Skip navigation

- Spring Updates
- For Employers
- In the Know
- Make An Appointment
- Internships
- Employer Connections
- CCE Programs
- Funding Programs
- Drop-in Hours
- Career Counseling Appointments
- Practice Interviews
- Programs & Services
- Design Your Next Steps
- Resumes & CVs
- Cover Letters
- Negotiating
- Career Advancement
- Graduate School
- Premium Resources
- Communications & Media
- Engineering & Technology
- Environment & Sustainability
- Financial Services
- International Affairs
- Non-Profits & Social Justice
- Psychology, Counseling, & Social Work
- Ways to Gain Experience
- Career Assessments
- Connect With Alumni
- Student Experiences
- First-Generation/Low-Income Students
- International Students
- Students with Disabilities
- Veteran Students
- LGBTQ Students
- Visiting Students
- Students of Color

How to Write a Personal Statement for a PhD Program Application
Personal statement guidelines, general guidelines to keep in mind:.
- One size does not fit all : Tailor your personal statement to each program and department you are applying to. Do your research to learn what is unique about each of your choices and highlight how this particular program stands out.
- Yes, it’s personal : Showcase your unique strengths and accomplishments. Explain what influenced your personal decisions to pursue the program. Ask yourself, could this be applied to your friend or neighbor? If so, you need to be more specific and provide examples. Saying that you are a “good scientist” isn’t enough. Provide examples of your previous research experience, projects you’ve completed, and what technical skills you learned. Explain how you overcame any challenges along the way.
- Set aside enough time : Although personal statements are generally short in length (approx. 700 words; 1-2 pages), give yourself ample time to write a strong, well-written statement. It takes more time than you think to develop a final draft for submission.
- Focus on your spelling, grammar, and vocabulary : It’s important to present a well-written statement with good grammar and vocabulary. Write concrete, succinct sentences that flow well. Avoid flowery language. Visit the Writing Center for additional review and feedback.
- Proofread one more time: Check your grammar and spelling again before submitting your final draft. Ask a friend, professor, or advisor to proofread your final draft one more time before sending it in.
YOUR PERSONAL STATEMENT SHOULD ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS:
- Why do you want to complete further research in this field? Write down a list of reasons as to why you are interested in pursuing further study in the field. When did you become interested in the field and what knowledge have you gained so far? Describe how your previous work provided the foundation and for further study.
- Why have you chosen to apply to this particular university ? Does the institution have a particular curriculum, special research facilities/equipment, or interesting research that appeal to you?
- What are your strengths ? Demonstrate how you stand out from other candidates. Highlight relevant projects, dissertations thesis or essays that demonstrate your academic skills and creativity. Include IT skills, research techniques, awards, or relevant traveling/ study abroad experience.
- What are your transferable skills? Be sure to emphasize transferable skills such as communication, teamwork, and time management skills. Give examples of how you have demonstrated each of these with specific examples.
- How does this program align with your career goals? It’s okay if you don’t know the exact career path you plan to take after completing your PhD. Provide an idea of the direction you would like to take. This demonstrates commitment and dedication to the program.
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
For examples of successful personal statements, visit the Online Writing Lab (OWL) .
Privacy Policy Accessibility Notice of Non-Discrimination Terms of Use
Writing Your Personal Statements
Your personal statement must demonstrate to the admissions committee that you have considered graduate school and their specific program seriously. It’s your opportunity to summarize your academic and research experiences. You must also communicate how your experiences are relevant to preparing you for the graduate degree that you will be pursuing and explain why a given program is the right one for you.
The personal statement is where you highlight your strengths. Make your strengths absolutely clear to the reviewers, because they will often be reading many other statements. Your self-assessments and honest conversations with peers and advisors should have also revealed your strengths. But you must also address (not blame others for) weaknesses or unusual aspects of your application or academic background.
Your personal statement should focus on two main aspects: your competence and commitment.
1. Identify your strengths in terms of competence that indicate that you will succeed in the grad program and provide examples to support your claims. Start your statement by describing your strengths immediately. Because faculty will be reading many statements, it’s important to start off with your strengths and not “bury your lede.” Consider traits of successful graduate students from your informational interviews, and identify which of these traits you have. These traits could involve research skills and experiences, expertise in working with techniques or instruments, familiarity with professional networks and resources in your field, etc.
- Check your responses from the exercises in the self-assessment section. You may wish to consult notes from your informational interviews and your Seven Stories . Write concise summaries and stories that demonstrate your strengths, e.g. how your strengths helped you to achieve certain goals or overcome obstacles.
- Summarize your research experience(s). What were the main project goals and the “big picture” questions? What was your role in this project? What did you accomplish? What did you learn, and how did you grow as a result of the experience(s)?

My research examines the interplay between U.S. domestic politics and foreign policy during the Cold War. As a native New Yorker, I saw firsthand how dramatically my city changed after 9/11, which prompted my early interest in U.S. policy at home and abroad. As an undergraduate at the City College of New York, I planned to study international relations with a focus on U.S. foreign affairs. I also quickly became involved in student activist groups that focused on raising awareness about a wide range of human rights issues, from the Syrian refugee crisis to asylum seekers from Central America.
The more I learned about the crises in the present, the more I realized that I needed a deeper understanding of the past to fully grasp them. I decided to pursue a PhD in history in order to gain a clearer understanding of human rights issues in the present and to empower young student-activists like myself.
— Vannessa Velez, PhD candidate in History
Addressing weaknesses or unusual aspects
- Identify weaknesses or unusual aspects in your application—e.g., a significant drop in your GPA during a term; weak GRE scores; changes in your academic trajectory, etc. Don’t ignore them, because ignoring them might be interpreted as blind spots for you. If you’re unsure if a particular issue is significant enough to address, seek advice from faculty mentors.
- Explain how you’ll improve and strengthen those areas or work around your weakness. Determine how you will address them in a positive light, e.g., by discussing how you overcame obstacles through persistence, what you learned from challenges, and how you grew from failures. Focusing on a growth mindset or grit and this blog on weaknesses might also help.
- Deal with any significant unusual aspects later in the statement to allow a positive impression to develop first.
- Explain, rather than provide excuses—i.e., address the issue directly and don’t blame others (even if you believe someone else is responsible). Draft it and get feedback from others to see if the explanation is working as you want it to.
- Provide supporting empirical evidence if possible. For example, “Adjusting to college was a major step for me, coming from a small high school and as a first-generation college student. My freshman GPA was not up to par with my typical achievements, as demonstrated by my improved GPA of 3.8 during my second and third years in college."
- Be concise (don’t dwell on the issues), but also be complete (don’t lead to other potentially unanswered questions). For example, if a drop in grades during a term was due to a health issue, explain whether the health issue is recurring, managed now with medication, resolved, etc.
2. Explain your commitment to research and their graduate program, including your motivation for why you are applying to this graduate program at this university. Be as specific as possible. Identify several faculty members with whom you are interested in working, and explain why their research interests you.
- Descriptions of your commitment should explain why you’re passionate about this particular academic field and provide demonstrations of your commitment with stories (e.g., working long hours to solve a problem, overcoming challenges in research, resilience in pursuing problems). Don’t merely assert your commitment.
- Explain why you are applying to graduate school, as opposed to seeking a professional degree or a job. Discuss your interest and motivation for grad school, along with your future career aspirations.

I am definitely not your traditional graduate student. As a biracial (Native American and white), first-generation PhD student from a military family, I had very limited guidance on how best to pursue my education, especially when I decided that graduate school was a good idea. I ended up coming to this PhD in a very circuitous manner, stopping first to get a JD and, later, an MFA in Young Adult Literature. With each degree, I took time to work and apply what I’d learned, as a lawyer and as an educator. Each time, I realized that I was circling around questions that I couldn’t let go of—not just because I found them to be fascinating, but because I did (and still do!) feel that my research could help to bridge a gap that desperately needs bridging. Because my work is quite interdisciplinary, I strongly feel that I wouldn’t have been able to pursue this line of research without the degrees and life experience I gained before coming to this program.
— Jamie Fine, PhD candidate in Modern Thought and Literature
Statement of Purpose: subtle aspects
- Think in terms of engaging faculty in a conversation rather than pleading with them that you should be admitted. Ask reviewers to read drafts with this concern in mind.
- With later drafts, try developing an overall narrative theme. See if one emerges as you work.
- Write at least 10 drafts and expect your thinking and the essay to change quite a bit over time.
- Read drafts out loud to help you catch errors.
- Expect the "you' that emerges in your essay to be incomplete. . . that’s OK.
- You’re sharing a professional/scholarly slice of "you."
- Avoid humor (do you really know what senior academics find funny?) and flashy openings and closings. Think of pitching the essay to an educated person in the field, but not necessarily in your specialty. Avoid emotionally laden words (such as "love" or "passion"). Remember, your audience is a group of professors! Overly emotional appeals might make them uncomfortable. They are looking for scholarly colleagues.
© Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305
Did you know? Advising Appointments are available year-round and throughout the summer!
- Undergraduates
- Ph.Ds & Postdocs
- Prospective Students & Guests
- What is a Community?
- Student Athletes
- First Generation and/or Low Income Students
- International Students
- LGBTQ Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Veterans
- Exploring Careers
- Advertising, Marketing & PR
- Finance, Insurance & Real Estate
- General Management & Leadership Development Programs
- Law & Legal Services
- Startups, Entrepreneurship & Freelance Work
- Environment, Sustainability & Energy
- Media & Communications
- Policy & Think Tanks
- Engineering
- Healthcare, Biotech & Global Public Health
- Life & Physical Sciences
- Programming & Data Science
- Graduate School
- Health Professions
- Business School
- Meet with OCS
- Student Organizations Workshop Request
- OCS Podcast Series
- Office of Fellowships
- Navigating AI in the Job Search Process
- Cover Letters & Correspondence
- Job Market Insights
- Professional Conduct & Etiquette
- Professional Online Identity
- Interview Preparation
- Resource Database
- Yale Career Link
- Jobs, Internships & Other Experiences
- Gap Year & Short-Term Opportunities
- Planning an International Internship
- Funding Your Experience
- Career Fairs/Networking Events
- On-Campus Recruiting
- Job Offers & Salary Negotiation
- Informational Interviewing
- Peer Networking Lists
- Building Your LinkedIn Profile
- YC First Destinations
- YC Four-Year Out
- GSAS Program Statistics
- Statistics & Reports
- Contact OCS
- OCS Mission & Policies
- Additional Yale Career Offices
Writing Personal Statements for Graduate School
- Share This: Share Writing Personal Statements for Graduate School on Facebook Share Writing Personal Statements for Graduate School on LinkedIn Share Writing Personal Statements for Graduate School on X
Personal Statements
Preparing a well-written and effective personal statement (sometimes referred to as statements of purpose or personal essays) that clearly articulates your preparation, goals, and motivation for pursuing that specific graduate degree is critically important. You will need to spend a considerable amount of time and effort in crafting these statements. The focus, structure, and length of personal statements vary from program to program. Some will have prompts or questions you need to answer, while others will leave the topic open-ended. The length varies widely as well. Read instructions carefully and make sure to adhere to all parameters laid out in the application guidelines.
Clear writing is the result of clear thinking. The first and most important task is to decide on a message. Consider carefully which two or three points you wish to impress upon the reader, remembering that your audience is composed of academics who are experts in their fields. Your statement should show that you are able to think logically and express your thoughts in a clear and concise manner. Remember that the reader already has a record of your activities and your transcript; avoid simply restating your resume and transcript. Writing your statement will take time; start early and give yourself more than enough time for revisions. If no prompts are given, you can use the questions below to begin brainstorming content to include in your statement; for more information, see our Writing Personal Statement presentation Prezi and our three-minute video on Writing Personal Statements .
- What experiences and academic preparation do you have that are relevant to the degree you’re seeking?
- Why are you choosing to pursue a graduate degree at this time?
- Why do you want to pursue this particular degree and how will this degree and the specific program fit into your career plans and your long-term goals?
- What specific topics are you aiming to explore and what does the current literature say about those topics?
After you’ve written a first draft, start the work of editing, refining, simplifying, and polishing. Provide specific examples that will help illustrate your points and convey your interests, intentions, and motivations. Is any section, sentence, or word superfluous, ambiguous, apologetic, or awkward? Are your verbs strong and active? Have you removed most of the qualifiers? Are you sure that each activity or interest you mention supports one of your main ideas? Spelling and grammatical errors are inexcusable. Don’t rely on spell-check to catch all errors; read your statement aloud and have it reviewed by multiple people whose opinion you trust. If possible, have your statement reviewed by a writing tutor. For individual assistance with writing your personal statement, consult with the writing tutor in your residential college or the Writing Center within the Yale Center for Teaching and Learning .
Office of Career Strategy
Visiting yale.
How to Write a Stand-Out Personal Statement for Your Graduate School Application

