
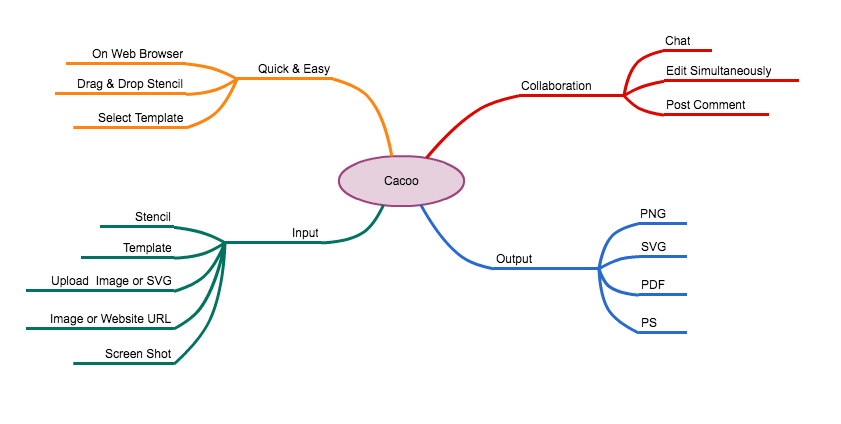
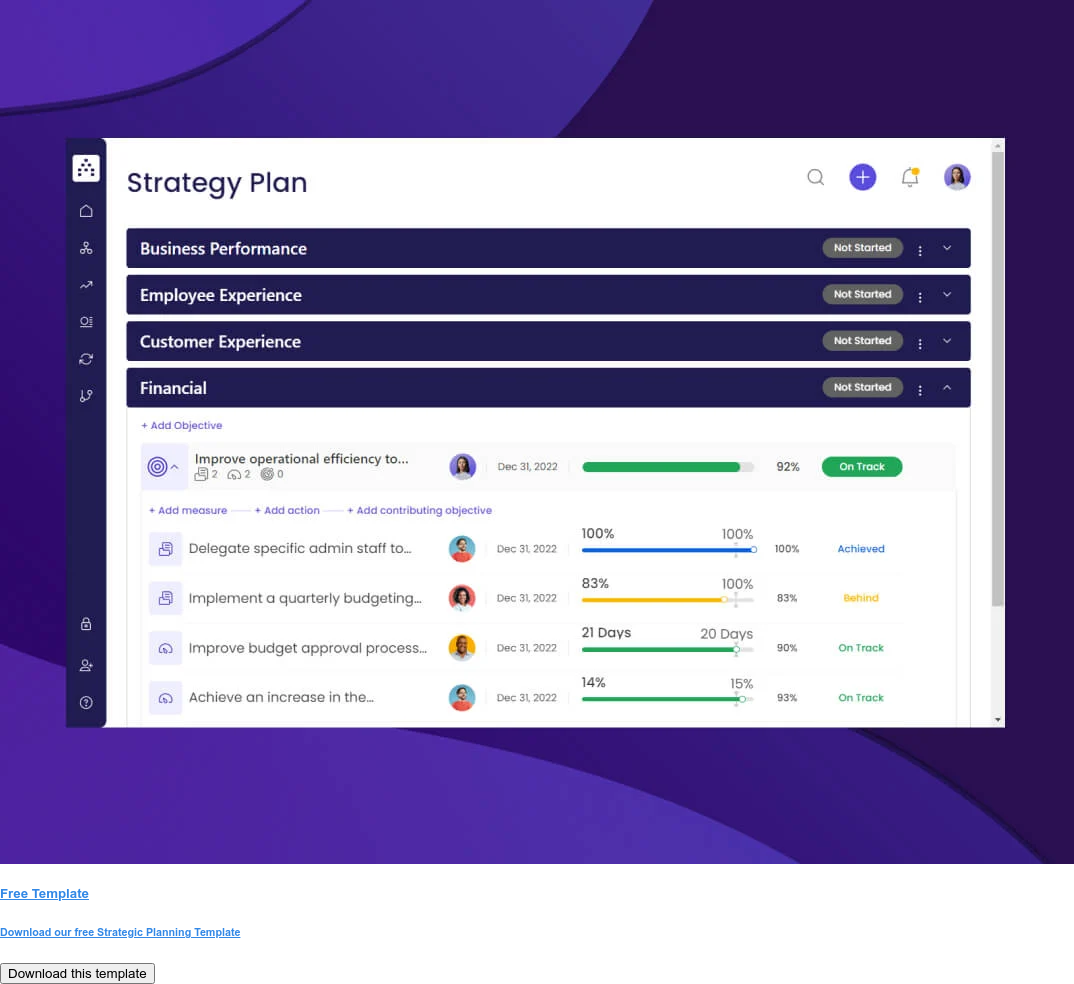
More Like this
Examples of strategic objectives, what are strategic objectives.
Strategic objectives create the big areas of focus for what your organization must focus on to achieve its vision of success. They create the top layer of your organizational strategy and strategic plan’s framework.
They are the big business objectives you must focus on for the next 3- to 5-years.
Strategic objectives are often one of the most challenging components of a strategic plan. They bridge your big, bold vision and the annual goals and actions needed to achieve it.
Download the Free Guide Here
We’ve put this guide together to show you how to develop your strategic plan’s objectives!
Tip The best strategic objectives are built from your SWOT Analysis and Vision Statement. Check out our guides if you need to complete those planning elements first.
Defining Strategic Objectives

Video Transcript – Strategic Objectives Defined
Hi, everyone, its Erica from OnStrategy.
Welcome to today’s whiteboard session on defining strategic objectives. From my point of view, strategic objectives are the hardest part of strategic planning. And why is that? That’s because they’re really in between a big vision and translating that big vision into annual goals or actions. And they make the bridge between the big idea and what’s actually getting done this year, this quarter this week. So strategic objectives serve such an important purpose. And they can take a little bit to get right. This is a two part series, check out this one first.
So we’re going to go through what they are. And the other one, we’re going to talk about how to build them. So let’s define strategic objectives. First of all, you can call them anything you want. We’ve heard them called strategic priorities, strategic goals, pillars, planks, kumquats, oranges, it doesn’t really matter. Today, we’re going to call them strategic objectives. And we are defining them as broad statements of direction. And again, they’re little mini vision statements that translate your vision into a bridge to build an annual plan.
Okay, so broad statements. That’s the that’s the idea. Let’s look at the anatomy of so here’s an example of a really good strategic objective. We like to start with a label. So what is it market share or market growth, let’s just say that, followed by a colon, a strong verb, and a statement of impact, in this case, strengthen our competitive advantage or position. Super simple, this is a little bit generic, you could continue the sentence if you want to, to make it a little more relevant to your organization. But you know, quick talking points, one of the strategic objectives for the organization is market growth. And what we’re trying to get done is strengthening our competitive position. Great.
Then underneath that, and I don’t have it fully built out here. But we like to actually build out an intent, couple of sentences, maybe even a paragraph, and this is really the the sense of where are you trying to go with this strategic objective, it really starts to bring it to life. And we like to have three sections in that intent statement. Where are you now, in the context of this, this strategic objectives in this case, your competitive position, you know, strategic plans have a lifespan.
And so it’s nice to know at the time in which you wrote it, where are you now a couple of sentences? What are the shifts that are needed in order to actually realize strengthening your competitive position? In this case, this will help you build great goals and initiatives? And then what’s the approach? What’s your method for strengthening competitive your competitive position. And by that, I mean, organic acquisitive, those types of things. So you could envision your intent statement, having, you know, a couple of sentences here, a couple of sentences here, and a couple of sentences here. Okay.
How do you use your strategic objectives? There are two really great ways to use them. Number one is you’re going to roadmap your strategic objectives by year and what we mean by that is this starts to become your framework for how do you actually build a plan that has a horizon. Now, in agile planning, it’s hard to have a really long horizon, but you do have a direction. So when this starts to build out your swim lanes, your strategic objectives, start to build out your swim lanes for your plan.
The second thing that you use your strategic objectives for are is building out your annual plan. So of course, for each strategic objective, you’ll have a handful of annual statements. In this case, I’m calling them goals, what are you actually going to achieve in the you know, the year that you’re in in order to move this objective forward? And then so on and so forth. So it starts your cascade? So a really nice thing to think about is strategic objectives answer the question where, and then following under that is the what, and then following under that is the how doesn’t matter what you call them? But absolutely, those are the components that make a strat plan go from a big idea to actually something that’s producing results.
And that’s all we have for you today. Check out part two for an example of how to build a framework with your strategic objectives. Don’t forget, subscribe to our social channels. Happy strategizing.
Strategic goals, priorities, pillars, planks, and strategic objectives— they’re all the same thing! Whatever you call them, they’re a critical component of your plan. For this whitepaper, we’re going to call them strategic objectives.
Strategic objectives are broad statements of direction that create a bridge from your vision to the annual plan or goals. We like to refer to strategic goals or strategic objectives as “mini vision statements” because they should support your overall vision of success but break it down into manageable and actionable focus areas.
Get the Free Guide to Build Your Strategic Objectives (with Examples!)
Ideally, strategic objectives should be broad, 3-year(ish) statements that address the core functional areas of your organization. We’re fans of Kaplan and Norton’s Balanced Scorecard® which guides strategic objectives and the strategic planning process around four key components of your organization, including:
- Financial Objectives: The financial performance of your organization.
- Customer: Your customer experience, satisfaction, and projects you provide to your customer.
- Internal Process/Operational: How your run an efficient organization.
- Learning and Growth: How you support your team members and stakeholders.
Having a strategic objective for each of the Balanced Scorecard perspectives ensures your business strategy is holistic and comprehensive.
Answer These Questions to Create Intent for Your Strategic Objectives
One of the things we like to complete as we build our new strategic objectives is a statement of intent. We include the answer to the following questions as a short paragraph with each strategic objective to clarify intent:
- Where are we now & where do we need to be in X years?
- What strategic shifts are needed to get there?
- What is our approach to achieve success?
Answering these core questions will help you create your new strategic objectives with clarity about what you’re seeking to achieve and what the cascading goals or OKRs need to focus on.
The Anatomy of a Strategic Objective

Strategic objectives or goals should start with a label. The label should clearly identify what it is you’re seeking to achieve. In this example, we’re seeking to achieve Customer Retention.
Begin your SO’s descriptive statement with a ‘power’ verb: a strong, action-oriented verb. Think “Create” or “Increase,” not passive verbs like, “Confirm” or “Facilitate.”
Statement of Impact
A short description of what you will achieve and how it will impact the organization. This should answer the intent questions from the previous section.
Building a Strategic Framework

With an understanding of the anatomy of a strategic objective, you can build the framework of your strategic management plan. As we’ve mentioned, strategic objectives are the bridge between your big, bold vision and your annual execution of goals and initiatives.
They Are Multi-Year in Nature
No matter what you call them—strategic objectives, long-term business goals, strategic goals—they must be multi-year in nature. You can choose three- to five-year objectives—it’s really about what works best for your organization.
Pro Tip: Annual goals are cascaded from the Strategic Objectives. Check out our guide on SMART goals if you need help writing your goals.
Your Framework Has 6 or Fewer Strategic Objectives
Pro Tip: Unsure how to prioritize your opportunities as you create your Strategic Objectives? Check out this exercise on prioritizing strategic objectives to help.
They Provides Company-wide Direction
It is not a mish-mash of department goals, example: balanced scorecard framework.
This is a traditional balanced scorecard framework. We like this framework because it covers all aspects of an organization and creates a balanced plan:
Tip It is essential to not use words that you found in someone else’s strategic plan! Use the words that are relevant to your organization and its culture and the message you want to send to your team about the investment the plan is making in them and the organization’s future.
Example: Themed Framework
A different way to think about creating a framework is theming your strategic objectives. Here’s what that might look like:
Strategic Objectives Examples:
We prefer to organize these types of strategic objectives into these four buckets and have provided some examples of each:
Financial Strategic Objectives
- Financial Growth: To exceed $10 million in the next 10 years.
- Financial Growth: To increase revenue by 10% annually.
- Financial Efficiency: To decrease expenses by 5%.
- Financial Efficiency: To increase net profit by 10% annually.
Customer/Constituent Strategic Objectives
- Current Customers: Expand sales to existing customers.
- Current Customers: Increase customer retention.
- Current Customers: Achieve and maintain outstanding customer service.
- Current Customers: Develop and use a customer database.
- New Customers: Introduce existing products into a new market.
- New Customers: Introduce new products to new and existing markets.
- New Customers: To expand sales to the global marketplace.
- Customer Services: Improve our service approach for new and existing customers.
Internal/Operational Strategic Objectives
- Product/Service/Program Management: To have all product meet standard of excellence guidelines. (Some businesses prefer to list their individual products or services as separate objectives.)
- Operations Management: Capitalize on physical facilities (location, capacity, etc.).
- Operations Management: Increase community outreach.
- Technology Management: Increase efficiencies through use of wireless or virtual technology.
- Communication Management: Improve internal communications.
- Customer Management: To execute and maintain a CRM process that is producing results.
- Marketing Management: Develop and implement a promotional plan to drive increased business.
- Alliance Management: Establish one new strategic alliance annually.
- Channel Management: Improve distributor and/or supplier relationships.
People/Learning Strategic Objectives
- People: Employ professionals who create success for customers.
- Training: To develop the leadership abilities and potential of our team.
- Culture: To align incentives and staff rewards with performance.
- Knowledge: To continually learn and adopt current best practices.
Bonus – AI Stragic Objectives
- AI Reskill: Re-skill and retool our team to work more efficiently with AI while protecting our workforce.
- AI Efficiency: Create 25% more efficiency using generative AI.
- AI Product Shift: Enter a new market with a new product not previously possible without AI.
Remember, these are just examples of strategic objectives. Sometimes seeing an example makes understanding the process easier.
Build Your Plan, Objectives, Strategic Goals, and KPIs in a single Dashboard with the StrategyHub
Most CEOs struggle with shifting demands that make keeping their long-term vision connected to weekly priorities chaotic. So we created a framework and software with dashboards to make adapting strategy, goals, and priorities easy. When your team contributes directly to the big picture, you deliver results consistently. Try it for free here.
35 Comments
very greatful with the source of information provided to me.it has helped me as a student of project planning and entrepreneurship to do the work in relation to my course assignment.
Makes it easy for me as a student to have a grip of what objectives are and in particular the way they are spelt out. As a PR student am now able answer at least some questions about PR objectrives
This is also very helpful to me…as a student of Company Management. Thanks a lot.
This is very detailed, relevant information and very useful to me as a new entrepreneur in organizational consulting! Thank you so much
very interesting and useful
Very informative and educative!
This would really help me in my Strategic Management paper. Thank you!
this is useful information. i have benefited from it on my studies and strategic objectives planning in my small business.
Thank You 🙂
Thank you for sharing such helpful information. I have learnt a lot:-)
Hey there!!
found it very good and informative. it educates me to set something strategically for the benefit of my organisation and to grow it.
further more i would like to know every organisation having different departments to fulfill particular requirements. say purchase/procurement, finance/accounts, personnel management/HR. I request you to guide on departmental stratagic ideas too.
Thanks a ton..
Regards Amit
very useful information for strategic planning. the information has assisted me greatly to review ma companys’ strategic plan
This is great stuff!!!
Thanks! Very concise and helpful!
Thanks for positing. Its really very useful info.
Don’t objectives need to be SMART?
yes, they need to be. Are they not?
A well thought out document. Found interesting and useful
very informative. thank you very much. 🙂
I find this very helpful and just in time for my strategic assignment. Thank you and continue providing such information.
This is very helpful to me especially now that im doing an assessment on marketing plan
It was very nice common strategic objectives to start with. Also can add Improve Market Share Increase, Share Holder Value, Brand Image, Customer Satisfaction, Return on Investment (ROI), Decrease Production Time, Increase Quality of the product, Safety Measures like Decrease Accidents, Environmental Measures etc. This will help for new companies.
Thank you so much! I found this article very much helpful to complete my strategy-management assignment.
thanksyouve helpd me through to answermy appraisal form atwork
Splendid. Really needed this to improve services for my starting business. Sincerely grateful. Keep it up!
This was very insightful and helpful. Thanks
This was very helpful . Sincere thanks
Really a great stuff as it has helped me as a fresh entrepreneur. Thanks a lot.
i am glad to see that kind of techniques. these are helpful for a entrepreneur.
very useful for my strategic analysis of a Ghanaian insurance company. thanks
very insightful read, thank you
Can a strategic plan like for instance Operational Excellence tie into objectives and tactics? If so, how?
Spectacular work <3 very helpful for my studies. Thoroughly enjoyed
Amazing! Thanks, Everything Strategy, for this helpful blog. I am now knowledgeable about the strategic objectives. I am motivated to pursue my success in the future. Thank you so much!
Hi, The article is well written and worth reading. Thank you for sharing the valuable information. Please keep sharing more about Financial Goals For A Business!
Comments Cancel
Join 60,000 other leaders engaged in transforming their organizations., subscribe to get the latest agile strategy best practices, free guides, case studies, and videos in your inbox every week..

