Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .

Environmental economics
- Ecology and environmental sciences
- Bioeconomics
- Get an email alert for Environmental economics
- Get the RSS feed for Environmental economics
Showing 1 - 13 of 197
View by: Cover Page List Articles
Sort by: Recent Popular
Can urban e-commerce transformation improve economic resilience? a quasi-natural experiment from China
Xiekui Zhang, Tongsheng Tang, Erhang Mo
Studying regional low-carbon development: A case study of Sichuan Province in China
Genjin Sun, Rui Gao, [ ... ], Cuilan Li
Research on the impact of pilot free trade zones on urban green development: A case study based on the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China
Weiwei Wu, Xiaoyong Tian, Yating Liu, Weitong Huang
A time-varying analysis between economic uncertainty and tourism development in Singapore
Bui Hoang Ngoc, Canh Chi Hoang, Nguyen Huynh Mai Tram
Research on the impact of regional integration policy on carbon emissions——Taking the Yangtze River Economic Belt as an example
Yuxing Xu, Muhua Cui
Construction and application of economic resilience evaluation model for megacities
Chenhuan Kou, Donghan Meng, Xiuli Yang
Agricultural production and air pollution: An investigation on crop straw fires
Kai Zhao, Xiaohui Tian, Wangyang Lai, Shuai Xu
Nexus of green energy, financial inclusion, militarization, and environmental sustainability: A global perspective
Muhammad Ramiz Murtaza, Fan Hongzhong, [ ... ], Sinisi Crenguta Ileana
Green innovation and enterprise digital transformation: Escape from the “dilemma” of development and governance choices
Jinghuai She, Qi Zhang
Ecological niche measurement and high-quality development of "the Belt and Road" core area
Hang Zhang, Nurguli Abdusuli
Investigation on the strategy of business administration level of enterprises in the new economic environment
Zhuolin Xiao
Caribbean red snapper fishing performance indicators in Brazilian amazon shelf: Is it the beginning of the end of a fishing system?
Niedja Mescouto, Ualerson Iran Peixoto, [ ... ], Bianca Bentes
The impact of technological innovation on the green digital economy and development strategies
Yanlin Liu, Yaoguang Yang, Xiyue Zhang, Yaohui Yang
Connect with Us
- PLOS ONE on Twitter
- PLOS on Facebook

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
JavaScript appears to be disabled on this computer. Please click here to see any active alerts .
Environmental Economics Research Inventory - NCEE EERI Series
EPA's National Center for Environmental Economics (NCEE) publishes a working paper series on research in environmental economics. Paper topics include environmental management, resources and conservation, agriculture, global issues, institutional issues, and other topics. These papers are either authored by NCEE economists or produced with funding from NCEE.
The working papers are distributed for purposes of information and discussion. The opinions and findings expressed in these papers are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of EPA or NCEE. NCEE is committed to maintaining a high standard of quality in the NCEE Working Paper Series, and each paper must receive a favorable peer review prior to publication in the series.
Any questions regarding the EERI Series can be addressed to Keith Sargent ( [email protected]) .
- Environmental Economics Home
- Overview of Environmental Economics
- Current EPA Guidelines for Preparing Economic Analyses (2016)
- Environmental Economics Reports
- Current Environmental Economic Topics
- EPA Datasets
- EPA Handbook on Land Cleanup and Reuse
- Peer Review of TSD: Social Cost of Greenhouse Gas Estimates (2023)
- Retrospective Study of the Costs of EPA Regulations
Environmental Economics, Regulation, and Innovation
This paper provides a primer on the economics of environmental innovation. Our intention is not to write a pure review paper, but to also provide an up-to-date textbook treatment on the issue. Thus, we start by defining the marginal costs of both emissions and of emissions abatement. We then analyze theoretically how innovation may affect marginal abatement costs. We also cover the different modelling choices with respect to how the innovation process is represented mathematically and how different environmental policy measures could affect environmental innovation. Our theoretical propositions are all illustrated with examples from the empirical literature. A special emphasis is placed on the recent literature on directed technical change and the potential impact of government intervention in the research and development choices of private firms.
A revised version of this paper will appear in the forthcoming Handbook on Innovation and Regulation by Edward Elgar Publishing We thank Pontus Braunerhjelm, editor of the Handbook, for excellent comments and many good suggestions on earlier drafts. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
More from NBER
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .

Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Environmental economics articles within Nature Climate Change
Brief Communication | 21 May 2024
Cross-border CO 2 transport decreases public acceptance of carbon capture and storage
Carbon removal using carbon capture and storage (CCS) remains controversial. This study finds that cross-border CO 2 transport would hinder public acceptance of CCS, associated with the perceived unfairness.
- Sven Anders
- , Ulf Liebe
- & Juergen Meyerhoff
Research Highlight | 10 May 2024
Emergency loan
- Lingxiao Yan
News & Views | 17 April 2024
Going beyond averages
Global projections of the economic impacts of climate change have usually focused on rising average temperatures. Now, two studies depict more complex and gloomier scenarios by incorporating variability in temperature and precipitation.
- Matteo Coronese
Article 17 April 2024 | Open Access
Climate damage projections beyond annual temperature
Existing global economic damage assessments only focus on the impacts induced by annual temperature changes. Including variability and extremes of temperature and precipitation in climate damage projections raises global gross domestic product losses and exacerbates global disparities of economic damage.
- Paul Waidelich
- , Fulden Batibeniz
- & Sonia I. Seneviratne
Policy Brief | 28 March 2024
Global corporate tax competition leads to unintended yet non-negligible climate impacts
The worldwide trend of decreasing corporate tax in recent years has contributed to an increase in global carbon emissions, but implementing a global minimum tax rate of 15% could partially mitigate this impact. Policymakers should coordinate corporate tax policies with climate regulations.
- , Zengkai Zhang
- & Yi Lu
Perspective | 28 March 2024
Designing water markets for climate change adaptation
Global climate change will continue to reconfigure water resources and lead to more extreme events. Water markets may provide a low-cost adaptation tool. This Perspective discusses the opportunities and challenges for surface and groundwater markets to manage water resources.
- Ellen M. Bruno
- & Katrina Jessoe
Article | 28 March 2024
Global corporate tax competition challenges climate change mitigation
Countries use corporate tax cuts to attract foreign investment, which reshapes patterns of global production. This research shows that such competition will lead to higher carbon emissions and shift them to developing countries, while a global minimum tax could help alleviate these problems.
Article | 03 January 2024
The social costs of hydrofluorocarbons and the benefits from their expedited phase-down
Hydrofluorocarbons are a class of important greenhouse gases, and quantitative estimates of their social cost are still lacking. This research develops a set of direct estimates of their economic costs and shows their rapid phase-down could lead to large climate benefits.
- , Lisa Rennels
- & Bryan Parthum
Research Highlight | 03 November 2023
Disaster and capital stock
Perspective | 30 October 2023
Realizing the social value of impermanent carbon credits
Nature-based solutions are essential to avoid climate crisis, yet how best to estimate their long-run effects is unclear. Here the authors propose a new dynamic accounting method that captures the impermanence of these carbon impacts, allowing investors to make robust comparisons across projects.
- Andrew Balmford
- , Srinivasan Keshav
- & Tom Swinfield
Research Highlight | 04 August 2023
Economics of adaptation
- Bronwyn Wake
Article | 17 July 2023
Co-firing plants with retrofitted carbon capture and storage for power-sector emissions mitigation
Coal–biomass co-firing power plants with retrofitted carbon capture and storage are seen as a promising decarbonization solution for coal-dominant energy systems. Framework with spatially explicit biomass sources, plants and geological storage sites demonstrate its effectiveness in China.
- Jing-Li Fan
- , Jingying Fu
- & Xi Lu
Analysis 06 July 2023 | Open Access
The historical social cost of fossil and industrial CO 2 emissions
Historical CO 2 emissions could lead to future climate damages and harm human inclusive wealth. This analysis proposes the concept of climate wealth borrowing and quantifies the country-specific present value of climate change impacts arising from energy and industrial CO 2 emissions of the period of 1950–2018.
- Wilfried Rickels
- , Felix Meier
- & Martin Quaas
Comment | 26 June 2023
Green premiums are a challenge and an opportunity for climate policy design
Adjusting green public support programmes to green premiums can reduce public spending, yet this is challenged by uncertainty. Underfunding green technologies can delay the green transition, and overfunding them can increase transition costs. Both risks of under- and overfunding can be reduced using responsive adjustments.