While deciding to embark on the path to graduate school is an exciting first step toward advancing your career, the application process can sometimes feel daunting and confusing.
One major part of the application that most schools require is a personal statement. Writing a personal statement can be an arduous task: After all, most people don’t necessarily enjoy writing about themselves, let alone at length.
A compelling personal statement, however, can help bring your application to the top of the admissions pile. Below, we’ve outlined what you need to know about crafting a personal statement to make your application shine.
What Is a Personal Statement?
The point of a personal statement is for the admissions board to gain a deeper understanding of who you are apart from your education and work experience. It explains why you’re the right fit for the program and a worthwhile applicant. It’s also an opportunity to highlight important factors that may not be readily available in the rest of your application.
A personal statement is different from a statement of purpose (if you’re asked for that as well). A statement of purpose will touch on your academic and career goals, as well as your past credentials. While those should also be discussed in your personal statement, it’s more about your life experiences and how they’ve shaped you and your journey to graduate school.
Questions to Ask Yourself Before Writing a Personal Statement
Before you start crafting your essay, there are a few prompts you can ask yourself to help clarify what you want to accomplish.
- What are the key points you want to communicate about yourself?
- What personal characteristics or skills do you have that make you a strong candidate for this field?
- What exactly are your career goals, and how does graduate school play into them?
- What have you learned about this field already? When did you first choose to follow this path, and what do you enjoy about it?
- What do you think is important for the admissions board to know specifically about you?
- Are there any discrepancies or causes for concern in your application you need to address? For example, is there a career and schooling gap, or a low GPA at one point? This is the time to discuss whether a personal hardship may have affected your academics or career.
- Have you dealt with any unusual obstacles or difficulties in your life? How have they affected and shaped you?
- What sets you apart and makes you unique from other graduate school applicants?
- What factors in your life have brought you to where you are today?
Top Tips for Writing a Graduate School Personal Statement
Pick a few points to emphasize about yourself . Introduce yourself to the admissions board. Select key factors about your background that you want the university to know — elements that reveal what kind of person you are and demonstrate why you’re a strong candidate for the school and field of study.
Be very specific . Again, a personal statement is all about communicating what distinguishes you from other applicants. To accomplish that, you need to share specific anecdotes that underscore your statements. If you say you’re a strong leader, present an example of a time you’ve proven that skill through work, school or your personal life. These specific, personal stories provide a deeper understanding of who you are and prove your intentions.
Do your research . Demonstrate what attracted you to the program. If there is a specific faculty member or class that caught your attention, or another aspect of the program that greatly interests you, convey it. This shows you’ve truly researched the school and have a passion for the program.
“Whatever the topic may be, I would recommend writing in a manner that reflects or parallels the institution’s and/or department’s missions, goals and values,” said Moises Cortés, a graduate/international credentials analyst for the Office of Graduate Admission at USC .
Address any gaps or discrepancies . Explain any factors that may have impacted your academic career. If you had an illness or any other personal hardships that affected your grades or work, discuss them. If there is a discrepancy between your grades and your test scores, you can also take the time to go over any extenuating circumstances.
Strike the right tone . While it’s important to give readers a glimpse of your personality, avoid oversharing or revealing intimate details of your life experiences. You should also avoid making jokes or using humorous cliches. Maintain a professional tone throughout your writing.
Start strong and finish strong . As with any piece of writing, you want to draw in your readers immediately. Make sure to start off with an interesting and captivating introduction. Similarly, your conclusion should be a well-written, engaging finish to the essay that highlights any important points.
“ For a personal statement, I think the first and last paragraphs are most important and should always relate the program they are applying to their own experiences and ideas,” Hoon H. Kang, a graduate/international credential analyst with the Office of Graduate Admission, told USC Online.
Proofread, proofread and proofread again . We can’t emphasize enough the importance of rereading your work. Your personal statement is also an analysis of your writing skills, so ensure you have proper grammar and spelling throughout. In addition, we recommend having multiple people look over your statement before submission. They can help with the proofreading (a second person always catches a mistake the writer may miss), give advice about the statement’s structure and content, and confirm it’s the proper recommended length.
Once you’ve considered all of the above and reviewed and edited your personal statement to perfection, it’s time to submit and check off any remaining application requirements, including your resume and letters of recommendation .
Personal statements are arguably one of the most challenging aspects of applying to graduate school, so make sure to revel in this accomplishment and acknowledge your successes.
For more information, visit the Office of Graduate Admission at USC and explore USC Online ’s master’s degrees, doctoral programs and graduate certificates.
Testimonials
Free Resources
PrepScholar GRE Prep
Gre prep online guides and tips, how to write a stand-out personal statement for grad school.
If you’re applying to graduate school, you’ll likely need to write a personal statement. But what exactly is a graduate school personal statement? And what should you write about to give yourself your best shot at admission?
In this guide, we teach you how to write a personal statement for grad school, step by step. But first, let’s go over how the personal statement differs from the statement of purpose as well as what schools look for in a great graduate school essay.
What Is a Graduate School Personal Statement?
A graduate school personal statement is an admission essay that typically focuses on your personal reasons for wanting to enter a grad program and particular field of study. Essentially, you must tell the story of who you are and how you developed your current research interests.
So is a personal statement for graduate school the same thing as a statement of purpose? Well, not always (though it can be). Here are the general distinctions between the two essay types:
- Statement of purpose: A formal essay that summarizes your academic and professional background, research interests, and career goals. In this essay, you’ll usually explain your reasons for applying to grad school and why you believe the program is a good fit for you (as well as why you’re a good fit for it!).
- Personal statement: A less formal essay that focuses on your passion and motivation for wanting to enter your chosen field and program. This statement is typically more flexible than the statement of purpose, with a bigger emphasis on storytelling. Schools often encourage applicants to discuss (relevant) challenges in their lives and how they’ve overcome them.
Both the graduate school personal statement and statement of purpose are usually anywhere from one to three double-spaced pages long, depending on the program you’re applying to.
Below is a chart comparing the personal statement and statement of purpose:
Usually, the personal statement and statement of purpose are considered two different graduate school essay types.
But this isn’t always the case. While some schools consider the personal statement and statement of purpose two distinct essays, others use the names interchangeably.
For example, Michigan State University’s College of Engineering considers them two distinct essays, while The Ohio State University uses “personal statement” to describe what is essentially a statement of purpose.
Many schools require just one essay (and it’ll usually be the statement of purpose, as it’s the more academic one). But some, such as the University of Michigan , ask for both a personal statement and statement of purpose, while others, such as Notre Dame’s Creative Writing MFA program , want an essay that combines the features of both!
Ultimately, the type of graduate school essay you submit will depend entirely on where you’re applying.

What Do Schools Look For in a Personal Statement?
Many grad schools require a personal statement in order to learn more about you, your interests, your struggles, and your motivations for wanting to enter a field of study. Through this essay, schools can get to know you on a deeper, more intimate level and learn about you in ways they can’t through transcripts and letters of recommendation alone.
But what specifically do universities look for in a great personal statement for graduate school? Here are some of the most important elements to include in your essay.
A Compelling Story
First off, your personal statement must tell a story. After all, this essay is basically your autobiography: it introduces who you are, your interests and motivations, and why you’ve decided to apply to grad school.
Unlike the statement of purpose, the personal statement should focus mostly on your personal history, from your failures to your triumphs. All experiences should tie back to your field or research area, emphasizing what you’ve learned and what this means in terms of your potential as a grad student.
Since you’re talking about yourself, be conversational in your storytelling: use an authentic voice, open up about your experiences, and maybe even throw in a joke or two. Though you’re still writing an essay for school, it’s generally OK to be a little more informal here than you would in a statement of purpose.
That said, there are a couple of things you absolutely shouldn’t do in your personal statement.
- Open your essay with a quotation. Professors have heard the quotation before and don’t need (or want) to hear it again. Plus, quotations often take up too much space in an already short essay!
- Use clichés. Think of unique ways to tell your story and grab readers’ attention. Schools want to see you can be creative yet honest about yourself, so avoid clichés like the plague (see what I did there?).
- Get too creative. Your goal is to look like a serious, committed applicant—not a wacky risk taker—so write clearly and avoid any unnecessary distractions such as images, colors, and unprofessional fonts.
Most importantly, remember that your graduate school personal statement should focus on your successes. Try to use strong, encouraging words and put positive twists on difficult experiences whenever possible. It’s OK to mention your setbacks, too—just as long as you’re discussing how you ultimately overcame (or plan to overcome) them.
Inspirations for Your Research Interests
Schools don’t only want to see clearly defined research interests but also why you have these particular interests. While the statement of purpose elaborates on your professional goals, the personal statement explains what personally motivated you to explore your interests.
For example, in my personal statement for a Japanese Studies MA program, I wrote about my hot-and-cold relationship with the Japanese language and how a literature class and a stint abroad ultimately inspired me to keep learning.
Don’t make the mistake of going way back to the beginning to start your essay. Many applicants open their statements with something along the lines of “I fell in love with psychology when I was ten years old” or “It all started when I was in high school.” But these broad statements lack the creativity and zest needed to secure an acceptance, so avoid them at all costs.

Your Motivation for Applying to Grad School
Your statement of purpose should explain why grad school is a practical next step in your professional life—but your personal statement should focus on what personally motivates you to take this step.
Generally, schools want answers to the following questions:
- Why is grad school an appropriate step for you now?
- How will a graduate degree help you achieve your goals?
- Why didn’t you apply to grad school earlier (if you took time off after undergrad)?
- Were there any struggles or problems you faced that prevented you from applying to grad school before?
Be honest about why you’re applying, both to grad school and the program in particular. In my graduate school essay, I discussed how my passion for Japanese literature and desire to translate it inspired me to seek advanced language training at the graduate level.
Strong Writing Skills
A great personal statement shows that you can write cogently and coherently. After all, strong writing skills are imperative for success as a grad student!
So in addition to telling a good story, make sure you use correct grammar, spelling, punctuation, and capitalization. Use paragraphs to break up your thoughts, too. Because the personal statement is slightly less formal than the statement of purpose, feel free to play around a little with paragraph form and length.
Also, remember that good writing doesn’t necessarily equal big words. You’re writing about yourself, so use words that come naturally to you. Don’t grab a thesaurus and start throwing in a bunch of high-level vocabulary wherever you can; this will make your essay sound less authentic, not to mention stiff.
On the other hand, don’t get too colloquial. You’ll lose respect if you start inserting conversational words such as “gonna” and “gotta.” Therefore, look for the middle ground and write from there.
Want to improve your GRE score by 7 points? We have the industry's leading GRE prep program. Built by world-class instructors with 99th percentile GRE scores , the program learns your strengths and weaknesses through machine learning data science, then customizes your prep program to you so you get the most effective prep possible.
Try our 5-day full access trial for free:
Explanations for Any Hiccups in Your Academic Career
Lastly, the personal statement gives applicants a chance to explain any problems or changes in their academic histories, such as low grades or gaps in education.
Because transcripts and resumes are severely limited in what information they give, schools often use the personal statement to understand your reasons for abrupt changes in your resume and/or transcripts, and to see how you’ve overcome these barriers in your education (and life).
Essentially, a personal statement equalizes the playing field by giving you full rein to explain yourself and emphasize your success over any struggles you’ve had.

