Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Academic Research Writing: Chapter 3 Methodology, General Lecture Notes


Related Papers
Stevejobs.education
Dr. David Annan
Very often, little attention is paid to how students have to prepare and understand the processes of conducting research and mostly young scholars struggle in the early stages in the university career about what is required of them and how to present their proposal to their supervisors. Keeping this in mind, the purpose of this guidebook is to offer a critical and practical mind map introduction to research writing to assist researchers in creating an appropriate design for their research studies and to offer the simplest guide of creating a logical orientated research. The book is made using simple graphs to explain what is expected of researchers at each stage of their research writing to enable them to understand if any a missing link when conducting their research. The book is mostly content mind-map and figures to make it easier for the researcher to understand what is expected of them from the stages of their research to completion. It presents the basic tenets of methodological steps so that the researcher can become familiar with how to conduct research and what techniques to use in their choice for research writing.
Dhirawit Pinyonatthagarn
budianto rosidi
Dr Dare E Ajayi
The complexities and diversities of human nature and challenges necessitated the need to discover and identify ways to solving and meeting human and academic problem needs. The existence of problems gave rise to the the need for research. The book takes researchers and students through the latest and best research practice through the adoption of simple, adoptable and practicable research models for academic and contemporary research writing.
Marivic Sumagaysay
Roohullah Nawandish
Andrew Johnson
This chapter excerpt describes the processes of writing a review of the literature for an academic article.
This 7-minute mini-lecture describes the basic elements of quantitative research and qualitative research. This provides a foundation for understanding educational research.
Bozhena Tikhonova
Vidyodaya Journal of Management
N.J. Dewasiri
Scholarly or academic writing is clear, concise, planned, coherent, and backed up by evidence. Its purpose is to aid the reader’s understanding. Hence, it consists of a formal style and tone. Further, it does not require the use of long sentences and instead uses clear and concise language with simple vocabulary. Research report writing is an integral part of academic writing. Hence, both academic and research report writing play a vital role in developing a multitude of researchers across the globe. The authors of the book entitled “A Guide to Academic Writing and Research Reports” identified such a role to develop prolific researchers amongst the student community both within and outside the university in Sri Lanka.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Lecture Notes on Software Engineering
Haifa Mohammed
Aditya Mukherjee
LRCW 4, Late Roman Coarse Wares, Cooking Wares and Amphorae in the Mediterranean, Archaeology and archaeometry (Thessaloniki April 2011), BAR International Series 2616: 451-467
Paul Reynolds , Evangelos Pavlidis
Kirtikumar Randive
Muhammad Zuhdi
Lulu Schulerin
Dr. Uday Dokras
In Gontier, N., Lock, A., Sinha, C. The Oxford Handbook of Human Symbolic Evolution. Oxford, Oxford University Press.
Nathalie Gontier
Nile Magazine
Nile Magazine - Jeff Burzacott, Editor
Mukesh Kumar
Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems
Javier Andrade
crumuel marqueso
Sabahattin Gürsoy
Jurnal Biology Education
kiswanto kiswanto
Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing
Sergio Salazar
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Talita Laurentino
Revista de Arqueologia
Andres Zarankin
Marcello Allegretti
Jurnal Pengabdian Masyarakat
Cholina Siregar
Norsk filosofisk tidsskrift
David C. Vogt
International Journal of Child Health and Nutrition
Sergi Masip
Revista USP
Sérgio Soares
Internal and Emergency Medicine
RENATA VECCHIETTI
Jean-Claude Dumoncel
utgrr efdddsa
American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology
Christopher Simons
ELLITE: Journal of English Language, Literature, and Teaching
Fitrotul Mufaridah
International Journal of Psychology : a Biopsychosocial Approach
Jurga Misiūnienė
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Your browser does not support HTML5 or CSS3
To best view this site, you need to update your browser to the latest version, or download a HTML5 friendly browser. Download: Firefox // Download: Chrome
Pages may display incorrectly.
PowerPoint Slides
Download all.
Download all the slides for chapters 1-45 .
Download chapter 1 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 2 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 3 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 4 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 5 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 6 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 7 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 8 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 9 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 10 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 11 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 12 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 13 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 14 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 15 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 16 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 17 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 18 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 19 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 20 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 21 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 22 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 23 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 24 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 25 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 26 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 27 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 28 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 29 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 30 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 31 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 32 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 33 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 34 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 35 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 36 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 37 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 38 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 39 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 40 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 41 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 42 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 43 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 44 PowerPoint Slides.
Download chapter 45 PowerPoint Slides.

