- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Contentious Politics and Political Violence
- Governance/Political Change
- Groups and Identities
- History and Politics
- International Political Economy
- Policy, Administration, and Bureaucracy
- Political Anthropology
- Political Behavior
- Political Communication
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Philosophy
- Political Psychology
- Political Sociology
- Political Values, Beliefs, and Ideologies
- Politics, Law, Judiciary
- Post Modern/Critical Politics
- Public Opinion
- Qualitative Political Methodology
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- World Politics
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter

Article contents
Global migration: causes and consequences.
- Benjamin Helms Benjamin Helms Department of Politics, University of Virginia
- and David Leblang David Leblang Department of Politics, Frank Batten School of Leadership and Public Policy, University of Virginia
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190228637.013.631
- Published online: 25 February 2019
International migration is a multifaceted process with distinct stages and decision points. An initial decision to leave one’s country of birth may be made by the individual or the family unit, and this decision may reflect a desire to reconnect with friends and family who have already moved abroad, a need to diversify the family’s access to financial capital, a demand to increase wages, or a belief that conditions abroad will provide social and/or political benefits not available in the homeland. Once the individual has decided to move abroad, the next decision is the choice of destination. Standard explanations of destination choice have focused on the physical costs associated with moving—moving shorter distances is often less expensive than moving to a destination farther away; these explanations have recently been modified to include other social, political, familial, and cultural dimensions as part of the transaction cost associated with migrating. Arrival in a host country does not mean that an émigré’s relationship with their homeland is over. Migrant networks are an engine of global economic integration—expatriates help expand trade and investment flows, they transmit skills and knowledge back to their homelands, and they remit financial and human capital. Aware of the value of their external populations, home countries have developed a range of policies that enable them to “harness” their diasporas.
- immigration
- international political economy
- factor flows
- gravity models
Introduction
The steady growth of international labor migration is an important, yet underappreciated, aspect of globalization. 1 In 1970 , just 78 million people, or about 2.1% of the global population, lived outside their country of birth. By 1990 , that number had nearly doubled to more than 150 million people, or about 2.8% of the global population (United Nations Population Division, 2012 ). Despite the growth of populist political parties and restrictionist movements in key destination countries, the growth in global migration shows no signs of slowing down, with nearly 250 million people living outside their country of birth as of 2015 . While 34% of all global migrants live in industrialized countries (with the United States and Germany leading the way), 38% of all global migration occurs between developing countries (World Bank, 2016 ).
Identifying the causes and consequences of international labor migration is essential to our broader understanding of globalization. Scholars across diverse academic fields, including economics, political science, sociology, law, and demography, have attempted to explain why individuals voluntarily leave their homelands. The dominant thread in the labor migration literature is influenced by microeconomics, which posits that individuals contemplating migration are rational, utility-maximizing actors who carefully weigh the potential costs and benefits of leaving their country of origin (e.g., Borjas, 1989 ; Portes & Böröcz, 1989 ; Grogger & Hanson, 2011 ). The act of migration, from this perspective, is typically conceptualized as an investment from which a migrant expects to receive some benefit, whether it be in the form of increased income, political freedom, or enhanced social ties (Schultz, 1961 ; Sjaastad, 1962 ; Collier & Hoeffler, 2014 ).
In this article we go beyond the treatment of migration as a single decision and conceive of it as a multifaceted process with distinct stages and decision points. We identify factors that are relevant at different stages in the migration process and highlight how and when certain factors interact with others during the migration process. Economic factors such as the wage differential between origin and destination countries, for example, may be the driving factor behind someone’s initial decision to migrate (Borjas, 1989 ). But when choosing a specific destination, economic factors may be conditioned by political or social conditions in that destination (Fitzgerald, Leblang, & Teets, 2014 ). Each stage or decision point has distinguishing features that are important in determining how (potential) migrants respond to the driving forces identified by scholars.
This is certainly not a theoretical innovation; migration has long been conceived of as a multi-step process, and scholars often identify the stage or decision point to which their argument best applies. However, most interdisciplinary syntheses of the literature on international labor migration do not provide a systematic treatment of this defining feature, instead organizing theoretical and empirical contributions by field of study, unit or level of analysis, or theoretical tradition (e.g., Portes & Böröcz, 1989 ; Massey et al., 1993 ; European Asylum Support Office, 2016 ). Such approaches are undoubtedly valuable in their own right. Our decision to organize this discussion by stage allows us to understand this as a process, rather than as a set of discrete events. As a result, we conceptualize international labor migration as three stages or decision points: (a) the decision to migrate or to remain at home, (b) the choice of destination, and (c) the manner by which expatriates re-engage—or choose not to re-engage—with their country of origin once abroad. We also use these decision points to highlight a number of potential new directions for future research in this still-evolving field.
Figure 1. Global migration intentions by educational attainment, 2008–2017.
Should I Stay or Should I Go, Now?
The massive growth in international labor migration in the age of globalization is remarkable, but the fact remains that over 95% of the world’s population never leave their country of origin (United Nations Population Division, 2012 ). Figure 1 shows the percentage of people who expressed an intention to move abroad between 2008 and 2017 by educational attainment, according to data from the Gallup World Poll. Over this time period, it appears that those who were highly educated expressed intent to migrate in greater numbers than those who had less than a college education, although these two groups have converged in recent years. What is most striking, however, is that a vast majority of people, regardless of educational attainment, expressed no desire to move abroad. Even though absolute flows of migrants have grown at a near-exponential rate, relative to their non-migrating counterparts, they remain a small minority. What factors are important in determining who decides to migrate and who decides to remain at home? 2
From Neoclassical Economics to the Mobility Transition
Neoclassical economic models posit that the primary driving factor behind migration is the expected difference in wages (discounted future income streams) between origin and destination countries (Sjaastad, 1962 ; Borjas, 1989 ; Clark, Hatton, & Williamson, 2007 ). All else equal, when the wage gap, minus the costs associated with moving between origin and destination, is high, these models predict large flows of labor migrants. In equilibrium, as more individuals move from origin to destination countries, the wage differential narrows, which in turn leads to zero net migration (Lewis, 1954 ; Harris & Todaro, 1970 ). Traditional models predict a negative monotonic relationship between the wage gap and the number of migrants (e.g., Sjaastad, 1962 ). However, the predictions of neoclassical models are not well supported by the empirical record. Empirical evidence shows that, at least in a cross-section, the relationship between economic development and migration is more akin to an inverted U. For countries with low levels of per capita income, we observe little migration due to a liquidity constraint: at this end of the income distribution, individuals do not have sufficient resources to cover even minor costs associated with moving abroad. Increasing income helps to decrease this constraint, and consequently we observe increased levels of emigration as incomes rise (de Haas, 2007 ). This effect, however, is not monotonic: as countries reach middle-income status, declining wage differentials lead to flattening rates of emigration, and then decreasing rates as countries enter later stages of economic development. 3
Some research explains this curvilinear relationship by focusing on the interaction between emigration incentives and constraints : for example, increased income initially makes migration more affordable (reduces constraints), but also simultaneously reduces the relative economic benefits of migrating as the wage differential narrows (as potential migrants now have the financial capacity to enhance local amenities) (Dao, Docquier, Parsons, & Peri, 2016 ). The theoretical underpinnings of this interaction, however, are not without controversy. Clemens identifies several classes of theory that attempt to explain this curvilinear relationship—a relationship that has been referred to in the literature as the mobility transition (Clemens, 2014 ). These theories include: demographic changes resulting from development that also favor emigration up to a point (Easterlin, 1961 ; Tomaske, 1971 ), the loosening of credit restraints on would-be migrants (Vanderkamp, 1971 ; Hatton & Williamson, 1994 ), a breakdown of information barriers via the building of transnational social networks (Epstein, 2008 ), structural economic changes in the development process that result in worker dislocation (Zelinsky, 1971 ; Massey, 1988 ), the dynamics of economic inequality and relative deprivation (Stark, 1984 ; Stark & Yitzhaki, 1988 ; Stark & Taylor, 1991 ), and changing immigration policies in destination countries toward increasingly wealthy countries (Clemens, 2014 ). While each of these play some role in the mobility transition curve, Dao et al. ( 2016 ) run an empirical horse race between numerous explanations and find that changing skill composition resulting from economic development is the most substantively important driver. Economic development is correlated with an increase in a country’s level of education; an increase in the level of education, in turn, is correlated with increased emigration. However, traditional explanations involving microeconomic drivers such as income, credit constraints, and economic inequality remain important factors (Dao et al., 2016 ). The diversity of explanations offered for the mobility transition curve indicates that while most research agrees the inverted-U relationship is an accurate empirical portrayal of the relationship between development and migration, little theoretical agreement exists on what drives this relationship. Complicating this disagreement is the difficulty of empirically disentangling highly correlated factors such as income, skill composition, and demographic trends in order to identify robust causal relationships.
Political Conditions at the Origin
While there is a scholarly consensus around the mobility transition and the role of economic conditions, emerging research suggests that the political environment in the origin country may also be salient. We do not refer here to forced migration, such as in the case of those who leave because they are fleeing political persecution or violent conflict. Rather, we focus on political conditions in the homeland that influence a potential migrant’s decision to emigrate voluntarily. Interpretations of how, and the extent to which, political conditions in origin countries (independent of economic conditions) influence the decision to migrate have been heavily influenced by Hirschman’s “Exit, Voice, and Loyalty” framework (Hirschman, 1970 , 1978 ). Hirschman argues that the opportunity to exit—to exit a firm, an organization, or a country—places pressure on the local authorities; voting with one’s feet forces organizations to reassess their operations.
When applied to the politics of emigration, Hirschman’s framework generates two different hypotheses. On the one hand, politicians may allow, encourage, or force the emigration of groups that oppose the regime as a political safety valve of sorts. This provides the government with a mechanism with which to manage potential political challengers by encouraging their exit. On the other hand, politicians—especially those in autocracies—may actively work to prevent exit because they fear the emigration of economic elites, the highly skilled, and others who have resources vital to the survival of the regime. 4
A small number of studies investigate how local-level, rather than national, political circumstances affect a potential migrant’s calculus. The limited empirical evidence currently available suggests that local conditions are substantively important determinants of the emigration decision. When individuals are highly satisfied with local amenities such as their own standard of living, quality of public services, and overall sense of physical security, they express far less intention to migrate compared with highly dissatisfied individuals (Dustmann & Okatenko, 2014 ). Furthermore, availability of public transport and access to better education facilities decreases the propensity to express an intention to emigrate (Cazzuffi & Modrego, 2018 ). This relationship holds across all levels of wealth and economic development, and there is some evidence that satisfaction with local amenities matters as much as, or even more than, income or wealth (Dustmann & Okatenko, 2014 ).
Political corruption, on both national and local levels, also has substantively important effects on potential migrants, especially those who are highly skilled. Broadly defined as the use of public office for political gain, political corruption operates as both a direct and an indirect factor promoting emigration. 5 Firstly, corruption may have a direct effect on the desire to emigrate in that it can decrease the political and economic power of an individual, leading to a lower standard of living and poorer quality of life in origin countries. If the reduction in life satisfaction resulting from corruption is sufficiently high—either by itself or in combination with other “push” factors—then the exit option becomes more attractive (Cooray & Schneider, 2016 ). Secondly, corruption also operates through indirect channels that influence other push factors. Given the large literature on how political corruption influences a number of development outcomes, it is conceivable that corruption affects the decision-making process of a potential migrant through its negative effect on social spending, education, and public health (Mo, 2001 ; Mauro, 1998 ; Gupta, Davoodi, & Thigonson, 2001 ).
The combination of its direct and indirect impacts means that corruption could be a significant part of a migrant’s decision-making process. At present there is limited work exploring this question, and the research does not yield a consensus. Some scholars argue that political corruption has no substantive effect on total bilateral migration, but that it does encourage migration among the highly skilled (Dimant, Krieger, & Meierrieks, 2013 ). This is the case, the argument goes, because corruption causes the greatest relative harm to the utility of those who have invested in human capital, who migrate to escape the negative effect on their fixed investment. In contrast, others find that a high level of corruption does increase emigration at the aggregate level (Poprawe, 2015 ). More nuanced arguments take into account the intensity of corruption: low to moderate levels of corruption lead to increased emigration of all groups, and especially of the highly skilled. But at high levels of corruption, emigration begins to decrease, indicating that intense corruption can act as a mobility constraint (Cooray & Schneider, 2016 ). All of these existing accounts, however, employ state-level measures of corruption by non-governmental organizations, such as those produced by Transparency International. Scholars have yet to harness micro-level survey data to explore the influence of personal corruption perception on the individual’s decision-making process.
The Land of Hopes and Dreams
Given that an individual has decided to emigrate, the next decision point is to choose a destination country. Advanced industrial democracies, such as those in the OECD, are major migrant-receiving countries, but so are Russia and several Gulf countries including Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates (World Bank, 2016 ). A country’s constellation of political, economic, and social attributes is crucial to understanding an emigrant’s choice of destination. Potential migrants weigh all of these factors simultaneously when choosing a destination: will the destination allow political rights for the migrant and their children, is access to the labor market possible, and does the destination provide an opportunity for reunification with friends and family? In this section we focus on the non-economic factors that draw migrants to certain countries over others. In addition, we emphasize how skill level adds layers of complexity to a migrant’s calculus.
Political Environment, Both Formal and Informal
As noted earlier, traditional neoclassical models and their extensions place wage differentials and associated economic variables at the heart of a migrant’s choice. Gravity models posit that migrants choose a destination country based on their expected income—which itself is a function of the wage rate and the probability of finding employment in the destination—less the costs associated with moving (Ravenstein, 1885 ; Todaro, 1969 ; Borjas, 1989 ). A rigid focus on economic factors, however, blinds us to the empirical reality that a destination country’s political environment influences what destination a migrant chooses (Borjas, 1989 ). A country’s legal and political rights structure for migrants, as well as its level of tolerance for newcomers, is critical to migrants discriminating between an array of potential destinations. Fitzgerald, Leblang, and Teets ( 2014 ) argue, for example, that states with restrictive citizenship policies and strong radical right anti-immigrant parties will receive fewer migrants, while states with relatively liberal citizenship requirements and weak radical right political movements will receive more migrants. In the rational actor framework, migrants seek countries with hospitable political environments to maximize both their political representation in government and their access to labor market opportunities as a result of citizenship rights and social acceptance (Fitzgerald et al., 2014 ).
Using a broad sample of origin countries and 18 destination countries, they find that relative restrictiveness of citizenship policies and level of domestic support for the radical right are substantively important determinants of global migratory flows. Further, they find that these political variables condition a migrant’s choice of destination: the relative importance of economic factors such as the unemployment rate or the wage differential diminishes as a destination country’s political environment becomes more open for migrants. In other words, when migrants are choosing a destination country, political considerations may trump economic ones—a finding that is an important amendment to the primarily economics-focused calculus of the initial stage of the immigration decision.
However, prior to choosing and entering a destination country, a migrant must also navigate a country’s immigration policy—the regulation of both migrant entry and the rights and status of current migrants. While it is often assumed that a relatively more restrictive immigration policy deters entry, and vice versa, a lack of quantitative data has limited the ability of scholars to confirm this intuition cross-nationally. Money ( 1999 ) emphasizes that the policy output of immigration politics does not necessarily correlate with the outcome of international migrant flows. There are a number of unanswered questions in this field, including: is immigration policy a meaningful determinant of global flows of migration? Do certain kinds of immigration policies matter more than others? How does immigration policy interact with other political and economic factors, such as unemployment and social networks?
Only a handful of studies analyze whether or not immigration policy is a significant determinant of the size and character of migratory flows. Perhaps the most prominent answer to this question is the “gap hypothesis,” which posits that immigration rates continue to increase despite increasingly restrictive immigration policies in advanced countries (Cornelius & Tsuda, 2004 ). Some subsequent work seems to grant support to the gap hypothesis, indicating that immigration policy may not be a relevant factor and that national sovereignty as it relates to dictating migrant inflows has eroded significantly (Sassen, 1996 ; Castles, 2004 ). The gap hypothesis is not without its critics, with other scholars arguing that the existing empirical evidence actually lends it little or no support (Messina, 2007 ).
A more recent body of literature does indicate that immigration policy matters. Brücker and Schröder ( 2011 ), for example, find that immigration policies built to attract highly skilled migrants lead to higher admittance rates. They also show that diffusion processes cause neighboring countries to implement similar policy measures. Ortega and Peri ( 2013 ), in contrast to the gap hypothesis literature, find that restrictive immigration policy indeed reduces migrant inflows. But immigration policy can also have unintended effects on international migration: when entry requirements increase, migrant inflows decrease, but migrant outflows also decrease (Czaika & de Haas, 2016 ). This indicates that restrictive immigration policy may also lead to reduced circular migrant flows and encourage long-term settlement in destination countries.
Disaggregating immigration policy into its different components provides a clearer picture of how immigration policy may matter, and whether certain components matter more than others. Immigration policy is composed of both external and internal regulations. External regulations refer to policies that control migrant entry, such as eligibility requirements for migrants and additional conditions of entry. Internal regulations refer to policies that apply to migrants who have already gained status in the country, such as the security of a migrant’s legal status and the rights they are afforded. Helbling and Leblang ( 2017 ), using a comprehensive data set of bilateral migrant flows and the Immigration Policies in Comparison (IMPIC) data set, find that, in general, external regulations prove slightly more important in understanding migrant inflows (Helbling, Bjerre, Römer, & Zobel, 2017 ). This indicates that potential migrants focus more on how to cross borders, and less on the security of their status and rights once they settle. They do find, however, that both external and internal components of immigration are substantively important to international migrant flows.
The effects of policy, however, cannot be understood in isolation from other drivers of migration. Firstly, poor economic conditions and restrictive immigration policy are mutually reinforcing: when the unemployment rate is elevated, restrictive policies are more effective in deterring migrant flows. An increase in policy effectiveness in poor economic conditions suggests that states care more about deterring immigration when the economy is performing poorly. Secondly, a destination country’s restrictive immigration policy is more effective when migrants come from origin countries that have a common colonial heritage. This suggests that cultural similarities and migrant networks help to spread information about the immigration policy environment in the destination country. Social networks prove to be crucial in determining how much migrants know about the immigration policies of destination countries, regardless of other cultural factors such as colonial heritage or common language (Helbling & Leblang, 2017 ). In summary, more recent work supports the idea that immigration policy of destination countries exerts a significant influence on both the size and character of international migration flows. Much work remains to be done in terms of understanding the nuances of specific immigration policy components, the effect of policy change over time, and through what mechanisms immigration policy operates.
Transnational Social Networks
None of this should be taken to suggest that only political and economic considerations matter when a potential migrant contemplates a potential destination; perhaps one of the biggest contributions to the study of bilateral migration is the role played by transnational social networks. Migrating is a risky undertaking, and to minimize that risk, migrants are more likely to move to destinations where they can “readily tap into networks of co-ethnics” (Fitzgerald et al., 2014 , p. 410). Dense networks of co-ethnics not only help provide information about economic opportunities, but also serve as a social safety net which, in turn, helps decrease the risks associated with migration, including, but not limited to, finding housing and integrating into a new community (Massey, 1988 ; Portes & Böröcz, 1989 ; Portes, 1995 ; Massey et al., 1993 ; Faist, 2000 ; Sassen, 1995 ; Light, Bernard, & Kim, 1999 ). Having a transnational network of family members is quite important to destination choice; if a destination country has an immigration policy that emphasizes family reunification, migrants can use their familial connections to gain economically valuable permanent resident or citizenship status more easily than in other countries (Massey et al., 1993 , p. 450; Helbing & Leblang, 2017 ). When the migrant is comparing potential destinations, countries in which that migrant has a strong social network will be heavily favored in a cost–benefit analysis.
Note, however, that even outside of a strict rational actor framework with perfect information, transnational social networks still may be quite salient to destination choice. An interesting alternative hypothesis for the patterns we observe draws on theories from financial market behavior which focus on herding. Migrants choosing a destination observe the decisions of their co-ethnics who previously migrated and assume that those decisions were based on a relevant set of information, such as job opportunities or social tolerance of migrants. New migrants then choose the same destination as their co-ethnics not based on actual exchanges of valuable information, but based solely on the assumption that previous migration decisions were based on rational calculation (Epstein & Gang, 2006 ; Epstein, 2008 ). This is a classic example of herding, and the existing empirical evidence on the importance of transnational social networks cannot invalidate this alternative hypothesis. One could also explain social network effects through the lens of cumulative causation or feedback loops: the initial existence of connections in destination countries makes the act of migration less risky and attracts additional co-ethnics. This further expands migrant networks in a destination, further decreasing risk for future waves of migrants, and so on (Massey, 1990 ; Fussel & Massey, 2004 ; Fussel, 2010 ).
No matter the pathway by which social networks operate, the empirical evidence indicates that they are one of the most important determinants of destination choice. Potential migrants from Mexico, for example, who are able to tap into existing networks in the United States face lower direct, opportunity, and psychological costs of international migration (Massey & Garcia España, 1987 ). This same relationship holds in the European context; a study of Bulgarian and Italian migrants indicates that those with “social capital” in a destination community are more likely to migrate and to choose that particular destination (Haug, 2008 ). Studies that are more broadly cross-national in nature also confirm the social network hypothesis across a range of contexts and time periods (e.g., Clark et al., 2007 ; Hatton & Williamson, 2011 ; Fitzgerald et al., 2014 ).
Despite the importance of social networks, it is, again, important to qualify their role in framing the choice of destinations. It seems that the existence of co-ethnics in destination countries most strongly influences emigration when they are relatively few in number. Clark et al. ( 2007 ), in their study of migration to the United States, find that the “friends and relatives effect” falls to zero once the migrant stock in the United States reaches 8.3% of the source-country population. In addition, social networks alone cannot explain destination choice because their explanatory power is context-dependent. For instance, restrictive immigration policies limiting legal migration channels and family reunification may dampen the effectiveness of networks (Böcker, 1994 ; Collyer, 2006 ). Social networks are not an independent force, but also interact with economic and political realities to produce the global migration patterns we observe.
The Lens of Skill
For ease of presentation, we have up to now treated migrants as a relatively homogeneous group that faces similar push and pull factors throughout the decision-making process. Of course, not all migrants experience the same economic, political, and social incentives in the same way at each stage of the decision-making process. Perhaps the most salient differentiating feature of migrants is skill or education level. Generally, one can discuss a spectrum of skill and education level for current migrants, from relatively less educated (having attained a high school degree or less) to relatively more educated (having attained a college or post-graduate degree). The factors presented here that influence destination choice interact with a migrant’s skill level to produce differing destination choice patterns.
A migrant’s level of education, or human capital, often serves as a filter for the political treatment he or she anticipates in a particular destination country. For instance, the American public has a favorable view of highly educated migrants who hold higher-status jobs, while simultaneously having an opposite view of migrants who have less job training and do not hold a college degree (Hainmueller & Hiscox, 2010 ; Hainmueller & Hopkins, 2015 ). Indeed, the political discourse surrounding migration often emphasizes skill level and education as markers of migrants who “should be” admitted, across both countries and the ideological spectrum. 6 While political tolerance may be a condition of entry for migrants in the aggregate, the relatively privileged status of highly educated and skilled migrants in most destination countries may mean that this condition is not as salient.
While it is still an open question to what extent immigration policy influences international migration, it is clear that not all migrants face evenly applied migration restrictions. Most attractive destination countries have policies that explicitly favor highly skilled migrants, since these individuals often fill labor shortages in advanced industries such as high technology and applied science. Countries such as Australia, Canada, and New Zealand all employ so-called “points-based” immigration systems in which those with advanced degrees and needed skills are institutionally favored for legal entry (Papademetriou & Sumption, 2011 ). Meanwhile, the United States maintains the H-1B visa program, which is restricted by educational attainment and can only be used to fill jobs in which no native talent is available (USCIS). Even if destination countries decide to adopt more restrictive immigration policies, the move toward restriction has typically been focused on low-skilled migrants (Peters, 2017 ). In other words, even if immigration policy worldwide becomes more restrictive, this will almost certainly not occur at the expense of highly skilled migrants and will not prevent them choosing their most preferred destination.
Bring It on Home to Me
This article began by asserting that international labor migration is an important piece of globalization, as significant as cross-border flows of capital, goods, and services. This section argues that migrant flows enhance flows of capital and commodities. Uniquely modern conditions such as advanced telecommunications, affordable and efficient international travel, and the liberalization of financial flows mean that diasporas—populations of migrants living outside their countries of origin—and home countries often re-engage with each other (Vertovec, 2004 ; Waldinger, 2008 ). This section reviews some of the newest and most thought-provoking research on international labor migration, research that explores diaspora re-engagement and how that re-engagement alters international flows of income, portfolio and foreign direct investment (FDI), trade, and migratory flows themselves.
Remittances
As previously argued, migration is often driven by the prospect of higher wages. Rational, utility-maximizing migrants incur the cost of migration in order to earn increased income that they could not earn at home. But when migrants obtain higher wages, this additional increment to income is not always designated for individual consumption. Often, migrants use their new income to send remittances, direct transfers of money from one individual to another across national borders. Once a marginal financial flow, in 2015 remittances totaled $431 billion, far outpacing foreign aid ($135 billion) and nearly passing private debt and portfolio equity ($443 billion). More than 70% of total global remittances flow into developing countries (World Bank, 2016 ). In comparison with other financial flows such as portfolio investment and FDI, remittances are more impervious to economic crises, suggesting that they may be a countercyclical force to global downturns (Leblang, 2017 ).
Remittances represent one of the most common ways in which migrants re-engage with their homeland and alter both global income flows and distribution. Why do migrants surrender large portions of their new income, supposedly the very reason they migrated in the first place, to their families back home? New economics of labor migration (NELM) theory argues that immigration itself is motivated by a family’s need or demand for remittances—that remittances are an integral part of a family’s strategy for diversifying household financial risk (Stark & Bloom, 1985 ). Remittances “are a manifestation of informal contractual agreements between migrants and the households from which they move,” indicating that remitting is not an individual-level or purely altruistic action but rather occurs in a larger social context, that of one’s immediate or extended family (European Asylum Support Office, 2016 , p. 15).
The impact of migrant remittances on countries of origin is multifaceted yet somewhat ambiguous. Most scholarly work focuses on whether remittances positively or negatively influence existing economic conditions. A number of studies find that remittances modestly reduce poverty levels in developing countries (Adams & Page, 2005 ; Yang & Martinez, 2006 ; Acosta, Calderon, Fajnzybler, & Lopez, 2008 ; Lokshin, Bontch-Osmolovski, & Glinskaya, 2010 ). On other measures of economic well-being, such as growth, inequality, and health, the literature is quite mixed and no definitive conclusions can be drawn. For instance, some studies find that remittances encourage investment in human capital (Yang, 2008 ; Adams & Cuecuecha, 2010 ), while others find no such effect and suggest that families typically spend remittances on non-productive consumption goods (Chami, Fullenkamp, & Jahjah, 2003 ). Here we can only scratch the surface of the empirical work on remittances and economic outcomes. 7
Some of the most recent research in the field argues that remittances have a distinct political dimension, affecting regime support in developing countries and altering the conditions in which elections are held. Ahmed ( 2012 ), grouping remittances with foreign aid, argues that increased remittances allow autocratic governments to extend their tenure in office. These governments can strategically channel unearned government and household income to finance political patronage networks, which leads to a reduced likelihood of autocratic turnover, regime collapse, and mass protests against the regime. More recent research posits nearly the exact opposite: remittances are linked to a greater likelihood of democratization under autocratic regimes. Escriba-Folch, Meseguer, and Wright ( 2015 ) argue that since remittances directly increase household incomes, they reduce voter reliance on political patronage networks, undermining a key tool of autocratic stability.
Remittances may also play an important role in countries with democratic institutions, yet more research is needed to fully understand the conditions under which they matter and their substantive impact. Particularly, remittances may alter the dynamics of an election as an additional and external financial flow. There is evidence of political remittance cycles : the value of remittances spikes in the run-up to elections in developing countries. The total value of remittances to the average developing country increases by 6.6% during election years, and by 12% in elections in which no incumbent or named successor is running (O’Mahony, 2012 ). The effect is even larger in the poorest of developing countries. Finer-grained tests of this hypothesis provide additional support: using monthly and quarterly data confirms the existence of political remittance cycles, as well as using subnational rather than cross-national data (Nyblade & O’Mahony, 2014 ). However, these studies do not reveal why remittances spike, or what the effects of that spike are on electoral outcomes such as vote share, campaign financing, and political strategy.
Remittances represent a massive international financial flow that warrants more scholarly attention. While there are numerous studies on the relationship between remittances and key economic indicators, there remains much room for further work on their relationship to political outcomes in developing countries. Do remittances hasten the downfall of autocratic regimes, or do they contribute to autocratic stability? In democratic contexts, do remittances substantively influence electoral outcomes, and if so, which outcomes and how? Finally, do remittances prevent even more migration because they allow one “breadwinner from abroad” to provide for the household that remains in the homeland? While data limitations are formidable, these questions are important to the study of both international and comparative political economy.
Bilateral Trade
The argument that migrant or co-ethnic networks play an important role in international economic exchange is not novel. Greif ( 1989 , 1993 ) illustrates the role that the Maghrebi traders of the 11th century played in providing informal institutional guarantees that facilitated trade. This is but a single example. Cowen’s historical survey identifies not only the Phoenicians but also the “Spanish Jews [who] were indispensable for international commerce in the Middle Ages. The Armenians controlled the overland route between the Orient and Europe as late as the nineteenth century . Lebanese Christians developed trade between the various parts of the Ottoman empire” (Cowen, 1997 , p. 170). Rauch and Trindade ( 2002 ) provide robust empirical evidence linking the Chinese diaspora to patterns of imports and exports with their home country.
A variety of case studies document the importance of migrant networks in helping overcome problems of information asymmetries. In his study of Indian expatriates residing in the United States, Kapur ( 2014 ) documents how that community provides U.S. investors with a signal of the work ethic, labor quality, and business culture that exists in India. Likewise, Weidenbaum and Hughes ( 1996 ) chronicle the Bamboo Network—the linkages between ethnic Chinese living outside mainland China and their homeland—and how these linkages provide superior access to information and opportunities for investment.
Connections between migrant communities across countries affect cross-national investment even when these connections do not provide information about investment opportunities. In his work on the Maghrebi traders of the 11th century , Greif argues that this trading network was effective because it was able to credibly threaten collective punishment by all merchants if even one of them defected (Greif, 1989 , 1993 ). Grief shows that this co-ethnic network was able to share information regarding the past actions of actors (they could communicate a reputation)—something that was essential for the efficient functioning of markets in the absence of formal legal rules. Weidenbaum and Hughes reach a similar conclusion about the effectiveness of the Bamboo Network, remarking that “if a business owner violates an agreement, he is blacklisted. This is far worse than being sued, because the entire Chinese networks will refrain from doing business with the guilty party” (Hughes, 1996 , p. 51).
Migrants not only alter the flow of income by remitting to their countries of origin, but also influence patterns of international portfolio investment and FDI. Most existing literature on international capital allocation emphasizes monadic factors such as the importance of credible commitments and state institutional quality, failing to address explicitly dyadic phenomena that may also drive investment. Diaspora networks, in particular, facilitate cross-border investment in a number of ways. They foster a higher degree of familiarity between home and host countries, leading to a greater preference for investment in specific countries. Diaspora networks can also decrease information asymmetries in highly uncertain international capital markets in two ways. Firstly, they can provide investors with salient information about their homeland, such as consumer tastes, that can influence investment decision-making. Secondly, they can share knowledge about investment opportunities, regulation and procedures, and customs that decrease transaction costs associated with cross-border investment (Leblang, 2010 ). This place of importance for migrants suggests to the broader international political economy literature the importance of non-institutional mechanisms for channeling economic activity.
Although the hypothesized link between migrants and international investment has only recently been identified, the quantitative evidence available supports that hypothesis. Leblang ( 2010 ), using dyadic cross-sectional data, finds that diaspora networks “have both a substantively significant effect and a statistically significant effect on cross-border investment,” including international portfolio investment and FDI (p. 584). The effect of bilateral migratory flows correlates positively with the degree of information asymmetry: when informational imperfections are more pervasive in a dyad, migrants (especially the highly skilled) play a disproportionately large role in international capital allocation (Kugler, Levinthal, & Rapoport, 2017 ). Other quantitative studies find substantively similar results for FDI alone (e.g., Javorcik, Özden, Spatareanu, & Neagu, 2011 ; Aubry, Rapoport, & Reshef, 2016 ).
Many questions still remain unanswered. Firstly, does the effect of migrants on investment follow the waves of the global economy, or is it countercyclical as remittances have been shown to be? Secondly, how does this additional investment, facilitated by migrants, affect socioeconomic outcomes such as inequality, poverty, and economic development (Leblang, 2010 )? Does the participation of migrants lead to more successful FDI projects in developing countries because of their ability to break down information barriers? Within portfolio investment, do migrants lead to a preference for certain asset classes over others, and if so, what are the effects on bilateral and international capital markets? These are just a few directions in an area ripe for additional research.
Return Migration and Dual Citizenship
Besides financial flows, migrants themselves directly contribute to global flows of capital by returning to their countries of origin in large numbers. This phenomenon of return migration—or circular migration—can come in a few temporal forms, including long-term migration followed by a permanent return to a country of origin, or repeat migration in which a migrant regularly moves between destination and origin countries (Dumont & Spielvogel, 2008 ). While comparable data on return migration is scarce, some reports suggest that 20% to 50% of all immigrants leave their destination country within five years after their arrival (e.g., Borjas & Bratsberg, 1996 ; Aydemir & Robinson, 2008 ; Bratsberg, Raaum, & Sørlie, 2007 ; Dustmann & Weiss, 2007 ). An independent theoretical and empirical account of return migration does not yet exist in the literature and is beyond the scope of this paper. But in the rational actor framework, motivations to return home include a failure to realize the expected benefits of migration, changing preferences toward a migrant’s home country, achievement of a savings or other economic goal, or the opening of additional employment opportunities back home due to newly acquired experience or greater levels of economic development (Dumont & Spielvogel, 2008 ).
While most migration literature treats the country of origin as a passive actor that only provides the conditions for migration, new literature on return migration gives home country policies pride of place. Origin countries can craft policies that encourage diaspora re-engagement, incentivizing individuals to return home. Dual citizenship, for example, is an extension of extraterritorial rights, allowing migrants to retain full legal status in their home country. Dual citizenship “decreases the transaction costs associated with entering a host country’s labor market and makes it easier for migrants to return home” (Leblang, 2017 , p. 77). This leads migrants to invest their financial resources in the form of remittances back home as well as their valuable human capital. When states provide such extraterritorial rights, expatriates are 10% more likely to remit and 3% more likely to return home. Dual citizenship is also associated with a doubling of the dollar amount of remittances received by a home country (Leblang, 2017 ). These striking results suggest that in addition to the power of migrants to affect cross-border flows of money and people, countries of origin can also play a significant role.
Conclusion and Future Directions
This brief article has attempted to synthesize a broad range of literature from political science, economics, sociology, migration studies, and more to construct an account of international labor migration. To do so, the migratory process was broken down into distinct stages and decision points, focusing particularly on the decision to migrate, destination choice, and the re-engagement of migrants with their homeland. In doing so, the article also discussed the interlinkages of international migration with other fields of study in international political economy, including cross-border financial flows, trade, and investment. Through a multiplicity of approaches, we have gained a greater understanding of why people decide to move, why they decide to move to one country over another, and how and why they engage with the global economy and their homeland. Despite this intellectual progress, there remain many paths for future research at each stage of the migratory process; we highlight just a few of them here.
We know that income differentials, social ties, and local political conditions are important variables influencing the migration process. Yet the question remains: why do a small but growing number of people choose to leave while the overwhelming majority of people remain in their country of birth? Here, individual- or family-level subjective characteristics may be significant. There are a handful of observational studies that explore the relationship between subjective well-being or life satisfaction and the intention to migrate, with the nascent consensus being that life dissatisfaction increases the intention to migrate (Cai, Esipova, Oppenheimer, & Feng, 2014 ; Otrachshenko & Popova, 2014 ; Nikolova & Graham, 2015 ). But more research on intrinsic or subjective measures is needed to understand (a) their independent importance more fully and (b) how they interact with objective economic, political, and social factors. For instance, do those who are more optimistic migrate in larger numbers? Do minority individuals who feel they live in an environment in which diversity is not accepted feel a greater urge to leave home? Synthesizing these types of subjective variables and perceptions with the more prominent gravity-style models could result in a more complete picture of the international migration process.
For the “typical” migrant, one who is relatively less educated than the population in the chosen destination and does not have specialized skills, social networks are key to minimizing the risk of migrating and quickly tapping into economic opportunities in destination countries. Does this remain true for those who are highly educated? Although little empirical research exists on the topic, greater human capital and often-accompanying financial resources may operate as a substitute for the advantages offered by social networks, such as housing, overcoming linguistic barriers, and finding gainful employment. This would indicate that the “friends and family effect” is not as influential for this subset of migrants. Economic considerations, such as which destination offers the largest relative wage differential, or political considerations, such as the ease of quickly acquiring full citizenship rights, may matter more for the highly skilled. Neoclassical economic models of migration may best capture the behavior of migrants who hold human capital and who have the financial resources to independently migrate in a way that maximizes income or utility more broadly.
Since we have focused on international migration as a series of discrete decision points in this article, we have perhaps underemphasized the complexity of the physical migration process. In reality, migrants often do not pick a country and travel directly there, but travel through (perhaps several) countries of transit such as Mexico, Morocco, or Turkey along the way (Angel Castillo, 2006 ; Natter, 2013 ; Icduygu, 2005 ). There is little existing theoretical work to understand the role of transit countries in the migratory process, with much of it focusing on the potential for cooperation between destination and transit countries in managing primarily illegal immigration (Kahana & Lecker, 2005 ; Djajic & Michael, 2014 ; Djajic & Michael, 2016 ). Another related strand of the literature focuses on how wealthy destination countries are “externalizing” their immigration policy, encompassing a broader part of the migratory process than simply crossing a physically demarcated border (Duvell, 2012 ; Menjivar, 2014 ). But many questions remain, such as the following: how do we understand those who desire to enter, say, the United States, but instead relocate permanently to Mexico along the way? How do countries of transit handle the pressure of transit migrants, and how does this affect economic and political outcomes in these countries?
Finally, the focus of nearly all literature on international migration (and this article as a byproduct) implicitly views advanced economies as the only prominent destinations. However, this belies the fact that 38% of all migration stays within the “Global South” (World Bank, 2016 ). While there is certainly some literature on this phenomenon (see Ratha & Shaw, 2007 ; Gindling, 2009 ; Hujo & Piper, 2007 ), international political economy scholars have yet to sufficiently tackle this topic. The overarching research question here is: do the same push and pull factors that influence the decision to migrate and destination choice apply to those who migrate within the Global South? Do we need to construct new theories of international migration with less emphasis on factors such as wage differentials and political tolerance, or are these sufficient to understand this facet of the phenomenon? If we fail to answer these questions, we may miss explaining a significant proportion of international migration with its own consequences and policy implications.
- Abreu, A. (2012). The New Economics of Labor Migration: Beware of Neoclassicals Bearing Gifts. Forum for Social Economics , 41 (1), 46–67.
- Acosta, P. , Calderon, C. , Fajnzybler, P. , & Lopez, H. (2008). What Is the Impact of International Remittances on Poverty and Inequality in Latin America? World Development , 36 (1), 89–114.
- Adams, R., Jr. (2011). Evaluating the Economic Impact of International Remittances on Developing Countries Using Household Surveys: A Literature Review. Journal of Development Studies , 47 (6), 809–828.
- Adams, R., Jr. , & Cuecuecha, A. (2010). Remittances, Household Expenditure and Investment in Guatemala. World Development , 38 (11), 1626–1641.
- Adams, R., Jr. , & Page, J. (2005). Do International Migration and Remittances Reduce Poverty in Developing Countries? World Development , 33 (10), 1645–1669.
- Ahmed, F. Z. (2012). The Perils of Unearned Foreign Income: Aid, Remittances, and Government Survival. American Political Science Review , 106 (1), 146–165.
- Akerman, S. (1976). Theories and Methods of Migration Research. In H. Runblom & H. Norman (Eds.), From Sweden to America: A History of the Migration . Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
- Angel Castillo, M. (2006). Mexico: Caught Between the United States and Central America . Migration Policy Institute.
- Aubry, A. , Rapoport, H. , & Reshef, A. (2016). Migration, FDI, and the Margins of Trade. Mimeo . Paris School of Economics.
- Aydemir, A. , & Robinson, C. (2008). Global Labour Markets, Return, and Onward Migration. Canadian Journal of Economics , 41 (4), 1285–1311.
- Böcker, A. (1994). Chain Migration over Legally Closed Borders: Settled Immigrants as Bridgeheads and Gatekeepers. Netherlands Journal of Social Sciences , 30 (2), 87–106.
- Borjas, G. J. (1989). Economic Theory and International Migration. International Migration Review , 23 (3), 457–485.
- Borjas, G. J. , & Bratsberg, B. (1996). Who Leaves? The Outmigration of the Foreign-Born. Review of Economics and Statistics , 41 (4), 610–621.
- Bratsberg, B. , Raaum, O. , & Sørlie, K. (2007). Foreign-Born Migration to and from Norway. In Ç. Özden & M. Schiff (Eds.), International Migration, Economic Development and Policy . New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Brücker, H. , & Schröder, P. J. H. (2011). Migration regulation contagion. European Union Politics , 12 (3), 315–335.
- Cai, R. , Esipova, N. , Oppenheimer, M. , & Feng, S. (2014). International Migration Desires Related to Subjective Well-Being. IZA Journal of Migration , 3 (8), 1–20.
- Castles, S. (2004). Why Migration Policies Fail. Ethnic and Racial Studies , 27 (2), 205–227.
- Cazzuffi, C. , & Modrego, F. (2018). Place of Origin and Internal Migration Decisions in Mexico. Spatial Economic Analysis , 13 (1), 1–19.
- Chami, R. , Fullenkamp, C. , & Jahjah, S. (2003). Are Immigrant Remittance Flows a Source of Capital for Development ? IMF Working Paper 03/189.
- Clark, X. , Hatton, T. J. , & Williamson, J. G. (2007). Explaining US Immigration, 1971–1998. Review of Economics and Statistics , 89 (2), 359–373.
- Clemens, M. A. (2014). Does Development Reduce Migration ? IZA Discussion Paper No. 8592.
- Collier, P. , & Hoeffler, A. (2014). Migration, Diasporas and Culture: An Empirical Investigation . Unpublished manuscript.
- Collyer, M. (2006). When Do Social Networks Fail to Explain Migration? Accounting for the Movement of Algerian Asylum-Seekers to the UK. Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies , 31 (4), 699–718.
- Constant, A. , & Massey, D. S. (2002). Return Migration by German Guestworkers: Neoclassical versus New Economic Theories. International Migration , 4 0(4), 5–38.
- Cooray, A. , & Schneider, F. (2016). Does Corruption Promote Emigration? An Empirical Examination. Journal of Population Economics , 29 , 293–310.
- Cornelius, W. A. , & Tsuda, T. (2004). Controlling Immigration: The Limits of Government Intervention . Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Cowen, R. (1997). Global Diasporas: An Introduction . London: Routledge.
- Czaika, M. , & de Haas, H. (2016). The Effect of Visas on Migration Processes. International Migration Review , 51 (4), 893–926.
- Dao, T. H. , Docquier, F. , Parsons, C. , & Peri, G. (2018). Migration and Development: Dissecting the Anatomy of the Mobility Transition. Journal of Development Economics , 132 , 88–101.
- Dao, T. H. , Docquier, F. , Parsons, C. , & Peri, G. (2016). Migration and Development: Dissecting the Anatomy of the Mobility Transition . IZA Discussion Paper No. 10272.
- De Haas, H. (2007). Turning the Tide? Why Development Will Not Stop Migration. Development and Change , 38 , 819–841.
- Dimant, E. , Krieger, T. , & Meierrieks, D. (2013). The Effect of Corruption on Migration, 1985–2000. Applied Economics Letters , 20 (13), 1270–1274.
- Djajic, S. , & Michael, M. S. (2014). Controlling Illegal Immigration: On the Scope for Cooperation with a Transit Country. Review of International Economics , 22 (4), 808–824.
- Djajic, S. , & Michael, M. S. (2016). Illegal Immigration, Foreign Aid, and the Transit Countries. CESifo Economic Studies , 572–593.
- Dumont, J.-C. , & Spielvogel, G. (2008). Return Migration: A New Perspective. International Migration Outlook 2008 . OECD, 166–212.
- Dustmann, C. , & Okatenko, A. (2014). Out-Migration, Wealth Constraints, and the Quality of Local Amenities. Journal of Development Economics , 110 , 52–63.
- Dustmann, C. , & Weiss, Y. (2007). Return Migration: Theory and Empirical Evidence from the UK. British Journal of Industrial Relations , 45 (2), 236–256.
- Duvell, F. (2012). Transit Migration: A Blurred and Politicized Concept. Population, Space and Place , 18 , 415–427.
- Easterlin, R. A. (1961). Influences in European Overseas Emigration Before World War I. Economic Development and Cultural Change , 9 (3), 331–351.
- Epstein, G. (2008). Herd and Network Effects in Migration Decision-Making. Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies , 34 (4), 567–583.
- Epstein, G. , & Gang, I. (2006). The Influence of Others on Migration Plans. Review of Development Economics , 10 (4), 652–665.
- Escriba-Folch, A. , Meseguer, C. , & Wright, J. (2015). Remittances and Democratization. International Studies Quarterly , 59 (3), 571–586.
- European Asylum Support Office . (2016). The Push and Pull Factors of Asylum-Related Migration: A Literature Review .
- Faist, T. (2000). The Volume and Dynamics of International Migration and Transnational Social Space . New York: Oxford University Press.
- Fitzgerald, J. , Leblang, D. , & Teets, J. C. (2014). Defying the Law of Gravity: The Political Economy of International Migration. World Politics , 66 (3), 406–445.
- Fussel, E. (2010). The Cumulative Causation of International Migration in Latin America. Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science , 630 , 162–177.
- Fussel, E. , & Massey, D. (2004). The Limits to Cumulative Causation: International Migration from Mexican Urban Areas. Demography , 41 (1), 151–171.
- Gindling, T. H. (2009). South–South Migration: The Impact of Nicaraguan Immigrants on Earnings, Inequality, and Poverty in Costa Rica. World Development , 37 (1), 116–126.
- Gould, J. D. (1979). European Inter-Continental Emigration 1815–1914: Patterns and Causes. Journal of European Economic History , 8 (3), 593–679.
- Greif, A. (1989). Reputation and Coalitions in Medieval Trade: Evidence on the Maghribi Traders. Journal of Economic History , 49 (4), 857–882.
- Greif, A. (1993). Contract Enforceability and Economic Institutions in Early Trade: The Maghribi Traders’ Coalition. American Economic Review , 83 (3), 525–548.
- Grogger, J. , & Hanson, G. H. (2011). Income Maximization and the Selection and Sorting of International Migrants. Journal of Development Economics , 95 , 42–57.
- Gupta, S. , Davoodi, H. , & Tiongson, E. (2001). Corruption and the Provision of Healthcare and Education Services. In A. Jain (Ed.), The Political Economy of Corruption . New York: Routledge.
- Hainmueller, J. , & Hiscox, M. J. (2010). Attitudes toward Highly Skilled and Low-Skilled Immigration: Evidence from a Survey Experiment. American Political Science Review , 104 (1), 61–84.
- Hainmueller, J. , & Hopkins, D. J. (2015). The Hidden Immigration Consensus: A Conjoint Analysis of Attitudes toward Immigrants. American Journal of Political Science , 59 (3), 529–548.
- Harris, J. R. , & Todaro, M. P. (1970). Migration, Unemployment and Development: A Two-Sector Analysis. American Economic Review , 60 (1), 126–142.
- Hatton, T. J. , & Williamson, J. G. (1994). What Drove the Mass Migrations from Europe in the Late Nineteenth Century? Population and Development Review , 20 (3), 533–559.
- Hatton, T. J. , & Williamson, J. G. (2011). Are Third World Emigration Forces Abating? World Development , 39 (1), 20–32.
- Haug, S. (2008). Migration Networks and Migration Decision-Making. Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies , 34 (4), 585–605.
- Helbling, M. , Bjerre, L. , Römer, F. , & Zobel, M. (2017). Measuring Immigration Policies: The IMPIC-Database. European Political Science, 16 (1), 79–98.
- Helbling, M. , & Leblang, D. (forthcoming). Controlling Immigration? European Journal of Political Research .
- Hirschman, A. O. (1970). Exit, Voice, and Loyalty: Responses to Decline in Firms, Organizations, and Sates . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Hirsh, A. O. (1978). “Exit, Voice, and the State.” World Politics , 31 (1), 90–107.
- Hujo, K. , & Piper, N. (2007). South–South Migration: Challenges for Development and Social Policy. Development , 50 (4), 1–7.
- Icduygu, A. (2005). Transit Migration in Turkey: Trends, Patterns, and Issues . Euro-Mediterranean Consortium for Applied Research on International Migration Research Report 2005/04.
- Javorcik, B. , Özden, C. , Spatareanu, M. , & Neagu, C. (2011). Migrant Networks and Foreign Direct Investment. Journal of Development Economics , 94 , 231–241.
- Kahana, N. , & Lecker, T. (2005). Competition as a Track for Preventing Illegal Immigration. Economics of Governance , 6 , 33–39.
- Kapur, D. (2014). Political Effects of International Migration. Annual Review of Political Science , 17 , 479–502.
- Kugler, M. , Levinthal, O. , & Rapoport, H. (2017). Migration and Cross-Border Financial Flows . World Bank Policy Research Working Paper 8034.
- Leblang, D. (2010). Familiarity Breeds Investment: Diaspora Networks and International Investment. American Political Science Review , 104 (3), 584–600.
- Leblang, D. (2017). Harnessing the Diaspora: Dual Citizenship, Migrant Return, and Remittances. Comparative Political Studies , 50 (1), 75–101.
- Lewis, A. W. (1954). Economic Development with Unlimited Supplies of Labor. The Manchester School , 22 (2), 139–191.
- Lichter, D. T. (1983). Socioeconomic Returns to Migration among Married Women. Social Forces , 62 (2), 487–503.
- Light, I. , Bernard, R. B. , & Kim, R. (1999). Immigrant Incorporation in the Garment Industry of Los Angeles. International Migration Review , 33 (1), 5–25.
- Lokshin, M. , Bontch-Osmolovski, M. , & Glinskaya, E. (2010). Work-Related Migration and Poverty Reduction in Nepal. Review of Development Economics , 14 (2), 323–332.
- Massey, D. S. (1988). Economic Development and International Migration in Comparative Perspective. Population and Development Review , 14 (3), 383–413.
- Massey, D. S. (1990). Social Structure, Household Strategies, and the Cumulative Causation of Migration. Population Index , 56 (1), 3–26.
- Massey, D. S. , Arango, J. , Hugo, G. , Kouaouci, A. , Pellegrino, A. , & Taylor, J. E. (1993). Theories of International Migration: A Review and Appraisal. Population and Development Review , 19 (3), 431–466.
- Massey, D. S. , & Garcia España, F. (1987). The Social Process of International Migration. Science , 237 (4816), 733–738.
- Mauro, P. (1998). Corruption and the Composition of Government Expenditure. Journal of Public Economics , 69 , 263–279.
- Menjivar, C. (2014). Immigration Law Beyond Borders: Externalizing and Internalizing Border Controls in an Era of Securitization. Annual Review of Law and Social Science , 10 , 353–369.
- Messina, A. M. (2007). The Logics and Politics of Post-WWII Migration to Western Europe . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Mincer, J. (1978). Family Migration Decisions. Journal of Political Economy , 86 (51), 749–773.
- Miller, M. K. , & Peters, M. E. (2018). Restraining the Huddled Masses: Migration Policy and Autocratic Survival . British Journal of Political Science .
- Mo, P. H. (2001). Corruption and Economic Growth. Journal of Comparative Economics , 29 , 66–79.
- Money, J. (1999). Fences and Neighbors: The Political Geography of Immigration Control . Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- Morrison, D. R. , & Lichter, D. T. (1988). Migration and Female Employment. Journal of Marriage and Family , 50 (1), 161–172.
- Natter, K. (2013). The Formation of Morocco’s Policy Towards Irregular Migration (2000–2007): Political Rationale and Policy Processes. International Migration , 52 (5), 15–28.
- Nikolova, M. , & Graham, C. (2015). Well-Being and Emigration Intentions: New Evidence from the Gallup World Poll. Unpublished manuscript.
- Nyblade, B. , & O’Mahony, A. (2014). Migrants Remittances and Home Country Elections: Cross-National and Subnational Evidence. Studies in Comparative International Development , 49 (1), 44–66.
- O’Mahony, A. (2012). Political Investment: Remittances and Elections. British Journal of Political Science , 43 (4), 799–820.
- Ortega, F. , & Peri, G. (2013). The Effect of Income and immigration Policies on International Migration. Migration Studies , 1 (1), 47–74.
- Otrachshenko, V. , & Popova, O. (2014). Life (Dis)satisfaction and the Intention to Migrate: Evidence from Central and Eastern Europe. Journal of Socio-Economics , 48 , 40–49.
- Papademetriou, D. , & Sumption, M. (2011). Rethinking Points Systems and Employer-Based Selected Immigration . Migration Policy Institute.
- Peters, M. (2017). Trading Barriers: Immigration and the Remaking of Globalization . Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Poprawe, M. (2015). On the Relationship between Corruption and Migration: Evidence from a Gravity Model of Migration. Public Choice , 163 , 337–354.
- Portes, A. (Ed.). (1995). The Economic Sociology of Immigration . New York: Russell Sage Foundation.
- Portes, A. , & Böröcz, J. (1989). Contemporary Immigration: Theoretical Perspectives on its Determinant and Modes of Incorporation. International Migration Review , 23 (3), 606–630.
- Rapoport, H. , & Docquier, F. (2006). The Economics of Migrants’ Remittances. In S.-C. Kolm & J. M. Ythier (Eds.), Handbook on the Economics of Giving, Altruism and Reciprocity . New York: Elsevier-North Holland.
- Ratha, D. , & Shaw, W. (2007). South-South Migration and Remittances . World Bank WP 102.
- Rauch, J. E. , & Trindade, V. (2002). Ethnic Chinese Networks in International Trade. Review of Economics and Statistics , 84 (1), 116–130.
- Ravenstein, E. G. (1885). The Laws of Migration. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society of London , 48 (2), 167–235.
- Sassen, S. (1995). Immigration and Local Labour Markets. In A. Portes (Ed.), The Economic Sociology of Immigration . New York: Russell Sage Foundation.
- Sassen, S. (1996). Losing Control? Sovereignty in the Age of Globalization . New York: Columbia University Press.
- Schultz, T. W. (1961). Investment in Human Capital. American Economic Review , 51 (1), 1–17.
- Severin, T. , & Martin, M. (2018). German Parties Edge Closer to Coalition with Migration Deal . Reuters, February 2.
- Sjaastad, L. A. (1962). The Costs and Returns of Human Migration. Journal of Political Economy , 70 (5), 80–93.
- Stark, O. (1984). Rural-To-Urban Migration in LDCs: A Relative Deprivation Approach. Economic Development and Cultural Change , 32 (3), 475–486.
- Stark, O. , & Bloom, D. E. (1985). The New Economics of Labor Migration. American Economic Review , 75 (2), 173–178.
- Stark, O. , & Levhari, D. (1982). On Migration and Risk in LDCs. Economic Development and Cultural Change , 31 (1), 191–196.
- Stark, O. , & Taylor, J. E. (1991). Migration Incentives, Migration Types: The Role of Relative Deprivation. The Economic Journal , 101 (408), 1163–1178.
- Stark, O. , & Yitzhaki, S. (1988). Migration as a Response to Relative Deprivation. Journal of Population Economics , 1 (1), 57–70.
- Taylor, J. E. (1999). The New Economics of Labour Migration and the Role of Remittances in the Migration Process. International Migration , 37 (1), 63–88.
- Todaro, M. P. (1969). A Model of Labor Migration and Urban Employment in Less Developed Countries. American Economic Review , 59 (1), 138–148.
- Tomaske, J. A. (1971). The Determinants of Intercountry Differences in European Emigration: 1881–1900. Journal of Economic History , 31 (4), 840–853.
- Transparency International . (2018). What is corruption
- United Kingdom Independence Party . (2015). UKIP Launches Immigration Policy .
- United Nations Population Division . (2012). Trends in Total Migrant Stock .
- United Nations Population Division . (2013). International Migration: Age and Sex Distribution. Population Facts, September.
- United States Citizenship and Immigration Services . (2018). H-1B Fiscal Year 2018 Cap Season .
- USA Today . (2014) (20 November). Full Text: Obama’s Immigration Speech .
- Vanderkamp, J. (1971). Migration Flows, Their Determinants and the Effects of Return Migration. Journal of Political Economy , 79 (5), 1012–1031.
- Vertovec, S. (2004). Migrant Transnationalism and Modes of Transformation. International Migration Review , 38 (3), 970–1001.
- Waldinger, R. (2008). Between “Here” and “There”: Immigrant Cross-Border Activities and Loyalties. International Migration Review , 42 (Spring), 3–29.
- Weidenbaum, M. , & Hughes, S. (1996). The Bamboo Network: How Expatriate Chinese Entrepreneurs are Creating a New Economic Superpower in Asia . New York: Martin Kessler Books.
- World Bank . (2016). Migration and Remittances Factbook 2016 . 3rd ed. Washington, DC: World Bank Group.
- Yang, D. (2008). International Migration, Remittances, and Household Investment: Evidence from Philippine Migrants’ Exchange Rate Shocks. The Economic Journal , 118 (528), 591–630.
- Yang, D. , & Martinez, C. (2006). Remittances and Poverty in Migrants Home Areas: Evidence from the Philippines. In C. Ozden & M. Schiff (Eds.), International Migration, Remittances and the Brain Drain . Washington, DC: World Bank.
- Zaiceva, A. , & Zimmerman, K. (2014). Migration and the Demographic Shift. IZA Discussion Paper #8743 .
- Zelinsky, W. (1971). The Hypothesis of the Mobility Transition. Geographical Review , 61 (2), 219–249.
1. Our use of the term international labor migration follows academic and legal conventions; we use the term migration to refer to the voluntary movement of people across national borders, either in a temporary or permanent fashion. This excludes any discussion of refugees, asylum seekers, or any other groups that are forced to migrate.
2. We do not have space in this article to delve into the theoretical and empirical work unpacking the effect of demographic characteristics—age, gender, marital status, household size, and so forth on the migration decision and on subsequent flows of migrants. For comprehensive reviews, see Lichter ( 1983 ), Morrison and Lichter ( 1988 ); United Nations Population Division ( 2013 ); and Zaiceva and Zimmerman ( 2014 ).
3. Zelinsky ( 1971 ) originally identified this relationship and termed it mobility transition curve . A wealth of empirical work supports Zelinsky’s descriptive theory in a number of contexts (see Akerman, 1976 ; Gould, 1979 ; Hatton & Williamson, 1994 ; and Dao et al., 2016 ).
4. For a review of the arguments as well as some empirical tests, see Miller and Peters ( 2018 ) and Docquier, Lodigiani, Rapoport, and Schiff ( 2018 ).
5. Transparency International. “What is corruption?”
6. For example, former United Kingdom Independence Party leader Nigel Farage has called for the United Kingdom to adopt an immigration system that only allows in highly skilled migrants (“UKIP launches immigration policy”). In 2014, US President Barack Obama emphasized that he wanted to attract international students to American universities and that they “create jobs, businesses, and industries right here in America” (USA Today: “Full text: Obama’s immigration speech”). A key issue in Germany’s 2018 government formation was the creation of skill-based migration laws (Severin & Martin, 2018 ).
7. For a more comprehensive review, see Rapoport and Docquier ( 2006 ); and Adams ( 2011 ).
Related Articles
- Space, Mobility, and Legitimacy
- Immigration and Foreign Policy
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Politics. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 08 May 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|109.248.223.228]
- 109.248.223.228
Character limit 500 /500
Migration as a Social Problem
Sociologists have over a long time studied tribulations of migration and its consequences across and within cultures. Migration is defined in a number of ways but for this paper, it shall be used to refer to the movement of persons from one country or locality to another as defined by the free online Dictionary. Other words that are closely related to migration are immigration (migration into a place) and emigration (migrating from a place) over the years migration has brought with it mixed reactions and results; it, therefore, becomes difficult to conclude whether it brings problems or blessings. New immigration laws are set up to stabilize the general living conditions of migrants and immigrants.
The tradition of migration has continued over time and now it is time to examine the new and changing faces of it. Usually, the main supposition in studying migrants is that the central culture into which they migrate wields pressure to change through culture, organizations, and personal relations; however, incoming migrants resist the pressure to change. Therefore the most common model is whereby the migrants are marginalized socially, politically, and even economically, in addition to the conflict that the immigrants face. The migration phenomenon also tries to point out that when the four estates of society (government, military, church, and media) fail to function then the citizen is left with no option but to move to another place. It is at this time that the basic needs of that individual cannot be met by the structure of the society he/she belongs (Pugad ng Muharlika, 2008).
As identified by some readings, there are only two main things that make a citizen of a country migrate; the threat to peace and order in a region which may, in turn, endanger human life, and when one is unable to make both ends meet. However, these causes have been reviewed and amplified such that what we have today is many factors depending on where the individual comes from and where he is destined for, the reasons for leaving his homeland, and so on. The most common sources of migration include famine, unemployment, wars, and political persecution. These factors therefore will assist the receiving government to help the immigrants accordingly. For example, in a case where the immigrants are refugees of war, the government will need more than just humanitarian but also psychological assistance. On the other hand, if the immigrants have gone to pursue further education, their requirements from the government will not be as much as their refugee counterparts.
As an issue of social, economic, and political issues, migration has attracted a lot of responses from different people, individuals, and groups. The most dominant social problems result from the place of destination to within the place of destination. This implies migration within and outside the country. The major problems of migration include poverty, acculturation, education, social adjustment, employment, housing, and family difficulties. These problems are understood in different ways; how they affect the migrants, immigrants, their origin, and destination. Family problems that affect the immigrants include departing from the support system of the extended family. Suppose one goes away from his/her home, it is quite automatic that at one time that particular individual will feel homesick and miss the company of the immediate relatives. In case the migrant’s main aim was to look for a job in his destination then he misses it, he undergoes stress and financial difficulties in such events. There is also the problem of differing awareness about the concepts of basic human rights. Poverty among immigrants in the US continues to take an ascending motion because of the rapid increase in the numbers of these groups of people.
It is of great significance to incorporate other policies with the government policy to have a better way of solving this problem. There are policies designed to express the needs of migrants and immigrants even though they are heavily inclined towards the support of the smooth operation of local control and administration. Providing direct services by offering education to migrants and immigrants is a sure way of solving the problems of this group of people. This is because; amongst the critical issues that affect the migrants and immigrants are is basic literacy and an effective way of achieving this goal in a population that is always on the move.
Countries that experience a high number of refugees, for example, the US, should allow a flexible quota system that would be responsive to the variations in labor needs. The government should look more closely at the various migrant groups; their needs and how to advance them the required aid accordingly. The government should also attend to the social welfare issues of the immigrants (Dail P.W. 1988).
In cases where there exist cases of migration in nations that are close to one another, for example, Zimbabwe and South Africa or Mexico and the USA, the solution is not usually easy and it greatly depends on how far the governments involved are willing to go to work together in developing public policies of both counties’ interest. For the United States and Mexico, a long time compromise between the two governments can guarantee to venture into the Mexican economy to harmonize and keep a good balance in both labor markets.
According to Dr. Demetrios Papademetriou, migration is dreaded by the nations of destination because of the negative impacts that it is associated with; illegality, creation of divided communities, and labor market displacement. He discussed that the USA fell short of adequate legal channels to let people work in the country as he responded to illegality. He also added that the labor market on the other hand could absorb more people than it does currently and that the slow administrative process was responsible for slowing down immigration.
The impact of immigrants on the society of any given society and its economy is assessed and many nations have come up with ways to try and put migration under considerable control. Furthermore, the affected nations have accordingly made policies to deal with problems that might come up as a result of migration.
Aydin. R, Elvers. C 2006 World Migration: Economic and Social Impacts Challenges for implementing the recommendations of the Global Commission on International Migration in Germany and the United States.
Castaneda. D Economic and political perspective of migration in North America.
Rosenberg M, Ralph H. T 1990 Social Psychology: Sociological Perspectives .
Sociological perspective of migration, structural functionalism and the four estates of society .
Dail P.W 1988 NCBI Immigration and migration in America: social impact and social Response .
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, October 20). Migration as a Social Problem. https://studycorgi.com/migration-as-a-social-problem/
"Migration as a Social Problem." StudyCorgi , 20 Oct. 2021, studycorgi.com/migration-as-a-social-problem/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) 'Migration as a Social Problem'. 20 October.
1. StudyCorgi . "Migration as a Social Problem." October 20, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/migration-as-a-social-problem/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Migration as a Social Problem." October 20, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/migration-as-a-social-problem/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "Migration as a Social Problem." October 20, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/migration-as-a-social-problem/.
This paper, “Migration as a Social Problem”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: December 13, 2023 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Problems and solutions to the international migrant crisis
Chris mckenna and chris mckenna office of communications brennan hoban bh brennan hoban office of communications.
December 18, 2017
For more information on refugees, migrants, and internally displaced persons, click here , and consider signing up for “ This Week in Foreign Policy ,” a weekly roundup of the most important stories and analysis from the Foreign Policy program at Brookings.
On December 4, 2000, the United Nations declared December 18 as International Migrants Day . The U.N. did so to recognize the increasing number of migrants around the world and to reaffirm member nations’ commitments to migrants’ freedoms and human rights.
Nearly two decades later, compounding issues around the world have led to over 65 million people displaced abroad or within their own borders—the most ever recorded by the United Nations Commission on Human Rights (UNHCR). In recognition of the complexity of this issue and the millions of people displaced around the world, we want to highlight what Brookings scholars are saying about the greatest challenges and successes in global migration today.
The state of refugees, migrants, and internally displaced people by the numbers
In an episode of the Brookings Cafeteria podcast earlier this year, Jessica Brandt, fellow in Institutional Initiatives, provided context on the scale of the global refugee crisis and identified steps that the United States and international community should take in order to provide relief. Citing data from a UNHCR report , Brandt pointed out that on average, 24 people per minute, per day worldwide were forced to flee their home in 2015. About 1 out of every 113 people worldwide were either asylum seekers, refugees, or internally displaced, and about half of the world’s refugee population was under the age of 18.
Two-thirds of the world’s displaced population actually remain within the borders of their own country, as Elizabeth Ferris, nonresident senior fellow in the Foreign Policy program, points out. In June, Ferris unpacked the numbers of global refugees , and noted that the internationally displaced population—which accounts for most of the growth in overall global displacement—has grown from 25 million in 1992 to 40.3 million in 2016 (although at least some of that increase is likely due to greater awareness of internal displacement and better tracking).
The Syrian civil war
After almost 7 years of civil war, half of Syria’s population has been displaced, creating over 6 million refugees, about a third of the world’s total refugee population . Turkey hosts half of these refugees, with large numbers in Lebanon and Jordan, too, the “frontline” states on Syria’s border . Lebanon hosts more than 1 million refugees, which amounts to more than one in five people in the country. In Jordan, that number is one in ten at least.
According to Brandt and co-author Robert McKenzie, large flows of displaced people into these neighboring states causes real strains. They note “the sheer scale of the refugee crisis poses unparalleled humanitarian, economic, and political challenges in an already fragile region.”
Many of these refugees have limited access to labor market opportunities, education, and other public goods and, according to Brandt and McKenzie, are often forced to work in the “grey economy” where they are vulnerable to exploitation. They write that lack of resources available for refugees, “compounded by a myriad of legal, bureaucratic, and administrative challenges,” makes it difficult for international NGOs to provide humanitarian assistance on-the-ground.
Just last week, Brookings hosted an event with a young Syrian refugee, Saria Samakie, who candidly discussed his story and experience as a refugee in America. In the short clip below, Samakie answers a question from the audience on when and under what conditions he believes people will begin to return to Syria.
Other crises around the globe
While Syria is understandably a focal point in the refugee crises, there are many other parts to the world’s migration story. We should not overlook the people attempting to cross the Mediterranean from Libya to Italy , Rohingya Muslims in Myanmar fleeing religious persecution into Bangladesh and India, and thousands of Dominicans stateless in the Caribbean , about each of which Brookings scholars have written.
After Syria, more refugees come from Afghanistan than any other country in the world. Many are in Pakistan, but in a recent analysis, Brookings Nonresident Fellow Madiha Afzal explains how over 600,000 have already repatriated back to a country that is still under attack by the Afghan Taliban. According to Afzal, this “voluntary” repatriation is often enforced through police extortion, bribery, and the confiscation of legal documents, and supported by Pakistan’s narrative that Afghan refugees are economic burdens, criminals, and terrorists.
Cities are on the frontlines and should be part of the solution
Now more than ever, refugees are going to cities and they are staying longer. Cities would like to step up and play an even bigger role in the U.N.’s global compact on migration, but President Trump “wants out,” in the words of Jessica Brandt.
Brookings Centennial Scholar Bruce Katz and Jessica Brandt explain that many of the elements critical to an effective emergency response, as well as to long-term integration, are designed, delivered, and financed at the local level . Those elements include housing, healthcare, education, skills training, and social services of every sort.
Today, roughly 60 percent of the world’s 22 million refugees and 80 percent of the world’s internally displaced population reside in cities rather than in camps. This puts a heavy strain on cities, especially as the length of displacement increases. During the early 1990s, the average length of displacement was nine years. Today, it is roughly 20. At the end of last year, more than 11 million refugees—two-thirds of the global total—were in a protracted situation.
Brandt explains that cities need a seat at the table when developing an approach to the refugee and migrant crisis. She also argues that the UNHCR should incorporate towns and cities with sizeable refugee populations into the testing and development of new approaches. UNHCR should also encourage U.N. member states to engage in meaningful collaboration with municipal authorities by facilitating the flow of technical expertise and resources to towns and cities. Likewise, Brandt recommends that the international humanitarian community should develop ways to source innovative approaches to refugee integration directly from cities.
The politics of migration and the refugee crises
In his first year in office, President Trump has tried on multiple occasions to fulfill his campaign promise of “a total and complete shutdown of Muslims entering the United States.” Brookings experts have written extensively ( here , here , and here ) on the different renditions of these travel bans, issued via executive order, as well as their battles in court . As it stands today, the Supreme Court has granted a full stay on the third version of Trump’s executive order while its legality is being challenged in appeals courts.
Brookings scholars rebutted arguments that these orders are necessary to ensure the safety and security of Americans. As Brandt explained on the Brookings Cafeteria podcast in March, America already has an extremely thorough vetting system for refugees, and of the nearly 860,000 refugees resettled by the United States since 9/11 only three individuals have been convicted on terrorism-related charges (all were for plots outside of the United States and none were successful).
Nonetheless, Americans are split in their support for refugee resettlement within the United States . A survey conducted during the 2016 presidential race by Brookings Nonresident Senior Fellow Shibley Telhami showed that only 59 percent of Americans support the United States taking in refugees from conflict-prone areas in the Middle East after they have been screened for security risks. Studies also show that Europeans are more likely to be opposed to immigration than people from any other continent .
In contrast with some of President Trump’s assertions from the campaign trail, David M. Rubenstein Fellow Dany Bahar illustrates the positive link between immigration and economic growth . Bahar explains that while immigrants represent about 15 percent of the general U.S. workforce, they account for around a quarter of entrepreneurs and a quarter of investors in the United States, and that over one-third of new firms have at least one immigrant entrepreneur in its initial leadership team.
Related Content
Khalid Koser
July 2, 2012
Jessica Brandt
September 20, 2016
September 23, 2016
Vanda Felbab-Brown, Fred Dews
November 9, 2023
Kemal Kirişci
September 25, 2023
Reva Dhingra, Sophie Roehse
August 22, 2023
The biggest issues facing migrants today - and what we can do to solve them

