
- How We're Funded
- Staff Directory
- Board of Directors

What’s the Latest Research in Development Economics? A Roundup from NEUDC 2021
Recommended.
Last weekend was the North East Universities Development Consortium annual conference . Researchers—mostly economists—presented nearly 200 papers on topics from agriculture to COVID to marriage to microfinance. It’s a great introduction to a wide range of current development economics research.
As a crash course for you (and for us), we’ve produced a brief takeaway from each paper. Of course, these are our takeaways, and yours may differ. If you’re interested in the topic, we encourage you to read the papers . Some of the papers present preliminary results, so you may want to take a look before—you know—redesigning your monetary policy based on our tweet-sized summary. Finally, we made a judgment call about where to place papers: for example, does a study on the impact of a health intervention on education outcomes go under health or education? So you may as well just read the whole post.
The evidence comes from all over the world, as you can see in Figure 1 below. (We’ve sorted the papers by topic below, you can also find all the papers sorted by country .) By far, the most studies come from India (35 studies!), Brazil (18), China (14), Mexico (11). Relative to the same conference last year , India holds a similar position relative to Brazil and Mexico, but China is much more represented.
In terms of research methods, the most commonly used approach was fixed effects estimation (49 studies), followed by randomized controlled trials (42), difference-in-differences (29), regression discontinuity (21), and instrumental variables (19) (Figure 2).
Figure 2. What methods do studies use?
The referenced media source is missing and needs to be re-embedded.
Source: This chart draws on a sample of 185 studies from the NEUDC 2021 conference. Some studies used more than one method.
Without further ado, here are 185 paper microsummaries! For most papers, we indicate the methodology. If you had a different takeaway from a paper, share your thoughts in the comments!
Guide to the methodological hashtags
#DID = Difference-in-differences #FE = Fixed effects #IV = Instrumental variables #LIF = Lab in the field #PSM = Propensity score matching #RCT = Randomized controlled trial #RD = Regression discontinuity
Households and human capital
Education and early childhood development.
A large-scale home visiting intervention in Bangladesh was integrated into the national nutrition program. While service providers partly substituted away from nutrition counseling and towards early childhood development counseling, both cognitive and nutritional outcomes improved. ( Bos et al. ) #FE
Scheduling the school calendar such that exams fall during harvest season inflated dropouts among rural youth by between 6.5 and 8.4 percent in Bangladesh. ( Ito and Shonchoy ) #DID
Livestock insurance for pastoral communities in northern Kenya and southern Ethiopia decreased children's work and increased their schooling. ( Son ) #RCT
An after-school curriculum to strengthen teenagers' character in three countries of Central America reduced misbehavior at school. ( Dinarte, Egana-delSol, and Martinez A. ) #RCT
Poorer college applicants in China are less strategic in their college priority ranking, potentially exacerbating educational inequality. ( Wang, Wang, and Ye )
Providing students starting their senior year of high school in Argentina with information on their chances of graduating (given their current academic performance) increases timely graduation, especially for the worst performing students. ( Lopez ) #RCT
In areas of Mexico with more manufacturing jobs, conditional cash transfers had less of a positive impact on education, particularly for youth old enough to work in the factories. ( Molina and Vidiella-Martin ) #RCT
A voucher reform that increased government subsidies for disadvantaged students in Chile actually resulted in increased fees for those students at private schools. ( Cañedo-Riedel and Sánchez )
In Nepal, government expenditures on a year of primary or secondary school are roughly equal to the average increased taxes that someone with an additional year of schooling later pays (i.e., the fiscal externality). For tertiary education, the gains outweigh the costs. ( Bleakley and Gupta )
Cash grants to public school councils in rural Pakistan increased learning in both public and private schools. ( Andrabi et al. ) #RCT
Attending a high-quality public “model” school in India boosts test scores in math, science, and social science. ( Kumar ) #RD
Free after-school tutoring to primary school students in rural Bangladesh boosts test scores of their peers. Targeting tutoring to students who are more socially central leads to bigger effects. ( Islam et al.) #RCT
“Over-the-phone mentoring and homeschooling support delivered by volunteers” in Bangladesh “improved the learning outcomes of treated children by 0.75 SD and increased homeschooling involvement of treated mothers by 0.64 SD.” ( Hassan et al. ) #RCT
When men in Colombia “just miss the cutoff to enroll in their” preferred university major, they’re likely to retake the exam. Women, on the other hand, are more likely to “enroll in a less preferred major” right away. This difference can explain “about half of the gender-earnings gap among college-educated workers in Colombia.” ( Franco and Hawkins ) #RD
“An extra friend aspiring to go to college [in Brazil] increases the likelihood that the average student will also aspire to it by 11.39 percent.” ( Gagete-Miranda ) #IV
Affirmative action for undergraduate law studies in Brazil more than doubled the chance that beneficiaries went on to become certified lawyers and employed, with no apparent negative impacts on outcomes for "applicants displaced by the policy." ( Ribeiro and Estevan ) #RD
When the proportion of low-income students at a Colombian university tripled, the social networks of wealthy students changed, but only a little. ( Velasco ) #DID
State-sponsored education in 19th-century France led to most people speaking the same language, with persistent impacts on national identity and preferences for political centralization. ( Blanc and Kubo ) #RD
“Providing a free lunch to all students leads to improvements in academic achievement on average” in South Korea. ( Kim ) #DID
Automated, “interactive phone calls intended to encourage parents of first-graders in Kenya to read at home with their children” increased oral reading fluency by between 1.5-2 words per minute over 5 weeks. ( Esposito and Sautmann ) #RCT
Children in rural India attended school less when their families faced greater risk to their incomes, but the National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGA) may offset those impacts. ( Foster and Gehrke ) #FE
The introduction of mobile broadband internet had no impact on children's test scores in Brazil. ( Bessone, Dahis, and Ho )
Individuals growing up in parts of the United States with more robots “are more likely to have a Bachelor’s degree and tend to major in subjects where the prevalence of routine-related occupations is lower.” ( Carrillo and Iglesias ) #DID
A one standard deviation (SD) increase in temperature during exams in Brazil decreases the average exam score by 0.036 SD. The higher the stakes, the smaller the effects because exam takers exert more effort. ( Melo and Suzuki ) #FE
Public schools in Chile appoint more effective principals after increasing competitiveness and transparency of their selection process. ( Muñoz and Prem ) #DID
A bicycle can transform a girl’s life: in Zambia, bicycle provision reduced average commuting time to school by 35 percent, late arrival by 66 percent, and decreased absenteeism by 27 percent. It also had positive effects on grade transition, math test scores, girls’ self-reported feelings of control over their lives and, “for those who received bicycles with a small cost to her family, higher levels of aspirations, self-image, and a desire to delay marriage and pregnancy.” ( Fiala et al. ) #RCT
In Somalia, female role models impact boys’ and girls’ attitudes on gender equality but not students’ aspirations to attend colleges. ( Kipchumba et al. ) #RCT
An experiment in boarding schools in Peru showed that similarity increases the likelihood of friendships and proximity fosters more diverse friendships. ( Gitmez and Zárate ) #FE
COVID-19 lockdowns in Bangladesh led to more chores for girls, and job loss among parents increased the likelihood of "marriage-related discussions" for daughters. ( Makino, Shonchoy, and Wahhaj )
The Ugandan COVID-19 "lockdown, one of Africa’s strictest, impacted female workers more severely than male workers by disproportionately reducing their employment rate, shifting them to economic sectors in which they are less productive, and widening the gender pay gap." ( Alfonsi, Namubiru, and Spaziani )
On a COVID-19 mutual aid platform in Indonesia, donors are more likely to give a donation when given a smaller choice set of potential beneficiaries, and they prefer to donate to self-reported breadwinners and females. ( Hilmy, Lim, and Riyanto ) #FE
Phone calls and SMS messages to parents, encouraging them to support their children while schools were closed for COVID, increased learning in Botswana. ( Angrist, Bergman, and Matsheng ) #RCT
“A sizeable one-time-only emergency cash transfer ($526 PPP) targeted at self-employed, sub-employed, and informal sector workers [in Mexico] during the COVID-19 pandemic” increased mental health and food security but did not increase individuals’ likelihood of staying home or otherwise supporting public health policies. ( Cañedo, Fabregas, and Gupta ) #RD
Rural pensions in China boosted child weight, "largely driven by grandfathers’ pension receipt on grandsons." ( Yang and Chen ) #FE
"Living in a household experiencing food insecurity is associated with lower levels of psychological well-being" in Lebanon. ( Alloush and Bloem ) #IV
A nutritional support program in Ethiopia boosted beneficiaries' emotional state and stability, although labor productivity remained unaffected. ( Park and Kim ) #LIF
Girls receiving the Child Support Grant in South Africa were less likely to be underweight and also less likely to be obese. ( Sen and Villa ) #RD
Inequality between households within the same community is an important driver of inequality in women and children’s nutritional status. Sanitation infrastructure and health facility quality in South Asia matter for nutritional outcomes—but wealthier women can travel to receive better care. ( Brown et al. ) #FE
Health (including mental health)
Among Rohingya refugees living in Bangladesh, providing counseling, psychological education, and play activities for children reduced depression, increased happiness, and boosted child development. ( Islam et al. ) #RCT
Exposure to arsenic-contaminated water is bad for children's health, but in India, it's especially bad for younger sisters, potentially because of pre-existing malnutrition. ( Aggarwal and Barua ) #IV
Pharmacotherapy for adults in India increases investment in their children's education. ( Angelucci and Bennett ) #RCT
Encouraging smokers in rural Bangladesh to record their tobacco expenditures led them to buy cheaper, smokeless tobacco. Showing graphic posters of the effects of tobacco reduced expenditure for more educated smokers. ( Fakir and Bharati ) #RCT
“Within a government health insurance program that entitles 46 million poor individuals to free hospital care in Rajasthan, India … females account for only 33% of hospital visits among children and 43% among the elderly…. In the presence of gender bias, increasing access to and subsidizing social services may increase levels of female utilization but fail to address gender inequalities without actions that specifically target females.” ( Dupas and Jain )
Among “maternity care workers in primary health clinics in Nigeria… both rewards and penalties increase time on task by 11 percent, overall performance by six-to-eight percent, and directly incentivized performance by twenty percent.” Performance on tasks without incentives also improved. ( Bauhoff and Kandpal ) #RCT
“The current vaccination completion rate is low in states [of India] where forced sterilization was high” in the 1970s. “Places more exposed to forced sterilization in 1976-77 have higher child mortality today.” ( Sur ) #IV
How do drug procurement processes affect price, delivery, and shipment time? Across 100+ countries, “pooling internationally is most effective for small buyers and more concentrated markets, and pooling within-country is most effective for large buyers and less concentrated markets.” ( Wang and Zahur ) #IV
Hand-hygiene ‘edutainment’ within popular dramas in Bangladesh improved handwashing and child health. ( Hussam et al. ) #RCT
Evidence from 140 countries show that “epidemic exposure in an individual’s “impressionable years” (ages 18 to 25) has a persistent negative effect on confidence in political institutions and leaders, and on the public health system.” ( Eichengreen, Saka, and Aksoy ) #FE
Fertility and family planning
Providing vouchers in rural India for women to seek subsidized family planning services, either just for themselves or for them and their friends, boosted use of modern contraceptive methods. ( Anukriti, Herrera-Almanza, and Karra ) #RCT
A comprehensive family planning package in urban Malawi ("counseling, free transport to a clinic, and financial reimbursement for family planning services" over two years) decreased stunting by about 7 percent. Cognitive development also rose. ( Maggio, Karra, and Canning ) #RCT
A family planning campaign in Burkina Faso increased contraceptive use by 5.9 percentage points and births fell by 10 percent. ( Glennerster, Murray, and Pouliquen ) #RCT
In Brazil, agricultural “technological change that eliminates female jobs also increases fertility.” ( Moorthy ) #DID
Can improved counseling increase willingness to pay for modern contraceptives? In Cameroon, discounts increased update by 50 percent while shared decision-making (i.e., better information tailored to individual needs) tripled the share of clients adopting a contraceptive at full price. ( Athey et al. ) #RCT
In Malawi, women who received targeted counseling were 15.6 percent less likely to use their stated ideal contraceptive method. With husbands present at the counselling session, women were 13.5 percent less likely to change their stated ideal method. ( Karra and Zhang ) #RCT
Households and marriage
"Participation in Oportunidades [in Mexico] increased mothers’ bargaining power by almost 24%, associated with a 20% increase in their individual welfare." ( Flores ) #DID
An increase in community violence in Mexico led to a decrease in women's decision-making power. ( Hernandez-de-Benito )
In Ethiopia, a legal reform that provides for more equal division of property between wives and husbands in the case of divorce leads to higher consumption levels, particularly where non-land assets are divided more equally than land assets. ( Kieran ) #FE
Across 28 sub-Saharan African countries over the last 30 years, "at any given time more than 10% of children ages 5-16, the majority of them girls, were living with no parent present." ( McGavock )
In India’s marriage market, women prefer men who have completed primary school, while men are not looking for highly educated women. ( Beauchamp, Calvi, and Fulford )
Mobility restrictions in colonial Mozambique led young men to marry earlier and to women of similar age. “Because smaller age disparities reduce HIV risk”, “it is nearly 50 percent lower in those regions.” ( Denton-Schneider ) #RD
In sub-Saharan Africa, the effect of droughts on child marriage is weaker where polygyny is more commonly practiced. ( Tapsoba ) #FE
In China, early marriage reduces women’s progressive gender role attitudes. ( Wu ) #IV
Does it matter whether we discover information by ourselves or hear it from our spouse? For women in India, it’s the same. Men’s beliefs respond less than half as much to information that was discovered by their wife. Husbands put less weight on their wife’s signals even when it is “perfectly shared with them.” ( Conlon et al. ) #FE
After Cambodia’s World Trade Organization (WTO) accession, men in districts facing larger tariff reductions experienced a significant decline in paid employment, whereas women increased their entry into the labor force. This increased intimate partner violence, without changes in marriage, fertility, psychological distress, or household consumption. ( Erten and Keskin ) #FE
In India, mineral deposits—when it comes with sharing of mining royalties with local groups to support investment in vulnerable populations—improve women’s outcomes: “there is reduced acceptance of physical violence and women report fewer barriers to accessing healthcare.”( Guimbeau et al. ) #IV
A female empowerment program—with psychosocial therapy and vocational skills training—in Monrovia, Liberia, reduced the share of women who experienced emotional, physical, and sexual intimate partner violence. One channel: the business training was highly effective, increasing labor supply by 37 percent. ( Sungho Park and Kumar ) #RCT
Migration and refugees
Slavery-intensive districts opposed emancipation in 19 th century Brazil. There was “more support for emancipation where immigrants provided an alternative source of labor” and “where enslaved persons could more easily escape.” ( Seyler and Silve ) #IV
A one SD decrease in soil moisture leads to a 2 percentage point drop in the probability of international migration from West Africa to Europe, equivalent to a 25 percent decrease in the number of international migrants. ( Martínez Flores, Milusheva, and Reichert ) #FE
Adolescents in the households of return migrants in Mexico have a higher probability to attend school, and a lower probability to work or to work and attend school at the same time. ( Chakraborty ) #IV
In the US, “unemployment among low-skilled natives and local welfare expenditure per capita increase in the short-run with low-skilled immigration, but those effects fade through time, while voting is shifted towards republicans in the short run, but only partially attenuate.” ( Oliveira ) #IV
Regularization of Venezuelan migrants in Colombia (with the PEP visa) led to 18 percent and 24.5 percent higher consumption and income per capita compared to other migrants. They also have access to safety nets and financial services, better labor conditions, less food insecurity and better integration in the Colombian society. ( Ibáñez et al. ) #RD
In the Tigray region of Ethiopia, interaction with a migrant significantly improves attitudes towards them. ( Bezabih et al. ) #RCT
Working and saving
Banking and credit.
"Substantial credit creation and destruction exist at all phases of the business cycle" in India. "The annual average of gross and excess credit reallocation in India is even higher than the prior work on the U.S." ( Saini )
In Brazil, privatized branches reduce their lending supply alongside branch closure that adversely impacts bank access, especially in less developed locations. ( Mariani ) #FE
Increasing access to digital loans in Nigeria improves subjective well-being but does not significantly impact other measures of welfare. ( Björkegren et al. ) #RCT
In the 2000s in India, “banks with stronger deposit franchises significantly increased exposure to sectors characterized by long-term advances and rigid rates, whereas banks with weaker franchise increased exposure to sectors with flexible interest rates. Subsequently, banks with lower sensitivity to market interest rates have higher nonperforming loans.” ( Kulkarni and Singh ) #DID
In the absence of the 1997 financial crisis, “there would have been 20 percent more [bank] branches and 9.3 percent more markets [in Thailand] with at least one branch after ten years.” Access to loans would have increased by 13.7 percentage points ( Rysman, Townsend, and Walsh ) #FE
Rural banks in Indian villages decrease informal borrowing and increase formal loans, insurance, and savings products. This reduces poverty rates and stress, and increases non-agriculture self-employment, business income, and wage income. ( Barboni, Field, and Pande )
Access to microcredit in rural China reduced informal borrowing and raised the value of autarky (i.e., economic self-reliance). “Program members relied less on informal financial networks for insuring against shocks when they anticipated having access to credit from the village banks.” ( Cai ) #RCT
Performance-contingent contracts in Kenya have positive impacts on micro-distributor profits. ( Cordaro et al. ) #RCT
After a five-hour financial literacy program in rural Uganda, small business owners were more likely to have savings in their mobile money account or formal savings, and smaller outstanding loans. ( Hamdan et al. ) #RCT
Cash transfers
Unconditional cash transfers in Indonesia led recipients to be “2 to 3 percent less likely to be employed and, among those employed, 3 to 6 percent less likely to be in formal work following receipt of the transfer.” ( Pritadrajati ) #DID
Household exposure to Uganda’s social pension program improves child nutrition and increases educational investment in kin-based societies. There is no impact on children in societies organized by social groups based on age, where intergenerational ties are weak. ( Moscona and Seck ) #DID
The New Rural Pension Scheme (NRPS) in rural China “reduces labor supply, and the receipt of NRPS benefits lowers labor force participation by 9 percent.” ( Nikolov and Wang ) #RD
A cash transfer program in the Philippines reduced non-partner domestic violence (e.g., husband’s relatives), with no effect on intimate partner violence or violence outside home. Suggested mediating channels include stress reduction, increase in empowerment and bargaining power, and strengthening of social networks. ( Dervisevic, Perova, and Sahay ) #RD
Firms and microenterprises
“Spanish firms have lower productivity growth…than German firms…. financial frictions account for 11% of the aggregate productivity growth difference.” ( Sui ) #IV #FE
“Aggregate reallocation is procyclical,” which is “puzzling given the documented fact that the benefits to reallocation are countercyclical.” But “this procyclicality is entirely driven by reallocation of bundled capital.” ( Yang )
Fast-food chains in the US may intentionally target areas with higher obesity rates: "every 1% increase in obesity rate results in 3.8-4.3 additional branch openings." ( Chopra ) #PSM
Using data from India’s largest job website, growing demand for machine learning skills—a proxy for the adoption of artificial intelligence—"has a direct negative impact on the total number of vacancies posted by” firms. It also reduces wages for most jobs. ( Copestake, Pople, and Stapleton ) #FE
A three-week mini-masters of business administration (MBA) program for Ugandan high school students had positive impacts on earnings and business profits 3.5 years later, regardless of whether the training focused on hard skills or soft skills. ( Chioda et al. ) #RCT
In China, “individuals with higher college entrance exam scores … are less likely to create firms; however, when they do, their firms are more successful than those of their lower-score counterparts.” ( Bai et al. ) #FE
The improvement of the quality of legal courts in India has a disproportionately large impact on investment decisions of individuals from disadvantaged castes. ( Chakraborty et al. ) #FE