Chapter 3 Research
Mar 18, 2019
320 likes | 649 Views
Chapter 3 Research. A Scientific Approach. Provides systematic ways of investigating claims in ways that improve on casual observations Requires that theories be backed up by empirical evidence from controlled studies and that observations be checked and repeated before conclusions are drawn.
Share Presentation
- research designs
- mediating variables
- highly structured
- child psychopathology research
- epidemiological research addresses questions

Presentation Transcript
Chapter 3Research
A Scientific Approach • Provides systematic ways of investigating claims in ways that improve on casual observations • Requires that theories be backed up by empirical evidence from controlled studies and that observations be checked and repeated before conclusions are drawn
Scientific Approaches to Research (cont.) Figure 3.1 The research process in abnormal child psychology.
Skepticism in Child Psychopathology Research • Reasons: • experts on childhood disorders frequently disagree • findings often in conflict with one another • research has led to different treatment recommendations, and some treatments shown to have no effect • conclusions are often qualified, with no definitive answers • findings often dismissed because of exceptions or personal experiences to the contrary
Common Research Topics • Nature and Distribution of Childhood Disorders • epidemiological research addresses questions about the nature and distribution of childhood disorders • incidence rates: the extent to which new cases of a disorder appear over a specified time period • prevalence rates: all cases, whether new or previously existing, that are observed during a specified time period
Common Research Topics (cont.) • Correlates, Risks, and Causes • correlated variables are associated at a particular point in time with no clear proof that one precedes the other • risk factor: variable that precedes an outcome of interest and increases the chances that the outcome will occur • protective factor: variable that precedes an outcome of interest and decreases the chances that the outcome will occur
Common Research Topics (cont.) • Moderating and Mediating Variables • moderating variable: a factor that influences the direction or strength of the relationship between other variables of interest • mediating variable: the process, mechanism, or means through which a variable produces a particular outcome; describes what happens at the psychological or neurobiological level to explain how one variable results from another
Common Research Topics (cont.) Figure 3.2 Mediating variables: The type of discipline used by mothers on days they are feeling distressed mediates the relationship between maternal distress and child behavior problems.
Common Research Topics (cont.) • Outcomes associated with childhood problems • Interventions • treatment efficacy: refers to whether or not a treatment can produce changes under well-controlled conditions • treatment effectiveness: refers to whether the treatment can be shown to work in actual clinical practice, rather than in laboratory conditions
Standardization, Reliability, and Validity • Standardization • the process by which a set of norms is specified for a measurement procedure so that it can be used consistently across different assessments • Reliability • the consistency of a measure, either across raters or time • Validity • the extent to which the method actually measures the construct of interest
Forms of Measurement • Reporting • includes unstructured clinical interviews, highly structured interviews, and questionnaires • inaccuracies may occur because of inability to recall events, selective recall or bias, and intentional distortions • requires a certain level of verbal ability, therefore often not considered reliable with children under age 7 or 8
Forms of Measurement (cont.) • Psychophysiology and Neuroimaging • physiological responses often recorded include heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, pupil dilation, and electrical skin conductance • limitations of physiological measures include inconsistency, high level of inference often involved, and susceptibility to extraneous influences • electroencephalogram (EEG) measures electrical activity of the brain • neuroimaging procedures examine the structure and/or function of the brain
Forms of Measurement (cont.) • Observation • may range from unstructured, naturalistic observations to highly structured • compared to naturalistic observations, structured observations are often cost-effective, allow for focused attention, are useful for studying infrequent behavior, and allow for greater control over the situation • major limitation is that one cannot be certain the observations are a representative sample of behavior
