
How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 10 min read

How to Structure a Presentation
Choosing the best format for your audience.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Have you ever sat through a rambling, disorganized presentation? If so, you probably found it hard to follow what the speaker was saying.
When presentations don't flow well, it's easy for audiences to get lost. This is why it's important to think carefully about the structure and organization of your presentation.
In this article, we'll explore some common structures that you can use next time you speak in front of other people.
The Importance of Structure
Without a defined structure, your audience may not be able to follow your presentation. When this happens, your opportunity is lost, the communication fails, and your reputation takes a hit. For example, if your aim is to persuade people, you'll want to use a different approach from the one you'd use if you wanted to demonstrate how a product works.
Many factors can influence your choice of structure, but the most important consideration is your presentation's purpose or goal. You need to identify what you want to achieve – do you want to inspire, motivate, inform, persuade, or entertain people?
Your audience's needs also affect the structure you choose. For example, those who are new to your topic need more background information than people with more expertise and experience. So, in this case, you'd want to choose an approach that gives you ample time to explain the context of your subject, as well as to reinforce your main points.
Structures to Consider
Below, we outline several structures that you can use to organize your presentation.
1. Open – Body – Conclusion
The Open – Body – Conclusion approach is one of the most practical structures you can use for presentations. (Click here to download a worksheet that helps you use it.)
People often call it the "tell 'em" approach, because you:
- Tell audience members what you're going to tell them (introduction).
- Tell them (body).
- Tell them what you told them (conclusion).
This structure is simple, effective and easy to remember. Its repetitive nature allows you to reinforce your points, which helps others remember them. It is also flexible: you can adjust the introduction and body to persuade, motivate, educate, or entertain them.
One downside, however, is that repetition can quickly bore people. The approach is also "old hat" to many, which can cause them to lose interest. If you choose to use it, balance repetition with plenty of interesting facts, images, anecdotes, or stories to hold your audience's interest.
Let's look at each stage of the Open – Body – Conclusion structure in detail and discuss the elements that you need to include in each. We'll start with the body, rather than the introduction, because the rest of your presentation will be based on that.
The body of your presentation needs to contain your key points. You should present these in a logical order, so that your audience can follow them easily.
Keep in mind that the body should comprise a limited number of ideas: the more you try to include, the fewer people will remember. A good guide is to cover three to five main points, but no more.
When organizing your ideas, use the chunking principle to put the information into specific units. This will make the concepts easier to grasp, and help people remember what you have told them.
Make sure that you back up your main points with facts. Use good information-gathering strategies in your research, and consider citing the sources that you use. To add credibility to your presentation, consider using the following information to support your ideas:
- Data, facts or statistics.
- Images or diagrams.
- Stories and examples.
- Quotes or testimonials from experts or industry leaders.
Reliable sources will strengthen your credibility , and build trust with your audience.
Your opening, or introduction, has two main purposes: to grab your audience's attention, and to cover the key points that you intend to talk about.
Instead of telling people what you plan to say, you can use a different approach and explain why they are there. What will they learn from your presentation, and how will the content benefit them?
It's also important to get their attention right from the beginning. You can do this in several ways:
- Tell a story.
- Ask a rhetorical question.
- Play a short video.
- Make a strong or unexpected statement.
- Challenge your audience.
- Use a quotation or example.
- Appeal to people's self-interest.
- Request a specific action.
- Use suspense.
If you plan to answer questions at the end of your presentation, it's a good idea to mention this in the introduction, so people don't interrupt you mid-flow.
Many presenters overlook the importance of a conclusion – but the statements you finish with are what many audience members will remember best.
With the "tell 'em" approach, your conclusion summarizes the main points in the body of your presentation. If you want people to take action, be specific about what you want them to do.
Think carefully about how you want them to feel once you've finished; your conclusion is a great opportunity to reinforce this. Why not inspire them with a great story, a quote or a compelling call to action?
2. The Sandwich Approach
The Sandwich Approach is a variation of the Open – Body – Conclusion structure. This three-part structure covers:
- Advantages and/or benefits of your message or idea.
- Risks and concerns.
- How the benefits manage or eliminate those risks.
This approach is effective when you want to persuade audience members, or change their minds.
Having evidence to support your position is critical. However, factual data and reams of spreadsheets and charts are not highly persuasive. What people respond to is "vivid" evidence that brings your concept or argument to life.
To brush up on your persuasion skills, look at The Rhetorical Triangle . This tool asks you to consider your communication from three perspectives: those of the writer, the audience and the context. It's a method that builds credibility, and helps you ensure that your arguments are logical.
3. Monroe's Motivated Sequence
Monroe's Motivated Sequence is another good structure to use when you need to motivate or persuade. This sequence consists of five key steps:
- Getting your audience's attention – Use an interesting "hook" or opening point, such as a shocking statistic. Be provocative and stimulating, not boring and unemotional.
- Creating a need – Convince the audience there's a problem, explain how it affects them. Persuade them that things need to change.
- Defining your solution – Explain what you think needs to be done.
- Describing a detailed picture of success (or failure) – Give people a vision; something they can see, hear, taste, and touch.
- Asking the audience to do something straight away – Get them involved right from the start. If you do this, it's then much easier to keep them engaged and active in your cause.
4. Demonstration Structure
Use a simple demonstration structure when you are unveiling a new product or service.
Start by explaining why the product or service is so good. What makes it special? What problem will it solve for people?
Next, demonstrate what it does. How you do this will depend on your product but, whatever you do, make sure it works! Bring any important points to the audience's attention and provide helpful tips, where appropriate. Show them the results, and finish by giving them useful information, a good understanding of your topic, and something to remember.
Don't get too wrapped up in the detail; remember to keep it simple. Your presentation will be more powerful and your audience will remember more if you highlight just a few of the most important features. This will whet their appetite, and leave them wanting to know more.
5. Opportunity, Benefits, Numbers Structure
The Opportunity, Benefits, Number (OBN) structure is useful when you face busy people who want to hear what you have to say in the shortest time possible.
To use this structure, give audience members a quick summary of the opportunity that they need to consider, and outline the benefits that they can expect. Then, show them the numbers that back up your claims. [1]
For example, imagine you are explaining why your company should implement a new performance management system. First, you might give some background on the proposal – for example, you want to drive a high-performance culture. Then, you could explain the benefits, such as improving organizational performance and profits. Finally, you could compare the cost of bringing the system in with the predicted return on investment, based on a similar system at another organization.
Presentations that lack a clear flow are confusing and ineffective. This is why it's important to pay careful attention when choosing the most appropriate structure.
Different structures fulfill different purposes. Before you begin, think about why you are giving your presentation. Do you want to inform, persuade, inspire, or entertain your audience?
The most common structure for presentations is Open – Body – Conclusion. This is often effective because it gives you the opportunity to repeat your key points a number of times. However, other structures can be more appropriate, depending on the circumstances, such as when you're trying to persuade an audience, demonstrate a product, or provide information in the most time-efficient way.
Download Worksheet
[1] Martinuzzi, B. (2013). '11 Ways to Structure a Knockout Presentation,' from American Express OPEN Forum [online]. Available here . [Accessed 7 August 2014.]
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Managing ambiguity.
This Article Shows the Challenges of Ambiguity and What Strategies Minimize its Impact
Top Techniques for Creative Thinking
Simple Ways to Be More Creative
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Gain essential management and leadership skills
Busy schedule? No problem. Learn anytime, anywhere.
Subscribe to unlimited access to meticulously researched, evidence-based resources.
Join today and take advantage of our 30% offer, available until May 31st .
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Kees van der Heijden - The Sixth Sense