Leading strategy? Join our FREE community.
Become a member of the chief strategy officer collaborative..
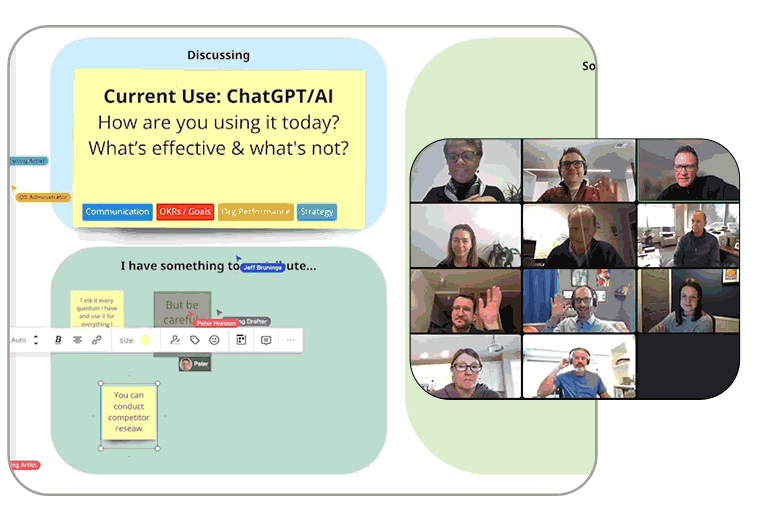
Free monthly sessions and exclusive content.
Do you want to 2x your impact.
How to make a business plan
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Business strategy |
- What is strategic planning? A 5-step gu ...
What is strategic planning? A 5-step guide

Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. In this article, we'll guide you through the strategic planning process, including why it's important, the benefits and best practices, and five steps to get you from beginning to end.
Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. The strategic planning process informs your organization’s decisions, growth, and goals.
Strategic planning helps you clearly define your company’s long-term objectives—and maps how your short-term goals and work will help you achieve them. This, in turn, gives you a clear sense of where your organization is going and allows you to ensure your teams are working on projects that make the most impact. Think of it this way—if your goals and objectives are your destination on a map, your strategic plan is your navigation system.
In this article, we walk you through the 5-step strategic planning process and show you how to get started developing your own strategic plan.
How to build an organizational strategy
Get our free ebook and learn how to bridge the gap between mission, strategic goals, and work at your organization.
What is strategic planning?
Strategic planning is a business process that helps you define and share the direction your company will take in the next three to five years. During the strategic planning process, stakeholders review and define the organization’s mission and goals, conduct competitive assessments, and identify company goals and objectives. The product of the planning cycle is a strategic plan, which is shared throughout the company.
What is a strategic plan?
![strategies business plan objectives [inline illustration] Strategic plan elements (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/7d1f14e4-b008-4ea6-9579-5af6236ce367/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A strategic plan is the end result of the strategic planning process. At its most basic, it’s a tool used to define your organization’s goals and what actions you’ll take to achieve them.
Typically, your strategic plan should include:
Your company’s mission statement
Your organizational goals, including your long-term goals and short-term, yearly objectives
Any plan of action, tactics, or approaches you plan to take to meet those goals
What are the benefits of strategic planning?
Strategic planning can help with goal setting and decision-making by allowing you to map out how your company will move toward your organization’s vision and mission statements in the next three to five years. Let’s circle back to our map metaphor. If you think of your company trajectory as a line on a map, a strategic plan can help you better quantify how you’ll get from point A (where you are now) to point B (where you want to be in a few years).
When you create and share a clear strategic plan with your team, you can:
Build a strong organizational culture by clearly defining and aligning on your organization’s mission, vision, and goals.
Align everyone around a shared purpose and ensure all departments and teams are working toward a common objective.
Proactively set objectives to help you get where you want to go and achieve desired outcomes.
Promote a long-term vision for your company rather than focusing primarily on short-term gains.
Ensure resources are allocated around the most high-impact priorities.
Define long-term goals and set shorter-term goals to support them.
Assess your current situation and identify any opportunities—or threats—allowing your organization to mitigate potential risks.
Create a proactive business culture that enables your organization to respond more swiftly to emerging market changes and opportunities.
What are the 5 steps in strategic planning?
The strategic planning process involves a structured methodology that guides the organization from vision to implementation. The strategic planning process starts with assembling a small, dedicated team of key strategic planners—typically five to 10 members—who will form the strategic planning, or management, committee. This team is responsible for gathering crucial information, guiding the development of the plan, and overseeing strategy execution.
Once you’ve established your management committee, you can get to work on the planning process.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment
Before you can define where you’re going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
To do this, your management committee should collect a variety of information from additional stakeholders, like employees and customers. In particular, plan to gather:
Relevant industry and market data to inform any market opportunities, as well as any potential upcoming threats in the near future.
Customer insights to understand what your customers want from your company—like product improvements or additional services.
Employee feedback that needs to be addressed—whether about the product, business practices, or the day-to-day company culture.
Consider different types of strategic planning tools and analytical techniques to gather this information, such as:
A balanced scorecard to help you evaluate four major elements of a business: learning and growth, business processes, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
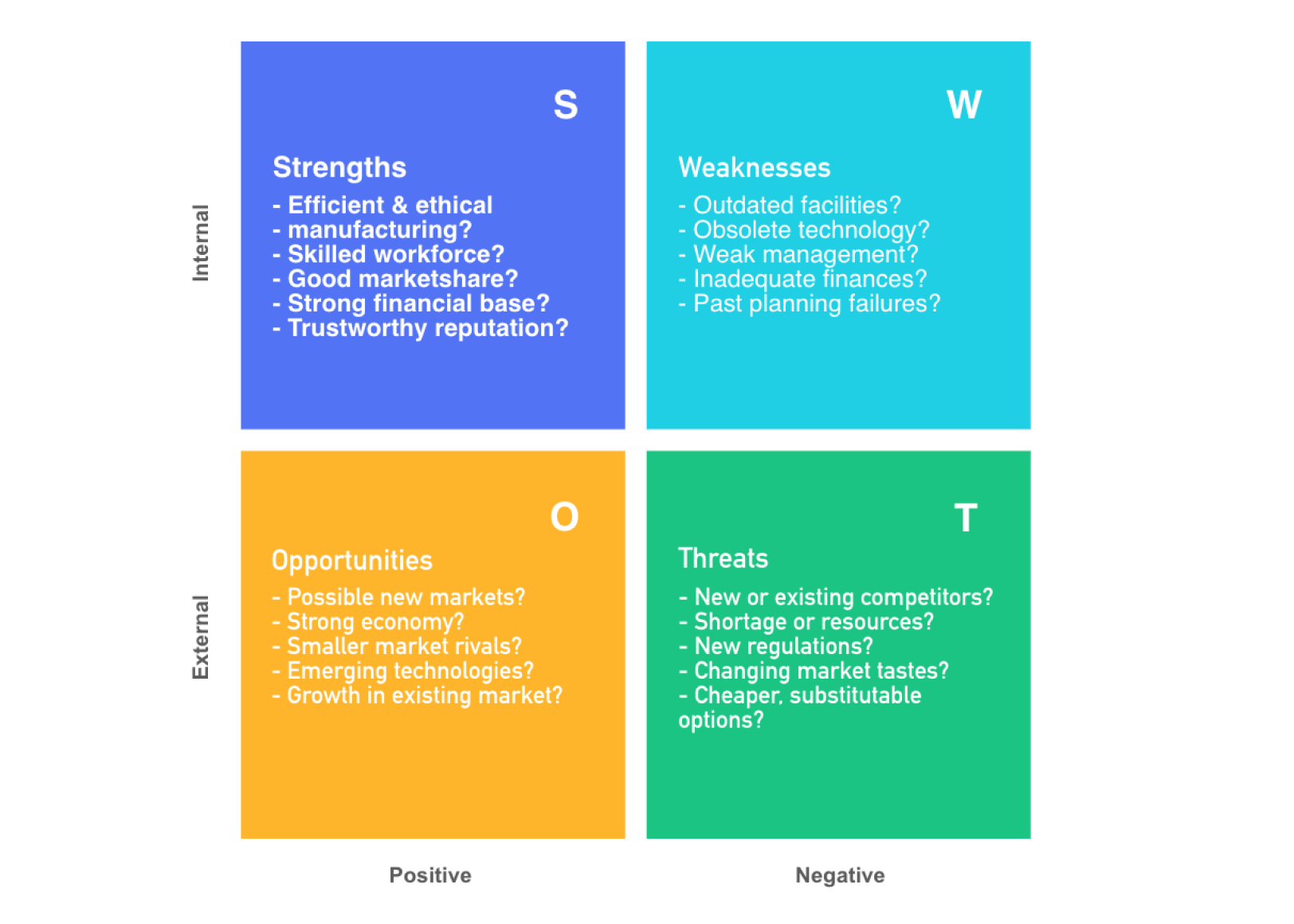
A SWOT analysis to help you assess both current and future potential for the business (you’ll return to this analysis periodically during the strategic planning process).
To fill out each letter in the SWOT acronym, your management committee will answer a series of questions:
What does your organization currently do well?
What separates you from your competitors?
What are your most valuable internal resources?
What tangible assets do you have?
What is your biggest strength?
Weaknesses:
What does your organization do poorly?
What do you currently lack (whether that’s a product, resource, or process)?
What do your competitors do better than you?
What, if any, limitations are holding your organization back?
What processes or products need improvement?
Opportunities:
What opportunities does your organization have?
How can you leverage your unique company strengths?
Are there any trends that you can take advantage of?
How can you capitalize on marketing or press opportunities?
Is there an emerging need for your product or service?
What emerging competitors should you keep an eye on?
Are there any weaknesses that expose your organization to risk?
Have you or could you experience negative press that could reduce market share?
Is there a chance of changing customer attitudes towards your company?
Step 2: Identify your company’s goals and objectives
To begin strategy development, take into account your current position, which is where you are now. Then, draw inspiration from your vision, mission, and current position to identify and define your goals—these are your final destination.
To develop your strategy, you’re essentially pulling out your compass and asking, “Where are we going next?” “What’s the ideal future state of this company?” This can help you figure out which path you need to take to get there.
During this phase of the planning process, take inspiration from important company documents, such as:
Your mission statement, to understand how you can continue moving towards your organization’s core purpose.
Your vision statement, to clarify how your strategic plan fits into your long-term vision.
Your company values, to guide you towards what matters most towards your company.
Your competitive advantages, to understand what unique benefit you offer to the market.
Your long-term goals, to track where you want to be in five or 10 years.
Your financial forecast and projection, to understand where you expect your financials to be in the next three years, what your expected cash flow is, and what new opportunities you will likely be able to invest in.
Step 3: Develop your strategic plan and determine performance metrics
Now that you understand where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to put pen to paper. Take your current business position and strategy into account, as well as your organization’s goals and objectives, and build out a strategic plan for the next three to five years. Keep in mind that even though you’re creating a long-term plan, parts of your plan should be created or revisited as the quarters and years go on.
As you build your strategic plan, you should define:
Company priorities for the next three to five years, based on your SWOT analysis and strategy.
Yearly objectives for the first year. You don’t need to define your objectives for every year of the strategic plan. As the years go on, create new yearly objectives that connect back to your overall strategic goals .
Related key results and KPIs. Some of these should be set by the management committee, and some should be set by specific teams that are closer to the work. Make sure your key results and KPIs are measurable and actionable. These KPIs will help you track progress and ensure you’re moving in the right direction.
Budget for the next year or few years. This should be based on your financial forecast as well as your direction. Do you need to spend aggressively to develop your product? Build your team? Make a dent with marketing? Clarify your most important initiatives and how you’ll budget for those.
A high-level project roadmap . A project roadmap is a tool in project management that helps you visualize the timeline of a complex initiative, but you can also create a very high-level project roadmap for your strategic plan. Outline what you expect to be working on in certain quarters or years to make the plan more actionable and understandable.
Step 4: Implement and share your plan
Now it’s time to put your plan into action. Strategy implementation involves clear communication across your entire organization to make sure everyone knows their responsibilities and how to measure the plan’s success.
Make sure your team (especially senior leadership) has access to the strategic plan, so they can understand how their work contributes to company priorities and the overall strategy map. We recommend sharing your plan in the same tool you use to manage and track work, so you can more easily connect high-level objectives to daily work. If you don’t already, consider using a work management platform .
A few tips to make sure your plan will be executed without a hitch:
Communicate clearly to your entire organization throughout the implementation process, to ensure all team members understand the strategic plan and how to implement it effectively.
Define what “success” looks like by mapping your strategic plan to key performance indicators.
Ensure that the actions outlined in the strategic plan are integrated into the daily operations of the organization, so that every team member's daily activities are aligned with the broader strategic objectives.
Utilize tools and software—like a work management platform—that can aid in implementing and tracking the progress of your plan.
Regularly monitor and share the progress of the strategic plan with the entire organization, to keep everyone informed and reinforce the importance of the plan.
Establish regular check-ins to monitor the progress of your strategic plan and make adjustments as needed.
Step 5: Revise and restructure as needed
Once you’ve created and implemented your new strategic framework, the final step of the planning process is to monitor and manage your plan.
Remember, your strategic plan isn’t set in stone. You’ll need to revisit and update the plan if your company changes directions or makes new investments. As new market opportunities and threats come up, you’ll likely want to tweak your strategic plan. Make sure to review your plan regularly—meaning quarterly and annually—to ensure it’s still aligned with your organization’s vision and goals.
Keep in mind that your plan won’t last forever, even if you do update it frequently. A successful strategic plan evolves with your company’s long-term goals. When you’ve achieved most of your strategic goals, or if your strategy has evolved significantly since you first made your plan, it might be time to create a new one.
Build a smarter strategic plan with a work management platform
To turn your company strategy into a plan—and ultimately, impact—make sure you’re proactively connecting company objectives to daily work. When you can clarify this connection, you’re giving your team members the context they need to get their best work done.
A work management platform plays a pivotal role in this process. It acts as a central hub for your strategic plan, ensuring that every task and project is directly tied to your broader company goals. This alignment is crucial for visibility and coordination, allowing team members to see how their individual efforts contribute to the company’s success.
By leveraging such a platform, you not only streamline workflow and enhance team productivity but also align every action with your strategic objectives—allowing teams to drive greater impact and helping your company move toward goals more effectively.
Strategic planning FAQs
Still have questions about strategic planning? We have answers.
Why do I need a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is one of many tools you can use to plan and hit your goals. It helps map out strategic objectives and growth metrics that will help your company be successful.
When should I create a strategic plan?
You should aim to create a strategic plan every three to five years, depending on your organization’s growth speed.
Since the point of a strategic plan is to map out your long-term goals and how you’ll get there, you should create a strategic plan when you’ve met most or all of them. You should also create a strategic plan any time you’re going to make a large pivot in your organization’s mission or enter new markets.
What is a strategic planning template?
A strategic planning template is a tool organizations can use to map out their strategic plan and track progress. Typically, a strategic planning template houses all the components needed to build out a strategic plan, including your company’s vision and mission statements, information from any competitive analyses or SWOT assessments, and relevant KPIs.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. business plan?
A business plan can help you document your strategy as you’re getting started so every team member is on the same page about your core business priorities and goals. This tool can help you document and share your strategy with key investors or stakeholders as you get your business up and running.
You should create a business plan when you’re:
Just starting your business
Significantly restructuring your business
If your business is already established, you should create a strategic plan instead of a business plan. Even if you’re working at a relatively young company, your strategic plan can build on your business plan to help you move in the right direction. During the strategic planning process, you’ll draw from a lot of the fundamental business elements you built early on to establish your strategy for the next three to five years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. mission and vision statements?
Your strategic plan, mission statement, and vision statements are all closely connected. In fact, during the strategic planning process, you will take inspiration from your mission and vision statements in order to build out your strategic plan.
Simply put:
A mission statement summarizes your company’s purpose.
A vision statement broadly explains how you’ll reach your company’s purpose.
A strategic plan pulls in inspiration from your mission and vision statements and outlines what actions you’re going to take to move in the right direction.
For example, if your company produces pet safety equipment, here’s how your mission statement, vision statement, and strategic plan might shake out:
Mission statement: “To ensure the safety of the world’s animals.”
Vision statement: “To create pet safety and tracking products that are effortless to use.”
Your strategic plan would outline the steps you’re going to take in the next few years to bring your company closer to your mission and vision. For example, you develop a new pet tracking smart collar or improve the microchipping experience for pet owners.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. company objectives?
Company objectives are broad goals. You should set these on a yearly or quarterly basis (if your organization moves quickly). These objectives give your team a clear sense of what you intend to accomplish for a set period of time.
Your strategic plan is more forward-thinking than your company goals, and it should cover more than one year of work. Think of it this way: your company objectives will move the needle towards your overall strategy—but your strategic plan should be bigger than company objectives because it spans multiple years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a business case?
A business case is a document to help you pitch a significant investment or initiative for your company. When you create a business case, you’re outlining why this investment is a good idea, and how this large-scale project will positively impact the business.
You might end up building business cases for things on your strategic plan’s roadmap—but your strategic plan should be bigger than that. This tool should encompass multiple years of your roadmap, across your entire company—not just one initiative.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a project plan?
A strategic plan is a company-wide, multi-year plan of what you want to accomplish in the next three to five years and how you plan to accomplish that. A project plan, on the other hand, outlines how you’re going to accomplish a specific project. This project could be one of many initiatives that contribute to a specific company objective which, in turn, is one of many objectives that contribute to your strategic plan.
What’s the difference between strategic management vs. strategic planning?
A strategic plan is a tool to define where your organization wants to go and what actions you need to take to achieve those goals. Strategic planning is the process of creating a plan in order to hit your strategic objectives.
Strategic management includes the strategic planning process, but also goes beyond it. In addition to planning how you will achieve your big-picture goals, strategic management also helps you organize your resources and figure out the best action plans for success.
Related resources

How to create a CRM strategy: 6 steps (with examples)
What is management by objectives (MBO)?