The entry of chain stores (like 7-11 or Circle-K) into Mexican neighborhoods reduced the number of neighborhood shops, but mostly from fewer newer neighborhood shops opening than usual rather than a bunch going out of business. ( Talamas Marcos ) #IV
In India, managers of firms with the same group identity (family lineage, native language, place of origin, and caste) as the board earn higher compensation. ( Aswani )
Reliability matters for firm-level trading patterns. In Rwanda, ‘good firms’—exporters, multinational companies, large firms, and suppliers to exporters and other multinational companies—are considered more reliable. Reliability matters for the supply chain and supplying a multinational company increases overall seller reliability. ( Nigam and Tan ) #FE
In the Dominican Republic, 20 percent of workers who change firms move to a buyer or supplier of their original employer. Hiring firms experience strong sales and productivity growth. ( Cardoza et al. ) #FE
In China, “historical family culture, as measured by genealogy density, is positively correlated with the share of family firms in counties.” ( Xie and Yuan ) #IV
While rural communities in India can solve internal collective action problems to improve production quality, they are not free from internal market frictions. ( Rao and Shenoy ) #DID
In Mozambique, while female telephone sales representatives working with M-Pesa, a leading mobile money provider in Sub-Saharan Africa, registered fewer clients with new SIM cards, they were more likely to convert these new mobile phone clients to M-Pesa, resulting in similar overall enrollments of new M-Pesa clients. ( Karra et al. ) #RCT
Contracts between the largest oil companies and petro-rich economies with weak institutions go through more changes later in the process (i.e., are backloaded) relative to countries with strong institutions. ( Paltseva, Toews, and Troya-Martinez ) #FE
Labor (including child labor)
A six-month wage incentive for secondary school graduates in Mexico gets youth into the labor market sooner then they'd enter otherwise (without pulling them away from education). ( Abel et al. ) #RCT
A new model to simulate the “the potential impacts of automation” finds big inequality impacts: Automation “raises 2050 wages of high-skilled American workers by 28.8 percent and lowers 2050 wages of low-skilled American workers by 22.8.” ( Benzell et al. )
Do “rickshaw-pullers from Bangladesh exert more effort in their work when they have more family dependents to support?” Yes. ( Aziz )
Most firms in Ethiopia use social networks to find new employees. Subsidizing the formalization of their search (through online and physical posting of job ads) had no effect on the total vacancies that firms created, but it did lead to more “white collar, professional positions.” ( Hensel, Tekleselassie, and Witte ) #RCT
“Offering part-time employment opportunities” in Ethiopia, compared to full-time employment, “attracts less able applicants, who exhibit lower productivity as measured by data entry speed and accuracy during an internship.” ( Kim, Kim, and Zhu ) #RCT
A women’s self-help group lending program in rural Bihar, India, reduced participation in agricultural wage labor for women from disadvantaged caste groups, while those from privileged caste groups increased their participation in self-employment. ( Surendra ) #DID
Uber is used by drivers to buffer against adverse weather shocks: a one SD increase in the intensity of an agricultural shock in Uganda increases time online by 5.1 hours in the month of the adverse weather event (a 6 percent increase over average hours). ( Michuda ) #FE
In India, a mother-in-law’s death reduces her daughter-in-law’s labor force participation by 10 percent. ( Khanna and Pandey ) #FE
In India, “job ads with a high female association use words in the job text that reflect gender stereotypes in job attributes, offer lower wages, and attract a high share of female applications.” ( Chaturvedi, Mahajan, Siddique ) #FE
After a commodity price boom in Brazil, labor was reallocated away from agriculture towards the manufacturing sector in locations more exposed to the commodities boom. ( Laskievic ) #IV
Poverty Measurement
Limitations of big data: Call Detail Records in Haiti fail as an alternative basis for either targeting or evaluation. Predicted outcomes are too noisy to differentiate between targeted cash transfer beneficiaries or to detect changes in food security. ( Barriga Cabanillas et al. ) #RD
Despite large post-disaster reconstruction programs after the 2004 tsunami in Aceh, Indonesia, the economic status of those living in heavily damaged areas did not keep up. This is partly driven by much higher inflation rates in those areas. ( Lawton et al. ) #FE
In Mexico, “combining survey and sub-area level satellite data using household-level empirical best models, while not always preferable to older census-based poverty estimates, significantly improves the accuracy and precision of survey-based estimates of monetary poverty.” ( Newhouse et al. )
What information do community members have and use for social benefits targeting? In Purworejo, Central Java, community members use longer-term wealth information to predict dynamic welfare and to target social benefits. This may be useful in identifying long-term poverty but less so to identify short-term distress. ( Trachtman, Permana, and Sahadewo ) #LIF
Governments, institutions, and conflict
“A decrease by one percent of the US family planning aid induces a decrease by 0.101 percent from the other donors on average.” ( Ferrière ) #IV
Local labor unrest in China increases allocation of Chinese foreign aid projects to large state-owned firms in the area, and employment by these firms increases. Overall, Chinese aid has positive effects on GDP, capital formation, consumption, and employment in the aid receiving country. ( Mueller ) #FE
In areas with high malaria exposure, there are fewer Chinese aid projects and Chinese workers. ( Cervellati et al. ) #DID
Conflict and crime
In Brazil, “municipalities more exposed to illegal mining experienced extra 8 homicides per 100,000 people” (an increase of about 20 percent) after government capacity to monitor gold laundering was reduced. ( Pereira and Pucci ) #DID
Districts in Peru affected by the Mining Mita (a colonial labor-coercion institution) experience more social unrest and violent conflict today. ( Huaroto and Gallego ) #RD
In Africa, droughts in the territory of seasonally migrant populations that herd livestock lead to conflict in neighboring areas, especially in agricultural areas and during the wet season. “Effects are muted in the presence of irrigation aid projects, but not in the presence of other forms of foreign aid.” ( McGuirk and Nunn ) #FE
Post-war sex ratios (with fewer men) in Paraguay are “associated with higher out-of-wedlock births, more female-headed households, better female educational outcomes, higher female labor force participation, and more gender-equal gender norms.” ( Alix-Garcia et al. ) #FE
Reparations for survivors of human rights violations in Colombia improve their lives with positive gains in wage earnings, health, and consumption. Survivors also “invest in their children’s human capital, improving college attendance and test scores.” ( Guarin Galeano )
“Do agricultural producers forgo otherwise profitable investments due to civil conflict?” In Colombia, the answer is yes. Credit disbursement increases after a peace agreement due to changes in returns to investment. ( de Roux and Martínez ) #DID
A 2016 non-aggression pact between gangs in El Salvador led to a large reduction in violence, but increased extortion rates by 15 percent to 20 percent. Much of the increase was passed on to retailers and consumers with observed increases in prices for pharmaceutical drugs and hospital visits for chronic illnesses. ( Brown et al. ) #DID
Buildings constructed when the county officials had connections to their superiors at the prefecture level (in terms of having the same hometown) were 83 percent more likely to collapse during the 2008 Sichuan earthquake relative to the no-connection benchmark. ( Cao ) #DID
In Indonesia, performance appraisals of teachers reduce generosity (as proxied by willingness to make a donation to their own school) at the workplace and increase dishonest behavior, especially when appraisals are linked to financial sanctions. ( Ibanez et al. ) #FE
“Campaign contributions buy forbearance from enforcement of environmental regulations.” Deforestation in Colombia is significantly higher in municipalities that elect donor-funded as opposed to self-funded politicians. ( Harding et al. ) #RD
In Pakistan and India, public officials use personal funds to complement official funding for public services, and part of these funds come from bribes. ( Aman-Rana, Minaudier, and Sukhtankar )
In Brazil, audits increase the number of public employee hires, especially among municipalities in which audits uncovered higher corruption. Mayors hire additional employees as a form of patronage to compensate for audit-related electoral support loss. Additional hires do not positively affect public good and services provision. ( Gonzales ) #DID
In Mexico, partisan alignment between the municipal and federal government increased allocation of an infrastructure program, and increased misuse of federal funds only in municipalities receiving the program. ( Garfias, Lopez-Videla, and Sandholtz ) #RD
In West Bengal, India, “areas controlled by the state’s ruling party receive systematically higher welfare allocations, both in election and non-election years, and yield more votes for the ruling party in the next national election.” ( Shenoy and Zimmermann ) #RD
In India, “the state government channels disproportionate funds to politically-aligned jurisdictions in water-stressed areas and consequently gains votes in subsequent elections.” ( Mahadevan and Shenoy ) #RD
Joining a WhatsApp group organized by political parties in Tamil Nadu, India, increases political knowledge and affects political preferences towards the party affiliated by the WhatsApp group. Effects are stronger when horizontal communication between group members is enabled. ( Carney ) #RCT
During 2018 election in Russia, “video monitoring reduces reported voter turnout by 5.2 percent and votes for the incumbent (autocrat) by 8.3 percent, suggesting a decrease in fraud.” ( Faikina ) #RD
Candidates during 2012 and 2016 Brazilian municipal elections with an electoral advantage (i.e., frontrunners) are substantially more likely to receive a campaign attack than candidates with lower electoral ranking. ( Nakaguma and Souza ) #RD
Providing information about criminal cases and charges of legislative candidates in India increases votes for candidates with no criminal charges and reduces votes for candidates charged for crimes. ( George, Gupta, and Neggers ) #FE
In India, term-limited village presidents provide relatively fewer public goods to heavily populated streets (with many potential votes), and instead allocate more public goods to the streets of the landed elite. ( Brown, Genicot, and Kochhar ) #FE
In the DRC, high-ability tax collectors exert greater effort when matched with other high-ability collectors. Implementing the optimal assignment in terms of ability of tax collectors with (i) teams, and (ii) neighborhoods, would increase tax compliance by 37 percent relative to the status quo (random) assignment. But: governments would have to replace 62 percent of low-ability tax collectors or increase performance wages by 69 percent. ( Bergeron et al. ) #FE
After India switched from sales tax to a value-added tax, gross sales increase by 45 percent. ( Agrawal and Zimmermann ) #DID #FE
Water and sanitation
Incentives for caretakers to maintain community toilets in Indian slums led to improved quality of the facilities and more people paying the contributory fee, but also demanding even better operation and maintenance. ( Armand, Augsburg, and Bancalari ) #RCT
Building a bunch of latrines in India actually made the quality of river water worse, but only in states with less sewage treatment plant capacity. ( Motohashi ) #DID
A mixed team of Hindu and Muslim workers in India is less productive in high-dependency tasks, but this effect vanishes in four months. In low-dependency tasks, diversity does not affect productivity. Mixing improves out-group attitudes for Hindu workers in high-dependency tasks. ( Ghosh ) #FE
One SD increase in RecordTV, a church-affiliated TV channel in Brazil, signal strength leads to an increase of 0.9 percentage points in the share of Pentecostals. This religious adherence leads to higher fertility rates, lower female labor force participation, lower homicide rates, and more votes for Pentecostal candidates. ( Buccione and Mello ) #FE
A zoning reform in urban Brazil that increased the amount of construction allowed led to a 1.4 percent increase in housing stock and a reduction in housing prices. "College educated and higher income households gain the most from the reform." ( Anagol, Ferreira, and Rexer ) #RD
“Fuel standards and gasoline content regulations are widely adopted by policymakers to reduce urban pollution and emission.” Are consumers willing to pay for it? In China, consumers will pay 3.9 percent of the gas price for higher standards. Premium gas consumers will pay more. ( Wang, Zhou, and Zhang ) #DID #RD
Entry deregulations reforms in Guangdong, China, increased firm entry by 25 percent and firm exit by 8.7 percent. Productivity of post-reform entrants is higher likely due to easing of financial constraints and more intense market competition. ( Barwick et al. ) #DID
Reducing cost of formalizing a firm in Brazil increased the number of active formal firms by 60 percent and formal firm registration in eligible industries by 161 percent. Overall formality rate of micro entrepreneurs increased from 17 percent to 32 percent. ( De Farias and Rocha ) #FE
Agriculture and the environment
Agriculture and land.
Farmers in Malawi contribute more to a soil test of someone else's land if they perceive the land to be similar to their own. ( Berazneva et al. ) #RCT
Some measures of wheat quality are easily observed; others aren't. In Ethiopia, large markets only reward easily observed quality, but markets that have grain millers or farmer cooperatives on site reward hard-to-observe quality measures. ( Do Nascimento Miguel )
In Tanzania and Mozambique, drought-tolerant maize seeds combined with insurance mitigated the impact of midseason drought. Farmers learned from this experience and increased future investments. ( Boucher et al. ) #RCT
“The poorest districts in Africa are more likely to have better (not worse) soil quality and … land fertility is higher in districts with worse roads…. Transportation costs are the main drivers of poverty in Africa… Isolation might turn soil quality into a curse.” ( Wantchekon et al. ) #IV
"Increased access to irrigation" in India "significantly boosts agricultural land production." ( Boudot-Reddy and Butler ) #RD
Including women in agricultural extension training for growing rubber in Côte d'Ivoire dramatically boosted investment in new crops and made it possible to maintain previous productivity on older crops. ( Donald, Goldstein, and Rouanet ) #RCT
Fertilizer in Tanzania is rarely adulterated. An information campaign telling farmers that the fertilizer was high quality increased fertilizer use a lot. ( Michelson, Magomba, and Maertens ) #RCT
Cashew producers in Guinea Bissau who received text messages with up-to-date market news and advice earned 21 percent more than other farmers. ( Pereira et al. ) #RCT
Do cotton farmers in Pakistan “learn from cultivation experience about the pest resistance of their seeds”? Not so much. It turns out that “parsing out and processing information from cultivation experience alone” is difficult. ( Ahmad )
If you start the bidding at a higher level in auctions among "commercial agricultural producers in the US," final bids end up higher. (It's what behavioral economists call "anchoring.") ( Ferraro et al. ) #RCT
Inappropriateness of technology adapted as proxied by crop pests and pathogens mismatch reduces global agricultural productivity by 40 to 55 percent, and increases global disparities in the same by 10 to 15 percent ( Moscona and Sastry ) #FE
In US counties with historically heterogenous soil, community ties are weaker, implying that “social learning is an important determinant of social structure.” ( Raz ) #DID
In the long run, labor and capital being mobile, agricultural gains may not “generate structural change in the exact locations in which [agricultural gains] occur.” Agricultural productivity gains improve consumption and education, but there are no gains to nonfarm employment or consumption for landless households in India. ( Asher et al. ) #RD
In India: “1) rural land holding concentration is higher close to urban areas and decreases with distance from urban centers, 2) the increase in land concentration near urban areas is due to fewer medium sized farmers (i.e., more small and large farmers near urban areas), and 3) the distance to urban area-land holding concentration relationship depends positively on the size of the urban area.” ( Rao, Eberhard, and Bharadwaj ) #FE
In Ghana, increases in staple crop price variability led to forest loss because of increased cultivation of cocoa. ( Krah ) #FE
In Mexico and Indonesia, as average heat and precipitation rise, people's aversion to risk falls. But as variation in heat and precipitation rise, aversion to risk rises. (Higher risk aversion correlates with fewer risky behaviors like smoking or migrating.) ( Howden and Levin ) #FE
By 2080, “climate change is estimated to displace 12 percent” of the population of sub-Saharan Africa and “reduce real GDP by 4 percent.” ( Conte ) #FE
Projected increases in the frequency of droughts over the next 30 years in India “will induce landowning households to allocate 2 percent more labor to agriculture and induce landless households to reduce their agricultural labor. The net effect is a 1 percent to 2 percent reduction in agricultural labor.” ( Basu ) #FE
In China, appealing a firm’s violations of pollution standards through social media increased both regulatory oversight and firm compliance, which reduced subsequent violations by 40 percent and air and water pollution emissions by 13 percent and 4 percent, respectively. Appealing to the regulator through private channels only caused a marginal improvement in environmental outcomes. ( Buntaine et al. )
In Uganda, “higher ability managers do not avoid polluted areas, but better adapt to pollution by protecting their workers through both provision of equipment and flexibility in work schedules.” ( Bassi et al. ) #FE
Air pollution in Beijing reduces local traffic which in turn decreases restaurant revenue. ( Liu, Rahman, and Wang ) #IV
Macroeconomics
Growth and inequality.
In the early 2000s, basic internet availability led "to about two percentage points higher economic growth" in towns across sub-Saharan Africa. ( Goldbeck and Lindlacher ) #DID
The extinction of “megaherbivores” (i.e., really big plant-eating animals) brought on the Neolithic Revolution, when a society shifted from forging to agricultural. ( Kumagai ) #IV
“Towns that shortly after the conquest” of the former Kingdom of Granada by the Catholic monarchs “were granted to nobles are relatively poorer today.” ( Oto-Peralías ) #FE
In railroad towns in Brazil, a long historical time as a railroad endpoint predicts a large city size today. ( Barsanetti ) #FE #IV
In colonial Mexico, when the Spanish crown improved its ability to observe local economic production, the transition to direct rule increased in mining districts, leading to greater investments to improve fiscal legibility (“the ability of a central government to observe local economic conditions for the purposes of taxation, shapes political centralization”) over the long term. ( Garfias and Sellars ) #DID
Municipalities in Brazil that fail to receive the revenues they expected from a resource discovery “suffer significant declines in per capita investment and public goods spending after ten years. In contrast, municipalities where discoveries are realized enjoy significant growth in per capita revenues and spending.” ( Katovich ) #DID
Korea’s promotion of heavy and chemical industries in the 1970s led to significant growth among targeted industries/regions. However, their total factor productivity did not grow faster because of resource misallocation across plants. ( Kim, Lee, and Shin ) #DID
Differences between men and women in occupational and sectoral choices and in wages are largest in poor countries and converge over the development process. ( Chiplunkar and Kleineberg ) #FE
“The geographic prevalence of domesticable transport animals, but not of other domesticable animals, strongly predicts the emergence of early long-distance trade routes.” Much later, “at the onset of the industrial era, ethnic groups living in regions historically also home to domesticable transport animals were more involved in trade and had built more complex hierarchical structures.” ( Link ) #FE
“A 10 percent decline in inter-state border frictions in India leads to welfare gains ranging between 1 percent and 8 percent across districts.” ( Panigrahi ) #FE
Ratifying an international trademark agreement led to welfare gains in Africa (from Chinese exports). ( Kuroishi ) #DID
China’s accession to the WTO (and implementation of import tariff cuts) improved female labor market conditions relative to males. It changed assortative mating patterns, improved education, and reduced women’s number of children, especially among high-skilled women. ( Luo and Zou ) #FE
In Vietnam, “US tariff reductions led to a decrease in the likelihood of being self-employed or working in an informal business and increased employment in foreign owned firms.” ( Asghar and McCaig ) #FE
Economic sanctions in Iran led to an overall decline in manufacturing employment growth rate by 16.4 percentage points. Effects are driven by labor-intensive industries and those that depend on imported inputs. ( Moghaddasi Kelishomi and Nisticò )
Following China’s accession to the World Trade Organization, Chinese cities more exposed to trade liberalization sent more students to US universities. Educational exports dampened trends in regional inequality. “Recent trade wars could cost US universities about $1.6 bn in tuition revenue.” ( Khanna et al. ) #IV
After Brazil’s tariff reform in the 1990, “regions specialized in adult-specific industries had lower growth in schooling and higher increases in child labor, especially in paid works.” Results translated into persistent effects on human capital formation and a structural transformation in employment composition. ( Viaro and Nakaguma ) #FE
The order of authors on this blog was determined by a virtual coin flip . This blog post benefited from research assistance from Amina Mendez Acosta and editing by Jeremy Gaines . It also appears on the Development Impact blog .
CGD blog posts reflect the views of the authors, drawing on prior research and experience in their areas of expertise. CGD is a nonpartisan, independent organization and does not take institutional positions.
View the discussion thread.
More Reading

Ideas to action: independent research for global prosperity
© 2024 Center for Global Development | Privacy Notice and Cookie Policy
Sign up to get weekly development updates:
Articles on Economic development
Displaying 1 - 20 of 134 articles.

