SOC scale were introduced to the Czech audience in the early 90s by a Czech psychologist Jaro Křivohlavý. His work included the Czech translation of the SOC-29 scale [ 24 ] and the application of the concept in research on resilience [ 25 ] and behavioral medicine [ 26 ]. Unfortunately, the early Czech translation of the scale by Křivohlavý is not available electronically, nor could we locate it in library repositories. Later studies examined SOC-29 in relation to resilience [ 27 , 28 ] and self-reported health [ 29 , 30 ], however, it is not clear which translation of SOC-29 the authors used in the studies. A new Czech translation of the SOC-13 scale has recently been developed by the authors of this paper to examine the protective role of SOC for mental health during the COVID-19 crisis [ 31 ]. In line with earlier studies [ 9 ], SOC was identified as an important protective resource for individual mental health. This recent Czech translation of the SOC-13 scale [ 31 ] is the subject of the present study.
Present study
Our study aims to investigate the psychometric properties of the SOC-13 scale within a representative sample of the Czech adult population. Specifically, we will examine the factorial structure of the SOC-13 scale to understand its underlying dimensions and evaluate its internal consistency to ensure its reliability as a measure of SOC. Additionally, we aim to assess criterion validity by examining the scale’s association with established measures of positive and negative mental health outcomes - the Mental Health Continuum [ 32 ] and Generalized Anxiety Disorder [ 33 ]. We anticipate a strong correlation between these measures and the SOC construct [ 6 ]. Furthermore, we will investigate demographic variations in SOC, considering factors such as age, gender, and education. Understanding these variations will provide valuable insights into the applicability of the SOC-13 scale across different population subgroups. Finally, we will explore whether alternative short versions of the SOC scale should be preferred over the 13-item version. This analysis will help determine the most efficient version of the SOC scale for future research.
Study design and data collection
Our study design is a cross-sectional online survey of the Czech adult population. We contracted a professional agency DataCollect ( www.datacollect.cz ) to collect data from a representative sample for our study. Participants were recruited using quota sampling. The inclusion criteria were: being of adult age (18+), speaking the Czech language, and having permanent residence in the Czech Republic. Exclusion criteria related to study participation were predetermined to minimize the risk of biases in the collected data. The order of items in all measures was randomized and we implemented two attention checks in the questionnaire (e.g. “Please, choose option number 2”). Participants were excluded if they did not finish the survey, completed the survey in less than five minutes, did not pass the attention checks, or gave the same answer to more than 10 consecutive items. Data collection was conducted via the online platform Survey Monkey between November 2021 and December 2021.
Translation into the Czech language
Translation of the SOC scale was carried out by the authors of the paper with the help of a qualified translator. We followed the translation guidelines provided on the website of the Society for Research and Theory on Salutogenesis ( www.stars-society.org ), where the original English version of the SOC scale is available for download. Two translations were conducted independently, then compared and checked for differences. Based on this comparison, the agreed version of the scale was back translated into English by a Czech-English translator. The final version was checked for resemblance to the original version in content and in form. Although we used only the short version of the scale in our study (i.e., SOC-13), the translation included the full SOC-29 scale. The Czech translation of the full SOC scale is available as supplementary material.
Sense of coherence. We used the short version of the Orientation to Life Questionnaire [ 3 ] to assess SOC. The measure consists of 13 items evaluated on a 7-point Likert-type scale with different response options. Five items measure comprehensibility (e.g., “Does it happen that you experience feelings that you would rather not have to endure?”), four items measure manageability (e.g., “Has it happened that people whom you counted on disappointed you?”), and four items measure meaningfulness (e.g., “Do you have the feeling that you really don’t care about what is going on around you?”). In our sample, Cronbach’s alpha for the full scale was α = 0.88, for comprehensibility α = 0.76, manageability α = 0.72, and meaningfulness α = 0.70.
Mental health continuum - short form (MHC-SF; 32). This scale consists of 14 items that capture three dimensions of well-being: (i) emotional (e.g. “During the past month, how often did you feel interested in life?”); (ii) social (e.g. “During the past month, how often did you feel that the way our society works makes sense to you?”); (iii) psychological (e.g. “During the past month, how often did you feel confident to think or express your own ideas and opinions?”). The items assess the experiences the participants had over the past two weeks, the response options ranged from 1 (never) to 6 (every day). Internal consistency of the scale was α = 0.90.
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD; 33). The scale consists of seven items that measure symptoms of anxiety over the past two weeks. Sample items include, e.g. “Over the past two weeks, how often have you been bothered by the following problems?” (i) “feeling nervous, anxious, or on edge”, (ii) “worrying too much about different things”, (iii) “becoming easily annoyed or irritable”. The response options ranged from 0 (not at all) to 3 (almost every day). Internal consistency of the scale was α = 0.92.
Sociodemographic characteristics included age, gender, and level of education (i.e., primary/vocational, secondary, tertiary).
Analytical procedure
Data analysis was conducted in R [ 34 ]. For confirmatory factor analysis, we used the cfa function of the lavaan package 0.6–16 [ 35 ]. We compared a one-factor model of SOC-13 to a correlated three-factor model (correlated latent factors comprehensibility, manageability, and meaningfulness) and a bi-factor model (general SOC dimension and specific dimensions comprehensibility, manageability, meaningfulness). Based on the empirical findings we further assessed the fit of alternative shorter versions of the SOC scale. We assessed the model fit using the comparative-fit index (CFI), Tucker-Lewis index (TLI), root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA), and standardized root mean square residual (SRMR) with the conventional cut-off values. The goodness-of-fit values for CFI and TLI surpassing 0.90 indicate an acceptable fit and exceeding 0.95 a good fit [ 36 ]. A value under 0.08 for RMSEA and SRMR indicates a good fit [ 37 ]. Nested models were compared using chi-square difference tests and the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC). Models with lower BIC values should be preferred over models with higher BIC values [ 38 ]. All models were fitted using maximum likelihood estimation.
Further, we used the cor function of the stats package 4.3.2 [ 34 ] for Pearson correlation analysis to explore the association between SOC-13 and age, the t.test function of the same package for between groups t-test for differences based on gender, and the aov function with posthoc tests of the same package for one-way between-subjects ANOVA to test for differences based on level of education. To examine the criterion validity of the scale, we used the cor function for Pearson correlation analysis to examine the associations between SOC-13, MHC-SF, and GAD. We conducted the same analyses for the alternative short versions of the scale.
Participants
The median survey completion time was 11 min. In total, 676 participants started the survey and 557 completed it. Of those, 56 were excluded due to exclusion criteria. One additional respondent was excluded because of dubious responses on demographic items (e.g., 100 years old and a student), and two respondents were excluded for not meeting the inclusion criteria (under 18 years old). The final sample included N = 498 participants. Of those, 53.4% were female, the average age was 49 years ( SD = 16.6; range = 18–86), 43% had completed primary, 35% secondary, and 22% tertiary education. The sample is a good representation of the Czech adult population Footnote 1 with regard to gender (51% females), age ( M = 50 years), and education level (44% primary, 33% secondary, 18% tertiary). Representativeness was tested using chi-squared test which yielded non-significant results for all domains.
Descriptive statistics
In Table 1 , we present an inter-item correlation matrix along with skewness, kurtosis, means and standard deviations of single items for SOC-13. Item correlations ranged from r = 0.07 (items 2 and 4) to r = 0.67 (items 8 and 9). Strong and moderately strong correlations were found also across the three SOC dimensions (e.g., r = 0.77 comprehensibility and manageability).
- Confirmatory factor analysis
A one-factor model showed inadequate fit to the data [χ2(65) = 338.2, CFI = 0.889, TLI = 0.867, RMSEA = 0.092, SRMR = 0.062]. Based on existing evidence [ 6 ], we specified residual covariance between items 2 and 3 and tested a modified one-factor model. The model showed an acceptable fit to the data [χ2(64) = 242.6, CFI = 0.927, TLI = 0.911, RMSEA = 0.075, SRMR = 0.050], and it was superior to the one-factor model (Δχ2 = 95.5, Δ df = 1, p < 0.001).
A correlated three-factor model showed an acceptable fit considering CFI and SRMR [χ2(63) = 286.6, CFI = 0.909, TLI = 0.885, RMSEA = 0.085, SRMR = 0.058]. The model was superior to the one-factor model (Δχ2 = 51.5, Δ df = 2, p < 0.001), however, it was inferior to the modified one-factor model (ΔBIC = -56). We further tested a modified three-factor model with residual covariance between items 2 and 3 which showed an acceptable fit to the data based on CFI and TLI and a good fit based on RMSEA and SRMR [χ2(62) = 191.7, CFI = 0.947, TLI = 0.932, RMSEA = 0.066, SRMR = 0.046]. The model was superior to the three-factor model (Δχ2 = 97.1, Δ df = 1, p < 0.001) as well as to the modified one-factor model (Δχ2 = 50.9, Δ df = 3, p < 0.001). See Fig. 1 for a detailed illustration of the model.
Finally, we tested a bi-factor model with one general SOC factor and three specific factors (comprehensibility, manageability, meaningfulness), however, the model was not identified.
Correlated three-factor model of SOC-13 with residual covariance between item 2 and item 3
Alternative short versions of the SOC scale
We further tested the fit of alternative shorter versions of the SOC scale by systematically removing poorly performing items. In SOC-12, item 2 was excluded (“Has it happened in the past that you were surprised by the behavior of people whom you thought you knew well?”). This item measures comprehensibility, hence SOC-12 has even distribution of items for each dimension (i.e., comprehensibility, manageability, meaningfulness). Item 2 has previously been identified as problematic [ 6 ] and also in our sample it did not perform well in any of the fitted SOC-13 models (i.e., low factor loading and explained variance). A one-factor SOC-12 model showed an acceptable fit to the data based on CFI and TLI and a good fit based on RMSEA and SRMR [χ2(54) = 221.1, CFI = 0.927, RMSEA = 0.079, SRMR = 0.048]. A correlated three-factor model showed an acceptable fit based on CFI and TLI and a good fit based on RMSEA and SRMR [χ2(52) = 171.1, CFI = 0.948, TLI = 0.932, RMSEA = 0.069 SRMR = 0.043]. The model was superior to the one-factor model (Δχ2 = 50, Δ df = 3, p < 0.001). Bi-factor model was not identified.