How to Encourage Diverse Perspectives
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
168 hours: you have more time than you think.
Laura Vanderkam
Book Insights
Rationalizing Your Project Portfolio
Delivering Strategic Benefits With Limited Resources
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Voluntary teams.
The Characteristics of Voluntary Teams and Some Tips for Managing Them
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
Blog > How to structure a good PowerPoint Presentation
How to structure a good PowerPoint Presentation
08.09.21 • #powerpoint #tips.
When creating presentations, it is particularly important that they are well organized and have a consistent structure.
A logical structure helps the audience to follow you and to remember the core information as best as possible. It is also important for the presenter, as a good presentation structure helps to keep calm, to stay on the topic and to avoid awkward pauses.
But what does such a structure actually look like? Here we show you how to best organize your presentation and what a good structure looks like.
Plan your presentation
Before you start creating your presentation, you should always brainstorm. Think about the topic and write all your ideas down. Then think about the message you want to communicate, what your goal is and what you want your audience to remember at the end.
Think about who your audience is so that you can address them in the best possible way. One possibility is to start your presentation with a few polls to get to know your audience better. Based on the results, you can then adapt your presentation a little. Use the poll function of SlideLizard and have all the answers at a glance. SlideLizard makes it possible to integrate the polls directly into your PowerPoint presentation which helps you to avoid annoying switching between presentation and interaction tool. You can keep an eye on the results while the votes come in and then decide whether you want to share them or not.
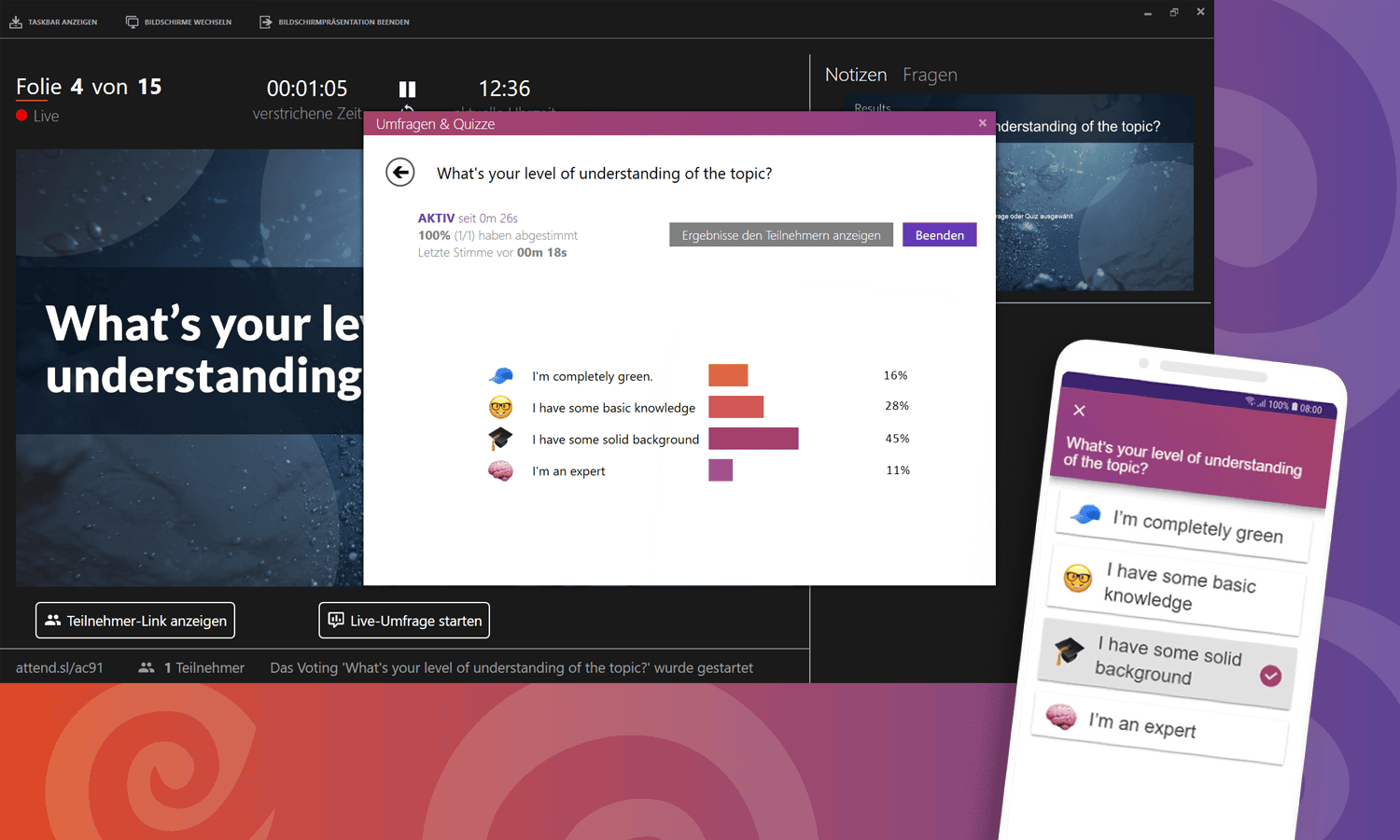
- an informative
- an entertaining
- an inspiring
- or a persuasive presentation?
Typical Presentation Structure
The basic structure of a presentation is actually always the same and should consist of:
Introduction
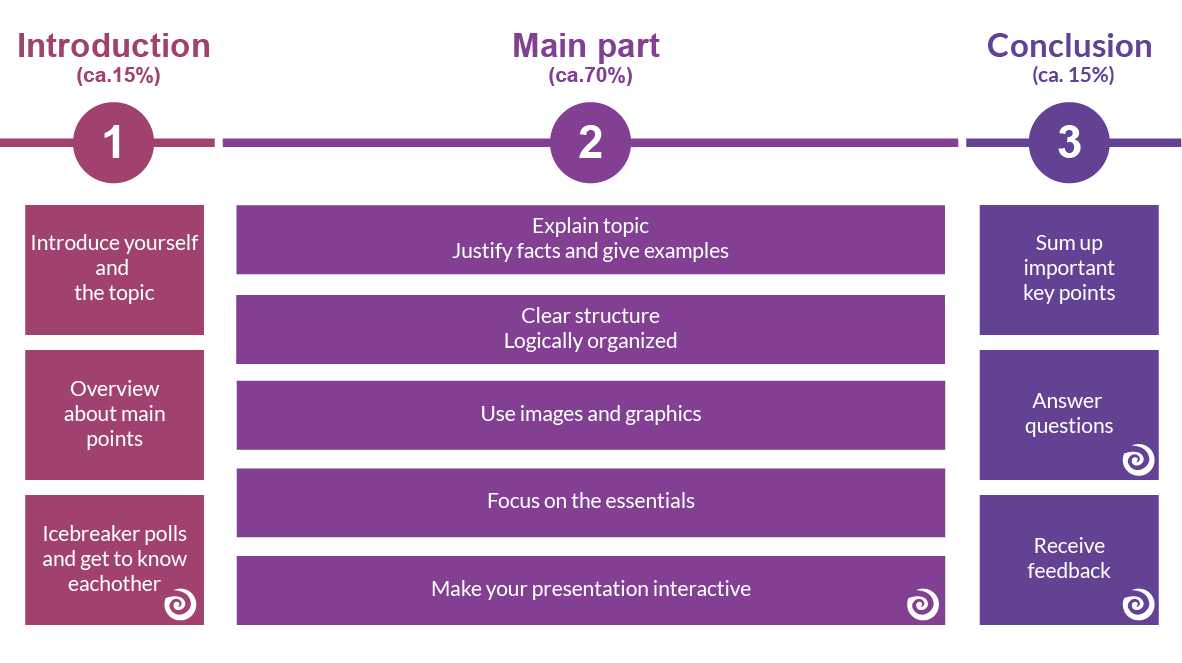
Make sure that the structure of your presentation is not too complicated. The simpler it is, the better the audience can follow.
Personal Introduction
It is best to start your presentation by briefly introducing yourself which helps to build a connection with your audience right away.
Introduce the topic
Then introduce the topic, state the purpose of the presentation and provide a brief outline of the main points you will be addressing.
Mention the length
In the introduction, mention the approximate length of the talk and then also make sure you stick to it.
The introduction should be no longer than two slides and provide a good overview of the topic.
Icebreaker Polls
According to studies, people in the audience only have an average attention span of 10 minutes, which is why it is important to increase their attention right at the beginning and to arouse the audience's interest. You could make a good start with a few icebreaker polls for example. They lighten the mood right at the beginning and you can secure your audience's attention from the start.
For example, you could use SlideLizard to have all the answers at a glance and share them with your audience. In addition, the audience can try out how the polls work and already know how it works if you include more polls in the main part.
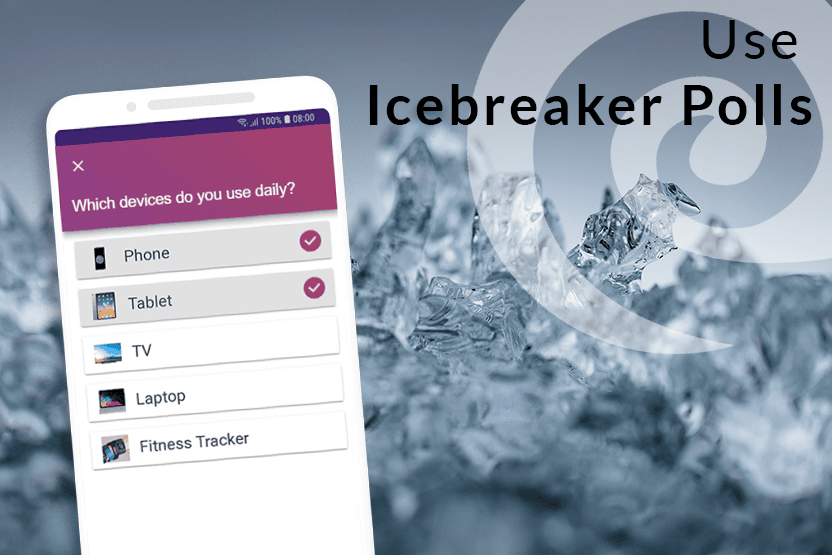
Get to know your audience
As mentioned earlier, it is always useful to think about who your audience actually is. Ask them questions at the beginning about how well they already know the topic of your presentation. Use SlideLizard for this so that you have a clear overview about the answers. You can use both single- and multiple-choice questions or also open questions and display their results as a WordCloud in your presentation, for example.
Include a quote
To make the beginning (or the end) of your presentation more exciting, it is always a good idea to include a quote. We have selected some powerful quotes for PowerPoint presentations for you.
Present your topic
The main part of a presentation should explain the topic well, state facts, justify them and give examples. Keep all the promises you made earlier in the introduction.
Length and Structure
The main part should make up about 70% of the presentation and also include a clear structure. Explain your ideas in detail and build them up logically. It should be organized chronologically, by priority or by topic. There should be a smooth transition between the individual issues. However, it is also important to use phrases that make it clear that a new topic is starting. We have listed some useful phrases for presentations here.
Visualize data and statistics and show pictures to underline facts. If you are still looking for good images, we have selected 5 sources of free images for you here.
Focus on the essentials
Focus on what is most important and summarize a bit. You don't have to say everything about a topic because your audience won’t remember everything either. Avoid complicated sentence structure, because if the audience does not understand something, they will not be able to read it again.
Make your presentation interactive
Make your presentation interactive to keep the attention of your audience. Use SlideLizard to include polls in your presentation, where your audience can vote directly from their smartphone and discuss the answers as soon as you received all votes. Here you can also find more tips for increasing audience engagement.
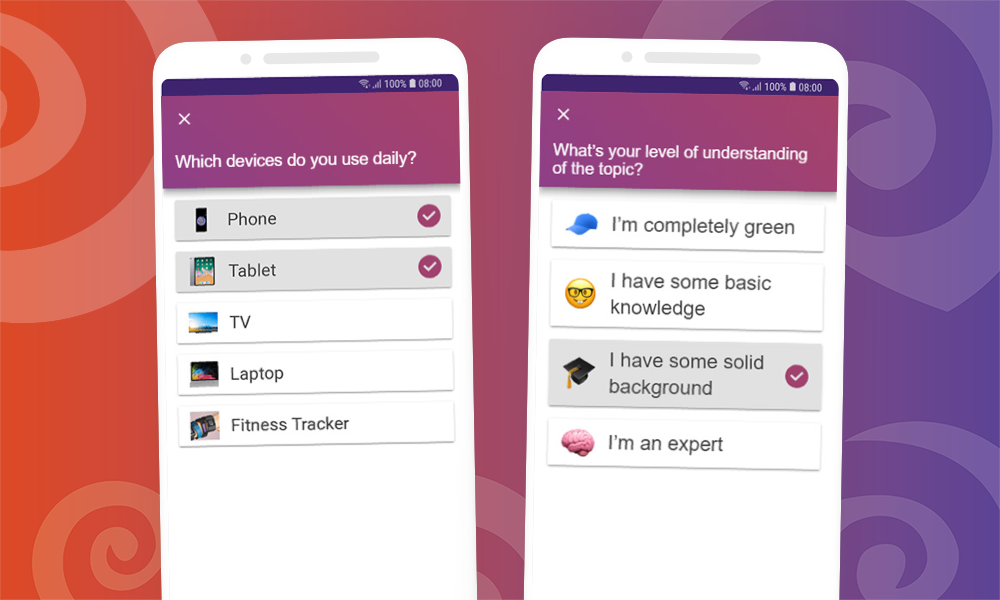
Repeat the main points
The conclusion should contain a summary of the most important key points. Repeat the main points you have made, summarize what the audience should have learned and explain how the new information can help in the future.
Include a Q&A part
Include a Q&A part at the end to make sure you don't leave any questions open. It's a good idea to use tools like SlideLizard for it. Your audience can ask anonymous questions and if there is not enough time, you can give them the answers afterwards. You can read more about the right way to do a question slide in PowerPoint here.
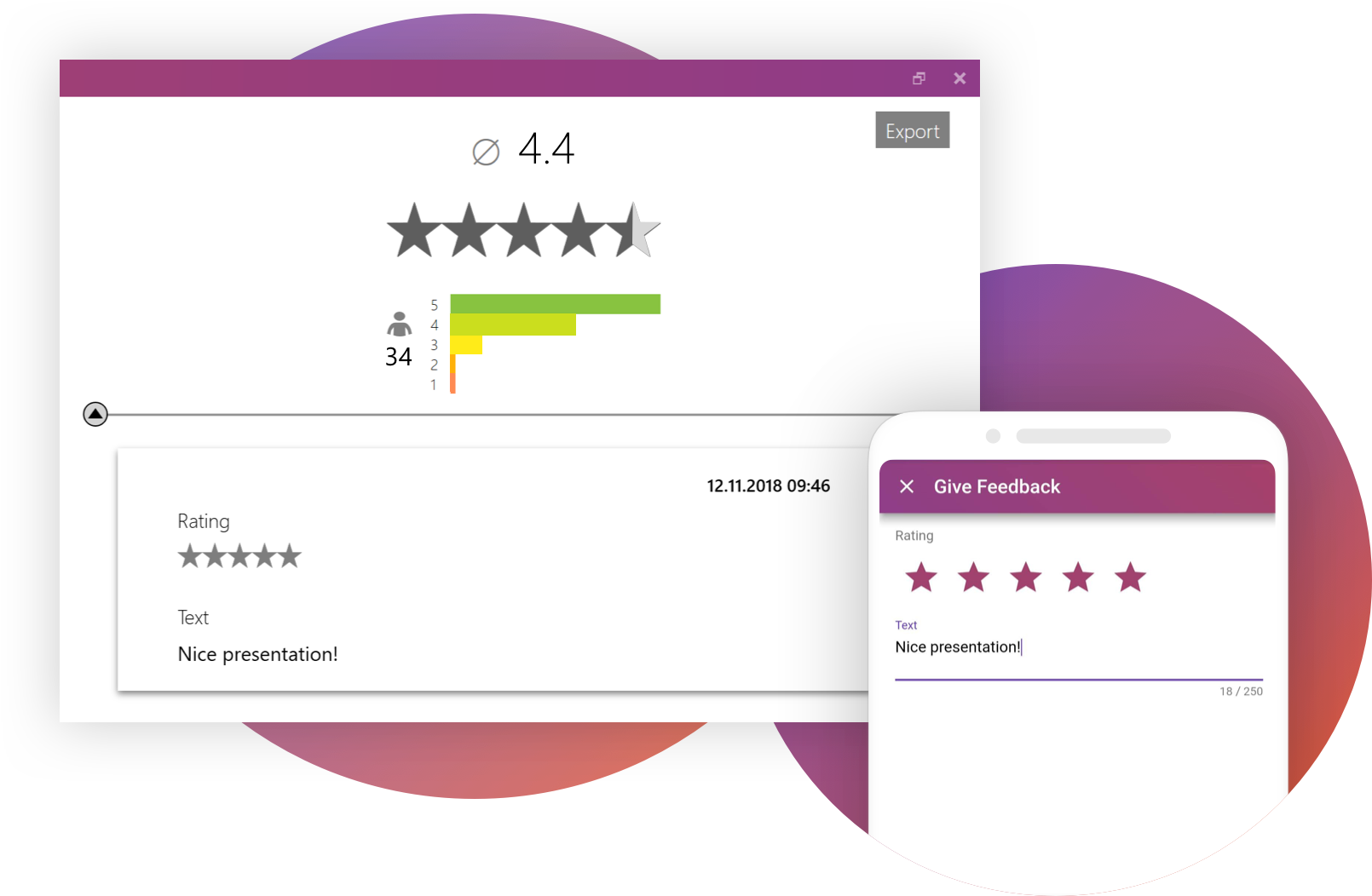
Get Feedback
It is also important to get feedback on your presentation at the end to keep improving. With SlideLizard you can ask your audience for anonymous feedback through star ratings, number ratings or open texts directly after your presentation. You can then export the responses and analyse them later in Excel.
Presentation style
Depending on the type of presentation you give, the structure will always be slightly different. We have selected a few different presentation styles and their structure for you.
Short Presentation

If you are one of many presenters on the day, you will only have a very limited time to present your idea and to convince your audience. It is very important to stand out with your presentation.
So you need to summarize your ideas as briefly as possible and probably should not need more than 3-5 slides.
Problem Solving Presentation
Start your presentation by explaining a problem and giving a short overview of it.
Then go into the problem a little more, providing both intellectual and emotional arguments for the seriousness of the problem. You should spend about the first 25% of your presentation on the problem.
After that, you should spend about 50% of your presentation proposing a solution and explaining it in detail.
In the last 25%, describe what benefits this solution will bring to your audience and ask them to take a simple but relevant action that relates to the problem being discussed.
Tell a Story

A great way to build an emotional connection with the audience is to structure a presentation like a story.
In the introduction, introduce a character who has to deal with a conflict. In the main part, tell how he tries to solve his problem but fails again and again. In the end, he manages to find a solution and wins.
Stories have the power to win customers, align colleagues and motivate employees. They’re the most compelling platform we have for managing imaginations. - Nancy Duarte / HBR Guide to Persuasive Presentations
Make a demonstration

Use the demonstration structure to show how a product works. First talk about a need or a problem that has to be solved.
Then explain how the product will help solve the problem and try to convince your audience of the need for your product.
Spend the end clarifying where and when the product can be purchased.
Chronological structure

When you have something historical to tell, it is always good to use a chronological structure. You always have to ask yourself what happens next.
To make it more interesting and exciting, it is a good idea to start by telling the end of something and after that you explain how you got there. This way you make the audience curious and you can gain their attention faster.
Nancy Duarte TED Talk
Nancy Duarte is a speaker and presentation design expert. She gives speeches all over the world, trying to improve the power of public presentations.
In her famous TED Talk "The Secret Structure of Great Talks" she dissects famous speeches such as Steve Jobs' iPhone launch speech and Martin Luther King's "I have a dream" speech. In doing so, she found out that each presentation is made up of 4 parts:
- What could be
- A moment to remember
- Promise of “New Bliss”
Related articles
About the author.

Helena Reitinger
Helena supports the SlideLizard team in marketing and design. She loves to express her creativity in texts and graphics.
Get 1 Month for free!
Do you want to make your presentations more interactive.
With SlideLizard you can engage your audience with live polls, questions and feedback . Directly within your PowerPoint Presentation. Learn more

Top blog articles More posts

How to find the best font for your PowerPoint presentation

How to create a custom Theme design in PowerPoint
Get started with Live Polls, Q&A and slides
for your PowerPoint Presentations
The big SlideLizard presentation glossary
A podcast is an audio or video contribution that can be listened to or viewed via the Internet. Podcasts can be used for information on specific topics but also for entertainment.
Slide Master
To create your own Template in PowerPoint it is best to use the Slide Master. After updating the Slide Master with your design, all slides (fonts, colours, images, …) adapt to those of the Slide Master.
Slide Layouts
PowerPoint has different types of Slide Layouts. Depending on which type of presentation you make, you will use more or less different slide layouts. Some Slide Types are: title slides, section heading slides, picture with caption slides, blank slides.
Eulogy Speech
A eulogy speech is given at a funeral. It is given by familiy members or friends of the deceased. The aim is to say goodbye and pay tribute to the person who has passed away.
Be the first to know!
The latest SlideLizard news, articles, and resources, sent straight to your inbox.
- or follow us on -
We use cookies to personalize content and analyze traffic to our website. You can choose to accept only cookies that are necessary for the website to function or to also allow tracking cookies. For more information, please see our privacy policy .
Cookie Settings
Necessary cookies are required for the proper functioning of the website. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information about the number of visitors, etc.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides How To Make a Good Presentation [A Complete Guide]
How To Make a Good Presentation [A Complete Guide]
Written by: Krystle Wong Jul 20, 2023

A top-notch presentation possesses the power to drive action. From winning stakeholders over and conveying a powerful message to securing funding — your secret weapon lies within the realm of creating an effective presentation .
Being an excellent presenter isn’t confined to the boardroom. Whether you’re delivering a presentation at work, pursuing an academic career, involved in a non-profit organization or even a student, nailing the presentation game is a game-changer.
In this article, I’ll cover the top qualities of compelling presentations and walk you through a step-by-step guide on how to give a good presentation. Here’s a little tip to kick things off: for a headstart, check out Venngage’s collection of free presentation templates . They are fully customizable, and the best part is you don’t need professional design skills to make them shine!
These valuable presentation tips cater to individuals from diverse professional backgrounds, encompassing business professionals, sales and marketing teams, educators, trainers, students, researchers, non-profit organizations, public speakers and presenters.
No matter your field or role, these tips for presenting will equip you with the skills to deliver effective presentations that leave a lasting impression on any audience.
Click to jump ahead:
What are the 10 qualities of a good presentation?
Step-by-step guide on how to prepare an effective presentation, 9 effective techniques to deliver a memorable presentation, faqs on making a good presentation, how to create a presentation with venngage in 5 steps.
When it comes to giving an engaging presentation that leaves a lasting impression, it’s not just about the content — it’s also about how you deliver it. Wondering what makes a good presentation? Well, the best presentations I’ve seen consistently exhibit these 10 qualities:
1. Clear structure
No one likes to get lost in a maze of information. Organize your thoughts into a logical flow, complete with an introduction, main points and a solid conclusion. A structured presentation helps your audience follow along effortlessly, leaving them with a sense of satisfaction at the end.
Regardless of your presentation style , a quality presentation starts with a clear roadmap. Browse through Venngage’s template library and select a presentation template that aligns with your content and presentation goals. Here’s a good presentation example template with a logical layout that includes sections for the introduction, main points, supporting information and a conclusion:

2. Engaging opening
Hook your audience right from the start with an attention-grabbing statement, a fascinating question or maybe even a captivating anecdote. Set the stage for a killer presentation!
The opening moments of your presentation hold immense power – check out these 15 ways to start a presentation to set the stage and captivate your audience.
3. Relevant content
Make sure your content aligns with their interests and needs. Your audience is there for a reason, and that’s to get valuable insights. Avoid fluff and get straight to the point, your audience will be genuinely excited.
4. Effective visual aids
Picture this: a slide with walls of text and tiny charts, yawn! Visual aids should be just that—aiding your presentation. Opt for clear and visually appealing slides, engaging images and informative charts that add value and help reinforce your message.
With Venngage, visualizing data takes no effort at all. You can import data from CSV or Google Sheets seamlessly and create stunning charts, graphs and icon stories effortlessly to showcase your data in a captivating and impactful way.