The contribution immigrants make to their host communities is huge. So why are they still so misunderstood? Image: REUTERS/ Juan Medina
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Ratna Omidvar

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Migration is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:.
In the management of global migration, the world is clinging to outdated infrastructure and patterns of mobility, says Canadian senator Ratna Omidvar, member of the Global Future Council on Migration. The contribution immigrants make to their host communities is not widely understood, and countries need to begin showing an interest in all migrants, not just skilled labour.
How do you see the state of migration today?
In the management of global migration, we are clinging to outdated infrastructure and patterns of mobility. We operate reactively instead of planning for the future.
I look back at the major migration trends of the last decade, and I wonder what could be different had we been prepared. The last decade gave us the largest number of displaced people since the Second World War, a steadily rising death toll in the Mediterranean, populist politics that traded on fear of immigration, and new environmental factors driving people from their homes. With the clarity of hindsight, planning for these realities could have strengthened the wellbeing of host communities, supported immigrants to move and prosper, and even saved lives.
Which issues related to migration do you perceive to be misunderstood or inadequately appreciated?
The evidence of the contributions immigrants can make to their host communities is not widely understood or accepted. This is true of both camps: those who think immigration is bad, and those who think it is good. The impact of immigration on communities is nuanced, and in many studies we see evidence of different outcomes due to different policy and social contexts. Robert Putnam found evidence of ebbing trust leading people to “hunker down” in diverse American communities, while Keith Banting found the opposite effect in equally diverse Canadian communities, where trust and engagement bloomed alongside immigration.
Sometimes, perception and reality are at odds. For example, a community or country may demonstrate positive gains from immigration but public opinion stubbornly disagrees. Where these contradictions persist, it is important to think about how to change perceptions.

What will be the most significant migration issues over the next 10 years?
One is the integration of displaced populations. Over 65 million people are currently displaced. The majority – 54% or 35 million – come from Somalia, Afghanistan and Syria. Their displacement will be long-term. They are in need of the basics of survival, employment opportunities, services, and community. Planning for integration instead of displacement means a shift from building temporary solutions to permanent infrastructure.
A second is tackling inequality in destination communities. Dissatisfaction at home and disillusionment with globalisation is a driving political force behind the recent rejectionist movement in countries that have swung towards closed-border nationalism. Inequality that builds a “marginalized majority” of native citizens boosts the power of anti-immigration narratives.
A third significant issue is preparing cities for ecological migration. The changing climate is causing people to move in mass and sometimes invisible numbers. City planners have not kept pace and internal migrants especially in the Global South are landing in slums and informal housing. As thinkers like Katherine Boo and Doug Saunders have documented, the fortunes of those who land in slums depend on policies that keep them in or help them out. Will these increasingly populated places of arrival become permanent homes, or temporary launch pads?
Fourth, planning for new patterns of resettlement should be a high priority. It is becoming clear that resettlement models in traditional destination countries like Canada, Australia and parts of Europe are in need of a refresh. They were built for cities not yet transformed by the defining socio-economic trends of the past decades: the growth of informal jobs, and the passage of poverty from inner cities to suburbs. Urban planning for integration means changing the physical centres of gravity in settlement.

What do you think the Global Future Council on Migration can contribute to the global effort to help migrants?
Given the diversity of members and contributors, I believe the Council on Migration has a major role in framing the conversation, and injecting facts and evidence into the political conversations that tend towards emotional arguments. I hope that we can deepen public understanding of the benefits of migration, diversity and inclusion. We must do this soberly: migration is not a silver bullet to our problems, but it can lead to shared prosperity for migrants and for host communities under the right conditions.
Using our diversity, we can also find the global good practices that can be replicated in other jurisdictions, such as Germany’s upskilling for refugees in universities and the trades, or Canada’s private sponsorship of refugees programme.
What more needs to be done for migrants?
It’s incredible to imagine that, because of visa restrictions, people are willing to risk their lives to find safety and opportunity. They will pay ten times what a legal trip on an airplane would cost, huge sums of money, to make dangerous overland trips or flee on unsafe boats. This is because we are intentionally making it difficult for people to migrate. We need more channels of safe, legal migration.
Regarding refugees in particular, resettlement commitments need to be honoured and raised. Countries taking part in the leader’s summit in New York in September committed to roughly doubling the number of refugees they collectively admit through resettlement or other third country admission programmes to more than 360,000 refugees. This is a significant number, but it amounts to under 2% of the 21.3 million refugees registered with the UN.
What do you think the migration situation will be by 2030?
Unless we fix issues of global governance, migration risks tearing the EU apart. We are going to see the hardening of attitudes in certain regions because they don’t see the opportunity in migration. Part of that comes from the fact that people only see migration as a good thing when we think of the highly skilled. But highly skilled people are more likely to come, settle, and then get recruited elsewhere. The long-term solution is to give a hand out to people now. The payoff is that their children will succeed, and those children will build the next generation of lawyers, doctors and create prosperity in those countries.
In Canada, we have taken that approach. Once people get here, after a rigorous screening process, we throw the government behind them. We educate and upskill them where needed, teach them the national languages, help them get jobs and integrate into society. Finally, we put them on the path to citizenship.
Global migration will continue to become even more normalised. There will be leading countries that realise long-term solutions for integration helps natives and newcomers to prosper. There will be problems along the way, but I think we might be quite surprised by what happens next. We might see countries not currently on the map stepping up and becoming big players.
Have you read?
2030: the rise of compassion, or a world of warships and walls, much more than cash: how businesses can help with the refugee crisis, immigrants don't harm economies. in fact, the opposite may be true.
What would be your ideal migration scenario in 2030?
By that time, I hope that displaced people worldwide are considered a mainstream source for immigration to countries in need of economic and population growth. There are over 65 million displaced people, and yet advanced and emerging economies alike are struggling with labour shortages.
Second, I would like to see a global governance system that qualifies people professionally. One hurdle that still remains for migrants is coming to a new country where their qualifications are not recognized. On top of this type of structural barrier, we know that immigrants face discrimination and bias, which impacts their work and well-being. By 2030, I want people who move from one city to another not to have to worry about the colour of their skin or the barriers to requalify in their field of training. They will worry about what someone who moves from Toronto to Ottawa worries about: the restaurants, the rent, the weather.
The Annual Meeting of the Global Future Councils is taking place on 13-14 November in Dubai.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Global Cooperation .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

How global joint ventures can thrive in times of turmoil
Rahul Khubchandani and Ed Gore-Randall
May 2, 2024

What bullet-proof Kevlar teaches us about cooperation and resilience
Aba Schubert
April 26, 2024

Japan and the Middle East: Japan can be a bridge in an era of global fragmentation and conflict
Kiriko Honda
April 25, 2024

Practice of long-term thinking: How to leverage foresight to address the transformational challenges ahead
Lasse Jonasson
April 24, 2024

Unlocking Africa's $1 trillion food economy: The role of global aid and sustainable technology

Energy for development: Everything you need to know from #SpecialMeeting24
Ella Yutong Lin and Kate Whiting
April 23, 2024
Guest Essay
The critical challenges of migration and displacement

National Autonomous University of Mexico, Wednesday, 18 October 2017. Statement by the ICRC President, Peter Maurer .
Migration and internal displacement are among the most pressing topics on the international agenda today. In my meeting with leaders from across the international community, from governments and business, and migration is one of the most frequent topics of conversation.
While many aspects of migration and displacement are relatively uncontroversial, it is the aspect of uncontrolled, poorly managed irregular migration and population displacement, which leads to policy controversy.
While worldwide more than 250 million people live outside their home country, it is the estimated 65 million people who have been displaced by violence and conflict and those who are forced by other circumstances to choose irregular pathways of migration often outside legal frameworks foreseen for migration that represent a population of particular concern.
Of the 65 million people displaced by violence and war, just over 20 million are refugees, while the remaining majority are displaced in their own countries, often more than once.
This region, Mexico and Central America, is no exception. One of the major flows of migrants happens right here and in particular in the Northern Triangle. The link between the root causes, the basic drivers and actual migration are rather complex; migration happens due to a series of factors and mixed migration happens as a consequence of inequalities in welfare and security and often happens in more than one way.
Often, policies trying to reduce migration have an adverse effect. Migration flows, displacements by violence and other pressures on a dignified life, are creating vulnerabilities of great concern for the ICRC and the Red Cross Red Crescent Movement as a whole. ICRC's mandate is to protect and assist people affected by armed conflict and other situations of violence. People being forced to move by violence and insecurity – be it related to armed conflict or other drivers of violence – is a critical humanitarian priority.
Global concerns
Through its delegations in almost 100 countries the ICRC is present at the places of origin of many migrants and internally displaced persons. The ICRC has a fairly accurate understanding of the needs arising in all phases of displacement and together with Movement partners can tailor its response to the specific needs of each context.
The ICRC works in close proximity to the people concerned, whether they are IDPs, refugees or migrants who have crossed the border into a foreign country . This work is regularly carried out in cooperation with the local national society of the Red Cross or the Red Crescent, and sometimes other partner institutions such as the UNHCR.
The reasons why people decide to migrate are multiple and complex. They include the absence of employment opportunities in their countries of origin, the scarcity of health and education services, or the desire to reunite with family members already in other countries: they are a combination of choice and constraints. But we cannot overlook that armed conflict and other situations of violence are major drivers forcing people to leave their homes. Whatever the motives, mixed population flows are the result and a phenomenon, which challenges policy making today. The situation is exacerbated when laws are violated. If international humanitarian laws were fully respected in armed conflict, people would be much less exposed to the humanitarian consequences they invariably face.
Respecting the law would go a long way in preventing people from having to leave their homes in the first place. And it would dramatically reduce the plight encountered by those who have left. Respecting and ensuring respect of the law are essential for addressing a root cause of the human cost generated by forced displacement.
Once on their journey, migrants and IDPs face multiple risks and high degrees of vulnerability. When they reach their destination they often face difficulties in accessing health care, housing, education or employment. They may become easy targets for abuse, extortion and exploitation due to a lack of a protective family network, a lack of information or missing documents. Many suffer accidents or illness and cannot benefit from medical care. Some lose contact with their families. Thousands die or disappear along the way every year. Many are held in prolonged detention for having entered or stayed irregularly in a foreign country, in disregard of the fact that detention should always be an exceptional measure of last resort and limited in time.
Concerns in Mexico and Central America
In Mexico and Central America, the ICRC together with Red Cross National Societies, work to prevent and mitigate these consequences.
We provide direct assistance along the migratory routes, including food and water, medical assistance and information about potential hazards along the journey. People can also receive support to contact their families.
Maintaining family links is crucial. For every missing migrant, there is a family living in uncertainty ‒ not knowing if their relative is dead or alive. Alongside the emotional turmoil linked to the disappearance and to the search, missing migrants' families can face numerous practical challenges that put their daily life on hold. This is an invisible but very painful humanitarian consequence of migration.
The ICRC's work furthermore involves support given to shelters, including in the form of rehabilitating infrastructure, so that living conditions of migrants staying there are dignified, as well as specific support to strengthen their understanding of the needs of migrant persons and in consequence their networking and routes of attention for these persons.
Another line of work consists of providing assistance to migrants who were severely wounded and are in need of artificial limbs or other devices they can receive from the Mexican Red Cross Society in centers supported by the ICRC.
The ICRC also visits places where migrants are being detained. We aim to ensure people's treatment and their living conditions are compliant with international law and standards. Particular attention is given to preventing children from being detained.
At an institutional level, ICRC's frontline work with migrants is complemented by efforts to ensure legal frameworks and policies comply with requirements stemming from international law, to guarantee dignity and safety, and reduce and prevent suffering. ICRC works with governments and parliaments to ensure legislative frameworks, policies and practice are in conformity with international law.
Similar approaches are taken with respect to internally displaced persons. In some situations, there is indeed a continuum between internal displacement and migration.
For some people, internal displacement may only be a first stage in further movement as they may be driven to continue their journey to a foreign country, if, for example they are unable to find protection inside their own country. In such situations, the challenges posed by internal displacement and migration may be connected.
Whatever the legal classification in which people displaced fall, the fundamental point is that they are protected from abuse and have their humanitarian needs met. We must start first by asking 'what are the humanitarian needs and vulnerabilities?' and then applying a generous interpretation of the relevant protection regime. This requires the international community and others involved to adopting a holistic and coordinated approach that maximizes protection for both IDPs and migrants.
Global Compact on Migration
Let me add a few thoughts about our work related to the Global Compact for Safe, Regular and Orderly Migration. Today this is one of the most ambitious endeavours to make a difference in the situation of migrants. The idea of the compact was supported by 193 States in the New York Declaration of 2016 and is a promising undertaking.
The ICRC is closely following the development of this new instrument, which should be adopted in September 2018. From our perspective, there are in particular three issues to watch for.
- The first is that there can be no compromise on existing obligations under international law. States must respect such obligations, including by having legislation and procedures in place that provide adequate safeguards to protect the safety and dignity of migrants. This includes abiding with international law and standards when force is being used by law enforcement officials, in strict compliance with the principles and requirements of legality, necessity, proportionality, precaution and accountability. It also includes respecting the principle of non-refoulement in all circumstances. This would entail, in particular, that domestic legislation and procedures ensure that no person is ever being returned if there are substantial grounds to believe that she or he would be in danger of being subjected to violations of certain fundamental rights in the country of return.
- The second issue is that national and international responses must be guided by the needs of migrants in terms of assistance and protection. Such needs encompass those stemming from family separation, unaccompanied minors, missing persons and deprivation of liberty.
- Third, an emphasis should be put on the prevention of forced displacement in armed conflict and other situations of violence, in particular through greater respect for the law and through more efforts to prevent and resolve such situations.
In conclusion, it is essential to have an appreciation for the complicated origins of migration: poverty, injustice, exclusion, armed conflict, violence, among others.
In the face of this reality, no country on their own can propose durable solutions and seek effective measures in accordance with national and international law that can respect for the rights of migrants and mitigate the undesirable humanitarian consequences of migration.
It is a critical public problem that requires coordinated and ambitious solutions at local, regional and global levels. This is why there needs to be a collaborative approach among States aimed at the well-being of individuals, and not to deter migration and punish those who decide to leave their communities. Security concerns must be balanced against humanitarian considerations.
We are hopeful that the Global Compact for Safe, Orderly and Regular Migration can strengthen the commitments of the 2016 Declaration, and provide a more predictable and humane response to the needs of people on the move everywhere. With this in mind, the ICRC and its partners in the Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement will remain engaged in this important process.
We also remain committed to contributing to the development of the Global Compact on Refugees, working with UNHCR who is entrusted with producing a draft.
There is certainly much work to do in the coming months. The two compacts may well be a turning point in how effectively States and the wider international community address the humanitarian consequences related to migration, refugees and IDPs.
- Social Justice
- Environment
- Health & Happiness
- Get YES! Emails
- Teacher Resources

- Give A Gift Subscription
- Teaching Sustainability
- Teaching Social Justice
- Teaching Respect & Empathy
- Student Writing Lessons
- Visual Learning Lessons
- Tough Topics Discussion Guides
- About the YES! for Teachers Program
- Student Writing Contest
Follow YES! For Teachers
Eight brilliant student essays on immigration and unjust assumptions.
Read winning essays from our winter 2019 “Border (In)Security” student writing contest.

For the winter 2019 student writing competition, “Border (In)Security,” we invited students to read the YES! Magazine article “Two-Thirds of Americans Live in the “Constitution-Free Zone” by Lornet Turnbull and respond with an up-to-700-word essay.
Students had a choice between two writing prompts for this contest on immigration policies at the border and in the “Constitution-free zone,” a 100-mile perimeter from land and sea borders where U.S. Border Patrol can search any vehicle, bus, or vessel without a warrant. They could state their positions on the impact of immigration policies on our country’s security and how we determine who is welcome to live here. Or they could write about a time when someone made an unfair assumption about them, just as Border Patrol agents have made warrantless searches of Greyhound passengers based simply on race and clothing.
The Winners
From the hundreds of essays written, these eight were chosen as winners. Be sure to read the author’s response to the essay winners and the literary gems that caught our eye.
Middle School Winner: Alessandra Serafini
High School Winner: Cain Trevino
High School Winner: Ethan Peter
University Winner: Daniel Fries
Powerful Voice Winner: Emma Hernandez-Sanchez
Powerful Voice Winner: Tiara Lewis
Powerful Voice Winner: Hailee Park
Powerful Voice Winner: Aminata Toure
From the Author Lornet Turnbull
Literary Gems
Middle school winner.
Alessandra Serafini
Brier Terrace Middle School, Brier, Wash.