- Till Köveker
- , Olga Chiappinelli
- & Xi Sun
Policy Brief | 26 June 2023
State of global land regulation inadequate to control biofuel land-use-change emissions
Under current land-use regulation, carbon dioxide emissions from biofuel production exceed those from fossil diesel combustion. Therefore, international agreements need to ensure the effective and globally comprehensive protection of natural land before modern bioenergy can effectively contribute to achieving carbon neutrality.
- Leon Merfort
- , Nico Bauer
- & Elmar Kriegler
Research Highlight | 09 May 2023
Carbon taxes and inflation
News & Views | 04 May 2023
Principles of decarbonization politics
Climate change mitigation politics is not delivering on climate targets. Recent research suggests that a general formal framework that represents the behaviour of citizens, consumers, firms and parties explains why.
- Linus Mattauch
- & Sugandha Srivastav
News & Views | 23 March 2023
Strong climate action is worth it
An immediate and rapid reduction in global emissions is required for many reasons. Integrated research supports the economic case for strong near-term climate action, even before accounting for expected negative impacts on biodiversity, health and tipping points.
- Jarmo S. Kikstra
- & Paul Waidelich
Article | 23 March 2023
New damage curves and multimodel analysis suggest lower optimal temperature
Cost-benefit analysis of climate change depends heavily on the damage function used, and it is difficult to get credible information. Multimodel comparison with newly developed bottom-up damage functions indicates the optimal temperature could be much lower than previously estimated.
- Kaj-Ivar van der Wijst
- , Francesco Bosello
- & Detlef van Vuuren
Research Highlight | 08 March 2023
Trade barriers
Research Briefing | 23 February 2023
Flood risks are insufficiently priced into housing markets but better pricing would leave some worse off
We estimate that US residential properties exposed to flood risks are overvalued by close to US$200 billion. We discuss where these properties are located, and who stands to lose the most from housing prices that better reflect climate risks.
Article 16 February 2023 | Open Access
Unpriced climate risk and the potential consequences of overvaluation in US housing markets
Natural hazards exacerbated by climate change pose serious risks to property markets in the United States. Ignoring these risks could create instability in housing values. This research shows the magnitude of unpriced flood risk and who stands to lose from housing prices that reflect climate risks.
- Jesse D. Gourevitch
- , Carolyn Kousky
- & Joakim A. Weill
Research Highlight | 08 February 2023
India’s financial system
Article | 06 February 2023
Coal-exit alliance must confront freeriding sectors to propel Paris-aligned momentum
Coal phase-out is an irreplaceable part of the overall mitigation effort and bottom-up momentum has emerged to accelerate the process. With a new approach considering political feasibility, this research shows the potential spillover risks that may undermine the sectoral actions.
- Stephen L. Bi
- & Jessica Jewell
Research Highlight | 12 January 2023
Science-based targets
Research Highlight | 01 December 2022
Directed climate innovation
Policy Brief | 24 October 2022
Climate-proofing the National Flood Insurance Program
Reforms are required to maintain a healthy and robust flood insurance market under future climate conditions for the United States. Therefore, policymakers should implement premiums that reflect flood risk and incentivize household-level risk reduction, complemented with regional flood adaptation investments.
- Lars T. de Ruig
- , Toon Haer
- & Jeroen C. J. H. Aerts
Article | 24 October 2022
How the USA can benefit from risk-based premiums combined with flood protection
The National Flood Insurance Program is a key tool for managing growing flood risk in the USA. This research shows that premiums based on local risk, rather than national averages, will generate large societal benefits, and investments in large-scale adaptation infrastructure will enhance these impacts.
Comment | 05 September 2022
Pragmatic cost–benefit analysis for infrastructure resilience
Infrastructure investment needs to account for climate change globally, yet most day-to-day projects are small and poorly served by economic assessment processes. Four simple adjustments to cost–benefit analysis practices would greatly improve decision making for future infrastructure resilience.
- Russell M. Wise
- , Tim Capon
- & Mark Stafford-Smith
Research Highlight | 01 September 2022
Ranchers and dry season
Research Highlight | 02 August 2022
Impacts on tourism demand
- Carmen Dayrell
Research Highlight | 07 July 2022
Prices with quantities
Comment | 27 June 2022
Accounting for ecosystem service values in climate policy
Ecosystem services are often omitted from climate policy owing to difficulties in estimating the economic value of climate-driven ecosystem changes. However, recent advances in data and methods can help us overcome these challenges and move towards a more comprehensive accounting of climate impacts.
- Hannah Druckenmiller
Value wild animals’ carbon services to fill the biodiversity financing gap
Incorporating the carbon services of wild animals into financial markets has the potential to benefit both climate and conservation through the development of carbon offsets that are equitable and nature positive. However, for this paradigm to be successful, many challenges regarding science, finance and law still need to be overcome.
- Fabio Berzaghi
- , Thomas Cosimano
- & Ralph Chami
Research Highlight | 08 June 2022
Governance modes
Research Briefing | 26 May 2022
Fossil-fuel stranded asset risks held by individuals in OECD countries and non-OECD governments
A model based on plausible changes in expectations of future oil and gas demand identifies the ultimate financial owners of potential stranded assets to be predominantly OECD-based individual investors (through pension funds and shareholdings) and governments of non-OECD countries.
News & Views | 31 March 2022

Assessing nuclear phase-out
Controversy remains as to whether nuclear power should be part of a sustainable future energy mix. Phasing out nuclear too rapidly could lead to substantial health damages from air pollution.
- Sebastian Rausch
Research Highlight | 09 March 2022
Adaptation funding
Research Highlight | 08 February 2022
Firm emissions reduction
Policy Brief | 29 November 2021
Protecting the poor with a carbon tax and equal per capita dividend
We find that if all countries adopt the necessary uniform global carbon tax and then return the revenues to their citizens on an equal per capita basis, it will be possible to meet a 2 °C target while also increasing wellbeing, reducing inequality and alleviating poverty. These results indicate that it is possible for a society to implement strong climate action without compromising goals for equity and development.
- Mark Budolfson
- , Francis Dennig
- & Stéphane Zuber
Analysis | 29 November 2021
Climate action with revenue recycling has benefits for poverty, inequality and well-being
Climate policy analyses often ignore the possibility of progressive redistribution of carbon tax revenues and assume that mitigation cost will burden the poor in the short term. Integrated Assessment Model (IAM) estimation suggests such redistribution could reduce inequality, alleviate poverty and increase well-being globally.
News & Views | 22 November 2021
Risk transfers support adaptation
Finding effective ways to support rural communities in adapting to climate change is critical for building climate-resilient societies. Now research shows the potential of risk-transfer policies for improving adaptation and securing the livelihoods of smallholder farmers.
- Roman Hoffmann
Policy Brief | 28 October 2021
Freely available deforestation alerts can reduce emissions from land-use change
Subscriptions to a free, weekly deforestation alert system available on the simple interface Global Forest Watch reduced deforestation in the protected areas and logging concessions of tropical African forests. This suggests that freely available near-real-time forest monitoring systems can help reduce emissions from deforestation if they are integrated with forest policies.
- Fanny Moffette
- , Jennifer Alix-Garcia
- & Amy H. Pickens
To achieve deep cuts in US emissions, state-driven policy is only slightly more expensive than nationally uniform policy
Using a multi-sector model of human and natural systems, we find that the nationwide cost from state-varying climate policy in the United States is only one-tenth higher than that of nationally uniform policy. The benefits of state-led action — leadership, experimentation and the practical reality that states implement policy more reliably than the federal government — do not necessarily come with a high economic cost.
- , Gokul Iyer
- & David G. Victor
News & Views | 25 October 2021
The hidden benefits of high-speed rail
Improvements in public transport are often regarded as essential to combat climate change. A study investigating the Chinese high-speed rail system suggests that these benefits could operate through channels other than those that one might expect.
- Armin Schmutzler
Article | 25 October 2021
Impact of high-speed rail on road traffic and greenhouse gas emissions
Intercity high-speed rail (HSR) can have large climate benefits with its high energy efficiency. This study explores the substitution effects of HSR on road traffic in China, which can be translated to an annual reduction of 14.76 million tons of CO 2 -equivalent emissions.
