
About Systematic Reviews

The Difference Between Narrative Review and Systematic Review

Automate every stage of your literature review to produce evidence-based research faster and more accurately.
Reviews in scientific research are tools that help synthesize literature on a topic of interest and describe its current state. Different types of reviews are conducted depending on the research question and the scope of the review. A systematic review is one such review that is robust, reproducible, and transparent. It involves collating evidence by using all of the eligible and critically appraised literature available on a certain topic. To know more about how to do a systematic review , you can check out our article at the link. The primary aim of a systematic review is to recommend best practices and inform policy development. Hence, there is a need for high-quality, focused, and precise methods and reporting. For more exploratory research questions, methods such as a scoping review are employed. Be sure you understand the difference between a systematic review and a scoping review , if you don’t, check out the link to learn more.
When the word “review” alone is used to describe a research paper, the first thing that should come to mind is that it is a literature review. Almost every researcher starts off their career with literature reviews. To know the difference between a systematic review and a literature review , read on here. Traditional literature reviews are also sometimes referred to as narrative reviews since they use narrative analysis to synthesize data. In this article, we will explore the differences between a systematic review and a narrative review, in further detail.
Learn More About DistillerSR
(Article continues below)
Narrative Review vs Systematic Review
Both systematic and narrative reviews are classified as secondary research studies since they both use existing primary research studies e.g. case studies. Despite this similarity, there are key differences in their methodology and scope. The major differences between them lie in their objectives, methodology, and application areas.
Differences In Objective
The main objective of a systematic review is to formulate a well-defined research question and use qualitative and quantitative methods to analyze all the available evidence attempting to answer the question. In contrast, narrative reviews can address one or more questions with a much broader scope. The efficacy of narrative reviews is irreplaceable in tracking the development of a scientific principle, or a clinical concept. This ability to conduct a wider exploration could be lost in the restrictive framework of a systematic review.
Differences in Methodology
For systematic reviews, there are guidelines provided by the Cochrane Handbook, ROSES, and the PRISMA statement that can help determine the protocol, and methodology to be used. However, for narrative reviews, such standard guidelines do not exist. Although, there are recommendations available.
Systematic reviews comprise an explicit, transparent, and pre-specified methodology. The methodology followed in a systematic review is as follows,
- Formulating the clinical research question to answer (PICO approach)
- Developing a protocol (with strict inclusion and exclusion criteria for the selection of primary studies)
- Performing a detailed and broad literature search
- Critical appraisal of the selected studies
- Data extraction from the primary studies included in the review
- Data synthesis and analysis using qualitative or quantitative methods [3].
- Reporting and discussing results of data synthesis.
- Developing conclusions based on the findings.
A narrative review on the other hand does not have a strict protocol to be followed. The design of the review depends on its author and the objectives of the review. As yet, there is no consensus on the standard structure of a narrative review. The preferred approach is the IMRAD (Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion) [2]. Apart from the author’s preferences, a narrative review structure must respect the journal style and conventions followed in the respective field.
Differences in Application areas
Narrative reviews are aimed at identifying and summarizing what has previously been published. Their general applications include exploring existing debates, the appraisal of previous studies conducted on a certain topic, identifying knowledge gaps, and speculating on the latest interventions available. They are also used to track and report on changes that have occurred in an existing field of research. The main purpose is to deepen the understanding in a certain research area. The results of a systematic review provide the most valid evidence to guide clinical decision-making and inform policy development [1]. They have now become the gold standard in evidence-based medicine [1].
Although both types of reviews come with their own benefits and limitations, researchers should carefully consider the differences between them before making a decision on which review type to use.
- Aromataris E, Pearson A. The systematic review: an overview. AJN. Am J Nurs. 2014;114(3):53–8.
- Green BN, Johnson CD, Adams A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. J Chiropratic Medicine 2006;5:101–117.
- Linares-Espinós E, Hernández V, Domínguez-Escrig JL, Fernández-Pello S, Hevia V, Mayor J, et al. Metodología de una revisión sistemática. Actas Urol Esp. 2018;42:499–506.
3 Reasons to Connect


Literature Review: Traditional or narrative literature reviews
Traditional or narrative literature reviews.
- Scoping Reviews
- Systematic literature reviews
- Annotated bibliography
- Keeping up to date with literature
- Finding a thesis
- Evaluating sources and critical appraisal of literature
- Managing and analysing your literature
- Further reading and resources
A narrative or traditional literature review is a comprehensive, critical and objective analysis of the current knowledge on a topic. They are an essential part of the research process and help to establish a theoretical framework and focus or context for your research. A literature review will help you to identify patterns and trends in the literature so that you can identify gaps or inconsistencies in a body of knowledge. This should lead you to a sufficiently focused research question that justifies your research.
Onwuegbuzie and Frels (pp 24-25, 2016) define four common types of narrative reviews:
- General literature review that provides a review of the most important and critical aspects of the current knowledge of the topic. This general literature review forms the introduction to a thesis or dissertation and must be defined by the research objective, underlying hypothesis or problem or the reviewer's argumentative thesis.
- Theoretical literature review which examines how theory shapes or frames research
- Methodological literature review where the research methods and design are described. These methodological reviews outline the strengths and weaknesses of the methods used and provide future direction
- Historical literature review which focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
References and additional resources
Baker, J. D. (2016) The purpose, process and methods of writing a literature review: Editorial . Association of Operating Room Nurses. AORN Journal, 103 (3), 265-269. doi:10.1016/j.aorn.2016.01.016
- << Previous: Types of literature reviews
- Next: Scoping Reviews >>
- Last Updated: May 12, 2024 12:18 PM
- URL: https://libguides.csu.edu.au/review

Charles Sturt University is an Australian University, TEQSA Provider Identification: PRV12018. CRICOS Provider: 00005F.
Subject Guides
Literature Review and Evidence Synthesis
- Reviews as Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
What is a Narrative Literature Review
Narrative review process.
- Integrative Review
- Scoping Review This link opens in a new window
- Systematic Review This link opens in a new window
- Other Review Types
- Subject Librarian Assistance with Reviews
- Grey Literature This link opens in a new window
- Tools for Reviews
Subject Librarians
Find your Subject Librarian Here

A narrative literature review is an integrated analysis of the existing literature used to summarize a body of literature, draw conclusions about a topic, and identify research gaps. By understanding the current state of the literature, you can show how new research fits into the larger research landscape.
A narrative literature review is NOT:
- Just a summary of sources
- A review of everything written on a particular topic
- A research paper arguing for a specific viewpoint - a lit review should avoid bias and highlight areas of disagreements
- A systematic review
Purposes of a narrative literature review:
- Explain the background of research on a topic
- Demonstrate the importance of a topic
- Suggest new areas of research
- Identify major themes, concepts, and researchers in a topic
- Identify critical gaps, points of disagreement, or flawed approaches for a research topic
1. Choose a topic & create a research question
- Use a narrow research question for more focused search results
- Use a question framework such as PICO to develop your research question
- Breakdown your research question into searchable concepts and keywords
- Research skills tutorials : How to choose a topic
- Ask a librarian for assistance
2. Select the sources for searching & develop a search strategy
- Identify databases to search for articles relevant to your topic
- Ask a librarian for recommended databases
- Develop a comprehensive search strategy using keywords, controlled vocabularies and Boolean operators
- Research skills tutorials: How to develop a search strategy
3. Conduct the search
- Use a consistent search strategy between databases
- Document the strategies employed to keep track of which are more successful
- Use a citation manager to organize your search results
- Ask a librarian for help or refer to the Research skills tutorials
4. Review the references
- Review the search results for relevant articles that answer your research question
- Review the bibliography of all relevant articles for additional sources
- Consider developing subfolders in the citation manager to organize sources by topic
- Use interlibrary loan for any articles without full text access
5. Summarize findings
- Synthesize the findings from the articles into a final paper
- The final paper should cover the themes identified in the research, explain any conflicts or disagreements, identify research gaps and potential future research areas, explain how this narrative review fits within the existing research and answer the research question .
For additional information :
Hempel. (2020). Conducting your literature review. American Psychological Association .
- Buchholz, & Dickins, K. A. (2023). Literature review and synthesis : a guide for nurses and other healthcare professionals . Springer Publishing Company, LLC.
- Coughlan, Michael, and Patricia Cronin. Doing a Literature Review in Nursing, Health and Social Care . 2nd edition., SAGE, 2017.
- Nundy, S., Kakar, A., Bhutta, Z.A. (2022). How to Do a Review of the Literature? . In: How to Practice Academic Medicine and Publish from Developing Countries?. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5248-6_18
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliography
- Next: Integrative Review >>
- Last Updated: May 15, 2024 12:32 PM
- URL: https://libraryguides.binghamton.edu/literaturereview
- share facebook
- share twitter
- share pinterest
- share linkedin
- share email
University Libraries University of Nevada, Reno
- Skill Guides
- Subject Guides
Systematic, Scoping, and Other Literature Reviews: Overview
- Project Planning
What Is a Systematic Review?
Regular literature reviews are simply summaries of the literature on a particular topic. A systematic review, however, is a comprehensive literature review conducted to answer a specific research question. Authors of a systematic review aim to find, code, appraise, and synthesize all of the previous research on their question in an unbiased and well-documented manner. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) outline the minimum amount of information that needs to be reported at the conclusion of a systematic review project.
Other types of what are known as "evidence syntheses," such as scoping, rapid, and integrative reviews, have varying methodologies. While systematic reviews originated with and continue to be a popular publication type in medicine and other health sciences fields, more and more researchers in other disciplines are choosing to conduct evidence syntheses.
This guide will walk you through the major steps of a systematic review and point you to key resources including Covidence, a systematic review project management tool. For help with systematic reviews and other major literature review projects, please send us an email at [email protected] .
Getting Help with Reviews
Organization such as the Institute of Medicine recommend that you consult a librarian when conducting a systematic review. Librarians at the University of Nevada, Reno can help you:
- Understand best practices for conducting systematic reviews and other evidence syntheses in your discipline
- Choose and formulate a research question
- Decide which review type (e.g., systematic, scoping, rapid, etc.) is the best fit for your project
- Determine what to include and where to register a systematic review protocol
- Select search terms and develop a search strategy
- Identify databases and platforms to search
- Find the full text of articles and other sources
- Become familiar with free citation management (e.g., EndNote, Zotero)
- Get access to you and help using Covidence, a systematic review project management tool
Doing a Systematic Review
- Plan - This is the project planning stage. You and your team will need to develop a good research question, determine the type of review you will conduct (systematic, scoping, rapid, etc.), and establish the inclusion and exclusion criteria (e.g., you're only going to look at studies that use a certain methodology). All of this information needs to be included in your protocol. You'll also need to ensure that the project is viable - has someone already done a systematic review on this topic? Do some searches and check the various protocol registries to find out.
- Identify - Next, a comprehensive search of the literature is undertaken to ensure all studies that meet the predetermined criteria are identified. Each research question is different, so the number and types of databases you'll search - as well as other online publication venues - will vary. Some standards and guidelines specify that certain databases (e.g., MEDLINE, EMBASE) should be searched regardless. Your subject librarian can help you select appropriate databases to search and develop search strings for each of those databases.
- Evaluate - In this step, retrieved articles are screened and sorted using the predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria. The risk of bias for each included study is also assessed around this time. It's best if you import search results into a citation management tool (see below) to clean up the citations and remove any duplicates. You can then use a tool like Rayyan (see below) to screen the results. You should begin by screening titles and abstracts only, and then you'll examine the full text of any remaining articles. Each study should be reviewed by a minimum of two people on the project team.
- Collect - Each included study is coded and the quantitative or qualitative data contained in these studies is then synthesized. You'll have to either find or develop a coding strategy or form that meets your needs.
- Explain - The synthesized results are articulated and contextualized. What do the results mean? How have they answered your research question?
- Summarize - The final report provides a complete description of the methods and results in a clear, transparent fashion.
Adapted from
Types of reviews, systematic review.
These types of studies employ a systematic method to analyze and synthesize the results of numerous studies. "Systematic" in this case means following a strict set of steps - as outlined by entities like PRISMA and the Institute of Medicine - so as to make the review more reproducible and less biased. Consistent, thorough documentation is also key. Reviews of this type are not meant to be conducted by an individual but rather a (small) team of researchers. Systematic reviews are widely used in the health sciences, often to find a generalized conclusion from multiple evidence-based studies.
Meta-Analysis
A systematic method that uses statistics to analyze the data from numerous studies. The researchers combine the data from studies with similar data types and analyze them as a single, expanded dataset. Meta-analyses are a type of systematic review.
Scoping Review
A scoping review employs the systematic review methodology to explore a broader topic or question rather than a specific and answerable one, as is generally the case with a systematic review. Authors of these types of reviews seek to collect and categorize the existing literature so as to identify any gaps.
Rapid Review
Rapid reviews are systematic reviews conducted under a time constraint. Researchers make use of workarounds to complete the review quickly (e.g., only looking at English-language publications), which can lead to a less thorough and more biased review.
Narrative Review
A traditional literature review that summarizes and synthesizes the findings of numerous original research articles. The purpose and scope of narrative literature reviews vary widely and do not follow a set protocol. Most literature reviews are narrative reviews.
Umbrella Review
Umbrella reviews are, essentially, systematic reviews of systematic reviews. These compile evidence from multiple review studies into one usable document.
Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal , vol. 26, no. 2, 2009, pp. 91-108. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x .
- Next: Project Planning >>