5. Clear and concise communication
Keep your language simple, and avoid jargon or complicated terms. Communicate your ideas clearly, so your audience can easily grasp and retain the information being conveyed. This can prevent confusion and enhance the overall effectiveness of the message.
6. Engaging delivery
Spice up your presentation with a sprinkle of enthusiasm! Maintain eye contact, use expressive gestures and vary your tone of voice to keep your audience glued to the edge of their seats. A touch of charisma goes a long way!
7. Interaction and audience engagement
Turn your presentation into an interactive experience — encourage questions, foster discussions and maybe even throw in a fun activity. Engaged audiences are more likely to remember and embrace your message.
Transform your slides into an interactive presentation with Venngage’s dynamic features like pop-ups, clickable icons and animated elements. Engage your audience with interactive content that lets them explore and interact with your presentation for a truly immersive experience.

8. Effective storytelling
Who doesn’t love a good story? Weaving relevant anecdotes, case studies or even a personal story into your presentation can captivate your audience and create a lasting impact. Stories build connections and make your message memorable.
A great presentation background is also essential as it sets the tone, creates visual interest and reinforces your message. Enhance the overall aesthetics of your presentation with these 15 presentation background examples and captivate your audience’s attention.
9. Well-timed pacing
Pace your presentation thoughtfully with well-designed presentation slides, neither rushing through nor dragging it out. Respect your audience’s time and ensure you cover all the essential points without losing their interest.
10. Strong conclusion
Last impressions linger! Summarize your main points and leave your audience with a clear takeaway. End your presentation with a bang , a call to action or an inspiring thought that resonates long after the conclusion.
In-person presentations aside, acing a virtual presentation is of paramount importance in today’s digital world. Check out this guide to learn how you can adapt your in-person presentations into virtual presentations .
Preparing an effective presentation starts with laying a strong foundation that goes beyond just creating slides and notes. One of the quickest and best ways to make a presentation would be with the help of a good presentation software .
Otherwise, let me walk you to how to prepare for a presentation step by step and unlock the secrets of crafting a professional presentation that sets you apart.
1. Understand the audience and their needs
Before you dive into preparing your masterpiece, take a moment to get to know your target audience. Tailor your presentation to meet their needs and expectations , and you’ll have them hooked from the start!
2. Conduct thorough research on the topic
Time to hit the books (or the internet)! Don’t skimp on the research with your presentation materials — dive deep into the subject matter and gather valuable insights . The more you know, the more confident you’ll feel in delivering your presentation.
3. Organize the content with a clear structure
No one wants to stumble through a chaotic mess of information. Outline your presentation with a clear and logical flow. Start with a captivating introduction, follow up with main points that build on each other and wrap it up with a powerful conclusion that leaves a lasting impression.
Delivering an effective business presentation hinges on captivating your audience, and Venngage’s professionally designed business presentation templates are tailor-made for this purpose. With thoughtfully structured layouts, these templates enhance your message’s clarity and coherence, ensuring a memorable and engaging experience for your audience members.
Don’t want to build your presentation layout from scratch? pick from these 5 foolproof presentation layout ideas that won’t go wrong.

4. Develop visually appealing and supportive visual aids
Spice up your presentation with eye-catching visuals! Create slides that complement your message, not overshadow it. Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words, but that doesn’t mean you need to overload your slides with text.
Well-chosen designs create a cohesive and professional look, capturing your audience’s attention and enhancing the overall effectiveness of your message. Here’s a list of carefully curated PowerPoint presentation templates and great background graphics that will significantly influence the visual appeal and engagement of your presentation.
5. Practice, practice and practice
Practice makes perfect — rehearse your presentation and arrive early to your presentation to help overcome stage fright. Familiarity with your material will boost your presentation skills and help you handle curveballs with ease.
6. Seek feedback and make necessary adjustments
Don’t be afraid to ask for help and seek feedback from friends and colleagues. Constructive criticism can help you identify blind spots and fine-tune your presentation to perfection.
With Venngage’s real-time collaboration feature , receiving feedback and editing your presentation is a seamless process. Group members can access and work on the presentation simultaneously and edit content side by side in real-time. Changes will be reflected immediately to the entire team, promoting seamless teamwork.
7. Prepare for potential technical or logistical issues
Prepare for the unexpected by checking your equipment, internet connection and any other potential hiccups. If you’re worried that you’ll miss out on any important points, you could always have note cards prepared. Remember to remain focused and rehearse potential answers to anticipated questions.
8. Fine-tune and polish your presentation
As the big day approaches, give your presentation one last shine. Review your talking points, practice how to present a presentation and make any final tweaks. Deep breaths — you’re on the brink of delivering a successful presentation!
In competitive environments, persuasive presentations set individuals and organizations apart. To brush up on your presentation skills, read these guides on how to make a persuasive presentation and tips to presenting effectively .

Whether you’re an experienced presenter or a novice, the right techniques will let your presentation skills soar to new heights!
From public speaking hacks to interactive elements and storytelling prowess, these 9 effective presentation techniques will empower you to leave a lasting impression on your audience and make your presentations unforgettable.
1. Confidence and positive body language
Positive body language instantly captivates your audience, making them believe in your message as much as you do. Strengthen your stage presence and own that stage like it’s your second home! Stand tall, shoulders back and exude confidence.
2. Eye contact with the audience
Break down that invisible barrier and connect with your audience through their eyes. Maintaining eye contact when giving a presentation builds trust and shows that you’re present and engaged with them.
3. Effective use of hand gestures and movement
A little movement goes a long way! Emphasize key points with purposeful gestures and don’t be afraid to walk around the stage. Your energy will be contagious!
4. Utilize storytelling techniques
Weave the magic of storytelling into your presentation. Share relatable anecdotes, inspiring success stories or even personal experiences that tug at the heartstrings of your audience. Adjust your pitch, pace and volume to match the emotions and intensity of the story. Varying your speaking voice adds depth and enhances your stage presence.

5. Incorporate multimedia elements
Spice up your presentation with a dash of visual pizzazz! Use slides, images and video clips to add depth and clarity to your message. Just remember, less is more—don’t overwhelm them with information overload.
Turn your presentations into an interactive party! Involve your audience with questions, polls or group activities. When they actively participate, they become invested in your presentation’s success. Bring your design to life with animated elements. Venngage allows you to apply animations to icons, images and text to create dynamic and engaging visual content.
6. Utilize humor strategically
Laughter is the best medicine—and a fantastic presentation enhancer! A well-placed joke or lighthearted moment can break the ice and create a warm atmosphere , making your audience more receptive to your message.
7. Practice active listening and respond to feedback
Be attentive to your audience’s reactions and feedback. If they have questions or concerns, address them with genuine interest and respect. Your responsiveness builds rapport and shows that you genuinely care about their experience.

8. Apply the 10-20-30 rule
Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it!
9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule
Simplicity is key. Limit each slide to five bullet points, with only five words per bullet point and allow each slide to remain visible for about five seconds. This rule keeps your presentation concise and prevents information overload.
Simple presentations are more engaging because they are easier to follow. Summarize your presentations and keep them simple with Venngage’s gallery of simple presentation templates and ensure that your message is delivered effectively across your audience.

1. How to start a presentation?
To kick off your presentation effectively, begin with an attention-grabbing statement or a powerful quote. Introduce yourself, establish credibility and clearly state the purpose and relevance of your presentation.
2. How to end a presentation?
For a strong conclusion, summarize your talking points and key takeaways. End with a compelling call to action or a thought-provoking question and remember to thank your audience and invite any final questions or interactions.
3. How to make a presentation interactive?
To make your presentation interactive, encourage questions and discussion throughout your talk. Utilize multimedia elements like videos or images and consider including polls, quizzes or group activities to actively involve your audience.
In need of inspiration for your next presentation? I’ve got your back! Pick from these 120+ presentation ideas, topics and examples to get started.
Creating a stunning presentation with Venngage is a breeze with our user-friendly drag-and-drop editor and professionally designed templates for all your communication needs.
Here’s how to make a presentation in just 5 simple steps with the help of Venngage:
Step 1: Sign up for Venngage for free using your email, Gmail or Facebook account or simply log in to access your account.
Step 2: Pick a design from our selection of free presentation templates (they’re all created by our expert in-house designers).
Step 3: Make the template your own by customizing it to fit your content and branding. With Venngage’s intuitive drag-and-drop editor, you can easily modify text, change colors and adjust the layout to create a unique and eye-catching design.
Step 4: Elevate your presentation by incorporating captivating visuals. You can upload your images or choose from Venngage’s vast library of high-quality photos, icons and illustrations.
Step 5: Upgrade to a premium or business account to export your presentation in PDF and print it for in-person presentations or share it digitally for free!
By following these five simple steps, you’ll have a professionally designed and visually engaging presentation ready in no time. With Venngage’s user-friendly platform, your presentation is sure to make a lasting impression. So, let your creativity flow and get ready to shine in your next presentation!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Presentation Structures: Everything You Need to Organize Your Talk
Hrideep barot.
- Presentation , Public Speaking , Speech Writing

A presentation structure includes an introduction, context, main body, conclusion, and scope for questions. Depending on the type of presentation you’re doing, this format can change. The article discusses various considerations for each section of a presentation structure.
For presentations to be understood and create a good impression, they can’t be haphazard. It has to have some sort of pre-planned presentation structure that is both logical and simple enough. Depending on the type of presentation you’re doing, there are likely some basic frameworks available that people tend to follow. Before we delve into the format, let’s consider key points to consider when planning a presentation.
How do you structure and plan a presentation?
We plan a presentation by considering the type of presentation, who our audience is, ideating the purpose, and formulating subtopics through research.
Consider the type of presentation
This leads to understanding the ideal flow to convey your content best. For instance, for persuasive presentations, you could use creative ways to convey what is best about a product, such as starting with a story about how it has helped many people achieve something.
On the other hand, for a progress presentation at your workplace, you might have conventions about what is expected, which must be followed precisely.
A few other types of presentations include:
- Informative presentations
- Instructive presentations
- Motivational presentations
- Analytical presentations
You might also want to consider if you want audience interaction and put that into the structure accordingly. While some allow questions mid-presentation for smaller audiences, it is typically left towards the end.
Consider your audience’s knowledge level and interests
This will determine if you can assume a particular knowledge base and not include it in your presentation structure or if you have to start off with basics and build up on that.
For instance, if you’re teaching 1st-year students about something, you might start with basics. But for graduates, a similar format would be unnecessary as they might have already learned about it.
Similarly, if your purpose is to deliver something entertaining, knowing about the interests and values of your audience helps a ton.
The most simple way is demographics. It’s typically quite easy to find out the expected age group, gender, etc of the audience. This information can help you have a basic idea of the sort of experiences they go through, which helps formulate an understanding.
Consider the purpose of your presentation
While this may seem obvious, many of us lose track of the main purpose and spend too much time on remotely related content. This diverts attention from the topic and might even cause boredom.
For example, if you’re advocating for some social action, it would be beneficial to stay on the topic itself, like the pros, cons, what can be done practically, etc. Instead, if the presenters spend more time criticizing others, the presentation will fall short of its purpose.
Few other examples of different purposes your presentation could have:
- Entertainment
- Providing information
- Telling your story
- Proposing ideas
- Discussing future plans for the company
Research your topic and start noting down the subtopics
Skip this if you already know exactly what needs to be a part of your presentation, and plan to include just that. While looking up your topic, you’ll discover the various sub-topics within that field. After you start noting them down, you can organize later what comes under which to build a structure.
Here is a guide on short presentations that you might be interested in.
So with these three considerations and subtopics in mind, we’re good to go over to decide our final structure.

What is the best presentation form?
The best presentation format is one that includes the introduction, context, main body, conclusion, and questions.
Here, we will discuss a template or structure for a typical presentation.
Introduction
- Greet the audience and introduce yourself, e.g., what you do and why you’re here
- The purpose of your presentation
- The flow or outline gives a sense of what they can expect
- Depending on the topic and audience, you might have to provide more or less context about your topic
- This could include a brief history, terminologies, the current market status, the current status of the field, etc.
- Includes the full depth of the primary purpose of the presentation
- All major chunks of data, including examples, evidence like research studies, etc, are included here
- Care needs to be taken at times to ensure that your introduction and context are not taking up so much time that the main body isn’t receiving enough attention. Ever wonder if a presentation can be too short? Check out this article .
- Bring emphasis to the main takeaways
- Thank your audience if they have been a good one
- Take questions and encourage healthy discussion
- End with sharing ways they can address their questions later
To make sure that the structure works out, it is important that you practice your presentation. This will also tell you if you’re falling within the time constraints. Here is a guide on how you can go about practicing your presentation.
5 Ways to Structure Your Presentation
The five ways include ordered, problem-solution, comparative, storytelling, and demonstrating structures.
1. Ordered Structure
The presentation follows a logical sequence starting with an introduction, main points, and then conclusions. This is what this article has focused on, as it’s the most straightforward method and tends to be very clear for the audience. However, for presentations that do not follow a clear progression, this may not be useful.
2. Problem-Solution Structure
This is useful when persuading the audience. You explain the problem (+ its importance and impact) and then provide a solution that motivates the audience to take it. This could be in the form of a product, a particular method of communication, some technical thing, etc. There should be a decent amount of time spent on the benefits of the solution as well as the exact “How?” to implement it to make the audience convinced. It helps to address any questions or barriers you expect them to have during the speech itself.
3. Comparative Method
This is useful when you want to highlight the benefits of something over alternatives . It is ideal to first fully address the alternatives by talking about their benefits and limitations. Then you lastly talk about the solution that you possess that effectively addresses the other limitations or is in some way a better choice than others, based on your arguments.
Alternatively, if you do not want to highlight the benefits of something particular and just form a comparison that demonstrates the pros and cons of different subjects in an unbiased manner, this technique is still used. For instance, how the main benefit of a product is practically useful for the consumer in comparison to the main benefit of another product can be discussed.
4. Storytelling Structure
This is useful when your goal is just to tell a story. This could be to explain the context or history of a company. It could also serve to talk about yourself and how you got there. A story will typically have an introduction, a complicating factor that introduces some challenges, and then an ending that highlights the importance of some action or belief.
You may also go in a timewise order when explaining a story. This might take away from the thrill but is useful nonetheless when it is required for the audience to properly understand what is being conveyed. Storytelling can be done in various ways, so feel free to find your own structure.
5. Demonstration Structure
This is useful when demonstrating products or services . The benefits of the product/service are highlighted and it is demonstrated showing those capabilities. The goal should be on persuading the audience that it is useful to them for their needs.
How to structure a scientific presentation?
Structuring a scientific presentation typically includes an introduction, methods, results, and discussion.
This typically follows the below format, but depending on the university/conference guidelines, you’ll have to adjust accordingly. The rest of the sub-topics revolves around these sections.
- Introduction/Background
- Literature review (if applicable)
- Acknowledgments (often optional)
After this, time is given to take questions.
How do you structure a presentation script?
The presentation never includes the full extent of the information. It’s just a concise version of what you’re speaking that adds as a visual aid at times while also highlighting major points.
The script is where the major content lies. The structure remains the same, but the content is greater in depth .
Sample Presentation Script
To make it easier for you to understand how you can structure your presentation script, here is a sample script for a presentation on the topic: Importance of Public Speaking.
This follows the same flow introduced earlier- introduction, context, main body, conclusion, and questions.
Title: Importance of Public Speaking
Slide 1: Why is Public Speaking Important?
Greetings, ladies, and gentlemen. Today, I will be exploring the importance of public speaking. My name is John, and I’m thrilled to discuss with you how improving our public speaking abilities may make a significant difference in our quality of life in the personal, social, and professional domains.
Slide 2: Introduction
Public speaking involves persuading an audience with a well-organized message. It is an essential part of our daily lives. We use it when we make conversation in social groups as well as when we address enormous crowds at social gatherings. It is a highly multifaceted and effective tool.
I will start off by giving some information about the context, moving on to its benefits, which is the main crux of our presentation, and then we will spend some time concluding.
Slide 3: Context
Effective communication is essential in our globally interconnected society. Speaking in front of an audience enables us to express our views and thoughts clearly and firmly. It facilitates the development of solid bonds and influences others, and acts as a catalyst for constructive change. Public speaking may open doors of opportunity and propel achievement for anyone, whether they are a student, professional, or member of the community.
Slide 4: Personal Development
Public speaking increases self-esteem and confidence, which are quite rudimentary to our self-efficacy. Effective communication skills help us to be more assertive and feel more in control of our lives. Research suggests that having an internal locus of control (i.e., feeling in control) leads to better outcomes in our personal lives as well as greater mental health. As we organize our ideas and arguments through public speaking, it improves critical thinking and organizational abilities. Furthermore, as we interact with others during talks and Q&A sessions, public speaking also enhances our listening abilities.
Slide 5: Professional Advancement
The ability to speak in front of an audience effectively is highly essential in most workplaces.
You ask Why? Well, it is because we are better able to communicate our qualifications and worth to potential employers, which enhances our performance in job interviews. Secondly, our influence within organizations grows when we can make a strong case for our points in meetings and conferences.
Next, for leadership positions, where success depends on inspiring and motivating others, public speaking is critical. And in general, you’ll need public speaking in any meeting or any talk you would typically deliver in front of a bunch of people.
Slide 6: Conclusion
Public speaking is a sought-after, multifaceted, and handy skill across many settings. It gives us the ability to inspire others, tell our stories, and make a lasting impression. Strong public speaking abilities help us communicate clearly and lead with influence in many facets of our lives.
Slide 7: Questions
I appreciate everyone here for being a great audience and cooperating wonderfully throughout the presentation. Now I will be taking any questions you all have. Feel free to discuss this now or reach out to me after the session is over.
Slide 8: Thank you
I want to thank you all for being here today.
I hope that the presentation did well to emphasize the importance of public speaking and perhaps motivated at least some of you to work on improving your abilities. We will end here.
[End of presentation]
Here are some tips for delivering an effective presentation.
We considered a few key points for presentation structure and the typical format that can be followed. We also covered five ways you can structure your presentation and the format for a scientific presentation. Lastly, we covered a sample script for presentations.
Public speaking coaching is a great way to increase your skills and get better at presentations as well.
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

Lost Voice? Here’s How to Recover Sore Throat and Speak Again

7 Keys to Emcee Like a Pro: Unlock Your Hosting Potential

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.