- & Mandi Xu
Article | 07 October 2021
Trade-linked shipping CO 2 emissions
More than 80% of trade by volume occurs via maritime shipping, with growing pressure to reduce associated GHG emissions. The top 10 single-direction trade pairs account for nearly 20% of emissions; optimizing trade patterns could reduce emissions by 38% of current totals.
- Xiao-Tong Wang
- & Ke-Bin He
News & Views | 30 September 2021
Do climate dynamics matter for economics?
Economic models of climate change are the basis for climate policy design. However, incorrect representation of physical dynamics in these models could lead to biased advice.
- Richard S. J. Tol
Research Highlight | 01 September 2021
Information Services
Article | 23 August 2021
The surprisingly inexpensive cost of state-driven emission control strategies
The nationwide cost of cutting emissions can be affected by local policies. This study considers the differences across the US states, with integrated assessment model results showing that varying state policies only increases nationwide costs by about 10%.
Browse broader subjects
- Environmental social sciences
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Environmental Economics Research Paper Topics

This comprehensive guide to environmental economics research paper topics is designed to assist students and researchers in selecting a subject for their study. Environmental economics, a field at the intersection of economics and environmental science, offers a wide array of topics that explore the economic aspects of environmental issues. From policy and natural resource economics to sustainability and climate change, this guide provides a diverse list of topics to inspire your research journey. Additionally, it offers expert advice on choosing a topic and writing a research paper in environmental economics. The guide also introduces iResearchNet’s writing services, which offer custom research papers on any topic in environmental economics, ensuring high-quality, in-depth research, and timely delivery.
Environmental economics is a fascinating field that combines the principles of economics with the study of environmental issues. It seeks to understand the economic impacts of environmental policies and to develop solutions that can balance economic growth with environmental sustainability. Here is a comprehensive list of environmental economics research paper topics that you can explore:
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Environmental Policies and Economic Growth
- The impact of environmental regulations on economic growth.
- The role of green taxes in promoting sustainable development.
- The economic benefits of renewable energy policies.
- The cost-effectiveness of carbon pricing mechanisms.
- The impact of environmental policies on job creation.
- The role of government subsidies in promoting green technologies.
- The economic implications of the Paris Agreement.
- The effect of environmental policies on industrial competitiveness.
- The role of environmental policies in shaping market behavior.
- The economic feasibility of transitioning to a circular economy.
Natural Resource Economics
- The economic valuation of natural resources.
- The role of property rights in natural resource management.
- The economic implications of overfishing.
- The impact of mineral extraction on local economies.
- The economics of water scarcity.
- The role of economic incentives in promoting sustainable forestry.
- The impact of climate change on agricultural economics.
- The economic costs and benefits of biodiversity conservation.
- The role of natural resources in economic development.
- The economic implications of soil degradation.
Environmental Cost-Benefit Analysis
- The use of cost-benefit analysis in environmental decision making.
- The challenges of monetizing environmental benefits.
- The role of discount rates in environmental cost-benefit analysis.
- The use of cost-effectiveness analysis in environmental policy.
- The limitations of cost-benefit analysis in addressing environmental justice issues.
- The role of cost-benefit analysis in climate change mitigation strategies.
- The use of multi-criteria analysis in environmental decision making.
- The role of risk analysis in environmental cost-benefit analysis.
- The impact of uncertainty on environmental cost-benefit analysis.
- The use of cost-benefit analysis in ecosystem service valuation.
Economics of Climate Change
- The economic impacts of climate change.
- The role of carbon markets in mitigating climate change.
- The economic feasibility of climate change adaptation strategies.
- The impact of climate change on global trade.
- The role of climate finance in promoting low-carbon development.
- The economic implications of sea level rise.
- The impact of climate change on agricultural productivity.
- The role of economic modeling in climate change projections.
- The economic costs and benefits of geoengineering.
- The impact of climate change on energy economics.
Environmental Justice and Economics
- The economic dimensions of environmental justice.
- The role of economic inequality in environmental degradation.
- The impact of environmental policies on marginalized communities.
- The role of green jobs in promoting environmental justice.
- The economic implications of environmental racism.
- The impact of environmental displacement on economic wellbeing.
- The role of economic empowerment in promoting environmental justice.
- The economic costs of environmental health disparities.
- The impact of environmental gentrification on urban economies.
- The role of economic policy in addressing environmental justice issues.
Green Economy and Sustainable Development
- The economic benefits of transitioning to a green economy.
- The role of green jobs in sustainable development.
- The economic implications of sustainable consumption and production.
- The impact of green growth strategies on economic competitiveness.
- The role of green finance in promoting sustainable development.
- The economic implications of the circular economy.
- The impact of green innovation on economic growth.
- The role of sustainable tourism in the green economy.
- The economic feasibility of green infrastructure projects.
Environmental Economics and Policy
- The economic impacts of environmental regulations.
- The role of economic incentives in environmental policy.
- The impact of environmental taxes on economic behavior.
- The role of trade policy in environmental protection.
- The economic implications of the polluter pays principle.
- The impact of environmental subsidies on market behavior.
- The role of economic instruments in biodiversity conservation.
- The economic feasibility of ecosystem service payments.
- The impact of environmental policy on economic competitiveness.
- The role of economic analysis in environmental policy making.
Economics of Energy and Environment
- The economic impacts of renewable energy policies.
- The role of energy economics in environmental sustainability.
- The impact of fossil fuel subsidies on the environment.
- The role of energy efficiency in economic growth.
- The economic implications of the energy transition.
- The impact of energy prices on environmental quality.
- The role of energy policy in climate change mitigation.
- The economic feasibility of carbon capture and storage.
- The impact of energy security on environmental sustainability.
- The role of energy markets in environmental protection.
Environmental Economics and Agriculture
- The economic impacts of agricultural pollution.
- The role of agricultural economics in environmental sustainability.
- The impact of agricultural subsidies on the environment.
- The role of sustainable agriculture in economic development.
- The economic implications of organic farming.
- The impact of agricultural trade on the environment.
- The role of agricultural policy in environmental protection.
- The economic feasibility of agroecology.
- The impact of agricultural innovation on environmental sustainability.
- The role of agricultural markets in environmental protection.
Environmental Economics and Urbanization
- The economic impacts of urban pollution.
- The role of urban economics in environmental sustainability.
- The impact of urban sprawl on the environment.
- The role of sustainable urban development in economic growth.
- The economic implications of urban green spaces.
- The impact of urban transportation on environmental quality.
- The role of urban planning in environmental protection.
- The economic feasibility of green buildings.
- The impact of urbanization on biodiversity.
- The role of urban infrastructure in environmental protection.
These environmental economics research paper topics cover a wide range of issues in the field of environmental economics, from policy and law to energy and agriculture. They provide a starting point for your research and can be tailored to fit your specific interests and the requirements of your assignment. Remember, choosing the right topic is the first step in writing a successful research paper. So take your time, explore these topics, and choose one that you find interesting and meaningful.
Environmental Economics Research Guide
Environmental economics is a vital field that examines the interplay between economic systems and the environment. As our world faces increasingly complex environmental challenges, understanding the economic dimensions of these issues becomes crucial for developing effective solutions. This page aims to provide a comprehensive resource for students studying environmental science and seeking research paper topics in the field of environmental economics.
Environmental economics focuses on analyzing the costs and benefits associated with environmental policies, natural resource management, pollution control, and sustainable development. It explores the ways in which economic activities impact the environment and how environmental factors influence economic decision-making. By studying environmental economics, students gain insights into the intricate relationship between human activities and the natural world, enabling them to propose informed strategies for sustainable development.
For students pursuing a degree in environmental science, conducting research in environmental economics offers a unique perspective on addressing environmental challenges. It provides a framework to assess the economic implications of environmental issues and develop innovative solutions that balance ecological sustainability and economic prosperity. Research papers in environmental economics not only contribute to the academic discourse but also equip students with the knowledge and skills necessary to effect positive change in their future careers.
The purpose of this page is to serve as a valuable resource for students seeking inspiration and guidance for their research papers in environmental economics. We aim to provide a curated list of diverse research paper topics, expert advice on topic selection, and practical tips on writing an effective environmental economics research paper. Additionally, we introduce the writing services offered by iResearchNet, providing students the opportunity to order custom research papers tailored to their specific needs.
By exploring the topics and advice presented on this page, students will be equipped with the tools and insights necessary to delve into the fascinating field of environmental economics. Whether you are interested in studying the economic impact of climate change, analyzing environmental policies, or exploring sustainable development strategies, this page will help you navigate the vast landscape of environmental economics research.
