- MY LCI Login
- LCI Design & LCI Engineering Design Award
- Our Mission & Vision
- Our Strengths
- History of LCI
- How We Serve
- Board of Directors
- LCI Congress 2024
- Lean in Design Forum 2024
- Respect For People
- Communities
- New to Lean
- Learn by Pathway
- For Designers
- For Constructors
- Field Crew Huddle
- Assessments
- Classroom Learning
- Instructor Program
- LCI Publications
- Learning Videos
- Partner Programs
- Simulations
- Certification FAQs
- Certification Practice Quiz
- Designation Directory

- Lean Construction
- Lean Design
- Lean Project Delivery
- What is Lean?
- Founder’s White Papers
- Lean Construction Journal
- LCI Research
- Newsletter Archives
- Past Event Presentations
- Blog & Buzz
- Lean Consultant Members
- Member Directory

A3: Thinking, Reports, Examples & Templates
A3 thinking.
An Introduction to A3
In the design and construction industry – as in all industries – complex problems arise daily. Each project contains hundreds of decisions containing thousands of variables, and sorting them out to arrive at the best outcome is critical.
A3 problem solving provides teams with a strategy to effectively and efficiently deal with problems that they encounter and decisions that need to be reached. In true Lean fashion, A3 process improvement brings the entire team into the collaborative problem-solving process and allows teams to embrace out-of-the-box solutions.

What is A3?
An A3 is a one-page report prepared on a single 11 x 17 sheet of paper that adheres to the discipline of PDCA thinking as applied to collaborative problem solving, strategy development or reporting. The A3 includes the background, problem statement, analysis, proposed actions, and the expected results.
The History
A3 thinking was developed by Toyota in the 1940s. Toyota believed that any problem should be capable of being explained and solved using one sheet of paper (an 11 x 17 sheet being the largest sized paper that is capable of being faxed and closest in size to the traditional A3).
The company also believed that if a problem is too complex to fit onto an A3 report, it should be broken down into smaller bits that would be solved individually. If your problem cannot fit onto an A3, you should reconsider the scope of what you are hoping to accomplish.
Who Uses A3 Strategies?
Today, A3 strategies are deployed across various industries that employ Lean thinking such as:
- Design & Construction
- Manufacturing
- Project Management
- Engineering & Architecture
- Service Industries
LCI’s Meaning of A3
A3 thinking is an extremely useful tool when utilized correctly. By distilling the entirety of a problem on a single sheet of paper, A3 Lean thinking forces team members to collaborate and rationalize through the problem solving process. A3 thinking makes for more effective problem solving and produces written explanations that can then be passed on to senior management. An effectively completed A3 report will also build management’s confidence in the team and its ability to solve problems.
A3 Reporting
A well-written A3 report should show and explain the consideration that went into the counter-measure to the problem listed. Properly executed plans include the input of team members from all across the stakeholder spectrum and should allow members to emerge as leaders in its problem solving. A3 papers can also be referenced later, allowing the lessons learned during the process to be shared with future project teams.
Understanding A3 Thinking
A3 thinking does not provide a solution to the problem your team is facing. Rather, it guides your team’s process to help it reach the best possible countermeasure with the tools it has at its disposal.
An A3 report is to be filled out by one person on the team – the “champion” – who will gather assessments and intel from other members in a collaborative fashion. Bringing all of the knowledge and expertise of the team to bear when solving a problem is the best way to come to a satisfying outcome.
Problem Solving: An A3 Process
A3 thinking allows for many different types of decision-making. But ultimately, all decisions are fundamentally a form of problem solving. For example, A3 thinking can be deployed to guide the team in optimizing decisions during the design phase, or for solving a constructability challenge.
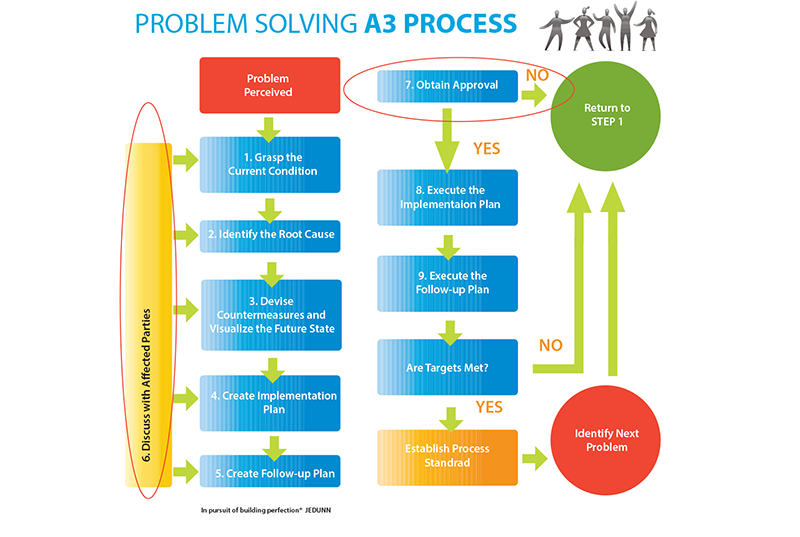
The First Step to A3 Thinking
The first step of the A3 process for problem solving is to correctly identify the problem. From unexpected lead times on materials to communication breakdowns among design teams, “problems” are in no short supply in the design and construction industry. Before engaging in A3, ask yourself the following questions about the problem you are working to solve.
Questions to Facilitate the Process
- What are you trying to address or solve?
- What is the current situation?
- What are clear Conditions of Satisfaction (CoS) I can develop?
- Where can I brainstorm and analyze the 5 whys/root cause ideas?
- What’s a recommendation I can put forth?
- What is my plan to implement the recommendation above (if applicable)?
State plan to check and adjust using the PDCA cycle.
More on the PDCA Cycle
PDCA stands for Plan, Do, Check, Adjust. Explore each element of this acronym for more information about how it supports both the problem solving questions above as well as A3 problem solving as a whole.
Identify an issue in your process and exercise continuous improvement by planning your course of change.
Perform your case study by applying the corrective actions outlined in the “plan” stage in an experimental manner.
Follow the performance of your experiment and measure it to determine whether it is having the desired effect.
If your plan worked, implement the change to the necessary areas of your process. If it did not, determine what you will do differently next time and repeat the cycle.
A3 Reports for Solutions
While A3 reports broadly follow the PDCA cycle, the actual journey of an A3 process is a bit more granular. Let’s analyze the various steps and sections of an A3 report.
Describe the problem, theme, or issue. List out all of the details including the champion’s name, date, and the names of all of the collaborators who will be helping with the report.
Establish the business context & importance. Provide additional information on the problem being addressed.
Current State
Describe what is currently known about the problem. Note potential variables and roadblocks that may stop your team from solving this problem and additional information you hope you acquire.
Future State or Goal
Identify the desired outcome for your experiment. Identify the Conditions of Satisfaction (CoS) for the project.
Analyze the situation and underlying cause.
Recommendation
Provide a recommendation for process improvement that your team can implement for the future.
Create a follow-up/review process.
A3 Examples
A3 thinking is frequently applied in Lean design and Lean construction during all phases of the process for the purposes of making sound decisions. In the example below, A3 thinking is applied to the process of learning Lean design and construction techniques.

A3 Template
The Lean Construction Institute seeks to educate companies all throughout the design and construction industry on Lean practices and methods. Here is our A3 template which you can use to guide your decision-making processes.
A3 Training
The Lean Construction Institute offers A3 training as well as tools , events , education , and networking opportunities for Lean practitioners in design and construction all around the world. Whether you’re a Lean expert or are just learning about Lean for the first time, LCI can provide the tools you need for problem solving and continuous improvement in your business.
Lean Assessments
How strong is your Lean knowledge? Take a Lean assessment to determine your current state so you have a baseline for improvement. Lean assessments are available for individuals, teams, and organizations alike. Whether you’re new to Lean or are an experienced Lean practitioner, Lean assessments are a great way to get started at LCI!

William R. (Bill) Seed, Executive Editor

Executive Editors: Kristin Hill, Katherine Copeland and Christian Pikel
More lean topics.
From 5s to IPD, explore more popular Lean design and construction topics below.


- Guide: A3 Problem Solving
Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is an experienced continuous improvement manager with a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt and a Bachelor's degree in Business Management. With more than ten years of experience applying his skills across various industries, Daniel specializes in optimizing processes and improving efficiency. His approach combines practical experience with a deep understanding of business fundamentals to drive meaningful change.
- Last Updated: June 13, 2023
- Learn Lean Sigma
Problem-solving is one of the key tools a successful business needs to structure improvements and one I have been using to solve problems in a structured way in my career at a range of businesses over the years. When there is a problem in business that is leading to increased costs, waste , quality issues, etc., it is necessary to address these problems. A3 structured problem solving is a Lean Six Sigma methodology that has been designed and developed to support continuous improvement and solve complex business problems in a logical and structured process.
The guide will give you a full understanding of what A3 Problem solving is and a breakdown of all the steps of how to apply it within your business with an example of where I have made improvements with it previously.
Table of Contents
Importance of a3 in lean management.
The A3 problem-solving method is a key tool in Lean Six Sigma and continuous improvement in business, and in my experience, it is often the standard approach all improvement activities must follow and is particularly popular in the automotive industry. This is because of the following:
Focus on Root Causes : Rather than applying a quick fix to a problem or jumping to conclusions and solutionizing, A3 requires gaining a deep understanding of the root causes of the problem. By addressing these root causes, the chances of recurrence is reduced.
Standardization : With a consistent format, the A3 process ensures that problems are approached in a standardized way, regardless of the team or department. This standardization creates a common language and understanding across the organization and ensures all problems are addressed to the same standard and approach.
Team Involvement : An A3 isn’t an individual process. It requires a cross-functional team to work together on problem-solving, ensuring that a range of perspectives and expertise is considered. This collective approach builds a stronger understanding of the problem and ensures that solutions are well-rounded and robust.
Visual Storytelling : The A3 report serves as a visual storyboard, making it easier for stakeholders at all levels to understand the problem, the analysis, and the countermeasures. This visualization enhances communication and drives alignment.
The 6 Steps of A3 Problem Solving (With Real Example)
The A3 problem-solving process can initially seem difficult if you have never done one before and particularly if you have never been a team member in one. To help you with this we will break down the 6 steps into manageable activities, followed by a real-life example to help you apply this method within your business.
As a side note, the A3 problem-solving process was actually one of the first Lean Six Sigma tools I learned to use three weeks into my continuous improvement career after being thrown into the deep end due to resource availability, so I can understand how difficult it can be to understand.
Step 1: Describe the problem
Problem description.
The problem description is an important first step in the process as it ensures a common understanding with the team of what the issue is that needs to be addressed. This can be done by using a technique called the 5W1H Is/Is Not method to help gain a clear understanding of the problem.
To understand the 5W1H Is/Is Not the Process, check out our guide for details of that technique. However, in short, it’s about asking key questions about the problem, for example, “What IS the problem?” and “What IS NOT the problem?”
Let’s say you have been asked to look into a problem where “Machine downtime on the automotive assembly line has increased by 30% over the past three months, leading to production delays and increased costs.”
An example of a 5W1H Is/Is Not on this may result in the following output:
Based on this we can create a clear problem description as the focus of the project that give the team a clear and common understanding of the issue looking to be resolved in the next steps of the process. The problem description could then be written as:
“Over the past three months, machine downtime on Automotive Assembly Line No.3 has increased by 30%. This has predominantly affected the assembly line workers and leads, leading to production delays and higher labour costs. “
Current Condition
Next is demonstrating the current condition and demonstrating the impact on the business. This can often be done with data and charts to back up the problem that might show trends or changes in outputs.
This might look something like the below and demonstrate a good baseline for confirming the improvement at the end of the A3

Containment Actions
Next is containment actions. Since you have identified a problem, there is likely an impact on the business or the customer. As a team, you should consider what can be done to limit or eliminate this problem in the short term. Remember this is just a containment action and should not be seen as a long-term fix.
In our situation we decided to “Implement temporary overtime shifts to meet production goals, leading to an increase in labor costs.”
At this stage, the A3 should look similar to the one below; you can use charts and graphics to represent the current state as well if they fit within the limit area. Remember, we must include the content of the A3 within the 1-page A3 Document.