Ask a Librarian
How can I help you today?
A live human is ready to help.

Find & Cite | Research Help | Collections | Services | About
- Cook Library
- Research Guides
Planning For Your Expert Literature Review
Narrative literature reviews.
- Types of Expert Literature Reviews
Further Reading
- Standards and Guidelines
- The Systematic Review Process
- Review Tools and Platforms
- Screening Tools and Software This link opens in a new window
- Where to Publish
- Searching for Evidence in the Health Professions This link opens in a new window
Narrative or traditional literature reviews can take many shapes and forms. They do not need to follow any specific guideline or standard. A narrative literature view may be assigned as part of your coursework or capstone.
A narrative literature review can be a first step to building on other research in the field. After all, if it's a topic that you're interested in, you need to know what's already been done, right?
Your Narrative Literature Review Should Have...
- A clearly defined topic
- A search for relevant literature
- A logical organization structure
- An interpretation and discussion of the selected relevant literature
A common structure for narrative literature reviews is IMRaD, or:
- Introduction
- What is your topic?
- What are you interested in finding out?
- Why did you select this topic?
- How did you look for the literature?
- Where did you look?
- What search terms did you use?
- What kind of literature did you find?
- Did the literature you found change your opinion on the topic?
- Did you find out something new?
- What were the key concepts?
- and Discussion
- Evaluate and summarize the major concepts
- Connect the major concepts to future research potential
While the structure above may be sufficient for your topic, you may also consider using the similar but more robust structure IAMRDC, or:
- Ferrari, R. (2015). Writing narrative style literature reviews. Medical Writing, 24 (4), 230-235. https://doi.org/10.1179/2047480615Z.000000000329
- Sollaci, L. B., & Pereira, M. G. (2004). The introduction, methods, results, and discussion (IMRAD) structure: a fifty-year survey. Journal of the Medical Library Association 92 (3), 364–367. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC442179/
- << Previous: Types of Expert Literature Reviews
- Next: Standards and Guidelines >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 9:52 AM
- URL: https://towson.libguides.com/expert-reviews
Types of Reviews
In this guide.
- Common Types of Reviews
- Narrative Reviews
- Scoping Reviews
- Systematic Reviews
- Rapid Reviews
- Umbrella Reviews
- Clinical Practice Guidelines
- Full Infographic Series

What are they?
(AKA Literature Reviews)
Narrative Reviews involve looking at literature across a specific topic and synthesizing what you have learned. You can either look at one specific database, or across multiple databases.
You aren’t expected to become a subject expert, but you should have a pretty good concept of the topic once the review is completed.
How long might it take to complete?
Typically takes less than a month.
Is a team required?
A team is not required for this type of review.
What are the protocols that are preferred or required?
There are no specific protocols required.
When would you use this type of review?
Narrative Reviews can be submitted on their own as an article, or can be a part of a more in-depth project, like a book chapter, thesis, or dissertation.
Is there an example?
Kuwabara AM, Tenforde AS, Finnoff JT, Fredericson M. Iron deficiency in athletes: a narrative review. PM R. 2022;14(5):620-642. doi:10.1002/pmrj.12779

- << Previous: Common Types of Reviews
- Next: Scoping Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Oct 4, 2023 4:22 PM
- URL: https://laneguides.stanford.edu/types-of-reviews
The Literature Review
- Narrative Review
- Systematic Review
- Scoping Review
Writing your Literature Review
Once you have developed a body of literature to draw from, you can begin writing your literature review. There is no set format for a narrative literature review, and it can vary across fields. However, you will typically see the following elements:
- Sections you might see in a typical research paper including Introduction, background, (possibly) methods, Main/Body, and Conclusion
- Some logical structure of sections (i.e. by time period, by areas of the field, by approach of article etc.)
- Analysis of the relative value of contributions across different sources
- section on areas for further development or further research suggestions
Need writing help? Head to the Graduate Writing Center for help with your literature review!
What is a narrative literature review.
Narrative Literature Reviews are works in which the author reviews a body of literature on a topic and synthesizes the information into a clear narrative that demonstrates the general context of the field . They can also be called a Traditional Literature Review. Compared to Systematic and Scoping reviews, Narrative literature reviews do not use an established method or protocol, but rather take a broad, unspecified approach to what sources are selected to represent the field. Typically narrative literature reviews use peer-reviewed journal articles as their source of scholarship to review, but this might vary based on the individual assignment or review you are conducting. Below are some key elements of a Narrative Lit Review:
- Places the topic within an existing context
- Describes relationships between and around sources cited
- Typically includes critical analysis
- Organizes ideas by theme and/or relevance
- Demonstrates author's knowledge
Staying Organized
Use a reference management software.
Reference Managers are tools that can help you keep track of the scholarly articles you are collecting and reading for your literature review. They can also help you generate citations and bibliographies within your writing. Use the Reference Management Software Guide linked below to learn more about how to get started with one.
Reference Management Research Guide
Keep your search terms in a document or spreadsheet.
Although in Narrative Lit Reviews you are not required to keep detailed reports on your search strategy, it is still important to keep track of the terms you are searching and include information about them to be sure you are casting the widest net possible. Organize your search terms in a way that makes sense to you. As an example, you could keep tabs on:
- Broader terms
- Narrower terms
- Filters that work / filters that don't
- Search strings you can copy and paste directly into search engines and databases
The Research Process
Start with an exploratory/preliminary search.
Use a couple key terms about your topic to try searching without keeping track to see whats out there. This is also a good time to search for already existing reviews on your topic and see if something similar has already been completed. After doing a preliminary search in your general topic, you can begin thinking about your specific research question.
Drafting a Research Question
To start drafting your research question, it may be helpful to consider how your topic fits within a couple of different broad overlapping fields of research. For example, the research question illustrated below asks about identity perspectives from Asian American students in high schools. Each individual topic in this question is its own circle, and the intersection of these circles is the main focus of the literature review. There could be more circles added for each new dimension I would like to add to my research question whether it be a location (i.e. New York City), a clarifying detail (i.e. generational identity), or other form of context.
As you are searching, use the different dimensions of your research question to find individual areas of research, For example, I may want to look at the literature around just the identity of Asian American students, or maybe just look at identity formation in High School. Then, in my literature review, I can synthesize these various fields to explain the different backgrounds and how they all converge around my central topic, the middle of the diagram.

Image from Tips and Strategies for Writing a Dissertation Proposal on Ashe Grads blog.
Conducting your Search
Once you have your research question and key terms from that research question, you can start your formal searching process. In narrative literature reviews it is less important to be comprehensive in checking every possibly relevant result, but more focused on making sure the results you are getting are representative of the fields you are analyzing.
Books in the Libraries to Help with you Narrative Lit Review
Literature Review and Research Design: A Guide to Effective Research Practice
They Say / I Say: The Moves That Matter in Academic Writing, with Readings
The Literature Review: Six Steps to Success
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Systematic Review >>
- Last Updated: Mar 20, 2024 12:38 PM
- URL: https://tc-columbia.libguides.com/review
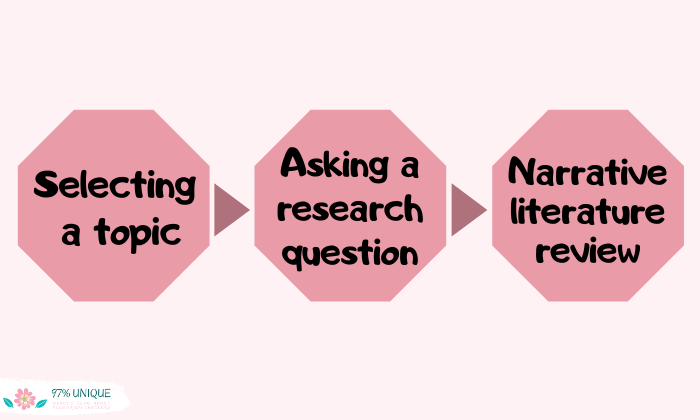
Composing an Authentic, Academic Narrative Literature Review: How to Evaluate Scholarly Articles and Write a Thorough Narrative Literature Review

Over the course of many years of teaching, I’ve found that both my students and I struggle with our course unit on research writing. It’s boring, it’s difficult, and we all undoubtedly become aggravated with each other throughout the process.
If you’ve ever experienced a lesson burnout, like I have so many times, you know how frustrating it can be for both teacher and students. Unless you’ve written tons of research papers in your lifetime, they can seem like a daunting task. This is especially true for middle school and high school students who are likely just learning how to do so.
If your students are embarking on a research project, one of their first steps in the research process will be completing a comprehensive narrative literature review.
Ironically, I’ve had to do my own narrative literature review of sorts to bring you the resources you’ll find herein. Of note, after you’ve made it to the end of this post, you’ll be able to effectively guide your students in composing a narrative literature review by focusing on these basic tenets:
What is a narrative literature review?
- Systematic vs. Narrative literature reviews.
- The different types of narrative literature reviews.
- Steps in writing a narrative literature review.
Defining, Differentiating, and Composing a Narrative Literature Review
Essentially, it is a step in the research process that follows selecting a topic and asking a research question. Before developing an engaging thesis, a researcher has to ascertain that scholarly literature exists in support of their proposed thesis.
For students who have grown up with the ability to simply Google a wealth of information and receive desired results in a moment’s time, vetting sources may seem like a foreign concept. Teaching your students how to write this type of work will teach them how to scrutinize sources.
But what is a narrative literature review? According to top researchers, “A literature review is a type of research article published in a professional peer-reviewed journal.” These articles are published in vetted, scholarly journals that you and your students can trust as fact.
In essence, your students select a research topic then hit the databases in search of reputable, trustworthy journal articles that answer their research query and support their anticipated position on that topic. By reviewing the existing literature on the selected topic, students can be sure there is proven data and a body of existing knowledge that supports their thesis.
According to J.D. Baker, a professor at Charles Sturt University, acquiring current and relevant literature on a given topic is, “…an essential part of the research process [that] help[s] to establish a theoretical framework and focus or context for your research.” For this reason, the narrative literature review may very well be one of the most important steps in the research process.