We invite you to embark on this exciting journey of exploring environmental economics research paper topics and discovering the potential to make a meaningful impact on the environmental challenges of our time.
Choosing an Environmental Economics Topic
Choosing the right research paper topic is a crucial step in the process of writing an impactful and successful environmental economics research paper. With the vast scope of environmental economics, it is essential to select a topic that is not only interesting but also relevant, feasible, and has the potential to contribute to the field. Here are ten expert tips to help you navigate the process of choosing environmental economics research paper topics:
- Identify your Interests : Start by identifying your personal interests within the field of environmental economics. Think about the environmental issues that resonate with you, such as climate change, natural resource management, pollution control, or sustainable development. Choosing a topic that genuinely interests you will make the research process more enjoyable and motivating.
- Stay Updated with Current Issues : Keep yourself informed about the latest environmental issues and developments in environmental economics. Follow reputable news sources, academic journals, and research publications to stay abreast of emerging trends, debates, and areas of active research. This will enable you to select topics that are timely and relevant.
- Conduct Preliminary Research : Before finalizing a research topic, conduct preliminary research to gain a broad understanding of the existing literature in the field. Review academic papers, books, and reports related to environmental economics to identify gaps in knowledge and potential research areas that warrant further exploration.
- Narrow Down the Scope : Environmental economics is a vast field, and it is essential to narrow down the scope of your research topic. Focus on a specific aspect, problem, or geographic region that you can realistically address within the scope of your research paper. Narrowing down the topic will allow you to delve deeper and provide a more comprehensive analysis.
- Consult with Your Advisor : Seek guidance from your academic advisor or faculty members specializing in environmental economics. They can provide valuable insights, suggest potential research topics, and offer guidance on selecting a topic that aligns with your academic goals and interests.
- Consider the Research Gap : Look for areas in environmental economics where there is a research gap or limited literature available. Identifying gaps in the existing body of knowledge will allow you to contribute to the field by conducting original research and generating new insights.
- Balance Practicality and Significance : When choosing a research topic, consider the practicality of data collection and analysis. Ensure that you have access to relevant data sources and research methods required to investigate the topic effectively. Additionally, evaluate the potential significance of the research topic in addressing real-world environmental challenges.
- Engage in Discussions and Seminars : Participate in discussions, seminars, and conferences related to environmental economics. Engaging with peers and experts in the field will expose you to diverse perspectives and help you discover potential research topics and areas of interest that you may not have considered before.
- Seek Interdisciplinary Approaches : Environmental economics often intersects with other disciplines such as ecology, policy studies, sociology, and public health. Consider incorporating interdisciplinary approaches into your research topic to explore the interconnectedness between environmental and social factors, which can provide a more holistic understanding of the issues at hand.
- Reflect on Practical Applications : Reflect on the practical applications of your research topic. Consider how your findings and analysis can contribute to policy development, inform decision-making processes, or propose sustainable solutions. Topics that have practical implications and can make a positive impact in real-world contexts tend to be more compelling and meaningful.
By following these expert tips, you will be well-equipped to choose a compelling and relevant environmental economics research paper topic that aligns with your interests, addresses knowledge gaps, and has the potential to contribute to the field. Remember to consult with your academic advisor throughout the process to ensure that your chosen topic aligns with the requirements and objectives of your research paper.
How to Write an Environmental Economics Research Paper
Writing an environmental economics research paper requires a systematic and well-structured approach to effectively communicate your research findings and contribute to the field. Here are ten essential tips to help you navigate the process of writing an impactful environmental economics research paper:
- Understand the Research Question : Start by clearly understanding the research question or objective of your paper. Identify the specific problem or issue you aim to address and formulate a concise and focused research question. This will serve as the guiding principle throughout your research and writing process.
- Conduct In-depth Literature Review : Before delving into your own research, conduct a comprehensive literature review to familiarize yourself with the existing body of knowledge. Identify key theories, concepts, methodologies, and empirical studies relevant to your research question. This will help you establish the context for your research and identify research gaps to address.
- Develop a Solid Research Methodology : Choose an appropriate research methodology that aligns with your research question and objectives. Whether it’s quantitative, qualitative, or a combination of both, ensure that your chosen methodology allows you to collect and analyze data effectively to answer your research question.
- Collect and Analyze Data : Depending on your research question, collect relevant data from credible sources. This may include primary data collected through surveys, interviews, or experiments, or secondary data from academic journals, government reports, or databases. Analyze the data using appropriate statistical or qualitative analysis techniques to derive meaningful insights.
- Organize Your Paper : Structure your research paper in a logical and coherent manner. Start with an introduction that provides background information, states the research question, and outlines the paper’s structure. Follow this with a literature review, methodology section, presentation and analysis of findings, discussion of results, and a conclusion that summarizes your key findings and their implications.
- Provide Clear and Concise Writing : Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and accessible to your target audience. Use plain language and avoid unnecessary jargon. Clearly articulate your arguments, provide sufficient evidence, and use appropriate citations to support your claims. Use subheadings, bullet points, and paragraph breaks to improve readability.
- Support Your Arguments with Evidence : Back up your claims and arguments with reliable evidence. Use empirical data, case studies, academic research, and real-world examples to support your analysis. Be critical of your sources and ensure they are reputable and peer-reviewed.
- Engage in Critical Analysis : Demonstrate critical thinking skills by analyzing and interpreting your findings in the context of existing literature and theories. Identify strengths, limitations, and potential biases in your research. Discuss alternative explanations and consider counterarguments to strengthen the validity of your research.
- Discuss Policy Implications : Environmental economics research often has policy implications. Discuss the implications of your research findings for environmental policies, regulations, or economic decision-making. Highlight the potential benefits and challenges of implementing your research outcomes in real-world scenarios.
- Revise and Edit : Revise and edit your research paper thoroughly before final submission. Pay attention to clarity, grammar, spelling, and formatting. Read your paper multiple times, seek feedback from peers or advisors, and make necessary revisions to improve the overall quality and coherence of your work.
By following these tips, you can effectively write an environmental economics research paper that is well-structured, evidence-based, and contributes to the understanding of environmental issues from an economic perspective. Remember to maintain a systematic approach, stay focused on your research question, and continuously refine your writing through feedback and revisions.
Custom Research Paper Writing Services
When it comes to writing a custom environmental economics research paper, iResearchNet is here to assist you. Our writing services offer a range of features that ensure the highest quality and professionalism in delivering customized research papers. By ordering a custom paper from us, you can benefit from the following:
- Expert Degree-Holding Writers : We have a team of experienced writers with advanced degrees in environmental economics and related fields. They possess the expertise and knowledge to write high-quality research papers tailored to your specific requirements.
- Custom Written Works : Each research paper we deliver is 100% original and tailored to your unique needs. Our writers follow your instructions and conduct thorough research to provide you with a custom-written paper that meets your academic standards.
- In-depth Research : Our writers are skilled in conducting in-depth research on environmental economics topics. They access reputable academic sources, scholarly journals, and up-to-date research databases to ensure your paper is well-informed and based on the latest findings in the field.
- Custom Formatting : We understand the importance of adhering to specific formatting styles. Whether it’s APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, Harvard, or any other style, we ensure that your research paper is formatted correctly, including citations, references, and bibliography.
- Top Quality : Our commitment to quality is unwavering. We strive to deliver research papers that meet the highest standards of excellence. Our rigorous quality control measures ensure that your paper is well-written, well-structured, and free from errors.
- Customized Solutions : We recognize that every research paper is unique. Our writers work closely with you to understand your specific requirements and tailor the paper accordingly. We take into account your research question, objectives, and any specific guidelines provided by your institution.
- Flexible Pricing : We offer competitive and flexible pricing options to accommodate your budget. Our pricing structure considers factors such as the complexity of the research paper, deadline, and additional services required. We strive to provide affordable solutions without compromising on quality.
- Short Deadlines : We understand that deadlines can be tight. That’s why we offer short deadlines of up to 3 hours for urgent research paper requests. Our dedicated team works efficiently to ensure timely delivery, even for tight schedules.
- Timely Delivery : We value your time and strive to deliver your research paper within the agreed-upon deadline. Our writers and support team work collaboratively to ensure your paper is completed and delivered to you on time.
- 24/7 Support : Our customer support team is available round-the-clock to assist you with any queries or concerns you may have. Whether it’s assistance with placing an order, tracking your paper’s progress, or addressing any post-delivery concerns, we are here to support you.