How to make a great presentation
Stressed about an upcoming presentation? These talks are full of helpful tips on how to get up in front of an audience and make a lasting impression.

The secret structure of great talks

The beauty of data visualization

TED's secret to great public speaking

How to speak so that people want to listen

How great leaders inspire action
Home Blog Business Presentation Structure Guidelines for Effective Communication
Presentation Structure Guidelines for Effective Communication
In the business world, a presentation is so much more than just a bunch of slides or points—it’s a golden opportunity. It can sway decisions, propel change, or bring people together. How you structure your presentation is absolutely critical in getting your ideas across clearly and compellingly.
When you’ve got a structured presentation just right, it’s like you’re taking your audience by the hand and guiding them through your thoughts, making sure they pick up all the important bits along the way. Moreover, it speaks of your degree of professionalism and how much knowledge you bear on the topic in question.
Therefore, nailing your presentation structure isn’t just helpful; it’s downright necessary to get the results you’re after. Whether you’re pitching a new concept to the investors, sharing the latest findings with your team, or taking the stage at a conference, how you lay out your content becomes the language you use to interact with your audience. Get to know all that’s required to create a powerful presentation structure that will guarantee success in business meetings, academic dissertations, or motivational talks .
Table of Contents
What is a Presentation Structure
Introduction, techniques to structure your presentation, common mistakes to avoid when designing a presentation structure, final words.
Let’s compare a presentation structure to a business plan . Just as a business plan is essential for guiding a company’s strategy and ensuring all aspects of the business are aligned toward common goals, a presentation structure is crucial for organizing the content and delivery of your talk.
The presentation structure lays out a clear and logical sequence of information, akin to the sections of a business plan that outline the company’s mission , market analysis , and financial projections. This clear sequence ensures that your audience can easily follow and understand your message, maximizing the impact your speech can deliver and influencing your target audience.
Key Elements of a Presentation Structure
The easiest way to study a presentation structure is to subdivide it into sections. Basically, every presentation has a structure that follows this formula: Introduction > Body > Conclusion.
The introduction is the first section of the presentation and sets the tone for the rest of the presentation. It should be attention-grabbing and make the audience want to listen to the rest of the presentation.
When defining how to start a presentation , these are the best tips we recommend you implement.
Start with a Hook
Kick off your introduction with a strong hook that grabs your audience’s attention. This could be an intriguing fact, a thought-provoking question, or a compelling story related to your topic. A captivating opening will make your audience want to listen and engage with your presentation.
Clearly State Your Topic
Be clear and concise when stating your topic. Your audience should immediately understand what your presentation is about and what they can expect to learn. A clear statement of your topic sets the stage and provides a roadmap for the rest of your presentation.
Establish Credibility
Take a moment to establish your credibility by briefly sharing your qualifications or experience related to the topic. This helps to build trust and rapport with your audience, and it shows that you are knowledgeable and well-prepared.
Engage Your Audience
Make your audience part of the presentation by engaging them from the start. Ask a question, encourage participation, or invite them to think about how the topic relates to their own experiences. Engagement helps to create a connection between you and your audience. Using a surprise factor is an alternative if you feel the topic you’re about to present may not fully resonate with the target audience.
Preview Main Points
End your introduction by briefly previewing the main points you will cover in your presentation. This provides a clear structure for your audience to follow and helps them understand what to expect in the body of your presentation. An agenda slide is the perfect tool for this purpose.
The body is the main part of the presentation and provides the content and information that the audience came to hear. It should feature the main points and details supporting your presentation’s objective. Depending on your topic, this could include data, arguments, case studies, examples, or demonstrations. Each main point should be clear and distinct, with evidence or examples substantiating it. The content should be tailored to your audience’s level of knowledge and interest.
Different presentations call for various structures. For example, a Product Presentation ’s structure should start by dividing the content into clear sections or headings. For instance, if presenting a new software tool, sections could include its features, benefits, and user feedback.

On the other hand, a Persuasive Presentation begins with stating the current situation or problem, followed by proposed solutions, evidence supporting those solutions, and the benefits of adopting your proposition.
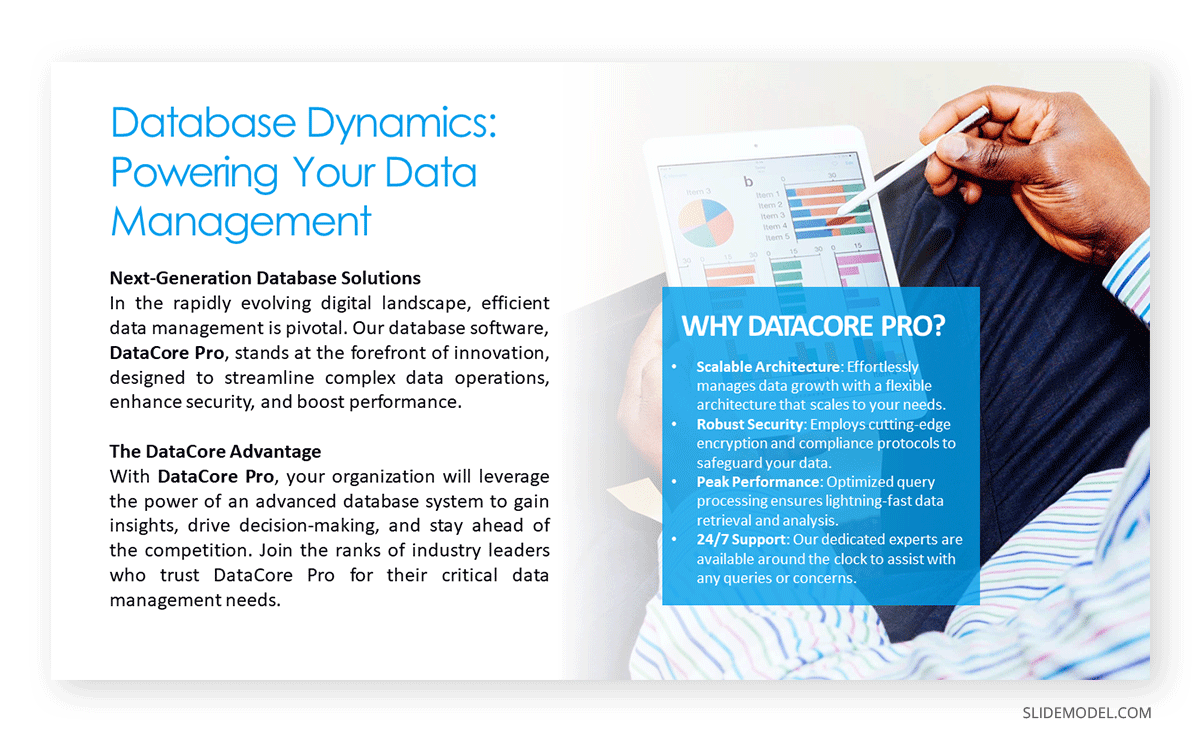
Workshop or Training Presentations begin with an overview of what will be taught, followed by step-by-step instructions, examples, demonstrations, and summaries or quizzes after each major section.
One essential aspect is to plan the multimedia elements to include in your presentation, including audio, images, and video, depending on the presentation style you aim to deliver. Through our expertise, we want to share some tips on how to plan this kind of content:
- Using relevant content: Each image should be related to its accompanying content. Avoid using images just for decoration. If using videos, dedicate an entire slide to them rather than sticking them to a corner of your slide. Plan a powerful hook to connect your thoughts with these visual aids.
- Quality: Ensure all images are of high resolution and can be clearly viewed, even from a distance. Avoid pixelated or distorted images.
- Simplicity: Infographics and diagrams should be easy to understand. If presenting data, use simple charts or graphs instead of complex tables. Limit the amount of text on each slide to ensure clarity. This rule of simplicity also applies to written content and the structure of your speech. Use the Feynman Technique as a time-saver approach to simplify content to reach any knowledgeable audience.
- Consistency: A common cause of presentation failures is to distract the audience with an unprofessional look. Maintain a consistent style and color scheme for all images to give your presentation a polished and professional feel.
Along the path of creating these media elements, you can rethink your strategy for disclosing content. In general lines, you should present your points in a logical order, often from the most to least important or in a chronological sequence. This helps the audience follow along and build understanding step by step. Well-known practices like the storytelling technique follow this approach to maximize audience engagement.
Transition smoothly between points. Phrases like “moving on,” “in addition,” or “on the other hand” can guide your audience through your narrative. Break up long sections of spoken content with anecdotes, questions, or short videos. Such an approach adds variety and keeps the audience engaged.
A well-structured conclusion is the linchpin that holds your presentation together, reinforcing your main points and leaving a lasting impression on your audience. It is your final opportunity to communicate your message and encourage audience engagement. So, before you consider how to end a presentation , here are some powerful tips to ensure you conclude your presentation with impact.
End with a Strong Statement or Quote
This technique is commonly used in motivational presentations, where the speaker leaves the audience with a slide containing a quote related to the topic of the presentation, something that evokes inner reflection about the topic discussed.

Conclude your presentation with a strong, memorable statement or a powerful quote that ties back to your main message. This adds weight to your argument and leaves a lasting impression on your audience. If you aim to surprise your audience, silence can also be a strong statement if your presentation has to raise awareness about a problem.
Incorporate a Call-to-Action
Clearly communicate to your audience what you want them to do next. Whether it’s to adopt a new perspective, take specific action, or continue the conversation outside of the presentation, a clear call to action drives engagement and encourages your audience to act upon your message.
Ask Thought-Provoking Questions
Pose thought-provoking questions that stimulate reflection and discussion. This opens the door for audience participation and engagement and allows you to interact with the audience in a Q&A session, or reach after your presentation concluded to network.

Additional Resources and Contact Info
Offer resources such as articles, websites, or books for those interested in exploring your topic further. This not only adds value to your presentation but also encourages the audience to engage with the content beyond the presentation itself.
Consider the way you leave a communication channel open with your audience. This can be in the format of a deliverable, writing down your contact data in the “Thank You” slide , or simply via speech to inform where they can know more about you and your work.
We already discussed the basic Introduction-Body-Conclusion framework for a presentation, but there are alternative approaches that can help you structure your talk.
Problem-Solution Framework
The Problem-Solution Framework is a compelling method to structure presentations, particularly when aiming to persuade or inform an audience about addressing specific challenges. The framework operates on a simple yet impactful premise: initially, highlight a problem or challenge that needs addressing and subsequently propose a viable solution or set of solutions.
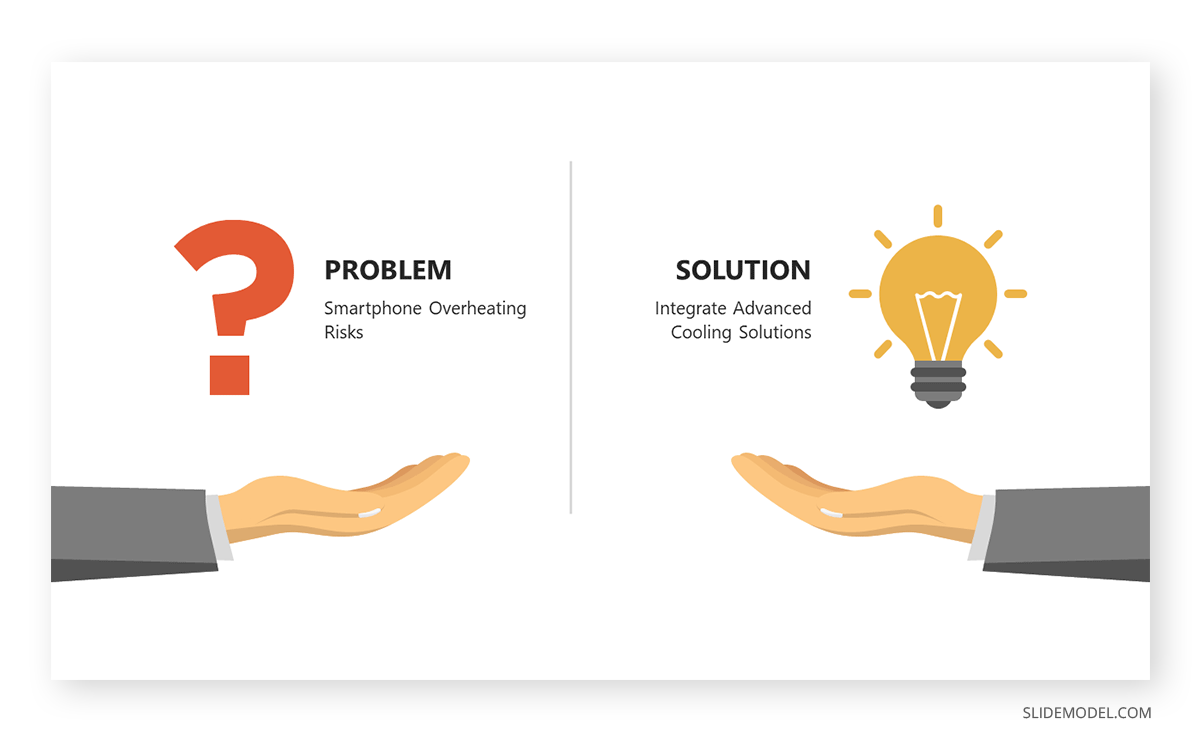
Starting with the problem establishes a context, engages the audience by highlighting pain points or challenges they may recognize, and creates a desire for resolution. It sets the stage for the solution to be perceived as necessary and valuable.
The solution phase offers that much-needed resolution. By presenting a clear, actionable solution or set of recommendations, the presenter provides a pathway to overcome the identified challenge. This structure is not only logical but also highly persuasive, as it appeals to the audience’s desire for resolution and improvement. In essence, the Problem-Solution Framework is both a guide for content organization and a psychological tool for persuasion.
Chronological Structure
The Chronological Structure is an intuitive and organized approach to presenting information based on a sequence of events or a progression in time. Whether recounting historical events, outlining the stages of a project, or narrating a personal story, this structure follows a clear beginning, middle, and end sequence. By presenting details in the order they occurred, the audience can easily follow the narrative, making connections between events and understanding causality.
This structure is especially effective when the timeline of events is crucial to the narrative or when showcasing developments, evolutions, or growth over time. It provides clarity and eliminates confusion that might arise from a non-linear presentation. Moreover, by anchoring information on a timeline, the Chronological Structure aids memory retention, as the audience can mentally “map out” the journey of events. In sum, this method offers clarity and a compelling narrative arc, ensuring audience engagement from start to finish.
Comparative Structure
The Comparative Structure is a strategic approach to presentations that hinges on juxtaposing two or more elements, ideas, or solutions side by side. By examining similarities and differences, this method illuminates unique qualities, advantages, or drawbacks inherent in each element. Often employed in business scenarios like product comparisons, market analysis, or debates, the comparative structure helps audiences critically analyze options and make informed decisions.
Presenters utilizing this structure typically start by introducing the elements for comparison. They then delve into detailed analysis, often using criteria or metrics to maintain objective evaluations. Visual aids like Venn diagrams or comparison charts can enhance clarity and visual appeal.
The strength of the Comparative Structure lies in its ability to foster critical thinking. By directly contrasting items, audiences are engaged, encouraged to weigh pros and cons, and ultimately arrive at a deeper understanding or more nuanced perspective on the subject matter.
Matrix Structure
The Matrix Structure offers an approach to organizing presentations by segmenting information into distinct categories or sections, akin to a grid or matrix. Instead of a linear flow, topics are grouped by themes, criteria, or any relevant classification, allowing for simultaneous exploration of multiple facets of a subject. Think of it as viewing a topic through various lenses concurrently.
For instance, in a business setting, a product might be examined in terms of design, functionality, market positioning, and customer feedback. Each of these constitutes a segment in the matrix.
Visually, the matrix can be represented using tables, grids, or quadrant charts, making the content easily digestible and engaging. A key advantage of this structure is its flexibility; presenters can delve deep into one segment or provide a broader overview of all areas, depending on the audience’s needs. Ultimately, the Matrix Structure ensures a comprehensive and multifaceted examination of a topic, providing depth and breadth in analysis.