Neediest areas are being shortchanged on government funds − even with programs designed to benefit poor communities
Eric Stokan , University of Maryland, Baltimore County ; Aaron Deslatte , Indiana University , and Michael Overton , University of Idaho

How the ‘Mexican miracle’ kickstarted the modern US–Mexico drugs trade
Nathaniel Morris , UCL

Industrialisation is still vital to economic development but some countries are struggling to reap its benefits
Jostein Hauge , University of Cambridge

Poor men south of Richmond? Why much of the rural South is in economic crisis
Peter A. Coclanis , University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and Louis M. Kyriakoudes , Middle Tennessee State University

India could soon be the world’s third biggest economy – NZ needs to build the trade relationship urgently
Rahul Sen , Auckland University of Technology

How Indigenous economic development corporations can support a just, low-carbon energy transition
Christina E. Hoicka , University of Victoria and Matthew Foss

Tribes in Maine left out of Native American resurgence by 40-year -old federal law denying their self-determination
Joseph Kalt , Harvard Kennedy School ; Amy Besaw Medford , Harvard Kennedy School , and Jonathan B. Taylor , Harvard Kennedy School

Community-based economic development is the key to a strong pandemic recovery
Audrey Jamal , University of Guelph

Expanded access to solar power in Africa can stimulate economic development – but there are risks
Ben Radley , University of Bath

Street traders in South Africa play a vital role: how their rights can be protected
Nonhlanhla Ngcobo , North-West University ; Anél du Plessis , North-West University , and Oliver Fuo , North-West University

What drives Chinese migrants to Ghana: it’s not just an economic decision
Jinpu Wang , Syracuse University

Small oil producers like Ghana, Guyana and Suriname could gain as buyers shun Russian crude
Jennapher Lunde Seefeldt , Augustana University

Got $1.2T to invest in roads and other infrastructure? Here’s how to figure out how to spend it wisely
Anna Nagurney , UMass Amherst

South African local government elections: why a great deal hangs on the outcome
Dirk Kotze , University of South Africa

Municipalities can play a key role in South Africa’s economic development. Here’s how
Johann Kirsten , Stellenbosch University and Helanya Fourie , Stellenbosch University

COVID: poorest countries should have stopped short of full workplace closures – economist
Mehdi Shiva , University of Oxford

If China’s middle class continues to thrive and grow, what will it mean for the rest of the world?
Amitrajeet A. Batabyal , Rochester Institute of Technology

Pandemic recovery will take more than soaring growth – to fuel a more equitable economy, countries need to measure the well-being of people, too
Bas van Bavel , Utrecht University and Auke Rijpma , Utrecht University

Many African countries had a surprise manufacturing surge in 2010s – it bodes well for the years ahead
Gaaitzen de Vries , United Nations University ; Emmanuel B Mensah , University of Groningen ; Hagen Kruse , University of Groningen , and Kunal Sen , United Nations University

Why the EU’s global fishing activities can’t be called sustainable yet
Andrew Frederick Johnson , Heriot-Watt University and Ingrid Kelling , Heriot-Watt University
Related Topics
- Development
- Economic growth
- Global perspectives
- Manufacturing
- Peacebuilding
- South Africa
- Sustainable development
Top contributors
Professor of Rural-Urban Policy, The Ohio State University
Assistant Professor in Development Studies, University of Cambridge
Associate Vice President (External Engagement); Chair Professor of Business Analytics;, University of Surrey
Senior Lecturer in International Business, Birkbeck, University of London
Professor and Eugene M. Isenberg Chair in Integrative Studies, UMass Amherst
Research Fellow, The Australasian Centre for Resilience Implementation for Sustainable Communities, Charles Darwin University
Academic Director, School for International Training, The University of Melbourne
Professor of Environment and Society, University of Essex
Research Fellow New South Institute, Emeritus Professor at The Nelson Mandela School of Public Governance, University of Cape Town
Assistant Professor of Human Development and Family Science, The Ohio State University
Visiting Assistant Professor, University of Arizona
Professorial Fellow, University of Canberra
Lecturer and Researcher, School of Social Sciences, Monash University
Professor of Sport and Geopolitical Economy, SKEMA Business School
Emertius Professor, University of Tasmania
- X (Twitter)
- Unfollow topic Follow topic
Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- Prof. Esther Duflo
- Prof. Benjamin Olken
Departments
As taught in.
- Developmental Economics
- Microeconomics
Learning Resource Types
Development economics, course description.