Step 2: Set the A3 Goals
The next step of the A3 is to, as a team, set the goal for the project. As we have a clear understanding of the current condition of the problem, we can use that as our baseline for improvement and set a realistic target for improvement.
A suggested method for setting the Target condition would be to use the SMART Target method.
If you are not familiar with SMART Targets , read our guide; it will cover the topic in much more detail. In short, a SMART target creates a goal statement that is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound.
By doing this you make it very clear what the goal of the project is, how it will be measured, it is something that can be achieved, relevant to the needs of the business and has a deadline for when results need to be seen.
For our A3 we decided that the goal would be “Our goal is to achieve at least a 20% reduction in machine downtime on Automotive Assembly Line No.3, lowering it from 90 minutes to no more than 72 minutes per day per machine, within the next 60 days. This reduction is crucial for increasing productivity and reducing labour costs, aligning with our overall business objectives.”
I also recommend using charts in this section to visualize the benefit or improvement to ensure you have stakeholder and sponsor support. Visuals are much easier and faster for people to understand.

At this point, your A3 might look something like the one below, with the first 1/4 or section complete. The next step is to move on to the root cause analysis to get to the root of the problem and ensure the improvement does not focus on addressing the symptoms of the problem.

Step 3: Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is the next step in the process, often referred to as gap analysis, as this step focuses on how to get to the goal condition from the current condition.
Tip: If at this point you find the team going off-topic and focusing on other issues, Ask the question, “Is this preventing us from hitting our goal statement?” I have found this very useful for keeping on track in my time as an A3 facilitator.
For root cause analysis, a couple of key tools are usually used: a fishbone diagram and a five-why Analysis . Again, we won’t go into the full details of these tools within this guide, as they have been covered in extensive detail in their own guides.
But the aim at this point is as a team, to brainstorm what is preventing us from achieving our target condition. This is done by allowing all members of the team to input the reasons they think it is not being achieved. These inputs are often written on sticky notes and placed on the fishbone diagram. Following this, you may have results similar to the ones below. Note: it is important that the inputs are specific so they can be understood. e.g. “Calibration” alone is not specific to how it’s causing the problem; specify it with “Calibration: Inaccurate measurements affecting machine settings.”

After the fishbone diagram has been populated and the team has exhausted all ideas, the team should then vote on the most likely cause to explore with a 5 Whys analysis. This is done because, due to resource limitations, it is unlikely all of the suggestions can be explored and actioned.
In this situation the team decided the “lack of preventative machines: machines not being serviced regularly” was the cause of increased downtime. This was explored with the 5 Whys to get to the root cause of why Assembly Line 3 did not have preventative maintenance implemented.
The result of this root cause analysis can be seen below, and you may end up with more ideas on the fishbone, as generally there are a lot of ideas generated by a diverse team during brainstorming.

Step 4: Solutions and Corrective Actions
Now that we understand what the root cause of the problem is, we need to address it with solutions and corrective actions. Again, as a team, consider the root cause of the problem and discuss what actions need to be taken by the team, who will do them, and when they will be done. The result should be an action plan, for example, like the one below:

This action plan needs to be carried out and implemented.
The result of this section will likely just be an action list and look like the below section.

Step 5: Validate Solution and Standardize
Within step 5 it is time to collect data to validate and confirm the actions that have been implemented resulting in solving the problem and meeting the target state of the problem. This is done by continuing to collect data that demonstrates the problem in the baseline to see if the problem is being reduced.
For example, below, the project team continued to collect Assembly Line 3 downtime data on a weekly basis. Initially, there was a steady reduction, likely due to the focus of the project on the problem, which had some impact. However, once the majority of the action was implemented, a huge drop in product downtime was seen, exceeding the target. This showed the actions have been successful

If, in the validation stage, you find that the improvement required is not being made, you should go back to step 3 and reconsider the root cause analysis with the team, pick another area to focus on, and create an action plan for that following the same steps.

Step 6: Preventive Actions and Lessons Learned
In step 6 after the confirmation of project success you should look at preventive actions and lessons learned to be shared from this project:
- Preventive Action: The new preventive maintenance schedule will be standardized across all assembly lines. This will prevent other lines having similar issues and make further improvements
- Lessons Learned: A formal review will be conducted to document the process, including challenges faced and how they were overcome, which will then be archived for future reference.
In our project, this looked like the one below and will be used as a reference point in the future for similar issues.

And that is the successful completion of a structured A3 problem-solving technique.
The complete A3 looks like the below image. Yours may slightly differ as the problem and information vary between projects.

Downloadable A3 Reporting Template
To support you with your A3 problem solving, you can download our free A3 problem solving report from the template section of the website.

Problem-solving is important in businesses, specifically when faced with increased costs or quality issues. A3 Structured Problem Solving, rooted in Lean Six Sigma, addresses complex business challenges systematically.
Originally from Toyota’s lean methodology, A3, named after the 11″x17″ paper size, visually maps problem-solving processes. This method ensures concise communication and focuses on crucial details, as illustrated by the provided example.
Emphasized in Lean Management, A3 stresses understanding root causes, standardization across teams, team collaboration, and visual representation for clarity. This tool is not only a guide to understanding the issue but is a standardized format ensuring robust solutions. Particularly for novices, breaking down its six steps, from problem description to setting A3 goals and root cause analysis, provides clarity. Visual aids further enhance comprehension and alignment across stakeholders.
- Sobek II, D.K. and Jimmerson, C., 2004. A3 reports: tool for process improvement. In IIE Annual Conference. Proceedings (p. 1). Institute of Industrial and Systems Engineers (IISE).
- Matthews, D.D., 2018. The A3 workbook: unlock your problem-solving mind . CRC Press.
Q: What is A3 problem solving?
A: A3 problem solving is a structured approach used to tackle complex problems and find effective solutions. It gets its name from the A3-sized paper that is typically used to document the problem-solving process.
Q: What are the key benefits of using A3 problem solving?
A: A3 problem solving provides several benefits, including improved communication, enhanced teamwork, better problem understanding, increased problem-solving effectiveness, and the development of a culture of continuous improvement.
Q: How does A3 problem solving differ from other problem-solving methods?
A: A3 problem solving emphasizes a systematic and structured approach, focusing on problem understanding, root cause analysis, and the development and implementation of countermeasures. It promotes a holistic view of the problem and encourages collaboration and learning throughout the process.
Q: What are the main steps in the A3 problem-solving process?
A: The A3 problem-solving process typically involves the following steps: problem identification and description, current condition analysis, goal setting, root cause analysis, countermeasure development, implementation planning, action plan execution, and follow-up and evaluation.
Q: What is the purpose of the problem identification and description step?
A: The problem identification and description step is crucial for clarifying the problem, its impact, and the desired outcome. It helps establish a common understanding among the team members and ensures everyone is working towards the same goal.

Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.
Free Lean Six Sigma Templates
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.