Validity of Studies • Internal validity • the extent to which a particular variable, rather than extraneous influences, accounts for the findings • may be threatened by maturation, effects of testing, an subject selection biases • External validity • the extent to which findings can be generalized to other people, settings, times, measures, and characteristics • may be threatened by subject reactivity to participation, the setting, and the time measurements are made
Identifying the Sample • A careful definition of the sample is critical for comparability of findings across studies • Must consider comorbidities among the sample • Random selection is rare in child psychopathology studies; often need to use a sample of convenience
General Approaches to Research • Nonexperimental vs Experimental Research • in true experiments, researchers have maximum control over the independent variable, subjects are randomly assigned, and possible sources of bias are controlled • correlational studies only examine relationships among variables- causality cannot be determined • natural experiments involve comparisons between conditions that already exist
General Approaches to Research (cont.) • Prospective vs Retrospective Research • real-time prospective designs: sample is followed longitudinally over time; time consuming and susceptible to sample attrition • retrospective designs: sample is asked for information relating to an earlier time period; highly susceptible to recall bias and distortion • Analogue Research • evaluation of a specific variable under conditions that only resemble the situation to which one wishes to generalize
Research Designs • Case Studies • intensive and usually anecdotal observations and analyses of an individual child; rich sources of descriptive information • often viewed as unscientific and flawed because of uncontrolled methods and selective biases, as well as the inherent difficulties in integrating observations, drawing valid inferences, and generalizing from one child to other children
Research Designs (cont.) • Single-Case Experimental Designs • often used to evaluate the impact of treatments • involves repeated assessment of behavior over time, replication of treatment effects within the same subject, and the subject serving as own control • common examples are the A-B-A-B (reversal) design and the multiple-baseline design • weaknesses: possible interactions between treatment and subject characteristics, limited generality of findings, and subjectivity and inconsistency of visual inspection of the data
Research Designs (cont.) • Between-Group Comparison Designs • involves comparisons between experimental and control groups • Cross-Sectional Studies • individuals at different ages or stages of development are studied at the same point in time • often efficient and less susceptible to attrition and practice effects • do not allow for inferences regarding change in the individual and are susceptible to cohort effects
Research Designs (cont.) • Longitudinal Studies • same individuals are studied at different ages or stages of development • allows for identification of patterns that are common to all children and for tracking differences in developmental paths • disadvantages include time commitment, increased costs, aging effects, cohort effects, period effects, and practice effects
Qualitative Research • Purpose is to describe, interpret, and understand the phenomenon of interest in the context in which it is experienced • Although intensive and intimate, may be biased by researcher’s values and preferences, and findings cannot be generalized to other individuals
Ethical and Pragmatic Issues • Informed Consent and Assent • informed consent must be obtained from parents • child’s assent must be obtained when child is around age 7 or older • Voluntary Participation • participation in research must be voluntary • may be compromised by subtle pressure and coercion
Ethical and Pragmatic Issues (cont.) • Confidentiality and Anonymity • disclosed information must be kept confidential • individuals must be advised about any exceptions to confidentiality • disclosures of abuse common problem in child research • Non-harmful procedures • no research procedures may be used that may harm a child physically or psychologically
Ethical and Pragmatic Issues (cont.) • Other Ethical and Pragmatic Concerns • may arise when research involves potentially invasive procedures, deception, the use of punishment, the use of incentives • final responsibility of ethical integrity is with the investigator
- More by User

Ethics in Social Research (Babbie Chapter 3)
Geography 237a Research Methods. Ethics in Social Research (Babbie Chapter 3). no harm informed consent confidentiality anonymity deception debriefing case studies. Ethics Terminology. no harm do not endanger physically, psychologically or socially do not embarrass
1.78k views • 6 slides