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare

What’s the Latest Research in Development Economics? A Roundup from NEUDC 2023
Almedina music, david evans.
There are so many studies regarding so many aspects of development economics that it can be difficult to keep up. Last week was the North East Universities Development Consortium annual conference , often called NEUDC. Researchers presented more than 130 papers across a wide range of topics, from agriculture to education and from labor to climate; almost all of the studies are available for download . This is a great snapshot of the latest research in development economics.
Where the studies are from and what methods they use
The studies take place all over the world (Figure 1). India has more than twice as many studies (23) than the next highest country, Brazil (with 10 studies). Kenya has eight, Indonesia has six, and Bangladesh, Malawi, and Pakistan each have five. A total of 43 countries are represented (not even including regional or cross-country studies that include dozens of countries). If you examine the studies per country population, the top countries are Guinea-Bissau, Uruguay, Malawi, Chile, and Jordan. (Guinea-Bissau and Uruguay just have one study each but have smaller populations.)
Figure 1. Where are recent development economics studies focused?
Source: This map draws on a sample of more than 135 studies from the NEUDC 2023 conference. We categorized studies and excluded those that covered more than three countries (often broad global or regional analyses).
The research continues to draw on a wide range of empirical strategies—i.e., not just randomized controlled trials, or RCTs (Figure 2). RCTs are the single largest group, but there are still lots of studies using difference-in-differences, fixed effects, and regression discontinuity.
Figure 2. What empirical methods do recent development economics papers use?
Source: This figure draws on 124 studies for which we found it easy to ascertain and categorize the empirical strategy. Some studies used multiple methods, in which case we categorized the two main methods we found.
What we learned from 130+ NEUDC studies
We went through each study, and we provide a micro-summary below. Obviously these are just our quick takes. Many studies have more than one thing to teach us, so if our microsummary piques your interest, click the link to the study! Also, take these micro-summaries with a grain of salt: some of these studies are still preliminary (that’s indicated on the front page of the studies themselves), and we also largely take the studies’ claims at face value (we aren’t peer reviewers). Still, there’s a lot of exciting research here, teaching us more about both problems and solutions in low- and middle-income countries (and beyond). We hope you learn as much reading them as we did writing them!
Guide to the methodological hashtags:
Households and human capital
Education and early childhood development.
- Schools in Chile with more poor students tend to have lower test scores. A program that provides extra funding to those schools benefits disadvantaged students at both low and high levels of support. The results for advantaged students in the same schools are less consistent. (Cerda) #RD
- A school voucher program in India benefits recipients, but because voucher amounts are linked to schools' tuition fees, schools have an incentive to raise their fees, which hurts non-beneficiary students. The net effect is still positive, but failing to account for the effect on non-beneficiaries would dramatically overstate the benefits. (Sahai) #DID
- A ten-hour virtual training to help teachers in India better manage emotions, set goals, and solve problems led to a greater belief that they could boost students' learning and put more effort in their teaching. (Kaur) #RCT
- Lots of families in western Kenya don't have books to read to their kids. When those storybooks were offered, the vast majority of families took them. The more expensive they were, the less likely people were to buy them; but even with a low subsidy, more than 90 percent of families bought them. But three months later, kids still didn't have stronger vocabularies. (Bonds, Hamory, and Ochieng) #RCT
- In Tanzania, 10 percent more stagnant water increases diarrhea incidence among children by 30 percent and reduces test scores by 7 percent of a standard deviation. Access to improved sanitation and water sources mitigates the effect of stagnant water on these health and learning outcomes, but this effect increases with high temperatures and population density. (Berggreen and Mattisson) #DID
- A “learning how to learn” approach in Uganda raised the pass rate in the national exam (progression from primary to secondary school) from 51 percent to 71 percent. The approach “trained teachers to teach students to learn like scientists: posing sharp questions, framing specific hypotheses, using evidence and data gathered from everyday life whenever possible.” (Ashraf, Banerjee, and Nourani) #RCT
- In Chile, “classroom peers and older high school peers significantly shape students’ choices of college majors in male-dominated fields.” (Valdebenito) #RD
- In Peru, a 20-minute interaction between engineering students and high school students increased students’ preferences towards engineering, especially among female students with high math aptitude. (Agurto et al.) #RCT
- In India, primary students taught by college students scored 0.34 SD higher in math, 0.22 SD in science, and 0.15 SD in language higher than those taught by regular teachers. (Ganimian, Mbiti, and Mishra) #RCT
- A country-wide effort to improve toilet access and other aspects of sanitation in India (the "Clean India Mission") boosted children's math—but not literacy—scores. Results are similar for boys and girls. (Karmakar and Villa) #DID #ES
- Eleven months after introducing a program in India to encourage teachers to blend their teaching with high-quality videos, student math scores got worse, teachers taught less effectively (e.g., they gave worse feedback to students and monitored student learning less), and students had worse attitudes towards science and math. (de Barros) #RCT
- In the Dominican Republic, all Major League Baseball teams run training academies for adolescent boys. Despite public perceptions that this leads youth to undervalue formal education, exposure to these academies has no measurable impact on school attendance. (Marein and Palsson) #DID
- A common policy to get more underrepresented groups into college is to rank students within high schools (so that kids from poorer high schools have a shot). But in Chile, high school students switch schools to game the system, such that the current policy had a tiny impact, which would have been more than five times as large if students weren't switching schools. (Concha-Arriagada) #FE
- With the introduction of a new bus line and a new train line in Lima (Peru), "a 17 percent reduction in commuting time to college increases enrollment rates by 6 percent," with that mostly driven by enrollment in private colleges. Boys are willing to travel 50 percent longer than girls to attend a better college. (Alba-Vivar) #DID
- Study groups in Chinese primary schools boost student achievement. The effects are biggest for kids who were previously not doing so well in school but who are in high-achieving study groups. It also boosts those kids' level of motivation. (Gao et al.) #IV
- An additional year of education for women in India led to "a 27% decrease in less severe physical domestic violence, a 9% decrease in sexual violence, and a 10% decrease in injuries due to domestic violence." This was likely due to women finding better partners, improved attitudes, and potentially a higher likelihood of reporting violence. (Bergonzoli, Bahure, and Agarwal) #RD
- Higher export prices for crops grown by women in Peru reduce "domestic violence, including severe physical violence and female homicide... The effects are stronger in districts with more unequal gender norms." (Frankenthal) #FE
- In India, short-term exposure to domestic violence doesn't seem to affect women's attitudes about violence, but over time, women who experience violence are more likely to tolerate violence—potentially as a coping mechanism. (Frezza) #RD
- Girls' clubs for adolescents in Côte d'Ivoire alone boosted some girls' mental health but not employment outcomes. Adding separate clubs for husbands and future husbands boosted employment and sexual and reproductive health outcomes. (Boulhane et al.) #RCT
- Women living in neighborhoods with low risk of harassment or assault on the streets are 8.5 percentage points more likely to participate in the labor market relative to women in higher risk neighborhoods—in Indonesia and India. (Cahill) #PSM
- A successful school-expansion program in India “increased voter prioritization of leader competence over gender, boosting the share of women among candidates and state parliamentarians and the overall capability of elected officials.” (Anukriti, Calvo, and Charavarty) #RD
- In Pakistan, providing correct information about support for women voting in society to men does not change the turnout of women, while providing the same information to women or both lowers female turnout. “This blow-back effect is caused by men discouraging women from political participation because they believe women will act according to their own (and different from men’s) preferences.” (Gulzar, Khan, and Sonnet) #FE
- An anti-poverty program in Malawi improved households’ consumption, food security, and dietary diversity outcomes, regardless of whether men or women were targeted and whether a gender transformative training was incorporated in the program. (Bedi, King, and Vaillant) #RCT
- A conditional cash transfer (CCT) program in Peru reinforced traditional gender-role attitudes among children, especially girls. Beneficiary mothers spent more time on home production, and this priority could be a channel for perpetuating traditional gender role attitudes. (Luong) #RD
- Families historically exposed to higher levels of slavery in Guadeloupe and Martinique tend to be more matrifocal, with weaker fathers after emancipation. These families also face higher child mortality, stemming from poorer family environments rather than local conditions. (Beigelman) #FE
- “On an online marriage market platform in India, ... working women are 14.5% less likely to receive interest from male suitors... Women employed in ‘masculine’ occupations are 3.2% less likely to elicit interest from suitors relative to those in ‘feminine’ occupations.” (Afridi et al.) #RCT
- Providing "mentored girls' clubs, life skills, and vocational training" to adolescent girls in northern Nigeria reduced marriage two years after the intervention by 65 percentage points! A major reason is that it boosted girls' likelihood of staying in school. (Cohen, Abubakar, and Perlman) #RCT
- A radio campaign against female genital cutting in Egypt reduced cutting by 13 percent. But those girls also saw their bride prices fall by nearly a quarter and child marriages rose. Across Africa, cutting is more common in settings with bride price. (Khalifa) #DID
- Several years after the start of a cash transfer program in Malawi, those who benefited as adolescent girls were more likely to move longer distances for marriage, and those moves happened over a longer period of time, into young women's mid-twenties. (Ibrahim) #RCT
- Parents in Pakistan prefer grooms who are relatives; they also prefer marriages where their daughters will have more freedom (e.g., to leave the house unaccompanied or to make health decisions independently). (Calvi, Farooqi, and Kandpal) #SurveyExperiment
- In Lahore (Pakistan), women are more likely to sign up for a job search platform than they are to take a job. For less-educated job seekers, jobs with explicit gender requirements are more likely to exclude women. Women with more education are more selective about jobs, but the jobs themselves are less likely to be gender-restrictive. (Gentile et al.) #RCT
- Offering women in West Bengal (India) the ability to multitask work with childcare and to work from home boosts labor market participation, especially for those from more traditional households. Flexible work also increases women's likelihood of accepting out-of-home work later. (Ho, Jalota, and Karandikar) #RCT
- Increasing the minimum wage by nearly a quarter in Morocco narrowed the gender pay gap in the formal sector by about a quarter. But it also led a small fraction of women (but not men) to leave the formal labor market. (Paul-Delvaux) #DID
- In India, horizontal communication between cisgender participants reduces discrimination against transgender people: when involved in a group discussion with two neighbors, there is no longer discrimination at all on average, even when making private choices. This effect is 1.7x larger than top-down communication that informs participants about the legal rights of transgender persons. (Webb) #RCT
- In a lab in the field experiment in Bangladesh, the “less capable women are perceived compared to men, the less they are involved in decision-making. After the information treatment (on women’s abilities), individuals with the lowest perceptions about the wife’s skills are 20 percent more likely to make allocations in her favor.” (Nani) #RCT
- Employers in Bangladesh discriminate paternalistically, i.e., they restrict women’s employment choices to protect them from what employers perceive as unsafe. Informing about safe worker transport at the end of the shift increases demand for female labor by 22 percent and female labor supply by 15 percent. (Buchmann, Meyer, and Sullivan) #RCT
- Offering female entrepreneurs in Jordan access to virtual storefronts by (1) creating and managing Facebook pages for their businesses and (2) offering them digital marketing training created in collaboration with local influencers, increased business survival and revenues. Effects are driven by women with low physical mobility due to social norms at baseline. (Alhorr) #RCT
Health (including mental health)
- Sharing information about either "the prevalence of mental health issues and the efficacy of treatment" or "the mental health struggles of a Nepali celebrity and how he benefited from treatment" boosted people's stated willingness to seek mental health treatment and to pay for counseling. The effects were biggest for those with "less severe symptoms of depression and anxiety." (Lacey et al.) #RCT
- Sometimes people are uncertain about how risky a behavior is. In Malawi, people with greater uncertainty about how risky regular unprotected sex with an HIV-infected partner update their beliefs more drastically in response to new information. (Kerwin and Pandey) #RCT
- Groups of friends among Syrian refugees in Jordan are good at identifying who needs mental health support. Sometimes friends don't want to share info about mental health services because of stigma, but if you nudge the sharers to disclose that they're being financially compensated for sharing the info, they're more likely to share it. (Smith) #RCT
- Home visits inviting adults in Kenya to get vaccinated against COVID increased vaccine doses by ten percent, especially among women and people with less education or income. Announcing the home visit ahead of time (so people could either making a point of being home for the appointment or being out to avoid it) further boosted vaccinations. (Carney et al.) #RCT
- Providing frontline health workers in Guinea-Bissau "with evidence of their program’s effectiveness in improving local health indicators" significantly boosted the effort of health workers, even six months later. (Fracchia) #RCT
- A "mother and child health and family planning program in Bangladesh" boosted height in adulthood for those who participated as children (as well as education among the men). In the next generation, daughters of beneficiaries tend to be taller and have better cognitive development. (Barham et al.) #DID
- Introducing “a competitive selection system for recruiting CEOs in public hospitals in Chile reduced hospital mortality by 8%”, driven by hospitals in which the new CEOs had managerial qualifications. “These CEOs improved operating room efficiency and reduced staff turnover.” (Otero and Muñoz) #DID
- In Rajasthan (India), posting of a mid-level health care provider increased the monthly patient load by 68 percent. The number of patients diagnosed with hypertension and diabetes at treatment facilities increased as well. After one year, elderly deaths declined by 12 percent. (Agte and Soni) #DID
Migration and refugees
- Mexican regions experiencing larger inflows of Mexican low-skilled deportees have higher rates of firm creation, firm survival, and revenue. (Osuna-Gomez and Medina-Cortina) #FE
- In Vietnam, the Ho Khau reform, which reduced migration barriers, had more impact on reducing spatial inequality than place-based incentives. (Huynh) #DID
- In Uganda, “landslides increase long-term displacement and migration, and affected households have substantially worse economic and mental health outcomes years afterward.” (Baseler and Hennig) #FE #DID
- In the Philippines, typhoons increase international migration from affected municipalities, and incentivize migrants to leave for lower paying overseas jobs. (Murathanoglu) #FE
- Municipalities from which more Moroccan soldiers were deployed to France before independence were more likely to send emigrants to France after independence. But this wasn’t true with those sent to Algeria. (Salem and Seck) #FE
Safety nets (including cash transfers and peer support)
- How do you target disaster aid to households? In post-2015 earthquake Nepal, the “property damage criterion excludes many liquidity-constrained households that have high demand for aid, and it includes wealthy, well-insured households that have low demand.” Dividing aid equally among all affected households has larger welfare gains. (Gordon, Hashida, and Fenichel) #RD
- In Mumbai (India), residents who received a subsidy that could only be used for rice or wheat spent less on packaged snacks. The effect was bigger in households with children. (Aouad, Ramdas, and Sungu) #RCT
- With access to safety nets, middle-income households in Colombia are more likely to borrow from formal lenders, and in the long run, they substitute away from predatory loans toward formal loans when experiencing severe shocks. (Álvarez et al.) #RD
- An unconditional grant to poor kids in South Africa reduced the likelihood that girls would be underweight or obese, but it boosted the likelihood that they'd be overweight. There were no substantive effects for boys on average. (Chakraborty and Villa) #RD
- Peer groups in Nepal where most people know each other don't necessarily choose a peer monitor in lab games. But groups where few people are immediately connected do. (Iacobelli and Singh) #RCT #DID
- Using data from six low- and middle-income countries, a proxy means test (PMT)—i.e., using a short list of household characteristics to decide if a household is poor—fails to accurately predict eligibility for social protection programs: “the accuracy of the PMT prediction algorithm decreases steadily over time, by roughly 1.7 percentage points per year,” even though the PMT model is updated only every 5-8 years. (Aiken, Ohlenburg, and Blumenstock)
Working and saving
Banking and credit.
- Encouraging commercial banks in India to increase lending to minority borrowers in “minority concentration” districts in India increased minorities’ access to bank credit. (Khan and Ritadhi) #RD
- In Kenya and Pakistan, equity-like contracts stimulate more profitable investments. Risk preferences play an important but nuanced role: loss-averse individuals prefer equity; however, individuals exhibiting non-linear probability weighting prefer debt. (Meki) #RCT
- In Ghana, individual incentives increased adoption of a new technology; adding endorsement by a trusted peer doubles the impact of the individual subsidy. (Riley, Shonchoy, and Darko Osei) #RCT
- Lots of people in urban India don't have access to credit for when there's a financial crunch or to professionals for mental health problems. Many would like to talk to the people they know, but—from a survey—68 percent underestimate others' willingness to engage on these topics. Helping people realize that boosts sign-ups for potential savings groups or for a potential program to get trained to be a volunteer to listen to other people's anxieties. (Jain and Khandelwal) #RCT
Firms and microenterprises
- Fifteen years after the Indian Ocean tsunami, Indonesian business owners exposed to the tsunami had lower levels of capital and profits than those not exposed. These effects were biggest in rural areas. (Lombardo, Frankenberg, and Thomas) #FE
- Providing firms in Addis Ababa (Ethiopia) with more information about candidates with college degrees led firms to hire faster, but they often hired candidates without college degrees and downgraded their expectations about college graduate productivity. (Wu and Wang) #RCT
- For US firms, entering the whaling industry entails lots of sunk costs such that firms are slow to enter but also slow to leave the market. (Yun)
- In Kenya, “informality is particularly prevalent in downstream economic activities and smaller regional markets.” (Wiedemann et al.) #DID #SC
- Vendors in the Kolkata (India) vegetable market subsidized to sell additional produce earned over 60 percent higher profits, after excluding the value of the subsidy. And yet, “after the subsidy ended vendors largely stopped selling the additional produce” which may reflect “social or private preferences”. (Banerjee et al.) #RCT
- In Tanzania, rural firms smooth both negative and positive input price shocks more than urban firms. Urban firms pass nearly 95 percent of input price increases to customers, while rural firms pass only 55 percent of input price increases. (Rudder) #FE
- Some firms in Sri Lanka have much higher returns to inputs than others, and new econometric tools to test how much putting inputs into the wrong firms affects growth suggest that output could quadruple with better allocation of resources. (Hughes and Majerotvitz) #RCT
- When steam power started replacing water power in the United States, water-powered mills shut down rather than transforming to steam mills, suggesting that shifting technologies is costly. (Hornbeck et al.) #FE
- In Malawi, a survey of shopkeepers shows that they have widely varying strengths across different dimensions of productivity (like attracting customers, managing a storefront, and maintaining inventory across many products). So a one-size-fits-all management training intervention may have disappointing results. (Huntington, de la Parra, and Shenoy)
Labor (including child labor)
- In Uganda, an experiment with job referrals reveals that gender discrimination exists in both directions (favoring the majority gender in a given sector) but that it's worse in male-dominated sectors. But when men can make referrals anonymously, they discriminate less. (Alfonsi and Ferreira) #RCT
- A subsidy to help people find jobs in Ethiopia seems to have smaller effects when more people participate (i.e., general equilibrium effects). The net impact on people's wellbeing still seems to be positive. (Van Vuren) #RCT
- If the unemployment rate is 1 percent higher at the time a person first starts looking for a job in Indonesia, that person is likely to have worse long-term economic prospects: 21 percent lower income and 7 percent lower likelihood of being employed. These effects are smaller than those in high-income settings. (Marshan) #FE
- When farmers in Burundi train their workers, they don't capture all the benefits, since the workers often take those skills and work for others. A contract that keeps workers with the same employer boosts employers' willingness to train massively (by 50 percentage points). (Cefala et al.) #RCT
- A comprehensive training and mentoring program targeted to youth at risk in Rio de Janeiro (Brazil) boosts employment among men but it also—surprisingly—boosts fertility and subsequently welfare receipts among women. (Barros et al.) #RCT
- How much a person is willing to work may in part just be driven by getting used to working. In Chennai (India), providing casual workers with incentives to work over a couple of months boosted how much they worked during that time (by 23 percent), and those same workers worked 16 percent in the following two months, after incentives were removed. (Cefala et al.) #RCT
Governments, institutions, and conflict
Conflict and crime.
- Which connections do people value most in times of crisis? During social unrest in Haiti, daily contacts decrease but total talk time remains constant. Checking in on close friends, family, and others remains a priority. (Putman and Lybbert) #DID
- Historical genocide violence of the Cambodian population impacts today’s household wealth and village-level poverty rates, driven by lower human capital, limited structural transformation, and restricted public goods provision. (Mehrotra) #IV
- In Rio de Janeiro (Brazil), installing peacemaker units of police officers reduced crime rates, which boosted available credit, which in turn further reduced crime. (Tomkowski, Monteiro, and Caluz) #DID
- Sanctioning public acts of repression, such as beating or arrests of protesters, can encourage a regime to prevent protest through less-public means, such as obstruction or harassment of organizers (based on data from 150 countries). (Andirin et al.) #FE
- The political leaning of Brazilian players during the 2022 World Cup affected fans’ reactions depending on their political alignment. Celebrations after goals scored by a player were more intense among politically congruent fans. (Ajzenman, Ferman and Sant'Anna) #RCT
- In southern Ethiopia, areas with more droughts also have more violent conflict. But when herders get and use insurance to protect against drought, it reduces conflict significantly (between 17 and 50 percent). (Sakketa, Maggio, and McPeak) #RCT
- A law in Brazil requiring firms with more than a hundred workers to reserve at least two percent of their job openings for people with disabilities increased employment of people with disabilities. When firms got fined for not meeting the quota, nearby firms—even those not covered by the law—also boosted their disability employment. (Berlinski and Gagete-Miranda) #DID
- In Uruguay, introducing individual retirement accounts as a complement to the traditional defined benefit pension led more people to work into their fifties. It also may have reduced tax evasion. In early old age, people had similar income levels across the two systems, but when people had the chance to go back to the defined benefit system, many did. (Lauletta and Bérgolo) #RD
- If the government doesn't enforce people sticking to contracts, how do they work? Gamblers on horse races in Pakistan provide a window, since such betting is illegal and so the government doesn't enforce the contracts. "Even in the absence of legal enforcement authority, personal relationships, and violence, more than 70% of gamblers fulfill their contractual obligations." (Mehmood and Chen) #RCT
- South African municipalities with higher historical exposure to post-apartheid Truth and Reconciliation Commissions on media have lower levels of violence today. (Gautier, Horta-Saenz, and Russo) #FE
- Losing a sibling during the 1994 Rwandan Genocide leads to more schooling and more siblings born after the genocide. (Gautier) #IV
Regulation, tax, and government
- In Indonesia, “electoral defeats of the incumbent village head increase turnover in the village bureaucracy and reduce nepotism.” (Bazzi et al.) #RD
- In India, after a bureaucrat is transferred to an important ministry with the power to make influential policies, the annual growth rate of the value of the bureaucrat’s assets is 10 percent higher, and it’s 4.4 percent higher for the number of their assets. (Chaudhury and Yuan) #DID
- In China, “over 65% scoring auctions in public procurement show evidence of scoring rule manipulation.” (Chen) #FE
- In Brazil, “high-ability students in (anti-corruption) audited municipalities are less likely to choose majors tailored toward public sector careers, such as business administration and law.” (Xun) #DID
- In rural Bangladesh, the introduction of Village Courts more than doubled the share of disputes resolved in state-sanctioned courts, but the informal dispute resolution mechanism “shalish” remains most used. (Mattsson and Mobarak) #RCT
- A comparative welfare analysis of 40 policies implemented in low- and middle-income countries since 1997 shows that the marginal value is low. (Morris)
- Successful democratizations lead to substantial redistribution: the size of the public sector grows, income inequality falls, and the labor share of income rises, according to data from 90 countries. (Miller) #DID
- In India, “local democracy aligns spending more closely with citizen preferences, but these gains accrue more to men, upper castes, and other advantaged social groups.” (Arora et al.) #FE #DID
- In Brazil, “when a young politician is in office, there is a reduction in deforestation and greenhouse gas emissions without significant effects on local GDP.” (Dahis, de las Heras, Saavedra) #RD #DID
- Appointing “a new city party secretary (PS), who serves as the leader of the local Chinese Communist Party (CCP) organization, is associated with a significant increase in the revealed comparative advantage in industries where the PS’s previous work location exhibited better performance.” (Lin et al.) #FE
- Electoral turnovers improve country performance. “Electing new leaders leads to more policy change, it improves governance, and it reduces perceived corruption,” based on data from over 4,000 national elections since 1945. (Marx, Pons, and Rollet) #RD
- In Senegal, bureaucrats with full discretion for building the lists of potential property tax payers tend to undervalue properties, and they do so even more for higher-value properties, resulting in a regressive tax profile. “In contrast, a rule-based system where bureaucrats record property characteristics (not values) that an algorithm then uses to compute values, significantly reduces this tax gap.” (Knebelmann, Pouliquen, and Sarr) #RCT
- In Uzbekistan, mandating the use of online electronic fiscal devices, which provide regulators with real-time information on business transactions, increases company revenue reports to tax authorities by 13 percent. Adding a direct communication channel with citizens and financial rewards to act as enforcement agents increases firms’ reported revenues by an additional 34 percent. (Kobilov) #DID
- Research projects developed in partnership with policymakers are 17 to 20 percentage points more likely to result in observed policy change. (Bonargent)
- Do religions codify ecological principles? In Benin, a 1 SD increase in African Traditional Religions adherence has a 0.4 SD positive impact on forest cover change. (Deopa and Rinaldo) #IV
- When Israel reduced child allowances to large families in 2003, Jewish families substituted by enrolling their young boys in ultra-Orthodox religious schools. In the long-term, fewer boys enrolled in high schools, without affecting families’ fertility or labor supply decisions. The reform led to a 13 percent decline in completed fertility among Arab families. (Gershoni et al.) #RD
- In Brazil, exposure to a church-affiliated TV channel increases fertility rates, lowers female labor force participation, lowers schooling for young women in the next generation, and leads to more votes for Pentecostal candidates. (Mello and Buccione) #DID
- In Brazil, the removal of progressive Catholic leaders halted the land invasion movement, a conflict in which poor and landless peasants invaded large landholdings to force land redistribution. (Martinez-Bravo, Solá, and Tuñón) #FE
- Hate or fear? In the ongoing conflict between Christians and Muslims in Jos (Nigeria), fear explains 76 percent, and hate 24 percent of the non-cooperative behavior. (Ortiz) #RCT
- Climate change leads to welfare losses of 4.8 percent of GDP across 271 regions in sub-Saharan Africa, with country-level losses as high as 43.8 percent of GDP. “Lowering trade costs can offset these losses by connecting deficit regions to surplus regions and the world market.” (Porteous)
- In South Korea, under a better bureaucrat, exports increased by 40 percent. "In subsequent appointments, exports increase in products with greater bureaucrat experience." (Barteska and Lee) #FE
- Giving information on tariff costs and local prices to traders (via a cell phone platform) at the Kenya-Uganda border increases switching across markets and routes, leading to large increases in traders’ profits and significant formalization of trade. (Wiseman) #RCT
Agriculture, infrastructure, and the environment
Agriculture and land.
- In India, redistribution of land ownership led to an overall increase in durable asset ownership, nonfarm employment and years of schooling, including among lower-caste descendants of households that did not receive land. (Batra) #RD
- Households’ agricultural production in Côte d’Ivoire improves during the agricultural season overlapping with oxen delivery, and increases in land holdings and input use in the subsequent season. (Brudevold-Newman, Donald, and Rouanet) #RCT
- In Kenya, an information campaign (training farmers to identify hybrid maize seeds that are quality-verified) improved farmers' purchasing decisions and led to gains in maize yields. While improved information caused sellers to exit the market, there are no effects on prices or quality among stayers. (Hsu and Wambugu) #RCT
- Increasing agricultural technologies cannot rely on market prices as a mechanism for targeting high-return farmers. In Bangladesh, when farmers receive a new wheat seed variety for free, they adopt it as much as farmers that chose to buy it at a subsidized price. (Mahmoud) #RCT
- Improving the allocation of inputs (like land, labor, and credit) across farms in Thailand could boost productivity by more than a third. But improving allocation of multiple inputs is more productive than focusing entirely on improving allocation of just one input. (Silver)
- A government program to subsidize the price of fertilizer encouraged farmers to specialize based on their comparative advantage: some boosted their agricultural yields; others left agriculture. (Diop) #DID
- Social networks are key to people adopting new agricultural technology. But in Malawi (and a theoretical model predicts similar results elsewhere), using people with lots of connections to get farmers to adopt new seeds works best when lots of farmers in the network have similar farms (so that the seeds are similarly likely to work). (Chakraborty) #FE
Climate and pollution
- Increasing water prices led to a decline in water use of richer households in Cape Town (South Africa). However, richer households substituted municipal water with privately drilled groundwater. (Cole et al.)
- In Mozambique, “providing information on flood risk [such as physical damage and disease outbreaks] increased the implementation of suggested mitigation strategies.” (Leefers) #RCT
- In the Philippines, large-scale tree planting reduced regional poverty and increased economic activity. (Pagel and Sileci) #DID
- In Vietnam, rising temperatures lead more workers to move from agriculture into other industries, both in the short run and the long run. (Pham) #FE
- Reducing localized emissions from vehicles within India’s 10 largest cities leads to a 3 times larger GDP gain than a policy controlling agricultural fires. “Further accounting for labor reallocation leads to a 6 times larger GDP gain.” (Tiwari)
- In Colombia, “extreme temperature events increase the frequency of land sales and decrease the average farm size within municipalities.” (Arteaha et al.) #FE
- In India, industrial water pollution does not seem to affect crop yields. Farmers respond to industrial water pollution by switching irrigation sources from surface water to (costly) groundwater and expanding irrigation. (Hagerty and Tiwari) #RD
- To address sea level rise, the Indonesian government proposed a sea wall. Moral hazard generates severe lock-in and limits migration inland, even over the long run. (Hsiao) #RD
- The 2009 tightening of environmental standards in the US shifted used lead-acid battery recycling, an industry that emits large amounts of lead pollution, to Mexico. Lead pollution exposure reduced students’ text scores by 0.05-0.09 standard deviations. (Litzow et al.) #DID
- The Green Municipalities Program in the Brazilian Amazon (PMV) increased secondary forest cover (in places that have been previously deforested) by 9 percent. (Shinde et al.) #DID
- In Nairobi (Kenya), improved stove ownership reduced high-frequency particulate matter (PM) exposure from 122 µg/m3 to 49 µg/m3, with a 0.24 SD reduction in self-reported respiratory health symptoms. (Berkouwer and Dean) #RCT
- The beef cattle sector drives deforestation worldwide. In the Brazilian Amazon, large intermediaries drive down prices for farmer and cattle supply, but the deforestation frontier is largely competitive and thus emissions remain unaffected. (Barrozo) #IV
Infrastructure and transport
- Chinese infrastructure projects significantly increased nighttime light in the African recipient regions, and the effects persist over time. World Bank projects, however, did not exhibit significant impacts on nighttime light. World Bank and Chinese infrastructure projects both positively influence women’s education attainment and health. (Chai and Tang)
- Motortaxi drivers in Uganda admire other drivers who speed. Drivers are more likely to want financial incentives to limit speeding if those incentives are visible, so they can use them to justify their reduced speed to other drivers. (Raisaro) #RCT
- In Mexico, urban localities that spent an additional month downwind from a 0.1 degree × 0.1 degree grid cell that has adopted conservation agriculture experience a 1.3 percent reduction in the number of infant deaths. (Ferguson and Govaerts) #ES #DID
- Discontinuous incentives around the range thresholds of Chinese driving-range-based subsidies made low-end electric vehicle manufacturers’ invest in reducing the production costs of driving ranges by 30 percentage points. (Zhang) #FE
- “Commuters in Jakarta (Indonesia) are 2-4 times more sensitive to wait time compared to time on the bus, and inattentive to long routes.” (Kreindler et al.) #DID
- “Winning random lotteries for the ownership of condominium houses in Ethiopia leads to significant gains in educational attainment: educational enrollment increases by 4.5-11%, secondary school completion rates by 10.5% and post-secondary attendance rates by 16%.” (Agness and Getahun) #IV
The order of authors on this blog was determined by a virtual coin flip. This blog post benefited from research assistance by Amina Mendez Acosta and editing by Jeremy Gaines . A version of this post will also appear on the CGD Blog.