Broken Promises
“…Give me your tired, your poor,
Your huddled masses yearning to breathe free,
The wretched refuse of your teeming shore.
Send these, the homeless, tempest-tossed to me,
I lift my lamp beside the golden door!”
These words were written by Emma Lazarus and are inscribed on the base of the Statue of Liberty. And yet, the very door they talk about is no longer available to those who need it the most. The door has been shut, chained, and guarded. It no longer shines like gold. Those seeking asylum are being turned away. Families are being split up; children are being stranded. The promise America made to those in need is broken.
Not only is the promise to asylum seekers broken, but the promises made to some 200 million people already residing within the U.S. are broken, too. Anyone within 100 miles of the United States border lives in the “Constitution-free zone” and can be searched with “reasonable suspicion,” a suspicion that is determined by Border Patrol officers. The zone encompasses major cities, such as Seattle and New York City, and it even covers entire states, such as Florida, Massachusetts, and New Jersey. I live in the Seattle area, and it is unsettling that I can be searched and interrogated without the usual warrant. In these areas, there has been an abuse of power; people have been unlawfully searched and interrogated because of assumed race or religion.
The ACLU obtained data from the Customs and Border Protection Agency that demonstrate this reprehensible profiling. The data found that “82 percent of foreign citizens stopped by agents in that state are Latino, and almost 1 in 3 of those processed are, in fact, U.S. citizens.” These warrantless searches impede the trust-building process and communication between the local population and law enforcement officers. Unfortunately, this lack of trust makes campaigns, such as Homeland Security’s “If You See Something, Say Something,” ineffective due to the actions of the department’s own members and officers. Worst of all, profiling ostracizes entire communities and makes them feel unsafe in their own country.
Ironically, asylum seekers come to America in search of safety. However, the thin veil of safety has been drawn back, and, behind it, our tarnished colors are visible. We need to welcome people in their darkest hours rather than destroy their last bit of hope by slamming the door in their faces. The immigration process is currently in shambles, and an effective process is essential for both those already in the country and those outside of it. Many asylum seekers are running from war, poverty, hunger, and death. Their countries’ instability has hijacked every aspect of their lives, made them vagabonds, and the possibility of death, a cruel and unforgiving death, is real. They see no future for their children, and they are desperate for the perceived promise of America—a promise of opportunity, freedom, and a safe future. An effective process would determine who actually needs help and then grant them passage into America. Why should everyone be turned away? My grandmother immigrated to America from Scotland in 1955. I exist because she had a chance that others are now being denied.
Emma Lazarus named Lady Liberty the “Mother of Exiles.” Why are we denying her the happiness of children? Because we cannot decide which ones? America has an inexplicable area where our constitution has been spurned and forgotten. Additionally, there is a rancorous movement to close our southern border because of a deep-rooted fear of immigrants and what they represent. For too many Americans, they represent the end of established power and white supremacy, which is their worst nightmare. In fact, immigrants do represent change—healthy change—with new ideas and new energy that will help make this country stronger. Governmental agreement on a humane security plan is critical to ensure that America reaches its full potential. We can help. We can help people in unimaginably terrifying situations, and that should be our America.
Alessandra Serafini plays on a national soccer team for Seattle United and is learning American Sign Language outside of school. Her goal is to spread awareness about issues such as climate change, poverty, and large-scale political conflict through writing and public speaking.
High School Winner
Cain Trevino
North Side High School, Fort Worth, Texas

Xenophobia and the Constitution-Free Zone
In August of 2017, U.S. Border Patrol agents boarded a Greyhound bus that had just arrived at the White River Junction station from Boston. According to Danielle Bonadona, a Lebanon resident and a bus passenger, “They wouldn’t let us get off. They boarded the bus and told us they needed to see our IDs or papers.” Bonadona, a 29-year-old American citizen, said that the agents spent around 20 minutes on the bus and “only checked the IDs of people who had accents or were not white.” Bonadona said she was aware of the 100-mile rule, but the experience of being stopped and searched felt “pretty unconstitutional.”
In the YES! article “Two-Thirds of Americans Live in the ‘Constitution-Free Zone’” by Lornet Turnbull, the author references the ACLU’s argument that “the 100-mile zone violates Fourth Amendment protections against unreasonable search and seizure.” However, the Supreme Court upholds the use of immigration checkpoints for inquiries on citizenship status. In my view, the ACLU makes a reasonable argument. The laws of the 100-mile zone are blurred, and, too often, officials give arbitrary reasons to conduct a search. Xenophobia and fear of immigrants burgeons in cities within these areas. People of color and those with accents or who are non-English speakers are profiled by law enforcement agencies that enforce anti-immigrant policies. The “Constitution-free zone” is portrayed as an effective barrier to secure our borders. However, this anti-immigrant zone does not make our country any safer. In fact, it does the opposite.
As a former student from the Houston area, I can tell you that the Constitution-free zone makes immigrants and citizens alike feel on edge. The Department of Homeland Security’s white SUVs patrol our streets. Even students feel the weight of anti-immigrant laws. Dennis Rivera Sarmiento, an undocumented student who attended Austin High School in Houston, was held by school police in February 2018 for a minor altercation and was handed over to county police. He was later picked up by Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) and held in a detention center. It is unfair that kids like Dennis face much harsher consequences for minor incidents than other students with citizenship.
These instances are a direct result of anti-immigrant laws. For example, the 287(g) program gives local and state police the authority to share individuals’ information with ICE after an arrest. This means that immigrants can be deported for committing misdemeanors as minor as running a red light. Other laws like Senate Bill 4, passed by the Texas Legislature, allow police to ask people about their immigration status after they are detained. These policies make immigrants and people of color feel like they’re always under surveillance and that, at any moment, they may be pulled over to be questioned and detained.
During Hurricane Harvey, the immigrant community was hesitant to go to the shelters because images of immigration authorities patrolling the area began to surface online. It made them feel like their own city was against them at a time when they needed them most. Constitution-free zones create communities of fear. For many immigrants, the danger of being questioned about immigration status prevents them from reporting crimes, even when they are the victim. Unreported crime only places more groups of people at risk and, overall, makes communities less safe.
In order to create a humane immigration process, citizens and non-citizens must hold policymakers accountable and get rid of discriminatory laws like 287(g) and Senate Bill 4. Abolishing the Constitution-free zone will also require pressure from the public and many organizations. For a more streamlined legal process, the League of United Latin American Citizens suggests background checks and a small application fee for incoming immigrants, as well as permanent resident status for Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) and Temporary Protected Status (TPS) recipients. Other organizations propose expanding the green card lottery and asylum for immigrants escaping the dangers of their home countries.
Immigrants who come to the U.S. are only looking for an opportunity to provide for their families and themselves; so, the question of deciding who gets inside the border and who doesn’t is the same as trying to prove some people are worth more than others. The narratives created by anti-immigrant media plant the false idea that immigrants bring nothing but crime and terrorism. Increased funding for the border and enforcing laws like 287(g) empower anti-immigrant groups to vilify immigrants and promote a witch hunt that targets innocent people. This hatred and xenophobia allow law enforcement to ask any person of color or non-native English speaker about their citizenship or to detain a teenager for a minor incident. Getting rid of the 100-mile zone means standing up for justice and freedom because nobody, regardless of citizenship, should have to live under laws created from fear and hatred.
Cain Trevino is a sophomore. Cain is proud of his Mexican and Salvadorian descent and is an advocate for the implementation of Ethnic Studies in Texas. He enjoys basketball, playing the violin, and studying c omputer science. Cain plans to pursue a career in engineering at Stanford University and later earn a PhD.
High School Winner
Ethan Peter
Kirkwood High School, Kirkwood, Mo.

I’m an expert on bussing. For the past couple of months, I’ve been a busser at a pizza restaurant near my house. It may not be the most glamorous job, but it pays all right, and, I’ll admit, I’m in it for the money.
I arrive at 5 p.m. and inspect the restaurant to ensure it is in pristine condition for the 6 p.m. wave of guests. As customers come and go, I pick up their dirty dishes, wash off their tables, and reset them for the next guests. For the first hour of my shift, the work is fairly straightforward.
I met another expert on bussing while crossing the border in a church van two years ago. Our van arrived at the border checkpoint, and an agent stopped us. She read our passports, let us through, and moved on to her next vehicle. The Border Patrol agent’s job seemed fairly straightforward.
At the restaurant, 6 p.m. means a rush of customers. It’s the end of the workday, and these folks are hungry for our pizzas and salads. My job is no longer straightforward.
Throughout the frenzy, the TVs in the restaurant buzz about waves of people coming to the U.S. border. The peaceful ebb and flow enjoyed by Border agents is disrupted by intense surges of immigrants who seek to enter the U.S. Outside forces push immigrants to the United States: wars break out in the Middle East, gangs terrorize parts of Central and South America, and economic downturns force foreigners to look to the U.S., drawn by the promise of opportunity. Refugees and migrant caravans arrive, and suddenly, a Border Patrol agent’s job is no longer straightforward.
I turn from the TVs in anticipation of a crisis exploding inside the restaurant: crowds that arrive together will leave together. I’ve learned that when a table looks finished with their dishes, I need to proactively ask to take those dishes, otherwise, I will fall behind, and the tables won’t be ready for the next customers. The challenge is judging who is finished eating. I’m forced to read clues and use my discretion.
Interpreting clues is part of a Border Patrol agent’s job, too. Lornet Turnbull states, “For example, CBP data obtained by ACLU in Michigan shows that 82 percent of foreign citizens stopped by agents in that state are Latino, and almost 1 in 3 of those processed is, in fact, a U.S. citizen.” While I try to spot customers done with their meals so I can clear their part of the table, the Border Patrol officer uses clues to detect undocumented immigrants. We both sometimes guess incorrectly, but our intentions are to do our jobs to the best of our abilities.
These situations are uncomfortable. I certainly do not enjoy interrupting a conversation to get someone’s dishes, and I doubt Border Patrol agents enjoy interrogating someone about their immigration status. In both situations, the people we mistakenly ask lose time and are subjected to awkward and uncomfortable situations. However, here’s where the busser and the Border Patrol officer’s situations are different: If I make a mistake, the customer faces a minor inconvenience. The stakes for a Border Patrol agent are much higher. Mistakenly asking for documentation and searching someone can lead to embarrassment or fear—it can even be life-changing. Thus, Border Patrol agents must be fairly certain that someone’s immigration status is questionable before they begin their interrogation.
To avoid these situations altogether, the U.S. must make the path to citizenship for immigrants easier. This is particularly true for immigrants fleeing violence. Many people object to this by saying these immigrants will bring violence with them, but data does not support this view. In 1939, a ship of Jewish refugees from Germany was turned away from the U.S.—a decision viewed negatively through the lens of history. Today, many people advocate restricting immigration for refugees from violent countries; they refuse to learn the lessons from 1939. The sad thing is that many of these immigrants are seen as just as violent as the people they are fleeing. We should not confuse the oppressed with the oppressor.
My restaurant appreciates customers because they bring us money, just as we should appreciate immigrants because they bring us unique perspectives. Equally important, immigrants provide this country with a variety of expert ideas and cultures, which builds better human connections and strengthens our society.
Ethan Peter is a junior. Ethan writes for his school newspaper, The Kirkwood Call, and plays volleyball for his high school and a club team. He hopes to continue to grow as a writer in the future.
University Winner
Daniel Fries
Lane Community College, Eugene, Ore.

Detained on the Road to Equality
The United States is a nation of immigrants. There are currently 43 million foreign-born people living in the U.S. Millions of them are naturalized American citizens, and 23 million, or 7.2 percent of the population, are living here without documentation (US Census, 2016). One in seven residents of the United States was not born here. Multiculturalism is, and always has been, a key part of the American experience. However, romantic notions of finding a better life in the United States for immigrants and refugees don’t reflect reality. In modern history, America is a country that systematically treats immigrants—documented or not—and non-white Americans in a way that is fundamentally different than what is considered right by the majority.
The Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment states,“No state shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any state deprive any person of life, liberty or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.” When a suspected undocumented immigrant is detained, their basic human rights are violated. Warrantless raids on Greyhound buses within 100 miles of the border (an area referred to by some as the “Constitution-free zone”) are clear violations of human rights. These violations are not due to the current state of politics; they are the symptom of blatant racism in the United States and a system that denigrates and abuses people least able to defend themselves.
It is not surprising that some of the mechanisms that drive modern American racism are political in nature. Human beings are predisposed to dislike and distrust individuals that do not conform to the norms of their social group (Mountz, Allison). Some politicians appeal to this suspicion and wrongly attribute high crime rates to non-white immigrants. The truth is that immigrants commit fewer crimes than native-born Americans. In fact, people born in the United States are convicted of crimes at a rate twice that of undocumented non-natives (Cato Institute, 2018).
The majority of immigrants take high risks to seek a better life, giving them incentive to obey the laws of their new country. In many states, any contact with law enforcement may ultimately result in deportation and separation from family. While immigrants commit far fewer crimes, fear of violent crime by much of the U.S. population outweighs the truth. For some politicians, it is easier to sell a border wall to a scared population than it is to explain the need for reformed immigration policy. It’s easier to say that immigrants are taking people’s jobs than explain a changing global economy and its effect on employment. The only crime committed in this instance is discrimination.
Human rights are violated when an undocumented immigrant—or someone perceived as an undocumented immigrant—who has not committed a crime is detained on a Greyhound bus. When a United States citizen is detained on the same bus, constitutional rights are being violated. The fact that this happens every day and that we debate its morality makes it abundantly clear that racism is deeply ingrained in this country. Many Americans who have never experienced this type of oppression lack the capacity to understand its lasting effect. Most Americans don’t know what it’s like to be late to work because they were wrongfully detained, were pulled over by the police for the third time that month for no legal reason, or had to coordinate legal representation for their U.S. citizen grandmother because she was taken off a bus for being a suspected undocumented immigrant. This oppression is cruel and unnecessary.
America doesn’t need a wall to keep out undocumented immigrants; it needs to seriously address how to deal with immigration. It is possible to reform the current system in such a way that anyone can become a member of American society, instead of existing outside of it. If a person wants to live in the United States and agrees to follow its laws and pay its taxes, a path to citizenship should be available.
People come to the U.S. from all over the world for many reasons. Some have no other choice. There are ongoing humanitarian crises in Syria, Yemen, and South America that are responsible for the influx of immigrants and asylum seekers at our borders. If the United States wants to address the current situation, it must acknowledge the global factors affecting the immigrants at the center of this debate and make fact-informed decisions. There is a way to maintain the security of America while treating migrants and refugees compassionately, to let those who wish to contribute to our society do so, and to offer a hand up instead of building a wall.
Daniel Fries studies computer science. Daniel has served as a wildland firefighter in Oregon, California, and Alaska. He is passionate about science, nature, and the ways that technology contributes to making the world a better, more empathetic, and safer place.
Powerful Voice Winner
Emma Hernandez-Sanchez
Wellness, Business and Sports School, Woodburn, Ore.

An Emotion an Immigrant Knows Too Well
Before Donald Trump’s campaign, I was oblivious to my race and the idea of racism. As far as I knew, I was the same as everyone else. I didn’t stop to think about our different-colored skins. I lived in a house with a family and attended school five days a week just like everyone else. So, what made me different?
Seventh grade was a very stressful year—the year that race and racism made an appearance in my life. It was as if a cold splash of water woke me up and finally opened my eyes to what the world was saying. It was this year that Donald Trump started initiating change about who got the right to live in this country and who didn’t. There was a lot of talk about deportation, specifically for Mexicans, and it sparked commotion and fear in me.
I remember being afraid and nervous to go out. At home, the anxiety was there but always at the far back of my mind because I felt safe inside. My fear began as a small whisper, but every time I stepped out of my house, it got louder. I would have dreams about the deportation police coming to my school; when I went to places like the library, the park, the store, or the mall, I would pay attention to everyone and to my surroundings. In my head, I would always ask myself, “Did they give us nasty looks?,” “Why does it seem quieter?” “Was that a cop I just saw?” I would notice little things, like how there were only a few Mexicans out or how empty a store was. When my mom went grocery shopping, I would pray that she would be safe. I was born in America, and both my parents were legally documented. My mom was basically raised here. Still, I couldn’t help but feel nervous.
I knew I shouldn’t have been afraid, but with one look, agents could have automatically thought my family and I were undocumented. Even when the deportation police would figure out that we weren’t undocumented, they’d still figure out a way to deport us—at least that was what was going through my head. It got so bad that I didn’t even want to do the simplest things like go grocery shopping because there was a rumor that the week before a person was taken from Walmart.
I felt scared and nervous, and I wasn’t even undocumented. I can’t even imagine how people who are undocumented must have felt, how they feel. All I can think is that it’s probably ten times worse than what I was feeling. Always worrying about being deported and separated from your family must be hard. I was living in fear, and I didn’t even have it that bad. My heart goes out to families that get separated from each other. It’s because of those fears that I detest the “Constitution-free zone.”
Legally documented and undocumented people who live in the Constitution-free zone are in constant fear of being deported. People shouldn’t have to live this way. In fact, there have been arguments that the 100-mile zone violates the Fourth Amendment, which gives people the right to be protected from unreasonable searches and seizures of property by the government. Unfortunately, the U.S. Supreme Court has consistently upheld these practices.
One question that Lornet Turnbull asks in her YES! article “Two-Thirds of Americans Live in the ‘Constitution-Free Zone’” is, “How should we decide who is welcome in the U.S and who is not?” Instead of focusing on immigrants, how about we focus on the people who shoot up schools, rape girls, exploit women for human sex trafficking, and sell drugs? These are the people who make our country unsafe; they are the ones who shouldn’t be accepted. Even if they are citizens and have the legal right to live here, they still shouldn’t be included. If they are the ones making this country unsafe, then what gives them the right to live here?
I don’t think that the Constitution-free zone is an effective and justifiable way to make this country more “secure.” If someone isn’t causing any trouble in the United States and is just simply living their life, then they should be welcomed here. We shouldn’t have to live in fear that our rights will be taken away. I believe that it’s unfair for people to automatically think that it’s the Hispanics that make this country unsafe. Sure, get all the undocumented people out of the United States, but it’s not going to make this country any safer. It is a society that promotes violence that makes us unsafe, not a race.
Emma Hernandez-Sanchez is a freshman who is passionate about literature and her education. Emma wan ts to inspire others to be creative and try their best. She enjoys reading and creating stories that spark imagination.
Powerful Voice Winner
Tiara Lewis
Columbus City Preparatory Schools for Girls,
Columbus, Ohio

Hold Your Head High and Keep Those Fists Down
How would you feel if you walked into a store and salespeople were staring at you? Making you feel like you didn’t belong. Judging you. Assuming that you were going to take something, even though you might have $1,000 on you to spend. Sometimes it doesn’t matter. This is because people will always judge you. It might not be because of your race but for random reasons, like because your hair is black instead of dirty blonde. Or because your hair is short and not long. Or just because they are having a bad day. People will always find ways to bring you down and accuse you of something, but that doesn’t mean you have to go along with it.
Every time I entered a store, I would change my entire personality. I would change the way I talked and the way I walked. I always saw myself as needing to fit in. If a store was all pink, like the store Justice, I would act like a girly girl. If I was shopping in a darker store, like Hot Topic, I would hum to the heavy metal songs and act more goth. I had no idea that I was feeding into stereotypes.
When I was 11, I walked into Claire’s, a well-known store at the mall. That day was my sister’s birthday. Both of us were really happy and had money to spend. As soon as we walked into the store, two employees stared me and my sister down, giving us cold looks. When we went to the cashier to buy some earrings, we thought everything was fine. However, when we walked out of the store, there was a policeman and security guards waiting. At that moment, my sister and I looked at one another, and I said, in a scared little girl voice, “I wonder what happened? Why are they here?”
Then, they stopped us. We didn’t know what was going on. The same employee that cashed us out was screaming as her eyes got big, “What did you steal?” I was starting to get numb. Me and my sister looked at each other and told the truth: “We didn’t steal anything. You can check us.” They rudely ripped through our bags and caused a big scene. My heart was pounding like a drum. I felt violated and scared. Then, the policeman said, “Come with us. We need to call your parents.” While this was happening, the employees were talking to each other, smiling. We got checked again. The police said that they were going to check the cameras, but after they were done searching us, they realized that we didn’t do anything wrong and let us go about our day.
Walking in the mall was embarrassing—everybody staring, looking, and whispering as we left the security office. This made me feel like I did something wrong while knowing I didn’t. We went back to the store to get our shopping bags. The employees sneered, “Don’t you niggers ever come in this store again. You people always take stuff. This time you just got lucky.” Their faces were red and frightening. It was almost like they were in a scary 3D movie, screaming, and coming right at us. I felt hurt and disappointed that someone had the power within them to say something so harsh and wrong to another person. Those employees’ exact words will forever be engraved in my memory.
In the article, “Two-Thirds of Americans Live in the ‘Constitution-Free Zone’,” Lornet Turnbull states, “In January, they stopped a man in Indio, California, as he was boarding a Los Angeles-bound bus. While questioning this man about his immigration status, agents told him his ‘shoes looked suspicious,’ like those of someone who had recently crossed the border.” They literally judged him by his shoes. They had no proof of anything. If a man is judged by his shoes, who else and what else are being judged in the world?
In the novel To Kill a Mockingbird , a character named Atticus states, “You just hold your head high and keep those fists down. No matter what anybody says to you, don’t you let’em get your goat. Try fighting with your head for a change.” No matter how much you might try to change yourself, your hairstyle, and your clothes, people will always make assumptions about you. However, you never need to change yourself to make a point or to feel like you fit in. Be yourself. Don’t let those stereotypes turn into facts.
Tiara Lewis is in the eighth grade. Tiara plays the clarinet and is trying to change the world— one essay at a time. She is most often found curled up on her bed, “Divergent” in one hand and a cream-filled doughnut in the other.
Hailee Park
Wielding My Swords
If I were a swordsman, my weapons would be my identities. I would wield one sword in my left hand and another in my right. People expect me to use both fluently, but I’m not naturally ambidextrous. Even though I am a right-handed swordsman, wielding my dominant sword with ease, I must also carry a sword in my left, the heirloom of my family heritage. Although I try to live up to others’ expectations by using both swords, I may appear inexperienced while attempting to use my left. In some instances, my heirloom is mistaken for representing different families’ since the embellishments look similar.
Many assumptions are made about my heirloom sword based on its appearance, just as many assumptions are made about me based on my physical looks. “Are you Chinese?” When I respond with ‘no,’ they stare at me blankly in confusion. There is a multitude of Asian cultures in the United States, of which I am one. Despite what many others may assume, I am not Chinese; I am an American-born Korean.
“Then… are you Japanese?” Instead of asking a broader question, like “What is your ethnicity?,” they choose to ask a direct question. I reply that I am Korean. I like to think that this answers their question sufficiently; however, they think otherwise. Instead, I take this as their invitation to a duel.
They attack me with another question: “Are you from North Korea or South Korea?” I don’t know how to respond because I’m not from either of those countries; I was born in America. I respond with “South Korea,” where my parents are from because I assume that they’re asking me about my ethnicity. I’m not offended by this situation because I get asked these questions frequently. From this experience, I realize that people don’t know how to politely ask questions about identity to those unlike them. Instead of asking “What is your family’s ethnicity?,” many people use rude alternatives, such as “Where are you from?,” or “What language do you speak?”
When people ask these questions, they make assumptions based on someone’s appearance. In my case, people make inferences like:
“She must be really good at speaking Korean.”
“She’s Asian; therefore, she must be born in Asia.”
“She’s probably Chinese.”
These thoughts may appear in their heads because making assumptions is natural. However, there are instances when assumptions can be taken too far. Some U.S. Border Patrol agents in the “Constitution-free zone” have made similar assumptions based on skin color and clothing. For example, agents marked someone as an undocumented immigrant because “his shoes looked suspicious, like those of someone who had recently crossed the border.”
Another instance was when a Jamaican grandmother was forced off a bus when she was visiting her granddaughter. The impetus was her accent and the color of her skin. Government officials chose to act on their assumptions, even though they had no solid proof that the grandmother was an undocumented immigrant. These situations just touch the surface of the issue of racial injustice in America.
When someone makes unfair assumptions about me, they are pointing their sword and challenging me to a duel; I cannot refuse because I am already involved. It is not appropriate for anyone, including Border Patrol agents, to make unjustified assumptions or to act on those assumptions. Border Patrol agents have no right to confiscate the swords of the innocent solely based on their conjectures. The next time I’m faced with a situation where racially ignorant assumptions are made about me, I will refuse to surrender my sword, point it back at them, and triumphantly fight their ignorance with my cultural pride.
Hailee Park is an eighth grader who enjoys reading many genres. While reading, Hailee recognized the racial injustices against immigrants in America, which inspired her essay. Hailee plays violin in her school’s orchestra and listens to and composes music.
Aminata Toure
East Harlem School, New York City, N.Y.

We Are Still Dreaming
As a young Muslim American woman, I have been labeled things I am not: a terrorist, oppressed, and an ISIS supporter. I have been accused of planning 9/11, an event that happened before I was born. Lately, in the media, Muslims have been portrayed as supporters of a malevolent cause, terrorizing others just because they do not have the same beliefs. I often scoff at news reports that portray Muslims in such a light, just as I scoff at all names I’ve been labeled. They are words that do not define me.
In a land where labels have stripped immigrants of their personalities, they are now being stripped of something that makes them human: their rights. The situation described in Lornet Turnbull’s article, “Two-Thirds of Americans are Living in the ‘Constitution-Free Zone’,” goes directly against the Constitution, the soul of this country, something that asserts that we are all equal before the law. If immigrants do not have protection from the Constitution, is there any way to feel safe?
Although most insults are easy to shrug off, they are still threatening. I am ashamed when I feel afraid to go to the mosque. Friday is an extremely special day when we gather together to pray, but lately, I haven’t been going to the mosque for Jummah prayers. I have realized that I can never feel safe when in a large group of Muslims because of the widespread hatred of Muslims in the United States, commonly referred to as Islamophobia. Police surround our mosque, and there are posters warning us about dangerous people who might attack our place of worship because we have been identified as terrorists.
I wish I could tune out every news report that blasts out the headline “Terrorist Attack!” because I know that I will be judged based on the actions of someone else. Despite this anti-Muslim racism, what I have learned from these insults is that I am proud of my faith. I am a Muslim, but being Muslim doesn’t define me. I am a writer, a student, a dreamer, a friend, a New Yorker, a helper, and an American. I am unapologetically me, a Muslim, and so much more. I definitely think everyone should get to know a Muslim. They would see that some of us are also Harry Potter fans, not just people planning to bomb the White House.
Labels are unjustly placed on us because of the way we speak, the color of our skin, and what we believe in—not for who we are as individuals. Instead, we should all take more time to get to know one another. As Martin Luther King Jr. said in his “I Have a Dream” speech, we should be judged by the content of our character and not the color of our skin. To me, it seems Martin Luther King Jr.’s dream is a dream that should be a reality. But, for now, we are dreaming.
Aminata Toure is a Guinean American Muslim student. Aminata loves spoken-word poetry and performs in front of hundreds of people at her school’s annual poetry slam. She loves writing, language, history, and West African food and culture. Aminata wants to work at the United Nations when she grows up.
From the Author
Dear Alessandra, Cain, Daniel, Tiara, Emma, Hailee, Aminata and Ethan,
I am moved and inspired by the thought each of you put into your responses to my story about this so-called “Constitution-free zone.” Whether we realize it or not, immigration in this country impacts all of us— either because we are immigrants ourselves, have neighbors, friends, and family who are, or because we depend on immigrants for many aspects of our lives—from the food we put on our tables to the technology that bewitches us. It is true that immigrants enrich our society in so many important ways, as many of you point out.
And while the federal statute that permits U.S. Border Patrol officers to stop and search at will any of the 200 million of us in this 100-mile shadow border, immigrants have been their biggest targets. In your essays, you highlight how unjust the law is—nothing short of racial profiling. It is heartening to see each of you, in your own way, speaking out against the unfairness of this practice.
Alessandra, you are correct, the immigration system in this country is in shambles. You make a powerful argument about how profiling ostracizes entire communities and how the warrantless searches allowed by this statute impede trust-building between law enforcement and the people they are called on to serve.
And Cain, you point out how this 100-mile zone, along with other laws in the state of Texas where you attended school, make people feel like they’re “always under surveillance, and that, at any moment, you may be pulled over to be questioned and detained.” It seems unimaginable that people live their lives this way, yet millions in this country do.
You, Emma, for example, speak of living in a kind of silent fear since Donald Trump took office, even though you were born in this country and your parents are here legally. You are right, “We shouldn’t have to live in fear that our rights will be taken away.”
And Aminata, you write of being constantly judged and labeled because you’re a Muslim American. How unfortunate and sad that in a country that generations of people fled to search for religious freedom, you are ashamed at times to practice your own. The Constitution-free zone, you write, “goes directly against the Constitution, the soul of this country, something that asserts that we are all equal before the law.”
Tiara, I could personally relate to your gripping account of being racially profiled and humiliated in a store. You were appalled that the Greyhound passenger in California was targeted by Border Patrol because they claimed his shoes looked like those of someone who had walked across the border: “If a man is judged by his shoes,” you ask, “who else and what else are getting judged in the world?”
Hailee, you write about the incorrect assumptions people make about you, an American born of Korean descent, based solely on your appearance and compared it to the assumptions Border Patrol agents make about those they detain in this zone.
Daniel, you speak of the role of political fearmongering in immigration. It’s not new, but under the current administration, turning immigrants into boogiemen for political gain is currency. You write that “For some politicians, it is easier to sell a border wall to a scared population than it is to explain the need for reformed immigration policy.”
And Ethan, you recognize the contributions immigrants make to this country through the connections we all make with them and the strength they bring to our society.
Keep speaking your truth. Use your words and status to call out injustice wherever and whenever you see it. Untold numbers of people spoke out against this practice by Border Patrol and brought pressure on Greyhound to change. In December, the company began offering passengers written guidance—in both Spanish and English—so they understand what their rights are when officers board their bus. Small steps, yes, but progress nonetheless, brought about by people just like you, speaking up for those who sometimes lack a voice to speak up for themselves.
With sincere gratitude,
Lornet Turnbull