CHAPTER 3-3
CHAPTER 3-3. MIDDLE COLONIES. Graphic Organizer. CHAPTER 3-3. EQ: How did the Middle Colonies Develop?. ENGLAND & THE MIDDLE COLONIES. Middle Colonies. NEW YORK. Pennsylvania. New Jersey. Delaware. England and the Colonies. IDENTIFYING. England & the Colonies. Comparing.
1.39k views • 13 slides

Chapter 3 Internet Consumers and Market Research
Chapter 3 Internet Consumers and Market Research. Learning Objectives. Describe the essentials of consumer behavior Describe the characteristics of Internet surfers and EC purchasers Understand the process of consumer purchasing decision making
765 views • 43 slides

CHAPTER 3 RESEARCH TRADITIONS
CHAPTER 3 RESEARCH TRADITIONS. ONTOLOGY AND EPISTEMOLOGY Ontology refers to the philosophy of the existence and nature of phenomena. Epistemology is the branch of philosophy that deals with how knowledge of such phenomena is acquired, and what counts as knowledge. . POSITIVISM
548 views • 19 slides

Educational Research Chapter 3
Educational Research Chapter 3. Research Problem. Systematic Research begins with a research problem - begin with a general topic and then narrow it down to a specific statement of the research problem Sources of problems : Experience Deductions from theory Related Literature
1.46k views • 9 slides

Chapter 3 The Research Process
Chapter 3 The Research Process. © Nursing Research: An Introduction by Pam Moule and Margaret Goodman (2009, SAGE). Learning outcomes. To understand the stages of the research process. To appreciate that the stages are not always applied in all research in a uniform way.
452 views • 9 slides


Chapter 3 Research Methods and Theory Development
Chapter 3 Research Methods and Theory Development. Frank Schmalleger PowerPoint presentation created by Ellen G. Cohn, Ph.D. The Science of Criminology. John Laub’s three eras
1.03k views • 38 slides

Chapter 3-3
6d. Know how water, carbon, & nitrogen cycle between abiotic resources and organic matter in the ecosystem and how oxygen cycles through photosynthesis and respiration. Chapter 3-3. Key Terms.
274 views • 12 slides

CHAPTER 3 Research in Psychology: Methods and Design
CHAPTER 3 Research in Psychology: Methods and Design. Chapter Objectives . Describe the defining features of a theory in psychology
751 views • 15 slides

Chapter 3: Ethical Treatment of Research Participants
Chapter 3: Ethical Treatment of Research Participants. Responsibility for ethical research Researcher, IRB Ethical considerations in planning research Risks, voluntary participation, informed consent, deception Ethical considerations in data collection Avoid harm, withdrawal of consent
510 views • 12 slides

Research 3. 1. Open System. Energy and matter can enter or leave the system There is always interaction between the internal and external elements Ex: Greenhouse. Closed System. Energy can leave or enter the system, however matter cannot
294 views • 17 slides

Chapter 3 Chapter 3
Chapter 3 Chapter 3. New Key learning Skills. Chapter 3 Lessons. Lesson 3-1: Home Keys (fdsa jkl;) Lesson 3-2: Review Lesson 3-3: New Keys h and e Lesson 3-4: New Keys i and r Lesson 3-5: Review Lesson 3-6: New Keys o and t Lesson 3-7: New Keys n and g
968 views • 51 slides

Chapter 3 Research. Getting information from a variety of sources finding great ideas on the web Getting your research for free. Getting Sources. An old philosopher once said that its more interesting to hear a speaker who met an old philosopher than a speaker who read about one.
254 views • 11 slides
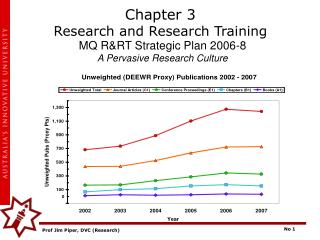
Chapter 3 Research and Research Training
Chapter 3 Research and Research Training. MQ R&RT Strategic Plan 2006-8 A Pervasive Research Culture. Chapter 3 Research and Research Training A Pervasive Research Culture. Chapter 3 Research and Research Training A Pervasive Research Culture.
148 views • 7 slides

