Topics on Economics of Education

Journal Title
Journal issn, volume title, repository usage stats.
This dissertation consists of two separate essays on economics of education. First, the role of teacher-student interactions is analyzed. Teacher effectiveness is generally characterized by a single effect that is common across students. However, educators are multi-task agents that choose how to allocate their efforts among pupils. Some teachers may target their courses towards the top students in the class while others to the bottom, leading to different complementarity effects. Moreover, the introduction of accountability programs, such as No Child Left Behind (NCLB), could induce a reallocation of teacher's efforts, affecting the dynamics of student-teacher interactions. This study shows that the role of complementarities is key from a policy perspective. In this regard, an analytical framework and a novel iterative algorithm are implemented in order to characterize and quantify these effects. Results indicate that interaction effects played a crucial role in shaping the distribution of student achievement, especially after the implementation of NCLB. While more than half of the total gains in test scores experienced by the bottom third of the student achievement distribution post NCLB are due to adjustments in teacher-student complementarities, those with the very highest abilities have seen decreases in their performance.
In the second essay, gender disparities in educational attainment are explored across races. The sizable gender gap in college enrollment, especially among African Americans, constitutes a puzzling empirical regularity that may have serious consequences on marriage markets, male labor force participation and the diversity of college campuses. For instance, only 35.7 percent of all African American undergraduate students were men in 2004. Results show that, while family background characteristics cannot account for the observed gap, proxy measures for non-cognitive skills are crucial to explain it.
Description
Aucejo, Esteban Matias (2012). Topics on Economics of Education . Dissertation, Duke University. Retrieved from https://hdl.handle.net/10161/5791 .
Collections

Dukes student scholarship is made available to the public using a Creative Commons Attribution / Non-commercial / No derivative (CC-BY-NC-ND) license .
- Faculty of Arts and Sciences
- FAS Theses and Dissertations
- Communities & Collections
- By Issue Date
- FAS Department
- Quick submit
- Waiver Generator
- DASH Stories
- Accessibility
- COVID-related Research
Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- By Collections
- By Departments
Essays on the Economics of Education
Citable link to this page
Collections.
- FAS Theses and Dissertations [6136]
Contact administrator regarding this item (to report mistakes or request changes)
Economics and Education PhD
Doctor of philosophy in economics and education.

Admissions Information
Displaying requirements for the Spring 2024, Summer 2024, and Fall 2024 terms.
Doctor of Philosophy
- Points/Credits: 75
- Entry Terms: Fall
Application Deadlines
Select programs remain open beyond our standard application deadlines , such as those with an extended deadline or those that are rolling (open until June or July). If your program is rolling or has an extended deadline indicated above, applications are reviewed as they are received and on a space-available basis. We recommend you complete your application as soon as possible as these programs can close earlier if full capacity has been met.
Application Requirements
Additional degree information.
Program Guide
Doctoral Program Worksheet
Requirements from the TC Catalog (AY 2023-2024)
Displaying catalog information for the Fall 2023, Spring 2024 and Summer 2024 terms.
View Full Catalog Listing
This 75-point degree program is intended for individuals who want to acquire advanced training in the theory, methods, and practices in the economics of education. It is a highly selective program to prepare individuals for leadership roles in teaching, research, or administrative settings.
The coursework for this program consists of three parts: core courses, courses in research methods, and courses in a specialized area of study, such as higher education, early childhood education, field experimentation, or a regional focus. Students work on their dissertation under the guidance of faculty advisors within the program; additional members of the dissertation committee may be drawn from other TC Departments, and at least one committee member must be from Columbia University’s Graduate School of Arts and Sciences. All degrees are conferred by Columbia University. https://www.tc.columbia.edu/education-policy-and- social-analysis/economics-and-education/degrees/doctor-of-philosophy- in-economics-and-education-econ/
Admission to the Ph.D. program is highly selective. All applications to enter the program are evaluated on an individual and holistic basis. However, the curriculum of the degree program assumes that students have some previous coursework in economics and statistics, possess intellectual maturity, and demonstrate an interest in education policy and practice. Compelling applications for admission demonstrate the applicant’s capacity for success and also clearly explain how the Economics and Education curriculum fits with the applicant’s past experiences and future goals.
- View Other Degrees
Program Director : Professor Alex Eble
Teachers College, Columbia University 212 Zankel, Suite B
Contact Person: Katherine Y. Chung, Program Manager
Phone: (212) 678-3677 Fax: (212) 678-3677
Email: kc2610@tc.columbia.edu
Economics of Education

Caroline Hoxby

- DigitalGeorgetown Home
- Georgetown University Institutional Repository
- Georgetown College
- Department of Economics
Graduate Theses and Dissertations - Economics

Creators Titles By Creation Date
Search within this collection:
Browse All Items
Most Recent Submissions

Essays on Unequal Wealth Accumulation over the Business Cycle

Essays on Safe Assets and the Macroeconomy

Essays in Education, Mobility, and Political Economy

Essays on Mortgage Curtailment

Essays in Oligopoly Pricing Behavior
- Cadmus Home
- Department of Economics (ECO)
Essays in economics of education
Retrieved from Cadmus, EUI Research Repository
Show full item record
Files associated with this item

Collections
Browse Econ Literature
- Working papers
- Software components
- Book chapters
- JEL classification
More features
- Subscribe to new research
RePEc Biblio
Author registration.
- Economics Virtual Seminar Calendar NEW!