Other Guides
Was this helpful.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
- Patient safety and quality improvement
- Patient safety and CQI resources
- A3 problem solving tools
Guide to an A3 problem solving report
An A3 problem solving report is usually structured as follows:
PROBLEM STATEMENT
State the problem you want to address in one or two sentences. Address the problem from a service user point of view. Only include details that can be observed and quantified from the current situation.
CURRENT STATE
Determine your current state by answering the following questions: What is the problem? Why are you trying to resolve it? Support your answers with evidence. It is useful to express your answers visually through mapping or charting your information (e.g. value stream map, statistical process control chart , spaghetti map , pareto chart, process flowchart ).
FUTURE STATE
Provide a statement that represents the situation you envision achieving as a result of the improvement. From this, create SMART goals for your intervention (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and time-bounded).
ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS
In order to improve the situation, you need to know why the problem exists. Identify contributory causes and root causes using tools such as ‘5 whys’ or fishbone (Ishikawa) diagram .
DETERMINE COUNTERMEASURES
Define and list the actions needed to achieve your planned improvement, taking into account their anticipated effectiveness, cost and time requirements. Each action should contribute to your envisioned future state.
IMPLEMENTATION PLAN
Make an action plan (use a Gantt chart or other project management system) to document how the improvements will be made, by whom and by when. In this way, you will be able to track progress and maintain accountability for each action.
EVALUATION OF RESULTS AND PROCESS
Provide details of the improvements achieved, using quantitative data if possible (e.g. run chart ). Record reflections on your team’s learning from the process.
FOLLOW-UP ACTIONS
Make an action plan to record the effectiveness of the changes. Be specific: what will be measured, by whom and for how long? Think about how you will disseminate the information. Set a date for review of implementation. Additional actions to sustain or refine the improvement are identified here.
Action plan structure
- Consultancy
- Online Courses
SIGN UP TODAY
- Lean , Lean Culture , Lean Training , Lean Wiki , Tools
A Deep Dive into the A3 Problem-Solving Approach
- 11 mins to read
- June 20, 2023
- By Reagan Pannell
In today’s fast-paced and fiercely competitive business world, organisations must find ways to continuously adapt, evolve, and excel. Amidst the myriad methods and techniques for achieving improvements and driving continuous improvement, few have proven as profound and transformative as Toyota’s A3 problem-solving approach.
A significant driving force behind the company’s rise to global prominence, the A3 process fosters a culture where problems are embraced as opportunities for growth and learning. In this article, we’ll explore the origins and underlying principles of the A3 approach and uncover the secrets to its success in unlocking the power of improvements.
Understanding the A3 Approach
The A3 methodology is an integral part of the Toyota Production System (TPS), a set of principles and practices that have shaped the company’s approach to manufacturing, management, and continuous improvement over the years. Named after the A3 sheet of paper that was historically used to capture the plan, analysis, and follow-up on a single page, the A3 process represents a simple, yet powerful, tool for addressing complex challenges and discovering lasting solutions.
At its core, the A3 approach is rooted in three key elements:
1. Thorough problem analysis: The foundation of the A3 process lies in digging deep to diagnose the true nature and root cause of an issue, rather than jumping to hastily devised fixes that merely address symptoms.
2. Structured documentation: The A3 report serves as both a communication tool and an iterative planning device, with each section building on the previous ones to guide problem solvers through a comprehensive analysis, solution development, and execution process. It’s the foundation of good continuous improvement.
3. Cyclical learning and improvement: Leadership and employees alike are encouraged to commit to hypothesis-driven inquiry, observation, experimentation, and reflection, leading to a culture that actively seeks and leverages opportunities for growth by solving problems.
How to Implement the A3 Process in Your Organisation
The Lean Thinking A3 approach can be distilled into seven essential steps:
1. Identify the problem:
Clearly articulate and define the issue at hand, avoiding the temptation to jump to solutions or assume important facts to be self-evident..
When identifying the problem, it is important to ensure that all relevant stakeholders in the organisation are consulted. This helps to ensure that the issue is accurately described and understood from multiple perspectives. A thorough problem analysis should also include conducting research into possible causes or root issues, and clearly documenting any observed symptoms of the problem. Additionally, it is essential to identify any major risks associated with not finding a solution and recognise any constraints (both external and internal) that may exist which could limit potential solutions. Lastly, it is important to consider any potential opportunities which may arise from addressing the issue that may have been overlooked at first glance. This is the problem statement part which is a critical component that identifies the difference between the current condition and the target condition.
At this stage, we are not looking at how to solve problems being faced or at the potential solution to solving problems. It’s about developing a good understanding of how the actual results differ from the expected results and providing an in-depth systematic approach to process improvement and developing problem-solving skills.
2. Establish the context and background:
Provide a high-level overview of the problem, describing the stakeholders involved, relevant data, and the broader organisational context in which the challenge has arisen..
It is important to ensure that all stakeholders are properly considered when identifying any potential solutions as their perspectives can play a vital role in determining an effective solution. All related data should be thoroughly analysed to understand the full scope of potential solutions. This includes resources, costs, timelines, and any legal or regulatory issues that may need to be considered. Additionally, it is important to consider how well-proposed solutions fit within existing organisational policies and procedures as this could impact implementation success. Finally, understanding how proposed solutions would interact with other initiatives or processes currently taking place in the organisation can help inform decisions about whether or not they are viable options. It may include conducting some value stream mapping to dig deeper into the current state.
It is important to fully explore any underlying factors that may be contributing to the issue at hand and ensure in-depth problem analysis. This includes looking deeper into existing systems, structures, and processes related to the problem in order to identify potential areas of improvement or optimisation. Additionally, it is essential to consider any relevant industry trends or external influences that could impact how the problem manifests within the organisation.
When analysing a problem, collecting data from various sources is important to get a more comprehensive understanding of how a particular issue can be addressed. This includes mapping the current process using the VSM, SIPOC, Process Mapping or Flowcharting techniques. Additionally, interviews and surveys can be conducted with stakeholders to gain insights into how they perceive the issue and their perspectives on potential solutions. Lastly, it is important to observe any real-world activities related to the problem to uncover key areas where time, effort, resources, money etc is being wasted. This is the time improvement that may not have been identified otherwise.
GB MASTERCLASS COURSE
Get access to our free gb mastercourse classes, free course previews, fundamentals of lean.
Ready to start your journey into the world of Lean with this free course?
FREE COURSE
Lean Thinking
A Lean focused continious improvement certification course
LSS Yellow Belt
Propel your career forward, tackle complex problems and drive change
LEAN SIX SIGMA GREEN BELT
Get 3-days free access to our green belt course, accelerate your career, 3. set a goal:, now that you have identified the problem and outlined the relevant context, it is time to set a project goal or outcome..
This involves clearly articulating the desired state of affairs and any key deliverables of the proposed solution. Whether it is reducing operational costs, increasing efficiency, improving customer experience, or something else entirely – defining specific objectives with measurable metrics can help ensure that project teams stay focused and remain aligned on their ultimate destination.
At this stage, it is also important to consider how long it will take to reach the desired outcome. Establishing an implementation timeline will help safeguard progress and provide a framework for tracking results along the way. Setting milestones for achieving particular goals at certain points in time can be especially helpful in keeping teams accountable throughout the process. Additionally, having a plan for evaluating success after reaching the end target will allow stakeholders to gain further insights into how effective their approach has been in addressing underlying problems, as well as how well-proposed solutions have fared once implemented.
4. Investigate root causes:
Use a variety of techniques (e.g., the 5 whys, fishbone diagrams, pareto charts) to probe the problem’s underlying causes and avoid settling on proximate reasons..
The process of identifying root causes is essential when using data-driven tools. We always want to find the simplest root cause approach.
One of the most widely used methods for root cause analysis is the ‘5 Whys’ technique. This method involves asking a series of ‘why’ questions to determine the underlying cause of a particular symptom or issue. The goal is to keep asking “Why?” until you reach an answer that can provide insight into how to address the problem and prevent it from occurring in the future.
Another commonly used tool for root cause analysis is the fishbone diagram (also known as Ishikawa diagrams). This approach involves visualising all potential causes which could be causing a symptom or issue in a logical format, allowing users to identify patterns and uncover links between root causes and their respective effects. This technique can be helpful in identifying and focusing on key areas for improvement, as well as helping to identify interdependencies between components within an organisation’s systems.
Finally, Pareto Charts are useful for analysing data collected from surveys, interviews, observations, etc., concerning the severity or frequency of occurrence. This type of chart helps users quickly identify which factors are contributing most significantly towards an issue, allowing them to focus resources towards addressing those areas first and foremost. Additionally, Pareto charts can also be used to prioritise different solutions based on their estimated effectiveness in addressing an issue.
In conclusion, understanding the root cause of an issue through rigorous techniques such as 5 Whys, fishbone diagrams, and Pareto charts provides invaluable insight into how best to address it effectively while preventing it from reoccurring in the future. By leveraging these tools along with other data-led approaches such as process mapping and flowcharting, organisations can ensure that any proposed solutions are well-informed by both qualitative and quantitative data sources as well as ensure they are building consensus across the entire organisation.
5. Countermeasures:
Identify the right countermeasures (corrective actions) to implement that will directly impact the root causes identified..
Brainstorming is a useful tool for identifying potential improvements. It involves coming up with ideas and solutions in an open and collaborative manner, without judgement or criticism. By allowing team members to share their thoughts freely, brainstorming can help uncover innovative solutions that may have otherwise gone unnoticed. Additionally, looking at how waste reduction, flow and pull can be used to improve processes can also provide valuable insights into where improvement opportunities lie.
Brainstorm potential solutions that directly target the root causes and create detailed action plans for implementation, complete with assigned roles, responsibilities, and timelines.
Once the countermeasures are identified, it is important to design an implementation plan and assign roles & responsibilities. This will help ensure that all stakeholders understand their part in the implementation and can work together to achieve the desired outcome. Additionally, it is important to track progress along the way – setting measurable milestones that can be tracked against goals established during the initial problem-solving phase will help keep teams accountable and allow for course corrections if needed.
By utilising A3 Problem Solving Tools such as a template, organisations can easily document and share their analyses with relevant stakeholders throughout each stage of the project. Having detailed record-keeping like this also helps teams stay on target over time while providing insights into how proposed solutions may need to be re-evaluated down the line. This implementation plan provides the entire organisation with a clear project status on a one-page report.
6. Evaluate the results:
Measure the impact of your countermeasures against the problem, using well-defined success criteria, key performance indicators, or other relevant metrics..
Once the countermeasures have been implemented, it is essential to measure and evaluate their success. This can be done by tracking performance against the initial objectives established during the goal phase, as well as establishing key performance indicators to gauge how well the proposed solutions have fared.
Additionally, stakeholders should also consider conducting a post-implementation evaluation in order to assess how successful their approach has been in addressing underlying issues and determining what lessons can be learned from the experience. This will enable teams to identify strengths and weaknesses within their existing processes and make any necessary adjustments going forward. By understanding the outcomes of their improvements, organisations are able to gain valuable insights into how well they’ve succeeded in achieving their goals and ensure continued success moving forward.
Once the countermeasures have been implemented and their success measured, it is important to compare the results against the initial objective. This can be done in a variety of ways, including graphical analysis such as charts, process maps or flow diagrams. Graphical analysis helps to visualise the differences between results achieved before and after the implementation of new measures in a meaningful way. It also provides an increased level of clarity when assessing whether the desired outcomes have been achieved or not.
Process maps can be useful in understanding how changes made during the improvement phase have impacted processes within an organisation. By mapping out existing processes and then comparing them against those following implementation of countermeasures, teams can easily pinpoint where improvements were made and analyse how they led to improved performance overall.
Charts, on the other hand, enable users to quickly identify trends that may have emerged from data collected during the project. For example, if performance metrics are tracked before and after countermeasures are implemented, users can use charts and graphs to more clearly observe any patterns that may indicate an improvement or regression in performance over time – providing further insights into which areas need further attention or adjustment moving forward.
Finally, dashboard views provide an effective means of displaying results at a glance while highlighting any anomalies that might warrant further investigation. Dashboards allow stakeholders to gain access to important information quickly and easily while also helping them keep track of progress towards goals set out during initial problem-solving phases. Additionally, because dashboards support data visualisation capabilities they offer a highly interactive user experience which can help teams understand underlying trends with greater clarity and precision.
7. Standardise and share:
If a countermeasure proves successful, integrate it into the organisation’s standard operating procedures and share it with other teams as a best practice..
Once the countermeasures have been successfully implemented and measured against the initial objectives, these changes need to be integrated into the organisation’s standard operating procedures (SOPs) and shared with other teams as best practices. This will ensure that any improvements made during the problem-solving phase are consistently applied across all teams within the organisation.
In order to ensure that these improvements become part of the organisation’s long-term strategy, process maps should be updated to reflect the new improved way of working. Process maps provide a visual representation of how workflows are structured within an organisation, and by updating them in line with newly-implemented countermeasures, organisations can ensure that their processes continue to remain up-to-date and efficient moving forward. It may also be necessary to build a follow-up plan if not all tasks are fully completed as well as develop a Lean-focused PDCA cycle to ensure long-term effective collaboration on the solutions that were implemented.
Process documentation should also be updated in order to keep track of changes made during problem-solving. By documenting not just the solutions that were proposed but also why they were proposed, teams can gain valuable insights into their decision-making process which they can leverage for similar future problems.
Furthermore, it is important to update key performance indicators (KPIs) to accurately reflect any progress made during problem-solving. By tracking performance against objectives established before and after countermeasures were implemented, organisations will be able to identify any areas that may still need improvement or require further adjustment going forward. Additionally, tracking KPIs over time will help teams understand whether or not their current strategies are leading them towards meeting their goals in a timely manner or if additional measures may need to be taken in order to achieve desired results more quickly.
Finally, organisations should share successful solutions with other teams in order to promote collaboration and knowledge sharing amongst stakeholders throughout different parts of the business. This will allow for ideas generated through one team’s problem-solving efforts to benefit multiple departments – helping foster creativity and innovation while ensuring that everyone is on board with necessary changes being made throughout the organisation. The last step is key to Toyota’s PDCA management system designed for the entire organisation.
By breaking down the problem-solving process into these seven discrete stages, the A3 method offers practitioners a comprehensive, end-to-end framework for tackling complex challenges and driving improvements in any organisation.
- Lean Consultancy
- Corporate Training
Training the team on A3
To get A3 started, everyone in the entire organisation needs to learn how to use this single-sheet or single-page document. This means training people across all parts of the company so that everyone knows how to use the A3 Problem Solving Tool and A3 template. Training will help make sure that everyone follows a structured approach when using A3.
Getting the organisation fully onboard with A3 Problem Solving is not an easy task and will require a dedicated effort to ensure its successful implementation. To this end, it is important to start with specific areas of the business – whether it be operations, finance or marketing – by setting up targeted training sessions for both operational teams and senior managers. This will help everyone understand how and why A3 is used, as well as the potential benefits it can bring to their business.
Once everyone has mastered the basics of working with an A3 template, companies should look to regularly review and evaluate its effectiveness. This could include setting up quarterly reviews or running workshops where teams discuss successes and areas for improvement when using the A3 tool. Doing this will ensure that any issues are identified early on, allowing the team to quickly adjust accordingly.
At Leanscape, we understand that transitioning to A3 Problem Solving can be a daunting task. With our team of specialists, we can provide your teams with the necessary training and coaching to ensure that they are able to adapt quickly and efficiently. Our comprehensive approach to A3 will equip your team with the knowledge and skills needed to successfully use this powerful tool for improving performance in all areas of your business.
We are committed to helping you develop a culture of continuous improvement within your organisation by teaching best practices and providing guidance through every step of the problem-solving process. Through our specialised training programs, we will help your teams learn how to use the A3 template more effectively, as well as how to interpret data visualisations quickly and accurately – enabling them to take action swiftly when required. Our experienced coaches will also share insights from industry experts on how best to integrate countermeasures into standard operating procedures (SOPs) and process maps, keeping up-to-date with industry trends in order to stay ahead of the competition.
By leveraging Leanscape’s expertise in A3 Problem Solving, you can rest assured knowing that your team is in good hands. Our team is dedicated to providing you with the support needed for successful implementation so that you can achieve sustained performance improvements over time.
100% Free Fundamentals of Lean COURSE
Take our free course.
JOIN FOR FREE
Join our Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Certification Course
The implementation of A3 Problem Solving provides a comprehensive framework for organisations looking to successfully address complex problems in an efficient and cost-effective manner. By breaking down the problem-solving process into seven distinct stages, users can structure their approach and track the progress of their countermeasures over time.
In order to ensure successful implementation, organisations should dedicate time towards training their teams on how to use the A3 Problem Solving Tool and A3 template. This will give everyone a solid foundation for carrying out future problem-solving activities more effectively, as well as provide insights into the effectiveness of certain countermeasures over time.
Through Leanscape’s specialised training programs, you can ensure that your team is fully equipped with the necessary skills to successfully adopt and incorporate A3 Problem Solving into all areas of your business. Our experienced coaches are committed to helping you develop a culture of continuous improvement within your organisation – providing guidance through every step of the process
Final Thoughts
The A3 approach is an invaluable tool for unlocking the power of improvements within any organisation. By leveraging its structured framework and cyclical learning approach, businesses can remain agile and responsive to ever-changing conditions, allowing them to navigate change more successfully and emerge stronger than ever before. Ultimately, this makes Toyota’s A3 problem-solving process one of the most effective ways to ensure long-term success in today’s fast-paced and competitive market.
Our Newsletter
Reagan pannell.
Reagan Pannell is a highly accomplished professional with 15 years of experience in building lean management programs for corporate companies. With his expertise in strategy execution, he has established himself as a trusted advisor for numerous organisations seeking to improve their operational efficiency.
Our Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma White Belt Course
- Lean Thinking Business Course
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Course
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Course
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Course
Yellow Belt Course
View all courses, recent articles, the synergy of antifragility and lean thinking, 5 essential problem-solving strategies every business leader should know, unveiling the secrets of blue ocean strategy for business growth, the difference between strategy and strategic execution, small steps, big gains: the case for incremental improvement, maximising efficiency and profitability: exploring the benefits of lean consultancy, view all articles, green belt course, other articles, an introduction to process capability, redefining automation: prioritizing standardization and optimization, how to optimize your business processes for maximum efficiency and profit, what is ppm (parts per million) in lean six sigma, what is cycle time, thrive in the business world: lean six sigma yellow belt, what is the difference between lean & six sigma, what is 5s and what are the benefits, guidelines for effective meetings: strategies for successful meetings, what is kanban | kanban explained for beginners, the power of hansei: why japanese business leaders swear by this concept, what qualities do employers look for in potential employees.
- | lean , lean thinking , problem solving , toolkit , tools
Related Articles
A comprehensive guide to integrating hoshin kanri into strategic planning, what is a gemba walk gemba walks explained, agile project management: a comprehensive guide, how lean six sigma yellow belt will accelerate your career, 5 business benefits of lean six sigma, lean six sigma online courses.
FREE COURSE | YELLOW BELT | GREEN BELT | BLACK BELT | MASTERCLASS | WORKSHOPS
Lean Accelerator Progam
A Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Masterclass