Lornet Turnbull is an editor for YES! and a Seattle-based freelance writer. Follow her on Twitter @TurnbullL .
We received many outstanding essays for the Winter 2019 Student Writing Competition. Though not every participant can win the contest, we’d like to share some excerpts that caught our eye:
After my parents argued with the woman, they told me if you can fight with fists, you prove the other person’s point, but when you fight with the power of your words, you can have a much bigger impact. I also learned that I should never be ashamed of where I am from. —Fernando Flores, The East Harlem School, New York City, N.Y.
Just because we were born here and are privileged to the freedom of our country, we do not have the right to deprive others of a chance at success. —Avalyn Cox, Brier Terrace Middle School, Brier, Wash.
Maybe, rather than a wall, a better solution to our immigration problem would be a bridge. —Sean Dwyer, Lane Community College, Eugene, Ore.
If anything, what I’ve learned is that I don’t know what to do. I don’t know how to change our world. I don’t know how to make a difference, how to make my voice heard. But I have learned the importance of one word, a simple two-letter word that’s taught to the youngest of us, a word we all know but never recognize: the significance of ‘we.’ —Enna Chiu, Highland Park High School, Highland Park, N.J.
Not to say the Border Patrol should not have authorization to search people within the border, but I am saying it should be near the border, more like one mile, not 100. —Cooper Tarbuck, Maranacook Middle School, Manchester, Maine.
My caramel color, my feminism, my Spanish and English language, my Mexican culture, and my young Latina self gives me the confidence to believe in myself, but it can also teach others that making wrong assumptions about someone because of their skin color, identity, culture, looks or gender can make them look and be weaker. —Ana Hernandez, The East Harlem School, New York City, N.Y.
We don’t need to change who we are to fit these stereotypes like someone going on a diet to fit into a new pair of pants. —Kaylee Meyers, Brier Terrace Middle School, Brier, Wash.
If a human being with no criminal background whatsoever has trouble entering the country because of the way he or she dresses or speaks, border protection degenerates into arbitrariness. —Jonas Schumacher, Heidelberg University of Education, Heidelberg, Germany
I believe that you should be able to travel freely throughout your own country without the constant fear of needing to prove that you belong here . —MacKenzie Morgan, Lincoln Middle School, Ypsilanti, Mich.
America is known as “the Land of Opportunity,” but this label is quickly disappearing. If we keep stopping those striving for a better life, then what will become of this country? —Ennyn Chiu, Highland Park Middle School, Highland Park, N.J.
The fact that two-thirds of the people in the U.S. are living in an area called the “Constitution-free zone” is appalling. Our Constitution was made to protect our rights as citizens, no matter where we are in the country. These systems that we are using to “secure” our country are failing, and we need to find a way to change them. —Isis Liaw, Brier Terrace Middle School, Brier, Wash.
I won’t let anyone, especially a man, tell me what I can do, because I am a strong Latina. I will represent where I come from, and I am proud to be Mexican. I will show others that looks can be deceiving. I will show others that even the weakest animal, a beautiful butterfly, is tough, and it will cross any border, no matter how challenging the journey may be. —Brittany Leal, The East Harlem School, New York City, N.Y.
Get Stories of Solutions to Share with Your Classroom
Teachers save 50% on YES! Magazine.
Inspiration in Your Inbox
Get the free daily newsletter from YES! Magazine: Stories of people creating a better world to inspire you and your students.
- Meeting report
- Open access
- Published: 19 March 2019
Critical reflections, challenges and solutions for migrant and refugee health: 2nd M8 Alliance Expert Meeting
- Nefti-Eboni Bempong 1 ,
- Danny Sheath 1 ,
- Joachim Seybold 2 ,
- Antoine Flahault 1 ,
- Anneliese Depoux 3 &
- Luciano Saso 4
Public Health Reviews volume 40 , Article number: 3 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
29k Accesses
19 Citations
20 Altmetric
Metrics details
Throughout recent years, we have witnessed an increase in human migration as a result of conflict, political instability and changes in the climate. Despite the growing number of migrants and refugees, provisions to address their health needs remain inadequate and often unmet. Whilst a variety of instruments exist to assert and emphasise the importance for migrant and refugee health, the lack of shared priorities between partners and stakeholders results in poor access to healthcare and essential medicines.
In response to the growing health challenges faced by migrants and refugees, members of the M8 Alliance launched an annual Expert Meeting on Migrants ’ and Refugees ’ Health . This report is shaped by discussions from the second M8 Alliance Expert Meeting (Sapienza University of Rome, Italy, 15–16 June 2018) and is supported by supplementing literature to develop a framework addressing critical reflections, challenges and solutions of and for migrant and refugee health. This report aims to inform decision-making fostering a humanitarian, ethics and rights-based approach. Through a series of country-specific case studies and discussions, this report captures the most prominent themes and recommendations such as mental health, tuberculosis (TB) and best practices for increased access.
Narrative of migration: Moving lives
As a complex and social phenomenon, the process of migration has become increasingly political, with adequate healthcare often low on the list of priorities. Over the past decade, there has been an influx of migrants crossing borders, primarily due to political instability, military conflict and extreme climatic conditions. These events have been accompanied by a growing burden of disease, with data suggesting that infectious disease, accidents, injuries, musculoskeletal disorders and violence disproportionately affect migrant groups compared to long-settled populations in the European Union [ 1 ]. Amongst these health challenges, mental health disorders and TB remain a major problem. Disease prevalence varies between migrant groups, and therefore it is important to be aware of the different types of migrants that exist [ 1 ].
Whilst a refugee is a type of migrant, stark differences exist between refugees and other type of migrants. The Convention and Protocol relating to the status of Refugees defined refugees as “Individuals who, owing to a well-founded fear of being persecuted for reasons of race, religion, nationality, membership of a particular social group, or political opinion, are outside the country of their nationality, and are unable to, or owing to such fear, are unwilling to avail themselves of the protection of that country or return because of fear of persecution” [ 2 ]. Other migrant status may include international migrants, internal migrants, irregular migrants and tourists [ 3 ]. The main difference that exists between refugee populations (asylum seekers, resettled and relocated refugees) and other types of migrant groups is that refugees are survivors of persecution and multiple violent events, including war and torture, and their migration experience is forced [ 4 ]. The differences in these lived experiences may therefore have a profound effect on their overall wellbeing and in particular on their mental health [ 4 ]. In addition to categorising the type of migrant, the process of migration may also be categorized. Factors that dictate the type of migration include the following: boundary crossed (national, international, political, and administrative), duration of stay (temporary, permanent), distance (regional, national, and international) and lastly, the decision-making approach for migration [ 5 ]. The latter can be further subcategorised into voluntary, instigated or forced, or impelled [ 5 ]. Migration, both voluntary and forced, is increasing at an unprecedented rate, leaving many unanswered questions for public health. Therefore, migrant and refugee health requires a collective response, addressing health challenges by mobilizing stakeholders, trade unions and partners globally.
The migration process can increase migrant and refugees vulnerability to ill health, through increased exposure to risk factors (see Fig. 1 ). The process may be subcategorised into the following: pre-departure and at the border, travel and transit, host communities and return. Compulsory medical screening is often a major concern for migrants and refugees pre-departure or at the border, as unsuccessful screening could result in denial to enter their chosen host country. The purpose of screening is to address the introduction of potential health threats that may endanger the health of host populations, specifically for the case of infectious disease [ 6 , 7 ]. However, the legitimacy of medical screening has been questioned, as it disregards the moral and ethical implications, and also does not adequately address diseases with latent periods [ 8 ]. The migratory journey itself affects the health of many migrants, due to physical and environmental threats, the lack of access to the most basic services, alongside increased exposure to both violence and trauma having significant repercussions on their mental health [ 9 ].
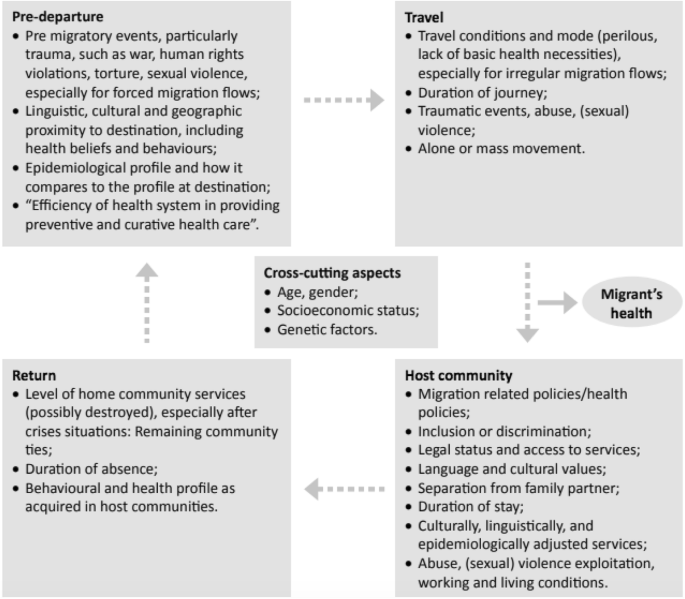
Aspects of the various migrant stages that can affect migrants’ health [ 9 ]
Once within the host country, there are still many obstacles hindering health for migrant populations, such as occupational health and safety. Migrants and refugees are more commonly exposed to occupational hazards via physical labour in occupations such as mining, agriculture and construction, whilst also having increased exposure to sexual exploitation [ 10 ]. Upon return to their country of origin, health problems that have been acquired in the host country may surface—this is especially true for mental health conditions, which may increase in severity [ 11 ].
Understanding the issue
The portrayal of migration in the media often leads to false beliefs, stereotypes, and negative perceptions of migrants and refugees. This widely circulating narrative often dilutes the severity of the phenomena, focusing only on negative aspects and shedding no light on the positives of migration. As a result, host societies often neglect to understand migration in its entirety (from departure to arrival and integration), especially within its political framework [ 1 ]. The Wroclaw Medical University , Poland , further explored public opinion regarding migration by Attitudes and opinions of Polish society about immigrants and refugees in Poland [ 12 ]. Results were drawn from a survey on public acceptance of refugees and migrants, including 367 respondents (of which 100 were within medical professions), conducted in cooperation with the Polish Association of Healthcare Managers (STOMOZ). Results of the survey seemed contradictory at times, indicating that many respondents perhaps misunderstood or misinterpreted the concept of migration. For instance, when asked if “every person should be able to move to another country fleeing war or prosecution” 62% of respondents answered “totally agree”, however when asked “would you feel uncomfortable if your new neighbour was an immigrant of refugee”, 54% of respondents answered “yes” [ 12 ]. This indicated that whilst respondents seemed to understand the reason for leaving, they were less receptive to the practical realities of migration.
Findings from the survey concluded that a possible reason for the negative opinions could be deduced to (1) misunderstanding of migration, (2) fear of an unknown situation or (3) stereotypes [ 12 ]. However, it is also important to note that the migrant population in Poland consists mostly of Ukrainian immigrants, who due to proximity have acclimatized well in Polish society. Similarities within the neighbouring regions, as well similarities in ethnicity, may have therefore accounted for some of the discrepancy between responses in this case [ 12 ]. Additionally, it is important to note that a rather small sample size of the Polish society were included in the survey and are thus not representative of the Polish society as a whole.
Evidence-based narrative on migration to promote reliability, coherence and consistency
In order to move beyond simply understanding migration and to better foster admission and integration, the narrative of migration needs to be transformed by evidence-based, reliable and sustainable data sets. A primary example in which migrant groups are often misrepresented is with regard to economic resources. Migrants are often perceived as a long-term drain on the economy, when in reality it is a short-term cost for long-term benefits. For example, whilst initial absorption may be costly, it has been estimated that in the UK, refugees are projected to grow the GDP more than two-fold (€126.6 bn) in the next 5 years, through the creation of jobs, increased demand for services and products, and also filling gaps in EU workforces [ 13 ]. Additionally, findings from Addressing the income gap of ethnic groups : impact of health on livelihoods conducted by the University of Economics in Bratislava demonstrated that proxies for migrant discrimination played a substantial role in explaining the poverty differences between migrants and nationals in the EU. Therefore, it remains imperative to change the narrative of migrants through the use of data, to support and promote the evidence on the positive effects of migration.
The inclusion of evidence-based tools also needs to be reinforced and adopted at country-level. In Italy, two guidelines, namely the Guidelines to control TB among migrants in Italy and Boarder checks kept in check , were developed in collaboration with the National Institute of Health, the National Institute for Health, Migration and Poverty, and the Italian Society of Migration Medicine to promote evidence-based guidance for decision-makers [ 14 ]. The guidelines were drawn from systematic and rigorous literature reviews, which aimed to draw recommendations and best practices focused primarily on infectious diseases, chronic-degenerative conditions, pregnancy and vaccinations [ 14 ]. Rewriting the true narrative of migration should be based on both values and human rights, in hopes of triggering further engagement and acceptance. Similarly, shaping perception is also part of the Global Compact, which as part of its framework, aims to “eliminate all forms of discrimination and promote evidence-based public disclosure to shape perceptions of migration” [ 15 ].
International frameworks and policy: Translating abstract concepts into sustainable action
Due to the political nature of migration and the implications for the economic and legal system, it remains essential that there are just and robust frameworks and policy to advocate for the human rights of migrant populations. In collaboration with the WHO framework of priorities and guiding principles to promote health of refugees and migrants, the Global Compact for Migration seeks to set out comprehensive and holistic guidelines for healthier lives of migrant and refugees [ 15 ]. Objective 15f in the Global Compact for Migration seeks to provide access to basic services for migrants and states the following:
Expand and enhance national health systems, incorporating the needs of migrants in national and local health care policies and plans, including by strengthening capacities for service provision, facilitating affordable and non-discriminatory access, reducing communication barriers, and training health care providers on culturally-sensitive service delivery, in order to promote physical and mental health of migrants and communities overall.
There is a clear link which exists between migration and development, not only demonstrated by the Global Compact acting as a response to the sustainable development goals, but also by the proliferation of universal health care for migrants and refugees in Iran. There has been an influx of Afghan refugees into Iran, which currently hosts 951,142 documented refugees and is estimated to also host 1.5 to 2 million undocumented refugees (see Fig. 2 ) [ 16 ]. In the case for documented refugees, insurance coverage for refugees is endorsed by Iran’s development programs, namely through the 6-year development plan (2016–2021; Article 70, number 5). Examples of free primary healthcare services in Iran include vaccinations, maternal and child health, family planning and psychological consultations [ 17 ]. Health is also a main pillar of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, as a healthier population will also reinforce greater financial sustainability.
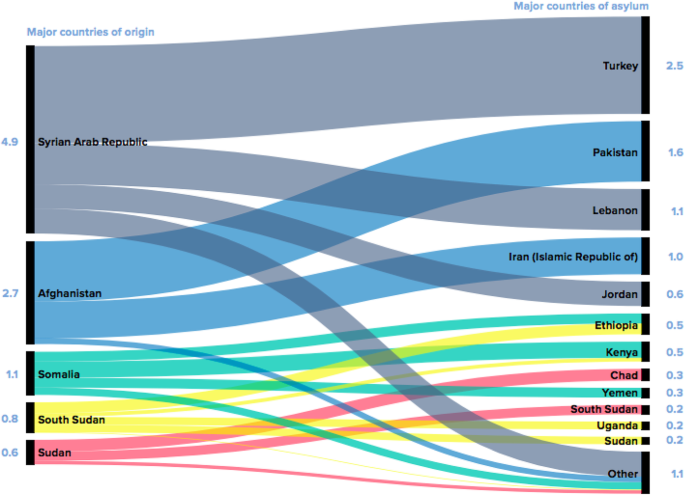
Where refugees from the top five countries of origin found asylum (UNHCR, 2015)
According to Lee’s push and pull theory, there may be various push and pull factors which influence migrants’ choice of host destination, and access to medicines may be categorised as a pull factor to migrate to said host country [ 18 ]. However, pull factors may be extremely conditional at times, widening the gap between expectation and reality. For instance, in France, a health protection scheme for undocumented migrants was created in 2000, named the State Medical Assistance [ 19 ]. Whilst the scheme had a period of entitlement for up to one renewable year, the legitimacy of assistance for undocumented migrants has been subject to debate and regular criticisms. The reasons for this being the requirements needed to access the healthcare are not only were undocumented migrants expected to have lived in the territory for over 3 months, but also beneficiaries were expected to bring forward supporting documents such as proof of identity, address of domiciliation and administrative documents proving their 3-month presence in France [ 19 ]. These criteria increase the difficulty to actually access these services, with only 10.2% of eligible candidates gaining effective access to medicine and primary health care services [ 19 ]. This echoes the need to have clearer laws and regulations, and research also concluded that it might be more beneficial to reintroduce undocumented migrants into a common law system opposed to maintaining a specific defined system for undocumented migrants [ 19 ].
- Mental health
Mental health remains a major challenge for migrant and refugee health, with a notable increase in schizophrenia, depression and anxiety. Due to the stress-inducing nature of migrations, difficulties may arise as a result of poor social skills, the concept of self and further exposure to psychological, social and biological vulnerabilities [ 20 ]. Mental health may afflict both children and adults, with exposure to violence, internalising difficulties and unaccompanied transit identified as the key risk factors for poor mental health in children [ 21 ]. Poor social interaction and integration have been hypothesised as key factors affecting mental health adjustment in adults [ 20 ]. Cultural shock plays a major role in reduced acclimatisation and has been hypothesised to occur in six stages: strain; sense of loss and feelings of deprivation; rejection by and members of the new culture; confusion in role and role expectation, values, feelings and self-identity; surprise, anxiety, disgust and indignation; and feelings of impotence [ 22 ]. Furthermore, the novel environment with uncertainties potentially caused by residence status, limited access to basic infrastructures and health services due to living conditions in provisional refugee shelters can cause emotional distress likely to increase prevalence rates of mental disorders amongst refugees in comparison to the general population [ 23 , 24 , 25 ]. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) has been observed in most migrant and refugee populations, due to the heterogenic nature of the migration process itself [ 20 ].
Trauma is especially prominent in refugee populations, often categorised as either “collective traumas”, which refer to shared injuries to a population’s social, cultural and physical ecologies [ 26 ], or “social suffering” described as “interconnected adversities on the level of individual, family, community and society” [ 27 ]. It is important to note that trauma may manifest pre-migration, but also post-migration and post-displacement adjustment [ 28 ]. Displacement and pre-migration situations of war and conflict may involve: witnessing or being subjected to torture, killings, atrocities, incarceration, starvation/deprivation, rape, sexual assault and physical beatings [ 28 ]. Trauma often results in PTSD, and the four main resettlement stressors predictive of PTSD have been identified as (1) social and economic strain, (2) loss of status corresponding with racism and discrimination, (3) threats and violence and (4) alienation [ 28 ]. However, exposure to other stressful and traumatising experiences may also contribute, such as abuse by law enforcement officers, separation from families and fear of detention and/or deportation. Trauma has also been associated with major depressive disorders and suicide [ 29 ]. To start healing from traumatic events, it requires refugees, both individually and collectively, to make meaning of their trauma [ 4 , 30 ].
More recently, the Centre for Civic Engagement and Community Service , at the American University of Beirut ( AUB ) launched the Ghata school project in Lebanon [ 31 ]. The aim of these schools was to produce a restorative built environment to impact refugee’s mental health, promoting the notion of a “safe place” via the following objectives: (1) to assess the frequency of mental health problems and trauma outcomes (PTSD, depression, anxiety) amongst children aged 12–14 attending Ghata versus tented schools; (2) to assess the perception of children and parents on their schools as a restorative built environment; and lastly, (3) to assess the need for mental health service interventions within the built environment [ 31 ]. The design of the Ghata unit is derived from refugees’ own shelter construction practices that are based on simplicity, portability, adaptability, scalability, climatic responsiveness and economic efficiency (see Fig. 3 ) [ 31 ]. AUB student volunteers assembled the first prototype in 2013, and two refugees built the second in six working hours; specifically choosing land in close proximity of refugee resettlements. Following rigorous simulation analysis, the project was scaled up across the country with support from the Ministry of Education. To date, 10 portable school campuses located within refugees’ informal tented settlements have been assembled, serving around 5000 students annually—with attendance rates over 80% [ 31 , 32 ].

Ghata school unit [ 31 ]
Results from the MHPSS surveys allowed informants to learn more about their experiences and trauma. For instance, 59.3% described their journey as “terrifying and scary”, whilst 35.6% shared their experience of seeing someone being “beaten up, shot or killed by another person”, and 45.8% admitting that they “felt like they were going to die” [ 31 ]. Ghata aims to fill the gap for needs and resource assessment, and it has also been noted that education can be used as an instrument to foster social integration, by increasing engagement and acceptance within resettled communities. Mental health within migrant communities remains a major challenge, and therefore it is important to also immobilise stakeholders and trade unions for an interagency approach. It is important to not only address the fear, anxiety and doubts pre-migration, but also assess mental health needs post-migration, guaranteeing cohesion of migrant communities.
- Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an airborne infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis , which affects the lungs most commonly, and is spread from person to person by coughing and sneezing [ 33 ]. TB is entirely preventable and treatable yet it is one of the top 10 causes of death globally, responsible for the deaths of 1.7 million in 2016, with most of these (over 95%) deaths occurring in low- and middle-income countries [ 34 ]. Clearly, TB disproportionally affects poor and vulnerable populations hence migrant populations are at a heightened risk of contracting the infection. Further, migration increases TB-related morbidity and mortality due to the conditions they are exposed to during migration itself including malnutrition, overcrowding in camps and treatment interruption, which can increase the risk of drug resistance [ 35 ]. Even when migrants reach their final destination countries, their TB-associated morbidity and mortality is elevated. This is particularly true for undocumented migrants where fear of deportation or detention prevents individuals seeking medical attention for diagnosis or treatment. Those that do identify themselves may end up in detention centres where conditions are often crowded, proliferating the spread of infection and disrupting access to treatment. The situation is not much better for migrants with legal status, whose access to care and treatment is often reliant on their working permits and health insurance, exposing a significant proportion of this group to inadequate services [ 35 ]. As an example, in Germany, the highest incidence of TB (18.2/100,000) was found in young adults aged 20 to 24 years (male 25.9 vs. female 9.7). Furthermore, TB was diagnosed significantly higher in the foreign population at all ages (42.6/100,000) compared to the general population (2.2/100,000) [ 36 ]. Therefore, all screening activities for tuberculosis should take into account that particularly migrated adolescents and young adults are at a much higher risk to be diagnosed with TB.
A particular migrant subgroup that requires attention is the unaccompanied asylum-seeking minors (UASM). UASM are defined as “third-country nationals or stateless persons below the age of 18, who arrive on the territory of the Member States unaccompanied by an adult responsible for them whether by law or custom, and for as long as they are not effectively taken into the care of such a person; it includes minors who are left unaccompanied after they have entered the territory of the Member States” [ 37 ]. Given the scale of migration amongst this vulnerable subgroup, it is important that they are not missed from screening and treatment programs.
At the 2014 World Health Assembly, the WHO End TB Strategy was introduced as a blueprint for countries to end the TB epidemic by reducing TB deaths and incidence and eliminating the terrible costs of the epidemic. The End TB Strategy outlines global impact targets to reduce TB deaths by 90%, to cut new cases by 80% between 2015 and 2030, and to ensure that no family is burdened with catastrophic costs due to TB [ 38 ]. This goal of 2030 is shaped somewhat by the inclusion of the End TB strategy in the health targets of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). WHO has gone a step further than this by setting the target of 95% reduction in deaths and a 90% decline in TB incidence globally by 2035; this is similar to current levels in low-TB incidence countries today and represents a commitment to bring high-burden countries in line with this.
The End TB Strategy faces a number of challenges on the path to achieving these goals, including the growing threat of multidrug resistance, but the status of TB amongst the migrant populations also represents a key challenge. In fact, these two challenges are not mutually exclusive, and migrant populations can accelerate the prevalence and spread of multidrug resistant TB as seen with the arrival of new strains of drug-resistant TB in the Western Cape province in South Africa, thought to be a result of the large migrant population [ 39 ]. Such introductions of new resistant strains of TB emphasise the need for the inclusion of strain data in screening and notification systems within countries with large migrant populations, when there are sufficient resources available [ 39 ].
A key component of the primary pillar for the End TB Strategy is systematic screening of contacts and high-risk groups, one such high-risk group is migrant populations, hence the importance of clear and effective screening procedures in the context of migrant and refugee health. Screening is defined as “a process of identifying apparently healthy people who may be at increased risk of a disease or condition. They can then be offered information, further tests and appropriate treatment to reduce their risk and/or any complications arising from the disease or condition” (UK National Screening Committee, 2012). Healthcare workers who are in contact with a person coming from a TB high-prevalence country (> 100/100.000) should collect TB history and check for any TB symptoms or signs as standard practice. If TB is suspected, full diagnostic exams should be carried out immediately, and full preventive therapy must be offered. As previously mentioned, there are challenges unique to the migrant population, particularly regarding unregistered migrants, and these permeate down to make effective and comprehensive screening difficult. UASM present a special case, where a more general medical screening is conducted, with more in-depth examinations carried out (e.g. X-rays) in cases of risk of TB exposure or suspected infection.
Adherence remains a challenge at all stages from comprehensive screening procedures to the completion of preventative and treatment courses. Adherence is favoured through integrated management of cases, but many challenges to achieving this exist. Preventive therapy is usually well accepted amongst migrants, but major obstacles that derive from a lack of information or bad communication and organisational problems still persist. For example, in Italy more than 40% of screened patients testing positive for possible TB infection fail to undergo follow-up diagnoses. Around 25% of those patients that do undergo diagnostic X-rays and test negative choose not to use preventive prophylaxis, and of those that do 64% still fail to complete the course. That said, such problems have started to be overcome in recent years, and whilst a 64% failure to complete figure is still too high, this is a marked improvement over recent years.
Whilst migration can have positive impacts—particularly for development, there are also a number of challenges that exist as a by-product of increased migration. A major problem is the effect of increased workload on humanitarian and health workers. Greece has experienced many health workers prone to burn out, resulting in the development of a brain drain culture (the emigration of highly trained or skilled persons). For instance, a thematic analysis “ Understanding healthcare access for refugees in Greece ” conducted by the Imperial College London highlighted how socio-cultural differences such as language acted as a major barrier in communicating. The study also noted a low presence of translators exacerbating the negative consequences. Within the Greek experience, in addition to inadequate staffing, the lack of coordination and changes in available healthcare provision also contributed to the burn out of healthcare workers [ 40 ]. The language barrier may also contribute to the lack of adherence to treatment, delays or misdiagnosis, unnecessary examinations and incorrect treatments [ 9 ]. Linguistic problems are closely tied with cultural issues. More recently, the need for “culturally competent” conduct has been pushed on the healthcare agenda, which in the case of migrant health, means putting aside personal biases and being familiar with the health, social, cultural, religious and gender-related issues regarding the experience of migrant populations [ 41 ].
Another persisting problem that has been noted is the increased incidence of work-related injuries—the ILO estimated that there were 2.3 million occupational fatalities from a variety of sources in 2014, globally [ 42 ]. The department of public health and infectious diseases at the Sapienza University of Rome concluded in their study Work-related injuries and mortality among immigrant workers in Italy : a national perspective , that occupational injuries have more frequently been observed in migrant populations with increased hazardous exposure, which may include physical, chemical, biological or increased levels of psychosocial stress. Migrants are often engaged in what is known as 3-D jobs, dirty, dangerous and demanding, in which they experience a combination of increased workplace demands, lack of safety standards and frequent workplace abuse [ 42 ].
Writing a true narrative of the migration experience remains a challenge, as the narrative of migration needs to be evidence based in order to promote a future in which we build with trust. Amongst the need to mobilise stakeholders and trade unions, shape perception via media outlets, and enhance international cooperation, many other challenges exist. It is therefore crucial that migrant and refugee health continues to be addressed, through shared priorities and the vision of involved partners and stakeholders. With a changing landscape in the climate and demographics, unpredictable political outcomes and the growing emergence of infectious disease outbreaks, migration will continue to occur, and therefore advocating for health for all and issuing calls for action remain of up most importance.
“Ultimately, the challenge is to make migration work for all.” -Antonio Vitorino, IOM Director General
Recommendations
The symposium highlighted several critical areas for action, including the following:
There is a need for an evidence-based narrative on migration to promote reliability, coherence and consistency.
Migrant and refugee health must become a shared priority mirrored in the commitment of member states to ensure access to healthcare for all.
The need to raise awareness of migrant group barriers to accessing care, and training health care professionals to overcome language barriers
Support social integration through education, housing and employment
Mladovsky P. “Migrant health in the EU.” Eurohealth- London- 13.1 (2007): 9.
UN General Assembly. Convention and protocol relating to the status of refugees. Geneva: UNHCR; 1951.
Google Scholar
Zimmerman C, Kiss L, Hossain M. Migration and health: a framework for 21st century policy-making. PLoS Med. 2011;8(5):e1001034.
Article Google Scholar
Matos L, Indart M, Park C, Leal IP. Meaning-making and psychological adjustment following refugee trauma. In: Actas do 12° Congresso Nacional de Psicologia da Saúde; 2018. p. 513–21.
Sinah BRK. Human migration: concepts and approaches. 2005. Available: http://www.mtafki.hu/konyvtar/kiadv/FE2005/FE20053-4_403-414.pdf . Last accessed 15/05/2018.
Cetron M and Simone P. Battling 21st-centry scourges with a 14th-century toolbox. Emerg Infect Dis J. 2004;10(11): 2053–2054. Available from: www.cdc.gov/ncidod/eid/vol10no11/04-0797_12.htm . 96 Last accessed: 15/10/2018.
Arcury TA, Quandt SA. Delivery of health services to migrant and seasonal farm workers. Annu Rev Public Health. 2007;28:345–63.
Coker. Compulsory screening of immigrants for tuberculosis and HIV. Br Med J. 2004;328:298–300.
International Migration, Health and Human Rights. IOM, WHO and UN Human Rights: https://www.ohchr.org/Documents/Issues/Migration/WHO_IOM_UNOHCHRPublication.pdf Last accessed: 16/10/2018.
Flyvholm M. Results from a Danish intervention project on immigrants in the cleaning trade, Barents Newsletter on Occupational Health and Safety. 2011; 14(2):46–47. Available from: www.ttl.fi/en/publications/electronic_journals/barents_newsletter/Documents/BarentsNewsletter2_2011.pdf. Human Rights Watch, World Report 2010, p. 346 (New York, 2010). Last accessed: 15/10/2018.
UNPD, IOM and UNIFEM. HIV Vulnerabilities of migrant women: from Asia to the Arab states. Colombo: UNDP Regional Centre in Colombo; 2008.
Mapping exclusion: Mental Health Europe. https://mhe-sme.org/mapping-exclusion/ Last accessed: 15/10/2018.
Legrain, P. Refugees work: A humanitarian investment that yields economic dividends. 2016. Available: http://www.opennetwork.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Tent-Open-Refugees-Work_V13.pdf . Last accessed 15/10/2018.
Marcea M, Baglio G, Tosti ME, Geraci S, Vella S, Villari P. The evidence-based approach in protecting the health of migrants and host communities: the Italian guidelines produced by ISS, INMP and SIMM; 2018.
Global Compact for Migration https://refugeesmigrants.un.org/sites/default/files/180713_agreed_outcome_global_compact_for_migration.pdf Last accessed: 16/10/2018.
UNHCR. Global trends: Forced displacement in 2015. Available: http://www.unhcr.org/statistics/unhcrstats/576408cd7/unhcr-global-trends-2015.html8June. Last accessed 20/08/2018. Last accessed: 16/10/2018.
Takian A, Akbari-Sari A. Sustainable health development becoming agenda for public health academia. Iran J Public Health. 2016;45(11):1502.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lee ES. A theory of migration. Demography. 1966;3(1):47–57.
Jean-Marie A, Azzedine F. Access to healthcare for undocumented migrants in France: a critical examination of state medical assistance. Public Health Rev. 2016.
Bhugra D. Migration and mental health. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2004;109(4):243–58.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Fazel M, Reed RV, Panter-Brick C, Stein A. Mental health of displaced and refugee children resettled in high-income countries: risk and protective factors. Lancet. 2012;379.
Oberg K. Culture shock: adjustment to new culture environments. Practical Anthropol. 1960;7:177–82.
Georgiadou E, Morawa E, Erim Y. High manifestations of mental distress in Arabic asylum seekers accommodated in collective centers for refugees in Germany. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017;14(6):E612.
Fazel M, Wheeler J, Danesh J. Prevalence of serious mental disorder in 7000 refugees resettled in western countries: a systematic review. Lancet. 2005;365:1309–14.
Porter M, Haslam N. Predisplacement and postdisplacement factors associated with mental health of refugees and internally displaced persons: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2005;294:602–12.
Saul J. Collective trauma, collective healing. New York and London: Routledge; 2014.
Kleinman A, Das V, Lock M, Lock MM. Social suffering. In: Univ of California press; 1997.
Bemak F, Chung RCY. Refugee trauma: culturally responsive counselling interventions. Journal of Counseling & Development. 2017;95(3):299–308.
Lindencrona F, Ekblad S, Hauff E. Mental health of recently resettled refugees from the Middle East in Sweden: the impact of pre-resettlement trauma, resettlement stress and capacity to handle stress. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2008;43(2):121–31.
Park CL. Making sense of the meaning literature: an integrative review of meaning making and its effects on adjustment to stressful life events. Psychol Bull. 2010;136(2):257.
Centre for Civic Engagement and Community Service, at the American University of Beirut (AUB). Ghata: a restorative built environment impacting refugees’ mental health in Lebanon. 2018.
Decreasing tensions between Lebanese and Syrian students in Zgharta. https://website.aub.edu.lb/ccecs/Documents/Success%20Story_Decreasing%20Tensions%20between%20Lebanese%20and%20Syrian%20Students%20in%20Zgharta.pdf
http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tuberculosis . Last accessed: 16/10/2018.
Goosby E, Jamison D, Swaminathan S, Reid M, Zuccala E. The Lancet Commission on tuberculosis: building a tuberculosis-free world. Lancet. 2018;391(10126):1132–3.
Tuberculosis prevention and care for migrants. http://www.who.int/tb/publications/WHOIOM_TBmigration.pdf . Accessed 16 OCt 2018.
Robert Koch Institut, Berlin, Germany: Bericht zur epidemiologie der tuberkulose in. Deutschland für 2016: https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/InfAZ/T/Tuberkulose/Download/TB2016.pdf?__blob=publicationFile Last accessed: 16/10/2018.
Council directive https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32004L0083 Last accessed: 16/10/2018.
Implementing the End the TB Strategy: The essentials http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/206499/9789241509930_eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y . Accessed 16 Oct 2018.
Theron G, Jenkins HE, Cobelens F, et al. Dara for action: collection and use of local data to end tuberculosis. Lancet. 2015;386:10010.
Khan MS, Osei-Kofi A, Omar A, Kirkbride H, Kessel A, Abbara A, Dar O. Pathogens, prejudice, and politics: the role of the global health community in the European refugee crisis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16(8):e173–7.
College of Nurses of Ontario. Practice guideline: culturally sensitive care, Ontario 2004. http://tools.hhr-rhs.ca/index.php?option=com_mtree&task=viewlink&link_id=8612&Itemid=109&lang=en . http://www.cno.org/globalassets/docs/prac/51040_culturesens.pdf . Accessed 16 Oct 2018.
Moyce SC, Schenker M. Migrant workers and their occupational health and safety. Annu Rev Public Health. 2018;39:351–65.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Sapienza University, Rome for hosting the meeting, and the German Embassy, Rome for its support of the event and the M8 Alliance. The authors thank the participants in the Expert Meeting for their contributions to the presentations and discussions, on which this report was drawn. Participant include: Jean-Marie André, Fabienne Azzedine, Lisa Matos, Alexander Krämer, Amirhoessein Takian, Aula Abbara, Giuseppe La Torre, Alessandra Talamo, Iwona Mazur, Piotr Karniej, Maurizio Marceca, Anna Paola Massetti, Paula Puskarova, Gillian Bentley, Rabih Shibli.
The funding source had no involvement in writing the manuscript or decision to submit the manuscript for publication. Authors had full access to all the data in the study, and also the final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Global Health, Faculty of Medicine, University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland
Nefti-Eboni Bempong, Danny Sheath & Antoine Flahault
Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Joachim Seybold
Centre Virchow-Villermé for Public Health Paris-Berlin–Paris Office, Paris, France
Anneliese Depoux
Faculty of Pharmacy and Medicine, Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy
Luciano Saso
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The idea was conceptualised by AF and LS. NB, DS, AD and LS drafted the first version of the report. NB and DS conducted the writing, and a final review for improvements to the manuscript was conducted by JS, AF, AD and LS. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nefti-Eboni Bempong .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Bempong, NE., Sheath, D., Seybold, J. et al. Critical reflections, challenges and solutions for migrant and refugee health: 2nd M8 Alliance Expert Meeting. Public Health Rev 40 , 3 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40985-019-0113-3
Download citation
Received : 25 October 2018
Accepted : 15 February 2019
Published : 19 March 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40985-019-0113-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Migrant health
- Refugee health
- Health policy
- M8 Alliance
Public Health Reviews
ISSN: 2107-6952
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
World history
Course: world history > unit 3, causes and effects of human migration.
- Key concepts: Human Migration
- Focus on causation: Human migration
- Migration is the movement of people from one place to another with the intent to settle
- Causes: In preindustrial societies, environmental factors, such as the need for resources due to overpopulation, were often the cause of migration
- Effects: As people migrated, they brought new plants, animals, and technologies that had effects on the environment
Causes of migration
- (Choice A) Temporary movement that follows seasonal weather patterns A Temporary movement that follows seasonal weather patterns
- (Choice B) Movement to a new region with the intent to settle there B Movement to a new region with the intent to settle there
- (Choice C) Continuous movement to follow resources C Continuous movement to follow resources
Causes of migration in Africa
Causes of migration in the pacific.
- (Choice A) Iron farming tools and weapons A Iron farming tools and weapons
- (Choice B) Long-term food preservation techniques B Long-term food preservation techniques
- (Choice C) Types of canoes that could sail in the open ocean C Types of canoes that could sail in the open ocean
Effects of migration
- (Choice A) Rats eating eggs and greatly reducing the bird population A Rats eating eggs and greatly reducing the bird population
- (Choice B) Intense storms that altered the landscape of the island B Intense storms that altered the landscape of the island
- (Choice C) Human activity, such as hunting and cutting down trees C Human activity, such as hunting and cutting down trees
- Jerry Bentley, et al, Traditions and Encounters , Vol. 1 (New York: McGraw Hill, 2015), 284.
- Douglas L. Oliver, Polynesia in Prehistoric Times (Honolulu: Bess Press, 2002), 32-35.
- Oliver, 232, 239.

Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page
QUÉ HACEMOS
Prioridades transversales (global).
- Where we work
- Take Action
- Data and Resources
- 2030 Agenda
About Migration
How to “solve” migration: A practical guide
The first thing to know is that migration is not a problem to be solved ; in fact, it is a powerful driver of sustainable development, for migrants and their communities. It brings significant benefits in the form of skills, strengthening the labor force, investment and cultural diversity, among others.
However, migration, especially when it is massive, involves challenges that, if properly managed, can turn these migratory movements into a source of growth for locals and newcomers. The challenge of managing migration has grown dramatically over the past few decades as more and more people are driven to move out of their homes by diverse economic, political, social and environmental factors.
To start with, most migratory movements are regular: they take place legally through regulator channels and legal means. By contrast, irregular migration occurs when a person enters, stays or works in a country without the necessary authorization or documents required under immigration regulations.
Migration is a social phenomenon caused by a broad variety of reasons including the search for better economic or educational opportunities, the desire for family reunification, climate change or disasters.
However, migration that is not safe, orderly and regular results in problems that the world is currently seeing unfold, like the thousands of migrants that have died or gone missing along dangerous migration routes; or the proliferation of migrant smuggling and human trafficking .
In response to the growth of irregular migratory movements many countries are looking towards border control as a solution: closing ports of entry to deter migration.
It is true that efficient border management policies and tools , help prevent irregular migration, dismantle organized criminal networks, and protect the rights of migrants. They are an essential part of migration governance, but not the only part.
Beyond border control, countries can approach migration from a holistic point of view which seeks to take advantage of its potential to boost countries´ economy while also addressing the risks of the process and the causes that drive people out of their countries.
Here are a few recommendations based on IOM’s Migration Governance Framework :
- Countries should promote stability, education and employment opportunities and reduce the drivers of forced migration, including by promoting resilience, thereby enabling individuals to make the choice between staying or migrating.
- The collection, analysis and use of credible data and information on, among other things, demographics, cross-border movements, internal displacement, diasporas, labor markets, seasonal trends, education and health is essential to create policies based on facts, that weighs the benefits and risks of migration.
- Regional cooperation , can help minimize the negative consequences of migration and preserve its integrity. It can also contribute to regional and global development goals by improving human capital through sustainable development and ensuring longer-term economic growth.
Migration has the potential to bring positive socioeconomic outcomes for both society and migrants. For countries to reap these benefits, their policies and practices need to advance the socioeconomic wellbeing of migrants and society, while adhering to adherence to international standards that respect, protect and fulfil the human rights of individuals within a state’s territory without discrimination based on nationality, race, gender, religion or migration status.
Blogs relacionados
3 key considerations for states to protect the health of migrants, social networks, migration, xenophobia: what is the discussion like in the region, 4 keys to boost the economic autonomy of migrant women entrepreneurs, 5 key actions to protect the lives of migrants in transit through the americas.
Migration updates
Subscribe to our newsletter
Immigration - Essay Examples And Topic Ideas For Free
Immigration refers to the movement of individuals from one country to another, often in search of better opportunities or to escape adversities. Essays on immigration could delve into the various causes of immigration, its impact on host and origin countries, and the policies governing immigration. Additionally, discussions might extend to the experiences of immigrants, and the global debates surrounding immigration and asylum. We’ve gathered an extensive assortment of free essay samples on the topic of Immigration you can find at PapersOwl Website. You can use our samples for inspiration to write your own essay, research paper, or just to explore a new topic for yourself.