In SOC-11, we removed item 3 (“Has it happened that people whom you counted on disappointed you?”), which measures manageability. The item had the lowest factor loading and the lowest explained variance in the one-factor SOC-12. A one-factor SOC-11 model showed a good fit to the data [χ2 (44) = 138.5, CFI = 0.955, TLI = 0.944, RMSEA = 0.066, SRMR = 0.038]. A correlated three-factor model was identified but not acceptable due to covariance between comprehensibility and manageability higher than 1 (i.e., Heywood case; 39).
In SOC-10, we removed item 1 (“Do you have the feeling that you don’t really care about what goes on around you?”), which measures meaningfulness. The item had the lowest factor loading and the lowest explained variance in one-factor SOC-11. A one-factor SOC-10 model showed a good fit to the data [χ2 (35) = 126.6, CFI = 0.956, TLI = 0.943, RMSEA = 0.072, SRMR = 0.039]. As in the case of SOC-11, a correlated three-factor model was identified but not acceptable due to covariance between comprehensibility and manageability higher than 1.
Finally, in SOC-9, we removed item 11 (“When something happened, have you generally found that… you overestimated or underestimated its importance / you saw the things in the right proportion”), which measures comprehensibility. The item had the lowest factor loading and the lowest explained variance in one-factor SOC-10. SOC-9 has an even distribution of three items for each dimension. A one-factor model showed a good fit to the data [χ2 (27) = 105.6, CFI = 0.959, TLI = 0.946, RMSEA = 0.076, SRMR = 0.038]. As in the previous models, a correlated three-factor model was identified but not acceptable due to covariance between comprehensibility and manageability higher than 1. See Fig. 2 for an illustration of one-factor SOC-9 model. Detailed results of the confirmatory factor analysis are shown in Table 2 . In Table 3 , we present the items of the SOC-13 (and SOC-9) scale with details about their facet structure.
One-factor model of SOC-9
Differences by gender, age, and education
Correlation analysis indicated that SOC-13 increases with age ( r = 0.32, p < 0.001), this finding was identical for all alternative short versions of the SOC scale (see Table 2 ). Further, the results of the two-tailed t-test showed that males ( M = 4.8, SD = 1.08) had a significantly higher SOC-13 score [ t (497) = 3.06, p = 0.002, d = 0.27] than females ( M = 4.5, SD = 1.07). A one-way between-subjects ANOVA did not show any significant effect of level of education on SOC-13 score [F(2, 497) = 1.78, p = 0.169, η p 2 = 0.022]. These results were similar for all alternative short versions of the SOC scale.
Criterion validity
We found a moderately strong positive correlation ( r = 0.61, p < 0.001) between SOC-13 and the positive mental health measure MHC, and a moderately strong negative correlation between SOC-13 and the negative mental health measure GAD ( r = -0.68, p < 0.001). These findings were similar for all alternative short versions of the SOC scale (see Table 4 ).
Our study examined the psychometric properties of the SOC-13 scale and its alternative short versions SOC-12, SOC-11, SOC-10, and SOC-9 in a representative sample of the Czech adult population. In line with existing studies [ 40 ], we found that SOC increases with age and that males score higher than females. In contrast to some prior findings [ 12 ], we did not find any significant differences in SOC based on the level of education. Further, we tested criterion validity using both positive and negative mental health outcomes (i.e., MHC and GAD). SOC had a strong positive correlation with MHC and a strong negative correlation with GAD, thus adding to the evidence about the criterion validity of the scale [ 6 , 40 ].
Analysis of the factor structure showed that a one-factor SOC-13 had an inadequate fit to our data, however, an acceptable fit was achieved for a modified one-factor model with specified residual covariance between item 2 (“Has it happened in the past that you were surprised by the behavior of people whom you thought you knew well?”) and item 3 (“Has it happened that people whom you counted on disappointed you?”). A correlated three factor model with latent factors comprehensibility, manageability, and meaningfulness showed a better fit than the one factor-model. However, it was also necessary to specify residual covariance between item 2 and item 3 to reach an acceptable fit for all fit indices. A recent Slovenian study [ 41 ] found a similar result and several prior studies (see 6 for an overview) have noted that items 2 and 3 of the SOC-13 scale are problematic. Although the items pertain to different SOC dimensions (item 2 to comprehensibility, item 3 to manageability), multiple studies [e.g., 20 , 42 , 43 ] have reported moderately strong correlation between them and this is also the case in our study ( r = 0.5, p < 0.001). The two items aptly illustrate the facet theory behind the scale construction as the SOC component represents only one building block of each item. Although items 2 and 3 theoretically pertain to different SOC components, they share the same elements from the other four facets (i.e., modality, source, demand, and time) which is reflected in the similarity of their wording. Therefore, they will necessarily share residual variance and this needs to be specified to achieve a good model fit. Drageset and Haugan [ 18 ] explain this similarity in that the people whom we know well are usually the ones that we count on, and feeling disappointed and surprised by the behavior of people we know well is closely related. Therefore, it should be theoretically justifiable to specify residual covariance between item 2 and item 3 as a possible solution to improve the fit. As we could show in our sample, the model fit significantly improved for both one-factor and three-factor solutions.
In addition, we examined the fit of alternative short versions of the SOC scale by systematically removing single items that performed poorly. First, in line with previous studies [ 6 ], we addressed the issue of residual covariance in SOC-13 by removing item 2, examining the factor structure of SOC-12. The remaining 12 items were equally distributed within the three SOC components with four items per each component. Interestingly, a one-factor model reached an acceptable fit and the fit further improved for a correlated three-factor model with latent factors of comprehensibility, manageability, and meaningfulness. Although correlated three-factor models were superior to one-factor models, we observed extreme covariances between latent variables, especially in case of comprehensibility and manageability (cov = 0.98). This suggests that the SOC components are not empirically separable and that, indeed, SOC is rather a one-dimensional global orientation with multiple components that are dynamically interrelated as Antonovsky proposed [ 2 ]. This notion was supported in a recent study that explored the dimensionality of the scale using a network perspective [ 16 ]. Our examination of SOC-11, SOC-10 and SOC-9 provided further support for a one-factor structure of the scale. All shorter versions yielded a good one-dimensional fit, however, we could not identify a correlated three-factor model fit due to the Heywood case. This refers to the situation when a solution that otherwise is satisfactory produces communality greater than one explained by the latent factor, which implies that the residual variance of the variable is negative [ 39 ]. In our case, this was true for the latent factors comprehensibility and manageability. However, we demonstrated that we could attain a good one-dimensional fit for all alternative short versions of SOC, and, importantly, they all showed comparable reliability and validity metrics to their longer counterpart SOC-13. In particular, SOC-9 shows very good fit indices and it performs equally well in validity analyses as SOC-13. Given these findings and existing evidence [ 5 ], we propose that future investigations may consider utilizing the SOC-9 scale instead of the SOC-13. It is interesting to point out that the majority of items that were removed for the shorter versions of the scale are negatively worded or reverse-scored (expect for item 11). This is in line with the latest research suggesting that such items can cause problems in model identification as they create additional method factors [ 44 , 45 , 46 ].
Finally, it is important to highlight that Antonovsky did not provide any information about the selection of the 13 items for the short version of the SOC scale [ 2 ]. For example, a detailed examination of the facet structure reveals that none of the items included in SOC-13 refers to future which is part of facet referring to time (i.e., past, present, future). Hence, considering the absence of explicit criteria for item selection in the SOC-13 scale, it would be interesting to gather data from diverse populations utilizing the full SOC-29 scale. Subsequently, through exploratory factor analysis, researchers could derive a new, theory- and empirical-driven, short version of the SOC scale.
Strengths and limitations
A clear strength of our study is that our findings are based on a representative sample that accurately reflects the Czech adult population. Moreover, we implemented rigorous data cleaning procedures, meticulously excluding participants who provided potentially careless or low-quality responses. By doing so, we ensured that our conclusions are based on high-quality data and that they are generalizable to our target population of Czech adults. Finally, we conducted a thorough back-translation procedure to achieve an accurate Czech version of the SOC scale and we carried out systematic testing of different short versions of the SOC scale.
However, our study also has some limitations. First, our conclusions are based on data from a culturally specific country and they may not be generalizable to other populations. It is important to note, however, that most of our findings are in line with multiple existing studies which supports the validity of our conclusions. Second, the data were collected during a later stage of the COVID-19 pandemic, which may have impacted particularly the mental health outcomes we used for criterion validity. It would be worthwhile to investigate whether the data replicate in our population outside of this exceptional situation. Third, it should be noted that we did not examine test-retest reliability of the scale due to the cross-sectional design of our study. Finally, self-reported data are subject to common method biases such as social desirability, recall bias, or consistency motive [ 47 ]. We aimed to minimize this risk by implementing various strategies in the questionnaire, such as randomization of items and the use of disqualifying items (e.g. “Please, choose option number 2”) to disqualify careless answers.
Our study contributes to decades of ongoing research on SOC, the main pillar of the theory of salutogenesis. In line with existing research, we found evidence for the validity of the SOC as a construct, but we could not identify a clear factorial structure of the SOC-13 scale. However, following Antonovsky’s conception of the scale, we believe it is theoretically sound to aim for a one-factor solution of the scale and we could show that this is possible with shorter versions of the SOC scale. We particularly recommend using the SOC-9 scale in future research which shows an excellent one-factor fit and validity indices comparable to SOC-13. Finally, since Antonovsky does not explain how he selected the items of the SOC-13 scale, it would be interesting to examine the possibility of developing a new one-dimensional short version based on exploratory factor analysis of the original SOC-29 scale.
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study and the R code used for the statistical analysis are available as supplementary material.
www.czso.cz .
Antonovsky A. The salutogenic model as a theory to guide health promotion. Health Promot Int. 1996;11(1).
Antonovsky A. Unraveling the mystery of Health how people manage stress and stay well. Jossey-Bass; 1987.
Antonovsky A. Health stress and coping. Jossey-Bass; 1979.