LSS Green Belt
The ultimate fast-track for future leadership
LSS Black Belt
Become an expert in change management and complex problem-solving.
Subscribe to Newsletter
Keep up to date to the latest insights, courses, training, webinars and more. Join our newsletter today.
Lean Accelerator Program
Discover the power of problem-solving, 15 min per day | 3-months | only €999 | learn from experts.

Continuous Improvement Toolkit
Effective Tools for Business and Life!
A3 Problem Solving Template

A3 thinking is a logical and structured approach to problem solving adopted by Lean organizations around the world. It can be used for most kinds of problems and in any part of the business. This A3 template uses a four stages model that is based on the PDCA management philosophy. It makes the problem-solving progress visible to the entire team while allowing the lessons to be learned by others.
This template is a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that you can use and modify to meet your specific requirements. For example, you may expand the implementation or follow-up plans by increasing the number of rows. The template is available in two variations: a user-friendly straightforward version, and a more detailed one that requires providing in-depth information.
A3 Template (32 KB)
A3 Template – Simple (216 KB)
A3 Template – Detailed (340 KB)
Related Templates

Written by:
CIToolkit Content Team


Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Must-Have A3 Report Templates with Samples and Examples

Kavesh Malhotra
We cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them – Albert Einstein.
Every organization, big and small, has to deal with problems occasionally. Such problems can test the leadership and team leaders' ability to tackle them. If the organization fails to deal with problems and find solutions, it can impact the business’s growth.
That’s where the problem-solving approach comes into play. A problem-solving approach is nothing but a process of analyzing and defining the problem, finding the best way around it, and fixing it. If done effectively, this approach can help organizations tackle any kind of problem they have to face.
But how exactly can you do it? Well, you can do it by utilizing problem-solving report templates. These templates can help you find the root causes of your problem, analyze them, and identify proposed countermeasures. The most important thing about these templates is that they ensure organizations do not go back to age-old and outdated practices to identify problem status and its solutions.
At Slide Team, our experts have crafted highly customizable, content-ready, and 100% editable templates to aid in problem-solving. Using these templates, organizations can find solutions to their problems.
So, let's take a look at these templates and understand how they can benefit you.
Template 1: Sample A3 Problem Solving Report Collection of Quality Control Templates
This template is a comprehensive solution that can help organizations find solutions to problems related to project management. The best part? This template is clean, crystal clear, and easy to understand. It divides the entire problem-solving approach into multiple sections. The first section focuses on the identification of the problem. Then, it goes on to identify root causes , the current situation, and the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle. The layout is divided into 4 categories: Materials, Processes/Methods, People, and Machines. Each category has multiple layers of "Why?" questions. This can offer a better understanding of the problem and effective solutions. Download it now and fix any problems that your organization is dealing with.

Download Now
Template 2: A3 Problem-Solving Example PPT Presentation
This clutter-free template can help teams understand a structured problem-solving process. The layout is super clean, which makes it easy for everyone to understand the issue. The template starts with the "Background" to understand the root causes behind the problem. Then comes the " Current Condition " section that pinpoints the exact situation. Then, the templates focus on "Goals/Targets." Then, the "Analysis" stage helps identify the root causes of the problem. The template then offers the solution in the " Proposed Countermeasure " section. A concrete "Plan" is then laid out for implementing these solutions. Finally, the "Follow-up" step ensures that the solutions are effective and the problem is resolved. Overall, this template can help teams analyze and fix any problem in their organization.

Template 3: A3 Problem-Solving PPT Design Templates
This template uses a logical layout to analyze and fix problems within any organization. The entire template is segmented into multiple sections. These sections include "Description of Current State," "Background & Supporting Data," and "Root Cause Analysis." Finally, it also has sections an "Action Plan" and "Check & Follow Up." The muted color palette with effective use of vibrant colors—red, teal, and green—helps highlight critical phases: Plan, Do, Check, Act. Such a layout ensures the template looks visually appealing and can simplify the entire problem-solving process. Overall, this dynamic template is an effective tool for project management and team collaboration for fixing any problem.

Template 4: A3 Problem-Solving Approach PPT Design Templates
This template takes a slightly different approach to fixing any problem. It utilizes the PDCS (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle for it. The cycle layout ensures the presentation looks clean, and viewers can understand the core content easily. All 4 phases of the cycle are highlighted using different color codes. This ensures the viewers can easily differentiate between these phases. The arrows indicate the flow of the process, jumping from one phase to the next. The design looks extremely eye-pleasing, dives deeper into the root causes of the problem, takes into account the current condition , and offers proposed countermeasures . Download it now and fix any problems that might arise within your organization.