Department of Economics, University of Sussex Business School
Economics phd theses.
- Publisher Info
- Serial Info
Corrections
Contact information of department of economics, university of sussex business school, serial information, impact factors.
- Simple ( last 10 years )
- Recursive ( 10 )
- Discounted ( 10 )
- Recursive discounted ( 10 )
- H-Index ( 10 )
- Euclid ( 10 )
- Aggregate ( 10 )
- By citations
- By downloads (last 12 months)
More services and features
Follow serials, authors, keywords & more
Public profiles for Economics researchers
Various research rankings in Economics
RePEc Genealogy
Who was a student of whom, using RePEc
Curated articles & papers on economics topics
Upload your paper to be listed on RePEc and IDEAS
New papers by email
Subscribe to new additions to RePEc
EconAcademics
Blog aggregator for economics research
Cases of plagiarism in Economics
About RePEc
Initiative for open bibliographies in Economics
News about RePEc
Questions about IDEAS and RePEc
RePEc volunteers
Participating archives
Publishers indexing in RePEc
Privacy statement
Found an error or omission?
Opportunities to help RePEc
Get papers listed
Have your research listed on RePEc
Open a RePEc archive
Have your institution's/publisher's output listed on RePEc
Get RePEc data
Use data assembled by RePEc
- Browse by author
- Browse by year
- Departments
- History of Thought
- Advanced search
Curriculum and Thesis
In their first and second years, PhD students are required to complete a series of core classes, coursework in their major and minor fields of study, and an advanced research methods course before proceeding to the thesis-writing stage.
Core courses
Students must satisfy the requirements in at least 10 of 12 half-semester first-year core courses (14.384 and 14.385 are considered second-year courses). The requirements can be met by earning a grade of B or better in the class or by passing a waiver exam.
Waiver exams are offered at the start of the semester in which the course is offered and graded on a pass-fail basis. Students who receive a grade of B- or below in a class can consult the course faculty to determine whether to take the waiver exam or re-take the course the following year. These requirements must all be satisfied before the end of the second year.
Course list
- 14.121: Microeconomic Theory I
- 14.122: Microeconomic Theory II
- 14.123: Microeconomic Theory III
- 14.124: Microeconomic Theory IV
- 14.380: Statistical Methods in Economics
- 14.381: Estimation and Inference for Linear Causal and Structural Models
- 14.382*: Econometrics
- 14.384*: Time Series Analysis (2nd year course)
- 14.385*: Nonlinear Econometric Analysis (2nd year course)
- 14.451: Dynamic Optimization Methods with Applications
- 14.452: Economic Growth
- 14.453: Economic Fluctuations
- 14.454: Economic Crises
*Courses 14.382, 14.384, and 14.385 are each counted as two half-semester courses.
Most students will also take one or more field courses (depending on whether they are waiving core courses) during their first year. Feel free to ask your graduate research officer, field faculty, and advanced students for advice on how you structure your first-year coursework.
Second year students must also successfully complete the two-semester course 14.192: Advanced Research Methods and Communication. The course, which is graded on a pass-fail basis, guides students through the process of writing and presenting the required second-year research paper.
Major field requirement
By the end of year two, PhD students must complete the requirements for two major fields in economics. This entails earning a B or better in two designated courses for each field. Some fields recommend additional coursework or papers for students intending to pursue research in the field.
Major fields must be declared by the Monday following the spring break of your second year. Your graduate registration officer must approve your field selections.
Minor field requirement
PhD students are also required to complete two minor fields, taking two courses in each field and earning a grade of B or better. Your graduate registration officer must approve your field selections.
Minor coursework is normally completed by the end of year two, but in some cases students can defer the completion of one field until after general exams. Students must consult with their graduate registration officer before making a deferment.
Options for minor fields include the eleven economics major fields, plus computation and statistics (from the interdisciplinary PhD in Economics and Statistics).
Students who wish to satisfy one of the minor field requirements by combining two courses from different fields–for example, environmental economics and industrial organization II–can petition the second-year graduate registration officer for permission.
At least one minor field should be from the department’s standard field list.
The fields in which the Department offers specialization and the subjects that will satisfy their designation as a minor field are given in the chart below. Some fields overlap so substantially that both cannot be taken by a student. In any event, the same subject cannot be counted towards more than a single minor field. Students must receive the approval of their Graduate Registration Officer for their designated major and minor fields.
List of fields
- Development
- Econometrics
- Industrial organization
- International
- Macroeconomics
- Organizational
- Political economy
- Public finance
- Computation and statistics (minor only)
Subjects satisfying major and minor requirements
Advanced economic theory.
Minor: Any subset adding up to two full semesters from 14.125, 14.126, 14.127, 14.130, 14.137, 14.147, 14.160, 14.281 and Harvard Ec 2059. Major: At least two of 14.125, 14.126, 14.281, and Harvard Ec 2059. Recommended for major: 14.126, 14.281, and at least one of 14.125, 14.127, 14.130, 14.147, and Harvard Ec 2059.
Econometrics and Statistics
Minor: 14.382 in addition to one of 14.384 or 14.385. Major: Any one of 14.386, 14.387, 14.388 in addition to one of 14.384 or 14.385. Recommended for major: 14.384 and 14.385. *Dual PhD in Economics and Statistics has an additional requirement of 14.386.
Economic Development
Major and minor: 14.771 and 14.772 or 14.773
Minor: Any two of 14.416J, 14.440J, 14.441J, 14.442J, 14.448. Major: 14.416J and 14.441J
Industrial Organization
Minor: 14.271 and 14.272 or 14.273. Major: 14.271 and 14.272 or 14.273. Recommended for major: 14.271, 14.272, and 14.273.
International Economics
Major and minor: 14.581 and 14.582
Labor Economics
Major: 14.661 and 14.662A. Minor: Two subjects chosen from 14.193, 14.661, and 14.662
Monetary Economics
Major and minor: Two subjects chosen from 14.461, 14.462, and 14.463
Organizational Economics
Major and minor: 14.282 and one of 14.283-284, 14.441J, or an approved substitute
Political Economy
Major and minor: 14.770 and 14.773
Public Economics
Major and minor: 14.471 and 14.472
General exams
MIT requires doctoral candidates to complete an advanced course of study that includes general exams at its completion. Beginning in 2019-20, the Economics Department will operationalize this requirement to include successful completion of: the core and other required courses; course exams and other requirements of courses in each of a student’s two major and two minor fields; the written research paper and oral presentation components of 14.192. Students may present for the general exams while having one remaining minor field to complete. The faculty will review these components together with the candidate’s overall course record to determine whether students have passed the general exam requirement and can proceed to the thesis writing stage.
Typical course schedule
Math Camp begins on the second Monday in August.
Fall Semester
14.121/14.122 (Micro Theory I/II) 14.451/14.452 (Macro Theory I/II) 14.380/14.381 (Statistical Method in Economics & Applied Econometrics) Field Course (major or minor)
Spring Semester
14.123/14.124 (Micro Theory III/IV) 14.453/14.454 (Macro Theory III/IV) 14.382 (Econometrics) Field Course (major or minor)
2-3 Field Courses 14.192 (Advanced Research and Communication) 14.384 or 14.385 (Advanced Econometrics)
3 Field Courses 14.192 (Advanced Research and Communication)
Years 3 and up
Field workshop Field lunch Thesis writing
Upon satisfying the core and field requirements, PhD candidates embark on original research culminating in a completed dissertation. A PhD thesis normally consists of three research papers of publishable quality. The thesis must be approved by a student’s primary and secondary thesis advisors, and by an anonymous third reader. These three faculty members will be the candidate's thesis committee and are responsible for its acceptance. Collaborative work is acceptable and encouraged, but there must be at least one paper in the dissertation without a co-author who was a faculty member when the research started.
Criteria for satisfactory progress
Third-year students.
- Meet regularly with their advisor
- Participate consistently in their primary field advising lunch, their primary field workshop, and the third-year student research lunch
- Complete their third-year paper
- Participate in third-year meetings organized by the thesis graduate research officer
Students should present on their research in progress at least once in both the third-year student research lunches and their field advising lunch. Presentations provide opportunities for early and broad feedback on research ideas and the chance to develop oral presentation skills. Research ideas or early stage work in progress is encouraged and expected.
Fourth-year and later students
- Participate consistently in their primary field advising lunch and their primary field workshop
- Present at least once per year in their field advising lunch or field workshop. A presentation each semester in the field advising lunch is strongly recommended by most fields; consult your advisors for more information
Satisfactory progress toward a dissertation will be evaluated based on progress assessments by the student’s primary advisor, regular participation in the lunches and workshops, and field lunch or workshop presentations that show continued progress.
Sub-navigation
- EENEE Coordinators
- Network Members
- Analytical Reports
- Policy Briefs
- Ad Hoc Questions
- Database of Researchers
- Conferences
- You are here: Topics
- European Perspective
- News Archive
You are here:
- Economics of Education
The economics of education is a wide-ranging and growing sub-field of economics. It encompasses topics such as research on returns to education in the labour market, efficiency of the education “industry”, effets of education on the growth of economies, and educational finance. It also encompasses all levels of education, ranging from pre-school learning over school and university education and training to lifelong learning.
The following list provides an encompassing overview of the various sub-fields of research in the economics of education and of the most important topics within each sub-field. To illustrate the kind of work performed under each of these headings, we present below a brief overview of some research undertaken by members of the EENEE network as examples of research in each category.
Each reference list contains three parts: first, a list of “Introductory Reading”, where somebody who does not know this literature might want to start from; second, a list of “Key References”, which may require some more knowledge of the field but might be viewed as belonging to the most important references in this literature; and third, a list of “Further Reading” in this literature, organized by date of publication. As far as possible, the lists provide an abstract for each entry, as well as a link to the publication or at least its publisher.
It is clear that these reference lists can never be exhaustive, particularly because the literature on the economics of education is so wide-ranging and continues to expand ever more rapidly. Thus, if you detected important omissions in the lists, particularly of introductions or overviews of particular topics, or if you want to post your own recent published articles and working papers, we would be most grateful if you could let us know by email to [email protected] .
- 0 Introductory and General Reading
- 1 Micro: Labour Markets
- 2 Micro: Schooling Quality and Educational Production
- 3 Macro: Human Capital
- 4 Educational Finance
- 5 Levels of Education
- 6 Training, Informal Learning and Lifelong Learning
- 7 Research and Knowledge Creation
- 8 Socio-Demographic Aspects
- 9 Economic Theories of Education
- 10 Comparative Economics of Education
- Reference lists
- Search references


_linkedin_partner_id = "1170812"; window._linkedin_data_partner_ids = window._linkedin_data_partner_ids || []; window._linkedin_data_partner_ids.push(_linkedin_partner_id); (function(){var s = document.getElementsByTagName("script")[0]; var b = document.createElement("script"); b.type = "text/javascript";b.async = true; b.src = "https://snap.licdn.com/li.lms-analytics/insight.min.js"; s.parentNode.insertBefore(b, s);})(); School of Education

Graduate Programs Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in Economic Education
This Ph.D. program is on moratorium and no longer accepting new students. This page is for students admitted to the program prior to Fall 2021.
An Interdisciplinary Program for Leaders in Economic Education
The doctorate in economic education is designed to train the next generation of leaders in this fast-growing field. It is a joint program of Lerner’s economics department and the School of Education.
The field of economic education focuses on developing and evaluating economic and financial literacy programs and curricula in the K-12 school system, universities and a wide variety of outreach programs.
Traditionally, professionals and scholars in this field have been trained in either economics or education, with little or no formal training in the other area. This is no longer adequate. The increasing complexity and importance of economics in today’s world requires scholars and leaders who have a deeper understanding of both disciplines.
The program draws on the strengths of the University of Delaware’s economics and education graduate programs and on UD’s nationally-recognized Center for Economic Education and Entrepreneurship.
Program Highlights
The curriculum is evenly balanced between coursework in economics and education. The elective options allow you to specialize in one area or the other, depending on your interests and strengths.
The program can be completed in four years following a B.A., although the typical student takes five years to complete the degree. Students with substantial prior graduate training in economics or education can complete the program in three years.
Program Coordinator: Elizabeth Farley-Ripple (Education) and Thomas Bridges (Economics)
Student Spotlight