Antonovsky A. The structure and Properties of the sense of coherence scale. Soc Sci Med. 1993;36(6):125–733.
Article Google Scholar
Eriksson M, Contu P. The sense of coherence: Measurement issues. The Handbook of Salutogenesis. Springer International Publishing; 2022. pp. 79–91.
Eriksson M. The sense of coherence: the Concept and its relationship to Health. The Handbook of Salutogenesis. Springer International Publishing; 2022. pp. 61–8.
Eriksson M, Lindström B. Antonovsky’s sense of coherence scale and the relation with health: a systematic review. J Epidemiol Community Health (1978). 2006;60(5):376–81.
Eriksson M, Lindström B. Antonovsky’s sense of coherence scale and its relation with quality of life: a systematic review. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2007;61(11):938–44.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mana A, Super S, Sardu C, Juvinya Canal D, Moran N, Sagy S. Individual, social and national coping resources and their relationships with mental health and anxiety: A comparative study in Israel, Italy, Spain, and the Netherlands during the Coronavirus pandemic. Glob Health Promot [Internet]. 2021;28(2):17–26.
Silverstein M, Heap J. Sense of coherence changes with aging over the second half of life. Adv Life Course Res. 2015;23:98–107.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Rivera F, García-Moya I, Moreno C, Ramos P. Developmental contexts and sense of coherence in adolescence: a systematic review. J Health Psychol. 2013;18(6):800–12.
Volanen SM, Lahelma E, Silventoinen K, Suominen S. Factors contributing to sense of coherence among men and women. Eur J Public Health [Internet]. 2004;14(3):322–30.
Guttman L. Measurement as structural theory. Psychometrika. 1971;3(4):329–47.
Guttman R, Greenbaum CW. Facet theory: its development and current status. Eur Psychol. 1998;3(1):13–36.
Shye S. Theory Construction and Data Analysis in the behavioral sciences. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass; 1978.
Google Scholar
Portoghese I, Sardu C, Bauer G, Galletta M, Castaldi S, Nichetti E, Petrocelli L, Tassini M, Tidone E, Mereu A, Contu P. A network perspective to the measurement of sense of coherence (SOC): an exploratory graph analysis approach. Current Psychology. 2024;12:1-3.
Bachem R, Maercker A. Development and psychometric evaluation of a revised sense of coherence scale. Eur J Psychol Assess. 2016;34(3):206–15.
Drageset J, Haugan G. Psychometric properties of the orientation to Life Questionnaire in nursing home residents. Scand J Caring Sci. 2016;30(3):623–30.
Kanhai J, Harrison VE, Suominen AL, Knuuttila M, Uutela A, Bernabé E. Sense of coherence and incidence of periodontal disease in adults. J Clin Periodontol. 2014;41(8):760–5.
Naaldenberg J, Tobi H, van den Esker F, Vaandrager L. Psychometric properties of the OLQ-13 scale to measure sense of coherence in a community-dwelling older population. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2011;9.
Luyckx K, Goossens E, Apers S, Rassart J, Klimstra T, Dezutter J et al. The 13-item sense of coherence scale in Dutch-speaking adolescents and young adults: structural validity, age trends, and chronic disease. Psychol Belg. 2012;52(4):351–68.
Lerdal A, Opheim R, Gay CL, Moum B, Fagermoen MS, Kottorp A. Psychometric limitations of the 13-item sense of coherence scale assessed by Rasch analysis. BMC Psychol. 2017;5(1).
Klepp OM, Mastekaasa A, Sørensen T, Sandanger I, Kleiner R. Structure analysis of Antonovsky’s sense of coherence from an epidemiological mental health survey with a brief nine-item sense of coherence scale. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2007;16(1):11–22.
Křivohlavý J. Sense of coherence: methods and first results. II. Sense of coherence and cancer. Czechoslovak Psychol. 1990;34:511–7.
Křivohlavý J. Nezdolnost v pojetí SOC. Czechoslovak Psychol. 1990;34(6).
Křivohlavý J. Salutogenesis and behavioral medicine. Cas Lek Cesk. 1990;126(36):1121–4.
Kebza V, Šolcová I. Hlavní Koncepce psychické odolnosti. Czechoslovak Psychol. 2008;52(1):1–19.
Šolcová I, Blatný M, Kebza V, Jelínek M. Relation of toddler temperament and perceived parenting styles to adult resilience. Czechoslovak Psychol. 2016;60(1):61–70.
Šolcová I, Kebza V, Kodl M, Kernová V. Self-reported health status predicting resilience and burnout in longitudinal study. Cent Eur J Public Health. 2017;25(3):222–7.
Šolcová I, Kebza V. Subjective health: current state of knowledge and results of two Czech studies. Czechoslovak Psychol. 2006;501:1–15.
Šípová I, Máčel M, Zubková A, Tušl M. Association between coping resources and mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study in the Czech Republic. Int J Environ Health Res. 2022;1–9.
Keyes CLM. The Mental Health Continuum: from languishing to flourishing in life. J Health Soc Behav. 2002;43(2):207–22.
Löwe B, Decker O, Müller S, Brähler E, Schellberg D, Herzog W, et al. Validation and standardization of the generalized anxiety disorder screener (GAD-7) in the General Population. Med Care. 2008;46(3):266–74.
R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2022.
Rosseel Y. Lavaan: an R Package for Structural equation modeling. J Stat Softw. 2012;48(2):1–36.
Bentler PM, Bonett DG. Significance tests and goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychol Bull. 1980;88(3):588–606.
Beauducel A, Wittmann WW. Simulation study on fit indexes in CFA based on data with slightly distorted simple structure. Struct Equ Model. 2005;12(1):41–75.
Raftery AE. Bayesian model selection in Social Research. Sociol Methodol. 1995;25:111–63.
Farooq R. Heywood cases: possible causes and solutions. Int J Data Anal Techniques Strategies. 2022;14(1):79.
Eriksson M, Lindström B. Validity of Antonovsky’s sense of coherence scale: a systematic review. J Epidemiol Community Health (1978). 2005;59(6):460–6.
Stern B, Socan G, Rener-Sitar K, Kukec A, Zaletel-Kragelj L. Validation of the Slovenian version of short sense of coherence questionnaire (SOC-13) in multiple sclerosis patients. Zdr Varst. 2019;58(1):31–9.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bernabé E, Tsakos G, Watt RG, Suominen-Taipale AL, Uutela A, Vahtera J, et al. Structure of the sense of coherence scale in a nationally representative sample: the Finnish Health 2000 survey. Qual Life Res. 2009;18(5):629–36.
Sardu C, Mereu A, Sotgiu A, Andrissi L, Jacobson MK, Contu P. Antonovsky’s sense of coherence scale: cultural validation of soc questionnaire and socio-demographic patterns in an Italian Population. Clin Pract Epidemiol Mental Health. 2012;8:1–6.
Chyung SY, Barkin JR, Shamsy JA. Evidence-based Survey Design: the Use of negatively worded items in surveys. Perform Improv. 2018;57(3):16–25.
Suárez-Alvarez J, Pedrosa I, Lozano LM, García-Cueto E, Cuesta M, Muñiz J. Using reversed items in likert scales: a questionable practice. Psicothema. 2018;30(2):149–58.
PubMed Google Scholar
van Sonderen E, Sanderman R, Coyne JC. Ineffectiveness of reverse wording of questionnaire items: let’s learn from cows in the rain. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(7).
Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB, Lee JY, Podsakoff NP. Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J Appl Psychol. 2003;88(5):879–903.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank to the team of Center of Salutogenesis at the University of Zurich for their helpful comments on the adapted version of the SOC scale.
MT received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No 801076, through the SSPH + Global PhD Fellowship Program in Public Health Sciences (GlobalP3HS) of the Swiss School of Public Health. Data collection was supported by the Charles University Strategic Partnerships Fund 2021. The University of Zurich Foundation supported the contribution of GB.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Division of Public and Organizational Health, Center of Salutogenesis, Epidemiology, Biostatistics and Prevention Institute, University of Zurich, Hirschengraben 84, Zurich, 8001, Switzerland
Martin Tušl & Georg F. Bauer
Department of Psychology, Faculty of Arts, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic
Ivana Šípová, Martin Máčel & Kristýna Cetkovská
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design of the study. MT wrote the manuscript, conducted data analysis, and contributed to data collection. MM and IS conducted data collection, contributed to data analysis, interpretation of results, edited and commented on the manuscript. KC and GB contributed to interpretation of results, edited and commented on the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Martin Tušl .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was conducted in accordance with the general principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and with the ethical principles defined by the university and by the national law ( https://cuni.cz/UK-5317.html ). Informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to the completion of the survey. Participation was voluntary and participants could withdraw from the study at any time without any consequences. For anonymous online surveys in adult population no ethical review by an ethics committee was necessary under national law and university rules. See: https://www.muni.cz/en/about-us/organizational-structure/boards-and-committees/research-ethics-committee/evaluation-request .