Wrapping Up
No organization is immune to problems. Every now and then, a new problem can arise. Only the organizations and teams that can tackle these problems survive in tough competition. That’s where these problem-solving approach templates can become your best buddies! They could help you understand the root causes of the problem and come up with effective solutions.
I hope you find the list of templates useful for your organization. Using them, you can showcase how you are willing to tackle a problem to your teams and stakeholders. Meanwhile, you can also take a look at our Top-10 maintenance Report templates that can help with your operational maintenance.
Related posts:
- Top 10 Problem Solving Templates with Samples and Examples
- How to Design the Perfect Service Launch Presentation [Custom Launch Deck Included]
- Quarterly Business Review Presentation: All the Essential Slides You Need in Your Deck
- [Updated 2023] How to Design The Perfect Product Launch Presentation [Best Templates Included]
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Yearly Achievement PPT Templates with Examples and Samples

Top Five 5 Circle Venn Diagram Templates with Examples and Samples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

A3 problem-solving reports — what they are and how to use them

The A3 problem-solving methodology is part of Lean practices. If you’re familiar with Lean principles for project management, you may have used A3 problem solving before. However, if you haven’t heard of A3, keep reading to learn what it is, where it comes from, and how it’s used to resolve problems and track success.
In this post, you’ll learn:
What is A3 problem solving?
- A3 problem solving reports explained
Why use the A3 process?
The a3 problem-solving process.
- A3 report examples
Start solving your problems with the A3 process
A3 problem solving is a structured, collaborative problem-solving approach that distills a problem onto a single piece of paper — that is commonly used in Lean management and Six Sigma methodologies. The name “A3” is derived from the standard size of the paper (11" x 17") that is traditionally used to document the process.
The A3 problem-solving approach originated at Toyota as part of the Toyota Production System, which pioneered the Lean manufacturing philosophy. The A3 approach helped standardize problem-solving processes while encouraging collaboration and communication within the organization. It also uses a plan-do-check-act (PDCA) cycle to help leaders within organizations achieve constant improvement and growth.
A3 problem-solving reports explained

An A3 report is a structured document that concisely summarizes the problem-solving process. This document will typically include a problem statement, analysis of the current situation, proposed countermeasures, and the results of the implemented solution. The A3 report is designed to communicate the problem and solution in a clear way so it can be easily shared and reviewed by others in the organization.
There are several benefits to using the A3 problem-solving process, including:
- Structured approach. The A3 process provides a framework for identifying and working through problems in a systematic way.
- Collaboration. Input from all team members is an important part of the A3 process.
- Visual representation. The A3 report is a clear and concise document that is easily scannable by all team members involved.
- Continuous improvement. This problem-solving process encourages continuous improvement by providing a better system for working through problems in your organization’s processes.
- Standardization. The A3 process is standardized and repeatable, so you can use it to work through problems from organizations of all sizes in any industry.
Let’s look at the A3 process so you can use it to address any problems you and your organization are facing.
The A3 problem-solving process typically involves the following steps:
- Background of the problem. The first step is to clearly identify the problem that needs to be solved and any past issues that may have led to the problem.
- Current situation. This step involves collecting data and analyzing the current situation to better understand the problem.
- Set targets and goals. In this step, set specific and measurable targets so you’re able to monitor the progress toward achieving your goals.
- Root cause analysis. A root cause analysis identifies what is actually causing the problem so that solutions will go beyond temporary, surface-level fixes.
- Countermeasures. Once the root cause has been identified, potential solutions are developed. This step involves evaluating different options and selecting the most effective countermeasure.
- Implementation. The selected countermeasure is then put in place, and its effectiveness is monitored to ensure it is solving the problem.
- Effect confirmation and follow-up. This step involves measuring the impact of the solution and identifying if any additional improvements can be made.
- Standardize the solution. If the solution is effective, it should be standardized and incorporated into the organization’s standard work process to avoid the problem in the future.
A3 report example
Now that we’ve covered the A3 problem-solving process, let’s look at an example of what a completed A3 report might look like:
Problem statement. The customer complaint rate for our company’s new product has been steadily increasing over the past three months. We need to identify the root causes of the problem and develop a plan to reduce the complaint rate to below 1%.
Background. Our company recently launched a new product, and initial customer feedback was positive. However, over the past three months, we have seen a steady increase in customer complaints. Our customer service team has been working to address each complaint as it comes in, but the overall complaint rate continues to rise. We need to identify the cause of the problem so that we can implement a solution that will address the issue at its source.
Current condition. As of the last reporting period, the customer complaint rate for our new product was 2.5%. Our goal is to reduce this rate to below 1%. Most of the complaints we receive are related to product defects or shipping issues.
Root cause analysis. To identify the root cause or causes of the problem, we conducted a thorough analysis of customer feedback and internal data. We found that the most common complaints were related to product defects and shipping issues. We also identified several contributing factors, including inadequate quality control processes and insufficient training for our shipping team.
Countermeasures: To address the root causes of the problem, we have developed the following countermeasures:
- Improve quality control processes. We will implement a more rigorous quality control process for our new product. This will involve additional inspections at each stage of the manufacturing process to ensure that defects are caught before the product is shipped to customers.
- Provide additional training. We will provide additional training for our shipping team to ensure that they are properly trained to handle the new product. This will include training on how to identify and handle fragile items and how to properly package products to prevent damage during shipping.
- Improve communication. We will improve communication between our customer service team and our manufacturing team to ensure that any product defects or shipping issues are identified and addressed in a timely manner.
Implementation plan : To implement these countermeasures, we have developed the following plan:
- Improve quality control processes. We will implement the new quality control process within the next 30 days. This will involve additional inspections at each stage of the manufacturing process.
- Provide additional training. We will provide additional training for our shipping team within the next 60 days. This will include both classroom and hands-on training.
- Improve communication. We will implement a new communication process between our customer service team and our manufacturing team within the next 30 days. This will include regular meetings to discuss any product defects or shipping issues.
Follow-up: To ensure that our countermeasures are effective, we will monitor the customer complaint rate for our new product monthly. We will also conduct periodic audits of our quality control process and shipping team training to ensure that they are being implemented correctly.
A3 problem solving works to help businesses in any industry better understand and solve problems they may be experiencing in their business processes. By providing a standardized framework for identifying solutions, A3 helps teams continuously improve and become more efficient.
If you want to start using A3 problem solving and Lean business management principles in your organization, read our guide to Lean management to learn more .
Adobe Workfront is a project management tool that makes it easy to connect, collaborate, and simplify workflows at scale. If you’re ready to give Lean management and A3 problem solving a try, learn how Workfront enterprise project management can assist your team .

This page uses JavaScript. Please make sure that JavaScript is enabled in your browser.
- kanban library
- pricing & sign up
Thank you! We have sent you an email with details about your accounts.
- Kanban Guide
- Introduction
- History of Kanban
- Agile Framework
- Kanban Fundamentals
- ⬞ Visualize the Workflow
- ⬞ Limit Work in Progress
- ⬞ Manage Flow
- ⬞ Make Policies Explicit
- ⬞ Improve Continuously
- Kanban Elements
- ⬞ Kanban Method
- ⬞ Kanban Card
- ⬞ Kanban Board
- ⬞ Kanban Software
- ⬞ Personal Kanban
- ⬞ Manufacturing
- ⬞ Business Management
- ⬞ Bottlenecks
- Lean Thinking
- ⬞ Lean & Kanban
- ⬞ Just-In-Time (JIT)
- ⬞ Lean Manufacturing
- ⬞ Theory of Constraints (TOC)
- ⬞ Water Spider
- ⬞ Hoshin Kanri
- ⬞ Toyota Kata
- ⬞ Lean Project Management
- ⬞ Lean Accounting
- Lean Methodology
- ⬞ 5S in Lean
- ⬞ Six Sigma
- ⬞ Gemba Walk
- ⬞ Poka-Yoke
- ⬞ The 5 Whys
- ⬞ Flowcharts
- ⬞ Fishbone Diagram
- ⬞ A3 Problem Solving
- ⬞ SIPOC (COPIS)
- ⬞ Design of Experiments
- Lean Metrics
- ⬞ Cumulative Flow
- ⬞ Cycle Time
- ⬞ Lead Time
- ⬞ Process Throughput
- ⬞ Root Cause Analysis
- ⬞ Takt Time
- Kanban Use Cases
What is A3 Problem Solving?

A3 problem solving is a Lean approach to reporting issues and presenting ways of addressing them. The simple method, developed by Toyota, bases on documenting a problem, together with its current outcome and a suggested change, on a single sheet of A3 paper (420x297mm), giving it the name. You can use it to make a process change proposal, report on project status, or solve a problem.
A3 takes from the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle . Though it appears to be a step-by-step process, the method tends to be used iteratively, with the problem and solution sections being cyclically updated.
Taiichi Ōno of Toyota was known for not appreciating reports longer than one page, which helped the proliferation of the A3 approach within the automotive giant’s offices. A3 is similar to the 8D report also widespread in the automotive industry, though typically for complaints management. Furthermore, the ability to quickly discern a problem and understand its solution is innate to Lean values.
Lean emphasizes visualization, with examples in value stream mapping and Kanban’s visual workflows. That made a single-page report presenting what is going on was a welcome addition to a Lean operation.
Through shared use of A3s to solve all problems and plan initiatives, companies can start to operate an A3 system thinking methodology: address difficulties, suggest change, innovate, and curate logical reasoning rooted in the current needs.
Why use the A3 approach to solving problems?
Lean provides a competitive advantage, strategic and operational benefits through its objective to increase the value delivered to the customer and to reduce waste. Engaging in a process that allows the team to find the correct, best solution in the shortest possible time is highly beneficial.
Understandably, some reports and proposals must contain extensive amounts of data, and they have their place in a business environment. But imagine the value and advantage that distilling this information to 1 page has. Consider how much faster decisions can be made based on that. Besides the time savings, the opportunity to use the systematic approach of PDCA supplements the problem-solving skills required to propose accurate solutions.
In preparing for battle I have always found that plans are useless, but planning is indispensable. Dwight Eisenhower
It’s the act of planning that is important, as it spells out all known obstacles, visualizes the action plan, and helps to foresee potential outcomes and issues along the way. While documenting your problem on an A3 piece of paper may or may not yield benefits, the act of implementing A3 thinking is what makes the difference.
The benefits of using A3 thinking are:
- Quicker problem solving through logical reasoning and application of a step-by-step, visual process. Demanding a root cause identification ensures that difficulties are dealt with, not just temporarily masked.
- Easier planning thanks to the application of objective, critical thinking promoted by the A3’s structure.
- Team development through repeated use of a structural tool to find root causes of problems and their best solutions. The use of one tool across all company levels also promotes cross-department collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Company growth A3 reports help maintain and keep company knowledge on record, helping to sustain good operating policies and build a strong growth culture rooted in solving a company’s actual problems, not abstract ideas.
How to create an A3 report?