- Absolute Privacy : We prioritize the privacy and confidentiality of our customers. All personal information and details of your order are treated with the utmost confidentiality. We never share your information with third parties, and all transactions are secured.
- Easy Order Tracking : We provide a user-friendly platform that allows you to easily track the progress of your order. You can communicate directly with your assigned writer, monitor the writing process, and receive updates on the status of your paper.
- Money Back Guarantee : We stand behind the quality of our work. If, for any reason, you are not satisfied with the final research paper, we offer a money back guarantee. Your satisfaction is our top priority, and we are committed to ensuring your academic success.
By choosing our writing services, you can rest assured that your environmental economics research paper will be handled by professionals who are dedicated to delivering customized and high-quality work. Our extensive features and commitment to excellence make us the ideal choice for students seeking reliable and professional assistance in their research paper endeavors.
Unlock Your Academic Success with iResearchNet!
Are you ready to take the next step towards achieving your academic goals in environmental economics? Don’t let the challenges of writing a research paper hold you back. Take advantage of our professional writing services at iResearchNet and order your custom environmental economics research paper today.
Why settle for generic research papers when you can have a paper tailored specifically to your requirements? Our team of expert degree-holding writers is ready to assist you in crafting a research paper that showcases your understanding of environmental economics concepts and explores your chosen topic in-depth. Whether you need a paper on pollution pricing mechanisms, environmental policy analysis, or sustainable resource management, we have the expertise to deliver outstanding results.
With our user-friendly platform and 24/7 support, the process of ordering your custom research paper is simple and hassle-free. Just provide us with the details of your assignment, including the topic, formatting requirements, and any specific guidelines. Our writers will meticulously research and develop your paper, ensuring that it meets your academic standards and reflects your unique perspective.
Take the leap and order your custom environmental economics research paper today. Experience the benefits of working with a trusted writing service and unlock your full potential in the field of environmental science. Let us assist you in making a significant impact through your research and contribute to the sustainable future of our planet.
Order now and embark on a rewarding academic journey with iResearchNet!
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
Environmental Economics
- Most Cited Papers
- Most Downloaded Papers
- Newest Papers
- Save to Library
- Last »
- Ecological Economics Follow Following
- Environmental Policy and Governance Follow Following
- Environmental Studies Follow Following
- Climate Change Follow Following
- Environmental Sustainability Follow Following
- Environmental Science Follow Following
- Economics Follow Following
- Energy Economics Follow Following
- Environmental Law Follow Following
- Resource Economics Follow Following
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- Academia.edu Publishing
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Faculty and Staff
- Faculty Focus
- Honors and Awards
- Student Spotlight
- Scholarships and Awards
- Enterprise Budgets
- Economic Perspective
Wu and Collaborators Receive AAEA Quality of Research Discovery Honorable Mention

ARE Department Head Junjie Wu was recently honored along with collaborators Kathleen Segerson and Chunhua Wang with the Agricultural & Applied Economics Association’s Quality of Research Discovery Award Honorable Mention for their 2023 paper, “ Is Environmental Regulation the Answer to Pollution Problems in Urbanizing Economies? ” published in the Journal of Environmental Economics and Management .

Severe air pollution in major cities of developing countries is a critical environmental issue, with almost all of the top 25 most polluted cities in the world located in these nations, and China and India accounting for most of them. Despite many implementing significant policy measures, their air pollution problems persist. In their paper, Wu, Segerson and Wang investigate why environmental quality improvements are challenging in emerging economies and seek to inform better policy design.
The paper introduces a model of an economy affected by pollution and agglomeration economies to evaluate the effectiveness of environmental policies. It compares uniform emission standards or taxes applied across all regions with differentiated standards that are stricter in more polluted areas. The analysis considers scenarios with fixed firm locations and those where firms can relocate based on profit, cost of living and environmental quality.
A key finding is that the interaction between environmental regulation and agglomeration economies contributes to persistent pollution in emerging economies. While regulations may be effective in the short term, firm relocation can undermine their effectiveness, potentially worsening pollution. This occurs because cleaner technologies lower agglomeration costs, leading to higher concentrations of economic activity that can offset the benefits of regulation, resulting in “environmental stagnation.”
The paper further explores this dynamic through empirical analysis of water pollution regulation in China, providing evidence that the impact of such regulation is influenced by agglomeration economies. It demonstrates that polluting firms incur lower abatement costs in regions with larger agglomeration economies, emphasizing the need to consider these factors when designing environmental policies. The findings offer insights into the challenges of achieving environmental improvements in developing countries and suggest crucial policy implications.
- News and Events
- environmental economics
More From Agricultural and Resource Economics

2 ARE Faculty Elected AAEA Section Chairs

Walden to Write New Book on Post-COVID NC Economy

Treme Receives CALS Nomination for Award for Excellence in Teaching
College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences
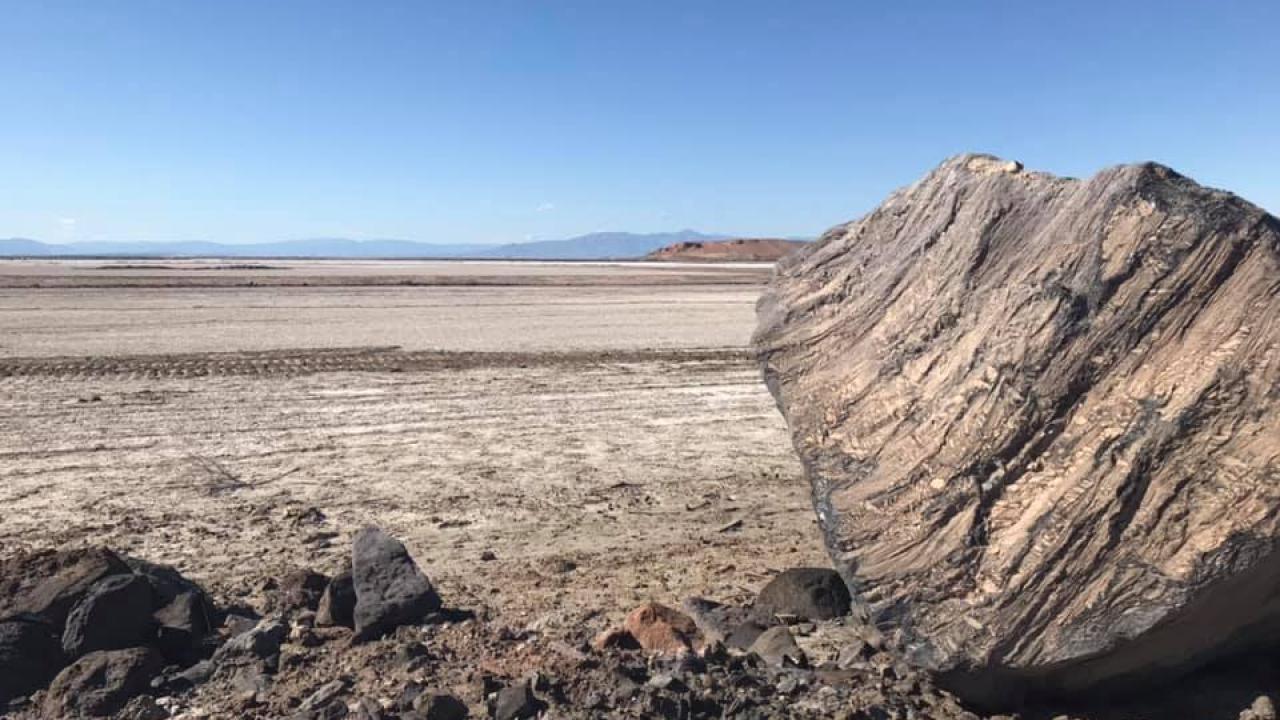

A Drying Salton Sea Pollutes Neighboring Communities
Research finds higher particulate pollution after water diverted to san diego.
- by Emily C. Dooley
- May 29, 2024
When desert winds stir up dust from the Salton Sea’s exposed lakebed, nearby communities suffer from increased air pollution. The deterioration coincides with reduced flows into California’s largest lake, a new research paper in the American Journal of Agricultural Economics finds.
Disadvantaged communities have been affected more than others in the areas near the Salton Sea, which has been shrinking for years, said the paper’s co-leading author Eric Edwards. He is an assistant professor of agricultural economics at University of California, Davis, who did the research while at North Carolina State University.