CHAPTER 3: The Marketing Research Process and Proposals
CHAPTER 3: The Marketing Research Process and Proposals. ESSENTIALS OF MARKETING RESEARCH Hair/Wolfinbarger/Ortinau/Bush. Information Research Process. Information research process is the systematic task steps in the gathering, analyzing, interpreting, and transforming
876 views • 19 slides

Chapter 3 The Research Endeavor
Chapter 3 The Research Endeavor. Case Studies. Detailed histories of individuals who have suffered some form of psychological disorder.
179 views • 10 slides

Chapter 3 The Marketing Research Process
Chapter 3 The Marketing Research Process. LEARNING OUTCOMES. Classify marketing research into one of three types List the major phases of the marketing research process Distinguish between the concepts of theory and hypothesis
331 views • 30 slides

Chapter 3 Clinical Assessment, Diagnosis, and Research Methods
Chapter 3 Clinical Assessment, Diagnosis, and Research Methods. Assessing Psychological Disorders. Purposes of Clinical Assessment To understand the individual To predict behavior To plan treatment To evaluate treatment outcome. Assessing Psychological Disorders (continued).
568 views • 53 slides

Chapter 3-3. Chang Chi-Chung 2015.07.03. Bottom-Up Parsing. L R methods ( Left-to-right , Rightmost derivation ) LR(0), SLR, Canonical LR = LR(1), LALR 最右推導 沒有右遞迴 明確性文法 Other special cases: Shift-reduce parsing Operator-precedence parsing. Bottom-Up Parsing. reduction.
709 views • 51 slides

RESEARCH METHODOLOGY CHAPTER 3-5 EXPLAINED AUDIO
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY CHAPTER 3-5 COMES WITH AUDIO EXPLANATIONS
77 views • 6 slides

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Chapter 3 Research Design.
Published by Gillian Stewart Modified over 8 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Chapter 3 Research Design."— Presentation transcript:

19/11/2007 9:15-11:15amAsian School of Business, Trivandrum Marketing Research Design: The Nuts and Bolts!!
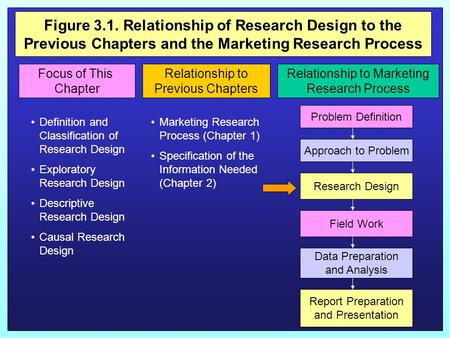
Figure 3.1. Relationship of Research Design to the Previous Chapters and the Marketing Research Process Figure 3.1Relationship to the Previous Chapter.

Secondary Data, Literature Reviews, and Hypotheses

Chapter 5 Research Design.

Chapter Three. Figure 3.1. Relationship of Research Design to the Previous Chapters and the Marketing Research Process Focus of This Chapter Relationship.

Chapter Three Research Design.

Recap Step 1: Identify and define the Problem or Opportunity

Research Design.

What Have We Covered So Far? Problem Formulation and Approach

2-1 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Two Defining the Marketing Research Problem and Developing an Approach.

Chapter Three Research Design Formulation.

The Proposal. The Final Product Introduction –Including your Management Question Literature Review Your Model –Research Questions –Hypotheses you plan.

Descriptive Research Spending major dollars, expecting major results.

Fundamentals of Market Research

Chapter Three Research Design. 3-2 Research Design: Definition A research design is a framework or blueprint for conducting the marketing research project.