Step 1: The title
It should focus on the problem you are trying to solve and not the solution you want to convey. Examples of titles are: “Decrease Team Misunderstanding of Task Instructions” or “Reduce Customer Complaints with Product XYZ” .
Step 2: Background
According to the authors of “Understanding A3 Thinking: A Critical Component of Toyota’s PDCA Management System” , one of the main strengths of Toyota is that they place importance on understanding a problem. Rather than rush onto a solution, Toyota takes the time to precisely understand what is going on. The principle of going on a Gemba walk attests to this need to perceive problems first-hand.
The report’s background section conveys important related facts and how the problem aligns with the company’s strategic objectives. Presenting this right there on the page helps minimize the cost that a board of highly paid executives would need to spend looking at a problem, without a guarantee of them understanding it, nor coming up with the right solution. Consider this checklist for your background section:
- Do I know the needs of my report’s audience?
- Have I provided enough context?
- Does what it presents align with the audience’s strategic goals?
- Can the background be explained in 30 seconds?
Step 3: Current condition
A correct definition and a good understanding of the problem is your path to finding the right solution. That makes working on defining the current condition 90 % of the A3 effort.
The objective here is to make sure everyone is aware of the problem, whether the report documents it appropriately, and whether anyone questions the report’s findings. The use of graphs, charts, or other visual aids is beneficial.
Step 4: Goal
Your target - if you hit it, you know that your problem-solving effort has been a success. But you need to know what metrics will measure success and what the definition of success is. An example could be “reducing customer complaints by 15%, as measured by call center statistics” .
Step 5: The root cause
The focus of the root cause section should be to differentiate between facts and opinions regarding a problem’s cause and effect. You can include your findings from 5 Whys exercises , an Ishikawa diagram , or any other result of your RCA efforts . If the root cause is not defined correctly, the problem will likely resurface, causing waste and negating the Lean principles.
Step 6: Countermeasures
The countermeasures should be the corrective actions to take for the root cause of the problem to be resolved. If not possible - without a process overhaul - you can use containment actions instead to stop the issue from directly impacting the customer. It is OK to address complex problems iteratively, along with the values of continuous improvement .
The section may include a table of the problem causes, actions taken, action owners, and the achieved results.
Step 7: Effect confirmation
Since the A3 exercise bases on the PDCA cycle, this section of your report should show the effort you expended to confirm your findings. The proof that you have indeed solved the problem. For example, software engineers include samples that replicate the bugs and verify they are no longer present after a fix.
If the exercise has not taken place yet, i.e., when you’re presenting a plan to gain approval, you should outline what exercises you will conduct to check if the aim is successful.
Step 8: Follow up actions
The final section should include any other actions that you might want to consider. A principle worth adhering to here is the “Shitsuke - sustain” step of the 5S plan . Consider what you should do to ensure the benefits of this exercise are maintained. And could they possibly be translated to other areas of the company?
An A3 problem-solving report will help you deliver information in a way that provides instant value and can quickly reduce waste.
The most important thing to remember is that the act of Lean problem solving is more important than creating an A3 document that may contain no valid data and be simply a tick on some corporate checklist.
The same is true of all Lean methods and tools - their application alone will not make your company Lean. To truly implement Lean principles, your company culture, thinking, and planning all have to transform.
Did you know?
A low-risk, tiny step in attempting a culture change in a company could be getting the teams to collaborate on digital Kanban Tool ® boards. Their WIP limits monitoring and process visualization stand a chance to slowly change people’s way of thinking towards more Lean patterns. Please enter valid URL This name is not available Please enter valid email address
Did you like this article?
Anything to change or improve - let us know.
Further reading
- Understanding A3 Thinking: A Critical Component of Toyota’s PDCA Management System (BOOK)
- Kanban Tool
- Pricing & sign up
- Kanban Tool On-Site
- Kanban Library
- Kanban Tool Support
- Integrations
- Developer API
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
© 2009-2024 Kanban Tool ® by Shore Labs . All rights reserved. | All other trademarks, logos and images mentioned on this site belong to their respective owners. | We use cookies on our website.
Kanban Tool is a visual management solution that helps companies visualize workflow, track project progress, and analyze and significantly improve business processes. Kanban Tool provides powerful online Kanban boards with seamless time tracking and insightful analytics. Our Kanban software works perfectly in any business process and is designed for teams that want to visualize work on a Kanban board .
- Data, AI, & Machine Learning
- Managing Technology
- Social Responsibility
- Workplace, Teams, & Culture
- AI & Machine Learning
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Big ideas Research Projects
- Artificial Intelligence and Business Strategy
- Responsible AI
- Future of the Workforce
- Future of Leadership
- All Research Projects
- AI in Action
- Most Popular
- The Truth Behind the Nursing Crisis
- Work/23: The Big Shift
- Coaching for the Future-Forward Leader
- Measuring Culture

The spring 2024 issue’s special report looks at how to take advantage of market opportunities in the digital space, and provides advice on building culture and friendships at work; maximizing the benefits of LLMs, corporate venture capital initiatives, and innovation contests; and scaling automation and digital health platform.
- Past Issues
- Upcoming Events
- Video Archive
- Me, Myself, and AI
- Three Big Points

Toyota’s Secret: The A3 Report
How toyota solves problems, creates plans, and gets new things done while developing an organization of thinking problem-solvers..
- Workplace, Teams, & Culture
- Innovation Strategy
- Quality & Service
- Organizational Behavior
While much has been written about Toyota Motor Corp.’s production system, little has captured the way the company manages people to achieve operational learning. At Toyota, there exists a way to solve problems that generates knowledge and helps people doing the work learn how to learn. Company managers use a tool called the A3 (named after the international paper size on which it fits) as a key tactic in sharing a deeper method of thinking that lies at the heart of Toyota’s sustained success.
A3s are deceptively simple. An A3 is composed of a sequence of boxes (seven in the example) arrayed in a template. Inside the boxes the A3’s “author” attempts, in the following order, to: (1) establish the business context and importance of a specific problem or issue; (2) describe the current conditions of the problem; (3) identify the desired outcome; (4) analyze the situation to establish causality; (5) propose countermeasures; (6) prescribe an action plan for getting it done; and (7) map out the follow-up process.
The leading question
Toyota has designed a two-page mechanism for attacking problems. What can we learn from it?
- The A3’s constraints (just 2 pages) and its structure (specific categories, ordered in steps, adding up to a “story”) are the keys to the A3’s power.
- Though the A3 process can be used effectively both to solve problems and to plan initiatives, its greatest payoff may be how it fosters learning. It presents ideal opportunities for mentoring.
- It becomes a basis for collaboration.
However, A3 reports — and more importantly the underlying thinking — play more than a purely practical role; they also embody a more critical core strength of a lean company. A3s serve as mechanisms for managers to mentor others in root-cause analysis and scientific thinking, while also aligning the interests of individuals and departments throughout the organization by encouraging productive dialogue and helping people learn from one another. A3 management is a system based on building structured opportunities for people to learn in the manner that comes most naturally to them: through experience, by learning from mistakes and through plan-based trial and error.
Get Updates on Transformative Leadership
Evidence-based resources that can help you lead your team more effectively, delivered to your inbox monthly.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up
Privacy Policy
About the Author
John Shook is an industrial anthropologist and senior advisor to the Lean Enterprise Institute, where he works with companies and individuals to help them understand and implement lean production. He is author of Managing to Learn: Using the A3 Management Process to Solve Problems, Gain Agreement, Mentor, and Lead (Lean Enterprise Institute), and coauthor of Learning to See (Lean Enterprise Institute). He worked with Toyota for 10 years, helping it transfer its production, engineering and management systems from Japan to its overseas affiliates and suppliers.
More Like This
Add a comment cancel reply.
You must sign in to post a comment. First time here? Sign up for a free account : Comment on articles and get access to many more articles.
Comments (22)
Sheila colinlak, patrick doyle, acta de constitución de proyecto ágil, un elemento diferenciador. | agilia, dave whaley, william harrod, howard s weinberg, systemental, khucxuanthinh.

A3 Problem Solving
– The A3 Report –
⇓ Introduction to A3
⇓ What is A3
⇓ Why Implement A3
⇓ How to Implement A3
⇓ A3 Services