“We have a dusty area, and any time there is wind, it’s going to pick up dust and move it around,” Edwards said. “We think this new dust is increasing the amount of pollution faced by disadvantaged communities in the region surrounding the lake.”
An overflowing river
The Salton Sea formed in 1905 after the Colorado River overflowed its banks and the floodwaters settled into what was known as the Salton Sink. It was primarily fed by water runoff from agricultural operations for almost a century. As the southern part of California struggled to meet growing water demand, the Imperial Irrigation District agreed to send water to San Diego for urban use.
Imperial, which supplies water to vast desert farms as well as seven towns and two special districts, is the largest user of Colorado River water. The agreement with San Diego required agricultural water users to increase efficiency and reduce their water consumption, which reduced water running into the Salton Sea, Edwards said.
The reductions increased the lake’s salt content, which is higher than in the Pacific Ocean . This also harmed wildlife habitats and created localized air pollution. The area is the subject of many environmental restoration projects.
Studying implications
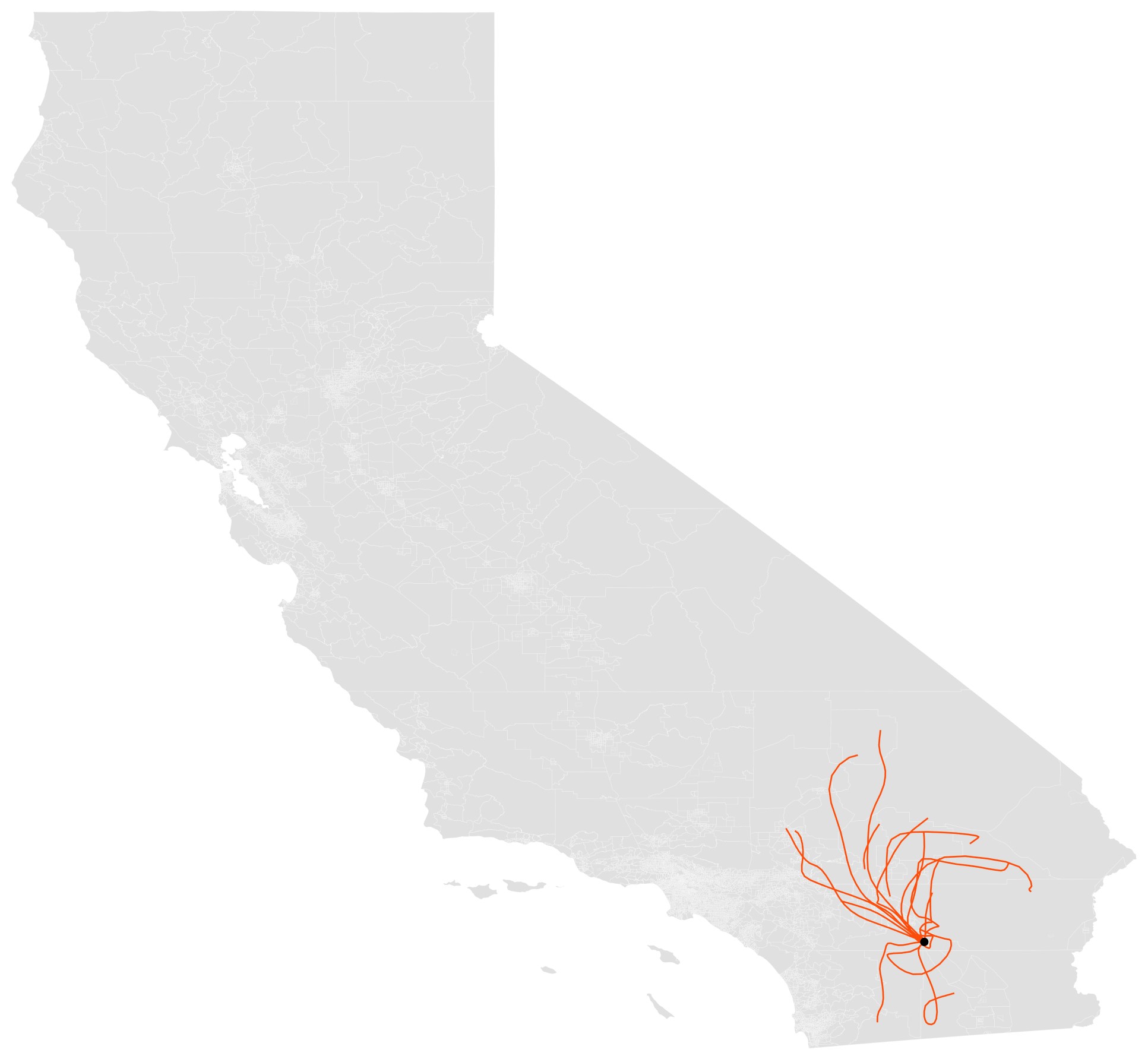
Edwards and others used a particle transport model to study the effects of changing water diversions on particulate pollution.
They found that the paths of fine particulate matter – which can cause asthma, heart and respiratory issues when inhaled – were associated with higher air pollution readings after Imperial began reducing runoff water to the Salton Sea around 2011 in order to transfer it to San Diego, a practice that continues today.
Researchers modeled lakebed exposure by dividing the lake’s shoreline into 1-square-kilometer grids and collected air pollution data daily for over 20 years, from 1998 to 2018. They added data about the exposed lakebed, or playa, and used a sophisticated physics model called HYSPLIT to factor in wind levels and particle size to track the movement of dust over time. State health screening information available by ZIP Code added more to the story by pinpointing disadvantaged areas, asthma rates and other vulnerabilities.
Lake levels were higher in 1998 before the transfers, so the change was not evident until later years, when the lakebed became more exposed.
“We show that during that post-2011, there is an increase in particles going through disadvantaged communities relative to non-disadvantaged communities, which are farther away from the sea,” Edwards said.
In the paper, the pollution paths are depicted on a map of the state. The Salton Sea is marked with a black dot, and red lines radiate from there to distances of 100 miles or more.
“From every exposed grid cell you have these paths predicting where the particles are going based on physics,” Edwards said. “That’s the path of emissions.”
Prior research suggests that dust particles from newly exposed playa are more susceptible to wind erosion.
“There’s lots of evidence that playa is particularly emissive in terms of dust,” Edwards said. “If it’s dry, those particles get picked up readily by the wind and create dust—and at rates higher than areas that have been exposed to the wind over long periods of time.”
Informing decision makers
Edwards said policymakers and regulators should consider the health and environmental impacts of water diversions in their decision making.
“The drying up of the Salton Sea has serious health consequences that have generally fallen on more disadvantaged populations, who may not be well equipped to advocate for policies that improve their health,” he said. “Policymakers need to think about how to facilitate the movement of water via market transactions, which are essential, while also accounting for potential negative effects on the environment.”
Ryan Abman from San Diego State University and Dana Hernandez-Cortes from Arizona State University contributed equally with Edwards to the research and journal article.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture supported this research.
Media Resources
- Eric Edwards, Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics, [email protected]
- Emily C. Dooley, College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, 530-650-6807, [email protected]
- Kat Kerlin, UC Davis News and Media Relations, 530-750-9195, [email protected]
- Susanne Clara Bard, San Diego State University Strategic Communications and Public Affairs, 202-441-8976, [email protected]
Primary Category
Environmental and economic analysis of the transformation of paper mill sludge treatment technologies in China
- Research Article
- Published: 27 May 2024
Cite this article

- Yanfei Lin 1 ,
- Guoxia Wei 2 ,
- Hanqiao Liu 1 ,
- Yuwen Zhu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2759-0656 1 ,
- Qianlong Han 1 ,
- Yunzhen Yang 1 &
- Yi Lian 3
83 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Paper mill sludge (PMS) is featured with a high content of cellulose and hemicellulose, and using its characteristics to make paperboard can achieve a high-value utilization of PMS, which has attracted growing interest. In this study, currently prevalent landfill, incineration technologies (generating heat and electricity by incineration), and three paperboard technologies (medium density fiberboard, pulp board, and corrugated paper) were evaluated and compared via life cycle assessment (LCA) and life cycle costing (LCC) methods. LCA results show that the PMS-to-pulp board outperforms others with an energy conservation and emission reduction (ECER) value of − 2.86 × 10 −8 , while the landfill exhibits the highest overall environmental impact with an ECER value of 4.80 × 10 −9 . LCC results reveal that the PMS-to-pulp board delivers the highest economic profit with $257.357, while the landfill is the lowest with $ − 35.63. The PMS paperboard technologies are more economically friendly than the incineration technologies due to additional electricity/steam consumption during the PMS pre-drying process in incineration. In addition, different scenarios were set up to explore national GHG emission reduction potential by increasing paperboard technologies application rate and reducing the proportion of landfill and incineration. The scenario analysis suggests that replacing 90% of landfill and incineration ratio with PMS paperboard technologies could tremendously improve the overall emission reduction performance with − 9.08 × 10 10 kg CO 2 eq. This result indicates that the PMS treatment technology transformation has a significant favorable impact on the achievement of the “carbon neutrality” target.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Similar content being viewed by others
Removal of toilet paper fibers from residential wastewater: a life cycle assessment
Municipal sewage sludge energetic conversion as a tool for environmental sustainability: production of innovative biofuels and biochar
Valorization of Primary Sludge and Biosludge from the Pulp Mill Industry in Uruguay Through Hydrothermal Carbonization
Data availability.