As one of the first few steps in the research process, a step that is likely a foreign task to your students, it’s imperative that the process is broken down into simplified, manageable tasks.
Rebecca Alber, blogger for Edutopia, discusses the importance of scaffolding projects for students. She expounds upon the pedagogy of breaking projects into manageable chunks and “providing concrete structure for each.”
By reading through and analyzing the body of knowledge on a given topic, researchers, like your students, can focus and justify their research. As discussed here , the thesis is the most important part of a research paper, but you can’t arrive at your thesis without a thorough narrative literature review.
In this video, research specialist, Sarah Bronson, explains what a narrative literature review does, how to plan it, and how to write a cohesive and proper review.
Systematic vs. Narrative Literature Reviews: Knowing the Difference
In short, the difference between a narrative literature review and a systematic literature review has to do with the search terms used and the methodology employed when searching databases.
According to those in the know, “A narrative literature review is fairly broad, as it involves gathering, critiquing and summarizing journal articles and textbooks about a particular topic.” In other words, you enter general search terms into a search engine and sift through the yielded articles.

Essentially, a narrative literature review summarizes and synthesizes the body of work on a topic. The review may be generally focused on a broad topic or a specific research question.
A systematic literature review, on the other hand, “tend[s] to use specific search terms and inclusion/exclusion criteria, whereas the criteria for narrative reviews may not be as strict.” This type of work is best employed by writers who have already focused their query and/or thesis. By including or excluding particular terms, a more pointed search return is gleaned.
In essence, the goal of a systematic literature review is to answer a focused objective question. To be clear, in this type of work, the researcher is working with a clearly defined question.
Check out this helpful video that further explicates the point and process of a systematic literature review. Cochrane provides insight into why, in some instances, a systematic review is more useful than its narrative counterpart.
Though both systematic and narrative literature reviews can be useful in producing desired and relevant research documents, knowing which method to use depends on your experience and how far into the research process you’ve gone.
If you are beginning preliminary research, you’ll likely only be able to perform a narrative literature review. You may have a general topic that you’d like to investigate before committing to a topic and a thesis.
However, if you’ve already focused your study and have a better grip on the direction you wish to go, then you may find the systematic review to be useful.
Again, the literature review is just one step in a series of interrelated steps that help students write a focused and cohesive research paper. In this article, you can take a look at later steps in the writing process.
Narrative Literature Reviews: Four Unique Approaches
According to Onwuegbuzie and Frels, there are four common types of narrative literature reviews. Essentially, literature reviews can be broken down into these four categories: general, methodological, theoretical, and historical. Let’s take a look at how they differ from one another.

A general literature review takes a close look at the most important and most current knowledge on a given topic. This type of work will form the basis for your thesis or dissertation; it’s what you’ll do before focusing your query.
Sources cited in a general literature review may include scholarly articles, governmental data, books, interviews, and websites. The general literature includes a summary and assessment of the literature.
A methodological literature review defines the methodology used to apprehend the literature. In other words, this type of paper outlines and explains research methods and parameters.

The methodological literature review analyzes how information was arrived at not necessarily what the literature asserts.
A theoretical literature review analyzes how theories inform research practices. Basically, this type of paper identifies pre-existing theories, the connection between and among them, how well scrutinized the theories are, and the development of new possible theories.
Finally, a historical literature review focuses on the emergence, development, and historical context of a research topic as it presents in a body of knowledge. To be clear, this type of literature review traces the history of a particular issue or theory and how it has evolved since its onset.
In this excellent resource featuring Leigh Hall of teachingacademia.com, Hall further explains the different types of narrative literature reviews. Hall explains the four types of reviews in further detail to help writers determine which is best suited for their research purposes.
Teachers should be clear about their expectations of students concerning which type of narrative literature review is expected of them. A closer look at which type of review is best suited to your students’ projects can help you, the teacher, in guiding your students.
As one of the most important steps in the research process, it’s imperative students can successfully complete a literature review before moving on in the research process.
Lisa L. Munro, Phd., a blogger who examines the importance of creating writing communities among our students, asserts the importance of, “writing a concise literature review just comprehensive enough for the purpose of an academic journal article.”
Narrative Literature Review: A Writer’s Checklist
The writing process is a step-by-step undertaking and some steps are more of a process than others. That’s especially true of composing a narrative literature review.

Essentially, a narrative literature review is a project in and of itself. A proper review adheres to the following steps.
Entitle your review as a “review of…” Titling your work this way lets your reader know exactly what you’re setting out to do in the subsequent paragraphs. However, as a researcher, doing so helps you keep your sources organized and makes it easy to refer back to that source.
Write a brief summary of the article and how it applies to your course of study. This step is where you synthesize the information gleaned from a particular source. It will provide you, the researcher, with an opportunity to decide if it’s useful information that will support your research query.
Your abstract should include a sentence about how the source applies to your own research, your purported thesis, a summary of the literature, and conclusions you’ve made based on your findings.
Introduction
The writer provides his/her rationale and objectives for the literature review. Your introduction should establish your topic of study and an explanation of why your research is important.
Describe the methods used in performing the research. Essentially this is a few sentences explaining the steps and mediums used to acquire your sources. This indicates whether or not your research comes from reputable sources.

Here is where you explain if you used computer databases along with the search terms you employed, scoured physical files at a given office building, read physical texts on a given topic, etc.
Discussion/Summary
The writer discusses his/her discoveries as well as an overall summary of the information. Without repeating what you’ve written in the other parts of your review, in the discussion, you summarize your main findings, interpret those findings, identify the strengths and weaknesses of the given source, compare your findings with other literature on the topic, explain how and if your findings answer your research query, and assert if your thesis is supported by the literature.
In this helpful tutorial, David Taylor, an online writing professor, walks you through the formatting of a literature review. He walks writers through the five-step process of completing a paper in less than 30 minutes.
As in writing any type of composition, students should be reminded to carefully proofread for clarity and correctness. I always suggest that students read their compositions aloud as readers will often hear mistakes before they see them.
A final consideration that students inevitably need to be reminded of is avoiding plagiarism. I find it’s helpful to define plagiarism for students so there’s no question about why copying another’s ideas is problematic.
There are many online plagiarism checkers for teachers and students to use to ensure work is entirely authentic. Check out this article for some tips and tricks for avoiding and identifying plagiarism.
Useful Resources
- What is a research paper?
- How to format a research paper
- 113 great research paper topics
- Writing an educational research paper: research paper sections
One of the most arduous tasks in a research project is gathering the right sources for your purpose. Help students understand how to search in the right places for articles and how to evaluate sources.
One of the questions my students rightfully ask is why they can’t use news media websites. News networks like CNN deliver the facts, don’t they? This article may help you and them to better recognize and evaluate credible source material.
A thorough narrative literature review will get your students off on the right foot. Everything after the literature review falls into place more readily when you have the right sources for your purpose.