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Tušl, M., Šípová, I., Máčel, M. et al. The sense of coherence scale: psychometric properties in a representative sample of the Czech adult population. BMC Psychol 12 , 293 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01805-7
Download citation
Received : 22 March 2023
Accepted : 21 May 2024
Published : 26 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01805-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Salutogenesis
- Sense of coherence
- Psychometrics
- Czech adult population
- Mental health
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]
College of Liberal Arts & Sciences
School of Chemical Sciences
- Student and Professional Organizations
- Welcome Alumni and Friends
- Alumni Database
- Donate to SCS
- Connect with the School of Chemical Sciences
- Corporate Relations Overview
- SCS Campus Awardees
- Chemistry News
- Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering News
- Celebrating our Sesquicentennial 1867 - 2017
- SCS Office Listings
- Staff Listing
- Chemistry Directory
- Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Directory
- Business Office
- Chemistry Library
- CORES (SCS Research and Service Facilities)
- Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Access
- Employment Opportunities
- Facilities Management Group
- Human Resources
- Receiving & Mailroom
- **Building Emergency**
- Academic Advising
- Career Services
- Copying and Printing Services
- Facilities Management
- Online Ordering/REACTION
- SCS Chemical Inventory Program
- Staff Listings
Sample Preparation

The sample should usually be solvent-free and pure. (Purity is not a requirement for GC/MS or LC/MS, and both ESI and MALDI can also handle moderate mixtures.) There should be no excess salts in your sample, especially for FAB, ESI, and MALDI. Buffers such as phosphate and HEPES are fatal to these techniques. Weigh out your sample into a small screw-top vial. For very small amounts of sample, a Reacti-Vial is best. This is especially true for oils. Oil smeared around the inside of a regular vial is very difficult to get out. For high molecular weight biomolecules, such as peptides, an Eppendorf-like tube is required. Use an inert cap liner, such as aluminum foil or Teflon, for screw-top vials since we may use a solvent which will leach plasticizers out of the caps. Solvent is always used for FD, FAB, ESI, MALDI, GC/MS, and LC/MS. Accurate weighing is mandatory for FD, ESI, MALDI, FAB, GC/MS, and LC/MS and is important for other techniques. The amounts required vary by ionization technique and instrument. As a quick rule of thumb, 1 mg is always enough. ESI and MALDI require very small amounts of sample. For specific amounts, see the ionization techniques section.
The reason we want pure samples for most techniques is that impure samples do not give good mass spectra. The mass spectrum of a mixture is a confusing jumble of molecular ions and fragments from each component. Also, the signal for any one component will be weaker than if it were pure. To make matters worse, the spectra of some components may be totally suppressed by the others.
Radioactive Sample Permissible Levels: The maximum permissible levels of radioactivity for samples submitted for normal MS analysis is 86 microcurie for 3 H and 43 microcurie for 14 C. This corresponds to 0.03% incorporation of tritium and 7% incorporation of carbon-14 in a 2 mg sample.
- Open access
- Published: 15 May 2024
The prevalence and mortality risks of PRISm and COPD in the United States from NHANES 2007–2012
- Christopher J. Cadham 1 na1 ,
- Hayoung Oh 2 na1 ,
- MeiLan K. Han 3 ,
- David Mannino 4 , 5 ,
- Steven Cook 6 ,
- Rafael Meza 7 ,
- David T. Levy 2 &
- Luz María Sánchez-Romero 2
Respiratory Research volume 25 , Article number: 208 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
484 Accesses
10 Altmetric
Metrics details
We estimated the prevalence and mortality risks of preserved ratio impaired spirometry (PRISm) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in the US adult population.
We linked three waves of pre-bronchodilator spirometry data from the US National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (2007–2012) with the National Death Index. The analytic sample included adults ages 20 to 79 without missing data on age, sex, height, BMI, race/ethnicity, and smoking status. We defined COPD (GOLD 1, 2, and 3–4) and PRISm using FEV 1 /FVC cut points by the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). We compared the prevalence of GOLD stages and PRISm by covariates across the three waves. We estimated adjusted all-cause and cause-specific mortality risks by COPD stage and PRISm using all three waves combined.
Prevalence of COPD and PRISm from 2007–2012 ranged from 13.1%-14.3% and 9.6%-10.2%, respectively. We found significant differences in prevalence by sex, age, smoking status, and race/ethnicity. Males had higher rates of COPD regardless of stage, while females had higher rates of PRISm. COPD prevalence increased with age, but not PRISm, which was highest among middle-aged individuals. Compared to current and never smokers, former smokers showed lower rates of PRISm but higher rates of GOLD 1. COPD prevalence was highest among non-Hispanic White individuals, and PRISm was notably higher among non-Hispanic Black individuals (range 31.4%-37.4%). We found associations between PRISm and all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR]: 2.3 95% CI: 1.9—2.9) and various cause-specific deaths (HR ranges: 2.0–5.3). We also found associations between GOLD 2 (HR: 2.1, 95% CI: 1.7–2.6) or higher (HR: 4.2, 95% CI: 2.7–6.5) and all-cause mortality. Cause-specific mortality risk varied within COPD stages but typically increased with higher GOLD stage.
Conclusions
The prevalence of COPD and PRISm remained stable from 2007–2012. Greater attention should be paid to the potential impacts of PRISm due to its higher prevalence in minority groups and its associations with mortality across various causes including cancer.
Introduction
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death in the US [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]. The clinical diagnosis of COPD requires a spirometry FEV 1 /FVC ratio of less than 0.7, representing the ratio of the maximum amount of air that the subject can forcibly expel during the first second following maximal inhalation (FEV 1 ) divided by the forced vital capacity (FVC). However, COPD is a progressive and chronic lung obstruction operating on a spectrum, and those not meeting the clinical COPD definition may still experience lung obstruction abnormalities.
Nomenclature for low lung function is heterogeneous [ 5 ]. Recently, Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry (PRISm), [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ] defined as those with an FEV 1 /FVC ratio greater or equal to 0.7 and FEV 1 less than 0.8, has been proposed as a pre-clinical COPD abnormal spirometry. PRISm replaces terms such as Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Diseases (GOLD)-Unclassified and restrictive spirometry [ 9 , 10 ]. PRISm serves as a more informative name that distinguishes the patterns of PRISm as different from restriction and non-specific abnormality [ 10 ]. PRISm is associated with increased cardiovascular mortality, physical strength limitations, higher body mass index (BMI), respiratory symptoms, diabetes, a history of stroke, and hypertension [ 4 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]. However, those with PRISm are not easily categorized into a specific disease pathway given its comorbidities [ 7 , 8 , 14 , 16 ] and the uncertainty of progression into a future COPD diagnosis [ 7 , 8 ]. With only 22.2%-35.8% of individuals with PRISm expected to be diagnosed with COPD within five years, [ 17 , 18 ] the causal pathway remains unclear, but those with PRISm are a population with poor health outcomes [ 6 ].
With an annual direct cost of $32 billion to the US healthcare system from COPD, [ 19 ] it is important to better understand the prevalence and mortality risks associated with different severity levels of abnormal spirometry. It is possible that addressing PRISm prior to a formal clinical COPD diagnosis could allow for preventative measures to help alleviate the physical burden of COPD for patients. Despite this, spirometry data are rarely collected in US population-based studies, making examinations of the prevalence and health risks of PRISm and COPD challenging.
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) Study collected spirometry data for three waves from 2007–2012. We used this data to examine the prevalence of PRISm and the different stages of COPD severity, and associations between PRISm and COPD severity and all-cause and cause-specific mortality using the NHANES Linked Mortality Files [ 20 ].
Study and data
Conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics at the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, NHANES is a nationally representative, cross-sectional survey of the civilian, non-institutionalized US population [ 21 ]. This study used three waves of data from NHANES: 2007–2008, 2009–2010, and 2011–2012 based on the availability of spirometry values. NHANES data were collected via household interviews and standardized physical examinations. Underrepresented subgroups such as Hispanic and Black populations, and low-income white persons were oversampled. The Asian racial/ethnic group was also oversampled in 2011–2012. NHANES sample selection and a more detailed survey description can be found elsewhere [ 22 ].
COPD and PRISm prevalence was estimated using a subset of US adults aged 20 to 79 eligible for spirometry tests [ 23 ]. Age limits of 20–79 were established based on Hankinson’s lung function predictive equation, which starts at ages 20 for males and 18 for women [ 24 ], and were capped at age 79 as the maximum eligible age for the NHANES spirometry. Response rate for the spirometry test was 77.3%, 87.3%, and 86.9% in 2007–2008, 2009–2010, and 2011–2012, respectively. The final prevalence analytic sample ( N = 4,237 in 2007–2008, N = 4,783 in 2009–2010, and N = 4,308 in 2011–2012) included those with complete spirometry values and no-missing data for the lung function predictive equation or covariates (age, sex, height, BMI, race/ethnicity, and smoking status [ N = 6,722 excluded (33%)]).
The final analytic sample for the mortality analyses ( N = 13,307) included all participants who met the inclusion criteria for the prevalence analysis and had vital status ascertained through the NHANES Linked Mortality Files, which links NHANES records to the National Death Index [ 20 ].
Spirometry, COPD, and PRISm definitions
The FVC, the FEV 1 , and FEV 1 /FVC were the spirometry values utilized for this analysis. Normal FEV 1 values were estimated using Hankinson’s [ 24 ] gender-specific, non-Hispanic White predictive equations (FEV 1 predicted for males = 0.5536–0.01303*age-0.000172*age^2 + 0.00014098*BMI^2 and FEV 1 predicted for females = 0.4333–0.00361*age-0.000194*age^2 + 0.00011496*BMI^2) for all race/ethnicities following the methodology of similar studies [ 25 ].
We decided against Hankinson’s race-specific equations, which were created and validated for the NHANES III Study, [ 24 ] as there is growing evidence that use of race-specific equations the underestimates the prevalence of COPD across racial groups [ 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 ].
To maximize our analytic sample, COPD diagnosis was based on pre-bronchodilator spirometry values data (respondents with pre-bronchodilator N = 20,050, respondents with post-bronchodilator N = 1,564); an approach consistent with other studies [ 30 ]. We defined COPD as recommended by the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) as FEV 1 /FVC ratio of less than 0.7 [ 31 ] and further classified into GOLD stages based on FEV 1 predicted values: GOLD 1 (FEV 1 ≥ 80%), GOLD 2 (50% < FEV 1 < 80%), and GOLD 3 + 4 (FEV 1 ≤ 50%). Preserved ratio impaired spirometry (PRISm) was defined as those with an FEV 1 /FVC value of ≥ 0.7 but with abnormal spirometry (i.e., FEV 1 < 80%) [ 16 ]. Individuals without PRISm or COPD were classified as GOLD 0 or normal spirometry.
Covariates were selected based on the inputs for the FEV 1 predictive equations: age, gender, smoking status, body mass index (BMI) and race/ethnicity [ 7 , 8 , 14 , 16 ]. For prevalence estimates, age was recoded as three age groups: 20–39, 40–64, and 65 + . Gender was defined as male or female. NHANES categorized race/ethnicity into five categories: non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, Mexican–American, Hispanic Other, and Other. For cigarette use status, we considered: “Have you smoked at least 100 + cigarettes in your lifetime?” and “Are you currently smoking?”. Current smokers smoked at least 100 + cigarettes in their lifetime and were currently smoking. Former smokers smoked at least 100 + cigarettes in their lifetime and did not currently smoke at the time of the survey. Never smokers were those who had not smoked 100 + lifetime cigarettes. BMI was categorized into three groups: normal (BMI < 25), overweight (25 ≤ BMI < 30), and obesity (BMI ≥ 30).