How to Write a Personal Statement for Grad School: 9-Step Guide
The personal statement is a fiercely important part of your grad school application. In this section, we teach you how to write a memorable personal statement for grad school so that you’ll have a better shot at getting accepted.
Step 1: Start Early
Personal statements (actually, grad school applications in general!) take a lot of work, so don’t put off writing your essay until the week before your deadline. Rather, try to start working on your essay at least two or three months before your application is due.
You might want to give yourself more time to write it if you’re currently in school or working a demanding job. Setting aside more time lets you work on your graduate school essay routinely without having to squeeze in too many hours each week.
If you only have a month or less until your application deadline, get started on your essay pronto! Though it’s possible to write a personal statement quickly, I recommend carving out more time so that you can put more thought and effort into what you write and how you present yourself. (Doing this also gives others more time to edit your essay for you! We’ll cover this more in later steps.)
Step 2: Read the Instructions
Perhaps the most important step is to read your program’s instructions for the personal statement. Not following these instructions could very well result in a rejection, so always read these first before you start writing! Most programs put their personal statement instructions on their application materials pages.
Your program should give you the following information:
- What type of content your personal statement should include or generally focus on (you might even get an actual prompt to answer!)
- How long your statement should be
- What type of heading, if any, you must include on your statement
- How to save and submit your statement (e.g., .docx, PDF, etc.)
For example, let’s say you’re applying to the History PhD program at UC Berkeley . In this case, your personal statement can’t exceed 1,000 words (three double-spaced pages). You must also answer this prompt :
Please describe how your personal background informs your decision to pursue a graduate degree. Please include information on how you have overcome barriers to access in higher education, evidence of how you have come to understand the barriers faced by others, evidence of your academic service to advance equitable access to higher education for women, racial minorities, and individuals from other groups that have been historically underrepresented in higher education, evidence of your research focusing on underserved populations or related issues of inequality, or evidence of your leadership among such groups.
On the other hand, if you were to apply for an MS in Mining, Geological, and Geophysical Engineering at the University of Arizona , your personal statement would follow these parameters:
Your personal statement is an opportunity to sell yourself, in terms of your research interests, research experience and research goals. Unless you have extensive research experience, most personal statements should be about two single-spaced pages. Your writing should be clear, concise, grammatically correct and professional in tone. You may convey some personal experiences that have led to your current interests or that make you a particularly promising candidate.
Clearly, grad programs can approach personal statements quite differently. Some schools consider them the same as statements of purpose and want a formal focus on academic and research interests, while others want applicants to explain more informally the challenges they’ve overcome to get to this point.
Simply put, follow your program’s directions exactly in order to give yourself your best shot at admission. And if any part of the instructions is unclear, don’t hesitate to contact your program!
Step 3: Figure Out Your Angle
Your “angle,” or focus, in your graduate school personal statement will depend on a few key factors:
- What your grad program wants you to write about
- Your field of study and research interests
- How much experience you have in your field
As I mentioned in step 2, it’s extremely important to read the personal statement instructions for your program. Many times these guidelines will tell you what to include in your essay, thereby clarifying what your overall angle needs to be.
Let’s look back at the example we used above for UC Berkeley’s doctoral program in history. If you were applying here and came from a low-income family, you could discuss how you’ve overcome these financial challenges in your life to get to where you are today.
No matter the prompt, you’ll need to discuss your research interests (to some degree) in your personal statement. How much you talk about your interests, however, will depend on whether you have to submit a separate statement of purpose. If so, you can focus less on your research plans and more on your passions and motivations for applying.
On the other hand, if your personal statement is essentially a statement of purpose, dive deep into your research interests—that is, be specific! For example, those applying to English lit programs should think about the works, eras, and writers they want to study, and why.
More broadly, though, try to answer the question of what you hope to accomplish, either during or after the program. Is there any particular project you want to do? Skills you want to improve? Field you want to break into?
Finally, always choose a positive angle. Use affirmative words and phrases to highlight both your successes and overall enthusiasm for the program.
Step 4: Ask Yourself, “Why This Program? Why This Field?”
Although the statement of purpose usually answers this question directly, you’ll likely need to address this in your personal statement as well—ideally, with a less academic and more conversational tone.
As you brainstorm, try to come up with answers to the following questions:
- What goals or experiences led you to apply to this program?
- How will this program help you grow on a personal level?
- What made you interested in this field? Why do you want to study it more?
- What are your research interests? How did you develop these interests?
- Are there any particular professors you wish to work with?
Step 5: Make an Outline
Now that you’ve brainstormed some ideas, it’s time to start outlining your essay.
Want to improve your GRE score by 7+ points?
Check out our best-in-class online GRE prep program . We guarantee your money back if you don't improve your GRE score by 7 points or more.
PrepScholar GRE is entirely online, and it customizes your prep program to your strengths and weaknesses . We also feature 2,000 practice questions , official practice tests, 150 hours of interactive lessons, and 1-on-1 scoring and feedback on your AWA essays.
Check out our 5-day free trial now:
How you choose to outline your statement is up to you. Some people like drawing bubble charts for organizing their thoughts, whereas others (like myself) prefer to write a list of rough ideas in the general order they want to present them.
Even if you’re not sure whether you want to include something, just add it to your outline anyway. You can always cut it out later as you draft and edit.
Step 6: Draft Your Essay
It’s now time to start writing! Once you’ve got your outline ready, work on expanding what you’ve written into full-fledged paragraphs.
In the beginning, it’s OK to write down anything you feel is relevant, but as you continue to draft, try to look for any extraneous information you can chop.
Remember, most personal statements will be short— usually one to two double-spaced pages—so you don’t want to risk exceeding your program’s word limit. Schools want to see that you can tell a story concisely yet effectively.
If you’re having trouble coming up with a way to open your statement, try skipping around as you draft. Go ahead and jump to a paragraph you have more ideas for—it’s perfectly OK! Just make sure you start to tie all of your ideas together the closer you get to finishing your draft.
On a related note, be careful not to copy any material from your statement of purpose (if you’re required to submit two separate essays). These statements may share a little overlap but should still focus on different aspects of your (academic) life, accomplishments, and goals.

Step 7: Get Feedback
Once you finish drafting, give your essay to people you trust for feedback. This could be a parent, friend, sibling, or mentor (such as a former or current professor).
Ask your editors to give you specific feedback on what you can change, both stylistically and technically, to make it more impactful. Ideally, they’ll also note any unclear, awkward, or redundant ideas/phrases and will offer you helpful suggestions for improvement.
If you’ve written a separate statement of purpose, see whether your editors are willing to check that essay over as well so that you can ensure there isn’t too much overlap between the two.
Step 8: Revise & Edit Your Essay
Once you get feedback, revise and edit your personal statement using your editors’ comments as a guide.
For example, if your editors told you your essay lacked detail, look for places in your writing where you can be more specific and that are likely to have a strong impact on the admission committee.
As you revise, keep an eye out for any awkward sentences or extraneous information. Personal statements are usually pretty brief and you don’t want to accidentally exceed the word limit. So when in doubt, take it out!
Step 9: Proofread
The final step is to proofread your draft. Start by using your computer’s spell check function to quickly find any glaring typos and grammatical errors.
Then, proofread your essay one sentence at a time. Since it’s easy to miss errors in your own writing, I recommend editing your essay from back to front (i.e., from the last sentence to the first sentence). Doing this prevents you from glossing over words and lets you pinpoint punctuation, spelling, and grammatical errors more easily.
In addition, check that you have page numbers on each page (if required—though I suggest adding them regardless) and a proper heading (again, if required) that meets the requirements of your program.
Before you submit it, see if you can get someone else (preferably one or all of your editors from step 7) to look over your final draft as well. If anyone spots a problem with your essay, go back to step 8. If you get all thumbs ups, read over your statement one last time and then turn it in without looking back! (Seriously, don’t read it again or you’re going to want to change something.)

The Key to a Great Graduate School Personal Statement
The personal statement is an essential part of your grad school application. Like the statement of purpose, it highlights your research interests, experiences, and goals.
But more importantly, the personal statement showcases your unbridled passion for your field, lets you reflect on challenges you’ve faced (and subsequently overcome), and answers the overarching question of why you want to attend grad school.
A great graduate school personal statement will normally include most or all of the following elements:
- A compelling story
- Inspirations for your research interests
- Your motivation for applying to grad school
- Strong writing skills
- Explanations for any changes or problems in your academic career
Above, we walked you through how to write a personal statement for grad school. To recap, here are the nine steps to follow:
- Start early—at least two or three months before your application is due
- Read your program’s instructions for the personal statement
- Figure out your angle by brainstorming ideas
- Ask yourself, “Why this program/field?”
- Make an outline using charts, a list, etc.
- Draft your essay
- Get specific feedback from multiple editors
- Revise and edit your essay
- Proofread (and get other people to proofread it, too!)
What’s Next?
Need to write a statement of purpose, too? Waste no time! Our expert guide offers tons of tips to help you come up with a statement of purpose that’s certain to impress admission committees.
Do your schools require a CV or resume? If you’re totally lost on where to begin, read our guides to learn how to put together a great CV or resume for grad school. And for extra help, check out our four original CV and resume templates !
What do you need to submit for your grad school application? Get the scoop on what kinds of materials you’ll need to prepare when applying to grad school .
Ready to improve your GRE score by 7 points?
Author: Hannah Muniz
Hannah graduated summa cum laude from the University of Southern California with a bachelor’s degree in English and East Asian languages and cultures. After graduation, she taught English in Japan for two years via the JET Program. She is passionate about education, writing, and travel. View all posts by Hannah Muniz

Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
Introduction
So you’ve decided to apply to a Ph.D. program—how exciting! While the application process can be harrowing at times, being accepted to a graduate school that is a good fit for your interests and skills is a privilege that will be well worth your efforts.
Before we get too wrapped up in the future, though, let’s return to the task at hand: writing a thoughtful personal statement that compellingly represents your academic journey and makes a persuasive case for your admission. This page will orient you to the process of writing a personal statement. The subsequent pages in this section will give you some general guidelines for constructing a convincing statement.
The advice on these pages is designed for students who are applying to Ph.D. programs in the U.S. While some of what we say may be applicable for graduate school applications to master’s degree programs, professional schools (like business school, law school, or medical school), or other kinds of courses of study, keep in mind that some (or many!) aspects of these applications may be different.
Although the title of this page mentions personal statements, the truth is that each department has different names for the essays they require for admission. Some departments require only a personal statement, others will ask for a personal statement and a research statement, still others will request only a statement of purpose (among other permutations!). While the personal statement, statement of research, and statement of purpose may seem like different essays altogether, this is not always the case. For this reason, it is critical that you read through the admissions guidelines for each program you are applying to. Carefully dissecting and understanding the criteria for each part of the application is an important part of applying to graduate school.
If you have any question about the kind of essay a school requires, your first defense should be your advisor (a professor in the field to which you are applying). Together, you can strategize about the requirements for the essay and can determine if you should reach out to the graduate coordinator for clarification.
That being said, this guide will focus primarily on personal statements, which we will define as essays in which applicants give details about their interest in an academic discipline and intellectual journey. Applicants may also be asked to write about challenges they have faced or the kinds of academic questions that most interest them. These statements’ main purpose is to convince admissions committee that the applicant is a good match for graduate work.
As you write your personal statement, be sure to read through these pages:
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
The Writing Process and a Suggested Timeline
Now that we know what we’re talking about, let’s think about how you will actually write this statement. What follows is a brief outline of one process for writing a personal statement. Keep in mind, though, that everyone is different. You may find that you are able to rigidly follow this process and timeline, but this also may not be the case.
Before you start your applications, think carefully about the kinds of writing you have done in the past. What kinds of writing processes have worked for you? What hasn’t? At what point in the day or week can you get the most work done? When are you not usually as productive?
Based on your answers to these kinds of questions, create a schedule for yourself and set deadlines for completing writing goals (like finishing a first draft of your personal statement, for example). Transcribe this schedule onto a physical calendar, your phone’s calendar application, or a boatload of sticky notes—whatever makes the most sense for you. Just make sure that you can see easily see your schedule in the places where you work.
One last note: try to build in extra time. Most students applying to Ph.D. programs are able to quickly write short essays, so you may be tempted to assume that you’ll also be able to write your personal statement without devoting too much time or effort to this process. Although personal statements are short, they’ll require more time than you might expect. This kind of writing is hard word—and can be emotional, especially because you’ll need to share your statement with tough critical reviewers. Sometimes, too, these reviewers may take a while to get back to you with feedback, so make sure that your schedule can accommodate these anomalies.
What follows is a suggested (and we think, realistic!) timeline for crafting a compelling personal statement based on the assumption that applications are due in December. Here, we’ve outlined a rough schedule that covers when you should start a particular element of the writing process, but we haven’t attempted to say how long each element will take. (For example, we say that you should write the first draft of your personal statement in August, but we don’t say how many hours you should devote to completing this draft.) We hope that you will use the schedule below to create your own calendar that includes your own estimates for the amount of time each element of the writing process will take. For example, you may want to schedule four two-hour writing sessions in August that you can use to write your first draft. Once you have a sense of how long it takes to write this kind of draft, you can tailor your calendar to your own writing habits.

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Proposals and dissertations.
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Incorporating Interview Data
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Research Papers
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
How to Write a Strong Personal Statement for Graduate School
- by Heidi Kerr and Paul David Terry
- November 10, 2020

You’ve made the exciting decision to pursue a graduate degree. Congratulations! There are a wide range of graduate programs to explore , and once you’ve selected the right program for you, it’s time to begin the graduate application process.
The statement of purpose and personal history statement are key components of the UC Davis graduate school application . With fewer than 4,000 characters allowed for each essay, these statements can seem particularly daunting. However, each one has a specific purpose for showcasing your academic journey and creating a holistic application.
Below, we’ve analyzed the differences between the statement of purpose and personal history statement and provided tips for writing these graduate school admissions essays.
Statement of Purpose and Personal History: What’s the Difference?

The statement of purpose shares your academic objectives with the admissions committee and explains why you want to obtain a graduate degree. The personal history statement provides background about who you are and how your experiences have shaped your interests and ability to overcome challenges. Each essay has specific goals to showcase your experience, passion and story.
How to Write a Strong Statement of Purpose
The statement of purpose should highlight your academic preparation , motivation and interests, along with any specializations and career goals that contribute to your program of study. As you write your statement of purpose, it should encompass some of the following:
- Academic and research experiences - Include any relevant academic studies or research pursuits, internships or employment, presentations, publications, teaching, and travel or study abroad experiences that prepare you for this graduate program. Explain your motivation or passion for these experiences and how they can enrich your graduate study.
- Interests, specializations, and career goals - Highlight your research interests, disciplinary subfields, area(s) of specialization, and professional objectives.
- Fit - Explain how your preparation, experiences, and interests match the specific resources and characteristics of your graduate program at UC Davis. Identify specific faculty within your desired graduate program with whom you would like to work and how their interests match your own.
The statement of purpose should also address why you want to pursue the particular graduate degree program at the university and what your goals are in pursuing a degree. Remember, the statement of purpose should explain exactly that, your purpose for becoming a graduate student. This is the primary way it stands apart from your personal history statement.
What to Include in Your Personal History Statement

The personal history statement helps the reader learn more about you as an individual and potential graduate student. Use this opportunity to describe how your personal background informs your decision to pursue a graduate degree. Tell a story that includes any experiences, challenges or opportunities relevant to your academic journey. Consider how your life experiences contribute to the social, intellectual, or cultural diversity within a campus community and your chosen field.
A strong personal history statement begins with an authentic voice and personal narrative. This can reflect your journey to graduate school, any obstacles you’ve encountered, and how you've overcome challenges. Talk about your personal goals and dreams. Explain what motivates and drives you toward this degree. The more your personal statement tells your school about you as an individual, the more it will stand out. Don't write something to impress someone else. This includes language, style and tone. Authenticity is important and resonates well. Tell the truth, in your voice, from your perspective. Use your story to connect.
More Tips and Resources for Applying to Graduate School
Applying to graduate school may be daunting to some, but UC Davis has a variety of resources to help you create a strong graduate school application. Check out the Applying to Graduate School: A Guide and Handbook for ideas and worksheets on how to construct your essays. Or visit our Office of Educational Opportunity and Enrichment Services website for more graduate school prep resources.
Paul David Terry is the assistant director of special interest and affinity networks and alumni diversity lead at the Cal Aggie Alumni Association. He oversees the UC Davis Health Improving OUTcomes blog and enjoys cycling and brewing ginger beer.
Heidi Kerr works as the content and media manager at UC Davis’ Graduate Studies. She has worked as a communications professional at multiple higher education institutions and is passionate about promoting student success.
The authors acknowledge current and former leaders from Pre-Graduate/Law Advising in Office of Educational Opportunity and Enrichment Services, especially Annalisa Teixeira, Ph.D. and Cloe Le Gall-Scoville, Ph.D., who granted us permission to reference Applying to Graduate School: A Guide and Workbook .
Subscribe to the Majors Blog

Primary Category
- Clinical Mental Health Counseling
- School Counseling
- Military and Veterans Counseling
- Social Justice Dashboard
- Tuition and Financial Aid
- Admissions FAQs
- Student Profile
- Counseling Licensure
- Mental Health Counselor Jobs
- School Counselor Jobs
- Online Student Experience
- Student Success
Get a Program Brochure
How to write your personal statement for graduate school.

Drafting a personal statement for graduate school can be a challenging prospect for even the most confident writers. Your “why” for pursuing a specific career path or for wanting to attend a specific school might be clear in your mind, but can be harder to put into words. Personal topics are often more challenging to structure and can easily go off the rails, meaning you will miss out on hitting key points that will demonstrate why you are a good fit for a particular program.
To make this process less daunting, let’s break it down into actionable steps that will help you shine.
Follow These 6 Steps to Write Your Personal Statement
As you consider your application to William & Mary’s Online Master of Education (M.Ed.) in Counseling program, follow these steps to ensure you hit the mark with your personal statement.
1. Research
Know the ins and outs of the program you are applying to, including the admissions requirements, curriculum and faculty before you start writing. The more you know about the program, the more you can highlight what stands out to you about the program and what seems relevant to your career goals. Note that the faculty members of the William & Mary School Education will be reviewing your application materials. You can get to know the specific faculty members involved with our online program by visiting the M.Ed. in Counseling faculty page .
As you research, you will want to make sure you understand what is being asked of you when it comes to the personal statement. Are there specific prompts you should be answering? Is there a page or world limit you need to be mindful of? Gather this information in the research step. We have outlined the specifics of the personal statement along with the other admission requirements in a useful guide .
It is also important to do your homework about the career you plan to pursue with this degree. What type of counselor do you want to be? Who do you want to work with? You will want to speak about why you want to pursue this career and what you hope to accomplish, and the more you know about your intended career path, the more specific you can be in your writing. Specifics will help your personal statement stand out.
Once you have gathered your external research, it’s time to look inward and reflect. This is the stage where you can put your thoughts on paper without worrying about structure. Review any prompts given and get your ideas around these on paper. Also, think about your career aspirations, past academic, professional and volunteer experience, leadership potential, collaborative skills and propensity to engage in reflective practice.
The guiding questions for your application to the M.Ed. in Counseling program are:
- What has led you to become interested in becoming a _____ (Clinical Mental Health, School, Clinical Mental Health – Military & Veterans) counselor?
- Why are you interested in pursuing your counselor education at William & Mary?
- How will your graduate degree in Counseling at William & Mary help you achieve your career goals?
- What strengths would you bring to your graduate studies at William & Mary?
- What do you think would be the greatest challenge(s) for you in your graduate studies at William & Mary? How would you address the challenge(s)?
Based on these prompts, you can see how the research step pays off, as you can address specifics in the program and in your career aspirations. You also have the opportunity to address your strengths here and in turn what you will bring to the program with those strengths.
Now that you have all of your thoughts on paper (or typed up on your computer), it is time to get organized. There are thousands of articles about how to create an outline online, but this does not have to be a big, formal process. The goal here is to get your notes from the research and reflection steps placed in a logical order that will take your reader from the introduction to the conclusion, leaving them convinced that you will be a great fit for the program.
Generally, you will want to hook your reader in the introduction. This is a great place to share a story that relates to your “why” for pursuing counseling and/or the program. Your body paragraphs will continue on what you have set up in the introduction, giving evidence of why the reviewers should admit you to the program. And then finally, you will wrap everything up in your conclusion.
Take your time with the outline to ensure you are hitting the points you want to cover within the ideal page range. For the William & Mary person statement, we are looking for two to three pages.
You may be surprised how fast this step can go if you have given ample attention to the proceeding steps. With your notes and outline in hand, sit down and tie everything together into a cohesive paper. You have already made it through your undergraduate career (or are in the home stretch to graduation). Lean on the skills you have used to write your papers up until now and trust yourself.
Generally, write your personal statement at a time and in an environment that is conducive to getting the words on to the page. Do you write better at night, or are you more of an early bird? Do you need silence when writing, or do you thrive in a busy cafe while listening to your favorite music? Set yourself up for success in the drafting process and know that getting started is often the most challenging part.
Reviewing your draft can be broken down further into two parts: 1. Reviewing for content, and 2. Reviewing for spelling and grammar.
Enlist someone you trust, whether it be a friend, family member, colleague or supervisor, to review the content itself. Do your ideas make sense and flow and in logical order? Can the reader follow your thoughts? Is the takeaway clear? The reviewer can pinpoint areas where you might have missed a key part of the prompt or did not explain yourself very well. If you are struggling with a certain section, talking through it can be a big help.
Once you have the content nailed down, it is time to proofread. You do not want to leave any careless errors on the page. If you do not consider spelling and grammar as strengths, enlist the help of someone you trust to handle this part of the review. It can be the same person who read for the content review, or someone entirely new. Fresh eyes never hurt when it comes to proofreading. When faculty and administrators read a personal statement, they want to see true excitement and a strong level of professionalism without being distracted by errors.
6. Finalize
Charles “Rip” McAdams, professor of Counselor Education at William & Mary, explained what faculty members are looking for when reviewing an applicant’s personal statement: “The goal is to determine if an applicant's decision to pursue graduate education in counseling reflects a realistic understanding of the professional counselor's role, as well as a genuine commitment to engaging in the rigorous academic and clinical preparation that will be required.”
If you feel you have demonstrated this in your statement, it is time to stop writing. You have put in the work, and after one final proof, your personal statement is ready to be sent off with the rest of your application.
Set Yourself Up for a Successful Application Process
As you prepare to apply for William & Mary’s Online Master of Education (M.Ed.) in Counseling , know that our admissions advisors are always on standby to answer your questions, clarify admissions requirements and review the list of materials we need from you. We have also compiled a number of resources to set you up for success throughout this process.
Visit the main admissions page to find the requirements. Check out our step-by-step How to Apply guide , which walks you through the process of applying through our online portal. You can also view the admissions timeline to get a better idea of how long the application process may take. Additionally, here is a blog post to help you consider what time of year you might want to start your graduate school journey.
We compiled a helpful list of admissions FAQs to assist in this process, but please reach out if you run into any questions. You can schedule a call with an admissions advisor here .
Return to Blog
William & Mary has engaged Everspring , a leading provider of education and technology services, to support select aspects of program delivery.
- Find & Compare Programs
Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership
Take the next step toward your career goals. Learn key information about the USC Rossier admission process and application requirements for the Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership program.