Erin Yetter
Erin Yetter, the first ever graduate of UD’s doctorate in economic education program, won the Journal of Economics Teaching’s 2016 Best Paper Award for her paper, “Using the Berenstain Bears to Teach Economics in the Elementary Classroom.” She works as an economic education specialist with the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, Louisville Branch where she writes curriculum materials, conducts professional development for teachers and continues to research student learning of economic concepts.
Program Faculty
Program requirements.
Graduate students are required to be registered for courses every semester, including the semester in which their degree is conferred, unless they are on an approved Leave of Absence. The program requires a minimum of 45 graduate-level credits.
Economic Theory & Statistical Methods Competency Courses
All students must demonstrate graduate-level competence in economic theory and in statistical methods by completing the following UD courses or by seeking waivers for previously completed coursework. The Department of Economics has sole authority to award waivers for economics courses and the School of Education has sole authority to award waivers for education courses.
- ECON 801 – Microeconomics
- ECON 802 – Macroeconomics
- ECON 803 – Applied Econometrics I
- ECON 804 – Applied Econometrics II
- EDUC 856 – Introduction to Statistical Inference
Required Courses
As indicated above, some students will also take additional courses in economic theory and in statistical methods.
- EDUC 805 – Proseminar in Education I
- EDUC 806 – Proseminar in Education II
- EDUC 850 – Qualitative Research in Educational Settings
- EDUC 812, 826, 865, 873 or 874
- EDUC 840 – Research Colloquium in Education
- 2 EDUC electives
- ECON 820 – Economics of Education Policy
- ECON 829 – Economic Education Curricula
- 2 ECON electives
- Free elective
- ECON/EDUC 964 and 969, dissertation (9 credits)
Sample Student Schedules
- Sample schedule for students with no course waivers
- Sample schedule for students with maximum course waivers (ECON801, 802, 803, 804, EDUC 856)
Career Opportunities
As a graduate of our program, you will have a wide range of professional and academic employment opportunities, including:
- University departments of economics and education
- Councils and centers for economic education (approximately 200 nationally, most affiliated with universities)
- Education units within regional Federal Reserve banks and other private sector businesses and foundations with an interest in economic and financial education
- School districts and state departments of education
- Education consulting and evaluation firms
Where Our Graduates Work
The doctorate in economic education is a relatively new program at the University of Delaware. Our first graduate completed her doctorate in 2013. She is currently employed as an economic education specialist with the Louisville Branch of the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis. Our second graduate completed her degree in 2016 and is on the faculty of the Department of Economics at Michigan State University. A recent 2017 graduate is currently employed in UD’s Center for Economic Education and Entrepreneurship.
Alumni Profile
Lauren ahlstrom.
“The Ph.D. in Economic Education program at UD was a great fit. My coursework and experiences at UD combined my love of economics with my passion for education and provided me with a strong foundation of skills as a scholar in my field. When I was beginning to write the literature review for my dissertation, a professor on my committee gave me some excellent advice. She encouraged me to think of the literature review like a funnel that should begin with a general overview of the research, moving to a narrower focus. As a result, I explored research outside of my primary field of economic education, which gave me a much broader perspective and understanding of the questions I was studying.”