Chapter Three Chapter Three.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This powerpoint presentation contains a brief overview of the contents of Chapter 3 or Research Methodology. You can also find a sample that shows the different components of Chapter 3. Kindly hit the like and subscribe buttons, thank you. An Overview of Chapter 3 - Research Methodology
Instruments. This section should include the instruments you plan on using to measure the variables in the research questions. (a) the source or developers of the instrument. (b) validity and reliability information. •. (c) information on how it was normed. •. (d) other salient information (e.g., number of. items in each scale, subscales ...
Chapter 3 by Jullia Morente on Prezi. Blog. April 18, 2024. Use Prezi Video for Zoom for more engaging meetings. April 16, 2024. Understanding 30-60-90 sales plans and incorporating them into a presentation. April 13, 2024.
Discuss the source of this strategy. 5. Discuss why it is an appropriate strategy. 6. Identify how the use of this strategy will shape the type of questions asked, the form of data collection, the steps and data analysis, and the final narrative. This section should include discussion about participants and the site.
research methodology chapter 3.ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
qualitative research, in general, and in your tra-dition or genre, in particular; hence, it is written in future tense. In the dissertation's chapter 3, you report on what you have already done. You write after the fact; hence, you write in past tense. As such, many of the sections of chapter 3 can be written only after you have
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY CHAPTER 3. Components of a research methodology 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Research instruments 3.3 Respondents 3.4 Research procedure. Published byMartha Craig Modified over 8 years ago. Embed. Download presentation ... Download ppt "RESEARCH METHODOLOGY CHAPTER 3. Components of a research methodology 3.1 Introduction 3.2 ...
Research Design and Methodology. Chapter 3 consists of three parts: (1) Purpose of the. study and research design, (2) Methods, and (3) Statistical. Data analysis procedure. Part one, Purpose of ...
Academic Research Writing: Chapter 3 Methodology, General Lecture Notes
3 Chapter 3. Methodology Ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. DSDSDASDA
Download ppt "CHAPTER 3: METHODOLOGY." Similar presentations ... Goals Discuss asking the right questions in the right way as part of an epidemiologic study. ... RESEARCH METHODOLOGY CHAPTER 3. Components of a research methodology 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Research instruments 3.3 Respondents 3.4 Research procedure. DR. DAWNE MARTIN MKTG 241 FEB. 15 ...
Research. Methods in. Education. Home; Resources; PowerPoint Slides; PowerPoint Slides. Download all. Download all the slides for chapters 1-45. ... Chapter 9. Download chapter 9 PowerPoint Slides. Download Chapter 9 (DOC) Chapter 10. Download chapter 10 PowerPoint Slides. Download Chapter 10 (DOC)
Chapter III - Research Methodology • In Descriptive research studies, like surveys and genetic studies, the chapter on research methodology include the following: 1. research method used 2. population and sampling 3. description of respondents 4. description of instruments used in the collection of data 5. validation of the instrument 6. how data were collected 7. how data were treated and ...
Writing Chapter 3 Research Methodology - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
Chapter 3Research . A Scientific Approach • Provides systematic ways of investigating claims in ways that improve on casual observations • Requires that theories be backed up by empirical evidence from controlled studies and that observations be checked and repeated before conclusions are drawn. Scientific Approaches to Research (cont.) Figure 3.1 The research process in abnormal child ...
Quantitative research: is concerned with objectivity, tight controls over the research situation, and the ability to generalize findings. Qualitative research: is concerned with the subjective meaning of an experience to an individual. Concepts are abstractions of particular aspects of human behavior or characteristics (e.g., pain, weight).
3.1 Introduction: the qualitative research paradigm This chapter discusses the planning and execution of the study and the overall ... As part of the extended-case studies methodology, in chapter 2 and later chapters the importance and significance of news agencies is discussed. This study therefore seeks not to "prove" the existence of
PARTS OF. TITLE PAGE The following. ABSTRACT • An abstract. INTRODUCTION • The first. AREA OF FOCUS •. RELATED LITERATURE • In. RESEARCH QUESTIONS • The. DATA ANALYSIS AND. INTERPRETATION OF DATA •.
Download ppt "Chapter 3 Research Design." Similar presentations . 19/11/2007 9:15-11:15amAsian School of Business, Trivandrum Marketing Research Design: The Nuts and Bolts!! ... Chapter Three Research Design. 3-2 Research Design: Definition A research design is a framework or blueprint for conducting the marketing research project.