The Effects of Illegal Immigration
Introduction Immigrants from all over look to the United States' as a possible new home in hopes at a chance at a better life. The United States is seen as a chance for economic prosperity and as an escape from a life of many disappointments and fears, so many immigrants will do whatever it takes to get themselves and their families here, even if it does include breaking the law. The United States' population includes approximately 43.7 million immigrants, which […]
Cons of Illegal Immigration
Millions of immigrants come to the United States. Illegal immigration has been an ongoing issue for many years. They may come here for a better life, job opportunities, better life, and many more reasons. These undocumented immigrants leave everything they have at home to come here. They risk a lot. They come for the better for themselves and their families. These immigrants come here for a purpose whether financial issues or the better. Many come for better education and job […]
Prejudice Towards Illegal Immigrants
Thesis: The Illegal immigrant are sometimes judged as harmful people who come to America and destroy this country. However, most of them are very hardworking people looking for a better life to support their families. Illegal immigrants come to the United States to keep their families safety Immigrants contribute to the United States workforce About 90 percent of undocumented immigrants in the nation work 2. If employers can keep wages down by hiring illegal immigrants, then these savings are presumably […]
We will write an essay sample crafted to your needs.
Illegal Immigration and its Effects on Society
Illegal immigration is a growing problem in the United States which causes many issues for citizens, such as job loss and higher taxes. It is undoubtedly an issue that needs to be addressed[1]. Illegal immigration leads to the drug trade in the United States and takes away many jobs from legal citizens[2]. Welfare is also something to consider when discussing illegal immigrants, considering that they can't legally be paid, so they are granted welfare, which also costs taxpayers more money[3]. […]
Illegal Immigration: Search of a Good Life
Illegal immigration to the United States is thriving due to the support of people needing to find a better life for themselves and families. The movement of immigration can be a positive impact on the politics and culture and economy wise. Yes it is more people coming into our country, but not all of its bad as everyone thinks it is. People of immigration bring new perspectives, experiences, and ideas to the communities. Immigrants start businesses, also earn income, and […]
Illegal Immigrants Deserve Civil Rights
Citizenship in the United States comes with a very significant and powerful advantage; civil rights. Under these rights, your freedom is protected from several infringements by the government. Many individuals are entitled to these rights, such as those born in the United States, while many individuals may not be granted all of these rights, such as illegal immigrants. There is a huge controversial debate surrounding illegal immigrants and whether they should have civil rights and liberties, and this debate is […]
What are the Effects of Illegal Immigration?
The United States of America is facing many challenges in regards to illegal immigration. By draining public funds, creating unfair competition for jobs (thereby lowering wages and working conditions), and by imposing unwanted strains on services designed to provide assistance to Americans, illegal immigration causes harm to legal residents. We are one of the only countries in the world where, in your stay, you retain many benefits, and are taken care of while you're here. Countless amount of people believe […]
Immigration Reform
Immigration reforms have been very controversial in United States of America. Way back in 1965, the United States made a law on issues of immigration which was aimed at allowing immigrants into United States. It was, however, stated that immigrants with possible skills to bring United States economy more benefits would be highly considered. With time even so, more immigrants began to come to United States with family chains being the main issue of concern. Once an individual is able […]
Illegal Immigrants: Huge Controversial in the United States
Year after year, numerous news stories emerge about illegal immigrants. The first prominent case involved two illegal immigrants who were arrested for speeding by two sheriff's deputies. The deputies ended up severely beating them, even though the arrested individuals were unarmed. ("Who does not like Immigrants?", n.d.) Many people empathized with them, while others showed no sympathy due to their illegal entry into the U.S. ("Who does not like Immigrants?", n.d.) This marked the beginning of escalating tensions. A significant […]
Managing Illegal Immigration to the United States
Basically, the goal to protect the country and its people has not changed and still lives on within the modern policies. As in the late 1800s, almost any given foreigner has the ability to become a legal resident, or a person (who lawfully lives in a country, state, etc.) of the United States. However, the process by which an individual can become a legal resident is much more complicated than it has been in years prior. In order to become […]
Illegal Immigration: Economy’s Boost
Many of us know that America is known as a great country because of its diversity. The cause of this diversity is the fact that America allowed immigrants to move to this country from their home countries which had an influence on our economy. However, not everyone in America is a legal immigrant. In October 1996, there were about five million illegal immigrants living in the United States, and the population of those immigrants was growing by about two hundred […]
Illegal Immigrant Population of the United States
As of 2018, according to FactCheck.org there are 12.5 million illegal immigrants living in the US. Immigration is not bad for a country if the country can support the people. Diversity lets us experience different cultures and be more open to different views. However, the problem with immigration is illegal immigration. Illegal immigration is a tough problem because finding the right solution for it can be so hard. Dealing with immigration is hard because you want to help the people […]
Illegal Immigration and President Donald Trump’s Zero Tolerance Policy
Illegal immigration, according to the Unites States of America is defined as when people who are foreigners and or immigrants try to enter the United States without the proper documentation needed to enter. During the summer of 2018, illegal immigration reached an all-time high due to President Donald Trump's zero tolerance policy. This crisis and the collapse of the border policy caused the Trump Administration to be very frustrated because this was an issue that was not going to be […]
Analyzing the Definition of Illegal Immigration and how Immigration has Affected American Value
Values The focus of our group for this project is illegal immigration and how it has shaped the mindset of people in America today. Our research question following the topic is, "To what extent has immigration affected American values and how do people define immigration?" For the purpose of this paper, this definition will serve as a guideline: Immigration is the action of coming to live permanently in a foreign country. Embedded in this definition is the questionable interpretation of […]
Immigration Policy of Donald Trump
On the 17th January 2017, at a campaign rally in Miami, President Donald Trump stated that A Trump administration will stop illegal immigration, deport all criminal aliens, and save American lives (poltifact.com). The president and his administration will do actions to keep the US clear and safe. Trump tried to deport about 11 million undocumented immigrants (Wessler). This is just so cruel to destroy people live by sending them back to totally strange country, to separate their family, and to […]
American Population and Illegal Immigration
America has always been known as the country who invites those less fortunate in, but at what cost? At what point will there be an end? There have been millions of people coming to the United States every year, fleeing from war torn countries and poverty, and the United States lets them in. They are supposed to be the country of freedom, but at a certain point it will need to stop. That point is now, the U.S. can no […]
Massive Influx of Illegal Immigrants in USA
There have been a large number of illegal immigrants entering the United States for many years. For the last few years in particular, there has been a massive influx of illegal immigrants crossing the Mexican border. Illegal immigration needs to be stopped because it places a huge burden on the economy od the United States. One reason is the illegal immigrants receive many free benefits. Another reason is the illegal immigrants work practices are causing wages in certain areas to […]
Termination of Racism and American Perception of Immigration Today
Robert F. Kennedy is deemed as an unusual rebel of the sorts. Kennedy came from a wealthy, politically oriented family and was strongly influenced by the administrative occupations held by his father Joe and brother Jack. Kennedy worked as the attorney general and senator for New York. He had a vast empathy for minorities. While running for President Kennedy was popular among the public as he perceived all people as human beings and had a family-man aura. Unfortunately, Kennedy's life […]
Immigration and Customs Enforcement
Illegal immigration has been occurring for many centuries and continues to take place today. When people cross the border without being authorized, this can lead to grave danger. There have been many incidents with illegal immigrants who were involved in identity theft and identity loans. Most importantly, it violates the IRCA (1986 Immigration Reform and Control Act). Although, illegal immigration might be beneficial to people crossing the border; it should not be tolerated at all. In this essay, I will […]
Is Illegal Immigration Good for our Country?
Illegal immigration is good because some immigrants are trying to give their children a better future than will have in the country that they came from. Some are immigrants might drug traffic. For example, mexico drug dealers bring drugs to the United States and sell them for possibly money, coke, ammo, or marijuana. Some other Immigrants who don't drug traffic to the United States of America are here to give them and their children a opportunity to succeed in their […]
Does Illegal Immigration Impact Texas?
How Illegal Immigration Impacts Texas Vincent M Messana Geography 1303 Lone Star College - Tomball Abstract This paper explores the impact of illegal immigration in the great state of Texas, the main topics will focus on the effects on the economy, why illegal immigrants come here/ why not come legally, are the illegal immigrants bringing crime, how are illegal immigrants affecting Texas culture how are there so many illegal immigrants still living in Texas and what is being done to […]
Are Immigrants Good for the Americans?
Illegal immigration is not beneficial to our country and we should not protect it. Legal immigration is alright but we should focus more on enforcing our laws rather than offer blanket forgiveness to those who have broken them. People coming to our country bring many issues along with them. While they are in search of better opportunities in this country, most of them come here illegally even though we have a system that they can apply for and enter legally. […]
Illegal Immigration and Crime
The United States border is always a topic when the subject is the illegal entry ( entering into a country ) in the United States. Some people defend that building a wall will reduce the criminal activities in the country, while others defend that to stop illegal entry, ( entering into a country) could lapse the United States economy (the process of people making, selling, and buying things). To state that whether criminal activities increases by illegal ( entering into […]
A Look into our Natio’s Criminal Justice System and Immigration Laws
Abstract This paper will take a look at how the criminal justice system, race, and immigration all relate to each other, and the outcomes of each, with examples from the films 13th and Documented. It will analyze mass incarceration within the criminal justice system and discuss why there are so many people locked up, and some locked up for crimes they did not even commit. It will then elaborate on race in the criminal justice system, and talk about the […]
International and U.S Helping IIlegal Immigration
The International and U.S aid are agencies that help out civilian foreign aid especially those countries who are considered 3rd world countries. Which have less than a 1st world country has, such as more job opportunities, money, education and overall less crime. The overall issue for 3rd world countries is that the crime rate is very high as well as the homicide rate. And as of now it is increasing. The U.S aid is part of the government, and helps […]
Illegal Immigration and Human Trafficking
Human trafficking comes in many different forms such as sex trafficking for the purpose of sexual exploitation. Sex exploitation is based on the interaction between a trafficker selling an individual, victim being smuggled to customers for sexual services. Labor trafficking includes situations of debt bondage, forced labor, and involuntary child labor. Labor trafficking uses violence, threats, lies, and other forms of coercion to force people to work against their will in which most cases have no knowledge on the activities […]
Biggest Problem in the United States of America is Illegal Immigrants
One of the biggest problems that is being discussed in the United States of America is illegal immigrants. An illegal immigrant is someone who lives or works in another country when they do not have the legal right to do so, this is according to the Cambridge dictionary. Now you made wonder why someone would just want to get up and leave their country to just work and live? Or why is this such a big issue in the United […]
Positive Effects of Immigration
In the past few years, the topic of immigration has been a cause for much conversation and debate. While many people have discussed the morals of immigration, many have also assessed how exactly immigration affects the United States at both smaller and larger levels. Currently, there is much debate among scholars, politicians, economists and citizens regarding immigration and the economic effects that arise from it. Immigration has been discussed at great lengths for the past few years, and based off […]
Benefits of Immigration Essay
Combined picture of five years Syrian boy Omran injured during the airstrike in Aleppo and unbreathing body, faced down of three years old Alan Kurdi founded drowned in Mediterranean sea become a symbol of emigrant crisis1. This artwork of Syrian artist Rehman Siddiq very spectacularly and emotionally illustrated dilemma of every immigrant - stay or run. Immigration crisis become a social phenomenon that keep spreading all over the world. From mass media we can hear basically about two main streams […]
Mexican Immigration
At the wake of 1930, the Great Depression hit the United States hard. There was a serious job crisis as well as food shortages that affected the Mexican immigrants as well as all American dwellers. During this time, most of the Mexican immigrants and the Mexicans Americans were subjected to additional threats and hostility as the American migrants believed the Mexicans were taking their jobs (Gratton & Merchant, 2013). The American government came up strongly with deportation threats and they […]
Related topic
Additional example essays.
- Socioautobiography Choices and Experiences Growing up
- A Class Divided
- Gender Inequality in Education
- Homelessness in America
- End Of Life Ethical Issues
- The Oppression And Privilege
- Macbeth Downfall in the Context of Violence
- "Just Walk on" by Brent Staples Summary: Racial Stereotypes and Their Impact
- Essay About Theme for English B
- Logical Fallacies in Letter From Birmingham Jail
- How the Roles of Women and Men Were Portrayed in "A Doll's House"
- Dogs Are Better Than Cats Essay
How To Write an Essay About Immigration
Understanding the intricacies of immigration.
Writing an essay on how to write an essay about immigration requires a deep understanding of the multifaceted nature of immigration itself. Immigration is a complex topic, encompassing legal, economic, cultural, and humanitarian aspects. It's essential to recognize that essays about immigration should address its diverse implications – from the challenges faced by immigrants to the impacts on host countries. This foundational understanding is crucial for guiding the exploration of how to approach various narratives, policies, and theories related to immigration. Consider including aspects such as the reasons behind immigration, the experiences of immigrants, the policies of different countries, and the societal reactions to immigration.
Structuring the Immigration Essay
The structure of your essay about writing an essay on immigration is key. Start with a compelling introduction that highlights the importance of accurately and empathetically discussing immigration. The thesis statement here should reflect the purpose of your guidance – whether to inform, argue, or analyze different aspects of immigration. The body of your essay should then be divided into coherent sections, each focusing on a key aspect of writing about immigration. Discuss how to construct an argument, the importance of using reliable data and sources, and the need for presenting a balanced view that considers both the challenges and contributions of immigrants. Ensure each part of the essay seamlessly connects to create a cohesive guide.
Addressing Challenges and Offering Strategies
In this part of the essay, focus on the challenges writers may face when crafting an essay on immigration and propose strategies to overcome these. One major challenge is the politicization of immigration, requiring a careful and unbiased approach. Another is the sensitivity of the topic, as it often involves vulnerable populations. Offer advice on maintaining objectivity while being empathetic, and stress the importance of cultural sensitivity. Suggest methods for thorough research and analysis, emphasizing the need to understand immigration laws and policies, as well as the socio-economic factors involved. Discuss the importance of acknowledging diverse perspectives and experiences in the essay to provide a comprehensive view of immigration.
Concluding with Purpose
The conclusion of your essay should do more than summarize the main points about writing an essay on immigration. It's an opportunity to reflect on the importance of understanding and discussing immigration in a responsible and informed manner. Emphasize the role of such essays in shaping public opinion and policy. Encourage writers to approach the topic of immigration with a commitment to fairness, accuracy, and empathy. A strong conclusion will not only wrap up your essay effectively but also inspire and guide future writers to approach the topic of immigration with the depth and respect it deserves.
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Apr 10, 2023
How To Write Essays About Immigration (With Examples)
Immigrants bring diverse perspectives and skills that can enrich our societies and economies. If you want to gain insight into the impact of immigration on society and culture, keep reading!
Immigration, a subject deeply woven into the fabric of global discussions, touches on political, economic, and social nuances. As globalization propels many to seek new horizons, understanding the multifaceted impacts of migration is crucial. Crafting a compelling essay on such a vast topic requires more than just research; it demands the delicate weaving of insights into a coherent narrative. For those keen on delivering a polished essay on immigration, considering assistance from a reliable essay writing tool can be a game-changer. This tool not only refines the craft of writing but ensures your perspectives on immigration are articulated with clarity and precision.
Here are our Top 5 Essay Examples and Ideas about Immigration:
The economic impact of immigration on host countries, introduction.
In many nations, immigration has been a hotly debated issue, with supporters and opponents disputing how it would affect the home nation. The economic impact of immigration on host countries is one of the essential components of this discussion. Immigration's economic effects may be favorable or harmful, depending on many circumstances.
This article will examine the economic effects of immigration on the receiving nations, examining both the advantages and disadvantages that immigration may have. You will better know how immigration impacts a nation's economy and the variables that influence it after this article.
Immigration's effects on labor markets
An essential component of the total economic impact of immigration is how it affects labor markets. Immigration may affect labor markets, including shifting labor supply and demand, opening new job possibilities, and perhaps affecting local employees' earnings and prospects. This section will examine how immigration affects labor markets in receiving nations.
The shift in the labor supply is one of immigration's most apparent effects on labor markets. When more employees are available in the host nation due to immigration, there may be more competition for open positions. In fields that serve immigrant populations, such as ethnic food shops or language schools, immigrants can also generate new jobs.
Another significant impact of immigration on labor markets is its effect on wages and income distribution. Some studies have suggested that immigration can reduce wages for native workers, particularly those who are less educated or have lower skill levels.
Immigrants can also contribute to economic growth and innovation, which can positively impact labor markets. Immigrants often have unique skills, experiences, and perspectives that can help drive innovation and create new job opportunities in the host country. Furthermore, immigrants are often more entrepreneurial and more likely to start businesses, which can generate new jobs and contribute to economic growth.
The effect of immigration on wages and income distribution
The effect of immigration on wages and income distribution is a crucial area of concern in the overall economic impact of immigration. Immigration can affect wages and income distribution in various ways, which can have significant implications for both native workers and immigrants. In this section, we will explore the effect of immigration on wages and income distribution in host countries.
One of the primary ways that immigration can impact wages and income distribution is by changing the supply and demand of labor. With an influx of immigrants, the labor supply increases, which can lead to increased competition for jobs. Some studies suggest that immigration harms wages for native workers, while others offer no significant effect.
Another way that immigration can impact wages and income distribution is through its effect on the composition of the workforce. Immigrants often fill low-skilled jobs in industries such as agriculture, construction, and hospitality, which tend to pay lower wages.
Immigration can also impact income distribution by contributing to the overall level of economic inequality in a host country. While immigration can lead to lower wages for some native workers, it can also lead to higher wages and increased economic mobility for some immigrants. Furthermore, immigrants may face various barriers to upward mobility, such as discrimination or lack of access to education and training. This can lead to increased income inequality between native and immigrant workers.
The contribution of immigrants to economic growth and innovation
Immigrants have historically played a significant role in driving economic growth and innovation in host countries. In this section, we will explore the contribution of immigrants to economic growth and innovation and the factors that enable them to do so.
One of the primary ways that immigrants contribute to economic growth is through their entrepreneurial activities. Immigrants are often more likely to start their businesses than native-born individuals, and these businesses can create jobs and drive economic growth. Immigrant entrepreneurs have contributed to developing industries such as technology, healthcare, and hospitality. Additionally, immigrants are often overrepresented in STEM fields, which is critical to driving innovation and economic growth.
Another way that immigrants contribute to economic growth is through their impact on the labor force. Immigrants tend to be more mobile than native-born individuals, which can lead to a more flexible and adaptable workforce. Immigrants also tend to fill critical roles in industries such as healthcare and agriculture, which are essential to maintaining the functioning of the economy. By filling these roles, immigrants contribute to the overall productivity and growth of the economy.
The costs and benefits of social welfare programs for immigrants
The issue of social welfare programs for immigrants has been a controversial topic in many host countries. In this section, we will explore the costs and benefits of social welfare programs for immigrants and the policy implications.
One of the primary benefits of social welfare programs for immigrants is that they can help reduce poverty and promote social inclusion. Immigrants often face significant barriers to economic mobility, such as language barriers and discrimination. Social welfare programs can help provide a safety net for those struggling to make ends meet and promote social cohesion by reducing inequalities.
However, social welfare programs for immigrants also come with costs. One concern is that these programs may attract immigrants primarily seeking to access social welfare benefits rather than contributing to the economy. This can strain public finances and create resentment among native-born individuals who feel their tax dollars are being used to support immigrants.
Another concern is that social welfare programs may create disincentives for immigrants to work and contribute to the economy. If the benefits of social welfare programs are too generous, some immigrants may choose to rely on them rather than seek employment. This can create long-term dependence and reduce overall economic productivity.
The impact of immigration on public finances and fiscal policies
The effect of immigration on public finances and fiscal policies is a topic of significant interest and debate. This section will explore how immigration affects public finances and how host countries can implement budgetary policies to manage the impact.
One way that immigration can impact public finances is through taxes. Immigrants who are employed and pay taxes can contribute to the tax base of the host country, which can provide additional revenue for public services and infrastructure. However, immigrants who are not employed or earn low wages may contribute fewer taxes, which can strain public finances.
Fiscal policies can be used to manage the impact of immigration on public finances. One guideline is to increase taxes on immigrants to offset the costs of public services they use. However, this can create a disincentive for highly skilled and educated immigrants to migrate to the host country. Another policy is to increase spending on public services to accommodate the needs of immigrants. However, this can strain public finances and lead to resentment among native-born individuals who feel their tax dollars are being used to support immigrants.
In conclusion, the economic impact of immigration is a complex issue with both costs and benefits for host countries. Immigration can impact labor markets, wages and income distribution, economic growth and innovation, social welfare programs, public finances, and fiscal policies.
The social and cultural implications of immigration
Immigration has social and cultural implications that affect both immigrants and host countries. The movement of people from one place to another can result in a blending of cultures, traditions, and ideas. At the same time, immigration can also result in social and cultural tensions as different groups struggle to integrate and adjust to new environments.
The social and cultural implications of immigration have become increasingly important in today's globalized world as the movement of people across borders has become more common. In this article, we will explore the various social and cultural implications of immigration and how they impact immigrants and host communities.
The impact of immigration on social cohesion and integration
Immigration has a significant impact on social cohesion and integration in host countries. Social cohesion refers to the degree to which members of a society feel connected and share a sense of belonging. In contrast, integration refers to the process by which immigrants become a part of the host society. Immigration can either enhance or hinder social cohesion and integration, depending on how it is managed and perceived by the host society.
Another factor that can impact social cohesion and integration is the level of diversity within the host society. Increased diversity can lead to greater cultural exchange and understanding but also social tensions and the formation of segregated communities. Promoting social interaction and cooperation among diverse groups can help mitigate these tensions and promote social cohesion.
The perception of immigrants by the host society also plays a significant role in social cohesion and integration. Negative stereotypes and discriminatory attitudes can hinder integration and create barriers to social cohesion. On the other hand, positive attitudes towards immigrants and their contributions to society can facilitate integration and promote social cohesion.
The role of language and communication in the integration of immigrants
Language and communication play a crucial role in integrating immigrants into host societies. Immigrants may need the ability to communicate effectively with others to overcome significant barriers to social and economic integration. Language and communication skills are essential for accessing education, finding employment, and participating in civic life.
Language is one of the primary barriers immigrants face when integrating into a new society. Without proficiency in the host country's language, immigrants may struggle to understand instructions, participate in conversations, and access essential services. This can lead to social isolation and hinder economic opportunities.
Language training programs are one way to address this issue. Effective language training programs can help immigrants learn the host country's language and develop the communication skills necessary for successful integration. These programs can also give immigrants the cultural knowledge and understanding essential to navigate the host society.
The effect of immigration on cultural diversity and identity
Immigration can significantly impact the cultural diversity and identity of both host societies and immigrant communities. The cultural exchange resulting from immigration can enrich societies and provide opportunities for learning and growth. However, immigration can also pose challenges to preserving cultural identities and maintaining social cohesion.
One of the primary ways in which immigration affects cultural diversity and identity is through the introduction of new customs, traditions, and beliefs. Immigrant communities often bring unique cultural practices, such as food, music, and art, that can enhance the cultural landscape of the host society. Exposure to new cultures can broaden the perspectives of individuals and communities, leading to greater tolerance and understanding.
The challenges and benefits of multiculturalism in host countries
Multiculturalism refers to the coexistence of different cultural groups within a society. It is a concept that has become increasingly important in modern societies characterized by race, ethnicity, religion, and language diversity.
Multiculturalism is often promoted to promote tolerance, social cohesion, and the celebration of diversity.
Challenges of multiculturalism
Multiculturalism presents a range of challenges that can impact host societies. These challenges include social division, discrimination, language barriers, and cultural clashes. For example, when immigrants share different values or traditions than the host society, this can lead to misunderstandings and conflict. Similarly, language barriers can limit communication and make it difficult for immigrants to integrate into the host society.
Benefits of multiculturalism
Multiculturalism can also bring a range of benefits to host societies. These benefits include increased cultural awareness and sensitivity, economic growth, and exchanging ideas and perspectives. For example, cultural diversity can provide opportunities for host societies to learn from different cultural practices and approaches to problem-solving. This can lead to innovation and growth.
Social cohesion
Social cohesion refers to the ability of a society to function harmoniously despite differences in culture, ethnicity, religion, and language. Multiculturalism can pose a challenge to social cohesion, but it can also promote it. Host societies can foster social cohesion by promoting the acceptance and understanding of different cultural groups. This can be achieved through policies and programs that promote intercultural dialogue, education, and community-building.
Discrimination and prejudice
Multiculturalism can also increase the risk of discrimination and prejudice. Discrimination can take many forms, including racial, religious, and cultural bias. Host societies can combat discrimination by implementing anti-discrimination laws and policies and promoting diversity and inclusion.
Economic benefits
Multiculturalism can also bring economic benefits to host societies. The presence of a diverse range of skills and talents can lead to innovation and economic growth. Immigrants can also get various skills and experiences contributing to the host society's economic development.
In conclusion, immigration has significant social and cultural implications for both host countries and immigrants. It affects social cohesion, integration, cultural diversity, and identity. Host countries face challenges and benefits of multiculturalism, including economic growth, innovation, and social change.
The role of immigration in shaping national identity
Immigration has always been a significant driver of cultural and social change, with immigrants often bringing their unique identities, values, and traditions to their new homes. As a result, immigration can play a crucial role in shaping national identity, as it challenges existing cultural norms and values and introduces new ideas and perspectives.
In this article, we will explore the role of immigration in shaping national identity, including its effects on cultural diversity, social cohesion, and political discourse. We will also discuss the challenges and opportunities presented by immigration to national identity and the importance of embracing a diverse and inclusive national identity in today's globalized world.
Immigration and the evolution of national identity
The relationship between immigration and national identity is complex, as immigration can challenge and reinforce existing national identities. As immigrants bring new cultural practices and values, they challenge the existing norms and values of the host society, prompting a re-evaluation of what it means to be part of that society. This can create a more inclusive and diverse national identity as different cultural traditions and practices are recognized and celebrated.
At the same time, the influx of new immigrants can also create a sense of fear and anxiety among some members of the host society, who may view the changes brought about by immigration as a threat to their cultural identity. This can lead to calls for stricter immigration policies and a more limited definition of national identity, which can exclude or marginalize certain groups.
The role of immigrants in shaping cultural diversity
Immigrants have played a significant role in shaping cultural diversity in many countries. Their arrival in a new land brings their customs, traditions, beliefs, and practices, which contribute to society's richness and vibrancy.
One of the key ways in which immigrants have shaped cultural diversity is through their contributions to the local community. Immigrants bring a wealth of knowledge, skills, and talents that can benefit the societies they move to. For example, they may introduce new cuisines, music, art, and literature that add to the cultural landscape of their new home. This can create a more diverse and inclusive society where different cultures are celebrated and appreciated.
Another important aspect of cultural diversity is the challenges immigrants face when adapting to a new culture. Moving to a new country can be a daunting experience, especially if the culture is vastly different from one's own. Immigrants may struggle with language barriers, cultural norms, and social customs that are unfamiliar to them. This can lead to feelings of isolation and exclusion, which can negatively impact their mental health and well-being.
The challenges of maintaining social cohesion amidst diversity
Strengthening social cohesion amidst diversity is a complex challenge many societies face today. Cultural, ethnic, religious, and language diversity can lead to tensions and conflicts if managed poorly.
One of the main challenges of maintaining social cohesion amidst diversity is the need to balance the interests of different groups. This involves recognizing and respecting the cultural, religious, and linguistic diversity of society while also promoting a sense of shared identity and common values. This can be particularly challenging in contexts with competing interests and power imbalances between different groups.
Another challenge is the need to address discrimination and prejudice. Discrimination can take many forms, including unequal access to education, employment, housing, hate speech, and violence. Prejudice and stereotypes can also lead to social exclusion and marginalization of certain groups. Addressing these issues requires a concerted effort from the government, civil society, and individuals to promote tolerance and respect for diversity.
Promoting inclusive policies is another crucial factor in maintaining social cohesion amidst diversity. This includes policies promoting equal opportunities for all, regardless of background. This can involve affirmative action programs, targeted social policies, and support for minority groups. Inclusive policies can also create a sense of belonging and ownership among different groups, which helps foster social cohesion.
In conclusion, immigration profoundly influences the formation of national identity. As individuals from various backgrounds merge into a new country, they not only introduce their distinct cultural and ethnic traits but also embark on a journey of personal growth and adaptation. This process mirrors the development of key skills such as leadership, character, and community service, essential for thriving in diverse environments. These attributes are not only vital for immigrants as they integrate into society but are also exemplified in successful National Honor Society essays , where personal growth and societal contribution are celebrated. Thus, the experiences of immigrants significantly enrich the societal tapestry, reflecting in our collective values, beliefs, and practices.
To sum it all up:
To recapitulate writing a five-paragraph essay about immigration can be challenging, but with the right approach and resources, it can be a rewarding experience. Throughout this article, we have discussed the various aspects of immigration that one can explore in such an essay, including the economic impact, social and cultural implications, and the evolution of national identity.
If you're looking for an AI-powered writing assistant to help you with your next writing project, sign up for Jenni.ai today. With its advanced language models and intuitive interface, Jenni.ai can provide you with personalized suggestions and feedback to improve your writing. Give it a try, Sign up for free and take your writing to the next level!
Try Jenni for free today
Create your first piece of content with Jenni today and never look back
417 Immigration Topics to Write about & Essay Examples
Welcome to our list of catchy immigration essay titles! Here, you will find a variety of immigration topics to write about as well as writing prompts and presentation ideas.
🔝 Top 10 Immigration Titles for Essays
📝 key points to use to write an outstanding immigration essay, 🏆 best immigration topic ideas & essay examples, 👍 good essay topics on immigration, 🎓 simple & easy immigration essay titles, 🥇 most interesting immigration topics to write about, 📌 immigration writing prompts, ✅ good research topics about immigration, ❓ immigration essay questions, ✨ creative titles for immigration essays, 🚀 immigration topics for presentation.
- How Migration Shapes Identities
- Assimilation vs. Multiculturalism
- Immigration Policies and Their Effects
- Global Responses the Refugee Crisis
- Immigration and Crime: Fact vs. Fiction
- Immigration’s Impact on Social Integration
- Educational Challenges and Opportunities for immigrants
- What Are the Health Impacts of Immigration?
- The Effects of Immigration on Family Separation
- What’s the Role of Immigrants in Entrepreneurship?
Immigration essay is a popular type of assignment in various topics, including politics and social sciences. In a globalized world, people can migrate from one country to another for work, study, and other reasons.
This post will discuss some points that you could include in your essay on immigration to earn a high mark!
First of all, you should provide some background information on the subject. For example, if you are writing an essay about immigration in the United States, describe and discuss the key periods when immigration was high. Try to think about the following questions:
- What motivates people to immigrate a certain country?
- Why is immigration higher in developed countries than in developing ones?
- What are some examples of government policies promoting or reducing immigration?
Secondly, you should cover the key pro/con immigration arguments. Whether your essay is argumentative, persuasive, or informative, you need to acknowledge that immigration has both advantages and disadvantages. Here is a list of questions that you might want to ask yourself while writing the paper:
- What influence does immigration have on the economy?
- Does immigration make it easier or harder for people to find employment?
- Why are some people against immigration, even when it’s legal?
The third point you should address in your essay is illegal immigration.
This is a significant topic in many countries, including the United States. To make sure that your paper receives an excellent mark, answer the following questions:
- What are the reasons that make people immigrate illegally?
- What are your country’s policies with regards to illegal immigrants?
- What impact do illegal aliens have on the economy and society?
- Why are some countries targeted by illegal immigrants more often than others?
- What can governments do to prevent illegal migration without violating human rights and freedoms?
One of the most important immigration essay topics is the immigrant experience. While many students write about immigration, they often fail to present a comprehensive view of the concept.
To avoid this mistake, consider what immigrants feel and experience when they decide to come to a different country. If you have a friend who is an immigrant, you can interview them. Here are a few ideas to think about:
- What are the most widespread challenges faced by immigrants?
- How do people plan their life in a different country?
- Do language barriers affect their relationships with other people, access to medical care, and education?
- How do immigrants adjust to a new culture?
- Can an immigrant integrate fully into the community?
Lastly, when thinking of essay topics about immigration, it is impossible to ignore the impact of immigration on society. Indeed, most essay titles in this area are focused on positive and negative social consequences of immigration. To cover this point in your paper, you may try to answer these questions:
- Does immigration facilitate social division and can this effect be prevented?
- Why do some people oppose cultural and racial diversity? What is cultural assimilation, and is it helpful to modern societies?
- How can cultural pluralism and multiculturalism influence communities in immigrant-rich countries?
- What can we do to ensure that immigration benefits all people, including native citizens?
Hopefully, this post has provided you with some things to talk about in your future immigration essays. Make sure to check sample papers and free essay titles about immigration on our website!
- Essay About Immigration Causes and Effects Some of the major causes of immigration in the current world include; Political unrests and wars This is one of the common causes of immigration in various regions of the world.
- Immigration: Advantages and Disadvantages It is important to mention how immigrants tend to affect the economy of the country. According to the statistics received from the US Bureau of Labor, the participation of foreigners in the workforce was 3.
- The History of Jamaicans Immigration to Canada The final section examines and discusses the migration of Jamaicans to Canada from 1960s to the financial year 2000. Despite the importation, the Maroons who in 1976 migrated to Halifax became the earliest Jamaicans to […]
- Thunder in the Sun – A Tale of Basque Gold-Rush Immigration The examination of the plot of Thunder in the Sun and credible sources focused on the Basques’ culture and immigration into the United States has revealed some inconsistencies in terms of historical evidence.
- Immigration: Where Did Your Ancestors Live? Officially, it is referred to as the Republic of Haiti, and the population of this country is approximately ten million people.
- Chinese Immigration to Cambodia in Personal Story Mom was forced to gather up some money from relatives who were already in the refugee camp to exchange for the release of my sister.
- Ferguson v. Canada: Citizenship and Immigration Case The applicant and the council counter this claim by stating that the officer’s dismissal was based on not finding evidence credible and failing to consider statements such as “Ms.
- Soledad Castillo’s Immigration to the USA To reach the USA at that time, the group of people Soledad was with had to stay invisible and quiet because the actions they took were illegal.
- The Texas Border, Security, and Immigration Immigration from Mexico is not thought to represent a violation of U.S.security, but the issue of the Texas border remains relevant and intriguing.
- Current Immigration Issues in the United States First of all, the goal of this speech is to inform the audience of the current immigration issues in the country and how they have been and are promised to be treated by the politicians.
- Immigration and Discrimination in the Workplace The ability to see a big picture and the need to appreciate the contribution of immigrants to U.S.economy will reduce the incidences of discrimination in the workplace.
- Analysis of Immigration Issues The lack of protection for the work of immigrants demands compared to people born in this country and who had the opportunity to get a job because the state protects them.
- Immigration in California: “Moving Still” by Francisco Jimenez The atmosphere of fear and poverty forced the families to break the rules and to overcome the frontier in the pursuit of welfare.
- Effect of Immigration on American Economy On the other side of the fence there business leaders and economists who asserted that immigrant workers can be a boon to the US economy.
- Irish-Catholic Immigration to America The importance of this event appeared from the fact that the Irish migration was one of the most significant contributors to the American immigrants’ inflow.