Prerequisites
In order to apply for this program, you must:
- Have a master’s degree, or equivalent, from a college or university that is regionally accredited or recognized by a ministry of education. The institution must have been accredited at the time your degree was conferred
- Have a minimum of three years of relevant, full-time work experience relevant to the concentration of interest
- Have leadership experience that demonstrates increasing responsibility
Program applications are reviewed on a rolling basis, but we encourage you to apply early.
*scholarship consideration priority deadlines
Application Instructions
Review the detailed instructions in the dropdowns for each section of the online application . If you need accommodation for any part of the application process, please contact the Office of Admission and Scholarships at [email protected]. We encourage you to submit your request for accommodation at least two weeks before the accommodation is needed so our team can make the necessary arrangements.
Where to find it on the application: My Application > Personal Information
- Enter your name as it appears on your government issued I.D. Indicate any alternate or previous names in the “other name” field (i.e. maiden name).
- Enter the email address USC Rossier should use to communicate with you throughout the application process.
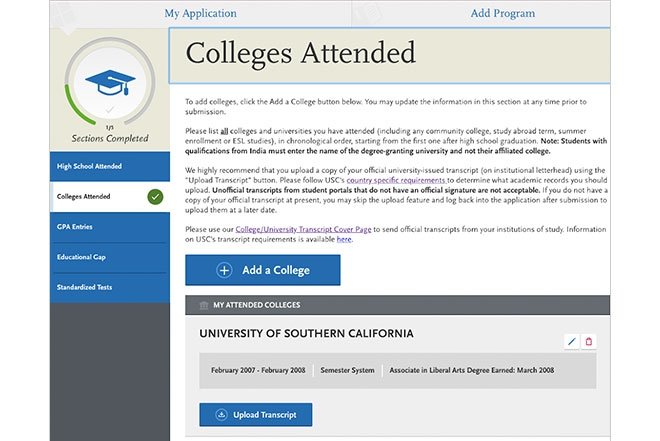
Where to find it on the application: My Application > Academic History > Colleges Attended > Add a College > Upload a Transcript
To expedite admission decisions, please upload registrar-issued transcripts from all attended institutions to the USC application portal. Official transcripts should be submitted separately to the USC Office of Graduate Admissions upon acceptance and submission of intent to enroll.
International students should refer to USC’s country specific requirements to determine which academic records they need to submit.
To Upload Your Transcript to The Application Portal
Login to your USC Application Portal and navigate to the Academic History section. Enter detailed information about your academic history from each institution you have attended.
Once you have saved this information, you will find an option to Upload a Transcript for each institution. You can upload only one PDF per institution. If the transcript consists of multiple pages, you must scan each page and merge them into a single PDF file. If you do not have access to a scanner, you can take clear photos of each page and combine them into one PDF.
There are various online services available to merge multiple files into a single PDF or convert photos into PDFs. Once you have uploaded your transcripts and completed all other sections of the application, you can proceed to submit your application.
Upon admission and submission of the statement of intent to enroll, you must submit degree-conferred transcripts from all attended institutions to the Office of Graduate Admissions.
Where to find it on the application: My Application > Supporting Information > Documents > CV/Resume
Your résumé should be detailed enough to help the admission committee understand the various experiences – extracurricular, leadership or volunteer – that have shaped your interest in the program. Outline your roles and responsibilities within each organization and highlight any special achievements or accomplishments. In the “Supporting Information” section of the application, select “Documents”. Select the “add document” button under “CV/Resume.”

Where to find it on the application: My Application > Program Materials > Documents
Essay responses will be used to evaluate your personal, professional and educational perspectives and experiences and the ability to effectively communicate ideas and organize written thoughts.
Responses to essay questions should be double-spaced with a 12-point font and one-inch margin on all sides. Include your full name at the beginning of each document. Upload each essay as a separate document in the appropriate section.
Personal Statement — 500 words or less
Your personal statement consists of a 500-word essay response. You will have the opportunity to provide an in-depth look at your background, professional goals, and highlight graduate-level written communication skills.
Write a personal statement that addresses how earning the Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership (EDL) degree in your concentration of interest will enable you to address inequities that interfere with learning opportunities and outcomes for students and/or employees in educational settings.
Upload your Personal Statement in the “Program Materials” section of the application under the tab “Documents.” Select the “add document” button under “Personal Statement” .

Leadership Description – 500 words or less
A key aim of the program is to graduate critically conscious leaders who will exert influence to bring about equity-oriented change in an educational context. Tell us about your leadership experiences to date. What type of formal or informal leadership roles have you held. What types of responsibilities have you carried? And what has been the scope of your influence? Please provide specific examples.
Upload your short answer essay in the “Program Materials” section of the application under the tab “Documents”. Select the “add document: button under “Writing Sample.”

Optional Essay – 250 words or less
To aid the admission committee in evaluating your application, use this essay to discuss anything in your academic and/or professional history that may require additional explanation. This essay is optional.
Upload your optional essay in the “Program Materials” section of the application under the tab “Documents.” Select the “add document” button under “Other.”

Where to find it on the application: My Application > Program Materials > Recommendations > Add Recommendation
USC Rossier requires two letters of recommendation to complete the application. Letters should come from supervisors and/or former instructors or faculty who can comment on significant contributions you have made in your workplace, your leadership skills as well as your commitment to life-long learning and your ability to perform well in doctoral-level coursework.
- To submit the names of your recommenders, go to the “Program Materials” section of the application and click on the tab “Recommendations.”
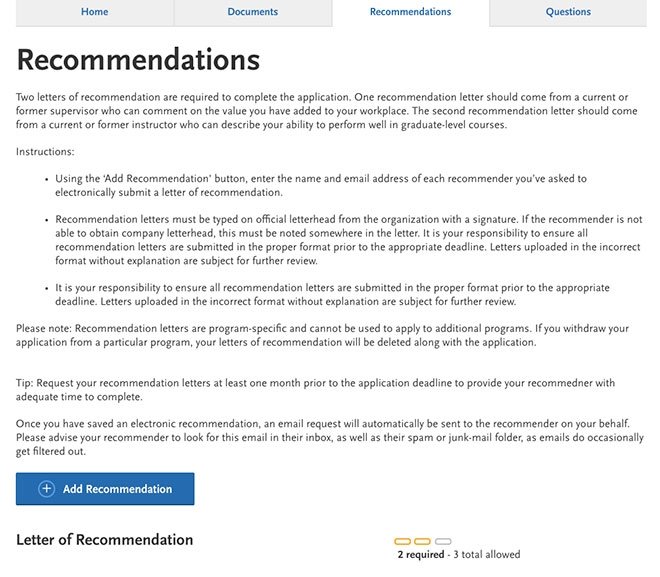
- Recommendation letters must be typed on official letterhead from the organization with a signature. If the recommender is not able to obtain company letterhead, this must be noted somewhere in the letter.
- It is your responsibility to ensure all recommendation letters are submitted in the proper format prior to the appropriate deadline. Letters uploaded in the incorrect format without explanation are subject to further review.
- Recommendations letters should be submitted by recommenders by the application deadline, but they are not required to be submitted at the time you submit your application.
Please note: recommendation letters are program-specific and cannot be used to apply to additional programs. If you withdraw your application from a particular program, your letters of recommendation will be deleted along with the application.
Where to find it: My Application > Program Materials > Kira Assessment
The recorded video response is an opportunity for you to demonstrate your communication skills in professional settings. The timed writing assessment will allow you to demonstrate your writing, critical thinking and analytical ability. No advance preparation is required for either assessment. You must complete both assessments during the same session. You are allowed to take each assessment one time only. For technical assistance with the video response or timed writing assessment, email [email protected].
- Click the “Open Kira Assessment” button on the “Kira Assessment” tab in the application. Note: clicking this link will NOT require you to take the assessment(s) immediately. You can register for the assessment(s) and return at any time to complete it.
- When the page opens, click the “Check In” button.
- Click the registration module. Your first and last name and email should pre-populate in the registration form. Agree to the terms of agreement and privacy policy and click the “Register” button. After you register, a link to Kira will also be sent to your email address for easy access at the time you choose to complete your assessment(s).
- Complete the device set up and practice modules to prepare for your assessment(s).
- Click the assessment module (final step) at the time you are ready to begin your assessment(s).
- Once completed, your assessments become part of your application and will be reviewed by the admission committee in conjunction with other application materials.
Video Response
- Record your responses using an internet-connected computer with a webcam.
- Dress professionally and behave as you would during an in-person interview.
- Make sure you have a pen and notepad available for taking notes on the prompt.
- Once you begin the assessment, you will be provided with two prompts, one at a time, followed by five minutes of prep time for each prompt.
- You will have two minutes to complete your response. There will be a countdown timer and a progress bar during preparation and response time so you can track how much time you have left. If you finish before time is up, you can submit your response using the “submit” button in the lower right corner. The system will automatically submit your response when the time is up.
Timed Writing Assessment
- Once you begin the assessment, you will be provided with the essay topic. You will have 45 minutes to compose and submit your response.
- Write your essay within the provided space in Kira; do not copy and paste from other documents.
- As a general guideline, the essay should be structured with an introduction containing a thesis statement, a body containing your major points and a conclusion.
- Do not use citations or conduct research on the topic while writing your response.
- There is no minimum or maximum word count, however, we recommend a length of 350 to 700 words.
- There will be a countdown timer and a progress bar during the response time so you can track how much time you have left. If you finish before time is up, you can submit your response using the “submit” button in the lower right corner. The system will automatically submit your response when the time is up.
USC Rossier welcomes international applicants. If your prior study was completed outside of the United States, you must have earned the equivalent of a United States bachelor’s degree to be eligible for admission. View the international application requirements based on your country of study .
International students whose native language is not English and who completed their undergraduate work outside of the United States are required to demonstrate proficiency in English as part of the application process. USC does not waive the English proficiency requirement for graduate degree(s) earned in the United States or other qualifying countries; requirements are based on the completion of undergraduate studies. For more information on English Proficiency requirements, English-language test waivers and other alternate accepted exams, please visit the USC Graduate Admission English-Language Proficiency page .
TOEFL or IELTS Test Scores Where to find it on the application: My Application > Academic History > Standardized Tests > Add a Test Score
International students whose native language is not English and who completed their undergraduate work outside of the United States are required to submit an official TOEFL or IELTS score as part of their application. You must have taken one of these tests within the past two years.
In order to be a competitive applicant, you should receive a TOEFL score at or above 100 iBT and an IELTS score at or above 6.5 with no less than a score of 6 on each band.
You may upload your test score report in the “Academic History” section of the application to be used in application review. However, only scores received electronically from the testing service are considered official. Official test scores should be sent from the testing agency directly to USC.
- TOEFL: To send official scores, use USC ETS code 4852. Please note that USC does not accept super-scoring for the TOEFL.
- IELTS: Select “University of Southern California” at the time of registration. Alternatively, provide this information to your testing center after taking the test.
For more information on English Proficiency requirements, English-language test waivers, and other alternate accepted exams, please visit the USC Graduate Admission page .
Your application materials will be reviewed by both the USC Rossier School of Education Office of Admission and Scholarships and the USC Office of Graduate Admissions.
- Refer to your USC Rossier personal portal for timely and accurate updates on your application status (including missing items).
- If your application is complete by the round application deadline, expect to receive notification of your admission decision by the corresponding notification date.
- You will receive a decision letter from both USC Rossier and the USC Office of Graduate admission.
Where to find it on the application: Submit Application Tab
Application fees must be paid by credit or debit card.
An application fee waiver is available to applicants who meet certain eligibility criteria. Eligibility criteria and instructions for obtaining a fee waiver can be found at the USC Graduate Admission website. If you choose to apply for a fee waiver you must:
- Start your online application but do not submit the application until the fee waiver is approved.
- Provide supporting documents to demonstrate qualification.
- Have your fee waiver request approved.
- Complete and submit your online application.
Tips Submit all application materials by the deadline . Incomplete applications may be delayed to the next application review. Skip ahead to the “Recommendations” section and use the application platform to send requests for letters of recommendation first . We recommend you complete this step right away to provide each recommender with the maximum amount of time to complete their letter. Follow the transcript submission instructions carefully. Please upload your registrar-issued transcripts from each institution attended to the USC application portal. Upon acceptance and submission of intent to enroll, you will need to submit official transcripts to the USC Office of Graduate Admissions separately.
Review Process
Your application to USC Rossier will be evaluated using a holistic review process. Academic preparation, professional work experience, personal achievement and commitment to the USC Rossier mission are each considered. No single attribute or characteristic guarantees admission to USC Rossier.
We seek applicants who will add to our vibrant learning community and whose goals, values and experiences align with the USC Rossier mission and program goals. We adhere to the university’s non-discrimination policy, and are committed to providing equal opportunity for all students.
As an applicant for this program, you will be automatically considered for limited USC Rossier scholarships, with priority consideration given to applicants who apply by the priority and regular deadlines. There is no need to submit a separate application. Recipients are selected based on academic achievement, demonstrated dedication to the USC Rossier mission and other distinguishing characteristics. All USC Rossier scholarships are awarded at the time of admission.
Document Submission Policy
Transcripts and all other application materials become the property of USC. The university does not return or duplicate materials for any reason whatsoever. The information and materials in your submitted application are made available only to the central Office of Admission and the admission committee of the academic department or professional school to which you have applied.
Frequently Asked Questions
USC Rossier students come from diverse academic backgrounds. Education or experience related to your program of interest can make you a more competitive applicant, however it is not required. If your bachelor’s or master’s degree is unrelated to the program for which you are applying, use your application to communicate your passion for working in your selected field and explain how your background and experience has prepared you to be successful and positively contribute to your chosen field.
The admission committee looks for leadership experiences that demonstrate increasing levels of responsibility. Exceptional applicants demonstrate long-term commitment to historically marginalized student populations.
No. At USC Rossier, the online and on-campus version of our programs are distinct with separate applications. If you would like to be considered for a program other than the program for which you have been admitted, you will need to reapply to that program.
No. Your diploma will read “Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership” only.
No. The program has one start date per academic year.
There is no minimum GPA required to apply to USC Rossier programs, but competitive applicants typically have a GPA of 3.0 or above. However, GPA is one of many elements evaluated in the admission committee’s comprehensive evaluation of candidates. In the application, you may use the optional essay to discuss anything in your academic and/or professional history that may require additional explanation.
If you would like to be considered for a program other than the program for which you have been admitted, you will need to re-apply for the new program. Please read the program requirements thoroughly, as they may be different from those specified for the program to which you were admitted. Your application will not be considered complete until all documents required for your new program are received.
Before applying for any program, it is recommended that you speak with an admission team member for assistance and direction in determining which program is the best fit for you.
Applicants are permitted to apply to up to three USC programs within the same academic year. When completing your online application, select all programs to which you would like to apply. Please read each program’s guidelines carefully, as each program may require different documents or methods of assessment. You will only need to complete program-specific questions for each additional program; you will not have to fill out the entire application multiple times.
If you decide you would like to apply to an additional program after submitting your initial application, you can log back into your application and add another program.
Application fees are required for each program to which you apply, but you will only need to submit transcripts and test scores (optional for most programs) once.
You can request to transfer up to six units of doctoral coursework completed at another institution that meet the requirements of the EDL program. Contact your academic advisor in the EdD program office to learn more.
GRE scores are neither required nor accepted for admission at USC Rossier.