For the prevalence analysis, COPD (Total, GOLD 1, GOLD 2 and GOLD 3–4) and PRISm were the outcomes of interest. For the mortality analysis, we estimated all-cause and cause-specific (i.e., cancer, cardiovascular disease, and chronic lower respiratory diseases) mortality for overall COPD, GOLD stages and PRISm.
Statistical analysis
For each of the NHANES wave used, we calculated the weighted [ 32 ] population prevalence estimates for each of the outcomes, as well as the prevalence by age, gender, smoking status, and race/ethnicity using full sample mobile examination center exam weight. Differences in the prevalence of disease point estimates and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were compared across the three waves. Cox proportional hazard models were estimated to examine all-cause and cause-specific mortality risks for COPD (overall COPD, GOLD 1, GOLD 2 and GOLD 3–4) and PRISm, adjusting for age (both categorically and continuously in separate analyses), gender, BMI, smoking status, and race/ethnicity. Weights were adjusted for mortality analyses to enable the pooling of all three survey waves [ 33 ]. Analyses were performed using STATA 17.0 and R 4.3.2.
Sensitivity analyses
Given recent debates over the merits of race-specific predicative equations for spirometry, [ 28 , 29 , 34 , 35 , 36 ] in addition to Hankinson’s non-Hispanic White predictive equation of lung function, we also applied a race-neutral reference equation to explore differences in COPD prevalence and mortality. We used the Global Lung Function Initiative’s (GLI) race-neutral predictive equation for this secondary analysis [ 35 ]. The race-neutral equation removes race-specific adjustments which may bias spirometry results and reflects the wide variation of lung function within and between populations.
In this secondary analysis, we estimated COPD (Total, GOLD 1, GOLD 2 and GOLD 3–4) and PRISm prevalence and all-cause mortality for COPD GOLD stages and PRISm. We also plotted the estimates from the GLI race-neutral predictive equation compared to the respective outcomes using the Hankinson non-Hispanic White predictive equation.
Table 1 presents the weighted demographics and COPD prevalence for 2007–2012 and each wave individually. Characteristics of the sample remained stable over the period.
Prevalence of COPD and PRISm
The overall prevalence estimates for COPD and PRISm are available in Table 1 and Fig. 1 : Panel A. Across all three waves, the prevalence of COPD was 13.8% (95% CI: 12.8%—14.9%) and PRISm 9.8% (95% CI: 8.9%—10.8%). Trends in COPD remained relatively stable from 2007 to 2012. Similar stability was seen among participants with PRISm. Prevalence estimates of COPD using spirometry were substantially higher than self-reported COPD at 5.9% (95% CI: 5.0%—6.9%) for 2007–2012 (Appendix 1 ).

COPD and PRISm prevalence by covariates and cohort waves. Legend: Figure 1 presents prevalence of each COPD GOLD stage and PRISm by subgroup and wave of NHANES. Point estimates and confidence intervals are available in Table 1 (overall estimates) and Appendices 2 – 6 (subgroups)
Prevalence of COPD and PRISm by gender, smoking status, BMI, age group, and race/ethnicity
Estimates of COPD and PRISm by gender show (Fig. 1 : Panel B; Appendix 2 ) that overall COPD was statistically significantly higher in males (range: 17.4%—17.9%), while PRISm was higher among females (range 10.5%—11.3%), albeit not significantly, for all survey waves. However, we did not observe significant differences in disease stages (Appendix 2 ).
Overall, the prevalence of COPD was statistically significantly higher among current and former cigarette users compared to never users (Fig. 1 : Panel C; Appendix 3 ). PRISm estimates were highest among current users for all years except 2011–2012 when the highest prevalence was among never users (10.9%, 95% CI: 8.7%—11.3%), but differences between groups were not statistically significant. Former users had the lowest rates of PRISm across all three waves of data, but the highest rates of GOLD 1 (range: 10.2%-11.6%), while current users reported the highest rates of GOLD 2 (range: 11.8%—12.9%) and GOLD 3–4 (range: 1.5%—3.1%).
COPD prevalence was lower for individuals with obesity compared to those with a BMI categorized as normal or overweight (Fig. 1 : Panel D, Appendix 4 ). The differences in prevalence were particularly notable for GOLD 1, which was roughly twice as high among normal-weight individuals compared to those with obesity. PRISm estimates across all three waves were higher for people with obesity than people with a normal BMI.
Estimates by age group showed increases in COPD with age and reported the highest prevalence among ages 65–79 (range: 28.1%-36.1%) (Fig. 1 : Panel E; Appendix 5 ). Conversely, PRISm prevalence was highest among ages 40–64 (range: 11.0%—11.9%) and lowest at ages 20–39 (range: 6.6%—8.9%).
Distinct patterns were observed for prevalence estimates by race/ethnicity (Fig. 1 : Panel F; Appendix 6 ). PRISm prevalence was higher among Non-Hispanic Black participants (range: 31.4%—37.4%), followed by those classified as having other race/ethnicity (range: 11.2%—20.4%). Conversely, non-Hispanic White participants had the highest prevalence of COPD across all three survey waves (range: 15.5%—17.5%), with GOLD 1 making up roughly half of those cases (range: 8.2%—9.3%). The prevalence of COPD and PRISm were roughly equal among Mexican Americans.
Mortality estimates
Of the 13,307 participants in the mortality analysis, 1,079 (8.15%) died, with a median follow-up of 9.4 years. In multivariable models adjusting for gender, race/ethnicity, age at screening exam, BMI, and smoking status, the risk of all-cause mortality was higher among those at GOLD 2 (HR: 2.1 95% CI: 1.7–2.6) or higher (HR: 4.2, 95% CI: 2.7–6.5) and for those at PRISm (HR: 2.3, 95% CI: 1.9–2.9) compared to GOLD 0 (Fig. 2 , Table 2 ).

COPD and PRISm survival curves by mortality outcome. Legend: Figure 2 presents Kaplan–Meier curves for each survival outcome by COPD GOLD stage and PRISm. Curves show the proportion of individuals still alive at a given time point. Shaded areas represent 95% confidence intervals
COPD stages and PRISm were also significant predictors of cause-specific mortality from cancer, cardiovascular disease, and chronic lower respiratory diseases. GOLD 2 was associated with a significant risk of cancer mortality (HR: 2.0, 95% CI: 1.4–2.8), as was PRISm (HR: 2.0, 95% CI: 1.2–3.2) compared with GOLD 0. GOLD3 + 4 (HR: 4.7, 95% CI: 2.3–9.8) showed the highest risk of cardiovascular mortality, followed by GOLD 2 (HR: 2.4, 95% CI: 1.6–3.7) and PRISm (HR: 2.4, 95% CI: 1.6–3.6) which conferred similar cardiovascular mortality risks. Finally, GOLD 3 + 4 (HR: 53.2, 95% CI: 14.0–202.0) and PRISm (HR: 5.3, 95% CI: 1.1–26.0) were both associated with an increased risk of chronic lower respiratory disease-related mortality when compared to GOLD 0.
We found no differences in estimates when using continuous age compared to categorical with the exception of the risk of mortality from chronic lower respiratory diseases among individuals with PRISm which was no longer statistically significant (Appendix 7 ).When comparing PRISm to any COPD (Appendix 8 and 9 ), mortality risks from PRISm trended higher than those of any COPD except for chronic lower respiratory disease-specific mortality.
Race-neutral predictive equation
When using the Global Lung Function Initiative (GLI) Race-Neutral predictive equation (Fig. 3 , Appendix 10 ), we find significantly lower estimates of PRISm. Both equations led to the same overall COPD prevalence. While we found no statistically significant differences in COPD GOLD stage between the two equations, there may be downstaging with the race-neutral equation. The race-neutral equation results show higher point-estimates for GOLD 1, and lower point-estimates for GOLD 2 and 3–4 relative to the Hankinson equation.

Comparison of COPD GOLD stage and PRISm prevalence estimates using Hankinson’s non-Hispanic White and the GLI race-neutral predictive equations. Legend: Figure 3 presents a forest plot that displays prevalence estimates and 95% confidence intervals of COPD GOLD stages and PRISm using weighted NHANES data from 2007–2012. These results are presented in tabular form in Appendix 10
Use of the race-neutral equation resulted in no statistically significant differences mortality outcomes (Appendices 11 and 12 ).
In a nationally representative dataset of US adults, our study found that from 2007–2012, COPD and PRISm trends were stable. The average prevalence of PRISm was 9.8% and 13.8% for COPD. Using race-neutral predictive equations, we found lower estimates of PRISm, but consistent estimates of COPD. By GOLD stages, we found that the prevalence of GOLD 1 was 6.9%, 6.0% for GOLD 2, and 0.9% for GOLD 3–4. Both COPD and PRISm were associated with greater all-cause mortality, with greater mortality risk at higher COPD stages. Further, despite having different demographic and cigarette smoking profiles, both COPD stages and PRISm were associated with an increased risk of cause-specific mortality outcomes, including cancer- and cardiovascular disease-specific mortality.
Our PRISm prevalence estimates were generally consistent with those reported in other national and international studies. Using data from the US National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) pooled cohort study, Wan et al. reported a PRISm prevalence of 8.5% between 1975–2018. Similarly, researchers found a PRISm prevalence of 11.0% in a United Kingdom population between 2006–2013, [ 37 ] while a cohort study from Rotterdam, Netherlands found a PRISm prevalence of 7.6% [ 4 ]. These prevalence estimates highlight the importance of monitoring PRISm trends using nationally representative surveys. Left unattended, PRISm could contribute to the increasing global chronic obstructive respiratory disease burden.