Modular Structure
The final model we will study is the Modular Structure. It takes content and packs it into modules, which can be arranged at any other the presenter requires them to be. Each module addresses a specific topic or idea and is designed to be self-contained, ensuring clarity even if presented independently or in a different order. This adaptability makes the modular approach especially valuable in dynamic settings, such as workshops or conferences, where audience feedback or time constraints might necessitate adjustments on the fly.
For example, in a corporate training session, different modules could cover distinct skills or topics. Based on the attendees’ prior knowledge or the session’s time limit, the presenter can prioritize, omit, or rearrange modules without compromising the integrity of each segment.
By adopting the Modular Structure, presenters gain flexibility without sacrificing depth. This approach fosters a responsive presentation style, allowing speakers to tailor content in real-time, ensuring maximum relevance and engagement for their audience.
Even well-seasoned presenters can fall prey to these common mistakes in terms of presentation structure. Let’s learn how to prevent them.
Overloading with Information
It’s tempting to include every bit of knowledge you have on a topic. Still, information overload can quickly disengage an audience. Prioritize key points and leave out extraneous details. As famous architect, Mies van der Rohe famously coined, “Less is More.”
Weak Transitions
Jumping abruptly from one point to another can disrupt the flow and confuse listeners. Ensure smooth transitions between sections, signaling shifts in topics or ideas to keep the narrative cohesive.
Dull Design
While content is king, visual appeal matters. Relying solely on walls of text or bland slides can lose your audience’s interest. Incorporate engaging visuals, charts, and multimedia elements to enhance your message and retain attention.
Ignoring the Call to Action
Concluding your presentation without guiding the audience on the next steps or what’s expected of them can be a missed opportunity. Whether it’s seeking feedback, prompting a discussion, or encouraging an action, always have a clear call to action.
Good communication is all about making your point clear, especially in presentations. We’ve talked about how the right structure can keep your audience hooked. But there’s more to it. Think about your presentation. Is it telling your story the way you want? Is it reaching your audience? Take a step back and really look at how you’re laying it out. Don’t just go with the flow – choose your format wisely. Remember, every presentation tells a story, and how you set it up matters a lot.

Like this article? Please share
Design, Presentation Approaches Filed under Business
Related Articles

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • April 23rd, 2024
How to Align Objects in Google Slides
Optimize your layouts by learning how to align objects in Google Slides presentations. Step-by-step guide with screenshots.

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 29th, 2024
How to Make a Fundraising Presentation (with Thermometer Templates & Slides)
Meet a new framework to design fundraising presentations by harnessing the power of fundraising thermometer templates. Detailed guide with examples.
Leave a Reply

A simple, engaging presentation structure that works every time

A simple, engaging presentation structure is like the air that your audience breaths: invisible, unnoticed and essential.
It will draw them into the content, and they will stay fully focused on what you have to say.
And if you don’t have a simple, engaging presentation structure your audience will suffer!
The benefits of this presentation structure
There are three key benefits, this presentation structure ensures that:
- The audience connects with your central message and key points
- You feel confident and in control
- You can flex the duration of the presentation to different circumstances
More on this last point a little later. Use my presentation structure and you’ll see how you can adapt it to a 1-minute elevator pitch or a 1-hour deep dive into the topic.
The ideal presentation structure
This presentation structure is deliberately simple (structure is not something that you should complicate!). At its highest level, it consists of the opening, content and closing.
Each of these three sections has a very specific purpose.
- The opening : deliver your central message and 3 key points
- The content : Dive into the detail of your 3 key points
- The closing : Recap your central message, Q&A, call to action

There’s more here on the benefits of this presentation structure from Inc’s 3 Tips from Aristotle article.
The opening
Let’s imagine for a moment that you’re proposing a 4-day working week for the whole company (with 5 days’ pay!), and your audience is the CEO and other C-level executives.
Open with your central message:
Good afternoon, I’m here to share with you how a 4-day working week can boost the profitability of the company. I realize that’s a big claim, let me tell you a little more about what I’ll be covering today.
Notice, you didn’t just mention the topic (4-day working week), you delivered your central message from the opening slide: that you can boost the productivity of the company. Motivate them to engage, ensure your central message is compelling to them , and deliver it right from the start.
Move to your agenda slide. This should be structured around 3 key points.
In this presentation I’ll be covering 3 points. How my proposal can: boost our productivity, reduce operating costs and increase revenues.
You’ve already hit your central message and key points. Then transition into the content.
Now, let me jump into the content, looking at our productivity first.
For added impact to your opening, explore how to use a presentation hook (to grab your audience!).
The content
Structure your content around the three key points to your central message.
Take a look at this ethos3.com article on the rule of three , here’s an extract:
Steve Jobs was famous for using the Rule of Three in his presentations. In 2011, he described the iPad 2 as “ thinner, lighter, and faster ” than the first. These three adjectives were massively effective; they said everything the audience needed to know.
Three points is complete and perfectly formed. If you use two points, it looks like you’re missing something, four key points and your audience will start to forget. Five, six or seven key points, and your audience will be lost!
Avoid a laundry list of topics (it’s lazy and it doesn’t help your audience!), distill your message into three key points.
The elevator pitch
Earlier I mentioned how this structure will help you flex the presentation to any duration. If you’re in the elevator, and someone asks you about this presentation, just use your ‘opening’ it’s a summary of your complete presentation.
A 4-day working week is a great opportunity to increase profitability. Let me tell you how, there are just 3 key things to know: it will boost our productivity, reduce operating costs and increase revenues. Is this your floor? OK, see you later!
The deep dive
Or, if you have an hour, use this structure to give yourself the confidence to expound on the topic. Talk about each key point in some detail, tell stories, share data, ask for input.
And if you’re doing this deep dive, add in some additional structure, to help the audience navigate. Summarize at the end of each key point, and transition to the next key point.
Use this kind of language to summarize:
That has been a great discussion about the first point I wanted to cover, how my proposal will boost productivity. Let me just summarize…
And this kind of language to transition to the next key point.
Now, as I mentioned, the next big benefit is increased productivity. There are several perspectives on this, let me take the next 20 mins to walk you through and share my experience, feel free to jump in any time…
That’s the beauty of this structure, it gives you control.
The closing
Finally, the closing. Use it to reinforce your central message and key support points, open the presentation for more questions, and your call to action.
Before you open the presentation for more questions, make sure you take a look at these simple and powerful techniques for confident Q&As .
Finally, your call to action. You do have a call to action, right? What is it that you want your audience to do, as a result of your presentation?
There should always be an action. Never present as a ‘briefing’ or ‘for information’. If that’s the case, then send an email. Presentations are expensive. (Take a look at the cost of meetings .)
Presentations can only be justified if there is clear business value, and business value comes from taking action.
Presentation structure, in summary
A great presentation structure is like air. Your audience won’t notice it, because they’ll be fully engaged with your central message and key points.
Keep your presentation structure simple:
- Open with a central message
- Structure your content around 3 key points
- Close with a call to action
Always have a call to action, that’s the business value.
Keep it simple, let your content shine!
Take the next step
Learn to become a great presenter with these effective presentation skills .

How To Write A Presentation 101 | Step-by-Step Guides with Best Examples | 2024 Reveals
Jane Ng • 05 April, 2024 • 11 min read
Is it difficult to start of presentation? You’re standing before a room full of eager listeners, ready to share your knowledge and captivate their attention. But where do you begin? How do you structure your ideas and convey them effectively?
Take a deep breath, and fear not! In this article, we’ll provide a road map on how to write a presentation covering everything from crafting a script to creating an engaging introduction.
So, let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a presentation , what should be in a powerful presentation.
- How To Write A Presentation Script
- How to Write A Presentation Introduction
Key Takeaways
Tips for better presentation.
- How to start a presentation
- How to introduce yourself

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
Presentations are all about connecting with your audience.
Presenting is a fantastic way to share information, ideas, or arguments with your audience. Think of it as a structured approach to effectively convey your message. And you’ve got options such as slideshows, speeches, demos, videos, and even multimedia presentations!
The purpose of a presentation can vary depending on the situation and what the presenter wants to achieve.
- In the business world, presentations are commonly used to pitch proposals, share reports, or make sales pitches.
- In educational settings, presentations are a go-to for teaching or delivering engaging lectures.
- For conferences, seminars, and public events—presentations are perfect for dishing out information, inspiring folks, or even persuading the audience.
That sounds brilliant. But, how to write a presentation?

- Clear and Engaging Introduction: Start your presentation with a bang! Hook your audience’s attention right from the beginning by using a captivating story, a surprising fact, a thought-provoking question, or a powerful quote. Clearly state the purpose of your presentation and establish a connection with your listeners.
- Well-Structured Content: Organize your content logically and coherently. Divide your presentation into sections or main points and provide smooth transitions between them. Each section should flow seamlessly into the next, creating a cohesive narrative. Use clear headings and subheadings to guide your audience through the presentation.
- Compelling Visuals: Incorporate visual aids, such as images, graphs, or videos, to enhance your presentation. Make sure your visuals are visually appealing, relevant, and easy to understand. Use a clean and uncluttered design with legible fonts and appropriate color schemes.
- Engaging Delivery: Pay attention to your delivery style and body language. You should maintain eye contact with your audience, use gestures to emphasize key points, and vary your tone of voice to keep the presentation dynamic.
- Clear and Memorable Conclusion: Leave your audience with a lasting impression by providing a strong closing statement, a call to action, or a thought-provoking question. Make sure your conclusion ties back to your introduction and reinforces the core message of your presentation.

How To Write A Presentation Script (With Examples)
To successfully convey your message to your audience, you must carefully craft and organize your presentation script. Here are steps on how to write a presentation script:
1/ Understand Your Purpose and Audience
- Clarify the purpose of your presentation. Are you informing, persuading, or entertaining?
- Identify your target audience and their knowledge level, interests, and expectations.
- Define what presentation format you want to use
2/ Outline the Structure of Your Presentation
Strong opening.
Start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience’s attention and introduces your topic. Some types of openings you can use are:
- Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: “Have you ever…?”
- Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: “Did you know that….?”
- Use a Powerful Quote: “As Maya Angelou once said,….”
- Tell a Compelling Story : “Picture this: You’re standing at….”
- Start with a Bold Statement: “In the fast-paced digital age….”
Main Points
Clearly state your main points or key ideas that you will discuss throughout the presentation.
- Clearly State the Purpose and Main Points: Example: “In this presentation, we will delve into three key areas. First,… Next,… Finally,…. we’ll discuss….”
- Provide Background and Context: Example: “Before we dive into the details, let’s understand the basics of…..”
- Present Supporting Information and Examples: Example: “To illustrate…., let’s look at an example. In,…..”
- Address Counterarguments or Potential Concerns: Example: “While…, we must also consider… .”
- Recap Key Points and Transition to the Next Section: Example: “To summarize, we’ve… Now, let’s shift our focus to…”
Remember to organize your content logically and coherently, ensuring smooth transitions between sections.
You can conclude with a strong closing statement summarizing your main points and leaving a lasting impression. Example: “As we conclude our presentation, it’s clear that… By…., we can….”
3/ Craft Clear and Concise Sentences
Once you’ve outlined your presentation, you need to edit your sentences. Use clear and straightforward language to ensure your message is easily understood.
Alternatively, you can break down complex ideas into simpler concepts and provide clear explanations or examples to aid comprehension.
4/ Use Visual Aids and Supporting Materials
Use supporting materials such as statistics, research findings, or real-life examples to back up your points and make them more compelling.
- Example: “As you can see from this graph,… This demonstrates….”
5/ Include Engagement Techniques
Incorporate interactive elements to engage your audience, such as Q&A sessions , conducting live polls, or encouraging participation. You can also spin more funs into group, by randomly dividing people into different groups to get more diverse feedbacks!
6/ Rehearse and Revise
- Practice delivering your presentation script to familiarize yourself with the content and improve your delivery.
- Revise and edit your script as needed, removing any unnecessary information or repetitions.
7/ Seek Feedback
You can share your script or deliver a practice presentation to a trusted friend, colleague, or mentor to gather feedback on your script and make adjustments accordingly.
More on Script Presentation

How to Write A Presentation Introduction with Examples
How to write presentations that are engaging and visually appealing? Looking for introduction ideas for the presentation? As mentioned earlier, once you have completed your script, it’s crucial to focus on editing and refining the most critical element—the opening of your presentation – the section that determines whether you can captivate and retain your audience’s attention right from the start.
Here is a guide on how to craft an opening that grabs your audience’s attention from the very first minute:
1/ Start with a Hook
To begin, you can choose from five different openings mentioned in the script based on your desired purpose and content. Alternatively, you can opt for the approach that resonates with you the most, and instills your confidence. Remember, the key is to choose a starting point that aligns with your objectives and allows you to deliver your message effectively.
2/ Establish Relevance and Context
Then you should establish the topic of your presentation and explain why it is important or relevant to your audience. Connect the topic to their interests, challenges, or aspirations to create a sense of relevance.
3/ State the Purpose
Clearly articulate the purpose or goal of your presentation. Let the audience know what they can expect to gain or achieve by listening to your presentation.
4/ Preview Your Main Points
Give a brief overview of the main points or sections you will cover in your presentation. It helps the audience understand the structure and flow of your presentation and creates anticipation.
5/ Establish Credibility
Share your expertise or credentials related to the topic to build trust with the audience, such as a brief personal story, relevant experience, or mentioning your professional background.
6/ Engage Emotionally
Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning.
Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations. Aim for clarity and brevity to maintain the audience’s attention.
For example, Topic: Work-life balance
“Good morning, everyone! Can you imagine waking up each day feeling energized and ready to conquer both your personal and professional pursuits? Well, that’s exactly what we’ll explore today – the wonderful world of work-life balance. In a fast-paced society where work seems to consume every waking hour, it’s vital to find that spot where our careers and personal lives harmoniously coexist. Throughout this presentation, we’ll dive into practical strategies that help us achieve that coveted balance, boost productivity, and nurture our overall well-being.
But before we dive in, let me share a bit about my journey. As a working professional and a passionate advocate for work-life balance, I have spent years researching and implementing strategies that have transformed my own life. I am excited to share my knowledge and experiences with all of you today, with the hope of inspiring positive change and creating a more fulfilling work-life balance for everyone in this room. So, let’s get started!”
🎉 Check out: How to Start a Presentation?