Write better AI prompts: A 4-sentence framework

What is content marketing? A complete guide
- Strategy & planning
How to set strategic goals (with 73 examples you can steal)
Georgina Guthrie
March 23, 2022
As a project manager, setting strategic goals for your team is an absolute must. By establishing objectives, you can ensure everyone (including yourself) is productive and moving in the right direction. It also means you can track progress and make real-time adjustments — which is incredibly difficult to do without clear metrics . In fact, without measurable goals, it’s near impossible to determine whether initiatives are working or not.
But what should these goals be?
What are strategic goals?
A strategic goal is a broad, long-term objective that a company strives to achieve. It can be something as general as becoming the top player in your industry or as specific as increasing market share by 20%.
There are different types of strategic goals (which we’ll explore in a little more detail later on), and each goal will involve metrics — the criteria you’ll use to measure progress.
Why are performance metrics important?
Metrics are important because they provide concrete evidence of whether a goal is being achieved. Without metrics, it can be difficult to determine whether things are working and how well. Metrics also help to identify areas of improvement and allow for targeted action.
Here are some common strategic goals metrics:
- Revenue growth : this metric measures how much revenue the company generates over some time. You can break it down by product, market, or other factors.
- Gross margin : this measures how much profit the company earns on each dollar of revenue. Gross margins are useful for tracking product profitability or comparing performance against competitors.
- Customer churn : churn refers to how many customers leave the company over a given period. It can identify areas of improvement and indicate which aspects of a service or product are driving away customers.
- Employee turnover : the opposite of retention, turnover measures how many employees leave the company over a given period. A high turnover rate often indicates that the company needs to improve its employee retention strategy or benefits package.
- Social media followers : this metric measures how many people follow your company on various social media platforms. Follower numbers help you determine the strength of the company’s brand awareness or engagement levels.
- Website visits : this metric shows how many people visit your company website over time. You can use this data to track the company’s online visibility or marketing efforts.
- Product launch success : this metric measures the success of a product release. You can use factors such as sales, customer feedback, and market share to understand product launch success clearly.
Strategic goals vs. strategic management: what’s the difference?
While both strategic goals and strategic management are important, they’re not the same thing.
- Strategic goals are the objectives a company aims to achieve.
- Strategic management is the process of setting and accomplishing those goals.
Think of strategic goals as the long-term outcome you envision — the things you want to achieve in three to five years. To achieve your goals, you need a well-defined process for developing and monitoring them. That’s where strategic management comes in.
Strategic goals vs. OKRs: what’s the difference?
OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) are a popular framework for setting strategic goals. But there are some key differences between OKRs and strategic goals.
Firstly, OKRs are typically shorter-term compared to strategic goals. Secondly, OKRs are more specific and quantitative, while strategic goals are broader and qualitative. Thirdly, OKRs are often used in performance-driven organizations, while strategic goals can be used in any organization.
Strategic goals vs. KPIs: what’s the difference?
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are a popular framework for measuring performance. Here’s where they differ from strategic goals.
KPIs are usually more narrow in scope than strategic goals. And while KPIs are highly specific and quantitative, strategic goals are more broad and qualitative. Also, KPIs are best suited for measuring operational performance , while strategic goals are better for measuring business performance overall.
Strategic goals vs. business goals:
There are some key similarities between strategic goals and business goals. Both are important for driving organizational success and must be measurable and achievable to offer the most value. But here’s where they differ:
- Strategic goals focus on long-term growth or performance, while business goals are more immediate targets you must hit to achieve bigger objectives.
- Business goals tend to be specific and quantitative, while strategic goals have a broader and more aspirational focus.
- Strategic goals encourage you to take a comprehensive approach to achieve organizational success. Business goals are more modular and focus on improving performance in individual business units or departments.
Which framework is right for your company?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question. The right goal-setting framework depends on your company’s size, culture, and industry. If unsure which model is right, speak with a business advisor or consultant for guidance. They can help you understand which operational factors impact your organization and choose a framework to drive progress.
How to set strategic goals
Now that we’ve covered some differences between strategic goals and other popular frameworks, let’s take a closer look at how to set effective strategic goals.
1. Start with the big picture
Start by thinking about the overall vision and mission of your company. What are you trying to achieve? Where do you want to be in three to five years? Once you have a general idea of where you want to go, you can start thinking about specific goals to help you get there.
2. Make them SMART
All goals should be SMART : that’s Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Your goals must be specific enough to be quantified and measured, achievable (not too easy or too difficult), and relevant to the company’s overall vision and mission. They should also have a specific timeframe for completion.
3. Communicate your goals to all employees
Make sure to communicate your goals to all employees, not just management. Employees need to understand what the company’s trying to accomplish and their role in achieving those objectives.
4. Hold everyone accountable
Holding employees accountable for meeting their goals is important to success. Use a system of rewards and penalties to motivate employees to stay on track.
5. Evaluate progress, and make changes as needed
Regularly evaluating progress is essential for managing the pace and success of your goals. If necessary, make changes based on what you learn from one milestone to the next.
Now, let’s get to some real-world examples.
73 strategic goal examples
We’ve split this list by goal type to make it easier to follow. Please note: the examples do not reflect Nulab’s goals; they’re here for educational purposes.
Strategic goals for finance
1) Increase revenue by 20% in the next three years 2) Reduce costs by 15% in the next 12 months 3) Invest in new technology that will improve our overall efficiency 4) Increase our market share by 5% in the next two years 5) Create a new product that will generate $1 million in revenue in the next 12 months 6) Diversify our revenue streams into two new markets 7) Become financially sustainable by 2023 8) Grow shareholder value by 20% in the next two years 9) Reduce marketing costs by 10% over the next year
Strategic goals for marketing
10) Increase website traffic by 25% in the next three months 11) Generate 1,000 leads through our website in the next six months 12) Double our social media following in the next six months 13) Increase customer satisfaction by five points in the next year 14) Increase brand awareness by 25% in the next year 15) Launch a new marketing campaign that generates a 10% ROI 16) Reach 10,000 people through our email list in the next six months 17) Secure two major partnerships in the next 12 months 18) Attend three industry tradeshows in the next year
Strategic goals for R&D
19) Develop a new product that will be in the market in 12 months 20) Patent our new technology by the end of the year 21) Increase our R&D budget by 15% in the next year 22) Hire two new senior scientists in the next six months 23) Double our current market share in the next three years 24) Develop a product that is fives times more efficient than our current products 25) Reduce the time to market for new products by 50% in the next year 26) Increase our customer base by 20% in the next year 27) Collaborate with two other companies in the next year
Strategic goals for employee productivity
28) Increase average billable hours per employee by 20% in the next three months 29) Streamline our billing process so that it takes employees less time to bill clients 30) Reduce customer support inquiries by 20% in the next month 31) Improve team productivity by 10% in the next three months 32) Implement a new CRM system that will make it easier for employees to find customer information 33) Create a training program for new employees that will shorten the learning curve 34) Hire two new customer service representatives in the next month 35) Allow employees to work from home one day a week 36) Give employees a 5% raise in the next three months
Strategic goals for innovation
37) Develop a new product that will be in the market in 12 months 38) Patent our new technology by the end of the year 39) Increase our R&D budget by 15% in the next year 40) Hire two new senior product designers in the next six months 41) Double our current market share in the next three years 42) Develop a product that is five times more efficient than our current products 43) Reduce the time to market for new products by 50% in the next year 44) Increase our customer base by 20% in the next year 45) Collaborate with two other companies in the next year
Customer-focused strategic goals
46) Increase customer satisfaction by five points in the next year 47) Decrease website bounce rate by 25% in the next three months 48) Generate 1,000 customer product reviews in the next six months 49) Secure a rating of 75% five-star reviews on Tripadvisor by the end of the quarter 50) Reduce refund time by one week by the end of next quarter 51) Host two focus groups in December to get feedback about the new product 52) Reduce customer call time wait by an average of three minutes in the next two months 53) Secure two major influencer partnerships in the next 12 months 54) Increase newsletter subscriptions by 20% by the end of 2022
Strategic goals for internal improvement
55) Increase average billable hours per employee by 20% in the next three months 56) Develop and implement new company core values by December 2023 57) Reduce staff turnover by 25% in the next six months 58) Increase employee satisfaction by 10% in the next six months 59) Implement a new training program for new employees 60) Give employees a raise of 5% in the next three months 61) Hire two new customer service representatives in the next month 62) Allow employees to work from home one day a week 63) Reduce the time it takes to process invoices by 50% in the next month 64) Implement new software that will improve team communication
Strategic goals to promote growth
65) Secure a new office space that is twice the size of our current one 66) Implement a new sales strategy that generates a 20% increase in sales in the next six months 67) Increase our customer base by 20% in the next year 68) Double our market share in the next three years 69) Collaborate with two other companies in the next year 70) Launch a new marketing campaign that generates a 10% ROI 71) Reach 10,000 people through our email list in the next six months 72) Secure two major partnerships in the next 12 months 73) Invest in a new advertising campaign
Final thoughts
Developing effective strategic goals is essential for any business, regardless of size or industry. By setting measurable, achievable objectives, you can ensure your company is moving fully ahead in the right direction and achieving its long-term goals.
As your organization or team grows and changes, choose tools that make collaborating and tracking your goal metrics as convenient as possible. By doing so, you’ll be able to work together as a team toward the success you and your business deserve.
Using a SWOT analysis to develop core business strategies
How to create an amazing elevator pitch using mind maps
Subscribe to our newsletter.
Learn with Nulab to bring your best ideas to life

How To Write A Strategic Plan That Gets Results + Examples

Are you feeling overwhelmed with the thought of writing a strategic plan for your business? Do you want to create a plan that will help you move your team forward with inspired alignment and disciplined execution? You're not alone.
Gone are the days of rigid, 5- or 10-year planning cycles that do not leave room for flexibility and innovation. To stay ahead of the curve, you need a dynamic and execution-ready strategic plan that can guide your business through the ever-evolving landscape.
At Cascade, we understand that writing a strategic plan can be dreadful, especially in today's unpredictable environment. That's why we've developed a simple model that can help you create a clear, actionable plan to achieve your organization's goals. With our tested and proven strategic planning template , you can write a strategic plan that is both adaptable and effective .
Whether you're a seasoned strategy professional or a fresh strategy planner, this guide will walk you through the process step-by-step on how to write a strategic plan. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive, easy-to-follow strategic plan that will help you align your organization on the path to success.
Follow this guide step-by-step or skip to the part you’re most interested in:
- Pre-Planning Phase: Build The Foundation
Cascade Model For Strategic Planning: What You Need To Know
- Key Elements of a Strategic Plan
How To Write A Strategic Plan In 6 Simple Steps
3 strategic plan examples to get you started, how to achieve organizational alignment with your strategic plan.
- Quick Overview of Key Steps In Writing A Strategic Plan
Create An Execution-Ready Strategic Plan With Cascade 🚀
*Editor’s note: This article is part of our ‘How to create a Strategy’ collection. At the end of this article, you’ll find a link to each piece within this collection so you can dig deeper into each element of an effective strategic plan and more related resources to master strategy execution.
Pre-Planning Phase: Build The Foundation
Before we dive into writing a strategic plan, it's essential to know the basics you should cover before the planning phase. The pre-planning phase is where you'll begin to gather the data and strategic insights necessary to create an effective strategic plan.
1. Run a strategic planning workshop
The first step is to run a strategic planning workshop with your team. Get your team in the room, get their data, and gather their insights. By running this workshop, you'll foster collaboration and bring fresh perspectives to the table. And that’s not all.
The process of co-creating and collaborating to put that plan together with stakeholders is one of the most critical factors in strategy execution . According to McKinsey’s research , initiatives in which employees contribute to development are 3.4 times more likely to be successful. They feel like the plan is a result of their efforts, and they feel ownership of it, so they're more likely to execute it.
💡 Tip: Use strategy frameworks to structure your strategy development sessions, such as GAP analysis , SWOT analysis , Porter’s Five Forces , Ansoff matrix , McKinsey 7S model , or GE matrix . You can even apply the risk matrix that will help you align and decide on key strategic priorities.
2. Choose your strategic planning model
Before creating your strategic plan, you need to decide which structure you will use. There are hundreds of ways to structure a strategic plan. You’ve likely heard of famous strategic models such as OKRs and the Balanced Scorecard .
But beyond the well-known ones, there's also a myriad of other strategic planning models ranging from the extremely simple to the absurdly complex.
Many strategic models work reasonably well on paper, but in reality, they don't show you how to write a strategic plan that fits your organization's needs.
Here are some common weaknesses most popular strategic models have:
- They're too complicated. People get lost in terminology rather than focus on execution.
- They don’t scale. They work well for small organizations but fail when you try to extend them across multiple teams.
- They're too rigid. They force people to add layers for the sake of adding layers.
- They're neither tangible nor measurable. They’re great at stating outcomes but lousy at helping you measure success.
- They're not adaptable. As we saw in the last years, the business environment can change quickly. Your model needs to be able to work in your current situation and adapt to changing economic landscapes.
Our goal in this article is to give you a simpler, more effective way to write a strategic plan. This is a tested and proven strategic planning model that has been refined over years of working with +20,000 teams around the world. We call it the Cascade Strategy Model.
This approach has proven to be more effective than any other model we have tried when it comes to executing and implementing the strategy .
It’s easy to use and it works for small businesses, fast-growing startups, as well as multinationals trying to figure out how to write a fail-proof strategic plan.
We’ve created a simple diagram below to illustrate what a strategic plan following the Cascade Model will look like when it's completed:
.jpeg)
Rather than a traditional roadmap , imagine your strategy as a flowchart. Each row is a mandatory step before moving on to the next.
We call our platform Cascade for a reason: strategy must cascade throughout an organization along with values, focus areas, and objectives.
Above all, the Cascade Model is intended to be execution-ready —in other words, it has been proven to deliver success far beyond strategic planning. It adds to a successful strategic management process.Key elements of a Strategic Plan
Key Elements Of A Strategic Plan
The key elements of a strategic plan include:
- Vision : Where do you want to get to?
- Values : How will you behave on the journey?
- Focus Areas : What are going to be your strategic priorities?
- Strategic objectives : What do you want to achieve?
- Actions and projects : How are you going to achieve the objectives?
- KPIs : How will you measure success?
In this part of the article, we will give you an overview of each element within the Cascade Model. You can follow this step-by-step process in a spreadsheet , or sign up to get instant access to a free Cascade strategic planning template and follow along as we cover the key elements of an effective strategic plan.
Your vision statement is your organization's anchor - it defines where you want to get to and is the executive summary of your organization's purpose. Without it, your strategic plan is like a boat without a rudder, at the mercy of strong winds and currents like Covid and global supply chain disruptions.
A good vision statement can help funnel your strategy towards long-term goals that matter the most to your organization, and everything you write in your plan from this point on will help you get closer to achieving your vision.
Trying to do too much at once is a surefire way to sink your strategic plan. By creating a clear and inspiring vision statement , you can avoid this trap and provide guidance and inspiration for your team. A great vision statement might even help attract talent and investment into your organization.
For example, a bike manufacturing company might have a vision statement like, “To be the premier bike manufacturer in the Pacific Northwest.” This statement clearly articulates the organization's goals and is a powerful motivator for the team.
In short, don't start your strategic plan without a clear vision statement. It will keep your organization focused and help you navigate toward success.
📚 Recommended read: How to Write a Vision Statement (With Examples, Tips, and Formulas)
Values are the enablers of your vision statement —they represent how your organization will behave as you work towards your strategic goals. Unfortunately, many companies throw around meaningless words just for the purpose of PR, leading to a loss of credibility.
To avoid this, make sure to integrate your organization’s core values into everyday operations and interactions. In today's highly-competitive world, it's crucial to remain steadfast in your values and cultivate an organizational culture that's transparent and trustworthy.
Companies with the best company cultures consistently outperform competitors and their average market by up to 115.6%, as reported by Glassdoor .
For example, a bike manufacturing company might have core values like:
- Accountability
These values reflect the organization's desire to become the leading bike manufacturer, while still being accountable to employees, customers, and shareholders.
👉 Here’s how to add vision and values to your strategic plan in Cascade:
After you sign up and invite your team members to collaborate on the plan, navigate to Plans and Teams > Teams page, and add the vision, mission and values. This will help you to ensure that the company’s vision, mission statement, and values are always at top of mind for everyone.
📚When you're ready to start creating some company values, check out our guide, How To Create Company Values .
3. Focus Areas
Your focus areas are the strategic priorities that will keep your team on track and working toward the company’s mission and vision. They represent the high-level areas that you need to focus on to achieve desired business outcomes.
In fact, companies with clearly defined priorities are more likely to achieve their objectives. According to a case study by the Harvard Business Review , teams that focus on a small number of key initiatives are more likely to succeed than those that try to do too much.
That’s also something that we usually recommend to our customers when they set up their strategic plan in Cascade. Rather than spreading your resources too thin over multiple focus areas, prioritize three to five.
Following our manufacturing example above, some good focus areas include:
- Aggressive growth
- Producing the nation's best bikes
- Becoming a modern manufacturer
- Becoming a top place to work
Your focus areas should be tighter in scope than your vision statement, but broader than specific goals, time frames, or metrics.
By defining your focus areas, you'll give your teams a guardrail to work within, which can help inspire innovation and creative problem-solving.
With a clear set of focus areas, your team will be better able to prioritize their work and stay focused on the most important things, which will ultimately lead to better business results.
👉Here’s how you can set focus areas in Cascade:
In Cascade, you can add focus areas while creating or importing an existing strategic plan from a spreadsheet. With Cascade’s Focus Area deep-dive functionality , you will be able to:
- Review the health of your focus areas in one place.
- Get a breakdown by plans, budgets, resources, and people behind each strategic priority.
- See something at-risk? Drill down into each piece of work regardless of how many plans it's a part of.

📚 Recommended read: Strategic Focus Areas: How to create them + Examples
4. Strategic Objectives
The importance of setting clear and specific objectives for your strategic plan cannot be overstated.
Strategic objectives are the specific and measurable outcomes you want to achieve . While they should align with your focus areas, they should be more detailed and have a clear deadline.
According to the 2022 State of High Performing Teams report , there is a strong correlation between goals and success not only at the individual and team level but also at the organizational level. Here’s what they found:
- Employees who are unaware of their company's goals are over three times more likely to work at a company that is experiencing a decline in revenue than employees who are aware of the goals.
- Companies with shrinking revenues are almost twice as likely to have employees with unclear work expectations.
Jumping straight into actions without defining clear objectives is a common mistake that can lead to missed opportunities or misalignment between strategy and execution.
To avoid this pitfall, we recommend you add between three and six objectives to each focus area .
It's here that we need to start being a bit more specific for the first time in your strategic planning process . Let's take a look at an example of a well-written strategic objective:
- Continue top-line growth that outpaces the industry by 31st Dec 2023.
This is too specific to be a focus area. While it's still very high level, it indicates what the company wants to accomplish and includes a clear deadline. Both these aspects are critical to a good strategic objective.
Your strategic objectives are the heart and soul of your plan, and you need to ensure they are well-crafted. So, take the time to create well-planned objectives that will help you achieve your vision and lead your organization to success.
👉Here’s how you can set objectives in Cascade:
Adding objectives in Cascade is intuitive, straightforward, and accessible from almost anywhere in the workspace. With one click, you’ll open the objective sidebar and fill out the details. These can include a timeline, the objective’s owner, collaborators, and how your objective will be measured (success criteria).
📚 Recommended read: What are Strategic Objectives? How to write them + Examples
5. Actions and projects
Once you’ve defined your strategic objectives, the next step is to identify the specific strategic initiatives or projects that will help you achieve those objectives . They are short-term goals or actionable steps you or your team members will take to accomplish objectives. They should leverage the company’s resources and core competencies.
Effective projects and actions in your strategic plan should:
- Be extremely specific.
- Contain a deadline.
- Have an owner.
- Align with at least one of your strategic objectives.
- Provide clarity on how you or your team will achieve the strategic objective.
Let's take a look at an example of a well-written project continuing with our bike manufacturing company using the strategic objective from above:
Strategic objective: Continue top-line growth that outpaces the industry by 31st Dec 2023.
Project: Expand into the fixed gear market by 31st December 2023.
This is more specific than the objective it links to, and it details what you will do to achieve the objective.
Another common problem area for strategic plans is that they never quite get down to the detail of what you're going to do.
It's easier to state "we need to grow our business," but without concrete projects and initiatives, those plans will sit forever within their PowerPoint templates, never to see the light of day after their initial creation.
Actions and projects are where the rubber meets the road. They connect the organizational strategic goals with the actual capabilities of your people and the resources at their disposal. Defining projects is a vital reality check every strategic plan needs.
👉Here’s how you create actions and projects in Cascade:
From the Objective sidebar, you can choose to add a project or action under your chosen objective. In the following steps, you can assign an owner and timeline to each action or project.
Plus, in Cascade, you can track the progress of each project or action in four different ways. You can do it manually, via milestones, checklists, or automatically by integrating with Jira and 1000+ other available integrations .
📚 Recommended read: How to create effective projects
Measuring progress towards strategic objectives is essential to effective strategic control and business success. That's where Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) come in. KPIs are measurable values that track progress toward achieving key business objectives . They keep you on track and help you stay focused on the goals you set for your organization.
To get the most out of your KPIs, make sure you link them to a specific goal or objective. In this way, you'll avoid creating KPIs that don't contribute to your objectives and distract you from focusing on what matters.
Ideally, you will add both leading and lagging KPIs to each objective so you can get a more balanced view of how well you're progressing. Leading KPIs can indicate future performance while lagging KPIs show how well you’ve done in the past. Both types of KPIs are critical for operational planning and keeping your business on track.
Think of KPIs as a form of signpost in your organization. They provide critical insights that inform business leaders of their organization’s progress toward key business objectives. Plus, they can help you identify opportunities faster and capitalize on flexibility.
👉Here’s how you can set and track KPIs in Cascade:
In Cascade , you can add measures while creating your objectives or add them afterward. Open the Objective sidebar and add your chosen measure.
When you create your Measure, you can choose how to track it. Using Cascade, you can track it manually or automatically. You can automate tracking via 1000+ integrations , including Excel spreadsheets and Google Sheets. In this way, you can save time and ensure that your team has up-to-date information for faster and more confident decision-making.
📚 Recommended reads:
- 10 Popular KPI Software Tools To Connect & Visualize Your Data (2023 Guide)
- How To Track KPIs To Hit Your Business Goals

Corporate Strategic Plan
Following the steps outlined above, you should end up with a strategic plan that looks something like this:

This is a preview of a corporate strategic plan template that is pre-filled with examples. Here you can use the template for free and begin filling it out to align with your organization's needs. Plus, it’s suitable for organizations of all sizes and any industry.
Once you fill in the template, you can also switch to the timeline view. You’ll get a complete overview of how the different parts of your plan are distributed across the roadmap in a Gantt chart view.