- Open access
- Published: 04 September 2016
Improving the peer review of narrative literature reviews
- Jennifer A. Byrne 1 , 2
Research Integrity and Peer Review volume 1 , Article number: 12 ( 2016 ) Cite this article
24k Accesses
70 Citations
29 Altmetric
Metrics details
As the size of the published scientific literature has increased exponentially over the past 30 years, review articles play an increasingly important role in helping researchers to make sense of original research results. Literature reviews can be broadly classified as either “systematic” or “narrative”. Narrative reviews may be broader in scope than systematic reviews, but have been criticised for lacking synthesis and rigour. The submission of more scientific manuscripts requires more researchers acting as peer reviewers, which requires adding greater numbers of new reviewers to the reviewing population over time. However, whereas there are many easily accessible guides for reviewers of primary research manuscripts, there are few similar resources to assist reviewers of narrative reviews. Here, I summarise why literature reviews are valued by their diverse readership and how peer reviewers with different levels of content expertise can improve the reliability and accessibility of narrative review articles. I then provide a number of recommendations for peer reviewers of narrative literature reviews, to improve the integrity of the scientific literature, while also ensuring that narrative review articles meet the needs of both expert and non-expert readers.
Peer Review reports
Over the past 30 years, the size of the published scientific literature has expanded exponentially [ 1 ]. While it has been argued that this rate of expansion is unsustainable [ 2 ], underlying factors such as greater numbers of scientists and scientific journals [ 3 ] are unlikely to change in the short term. The submission of more manuscripts for publication requires more peer reviewers, yet the current demand for capable, available manuscript reviewers is not being met [ 3 ]. This has serious adverse consequences for the validity of published research and overall trust in science [ 3 ].
Review articles help both experts and non-experts to make sense of the increasing volume of original publications [ 4 , 5 ]. Busy clinicians have a particular reliance upon review articles, because of their constant need for reliable, up-to-date information, yet limited available time [ 6 ]. Literature reviews can also help other content experts such as researchers and policymakers to identify gaps in their own reading and knowledge. However, literature reviews are also sought by readers with little or no prior understanding of the reviewed topic, such as researchers seeking to rapidly triage results from high-throughput analyses and students for whom literature reviews can represent entry points into a new field. For the benefit of both expert and non-expert readers, it is essential that review articles accurately synthesise the relevant literature in a comprehensive, transparent and objective manner [ 7 , 8 ].
Numbers of review articles are increasing in fields where this has been measured [ 4 ], as is the diversity of review types published [ 9 , 10 ]. Although there are now many review sub-types that can be distinguished based upon the literature search, appraisal, synthesis and analysis methods used [ 9 , 10 ], review articles can be broadly classified as either “systematic” or “narrative” [ 5 , 11 ]. Systematic reviews take defined approaches to the identification and synthesis of study findings and include other review sub-types such as evidence maps [ 12 ]. The systematic review is considered to be the gold standard of evidence synthesis, but also carries the potential disadvantages of narrow scope [ 11 ], and requiring more time and resources to prepare and update [ 7 ]. Narrative reviews, also referred to as “traditional reviews” [ 5 ] and “literature reviews” [ 9 ], constitute the majority of review articles published in some fields [ 7 ]. Other review sub-types, such as rapid and scoping reviews also present information in a narrative format [ 9 ]. Narrative reviews have been criticised for rarely employing peer-reviewed methodologies, or duplicate curation of evidence [ 5 ], and for often failing to disclose study inclusion criteria [ 11 ]. Despite these limitations, narrative reviews remain frequent within the literature, as they offer breadth of literature coverage and flexibility to deal with evolving knowledge and concepts [ 11 ]. In this article, I will provide advice regarding the peer review of narrative reviews, and the advice presented aims to be broadly applicable. I will not attempt to provide advice regarding the peer review of systematic reviews [ 13 , 14 ].
Given the broad readership of literature reviews, content and methodology experts as well as reviewers with less directly relevant expertise can play important roles in the peer-review process [ 15 ]. Peer reviewers with related content expertise are best placed to assess the reliability of the information presented, while other reviewers can ensure that this information remains accessible to readers with different levels of prior knowledge. However, whereas there are easily accessible guides for reviewers of primary research manuscripts [ 16 , 17 ], there are few similar resources available for reviewers of literature reviews [ 15 , 18 ]. This article therefore proposes a number of recommendations for peer reviewers (Table 1 ) to ensure that narrative literature review articles make the best possible contributions to their fields, while also meeting their readers’ often diverse needs.
Ask whether the literature review justifies its place in the literature
Lower than expected ratios between numbers of original publications and review articles suggest excessive numbers of reviews in some fields, which may contribute to the very problem that review articles aim to solve [ 4 ]. With rapidly rising publication rates in many fields [ 2 ], even content-expert peer reviewers should check publication databases for similar and/or overlapping review articles as part of the peer-review process. Pre-empting such scrutiny, authors should clearly define the review’s scope and what it intends to achieve [ 8 ]. If there have been other recent reviews of the same or similar topics, the authors should explain how their manuscript is unique. This could be through combining literature from related fields, by updating existing reviews in light of new research evidence [ 8 ], or because published reviews may have been subject to bias. A clear definition of a review’s scope is a recognised tool to reduce evidence selection bias [ 19 ]. Review authors can also define their subject by referring to literature reviews of related topics that will not be explored in depth. These definitions and statements should form part of an overall narrative structure that helps readers to anticipate and understand the information presented [ 20 ].
Ask whether the literature searches conducted were clearly defined
A criticism frequently levelled at traditional or narrative reviews is that they do not always state or follow rules regarding literature searches [ 5 , 7 , 11 ]. Providing evidence that comprehensive literature searches have been conducted, preferably according to pre-defined eligibility criteria [ 19 ], increases confidence that the review’s findings and conclusions are reliable, and have not been subject to selection bias. Ideally, any literature search choices made by the authors should be clearly stated, transparent and reproducible [ 11 ].
Check for citation breadth and balance
Consider whether the authors have cited a comprehensive range of literature or whether they have tended to cite papers that support their own point of view. If there are important papers that have not been cited, suggest to the authors that these be added, and explain why. If only a limited number of articles can be cited due to the journal’s requirements, check that these studies are representative of those available.
Where possible, verify that information has been summarised correctly
Many different types of citation errors can be identified in the research literature [ 21 , 22 ], and these may occur regardless of the journal impact factor [ 22 ]. The increasing size and complexity of primary reports [ 3 ] also render data extraction and summary more challenging. Realistically, it is unlikely that individual peer reviewers will have detailed knowledge of any full review topic [ 19 ]. Nonetheless, if you are a content expert, take time to cross-reference at least some individual statements to citations, for the particular benefit of non-expert readers. If your level of expertise means that you are unable to verify the accuracy of particular sections of the review, you should indicate this to your editor. Peer reviewers can also ask about data extraction methods, if these were not described in the manuscript. Adopting systematic review practices, such as duplicate independent data extraction, or independent data extraction and validation, can reduce content errors and increase reliability [ 19 ].
Check that original references have been cited
Authors sometimes incorrectly cite original studies, both in original manuscripts and reviews [ 23 , 24 ]. While checking the content, ask whether descriptions of original findings were referenced accordingly, as opposed to being incorrectly attributed to reviews [ 23 ].
Consider how studies were critically evaluated
Beyond correct data summary, narrative literature reviews should include critical data appraisal and some level of data synthesis. How this should be done varies according to the review scope and methodology [ 9 , 10 , 19 ]. While some narrative reviews reasonably focus on breadth as opposed to depth of literature coverage [ 10 ], limited or poor data appraisal risks placing undue emphasis on poor quality research [ 9 ]. Evaluating at least some aspects of the methods used by individual studies can improve reliability [ 7 ]. Similarly, ask how the authors have interpreted conflicting findings or studies with apparently outlying results [ 9 , 11 ].
Evaluate whether tables/figures/diagrams support the text
While not all literature reviews need to include figures or tables, these can help to summarise findings and make key messages clearer. Some detailed information may be best presented in tables, with a shorter summary within the text. Tables can improve the availability of quantitative data for cross-checking, better demonstrate the results of qualitative or quantitative data synthesis, and reassure both peer reviewers and readers that comprehensive, objective analyses have been performed. If figures or tables are included, these need to be original; otherwise, the authors need to have obtained permission to reproduce these from an original source.
Consider whether the review will help someone entering the field
Literature reviews are not always read by subject experts, and it is important that the peer-review process considers this. Reviewers who are not direct content experts may valuably request clarification of nomenclature and/or historical issues that may have seemed too obvious for the authors to have explained. Summary diagrams suggested by peer reviewers may help make a literature review more accessible to a broader audience.
Ask whether the review expands the body of knowledge
Ultimately, the goal of a literature review should be to further the body of knowledge [ 18 ]. Extending or developing ideas is clearly a difficult task, and is often the weakest section of a review [ 25 ]. Consider therefore whether the authors have derived and clearly presented new ideas and/or new research directions from any identified knowledge gaps. Having read the manuscript with fresh eyes, peer reviewers may have valuable ideas to contribute.
Do not forget the rules for reviewing manuscripts in general
The review of literature reviews has some particular considerations, but all the usual manuscript review rules also apply, such as managing conflicts of interest and allocating appropriate time [ 16 , 17 ]. Try to separate the assessment of language and grammar from the more important assessment of scientific quality and remain aware that expert reviewers risk bringing their own biases to the peer-review process [ 15 ].
Conclusions
More quality peer reviewers are needed within the scientific community [ 3 ], including those with the capacity and confidence to review narrative literature reviews. Although it has been difficult to identify predictors of peer-reviewer performance and effective training methods, younger reviewer age has been reproducibly associated with better quality manuscript reviews [ 26 , 27 ]. This association suggests that peer reviewers should be recruited relatively early in their careers, and encouraged to participate widely in manuscript review. Associations between younger peer-reviewer age and better manuscript reviews may also highlight the need for regular training, to ensure that the peer-review community remains up-to-date regarding new approaches to editing or reviewing manuscripts. Indeed, a recent industry survey reported that over three quarters of researchers were interested in further reviewer training [ 28 ]. I therefore hope that this article will add to existing resources [ 29 ] to encourage less experienced peer reviewers to extend their efforts towards narrative literature reviews.
Bornmann L, Mutz R. Growth rates of modern science: a bibliometric analysis based on the number of publications and cited references. J Assoc Inform Sci Tech. 2015;66(11):2215–22.
Google Scholar
Pautasso M. Publication growth in biological sub-fields: patterns, predictability and sustainability. Sustainability. 2012;4(12):3234–47.
Article Google Scholar
Siebert S, Machesky LM, Insall RH. Overflow in science and its implications for trust. Elife. 2015;4: doi: 10.7554/eLife.10825 .
Ketcham CM, Crawford JM. The impact of review articles. Lab Invest. 2007;87(12):1174–85.
Dijkers MP. Task Force on Systematic Reviews and Guidelines. The value of traditional reviews in the era of systematic reviewing. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2009;88(5):423–30.
McAlister FA, Clark HD, van Walraven C, Straus SE, Lawson FM, Moher D, et al. The medical review article revisited: has the science improved? Ann Intern Med. 1999;131(12):947–51.
Haddaway NR, Woodcock P, Macura B, Collins A. Making literature reviews more reliable through application of lessons from systematic reviews. Conserv Biol. 2015;29(6):1596–605.
Pautasso M. Ten simple rules for writing a literature review. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9(7):e1003149.
Grant MJ, Booth A. A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inform Lib J. 2009;26(2):91–108.
Paré G, Trudel M-C, Jaana M, Kitsiou S. Synthesizing information systems knowledge: a typology of literature reviews. Inform Management. 2015;52(2):183–99.
Collins JA, Fauser BCJM. Balancing the strengths of systematic and narrative reviews. Hum Reprod Update. 2005;11(2):103–4.
Miake-Lye IM, Hempel S, Shanman R, Shekelle PG. What is an evidence map? A systematic review of published evidence maps and their definitions, methods, and products. Syst Rev. 2016;5:28.
Higgins JPT, Green S. Handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. The Cochrane Collaboration, John Wiley & Sons Ltd; 2011.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700.
Oxman AJ. Checklists for review articles. BMJ. 1994;309(6955):648–51.
Bourne PE, Korngreen A. Ten simple rules for reviewers. PLoS Comput Biol. 2006;2(9):e110.
Nicholas KA, Gordon W. A quick guide to writing a solid peer review. Eos. 2011;92(28):233–4.
Jennex ME. Literature reviews and the review process: an editor-in-chief’s perspective. CAIS. 2015;36:8.
O’Connor A, Sargeant J. Research synthesis in veterinary science: narrative reviews, systematic reviews and meta-analysis. Vet J. 2015;206(3):261–7.
Docherty M, Smith R. The case for structuring the discussion of scientific papers. BMJ. 1999;318(7193):1224–5.
Davids JR, Weigl DM, Edmonds JP, Blackhurst DW. Reference accuracy in peer-reviewed pediatric orthopaedic literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(5):1155–61.
Awrey J, Inaba K, Barmparas G, Recinos G, Teixeira PG, Chan LS, et al. Reference accuracy in the general surgery literature. World J Surg. 2011;35(3):475–9.
Gavras H. Inappropriate attribution: the “lazy author syndrome”. Am J Hypertens. 2002;15(9):831.
Katz TJ. Propagation of errors in review articles. Science. 2006;313(5791):1236.
Webster J, Watson RT. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: writing a literature review. MIS Q. 2002;26:2.
Black N, van Rooyen S, Godlee F, Smith R, Evans S. What makes a good reviewer and a good review for a general medical journal? JAMA. 1998;280(3):231–3.
Callaham ML, Tercier J. The relationship of previous training and experience of journal peer reviewers to subsequent review quality. PLoS Med. 2007;4(1):e40.
Warne V. Rewarding reviewers- sense or sensibility? A Wiley study explained. Learned Pub. 2016;29(1):41–50.
COPE Ethical Guidelines for Peer Reviewers. Available: http://publicationethics.org/resources/guidelines-new/cope-ethical-guidelines-peer-reviewers . Accessed 10 Aug, 2016.
Download references
Acknowledgements
I thank Dr Mona Shehata (Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, Toronto, Canada) for discussions, Ms Sarah Frost for critical reading, reviewers of this manuscript for many constructive comments, and reviewers of past publications for feedback which also contributed towards the development of this manuscript.
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Authors’ contributions.
JAB drafted, wrote and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The author declares that she has no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Ethics approval and consent to participate, author information, authors and affiliations.
Molecular Oncology Laboratory, Children’s Cancer Research Unit, Kids Research Institute, The Children’s Hospital at Westmead, Locked Bag 4001, Westmead, 2145, NSW, Australia
Jennifer A. Byrne
The University of Sydney Discipline of Child and Adolescent Health, The Children’s Hospital at Westmead, Locked Bag 4001, Westmead, 2145, NSW, Australia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jennifer A. Byrne .
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Byrne, J.A. Improving the peer review of narrative literature reviews. Res Integr Peer Rev 1 , 12 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41073-016-0019-2
Download citation
Received : 17 June 2016
Accepted : 05 August 2016
Published : 04 September 2016
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41073-016-0019-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Peer review
- Narrative literature review
Research Integrity and Peer Review
ISSN: 2058-8615
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Chaos to Clarity: Structuring Your Literature Review Format
Master literature review format! Learn key sections, effective citation & analysis tips to write a strong academic review.
Ever wondered how to dive into a mountain of books and articles and come up with something that not just makes sense but shines new light on a topic? What if there was a way to neatly tie together all that information, spot what’s missing, and maybe even pave the way for discoveries?
That’s what you are going to learn in this article, literature reviews—a place where chaos meets order, and where your insights could set the stage for the next big thing. Let’s break down the literature review format , your essential guide to properly writing a literature review.
Dissecting Literature Review Format
There are 6 main sections to make a note of while writing a literature review. Those are:
The Introduction Section
Topic background, conceptual framework.
- Synthesis and Evaluation in Literature Reviews
- Conclusion for Your Literature Review
- Reference List in Your Literature Review
Also Read: Essential Components of a Literature Review
The introduction of your literature review is where you set the stage for the entire document. It’s your first opportunity to engage your readers and provide a clear blueprint of what your review will cover and why it matters. This section does more than merely introduce the topic; it establishes the context, defines the scope, and outlines the purpose and objectives of your literature review.
Things to keep in mind while writing an introduction:
- Craft a compelling opening
- Establish the Context and Justification
- Define the Scope and Objectives
- Lay out the Structure
- Give an overview of the Structure
The “Topic Background” section of a literature review serves as the cornerstone for understanding the evolution and current state of the subject matter. It is divided into two crucial sub-sections: Historical Context and Current State of the Topic .
Delving into these areas provides you with a comprehensive backdrop against which the literature review is framed, enriching the reader’s understanding of why the topic is of interest and what has influenced its development to the current state.
Historical Context

The Historical Context is fundamental in setting the stage for the entire literature review. This section is not just a chronology of events or developments; it’s a curated narrative that highlights the key milestones and turning points that have significantly impacted the topic.
By examining the historical evolution, the review establishes a timeline of how understanding and perspectives have shifted over the years.