Callah Darmali
Associate Director, Office of Admission and Scholarships
- [email protected]
- (213) 205-0609
- Search All Scholarships
- Exclusive Scholarships
- Easy Scholarships to Apply For
- No Essay Scholarships
- Scholarships for HS Juniors
- Scholarships for HS Seniors
- Scholarships for College Students
- Scholarships for Grad Students
- Scholarships for Women
- Scholarships for Black Students
- Scholarships
- Student Loans
- College Admissions
- Financial Aid
- Scholarship Winners
- Scholarship Providers
Student-centric advice and objective recommendations
Higher education has never been more confusing or expensive. Our goal is to help you navigate the very big decisions related to higher ed with objective information and expert advice. Each piece of content on the site is original, based on extensive research, and reviewed by multiple editors, including a subject matter expert. This ensures that all of our content is up-to-date, useful, accurate, and thorough.
Our reviews and recommendations are based on extensive research, testing, and feedback. We may receive commission from links on our website, but that doesn’t affect our editors’ opinions. Our marketing partners don’t review, approve or endorse our editorial content. It’s accurate to the best of our knowledge when posted. You can find a complete list of our partners here .
How to Write a Graduate School Personal Statement (with example!)

Varonika Ware is a content writer at Scholarships360. Varonika earned her undergraduate degree in Mass Communications at Louisiana State University. During her time at LSU, she worked with the Center of Academic Success to create the weekly Success Sunday newsletter. Varonika also interned at the Louisiana Department of Insurance in the Public Affairs office with some of her graphics appearing in local news articles.
Learn about our editorial policies

Bill Jack has over a decade of experience in college admissions and financial aid. Since 2008, he has worked at Colby College, Wesleyan University, University of Maine at Farmington, and Bates College.

Maria Geiger is Director of Content at Scholarships360. She is a former online educational technology instructor and adjunct writing instructor. In addition to education reform, Maria’s interests include viewpoint diversity, blended/flipped learning, digital communication, and integrating media/web tools into the curriculum to better facilitate student engagement. Maria earned both a B.A. and an M.A. in English Literature from Monmouth University, an M. Ed. in Education from Monmouth University, and a Virtual Online Teaching Certificate (VOLT) from the University of Pennsylvania.

Congratulations on finishing your bachelor’s degree, and starting the next chapter! You might be thinking about applying to graduate school, and fortunately, it’s very similar to applying to an undergraduate program. However, it’s probably been a few years since you’ve had to write an application essay, so you might be wondering how to write a personal statement for graduate school. If so, this guide is the perfect resource for you! Keep reading below to find out more, and don’t forget to check out the example of a graduate school personal statement.
What is a personal statement?
A personal statement is an essay that encapsulates your personal journey and how that’s shaped who you are as an applicant. They are typically 400-600 words, but can be longer or shorter.
Be sure not to confuse a personal statement with a statement of purpose as they are two different types of admissions essays. Use this as an opportunity to show colleges what you value and what’s turned you into an ideal student for your desired school.
What should I write about?
Personal statements are your chance to get, well, personal. While you should answer the prompt in its entirety, you should also write about yourself. Bring a personal element into your essay like family or a story of you overcoming an obstacle.
Ideally, your story should relate to what you’re trying to accomplish at your graduate school of choice. Tie it all together: your personal experiences, your desired major, and your ideal outcome.
Tips for writing a personal statement for graduate school
It’s important to start your graduate application as soon as you’re able. Usually, the first round of applications receive the best financial aid packages, so start early!
Starting sooner can also give you the time to outline your essay and get it read over by your support system. You’ll want it all to be perfect, so don’t rush.
Be transparent
Instead of telling admissions what you think they want to hear, be open and honest about yourself. You want them to understand you, and the only way to do that is to show who you actually are. Offer up personal stories or things that genuinely interest you so that you can show off your sparkling personality!
Be original
Graduate programs are often very competitive since there’s a smaller admissions pool. As a result, your essay should be as original as possible to stand out from the crowd. Tell your story in an organic way, and approach the given prompt with an open mind.
Related : How to write an essay about yourself
Check your work
It’s extremely important for you to proofread and check for correct spelling and grammar throughout your personal statement. Even simply reading your statement out loud can help you catch any errors and make sure your words flow together. You should also consider having mentors or people within your support system read over your essay to ensure your message is clear.
Common mistakes when writing a graduate school personal statement
Reusing your undergraduate essay .
Reusing your first supplemental essay as a template is a big mistake you want to avoid. Years have passed since then, and you’ve learned new skills and grown as a person and a student.
The experiences you previously wrote might not resonate with who you are today or tell the graduate team what they want to know about you. It may also have grammatical errors that you might not have noticed before, so take a little extra time to start from scratch and create something new.
Repeating what’s in your resume
It’s likely that your graduate school of choice will require you to upload a copy of your resume as part of your application. Therefore, the admissions committee will already know your professional background, so tell them something else about yourself or provide further depth to a job experience. Repeating yourself only tells them one thing, and you want to be the most well-rounded applicant that you can be.
Graduate school personal statement example
Prompt: Please discuss how your experiences, both personal and professional, have led you to pursue a graduate business degree at this time. What are your short- and long- term goals and how will this program and the J. Mack Robinson College of Business help you achieve these goals? (750 words max)
While many of the applications you receive will detail the many ways that person has been the first to do something, I pose a different perspective: hope to be the last. In other words, you might see me as a first-generation college student, but I see the makings of becoming the last generation to worry about generational wealth in my family.
Though it is true that I would be the first in my family to get my master’s degree, I’m hoping that my future success means I’ll be the last “first.” It’s not lost on me what this title means, but most of all, it signifies the dawn of an era. A dynasty bred from the struggles and achievements of those before it.
These are big shoes to fill, but I’ve never been afraid of a challenge and the things I’ve learned have helped me secure my future. For example, by observing different business models throughout the years, I found a secret about marketing: people love a product that loves them back. In my case, a product that’s always loved me back were books. I’d fallen in love with bookshelves and bookstores alike, so it only makes sense that a culmination of my love of marketing and books is the goal of one day working in book publishing. I want to know the inner workings of book promotion including design decisions and book tours. Eventually, I plan on working at one of the big publishers such as Penguin Random House, Harper Collins, or Macmillan.
Fortunately, I’ve been given opportunities to decide on my own path, which I hope to execute at Georgia State University. This school’s unique curriculum will be an asset to me since there are classes that specifically cater to buyer behavior, and that’s an area of study I’m particularly interested in. The Social Media Intelligence Lab and social media marketing class will hopefully give me an inside look into influencer marketing and its impact on product profitability. According to your mission statement, GSU educates future leaders, and I want to be a part of that.
As a mentor of mine once said, knowledge is meant to be shared, and if it isn’t, it’s control. I hope to build up the people around me with knowledge and experiences as I go out into the professional world just as I hope this program will do for me. If I’m accepted into this program, I plan on using my creativity and drive for not only my success, but for my family’s as well. There may be times I fall short of a goal, but failure isn’t an option. Each benchmark professors put in front of me will be conquered, and one day, I’ll be one of your notable alumni.
Why this essay works:
- The writer clearly researched the school and understands its values
- The prompt is answered completely and seamlessly
- The applicant knew their goals and thought of ways to achieve them at the college
- This statement communicates not only what the college gains from this applicant’s admission, but also what the applicant gains
- It’s also well within the word limit
Frequently asked questions about how to write a graduate school personal statement
Do i have to write a personal statement to get into graduate school, how long is graduate school, do i have to take an exam to get into graduate school, scholarships360 recommended.