This template will help you create a structured approach to the strategic planning process, focus on key strategic priorities, and drive accountability to achieve necessary business outcomes.
👉 Get your free corporate strategic plan template here.
Coca-Cola Strategic Plan
Need a bit of extra inspiration to start writing your organization’s strategic plan? Check out this strategic plan example, inspired by Coca-Cola’s business plan:

This template is pre-filled with Coca-Cola’s examples so you can inspire your strategic success on one of the most iconic brands on the planet.
👉 Grab your free example of a Coca-Cola strategic plan here.
The Ramsay Health Care expansion strategy
Ramsay Health Care is a multinational healthcare provider with a strong presence in Australia, Europe, and Asia.
Almost all of its growth was organic and strategic. The company founded its headquarters in Sydney, Australia, but in the 21st century, it decided to expand globally through a primary strategy of making brownfield investments and acquisitions in key locations.
Ramsay's strategy was simple yet clever. By becoming a majority shareholder of the biggest local players, the company expanded organically in each region by leveraging and expanding their expertise.
Over the last two decades, Ramsay's global network has grown to 460 locations across 10 countries with over $13 billion in annual revenue.
📚 Recommended read: Strategy study: The Ramsay Health Care Growth Study
✨ Bonus resource: We've created a list of the most popular and free strategic plan templates in our library that will help you build a strategic plan based on the Cascade model explained in this article. You can use these templates to create a plan on a corporate, business unit, or team level.
We highlighted before that other strategic models often fail to scale strategic plans and goals scales across multiple teams and organizational levels.
In an ideal world, you want to have a maximum of two layers of detail underneath each of your focus areas. This means you'll have a focus area, followed by a layer of objectives. Underneath the objectives, you'll have a layer of actions, projects, and KPIs.

If you have a single team that’s responsible for the strategy execution, this works well. However, how do you implement a strategy across multiple and cross-functional teams? And why is it important?
According to LSA research of 410 companies across 8 industries, highly aligned companies grow revenue 58% faster and are 72% more profitable. And this is what Cascade can help you achieve.
To achieve achieve organization-wide alignment with your strategic plan and impact the bottom line, there are two ways to approach it in Casade: through contributing objectives or shared objectives .
1. Contributing objectives
This approach involves adding contributing objectives that link to your main strategic objectives, like this:

For each contributing objective, you simply repeat the Objective → Action/Project → KPI structure as follows:

Here's how you can create contributing objectives in Cascade:
Option A: Create contributing objectives within the same plan
This means creating multiple contributing objectives within the same strategic plan that contribute to the main objective.
However, be aware that if you have a lot of layers, your strategic plan can become cluttered, and people might have difficulty understanding how their daily efforts contribute to the strategic plan at the top level.
For example, the people responsible for managing contributing objectives at the bottom of the plan ( functional / operational level ) will lose visibility on how are their objectives linked to the main focus areas and objectives (at a corporate / business level ).
This approach is best suited to smaller organizations that only need to add a few layers of objectives to their plan.
Option B: Create contributing objectives from multiple plans linking to the main objective
This approach creates a network of aligned strategic plans within your organization. Each plan contains a set of focus areas and one single layer of objectives, each with its own set of projects, actions, and KPIs. This concept looks like this:

This example illustrates an objective that is a main objective in the IT strategic plan , but also contributes to the main strategic plan's objective.
For example, let’s say that your main business objective is to improve customer satisfaction by reducing product delivery time by 25% in the next quarter. This objective requires multiple operational teams within your organization to work together to achieve a shared objective.
Each team will create its own objective in its plan to contribute to the main objective:
- Logistics team: Reduce the shipment preparation time by 30%
- IT team: Implement new technology to reduce manual handling in the warehouse
- Production team: Increase production output by hour for 5%
Here’s how this example would look like within Cascade platform:

Although each contributing objective was originally created in its own plan, you can see how each contributing objective relates to the main strategic objective and its status in real-time.
2. Shared objectives
In Cascade, shared objectives are the same objectives shared across different strategic plans.
For example, you can have an objective that is “Achieve sustainable operations”. This objective can be part of the Corporate Strategy Plan, but also part of the Operations Plan , Supply Chain Plan , Production Plan, etc. In short, this objective becomes a shared objective between multiple teams and strategic plan.
This approach helps you to:
- Cascade your business strategy as deep as you want across a near-infinite number of people while maintaining strategic alignment throughout your organization .
- Create transparency and a much higher level of engagement in the strategy throughout your organization since objective owners are able to identify how their shared efforts contribute to the success of the main business objectives.
The more shared objectives you have across your organization, the more your teams will be aligned with the overarching business strategy. This is what we call " alignment health ”.
Here’s how you can see the shared objectives in the alignment map and analyze alignment health within Cascade:

You get a snapshot of how is your corporate strategic plan aligned with sub-plans from different business units or departments and the status of shared objectives. This helps you quickly identify misaligned initiatives and act before it’s too late. Plus, cross-functional teams have better visibility of how their efforts contribute to shared objectives.
So whether you choose contributing objectives or shared objectives, Cascade has the tools and features to help you achieve organization-wide alignment and boost your bottom line.
Quick Overview Of Key Steps In Writing A Strategic Plan
Here’s a quick infographic to help you remember how everything connects and why each element is critical to creating an effective strategic plan:

This simple answer to how to write a strategic plan avoids confusing jargon and has elements that the whole organization can both get behind and understand.
💡Tip: Save this image or bookmark this article for your next strategic planning session.
If you're struggling to write an execution-ready strategic plan, the Cascade model is the solution you've been looking for. With its clear, easy-to-understand terminology, and simple linkages between objectives, projects, and KPIs, you can create a plan that's both scalable and flexible.
But why is a flexible and execution-ready strategic plan so important? It's simple: without a clear and actionable plan, you'll never be able to achieve your business objectives. By using the Cascade Strategic Planning Model, you'll be able to create a plan that's both tangible and measurable, with KPIs that help you track progress towards your goals.
However, the real value of the Cascade framework lies in its flexibility . By creating links between main business objectives and your teams’ objectives, you can easily scale your plan without losing focus. Plus, the model's structure of linked layers means that you can always adjust your strategy in response to new challenges or opportunities and keep everyone on the same page.
So if you want to achieve results with your strategic plan, start using Cascade today. With its unique combination of flexibility and focus, it's the perfect tool for any organization looking to master strategy execution and succeed in today's fast-paced business world.
Want to see Cascade in action? Get started for free or book a 1:1 demo with Cascade’s in-house strategy expert.
This article is part one of our mini-series "How to Write a Strategic Plan". This first article will give you a solid strategy model for your plan and get the strategic thinking going.
Think of it as the foundation for your new strategy. Subsequent parts of the series will show you how to create the content for your strategic plan.
Articles in our How to Write a Strategic Plan series
- How To Write A Strategic Plan: The Cascade Model (This article)
- How to Write a Good Vision Statement
- How To Create Company Values
- Creating Strategic Focus Areas
- How To Write Strategic Objective
- How To Create Effective Projects
- How To Write KPIs + Ultimate Guide To Strategic Planning
More resources on strategic planning and strategy execution:
- 6 Steps to Successful Strategy Execution
- 4-Step Strategy Reporting Process (With Template)
- Annual Planning: Plan Like a Pro In 5 Steps (+ Template)
- 18 Free Strategic Plan Templates (Excel & Cascade) 2023
- The Right Way To Set Team Goals
- 23 Best Strategy Tools For Your Organization in 2023
Popular articles

Viva Goals Vs. Cascade: Goal Management Vs. Strategy Execution

What Is A Maturity Model? Overview, Examples + Free Assessment

How To Implement The Balanced Scorecard Framework (With Examples)

The Best Management Reporting Software For Strategy Officers (2024 Guide)
Your toolkit for strategy success.

Need a business plan? Call now:
Talk to our experts:
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB1 Business Plan
- EB2 Visa Business Plan
- EB5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- UK Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- UK Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Planning
- Landlord Business Plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- eCommerce business plan
- Online Boutique Business Plan
- Mobile Application Business Plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food Delivery Business Plan
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Buy Side Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples
Goals and Objectives for Business Plan with Examples
Published Nov.05, 2023
Updated Apr.23, 2024
By: Jakub Babkins
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 2
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Table of Content
Every business needs a clear vision of what it wants to achieve and how it plans to get there. A business plan is a document that outlines the goals and objectives of a business, as well as the strategies and actions to achieve them. A well-written business plan from business plan specialists can help a business attract investors, secure funding, and guide its growth.
Understanding Business Objectives
Business objectives are S pecific, M easurable, A chievable, R elevant, and T ime-bound (SMART) statements that describe what a business wants to accomplish in a given period. They are derived from the overall vision and mission of the business, and they support its strategic direction.
Business plan objectives can be categorized into different types, depending on their purpose and scope. Some common types of business objectives are:
- Financial objectives
- Operational objectives
- Marketing objectives
- Social objectives
For example, a sample of business goals and objectives for a business plan for a bakery could be:
- To increase its annual revenue by 20% in the next year.
- To reduce its production costs by 10% in the next six months.
- To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
- To improve its customer satisfaction rating by 15% in the next month.
The Significance of Business Objectives
Business objectives are important for several reasons. They help to:
- Clarify and direct the company and stakeholders
- Align the company’s efforts and resources to a common goal
- Motivate and inspire employees to perform better
- Measure and evaluate the company’s progress and performance
- Communicate the company’s value and advantage to customers and the market
For example, by setting a revenue objective, a bakery can focus on increasing its sales and marketing efforts, monitor its sales data and customer feedback, motivate its staff to deliver quality products and service, communicate its unique selling points and benefits to its customers, and adjust its pricing and product mix according to market demand.
Advantages of Outlining Business Objectives
Outlining business objectives is a crucial step in creating a business plan. It serves as a roadmap for the company’s growth and development. Outlining business objectives has several advantages, such as:
- Clarifies the company’s vision, direction, scope, and boundaries
- Break down the company’s goals into smaller tasks and milestones
- Assigns roles and responsibilities and delegates tasks
- Establishes standards and criteria for success and performance
- Anticipates risks and challenges and devises contingency plans
For example, by outlining its business objective for increasing the average revenue per customer in its business plan, a bakery can:
- Attract investors with its viable business plan for investors
- Secure funding from banks or others with its realistic financial plan
- Partner with businesses or organizations that complement or enhance its products or services
- Choose the best marketing, pricing, product, staff, location, etc. for its target market and customers
Setting Goals and Objectives for a Business Plan
Setting goals and objectives for a business plan is not a one-time task. It requires careful planning, research, analysis, and evaluation. To set effective goals and objectives for a business plan, one should follow some best practices, such as:
OPTION 1: Use the SMART framework. A SMART goal or objective is clear, quantifiable, realistic, aligned with the company’s mission and vision, and has a deadline. SMART stands for:
- Specific – The goal or objective should be clear, concise, and well-defined.
- Measurable – The goal or objective should be quantifiable or verifiable.
- Achievable – The goal or objective should be realistic and attainable.
- Relevant – The goal or objective should be aligned with the company’s vision, mission, and values.
- Time-bound – The goal or objective should have a deadline or timeframe.
For example, using the SMART criteria, a bakery can refine its business objective for increasing the average revenue per customer as follows:
- Specific – Increase revenue with new products and services from $5 to $5.50.
- Measurable – Track customer revenue monthly with sales reports.
- Achievable – Research the market, develop new products and services, and train staff to upsell and cross-sell.
- Relevant – Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, profitability and cash flow, and market competitiveness.
- Time-bound – Achieve this objective in six months, from January 1st to June 30th.
OPTION 2: Use the OKR framework. OKR stands for O bjectives and K ey R esults. An OKR is a goal-setting technique that links the company’s objectives with measurable outcomes. An objective is a qualitative statement of what the company wants to achieve. A key result is a quantitative metric that shows how the objective will be achieved.
OPTION 3: Use the SWOT analysis. SWOT stands for S trengths, W eaknesses, O pportunities, and T hreats. A SWOT analysis is a strategic tool that helps the company assess the internal and external factors that affect its goals and objectives.
- Strengths – Internal factors that give the company an advantage over others.
- Weaknesses – Internal factors that limit the company’s performance or growth.
- Opportunities – External factors that allow the company to improve or expand.
- Threats – External factors that pose a risk or challenge to the company.
For example, using these frameworks, a bakery might set the following goals and objectives for its SBA business plan :
Objective – To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
Key Results:
- Research gluten-free cake market demand and preferences by month-end.
- Create and test 10 gluten-free cake recipes by next month-end.
- Make and sell 100 gluten-free cakes weekly online or in-store by quarter-end.
SWOT Analysis:
- Expertise and experience in baking and cake decorating.
- Loyal and satisfied customer base.
- Strong online presence and reputation.
Weaknesses:
- Limited production capacity and equipment.
- High production costs and low-profit margins.
- Lack of knowledge and skills in gluten-free baking.
Opportunities:
- Growing demand and awareness for gluten-free products.
- Competitive advantage and differentiation in the market.
- Potential partnerships and collaborations with health-conscious customers and organizations.
- Increasing competition from other bakeries and gluten-free brands.
- Changing customer tastes and preferences.
- Regulatory and legal issues related to gluten-free labeling and certification.
Examples of Business Goals and Objectives
To illustrate how to write business goals and objectives for a business plan, let’s use a hypothetical example of a bakery business called Sweet Treats. Sweet Treats is a small bakery specializing in custom-made cakes, cupcakes, cookies, and other baked goods for various occasions.
Here are some examples of possible startup business goals and objectives for Sweet Treats:
Earning and Preserving Profitability
Profitability is the ability of a company to generate more revenue than expenses. It indicates the financial health and performance of the company. Profitability is essential for a business to sustain its operations, grow its market share, and reward its stakeholders.
Some possible objectives for earning and preserving profitability for Sweet Treats are:
- To increase the gross profit margin by 5% in the next quarter by reducing the cost of goods sold
- To achieve a net income of $100,000 in the current fiscal year by increasing sales and reducing overhead costs
Ensuring Consistent Cash Flow
Cash flow is the amount of money that flows in and out of a company. A company needs to have enough cash to cover its operating expenses, pay its debts, invest in its growth, and reward its shareholders.
Some possible objectives for ensuring consistent cash flow for Sweet Treats are:
- Increase monthly operating cash inflow by 15% by the end of the year by improving the efficiency and productivity of the business processes
- Increase the cash flow from investing activities by selling or disposing of non-performing or obsolete assets
Creating and Maintaining Efficiency
Efficiency is the ratio of output to input. It measures how well a company uses its resources to produce its products or services. Efficiency can help a business improve its quality, productivity, customer satisfaction, and profitability.
Some possible objectives for creating and maintaining efficiency for Sweet Treats are:
- To reduce the production time by 10% in the next month by implementing lean manufacturing techniques
- To increase the customer service response rate by 20% in the next week by using chatbots or automated systems
Winning and Keeping Clients
Clients are the people or organizations that buy or use the products or services of a company. They are the source of revenue and growth for a company. Therefore, winning and keeping clients is vital to generating steady revenue, increasing customer loyalty, and enhancing word-of-mouth marketing.
Some possible objectives for winning and keeping clients for Sweet Treats are:
- To acquire 100 new clients in the next quarter by launching a referral program or a promotional campaign
- To retain 90% of existing clients in the current year by offering loyalty rewards or satisfaction guarantees
Building a Recognizable Brand
A brand is the name, logo, design, or other features distinguishing a company from its competitors. It represents the identity, reputation, and value proposition of a company. Building a recognizable brand is crucial for attracting and retaining clients and creating a loyal fan base.
Some possible objectives for building a recognizable brand for Sweet Treats are:
- To increase brand awareness by 50% in the next six months by creating and distributing engaging content on social media platforms
- To improve brand image by 30% in the next year by participating in social causes or sponsoring events that align with the company’s values
Expanding and Nurturing an Audience with Marketing
An audience is a group of people interested in or following a company’s products or services. They can be potential or existing clients, fans, influencers, or partners. Expanding and nurturing an audience with marketing is essential for increasing a company’s visibility, reach, and engagement.
Some possible objectives for expanding and nurturing an audience with marketing for Sweet Treats are:
- To grow the email list by 1,000 subscribers in the next month by offering a free ebook or a webinar
- To nurture leads by sending them relevant and valuable information through email newsletters or blog posts
Strategizing for Expansion
Expansion is the process of increasing a company’s size, scope, or scale. It can involve entering new markets, launching new products or services, opening new locations, or forming new alliances. Strategizing for expansion is important for diversifying revenue streams, reaching new audiences, and gaining competitive advantages.
Some possible objectives for strategizing for expansion for Sweet Treats are:
- To launch a new product or service line by developing and testing prototypes
- To open a new branch or franchise by securing funding and hiring staff
Template for Business Objectives
A template for writing business objectives is a format or structure that can be used as a guide or reference for creating your objectives. A template for writing business objectives can help you to ensure that your objectives are SMART, clear, concise, and consistent.
To use this template, fill in the blanks with your information. Here is an example of how you can use this template:
Example of Business Objectives
Our business is a _____________ (type of business) that provides _____________ (products or services) to _____________ (target market). Our vision is to _____________ (vision statement) and our mission is to _____________ (mission statement).
Our long-term business goals and objectives for the next _____________ (time period) are:
S pecific: We want to _____________ (specific goal) by _____________ (specific action).
M easurable: We will measure our progress by _____________ (quantifiable indicator).
A chievable: We have _____________ (resources, capabilities, constraints) that will enable us to achieve this goal.
R elevant: This goal supports our vision and mission by _____________ (benefit or impact).
T ime-bound: We will complete this goal by _____________ (deadline).
Repeat this process for each goal and objective for your business plan.
How to Monitor Your Business Objectives?
After setting goals and objectives for your business plan, you should check them regularly to see if you are achieving them. Monitoring your business objectives can help you to:
- Track your progress and performance
- Identify and overcome any challenges
- Adjust your actions and strategies as needed
Some of the tools and methods that you can use to monitor your business objectives are:
- Dashboards – Show key data and metrics for your objectives with tools like Google Data Studio, Databox, or DashThis.
- Reports – Get detailed information and analysis for your objectives with tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, or SEMrush.
- Feedback – Learn from your customers and their needs and expectations with tools like SurveyMonkey, Typeform, or Google Forms.
Strategies for Realizing Business Objectives
To achieve your business objectives, you need more than setting and monitoring them. You need strategies and actions that support them. Strategies are the general methods to reach your objectives. Actions are the specific steps to implement your strategies.
Different objectives require different strategies and actions. Some common types are:
- Marketing strategies
- Operational strategies
- Financial strategies
- Human resource strategies
- Growth strategies
To implement effective strategies and actions, consider these factors:
- Alignment – They should match your vision, mission, values, goals, and objectives
- Feasibility – They should be possible with your capabilities, resources, and constraints
- Suitability – They should fit the context and needs of your business
How OGSCapital Can Help You Achieve Your Business Objectives?
We at OGSCapital can help you with your business plan and related documents. We have over 15 years of experience writing high-quality business plans for various industries and regions. We have a team of business plan experts who can assist you with market research, financial analysis, strategy formulation, and presentation design. We can customize your business plan to suit your needs and objectives, whether you need funding, launching, expanding, or entering a new market. We can also help you with pitch decks, executive summaries, feasibility studies, and grant proposals. Contact us today for a free quote and start working on your business plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the goals and objectives in business.
Goals and objectives in a business plan are the desired outcomes that a company works toward. To describe company goals and objectives for a business plan, start with your mission statement and then identify your strategic and operational objectives. To write company objectives, you must brainstorm, organize, prioritize, assign, track, and review them using the SMART framework and KPIs.
What are the examples of goals and objectives in a business plan?
Examples of goals and objectives in a business plan are: Goal: To increase revenue by 10% each year for the next five years. Objective: To launch a new product line and create a marketing campaign to reach new customers.
What are the 4 main objectives of a business?
The 4 main objectives of a business are economic, social, human, and organic. Economic objectives deal with financial performance, social objectives deal with social responsibility, human objectives deal with employee welfare, and organic objectives deal with business growth and development.
What are goals and objectives examples?
Setting goals and objectives for a business plan describes what a business or a team wants to achieve and how they will do it. For example: Goal: To provide excellent customer service. Objective: To increase customer satisfaction scores by 20% by the end of the quarter.
At OGSCapital, our business planning services offer expert guidance and support to create a realistic and actionable plan that aligns with your vision and mission. Get in touch to discuss further!
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Ice Vending Machine Business Plan