The data that supports the findings of this study are available in the Supplementary Information.
Abbreviations
- Paper mill sludge
Medium density fiberboard
- Life cycle assessment
- Life cycle costing
Life cycle inventory
Chinese life cycle database
Energy conservation and emission reduction
Greenhouse gas
Bergamo J, Rossi E, Maffi JM et al (2020) Preparation and characterization of nanoencapsulated synthetic soybean oil derivative-an abundant and environmentally friendly phase change material-heat transfer analysis and applications. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 41:100794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2020.100794
Article Google Scholar
Chen G, Wang X, Li J et al (2019) Environmental, energy, and economic analysis of integrated treatment of municipal solid waste and sewage sludge: a case study in China. Sci Total Environ 647:1433–1443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.104
Article CAS Google Scholar
Cheng S, Long J, Evans B et al (2022) Non-negligible greenhouse gas emissions from non-sewered sanitation systems: a meta-analysis. Environ Res 212:113468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113468
China Statistical Yearbook 2021. https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/2021/indexeh.htm . Accessed 7 Apr 2024a
Cui RY, Hultman N, Cui D et al (2021) A plant-by-plant strategy for high-ambition coal power phaseout in China. Nat Commun 12:1468. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21786-0
De Azevedo ARG, Alexandre J, Xavier GDC, Pedroti LG (2018) Recycling paper industry effluent sludge for use in mortars: a sustainability perspective. J Clean Prod 192:335–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.011
De Azevedo ARG, Alexandre J, Marvila MT et al (2020) Technological and environmental comparative of the processing of primary sludge waste from paper industry for mortar. J Clean Prod 249:119336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119336
Faubert P, Barnabé S, Bouchard S et al (2016) Pulp and paper mill sludge management practices: what are the challenges to assess the impacts on greenhouse gas emissions? Resour Conserv Recycl 108:107–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.01.007
Furlani E, Maschio S (2018) Glazed tiles produced using paper sludge, glass cullet and a natural red clay: an experimental study. Int J Environ Stud 75:903–912. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207233.2018.1470404
Gievers F, Walz M, Loewe K et al (2022) Anaerobic co-digestion of paper sludge: feasibility of additional methane generation in mechanical–biological treatment plants. Waste Manage 144:502–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2022.04.016
Goel G, Kalamdhad AS (2017) An investigation on use of paper mill sludge in brick manufacturing. Constr Build Mater 148:334–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.05.087
Gong Y, Liu F, Liu H et al (2022) Environment–energy–economy analysis and related technical transition strategies for spent activated carbon regeneration in China. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 10:11512–11523. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c02855
Guo X, Yao Y, Zhao H et al (2021) Environmental impacts of functional fillers in polylactide (PLA)-based bottles using life cycle assessment methodology. Sci Total Environ 788:147852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147852
Guo X, Yao S, Wang Q et al (2022) The impact of packaging recyclable ability on environment: case and scenario analysis of polypropylene express boxes and corrugated cartons. Sci Total Environ 822:153650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153650
Han Q, Zhao H, Wei G et al (2024) Sustainable papermaking in China: assessing provincial economic and environmental performance of pulping technologies. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 12:4517–4529. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.3c07611
Havukainen J, Saud A, Astrup TF et al (2022) Environmental performance of dewatered sewage sludge digestate utilization based on life cycle assessment. Waste Manage 137:210–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.11.005
Hong J, Xu C, Hong J et al (2013) Life cycle assessment of sewage sludge co-incineration in a coal-based power station. Waste Manage 33:1843–1852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.05.007
Jadlovec M, Výtisk J, Honus S et al (2023) Pollutants production, energy recovery and environmental impact of sewage sludge co-incineration with biomass pellets. Environ Technol Innov 32:103400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2023.103400
Jiang H, Zhang Y, Bian K et al (2022) Is it possible to efficiently and sustainably remove microplastics from sediments using froth flotation? Chem Eng J 448:137692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.137692
Knapp S, Güldemund A, Weyand S, Schebek L (2019) Evaluation of co-firing as a cost-effective short-term sustainable CO2 mitigation strategy in Germany. Energ Sustain Soc 9:32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13705-019-0214-3
Li H, Jiang H-D, Dong K-Y et al (2020a) A comparative analysis of the life cycle environmental emissions from wind and coal power: evidence from China. J Clean Prod 248:119192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119192
Li J, Mei M, Han Y et al (2020b) Life cycle cost assessment of recycled paper manufacture in China. J Clean Prod 252:119868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119868
Li T, Wei G, Liu H et al (2023) Comparative study of electroplating sludge reutilization in China: environmental and economic performances. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:106598–106610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29849-z
Liu Y, Lin R, Ren J (2021) Developing a life cycle composite footprint index for sustainability prioritization of sludge-to-energy alternatives. J Clean Prod 281:124885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124885
Liu B, Han Z, Li J, Yan B (2022a) Comprehensive evaluation of municipal solid waste power generation and carbon emission potential in Tianjin based on grey relation analysis and long short term memory. Process Saf Environ Prot 168:918–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.10.065
Liu H, Liu T, Wei G et al (2022b) Environmental and economic assessment of rural domestic waste gasification models in China. Waste Manage 154:160–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2022.10.001
Liu H, Qiao H, Liu S et al (2023) Energy, environment and economy assessment of sewage sludge incineration technologies in China. Energy 264:126294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.126294
Maheswaran R, Marichelvam MK, Asok SP (2023) Development of value-added sustainable products from paper mill sludge: an experimental approach. Heliyon 9:e17517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17517
Mohammadi A, Sandberg M, Venkatesh G et al (2019) Environmental performance of end-of-life handling alternatives for paper-and-pulp-mill sludge: using digestate as a source of energy or for biochar production. Energy 182:594–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.06.065
Pasciucco F, Francini G, Pecorini I et al (2023) Valorization of biogas from the anaerobic co-treatment of sewage sludge and organic waste: life cycle assessment and life cycle costing of different recovery strategies. J Clean Prod 401:136762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136762
Shao J, Yuan X, Leng L et al (2015) The comparison of the migration and transformation behavior of heavy metals during pyrolysis and liquefaction of municipal sewage sludge, paper mill sludge, and slaughterhouse sludge. Biores Technol 198:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.147
van Hijfte L, Geurts M, Vallentgoed WR et al (2023) Alternative normalization and analysis pipeline to address systematic bias in NanoString GeoMx Digital Spatial Profiling data. iScience 26:105760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2022.105760
Wang Y, Zhou S, Huo H (2014) Cost and CO 2 reductions of solar photovoltaic power generation in China: perspectives for 2020. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 39:370–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.07.027
Wang Q, Liu W, Yuan X et al (2018) Environmental impact analysis and process optimization of batteries based on life cycle assessment. J Clean Prod 174:1262–1273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.059
Yang H, Guo Y, Fang N, Dong B (2023) Life cycle assessment of greenhouse gas emissions of typical sewage sludge incineration treatment route based on two case studies in China. Environ Res 231:115959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115959
Zambare VP, Christopher LP (2020) Integrated biorefinery approach to utilization of pulp and paper mill sludge for value-added products. J Clean Prod 274:122791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122791
Zhao H, Liu H, Wei G et al (2021a) Comparative life cycle assessment of emergency disposal scenarios for medical waste during the COVID-19 pandemic in China. Waste Manage 126:388–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.03.034
Zhao H-L, Wang L, Liu F et al (2021b) Energy, environment and economy assessment of medical waste disposal technologies in China. Sci Total Environ 796:148964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148964
Zhao H, Liu H, Wei G et al (2022) A review on emergency disposal and management of medical waste during the COVID-19 pandemic in China. Sci Total Environ 810:152302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152302
Download references
The authors would like to acknowledge the foundation of Tianjin Research Innovation Projects for Postgraduate Students (Grant no. 2022SKYZ208 and Grant no. 2022SKYZ180).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Energy and Safety Engineering, Tianjin Chengjian University, Tianjin, 300384, China
Yanfei Lin, Hanqiao Liu, Kai Li, Yuwen Zhu, Qianlong Han & Yunzhen Yang
College of Science, Tianjin Chengjian University, Tianjin, 300384, China
Tianjin Urban Planning and Design Institute Co, Ltd, Tianjin, 300000, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Yanfei Lin: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, writing—original draft. Guoxia Wei: writing—review and editing. Hanqiao Liu: conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing. Kai Li: methodology and editing. Yuwen Zhu: conceptualization, writing—review and editing. Qianlong Han: conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing. Yunzhen Yang: writing—review and editing. Yi Lian: writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yuwen Zhu .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kelvin Tsun Wai Ng
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (XLS 142 KB)
Supplementary file2 (doc 838 kb), rights and permissions.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Lin, Y., Wei, G., Liu, H. et al. Environmental and economic analysis of the transformation of paper mill sludge treatment technologies in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33708-w
Download citation
Received : 07 January 2024
Accepted : 13 May 2024
Published : 27 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33708-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- High-value utilization
- GHG emission reduction
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

COMMENTS
EPA's National Center for Environmental Economics (NCEE) publishes a working paper series on research in environmental economics. Paper topics include environmental management, resources and conservation, agriculture, global issues, institutional issues, and other topics. These papers are either authored by NCEE economists or produced with ...