10 Tips for Successful College Applications

Coalition vs. Common App: What is the difference?

College Application Deadlines 2023-2024: What You Need to Know
Trending now.

How to Convert Your GPA to a 4.0 Scale

PSAT to SAT Score Conversion: Predict Your Score

What Are Public Ivy League Schools?
3 reasons to join scholarships360.
- Automatic entry to our $10,000 No-Essay Scholarship
- Personalized matching to thousands of vetted scholarships
- Quick apply for scholarships exclusive to our platform
By the way...Scholarships360 is 100% free!

Writing an Effective Personal Statement for PhD Graduate Programs
Personal statements should be a reflection of your academic skills, success, and goals.
By Kaela Singleton Doctoral Candidate in Interdisciplinary Program in Neuroscience
A personal statement is one of the most important components of any doctoral graduate school application. This post will guide you with some general steps to get you started with generating a personal statement that is concise, reflects your academic success, and emphasizes your goals for graduate school. The individual graduate programs will provide writing prompts that detail exactly what you should address in your statement, so be sure you touch on everything that they want you to cover!
Before you start writing
- Update your CV: Having a complete list of your accomplishments will make it easier to include and exclude information from your personal statement. Your CV can be used as a timeline of your achievements, and therefore an outline to how your past experiences have prepared you for graduate school. For guidance on CV writing, see 7 Tips for Writing a Successful CV.
- Research Graduate Schools of Interest: Gain insight into the coursework, faculty, and student life for each program you are considering. Using the program website, generate a list of qualities that appeal to you about each school you’re applying to. Emphasize how and why these qualities contribute to your decision to apply to this program. This list should include research and faculty members that interest you as well as any other pros (i.e. location, cohort size, post-graduate jobs etc.)
- Create a team of editors: Your personal statement will be read by faculty members and graduate students studying different topics within the program. Therefore, your personal statement should be compelling to a broad audience. Ask peers, mentors and advisors from various disciplines well in advance to edit and provide feedback on your statement.
Now start writing
Introduction.
The goal is to engage your reader with a quick synopsis of who you are, what you want out of graduate school, and your qualifications to join this specific program.
- Introduce yourself and identify your academic interests: Provide a brief introduction of yourself and your academic interests. If you have a personal anecdote that explains how you became interested in science and research, start there. These “narrative hook” anecdotes engage the reader and set up a great platform to describe the motivation behind your experiences. Then go into your academic interests, which can be a couple of sentences broadly stating your research interests.
- Emphasize your skills and overall goals: Use both your research on the program and CV to highlight how your skill set will complement and grow from participation in this program. Speak in broad terms, showcasing how your goals align with the overall mission of the program.
THE BODY PARAGRAPHS
The goal is to expand on the points you mentioned within the introduction. Provide concrete examples of how past and present experiences led you to writing this application.
- Explain how you became interested in your particular scientific field: Highlight key moments that encouraged you to apply to graduate school. This can be the very start of your interests in the field or from skills and knowledge that you gained from internships, research experiences, or coursework and class discussions.
- Describe your prior research experiences and importantly what you learned from each experience: Provide a past experience where you used and developed a new skill that is pertinent to your ability to conduct research. Be sure to explain how this skill will be useful for your future in graduate school. It is critical to discuss what you learned from experience and to be as specific and concise as possible. For example: I worked with Dr. A at institution B. My work focused on C. The project entailed D, E and F techniques. From this experience, I learned G. This taught me F about my decision to attend graduate school.
In the conclusion paragraph, you should discuss what you learned about the graduate school program that you are applying for. Highlight specific faculty members or courses listed that excite you, and re-emphasize your goals.
- Summarize your qualifications and experiences: Bring everything together here. Emphasize the skills you currently have and how joining this program will aide in continuing your success.
- Personalize: In this final paragraph, include specific faculty and program qualities that appeal to you as an applicant. Show that you have researched specific faculty or courses that will aide in your future training. Also be sure to discuss your career goals.
- Edit: Proofread and edit. Send your statement out to friends, faculty advisors, and people outside of your discipline.
Personal statements should tell your story and be compelling across fields. Remember that a PhD program trains you to build and utilize scientific skills to advance research. You won’t want to try to convince the reader that you’ll cure cancer or discover the flu vaccine. Instead, focus on persuading readers that graduate training is right for you, and that the accompanying enrichment of your research skillset will help you reach your academic and professional goals.

More Career Advice
Learn from faculty, staff, postdocs, students and alumni through our Career Catalyst blog.
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- Office Directory
- Add or Edit Profile
- Financial Management Practices
- Development and Alumni Relations
- Benefits and Services
- Employee Appreciation Programs
- The Five Functions of DEI
- Communication
- Recruitment
- DEI Dashboard
- 2020 Report
- 2019 Report
- Student Ambassadors
- Education Library
- Education Technology Services
- Graduate Studies
- Courses and Workshops
- Video Production Guidelines
- Promotional Posting Guidelines
- Research and Development
- Records and Reporting
- Dean's Advisory Board
- Service, Leadership, and Outreach
- Student Success
- Diversity Plan
- 100th Anniversary Book
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Targeted Engagements
- Global Gateway for Teachers
- Overseas Short-Term Study Experiences
- External Grant Opportunities
- Our Global Reach
- Faculty and Student Int'l Engagement
- IU Global Gateways
- Indiana Global Education Outreach
- Int'l Partnerships
- Visiting Int'l Scholars
- Int'l Student Ambassadors
- Academic Programs
- International Journals
- News & Events
- Int'l Student Resources
- CAEP Annual Reporting Measures
- CAEP Accreditation Visit Call for Third-Party Comments
- SoE Data Dashboards (Faculty)
- Licensure Requirements
- Employment Outcomes
- Employer Evaluations
- Student Teaching Survey Reports
- Attrition & Completion Rates
- Graduate Survey Results
- Indiana Teachers of the Year
- Emergency Action Plan
- SoE Emergency Information
- School Violence
- Report Facility Issue
- Direct Admit Scholars
- TEP Application Guidelines
- Accessible Virtual Tour
- Field Trips
- Non-School of Education Scholarships
- Graduate Student Funding
- Student Emergency Fund
- Campus Financial Aid Resources
- INSPIRE Living-Learning Center
- All Programs
- License Additions
- Master's Programs
- Doctoral Programs FAQ
- Specialist Programs
- Certificate Programs
- Doctoral Minors
- Licensure Programs
- Transition to Teaching
- New Zealand
- Northern Ireland
- Navajo Nation Program
- Urban Program
- IU Bloomington Students
- Guest Campus Students
- Partner Campus Students
- Student Spotlights
- Teacher Spotlights
- Cost & Financial Aid
- Online Learning
- Tuition and Fees
- Registration
- Block Enrollment Course Information
- Student Teaching Registration Information
- Program Sheets
- Forms & Publications
- Credit Overload Request
- Four Year Plan
- Academic Calendar
- Undergraduate Bulletin
- Background Check
- Early Field Experiences
- Student Teaching Forms
- Preparation
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Student Organizations
- Counseling and Student Services
- Dean's List
- Report Your Concerns
- Scholarships
- Career Coaching
- Student Teaching Fair
- Health and Human Services Career Day
- Explore Possibilities
- Get Experience
- Stay Connected
- Professional Distinction
- Educator Wellbeing Distinction
- Workshops and Training
- Recruiting Policies
- Classroom Presentations
- Graduation Deadlines
- Leave Policy
- Online Students
- Graduation Application
- Guidelines for Multi-Article Dissertations
- G901 Permission Request
- Qualifying Examinations
- 2022 Scholars
- 2021 Scholars
- 2020 Scholars
- 2023 Scholars
- Program-Specific Information
- International Student Ambassadors
- Student Affiliates in School Psychology
- Dissertation & Thesis Announcements
- Approved Core Inquiry Courses
- Holmes Scholars Program
- Initial Licensure
- License Renewal
- Licensing Outside Indiana
- Knowledge Base
- Graduate Bulletin
- Teaching with Technology Lab
- Support Services
- Volunteering Opportunities
- Faculty Directory
- Counseling and Educational Psychology
- Curriculum and Instruction
- Chair's Welcome
- IST Conference
- Faculty Bookshelf
- Faculty Meetings
- Policies and Procedures
- Instructional Consulting
- In Memoriam
- Office of Research and Development
- 2023 Highlights
- Research Centers
- Funded Research
- Research Findings
- Translation to Practice
- Equity in Action
- Overview and Project Timeline
- Analysis in Progress
- Presentations
- Accomplishments
- Teacher Study Group
- "Creative Paths to Peace" Grant
- Proffitt Internal Grant Competition
- Proffitt Summer Faculty Fellowship Program
- Tilaar Faculty Support Fund
- Cost-Share and Matching Funds on External Grant Proposals
- Current Visiting Scholars
- Become a Visiting Scholar
- Visiting Scholar Policies
- COVID-19 Entry Updates
- Flexible Workspace
- Faculty & Staff Giving Campaign
- Donor Spotlights
- Get Involved
- Submit a Nomination
- Alumni Magazine
- Alumni Board of Directors
- Counseling and Wellness Clinic
- Learning and Developmental Evaluation Clinic
- Current Cohort
- Past Cohorts
- Nominate a Teacher
- How to Apply
- Armstrong Teacher Panel Archive
- Current Jacobs Educators
- Past Winners
- Advisory Board
- Teachers' Examples
- Research-to-Practice Briefs
- Speaker Series
- Baxter Online STEM Student Challenges
- Educating for Environmental Change (EfEC)
- Dual Language Immersion (DLI)
- Global Learning for Pre-Service Teachers Workshops
- Global Literacy Invitation Project
- Global STEAM
- In-Service Teachers Workshops
- Principals’ Academy on Internationalizing K-12 Schools
- School of Education Curriculum Internationalization
- Medical Research Education Project
- Project LIFT
- Saturday Art School
- Past Lesson Plans
- Partners in Education (PIE)
- Maker Mobile
- Past Mentors
- Screening and Training Process
- HOPE for Cadets
- AAC in Action
- Celebration of Excellence
- C&I Graduate Research Symposium
- Invited Sessions
- Visiting Bloomington
- Science Education Research Symposium
- Convocation
- Diggs Symposium
- Virtual Events
- Advisory Committee
- Education Law Resources
School of Education
Personal statements, personal statement criteria, higher education and student affairs, m.s.ed. in higher education and student affairs.
The personal statement should provide a concise reflection of why you are interested in becoming a student affairs professional. You may want to touch on what may have led to your desire to be a student affairs professional, and address anything you want the committee to know about your qualifications for the program. Finally, you may want to also address why you are interested in studying at Indiana University. The final statement should be double spaced and no more than 2 pages in length.
Ph.D. in Higher Education
Your personal goal statement is an important part of the review process for our faculty members as they consider your application. This statement allows faculty to learn about your background, work experience, and additional qualifications that make you a strong candidate for the program. It also serves as a platform for you to share your goals for graduate study, your interests in working with particular faculty members, and your thoughts about how IU’s program would help you reach your desired career outcome. This statement should be 500 words or less. You can upload your personal goal statement as a PDF file or as a Microsoft Word document (.doc or .docx) into the online application itself.
Start your life-changing journey
Additional links and resources.
- From the Dean
- Annual Report
- International Engagement
- Accreditation
- Measures of Success
- Emergency Preparedness
- Departments
- Instructor Resources
- Undergraduate
- Community of Teachers
- Research Initiatives
- Funding Opportunities
- Visiting International Scholars
- Undergraduate Portal
- Graduate Portal
- Academic Resources
- Career Connections
- Research Help
- Maker Education
- Youth Programs
- Award Programs
- CHG Counseling Services
- Staff Council
- Visit the School
- Alumni Spotlights
- Distinguished Alumni Award
Indiana University Bloomington School of Education
SoE Knowledge Base
SoE Intranet (Legacy)
Search Icon
Events See all →
Maggie nelson.