OGScapital at the National Citizenship and Immigration Conference

How to Start a Plumbing Business in 2024: A Detailed Guide

Vegetable Farming Business Plan

Trading Business Plan

How To Write A Textile Manufacturing Business Plan

Any questions? Get in Touch!
We have been mentioned in the press:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Search the site:
- Project management Track your team’s tasks and projects in Hive
- Time tracking Automatically track time spent on Hive actions
- Goals Set and visualize your most important milestones
- Resourcing Track time and assign teammates to projects
- Forms Gather feedback, project intake, client requests and more
- Proofing & Approvals Streamline design and feedback workflows in Hive
- See all features
- Analytics Gain visibility and gather insights into your projects
- Automations Save time by automating everyday tasks
- Hive Apps Connect dozens of apps to streamline work from anywhere
- Integrations Sync Hive with your most-used external apps
- Templates Quick-start your work in Hive with pre-built templates
- Download Hive Access your workspace on desktop or mobile
- Project management Streamline initiatives of any size & customize your workflow by project
- Resource management Enable seamless resourcing and allocation across your team
- Project planning Track and plan all upcoming projects in one central location
- Time tracking Consolidate all time tracking and task management in Hive
- Cross-company collaboration Unite team goals across your organization
- Client engagement Build custom client portals and dashboards for external use
- All use cases
- Enterprise Bring your organization into one unified platform
- Agency Streamline project intake, project execution, and client comms
- University Marketing Maximize value from your marketing and admissions workflows with Hive
- Nonprofits Seamless planning, fundraising, event execution and more
- Marketing Streamline your marketing projects and timelines
- Business operations Track and optimize strategic planning and finance initiatives
- Education Bring your institutions’ planning, fundraising, and more into Hive
- Design Use Hive to map out and track all design initiatives and assets
- On-demand demo Access a guided walk through Hive
- Customers More on how Teams are using Hive now
- FAQ & support articles Find answers to your most asked questions
- Hive University Become a Hive expert with our free Hive U courses
- Webinars Learn about Hive’s latest features
- Hive Community Where members discuss and answer questions in the community
- Professional Services Get hands-on help from our Professional Services team
- Hive Partners Explore partners services or join as a partner
- FEATURED WEBINAR
Time Tracking 101: The Basics
Learn how to utilize Hive's time tracking feature to increase productivity and efficiency in your work.
- Request Demo
- Get Started
What Are Strategic Objectives? Examples & How To Track Them
- Julie Simpson
- March 7, 2024
Table of Contents
Strategic objectives are an organization’s long-term goals to achieve its overall mission and vision. These objectives provide direction for the organization and serve as a roadmap for success.
If the term strategic objectives are not ringing any bells, you might have heard them discussed in another way. Also described as objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART ), these objectives guide an organization in decision-making and resource allocation .
You would want to incorporate strategic objectives within your organization for many reasons. They are more than just goals or daily tasks that you accomplish. They are components of your business’s strategy that require serious forethought and commitment.
In this article, we will discuss some of the steps your organization should take to build out strategic objectives, some examples to get you started, and a few ways to track your progress and measure your success.
Strategic objectives vs goals
Okay, so I initially thought both of these concepts were the same thing. So, if your brain goes there, you are not alone! However, after further review and research, goals and strategic objectives are two different processes.
While both goals and strategic objectives are related – they accomplish different concepts. Goals are broad, long-term aspirations that an organization aims to achieve, while strategic objectives are the SMART steps that support achieving those goals.
Essentially, goals are often qualitative and may be more abstract than strategic objectives. They provide a sense of direction for the organization and may be set for a long time horizon, such as five or ten years. Goals typically do not have a defined timeline for completion, and they may not be broken down into smaller, actionable steps.
Strategic objectives, however, are more concrete and can be extremely specific. They are the actionable steps that an organization takes to achieve its goals. They are often quantitative and SMART and may have a shorter time horizon, such as one to three years.
Goal example:
To become the leading provider of widgets in the southern region of Florida.
Strategic objective example:
Launch a new line of widgets within the next 12 months that are more efficient and cost-effective than the current widget offerings, targeting commercial and industrial customers.
6 Examples of strategic objectives
Strategic objectives vary depending on the organization’s size, industry, and goals. However, some common strategic objectives include increasing revenue, improving customer satisfaction , expanding market share, reducing costs, and enhancing operational efficiency. Examples of strategic objectives to grow your business include:
- Increase revenue
- Improve customer satisfaction
- Expand market share
- Reduce business costs
- Enhance operational efficiency
- Strengthen innovation and R&D
1. Increase Revenue
Increasing revenue is a common strategic objective for businesses. Using a strategic objective to achieve this could be through expanding into new markets, introducing new products or services, improving link building and marketing strategies, or increasing customer retention.
2. Improve Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is crucial to the success of any business. Customer satisfaction can be improved through providing efficient customer service , developing new products or services that meet customer needs or offering an upgraded personalized experience. Happy customers mean loyal customers! Customer support platforms helps businesses deliver fast, personalized help to keep customers satisfied.
3. Expand Market Share
Expanding market share is a way businesses scale and expand their product reach. Companies can do this through campaigns targeting new customer segments, acquiring competitors, or partnering with other businesses to get a foothold into new markets.
4. Reduce Costs
Reducing costs is a strategic objective that can help businesses improve profitability. Companies seeking to improve operational efficiency can look to renegotiate supplier contracts or outsource non-core functions. For example, you can decide to switch from your current costly communication channel to a more efficient and budget-friendly business phone service .
You can check out sites like TheNewWorkforce.com for more information on outsourcing your tasks.
5. Enhance Operational Efficiency
Improving operational efficiency is a strategic objective that can help businesses streamline processes and reduce costs. Companies may aim to achieve this objective by adopting new technologies, improving employee training, or implementing lean manufacturing processes.
6. Strengthen Innovation and R&D
Fostering innovation and R&D (research and development) is a strategic objective that encourages businesses to stay competitive and adapt to changing market demands. This goal can be achieved through allocating resources for R&D activities, encouraging creative thinking and idea generation , and promoting a culture of experimentation and continuous improvement.
How do you track your strategic objectives?
If you cannot track your strategic objectives, how do you know how much progress you are making toward achieving them? Strategic objectives are not just a “set it and forget it” process but must be constantly assessed and measured for success.
To ensure you meet and exceed your strategic objectives, follow these five tips to ensure you hit your objectives:
- Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Measurable metrics help organizations track progress towards their strategic objectives. Organizations should identify the most critical KPIs for each type of strategic objective proposed and establish specific benchmarks for success.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly monitoring your progress towards strategic objectives will help your organization identify areas that require improvement and make necessary adjustments.
- Communicate Results: Communicating results to stakeholders and peers can help organizations build support for their strategic objectives. It also allows the team to celebrate successes and discuss any setbacks.
- Adjust Strategies: As organizations track progress toward strategic objectives, opportunities arise that allow you to identify and adjust the strategies as needed. Organizations should be flexible and willing to change strategies to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
- Use tracking software: Using a project management software platform or goal-tracking tool will be your best friend. With so many moving parts for strategy, using a software platform that can communicate, pull reports, and automate your processes for time-savings, will help keep you on track and team members on the same page.
By implementing these tips into your process of tracking your strategic objectives, you will ensure that you are making steady progress toward achieving each goal. Doing this will set the pace for your strategic objectives and set you up for success. If you set up and follow through with your objectives, you are guaranteed to improve performance, achieve success, and build support for their mission and vision.
Using Hive To Set Your Goals
Are you ready to start making strategic goals with your team? You’re in luck — Hive’s newest (and most exciting) feature is Goals . Everyone wants to know how they’re moving their organization forward, and your team is more than just a project. With Goals, you can set various goals, visualize progress, and keep everyone aligned in one centralized dashboard. You can also:
- Create one, ten, twenty, or more goals for your team, so everyone understands what they’re contributing to.
- Centralize and automate your goal tracking and reporting.
- Pull data from other systems into Hive to streamline operations and reporting.
- Share your goal or goals, assign the goal to relevant teammates, track activity, and give yourselves a deadline.
- Understand how your team and organization are pacing towards an individual goal or a set of goals.
- Color-coded designations allow an easy understanding of “on-track” items.
- When it’s time to review progress, accomplishments, and achievements, easily export all relevant information.
Help your organization track strategic objectives. Get started today with a free 14-day trial of Hive !
Want to spread the word? Share on social
Get started with hive.
Test Hive out with a 2 week free trial.
Join the community!
Terms of Service
Privacy Policy
© 2015 – 2024 HIVE® INC.
Essential Guide to the Strategic Planning Process
By Joe Weller | April 3, 2019 (updated March 26, 2024)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, you’ll learn the basics of the strategic planning process and how a strategic plan guides you to achieving your organizational goals. Plus, find expert insight on getting the most out of your strategic planning.
Included on this page, you'll discover the importance of strategic planning , the steps of the strategic planning process , and the basic sections to include in your strategic plan .
What Is Strategic Planning?
Strategic planning is an organizational activity that aims to achieve a group’s goals. The process helps define a company’s objectives and investigates both internal and external happenings that might influence the organizational path. Strategic planning also helps identify adjustments that you might need to make to reach your goal. Strategic planning became popular in the 1960s because it helped companies set priorities and goals, strengthen operations, and establish agreement among managers about outcomes and results.
Strategic planning can occur over multiple years, and the process can vary in length, as can the final plan itself. Ideally, strategic planning should result in a document, a presentation, or a report that sets out a blueprint for the company’s progress.
By setting priorities, companies help ensure employees are working toward common and defined goals. It also aids in defining the direction an enterprise is heading, efficiently using resources to achieve the organization’s goals and objectives. Based on the plan, managers can make decisions or allocate the resources necessary to pursue the strategy and minimize risks.
Strategic planning strengthens operations by getting input from people with differing opinions and building a consensus about the company’s direction. Along with focusing energy and resources, the strategic planning process allows people to develop a sense of ownership in the product they create.

“Strategic planning is not really one thing. It is really a set of concepts, procedures, tools, techniques, and practices that have to be adapted to specific contexts and purposes,” says Professor John M. Bryson, McKnight Presidential Professor of Planning and Public Affairs at the Hubert H. Humphrey School of Public Affairs, University of Minnesota and author of Strategic Planning for Public and Nonprofit Organizations: A Guide to Strengthening and Sustaining Organizational Achievement . “Strategic planning is a prompt to foster strategic thinking, acting, and learning, and they all matter and they are all connected.”
What Strategic Planning Is Not
Strategic planning is not a to-do list for the short or long term — it is the basis of a business, its direction, and how it will get there.
“You have to think very strategically about strategic planning. It is more than just following steps,” Bryson explains. “You have to understand strategic planning is not some kind of magic solution to fixing issues. Don’t have unrealistic expectations.”
Strategic planning is also different from a business plan that focuses on a specific product, service, or program and short-term goals. Rather, strategic planning means looking at the big picture.
While they are related, it is important not to confuse strategic planning with strategic thinking, which is more about imagining and innovating in a way that helps a company. In contrast, strategic planning supports those thoughts and helps you figure out how to make them a reality.
Another part of strategic planning is tactical planning , which involves looking at short-term efforts to achieve longer-term goals.
Lastly, marketing plans are not the same as strategic plans. A marketing plan is more about introducing and delivering a service or product to the public instead of how to grow a business. For more about marketing plans and processes, read this article .
Strategic plans include information about finances, but they are different from financial planning , which involves different processes and people. Financial planning templates can help with that process.
Why Is Strategic Planning Important?
In today’s technological age, strategic plans provide businesses with a path forward. Strategic plans help companies thrive, not just survive — they provide a clear focus, which makes an organization more efficient and effective, thereby increasing productivity.

“You are not going to go very far if you don’t have a strategic plan. You need to be able to show where you are going,” says Stefan Hofmeyer, an experienced strategist and co-founder of Global PMI Partners . He lives in the startup-rich environment of northern California and says he often sees startups fail to get seed money because they do not have a strong plan for what they want to do and how they want to do it.
Getting team members on the same page (in both creating a strategic plan and executing the plan itself) can be beneficial for a company. Planners can find satisfaction in the process and unite around a common vision. In addition, you can build strong teams and bridge gaps between staff and management.
“You have to reach agreement about good ideas,” Bryson says. “A really good strategy has to meet a lot of criteria. It has to be technically workable, administratively feasible, politically acceptable, and legally, morally, and ethically defensible, and that is a pretty tough list.”
By discussing a company’s issues during the planning process, individuals can voice their opinions and provide information necessary to move the organization ahead — a form of problem solving as a group.
Strategic plans also provide a mechanism to measure success and progress toward goals, which keeps employees on the same page and helps them focus on the tasks at hand.
When Is the Time to Do Strategic Planning?
There is no perfect time to perform strategic planning. It depends entirely on the organization and the external environment that surrounds it. However, here are some suggestions about when to plan:
If your industry is changing rapidly
When an organization is launching
At the start of a new year or funding period
In preparation for a major new initiative
If regulations and laws in your industry are or will be changing
“It’s not like you do all of the thinking and planning, and then implement,” Bryson says. “A mistake people make is [believing] the thinking has to precede the acting and the learning.”
Even if you do not re-create the entire planning process often, it is important to periodically check your plan and make sure it is still working. If not, update it.
What Is the Strategic Planning Process?
Strategic planning is a process, and not an easy one. A key is to make sure you allow enough time to complete the process without rushing, but not take so much time that you lose momentum and focus. The process itself can be more important than the final document due to the information that comes out of the discussions with management, as well as lower-level workers.