- The Effects of Immigration in Texas The period between 200 and 2006 saw the population of the foreign-born in the Texas state increase by twenty-four percent and it was during this same period that the state gained over 650,000 immigrants bringing […]
- Free-rider Problem and Illegal Immigration The issue of free riding is inevitable in each and every country because of the presence of the presence of minors, tax evaders and illegal immigrants just to mention but a few.
- Is Immigration an Economic benefit to the Host Country? Economically, the rate of payment of tax to the host country is always lower than the services it provides to the immigrants.
- Immigration as Political Issue in the USA The country has been witnessing a surge in the number of immigrants, and it is estimated that the number of illegal immigrants superseded that of the legal ones.
- The IDEAL Immigration Policy Advocacy All IDEAL candidates, like most applicants nowadays, would be required to pay a processing fee in advance to cover the price of doing background checks and conducting visa interviews.
- Immigration in the United States and Canada in the Post Hart-Cella Act (1965) and Canadian Immigration (1976) Act Era Two basic factors motivate Immigration in the world; the first one is the reason to move from country of origin and second, the reason to move to a host country.
- Immigration in New York City and Its Effects Steele and Perkins examine the impact of the apparent volume of migrants in the neighborhood on the propensity to redistribute in New York City.
- The Maya Immigration to the United States Therefore, each narrative included in the article “Maya Youth in Los Angeles” by Alicia Ivonne Estrada helps a reader to determine the factors that affected the Maya immigration to the U.S.
- The Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada The IRB is comprised of the Immigration Appeal Division, the Immigration Division, and the Refugee Protection Division. The governor-in-council appoints the Chairperson of the IRB who is supported by the vice-chairperson and deputy chairperson.
- The National Immigration Enforcement The intention of ICE to employ their agents in sanctuary cities will only make the gap between the cities and enforcement agencies wider.
- Migration Patterns: American Immigration However, it is also crucial to refer to the effects of such processes, including the overview of local communities, the impact on the economy, and the overall development or lack thereof when multiple individuals move […]
- The Harvest of the Empire: Immigration in the US The situation has become more acute in the last few years because of global problems like the coronavirus. The entire economic development of the colonies was subordinated to the interests of Spain and Portugal.
- Climate Change and Immigration Issues Due to its extensive coverage of the aspects of climate migration, the article will be significant to the research process in acquiring a better understanding of the effects of climate change on different people from […]
- Immigration: The Key Challenges As evidenced in the four articles, the key challenges of immigration revolve around high unemployment, border militarization, and legality of DACA. The border agents, as explicated in the Carroll’s article, have doubled to 23,000 for […]
- Aspects of Immigration From Mexico to the United States In the 20th century, the employment of immigrants was an ambiguous decision due to the possibility of hiring a cheap labor force and the necessity of legal registration.
- Immigration in the US: Historical Background Therefore, it is likely that he would have supported the introduction of quotas and would have taken a position similar to Jefferson.
- The Immigration Crisis in Texas The clash between the federal government and the state of Texas over the implementation of immigration law and the exercise of these powers has been ongoing for decades now.
- The 0 Visa: Immigration Case Study The purpose of the work is to consider an example of a 0 visa case from a family of three people and the possible issues that an officer may encounter.
- Irish Immigration to America and the Slavery Despite the fact that the Irish encountered a great number of obstacles, the immigration of Irish people to the United States was advantageous not only to the immigrants but also to the United States.
- Discussion of Holocaust and Immigration In “Holocaust Education and Remembrance in Australia,” Suzanne D.and Suzanne H.discuss the adverse effects and after-issues of immigration among the Jewish community and how it led to the concept that the Holocaust had a long-lasting […]
- Phenomenon of Immigration Analysis The phenomenon of immigration is often viewed as a complex one due to the concerns and fears associated with the increase in the number of immigrants within a community.
- A Caribbean Immigration Policy in the United States Thus, United States policy has a significant influence on the economic and social condition of the Caribbean Islands. The Caribbean, the so-called third border of America, impacts the internal security of the United States.
- Immigration Controversy in the United States This might have a significant influence on the quality of decisions and the care provided to immigrants. The financial and emotional obstacles that children of immigrants encounter in a new nation are sometimes complex.
- Immigration in American Economic History Because of the discriminatory attitudes that existed in society, I was not able to find a high-paying job. Those were the physical challenges I had to face in the form of sickness and starvation.
- Migration to the Caribbean vs. African Immigration While the 19-20-th-centiury migration to the Caribbean historically has nothing to do with African immigration, the underlying cause of racism and discrimination case the main reason for migration connects the specified phenomena.
- Abolishing the Immigration and Customs Enforcement Detention Centers Although the abolition of ICE detention centers could potentially encourage the violation of the country’s immigration policies, they constitute a tool for racial subordination and exacerbate the problem of mass incarceration.
- The Irish Immigration to America in the 19th Century The increase in food production and income from the war led to increased fertility rates among the Irish. The abrupt end of the war in the early nineteenth century precipitated the emigration.
- Immigration System and Homeland Security The combined efforts of the agencies constituting the Department of Homeland Security in addressing the safety needs of American citizens have a predominant impact on the immigration system.
- Immigration and Homeland Security as Issues It is important to note that the issues of immigration and homeland security are the problem of the moral duty of the United States as a beacon of democracy and the safety of its current […]
- The Issue of Immigration and Immigration Policies Therefore, it is a moral duty and responsibility for a wealthy nation to help the poor, and immigrants mostly arrive in the United States to seek a better life and leave the poverty of their […]
- Geopolitics, Diplomacy and Small States: Immigration Challenges in Switzerland The current foreign policies of the country have remained ineffective in regulating the influx of foreigners in the country. The following are some of the specific challenges that are associated with the high rate of […]
- Globalization, Immigration, and Class Division It includes the widespread globalization of countries, diverse economic perception of each, and the acute ethical and legal side of the immigration issue.
- The Florence Project: Immigration According to a fellow volunteer at the Florence Project, one of the biggest non-profit organizations in Arizona, the need for social and emotional support for Mexican immigrants has been of utmost importance across the state […]
- The Immigration Stations of Ellis Island and Angel Island Although the Angel Island Immigration Station was often referred to as the “Ellis Island” of the West, the conditions in these sites were very different, and so was the treatment of the arriving immigrants.
- Alabama and California Immigration Policies The higher population of immigrants in California pushes the states to create a positive environment for the majority as opposed to Alabama.
- Waves of Immigration: Recognizing Race and Ethnicity In 1965, Congress overturned the discriminatory immigration quota system and passed legislation based on the principles of family reunification and the attraction of a highly-skilled workforce to the United States.
- Immigration: Social Issue Feeling Analysis From the global perspective, the most influencing countries in the world use visa and other conditions of entering the country as a migration regulating tool.
- The Problem of Immigration in the US Puerto Rico came to capitalism and imperialism, and the transformation of this territory into a state “under the wing” of the United States led to the loss of culture, tourism, and an increase in poverty […]
- Illegal Immigration Policies and Violent Crime The authors of this article discuss how illegal immigration and border enforcement influence the level of crime along the U.S.-Mexico border.
- Strategies for Solving the Issue of Illegal Immigration in the US The first one is enforcing the measures preventing it, and the second one is changing immigration policy in order to make legalization easier.
- Immigration: Life Chances and Difficulties Other factors are unsuitable weather conditions, persecution, threats to life or health, poverty in the country, risks of disease, and infection. Therefore, immigrants want to find a better place to live in order to improve […]
- The Crisis of Cultural Identity of Luxembourg Due to Massive Immigration The possibility of a city-wide display exhibiting the workmanship and specialties of Luxembourg could be a method for opening the secret of the nation’s way of life. There is an incredible blend of individuals who […]
- Resolving Mexico’s Immigration Crisis A stable rate of immigrants and refugees, particularly traveling in so ‘caravans’ coming from South and Central Americas into Mexico with the hopes of reaching the U.S.or finding permanent residence in Mexico at the least.
- Immigration, Cultural Encounters, and Cultural Clashes He also obeyed the religious traditions of his country by avoiding beef in his food, opting for milk and cornflakes as a meal.
- The Birth of Illegal Immigration In addition, Americans blamed Chinese immigrants for low wages and the unemployment rate, which further influenced the ban on Asians to move to the U.S.
- Immigration: Orientalism and Yellow Power The migration was propelled by drought and floods on the Opium trade between the Chinese and the British. The initial resistance against the Chinese started in 1875 with the enactment of the Page Act.
- Researching of Issue of Immigration Inclusion of this level helps to appreciate local policies and attitudes that can affect the immigrants and improve their quality of life.
- Biden Ends Workplace Immigration Raids, Reversing Trump Policy Firstly, the announcement will contribute immensely towards the integrity of most employers in the sense that it is going to push employers to pursue only documented immigrants for labor without putting excessive pressure on the […]
- Immigration: The Costs and Benefits According to the author, due to the prevailing ethnocentrism and the division of society into “us” and “outsiders,” the community often treats immigrants with prejudice.
- Analysis of DACA and Immigration Illegal immigration and its handling has always been a hot button topic in the US, especially after the events of 9/11 and the creation of the department of homeland security.
- Cost of Immigration Enforcement and Border Security Functional Components of the Incident Command System Out of the functions described in the table focusing on the NRF, the most useful and important one is definitely prevention of terrorist attacks and associated incidents.
- US Immigration Policy and Its Correlation to Structural Racism That may create breaches in the immigration policy and cause social instability that could endanger the status of immigrants and even negatively affect the lives of the nationals.
- Immigration, Social Construct, Race and Ethnicity As a result, the movement has impacted the United States positively and negatively, although the pros outweigh the cons. A social construct is defined as the thoughts or ideas established and accepted by individuals in […]
- Immigration to the US in Relation to Covid-19 Overall, the human right to change the place of residence should be upheld by the nations of the world. To conclude, the issues related to immigration should be of more significant concern to the world’s […]
- Ambiguous Loss: Immigration and Separation of Families To lessen the impact of ambiguous loss, immigrants and their families need therapy, community support, and advocacy for policy change to keep them safe.
- Impacts of Immigration and Urbanization Urbanization is a special term that describes the decreasing proportion of people who live in rural areas, the population shift from rural to urban areas, and the possible ways of societies’ adaption to these changes. […]
- The Implications of Immigration When considering the results of the process, both the sender and the receiver country must be discussed, as well as the implications for the migrants themselves.
- Aspects of Immigration Reform Creating a fair, legal, and humane immigration system requires the legalization of almost 11 million immigrants already staying in the country and the simplification of obtaining citizenship in the country.
- COVID-19 and Immigration Issues On March 20th, 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention of the US Department of Health and Human Services issued a special order to curb the spread of COVID-19.
- Homeland Security Analysis: The U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services The mission and duties of this agency are closely related to the September 11 events not to face similar losses and threats in the future.
- Immigration Policy in Germany and the United States Germany and the United States contrast each other in resolving the public issue of immigration. The immigration policies of Germany and the United States cater to specific key stakeholders.
- Immigration and Naturalization Service Officer Career For the present paper, I have selected to profile the careers of Custom Officer and Immigration and Naturalization Service Officer. However, the entry-level position for customs is often administrative assistant, who works mainly with documents […]
- Immigration: Benefits for the Nation or a Drain on Society? Immigration is a topical issue in the contemporary U.S., which has divided the community into two opposing camps.
- Immigration from Asia and India: Political Impacts In retrospect, the literature review of the issue at hand has shown that there is a significant gap in the study of the factors that shape immigrants’ ability to reconnect with their cultural roots.
- Immigration: Political Impacts and Social Changes Particularly, the author posits that the increase in the amount of labor force that immigration entails leads to the improved performance of local companies, hence the rise in GDP rates and the overall increase in […]
- Angel Island Immigration Station While European immigrants coming into the country at the beginning of the twentieth century were more familiar with Ellis Island of New York, the Orientals underwent the experience of the immigration station at Angel Island.
- Hearth and Home Perception in 19th-Century Victorians Due to Immigration Nevertheless, the Victorian perception of what constitutes the concept had undergone severe changes in the 19th century, when the heart of the British Empire saw a significant wave of migration into the metropolis from its […]
- Debate on Immigration Policy: Law Enforcement Practices It is presumed that a wise immigration policy performed by the representatives of the police departments is likely to stabilize the current set of things and to reduce the number of illegal unregistered immigration cases.
- Immigration Museum and Cultural Diversity in Australia History The timeline presenting the main periods of immigration which is exhibited in the gallery can help to understand the development of the cultural diversity in Australia from the historic point of view because various periods […]
- Immigration Debate: Literature Study The Size and Characteristics of the Unauthorized Migrant Population in the U. The Immigration Debate: Studies On The Economic, Demographic, And Fiscal Effects Of Immigration.
- Immigration Asylum and Nationality Law In the UK it is very easy to move from a temporary settlement to a permanent one and it has increased the levels of net migration to the brimming level.
- Immigration Policy, Border Security and Migrant Deaths The research design that was used to collect this data was to investigate the rate of deaths that were experienced among the immigrants since the enactment of the immigration policy.
- Immigration and Refugee Law in New Zealand Consequently, the refugee policy comes about due to the flow of obligations courtesy of the 1960 UNHCR Convention, that is to say, the provision of refugees’ protection.
- The Current Immigration and Customs Immigration has always been the backbone of American history and the country’s rich cultural and ethnic diversity. Immigration in the U.S.is overseen by the Department of Homeland Security and its various agencies.U.S.
- Immigration and Its Impact on Employment Opportunities of Local People On the macroeconomic level, the inflow of immigrants to a country leads to an expansion in the size of an economy.
- Immigration and the United States On the other hand, the approximated number of immigrants in the region is 58 million, and the group is projected to be the main source of the future labor force.
- The Immigration in Abu Dhabi Abu Dhabi, in particular, is a noteworthy case study subject due to its history as the center of the UAE government and its corresponding influence on the question of immigration in the nation.
- Immigration Programs in the US Despite its economic, military and cultural power and the concept of an American dream, the US is far from the land of hopes it is portrayed to be.
- US Politics of Immigration The representatives of the Democratic and the Republican Parties of the United States have opposite viewpoints on immigration-related issues. In conclusion, the views of Democrats and Republicans on immigration are completely different.
- Immigration and Multiculturalism: Flow of Workers This paper aims to address the question of whether the flow of workers makes a positive impact on the host country in the context of society and business.
- The Immigration Benefits Specialists define labour migration as an advantageous process that positively affects the development of the economy in countries of employment and the improvement of the quality of life of families of labour migrants in their […]
- Immigration in Canada and Ethnicity: New Perspectives Such a reality will continue to influence and affect the life outcomes of the greatest number of Canadian citizens with diverse backgrounds in the future.
- Immigration From Mexico to the United States In the present day, the immigration of Mexican citizens to the United States is a topic of considerably intense debates for various political and economic reasons.
- Role of Immigration in Development of Canadian History Changes to the Immigration Act in the 1960s and the Royal Commission recommendations that led to the bilingual framework and multiculturalism stance of the Canadian government signified the significant shift for the country from being […]
- The History of Immigration to the United States and the Nature of Racism The development of the idea of race and ethnicity along with the idea of racial antagonism has two main stages in the history of the United States.
- Immigrant Adaptation Patterns Generally, the main difference of this form of adaptation is in the fact that immigrants may continue having their own cultural perceptions as their connections with the motherland are still strong due to family ties, […]
- Mitt Romney Softens Stance on Immigration The minority vote, particularly the Latino, has been on the increase and could have an effect on the election by providing a margin of victory on some of the states such as Nevada, Colorado and […]
- Illegal Immigration Control in the Texas Although the public assigns immense powers to the governor’s office, Texas’ office of the governor enjoys weak institutional powers because of the constitution’s provision of multiple offices that server alongside the office of the governor.
- Chinese American Immigration The Chinese American immigration consists of two distinct periods: first wave occurred between the 1850s and 1880s and ended in the appearance of federal laws that restricted the immigration: and the second wave that started […]
- US Immigration: Mexico, Puerto Rico, and Philippines The origins of Philippines immigration lie in its historical and political links with the United States Philippines used to be first annexed by the United States in 1989 and then an insular area of the […]
- Immigration Of Mexicans Into The United States In The Early 20th Century In the book, “Becoming Mexican American: ethnicity, culture, and identity in Chicano Los Angeles 1900-1945”, the author, Sanchez, addresses various issues that led to the immigration of Mexican into the United States. Community crisis is […]
- Berlin: Music, Spies, and Turkish Immigration And I think that Berlin’s split during the XX century has also influenced the music that was produced and written here: in its core, it reflects the differences and similarities between the East and West.
- The Illegal Immigration Prevention Policy For example, one of the biggest of them would be the necessity to analyze all the gathered information. Therefore, it is safe to assume that there would be no shortage of information for the Chef […]
- The Immigration Crisis by Armando Navarro This is a strategy that has been incepted to reduce the immigration of the people especially in countries that have direct business transactions.
- Birthright Citizenship in the US This is whereby a foreigner travels to the United State for a short period for the sole reason of giving birth in the U.S.in order to guarantee the citizenship of the child.
- Failure of Immigration Laws in Pakistan and Its Influence on American Economy The military death and announcement of the Al Qaeda leader Osama Bin Laden by the president of the United States of America have raised eyebrows on the immigration policies of Pakistan as a sovereign nation.
- “Arizona Immigration Law Debate Triggers National Shockwaves” by Nowicki While the motives of the author are unknown, it is likely that proposing the debate as so contentious will cause the audience to be more enticed to read and more engaged in the material.
- Immigration: The Ethical Side So, in order to make it clear, the essay will touch upon ethical advantages and disadvantages of immigration for the countries of origin and for the US.
- Mexican-US Immigration: Causes and Effects The drift of Mexicans or Latinos into the US is begging for increased concerns recently, especially among Republicans and the concern around decision tables is to itemize and resolve causes and effects that are directly […]
- Current Immigration Patterns in Canada The refugee population is made up of the populace who come to seek refuge in Canada as well as the populace made up of persons brought to Canada by churches, private sponsors as well as […]
- Arizona’s 2010 Immigration Law and US Economy A challenge is thrown to this clause by the 2010 Arizona immigration Law in America. It is this very thing that the founding fathers of the American Constitution had feared and thus took steps to […]
- The American Immigration Debate In the context of the present discussion of the immigrant debate in the US, one should turn to the work of Brimelow who has offered a rather radical solution to the problem of immigration.
- Immigration Issues in the USA The USA is the country that was built up of immigrants at the period of British colonization about three centuries ago; people who could not find their happiness and welfare in the Old Land came […]
- Causes and Consequences of Immigration to Canada The Chinese and Japanese still kept their oriental culture while the rest of the immigrants adapted to the new way of living in Canada.
- The Problems of Immigration on the Example of an Interview With an Immigrant In his book, The Location of Culture, Hommi Bhabha, pointed out the fact that, by being constantly confronted by the realities of post-industrial living, ethnic immigrants eventually cease to think of their individuality in specifically […]
- European Neighborhood Policy Effectiveness As a Tool of Immigration Policy ENP Action Plans sets out the terms of engagement between the European Union and each of the nations and the relevant political and economic agenda with a timeline perspective.
- Ellis Island as an Immigration Station The minority of the un-admitted immigrants who had spent time and energy on the long journey to the Island led to the Island being referred to as “The Heartbreak Island” or the “The Island of […]
- Intercultural Communication, Culture Shock and Immigration in Literature Westerners on the other hand believe in individualism so much that they forget that harmonious living is important for personal and society’s development.
- Race Relations in Britain. Immigration Situation This was the first large-scale migration of colored immigrants as compared to the minimal migrations that Britain had gotten used to.
- Immigration, National Identity and Citizenship The essay then examines the issues of immigration and its link to national identity in America and the ethical dilemmas that denial of citizenship can cause to national philosophies of the Western world.
- The Role of Immigration in Australia: Positive and Negative The thing is that the immigration and multiculturalism, as a result, impact positively on the economy, security, and social stability in the country.
- Immigration and Assimilation in US The children do not live in the control of their parents and the parents give all freedom for them to decide their life and career of their own choice.
- Saenz’ Opinion on Comprehensive Legislation on Immigration In addition to this is the fact that, it would be in accordance with the respect for human rights that the country stands for.
- Russian Immigration to America after 1945 The first wave of migration of the Russians was in the second half of the nineteenth century and during the early 20th Century before the First World War.
- France: Position in the EU and Immigration The social framework of France is presupposed with the whole European trends in making social and economic programs for the citizens of the EU.
- Social Issues in Kuwait: Immigration Workforce Among the frequently highlighted issues in the country, one is the low productivity among the local workforce due to the high influence of favoritism and nepotism in promotions and merits.
- Hispanic Americans as Illegal Immigration Thus a historical loyalty to the Democratic Party is still sustained even today At 15% the Hispanic-American population of the United States makes up the fastest growing minority in the United States.
- Immigration Welfare Policy Analysis An unprecedented influx of immigrants Immigration has resulted in a lot of social, economic, and other problems and the need to have a strong and rational policy that is beneficial to both the immigrants and […]
- US Immigration in Late 19th Century In the late 19th century, following the stream of the “Gold Rush”, millions of immigrants entered the United States, most of them attracted by the opportunity to earn “easy money” and to escape the hardships […]
- Humanities. Immigration Issues in the United States The scope of the problem of illegal immigration in the United States has remained undefined due to the vagueness of the immigration policies.
- Jobs and the American Economy: The Issue of Immigration The issues of immigration to the USA, either legal or illegal are of great significance for the US government. Since the 1990s, lots of academic researches have tried to charge the extent to which immigration […]
- Catholic and Jewish Immigration in the United States The experiences and challenges of starting a new life in America were very different for both the Catholics and the Jews primarily because of their different social cultural and social economic disparities.
- Immigration in New York 1990-2008 The earliest debate regarding the distribution of powers over immigration between the federal and state governments arose in the context of the Alien Act of 1798.
- Immigration and Schools in the United States To understand the magnitude of the immigration and school issue, it is important to first understand the perspective that most people in the public domain, political and education circles, have on immigrants.
- The History of Canadian Immigration and Innovative Federal Immigration Policy Though this phenomenon has outlined in positive financial growth in Canada there are lots of fundamental complexities that immigrants usually have to challenge when immigrating to Canada comprising the underdevelopment of community services, difficulties in […]
- Canadian Immigration and Multiculturalism The number of Aboriginal peoples in the total Canadian population is growing. The third force consists of the racial and ethnic minorities that are not included in the Charter groups.
- French Immigration: Rights of Foreign-Born Citizens An analysis of the impact of immigrants on the average level and distribution of income among the native population shows that immigrants with higher levels of skill are more likely to raise the average level […]
- Women Study: Immigration and Mothering One of the most essential areas of such studies is immigration in relation to gender and specifically mothering.”Immigration and Mothering; Case Studies from Two Generations of Korean Immigrant Women” by Seungsook Moon is an attempt […]
- Immigration Restrictions in American History The opinions of politicians, scientists, and statesmen were opposite as some of them kept to the point of view that immigration was necessary for the development of American society, while others were convinced of the […]
- Immigration in Post-war France France is the only European country that has experienced a reduction of immigrants in Europe even though it has the highest number of immigrants.
- Illegal Immigration: Difference in Covering the Matter The aim of the paper is to discover the difference in covering the matter of illegal migration to Canary Islands from sub-Saharan including periodical issues, radio broadcasts, and a photo, in order not only to […]
- Immigration and Students in America For many students coming from Asian and post-soviet countries, the aim of immigration is to stay in the USA while European students want to receive good knowledge in technical and management spheres. The difference is […]
- Amending Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986 The arguments for the former side include the following: first is that there is an unprecedented increase in the inflow of illegal workers in the United States.
- Why Immigration Is a Problem When Amir came to rescue him, he is beaten by Assef and Sohrab hits Assef with a stone from the sling in the eye and it is when they manage to escape and go back […]
- Necessity of Immigration Reform in America Basically, immigration reform pertains to policies and programs that aim to improve the development of the quality of life that will aid in the adjustments of the immigrants.
- Open Immigration Borders Migration: Effects of Muslim Ideologically, the presence of the Muslim religion has affected the lives of the people of France in one way or the other.
- History of Puerto Rican Immigration to New York Amid the earliest Puerto Ricans to immigrate to New York were Spanish crown exiles both men and women, due to their political beliefs and resistance for the cause of Puerto Rican sovereignty In 1917 United […]
- Latino Migration: The Issue of the Mexican – US Immigration and the US Border Policies This policy brief is dedicated to a specific problem, namely the problem of the Latino migration, or, to be more exact, to the issue of the Mexican US immigration and the US border policies towards […]
- Immigration Asian Indians in America For American immigration history, it means that it coincides with the settlement of the country: the settlement of America was influenced more by the immigration processes rather than by the natural increase of the citizens.
- Americanism or Trans-National America: Immigration So according to Theodore Roosevelt that Americans must persist that if the immigrant reaches America in fine reliance turns out to be an American and incorporates himself to America and the citizens of America, one […]
- Immigration, Hispanics, and Mass Incarceration in the U.S. This article evaluates the effect of the 1986 Immigration Reform and Control Act, that led to the legalization of approximately 3 million immigrants had on the crime rates in the U.S.
- Immigration and Labor Law The majority of research findings suggest that despite the active work of the legislative branch on the improvement of immigration policies, the lives of both documented and undocumented foreigners are obstructed with multiple limitations and […]
- Immigration as a Source of Community Problems In order to address the immigration concern, one will have to create a more welcoming and inviting economic and social environment for immigrants, reducing the propensity toward a cross-cultural conflict and engaging the members of […]
- How Immigration Affects Global Business The purpose of this paper is to apply different case studies and thoughts to describe how immigration continues to affect global business.
- Problem of Immigration in the United States The history of the United States provides a variety of examples to support the idea that immigration is a source of economic and social benefits for the population.
- Federal Immigration Policy: Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals
- Immigration History of New York City: The Most Significant Center for New Arrivals
- Understanding Canadian Immigration Policy Change
- The Migrant and Immigration Issues in the US Society
- Health Policy and Immigration Issues in California
- The History of Korean American Immigration Experience
- Immigration Issues in the United States
- New Waves of Immigration to the United States
- Immigration in the United States
- Immigration and Crime Rates in the United States
- Immigration Effects on the Median Household Income
- Travel and New Land: Immigration Experience
- Labor Economy and Immigration
- The Immigration Museum: Cultural Diversity in Australia
- Immigration to the United States of America
- Immigration and Control Policies in the US
- International Immigration Flows: Economic Pressure
- Social Issues of the Immigration Journal
- Irish and German Immigration to the 19th-Century US
- Employment Law: Immigration Reform and Control Act
- Ethics of Illegal Immigration Effects on the US
- Immigration Effects on Marketing Activities in Canada
- Immigration Threats in the USA
- Immigration Influence on Israeli Residents’ Personality Traits
- Current International Interest: Immigration in the US
- Changes in Immigration Policy
- Fiscal Concerns and Public Attitude towards Immigration
- Illegal Immigration Issue in the USA
- Immigration Services Against Crime and Terrorism
- Muslim Immigration to European Countries
- Women’s Immigration and Its High Price
- The New Immigration Laws Creating a New Realty
- Donald Trump’s Immigration Speech
- Immigration Pros and Cons for the Immigrants Themselves
- Immigration in Britain and Social Cohesion
- Immigration as the Positive Economic Consequences in the USA
- Immigration and Urban Change in the USA
- Open Immigration, Its Benefits and Morality
- Illegal Immigration, Its Causes, Methods, Effects
- California’s Immigration Policy and Its Impacts
- Immigration in Trump’s Candidate Speech
- Immigration and Healthcare in the United States
- Immigration and Refugee Protection Act for Women
- Illegal Immigration Crisis: Problems and Solutions
- Reid Luhman’ View on History of Immigration to the US
- The Economics of Immigration
- Immigration Pros and Cons for the United States
- The Problems of Immigration: Muneera Qahtani Views
- A History of Immigration and Ethnicity in American Life
- German, Irish, and Jewish Migration to the US
- Identity, Immigration and American Public Opinion
- New York Times: Obama Vows to Push Immigration Changes
- Media View in Shaping Immigration
- The Canadian Contemporary Policy of Immigration
- Immigrants’ Human Rights in America: The Issue of Immigration as Old as the Country
- Immigration Effects in Patrick Buchanan’s The Death of the West
- How Immigration Relates to Post-Human and Globalization?
- Immigration in America: the Current Understanding
- Basque Immigration and Culture in Idaho
- Justice of Immigration in the United States
- Ontario Immigration Rates Growth
- Immigration, Voting and Naturalization Laws
- Reasons of Immigration Literature Growth
- Illegal Immigration as a Major Problem for the USA
- Operation Jump Start in Immigration Issues: Pros and Cons
- Immigration and Its Effects to the Middle East
- Relationship of Immigration and Median Household
- America and the Problem of Illegal Immigration
- Sheriff Joe’s Illegal Immigration in Arizona
- Immigration Laws in Arizona State
- Illegal Immigrants: Eviction or Amnesty
- UK Immigration in 2015
- Ethnic Groups in the US Immigration History
- Political Sciences: American Immigration
- Immigration Debate in the US
- Waves of Immigration to the United States
- Immigration Issues in Different Spheres
- Controversial Immigration Policy in Brazil
- Chinese Americans Immigration
- Illegal Immigration in the United States
- Illegal Immigration Problem in the United States
- Illegal Immigration in the USA
- Immigration and Deportation Processes
- Is the Legalization of Illegal Aliens a Good Solution to Illegal Immigration in America?
- Middle Eastern Immigrants in Australia
- Immigration as Social Issue in Australia
- The Aspects of Immigration into Australia
- Role of Frontex in Combating Illegal Immigration in the European Union Territory
- Illegal Immigration in the United States as an Economic Burden
- The Issue of Muslims’ Immigration to Australia
- Stopping Illegal Immigration: Border Security
- Analysis of Race and Ethnicity in U.S. Immigration History
- History of Immigration to the United States
- Arab Immigration in USA
- U.S. Immigration Reform Policy Circa 2001 to Present
- Domestic and Immigration Policies
- Immigration and Changes in British Society around the Time Period the Novel is Set
- Bridging People Together: When Immigration Issue Comes to the Forth
- Immigration and Multiculturalism in Australia
- Economics and Immigration in Japan
- Comparing Sweden Immigration Policy with German Immigration Policy
- Immigration and Illegal Foreigners in Japan
- Legal Mexican Immigration Wave Since 1965
- Immigration to Australia (Arabic Case)
- Impact of the DREAM Act on Immigration in America
- Immigration of Filipino Nurses to the United States
- History of Immigration in the United States
- Immigration to the US After the Second World War
- Women and Immigration Challenges
- Immigration Reform in the United States
- Immigration Admission and Control Polices
- Immigration Policies and Economy
- Types of Diasporas: Articles Analysis
- Public Opinion on Immigration and Ethnic Relations in the US
- African Americans: Immigration and Ethnic Relations
- Effects of illegal immigration on the economy of the United States and the measures that be taken to minimize the effect
- Controversy Surrounding Immigration
- How Has Immigration Transformed the Life and Culture of London Over the Past 150 Years?
- Canadian Immigration Policies: Points-Based System
- U.S. Immigration Encouragement
- Errors Made by the United States Citizen and Immigration Service When Processing Immigration Forms
- Socio-Economic Benefits of Immigrant Population in the US and Canada
- Immigration in the Film ‘The Guest worker’
- Illegal Immigration to the United States
- Economic advantages and disadvantages of immigration into the U.S.
- Economic of Immigration and Economics of Mexico
- Sweden and Denmark: Immigration policies
- The Impacts of Illegal Immigration on the Country of Destination
- Age at Immigration and Second Language Proficiency Among Foreign-born Adults by Gillian Stevens
- Immigration Specificity of ELLs in Canada and the USA
- Immigration Reform and the Economic Impact
- Immigration Reform in US Government
- Why US Attracts Immigration From All Over the World
- Immigration Issues in Alfonso Gonzales’s Book “Reform Without Justice: Latino Migrant Politics and the Homeland Security State”
- Justice Theories and American Immigration System
- Political Immigration as Addressed in City on the Edge: The Transformation of Miami
- Impact of Immigration on the Geography of Canada
- Immigration: “City on the Edge” and “Friends or Strangers”
- The Political Affairs and Strategies of Immigration Laws in the State of North Carolina
- Immigration Bill in US
- Immigration bias on Hispanics in North Carolina
- Myths About Immigration in the U.S.
- Immigration, Socioeconomic and Upward Mobility and Cultural Assimilation
- United States Immigration History
- Concept of Race and Ethnicity in U.S. Immigration History
- The Root Cause of Racism and Ethnic Stratification in the US
- A Speech Touching on Immigration Reforms
- Women Immigration to US
- American Immigration History
- History of Immigration and Its Timeline in the United States
- History of Immigration – United States
- Rights of Immigrants and Immigration Policy
- Globalisation, Immigration, Race and Ethnicity in Vancouver
- Immigration Debate: Romney & Obama
- Immigration’s Influence on the USA
- Economic Consequences of Immigration
- Economic Consequences of Immigration on Socioeconomic Activities
- Immigration in the Contemporary American Society
- Factor that Cause Immigration
- Consequences of Immigration
- Positive Economic Consequences of Immigration vs. Negative Socioeconomic Consequences of Unskilled Immigrants
- The Issue of Illegal Immigration
- Coming to America: An Exploration of Immigration
- Annotation of Immigration Effects on Homicide Offending for Total and Race/Ethnicity-Disaggregated Populations
- Anti-Anti Immigration: Principles to Make Migration Work
- The Impact of Immigration on the American Society and Culture
- Immigration Policy: Government Approach and Solutions
- Migration, Immigration, and Emigration, and their Effects on Religion, Women, and Minorities in Egypt
- Illegal Immigration: Views of Policy Makers, Media and General Public
- The Impact of Immigration on the Economy of the USA
- The Chief Tool of the “White Australian Policy” was the Immigration Restriction Act, 1901
- The Immigration History in the United States
- Argument for Measures to Control Illegal Immigration
- The Immigration Status for Students
- History of the Illegal Immigration into the U.S.
- The History of Canada, Its Position on Immigration
- Economic Contribution of Slaves and Present Day Legal and Illegal Immigration
- Legal Immigration versus Illegal Immigration in America
- Crossing Borders: Immigration Issue
- Immigration and Crime Rate
- Pros and Cons of Immigration for the Immigrants
- Implications of Illegal Immigration in the US
- Immigration Admissions and Control Policies
- Immigration Policies Challenges
- Analyzing the Issue of Illegal Immigration in the US
- Immigration and Ethnic Relations
- World Publics Welcome Global Trade – But Not Immigration
- Arizona Immigration Law Reform
- The Fact of Immigration in the US and Media Reaction
- Arizona Immigration Law: What For?
- Maria Full of Grace and De Nadie: Immigration in Terms of Shots and Angles
- Are Attitudes Towards Immigration Changing in Europe?
- Should Anti Immigration Measures Between the Us and Mexico Be?
- Are There Valid Economic Grounds for Restricting Immigration?
- Can Illegal Immigration Ever Be Solved?
- Does Education Affect Attitudes Towards Immigration?
- Should Nations Restrict Immigration?
- Why Do Americans Think Immigration Hurts the Economy?
- Can Illegal Immigration Lead to Terrorism?
- Can Immigration Alleviate the Demographic Burden?
- Does Immigration Affect Demand for Redistribution?
- Should America Encourage Immigration?
- Can Immigration Compensate for Europe’s Low Fertility?
- Are Concerns Over Immigration to Do With Culture of Economic Reasons?
- Can Immigration Reduce Imbalances Among Labor Markets?
- Does Immigration Affect the American Economy?
- Can Immigration Slow U.S. Population Aging?
- Can Old Immigration Theories Be Applied to New Immigrants?
- How Unification and Immigration Affected the German Income Distribution?
- Can Selective Immigration Policies Reduce Migrants’ Quality?
- Can Immigration Mitigate the Rising Pension Burden in Europe?
- Does Border Enforcement Protect U.S. Workers From Illegal Immigration?
- How Was Immigration Throughout the 1960s?
- Does Educational Choice Erode the Immigration Surplus?
- Should Countries Implement Immigration Quotas?
- Does Europe Need Mass Immigration?
- Can Immigration Save Our Social Protection System?
- Does Immigration Affect Public Education Expenditures?
- How Should the United States Treat the Present Day Immigrants?
- Should Immigration Standards Tougher?
- Who Has the Most Impact on Illegal Immigration Policy?
- Immigrant Stories: A Visual Journey
- How Cultural Identity is Redefined in Modern Immigration
- How Immigration Transforms Culinary Traditions
- Symbolism of Borders, Walls, and Bridges in Immigration Narratives
- Analysis of Science Fiction Works on Alien Immigration
- Does Language Unite or Divide Communities?
- Ways to Depict the Emotions of Immigrant Experience
- Immigration Stories in Song Form
- How Digital Technology Impacted Immigration
- The Possibility of Extraterrestrial Immigration
- Global Migration Patterns Throughout the 20th Century
- Immigration Policies Around the World: Comparison
- Push and Pull Factors of Immigration.
- The Impact of Immigration on Host Country’s Language.
- Approaches to Immigrant Inclusion.
- Challenges Faced by Refugees and Asylum Seekers
- The Role of Migrant Workers in a Country’s Economy
- Educational Opportunities for Immigrant Youth
- Myths and Reality of Undocumented Immigration
- How Immigration Detention Relates to Human Rights Concerns?
- Border Security and Migration Management Strategies
- How Do Migrants Negotiate Their Sense of Belonging?
- Humanitarian Issue of Family Separation
- Immigration Biases and Stereotypes in Media Representation
- Celebrating Diversity of Immigrants in Host Countries
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 25). 417 Immigration Topics to Write about & Essay Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/immigration-essay-examples/
"417 Immigration Topics to Write about & Essay Examples." IvyPanda , 25 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/immigration-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '417 Immigration Topics to Write about & Essay Examples'. 25 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "417 Immigration Topics to Write about & Essay Examples." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/immigration-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "417 Immigration Topics to Write about & Essay Examples." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/immigration-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "417 Immigration Topics to Write about & Essay Examples." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/immigration-essay-examples/.
- Globalization Essay Topics
- Social Security Paper Topics
- Social Democracy Essay Titles
- Population Titles
- Social Justice Essay Ideas
- Urbanization Ideas
- Refugee Paper Topics
- Social Problems Essay Ideas
- Social Responsibility Topics
- Colonization Essay Ideas
- Segregation Research Topics
- Immigration Reform Topics
- Human Trafficking Titles
- Cultural Identity Research Topics
- Demography Paper Topics
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Human Migration — The European Migrant Crisis
The European Migrant Crisis
- Categories: Human Migration
About this sample