In the US, there is a lack of COPD nationally representative prevalence estimated from spirometric values. This is partly due to NHANES being the only national health survey that collected spirometric values among those who collect COPD-associated data (i.e., the Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health, the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, and the National Health Interview Survey). Still, comparisons of our spirometric COPD estimates and those obtained from self-reported COPD data show that COPD prevalence as defined by spirometry is almost double that from self-reported measures. From 2011 to 2020, the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System reported a stable prevalence of around 6.0% [ 38 ]. Another study using NHANES self-reported data from 2007–2012 reported a COPD prevalence of 5.2% [ 39 ]. Similarly, we performed a sensitivity analysis using self-reported defined COPD from NHANES 2007–2012 and estimated a prevalence of 5.9% across this period (Appendix 6 ). Reliance on self-reported measures appears to underestimate the burden of COPD systematically. It has previously been reported that a substantial number of individuals, nearly 80%, with spirometry-defined COPD cannot be identified with self-reported questionnaires [ 40 , 41 ]. Furthermore, studies that compare self-report and spirometry results suggest that those with more regular contact with the healthcare system are more likely to be diagnosed with COPD, [ 39 ] which may bias prevalence estimates to those with better access to medical care.
Our stratified findings by sub-group covariates also revealed similar results to those in the literature. Self-report studies have suggested limited differences in COPD by gender, yet females may be more likely to be diagnosed with COPD [ 39 , 42 ]. However, using spirometry to define COPD, we found that females have a lower prevalence of COPD and a higher prevalence of PRISm than males. These results are consistent with previous studies that find a faster decline in FEV 1 among female smokers and overall increases in COPD prevalence among women [ 43 , 44 ]. The observed higher PRISm prevalence estimates among females than males could potentially reflect the faster decline in lung function.
As with previous studies, our estimates show that COPD prevalence increased by age group [ 45 , 46 , 47 ]. However, this was not the case for PRISm, with the highest prevalence at ages 40–64. Other studies in the US have also reported that a higher prevalence of PRISm is found in subjects aged 45 to 68 [ 16 , 48 ]. Those with PRISm in middle ages might transition to COPD before reaching age 65, therefore “diluting” the prevalence of PRISm at older ages as FEV 1 and FVC decline at different rates. Alternatively, individuals with PRISm may die at younger ages due to the increased mortality risk of PRISm [ 49 ]. Still, more evidence on the natural history of COPD and the role of PRISm in developing COPD is necessary.
Our results found that current cigarette users had the highest COPD prevalence, followed by former smokers and then never smokers, which is also consistent with previous literature [ 42 , 50 ]. While smoking is an established risk factor for COPD, other risk factors such as asthma and hazardous work conditions contribute to the prevalence of COPD among never smokers [ 51 ]. As with other sub-group categories, PRISm prevalence did not follow the same patterns as COPD when stratified by smoking status. Current and never users had higher PRISm prevalence, with former smokers having the lowest. This pattern might also be explained by the transition of PRISm to COPD.
COPD has been strongly associated with BMI. Our findings add to the evidence which shows, regardless of the COPD definition (i.e., self-reported or spirometry), that individuals with obesity showed a lower COPD prevalence. Published studies have reported that overweight and obese individuals are less likely to have GOLD stage 3–4 than individuals with a normal BMI [ 52 ]. This may be due in part to lower FVC and FEV 1 among people with obesity [ 53 ]. Alternatively, COPD patients with obesity report more symptoms and poorer quality of life than patients with a normal weight, [ 54 ] which may lead undiagnosed individuals with obesity to seek treatment earlier than those with normal BMI. Coupled with receiving more intense treatment, [ 55 ] those with obesity may see improved lung function. Previous studies have also found a substantially higher prevalence of PRISm among people with higher BMI [ 16 ].
COPD and PRISm prevalence stratified by race yielded several interesting results. Generally, the highest COPD prevalence was among non-Hispanic Whites, followed by non-Hispanic Blacks, those of other race/ethnicity, non-Mexican–American Hispanic individuals, and those in the Mexican–American racial category. Of note, non-Hispanic Blacks had the highest PRISm prevalence (30% +), resulting in a difference of around 20 percentage points between PRISm and COPD prevalence for this group. Previous studies have found inconsistent results on the relationship between race and PRISm/COPD prevalence [ 48 , 57 ]. More work is necessary to identify the extent to which racial/ethnic differences in COPD and PRISm prevalence exist and the root causes of these differences.
Through our survival analysis, we found that COPD and PRISm were both significantly associated with an increased mortality risk. PRISm was a consistent indicator of increased mortality risk from cancer, cardiovascular disease, and chronic lower respiratory disease, despite being comprised of fewer current and former smokers than COPD states.
When combined with findings from various countries and data sources, the results from our nationally representative study provide compelling evidence of the impact of COPD and PRISm on mortality. The increased mortality risk from PRISm has been corroborated by Yang et al., whose meta-analysis reports an increased risk of all-cause cardiovascular and respiratory-related mortality compared to normal spirometry [ 49 ]. In the US, Wan et al., reported that PRISm diagnosis is associated with an increased risk for all-cause, cardiovascular and respiratory mortality compared to individuals with normal spirometry using the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Pooled Cohort Study, a non-nationally representative sample [ 48 ]. Similar risks have also been reported for all-cause mortality in the UK using data from the UK BioBank, [ 37 ] for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the Netherlands, [ 4 ] and for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in Japan [ 58 ].
Less is known of the impacts of PRISm on cancer mortality. Our study’s results indicating a significant impact are the first such finding in a US general population. Nevertheless, these findings align with research from South Korea which found PRISm increased the risk of mortality from lung cancer [ 59 ].
Emerging evidence suggests that, like COPD, PRISm is a heterogeneous condition. Studies have indicated that PRISm can be categorized into restrictive PRISm (FEV1/FVC ≥ 0.7, FEV1 < 80%, and FVC < 80%) and non-restrictive PRISm (FEV1/FVC ≥ 0.7, FEV1 < 80%, and FVC ≥ 80%). This variability extends to differences in risk factors, [ 60 ] the likelihood of transitioning to airflow obstruction, exacerbations, and mortality risks for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality [ 61 , 62 , 63 ]. Therefore, future efforts should prioritize improving diagnostic approaches and mortality risks for individuals with this condition.
For COPD, our results show an increased risk of all-cause mortality as well as cardiovascular disease-specific mortality for GOLD 2 or higher. While we found evidence of significant increases in the risk of chronic lower respiratory disease-related mortality among GOLD 3–4 patients, the smaller number of individuals in this group limits confidence in these estimates, as is reflected in the large confidence intervals. Notably, we consistently find higher risk of mortality with PRISm than with GOLD 1 which questions the hypothesis that PRISm serves as a precursor state to COPD.
In recent years, a substantive body of research has demonstrated the bias associated with use of race-specific predictive equations [ 26 , 29 , 34 , 36 ]. As such, we avoided the use of race-specific equations in all our analyses and opted to use Hankinson’s non-Hispanic White predictive equation for all races and the GLI race-neutral predictive equation in a secondary analysis. Apart from lower rates of PRISm using the GLI equation, we find no statistically significant differences in COPD prevalence between these two approaches. However, the lower rates of PRISm with race-neutral equations, as well as higher trends of lower stages of COPD may suggest that race-neutral equations are downstaging patients. Regardless, this did not have impacts on mortality estimates. More research is needed, particularly evaluating the precision of race-neutral equations for the identification of PRISm.
This study has several limitations. First, our prevalence data are cross-sectional, and we cannot make inferences regarding the causal pathways of PRISm and COPD. Second, spirometry data were only available in the NHANES data between 2007–2012, limiting our ability to examine longer-term and more recent trends in COPD and PRISm prevalence as spirometry examination by NHANES was discontinued in 2013. Enhancing future research requires the collection of longitudinal spirometric data alongside additional nationally representative cross-sectional data. Broadening datasets to encompass spirometry results that reflect the current trends and diversity of the disease across the nation is essential. Third, we used pre-bronchodilator spirometry values due to sample size limitations for post-bronchodilator values in this study. While some research has found a non-significant discrepancy between the use of pre-bronchodilator or post-bronchodilator for air obstruction diagnosis, GOLD standards recommend the use of post-bronchodilator data [ 64 , 65 ]. Although there is still controversy on the estimated outcomes from each measure [ 66 ]. Previous studies using the NHANES data have been published with the same limitation, [ 11 , 15 ] and nationally representative data with post-bronchodilator data are needed. Furthermore, we defined COPD based on an FEV 1 /FVC ratio of 0.7, as is commonly done in research, rather than the lower limit of normal (LLN). FEV 1 /FVC ratio is age-dependent, and its utilization may result in misdiagnosed airflow obstruction [ 68 ]. Consequently, there is a possibility that our analysis may overestimate the prevalence of PRISm among younger individuals and underestimate PRISm among older individuals. Finally, we did not account for the potential impacts of measurement error in the spirometry [ 68 ].
Using a nationally representative sample of US adults with spirometry data between 2007–2012, we found that approximately 10% of the US adult population meet the criteria for PRISm, and 14% meet the criteria for COPD. Moreover, both PRISm and COPD were associated with an increased risk of all-cause and cause-specific mortality, demonstrating the importance of examining the potential impact of PRISm at the national level. Much remains unknown about PRISm and the extent to which it may progress to a formal COPD diagnosis; as such, increasing spirometric data collection is essential.
Availability of data and materials
All data used in this study is publicly available from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention through the National Center for Health Statistics which manages NHANES.
Ford ES. Trends in Mortality From COPD Among Adults in the United States. Chest. 2015;148:962–70.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
CDC. Leading Causes of Death in 2020. 2022; at https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/leading-causes-of-death.htm .
GOLD COPD Report 2020. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD); 2020. https://goldcopd.org/gold-reports/ .
Wijnant SRA, Roos ED, Kavousi M, Stricker BH, Terzikhan N, Lahousse L, et al. Trajectory and mortality of preserved ratio impaired spirometry: the Rotterdam Study. European Respiratory Journal 2020;55:.
Schiffers C, Mraz T, Breyer M-K, Hartl S, Breyer-Kohansal R, Wouters EFM. Restrictive Spirometry or PRISm: Does it Matter? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023;208:905–7.