6:30 p.m. - 10:00 a.m.
Kelly Writers House, 3805 Locust Walk
2024 Sachs Grant Awards

4:30 p.m. - 7:00 p.m.
The Arts Lounge at the Annenberg Center for the Performing Arts, 3680 Walnut St.
Alumni Weekend 2024

Various locations
268th Commencement

Franklin Field
Science & Technology
2024 tropical cyclone prediction
Michael mann and colleagues predict a record-breaking 33 named storms for the 2024 north atlantic hurricane season. it is the highest count ever projected..

For more than a decade, climate scientist Michael Mann of School of Arts & Sciences at the University of Pennsylvania and colleagues have annually combed through historical weather data, reviewed current oceanic and atmospheric conditions, and applied computational modeling to forecast of coming hurricane seasons.
The team, comprising Shannon Christiansen , a senior research coordinator in the Mann Group, and Michael Kozar, a former graduate researcher in the Mann Research Group , today released their prediction for the 2024 North Atlantic season, which spans from June 1 to Nov. 30. They forecast an unprecedented 33 named tropical cyclones, potentially ranging between 27 and 39.
“We’ve seen many hyperactive seasons over the past decade, and in just about all cases, like our prediction for this year, the activity is substantially driven by ever-warmer conditions in the tropical Atlantic tied to large-scale warming,” says Mann, Presidential Distinguished Professor in the Department of Earth and Environmental Science and director of the Penn Center for Science, Sustainability and the Media .
Mann says the annual prediction originally started out as a scientific exercise. It began as an undergraduate research project that Michael Kozar, then a Pennsylvania State University student, was doing under Mann’s guidance to improve the predictions other groups were making through a more appropriate statistical framework.
“This tropical cyclone project with Dr. Mann was my first exposure to meteorological research about 15 years ago,” Kozar says. “Working on this seasonal model as an undergraduate student helped confirm that I wanted to dedicate my career to better understanding and forecasting Atlantic tropical cyclones. So, it is always exciting to touch base with the team and revisit our work each spring to get an idea on how active the upcoming season might be.”
Kozar, now tropical cyclone forecaster at Moody’s Risk Management Solutions, still works with Mann every year to bolster the quality of the predictions, which now incorporate more advanced statistical models that have been refined to include a broader array of climate predictors and adjustments for historically undercounted storms.
The process and product
Christiansen explains that the forecast integrates several key climatic variables. “It takes into account the current Atlantic Sea Surface Temperatures (SSTs), which significantly influence hurricane development by providing the necessary heat and energy,” she says. “We also factor in the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) conditions, as shifts between El Niño and La Niña can dramatically alter atmospheric patterns that either enhance or suppress hurricane activity.”
Additionally, the researchers consider the mean conditions for the North Atlantic Oscillation, which affects weather patterns in the Atlantic. These climate predictors are gathered and put into the statistical model, enabling the researchers to produce a detailed range and best estimate of the named storms anticipated for the season.
This year’s predictions are influenced by particularly high sea surface temperatures in the North Atlantic Main Development Region (MDR), which, as of this month, are recorded at more than 1.9°C above average according to NOAA’s Coral Reef Watch. In addition, the forecast incorporates the anticipated development of moderate La Niña conditions, marked by a Niño 3.4 region anomaly of -0.5°C, and assumes average conditions for the North Atlantic Oscillation during the coming fall and winter. The Niño 3.4 region is a specific area in the central Pacific Ocean used to monitor and measure sea surface temperature anomalies as part of the ENSO diagnostic strategy.
Should ENSO conditions neutralize later in the year, the team predicts a slightly reduced activity of 30.5 +/- 5.5 storms, ranging from 25 to 36 storms, with the estimated 31 named storms as the most likely outcome. An alternative model, accounting for MDR sea surface temperature relative to the tropical average and incorporating the impact of negative ENSO conditions, suggests a lower activity with 19.9 +/- 4.5 named storms.
Why these matter
Mann cites three main reasons for why these results are of particular interest, saying, “first, from a preparation standpoint, these provide a lot of useful information as to whether those in areas impacted by Atlantic hurricanes should prepare for an especially active season.
“Second, these results underscore the seasonal relationship between climate and tropical cyclones, which helps to provide context for understanding how climate change is impacting hurricanes,” Mann says. “Since it’s the same basic relationships that are in play on seasonal and longer timescales, for instance, the warmth of the tropical Atlantic.”
Finally, it is an important demonstration of the strength of climate science models, Mann says. Scientists can make successful seasonal predictions based on the climate information they have, providing grounds for trust in longer-term climate predictions, particularly human-caused warming and its impacts.
Picturing artistic pursuits

Campus & Community
Penn celebrates operation and benefits of largest solar power project in Pennsylvania
Solar production has begun at the Great Cove I and II facilities in central Pennsylvania, the equivalent of powering 70% of the electricity demand from Penn’s academic campus and health system in the Philadelphia area.

Education, Business, & Law
Investing in future teachers and educational leaders
The Empowerment Through Education Scholarship Program at Penn’s Graduate School of Education is helping to prepare and retain teachers and educational leaders.

Arts, Humanities, & Social Sciences
‘The Illuminated Body’ fuses color, light, and sound
A new Arthur Ross Gallery exhibition of work by artist Barbara Earl Thomas features cut-paper portraits reminiscent of stained glass and an immersive installation constructed with intricately cut material lit from behind.

25 years of ‘LOVE’
The iconic sculpture by pop artist Robert Indiana arrived on campus in 1999 and soon became a natural place to come together.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A personal statement is a short essay of around 500-1,000 words, in which you tell a compelling story about who you are, what drives you, and why you're applying. To write a successful personal statement for a graduate school application, don't just summarize your experience; instead, craft a focused narrative in your own voice. Aim to ...
Set aside enough time: Although personal statements are generally short in length (approx. 700 words; 1-2 pages), give yourself ample time to write a strong, well-written statement. It takes more time than you think to develop a final draft for submission. Focus on your spelling, grammar, and vocabulary: It's important to present a well ...
Guidance for PhD applicants Faculty of Education, University of Cambridge. The 1,500 word personal statement is an important element of your application to doctoral study, whether full-time or part-time. It is one of several elements considered during the application process, alongside your research proposal and the references you provide.
Sample Personal Statement for Graduate School 3. PDF of Sample Graduate School Personal Statement 3 - Public Health. This is my successful personal statement for Columbia's Master's program in Public Health. We'll do a deep dive on this statement paragraph-by-paragraph in the next section, but I'll highlight a couple of things that ...
Your personal statement should focus on two main aspects: your competence and commitment. 1. Identify your strengths in terms of competence that indicate that you will succeed in the grad program and provide examples to support your claims. Start your statement by describing your strengths immediately. Because faculty will be reading many ...
Personal Statements. Preparing a well-written and effective personal statement (sometimes referred to as statements of purpose or personal essays) that clearly articulates your preparation, goals, and motivation for pursuing that specific graduate degree is critically important. You will need to spend a considerable amount of time and effort in ...
While deciding to embark on the path to graduate school is an exciting first step toward advancing your career, the application process can sometimes feel daunting and confusing.. One major part of the application that most schools require is a personal statement. Writing a personal statement can be an arduous task: After all, most people don't necessarily enjoy writing about themselves, let ...
How long should a PhD personal statement be? A PhD personal statement should be 400-500 words, fitting on one side of an A4 sheet of paper. Your university may set a specific word count or maximum length, so make sure to check the application details. Either way, you should aim to be disciplined and concise.
Step 3: Figure Out Your Angle. Your "angle," or focus, in your graduate school personal statement will depend on a few key factors: What your grad program wants you to write about. Your field of study and research interests. How much experience you have in your field.
Your personal statement needs to sell your unique qualifications, experiences and connections. Programs look for candidates with a strong point of view on what they want to learn and accomplish and a record of success. Even though it's called a 'personal' statement, skip the childhood story about seeing the ocean and wanting to become an ...
Nearly all doctoral programs and many master's degree programs in psychology require submission of a personal statement as part of the application package. In my experience advising students as well as serving as a graduate dean for many years, few things in the application process cause students as much anxiety and prompt so many questions.
This page will orient you to the process of writing a personal statement. The subsequent pages in this section will give you some general guidelines for constructing a convincing statement. The advice on these pages is designed for students who are applying to Ph.D. programs in the U.S. While some of what we say may be applicable for graduate ...
The more your personal statement tells your school about you as an individual, the more it will stand out. Don't write something to impress someone else. This includes language, style and tone. Authenticity is important and resonates well. Tell the truth, in your voice, from your perspective. Use your story to connect.
Personal Statement A personal statement is used in the graduate program admissions process to assess applicants. It describes your goals (e.g., research or study areas of interest) and intent for attending graduate school. EACH PROGRAM IS DIFFERENT statement or statement of research interests. You may also encounter essay questions that
Follow These 6 Steps to Write Your Personal Statement. As you consider your application to William & Mary's Online Master of Education (M.Ed.) in Counseling program, follow these steps to ensure you hit the mark with your personal statement. 1. Research. Know the ins and outs of the program you are applying to, including the admissions ...
Select the "add document" button under "Personal Statement". Leadership Description - 500 words or less. A key aim of the program is to graduate critically conscious leaders who will exert influence to bring about equity-oriented change in an educational context. Tell us about your leadership experiences to date.
Personal Statement for a Ph.D. in Literature. In August 2015, I completed my graduate degree and thesis for the Research Master's in Comparative Literary Studies at [university name2]. As a student in the Research Master's (RMA) program, my scholarly concerns were mostly focused on critical theory, cultural studies, and social discourse, built ...
Personal statements are your chance to get, well, personal. While you should answer the prompt in its entirety, you should also write about yourself. Bring a personal element into your essay like family or a story of you overcoming an obstacle. Ideally, your story should relate to what you're trying to accomplish at your graduate school of ...
Personal statements should tell your story and be compelling across fields. Remember that a PhD program trains you to build and utilize scientific skills to advance research. ... Biomedical Graduate Education Georgetown University Medical Center Medical and Dental Building, SE108. 3900 Reservoir Road NW Washington DC 20057-1411. Phone number P ...
Watch out for cliches like "making a difference," "broadening my horizons," or "the best thing that ever happened to me." 3. Stay focused. Try to avoid getting off-track or including tangents in your personal statement. Stay focused by writing a first draft and then re-reading what you've written.
How do you show you are applying psychological theory into your practice? How to write your personal statement for applying to the Educational Psychology Doc...
The personal statement should provide a concise reflection of why you are interested in becoming a student affairs professional. You may want to touch on what may have led to your desire to be a student affairs professional, and address anything you want the committee to know about your qualifications for the program.
This is an example personal statement for a Masters degree application in Education. See our guide for advice on writing your own postgraduate personal statement. Recent developments in the social and political landscapes have strongly highlighted the importance of education for children in schools. Studying an undergraduate degree in History ...
Personal development refers to the process of increasing one's self-awareness, associated increases of self-esteem, increasing skills, and fulfilling one's aspirations. The current paper reflects on these elements within the doctoral journey, for PhD students within the UK Higher Education system. The paper makes particular reference to frameworks to encourage and capture personal ...
The team, comprising Shannon Christiansen, a senior research coordinator in the Mann Group, and Michael Kozar, a former graduate researcher in the Mann Research Group, today released their prediction for the 2024 North Atlantic season, which spans from June 1 to Nov. 30. They forecast an unprecedented 33 named tropical cyclones, potentially ...