Words: 825 |
Published: Dec 12, 2018
Words: 825 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1258 words
2 pages / 1006 words
1 pages / 2055 words
1 pages / 479 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Human Migration
Europe is not obligated to accommodate immigration. Furthermore, immigration is ineffective in the global development policy (Carta et al. 2005). Europe is in the midst of witnessing the highest levels of immigration that seems [...]
Being an expatriate who longs to go back to the homeland and is able to do so on a regular basis does not have to rely on assimilating. Creating a new, comfortable life and network in an alien environment can be grueling, which [...]
Germany is currently home to some 15 million immigrants and their offspring born in the Countries. By statistical analysis, about 20 percent of the population have migration backgrounds and that makes Germany one of the European [...]
The population of America doubled from 1870 to 1900 as the population in the cities tripled.Cities grew up and out - cities built skyscrapers growing upwards with Louis Sullivan working on perfecting skyscrapers architecture [...]
“Immigrants Who Speak Indigenous Languages Encounter Isolation.” The New York Times,10 July 2014, www.nytimes.com/2014/07/11/nyregion/immigrants-who-speak-indigenous-mexican-languages-encounter-isolation.html. The writer uses [...]
In The Lonely Londoners by Samuel Selvon, Moses and Henry Oliver fight to overcome the discrimination they suffer due to prejudice in London towards immigrants. As insidious as the American South’s notoriously overt racism, [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Introduction. The steady growth of international labor migration is an important, yet underappreciated, aspect of globalization. 1 In 1970, just 78 million people, or about 2.1% of the global population, lived outside their country of birth.By 1990, that number had nearly doubled to more than 150 million people, or about 2.8% of the global population (United Nations Population Division, 2012).
The major problems of migration include poverty, acculturation, education, social adjustment, employment, housing, and family difficulties. These problems are understood in different ways; how they affect the migrants, immigrants, their origin, and destination. Family problems that affect the immigrants include departing from the support system ...
According to Afzal, this "voluntary" repatriation is often enforced through police extortion, bribery, and the confiscation of legal documents, and supported by Pakistan's narrative that ...
Inequality that builds a "marginalized majority" of native citizens boosts the power of anti-immigration narratives. A third significant issue is preparing cities for ecological migration. The changing climate is causing people to move in mass and sometimes invisible numbers. City planners have not kept pace and internal migrants especially ...
2016. 2023. Percentage of immigration court cases resolved per year. In the 2012 fiscal year, 207,000 immigration cases were resolved, or 39 percent of all cases. By 2023, the government managed ...
Introduction. Immigration is the foundation of the United States as a country. It was built on the labor, ideas, and cultural melting pot of immigrants coming to the US in the hopes of achieving the American dream, finding a new life, and establishing a home for their families. This report seeks to investigate whether the United States should ...
Migration and internal displacement are among the most pressing topics on the international agenda today. In my meeting with leaders from across the international community, from governments and business, and migration is one of the most frequent topics of conversation. ... It is a critical public problem that requires coordinated and ambitious ...
Explore how these issues and others shaped 2020, in our annual countdown of the Top 10 migration issues of the year. Click the links below to navigate to each issue: 1. COVID-19 Prompts Historic Halt to Global Mobility. 2. 2020 Deals Blows to Global Humanitarian Protection and the Notion of Burden-Sharing. 3.
For the winter 2019 student writing competition, "Border (In)Security," we invited students to read the YES! Magazine article "Two-Thirds of Americans Live in the "Constitution-Free Zone" by Lornet Turnbull and respond with an up-to-700-word essay.. Students had a choice between two writing prompts for this contest on immigration policies at the border and in the "Constitution-free ...
The slow and uneven recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic prompted new patterns of movement in parts of the world in 2021. New conflicts also erupted, ongoing crises smoldered, and migrants were often stuck in the middle. Our annual Migration Information Source Top 10 countdown reviews what we consider to be the year's most important migration trends and events.
Throughout recent years, we have witnessed an increase in human migration as a result of conflict, political instability and changes in the climate. Despite the growing number of migrants and refugees, provisions to address their health needs remain inadequate and often unmet. Whilst a variety of instruments exist to assert and emphasise the importance for migrant and refugee health, the lack ...
Rural to urban migration is higher in developing countries as compared to the developed nations. In Nigeria, a developing country, the population in cities is projected to rise from 1.9 billion to 3.9 billion between 2009 and 2030 (Ajaero & Onokala, 2013). This paper explains the causes and the impacts of migration of population from rural ...
A 2022 Gallup poll found that 70 percent of Americans surveyed considered immigration to be good for the United States, a 5 percent decrease from the year prior. At the same time, however, the ...
Overview. Migration is the movement of people from one place to another with the intent to settle. Causes: In preindustrial societies, environmental factors, such as the need for resources due to overpopulation, were often the cause of migration. Effects: As people migrated, they brought new plants, animals, and technologies that had effects on ...
The first thing to know is that migration is not a problem to be solved; in fact, it is a powerful driver of sustainable development, for migrants and their communities. It brings significant benefits in the form of skills, strengthening the labor force, investment and cultural diversity, among others. ... Migration is a social phenomenon ...
156 essay samples found. Immigration refers to the movement of individuals from one country to another, often in search of better opportunities or to escape adversities. Essays on immigration could delve into the various causes of immigration, its impact on host and origin countries, and the policies governing immigration.
Immigration Issues and Challenges. Immigration has been a hot-button issue in many countries around the world, with debates raging over the economic, social, and political impacts of immigration. In this essay, we will explore some of the key issues surrounding immigration, including the reasons people choose to immigrate, the challenges they ...
Immigrants often fill low-skilled jobs in industries such as agriculture, construction, and hospitality, which tend to pay lower wages. Immigration can also impact income distribution by contributing to the overall level of economic inequality in a host country. While immigration can lead to lower wages for some native workers, it can also lead ...
A. Economic factors. Economic opportunities are some of the most significant reasons why individuals choose to migrate. In countries with limited economic prospects, immigration is seen as a necessary means of improving their lives and the lives of their family members. Migrants also seek better job opportunities, higher wages, and a better ...
Immigration essay is a popular type of assignment in various topics, including politics and social sciences. In a globalized world, people can migrate from one country to another for work, study, and other reasons. This post will discuss some points that you could include in your essay on immigration to earn a high mark!
Published: Dec 12, 2018. The European migrant crisis highly increased in 2015 when rising numbers of people arrived in the EU travelling across the Mediterrean sea or overland through southeast Europe. These people include not only asylum seekers, but also economic migrants and some hostile agents, such as Islamic State agents, disguised as ...
In India, internal migration (fueled by an increasing rate of urbanization and rural-urban wage difference) is far greater than an external migration. India's urban population is expected to grow from 410 million in 2014 to 814 million by 2050. Instead of long term migration, there is a huge flow of short term migrants in the country.