Request More Information
Visit Campus
Awards and Scholarships
- Major and Minors
- Graduate Programs
- Prospective Students
- Academic Calendar
- Social Media
- 113 Willard Hall Education Building , Newark, DE 19716
- Phone: (302) 831-8695
- Fax: (302) 831-4110
- dissertation defense three essays education and labor economics eunseo kang
Dissertation Defense: “Three Essays in Education and Labor Economics”, Eunseo Kang
Eunseo Kang, PhD Candidate, University of California, Santa Barbara
Eunseo Kang is a PhD candidate in the Department of Economics at UC Santa Barbara. She graduated from Yonsei University in Seoul, Korea, with a BA in Economics. She is also pursuing an MA degree in the Statistics department with a specialization in Data Science. She has diverse work experience, including an internship as an Amazon Economist, where she analyzed large employee data. Before coming to UCSB, she worked in the fixed assets investment department at NH Life Insurance in Seoul, Korea.
This dissertation contains three chapters in education and labor economics. In Chapter 1, I study whether relative age effects among fourth graders on math and science test scores exist in developing countries and investigate whether they are similar across all countries with different levels of development. Students with different birthdays who are subject to the same school-entry cutoff date have different ages at school entry. This difference in maturity may affect a child’s outcomes in school because we might expect that students who are more mature relative to their peers will perform better; a phenomenon called `relative age effects'. While the focus of previous studies has been limited to developed countries, this study aims to provide evidence of relative age effects in the context of developing countries. Using Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study data and assigned relative age as an instrumental variable that is formed exogenously by this cutoff, I find that positive relative age effects on test scores exist in developing countries, but they are smaller than those in developed countries. I also explore the educational factors correlated to the magnitude of relative age effects using cross-country data.
In Chapter 2, I examine the impact of the inflow of international students on the first-time, full-time enrollment of domestic minority students in US Higher Education using data from IPEDS. Since foreign enrollment is an endogenous variable, I employ the instrumental variables approach, using the institution's historical share of international students and the year's non-immigrant visa issuance. I find that there is no significant effect of the influx of international students on the new enrollment of domestic minorities as a whole. However, when I divide the institutions by the level of state funding per student, I find that an additional influx of international students increases domestic minority FTFT enrollment by 0.65. I suggest that this is because institutions with relatively little reliance on government funding are more sensitive to the financial resources that international students bring in terms of determining the supply and demand of domestic minority enrollment.
In Chapter 3, we study how the academic achievement gap between different genders and socioeconomic groups within OECD countries has evolved over the years. Using TIMSS data for eighth graders from seventeen OECD countries from 1995 to 2019, we first confirm that trends in academic achievement have progressed towards gender equality, especially in science. Conversely, we find widening socioeconomic gaps, with high socioeconomic status (SES) groups showing greater improvements than low SES groups in both math and science test scores. When we examine the interaction between gender and socioeconomic groups to identify patterns driving these trends, we find that in many countries the low SES group shows greater improvements in the gender gap than the high SES group. While a widening SES achievement gap is observed for both genders, boys show a more pronounced increase in inequality than girls in many countries.
Event Details
Join us to hear Eunseo’s dissertation defense. She will be defending her dissertation, “Three Essays in Education and Labor Economics “. To access a copy of the dissertation , you must have an active UCSB NetID and password.
- Giving to Economics
- Contact & Directions
- Information
- Terms of Use
- Privacy
Department of Economics • College of Letters & Science • UC Santa Barbara 2023 © Regents of the University of California
- Open access
- Published: 08 May 2024
Measurement and analysis of change in research scholars’ knowledge and attitudes toward statistics after PhD coursework
- Mariyamma Philip 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 512 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
102 Accesses
Metrics details
Knowledge of statistics is highly important for research scholars, as they are expected to submit a thesis based on original research as part of a PhD program. As statistics play a major role in the analysis and interpretation of scientific data, intensive training at the beginning of a PhD programme is essential. PhD coursework is mandatory in universities and higher education institutes in India. This study aimed to compare the scores of knowledge in statistics and attitudes towards statistics among the research scholars of an institute of medical higher education in South India at different time points of their PhD (i.e., before, soon after and 2–3 years after the coursework) to determine whether intensive training programs such as PhD coursework can change their knowledge or attitudes toward statistics.
One hundred and thirty research scholars who had completed PhD coursework in the last three years were invited by e-mail to be part of the study. Knowledge and attitudes toward statistics before and soon after the coursework were already assessed as part of the coursework module. Knowledge and attitudes towards statistics 2–3 years after the coursework were assessed using Google forms. Participation was voluntary, and informed consent was also sought.
Knowledge and attitude scores improved significantly subsequent to the coursework (i.e., soon after, percentage of change: 77%, 43% respectively). However, there was significant reduction in knowledge and attitude scores 2–3 years after coursework compared to the scores soon after coursework; knowledge and attitude scores have decreased by 10%, 37% respectively.
The study concluded that the coursework program was beneficial for improving research scholars’ knowledge and attitudes toward statistics. A refresher program 2–3 years after the coursework would greatly benefit the research scholars. Statistics educators must be empathetic to understanding scholars’ anxiety and attitudes toward statistics and its influence on learning outcomes.
Peer Review reports
A PhD degree is a research degree, and research scholars submit a thesis based on original research in their chosen field. Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degrees are awarded in a wide range of academic disciplines, and the PhD students are usually referred as research scholars. A comprehensive understanding of statistics allows research scholars to add rigour to their research. This approach helps them evaluate the current practices and draw informed conclusions from studies that were undertaken to generate their own hypotheses and to design, analyse and interpret complex clinical decisions. Therefore, intensive training at the beginning of the PhD journey is essential, as intensive training in research methodology and statistics in the early stages of research helps scholars design and plan their studies efficiently.
The University Grants Commission of India has taken various initiatives to introduce academic reforms to higher education institutions in India and mandated in 2009 that coursework be treated as a prerequisite for PhD preparation and that a minimum of four credits be assigned to one or more courses on research methodology, which could cover areas such as quantitative methods, computer applications, and research ethics. UGC also clearly states that all candidates admitted to PhD programmes shall be required to complete the prescribed coursework during the initial two semesters [ 1 ]. National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS) at Bangalore, a tertiary care hospital and medical higher education institute in South India, that trains students in higher education in clinical fields, also introduced coursework in the PhD program for research scholars from various backgrounds, such as basic, behavioral and neurosciences, as per the UGC mandate. Research scholars undertake coursework programs soon after admission, which consist of several modules that include research methodology and statistical software training, among others.
Most scholars approach a course in statistics with the prejudice that statistics is uninteresting, demanding, complex or involve much mathematics and, most importantly, it is not relevant to their career goals. They approach statistics with considerable apprehension and negative attitudes, probably because of their inability to grasp the relevance of the application of the methods in their fields of study. This could be resolved by providing sufficient and relevant examples of the application of statistical techniques from various fields of medical research and by providing hands-on experience to learn how these techniques are applied and interpreted on real data. Hence, research methodology and statistical methods and the application of statistical methods using software have been given much importance and are taught as two modules, named Research Methodology and Statistics and Statistical Software Training, at this institute of medical higher education that trains research scholars in fields as diverse as basic, behavioural and neurosciences. Approximately 50% of the coursework curriculum focused on these two modules. Research scholars were thus given an opportunity to understand the theoretical aspects of the research methodology and statistical methods. They were also given hands-on training on statistical software to analyse the data using these methods and to interpret the findings. The coursework program was designed in this specific manner, as this intensive training would enable the research scholars to design their research studies more effectively and analyse their data in a better manner.
It is important to study attitudes toward statistics because attitudes are known to impact the learning process. Also, most importantly, these scholars are expected to utilize the skills in statistics and research methods to design research projects or guide postgraduate students and research scholars in the near future. Several authors have assessed attitudes toward statistics among various students and examined how attitudes affect academic achievement, how attitudes are correlated with knowledge in statistics and how attitudes change after a training program. There are studies on attitudes toward statistics among graduate [ 2 , 3 , 4 ] and postgraduate [ 5 ] medical students, politics, sociology, ( 6 – 7 ) psychology [ 8 , 9 , 10 ], social work [ 11 ], and management students [ 12 ]. However, there is a dearth of related literature on research scholars, and there are only two studies on the attitudes of research scholars. In their study of doctoral students in education-related fields, Cook & Catanzaro (2022) investigated the factors that contribute to statistics anxiety and attitudes toward statistics and how anxiety, attitudes and plans for future research use are connected among doctoral students [ 13 ]. Another study by Sohrabi et al. (2018) on research scholars assessed the change in knowledge and attitude towards teaching and educational design of basic science PhD students at a Medical University after a two-day workshop on empowerment and familiarity with the teaching and learning principles [ 14 ]. There were no studies that assessed changes in the attitudes or knowledge of research scholars across the PhD training period or after intensive training programmes such as PhD coursework. Even though PhD coursework has been established in institutes of higher education in India for more than a decade, there are no published research on the effectiveness of coursework from Indian universities or institutes of higher education.
This study aimed to determine the effectiveness of PhD coursework and whether intensive training programs such as PhD coursework can influence the knowledge and attitudes toward statistics of research scholars. Additionally, it would be interesting to know if the acquired knowledge could be retained longer, especially 2–3 years after the coursework, the crucial time of PhD data analysis. Hence, this study compares the scores of knowledge in statistics and attitude toward statistics of the research scholars at different time points of their PhD training, i.e., before, soon after and 2–3 years after the coursework.
Participants
This is an observational study of single group with repeated assessments. The institute offers a three-month coursework program consisting of seven modules, the first module is ethics; the fifth is research methodology and statistics; and the last is neurosciences. The study was conducted in January 2020. All research scholars of the institute who had completed PhD coursework in the last three years were considered for this study ( n = 130). Knowledge and attitudes toward statistics before and soon after the coursework module were assessed as part of the coursework program. They were collected on the first and last day of the program respectively. The author who was also the coordinator of the research methodology and statistics module of the coursework have obtained the necessary permission to use the data for this study. The scholars invited to be part of the study by e-mail. Knowledge and attitude towards statistics 2–3 years after the coursework were assessed online using Google forms. They were also administered a semi structured questionnaire to elicit details about the usefulness of coursework. Participation was voluntary, and consent was also sought online. The confidentiality of the data was assured. Data were not collected from research scholars of Biostatistics or from research scholars who had more than a decade of experience or who had been working in the institute as faculty, assuming that their scores could be higher and could bias the findings. This non funded study was reviewed and approved by the Institute Ethics Committee.
Instruments
Knowledge in Statistics was assessed by a questionnaire prepared by the author and was used as part of the coursework evaluation. The survey included 25 questions that assessed the knowledge of statistics on areas such as descriptive statistics, sampling methods, study design, parametric and nonparametric tests and multivariate analyses. Right answers were assigned a score of 1, and wrong answers were assigned a score of 0. Total scores ranged from 0 to 25. Statistics attitudes were assessed by the Survey of Attitudes toward Statistics (SATS) scale. The SATS is a 36-item scale that measures 6 domains of attitudes towards statistics. The possible range of scores for each item is between 1 and 7. The total score was calculated by dividing the summed score by the number of items. Higher scores indicate more positive attitudes. The SAT-36 is a copyrighted scale, and researchers are allowed to use it only with prior permission. ( 15 – 16 ) The author obtained permission for use in the coursework evaluation and this study. A semi structured questionnaire was also used to elicit details about the usefulness of coursework.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics such as mean, standard deviation, number and percentages were used to describe the socio-demographic data. General Linear Model Repeated Measures of Analysis of variance was used to compare knowledge and attitude scores across assessments. Categorical data from the semi structured questionnaire are presented as percentages. All the statistical tests were two-tailed, and a p value < 0.05 was set a priori as the threshold for statistical significance. IBM SPSS (28.0) was used to analyse the data.
One hundred and thirty research scholars who had completed coursework (CW) in the last 2–3 years were considered for the study. These scholars were sent Google forms to assess their knowledge and attitudes 2–3 years after coursework. 81 scholars responded (62%), and 4 scholars did not consent to participate in the study. The data of 77 scholars were merged with the data obtained during the coursework program (before and soon after CW). Socio-demographic characteristics of the scholars are presented in Table 1 .
The age of the respondents ranged from 23 to 36 years, with an average of 28.7 years (3.01), and the majority of the respondents were females (65%). Years of experience (i.e., after masters) before joining a PhD programme ranged from 0.5 to 9 years, and half of them had less than three years of experience before joining the PhD programme (median-3). More than half of those who responded were research scholars from the behavioural sciences (55%), while approximately 30% were from the basic sciences (29%).
General Linear Model Repeated Measures of Analysis of variance was used to compare the knowledge and attitude scores of scholars before, soon after and 2–3 after the coursework (will now be referred as “later the CW”), and the results are presented below (Table 2 ; Fig. 1 ).
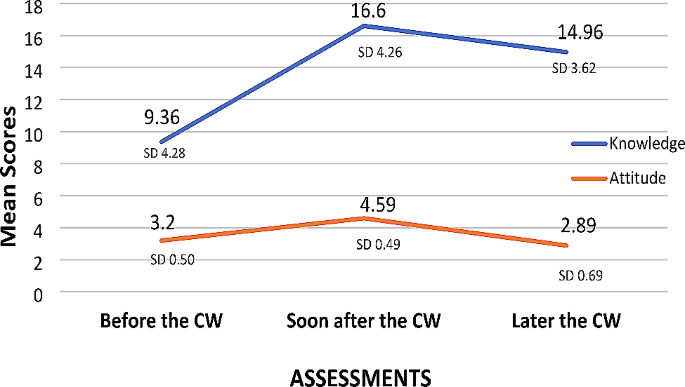
Comparison of knowledge and attitude scores across the assessments. Later the CW – 2–3 years after the coursework
The scores for knowledge and attitude differed significantly across time. Scores of knowledge and attitude increased soon after the coursework; the percentage of change was 77% and 43% respectively. However, significant reductions in knowledge and attitude scores were observed 2–3 years after the coursework compared to scores soon after the coursework. The reduction was higher for attitude scores; knowledge and attitude scores have decreased by 10% and 37% respectively. The change in scores across assessments is evident from the graph, and clearly the effect size is higher for attitude than knowledge.
The scores of knowledge or attitude before the coursework did not significantly differ with respect to gender or age or were not correlated with years of experience. Hence, they were not considered as covariates in the above analysis.
A semi structured questionnaire with open ended questions was also administered to elicit in-depth information about the usefulness of the coursework programme, in which they were also asked to self- rate their knowledge. The data were mostly categorical or narratives. Research scholars’ self-rated knowledge scores (on a scale of 0–10) also showed similar changes; knowledge improved significantly and was retained even after the training (Fig. 2 ).
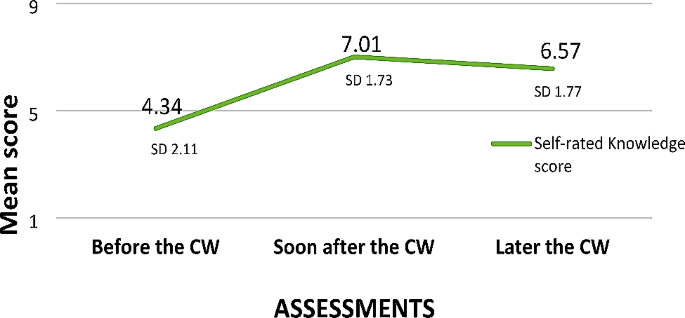
Self-rated knowledge scores of research scholars over time. Later the CW – 2–3 years after the coursework
The response to the question “ How has coursework changed your attitude toward statistics?”, is presented in Fig. 3 . The responses were Yes, positively, Yes - Negatively, No change – still apprehensive, No change – still appreciate, No change – still hate statistics. The majority of the scholars (70%) reported a positive change in their attitude toward statistics. Moreover, none of the scholars reported negative changes. Approximately 9% of the scholars reported that they were still apprehensive about statistics or hate statistics after the coursework.
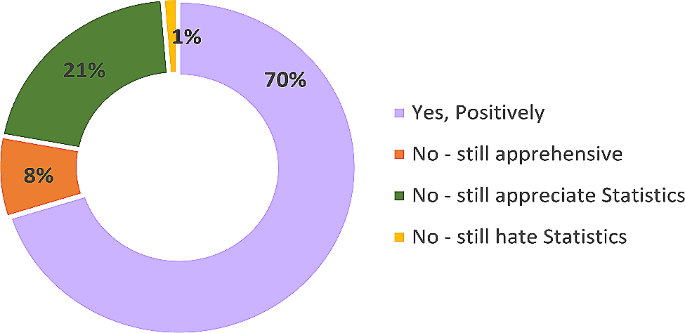
How has coursework changed your attitude toward statistics?
Those scholars who reported that they were apprehensive about statistics or hate statistics noted the complexity of the subject, lack of clarity, improper instructions and fear of mathematics as major reasons for their attitude. Some responses are listed below.
“The statistical concepts were not taught in an understandable manner from the UG level” , “I am weak in mathematical concepts. The equations and formulae in statistics scare me”. “Lack of knowledge about the importance of statistics and fear of mathematical equations”. “The preconceived notion that Statistics is difficult to learn” . “In most of the places, it is not taught properly and conceptual clarity is not focused on, and because of this an avoidance builds up, which might be a reason for the negative attitude”.
Majority of the scholars (92%) felt that coursework has helped them in their PhD, and they were happy to recommend it for other research scholars (97%). The responses of the scholars to the question “ How was coursework helpful in your PhD journey ?”, are listed below.
“Course work gave a fair idea on various things related to research as well as statistics” . “Creating the best design while planning methodology, which is learnt form course work, will increase efficiency in completing the thesis, thereby making it faster”. “Course work give better idea of how to proceed in many areas like literature search, referencing, choosing statistical methods, and learning about research procedures”. “Course work gave a good idea of research methodology, biostatistics and ethics. This would help in writing a better protocol and a better thesis”. “It helps us to plan our research well and to formulate, collect and plan for analysis”. “It makes people to plan their statistical analysis well in advance” .
This study evaluated the effectiveness of the existing coursework programme in an institution of higher medical education, and investigated whether the coursework programme benefits research scholars by improving their knowledge of statistics and attitudes towards statistics. The study concluded that the coursework program was beneficial for improving scholars’ knowledge about statistics and attitudes toward statistics.
Unlike other studies that have assessed attitudes toward statistics, the study participants in this study were research scholars. Research scholars need extensive training in statistics, as they need to apply statistical tests and use statistical reasoning in their research thesis, and in their profession to design research projects or their future student dissertations. Notably, no studies have assessed the attitudes or knowledge of research scholars in statistics either across the PhD training period or after intensive statistics training programs. However, the findings of this study are consistent with the findings of a study that compared the knowledge and attitudes toward teaching and education design of PhD students after a two-day educational course and instructional design workshop [ 14 ].
Statistics educators need not only impart knowledge but they should also motivate the learners to appreciate the role of statistics and to continue to learn the quantitative skills that is needed in their professional lives. Therefore, the role of learners’ attitudes toward statistics requires special attention. Since PhD coursework is possibly a major contributor to creating a statistically literate research community, scholars’ attitudes toward statistics need to be considered important and given special attention. Passionate and engaging statistics educators who have adequate experience in illustrating relatable examples could help scholars feel less anxious and build competence and better attitudes toward statistics. Statistics educators should be aware of scholars’ anxiety, fears and attitudes toward statistics and about its influence on learning outcomes and further interest in the subject.
Strengths and limitations
Analysis of changes in knowledge and attitudes scores across various time points of PhD training is the major strength of the study. Additionally, this study evaluates the effectiveness of intensive statistical courses for research scholars in terms of changes in knowledge and attitudes. This study has its own limitations: the data were collected through online platforms, and the nonresponse rate was about 38%. Ability in mathematics or prior learning experience in statistics, interest in the subject, statistics anxiety or performance in coursework were not assessed; hence, their influence could not be studied. The reliability and validity of the knowledge questionnaire have not been established at the time of this study. However, author who had prepared the questionnaire had ensured questions from different areas of statistics that were covered during the coursework, it has also been used as part of the coursework evaluation. Despite these limitations, this study highlights the changes in attitudes and knowledge following an intensive training program. Future research could investigate the roles of age, sex, mathematical ability, achievement or performance outcomes and statistics anxiety.
The study concluded that a rigorous and intensive training program such as PhD coursework was beneficial for improving knowledge about statistics and attitudes toward statistics. However, the significant reduction in attitude and knowledge scores after 2–3 years of coursework indicates that a refresher program might be helpful for research scholars as they approach the analysis stage of their thesis. Statistics educators must develop innovative methods to teach research scholars from nonstatistical backgrounds. They also must be empathetic to understanding scholars’ anxiety, fears and attitudes toward statistics and to understand its influence on learning outcomes and further interest in the subject.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
UGC Regulations on Minimum Standards and Procedure for the award of, M.Phil/Ph D, Degree R. 2009. Ugc.ac.in. [cited 2023 Oct 26]. https://www.ugc.ac.in/oldpdf/regulations/mphilphdclarification.pdf .
Althubaiti A. Attitudes of medical students toward statistics in medical research: Evidence from Saudi Arabia. J Stat Data Sci Educ [Internet]. 2021;29(1):115–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/10691898.2020.1850220 .
Hannigan A, Hegarty AC, McGrath D. Attitudes towards statistics of graduate entry medical students: the role of prior learning experiences. BMC Med Educ [Internet]. 2014;14(1):70. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-14-70 .
Hasabo EA, Ahmed GEM, Alkhalifa RM, Mahmoud MD, Emad S, Albashir RB et al. Statistics for undergraduate medical students in Sudan: associated factors for using statistical analysis software and attitude toward statistics among undergraduate medical students in Sudan. BMC Med Educ [Internet]. 2022;22(1):889. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-022-03960-0 .
Zhang Y, Shang L, Wang R, Zhao Q, Li C, Xu Y et al. Attitudes toward statistics in medical postgraduates: measuring, evaluating and monitoring. BMC Med Educ [Internet]. 2012;12(1):117. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-12-117 .
Bechrakis T, Gialamas V, Barkatsas A. Survey of attitudes towards statistics (SATS): an investigation of its construct validity and its factor structure invariance by gender. Int J Theoretical Educational Pract. 2011;1(1):1–15.
Google Scholar
Khavenson T, Orel E, Tryakshina M. Adaptation of survey of attitudes towards statistics (SATS 36) for Russian sample. Procedia Soc Behav Sci [Internet]. 2012; 46:2126–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.05.440 .
Coetzee S, Van Der Merwe P. Industrial psychology students’ attitudes towards statistics. J Industrial Psychol. 2010;36(1):843–51.
Francesca C, Primi C. Assessing statistics attitudes among College Students: Psychometric properties of the Italian version of the Survey of attitudes toward statistics (SATS). Learn Individual Differences. 2009;2:309–13.
Counsell A, Cribbie RA. Students’ attitudes toward learning statistics with R. Psychol Teach Rev [Internet]. 2020;26(2):36–56. https://doi.org/10.53841/bpsptr.2020.26.2.36 .
Yoon E, Lee J. Attitudes toward learning statistics among social work students: Predictors for future professional use of statistics. J Teach Soc Work [Internet]. 2022;42(1):65–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/08841233.2021.2014018 .
Melad AF. Students’ attitude and academic achievement in statistics: a Correlational Study. J Posit School Psychol. 2022;6(2):4640–6.
Cook KD, Catanzaro BA. Constantly Working on My Attitude Towards Statistics! Education Doctoral Students’ Experiences with and Motivations for Learning Statistics. Innov High Educ. 2023; 48:257–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10755-022-09621-w .
Sohrabi Z, Koohestani HR, Nahardani SZ, Keshavarzi MH. Data on the knowledge, attitude, and performance of Ph.D. students attending an educational course (Tehran, Iran). Data Brief [Internet]. 2018; 21:1325–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.08.081 .
Chau C, Stevens J, Dauphine T. Del V. A: The development and validation of the survey of attitudes toward statistics. Educ Psychol Meas. 1995;(5):868–75.
Student attitude surveys. and online educational consulting [Internet]. Evaluationandstatistics.com. [cited 2023 Oct 26]. https://www.evaluationandstatistics.com/ .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank the participants of the study and peers and experts who examined the content of the questionnaire for their time and effort.
This research did not receive any grants from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Biostatistics, Dr. M.V. Govindaswamy Centre, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), Bangalore, 560 029, India
Mariyamma Philip
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Mariyamma Philip: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Investigation, Writing- Original draft, Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mariyamma Philip .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study used data already collected data (before and soon after coursework). The data pertaining to knowledge and attitude towards statistics 2–3 years after coursework were collected from research scholars through the online survey platform Google forms. The participants were invited to participate in the survey through e-mail. The study was explained in detail, and participation in the study was completely voluntary. Informed consent was obtained online in the form of a statement of consent. The confidentiality of the data was assured, even though identifiable personal information was not collected. This non-funded study was reviewed and approved by NIMHANS Institute Ethics Committee (No. NIMHANS/21st IEC (BS&NS Div.)
Consent for publication
Not applicable because there is no personal information or images that could lead to the identification of a study participant.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Philip, M. Measurement and analysis of change in research scholars’ knowledge and attitudes toward statistics after PhD coursework. BMC Med Educ 24 , 512 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05487-y
Download citation
Received : 27 October 2023
Accepted : 29 April 2024
Published : 08 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05487-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Knowledge of statistics
- Attitude towards statistics
- PhD coursework
- Research scholars
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Health Care Economics
Explore the economic forces shaping us health care.
Taught by Harvard Medical School faculty, this Harvard Online course provides insights into the interactions between industries in the US health care sector and teaches what economic forces are shaping health care.