“There is not one favorite or perfect planning process,” says Jim Stockmal, president of the Association for Strategic Planning (ASP). He explains that new techniques come out constantly, and consultants and experienced planners have their favorites. In an effort to standardize the practice and terms used in strategic planning, ASP has created two certification programs .
Level 1 is the Strategic Planning Professional (SPP) certification. It is designed for early- or mid-career planners who work in strategic planning. Level 2, the Strategic Management Professional (SMP) certification, is geared toward seasoned professionals or those who train others. Stockmal explains that ASP designed the certification programs to add structure to the otherwise amorphous profession.
The strategic planning process varies by the size of the organization and can be formal or informal, but there are constraints. For example, teams of all sizes and goals should build in many points along the way for feedback from key leaders — this helps the process stay on track.
Some elements of the process might have specific start and end points, while others are continuous. For example, there might not be one “aha” moment that suddenly makes things clear. Instead, a series of small moves could slowly shift the organization in the right direction.
“Don’t make it overly complex. Bring all of the stakeholders together for input and feedback,” Stockmal advises. “Always be doing a continuous environmental scan, and don’t be afraid to engage with stakeholders.”
Additionally, knowing your company culture is important. “You need to make it work for your organization,” he says.
There are many different ways to approach the strategic planning process. Below are three popular approaches:
Goals-Based Planning: This approach begins by looking at an organization’s mission and goals. From there, you work toward that mission, implement strategies necessary to achieve those goals, and assign roles and deadlines for reaching certain milestones.
Issues-Based Planning: In this approach, start by looking at issues the company is facing, then decide how to address them and what actions to take.
Organic Planning: This approach is more fluid and begins with defining mission and values, then outlining plans to achieve that vision while sticking to the values.
“The approach to strategic planning needs to be contingent upon the organization, its history, what it’s capable of doing, etc.,” Bryson explains. “There’s such a mistake to think there’s one approach.”
For more information on strategic planning, read about how to write a strategic plan and the different types of models you can use.
Who Participates in the Strategic Planning Process?
For work as crucial as strategic planning, it is necessary to get the right team together and include them from the beginning of the process. Try to include as many stakeholders as you can.
Below are suggestions on who to include:
Senior leadership
Strategic planners
Strategists
People who will be responsible for implementing the plan
People to identify gaps in the plan
Members of the board of directors
“There can be magic to strategic planning, but it’s not in any specific framework or anybody’s 10-step process,” Bryson explains. “The magic is getting key people together, getting them to focus on what’s important, and [getting] them to do something about it. That’s where the magic is.”
Hofmeyer recommends finding people within an organization who are not necessarily current leaders, but may be in the future. “Sometimes they just become obvious. Usually they show themselves to you, you don’t need to look for them. They’re motivated to participate,” he says. These future leaders are the ones who speak up at meetings or on other occasions, who put themselves out there even though it is not part of their job description.
At the beginning of the process, establish guidelines about who will be involved and what will be expected of them. Everyone involved must be willing to cooperate and collaborate. If there is a question about whether or not to include anyone, it is usually better to bring on extra people than to leave someone out, only to discover later they should have been a part of the process all along. Not everyone will be involved the entire time; people will come and go during different phases.
Often, an outside facilitator or consultant can be an asset to a strategic planning committee. It is sometimes difficult for managers and other employees to sit back and discuss what they need to accomplish as a company and how they need to do it without considering other factors. As objective observers, outside help can often offer insight that may escape insiders.
Hofmeyer says sometimes bosses have blinders on that keep them from seeing what is happening around them, which allows them to ignore potential conflicts. “People often have their own agendas of where they want to go, and if they are not aligned, it is difficult to build a strategic plan. An outsider perspective can really take you out of your bubble and tell you things you don’t necessarily want to hear [but should]. We get into a rhythm, and it’s really hard to step out of that, so bringing in outside people can help bring in new views and aspects of your business.”
An outside consultant can also help naysayers take the process more seriously because they know the company is investing money in the efforts, Hofmeyer adds.
No matter who is involved in the planning process, make sure at least one person serves as an administrator and documents all planning committee actions.
What Is in a Strategic Plan?
A strategic plan communicates goals and what it takes to achieve them. The plan sometimes begins with a high-level view, then becomes more specific. Since strategic plans are more guidebooks than rulebooks, they don’t have to be bureaucratic and rigid. There is no perfect plan; however, it needs to be realistic.
There are many sections in a strategic plan, and the length of the final document or presentation will vary. The names people use for the sections differ, but the general ideas behind them are similar: Simply make sure you and your team agree on the terms you will use and what each means.
One-Page Strategic Planning Template
“I’m a big fan of getting a strategy onto one sheet of paper. It’s a strategic plan in a nutshell, and it provides a clear line of sight,” Stockmal advises.
You can use the template below to consolidate all your strategic ideas into a succinct, one-page strategic plan. Doing so provides you with a high-level overview of your strategic initiatives that you can place on your website, distribute to stakeholders, and refer to internally. More extensive details about implementation, capacity, and other concerns can go into an expanded document.
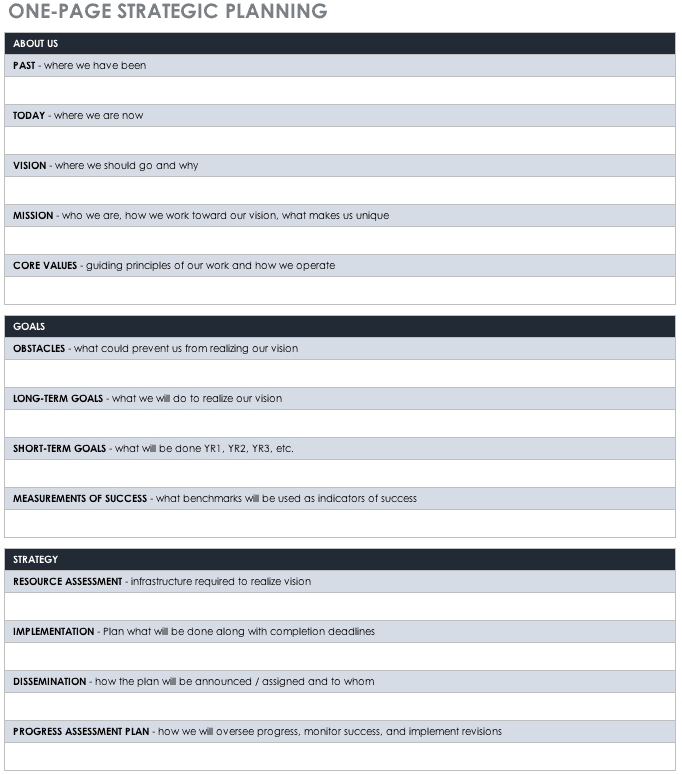
Download One-Page Strategic Planning Template Excel | Word | Smartsheet
The most important part of the strategic plan is the executive summary, which contains the highlights of the plan. Although it appears at the beginning of the plan, it should be written last, after you have done all your research.
Of writing the executive summary, Stockmal says, “I find it much easier to extract and cut and edit than to do it first.”
For help with creating executive summaries, see these templates .
Other parts of a strategic plan can include the following:
Description: A description of the company or organization.
Vision Statement: A bold or inspirational statement about where you want your company to be in the future.
Mission Statement: In this section, describe what you do today, your audience, and your approach as you work toward your vision.
Core Values: In this section, list the beliefs and behaviors that will enable you to achieve your mission and, eventually, your vision.
Goals: Provide a few statements of how you will achieve your vision over the long term.
Objectives: Each long-term goal should have a few one-year objectives that advance the plan. Make objectives SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, and time-based) to get the most out of them.
Budget and Operating Plans: Highlight resources you will need and how you will implement them.
Monitoring and Evaluation: In this section, describe how you will check your progress and determine when you achieve your goals.
One of the first steps in creating a strategic plan is to perform both an internal and external analysis of the company’s environment. Internally, look at your company’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as the personal values of those who will implement your plan (managers, executives, board members). Externally, examine threats and opportunities within the industry and any broad societal expectations that might exist.
You can perform a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis to sum up where you are currently and what you should focus on to help you achieve your future goals. Strengths shows you what you do well, weaknesses point out obstacles that could keep you from achieving your objectives, opportunities highlight where you can grow, and threats pinpoint external factors that could be obstacles in your way.
You can find more information about performing a SWOT analysis and free templates in this article . Another analysis technique, STEEPLE (social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, and ethical), often accompanies a SWOT analysis.
Basics of Strategic Planning
How you navigate the strategic planning process will vary. Several tools and techniques are available, and your choice depends on your company’s leadership, culture, environment, and size, as well as the expertise of the planners.
All include similar sections in the final plan, but the ways of driving those results differ. Some tools are goals-based, while others are issues- or scenario-based. Some rely on a more organic or rigid process.
Hofmeyer summarizes what goes into strategic planning:
Understand the stakeholders and involve them from the beginning.
Agree on a vision.
Hold successful meetings and sessions.
Summarize and present the plan to stakeholders.
Identify and check metrics.
Make periodic adjustments.
Items That Go into Strategic Planning
Strategic planning contains inputs, activities, outputs, and outcomes. Inputs and activities are elements that are internal to the company, while outputs and outcomes are external.
Remember, there are many different names for the sections of strategic plans. The key is to agree what terms you will use and define them for everyone involved.
Inputs are important because it is impossible to know where you are going until you know what is around you where you are now.
Companies need to gather data from a variety of sources to get a clear look at the competitive environment and the opportunities and risks within that environment. You can think of it like a competitive intelligence program.
Data should come from the following sources:
Interviews with executives
A review of documents about the competition or market that are publicly available
Primary research by visiting or observing competitors
Studies of your industry
The values of key stakeholders
This information often goes into writing an organization’s vision and mission statements.
Activities are the meetings and other communications that need to happen during the strategic planning process to help everyone understand the competition that surrounds the organization.
It is important both to understand the competitive environment and your company’s response to it. This is where everyone looks at and responds to the data gathered from the inputs.
The strategic planning process produces outputs. Outputs can be as basic as the strategic planning document itself. The documentation and communications that describe your organization’s strategy, as well as financial statements and budgets, can also be outputs.
The implementation of the strategic plan produces outcomes (distinct from outputs). The outcomes determine the success or failure of the strategic plan by measuring how close they are to the goals and vision you outline in your plan.
It is important to understand there will be unplanned and unintended outcomes, too. How you learn from and adapt to these changes influence the success of the strategic plan.
During the planning process, decide how you will measure both the successes and failures of different parts of the strategic plan.
Sharing, Evaluating, and Monitoring the Progress of a Strategic Plan
After companies go through a lengthy strategic planning process, it is important that the plan does not sit and collect dust. Share, evaluate, and monitor the plan to assess how you are doing and make any necessary updates.
“[Some] leaders think that once they have their strategy, it’s up to someone else to execute it. That’s a mistake I see,” Stockmal says.
The process begins with distributing and communicating the plan. Decide who will get a copy of the plan and how those people will tell others about it. Will you have a meeting to kick off the implementation? How will you specify who will do what and when? Clearly communicate the roles people will have.
“Before you communicate the plan [to everyone], you need to have the commitment of stakeholders,” Hofmeyer recommends. Have the stakeholders be a part of announcing the plan to everyone — this keeps them accountable because workers will associate them with the strategy. “That applies pressure to the stakeholders to actually do the work.”
Once the team begins implementation, it’s necessary to have benchmarks to help measure your successes against the plan’s objectives. Sometimes, having smaller action plans within the larger plan can help keep the work on track.
During the planning process, you should have decided how you will measure success. Now, figure out how and when you will document progress. Keep an eye out for gaps between the vision and its implementation — a big gap could be a sign that you are deviating from the plan.
Tools are available to assist with tracking performance of strategic plans, including several types of software. “For some organizations, a spreadsheet is enough, but you are going to manually enter the data, so someone needs to be responsible for that,” Stockmal recommends.
Remember: strategic plans are not written in stone. Some deviation will be necessary, and when it happens, it’s important to understand why it occurred and how the change might impact the company's vision and goals.
Deviation from the plan does not mean failure, reminds Hofmeyer. Instead, understanding what transpired is the key. “Things happen, [and] you should always be on the lookout for that. I’m a firm believer in continuous improvement,” he says. Explain to stakeholders why a change is taking place. “There’s always a sense of re-evaluation, but do it methodically.”
Build in a schedule to review and amend the plan as necessary; this can help keep companies on track.
What Is Strategic Management?
Strategic planning is part of strategic management, and it involves the activities that make the strategic plan a reality. Essentially, strategic management is getting from the starting point to the goal effectively and efficiently using the ongoing activities and processes that a company takes on in order to keep in line with its mission, vision, and strategic plan.
“[Strategic management] closes the gap between the plan and executing the strategy,” Stockmal of ASP says. Strategic management is part of a larger planning process that includes budgeting, forecasting, capital allocation, and more.
There is no right or wrong way to do strategic management — only guidelines. The basic phases are preparing for strategic planning, creating the strategic plan, and implementing that plan.
No matter how you manage your plan, it’s key to allow the strategic plan to evolve and grow as necessary, due to both the internal and external factors.
“We get caught up in all of the day-to-day issues,” Stockmal explains, adding that people do not often leave enough time for implementing the plan and making progress. That’s what strategic management implores: doing things that are in the plan and not letting the plan sit on a shelf.
Improve Strategic Planning with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Business growth
Business tips
Business objectives: How to set them (with 5 examples and a template)
As anyone who played rec league sports in the '90s might remember, being on a team for some reason required you to sell knockoff candy bars to raise funds. Every season, my biggest customer was always me. Some kids went door-to-door, some set up outside local businesses, some sent boxes to their parents' jobs—I just used my allowance to buy a few for myself.
Aside from initiative, what my approach lacked was a plan, a goal, and accountability. A lot to ask of an unmotivated nine-year-old, I know, but 100% required for anyone who runs an actual business.
Business objectives help companies avoid my pitfalls by laying the groundwork for all the above so they can pursue achievable growth.
Table of contents:
What are business objectives?
What you want the company to achieve
How you can measure success
Which players are involved in driving success
The timelines needed to plan, initiate, and implement steps
How, if successful, these actions can be integrated sustainably going forward
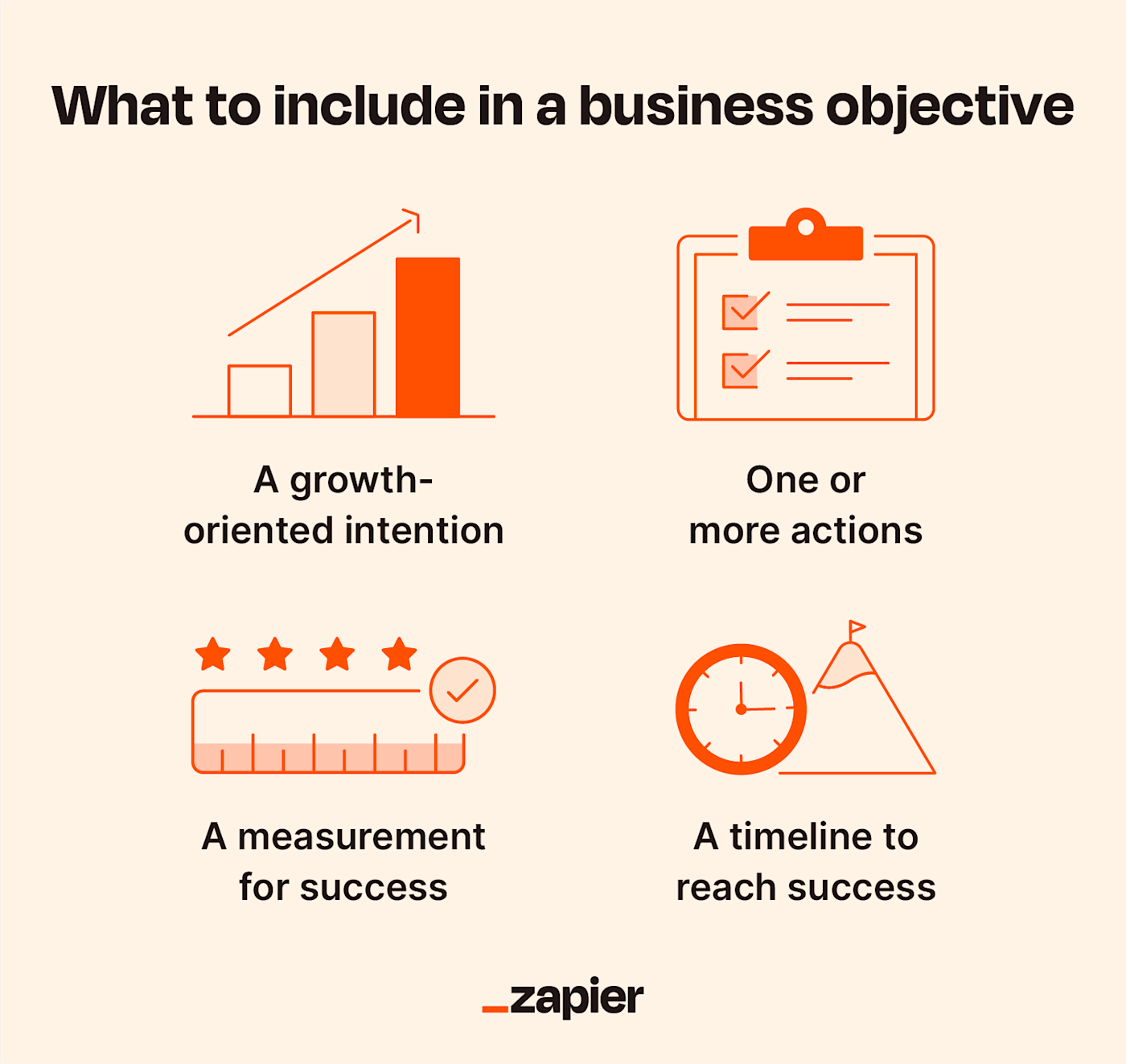
Business objectives vs. goals
Here's what that breakdown could have looked like for nine-year-old me selling candy for my little league team:
Business objective: I will increase my sales output by learning and implementing point-of-sale conversion frameworks. I'll measure success by comparing week-over-week sales growth to median sales across players on my baseball team.
Business goal: I will sell more candy bars than anyone on my team and earn the grand prize: a team party at Pizza Hut.
The benefits of setting business objectives
You might think it's good enough to continue working status quo toward your goals, but as the cliche goes, good enough usually isn't. Establishing and following defined, actionable steps through business objectives can:
Help establish clear roadmaps: You can translate your objectives into time-sensitive sequences to chart your path toward growth.
Set groundwork for culture: Clear objectives should reflect the culture you envision, and, in turn, they should help guide your team to foster it.
Influence talent acquisition: Once you know your objectives, you can use them to find the people with the specific skills and experiences needed to actualize them.
Encourage teamwork: People work together better when they know what they're working toward.
Establish accountability: By measuring progress, you can see where errors and inefficiencies come from.
Drive productivity: The endgame of an objective is to make individual team members and processes more effective.
How to set business objectives
Setting business objectives takes a thoughtful, top-to-bottom approach. At every level of your business—whether you're a massive candy corporation or one kid selling chocolate almond bars door-to-door—there are improvements to make, steps to take, and players with stakes (or in my case, bats) in the game.