Senior Economist, Education Global Practice

Senior Fellow, Center for Global Development
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added
Development Economics
The Development Economics Program studies the forces that contribute to economic development, particularly in less developed nations. It explores the role of decisions by households, firms, and governments, the effects of development aid policies, and the consequences of rising incomes in emerging economies.
Codirectors

Seema Jayachandran is a professor in the department of economics at Princeton University. Her research interests include health, education, labor markets, the environment, and political economy in developing nations. She has been an NBER affiliate since 2007.

Benjamin A. Olken is a professor in the department of economics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Director of the Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab. His research focuses on the political economy of developing nations, with particular emphasis on corruption. He has been an NBER affiliate since 2005.
Featured Program Content
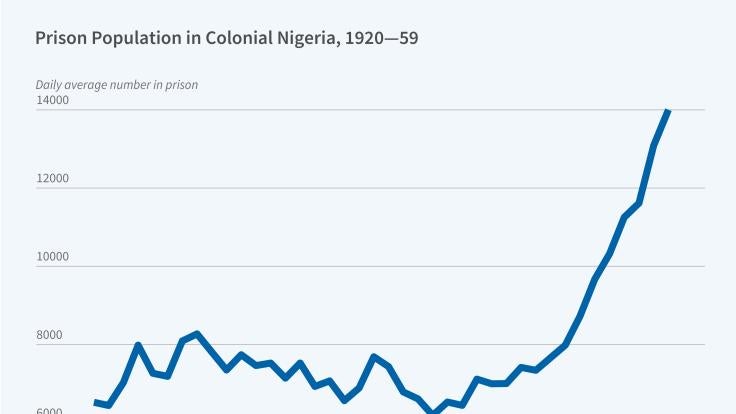
- Authors: Gabriel Kreindler , Arya Gaduh , Tilman Graff , Rema Hanna & Benjamin A. Olken
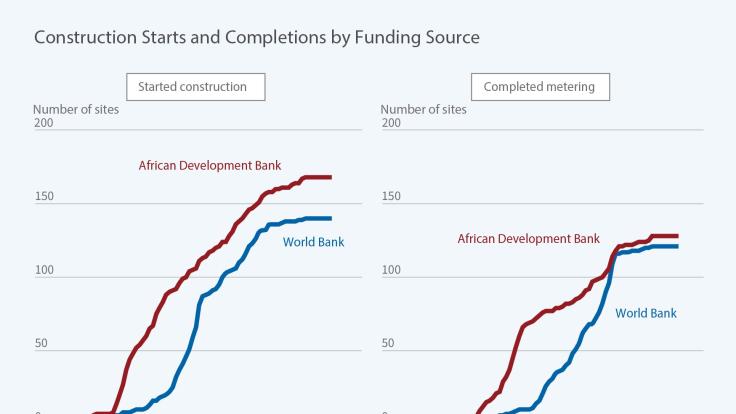
- Authors: Catherine Wolfram , Edward Miguel , Eric Hsu & Susanna B. Berkouwer
Current trends in economics: Implications for community and economic development in 2020 and beyond
In the next decade, what will be the most important advance or “big story” in community and economic development? In this article, we anticipate seven promising and aspirational contributions from the field of economics that may increase our chances of solving some of our most pressing challenges associated with poverty in low-income neighborhoods. In the past decade, our economy experienced the longest economic expansion on record but also declining economic mobility , rising income and wealth inequality, stagnating business formation , lower labor market dynamism , worsening rent burdens , and other developments that limited broad-based participation in economic growth and prosperity. Through research, analysis, and engagement, many economists seek to influence the policies that aim to reverse the developments damping the economic mobility and resilience of low-income households and disadvantaged neighborhoods. In other words, we seek to influence the trajectory of communities and their economic development. We wish to share our perspectives with those engaged in the areas of community outreach, organization, and development in the hopes of soliciting wider discussion and building a consensus on where our combined efforts may stand a greater chance of strengthening the economic well-being of all households.
Contribution #1: Evidence-based policy may shift the policy and practice of community and economic development.
Contribution #2: new knowledge of magnitudes may help direct scarce resources to more socially productive uses., contribution #3: analysis of market structure and regulation may strengthen consumer benefits and promote healthy innovation., contribution #4: economic analysis may help anticipate the full impact of policies affecting community development, including the intended and unintended consequences ., contribution #5: economic analysis may help anticipate risks in financial markets for low-income households and, in the course, help strengthen consumer financial protection policies., contribution #6: analysis of the changing structure of labor markets may guide more targeted and transformative policy interventions to strengthen employment opportunities., contribution #7: applying the methodological rigors of economic theory and quantitative analysis to topics in community and economic development may be even more widespread..
This article highlights seven promising and aspirational contributions from the field of economics for community and economic development in 2020 and beyond. As we said at the outset, we share our views in the hopes of soliciting others. Of course, there are many important aspects of community and economic development that are well outside of the purview of many economists. For example, community organizing, political advocacy, social activism, and creating a sense of belonging are important elements and worthy of their own discussions. Also, issues related to culture and organizational innovation are crucially important but also areas where economists are unlikely to make scholarly or analytical contributions. But together, we can all endeavor to take on the opportunities and challenges of community and economic development in the decade to come.
The views expressed in this post are our own and do not reflect those of the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago or the Federal Reserve System.
To sign up for updates or to access your subscriber preferences, please enter your contact information below.
- Email Address
Find Publications By:
Publication date, more by this author.
- Closing the Racial/Ethnic Gap in Refinancing in Chicago
- Closing Racial Economic Gaps During Covid-19
- Helping Homeowners During the Covid-19 Pandemic: Lessons from the Great Recession
Jonathan Lanning
- The Importance of Cars and Car Loans for People with Low and Moderate Incomes
- What Are the Consequences of Missed Payments on Consumer Debts?
- How Ford Motor’s Equal Pay Policies Reduced Overall Labor Market Discrimination
- Region & Community
- Style Guide
Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, 230 South LaSalle Street, Chicago, Illinois 60604-1413, USA. Tel. (312) 322-5322
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved.
Please review our Privacy Policy | Legal Notices
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Economics →

- 11 Apr 2024
- In Practice
Why Progress on Immigration Might Soften Labor Pains
Long-term labor shortages continue to stoke debates about immigration policy in the United States. We asked Harvard Business School faculty members to discuss what's at stake for companies facing talent needs, and the potential scenarios on the horizon.

- 01 Apr 2024
Navigating the Mood of Customers Weary of Price Hikes
Price increases might be tempering after historic surges, but companies continue to wrestle with pinched consumers. Alexander MacKay, Chiara Farronato, and Emily Williams make sense of the economic whiplash of inflation and offer insights for business leaders trying to find equilibrium.

- 29 Jan 2024
- Research & Ideas
Do Disasters Rally Support for Climate Action? It's Complicated.
Reactions to devastating wildfires in the Amazon show the contrasting realities for people living in areas vulnerable to climate change. Research by Paula Rettl illustrates the political ramifications that arise as people weigh the economic tradeoffs of natural disasters.

- 10 Jan 2024
Technology and COVID Upended Tipping Norms. Will Consumers Keep Paying?
When COVID pushed service-based businesses to the brink, tipping became a way for customers to show their appreciation. Now that the pandemic is over, new technologies have enabled companies to maintain and expand the use of digital payment nudges, says Jill Avery.

- 17 Aug 2023
‘Not a Bunch of Weirdos’: Why Mainstream Investors Buy Crypto
Bitcoin might seem like the preferred tender of conspiracy theorists and criminals, but everyday investors are increasingly embracing crypto. A study of 59 million consumers by Marco Di Maggio and colleagues paints a shockingly ordinary picture of today's cryptocurrency buyer. What do they stand to gain?

- 15 Aug 2023
Why Giving to Others Makes Us Happy
Giving to others is also good for the giver. A research paper by Ashley Whillans and colleagues identifies three circumstances in which spending money on other people can boost happiness.

- 13 Mar 2023
What Would It Take to Unlock Microfinance's Full Potential?
Microfinance has been seen as a vehicle for economic mobility in developing countries, but the results have been mixed. Research by Natalia Rigol and Ben Roth probes how different lending approaches might serve entrepreneurs better.

- 23 Jan 2023
After High-Profile Failures, Can Investors Still Trust Credit Ratings?
Rating agencies, such as Standard & Poor’s and Moody's, have been criticized for not warning investors of risks that led to major financial catastrophes. But an analysis of thousands of ratings by Anywhere Sikochi and colleagues suggests that agencies have learned from past mistakes.

- 29 Nov 2022
How Much More Would Holiday Shoppers Pay to Wear Something Rare?
Economic worries will make pricing strategy even more critical this holiday season. Research by Chiara Farronato reveals the value that hip consumers see in hard-to-find products. Are companies simply making too many goods?

- 21 Nov 2022
Buy Now, Pay Later: How Retail's Hot Feature Hurts Low-Income Shoppers
More consumers may opt to "buy now, pay later" this holiday season, but what happens if they can't make that last payment? Research by Marco Di Maggio and Emily Williams highlights the risks of these financing services, especially for lower-income shoppers.

- 01 Sep 2022
- What Do You Think?
Is It Time to Consider Lifting Tariffs on Chinese Imports?
Many of the tariffs levied by the Trump administration on Chinese goods remain in place. James Heskett weighs whether the US should prioritize renegotiating trade agreements with China, and what it would take to move on from the trade war. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 05 Jul 2022
Have We Seen the Peak of Just-in-Time Inventory Management?
Toyota and other companies have harnessed just-in-time inventory management to cut logistics costs and boost service. That is, until COVID-19 roiled global supply chains. Will we ever get back to the days of tighter inventory control? asks James Heskett. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 09 Mar 2022
War in Ukraine: Soaring Gas Prices and the Return of Stagflation?
With nothing left to lose, Russia's invasion of Ukraine will likely intensify, roiling energy markets further and raising questions about the future of globalization, says Rawi Abdelal. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 10 Feb 2022
Why Are Prices So High Right Now—and Will They Ever Return to Normal?
And when will sold-out products return to store shelves? The answers aren't so straightforward. Research by Alberto Cavallo probes the complex interplay of product shortages, prices, and inflation. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 11 Jan 2022
- Cold Call Podcast
Can Entrepreneurs and Governments Team Up to Solve Big Problems?
In 2017, Shield AI’s quadcopter, with no pilot and no flight plan, could clear a building and outpace human warfighters by almost five minutes. It was evidence that autonomous robots could help protect civilian and service member lives. But was it also evidence that Shield AI—a startup barely two years past founding—could ask their newest potential customer, the US government, for a large contract for a system of coordinated, exploring robots? Or would it scare them away? Harvard Business School professor Mitch Weiss and Brandon Tseng, Shield AI’s CGO and co-founder, discuss these and other challenges entrepreneurs face when working with the public sector, and how investing in new ideas can enable entrepreneurs and governments to join forces and solve big problems in the case, “Shield AI.” Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 06 May 2021
How Four Women Made Miami More Equitable for Startups
A case study by Rosabeth Moss Kanter examines what it takes to break gender barriers and build thriving businesses in an emerging startup hub. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 20 Apr 2021
- Working Paper Summaries
The Emergence of Mafia-like Business Systems in China
This study sheds light on the political pathology of fraudulent, illegal, and corrupt business practices. Features of the Chinese system—including regulatory gaps, a lack of formal means of property protection, and pervasive uncertainty—seem to facilitate the rise of mafia systems.
- 02 Feb 2021
Nonprofits in Good Times and Bad Times
Tax returns from millions of US nonprofits reveal that charities do not expand during bad times, when need is the greatest. Although they are able to smooth the swings of their activities more than for-profit organizations, nonprofits exhibit substantial sensitivity to economic cycles.

- 01 Feb 2021
Has the New Economy Finally Arrived?
Economists have long tied low unemployment to inflation. James Heskett considers whether the US economic policy of the past four years has shaken those assumptions. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 06 Jan 2021
Aggregate Advertising Expenditure in the US Economy: What's Up? Is It Real?
We analyze total United States advertising spending from 1960 to 2018. In nominal terms, the elasticity of annual advertising outlays with respect to gross domestic product appears to have increased substantially beginning in the late 1990s, roughly coinciding with the dramatic growth of internet-based advertising.
134 Economics Thesis Topics: Ideas for Outstanding Writing

Writing a thesis is not an easy task. For most of the students, it can be even intimidating, especially when you do not know where to start your research.
Here, we have provided an economics thesis topics list. After all, everyone knows that choosing the right idea is crucial when writing an academic paper. In economics, it can combine history, math, social studies, politics, and numerous other subjects. You should also have solid foundations and a sound factual basis for a thesis. Without these elements, you won’t be able to master your research paper.
The issue is:
It is not always clear what could be seen as an excellent economics thesis topic. Our experts can assist you with this challenge. This list contains some outstanding examples to get you started.
- ⭐ Thesis in Economics
- 🔥 Supreme Thesis Topics
- 👍 Bachelor’s Thesis
- 😲 Master’s Thesis
📊 Microeconomics
📈 macroeconomics.
- 🤔 Developmental
- 👨💼 Behavioral
- 💼 Financial
- 🌱 Agricultural
- 🤝 Sociology
- 📚 Ph.D. Topics
- 📝 How to Pick a Topic
⭐ What Does a Thesis in Economics Look Like?
A good thesis in economics is a blend between an empirical paper and a theoretical one. One of the essential steps in choosing a topic in economics is to decide which one you will write.
You may write, research, analyze statistical data and other information. Or build and study a specific economic model.
Or why not both!
Here are some questions you can ask when deciding what topic to choose:
- What has already been written on this topic?
- What economic variables will my paper study?
- Where should I look for the data?
- What econometrics techniques should I use?
- What type of model will I study?
The best way to understand what type of research you have to do is to write a thesis proposal. You will most probably be required to submit it anyway. Your thesis supervisor will examine your ideas, methods, list of secondary and primary sources. At some universities, the proposal will be graded.

After you get the initial feedback, you will have a clear idea of what to adjust before writing your thesis. Only then, you’ll be able to start.
🔥 Supreme Economics Thesis Topics List
- Fast fashion in India.
- The UK housing prices.
- Brexit and European trade.
- Behavioral economics.
- Healthcare macroeconomics.
- COVID-19’s economic impact.
- Global gender wage gap.
- Commodity dependence in Africa.
- International trade – developing countries.
- Climate change and business development.
👍 Economics Bachelor’s Thesis Topics
At the U.S. Universities, an undergraduate thesis is very uncommon. However, it depends on the Department Policy.
The biggest challenge with the Bachelor’s Thesis in economics concerns its originality. Even though you are not required to conduct entirely unique research, you have to lack redundant ideas.
You can easily avoid making this mistake by simply choosing one of these topics. Also, consider visiting IvyPanda essays database. It’s a perfect palce to conduct a brainstorming session and come up with fresh ideas for a paper, as well as get tons of inspiration.
- The impact of the oil industry on the economic development of Nigeria. The oil industry is vital for the economic development of Nigeria. In this thesis, students can discuss the notion of the resource curse. Analyze the reasons why general people are not benefiting from the oil industry. Why did it produce very little change in the social and economic growth of the country?
- Sports Marketing and Advertising: the impact it has on the consumers.
- Economic opportunities and challenges of investing in Kenya .
- Economic Development in the Tourism Industry in Africa. Since the early 1990s, tourism significantly contributed to the economic growth of African countries. In this thesis, students can talk about the characteristics of the tourist sector in Africa. Or elaborate on specific countries and how their national development plans look like.
- Globalization and its significance to business worldwide .
- Economic risks connected to investing in Turkey .
- The decline in employment rates as the biggest American economy challenge .
- The economics of alcohol abuse problems. In this thesis, students can develop several essential issues. First, they can examine how poverty is connected to alcohol abuse. Second, they can see the link between alcohol consumption and productivity. To sum up, students can elaborate on the economic costs of alcohol abuse.
- Causes and solutions for unemployment in Great Britain.
- Parallel perspective on Global Economic Order: China and America. This thesis can bring a comparative analysis of the economies to a new level. China and The US are the world’s two largest economies. These two countries have a significant impact on the global economic order. So, looking at the set of institutions, policies, rules can be constructive.
- The new international economic order after COVID-19
- Financial stability of the banking sector in China.
- New Electronic Payment Services in Russia.
- The influence of culture on different entrepreneurial behaviors.
- The impact of natural cultural practices on entrepreneurial activity.
- The relationships between national culture and individual behavior.
- The main reasons for salary inequalities in different parts of the U.S.
😲 Economics Master’s Thesis Topics
Student life can be fascinating, but it comes with its challenges. One of which is selecting your Master’s thesis topic.
Here is a list of topics for a Master’s thesis in economics. Are you pursuing MPhil in Economics and writing a thesis? Use the following ideas as an inspiration for that. They can also be helpful if you are working on a Master’s thesis in financial economics.
- The impact of visual aid in teaching home economics.
- The effect of income changes in consumer behaviors in America.
- Forces behind socio-economic inequalities in the United States. This thesis can explore three critical factors for socio-economic differences in the United States. In the past 30 years, social disparities increased in the United States. Some of the main reasons are technology, trade, and institutions.
- The relationships between economic growth and international development.
- Technological innovations and their influence on green and environmental products.
- The economics of non-solar renewable energy .