What You'll Learn
Why is health care spending so high in the US? What are the primary drivers of rising health care costs? What is the relationship between finance and health care? How does money shape your decision-making as a patient, provider, or payer? Is a sustainable healthcare architecture possible?
Even for those within the health care industry, the economics of the United States health care system are stunningly complex and can be challenging to navigate. In Health Care Economics, gain insights into the interactions between industries in the health care sector and learn what economic forces are shaping health care. You will cover core topics in health care economics, such as moral hazard and adverse selection, and examine how these forces, as well as the actions of patients, providers, and other key stakeholders, shape outcomes in the health care market.
Balancing the needs of patients and purchasers is a daily struggle for health care leaders and central to the success of any health care business. To make this happen, clinical, research, operational, and financial leaders need a shared understanding of the true drivers of health care spending, the policies that shape and define the sector, and how financial incentives impact both patient and provider behavior. This course will examine health care spending growth, considering new technologies and other economic factors, and explore the theoretical framework behind controlling spending growth through changes to benefit design and payment reform.
Delivered via Harvard Business School Online’s innovative course platform, Health Care Economics features real-world examples, interactive lessons, and conversations with industry experts. Led by Harvard Medical School professor Michael Chernew, PhD, Chair of The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC), this course allows you to gain a better understanding of core economic principles as you learn how to create more compelling programs, develop more effective growth strategies, negotiate better reimbursement contracts and partnerships, and advocate more effectively both inside and outside your organization.
The Harvard Medical School is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
The Harvard Medical School designates this enduring material for a maximum of 19.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™ . Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
Upon successful completion of the course, participants will have access to claim their credits through the Harvard Medical School’s continuing education platform.
The course is part of the Health Care Leadership Learning Path and will be delivered via HBS Online’s course platform . Learners will be immersed in real-world examples from experts at industry-leading organizations. By the end of the course, participants will be able to:
- Articulate the drivers of spending and spending growth in health care and evaluate how your organization’s strategy and decision-making processes impact total spending as well as value
- Describe approaches to getting the incentives right for both providers and patients and evaluate the impacts of changes to these incentives
- Understand risk and pooling as they relate to insurance markets and health benefit design
- Define the role of employers, insurers, and government in influencing the economics of health care markets, such as spending, access to care, and stability of insurance markets
- Explain how technology and patients’ and providers’ decisions contribute to high spending and spending growth, and how they impact their own organizations
Your Instructor
Michael Chernew, PhD, is the Leonard D. Schaeffer Professor of Health Care Policy at Harvard Medical School. Dr. Chernew’s research examines several areas related to improving the health care system, including studies of novel benefit designs, Medicare Advantage, alternative payment models, low-value care, and the causes and consequences of rising health care spending. Dr. Chernew is currently serving as Chair of the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC), where he previously served as the Vice Chair and as a Member. In 2000, 2004, and 2010, he served on technical advisory panels for the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) that reviewed the assumptions used by Medicare actuaries to assess the financial status of Medicare trust funds. He's a member of the Congressional Budget Office’s Panel of Health Advisors and Vice Chair of the Massachusetts Health Connector Board. Dr. Chernew is a member of the National Academy of Sciences, a research associate at the National Bureau of Economic Research, and a Senior Visiting Fellow at MITRE. He's currently a co-editor of the American Journal of Managed Care and on advisory boards for several private companies in the health care space, including Virta Health, Archway, and HEALTH[at]SCALE.
Real World Case Studies
Affiliations are listed for identification purposes only.