Introduction to A3 Problem Solving
In order for any business to be successful, they must strive to improve quality and efficiency as well as build a problem solving continuous improvement culture. The A3 Report is a very useful problem solving and continuous improvement tool. It was first used by Toyota and is quickly gaining popularity in industry today. Companies must start to view problems as opportunities for improvement. The A3 Report format allows the entire problem identification, clarification, analysis and resolution steps to be documented on one single sheet of paper.
What is A3 Problem Solving
The name “A3” is actually derived from a standard European paper size similar to 11” by 17”. The A3 Report is based upon the Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) Method. The PDCA process is sometimes referred to as the Deming Wheel or Deming Circle. The A3 Report incorporates this basic premise to problem solving and continuous improvement.
Why Implement A3 Problem Solving
Some problem solving tools involve numerous pages of information, multiple charts and graphs and lengthy reports. The A3 Report format can be used to more effectively communicate all of the pertinent information with greater visual impact. While the A3 Report is an effective communication tool, it is actually much more valuable as a problem solving and critical thinking tool that can be used to drive continuous improvement. The A3 Report fosters a problem solving / continuous improvement mindset within the participating team members. It is an excellent tool for managers and supervisors to share problem solving techniques with their teams. With resources being limited, completion of a formal A3 Report may not be applicable to every problem. Its use should be determined based upon the size of the problem and its impact on the business or organization. The A3 Report and the A3 way of thinking are valuable tools for Lean initiatives and for integrating a problem solving culture throughout the organization.
How to Implement A3 Problem Solving
The A3 Report usually consists of multiple steps following a PDCA structure of Plan, Do, Check, Act. The number of steps can vary due to the different formats being used for the A3 Report. The exact number of steps used is not as important as the end result. The A3 Report can utilize various forms depending upon the organizations needs and preferences. The following paragraphs provide information regarding the basic steps and some tools used to complete the A3. One thing that all of the forms seem to have in common is that they follow the PDCA problem solving process. The basic steps and where they fall into the PDCA structure are listed below:
- Define the Problem:
The first step is to define the problem or identify the need for improvement:
- Define the ideal state, the operational standard or the desired condition
- Describe the current situation or status
- How is the current status different from the desired state or operational standard?
- What value will be realized by completion of the A3 exercise?
- Containment:
In some A3 formats, a section is included for immediate countermeasures or containment actions. The purpose of containment is to prevent further problems from occurring or prevent the current problem from causing negative effects to other processes, products or departments.
- Breakdown the Problem:
Next, the team should breakdown or further define the problem. Ask any relevant 5W (What, When, Where, Who, Why) and 2H (How, How many / How often) questions. There also may be more than one issue contributing to the problem or more detail required to properly address the problem. Prioritize the issues and identify the point of occurrence or escape point.
- Define goals:
The A3 team should set goals regarding the improvement desired as a result of the exercise. This could include a percentage of improvement in process throughput, reduction in number of defects per unit or processing time. The goals should be specific, measureable, realistic, achievable and timely. Many companies are adopting the SMART goal approach.
- Root Cause Analysis:
The team should perform a Root Cause Analysis (RCA) of the problem by using various quality tools. The tools could include, but are not limited to data analysis or completing a Cause and Effect or Ishikawa diagram followed by a 5 Why exercise. Whatever method selected, it is important to get past the symptoms of the problem and down to the root cause.
- Countermeasures:
Permanent countermeasures or corrective actions must then be determined to address the root cause. The countermeasures must be clearly defined, achievable by the person responsible and have a due date. Corrective actions that do not have an owner or due date are seldom achieved.
- Implementation:
A plan for implementation of the corrective actions should be developed. The plan should include the team members, resources and time required to complete each task. In some cases, support from outside resources or test facilities are required. Some countermeasures may require repair or replacement of tooling or other capital expenditures. Therefore, proper levels of management should be kept informed throughout the process to assure adequate resources are available for implementing any corrective actions.
- Monitoring and Validation:
The A3 team should next confirm the effectiveness of the countermeasures. This can be accomplished in many ways, including but not limited to additional quality checks, Statistical Process Control (SPC) data, process or product audits and customer feedback.
- Standardize and Improve:
During this phase of the A3, the team should take action to standardize the process changes or improvements. The team must update all standard work, work instructions and process control plans, etc. In addition, it is a good practice to perform a short Things Gone Right / Things Gone Wrong (TGR/TGW) exercise and document in the A3 report what went well during the process and what could use improvement. The management team should also promote continuous improvement of the A3 tool within the organization.
Common problems to avoid with the A3 Report:
- The background is not well developed
- The problem statement is not well defined or unclear
- The ideal state or target condition is actually an action item, not the desired result
- Analysis does not drill down to the root cause(s)
- Ineffective countermeasures that will not prevent the problem from re-occurring
- Validation and monitoring methods are not well documented or there is a lack of evidence of improvement
Always remember that the A3 process and report are about fostering critical thinking. Encourage A3 thinking within your organization. The A3 process should be focused on improvement through developing the skills of the people. A3 thinking promotes problem solving, communication and mentoring of the teams.
The A3 Report is an effective visual tool for driving improvement and promoting a problem solving way of thinking. The format can and does vary depending upon the company or organization. The format you select is not as important as the results of the exercise. As long as the form contains the basic steps for problem identification, root cause analysis, corrective action and monitoring improvement or performance, it will be a very effective tool. The A3 Report has its roots in the automotive industry but is branching out into many different applications and industries from manufacturing to healthcare.
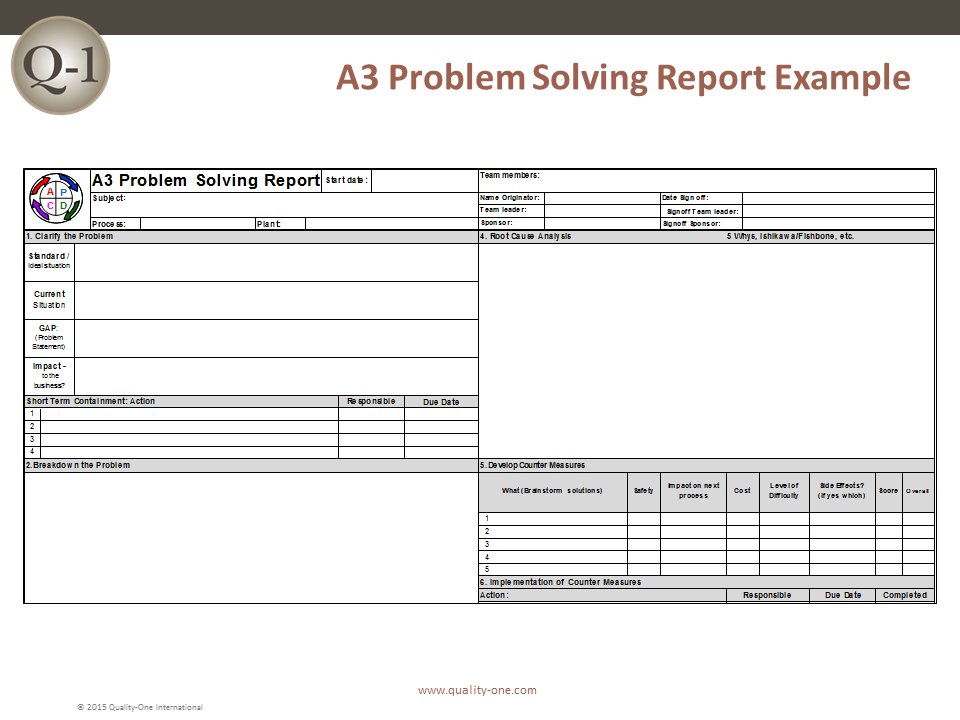
A3 Problem Solving Services
A3 Services from Quality-One include A3 Problem Solving Consulting, A3 Problem Solving Training and A3 Problem Solving Project Support, such as Facilitation and Auditing. Our experienced team of highly trained professionals will provide a customized approach for developing your people and processes based on your unique needs. Whether you need Consulting to assist in the design of your A3 process, Training to help understand and drive improvement through the A3 report, or hands-on Project Support for building and implementing your A3 process by utilizing our experienced Subject Matter Experts (SME) to work with your teams, Quality-One can help you promote A3 thinking in your organization.

Learn More About A3 Problem Solving
Quality-One offers Quality and Reliability Support for Product and Process Development through Consulting, Training and Project Support. Quality-One provides Knowledge, Guidance and Direction in Quality and Reliability activities, tailored to your unique wants, needs and desires. Let us help you Discover the Value of A3 Consulting, A3 Training or A3 Project Support.
Contact Us | Discover the Value!
(248) 280-4800 | [email protected]
Remember Me
- Don't have an account? Register
- Lost your password? Click here
- Already have an account? Log in
Streamline Problem Solving with Our A3 Report Template
Our A3 Report Template is crafted to help organizations simplify complex problem solving through structured analysis and documentation. Based on the principles of the Toyota Production System, this template empowers teams to encapsulate the entire Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle on a single page.
As you tailor your A3 Report format, focus on 3 essential elements:
- Structure the Layout : Organize information from problem identification to solution implementation in a clear, logical flow.
- Use Concise Communication : Summarize key points and ensure that every piece of information is relevant and actionable.
- Make it Visual : Utilizes diagrams and charts to visually represent problem-solving steps, making complex data easily understandable.
This free A3 Report Template is available as an editable Excel file, enabling you to customize it to align with your specific organizational needs. The file also includes two tabs featuring a simple and an advanced problem solving framework for you to utilize.
Tip for Usage: For printing, make sure to scale to 1 page wide in landscape format for ease of use.
Format: Excel (.xlsx)
Download instantly:
Lean Events and Training / Forms and Templates
Forms and Templates
Downloads for A3 problem solving, standard work , project management, and value stream mapping .
Problem Solving Templates

A3 Action Plan Form (from Getting the Right Things Done)
- The action plan template helps define the who, what, when, where, and how of a plan on one page.
- Helps track progress and highlight problems so action can be taken.
A3 Status Review Form (from Getting the Right Things Done)
- Top box provides an overview with respect to our critical end-of-pipe metrics.
- Second box provides an overview of activities, and usually reflects what’s been prescribed on the action plan of the right side of the strategy A3.

A3 Strategy Form (from Getting the Right Things Done)
- A strategy A3 is a one-page storyboard on 11-inch by 17-inch paper that helps tell the strategy “story.”
- Logic flows from top left to bottom right, and each box leads to the next one.
Detailed A3 Template (from Managing to Learn)
- Print this A3 template out to remind you of each section of the problem-solving A3 as you are creating your own.
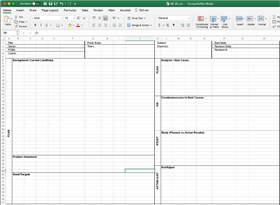
PDSA A3 Template (from On the Mend)
- A3 Template, in Excel, following the PDSA cycle.
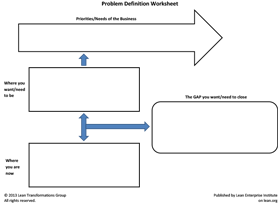
Problem Definition Worksheet
- This worksheet can help you breakdown the problem into a clearly defined gap as well as see how the problem aligns to the needs of the business or your True North purpose.
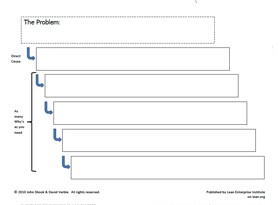
Root Cause Template
- This template gives you space to record the problem as well as the direct causes and underlying causes.

Four Types of Problems
Art Smalley

Managing to Learn: Using the A3 management process

Perfecting Patient Journeys
Beau Keyte , Tom Shuker and Judy Worth

Getting the Right Things Done
Pascal Dennis
Standard Work Templates
Standard Work Operator Balance Chart (OBC)
- The operator balance chart helps create continuous flow in a multi-step, multi-operator process by distributing operator work elements in relation to takt time.
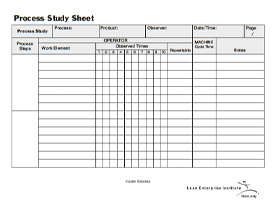
Standard Work Process Study Sheet
- The Process Study Sheet is used to define and record the time for work elements in a process.
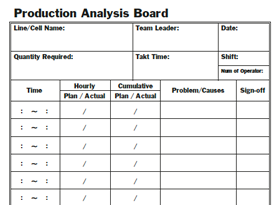
Standard Work Production Analysis Board
- A Production Analysis Board is a display that must be located at the exit of the cell (or the line) to show actual performance compared with planned performance on an hourly basis.
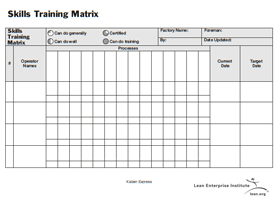
Standard Work Skills Training Matrix
- The Skills Training Matrix shows the required and attained skills of every operator.
- The training schedule also should be shown.
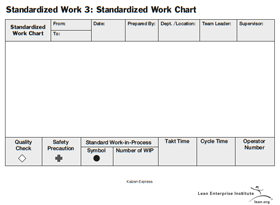
Standardized Work Chart
- The standardized work chart shows operator movement and material location in relation to the machine and overall process layout.
- It should show takt time, work sequence, and standard WIP.
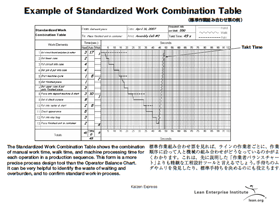
Standardized Work Combination Table
- The standardized work combination table shows the combination of manual work time, walk time, and machine processing time for each operation in a production sequence.
- This form is a more precise process design tool than the Operator Balance Chart.
- It can be very helpful to identify the waste of waiting and overburden, and to confirm standard.
Standardized Work Job Instruction Sheet
- The job instruction sheet is used to train new operations.
- It lists the steps of the job, detailing any special knack that may be required to perform the job safely with utmost quality and efficiency.
- It can also be useful for experienced operators to reconfirm the right operations.
Standardized Work Process Capacity Sheet
- The Process Capacity Chart is used to calculate the capacity of each machine to confirm true capacity and to identify and eliminate bottlenecks.
- Processing capacity per shift will be calculated from the available production time, completion time, and tool-change time (and other factors as necessary) for each work piece.
Waste Walk Template (from Perfecting Patient Journeys)
- Taking a “waste walk” is one way to make the waste visible again.
- A waste walk is simply a planned visit to where work is being performed to observe what’s happening and to note the waste. It differs from go-see activities in that you are specifically looking for waste.