The Journal of Environmental Economics and Management (JEEM) publishes theoretical and empirical papers addressing economic questions related to natural resources and the environment.To warrant publication in JEEM, papers must include carefully identified empirical findings, insightful theoretical analyses, or creative methodologies that are both novel and of broad interest to its readership.
Overview. The primary concern of Environmental & Resource Economics is the application of economic theory and methods to environmental issues and problems that require detailed analysis in order to improve management strategies. The contemporary environmental debate is in a constant state of flux, with new or relatively unexplored topics ...
The Review of Environmental Economics and Policy is an official journal of the Association of Environmental and Resource Economists and the European Association of Environmental and Resource Economists. REEP fills the gap between traditional academic journals and the general interest press by providing a widely accessible yet scholarly source ...
Research Open Access 29 May 2024 Communications Earth & Environment. ... Professor of Environmental Economics and Sustainability at Athens University of Economics and Business, ...
Economic and ecological systems are closely interlinked at a global and a regional level, offering a broad variety of important research topics in environmental and resource economics. The successful identification of key challenges for current and future research supports development of novel theories, empirical applications, and appropriate policy designs. It allows establishing a future ...
Research on the impact of pilot free trade zones on urban green development: A case study based on the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China Weiwei Wu, Xiaoyong Tian, Yating Liu, Weitong Huang A time-varying analysis between economic uncertainty and tourism development in Singapore
EPA's National Center for Environmental Economics (NCEE) publishes a working paper series on research in environmental economics. Paper topics include environmental management, resources and conservation, agriculture, global issues, institutional issues, and other topics. These papers are either authored by NCEE economists or produced with ...
Most read articles. Journal of Environmental Economics and Policy, Volume 13, Issue 1 (2024) See all volumes and issues. Volume 13, 2024Vol 12, 2023Vol 11, 2022Vol 10, 2021Vol 9, 2020Vol 8, 2019Vol 7, 2018Vol 6, 2017Vol 5, 2016Vol 4, 2015Vol 3, 2014Vol 2, 2013Vol 1, 2012. Select to download all citations or PDFs.
A progressive, human-centric journal which publishes pioneering research to support the UN SDGs and better facilitate the transition to a sustainable interaction between the economy, society and na...
This paper provides a contemporary analysis of how research issues have developed in the Journal of Environmental Economics and Management (JEEM) over the four decades of its existence.We have classified the articles in the journal along five dimensions: content, methods, environmental media, the regional dimension of studies, and cross-cutting issues.
The main purpose of the journal is twofold: to encourage (1) integration of theoretical studies and policy studies on environmental issues and (2) interdisciplinary works of environmental economics, environmental policy studies, and related fields on environmental issues. The journal also welcomes contributions from any discipline as long as ...
Environmental Economics, Regulation, and Innovation. Mads Greaker & David Popp. Working Paper 30415. DOI 10.3386/w30415. Issue Date September 2022. This paper provides a primer on the economics of environmental innovation. Our intention is not to write a pure review paper, but to also provide an up-to-date textbook treatment on the issue. Thus ...
Historical CO 2 emissions could lead to future climate damages and harm human inclusive wealth. This analysis proposes the concept of climate wealth borrowing and quantifies the country-specific ...
This paper provides a contemporary analysis of how research issues have developed in the Journal of Environmental Economics and Management (JEEM) over the four decades of its existence.We have classified the articles in the journal along five dimensions: content, methods, environmental media, the regional dimension of studies, and cross-cutting issues.
Recently, environmental issues have increased, whereas the Earth's natural resources have deteriorated. These problems have forced people and companies to engage in environmental economics to achieve sustainability. However, several barriers have been identified in the implementation of environmental economics. This literature review provides insights into environmental economics and the ...
This review systematically introduces the current main research directions of environmental macroeconomics. Environmental macroeconomics research aims to study the relationship between economic development and the ecological environment and ultimately achieve green outcomes. At the same time, maintaining a moderate economic scale within the environmental setting is vital to get rid of ...
Economic research is becoming a powerful tool to understand and inform policy and incentives related to climate change and energy use—and to assess the impact of environmental degradation and climate change on health, well-being, and productivity worldwide. At MIT, environmental economists are using cutting-edge techniques to weigh the impact ...
Economists. He won the European Association of Environmental and Resource Economics Erik Kempe Award for the best paper in 2004 and the German Society of Health Economics best paper award in 2013. His research articles have appeared in top eld and general economics outlets.
The paper is divided into three sections: (1) The scope and insight into Ecological and Environmental Economics; (2) the differences between the two subdisciplines in terms of; foundational ...
This comprehensive guide to environmental economics research paper topics is designed to assist students and researchers in selecting a subject for their study. Environmental economics, a field at the intersection of economics and environmental science, offers a wide array of topics that explore the economic aspects of environmental issues.
In environmental research, scholars consider the multifunctionality of co-production between metals [111], provide an overview of the metals inventoried in ecoinvent [101], perform sustainability analysis through exergy, thermo-economic and environmental footprint [103], establish the characterization factor based on the mining data [106], and ...
The paper deals with the analysis of methodology of Environmental Performance Index. The authors analyzed and systematized the main existing integrated indices, which were used for evaluation of environmental, social and economic situation in the countries.
ARE Department Head Junjie Wu was recently honored along with collaborators Kathleen Segerson and Chunhua Wang with the Agricultural & Applied Economics Association's Quality of Research Discovery Award Honorable Mention for their 2023 paper, "Is Environmental Regulation the Answer to Pollution Problems in Urbanizing Economies?" published in the Journal of Environmental Economics and ...
When desert winds stir up dust from the Salton Sea's exposed lakebed, nearby communities suffer from increased air pollution. The deterioration coincides with reduced flows into California's largest lake, a new research paper in the American Journal of Agricultural Economics finds.. Disadvantaged communities have been affected more than others in the areas near the Salton Sea, which has ...
Paper mill sludge (PMS) is featured with a high content of cellulose and hemicellulose, and using its characteristics to make paperboard can achieve a high-value utilization of PMS, which has attracted growing interest. In this study, currently prevalent landfill, incineration technologies (generating heat and electricity by incineration), and three paperboard technologies (medium density ...
The study aims to present a comprehensive assessment of India's electricity acts and power sector policies using a qualitative research design. The present study employs document analysis to explore the implications of the policies on social, technical, economic, and environmental dimensions. The challenges faced by the power sector and the policy implications of these challenges have also ...