MATTHEW HUTTER, MD, MPH

SANDHYA RAO, MD
Dr. Sandhya Rao is chief medical officer for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Massachusetts , the largest private health plan in Massachusetts. Learn from Rao about the challenges in health insurance today.

JOSEPH NEWHOUSE, PHD
Available discounts and benefits for groups and individuals.
Experience Harvard Online by utilizing our wide variety of discount programs for individuals and groups.
Past participant discounts.
Learners who have enrolled in at least one qualifying Harvard Online program hosted on the HBS Online platform are eligible to receive a 30% discount on this course, regardless of completion or certificate status in the first purchased program. Past Participant Discounts are automatically applied to the Program Fee upon time of payment. Learn more here .
Learners who have earned a verified certificate for a HarvardX course hosted on the edX platform are eligible to receive a 30% discount on this course using a discount code. Discounts are not available after you've submitted payment, so if you think you are eligible for a discount on a registration, please check your email for a code or contact us .
Nonprofit, Government, Military, and Education Discounts
For this course we offer a 30% discount for learners who work in the nonprofit, government, military, or education fields.
Eligibility is determined by a prospective learner’s email address, ending in .org, .gov, .mil, or .edu. Interested learners can apply below for the discount and, if eligible, will receive a promo code to enter when completing payment information to enroll in a Harvard Online program. Click here to apply for these discounts.
Gather your team to experience Health Care Economics and other Harvard Online courses to enjoy the benefits of learning together:
- Single invoicing for groups of 10 or more
- Tiered discounts and pricing available with up to 50% off
- Growth reports on your team's progress
- Flexible course and partnership plans
Learn more and enroll your team !
Who Will Benefit
Rising Leaders
Develop a comprehensive understanding of the health care landscape, including the key drivers of rising US health care spending.
Administrators and Policy Makers
Gain insights into strategic decisions around new business initiatives, health benefit plans, reimbursement contract negotiations, and care delivery models.
Understand the financial impacts of new technologies and services and how to create value-based care for patients.
Learner Testimonials
“This is an amazing course. The professor did a fantastic job dissecting the complexities of healthcare into chewable chunks.”
Howard H. Dinh, MD, FACC Medical Director, Cardiac Services, Greater Sacramento The Permanente Medical Group and Chief, Cardiology, Kaiser Permanente, South Sacramento
“This is now my fourth HBS online course that I have taken. I love that the format lets me learn asynchronously when I have time in my busy schedule. The HBS courses do a wonderful job encouraging interaction with peer learners which amplifies the learning. The HBS courses foster this peer engagement much more effectively than I have found in other online courses that I have taken.”
Denver Sallee III, MD Chief Financial Officer, Sibley Heart Center Cardiology and Associate Professor of Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine
“This is a very well designed course to understand the nuances of the US healthcare system economics. The videos and the guest talks were very helpful to understand the real world examples. The discussion surrounding the RAND experiment was very useful to understand many key concepts. Overall a very good course.”
Krishna K. Chotneeru, MPH Associate Director, Data Science & Statistics Alnylam Pharmaceuticals
Syllabus and Upcoming Calendars
Health Care Economics provides insights into the interactions between industries in the health care sector and teaches what economic forces are shaping health care.
Learning requirements: There are no required prerequisites to enroll in this course. In order to earn a Certificate of Completion from Harvard Online, participants must thoughtfully complete all 6 modules, including associated assessments, by stated deadlines.
Download Full Syllabus
Download October 2023 Calendar
Download January 2024 Calendar
- Why is health care so expensive?
- Why is health care spending growing?
- Make health care spending growth predictions.
- Compare US health care costs to costs in other countries.
- Analyze the math behind health care spending.
- Examine sources of waste in the health care industry.
- Explore the role of technology in health care spending growth.
- What role should patients play in making important choices about their care?
- What role should money play in the decisions of patients?
- Interpret demand curves.
- Explore willingness to pay for health care.
- Evaluate different solutions to inefficient consumption of care, such as moral hazard.
- What role should the provider play in determining care patterns?
- How do provider behavior and competition influence care?
- Analyze clinical decision-making.
- Recognize supplier-induced demand and the consequences of the medical arms race.
- Explore practice ownership trends.
- Determine whether prevention programs and care coordination are cost saving.
- What is the role of insurance in health care?
- Why is the risk pool for health insurance so important and how do we manage it?
- Explore risk preferences.
- Calculate actuarially fair premiums to understand what health insurance is and how it works.
- Examine solutions for solving some of the problems with insurance.
- Evaluate policy proposals for dealing with information asymmetry and adverse selection.
- How can we design insurance plans to promote efficient consumer decision-making?
- Explore patient decision-making in health care.
- Analyze different approaches for improving patient incentives.
- Understand the benefits of value based care and insurance.
- Strategies for implementing value-based healthcare and insurance designs.
- How do we structure payments to promote efficient provider decision-making?
- Explore provider decision-making in health care.
- Analyze different approaches for improving provider incentives.
Earn Your Certificate
Enroll today in Harvard Online's Health Care Economics course.
Still Have Questions?
What are the learning requirements? How do I list my certificate on my resume? Learn the answers to these and more in our FAQs.