Summary Of Key Historical Developments
This involves identifying and summarizing the major breakthroughs, shifts in thinking, or seminal works that have shaped the topic. It’s important to focus on developments that have a direct relevance to the current understanding and state of the subject. For example, if the topic is about the evolution of renewable energy technologies, this part would outline the initial discovery and use of renewable sources, significant technological innovations, and pivotal policy decisions that have influenced the field.
Relevance Of Historical Context To The Topic
After outlining the key historical developments, it’s crucial to connect these events to the present topic. This means discussing how past events have laid the groundwork for current theories, practices, or debates within the field. It involves analyzing the impact of historical milestones on the subject matter, and explaining how they have contributed to current knowledge, challenges, and research questions. This section makes it clear why understanding history is essential for anyone researching or studying the topic today.
Current State Of The Topic
Moving from the historical context, the review transitions to the present with the Current State of the Topic. This part assesses the latest research, trends, debates, and technological advancements that define the subject area at the moment.
Current Trends Or Updates
Here, the focus shifts to what is happening in the field right now. This could include recent research findings, emerging theories, new methodologies, or the latest technological innovations. The aim is to provide a snapshot of the current research landscape, identifying what themes, questions, or problems are being actively explored. For instance, in the context of digital marketing, this might involve discussing the rise of artificial intelligence in customer relationship management or the impact of social media trends on marketing strategies.
Impact Of These Trends On The Subject Matter
The final step is to assess the implications of these current trends for the topic. This includes considering how recent developments have advanced the field, the challenges they present, and the opportunities they open up for future research. It’s about connecting the dots between what’s happening now and what it means for the subject area moving forward. This not only helps to frame the research questions that the literature review will address but also sets the stage for identifying gaps in the current knowledge, thereby guiding the direction of future studies.
Also Read: What is a literature review? Get the concept and start using it
When doing a literature review, it’s essential to lay a solid foundation for your exploration through a well-defined conceptual framework. This framework acts as a compass, guiding your review’s direction by establishing the key concepts, theories, and perspectives that underpin your topic.
Definitions And Descriptions
Before diving into the depths of your literature review, it’s crucial to start with the basics. This means clearly identifying and defining the key concepts related to your topic. Think of this as setting the stage for your readers, ensuring they have a clear understanding of the fundamental terms and ideas you will be exploring.
Key Concepts Related To The Topic
Begin by listing the essential concepts central to your review. These are the building blocks of your topic, the terms that will repeatedly appear throughout your exploration.
Detailed Definitions And Their Relevance
Once you’ve identified these concepts, provide precise and comprehensive definitions for each. Don’t hesitate to explore different dimensions or interpretations of these terms, as this can enrich your readers’ understanding. More importantly, discuss why these concepts are crucial to your review. How do they shape the scope of your exploration? How do they relate to each other and to the broader topic? This step ensures that your readers are not just familiar with the terms but also understand their significance within your review’s context.
Theoretical Perspectives
With the key concepts clearly defined, it’s time to frame your literature review within relevant theoretical perspectives. This is where you align your exploration with existing theories, models, or frameworks that provide insights into your topic.
Important Theories Related To The Topic
Identify the theories that are foundational to your topic. These could range from well-established theories that have long guided research in your field to more contemporary models that offer new insights. For example, a review of organizational behavior might draw on theories of motivation, leadership styles, and organizational culture.
Evaluation Of These Theories And Their Influence On The Topic
After pinpointing the relevant theories, critically assess their contributions to the topic. Consider questions like: How have these theories shaped understanding of the topic? What insights do they offer, and where do they fall short? Are there controversies or debates surrounding these theories? This evaluation not only deepens your review’s analytical depth but also positions your work within the larger academic conversation.
Synthesis And Evaluation In Literature Reviews

The “Synthesis and Evaluation” section is where your literature review truly comes to life. Here, you’re not just summarizing what others have said; you’re weaving together diverse strands of research to present a cohesive picture of the topic at hand.
Comparison And Contrast Of Sources
Synthesizing the literature involves more than listing findings from various studies; it’s about drawing connections between them, highlighting areas of agreement and dispute, and weaving these into a narrative that adds depth and breadth to your understanding of the topic.
Comparative Analysis
Start by grouping your sources based on similarities in their findings, methodologies, or theoretical approaches. This clustering will help you identify trends and common themes across the literature. For example, if several studies have found similar outcomes under comparable conditions, these findings can be grouped to strengthen a particular argument or observation about the topic.
Contrasts Or Conflicts Among Sources
Equally important is the identification of discrepancies in the literature. Do some studies present findings that directly contradict others? Are there differences in how researchers have interpreted similar data? Highlighting these conflicts is crucial, as it can indicate areas where the topic is still evolving or where further research is needed. It also shows your ability to critically engage with the material, a hallmark of scholarly rigor.
Analysis Of Gaps In Literature
One of your primary tasks in the synthesis and evaluation section is to identify what’s missing in the current body of research. This requires a critical eye and a deep understanding of both your topic and the broader field in which it resides.
Identification Of Research Gaps
As you comb through the literature, ask yourself: What questions remain unanswered? Are there underexplored areas or populations? Perhaps certain methodologies have been overlooked, or theoretical perspectives have not been considered. Pinpointing these gaps is not a mere exercise in academic critique; it’s a vital step in advancing knowledge within the field.
Implications Of These Gaps For Future Research
Highlighting gaps in the literature sets the stage for future studies. It’s where you, as the reviewer, can suggest new research directions that could fill these voids or further explore the topic. Discussing the implications of these gaps not only enriches your review but also contributes to the ongoing scholarly conversation.
Conclusion For Your Literature Review
The conclusion of your literature review is where you bring together all the strands of your argument, synthesizing the insights gained and highlighting the significance of your findings. It’s not just a summary of what has been discussed; it’s an opportunity to underscore the relevance of the review, reflect on the broader implications of your synthesis and evaluation, and suggest directions for future research.
Summary Of Key Points
Start your conclusion by succinctly summarizing the main points and findings of your review. This isn’t about rehashing every detail but rather about distilling the essence of your exploration. Highlight the critical trends, themes, and conflicts you’ve uncovered, and remind your readers of the significance of these discoveries.
Relevance And Implications Of The Literature For The Topic
Next, focus on the relevance and implications of your findings. This involves stepping back to consider the bigger picture—how does your literature review contribute to the understanding of your topic? Discuss the impact of the trends and gaps you’ve identified on the field, and elaborate on how your synthesis of the literature advances or enriches existing knowledge.
Reflection On The Research Process
Reflecting on the research process itself can provide valuable insights. Consider discussing the challenges you encountered in navigating the literature, such as dealing with conflicting findings or the scarcity of research on certain aspects of your topic.
Directions For Future Research
One of the most critical aspects of your conclusion is to suggest directions for future research. Be as precise as possible, whether suggesting new methodologies, theoretical frameworks, or specific topics that warrant deeper investigation.
Final Thoughts
End your conclusion with a strong closing statement that reiterates the value of your literature review. Emphasize the importance of continued research on your topic and the potential it holds for advanced understanding within your field. A compelling conclusion reaffirms the significance of your work, leaving your readers with a clear sense of its contribution and the urgent need for further exploration.
Reference List In Your Literature Review
The Reference List is the backbone of your literature review, providing a comprehensive compilation of all the sources you’ve cited throughout your exploration. It’s not merely a formality but a crucial component that lends credibility and rigor to your work.
Importance Of Accuracy And Consistency
The cornerstone of a reliable Reference List is accuracy and consistency in citation style. Whether you’re adhering to APA , MLA , Chicago , or another academic citation format, it’s vital to apply the rules with precision. This includes correctly formatting author names, publication dates, titles, and publication details.
Organizing Your References
While different citation styles have their own rules for listing references, organizing them in a way that enhances readability and accessibility is universally beneficial. Alphabetical order by the author’s last name is the most common method, as it allows readers to easily locate sources.
Comprehensive Coverage
Your Reference List should be exhaustive, including every work you’ve cited in your review. This extends beyond journal articles and books to encompass reports, conference papers, online resources, and any other materials that have informed your analysis.
The Value Of Annotations
While not always required, providing brief annotations for key sources can add tremendous value to your Reference List. An annotated bibliography offers a succinct summary of each source’s main arguments, methodologies, and findings, as well as its relevance to your literature review.
Digital Accessibility
In today’s digital age, considering the accessibility of your referenced works can greatly enhance the utility of your Reference List. Whenever possible, include Digital Object Identifiers (DOIs) or stable URLs for online sources, ensuring readers can directly access the materials.
Also read: What Is A DOI? Exploring The Purpose And Importance
Reflecting On Ethical Scholarship
Finally, your Reference List is a reflection of ethical scholarship. By accurately citing all the sources that have informed your work, you’re honoring the intellectual property of other researchers and upholding the academic community’s standards of integrity and respect.
Crafting a meticulous Reference List is an essential aspect of your literature review that underscores the credibility, depth, and ethical foundation of your research. By adhering to the principles of accuracy, comprehensiveness, and accessibility, you not only facilitate further inquiry but also pay homage to the collective endeavor of knowledge advancement in your field.
Related Article: Navigating the AMA Citation Format: Best Tips for Referencing
In conclusion, writing a literature review involves meticulous structuring, beginning with an engaging introduction that sets the stage, followed by a detailed exploration of the topic’s background, including its historical context and current state.
A robust conceptual framework lays the groundwork for analysis, leading to a critical synthesis and evaluation of relevant literature.
The conclusion ties together the review’s key findings and implications, while the reference list meticulously catalogs all cited works. Mastering each section ensures a comprehensive and insightful review, essential for advancing academic understanding and contributing to scholarly discussions.
Related Article: Preliminary Literature Review: A Guide for Effective Research
Science Figures, Graphical Abstracts, And Infographics For Your Research
Revolutionize your research with infographics from Mind the Graph . From science figures, graphical abstracts to infographics, you can unleash the power of creative visuals with this user-friendly platform and make your research captivating.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Unlock Your Creativity
Create infographics, presentations and other scientifically-accurate designs without hassle — absolutely free for 7 days!
About Sowjanya Pedada
Sowjanya is a passionate writer and an avid reader. She holds MBA in Agribusiness Management and now is working as a content writer. She loves to play with words and hopes to make a difference in the world through her writings. Apart from writing, she is interested in reading fiction novels and doing craftwork. She also loves to travel and explore different cuisines and spend time with her family and friends.
Content tags