- The economic consequences of terrorism . Terrorism not only takes away lives and destroys property but also widely affects the economy. It creates uncertainty in the market, increases insurance claims, slows down investment projects, and tourism. This thesis can address all of the ways in which terrorism can affect economies.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) implementation in the Oil and Gas Industry in Africa.
- Use of incentives in behavioral economics.
- Economic opportunities and challenges of sustainable communities .
- Economics of nuclear power plants.
- Aid and financial help for emerging markets. This topic is very versatile. Students can look at both the positive and the adverse effects that funding has on the development. There are plenty of excellent examples. Besides, some theories call international help a form of neocolonialism.
- Multinational firms impact on economic growth in America .
- The effect of natural disasters on economic development in Asia.
- The influence of globalization on emerging markets and economic development.
📑 More Economics Thesis Topics: Theme
For some students, it makes more sense to center their search around a certain subject. Sometimes you have an econ area that interests you. You may have an idea about what you want to write, but you did not decide what it will be.
If that’s the case with you, then these economics thesis topics ideas are for you.
- An analysis of the energy market in Russia.
- The impact of game theory on economic development.
- The connection between minimum wage and market equilibrium.
- Gender differences in the labor market in the United States. This topic can shed light on gender differences in the labor market in the United States. In the past years, the overall inequality in labor in the markets decreased. However, there is still a lot of work that can be done.
- Economic reasons that influence the prices of oil .
- Relationship between the Lorenz curve and the Gini coefficient.
- Challenges of small businesses in the market economy.
- The changes in oil prices: causes and solutions . Universal economic principles do not always apply to the sale and purchase of the oil. The same happens with its cost. In the thesis, talk about what affects the prices. What are the solutions that can be implemented?
- The economic analysis of the impact of immigration on the American economy.

- Economic inequality as a result of globalization . Economic inequality becomes even more apparent on the global level. There is a common belief that globalization is the cause of that. Discuss what can be the solutions to these problems. This topic is vital to minimize the gap between the rich and the poor.
- The economic explanation of political dishonesty .
- Effect of Increasing Interest rates costs in Africa .
- The connection between game theory and microeconomics.
- Marketing uses in microeconomics.
- Financial liability in human-made environmental disasters.
- Banks and their role in the economy. Banks are crucial elements of any economy, and this topic covers why. You can explain how banks allow the goods and services to be exchanged. Talk about why banks are so essential for economic growth and stability.
- Inflation in the US and ways to reduce its impact.
- The connection between politics and economics.
- Income Dynamics and demographic economics.
- US Market Liquidity and macroeconomics.
- Macroeconomics and self-correction of the economy .
- The American economy, monetary policy, and monopolies .
- The importance of control in macroeconomics. One of the central topics in macroeconomics is grouped around the issue of control. It is quite reasonable that control over money and resources should become a topic of discussion.
- Analysis of Africa’s macroeconomics and its performance.
- Economics of education in developing markets.
- Problems and possible solutions for Japan macroeconomics .
- Comparative analysis of British macroeconomics concerning the US .
- Public policies and socio-economic disparities.
- The world problems through macroeconomic analysis. Indeed, macroeconomics is very complicated. There are many influences, details, and intricacies in it. However, it allows economists to use this complex set of tools to examine the world’s leading problems today.

- The connection between employment interest and money.
🤔 Development Economics
- Economics of development . This topic is very rich in content. First, explain what it is. Then pay particular attention to domestic and international policies that affect development, income distribution, and economic growth.
- The relation between development and incentive for migration.
- The impact of natural disasters on the economy and political stability of emerging markets.
- The economic consequences of population growth in developing countries.
- The role of industrialization in developing countries . The industrialization has been connected with the development. It promotes capital formation and catalyzes economic growth in emerging markets. In this thesis, you can talk about this correlation.
- Latin American economic development.
- Gender inequality and socio-economic development .
- Problems of tax and taxation in connection with economic growth.
- The economic impact of terrorism on developing markets.
- Religious decline as a key to economic development. Not everyone knows, but a lot of research has been done in the past years on the topic. It argues that decreased religious activity is connected with increased economic growth. This topic is quite controversial. Students who decide to write about it should be extra careful and polite.
👨💼 Behavioral Economics
- Risk Preferences in Rural South Africa.
- Behavioral Economics and Finance .
- Applied behavioral economics in marketing strategies. If you want to focus your attention on marketing, this topic is for you. Behavioral economics provides a peculiar lens to look at marketing strategies. It allows marketers to identify common behaviors and adapt their marketing strategies.
- The impact of behavioral finance on investment decisions.
- Behavioral Economics in Child Nutrition Programs in North Texas.
- Guidelines for Behavioral Economics in Healthcare Sector.
- Cognitive and behavioral theories in economics .
- Cross-cultural consumer behavior and marketing communication. Consumers are not only affected by personal characteristics, but also by the culture they are living in. This topic focuses on the extent it should determine marketing strategy and communication.
- Behavior implications of wealth and inequality.

- Optimism and pessimism for future behavior.
💼 Financial Economics
- Financial Economics for Infrastructure and Fiscal Policy .
- The use of the economic concept of human capital. Students can focus on the dichotomy between human and nonhuman capital. Many economists believe that human capital is the most crucial of all. Some approach this issue differently. Therefore, students should do their research and find where they stand on this issue.
- The analysis of the global financial crisis of 2020s. Share your thoughts, predictions, ideas. Analyze the economic situation that affects almost everyone in the world. This thesis topic will be fresh and original. It can help to start a good and fruitful conversation.
- The big data economic challenges for Volvo car.
- The connection between finance, economics, and accounting.
- Financial economics: Banks competition in the UK .
- Risk-Taking by mutual funds as a response to incentives.
- Managerial economics and financial accounting as a basis for business decisions.
- Stock market overreaction.

🌱 Agricultural Economics
- Agricultural economics and agribusiness.
- The vulnerability of agricultural business in African countries.
- Agricultural economics and environmental considerations of biofuels .
- Farmer’s contribution to agricultural social capital.
- Agricultural and resource economics. Agricultural and resource economics plays a huge role in development. They are subdivided into four main characteristics which in this topic, students can talk about: – mineral and energy resources; – soil resources, water resources; – biological resources. One or even all of them can be a focus of the thesis.
- Water as an economic good in irrigated agriculture.
- Agriculture in the economic development of Iran.
- The US Agricultural Food Policy and Production .
- Pesticides usage on agricultural products in California.

- An analysis of economic efficiency in agriculture. A lot of research has been done on the question of economic efficiency in agriculture. However, it does not mean there is no place for your study. You have to read a lot of secondary sources to see where your arguments can fit.
🤝Economic Sociology
- Theory, approach, and method in economics sociology.
- Economic sociology of capitalism. While economists believe in the positive effect capitalism has on the economy, the social effect is quite different. The “economic” part of the issue has been studied a lot. However, the sociology of it has been not. This thesis can be very intriguing to read.
- Political Economy and Economic Sociology.
- Gender and economic sociology .
- Progress, sociology, and economics.
- Data analysis in economics, sociology, environment .
- Economic sociology as a way to understand the human mind.
- Economic sociology of money.
- Economics, sociology, and psychology of security.
- Major principles of economic sociology. In the past decade, economic sociology became an increasingly popular field. Mainly due to it giving a new view on economics, human mind, and behavior. Besides, it explores relationships between politics, law, culture, and gender.
📚 The List of Ph.D. Topics in Economics
If you decide to go to grad school to do your Masters, you will likely end up getting a Ph.D. as well. So, with this plan in mind, think about a field that interests you enough during your Masters. Working with the same topic for both graduate degrees is easier and more effective.
This list of Ph.D. Topics in Economics can help you identify the areas you can work on.
- Occupational injuries in Pakistan and its effect on the economy. Injuries are the leading cause of the global burden of disability. Globally, Pakistan was ranked 9th populated country with a large number of unskilled workers. In this dissertation, consider the link between occupational injuries and their effects on the economy.
- The study of the Philippines’ economic development.

- Financial derivatives and climate change .
- Econometric Analysis of Financial Markets.
- Islamic Banking and Financial Markets .
- Health economics and policy in the UK.
- Health insurance: rationale and economic justification. In this dissertation, students can find different ways to explain and justify health insurance. Starting to philosophical to purely economic grounds. In the past years, there was a lot of discussion regarding the healthcare system for all. What are some of the economic benefits of that?
- Colombian economy, economic growth, and inequality.
- Benefits of mergers and acquisitions in agribusiness.
- Methods to measure financial risks when investing in Africa.
- The significance of financial economics in understanding the relationship between a country’s GDP and NDP.
- Network effects in cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrencies are not new anymore. However, it is still an original subject for a dissertation. Students can decide to choose several crypto coins and evaluate the importance of the network effect. This effect is particularly significant for Bitcoin. Explain why.
- The comparison of the Chinese growth model with the American growth model.
- An economic justification versus political expediency.
- Pollution Externalities Role in Management Economics .
📝 How to Select an Economics Thesis Topic
As your academic journey is coming to an end, it’s time to pick the right topic for your thesis. The whole academic life you were preparing to undertake this challenge.
Here is the list of six points that will help you to select an economics thesis topic:
- Make sure it is something you are genuinely interested in. It is incredibly challenging to write something engaging if you are not interested in the topic. So, choose wisely and chose what excites you.
- Draw inspiration from the previous student’s projects. A great place to start is by looking at what the previous students wrote. You can find some fresh ideas and a general direction.
- Ask your thesis advisor for his feedback. Most probably, your thesis advisor supervised many students before. They can be a great help too because they know how to assess papers. Before meeting with your professor, do some basic research, and understand what topic is about.
- Be original, but not too much. You do not want to spend your time writing about a project that many people wrote about. Your readers will not be interested in reading it, but your professors as well. However, make sure you do not pick anything too obscure. It will leave you with no secondary sources.
- Choose a narrow and specific topic. Not only will it allow you to be more original, but also to master a topic. When the issue is too broad, there is just too much information to cover in one thesis.
- Go interdisciplinary. If you find yourself interested in history, philosophy, or any other related topic, it can help you write an exceptional thesis in economics. Most of your peers may work on pure economics. Then, the interdisciplinary approach can help you to stand out among them.

Thank you for reading the article to the end! We hope this list of economics thesis topics ideas could help you to gather your thoughts and get inspired. Share it with those who may find it useful. Let us know what you think about it in the comment section below.
🔗 References
- Economics Thesis Topics List: Seminars Only
- How To Pick A Topic For Your Economics Research Project Or Master’s Thesis: INOMICS, The Site for Economists
- What Do Theses and Dissertations Look Like: KU Writing Center, the University of Kansas
- Writing Economics: Robert Neugeboren with Mireille Jacobson, University of Harvard
- Economics Ph.D. Theses: Department of Economics, University of Sussex Business School, IDEAS_RePEc
- World Economic Situation and Prospects 2018: United Nations
- Undergraduate Honors Theses: Department of Economics, University of California, Berkeley
- Economics Department Dissertations Collection: Economics Department, University of Massachusetts Amherst
- Topics for Master Theses: Department of Economics, NHH, Norwegian School of Economics
- Share via Facebook
- Share via Twitter
- Share via LinkedIn
- Share via email
The dilemma I faced in getting Thesis proposal for my M Phil programme is taken away. Your article would be a useful guide to many more students.Thank you for your guidance.
Thanks for the feedback, John! Your opinion is very important for us!
I wants it for msc thesis
These are very helpful and concise research topics which I have spent days surfing the internet to get all this while. Thanks for making research life experience easier for me. Keep this good work up.
Thank you, Idris!
Glad to hear that! Thank you for your feedback, Idris!
Excellent research
For research
A very well written, clear and easy-to-read article. It was highly helpful. Thank you!
Thanks for your kind words! We look forward to seeing you again!
Economic Development
These videos were released Nov. 24, 2015.
Part 1: Why Are Some Countries So Rich and Others So Poor?
The gap between rich and poor countries has grown exponentially since the days of Adam Smith. In the 1770s, rich countries were twice as well-off as poor countries. These days, GDP per capita is 35 times higher in rich countries than in poor. In this video, economist B. Ravikumar explains how he and other economists are looking at these cross-country income differences.
Part 2: Reducing Trade Barriers to Close the Gap between Rich and Poor Countries
If barriers to trade are removed, capital goods flow more freely across countries; this benefits all parties because they all can use their resources more efficiently. The removal of trade barriers could close the income gap between rich and poor countries by 50 percent, according to research conducted by economist B. Ravikumar and his colleagues.
Read the working paper, " Capital Goods Trade, Relative Prices, and Economic Development ."
Related Topics
Economists and experts talk about their research, topics in the news and issues related to the Fed. Views expressed are not necessarily those of the St. Louis Fed or the Federal Reserve System.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Research Reports and Publications
- Share this page
Through various programs, EDA funds and supports research and resources to shape economic development policies and inform economic development decision-making. Explore the research below:
ARPA Research
Research and evaluation, nacie reports and recommendations.
- EDA Program List
- Find Open Funding
- Resources & Tools
- Accessibility
- Commerce.gov
- EDA Archives
- Information Quality
- Massachusetts
- Operating Policies
- Privacy Policy

- Development & Economic Growth

New Global Empowerment Meeting Incubation Fund supports its first cohort of innovative projects focused on developing countries
Funding will support collaborations between researchers and local communities on the front lines of the climate crisis.

Harvard’s Growth Lab researchers diagnose South Africa’s decline and suggest tough choices to move forward

Juan Jimenez: Bringing real-world development and political experience to bear on complex challenges

Eliana La Ferrara: The world through a wider lens
- Poverty, Inequality & Opportunity
Who benefits? Experimental evidence on Saudi women’s take-up of unemployment assistance
Does a woman’s take-up of government benefits vary with her perception of how they will be shared within the household?
The Dollar versus the Euro as International Reserve Currencies
We begin by examining determinants of aggregate foreign exchange reserve holdings by central banks (size of issuing country’s economy and financial markets, ability of the currency to hold value, and
Addressing Challenges of a New Era: Against Rule-of-Thumb Economics
The most pressing economic problems of our time require pragmatic remedies closely tailored to context
Japan’s Economic Puzzle
In examining the economic landscape of Japan through a conventional lens, one might conclude that its performance is lackluster, particularly when compared to other advanced economies like the United
Watch & Listen

- Business & Regulation
What’s Next for the U.S. Economy? with Lawrence H. Summers
What is the outlook for the U.S. economy? Inflation. Interest rates. The budget deficit. In this Wiener Conference Call, former U.S. Secretary of the Treasury Lawrence H.

Goals and realities: What World Cup performances can teach us about development in African countries

COVID-19 and Developing Nations: The Economic Outlook

Will COVID-19 Remake the World?
Get smart & reliable public policy insights right in your inbox.
130 Excellent Economics Research Topics To Consider
Table of Contents
Are you an economics student searching for good topics for your research paper? If yes, then keep on reading this blog. To make the topic selection process easier for you, here we have suggested a list of the best economics research topics on various areas associated with the subject. In addition to that, we have also presented a brief overview of economics research paper topic selection and writing.
Quickly explore the entire list and choose any ideal topic for composing your economics thesis or dissertation.
Economics Research Paper Topic Selection and Writing
Have your professor asked you to submit an economics research paper? If yes, then topic selection is the first step you should do. In case, your supervisors had not suggested any research ideas, make sure to choose a unique economics research topic that you are interested in. The topic you choose should be understandable for you and your readers, and it should also have a wide research scope with the necessary information for crafting a comprehensive research paper or essay.
After you have selected a research topic for your economics assignment, sketch an outline with the research ideas that you have gathered. Then, with the help of the essay outline you have prepared, draft the research paper in a well-structured manner by including the essential elements such as the introduction, body, and conclusion.
The introduction paragraph of your research paper should have a catchy opening sentence, brief background information on the topic, and a strong thesis statement addressing the purpose of your research paper. After the introduction, in the body paragraphs, you should include innovative topic sentences and explain your arguments with supporting evidence in a way to persuade your reader. Then, you should finally close your research paper with an engaging conclusion that contains a brief summary of the main points.
List of the Best Economics Research Paper Topics
You may think that it is easy to choose a research topic for your economics research paper. But actually, it is not. As economics is a complex and broad subject, choosing a perfect research topic from it is a daunting task.
If you are asked to write an economics research paper or essay, then you can prefer to choose a topic from economics research areas such as macroeconomics, microeconomics, behavioral economics, agricultural economics, development economics, financial economics, and so on.
Here, we have sorted different categories of economics topics and have recommended a list of excellent economics research topic ideas for you to consider. Go through the entire list and pick a topic that is ideal for writing academic papers as per your instructor’s requirements.