1. Establish clear goals
You can't hit a home run without a fence, and you can't reach a goal without setting it. Before you start brainstorming your objectives, you need to know what your objectives will help you work toward.
Increase total revenue by 25% over the next two years
Reduce production costs by 10% by the end of the year
Provide health insurance for employees by next fiscal year
Grow design department to 10+ employees this year
Reach 100k Instagram followers ahead of new product launch
Implement full rebrand before new partnership announcement
Once you have these goals in place, you can establish individual objectives that position your company to reach them.
2. Set a baseline
Like a field manager before a game, you've got to set your baselines. (Very niche pun, I know.) With a definite goal in mind, the only way to know your progress is to know where you're starting from.
Analyzing your baselines could also help you recalibrate your goals. You may have decided abstractly that you want conversion rates to double in six months, but is that really possible? If your measurables show there's potentially a heavier lift involved than you expected, you can always roll back the goal performance or expand the timeline.
3. Involve players at all levels in the conversation
Too often, the most important people are left out of conversations about goals and objectives. The more levels of complexity and oversight, the more important it is to hear from everyone—yet the more likely it is that some will be excluded.
Let's say you want to reduce overhead by 5% over the next two years for your sporting goods manufacturing outfit. At a high level, your team finds you can reduce production costs by using cheaper materials for baseball gloves. A member of your sales team points out that the reduction in quality, which your brand is famous for, could lead to losses that offset those savings. Meanwhile, a factory representative points out that replacing outdated machines would be expensive initially but would increase efficiency, reduce defects, and cut maintenance costs, breaking even in four years.
By involving various teams at multiple levels, you find it's worth it to extend timelines from two to four years. Your overhead reduction may be lower than 5% by year two but should be much higher than that by year four based on these changes.
The takeaway from this pretty crude example is that it's helpful to make sure every team that touches anything related to your objective gets consulted. They should give valuable, practical input thanks to their boots- (or cleats-) on-the-ground experience.
4. Define measurable outcomes
An objective should be exactly that. Using KPIs (key performance indicators) to apply a level of objectivity to your action steps allows you to measure their progress and success over time and either adapt as you go along or stay the course.
How do you know if your specific objectives are leading to increased web traffic, or if that's just natural (or even incidental) growth? How do you know if your recruiting efforts lead to better candidates, or whether your employees are actually more satisfied? Here are a few examples of measurable outcomes to show proof:
Percentage change (15% overall increase in revenue)
Goal number (10,000 subscribers)
Success range (five to 10 new clients)
Clear change (new company name)
Executable action (weekly newsletter launch)
5. Outline a roadmap with a schedule
You've got your organizational goals defined, logged your baselines, sourced objectives from across your company, and know your metrics for defining success. Now it's time to set an actionable plan you can execute.
Your objectives roadmap should include all involved team members and departments and clear timelines for reaching milestones. Within your objectives, set action items with deadlines to stay on track, along with corresponding progress markers. For the objective of "increase lead conversion efficiency by 10%," that could look like:
May 15: Begin time logging
June 1: Register team members for productivity seminar
June 15: Integrate Trello for managing processes
June 15: Audit time log
August 1: Audit time log—goal efficiency increase of 5%
6. Integrate successful changes
You've successfully achieved your objectives—great! But as Yogi Berra famously said, "It ain't over till it's over," and it ain't over yet.
Don't let this win be a one-off accomplishment. Berra also said "You can observe a lot by just watching," and applying what you observed from this process will help you continue growing your company. Take what worked, and integrate it into your business processes for sustainable improvement. Then create new objectives, so you can continue the cycle.
Examples of business objectives and goals
Business objectives aren't collated plans or complicated flowcharts—they're short, impactful statements that are easy to memorize and communicate. There are four basic components every business objective should have:
A growth-oriented intention (improve efficiency)
One or more actions (implement monthly training sessions)
A measurement for success (20% increase)
A timeline to reach success (by end of year)
Our SaaS product's implementation team will grow to five during the next fiscal year. This will require us to submit a budget proposal by the end of the quarter and look into restructured growth tracks, new job posting templates, and revised role descriptions by the start of next fiscal year.
We will increase customer satisfaction for our mobile app product demonstrably by the end of the year by integrating a new AI chatbot feature. To measure the change in customer satisfaction, we will monitor ratings in the app store, specifically looking for decreases in rates of negative reviews by 5%-10% as well as increases in overall positive reviews by 5%-10%.
Each of our water filtration systems will achieve NSF certification ahead of the launch of our rebranding campaign. Our product team will establish a checklist of changes necessary for meeting certification requirements and communicate timelines to the marketing team.
HR will implement bi-annual performance reviews starting next year. Review timelines will be built into scheduling software, and HR will automate email reminders to managers to communicate to their teams.
Business objective template
Business objectives can be as simple as one action or as complex as a multi-year roadmap—but they should be able to fall into a clear, actionable framework.
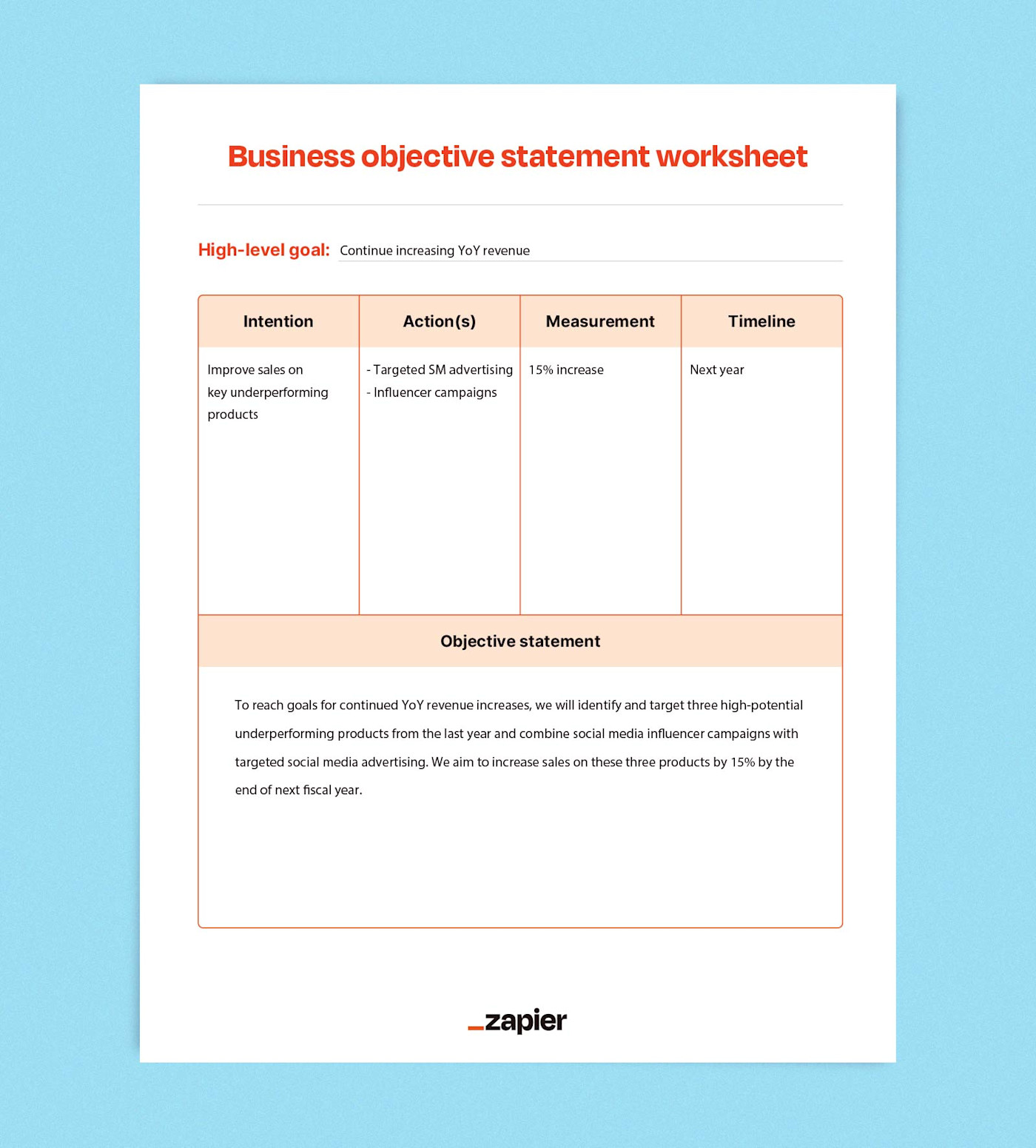
Tips for achieving business objectives
Calling your shot to the left centerfield wall and hitting a ball over that wall are two different things—the same goes for setting an objective and actualizing it.
Start with clear, attainable goals: Objectives should position your business to reach broader growth goals, so start by establishing those.
Align decisions with objectives: Once you set objectives, they should inform other decisions. Decision-makers should think about how changes they make along the way affect their objectives' timelines and execution.
Listen to team members at all levels: Those most affected by organizational changes can be the ones with the least say in the matter. Great ideas and insights can come from any level—even if they're only tangentially related to an outcome.
What makes business objectives so useful is that they can help you build a plan with defined steps to reach obtainable growth goals. As (one more time) Yogi Berra also once said, "You've got to be very careful if you don't know where you are going, because you might not get there."
As you outline your objectives, here are some guides that can help you find KPIs and improvement opportunities:
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Bryce Emley
Currently based in Albuquerque, NM, Bryce Emley holds an MFA in Creative Writing from NC State and nearly a decade of writing and editing experience. His work has been published in magazines including The Atlantic, Boston Review, Salon, and Modern Farmer and has received a regional Emmy and awards from venues including Narrative, Wesleyan University, the Edward F. Albee Foundation, and the Pablo Neruda Prize. When he isn’t writing content, poetry, or creative nonfiction, he enjoys traveling, baking, playing music, reliving his barista days in his own kitchen, camping, and being bad at carpentry.
- Small business
- Sales & business development
Related articles

How to start a successful side hustle

11 management styles, plus tips for applying each type
11 management styles, plus tips for applying...
Keep your company adaptable with automation
How to enrich lead data for personalized outreach
How to enrich lead data for personalized...
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Why Is Strategic Planning Important?

- 06 Oct 2020
Do you know what your organization’s strategy is? How much time do you dedicate to developing that strategy each month?
If your answers are on the low side, you’re not alone. According to research from Bridges Business Consultancy , 48 percent of leaders spend less than one day per month discussing strategy.
It’s no wonder, then, that 48 percent of all organizations fail to meet at least half of their strategic targets. Before an organization can reap the rewards of its business strategy, planning must take place to ensure its strategy remains agile and executable .
Here’s a look at what strategic planning is and how it can benefit your organization.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Strategic Planning?
Strategic planning is the ongoing organizational process of using available knowledge to document a business's intended direction. This process is used to prioritize efforts, effectively allocate resources, align shareholders and employees on the organization’s goals, and ensure those goals are backed by data and sound reasoning.
It’s important to highlight that strategic planning is an ongoing process—not a one-time meeting. In the online course Disruptive Strategy , Harvard Business School Professor Clayton Christensen notes that in a study of HBS graduates who started businesses, 93 percent of those with successful strategies evolved and pivoted away from their original strategic plans.
“Most people think of strategy as an event, but that’s not the way the world works,” Christensen says. “When we run into unanticipated opportunities and threats, we have to respond. Sometimes we respond successfully; sometimes we don’t. But most strategies develop through this process. More often than not, the strategy that leads to success emerges through a process that’s at work 24/7 in almost every industry.”
Strategic planning requires time, effort, and continual reassessment. Given the proper attention, it can set your business on the right track. Here are three benefits of strategic planning.
Related: 4 Ways to Develop Your Strategic Thinking Skills
Benefits of Strategic Planning
1. create one, forward-focused vision.
Strategy touches every employee and serves as an actionable way to reach your company’s goals.
One significant benefit of strategic planning is that it creates a single, forward-focused vision that can align your company and its shareholders. By making everyone aware of your company’s goals, how and why those goals were chosen, and what they can do to help reach them, you can create an increased sense of responsibility throughout your organization.
This can also have trickle-down effects. For instance, if a manager isn’t clear on your organization’s strategy or the reasoning used to craft it, they could make decisions on a team level that counteract its efforts. With one vision to unite around, everyone at your organization can act with a broader strategy in mind.
2. Draw Attention to Biases and Flaws in Reasoning
The decisions you make come with inherent bias. Taking part in the strategic planning process forces you to examine and explain why you’re making each decision and back it up with data, projections, or case studies, thus combatting your cognitive biases.
A few examples of cognitive biases are:
- The recency effect: The tendency to select the option presented most recently because it’s fresh in your mind
- Occam’s razor bias: The tendency to assume the most obvious decision to be the best decision
- Inertia bias: The tendency to select options that allow you to think, feel, and act in familiar ways
One cognitive bias that may be more difficult to catch in the act is confirmation bias . When seeking to validate a particular viewpoint, it's the tendency to only pay attention to information that supports that viewpoint.
If you’re crafting a strategic plan for your organization and know which strategy you prefer, enlist others with differing views and opinions to help look for information that either proves or disproves the idea.
Combating biases in strategic decision-making requires effort and dedication from your entire team, and it can make your organization’s strategy that much stronger.
Related: 3 Group Decision-Making Techniques for Success
3. Track Progress Based on Strategic Goals
Having a strategic plan in place can enable you to track progress toward goals. When each department and team understands your company’s larger strategy, their progress can directly impact its success, creating a top-down approach to tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) .
By planning your company’s strategy and defining its goals, KPIs can be determined at the organizational level. These goals can then be extended to business units, departments, teams, and individuals. This ensures that every level of your organization is aligned and can positively impact your business’s KPIs and performance.
It’s important to remember that even though your strategy might be far-reaching and structured, it must remain agile. As Christensen asserts in Disruptive Strategy , a business’s strategy needs to evolve with the challenges and opportunities it encounters. Be prepared to pivot your KPIs as goals shift and communicate the reasons for change to your organization.

Improve Your Strategic Planning Skills
Strategic planning can benefit your organization’s vision, execution, and progress toward goals. If strategic planning is a skill you’d like to improve, online courses can provide the knowledge and techniques needed to lead your team and organization.
Strategy courses can range from primers on key concepts (such as Economics for Managers ), to deep-dives on strategy frameworks (such as Disruptive Strategy ), to coursework designed to help you strategize for a specific organizational goal (such as Sustainable Business Strategy ).
Learning how to craft an effective, compelling strategic plan can enable you to not only invest in your career but provide lasting value to your organization.
Do you want to formulate winning strategies for your organization? Explore our portfolio of online strategy courses and download the free flowchart to determine which is the best fit for you and your goals.

About the Author
Business Objectives and Strategies
Business objectives (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});.

What is a Business Objective?
Business objectives are specific results that an organization seeks to achieve in pursuing its mission and vision.
The objectives of a business are the end results of planned activity. The achievement of objectives should result in the fulfillment of the mission and vision statement. This can be thought of as what society is giving back to the organization as it does the work of fulfilling its mission and vision.
Business objectives represent the results expected from pursuing certain strategies. Strategies represent the actions to be taken to accomplish long-term objectives. The time frame for objectives and strategies should be consistent, usually from two to five years.
Business objectives should be quantitative, measurable, realistic, understandable, challenging, hierarchical, obtainable, and congruent among organizational units. Each objective should also be associated with a timeline.
Objectives are commonly stated in terms such as growth in assets, growth in sales, profitability, market share, degree and nature of diversification, degree, and nature of vertical integration, earnings per share, and social responsibility.
Clearly established objectives offer many benefits. They provide direction, allow synergy, aid in evaluation, establish priorities, reduce uncertainty, minimize conflicts, stimulate exertion, and aid in both the allocation of resources and the design of jobs.
Objectives provide a basis for consistent decision-making by managers whose values and attitudes differ. Objectives serve as standards by which individuals, groups, departments, divisions, and entire organizations can be evaluated.
Business objectives are essential for organizational success because they state direction, aid in evaluation, create synergy, reveal priorities, focus coordination, and provide a basis for effective planning, organizing, motivating, and controlling activities.
In a multidimensional firm, business objectives should be established for the overall company and for each division.
Long-term objectives are needed at the corporate, divisional, and functional levels of an organization. They are an important measure of managerial performance. Without long-term objectives, an organization would drift aimlessly toward some unknown end. It is hard to imagine an organization or individual being successful without clear objectives. Success only rarely occurs by accident; rather, it is the result of hard work directed toward achieving certain objectives.
Types of Objectives
Two types of objectives are especially common in organizations: financial and strategic objectives.
Financial objectives include those associated with growth in revenues, growth in earnings, higher dividends, larger profit margins, greater return on investment, higher earnings per share, a rising stock price, improved cash flow, and so on.
Strategic objectives include things such as a larger market share, quicker on-time delivery than rivals, shorter design-to-market times than rivals, lower costs than rivals, higher product quality than rivals, wider geographic coverage than rivals, achieving technological leadership, consistently getting new or improved products to market ahead of rivals, and so on.
Although financial objectives are especially important in firms, oftentimes there is a trade-off between financial and strategic objectives such that crucial decisions must be made.
The dangers associated with trading off long-term strategic objectives with near-term bottom-line performance are especially severe if competitors relentlessly pursue increased market share at the expense of short-term profitability.
And there are other trade-offs between financial and strategic objectives, related to riskiness of actions, concern for business ethics, need to preserve the natural environment, and social responsibility issues.
Both financial and strategic objectives should include both annual and long-term performance targets.
Ultimately, the best way to sustain competitive advantage over the long run is to relentlessly pursue strategic objectives that strengthen a firm’s business position over rivals. Financial objectives can best be met by focusing first and foremost on the achievement of strategic objectives that improve a firm’s competitiveness and market strength.
Methods to Avoid
Management should avoid the following methods for setting objectives.
The first method is setting objectives by extrapolation.
This is the idea to keep on doing about the same things in the same ways because things are going well.
The second method is setting objectives for the crisis.
This is based on the belief that the true measure of good management is the ability to solve problems that occur every day. Managing by crisis is a form of reacting rather than acting and of letting events dictate what and when to make decisions.
The third method is setting objectives by subjective.
This is built on the idea that there is no general plan for which way to go and what to do; just do the best you can to accomplish what you think should be done.
The fourth method is setting objectives by hope.
This is because the future is laden with great uncertainty and that if we try and fail, then we hope our second (or third) attempt will succeed. Decisions are predicated on the hope that they will work, and the good times are just around the corner.
Strategies (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});