Literature Reviews
- Types of reviews
- Getting started
Types of reviews and examples
Choosing a review type.
- 1. Define your research question
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- 6. Write the review
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
- Meta-analysis
- Systematized
Definition:
"A term used to describe a conventional overview of the literature, particularly when contrasted with a systematic review (Booth et al., 2012, p. 265).
Characteristics:
- Provides examination of recent or current literature on a wide range of subjects
- Varying levels of completeness / comprehensiveness, non-standardized methodology
- May or may not include comprehensive searching, quality assessment or critical appraisal
Mitchell, L. E., & Zajchowski, C. A. (2022). The history of air quality in Utah: A narrative review. Sustainability , 14 (15), 9653. doi.org/10.3390/su14159653
Booth, A., Papaioannou, D., & Sutton, A. (2012). Systematic approaches to a successful literature review. London: SAGE Publications Ltd.
"An assessment of what is already known about a policy or practice issue...using systematic review methods to search and critically appraise existing research" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 100).
- Assessment of what is already known about an issue
- Similar to a systematic review but within a time-constrained setting
- Typically employs methodological shortcuts, increasing risk of introducing bias, includes basic level of quality assessment
- Best suited for issues needing quick decisions and solutions (i.e., policy recommendations)
Learn more about the method:
Khangura, S., Konnyu, K., Cushman, R., Grimshaw, J., & Moher, D. (2012). Evidence summaries: the evolution of a rapid review approach. Systematic reviews, 1 (1), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-1-10
Virginia Commonwealth University Libraries. (2021). Rapid Review Protocol .
Quarmby, S., Santos, G., & Mathias, M. (2019). Air quality strategies and technologies: A rapid review of the international evidence. Sustainability, 11 (10), 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102757
Grant, M.J. & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of the 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal , 26(2), 91-108. https://www.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
Developed and refined by the Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating Centre (EPPI-Centre), this review "map[s] out and categorize[s] existing literature on a particular topic, identifying gaps in research literature from which to commission further reviews and/or primary research" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 97).
Although mapping reviews are sometimes called scoping reviews, the key difference is that mapping reviews focus on a review question, rather than a topic
Mapping reviews are "best used where a clear target for a more focused evidence product has not yet been identified" (Booth, 2016, p. 14)
Mapping review searches are often quick and are intended to provide a broad overview
Mapping reviews can take different approaches in what types of literature is focused on in the search
Cooper I. D. (2016). What is a "mapping study?". Journal of the Medical Library Association: JMLA , 104 (1), 76–78. https://doi.org/10.3163/1536-5050.104.1.013
Miake-Lye, I. M., Hempel, S., Shanman, R., & Shekelle, P. G. (2016). What is an evidence map? A systematic review of published evidence maps and their definitions, methods, and products. Systematic reviews, 5 (1), 1-21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0204-x
Tainio, M., Andersen, Z. J., Nieuwenhuijsen, M. J., Hu, L., De Nazelle, A., An, R., ... & de Sá, T. H. (2021). Air pollution, physical activity and health: A mapping review of the evidence. Environment international , 147 , 105954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105954
Booth, A. (2016). EVIDENT Guidance for Reviewing the Evidence: a compendium of methodological literature and websites . ResearchGate. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.1562.9842 .
Grant, M.J. & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of the 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal , 26(2), 91-108. https://www.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
"A type of review that has as its primary objective the identification of the size and quality of research in a topic area in order to inform subsequent review" (Booth et al., 2012, p. 269).
- Main purpose is to map out and categorize existing literature, identify gaps in literature—great for informing policy-making
- Search comprehensiveness determined by time/scope constraints, could take longer than a systematic review
- No formal quality assessment or critical appraisal
Learn more about the methods :
Arksey, H., & O'Malley, L. (2005) Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology , 8 (1), 19-32. https://doi.org/10.1080/1364557032000119616
Levac, D., Colquhoun, H., & O’Brien, K. K. (2010). Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implementation Science: IS, 5, 69. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-5-69
Example :
Rahman, A., Sarkar, A., Yadav, O. P., Achari, G., & Slobodnik, J. (2021). Potential human health risks due to environmental exposure to nano-and microplastics and knowledge gaps: A scoping review. Science of the Total Environment, 757 , 143872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143872
A review that "[compiles] evidence from multiple...reviews into one accessible and usable document" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 103). While originally intended to be a compilation of Cochrane reviews, it now generally refers to any kind of evidence synthesis.
- Compiles evidence from multiple reviews into one document
- Often defines a broader question than is typical of a traditional systematic review
Choi, G. J., & Kang, H. (2022). The umbrella review: a useful strategy in the rain of evidence. The Korean Journal of Pain , 35 (2), 127–128. https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2022.35.2.127
Aromataris, E., Fernandez, R., Godfrey, C. M., Holly, C., Khalil, H., & Tungpunkom, P. (2015). Summarizing systematic reviews: Methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. International Journal of Evidence-Based Healthcare , 13(3), 132–140. https://doi.org/10.1097/XEB.0000000000000055
Rojas-Rueda, D., Morales-Zamora, E., Alsufyani, W. A., Herbst, C. H., Al Balawi, S. M., Alsukait, R., & Alomran, M. (2021). Environmental risk factors and health: An umbrella review of meta-analyses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Dealth , 18 (2), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020704
A meta-analysis is a "technique that statistically combines the results of quantitative studies to provide a more precise effect of the result" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 98).
- Statistical technique for combining results of quantitative studies to provide more precise effect of results
- Aims for exhaustive, comprehensive searching
- Quality assessment may determine inclusion/exclusion criteria
- May be conducted independently or as part of a systematic review
Berman, N. G., & Parker, R. A. (2002). Meta-analysis: Neither quick nor easy. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 2(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-2-10
Hites R. A. (2004). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the environment and in people: a meta-analysis of concentrations. Environmental Science & Technology , 38 (4), 945–956. https://doi.org/10.1021/es035082g
A systematic review "seeks to systematically search for, appraise, and [synthesize] research evidence, often adhering to the guidelines on the conduct of a review" provided by discipline-specific organizations, such as the Cochrane Collaboration (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 102).
- Aims to compile and synthesize all known knowledge on a given topic
- Adheres to strict guidelines, protocols, and frameworks
- Time-intensive and often takes months to a year or more to complete
- The most commonly referred to type of evidence synthesis. Sometimes confused as a blanket term for other types of reviews
Gascon, M., Triguero-Mas, M., Martínez, D., Dadvand, P., Forns, J., Plasència, A., & Nieuwenhuijsen, M. J. (2015). Mental health benefits of long-term exposure to residential green and blue spaces: a systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 12 (4), 4354–4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120404354
"Systematized reviews attempt to include one or more elements of the systematic review process while stopping short of claiming that the resultant output is a systematic review" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 102). When a systematic review approach is adapted to produce a more manageable scope, while still retaining the rigor of a systematic review such as risk of bias assessment and the use of a protocol, this is often referred to as a structured review (Huelin et al., 2015).
- Typically conducted by postgraduate or graduate students
- Often assigned by instructors to students who don't have the resources to conduct a full systematic review
Salvo, G., Lashewicz, B. M., Doyle-Baker, P. K., & McCormack, G. R. (2018). Neighbourhood built environment influences on physical activity among adults: A systematized review of qualitative evidence. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 15 (5), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050897
Huelin, R., Iheanacho, I., Payne, K., & Sandman, K. (2015). What’s in a name? Systematic and non-systematic literature reviews, and why the distinction matters. https://www.evidera.com/resource/whats-in-a-name-systematic-and-non-systematic-literature-reviews-and-why-the-distinction-matters/

- Review Decision Tree - Cornell University For more information, check out Cornell's review methodology decision tree.
- LitR-Ex.com - Eight literature review methodologies Learn more about 8 different review types (incl. Systematic Reviews and Scoping Reviews) with practical tips about strengths and weaknesses of different methods.
- << Previous: Getting started
- Next: 1. Define your research question >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/litreviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries

Enhancing Searching as Learning (SAL) with Generative Artificial Intelligence: A Literature Review
- Conference paper
- First Online: 01 June 2024
- Cite this conference paper