Whether you’re a seasoned speaker or new to the stage, understanding how to write a presentation that conveys your message effectively is a valuable skill. By following the steps in this guide, you can become a captivating presenter and make your mark in every presentation you deliver.
Additionally, AhaSlides can significantly enhance your presentation’s impact. With AhaSlides, you can use live polls , quizzes , and word cloud to turn your presentation into an engaging and interactive experience. Let’s take a moment to explore our vast template library !
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a presentation step by step .
You can refer to our step-by-step guide on How To Write A Presentation Script: Understand Your Purpose and Audience Outline the Structure of Your Presentation Craft Clear and Concise Sentences Use Visual Aids and Supporting Material Include Engagement Techniques Rehearse and Revise Seek Feedback
How do you start a presentation?
You can start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience’s attention and introduces your topic. Consider using one of the following approaches: Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: “Have you ever…?” Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: “Did you know that….?” Use a Powerful Quote: “As Maya Angelou once said,….” Tell a Compelling Story : “Picture this: You’re standing at….” Start with a Bold Statement: “In the fast-paced digital age….”
What are the five parts of a presentation?
When it comes to presentation writing, a typical presentation consists of the following five parts: Introduction: Capturing the audience’s attention, introducing yourself, stating the purpose, and providing an overview. Main Body: Presenting main points, evidence, examples, and arguments. Visual Aids: Using visuals to enhance understanding and engage the audience. Conclusion: Summarizing main points, restating key message, and leaving a memorable takeaway or call to action. Q&A or Discussion: Optional part for addressing questions and encouraging audience participation.

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides


Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Prepare for a Presentation, with Examples
February 15, 2021 - Dom Barnard
This guide covers everything you need to know to prepare for your presentation. including what you need to think about beforehand, during and after the presentation.
1. Rehearse, rehearse, rehearse (always aloud)
Once you have your presentation worked out, you will need to practice it, but even though you might think it’s the best way to have a flawless presentation, don’t memorise what you’re going to say.
That might sound like incredibly bad advice, but here’s why:
- If you memorise your speech, you’ll get stuck in thinking you can only deliver your ideas in that way, and that stifles your creativity, and the chance for new thoughts and ways to put things that come up as you speak.
Not only that, but every audience is different . Sometimes they laugh out loud, sometimes they sit and smile, and you never know which type of audience you’ll have until you’re live.
Practice Presentation Skills
Improve your public speaking and presentation skills by practicing them in realistic environments, with automated feedback on performance. Learn More
If you’re going off a memorised presentation, it’s much more difficult to break away from that to go with the flow on the day, and respond naturally to your audience.
- If you forget your speech in the middle of it, you will be thrown, and you’ll have more chance of complete brain freeze, which really will knock your confidence.
- Memorising your presentation gives you a false sense of security, which could leave you high and dry if something goes wrong. If you’ve only got your memorised speech, for example, what will you do if your PowerPoint freezes or your props break, and you can’t do what you were going to do?
Rehearse in front of colleagues, friends, a mirror, in virtual reality – always aloud. Make sure you spend plenty of time practising your presentation, it will make you feel much more relaxed if you know your material.
Courses where you can rehearse with interactive exercises:
- Essential Public Speaking
- How to Present over Video
Video showing how you can prepare for your presentation using virtual reality. Learn more about virtual reality training .
2. Memorise your opening line
Do, however, memorise your opening line. If you know how you’re going to begin, you’ll get a strong start and that will build your confidence.
Many speakers and stage actors find that the minute they’ve actually delivered their first line, the nerves are gone and they’re well into their stride.
3. Practise your speech from written notes
Writing your presentation out in your own handwriting will help you clarify your ideas and may well bring you new ones.
- How to Write a Speech to Engage your Audience
4. Practise presentation flow
As well as practising for the ideas and what you want to say, practise how you want your presentation to flow. Think of it almost as a symphony, with high points, slow movements and crescendos. If it’s important, think about how you want your audience to feel, what emotions you want them to have, and when.
5. The power of silence
Don’t be afraid to pause and use the power of silence. A good pause can have a huge emotional impact. It allows people to really absorb what you are saying and react, and it’s vital to pause if you’re using humour so that the next part of your presentation doesn’t get lost underneath people’s laughter.
For more on the ‘Power of the Pause’, watch this short from video Brian Tracy: The Power of the Pause
- 10 Effective Ways to use Pauses in your Speech
6. Have a backup
There’s nothing worse than the projector dying or finding that your laptop won’t communicate with the projector for some reason. If you know you have a backup, even if it’s only a pre-prepared flip chart, you’ll feel better, and you’ll be more confident.
7. Arrive early
Following on from that, arrive at least half an hour early so you aren’t feeling rushed, and so you have time to check your equipment and get your notes laid out ready to go. That gives you time to breathe and relax before you go on, knowing everything is as set as it can be.
8. Use physical props for a demo
Use physical props, if possible, for a demo. This can make you stand out and be more memorable among all the other speakers who only use PowerPoint, and it can add greatly to the impact of your presentation.
Video showing an example of using physical props during a live demo.
9. Structure your presentation
First, find out how much time you have to present, is it 10 minutes, 15, an hour? Prepare enough material for this time and have a couple of extra slides as backup – we tend to speak much quicker when nervous so you might find you finish your presentation too early. At some large conference events, timings may change on the day, be aware of this have a shorter version of your presentation in mind (i.e. know which slides to skip over).
- How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
- Examples of Corporate Presentation Structures
10. Prepare for questions
Have a few backup slides for questions you think will arise from your presentation. It is sometime a tactic to explain a section briefly in your speech, so that you get a question about it afterwards. If you don’t understand the question, ask for it to be rephrased.
If there are no questions, it is not an indication how good or bad your presentation was. You many have explain your material extremely well, or simply that people are tired at the end of the day and want to go home.
- Guide for Handling Questions after a Presentation
11. Prepare for where you are presenting
If you can, go to the room you are speaking in before the actual event. It gives you an idea of furniture layout, podium height, location, room size, audience size and lighting. You can then visualise the room while practising and avoid the shock of suddenly being faced with a huge room when you expected a tiny one.
Ask the organiser if you need any particular props, for example a table to help with your live demo.
Additional planning to think about before your presentation:
1. Purpose – what outcome are we trying to achieve? How can results be measured? What will success look like?
2. Topic – Novelty? Complexity? Technical?
3. People – Who should attend? What do they already know? How are they going to help?
4. Timing – When will it happen and how long will the presentation take?
5. Location – Where will the presentation be held? Do you have access to the correct facilities for the presentation?
6. Papers – Who is keeping minutes? Do you need to send out an agenda before the presentation? Background information required?
7. Visual aids – Is a projector required ? Boards?
8. Style – Structure or unstructured, discussion style? How assertive should you be? How should the meeting items be organised?
12. Choose the signals to give to your audience
Before the presentation, think about these 5 topics:
- Eye contact
- Facial gestures
- Body language
Decide how you will use each of these to reinforce your message. Use the table below for help.
Additional courses to help you prepare for your presentation:
- Presentation Skills Training Courses
Example from Steve Jobs
Think about these 10 techniques while you are preparing your presentation..

- Planning in Analog. Tell a story, create stunning visuals and videos to complement video, use demonstrations and other speakers, keep the audience engaged.
- Creating a Twitter-Friendly Description Single description sentence, condensed his message into 140 characters.
- Introduce the Enemy Story needs villains or a problem to be solved. Jobs highlighted IBM and useless mobile phones (during iPhone release) as his villains.
- Focusing on Benefits Keep reinforcing the benefits of your product, create top 10 lists, understand this is what customers care about.
- Sticking to Rule of Three Classic Literary technique, things are best remembered and reinforced in threes. Read this article on Literary Techniques for more detail.
- Sell Dreams, Not Products Create a vision people believe in, create a vision which will make people’s lives better
- Create Visual Slides Use as few words as possible and use colourful graphics on the slide to highlight points.
- Make Numbers Meaningful Compare large numbers to things people understand.
- Use Plain English Use easy to say and easy to remember words, keep it simple.
- Large Reveals Due to Apple secrecy, Jobs was able to deliver unexpected products to the world at his product launches.
This website uses cookies. Learn more
How to structure a PowerPoint presentation: A detailed guide
· Create Courses

How do you structure a PowerPoint presentation?
Introduction , the body , the conclusion , powerpoint presentation examples , graphy, the all-in-one course creation platform.
In this blog, you’ll understand the step-by-step guide on how you can structure a PowerPoint presentation effectively.
You might be a great presenter but suck at creating a structured presentation. The idea of outlining, selecting the right templates, and adding transitions is way out of your league.
However, creating a structured presentation is as important as the narration.
When information is presented logically, the retention rate automatically goes up. It becomes easier for a viewer to understand the meaning behind the words and create a flow of information.
Monetize your skills and extertise GOT YOUR CONTENT READY? GRAPHY IS ALL YOU NEED TO GET STARTED!
A report published by Standard Business says that people retain 40% more information when presented structurally.
So, here we are to help you understand how you should structure your PowerPoint presentation to make it likable and easy to digest.
Table of Contents
You can follow this standard structure while creating your PowerPoint presentations. A good presentation is always one that has a good storyline and narration. Let’s dive into detail on how to create a solid PowerPoint structure.
An introduction is the most crucial part of a presentation. It sets the tone for your audience and makes them comfortable. Before you start with your presentation, make sure to
- Introduce yourself
- Explain the purpose of this presentation
- And, what outcomes can your audience expect at the end of it?
This doesn’t have to be super-detailed, but it should build a connection with the person. You can include storytelling to gather attention and further move on to introducing the topic.
Here are some slides that you must include in your introduction:
- The title: Introduce the topic of the presentation and add a brief description
- Challenges/ objectives: Explain the goals or challenges you will target in the presentation. For example, I’ll “compare,” “evaluate,” and “analyze” this topic.
- Outcome: Your audience must know the results they can expect at the end of the presentation. For instance, at the end of this presentation, I hope to provide you with a….
- Table of Content: You can include a table of contents for your audience to know the topic of discussion in the presentation.
In the introduction, you can also tell the length of the talk or whether you want audience participation. Clarifying such small things can make presentations smoother and less awkward.
This is the part where you take your introduction forward and briefly discuss the key topics. You must organize these points to transition smoothly from one topic to another. The body of your presentation needs to be spot-on for your audience to understand the information given.
Here are some tips to consider when creating the body of your presentation:
- The length and structure of your slides are crucial to the body of your presentation. You can use the 5-5-5 and 10-20-30 rules to structure a PowerPoint presentation.
What is the 555 rule in PowerPoint?
The 555 rule says, to use at least
- 5 words on a single line.
- 5 lines of text on every slide
- 5 slides that use the mentioned rules in a row
The purpose of this 555 rule is to create a flow in presenting your information. This rule helps if you have to make a big presentation that requires heavy content and various slides. It will help you structure a presentation well and not overwhelm your audience with the information.
What is the 10 20 30 rule in PowerPoint?
The 10 / 20 / 30 rule in PowerPoint is fairly simple. It says that no PowerPoint presentation should have over 10 slides, be longer than 20 minutes, and have fonts smaller than 30 points.
Each of the rules helps the presenter form a balance between design and explanation. This helps to structure a PowerPoint presentation and create easy-to-digest slides.
- Use images more than words. The human brain processes visual stimuli 60 times faster than text. So, instead of writing lengthy paraphs, add photos or videos. If you think a concept is explainable through a photo, use it.
- Your presentation should be short and crisp. You don’t have to write everything about the topic in your slides. Include a few short-crisp sentences and use narration to explain the topic in depth.
- Try to organize your topics well. List points in order of numbers or alphabets put them in a time frame, or use transition words like next, then, and another for easy understanding. No matter how well you explain concepts, if your presentation lacks the translation to move from one topic to another, then it might not work.
In your conclusion, you can summarise the main points you have made and do a recap of what your audience has learned. Lastly, mention how this new information meets your objective for the presentation.
In conclusion, you must state your sources of information, like books, articles, or interviews with people.
Include a Q&A part to ask questions. This way, there isn’t any open-ended conversation, and your audience is clear about the points you made. If you cannot answer any question because of a lack of time, note it down to provide the solution through mail or phone.
End your presentation by thanking your audience for their precious time and asking for their feedback.
See how simple it is to structure a PowerPoint presentation. Now, look at a few examples of PowerPoint structures for your reference.
Powerpoint presentations are mostly referred to as bland and boring, but that’s not the case. If you structure it well, your presentations will become more like a learning opportunity than an endurance test. Here are some PowerPoint presentation examples you can refer to:
- Teacher education
Look at this slide deck , created for teachers on how to use Google Slides. It’s not overloading with information nor holding it back; it’s simply perfect. Most of the slides are image-oriented with practical examples to help the audience understand the basics of creating presentations in Google Slides.
- Zuroa sales deck
To see how storytelling works in presentation, refer to Zuroa’s sales desk . These slides are a perfect example of how you can make your audience relate to your issues. Including metrics and messages from well-known CEOs makes the slides authoritative.
- Trackmaven research deck
Creating a data-heavy presentation is quite tricky. Your audience can quickly accelerate from engaging to boring. Trackmaven excellently presents its report on the best time to post on social media. The presentation has more graphs than numbers or text. If you are looking for a reference for creating such data extensive topic, then, indeed, check this out.
- Officevibe collaboration examples
This slide deck increases awareness of the problem faced because of a disengaged team. The presentation has bright colors and unique designs that draw attention. Plus, it’s filled with relevant data to ensure the authority and seriousness of the issue.
They are excellent examples of how you can structure a PowerPoint presentation. If you notice, none of them are text-heavy. Instead, they have used visuals or videos to convey most of their information. Thus, the information presented is easy to digest and keeps the audience hooked until the end.
If you are looking to create your online course and sell it with minimum effort and easy-to-use features, then Graphy is the best place for you. Graphy has thousands of active content creators who have created their own online courses and monetized their skills. You can also do the same, and the best thing is that you can start for free.
Graphy offers a load of features that will definitely add stars to your success, features like:
- Branded website and mobile app
- Advanced-level marketing and sales tools and features
- Multi-layer content security
- Rich multimedia
- 24*7 customer support
- Customizable landing/sales pages
- Personalized course completion certificates for your learners
- Integrated payment gateways and country-specific pricing
Isn’t it amazing?
So join Graphy , just like 40,000+ creators.
Course platform
create your online course
online course platform india
PowerPoint presentation
structure a PowerPoint presentation
Top creators use Graphy to sell courses and memberships
Join 100K+ creators who have launched their online knowledge business using Graphy
You may also want to read

Top 7 Christmas Marketing Strategies to Boost Sales

9 Telegram Bots Every Telegram Channel Owner Must Have (2024 Updated)

How To Create a Paid Telegram Channel In 2024 (Updated)?