What is a Strategy?
Strategies are comprehensive plans that state how the organization will achieve its mission and objectives. It maximizes competitive advantage and minimizes competitive disadvantage.
Strategies are potential actions that require top management decisions and large amounts of the firms’ resources. In addition, strategies affect an organization’s long-term prosperity, typically for at least five years.
Strategies have multifunctional or multidivisional consequences and require consideration of both the external and internal factors facing the firm.
Strategy Types
There are usually 3 types of strategy and they form a hierarchy of strategy within an organization .
They are: (1) corporate strategy, which describes the company overall direction and attitude toward growth; (2) business strategy, which occurs at business unit or product level, and emphasizes improvement of the competitive position of the products and services of the company within the selected industry or market segment; and (3) functional strategy, which describes how each function achieve corporate and business unit strategy by creating and maintaining distinctive competences.
Strategy making is not just a task for top executives. Middle and lower-level managers too must be involved in the strategic planning process to the extent possible.
In large firms, the persons primarily responsible for having effective strategies at the various levels include the CEO at the corporate level; the president or executive vice president at the business level; and the respective chief finance officer (CFO), chief information officer (CIO), human resource manager (HRM), chief marketing officer (CMO), and so on, at the functional level.
In small firms, the persons primarily responsible for having effective strategies at the various levels include the business owner or president at the company level and then the same range of persons at the lower two levels, as with a large firm.
It is important to note that all persons responsible for strategic planning at the various levels ideally participate and understand the strategies at the other organizational levels.
This practice helps ensure coordination, facilitation, and commitment while avoiding inconsistency, inefficiency, and miscommunication.
Plant managers, for example, need to understand and be supportive of the overall corporate strategic plan (game plan) while the president and the CEO need to be knowledgeable of strategies being employed in various sales territories and manufacturing plants.
Many, if not most, organizations simultaneously pursue a combination of two or more strategies, but a combination strategy can be exceptionally risky if carried too far.
No organization can afford to pursue all the strategies that might benefit the firm. Difficult decisions must be made. Priority must be established. Organizations, like individuals, have limited resources. Both organizations and individuals must choose among alternative strategies and avoid excessive indebtedness.
Strategy Initiation
Strategy formulation is typically not a regular, continuous process. Humans tend to continue a particular course of action until something goes wrong or a person is forced to question his or her actions.
This period of strategic drift may result from inertia, or it may reflect the belief of management that the current strategy is still appropriate and needs only some fine-tuning. This phenomenon, called punctuated equilibrium, describes corporations as evolving through relatively long periods of stability (equilibrium periods) punctuated by relatively short bursts of a fundamental change (revolutionary periods).
Some sort of shock to the system is needed to motivate management to seriously reassess the situation of the organization. This triggering event can be (1) having a new CEO, (2) having an external intervention, (3) facing a threat of change in ownership, (4) having a performance gap, or (5) having a strategic inflection point.
Approaches to making Strategic Decisions
Strategic decisions are decisions that deal with the long-run future of an organization.
It has the 3 following characteristics: (1) Rare – strategic decisions are unusual and typically have no precedent to follow, (2) Consequential – strategic decisions commit sustainable resources and demand a great deal of commitment from the organization, and (3) Directive – strategic decisions set precedents for lesser decisions and future actions throughout the organization.
As organizations grow larger and more complex, with more uncertain environments, decisions become increasingly complicated to make. One of the distinguishing characteristics of strategic management is its emphasis on strategic decision-making.
In pursuit of such objectives, one will find themselves on a quest to follow a certain strategic decision-making framework. The following are the 4 most common approaches to strategic decision making.
Approach 1: Entrepreneurial Mode
Strategy decisions are made by one powerful individual. This type of decision usually focuses on opportunities; problems are secondary. Strategy is guided by the vision of the founder. The goal is about the growth of the organization.
Approach 2: Adaptive Mode
Strategy decisions that focus on reacting solutions to existing problems, rather than a proactive search for new opportunities. Strategy is made to move the corporation forward incrementally.
Approach 3: Planning Mode
Strategy decisions involve a systematic gathering of appropriate information for situation analysis, generation of feasible alternative strategies, and the rational selection of the most appropriate strategy. This planning mode includes both the proactive search for new opportunities and the reactive solution of existing problems.
Approach 4: Logical Incrementalism
Strategy decisions that combine planning, adaptive, and entrepreneurial modes. In this type of strategic decision-making, top management has quite a clear view of the mission and objectives of the organization. However, the actual strategy is allowed to emerge out of the debate, discussion, and experimentation. This approach can be useful when the external environment is changing quickly, or consensus and commitment within the internal environment are critical.
Process of making Strategic Decisions
The following are the 8 fundamental steps to the strategic decision-making process.
Step 1: Evaluate current performance results, in terms of (1) financial goals and (2) current mission, objectives, strategies, and policies.
Step 2: Review corporate governance, which is the performance of the board of directors and top management.
Step 3: Scan and assess the external environment to determine the strategic factors that pose Opportunities and Threats.
Step 4: Scan and assess the internal corporate environment to determine the strategic factors that are Strengths and Weaknesses.
Step 5: Analyze strategic factors (SWOT analysis) to pinpoint problem areas and review mission and objectives, if necessary.
Step 6: Generate, evaluate, and select the best alternative strategy in light of the analysis conducted previously.
Step 7: Implement selected strategies using programs, budgets, and procedures.
Step 8: Evaluate implemented strategies via activities of evaluation and control.
Further Reading
- How to Write Business Objectives? (indeed.com)
- Objectives of Business (economicsdiscussion.net)
- Business Objectives (cio-wiki.org)
- Demystifying Strategy: The What, Who, How, and Why (hbr.org)
- What The Heck Is A Strategy Anyway? (forbes.com)
- What Is Strategy (and Why Should You Care)? (braintraffic.com)
Related Concepts
- Business Mission and Vision
- Strategic Management Essentials
- Hitt, M. A., Ireland, D. R., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2016). Strategic Management: Concepts: Competitiveness and Globalization (12th ed.). Cengage Learning.
- Hitt, M. A., Ireland, D. R., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2019). Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases: Competitiveness and Globalization (MindTap Course List) (13th ed.). Cengage Learning.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Market Research
Business planning, website development, product or service selection, marketing and promotion, is it a good idea to start an online business, can i start an online business with $100, what are different types of online marketing strategies, the bottom line.
- Small Business
- How to Start a Business
How to Start an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
Crafting a Winning Business Plan: Setting Goals and Strategies
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/picture-53823-1434118722-5bfc2a8c46e0fb005119858e.jpg)
Katie Miller is a consumer financial services expert. She worked for almost two decades as an executive, leading multi-billion dollar mortgage, credit card, and savings portfolios with operations worldwide and a unique focus on the consumer. Her mortgage expertise was honed post-2008 crisis as she implemented the significant changes resulting from Dodd-Frank required regulations.
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide CURRENT ARTICLE
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
Oscar Wong / Getty Images
If you want to get into the online business game, it’s a good time to start. The COVID-19 pandemic reshaped online consumer spending, including how people shop online and how they research products.
Today, 76% of Americans buy products online. Furthermore, roughly a third of people purchase items online weekly. From setting up an ecommerce business to offering web design services, there are countless avenues to explore as an entrepreneur.
Below, we’ll walk through each step to building an online business.
Key Takeaways
- When starting an online business, comprehensive market research is critical for identifying your target audience and learning how to resonate with your customers and understand their needs.
- Creating a business plan is an important step for outlining your business goals. It also includes your product description, target market, and financial projections, among other core components.
- Building your website involves setting up a domain name, finding a hosting company, and designing a strong website with consistent branding that allows your customers to navigate it intuitively.
- Choosing the right product or service to sell is essential. It’s important to think about how you’re addressing an unmet need.
- Several digital marketing strategies can be utilized, from content marketing to paid advertising, to help your business grow.
Successful online entrepreneurs study hard in order to have a thorough understanding of their market. This is important for knowing exactly how to reach your target market , because these are the people who will buy your products and drive your business growth.
At its core, market research is about understanding your customers’ needs, pain points, and solutions. It is designed to help your business better meet these needs.
Steps to Conduct Market Research
Market research involves understanding key aspects of your current and future customers. To get a clear sense of your target market, outline the characteristics of your audience—for example, age, location, gender, income, job title, and key pain points.
Once you have identified your target audience, conduct research on the following topics, which will tell you about how they make decisions and how you can better position your business:
- What are the challenges that your target market faces?
- Where do they research a given product or service?
- What are their views on pricing for this product or service?
- What factors influence their decision to make a purchase?
- Who are your competitors?
To put this market research into action, there are a number of different avenues you can take:
- Focus groups
- Competitive analysis
- Brand awareness research
- Market segmentation research
Consider the following questions that may be asked in an interview or focus group to learn more about your audience:
- “How do you search for that product?”
- “How useful was it?”
- “What words do you use when you search on Google?”
When you have completed your market research, identify what you have learned as well as your next steps based on these insights.
Creating a business plan is a key first step for all business owners . It is important for companies looking to secure funding resources. It also serves as a blueprint to summarize your key business objectives and goals.
To write a business plan , incorporate these eight main sections, which are often found in traditional templates:
- Executive summary : This is typically a one-page section that explains your objectives and includes your mission statement, core team, and why your company is positioned for success.
- Company description : This describes what you offer, your competitive advantages, and your business goals.
- Market analysis : This is where you explain your target market, market size, market trends, and competitive landscape.
- Organization and management : Explain who is working on your team and their professional background and experience.
- Service or product line : Describe the product or service you are offering, including any copyright or plans for patenting.
- Marketing and sales : Discuss your marketing and sales strategy. Discuss your pricing, key metrics, and sales plan.
- Funding request : If you are a company looking for funding, here is where you outline the capital you are requesting and where it will be allocated.
- Financial projections : Include projections for your company’s revenue and expenses. Consider including an income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in this section.
A business plan is important because it helps clarify your action points, who you are, and what you offer, all in a coherent template.
Getting your business online is the next key step. In an ever-changing environment, it is important to know the tools, trends, and strategies for building a strong online presence to allow your business to grow.
Registering Your Domain
The first step is registering your name, or your website address. This can be in the form of your business name “.com.” To purchase your domain name, you can go to sites like GoDaddy or Namecheap . If you decide to build your website using WordPress, you will need to use a site such as these to host your website.
Web Hosting Companies
Alternatively, you can buy your domain name at a hosting company. These are companies like Shopify , Wix , or Amazon Web Services , that may also offer tools to build your website and release content on them.
Website Design
A well-designed website is important for many reasons. Using a website builder, such as Mailchimp or Squarespace , can allow you to choose a theme, customize your pages, create relevant content, and set up a payment page.
Other key aspects of your website design include its functionality, simplicity, and ease of use. Allowing your potential customers to navigate the site intuitively will be key to their experience. Brand consistency—in your logo, colors, and typeface, for example—is also key to creating a unified brand.
Another essential part of website design is its mobile application. You’ll want to ensure that your website runs smoothly on mobile, that images load properly, that the text is legible, and that buttons are intuitive to click.
This step focuses on how to choose the right product or service to sell. At the heart of this choice is the goal of solving a customer’s problem. But there are a number of strategies you can use to identify your product idea.
For example, you might consider analyzing companies with high-profit margins, products that align with your passion, burgeoning trends, items trending on online marketplaces, and/or customer reviews.
With this in mind, analyze how this product will get to your customers. Additionally, you may consider products that are not available in stores in your local market but are offered in communities such as Europe or Japan, for example.
Marketing strategy and promotion is an essential driver of business growth. As the digital landscape evolves, it’s important to have an effective marketing plan that resonates with changing consumer preferences and needs.
Here are questions that companies can consider as they create their marketing strategy, navigating today’s environment:
- Impact, value, and growth : What are the goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) that will measure success for your business? How will you explain the value that the business provides to its customers and/or society? Create an “elevator speech”—a 30-second description of what you offer and why it’s special.
- Customer need and brand promise : How does the brand meet a customer’s need through its products and services?
- Customer experience : How will the business deliver the best experiences at each stage of the customer journey?
- Organizational model : How will the business operate to serve the customer with the most impact?
These will help you understand what types of strategies can have real impact.
Types of Marketing Strategies
Consider the following digital marketing strategies that can be used for your online business:
- Email marketing
- Social media marketing
- Paid advertising
- Search engine optimization (SEO)
- Content marketing
- Influencer marketing
Each of these presents a different way to reach your target audience, drive conversions, or build brand awareness, depending on your marketing goals.
You need to determine that for yourself. But before starting an online business, it’s important to assess the time, investment, and resources you’ll need to get it off the ground. While the barrier to entry can be quite low, it’s worth considering your goals and strategies for making it a reality.
However, compared with starting up a traditional brick-and-mortar business, the risks of launching an online business may be reduced due to lower upfront costs such as rent, staff, and materials, among others.
The short answer: yes. While it depends on the type of business you hope to pursue, there are many ways to set up an online business at very little cost. For example, you could offer your services doing freelance work, photography, bookkeeping, or personal training. The primary costs involved include setting up your business website, which can cost as little as $2 to $20 each year with companies such as GoDaddy.
There are a number of digital marketing strategies that online businesses can use, such as content marketing, email marketing, paid advertising, SEO, and influencer marketing. Each of these strategies can be useful, depending on your product and goals.
Starting an online business can be a powerful way to launch a new product or service while reaching a wider audience. With market research, a solid business plan, a strong website, and a digital marketing strategy, you can get started in growing your company effectively. As customers increasingly make decisions virtually, building an online business is vital to any business owner’s success.
Pew Research Center. “ For Shopping, Phones Are Common and Influencers Have Become a Factor—Especially for Young Adults .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Market Research and Competitive Analysis .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Write Your Business Plan .”
Ogilvy. “ Getting Future Ready with Marketing Transformation ,” Page 15.
GoDaddy. “ How Much Does a Domain Name Cost? Find Out! ”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/shutterstock_222400081-5bfc47c7c9e77c00587d6bbf.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

Salesforce is closed for new business in your area.
More From Forbes
The lost art of business strategy and how to revive it.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Julius Černiauskas is the CEO at Oxylabs , a leading proxy networks and data gathering solutions provider.
Strategic thinking is vital in many fields, from sports to politics. Entrepreneurs and boards leading a business are expected to create sound strategies. Yet, too often, what is presented as a strategy in business needs more substance that addresses practical issues. Reviving the best practices of strategic thinking will take determinate leadership.
The Prevalence Of Bad Strategies
In today's business landscape, effective strategies are more of a rarity than the norm. A quick glance at what is commonly accepted as strategy reveals this reality. Many business leaders mistakenly equate a vision, mission and broad goals with strategy. While these elements are important for public-facing communication, true strategy involves much more than simply outlining desired outcomes.
One of the leading researchers in the field, Richard Rumelt, says that bad strategy spreads as a social contagion due to this tendency to present ambition for performance as a strategy. As it lacks any reference to obstacles and how they can be overcome, strictly speaking, there is no strategy here. However, having no strategy is better than mistaking this wishful thinking for strategy.
How A Bad Strategy Is Worse Than No Strategy
Using a wish list as a substitute for a strategy masks the absence of a genuine plan. In this scenario, ineffective strategy consumes valuable time and mental energy crafting superficial content that fails to guide action while hindering the development of a meaningful plan.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
Moreover, this prevalent approach to "strategizing" complicates internal communication about strategy. When individuals associate strategy solely with lofty mission statements or grand initiatives such as mergers and acquisitions, they overlook the strategic steps necessary for progress. These steps are often straightforward and logical, lacking immediate excitement. Reintroducing this seemingly mundane yet practical view of strategy can align all stakeholders and boost company morale.
4 Data-Driven Business Strategy Essentials
Reviving a sound strategy involves both complexity and simplicity. It's complex due to the inertia that impedes current strategic thought processes. However, it's also simple because there are only a few key essentials to prioritize. Aligning these elements involves underpinning decisions with relevant data.
1. Concentrating On Short-Term Specifics
If a strategy is too general, it can fail to guide action. For example, growing market share by becoming the most customer-centric company in the industry is not a complete strategy. There are hundreds of ways to be customer-centric. You need internal customer satisfaction data leveraged against competitive intelligence to specify the most customer-centric means in your particular circumstances.
Furthermore, while there are many forecasting methods, predictions need to be revised often. Thus, it is better to focus on short-term specifics. Think of it like using headlights at night down an unfamiliar road. By using these headlights to focus on your turns and avoid obstacles, you can more effectively and safely reach your intended destination.
2. Addressing Challenges
Strategy starts where smooth sailing ends. You do not need a strategy if there are no obstacles to achieving your goals. You simply need to complete the apparent course of action. For example, if you want to scale by entering new markets and you have limitless funds, there is no need for strategic thinking.
However, if you need new investments, you must address investor worries and distrust in the current economic conditions. Data on infrastructure critical to sustainable supply chains in the area, georeferenced labor market data and similar information are necessary to sway investors in this case.
When the main challenges are unclear, gathering competitive intelligence is a good place to start. Additionally, historical data might uncover trends to help deduce what challenges are likely when aiming for particular goals in specific circumstances.
3. Making Hard Choices
One of the most common barriers to a good strategy is the lack of will to choose a course of action. Choices can be difficult. They might involve shutting down pet projects or disappointing someone’s expectations and ambitions. It is impossible to know whether your chosen course was the best one possible. However, a decent and coherent strategy is enough to prevent pulling resources in different directions.
A significant part of leadership is making the hard choices to set the course without being sure it is correct, while others are certain you are wrong. Supporting the chosen strategy with data can help deal with pressures, internal and external. The more data-based your strategic decisions are, the better your chance of convincing stakeholders and achieving at least some measure of success.
4. Verifying It Is Actionable
Some people blame execution when a strategy fails. This separation of strategy and execution has long been recognized as detrimental to business management. It enables managers to avoid responsibility by claiming the plan was sound, but employees were not engaged, time ran out or the software tools were inadequate. However, effective planning should include ways to improve engagement, accurately estimate the necessary time and test the tools before incorporating them into the strategy.
Don’t create a strategy for a more prosperous or technologically advanced company. Develop a strategy tailored to your own company, ensuring it can be executed with the resources you have or can reasonably acquire.
Strategy is hard work. Success is not guaranteed, but you can improve your chances by ensuring the best use of your available data. It can help correctly allocate resources, get everyone within the company as well as investors on board and measure your progress. This can ultimately build a true, effective strategy where others only believe they've built one.
Forbes Technology Council is an invitation-only community for world-class CIOs, CTOs and technology executives. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A good strategic plan evolves and shifts as opportunities and threats arise. ... The most important element of a balanced scorecard is its alignment with your business strategy. ... (ROI) of the operational goals tied to each strategic objective. For example, if the strategic goal is "reach carbon-neutral status by 2030," you need to break ...
A business goal is a broad, long-term outcome that a company works toward.Goals usually inform which strategies that department leaders will implement. A business objective, however, is a specific, short-term outcome or action that helps the company achieve long-term goals.. Although the terms are often used interchangeably, goals and objectives are not the same.
Examples of financial strategic goals. These examples do not represent Asana's goals, and are merely included here for educational purposes. 11. Increase total revenue by $10M in the next three years. 12. Reduce cost by 12% to become a profitable company by 2024. 13.
3. Follow the "Verb + Adjective + Noun" format. The typical format of a strategic objective is "Verb + Adjective + Noun.". If you use this formula, your strategic objectives will create an action statement. Note that your strategic objectives should describe your strategy—not just a typical strategy.
They are the big business objectives you must focus on for the next 3- to 5-years. Strategic objectives are often one of the most challenging components of a strategic plan. They bridge your big, bold vision and the annual goals and actions needed to achieve it. ... Build Your Plan, Objectives, Strategic Goals, and KPIs in a single Dashboard ...
8. Critical success factors: Clarify the high-level goals you need to achieve in order to achieve your strategic goals. 9. Strategic management: Execute against your strategic plan in order to achieve your company goals. 10. Business goals: Set predetermined targets to achieve in a set period of time. 11.
Strategic business plan. A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment. Before you can define where you're going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
What Are Strategic Objectives? Strategic objectives are high-level and measurable goals outlining what an organization wants to achieve, with a clearly defined deadline.They help organizations create strategic roadmaps, initiatives, and projects that are aligned with the company's strategy and vision.. In Cascade's strategic planning model, strategic objectives populate your plan's Focus ...
Business unit strategic plans define and finalize business unit goals, objectives and initiatives, while cognizant of enterprise priorities and external trends. Operational plans deal with the short-term execution of specific projects and changes, as well as any operational tasks not contained in the strategic plan.
Strategic goals to promote growth. 65) Secure a new office space that is twice the size of our current one. 66) Implement a new sales strategy that generates a 20% increase in sales in the next six months. 67) Increase our customer base by 20% in the next year. 68) Double our market share in the next three years.
1. Run a strategic planning workshop. The first step is to run a strategic planning workshop with your team. Get your team in the room, get their data, and gather their insights. By running this workshop, you'll foster collaboration and bring fresh perspectives to the table. And that's not all.
4. Learning and Growth Opportunities. Another consideration while setting business goals and objectives is learning and growth opportunities for your team. These are designed to increase employee satisfaction and productivity. According to Strategy Execution, learning and growth opportunities touch on three types of capital: Human: Your ...
Social objectives. For example, a sample of business goals and objectives for a business plan for a bakery could be: To increase its annual revenue by 20% in the next year. To reduce its production costs by 10% in the next six months. To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
1. Increase Revenue. Increasing revenue is a common strategic objective for businesses. Using a strategic objective to achieve this could be through expanding into new markets, introducing new products or services, improving link building and marketing strategies, or increasing customer retention. 2.
To create a strategic objective, follow these steps: 1. Determine clear goals based on your vision. Before you make a strategic objective, decide on your overall goals and desired outcomes. Plan what areas are most important to your devolvement strategy. Think about how many objectives you need to achieve your overall vision.
Why Strategic Planning Fails. There are also plenty of organizations that do take steps to fulfill the requirements of strategic planning, yet still fail to see results. These strategies fail for many reasons, including: Lack of communication: This is a big one.Research shows that 95% of most companies' employees don't understand their organization's strategy, and 85% of executive ...
If your business is an architectural firm or a custom software developer company, this could be a good objective to ensure you are working with your customers to design critical solutions. Improve customer satisfaction: If customer satisfaction is critical in your company, this may be a good objective to hone in on.
Strategic planning is an organizational activity that aims to achieve a group's goals. The process helps define a company's objectives and investigates both internal and external happenings that might influence the organizational path. Strategic planning also helps identify adjustments that you might need to make to reach your goal.
There are four basic components every business objective should have: A growth-oriented intention (improve efficiency) One or more actions (implement monthly training sessions) A measurement for success (20% increase) A timeline to reach success (by end of year) Example objective #1: Percentage change.
Strategic planning is the art of formulating business strategies, implementing them, and evaluating their impact on organizational objectives. ... and redirecting marketing efforts in line with the strategy's goals and objectives. 3. Strategy Evaluation ... and money, a well-thought-out strategic plan efficiently fosters company growth, goal ...
Goals, Priorities and Strategies. Outlines the goals, priorities, and strategies to meet the mission. 3 -4 overarching goals aligned with mission. Priorities, activities, objectives, strategies are in more depth, have more specificity - each goal could have a few different objectives / strategies associated with it.
Benefits of Strategic Planning. 1. Create One, Forward-Focused Vision. Strategy touches every employee and serves as an actionable way to reach your company's goals. One significant benefit of strategic planning is that it creates a single, forward-focused vision that can align your company and its shareholders.
The following are the 8 fundamental steps to the strategic decision-making process. Step 1: Evaluate current performance results, in terms of (1) financial goals and (2) current mission, objectives, strategies, and policies. Step 2: Review corporate governance, which is the performance of the board of directors and top management.
To align marketing strategies with business objectives, start by clearly defining your business goals. These should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Creating a business plan is an important step for outlining your business goals. It also includes your product description, target market, and financial projections, among other core components.
A strategic plan may cover multiple years and be updated periodically. The organization may use a variety of methods of measuring and monitoring progress towards the strategic objectives and measures established, such as a balanced scorecard or strategy map. Organizations may also plan their financial statements (i.e., balance sheets, income ...
Sales forecasts touch virtually all departments in a business. For example, the finance department uses sales forecasts to decide how to make annual and quarterly investments. Product leaders use them to plan demand for new products. And the HR department uses forecasts to align recruiting needs to where the business is going.
Using a wish list as a substitute for a strategy masks the absence of a genuine plan. In this scenario, ineffective strategy consumes valuable time and mental energy crafting superficial content ...