Related Courses
Digital health.
Digital technologies and big data offer tremendous opportunities to improve health care.
Health Care Strategy
Learn from HBS Professor Leemore Dafny how to align the principles of business strategy with the unique challenges and structures of health care organizations to capture value, define your mission, and lead your organization to success.
Innovations in Teamwork for Health Care
In this course, experts from Harvard Business School and the T.H. Chan School of Public Health teach learners to implement a strategy for organizational teamwork in health care.
RIT graduate pursues Ph.D. across time zones
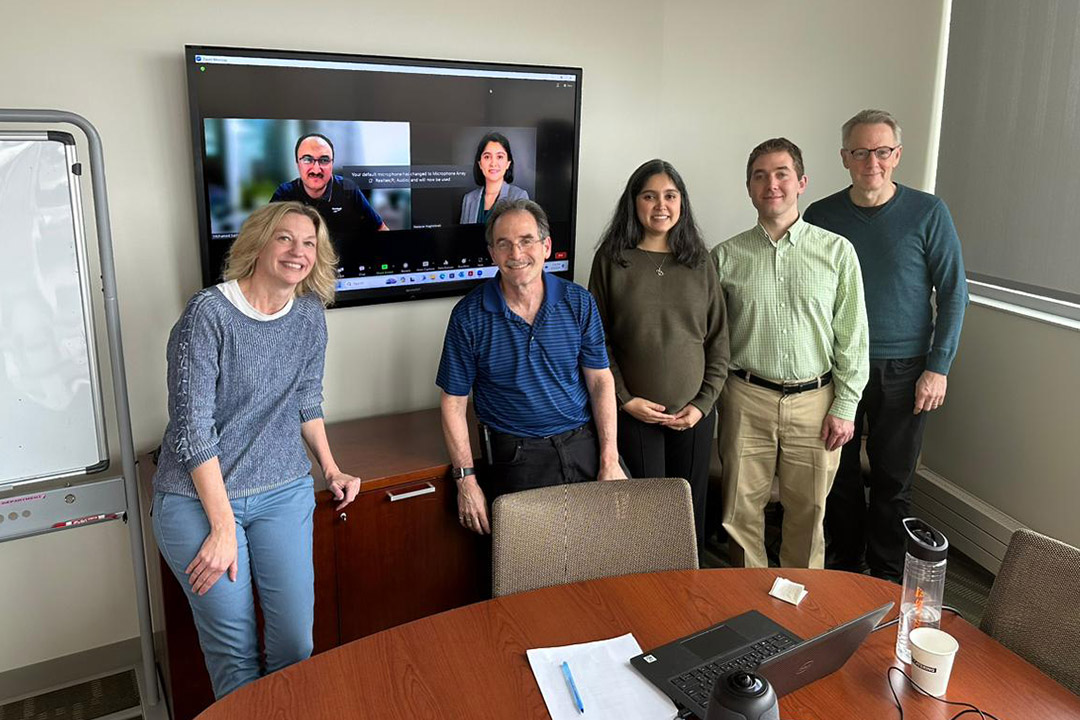

Nastaran Nagshineh, center, defended her Ph.D. thesis at RIT in April. Faculty from RIT’s Rochester and Dubai campuses served on her thesis committee and include, from left to right, Kathleen Lamkin-Kennard, Steven Weinstein, Nathaniel Barlow, and David Kofke (a professor at the University at Buffalo). Mohamed Samaha participated remotely and appears on the video screen behind the group and alongside Nagshineh’s picture.
Nastaran Nagshineh is one of the first Ph.D. candidates to bridge RIT’s Rochester and Dubai campuses. Her accomplishment creates a path for future students at the university’s international campuses.
Nagshineh completed her Ph.D. in mathematical modeling while working full time as a mathematics lecturer at RIT Dubai in the United Arab Emirates, teaching as many as five classes a semester. She described her Ph.D. journey as “an exercise in perseverance” due to competing demands and long days. Rochester is eight hours behind Dubai, and the time difference meant many late-night classes and meetings.
“I saw this collaboration as an opportunity, rather than as a challenge, because my primary adviser, Dr. Steven Weinstein (RIT professor of chemical engineering), and my co-adviser, Dr. Mohamed Samaha (RIT Dubai associate professor of mechanical engineering), both have the same area of research interest,” she said. “They both worked toward my success.”
Nagshineh is one of 67 RIT Ph.D. students who defended their thesis this academic year and who will earn their doctorate. RIT awarded 63 Ph.D. degrees in 2023.
In 2020-2021, RIT’s Graduate School met and surpassed the university’s goal of conferring 50 Ph.D. degrees during an academic year. That number will continue to grow as students cycle through the seven new Ph.D. programs that RIT has added since 2017, said Diane Slusarski , dean of RIT’s Graduate School.
Meeting these goals puts RIT on a path toward achieving an “R1,” or research-intensive designation, from the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Learning. RIT is currently ranked as an R2 institution . Many factors go into changing a university’s status, including research investment and maintaining a three-year average of 70 Ph.D. degrees awarded per year, according to Slusarski.
“We have met the goals of the strategic plan, and now we look forward to contributing to the research innovation in the future,” Slusarski said. “We want to help the new programs thrive and win national research awards.”
RIT’s emphasis on high-level research is seen in Nagshineh’s Ph.D. work. She applies mathematical modeling to the field of fluid dynamics. Her research has been published in top-tier journals and has gained notice, said Weinstein, her thesis adviser.
Weinstein describes Nagshineh’s accomplishments as “a testament to a fantastic work ethic and commitment” and is inspirational to younger students at Rochester and Dubai.
“The collaboration between RIT Dubai/Rochester has continued,” he said. “Another paper was submitted a few weeks ago with Mohamed Samaha and Nate Barlow (RIT associate professor in the School of Mathematics and Statistics) as co-authors, as well as Cade Reinberger, a younger Ph.D. student in my research group.”
Mathematical modeling is one of RIT’s newer Ph.D. degree programs, and Nagshineh is among its earliest graduates. The program has doubled in size since it began accepting students in 2017, Slusarski said. This past fall, the mathematical modeling program had 35 students, with two graduating this year.
Altogether, RIT has 13 Ph.D. degree programs currently enrolling 438 students, with computing and information sciences accounting for the largest with 117 students. RIT’s other Ph.D. programs include astrophysical sciences and technology , biomedical and chemical engineering , business administration , color science , electrical and computer engineering, imaging science , mechanical and industrial engineering , microsystems engineering , and sustainability .
New programs in cognitive science and physics will launch in the fall.
The growth in RIT graduate education—with more than 3,000 master’s and doctoral students—reflects a demographic change in the student population, Slusarski said. “We have a higher percentage of women in the graduate programs than we have for RIT undergraduate programs.”
RIT’s graduate programs enroll 42 percent women, according to Christie Leone , assistant dean for the Graduate School.
Nagshineh, who also holds an MS in electrical engineering from RIT Dubai, welcomes her role as a mentor to other women students on both campuses.
“As a young woman in an Arabic country, the power of women is often underestimated and undervalued, and I hope to serve as a role model to female students, especially those that question their path,” Nagshineh said.
She plans to continue in her career as a professor and a researcher. “I would like to pursue a research program where I can advise my own students and teach them more deeply.”
Recommended News
May 10, 2024

Design icon Patricia Moore inspires RIT graduates to embrace change and forge paths of impact
While sharing insights from her own transformative journey, Patricia Moore, a distinguished designer and trailblazing alumna of the class of 1974, encouraged this year’s RIT graduates to embrace the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead and answer the call for change.

Bright Spot: Inspiration for young scholars
WHAM-TV features Katrina Overby, assistant professor in the School of Communication, as its Bright Spot.
May 8, 2024

More than monarchs: Red admirals appear in Rochester with spring
The Democrat and Chronicle talks to Kaitlin Stack Whitney, assistant professor in the Department of Science, Technology, and Society, about the early arrival and habits of the red admiral butterfly in Monroe County, highlighting its migration patterns, habitat range, and behavior.
May 7, 2024

Comics go to College
The comics collection at RIT is growing by leaps and bounds and the new Kubert Lounge and Gallery makes it a visible presence on campus. The interdisciplinary art form is right at home at RIT.
- Share on twitter
- Share on facebook
Cutting graduate route an ‘economic own goal’, warn businesses
Universities losing income from international students would have to slash their r&d spending, letter to chancellor warns.
- Share on linkedin
- Share on mail