Group Presentations
46 How to structure your presentation
Lucinda Atwood and Christian Westin
This chapter teaches you a quick, easy way to create effective presentations. You’ll also learn how to use valid resources and avoid plagiarism.
There are lots of ways to structure a presentation, but we like this one best. It’s clear, simple and fits most presentations.
In this part of your presentation, you’ll capture the audience’s attention, tell them who you are, and give them a preview of your presentation.
- Grabber/hook (Goes before or after the self-introduction) A very brief and interesting statement or question that grabs the audience’s attention. See Grabber Types below for more details.
- Self-introduction (Goes before or after the grabber ) Tell the audience your name and credentials. For example: I’m Minh and I’ve been a professional presenter for 10 years.
- Thesis The main point or argument of your presentation. Be brief and precise, not general or vague. For example: I’m going to show you how practicing your presentation 10 times will improve your grade by 20%.
- Overview of main points Briefly outline the main points that you’ll cover in your presentation. To help your audience, do list these in same order that you’ll deliver them later on. For example: First, we’ll talk about what makes presentations great, then I’ll share some data on how practice affects your confidence and performance, and finally we’ll look at how to practice.
In this part of your presentation, you’ll deliver the detailed information of your presentation.
- Key point 1 A major point that supports your thesis and may have supporting sub-points
- Key point 2 Another major point that supports your thesis and may have supporting sub-points
- Key point 3 The final major point that supports your thesis and may have supporting sub-points
In this part you’ll remind the audience of what you told them, and tell them what to do next.
- Summary of main points (Can be merged with your conclusion) Clearly restate your three main points in the same order you delivered them. It’s the same as your overview but in past tense. First, I described what makes presentations great, then I shared data on how practice affects confidence and performance, and finally we looked at how to practice.
- Conclusion Restate your thesis in past tense. For example: I’m showed you that practicing your presentation 10 times will improve your grade by 20%.
- Call to action Give your audience clear, active and compelling direction, based on what you told them. For example: Practice your presentations ten times and start collecting those A-plusses!
Grabber types
Remember that the grabber’s job is grabbing the audience’s attention, so it must be surprising, fascinating or intriguing. It must also be related to your presentation’s topic. Here are some descriptions and examples:
You can also mix and match grabbers. For example, you could show an image and ask the audience to guess what it is.
The length of your grabber is relative to your total presentation time. For a 2-minute presentation, it should be quite brief – maybe one sentence. For a 16-minute team presentation, a 45-60 second grabber would be appropriate.
Outline your presentation
The fastest way to create a successful presentation is to start with an outline. Y ou’ll need two outlines: a preparation outline, and a speaking outline.
Preparation outlines are comprehensive outlines that include all of the information in your presentation. Our presentation outline will consist of the content of what the audience will see and hear. Eventually, you will move away from this outline as you develop your materials and practice your presentation.
Your speaking outline will contain notes to guide you and is usually not shared with your audience. It will summarize the full preparation outline down to more usable notes. You should create a set of abbreviated notes for the actual delivery.
Use an outline, not a script; this will allow you to be more natural and let you look at the audience or camera. Reading is a guaranteed way to make your presentation boring.
The easiest way to create your outline is to work in this order:
- Determine your thesis and write this as a full sentence
- Determine your 3 Main Points
- Add key supporting points for each of your Main Points
- Complete the other parts – introduction, grabber, call to action, etc.
Working in this order is fast because it’s easier to create the conclusion and grabber when you’ve already decided on the content. Also, after you have the main structure it’s easy to add details, examples, and stories that make your presentation interesting and convincing.
You can use your presentation outline as a starting point to developing your speaking outline. It’s a good idea to make speaking notes to align with your main points and visuals in each section.
UNC Libraries Presentation Planning Worksheet
Using Examples and Scenarios
Presenters will often use examples and scenarios to help illustrate the their message. The main difference between examples and scenarios is that while both help “show” the audience what you mean, an example is the “thing” itself, while a scenario would include more detail about the sequence or development of events. Scenarios also tend to be longer and more nuanced.
An ‘example’ of a sales target might be: to sell 500 units in 30 days. A ‘scenario’ might be described as: Company A is selling vacuums to the Atlantic Canada region. They are trying to increase their sales, and so have set a target of 500 units in the region in 30 days, using a sales incentive program for employees and promoting a sale at local stores.
A Word About Storytelling
Storytelling can be an effective way to convey your message to your audience. Stories are a fundamental part of the human experience, and, if well-told, can resonate with listeners. Some of the most inspiring TEDTalks speakers use storytelling effectively in their presentations. You can find out more about how to incorporate storytelling techniques into presentations from the TEDTAlk speakers directly.

Read the following blog post from Nayomi Chibana (2015).
http://blog.visme.co/7-storytelling-techniques-used-by-the-most-inspiring-ted-presenters/
Test your knowledge
How to structure your presentation Copyright © by Lucinda Atwood and Christian Westin is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center
How to Start a Presentation [+ Examples]
Published: September 13, 2023
The first step in mastering the art of delivering powerful presentations is understanding how to start a presentation properly.

In this post, you'll discover strategies for crafting a solid presentation opening, designing an impactful opening slide, and delivering a memorable presentation.
![how to structure your presentation with examples → Free Download: 10 PowerPoint Presentation Templates [Access Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/2d0b5298-2daa-4812-b2d4-fa65cd354a8e.png)
Table of Contents
Why Your Presentation Opening Matters
How to start a presentation, opening slide examples, best practices for starting a presentation.
The opening of your presentation sets the tone for your entire session.
Within the first few minutes, most of your audience will decide whether they find your expertise, experience, and topic compelling enough to warrant their attention.
Think of it this way: Your opening is a preview of your presentation like a trailer is a preview of a movie. If the five-minute trailer isn’t engaging or impactful, why should the audience bother sitting through the half-hour movie?
Your opening shapes the expectations of your audience and entices them to stay engaged throughout the session.
And although you’ll still need to work to maintain their attention, getting it right from the start will spare you the challenge of re-engaging a disinterested audience right from the beginning of your presentation.
This opening statement is powerful because rather than lead with his “credentials” or “accolades,” as the audience most likely expects, he defies that expectation.
He creates a sense of intrigue that instantly piques the audience's curiosity and compels them to pay closer attention.
Infuse humor.
In Tom Thum's TedTalk titled Beatbox Brilliance , he sets a lighthearted tone by stepping on stage wearing oversized sunglasses and declaring, “My name is Tom, and I've come here today to come clean about what I do for money.”
As you might expect, this humorous approach not only elicits laughter but also surprises the audience, who are intrigued and pleasantly surprised at the tone he sets for the presentation.
Ask a question.
Graham Shaw's presentation titled “ Why people believe they can’t draw - and how to prove they can ” begins with, “Hi, I've got a question for you - how many people here would say they can draw?”
Seeing as this is a relatively lighthearted question that’s simple to answer, the audience responds immediately.
Now, what makes this a powerful opening technique is that Graham then goes on to say:
“When people say they can’t draw, I think it's more to do with beliefs rather than talent and ability. When you say you can’t draw, that’s just an illusion, and today I’d like to prove that to you.”
By immediately challenging a widely held belief among the audience and promising to debunk it during the presentation, he employs a powerful technique that keeps the audience fully engaged.
This approach makes the audience feel “invested” in the outcome of the presentation and curious as to whether he can back up his claim.
2. Tell your audience why they should be listening to you.
Getting your audience’s attention is just one part of the equation. Once you have it, you must also explain why they should “keep” listening to you. Here are some ways to do this:
Highlight relevant personal experience.
In Phil Waknell’s opening section, he talks about how he’s spent the last ten years helping conference speakers, business leaders, and entrepreneurs prepare and deliver powerful presentations .
This immediately signals to the audience that he’s someone worth listening to and positions him as a credible source of insights based on the wealth of experience he has gathered.
Highlight your expertise.
During the opening section of Dr. Lara Boyd’s presentation titled “ After watching this, your brain will not be the same ,” she says, “I’m Dr. Lara Boyd, and I’m a brain researcher here at the University of British Columbia.”
Sharing her credentials as a brain researcher is crucial to gaining her audience's trust — especially considering the technicality of her topic.
But even while creating presentations outside fields like brain research, sharing qualifications and credentials in your opening section can be a powerful technique.
This helps you position yourself as a credible authority and reinforcing your audience's confidence in your ability to deliver valuable information.
Tell your audience what’s in it for them.
In Mel Robbins’ opening section for her presentation titled “ How to stop screwing yourself over ,” she ends her introduction by saying:
“I’m here for you. I’m going to tell you everything I know in less than 18 minutes about how to get what you want.”
Although she started the section by highlighting her experiences and expertise, she went further by explicitly stating the benefits her audience can expect from her presentation.
Doing this is a great way to create a compelling reason for your audience to invest their time and attention and emphasize the value of the presentation you’re about to deliver.
3. Introduce your topic.
If your topic is relatively simple to grasp or your audience is particularly knowledgeable, introducing your topic can be as easy as “Today, I’m going to be talking to you about how we’ve built a six-figure software company in 6 months.”
However, if your topic is more complex or unfamiliar to the audience, you must do a bit more heavy lifting in your opening section.
For example, Sam Bern’s “ My philosophy for a happy life ” presentation discusses how he lives a happy life despite having Progeria disease.
However, because this condition might be unfamiliar to some audience members, he takes some time in his opening section to talk about the illness before delving into the meat of his presentation.
Similarly, if you’re presenting on a complex topic or to an audience that isn’t knowledgeable, it’s essential to consider this when crafting your opening section.
4. Leverage storytelling.
Stories can create immersive experiences that captivate the audience and convey a core message.
For example, in the opening section of Sam Bern's presentation, he tells a story about his struggles while trying to achieve his goal of becoming a drummer in his school marching band, despite living with Progeria disease.
This sets the tone for his entire presentation by conveying an inspiring message of fighting against and succeeding despite the odds.
Another great example is the opening section of Josh Kaufman’s presentation, titled “ The First 20 Hours — how to learn anything ,” where he tells a story about his experience as a time-strapped first-time parent.
This story enhances the presentation as Josh eventually shares that this experience triggered his interest in studying how to become an efficient learner.
Finally, Amy Morins’s presentation “ The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong ” is another excellent example of leveraging storytelling.
Amy starts her presentation with a thought-provoking story about observing a Facebook friend's seemingly perfect life.
She then highlights how such comparisons can lead to negative thought patterns and emphasizes the importance of cultivating mental resilience.
This relatable story not only resonates with her audience but also sets the stage for her message on building inner strength.
All these presentations are great examples that highlight how incorporating story-telling in your openings can be a powerful tool for creating memorable and impactful presentations.
Your presentation slides play a crucial role in determining the impact and effectiveness of your presentation.
In this section, you’ll find examples of 8 powerful opening slides across various use cases that not just support but enhance the presentation openings:
1. “ Blackboard is Getting an Upgrade ”
Although these are very different methods of injecting humor at the start of a presentation, they show how infusing humor can be a powerful tool for adding a touch of personality and creating a more enjoyable presentation for the audience.
4. Keep it short and sweet.
While it's important not to rush through the start of your presentation, keeping your opening concise is equally important. But remember, concise does not mean sacrificing substance; it simply means delivering information efficiently.
Essentially, you want an opening section that allows you to create a solid initial impression without losing the audience's interest.
So, how long should this opening secretion be?
Most successful presentation openings are under three minutes, and many are shorter, often clocking in at under one minute.
5. Embrace authenticity.
Contrary to popular belief, there isn't a specific personality that makes someone a better presenter. In fact, the most impactful presentations have been delivered by individuals with diverse characters.
Take, for instance, the contrasting styles of Tom Thum’s irreverent humor and animated mannerisms and Sam Bern, who adopts a relaxed and conversational approach. Despite their differences, both speakers have garnered millions of views for their talks.
So, rather than emulating or mimicking their presentations, the key takeaway is to embrace authenticity.
Allow your personality to shine through, lean on your strengths, and be human in your delivery.
Mastering the Art of Captivating Presentations
Starting a presentation is a skill that is as much an art as it is a science. Thankfully, it is also a skill that can be learned and honed.
By implementing the strategies in this guide and refining them through experience, you’ll become a master at delivering impactful presentations that command attention and leave a lasting impression.
All from the moment you step onto the stage.
![how to structure your presentation with examples Blog - Beautiful PowerPoint Presentation Template [List-Based]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/013286c0-2cc2-45f8-a6db-c71dad0835b8.png)
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![how to structure your presentation with examples How to Create the Best PowerPoint Presentations [Examples & Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/powerpoint.webp)
How to Create the Best PowerPoint Presentations [Examples & Templates]
![how to structure your presentation with examples 17 PowerPoint Presentation Tips From Pro Presenters [+ Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/powerpoint-design-tricks_7.webp)
17 PowerPoint Presentation Tips From Pro Presenters [+ Templates]
![how to structure your presentation with examples How to Write an Ecommerce Business Plan [Examples & Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/ecommerce%20business%20plan.png)
How to Write an Ecommerce Business Plan [Examples & Template]
![how to structure your presentation with examples How to Create an Infographic in Under an Hour — the 2024 Guide [+ Free Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Make-infographic-hero%20%28598%20%C3%97%20398%20px%29.jpg)
How to Create an Infographic in Under an Hour — the 2024 Guide [+ Free Templates]
![how to structure your presentation with examples 20 Great Examples of PowerPoint Presentation Design [+ Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/powerpoint-presentation-examples.webp)
20 Great Examples of PowerPoint Presentation Design [+ Templates]

Get Buyers to Do What You Want: The Power of Temptation Bundling in Sales

How to Create an Engaging 5-Minute Presentation

120 Presentation Topic Ideas Help You Hook Your Audience

The Presenter's Guide to Nailing Your Next PowerPoint
![how to structure your presentation with examples How to Create a Stunning Presentation Cover Page [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/presentation-cover-page_3.webp)
How to Create a Stunning Presentation Cover Page [+ Examples]
Download ten free PowerPoint templates for a better presentation.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Directories
Structuring your presentation
Having worked out your key message and main points, the next stage is to structure the content of your presentation. Just like other forms of academic writing, a presentation can be divided into three parts: an introduction detailing the purpose and structure of the talk; a body covering the main points; and a conclusion summarising and highlighting the significance of your talk. A template for your talk is given in the Presentations structure document.
Introduction
You may wish to capture the audience's interest and attention with a story or commentary on a current development that raises an important question / problem / dilemma. Or, you may first wish to frame your talk with brief context / background, and then swiftly transition into a concise explantion of the issue / problem or debate that your key message addresses. In either case, the next step in your introduction is to clearly state the purpose or key message of the talk, for example using the following prompts.
- 'Today I would like to talk about a highly contested issue...'
- 'This question is central to understanding...'
- 'I will make the case that...'
If necessary, limit the scope of the presentation:
- 'Although there are several theories, this talk will only focus on two ...'
- 'focuses only on the private sector as opposed to the public sector ...'
- 'Implementation, rather than policy formation, will be considered ...'
Signpost the structure/approach of the talk:
- 'My case is based on three main points. Firstly...The second point is that...This will then lead me to...Finally...'
This part of the talk provides the support for your main message. You should discuss each of your main points in a clear and logical order. As you do, be sure to explain how these points relate to each other and your key message:
- 'Turning to the next point...'
- 'Another important consideration is that...'
- 'Having examined...I'd now like to talk about...'
All necessary concepts and terms need to be defined and explained before being used. Examples can be used to effectively illustrate your points.
Signpost that you have reached the end of the talk:
- 'In conclusion...'
- 'I'd like to finish by...'
Summarise the key points covered. In the process, remind the audience of the significance of the topic, the aims of your talk and demonstrate how you have met the aims. Thank the audience for their attention and invite them to comment or ask questions.
Acknowledging others ideas
As with all academic work, if you use other people's ideas, images, data etc, then you must appropriately acknowledge it in your presentation. You do this through your spoken words or supply references on your visual aids. In text references can be kept brief to enable the audience to read. You should also include a reference list slide at the end of your presentation. See referencing resources for more information.
Working with visual aids >>
Presentations
Working with visual aids
Delivering the presentation
Reference Documents
- Simple presentation template (DOCX, 64.34 KB)
- Detailed presentation template (DOCX, 66.58 KB)
Use contact details to request an alternative file format.
- ANU Library Academic Skills
- +61 2 6125 2972

3 Great Examples of Slide Structure from McKinsey, Bain, and BCG

By Paul Moss
Consulting firms all around the world consistently rely on the pyramid principle to build high-quality presentations with proper slide structure..
Consulting firms like McKinsey, Bain, and BCG rely on proper slide structure to communicate insights to their clients. In this post, I’ll show you exactly how they use the Pyramid Principle to structure their slides, and why it makes such a big difference in the clarity of their presentations.
If you’re new to this blog, make sure you check out our other consulting slide breakdowns . And when you’re ready, take a look at our advanced PowerPoint and presentation building courses where you can learn to create presentations like a top-tier consultant.