Han MK, Agusti A, Celli BR, Criner GJ, Halpin DMG, Roche N, et al. From GOLD 0 to Pre-COPD. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;203:414–23.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wan E s., Balte P, Cassano P a., Couper D, Jacobs D, Kalhan R, et al. Prevalence and Longitudinal Risk Patterns Associated with Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry (PRISm): The NHLBI Pooled Cohorts Study. C43 COPD AND POPULATION HEALTH American Thoracic Society; 2019. p. A4873–A4873. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm-conference.2019.199.1_MeetingAbstracts.A4873 .
Adibi A, Sadatsafavi M. Looking at the COPD spectrum through “PRISm.” Eur Respir J. 2020;55:1902217.
Wan ES, Castaldi PJ, Cho MH, Hokanson JE, Regan EA, Make BJ, et al. Epidemiology, genetics, and subtyping of preserved ratio impaired spirometry (PRISm) in COPDGene. Respir Res. 2014;15:89.
Wan ES. The Clinical Spectrum of PRISm. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;206:524–5.
Mannino DM, Buist AS, Petty TL, Enright PL, Redd SC. Lung function and mortality in the United States: data from the First National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey follow up study. Thorax. 2003;58:388–93.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
VazFragoso CA, Gill TM, McAvay G, Yaggi HK, Van Ness PH, Concato J. RESPIRATORY IMPAIRMENT AND MORTALITY IN OLDER PERSONS: A NOVEL SPIROMETRIC APPROACH. J Investig Med. 2011;59:1089–95.
Article Google Scholar
Tran T, Kinney GL, Comellas AP, Hoth KF, Baldomero AK, Wilson C, et al. Prevalence of Abnormal Spirometry in Ever Smokers with No Known Obstructive Lung Disease. A102 ASSESSMENT OF RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY American Thoracic Society; 2022. p. A2213–A2213. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm-conference.2022.205.1_MeetingAbstracts.A2213 .
Mannino DM, Holguin F, Pavlin BI, Ferdinands JM. Risk factors for prevalence of and mortality related to restriction on spirometry: findings from the First National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and follow-up. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2005;9:613–21.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Mannino DM, Ford ES, Redd SC. Obstructive and restrictive lung disease and functional limitation: data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination. J Intern Med. 2003;254:540–7.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Schwartz A, Arnold N, Skinner B, Simmering J, Eberlein M, Comellas AP, et al. Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry in a Spirometry Database. Respir Care. 2021;66:58–65.
Wan ES, Hokanson JE, Regan EA, Young KA, Make BJ, DeMeo DL, et al. Significant Spirometric Transitions and Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry Among Ever Smokers. Chest. 2022;161:651–61.
Wan ES, Fortis S, Regan EA, Hokanson J, Han MK, Casaburi R, et al. Longitudinal Phenotypes and Mortality in Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry in the COPDGene Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198:1397–405.
Løkke A, Lange P, Lykkegaard J, Ibsen R, Andersson M, de Fine LS, et al. Economic Burden of COPD by Disease Severity – A Nationwide Cohort Study in Denmark. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021;16:603–13.
National Center for Health Statistics Division of Analysis and Epidemiology. Continuous NHANES Public-use Linked Mortality Files, 2019. Hyattsville, Maryland. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data-linkage/mortality-public.htm . doi: https://doi.org/10.15620/cdc:117142 .
National Center for Health Statistics. NHANES - National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Homepage. 2022;at < https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm >.
Zipf G, Chiappa M, Porter KS, Ostchega Y, Lewis BG, Dostal J. National health and nutrition examination survey: plan and operations, 1999–2010. Vital Health Stat. 2013;1:1–37.
Google Scholar
Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J. 2005;26:319–38.
Hankinson JL, Odencrantz JR, Fedan KB. Spirometric Reference Values from a Sample of the General U.S. Population. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999;159:179–187.
Vollmer WM, Gislason Th, Burney P, Enright PL, Gulsvik A, Kocabas A, et al. Comparison of spirometry criteria for the diagnosis of COPD: results from the BOLD study. Eur Respir J. 2009;34:588–97.
Baugh AD, Shiboski S, Hansel NN, Ortega V, Barjaktarevic I, Barr RG, et al. Reconsidering the Utility of Race-Specific Lung Function Prediction Equations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;205:819–29.
Cooper BG, Stocks J, Hall GL, Culver B, Steenbruggen I, Carter KW, et al. The Global Lung Function Initiative (GLI) Network: bringing the world’s respiratory reference values together. Breathe (Sheff). 2017;13:e56–64.
Kaminsky DA. Is There a Role for Using Race-Specific Reference Equations? Yes and No. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;205:746–8.
Regan EA, Lowe ME, Make BJ, Curtis JL, Chen QG, Crooks JL, et al. Early Evidence of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Obscured by Race-Specific Prediction Equations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024;209:59–69.
Ford ES, Mannino DM, Wheaton AG, Giles WH, Presley-Cantrell L, Croft JB. Trends in the Prevalence of Obstructive and Restrictive Lung Function Among Adults in the United States. Chest. 2013;143:1395–406.
GOLD COPD 2019 Report. 2019;
CDC. NHANES Response Rates and Population Totals. at < https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/ResponseRates.aspx >.
Johnson CL, Paulose-Ram R, Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kruszon-Moran D, Dohrmann SM, et al. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: Analytic guidelines, 1999–2010. 2013;at < https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/analyticguidelines/99-10-analytic-guidelines.pdf >.
Moffett AT, Bowerman C, Stanojevic S, Eneanya ND, Halpern SD, Weissman GE. Global, Race-Neutral Reference Equations and Pulmonary Function Test Interpretation. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6: e2316174.
Bowerman C, Bhakta NR, Brazzale D, Cooper BR, Cooper J, Gochicoa-Rangel L, et al. A Race-neutral Approach to the Interpretation of Lung Function Measurements. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023;207:768–74.
Ekström M, Mannino D. Race-specific reference values and lung function impairment, breathlessness and prognosis: Analysis of NHANES 2007–2012. Respir Res. 2022;23:271.
Higbee DH, Granell R, Davey Smith G, Dodd JW. Prevalence, risk factors, and clinical implications of preserved ratio impaired spirometry: a UK Biobank cohort analysis. Lancet Respir Med. 2022;10:149–57.
CDC. National Trends in COPD. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Data and Statistics 2022;at < https://www.cdc.gov/copd/data-and-statistics/national-trends.html >.
Tilert T, Paulose-Ram R, Howard D, Butler J, Lee S, Wang MQ. Prevalence and factors associated with self-reported chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among adults aged 40–79: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2007–2012. EC Pulmonol Respir Med. 2018;7:650–62.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Borlée F, Yzermans CJ, Krop E, Aalders B, Rooijackers J, Zock J-P, et al. Spirometry, questionnaire and electronic medical record based COPD in a population survey: Comparing prevalence, level of agreement and associations with potential risk factors. In: Leroyer C, editor. PLoS One 2017;12:e0171494.
Shahab L, Jarvis MJ, Britton J, West R. Prevalence, diagnosis and relation to tobacco dependence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a nationally representative population sample. Thorax. 2006;61:1043–7.
Cook SF, Hirschtick JL, Fleischer NL, Arenberg DA, Barnes GD, Levy DT, et al. Cigarettes, ENDS Use, and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Incidence: A Prospective Longitudinal Study. Am J Prev Med. 2023;65:173–81.
Barnes PJ. Sex Differences in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Mechanisms. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193:813–4.
Gan WQ, Man SFP, Postma DS, Camp P, Sin DD. Female smokers beyond the perimenopausal period are at increased risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir Res. 2006;7:52.
Kurth L, Doney B, Halldin C. Prevalence of airflow obstruction among ever-employed US adults aged 18–79 years by longest held occupation group: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2008. Occup Environ Med. 2016;73:482–6.
Raherison C, Girodet P-O. Epidemiology of COPD. Eur Respir Rev. 2009;18:213–21.
Wang Z, Li Y, Lin J, Huang J, Zhang Q, Wang F, et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and mortality of COPD in young people in the USA: results from a population-based retrospective cohort. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2023;10: e001550.
Wan ES, Balte P, Schwartz JE, Bhatt SP, Cassano PA, Couper D, et al. Association Between Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry and Clinical Outcomes in US Adults. JAMA. 2021;326:2287–98.
Yang S, Liao G, Tse LA. Association of preserved ratio impaired spirometry with mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir Rev. 2023;32: 230135.
Stang P, Lydick E, Silberman C, Kempel A, Keating ET. The prevalence of COPD: using smoking rates to estimate disease frequency in the general population. Chest. 2000;117:354S-S359.
Celli BR, Halbert RJ, Nordyke RJ, Schau B. Airway obstruction in never smokers: results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Med. 2005;118:1364–72.
Putcha N, Anzueto AR, Calverley PMA, Celli BR, Tashkin DP, Metzdorf N, et al. Mortality and Exacerbation Risk by Body Mass Index in Patients with COPD in TIOSPIR and UPLIFT. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2022;19:204–13.
Jones RL, Nzekwu M-MU. The effects of body mass index on lung volumes. Chest 2006;130:827–833.
Cecere LM, Littman AJ, Slatore CG, Udris EM, Bryson CL, Boyko EJ, et al. Obesity and COPD: associated symptoms, health-related quality of life, and medication use. COPD. 2011;8:275–84.
Collins BF, Ramenofsky D, Au DH, Ma J, Uman JE, Feemster LC. The Association of Weight With the Detection of Airflow Obstruction and Inhaled Treatment Among Patients With a Clinical Diagnosis of COPD. Chest. 2014;146:1513–20.
Verberne LDM, Leemrijse CJ, Swinkels ICS, Van Dijk CE, De Bakker DH, Nielen MMJ. Overweight in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease needs more attention: a cross-sectional study in general practice. npj Prim Care Resp Med 2017;27:63.
VazFragoso CA, Gill TM, McAvay G, Yaggi HK, Van Ness PH, Concato J. Respiratory Impairment and Mortality in Older Persons: A Novel Spirometric Approach. J Investig Med. 2011;59:1089–95.