Cutting the graduate visa route would have a serious impact on UK research and innovation and damage the wider economy, business and university leaders have warned.
Ahead of the publication of a pivotal Migration Advisory Committee (MAC) report into the UK’s post-study work visa, 17 leaders from Chambers of Commerce and business networks from across the UK have written to the chancellor to warn against watering it down or scrapping it altogether .
It is the latest attempt by the sector to exert influence over the government on what has become a crunch issue, with protecting the visa widely seen as one of the only ways of averting further financial turmoil in the sector.
The letter, coordinated by the University Alliance group of universities, has also been signed by leaders from the Russell Group and Universities UK.
It argues that if the government were to place any restrictions on the graduate visa route, it would have a “serious impact upon R&D capacity and return on government investment, besides causing damage to the wider economy”.
The higher education sector is the second largest investor in research in the UK, spending £5.6 billion on research in 2021.
The letter argues that because most of this investment is generated by tuition fee income from overseas recruitment, fewer international students in the UK will mean reduced investment in R&D.
Vivienne Stern, chief executive of Universities UK, said the UK seems “intent on dismantling” all the benefits that international students bring to the country, and warned that any changes to the graduate route will inevitably mean a decline in the UK’s research power.
“Universities of all shapes and sizes will need to make difficult choices about where to invest diminishing resources,” added Ms Stern. “This will mean further cuts to staffing, courses and research investment.”
“The business community and the higher education sector alike are worried about this because we know what it means: a crushing blow to our local economies.”
The letter cites data collated by IDP Connect that indicates that if the graduate route were removed, 45 per cent of international students would study elsewhere.
Jane Harrington, vice-chancellor of the University of Greenwich and chair of University Alliance, said restricting the graduate route would make UK universities less globally competitive.
“The government would need to find ways of covering the significant losses to research funding and wider export income caused by declining international student numbers. “This would be an extraordinary economic own goal.”
Register to continue
Why register?
- Registration is free and only takes a moment
- Once registered, you can read 3 articles a month
- Sign up for our newsletter
Or subscribe for unlimited access to:
- Unlimited access to news, views, insights & reviews
- Digital editions
- Digital access to THE’s university and college rankings analysis
Already registered or a current subscriber? Login
Related articles

Last-ditch bid to save UK graduate visa as critics circle
Even a favourable MAC report may not relieve political pressure on government to act further on international student numbers, risking ‘enormous damage right across the sector’

MAC visa review will ‘struggle with’ ministers’ ‘integrity’ query
MAC chair clarifies graduate visa review will define abuse purely as ‘breach of the immigration rules’
You might also like

Malaysia policymakers push for improved post-study work rights
Malaysia is learning from top student destinations like Australia and Canada when it comes to creating balanced immigration rules for foreign students

Tensions rise over Australian university encampments
Temperatures soar despite the winter chills, as each side accuses its opponents of extremism

Minister: Stellenbosch refusal to urge Gaza ceasefire ‘is racist’
University insists senate decision to refrain from institutional stance safeguards academic freedom
Featured jobs

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Dissertation Advisor: Professor David Deming Author: Kirsten Slungaard Mumma Essays on the Economics of Education Abstract This dissertation consists of three essays in the economics of education. The first essay considers the impact of charter school openings on student achievement, behavior, and demographics in the traditional public sector.
This dissertation consists of two separate essays on economics of education. First, the role of teacher-student interactions is analyzed. Teacher effectiveness is generally characterized by a single effect that is common across students. However, educators are multi-task agents that choose how to allocate their efforts among pupils. Some teachers may target their courses towards the top ...
Dissertation Advisor: Author: Christopher Avery Andrew Bacher-Hicks Essays on the Economics of Education Abstract This dissertation includes three essays in the field of economics of education. The first essay estimates the impact of New York City's stop and frisk policing strategy on student's long-run ed-ucational attainment.
Abstract. This dissertation consists of three essays in the economics of education. The first essay considers the impact of charter school openings on student achievement, behavior, and demographics in the traditional public sector. Using longitudinal school- and student-level data, I estimate the effect of charter school openings on ...
This doctoral thesis builds on a rich literature investigating how education policy affects students' learning, motivation, investment, and decision-making—all of which are determinants of the productivity of education systems. Over the past decades, the education field has yielded one of
Abstract. This thesis consists of three chapters that investigate how the institutions and organization of schools affect their performance, and how neighbors and siblings affect human capital investment decisions. Chapter 1 studies whether the effect of a reform that substantially increased daily instruction time in Chilean primary schools ...
This thesis studies aspects related to the role of schools characteristics and their governance on students' learning outcomes. The thesis contains three chapters. The first chapter explores the effect of exposing students to more science in high school on their enrolment and persistence in STEM majors at university. It exploits the different timing in the implementation of a reform that ...
Economics and Education PhD; Doctor of Philosophy in Economics and Education. ... and practices in the economics of education. It is a highly selective program to prepare individuals for leadership roles in teaching, research, or administrative settings. ... additional members of the dissertation committee may be drawn from other TC Departments ...
Landau Economics Building . 579 Jane Stanford Way . Stanford, CA 94305 . Phone: 650-725-3266 . econ[at] stanford.edu(econ[at]stanford[dot]edu) . Connect with us on Twitter . Campus Map. "The Stanford Economics Department has two central missions: to train students at the undergraduate and graduate level in the methods and ideas of modern ...
Athanasopoulos, Thanos (2014) 3 essays on technological change and welfare. PhD thesis, University of Warwick. Azam, Kazim (2013) Copula methods in econometrics. PhD thesis, University of Warwick. Aoki, Yu (2012) Identification of causal effects using the 1995 earthquake in Japan : studies of education and health.
Essays in Education, Mobility, and Political Economy . Concha-Arriagada, Carolina (Georgetown University, 2023) In this dissertation, I apply theoretical and empirical analysis to three topics ranging from the economics of education, mobility, and political economy, mainly focusing on agents' decisions and the effects of those ...
This thesis consists of three independent essays in economics of education. In the first chapter, I investigate the connection between cultural identities and parental schooling decisions. By leveraging the case of the Basque Country (Spain), this essay studies how parents trade off academic quality for being educated in the regional language.
2020. 0420 Three essays in environmental economics. by Antonia Isabel Laurie Schwarz. 0320 Trade implications of transport cost in the Philippines. by Eugenia Go. 0220 Essays on the economics of mental health and well-being. by Anna Bencsik. 0120 Essays on political economy, inequality and development. by Marta Schoch.
3. Education can facilitate the diffusion of knowledge to successfully implement new technologies devised by others, which again can promote economic growth. Given this view that education drives growth, governments have responded by pouring their resources into education reform. Figure 1 below shows the amount of education spending in
Welcome to LSE Theses Online, the online archive of PhD theses for the London School of Economics and Political Science. LSE Theses Online contains a partial collection of completed and examined PhD theses from doctoral candidates who have studied at LSE. Please note that not all print PhD theses have been digitised. For a full catalogue of LSE ...
A PhD thesis normally consists of three research papers of publishable quality. The thesis must be approved by a student's primary and secondary thesis advisors, and by an anonymous third reader. These three faculty members will be the candidate's thesis committee and are responsible for its acceptance. Collaborative work is acceptable and ...
The economics of education is a wide-ranging and growing sub-field of economics. It encompasses topics such as research on returns to education in the labour market, efficiency of the education "industry", effets of education on the growth of economies, and educational finance. It also encompasses all levels of education, ranging from pre-school learning over school and university ...
The Dynamics of Research and Development: Identifying the Effect of Competition and Firm Size on Innovation Quality in High-Tech Industries. 1 Joint Concentrator: Computer Science and Economics. 3 Joint Concentrator: Economics and Math. 4 Joint Concentrator: ESPP and Economics.
Graduate Programs Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in Economic Education This Ph.D. program is on moratorium and no longer accepting new students. This page is for students admitted to the program prior to Fall 2021. An Interdisciplinary Program for Leaders in Economic Education The doctorate in economic education is designed to train the next generation of […]
This dissertation contains three chapters in education and labor economics. In Chapter 1, I study whether relative age effects among fourth graders on math and science test scores exist in developing countries and investigate whether they are similar across all countries with different levels of development.
Knowledge of statistics is highly important for research scholars, as they are expected to submit a thesis based on original research as part of a PhD program. As statistics play a major role in the analysis and interpretation of scientific data, intensive training at the beginning of a PhD programme is essential. PhD coursework is mandatory in universities and higher education institutes in ...
When students should write a PhD thesis they need to take various steps. Firstly, they need to choose the research topic and make sure that the professor supports it. Secondly, they need to ...
Michael Chernew, PhD, is the Leonard D. Schaeffer Professor of Health Care Policy at Harvard Medical School.Dr. Chernew's research examines several areas related to improving the health care system, including studies of novel benefit designs, Medicare Advantage, alternative payment models, low-value care, and the causes and consequences of rising health care spending.
There is a vibrant and prosperous future for M.A. and Ph.D. education not in radical transformation but in reconciliation—reconciliation between academic and applied domains of knowledge production, and in enabling lives as researchers and scholars both within the academy and beyond. Master's and Ph.D. graduates are eminently employable ...
Rutgers PhD student, Tamiah Brevard-Rodriguez, gave birth to her son and then hours later defended her dissertation to a committee over Zoom.
RIT awarded 63 Ph.D. degrees in 2023. In 2020-2021, RIT's Graduate School met and surpassed the university's goal of conferring 50 Ph.D. degrees during an academic year. That number will continue to grow as students cycle through the seven new Ph.D. programs that RIT has added since 2017, said Diane Slusarski, dean of RIT's Graduate School.
Cutting the graduate visa route would have a serious impact on UK research and innovation and damage the wider economy, business and university leaders have warned. Ahead of the publication of a pivotal Migration Advisory Committee (MAC) report into the UK's post-study work visa, 17 leaders from Chambers of Commerce and business networks from ...