FREE Slide Design Course
Enroll in our free 5-day email course and learn how to design slides like a McKinsey consultant.
Complete hands-on exercises , review a realistic consulting case study , and get personalized feedback from your instructor!
Plus get a free copy of our Top 50 PowerPoint Shortcuts for Consultants cheat sheet.
Learn More ➔
Success! Please check your email.
We respect your privacy. Unsubscribe anytime.
Table of Contents
What is the Pyramid Principle?
Put simply, the Pyramid Principle is just a structured way of communicating your ideas where you start with your main point and then work your way through the supporting details of that main point. It is represented pretty well with a pyramid because you start right at the top of the Pyramid and then move down to the bottom with more supporting details and data.

Let’s say I am trying to communicate the idea that LeBron James is my favorite player. I would first start with the main point, and then provide my three key arguments for why he is my favorite player. Then below that, I could provide supporting details for each key argument.
In this visualization, each idea is meant to summarize all the ideas below it. For example, the idea that Lebron James scores a lot of points summarizes the two supporting details about his career average of 27 points per game, and him being the 3rd highest all-time scorer.

This style of top-down communication works really well in a variety of settings, including email, face-to-face communication, and of course, PowerPoint presentations — which is what I’m going to focus on here.
BCG Example
The first example on our list is BCG . The slide is an excellent example of the Pyramid Principle because it is well-structured and clear. The slide title says “Melbourne seen as a cultural and creative city”, which is the main point the slide creator is trying to communicate (which is why it sits at the top of the slide in bold green letters).
Then they’ve split the main point into two key arguments: “Melbourne perceived by Australians as the country’s leading cultural city” and, “International travelers also perceive Melbourne as a creative city”. Then below each subtitle, there are four supporting points that are meant to provide support.

“Melbourne as a Global Cultural Destination” BCG
In this example the Pyramid Principle is quite easy to see. The title of the slide is the main point, the subtitles of the slide represent the key arguments, and the bullet points below that make up the supporting details and data. Each aspect of the slide fits into one of these three layers, and everything on the slide has a purpose.

By structuring the information in this way, BCG makes it easy for the audience to process the contents of the slide quickly and easily. There’s no question about what they’re trying to say, or why they’re trying to say it.
With data-heavy slides like this, it can be easy for the audience to get lost — especially if they’re trying to listen to a live speaker, read the words on the slide, and think critically about the slide’s message. Even for a smart person, this can be cognitive overload. Organizing the slide into digestible bites significantly reduces the mental load on the audience.
McKinsey Example
The next slide from McKinsey is also reasonably straightforward. It’s from a deck about high-growth emerging economies, which they refer to as “outperforming economies”.
The title of the slide says “A pro growth agenda of productivity, income, and demand propelled the outperforming economies”, and the slide itself shows the three areas that have propelled the growth for these emerging economies: productivity, growth, and demand.

“Outperformers: High-growth emerging economies and the companies that propel them” McKinsey, October 2018
There’s a few data points on the slide and a nice visual in the middle to break down the three main categories, making it pretty easy to spot the different layers in the Pyramid. So obviously, just like in our last slide, the main point will be represented by the title. That is what they want us to understand and take away from the slide first.
Then next the key argument level is also pretty clear with “higher productivity”, “boosting demand”, and “strong and inclusive growth” shown in bold text within each bracket (and also mentioned in the title). Then lastly, the bottom layer of the pyramid is represented by the various bullet points within each bracket (below the key arguments).

Altogether, it makes for a well structured slide with a clear message and clear supporting points. Despite not be organized visually in the same way as the BCG slide, the slide is very well structured and easy to understand.
Bain Example
Then lastly, we have a slide from Bain , and this one is slightly more complicated than the first two. The title says “Greater than 60% of growth in 2011 continues to come from new customers. However, share from existing customers improved.” The slide is all about the luxury goods market in China, and more specifically, they’re trying to show where the growth in the market is coming from.

“China Luxury Market Study” Bain & Company, December 2011
The BCG slide was organized neatly into the left and right sections of the slide, and in the McKinsey slide they were bolded with bullet points underneath. What’s tricky about this slide however, is that the Pyramid Principle is not clearly visible at first glance.
The title of the slide still represents the main point, and the key arguments are not emphasized visually, but logically they’re still present. The first key argument is that growth is coming from new customers, and the second key argument is that growth is coming from existing customers. Then if you look through the body of the slide, you’ll notice that everything falls into one of these two categories.

In the waterfall chart for example, notice how it is split into these two categories: new customers (as represented by the red columns), and then existing customers (as represented by the dark grey columns). Then on the right hand side of the slide, each of the bullet points can fit into one of the two categories.
For example, the first bullet says “China market is still supply driven; new store openings create new demand.” This clearly fits into the key argument about growth coming (in part) from new customers. Combined with the key argument about growth coming from existing customers, these two provide solid logical support for the main point.
So despite not having an easy visual layout like the previous two examples, this slide is well organized logically, and provides a nice structure that helps the audience clearly understand the main message, as well as the support for that main message.
You can watch a video version of this article on YouTube .
- Print Friendly
- Search entire site
- Search for a course
- Browse study areas
Analytics and Data Science
- Data Science and Innovation
- Postgraduate Research Courses
- Business Research Programs
- Undergraduate Business Programs
- Entrepreneurship
- MBA Programs
- Postgraduate Business Programs
Communication
- Animation Production
- Business Consulting and Technology Implementation
- Digital and Social Media
- Media Arts and Production
- Media Business
- Media Practice and Industry
- Music and Sound Design
- Social and Political Sciences
- Strategic Communication
- Writing and Publishing
- Postgraduate Communication Research Degrees
Design, Architecture and Building
- Architecture
- Built Environment
- DAB Research
- Public Policy and Governance
- Secondary Education
- Education (Learning and Leadership)
- Learning Design
- Postgraduate Education Research Degrees
- Primary Education
Engineering
- Civil and Environmental
- Computer Systems and Software
- Engineering Management
- Mechanical and Mechatronic
- Systems and Operations
- Telecommunications
- Postgraduate Engineering courses
- Undergraduate Engineering courses
- Sport and Exercise
- Palliative Care
- Public Health
- Nursing (Undergraduate)
- Nursing (Postgraduate)
- Health (Postgraduate)
- Research and Honours
- Health Services Management
- Child and Family Health
- Women's and Children's Health
Health (GEM)
- Coursework Degrees
- Clinical Psychology
- Genetic Counselling
- Good Manufacturing Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Speech Pathology
- Research Degrees
Information Technology
- Business Analysis and Information Systems
- Computer Science, Data Analytics/Mining
- Games, Graphics and Multimedia
- IT Management and Leadership
- Networking and Security
- Software Development and Programming
- Systems Design and Analysis
- Web and Cloud Computing
- Postgraduate IT courses
- Postgraduate IT online courses
- Undergraduate Information Technology courses
- International Studies
- Criminology
- International Relations
- Postgraduate International Studies Research Degrees
- Sustainability and Environment
- Practical Legal Training
- Commercial and Business Law
- Juris Doctor
- Legal Studies
- Master of Laws
- Intellectual Property
- Migration Law and Practice
- Overseas Qualified Lawyers
- Postgraduate Law Programs
- Postgraduate Law Research
- Undergraduate Law Programs
- Life Sciences
- Mathematical and Physical Sciences
- Postgraduate Science Programs
- Science Research Programs
- Undergraduate Science Programs
Transdisciplinary Innovation
- Creative Intelligence and Innovation
- Diploma in Innovation
- Transdisciplinary Learning
- Postgraduate Research Degree
Structure of a presentation

Supporting Study
Your go-to for support options, study resources, fun stuff and general help with being a student at UTS.
Get uni sorted now
A presentation:
- has an introduction, body and conclusion
- may include visual aids
- is usually followed by questions and discussions
- may also have a handout for the audience to take away.
Introduction
- The introduction should orient the audience to your subject and purpose. To capture interest and set up rapport, it should tell the audience what to expect.
- Be sure to carefully define the central point (or thesis) that is the basis of your talk and ensure that your supporting argument or information relates closely to it.
- If you are not proceeding from an already written assignment, it might help to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped, with the content coming out of the funnel. See the diagram below:
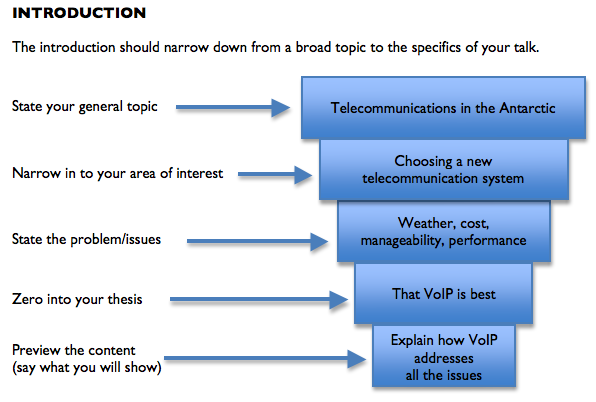
Useful language for presentations
Staging the introduction.
The body of the presentation should meet the promises of purpose and information made in the introduction.
The structure of the presentation is crucial.
Whether you organise:
- chronologically,
- by priority,
the body of your talk must proceed logically. The main points should be brought out one by one, with concise and relevant supportive evidence, statistics or examples and verbal ‘signposting’ of your progress through your argument or report.
You could present each important idea or point several times in different ways, because a listening audience needs several opportunities to fully absorb meaning.
You need to state clearly the links between your ideas and always signal when the next point is coming. If you think something is particularly important, say so and why.
If you don’t have a written assignment, it will help to think of your main points as paragraph topic sentences, each of which needs to be followed by supporting sentences and a conclusion.
Staging the body of your talk
Group presentations.
It may be that you are making a presentation as part of a group. Essentially the same information applies to group presentations as individual ones. It is important that they are logical and well structured as well as professional and meaningful. It is also doubly important that the group rehearse and practise together several times to ensure the presentation runs smoothly on the day.
Handing over to a co-presenter
Your talk may involve several speakers in your group presentation. You need to manage the handover smoothly and professionally, for example:
“I would like to conclude my discussion/report at this point and hand over to my partner/colleague XYZ who will examine/discuss/report the area/topic/perspective of…”
Similar to a written assignment, the conclusion again states your main points and what has been learned or shown but you also may raise implications inherent in the findings and offer creative recommendations.
Staging the conclusion
Back to top
UTS acknowledges the Gadigal people of the Eora Nation, the Boorooberongal people of the Dharug Nation, the Bidiagal people and the Gamaygal people, upon whose ancestral lands our university stands. We would also like to pay respect to the Elders both past and present, acknowledging them as the traditional custodians of knowledge for these lands.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there. Follow these steps: Signal that it's nearly the end of your presentation, for example, "As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…". Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation - "In this speech I wanted to compare…". 5.
Describing a detailed picture of success (or failure) - Give people a vision; something they can see, hear, taste, and touch. Asking the audience to do something straight away - Get them involved right from the start. If you do this, it's then much easier to keep them engaged and active in your cause. 4.
Length and Structure. The main part should make up about 70% of the presentation and also include a clear structure. Explain your ideas in detail and build them up logically. It should be organized chronologically, by priority or by topic. There should be a smooth transition between the individual issues.
Structure Your Presentation Like a Story. by. Nancy Duarte. October 31, 2012. PM Images/Getty Images. After studying hundreds of speeches, I've found that the most effective presenters use the ...
Apply the 10-20-30 rule. Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it! 9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule. Simplicity is key.
Hook, Meat and Payoff. This presentation structure, like The Drama, is deeply founded in the art of storytelling. While the Hero's Journey is more of a literary technique, Hook, Meat and Payoff is more like a spoken-word progression. Source. Create your own graphics with this drag-and-drop tool.
If you want your audience to stay engaged, you need to structure your ideas as a well-crafted story. Follow these three steps to clearly define your narrative before you start creating your slides ...
Here is a guide on how you can go about practicing your presentation. 5 Ways to Structure Your Presentation. The five ways include ordered, problem-solution, comparative, storytelling, and demonstrating structures. 1. Ordered Structure. The presentation follows a logical sequence starting with an introduction, main points, and then conclusions ...
The secret structure of great talks. From the "I have a dream" speech to Steve Jobs' iPhone launch, many great talks have a common structure that helps their message resonate with listeners. In this talk, presentation expert Nancy Duarte shares practical lessons on how to make a powerful call-to-action. 18:00.
The presentation structure lays out a clear and logical sequence of information, akin to the sections of a business plan that outline the company's mission, market analysis, and financial projections. This clear sequence ensures that your audience can easily follow and understand your message, maximizing the impact your speech can deliver and ...
Your audience won't notice it, because they'll be fully engaged with your central message and key points. Keep your presentation structure simple: Open with a central message. Structure your content around 3 key points. Close with a call to action. Always have a call to action, that's the business value. Keep it simple, let your content ...
Organize all the details you want to use in your presentation. After that, you can think about the key message you want to deliver. Also, knowing your audience can help you quickly engage with them. This way, you know the kind of presentation to deliver. Here are some of the purposes of presentations: For education.
Make a draft with the most important information you need to add and, thus, generate a good structure in your presentation. Get inspired by examples on the internet, but adapt them to your needs and audience. ... Step 1: Make a draft to structure your presentation. As we said before, writing a draft or script of your content will be vital to ...
Here is a quick look at how this structure looks like: The Wind Up - A summary of the current scenario. The Hurdle - The problem/issue that needs to be resolved. The Vision - A quick glimpse into the main idea on how the problem/issue can be solved. The Options - Illustrates two different options to solve the problem.
When it comes to presentation writing, a typical presentation consists of the following five parts: Introduction: Capturing the audience's attention, introducing yourself, stating the purpose, and providing an overview. Main Body: Presenting main points, evidence, examples, and arguments. Visual Aids: Using visuals to enhance understanding ...
4. Practise presentation flow. As well as practising for the ideas and what you want to say, practise how you want your presentation to flow. Think of it almost as a symphony, with high points, slow movements and crescendos. If it's important, think about how you want your audience to feel, what emotions you want them to have, and when. 5.
This helps to structure a PowerPoint presentation and create easy-to-digest slides. Use images more than words. The human brain processes visual stimuli 60 times faster than text. So, instead of writing lengthy paraphs, add photos or videos. If you think a concept is explainable through a photo, use it.
Self-introduction (Goes before or after the grabber) Tell the audience your name and credentials. For example: I'm Minh and I've been a professional presenter for 10 years. Thesis The main point or argument of your presentation. Be brief and precise, not general or vague.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
4. Keep it short and sweet. While it's important not to rush through the start of your presentation, keeping your opening concise is equally important. But remember, concise does not mean sacrificing substance; it simply means delivering information efficiently.
Try a unique presentation structure like this, or one of these seven that your audience is sure to love. ... This can be achieved by using interactive presentation examples and tools such as videos, live polls, quizzes, Q&A sessions, interactive games, and hands-on activities. By engaging with the audience in this way, presenters can create a ...
Presentation template. Having worked out your key message and main points, the next stage is to structure the content of your presentation. Just like other forms of academic writing, a presentation can be divided into three parts: an introduction detailing the purpose and structure of the talk; a body covering the main points; and a conclusion ...
The first example on our list is BCG. The slide is an excellent example of the Pyramid Principle because it is well-structured and clear. The slide title says "Melbourne seen as a cultural and creative city", which is the main point the slide creator is trying to communicate (which is why it sits at the top of the slide in bold green letters).
Body. The body of the presentation should meet the promises of purpose and information made in the introduction. The structure of the presentation is crucial. Whether you organise: chronologically, by priority, or theme. the body of your talk must proceed logically. The main points should be brought out one by one, with concise and relevant ...
Structure your interview presentation to make it appealing and impactful like the one below. Customize this template and make it your own! Edit and Download . 4. Pay Attention to Design ... Use the job interview presentation example below to craft a striking conclusion that leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Visme comes with a wide variety of charts and graphs templates you can use in your presentation.. 5. Use Presenter Notes. Visme's Presenter Studio comes with a presenter notes feature that can help you keep your slides succinct. Use it to pull out any additional text that the audience needs to understand the content.