Agricultural Economics Research Topics
- Farmer’s contribution to agricultural social capital.
- Agricultural economics and agribusiness.
- An analysis of economic efficiency in agriculture.
- Agricultural and resource economics.
- Agricultural economics and environmental considerations of biofuels.
- Analysis of food security and poverty status among households in Ehime Mbano
- Role of bank loans and credit facility in financing Nigerian agriculture sector: a case study of Nigeria agricultural cooperative and rural development bank
- Evaluation of the impact of micro-finance banks on the South African agriculture sector
- How poultry farming is becoming a veritable tool for the economic empowerment of South Africa?
- Critical analysis of the problems and prospects of agriculture financing in rural India
Behavioral Economics Research Paper Topics
- What does the economy of trust mean?
- How does the brain change when a person is striking a great deal?
- The impact of economic stability on the social life of a person
- The buying capacity and gender
- How does race relate to economic power?
- Big data and its implications for behavioral economics
- The impact of behavioral finance on investment decisions.
- Cognitive and behavioral theories in economics.
- Behavior implications of wealth and inequality.
- Using behavioral economics to help in reducing substance abuse
Development Economics Research Topics
- The relation between development and incentive for migration.
- The economic consequences of population growth in developing countries.
- The determinants of high-performing institutions in emerging economies
- The impact of globalization on income distribution in emerging economies
- The problems of tax and taxation in connection with economic growth.
- The economic impact of terrorism on developing markets.
- Investigate the relationship between family planning, labor force, and income fluctuations.
- The impact of natural disasters on the economy and political stability of emerging markets.
- Budgeting and decision-making by low-income earners in emerging economics
- The impact of multinational commodity trading through the development of economic perspective.
- Compare and contrast the impact of demand-pull inflation and cost-push inflation on a country’s economy
- Discuss the impact of multinational commodity trading through the perspective of development economics
- Discuss the concepts of mercantilism, linear stages of growth model, economic nationalism, and structural-change theory
- Investigate the relationship between unemployment and fluctuations in national income
- Compare and contrast the economic patterns of villages across Papua New Guinea
Environmental Economics Research Paper Topics
- Explain the energy markets’ economic potential.
- How does global warming affect economic growth?
- How technological advancement leads to economic growth
- Evolution of economic institutions concerning climate change
- Cost-benefit analysis of the regulation of the environment
- The economic perspectives of the distribution of natural resources across boundaries
- The relationship between financial subsidies and the generation of eco-friendly products
- Detailed analysis of the European Union Emission Trading System
- Why it’s important to analyze the economics of clean drinking water
- How wildlife protection affects the economy
Read more: Outstanding Environmental Science Topics for You to Consider
Financial Economics Research Topics
- Risk-taking by mutual funds as a response to incentives.
- Financial economics for infrastructure and fiscal policy.
- Managerial economics and financial accounting as a basis for business
- The analysis of the global financial crisis of 2020
- Stock market overreaction.
Health Economics Research Ideas
- How do chronic diseases affect the workforce and the economy?
- How can public hospitals optimize their revenue collection?
- The economics of the pharmaceutical industry
- How an unhealthy country translates into a poor country
- Is the world’s hunger affected by economics?
- How does perfect competition work in the pharmaceutical world?
- How does an infectious disease outbreak affect the economy?
- Is health insurance important?
- How is the economy affected by a smoking ban?
Research Paper Topics on International Trade
- What are the gains and losses of international trade for developing countries?
- The importance of international trade in developing countries
- The relationship between economic growth and international trade
- The impact of Brexit on small and middle businesses in the UK
- To what extent does a currency union affect trade?
- The roles of exchange rate and exchange rate regime in the US export.
- To what extent are the gains of less developed countries from trade liberalization exaggerated?
- Foreign direct investment in the United States: Determinants and impact
- The relationship between foreign direct investment and wages
- The effects of the banana crisis on the Jamaican and British economies
Macroeconomics Research Topics
- Global recession and factors that contribute to it.
- The relationship between Internet connectivity and productivity in the workplace.
- The relationship between economic growth and unemployment in your country.
- Income Dynamics and demographic economics.
- What should our government do to minimize the risks of future default?
- The connection between politics and economics.
- The world problems through macroeconomic analysis .
- US Market Liquidity and Macroeconomics.
- The structure, history, and activities of the World Bank.
- Economics of education in developing markets.
- Public policies and socio-economic disparities.
- Banks and their role in the economy.
- Problems and possible solutions for Japan macroeconomics.
- State regulation of the economy in foreign countries: main models of regulation.
- The effect of currency devaluation on small and medium firms
- A comparison of the United States unemployment to the rest of the world
- The relationship between common stock prices and inflation in your country.
- Macroeconomics and self-correction of the economy.
- Analysis of Africa’s macroeconomics and its performance.
- The implications of Internet banking on bank profitability.
Read more: Best Macroeconomics Research Topics and Ideas for Students
Microeconomics Research Topics
- Explain how competition influences the price.
- Opportunity costs explained from a microeconomics perspective
- Inflation sources and consequences explained
- The impact of demonetization on small and medium businesses
- The connection between the minimum wage and market equilibrium.
- Perfect competition in microeconomics
- Theories in microeconomics
- The effect of labor force participation on the economy and budget
- Economic inequality as a result of globalization.
- Explain the balance between supply and demand in microeconomics
- Dynamics of the Gini index as a reflection of the problem of inequality in income
- Privatization of Public Enterprises and its implications on economic policy and development
- How does the stock market work?
- The impact of game theory on economic development.
- The changes in oil prices: causes and solutions.
- Marketing uses in microeconomics.
- The economic explanation of political dishonesty.
- How company mergers and dissolutions impact the economy
- The role of tax collection agencies in microeconomics
- Different microeconomic models and how they face the effect of industry conditions
A Few More Microeconomics Research Ideas
- How exactly does Uber fit into the economy of trust?
- How does a person’s brain alter when they hit a big deal?
- missing practical human insights from big data and how this affects the economy.
- explaining how supply and demand are balanced in microeconomics
- Changes in economic institutions with regard to climate change
- Effects of greenhouses on economic growth
- Effects of climate change on economic growth
- Analysis of the European Union Emission Trading System in great detail
- Is resource management for waste scarce? A microeconomics explanation of opportunity costs
- Effects of wildlife protection on the economy
Interesting Economics Research Topics
- What role does entrepreneurship play in economic development?
- How do automation and artificial intelligence affect the labor market?
- Discuss the Economics of healthcare systems and policies in developing countries.
- Explain the effects of trade agreements on income distribution.
- How does foreign aid affect economic development?
- Explain the impact of monetary policy on financial markets and inflation.
- Discuss the effects of income inequality on social mobility.
- How does tax reform impact business investment?
- Explain the role of microfinance in alleviating poverty.
- How does behavioral economics impact personal savings habits?
From the list of economics research topics recommended in this blog, choose any topic of your choice and craft a top-quality research paper or essay. It is not necessary that you need to use the suggested topic as it is, you can also modify the research topic and write your academic paper. In case, you are unsure how to select the right topic and write a persuasive economics research paper, get in touch with us immediately.

Related Post

110 Hard Words to Spell for Students and Adults

Learn How to Avoid Passive Voice in 3 Simple Steps

117 Best Greek Mythology Essay Topics For Students
About author.
Jacob Smith
I am an Academic Writer and have affection to share my knowledge through posts’. I do not feel tiredness while research and analyzing the things. Sometime, I write down hundred of research topics as per the students requirements. I want to share solution oriented content to the students.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Featured Posts
140 Unique Geology Research Topics to Focus On
200+ outstanding world history topics and ideas 2023, 190 excellent ap research topics and ideas, 150+ trending group discussion topics and ideas, 170 funny speech topics to blow the minds of audience, who invented exams learn the history of examination, how to focus on reading 15 effective tips for better concentration, what is a rhetorical analysis essay and how to write it, primary school teacher in australia- eligibility, job role, career options, and salary, 4 steps to build a flawless business letter format, get help instantly.
Raise Your Grades with Assignment Help Pro
Trade Has Been a Powerful Driver of Economic Development and Poverty Reduction

From 1990 to 2017, developing countries increased their share of global exports from 16 percent to 30 percent; in the same period, the global poverty rate fell from 36 percent to 9 percent. Not all countries have benefited equally, but overall, trade has generated unprecedented prosperity, helping to lift some 1 billion people out of poverty in recent decades.
Trade has multiple benefits . Trade leads to faster productivity growth, especially for sectors and countries engaged in global value chains (GVCs). These links allow developing countries to specialize in making a single component, like a keyboard, rather than a finished product, like a personal computer. GVCs give them access to foreign technology, know-how, and investment. Trade eases the diffusion of technologies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and support adaptation – such as solar panels and wind turbines or drought-resistant seeds. Consumers enjoy a greater variety of goods and services at lower cost, though some firms and workers in individual sectors may see their livelihoods at risk through increased competitive pressures.
Despite these benefits, globalization is under fire. Critics blame it for the loss of manufacturing jobs in advanced economies, environmental degradation, and disruptions to supplies of vital goods like vaccines. These concerns, combined with geopolitical tensions, are prompting major players to raise barriers to trade and investment and to subsidize the domestic production of goods deemed essential and strategic. In 2022, many countries reacted to disruptions of food supplies from Ukraine by restricting exports of wheat, corn, and other foods. This tit-for-tat cycle only drove prices higher, briefly threatening a global food crisis.
Trade disputes and restrictions have weakened the rules-based global trading regime centered on the World Trade Organization. Smaller developing economies cannot be self-sufficient and need to export to import. They critically need to be able to compete at fair terms, a capacity that trade distortive subsidies and protectionist policies will hurt. To attract investment, they also critically need the certainty provided by a credible and coherent system of global trade rules. Furthermore, many developing countries don’t have the fiscal resources to counter steps taken by advanced countries to subsidize domestic production.
The World Bank estimates that a slump in investor confidence due to increased trade tensions among major players could push 30-50 million people into poverty by 2030, depending on the severity of protectionist policies put in place by advanced and developing economies. This compares with the 70 million people pushed into poverty in 2020 because of COVID-19.
How should developing and advanced economies respond? For now, trade restrictions and subsidies affect a small portion of global trade. There are still tremendous gains to be reaped from deeper and broader regional trade agreements. For example, the recently created African Continental Free Trade Area has the potential to lift 50 million people out of extreme poverty by 2035. Countries can boost trade by lowering the cost of moving goods across borders through streamlined border procedures and better infrastructure. They can also adopt policies that help them leverage rapid growth of trade in services, especially digital services.
The global trade system should address legitimate concerns about national security and reliable access to key goods, but not at the expense of development. It must distinguish between subsidies that provide public goods, like electric cars, and those that distort trade and disadvantage trade partners. Rules on the protection of intellectual property must ensure that subsidized technologies are made widely available. Exporters of food and other key goods must refrain from imposing restrictions in times of crisis; importers should permanently reduce or eliminate import tariffs to ensure adequate supply in good times and bad.
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .
Cornell Chronicle
- Architecture & Design
- Arts & Humanities
- Business, Economics & Entrepreneurship
- Computing & Information Sciences
- Energy, Environment & Sustainability
- Food & Agriculture
- Global Reach
- Health, Nutrition & Medicine
- Law, Government & Public Policy
- Life Sciences & Veterinary Medicine
- Physical Sciences & Engineering
- Social & Behavioral Sciences
- Coronavirus
- News & Events
- Public Engagement
- New York City
- Photos of the Week
- Big Red Sports
- Freedom of Expression
- Student Life
- University Statements
- Around Cornell
- All Stories
- In the News
- Expert Quotes
- Cornellians
New research initiative tackles pressing global development issues
By alison fromme cornell sc johnson college of business.
Fundamental challenges in food insecurity, poverty, agriculture, health, education and markets form the focus of Collaboration for International Development Economics Research (CIDER) , a new initiative launched by the Office of the Provost, the SC Johnson College of Business, the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, the College of Arts and Sciences and the Cornell Jeb E. Brooks School of Policy.
“CIDER builds on a long history of Cornell research and engagement in the economies of nations, particularly developing and emerging economies challenged by global economic forces,” said Provost Michael I. Kotlikoff. “This initiative expands the interdisciplinary focus of these efforts, bringing economists, social scientists, policy experts and agricultural experts together to pursue solutions to some of our most difficult global challenges.”
Hosted by the SC Johnson College, CIDER unites 24 faculty across campus and the world, along with students, staff, researchers and external partners, to create and share knowledge. CIDER’s activities will encompass research, workshops, seminars, internships, career mentoring and continuing-education coursework.
“We’re delighted to embark on this new collaborative effort in development economics,” said Andrew Karolyi, the Charles Field Knight Dean of the Cornell SC Johnson College of Business. “CIDER taps into existing expertise and a grand legacy of intellectual leadership at Cornell going back decades. I can’t wait to see the tangible impact CIDER makes on campus and around the world.”
CIDER’s inaugural faculty director is Chris Barrett , the Stephen B. and Janice G. Ashley Professor of Applied Economics and Management in the Charles H. Dyson School of Applied Economics and Management and professor in the Brooks School.
“We expect CIDER will further reinforce Cornell's already formidable reputation in this space,” Barrett said. The university’s impact in development economics was established over many decades and reinforced when standard measures of poverty and food insecurity were developed here in the 1980s. Now, CIDER provides a forum to collaborate on large-scale projects, advance policy-relevant research and train early career scholars and practitioners.
Through a workshop hosted by CIDER on May 10, the center is already encouraging new collaborations in East African dryland drought research, risk management and policy.
The World Bank, the African Development Bank, private organizations and multiple East African national governments are currently investing nearly $1 billion in the region to address drought, Barrett said.
“The efficacy and the impact of these massive investments can be directly influenced by research findings,” he said. “Indeed, research by Cornell and partners going back to the late 2000s underpins the initiative. We’re now working to produce timely policy-relevant, clearly communicated and rigorous research that can inform that effort.”
Among other presentations at the workshop, Karlijn Morsink , Utrecht University economist and CIDER-affiliated adjunct associate professor at the Dyson School, discussed her work leading the evaluation of World Bank programs in the region and share opportunities for Cornell faculty and student involvement.
“This workshop and the collaborations it represents offer just one example,” Barrett said. “We look to scale this type of effort across a range of different domains.”
CIDER will also support early career mentoring through two formal programs. Structural Transformation of Agriculture and Rural Spaces (STARS) , an existing Cornell program, previously paired early career researchers who earned degrees in Africa with mentors at Cornell and affiliated institutions. Now under CIDER’s umbrella, STARS is open to scholars across all low- and lower-middle-income countries.
Additionally, a predoctoral program for scholars who have not yet earned advanced degrees will provide one to three years of research experience and professional development training with core faculty. One predoctoral fellow already began work in January, and three more arrive this summer.
Building professional networks, increasing research capacity, disseminating best practices in the field and shaping early career researchers for the next generation are at the heart of CIDER’s mission, Barrett said. “This is a really exciting venture.”
Alison Fromme is a writer for the Cornell SC Johnson College of Business.
Media Contact
Lindsey knewstub.
Get Cornell news delivered right to your inbox.
You might also like

Gallery Heading

- Advisory Board
- Policy Dialogues
- Organigramme
- Intergovernmental Support
- Capacity Building
- Climate Action
- Global Partnerships
- Leaving No One Behind
- Science, Technology and Innovation
- Strengthening Institutions
- Publications
- Policy Briefs
- Working Papers
- Infographics
- UN DESA Voice
- World Economic Situation and Prospects As of Mid-2024
- World Economic Situation and Prospects as of mid-2024

Global economic prospects have improved since January, with major economies avoiding a severe downturn, bringing down inflation without increasing unemployment. However, the outlook is only cautiously optimistic. Higher-for-longer interest rates, debt sustainability challenges, continuing geopolitical tensions and ever-worsening climate risks continue to pose challenges to growth, threatening decades of development gains, especially for least developed countries and small island developing States.
According to the World Economic Situation and Prospects as of mid-2024 , the world economy is now projected to grow by 2.7 per cent in 2024 (+0.3 percentage points from the January forecast) and 2.8 per cent in 2025 (+0.1 percentage points from the January forecast). The upward revisions mainly reflect a better outlook in the United States, where the latest forecast points to 2.3 per cent growth in 2024, and several large emerging economies, notably Brazil, India and the Russian Federation. The outlook for China registers a small uptick with growth now expected to be 4.8 per cent in 2024. On the other hand, the economic outlook for Africa has deteriorated since the last release, with expected growth lowered by 0.2 percentage points for 2024, threatening adverse impacts for many of the world’s poor. On average, global growth in the coming years is expected to remain below the average of 3.2 per cent during 2010–2019.
Economic environment remains fragile for small island developing States
Economic prospects for small island developing States (SIDS) are projected to improve, with GDP growth increasing from 2.4 per cent in 2023 to 3.3 per cent in 2024, primarily driven by a sustained rebound in tourism. However, SIDS remain vulnerable to spikes in international commodity prices due to their high import dependency on essential goods. Frequent extreme weather events and high public debt also pose significant challenges.
“The SIDS outlook for 2024 is promising, but we mustn’t get complacent,” said Li Junhua, United Nations Under-Secretary-General for Economic and Social Affairs and Secretary-General of the fourth International Conference on Small Island Developing States, to be held in Antigua and Barbuda on 27–30 May 2024. “We need to think differently about our support to SIDS, mindful of their unique vulnerabilities. Through more effective partnerships and a more favourable international environment we can create the space that SIDS need to shore up their domestic capacities and build resilience for the future.”
Developing economies face persistent challenges despite global disinflationary trend
Although softening international commodity prices and tight monetary stances adopted by most central banks have set the global economy on a disinflationary path, several developing economies continue to grapple with stubbornly high inflation. Many developing economies also face challenges such as elevated borrowing costs, persistent exchange rate pressures, and lingering political instability.
The stagnant employment situation in developing economies contrasts with that of developed economies, particularly in North America, Europe and Japan, where unemployment rates remain near record lows. Furthermore, the near-term outlook for certain economies is clouded by potential intensification of geopolitical tensions and multiple conflicts across the world.
Harnessing potential of critical minerals for sustainable development
The report discusses how the growing use of critical minerals for accelerating the energy transition can also be an opportunity for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals in many developing countries. Countries endowed with critical mineral resources will, however, need smart policies, as well as effective implementation capacities to reap the benefits and avoid a renewed ‘resource curse’, the report underscored.
Moreover, international cooperation will remain crucial to facilitate technology transfers and financing to developing countries, combat illicit financial flows and ensure the supply of the critical minerals needed for the green transition. Many of these issues will be covered by the recently announced Secretary-General’s Panel on Critical Energy Transition Minerals, which will develop a set of common and voluntary principles to build trust and transparency, while accelerating the race to renewables.
Related Sustainable Development Goals