Kaizen Express
Toshiko Narusawa and John Shook
Lean Lexicon 5th Edition
Lean Enterprise Institute
Training Within Industry (TWI) Templates and Downloads
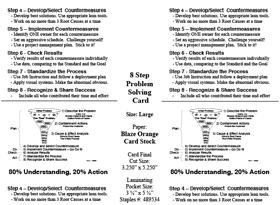
8-step TWI problem solving card - as presented by IBM
- 8-steps to problem solving handy pocket card printable.
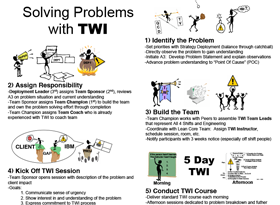
Solving Problems with TWI
- Solving problems with TWI deployment graphic.
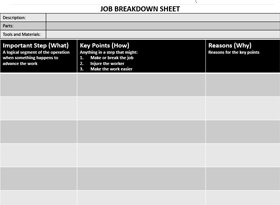
Template of Job Breakdown Sheet
- Job breakdown sheets are created to list the steps and highlight the main factors or key points that go into completing a job.
- It also provides reasons for these key points.

TWI Job Instruction Card
- TWI Job Instruction card in a handy pocket printable.

TWI Job Methods Card
- TWI Job Methods Card in a handy pocket printable.

TWI Job Relations Card
- TWI Job Relations Card in a handy pocket printable.

Lean Solutions
James (Jim) Womack, PhD and Dan Jones

Lean Thinking, 2nd Edition
Project Management Templates
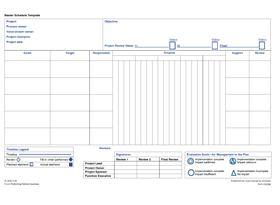
Master Schedule and Action Plan Template for One Goal (from Perfecting Patient Journeys)
- Use this template in your project tracking center so you can track both goals and action items on the same form.
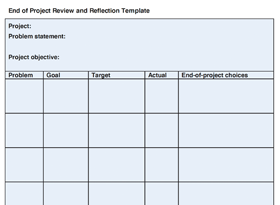
End of Project Review Template (from Perfecting Patient Journeys)
- The following template will help you capture your end-of-project reflections and make decisions about what to do next.
Master Schedule Template (from Perfecting Patient Journeys)
- This template will help you answer this question by letting you include the project goals with space to indicate whether each goal is on track as originally planned and whether the scheduled progress review has taken place.
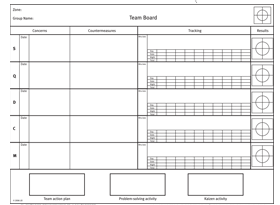
Team Board Form (from Getting the Right Things Done)
- A team board is a window on both routine and improvement work.
- The board on this template addresses both daily production and strategic issues, and is organized according to SQDCM—safety, quality, delivery, cost, and morale.

Value Proposition Template (from Perfecting Patient Journeys)
- Align the stakeholders around what will be included in addressing the problem,
- Identify the stakeholders who will be added to the project team and actively engaged in creating the current- and future-state value-stream maps,
- Identify additional stakeholders necessary to drive the implementation of the future state,
- Serve as an agreement—a proof of consensus—on the specific problem to be solved, and with the problem statement serve as authorization for the entire project.
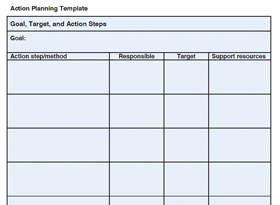
Action Planning Template (from Perfecting Patient Journeys)
- Identify the specific changes that need to be made and translate those changes into clearly stated goals and actions (i.e., the means) to achieve those goals.
- Identify the specific methods and action steps you think will help you achieve the goals. These action steps and targets constitute the action plan to achieve a specific goal.
Value-Stream Mapping Templates
Value-stream Mapping Icons for Excel
- At the request of some of our readers we have posted the most commonly used mapping icons so that they can be downloaded for Excel spreadsheets.
Learning to See
Mike Rother and John Shook

VSM Getting Started Set
Lean Enterprise Institute , Mike Rother and John Shook
Mapping to See: Value-Stream Improvement Workshop
Beau Keyte , Jim Luckman , Kirk Paluska , Guy Parsons , John Shook , Tom Shuker and David Verble
Improvement Kata / Coaching Kata
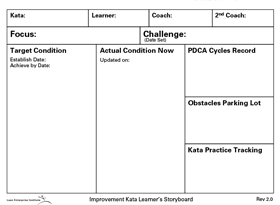
Improvement Kata Learner's Storyboard
Subscribe to get the very best of lean thinking delivered right to your inbox
Privacy overview.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Many Facets of A3. A standard paper size: At its most fundamental, "A3" is the international term for a sheet of paper 297 millimeters wide and 420 millimeters long.The closest U.S. paper size is the 11-by-17-inch tabloid sheet. A template: Many companies and individuals use an A3-sized document pre-printed with the steps needed to conduct lean problem-solving or improvement efforts ...
The A3 report provides an overview of the problem, data analysis, root causes, solutions, and results in a clear and concise manner. ... A3 Problem Solving is a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving that makes use of a one-page document called an A3 report to visually represent the process. The A3 report provides an overview of ...
The A3 Problem Solving Report (A3) is a problem solving and continuous improvement approach. Its name refers to a metric paper size designation that is roughly equivalent to an 11-inch by 17-inch sized paper, which is the largest size that will fit through a fax machine, and is
What is A3? An A3 is a one-page report prepared on a single 11 x 17 sheet of paper that adheres to the discipline of PDCA thinking as applied to collaborative problem solving, strategy development or reporting. The A3 includes the background, problem statement, analysis, proposed actions, and the expected results.
A3 Problem solving or A3 Structured Problem Solving as it is often referred to, is a systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and solving complex business problems. It was originally developed by Toyota as part of its lean methodology. The A3 is a problem-solving tool that encourages a collaborative and systematic approach to problem-solving.
The A3 report is an effective tool because it contains not only text, but also pictures, diagrams, and charts, all of which enrich and clarify the data and improve communication. The A3 report can be used for problem solving, but there also are two other ways of using it: a proposal A3 report and a storyboard A3 report. Each report has a ...
An A3 problem solving report is usually structured as follows: PROBLEM STATEMENT. State the problem you want to address in one or two sentences. Address the problem from a service user point of view. Only include details that can be observed and quantified from the current situation. CURRENT STATE. Determine your current state by answering the ...
the A3 Report goes hand-in-hand with steps 0-6 of the A3 Process. The purpose of the A3 Report is to: Document the learning, decisions, and planning involved with solving a problem ... Provide structure to problem-solving so as to maximize learning; The report (template) is designed to be printed on 11x17 inch paper (or two pieces of 8.5x11 ...
The A3 problem-solving approach is a powerful tool used to identify, analyze and solve issues. It consists of a comprehensive template which can be used to effectively unlock improvements and gain deeper insights into various situations. This article will discuss how this versatile technique can be used to help individuals unlock their ...
WHAT IS A3? On a literal level, A3 refers to a ledger size (11×17) piece of paper. But in the Lean Six Sigma world, it is a tool to help see the thinking behind the problem-solving. Don't mistake A3s as a document to be completed after the problem is solved. It's important to use the A3 while working through the problem.
Simple | Detailed. A3 thinking is a logical and structured approach to problem solving adopted by Lean organizations around the world. It can be used for most kinds of problems and in any part of the business. This A3 template uses a four stages model that is based on the PDCA management philosophy. It makes the problem-solving progress visible to the entire team while allowing the lessons to ...
Template 4: A3 Problem-Solving Approach PPT Design Templates. This template takes a slightly different approach to fixing any problem. It utilizes the PDCS (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle for it. The cycle layout ensures the presentation looks clean, and viewers can understand the core content easily.
equivalent to 11" x 17" (or B-sized) paper. Toyota actually uses several styles of A3 reports--for solving problems, for reporting project status, and for proposing policy changes--each having its own "storyline." We have focused on the problem-solving report simply because it is the most basic style, making it the best starting point. Why use it?
The A3 problem-solving process; A3 report examples; Start solving your problems with the A3 process; What is A3 problem solving? A3 problem solving is a structured, collaborative problem-solving approach that distills a problem onto a single piece of paper — that is commonly used in Lean management and Six Sigma methodologies. The name "A3 ...
When starting an A3 problem-solving initiative, you should consider the blank A3 merely as a guide leading you through the problem-solving process, one "box," or step, at a time. But at each stage, you must first think about and investigate the problem situation and only then record your thinking. However, do not expect to complete the ...
In the Lean Operating System, we achieve operational excellence by: Defining our standards. Continuously compare our operations against those standards. Engaging in aggressive and rigorous problem-solving when there is any deviation from the standard. Step 1: Identify the Problem. Step 2: Set the Target.
A3 problem solving is a Lean approach to reporting issues and presenting ways of addressing them. The simple method, developed by Toyota, bases on documenting a problem, together with its current outcome and a suggested change, on a single sheet of A3 paper (420x297mm), giving it the name. You can use it to make a process change proposal ...
A3 problem-solving is a solution-searching approach that involves addressing each aspect of an issue and writing it down. The method involves one sheet of paper, with sections that address each part of the problem, including ways that employees might resolve the issue. Employees can use A3 problem-solving to process a proposal, report on ...
An A3 is composed of a sequence of boxes (seven in the example) arrayed in a template. Inside the boxes the A3's "author" attempts, in the following order, to: (1) establish the business context and importance of a specific problem or issue; (2) describe the current conditions of the problem; (3) identify the desired outcome; (4) analyze ...
An A3 report or A3 Model is a problem-solving method typically used by managers and supervisors to identify, understand, and resolve problems in a business setting. Having evolved from the Toyota Production System's (TPS) lean management philosophy, it is now commonly used by various industries looking to improve their operational quality and ...
The A3 Report is a very useful problem solving and continuous improvement tool. It was first used by Toyota and is quickly gaining popularity in industry today. Companies must start to view problems as opportunities for improvement. The A3 Report format allows the entire problem identification, clarification, analysis and resolution steps to be ...
Our A3 Report Template is crafted to help organizations simplify complex problem solving through structured analysis and documentation. Based on the principles of the Toyota Production System, this template empowers teams to encapsulate the entire Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle on a single page. As you tailor your A3 Report format, focus on 3 ...
A3 Strategy Form (from Getting the Right Things Done) A strategy A3 is a one-page storyboard on 11-inch by 17-inch paper that helps tell the strategy "story.". Logic flows from top left to bottom right, and each box leads to the next one. Download.