Washio Y, Sakata S, Fukuyama S, Honda T, Kan-O K, Shibata M, et al. Risks of Mortality and Airflow Limitation in Japanese Individuals with Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;206:563–72.
Heo IR, Kim HC, Lee SJ, Yoo J-W, Ju S, Jeong YY, et al. Impact of coexistent preserved ratio impaired spirometry on the survival of patients with lung cancer: Analysis of data from the Korean Association for Lung Cancer Registry. Thoracic Cancer. 2021;12:2478–86.
Sun XW, Zhang LY, Li QY. Understanding Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry in Multiple Dimensions: Concerns over Restrictive Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023;208:1139.
Pan J, Adab P, Jiang CQ, Zhang WS, Zhu F, Jin YL, et al. All-cause and cause-specific mortality from restrictive and obstructive spirometric patterns in Chinese adults with and without dyspnea: Guangzhou Biobank Cohort Study. Respir Med. 2019;151:66–80.
Miura S, Iwamoto H, Omori K, Yamaguchi K, Sakamoto S, Horimasu Y, et al. Preserved ratio impaired spirometry with or without restrictive spirometric abnormality. Sci Rep. 2023;13:2988.
Guerra S, Carsin A-E, Keidel D, Sunyer J, Leynaert B, Janson C, et al. Health-related quality of life and risk factors associated with spirometric restriction. Eur Respir J. 2017;49:1602096.
Smith LJ. Postbronchodilator Reference Values: Should They Be the Norm? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023;208:356–7.
Mannino DM, Diaz-Guzman E, Buist S. Pre- and post-bronchodilator lung function as predictors of mortality in the Lung Health Study. Respir Res. 2011;12:136.
Sterk PJ. Let’s not forget: the GOLD criteria for COPD are based on post-bronchodilator FEV1. Eur Respir J. 2004;23:497–8.
Haynes JM. Basic spirometry testing and interpretation for the primary care provider. Can J Respir Ther 2018;54:.
Enright PL, Beck KC, Sherrill DL. Repeatability of Spirometry in 18,000 Adult Patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;169:235–8.
Download references
This project was funded through the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) grants K01CA260378 and U54CA229974. Mr. Cadham receives additional funding through pre-doctoral fellowships from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (DFD – 187708) and the PhRMA Foundation (AWD024330). The opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not reflect the views of the funders, the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Health and Human Services, the FDA or the United States government.
Author information
Christopher J. Cadham and Hayoung Oh contributed equally and are co-first authors.
Authors and Affiliations
School of Public Health, Department of Health Management and Policy, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
Christopher J. Cadham
Georgetown University-Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Washington, DC, USA
Hayoung Oh, David T. Levy & Luz María Sánchez-Romero
Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care, University of Michigan Health System, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
MeiLan K. Han
Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA
David Mannino
COPD Foundation, Miami, FL, USA
School of Public Health, Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
Steven Cook
BC Cancer Research Institute, Vancouver, Canada
Rafael Meza
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The authors contributed to the paper as follows: Conception and design: HO, CJC, MKH, LMSR. Methodology: HO, CJC, LMSR. Data curation: HO. Formal analysis: HO, CJC, LMSR. Original draft: HO, CJC, LMSR. Critical revision of manuscript: HO, CJC, MKH, DM, SC, RM, DTL, LMSR. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Luz María Sánchez-Romero .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable, this study uses publicly available anonymous data.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interest
CJC received research support funding from Imvaria, Inc. for unrelated work.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Cadham, C.J., Oh, H., Han, M.K. et al. The prevalence and mortality risks of PRISm and COPD in the United States from NHANES 2007–2012. Respir Res 25 , 208 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-024-02841-y
Download citation
Received : 15 January 2024
Accepted : 06 May 2024
Published : 15 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-024-02841-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Preserved ratio impaired spirometry
Respiratory Research
ISSN: 1465-993X
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Questionnaires vs. surveys. A survey is a research method where you collect and analyze data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.. Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives, placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
A questionnaire is defined a market research instrument that consists of questions or prompts to elicit and collect responses from a sample of respondents. This article enlists 21 questionnaire templates along with samples and examples. It also describes the different types of questionnaires and the question types that are used in these questionnaires.
As a research instrument, a questionnaire is ideal for commercial research because the data you get back is from your target audience (or ideal customers) and the information you get back on their thoughts, preferences or behaviors allows you to make business decisions. 6. A questionnaire can cover any topic.
We frequently test new survey questions ahead of time through qualitative research methods such as focus groups, cognitive interviews, pretesting (often using an online, opt-in sample), or a combination of these approaches. Researchers use insights from this testing to refine questions before they are asked in a production survey, such as on ...
A questionnaire is an important instrument in a research study to help the researcher collect relevant data regarding the research topic. It is significant to ensure that the design of the ...
There are several modes of questionnaire administration. The choice of mode depends on the research objectives, sample size, and available resources. Some common modes of administration include: Self-administered paper questionnaires: Participants complete the questionnaire on paper, either in person or by mail. This mode is relatively low cost ...
10. Test the Survey Platform: Ensure compatibility and usability for online surveys. By following these steps and paying attention to questionnaire design principles, you can create a well-structured and effective questionnaire that gathers reliable data and helps you achieve your research objectives.
1. Early questions should be easy and pleasant to answer, and should build rapport between the respondent and the researcher. 2. Questions at the very beginning of a questionnaire should explicitly address the topic of the survey, as it was described to the respondent prior to the interview. 3. Questions on the same topic should be grouped ...
writing questions and building the construct of the questionnaire. It also develops the demand to pre-test the questionnaire and finalizing the questionnaire to conduct the survey. Keywords: Questionnaire, Academic Survey, Questionnaire Design, Research Methodology I. INTRODUCTION A questionnaire, as heart of the survey is based on a set of
Filter by survey type. All our sample survey template questions are expert-certified by professional survey methodologists to make sure you ask questions the right way-and get reliable results. You can send out our templates as is, choose separate variables, add additional questions, or customize our questionnaire templates to fit your needs.
A questionnaire is a research instrument that consists of a set of questions or other types of prompts that aims to collect information from a respondent. A research questionnaire is typically a mix of close-ended questions and open-ended questions. Open-ended, long-form questions offer the respondent the ability to elaborate on their thoughts.
A questionnaire is a research tool that contains a series of questions used to gain information from respondents about their opinions, experiences, and behaviors. Questionnaires may elicit quantitative or qualitative data and be delivered online, by phone, on paper, or in person. First developed by Sir Francis Galton, a British anthropologist ...
How to make a questionnaire: Keep questions short and focused on one topic at a time. Use multiple choice questions to fit answers into a specific category. Use an open-ended question to capture comments. A Likert scale or MaxDiff question can be used for market research. Collect responses for your questionnaire using an email collector, anonymous link, or even a QR code.
The research questionnaire is one of the quantitative data-gathering methods a researcher can use in their research paper. 1. Market Research Questionnaire Template Example. Details. File Format. Size: 38 KB. Download. 2. Market Research Questionnaire Example.
However, the quality and accuracy of data collected using a questionnaire depend on how it is designed, used, and validated. In this two-part series, we discuss how to design (part 1) and how to use and validate (part 2) a research questionnaire. It is important to emphasize that questionnaires seek to gather information from other people and ...
A research questionnaire is a tool that consists of a series of standardized questions with the intent of collecting information from a sample of people. Think of it as a kind of written interview that follows a fixed scheme to ensure that data remains accurate.
This includes designing questions or using a premade template. Below are some of the best research survey examples, templates, and tips for designing these surveys. 20 research survey examples and templates. Specific survey questions for research depend on your goals. A research questionnaire can be conducted about any topic or interest.
A questionnaire is a research tool used to conduct surveys. It includes specific questions with the goal to understand a topic from the respondents' point of view. ... What are Survey Sample Sizes & How to Find Your Sample Size Jun 26, 2023 24 Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Survey Questions to Ask Your Employees Apr 05, 2023 Join 64,500 ...
However, for this study, a survey or a questionnaire was formed as a tool to collect the data using Google Form. This survey method was chosen because by analyzing a sample from a group, a survey ...
Questionnaires vs surveys. A survey is a research method where you collect and analyse data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.. Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives, placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
Sense of coherence (SOC) is a personal resource that reflects the extent to which one perceives the world as comprehensible, manageable, and meaningful. Decades of empirical research consistently show that SOC is an important protective resource for health and well-being. Despite the extensive use of the 13-item measure of SOC, there remains uncertainty regarding its factorial structure.
Sample Preparation. Preparing your sample for submission. The sample should usually be solvent-free and pure. (Purity is not a requirement for GC/MS or LC/MS, and both ESI and MALDI can also handle moderate mixtures.) There should be no excess salts in your sample, especially for FAB, ESI, and MALDI. Buffers such as phosphate and HEPES are ...
We estimated the prevalence and mortality risks of preserved ratio impaired spirometry (PRISm) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in the US adult population. We linked three waves of pre-bronchodilator spirometry data from the US National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (2007-2012) with the National Death Index. The analytic sample included adults ages 20 to 79 ...
I am currently conducting a survey on the acceptance of ChatGPT in academia, and your input would be incredibly valuable. Participants must either be current students or have previously studied and used ChatGPT. The questionnaire only takes about max. 5 Minutes to complete. Find the questionnaire here: https://sosci.univie.ac.at ...
Frequently asked questions The following are frequently asked questions about this role: What is a typical day like for a research intern? As a research intern, your day-to-day tasks can vary greatly depending on your project.However, you can expect a blend of data analysis, meetings with your team or supervisor, conducting experiments or studies and drafting reports of your findings.
In 2022, the Agricultural Resource Management Survey (ARMS) included a targeted sample of farms and ranches operated by socially disadvantaged producers. USDA, Economic Research Service researchers used this data to compare groups of farms based on the racial and ethnic characteristics of the farm operators.
The survey findings are a result of a three-step process. We first surveyed 6,273 Americans from a nationally representative online sample from Jan. 16 to 27, 2024, to understand the public's top-of-mind awareness of companies that either excel or falter in society. Respondents are asked which two companies — in their opinion — stand out as ...