Share This Publication
Global economic growth improves but ‘downsides’ lurk

Facebook Twitter Print Email
The global economic picture has improved since January, but vulnerabilities remain, the mid-year update of the World Economic Situation and Prospects report published on Thursday has revealed.
The world economy is forecast to grow by 2.7 per cent in 2024, up from 2.4 per cent projected at the start of the year. Growth will reach 2.8 per cent in 2025, representing a slight increase.
These changes are mainly due to better-than-expected performance in some large developed and emerging countries, notably Brazil, India, Russia and the United States.
Inflation down, wages up
Inflation is also down from the 2023 peak, said Shantanu Mukherjee of the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA), presenting the report to journalists in New York.
“In developed countries, tight labour markets are seeing wage increases for some parts of the population and also drawing people into the labor force, which is important,” he added.
However, the outlook is only cautiously optimistic in the face of higher-for-longer interest rates, debt sustainability risks and continuing geopolitical tensions.
Islands at risk
Ever-worsening climate shocks are also a challenge, threatening decades of development gains, especially for the world’s Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and small island developing States (SIDS).
Even though prospects for SIDS are being revised upwards to about 3.3 per cent each year, Mr. Mukherjee said this is still below the pre-pandemic average, meaning that “lost ground is still not being made up.”
In the case of Africa and LDCs in general, prospects are revised downward to about 3.3 per cent growth in 2024.
Concern for the continent
“This is particularly worrying because Africa is home to about 430 million living in extreme poverty and close to 40 per cent share of the global undernourished population,” he explained. Furthermore, two-thirds of the high inflation countries listed in the report are on the continent.
“At the same time, cause for concern is that African governments’ room to maneuver is also shrinking,” he continued.
“In 2024, over a quarter of public revenues on average in this continent went towards interest payments. That's again about 10 percentage points more than the average over the years immediately preceding the pandemic.”
For developing countries, on average, the debt situation is not as dire, but he was concerned that investment growth continues to fall.
These “downsides” are further compounded by risks such as inflation, which is both a symptom of the underlying fragility and a concern on its own.
Break the ‘resource curse’
The report also contains a special section on critical minerals such as lithium, nickel, cobalt and copper, that are essential for the transition to clean energy.
Countries that possess these resources will, however, need smart policies, as well as effective implementation capacities to reap the benefits.
Mineral-sector driven grown has in the past often been associated with environmental damage, stunted development of other sectors, poverty, conflict and other adverse outcomes collectively known as the “resource curse”.
“It is imperative for developing countries to design and implement well-targeted and timely economic, social, and environmental policies to optimize the benefits of their critical minerals endowments and avoid another cycle of resource curse,” the report said.
- World Economic Situation and Prospects Report
share this!
May 13, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
Research examines factors of resilient city development
by Higher Education Press
In recent years, with rapid urbanization, the global landscape of science and technology, industry, energy, and finance has undergone profound changes. Concurrently, emergencies or sudden events including natural disasters, human-induced disasters, and socio-economic crises are posing unrelenting threats to regional environment and security.
The concept of the "resilient city," as an important principle in contemporary urban planning, emphasizes that the capacity of urban systems to absorb the impacts and pressures caused by uncertain events while maintaining essential functions, structures, and characteristics.
The Resilient Cities Congress was initiated by ICLEI (International Council for Local Environment Initiatives)–Local Governments for Sustainability in 2010, as the first annual global forum dedicated to resilient cities studies.
In 2020, the Resilient Cities Congress was renamed the "Daring Cities," with the aim of building on the legacy of the Resilient Cities Congress series, enhancing the leadership role of governments, researchers, business leaders , and community organizers in urban decision-making process when responding to emergencies or sudden events, and forming new methods of urban governance and multi-stakeholder partnership models.
Drawing from the materials and scholarly work presented at these congresses, this research comprehensively reviews the evolution of resilient cities over the last decade through the lenses of policies and actions, summarizing the cutting-edge and current trends.
The work titled " From Resilient Cities Congress to Daring Cities: Policies, Actions, and Hot Trends of Resilient City Development " was published in the journal Landscape Architecture Frontiers .
Overall, the journey of global resilient cities unfolds in three phases of global commitment and framework establishment, path exploration and action, and experience translation and adaption. And after synthesizing the cases of global pioneering resilient city and regional construction cases from the Daring Cities, the experience of resilience actions can be summarized in five aspects:
- Multi-level governance and multi-stakeholder collaboration.
- Developing circular economy, and financing resilience and insuring cities.
- Nature-based solutions.
- Equal opportunities and access to basic services.
- Open data and strong data governance capability.
Throughout the previous Resilient Cities Congress series, the development of resilient cities in the past decade has evolved from theoretical exploration, framework establishment, and formulation of target strategies towards the implementation of regional and local actions and follow-up assessment, while integrating theoretical research into political decision-making that has in turn driven the progress of urban sustainable development.
Nowadays, with the development of big data and analytics technology, the construction of resilient cities not only requires deepening implementation at economic and social aspects, but also necessitates a series of effective measures in the field of cyber resilience to seize opportunities and mitigate risks, where information technology can and will play a vital role.
Looking ahead, it is crucial to further promote local resilience actions and practices, and to put more effort in filling the gaps of empirical research on resilient cities. It is of great practical significance to translate international resilience development results and action experience into localized efforts both in theory and practice at the national, regional, and city scales, so as to promote the full implementation of climate action and resilience building worldwide.
Provided by Higher Education Press
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Biologists travel with their mobile laboratory to study a wide range of mitochondrial functions in avian migration
12 minutes ago

Increasing drought puts the resilience of the Amazon rainforest to the test
22 minutes ago

Legacy of Indigenous stewardship of camas dates back more than 3,500 years, study finds
35 minutes ago
New 3D models reveal how warming climate affects underwater ocean tides
40 minutes ago

This modified stainless steel could kill bacteria without antibiotics or chemicals

Alaska's rusting waters: Pristine rivers and streams turning orange

New quantum dot approach can enhance electrical conductivity of solar cells

Genetic drift, not natural selection, identified as main factor driving speciation in endangered pupfish species

How cockroaches spread around the globe to become the pest we know today

Can coal mines be tapped for rare earth elements?
Relevant physicsforums posts, mt. vesuvius 1944 eruption light show -- static electricity.
2 hours ago
Pyramids built along dry river bed
May 18, 2024
The Secrets of Prof. Verschure's Rosetta Stones
May 16, 2024
A very puzzling rock or a pallasite / mesmosiderite or a nothing burger
May 8, 2024
M 4.8 - Whitehouse Station, New Jersey, US
What is global warming due to.
More from Earth Sciences
Related Stories

Are sponge cities a solution to growing urban flooding problems?
Oct 5, 2022

What next after 100 Resilient Cities funding ends?
Jun 6, 2019

Building African cities that cope with climate shocks—experts outline what it will take
Nov 30, 2023

Turning to nature to improve vital water treatment
Apr 22, 2024
Transforming urban sustainability: New study reveals cities' crucial contribution to meeting decarbonization goals
Aug 31, 2023
Defining a city using cell-phone data
Apr 5, 2024
Recommended for you
Satellite radar data uncover 'vigorous melting' at Antarctica's Thwaites Glacier

Record low Antarctic sea ice 'extremely unlikely' without climate change, says scientists
8 hours ago

Microplastics may slow the rate at which carbon is pulled from the sea surface to the depths
May 17, 2024

Differing values of nature can still lead to joined up goals for sustainability

Carbon pricing works, major meta-study finds
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
An official website of the United States government
- Special Topics
Research and Development Satellite Account
BEA is developing a new satellite account that measures research and development activity in a framework consistent with the measurement of gross domestic product (GDP) and other BEA statistics. The new statistics will provide a more comprehensive picture of the contribution of the R&D sector to the U.S. and state economies. In the first milestone of this ongoing project, BEA issued experimental statistics in May 2024. These statistics include R&D’s contribution to GDP (known as R&D value added) and associated R&D employment and compensation for the nation and all 50 states and the District of Columbia. These statistics can answer questions such as: Which states have the largest R&D value added? How many jobs in each state are supported by R&D activities? What are the leading R&D-producing industries across the nation? This work is conducted with data and support from the National Science Foundation’s National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics.
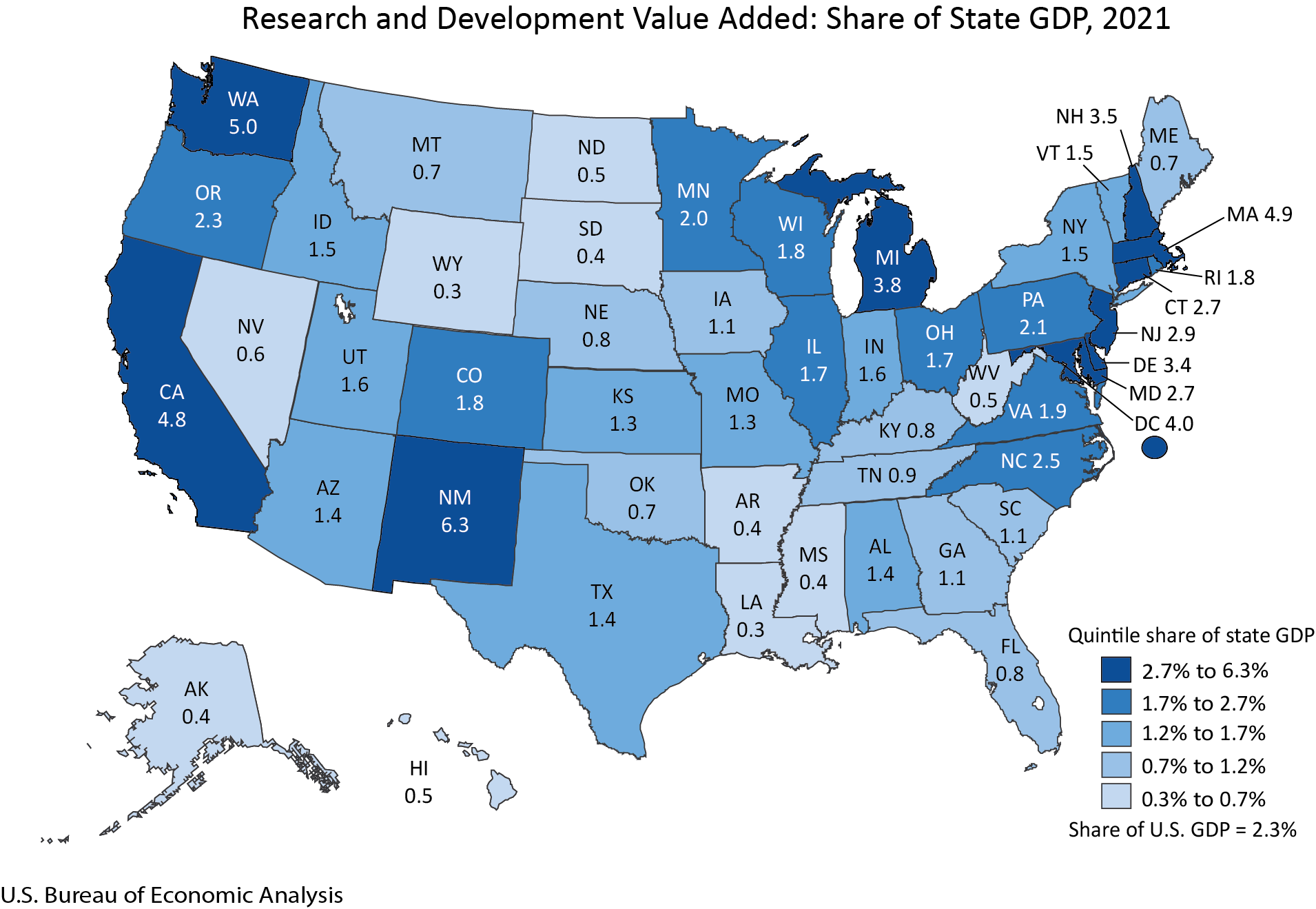
Data & Documentation
- R&D Value Added Data
- R&D Compensation Data
- R&D Employment Data
- Full Data Set
- Technical Document This document details BEA’s methodology for the experimental national and state-level R&D production statistics.
- Experimental R&D Value Added Statistics for the U.S. and States Now Available May 9, 2024
- Coming Soon: New R&D Value Added (and More) Statistics for the U.S. and States May 3, 2024
Background Material
- Presentation: Developing a Regional R&D Satellite Account BEA Advisory Committee Meeting, May 2023
- Background Materials: Concepts, Data, and Methods BEA Advisory Committee Meeting, May 2023
- National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics BEA’s statistics for the new R&D satellite account are being developed in collaboration with the National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics of the National Science Foundation
Archive: Previous R&D Satellite Account
- Measuring R&D in the National Economic Accounting System Survey of Current Business, November 2014
- Research and Development Satellite Account Update: New Estimates for Industry, Regional, and International Accounts Survey of Current Business, October 2007
- 2007 R&D Satellite Account Methodologies: Current-dollar GDP Estimates By Lisa Mataloni and Carol E. Moylan, December 2007
- Methodology for the Industry Estimates in the 2007 R&D Satellite Account By Carol A. Robbins, Felicia V. Candela, Mahnaz Fahim-Nader, and Gabriel W. Medeiros, December 2007
- Linking Frascati-based R&D Spending to the System of National Accounts By Carol A. Robbins, March 2006
- Full Archive of Previous R&D Satellite Account Materials 2006-2016
What is the R&D Satellite Account?
Measures the contribution of research and development to the U.S. and state economies through the value generated in production, the number of jobs the sector supports, and the compensation paid. R&D activity is attributed to the state where it is performed.
What’s a Satellite Account?

Contact Personnel
- Technical Ledia Guci 301-278-9788 [email protected]
- Media Connie O’Connell 301-278-9003 [email protected]
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- About Violence Prevention
- Resources for Action
- Cardiff Model
Violence Prevention

About The Public Health Approach to Violence Prevention
Violence Topics

About Adverse Childhood Experiences
About Child Abuse and Neglect
About Community Violence
About Firearm Injury and Death
About Intimate Partner Violence
About Sexual Violence
About Youth Violence
About Abuse of Older Persons
About Violence Against Children and Youth Surveys
About The National Intimate Partner and Sexual Violence Survey (NISVS)
About The National Violent Death Reporting System (NVDRS)
Featured Resources

Essentials for Parenting Teens

Essentials for Parenting Toddlers and Preschoolers

Cardiff Violence Prevention Model Toolkit
Violence is an urgent public health problem. CDC is committed to preventing violence so that everyone can be safe and healthy.
For Everyone
Public health.

COMMENTS
Source: This map draws on a sample of 139 studies from the NEUDC 2022 conference. Studies that covered more than three countries (often broad global or regional analyses) were excluded. Researchers draw on a wide range of empirical methods. Nearly a third of studies reported on the results of a randomized controlled trial (43 studies).
Development Economics; Development of the American Economy; Economic Fluctuations and Growth; Economics of Education; Economics of Health; ... All NBER research is categorized into topic areas that collectively span the field of economics. Featured Topics. COVID-19. Included in this topic.
Development Economics → New research on development economics from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including the between mental health and economic productivity, the "Argentina Paradox," and strategy and execution for emerging markets.
Last weekend was the North East Universities Development Consortium annual conference. Researchers—mostly economists—presented nearly 200 papers on topics from agriculture to COVID to marriage to microfinance. It's a great introduction to a wide range of current development economics research.
The Journal of Development Economics publishes original research papers relating to all aspects of economic development - from immediate policy concerns to structural problems of underdevelopment. The emphasis is on quantitative or analytical work, which is novel and relevant. The Journal does not … View full aims & scope $4190
Community-based economic development is the key to a strong pandemic recovery. Audrey Jamal, University of Guelph. Community wealth building is a direct response to extractive policies and aims to ...
The mission of Economic Development Quarterly is to promote research supporting the formulation of evidence-based economic development and workforce development policy, programs and practice in the United States. The focus of EDQ is high quality research in economic and workforce development policy and practice within the United States. This research can be scholarly, applied, or practice ...
This course provides rigorous introduction to core microeconomic issues in economic development, focusing on both key theoretical contributions and empirical applications to understand both why some countries are poor and on how markets function differently in poor economies. Topics include human capital (education and health); labor markets; credit markets; land markets; firms; and the role ...
This is a great snapshot of the latest research in development economics. Where the studies are from and what methods they use. The studies take place all over the world (Figure 1). India has more than twice as many studies (23) than the next highest country, Brazil (with 10 studies). Kenya has eight, Indonesia has six, and Bangladesh, Malawi ...
Development Economics. The Development Economics Program studies the forces that contribute to economic development, particularly in less developed nations. It explores the role of decisions by households, firms, and governments, the effects of development aid policies, and the consequences of rising incomes in emerging economies.
Economic Growth. New research on economic growth from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including whether the US economy can recapture the powerful growth rates of the past, how technology adoption affects global economies, and why India's economy is expected to overtake China's. Page 1 of 19 Results.
VoxDev. Development economics from research to practice. VoxDev is a platform for economists, policymakers, practitioners, donors, the private sector and others interested in development to discuss key policy issues. Expert contributors provide insightful commentary, analysis, and evidence on a wide range of policy challenges in formats that we hope are accessible to a wide audience interested ...
Many recent PhD candidates have applied rigorous and innovative methods to community and economic development topics in their dissertation work. Moreover, advances in machine learning and prediction may extend to research on these topics. Lastly, policymakers and the policy process may demand the rigor of economists in light of the shift at ...
The work program is organized around the following interrelated areas: Growth: Macro, regional (local), sectoral, firm growth; labor markets and human capital. Firms and Aggregate Outcomes : Allocation of production and finance; competition. Public economics/public finance: Domestic revenue mobilization, taxation, debt; government spending ...
Bibliometric units are researched from the Scopus database using keywords "economic development", "economic growth" and "poverty". The main contribution of this analysis is the review of existing ...
This study sheds light on the political pathology of fraudulent, illegal, and corrupt business practices. Features of the Chinese system—including regulatory gaps, a lack of formal means of property protection, and pervasive uncertainty—seem to facilitate the rise of mafia systems. 02 Feb 2021. Working Paper Summaries.
Economics Research Topics are as follows: The impact of technological change on income inequality. An analysis of the relationship between exchange rates and foreign direct investment. The effects of tax incentives on small business growth and development. The determinants of economic growth in developing countries.
Economic Development in the Tourism Industry in Africa. Since the early 1990s, tourism significantly contributed to the economic growth of African countries. ... How To Pick A Topic For Your Economics Research Project Or Master's Thesis: INOMICS, The Site for Economists; What Do Theses and Dissertations Look Like: KU Writing Center, the ...
The gap between rich and poor countries has grown exponentially since the days of Adam Smith. In the 1770s, rich countries were twice as well-off as poor countries. These days, GDP per capita is 35 times higher in rich countries than in poor. In this video, economist B. Ravikumar explains how he and other economists are looking at these cross ...
Research Reports and Publications. Share: Through various programs, EDA funds and supports research and resources to shape economic development policies and inform economic development decision-making. Explore the research below: ARPA Research Read More about ARPA ...
The Dollar versus the Euro as International Reserve Currencies. By Jeffrey Frankel. March 2024. We begin by examining determinants of aggregate foreign exchange reserve holdings by central banks (size of issuing country's economy and financial markets, ability of the currency to hold value, and. Development & Economic Growth.
Development Economics Research Topics. The relation between development and incentive for migration. The economic consequences of population growth in developing countries. The determinants of high-performing institutions in emerging economies. The impact of globalization on income distribution in emerging economies.
From 1990 to 2017, developing countries increased their share of global exports from 16 percent to 30 percent; in the same period, the global poverty rate fell from 36 percent to 9 percent. Not all countries have benefited equally, but overall, trade has generated unprecedented prosperity, helping to lift some 1 billion people out of poverty in recent decades.
The university's impact in development economics was established over many decades and reinforced when standard measures of poverty and food insecurity were developed here in the 1980s. Now, CIDER provides a forum to collaborate on large-scale projects, advance policy-relevant research and train early career scholars and practitioners.
Global economic prospects have improved since January, with major economies avoiding a severe downturn, bringing down inflation without increasing unemployment. However, the outlook is only cautiously optimistic. Higher-for-longer interest rates, debt sustainability challenges, continuing geopolitical tensions and ever-worsening climate risks continue to pose challenges to growth, threatening ...
The global economic picture has improved since January, but vulnerabilities remain, the mid-year update of the World Economic Situation and Prospects report published on Thursday has revealed. The world economy is forecast to grow by 2.7 per cent in 2024, up from 2.4 per cent projected at the start of the year.
In recent years, with rapid urbanization, the global landscape of science and technology, industry, energy, and finance has undergone profound changes. Concurrently, emergencies or sudden events ...
BEA is developing a new satellite account that measures research and development activity in a framework consistent with the measurement of gross domestic product (GDP) and other BEA statistics. The new statistics will provide a more comprehensive picture of the contribution of the R&D sector to the U.S. and state economies.
ACEs-related health consequences cost an estimated economic burden of $748 billion annually in Bermuda, Canada, and the United States. 8 Outcomes ACEs can have lasting effects on health and well-being in childhood and life opportunities well into adulthood. 9 Life opportunities include things like education and job potential.