- Kok Khiang Lim ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7118-6864 8 &
- Chei Sian Lee ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0891-6526 8
Part of the book series: Communications in Computer and Information Science ((CCIS,volume 2117))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction
Searching as Learning (SAL), a learning process with potential knowledge gain during searches in a digital environment, is an emerging field in human-computer interaction research, especially with recent technological advancements in generative artificial intelligence (GenAI). According to SAL, the act of searching for the information itself can be a valuable learning experience. Many studies have investigated SAL’s learning perspective and facets supported by traditional search systems (e.g., web browsers), to access, search, and retrieve information to fulfill users’ learning intentions. However, the applications of GenAI, as well as their roles and disruption to the existing SAL process, are unclear. To address this gap, this study aims to shed light on the applicability of GenAI in enhancing the SAL process by conducting a systematic literature review.
First, we seek to define the concepts of ‘learning’ and ‘searching’ by examining the components of SAL in the literature and then detailing how SAL would have occurred. Next, the systematic literature review, guided by PRISMA, uses the PICO (Population, Intervention, Comparison, and Outcome) framework to develop searchable keywords and guide the literature review. Five major databases were searched, and literature that fulfilled the PICO’s criteria was included for review. Preliminary analysis shows that GenAI could improve and ease SAL human-computer interfaces that inevitably change the process and influence users’ learning behavior, such as how information is retrieved and consumed. Consequently, these opportunities posed concerns about information reliability, accuracy, and long-term effects on user behavior.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Disclosure of Interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Choo, C.W., Detlor, B., Turnbull, D.: Information seeking on the web: an integrated model of browsing and searching. First Monday 5 (2000). https://doi.org/10.5210/fm.v5i2.729
Wildemuth, B.M., Freund, L.: Assigning search tasks designed to elicit exploratory search behaviors. In: Proceedings of the Symposium on Human-Computer Interaction and Information Retrieval, pp. 1–10 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1145/2391224.2391228
Vakkari, P.: Searching as learning: a systematization based on literature. J. Inf. Sci. 42 , 7–18 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/0165551515615833
Article Google Scholar
Dhillon, M.K.: Online information seeking and higher education students. In: Chelton, M., Cool, C. (eds.) Youth Information- Seeking Behavior II: Context, Theories, Models, and Issues, pp. 165–205. Scarecrow Press, Lanham (2007)
Google Scholar
Chiu, T.K.F.: Future research recommendations for transforming higher education with generative AI. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 6 , 100197 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2023.100197
Song, C.P., Song, Y.P.: Enhancing academic writing skills and motivation: assessing the efficacy of ChatGPT in AI-assisted language learning for EFL students. Front. Psychol. 14 , 1260843 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1260843
Malmström, H., Stöhr, C., Ou, A.W.: Chatbots and other AI for learning: a survey of use and views among university students in Sweden. Chalmers Stud. Commun. Learn. High. Educ. 1 (2023). https://doi.org/10.17196/cls.csclhe/2023/01
Abdaljaleel, M., et al.: A multinational study on the factors influencing university students’ attitudes and usage of ChatGPT. Sci. Rep. 14 , 1983 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-52549-8
Stahl, B.C., Eke, D.: The ethics of ChatGPT – exploring the ethical issues of an emerging technology. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 74 , 102700 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2023.102700
Wu, X., Duan, R., Ni, J.: Unveiling security, privacy, and ethical concerns of ChatGPT. J. Inf. Intell. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiixd.2023.10.007
Pollock, A., Berge, E.: How to do a systematic review. Int. J. Stroke 13 , 138–156 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1747493017743796
Gimenez, P., Machado, M., Pinelli, C., Siqueira, S.: Investigating the learning perspective of searching as learning, a review of the state of the art. In: 31st Brazilian Symposium on Computers in Education, pp. 302–311 (2020). doi: https://doi.org/10.5753/cbie.sbie.2020.302
Kuhlthau, C.: Guided inquiry: school libraries in the 21st century. Sch. Libr. Worldw. 16 , 1–12 (2001). https://doi.org/10.29173/slw6797
Flavell, J.: Metacognition and cognitive monitoring: a new area of cognitive-developmental inquiry. Am. Psychol. 34 , 906–911 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.34.10.906
Pressley, M.: Metacognition and self-regulated comprehension. In: Farstrup, A.E., Samuel, S.J. (eds.) What Research Has to Say About Reading Instruction, pp. 291–309. International Reading Association, Newark (2002)
Hoyer, J.v., Pardi, G., Kammerer, Y., Holtz, P.: Metacognitive judgments in searching as learning (SAL) tasks: Insights on (mis-) calibration, multimedia usage, and confidence. Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Search as Learning with Multimedia Information, pp. 3–10. Association for Computing Machinery, Nice (2019)
Marchionini, G.: Exploratory search: from finding to understanding. Commun. ACM 49 , 41–46 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1145/1121949.1121979
https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt/
Niedbał, R., Sokołowski, A., Wrzalik, A.: Students’ use of the artificial intelligence language model in their learning process. Procedia Comput. Sci. 225 , 3059–3066 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2023.10.299
American Psychological Association. https://www.apa.org/monitor/2023/06/chatgpt-learning-tool
Page, M.J., et al.: The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 10 , 89 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-021-01626-4
Fink, A.: Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper, 2nd edn. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks (2005)
Bach, T.A., Khan, A., Hallock, H., Beltrão, G., Sousa, S.: A systematic literature review of user trust in AI-enabled systems: an HCI perspective. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 40, 1–16 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2022.2138826
Floridi, L., Chiriatti, M.: GPT-3: Its nature, scope, limits, and consequences. Mind. Mach. 30 , 681–694 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11023-020-09548-1
Bandara, W., Miskon, S., Fielt, E.: A systematic, tool-supported method for conducting literature reviews in information systems. In: ECIS 2011 Proceedings 19th European Conference on Information Systems, pp. 1–13. AIS Electronic Library (AISeL)/Association for Information Systems (2011). https://eprints.qut.edu.au/42184/
Jo, H.: Understanding AI tool engagement: a study of ChatGPT usage and word-of-mouth among university students and office workers. Telematics Inform. 85 , 102067 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2023.102067
Jo, H., Park, D.H.: AI in the workplace: examining the effects of ChatGPT on information support and knowledge acquisition. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2023.2278283
Murgia, E., Abbasiantaeb, Z., Aliannejadi, M., Huibers, T., Landoni, M., Pera, M.S.: ChatGPT in the classroom: a preliminary exploration on the feasibility of adapting ChatGPT to support children’s information discovery. In: Adjunct Proceedings of the 31st ACM Conference on User Modeling, Adaptation and Personalization, pp. 22–27 (2023). doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/3563359.3597399
Pellas, N.: The effects of generative AI platforms on undergraduates’ narrative intelligence and writing self-efficacy. Educ. Sci. 13 , 1155 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13111155
Yilmaz, R., Karaoglan Yilmaz, F.G.: The effect of generative artificial intelligence (AI)-based tool use on students’ computational thinking skills, programming self-efficacy and motivation. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 4 , 100147 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2023.100147
Yilmaz, R., Karaoglan Yilmaz, F.G.: Augmented intelligence in programming learning: examining student views on the use of ChatGPT for programming learning. Comput. Hum. Behav. Artif. Hum. 1 , 100005 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chbah.2023.100005
Duong, C.D., Vu, T.N., Ngo, T.V.N.: Applying a modified technology acceptance model to explain higher education students’ usage of ChatGPT: a serial multiple mediation model with knowledge sharing as a moderator. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 21 , 100883 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2023.100883
Rahman, M.S., Sabbir, M.M., Zhang, D.J., Moral, I.H., Hossain, G.M.S.: Examining students’ intention to use ChatGPT: does trust matter? Aust. J. Educ. Technol. 39 , 51–71 (2023). https://doi.org/10.14742/ajet.8956
Songsiengchai, S., Sereerat, B.O., Watananimitgul, W.: Leveraging artificial intelligence (AI): Chat GPT for effective English language learning among Thai students. Kurdish Stud. 11 , 359–373 (2023). https://doi.org/10.58262/ks.v11i3.027
Wandelt, S., Sun, X., Zhang, A.: AI-driven assistants for education and research? a case study on ChatGPT for air transport management. J. Air Transp. Manag. 113 , 102483 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jairtraman.2023.102483
Al-Sharafi, M.A., Al-Emran, M., Iranmanesh, M., Al-Qaysi, N., Iahad, N.A., Arpaci, I.: Understanding the impact of knowledge management factors on the sustainable use of AI-based chatbots for educational purposes using a hybrid SEM-ANN approach. Interact. Learn. Environ. 31 , 7491–7510 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2022.2075014
Arif, M., Qaisar, N., Kanwal, S.: Factors affecting students’ knowledge sharing over social media and individual creativity: an empirical investigation in Pakistan. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 20 , 100598 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2021.100598
Bouton, E., Tal, S.B., Asterhan, C.S.C.: Students, social network technology and learning in higher education: visions of collaborative knowledge construction vs. the reality of knowledge sharing. Internet High. Educ. 49 , 100787 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2020.100787
Proper, H.A., Bruza, P.D.: What is information discovery about? J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 50 , 737–750 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4571(1999)50:9%3c737::AID-ASI2%3e3.0.CO;2-C
Lee, C.T., Pan, L.-Y., Hsieh, S.H.: Artificial intelligent chatbots as brand promoters: a two-stage structural equation modeling - artificial neural network approach. Internet Res. 32 , 1329–1356 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1108/INTR-01-2021-0030
Holzwarth, M., Janiszewski, C., Neumann, M.M.: The influence of avatars on online consumer shopping behavior. J. Mark. 70 , 19–36 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1509/JMKG.70.4.019
Randall, W.L.: Narrative intelligence and the novelty of our lives. J. Aging Stud. 13 , 11–28 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-4065(99)80003-6
Rieh, S.Y., Collins-Thompson, K., Hansen, P., Lee, H.-J.: Towards searching as a learning process: a review of current perspectives and future directions. J. Inf. Sci. 42 , 19–34 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/0165551515615841
Tayan, O., Hassan, A., Khankan, K., Askool, S.: Considerations for adapting higher education technology courses for AI large language models: a critical review of the impact of ChatGPT. Mach. Learn. Appl. 15 , 100513 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mlwa.2023.100513
Slyer, J.T.: Unanswered questions: implications of an empty review. JBI Evid. Synth. 14 , 1–2 (2016). https://doi.org/10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-002934
Yaffe, J., Montgomery, P., Hopewell, S., Shepard, L.D.: Empty reviews: a description and consideration of Cochrane systematic reviews with no included studies. PLoS ONE (2012). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036626
Abdel Aziz, M.H., Rowe, C., Southwood, R., Nogid, A., Berman, S., Gustafson, K.: A scoping review of artificial intelligence within pharmacy education. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 88 , 100615 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpe.2023.100615
Download references
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the National Research Foundation, Singapore under its AI Singapore Programme (AISG Award No: AISG-GV-2023-013).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Wee Kim Wee School of Communication and Information, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore
Kok Khiang Lim & Chei Sian Lee
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kok Khiang Lim .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
University of Crete and Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas (FORTH), Heraklion, Crete, Greece
Constantine Stephanidis
Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas (FORTH), Heraklion, Crete, Greece
Margherita Antona
Stavroula Ntoa
University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL, USA
Gavriel Salvendy
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Lim, K.K., Lee, C.S. (2024). Enhancing Searching as Learning (SAL) with Generative Artificial Intelligence: A Literature Review. In: Stephanidis, C., Antona, M., Ntoa, S., Salvendy, G. (eds) HCI International 2024 Posters. HCII 2024. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 2117. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61953-3_17
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61953-3_17
Published : 01 June 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-61952-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-61953-3
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Chiropr Med
- v.5(3); Fall 2006
Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade
Bart n. green.
a Associate Editor, National University of Health Sciences
Claire D. Johnson
b Editor, National University of Health Sciences
c Vice President of Academic Affairs and Program Development, Texas Chiropractic College
This document may be redistributed and reused, subject to certain conditions .
To describe and discuss the process used to write a narrative review of the literature for publication in a peer-reviewed journal. Publication of narrative overviews of the literature should be standardized to increase their objectivity.
In the past decade numerous changes in research methodology pertaining to reviews of the literature have occurred. These changes necessitate authors of review articles to be familiar with current standards in the publication process.
Narrative overview of the literature synthesizing the findings of literature retrieved from searches of computerized databases, hand searches, and authoritative texts.
An overview of the use of three types of reviews of the literature is presented. Step by step instructions for how to conduct and write a narrative overview utilizing a ‘best-evidence synthesis’ approach are discussed, starting with appropriate preparatory work and ending with how to create proper illustrations. Several resources for creating reviews of the literature are presented and a narrative overview critical appraisal worksheet is included. A bibliography of other useful reading is presented in an appendix.
Narrative overviews can be a valuable contribution to the literature if prepared properly. New and experienced authors wishing to write a narrative overview should find this article useful in constructing such a paper and carrying out the research process. It is hoped that this article will stimulate scholarly dialog amongst colleagues about this research design and other complex literature review methods.
Sources of support: This article is reprinted with permission. Its original citation is: Green BN, Johnson CD, Adams A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. J Sports Chiropr Rehabil 2001;15:5–19.
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 30 May 2024
The effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviours in adults with autism spectrum disorders (ASD): a systematic PRISMA review
- Jody Salter 1 , 2 &
- Sarah Blainey 1 , 3
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 316 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
43 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Previous research has suggested that the core features of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) may contribute to offending behaviours and increased vulnerability within the Criminal Justice System. To date, there is a paucity of evidence assessing the effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviour in adults with ASD but without co-occurring intellectual disability (ID) across a broad range of forensic settings. The lack of robust evidence is concerning, as limited effectiveness may contribute to an increased likelihood of prolonged incarceration, particularly in the most restrictive settings. A PRISMA systematic review was conducted with a narrative synthesis to: (a) evaluate the evidence of the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing recidivism, (b) assess whether the core features of ASD impact the effectiveness of these interventions, and (c) identify additional factors that may affect the effectiveness of interventions within this population. Seven studies involving ten male participants were identified. The findings suggest that interventions for offending behaviours in adults with ASD without intellectual disability (ID) are largely inadequate, and that core ASD features need to be considered. Additionally, a complex interplay of risk factors potentially impacting intervention effectiveness was suggested. Limitations include heterogeneity across intervention types, measures of effectiveness, and what constitutes effectiveness. Despite the limited number of studies and data quality, the review aligns with a growing body of literature highlighting vulnerability and a need for evidence-based interventions for people with ASD. The review also discusses the broader implications of ineffective interventions.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) represent a group of complex and highly heterogeneous neurodevelopmental disorders. A diagnosis of ASD is based on the presence of two core features: impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI), and restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs) [ 1 ].
Phenotypic manifestations of the core features often present with varying degrees of social disengagement, difficulties in establishing and sustaining relationships, social naivety, lack of eye contact, and difficulties in interpreting facial expressions [ 2 ]. RRBs manifest as intense and highly restrictive special interests, a strong inclination for environmental consistency [ 3 ], cognitive rigidity, and hyper-or hypo sensory responses to the environment [ 4 ].
Additional factors modulate and influence these core features, including the extent of sensory and motor impairments, language and cognitive abilities, adaptive functioning, gender and the presence of co-occurring psychiatric disorders [ 5 , 6 , 7 ]. The increasing recognition of ASD has resulted in significantly higher diagnosis rates across all age groups [ 8 ], which are currently estimated to be 1 in 57 in England [ 9 ]. Consequently, this increase in diagnoses has led to a greater representation of individuals with ASD within the criminal justice system (CJS).
ASD in the criminal justice system
An increasing body of research has highlighted the significant vulnerability experienced by individuals with ASD while navigating the CJS. This vulnerability becomes evident throughout multiple stages of the criminal justice process, ranging from initial encounters with police [ 10 ] through to police interviews [ 11 ], to court room proceedings [ 12 ] and prison services [ 13 ]. This heightened vulnerability is exacerbated by the reported general lack of understanding of ASD within the CJS, among both professionals and the general public [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 ].
Individuals with ASD and co-occurring intellectual disability (ID) are often identified and diverted from the criminal justice system (CJS). This is due to a recognition of their reduced culpability, a result of impairments in both intellectual and adaptive functioning [ 15 ]. In contrast, individuals with ASD but without co-occurring ID, the population on which this review focuses, exhibit significant deficits in adaptive functioning despite their intellectual capabilities. This difference is often referred to as the IQ functioning gap and is unique to individuals with ASD [ 17 ]. Despite impairments in adaptive functioning, this population is considered intellectually capable. Therefore, they are generally perceived as culpable and sufficiently competent to navigate the complexities of the CJS and receive a fair trial. This contrast raises further questions concerning culpability ranging from criminal responsibility to the appropriateness of sentencing.
Following conviction, when an offence has met the custody threshold, offenders with ASD are typically diverted to the community or prison. Alternatively, if detained under the Mental Health Act 1983 (the legislative framework governing mental healthcare and treatment in England and Wales), they may be detained in a secure hospital environment (classified as low, medium, or high security).
Estimating the prevalence of ASD within the UK prison population is difficult because of a lack of routine assessment; nonetheless, ASD is estimated to range between 1% and 4.4% [ 5 ]. Research has shown a disproportionately high prevalence of ASD in secure hospital settings (6.5%), exceeding the estimate for the general population [ 18 ].
Qualitative studies examining the experiences of prisoners with ASD without co-occurring ID have highlighted their increased vulnerability to bullying, exploitation, and social anxiety in prison [ 13 ]. In addition, research aimed at evaluating the prevalence of the broader autistic phenotype among a prison population, as well as comparing their mental health characteristics to those without, revealed a significant risk of self-harm and suicide in individuals presenting with autistic traits. Within this cohort, of the 240 prisoners assessed, 46 displayed significant autistic traits, with 12 meeting the diagnostic criteria for ASD. Notably, only two of these individuals had been previously recognised by the prison as having ASD. This finding highlights the under recognition of ASD and emphasises the heightened vulnerability of this population to a range of mental health risks within the prison environment [ 5 ].
Although it may be logical to assume that a secure hospital setting may better meet the treatment needs of people with ASD than a prison setting, current evidence suggests otherwise. Concerns have been raised, including the high likelihood of long-term seclusion in people with ASD compared to those without ASD [ 19 ] and significantly longer than average stays within secure hospital settings [ 20 ].
Despite several initiatives aimed at improving the recognition of ASD within the prison population [ 21 ], a recent UK government report on ‘neurodiversity’ [ 22 ], a term encompassing various conditions that fall into the broader category of neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) including ASD, highlighted three notable areas of concern. These included a greater likelihood of neurodivergent individuals being held on remand, inappropriately pleading guilty, and judges often failing to recognise a defendant’s neurodivergence as a mitigating factor when sentencing. These findings demonstrate that much work is needed to address the challenges faced by individuals with ASD and neurodivergent conditions in the CJS.
ASD and risk of offending
While there is insufficient evidence to suggest that individuals with ASD are at greater risk of engaging in offending behaviours [ 23 ], it has been suggested that the core features of ASD may contribute to the risk of offending behaviours [ 24 , 25 ]. Risk factors for offending behaviour in the general population are associated with the cumulative influence of various factors, including alcohol and drug abuse, low socioeconomic status, mental disorders, adversity, child abuse, and traumatic brain injury [ 26 , 27 , 28 ]. Less is known about the risk factors for offending behaviour within the ASD population, with the exception of co-occurring psychiatric disorders, such as personality disorders and psychosis [ 5 ].
Research suggests that individuals diagnosed with ASD early in life face barriers to services throughout their lifespan, resulting in unmet education, health, and therapeutic needs [ 29 , 30 ]. Research suggests that certain demographic groups, such as women [ 31 , 32 ], individuals from ethnic minorities, and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds [ 9 , 33 ], are far more likely to be underdiagnosed. This in turn increases the risk of unmet needs [ 34 , 35 ]. These factors may contribute as variables that collectively increase the overall cumulative risk of engaging in offending behaviours.
Forensic interventions
Interventions for offending behaviour often use cognitive-behavioural techniques to reduce recidivism, with an emphasis on perspective-taking, self-and relationship management, and problem solving. In the United Kingdom, the Ministry of Justice requires a sufficient evidence base for the accreditation of forensic interventions. This accreditation aims to promote high-quality programs in prisons and community settings to reduce recidivism [ 36 ].
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is widely recognised as one of the most effective interventions for offending behaviours [ 37 ]. There is evidence that CBT reduces recidivism by 20–30% in the general offending population [ 38 , 39 ]. However, there is little evidence to support the effectiveness of such interventions for offending behaviour in forensic secure settings, often yielding inconsistent findings [ 40 ].
Beyond forensic settings, evidence suggests that adapted CBT is effective for individuals with ASD [ 41 , 42 ]. These adjustments are necessary due to the core features of ASD and challenges in areas such as perspective taking and cognitive rigidity, both of which are conducive to successful therapeutic outcomes in this population [ 43 ]. Additionally, evidence supports the use of social skills training [ 44 ] and group-based social skills interventions in adults with ASD [ 41 ] However, there is no consensus regarding the specific adaptations most beneficial for individuals with ASD.
Furthermore, the lack of appropriate outcome measures has been reported to be a barrier to determining the effectiveness of interventions within secure forensic hospital settings [ 45 , 46 , 47 ]. Despite the evidence for CBT use within the general offender population and for individuals with ASD outside forensic settings, there are reports that the implementation of these interventions is not effective for individuals detained within secure hospital settings [ 19 , 48 , 49 ].
The increasing recognition of the vulnerability of individuals with ASD within the CJS highlights the urgent need for a systematic evaluation of the effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviours in adults with ASD. While previous research has examined interventions for individuals with ASD and co-occurring ID [ 49 ], a significant research gap remains regarding the effectiveness of forensic interventions for individuals with ASD but without co-occurring ID [ 14 ].
This systematic review aims to address this gap by conducting a comprehensive evaluation of intervention effectiveness in an ASD population without co-occurring ID.
Research aims
This systematic review is guided by the following research objectives:
To systematically review and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviours in adults with ASD without co-occurring ID, as reported in the literature;
To ascertain whether the core features of ASD impact the effectiveness of the identified interventions; and.
To identify additional risk factors that may impact the effectiveness of interventions in this population.
Inclusion criteria
Each potentially eligible study was screened based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria described in the PICO framework below [ 50 ].
Population.
Participants included adults aged 18 years and older diagnosed with ASD, as defined by the authors in the literature. Studies involving participants with co-occurring ASD and ID and those that did not differentiate between these two populations were excluded.
Intervention & Outcomes.
Our review aimed to identify studies that objectively and/or subjectively measured the effectiveness of therapeutic or pharmacological interventions for reducing recidivism in individuals with ASD exhibiting offending behaviours. These included interventions delivered in all categories, namely, prisons, probation supervision, and secure hospitals.
Study Design and Comparison.
All primary research studies were included, regardless of publication date or country of origin. Studies that were peer-reviewed (e.g., grey literature and conference abstracts), systematic reviews, and those not published in English were excluded. An inclusion-exclusion criterion related to the type of comparison conducted in individual studies was not imposed.
Search strategy
The search was conducted on the 27th of March 2021 across five databases, covering a broad timeframe and utilising international terminology. The databases included:
Embase (1974 to 2021).
Ovid MEDLINE(R) and Epub ahead of print, In-process, In data-review and other Non-Indexed Citations.
Ovid MEDLINE(R) Daily.
Global Health (1973 to March 2021).
APA PsychInfo (1806 to February 2021).
Furthermore, a web-based search using Google Scholar was conducted with the same search terms. The first 15 pages of results were manually reviewed; however, no additional studies meeting the inclusion criteria were found. Additionally, the reference lists and citations of relevant reviews were manually checked, but this did not yield any further eligible studies.
Data selection and extraction
The data selection and extraction processes consisted of two stages:
During Stage 1, potential eligible studies were screened based on their titles and abstracts against the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Owing to the limited number of results, the screening process was performed manually and repeated one week later to increase accuracy.
Stage 2 involved a comprehensive review of the full texts of the selected studies to confirm their alignment with the inclusion criteria. Relevant data were extracted and organised into spreadsheets using Microsoft Excel.
PRISMA flow diagram of searches of databases and registers only
Consistent with the primary aim of this systematic review, the first outcome measure is the effectiveness of the identified forensic interventions, measured by a reduction in recidivism. While reducing recidivism is the principal goal of forensic interventions, it is often viewed as a proxy measure that may not fully capture the complexity of offending behaviours, particularly in cases of crossover crime [ 46 , 51 ]. To address this limitation, additional relevant measures contributing to reduced recidivism were collected to allow for a preliminary assessment of intervention effectiveness. These additional measures included variables such as a reduction in security levels within institutional settings (i.e., medium to low security) or significant positive changes compared to baseline measurements recorded before and after the intervention.
The second aim of this review was to examine whether the core features of ASD present barriers to the rehabilitation process. To achieve this objective, data concerning the interactions between impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI) and restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs) in relation to interventions within individual studies, as described by clinicians were collected and analysed.
Thirdly, this review aimed to identify additional risk factors described within findings that may influence the effectiveness of the interventions. The aim of the analysis is to provide a more comprehensive understanding of collective risk factors and their interactions with intervention effectiveness assessed through narrative synthesis. In addition, the data collected included the study design, author, and country of origin. When reported, participant demographics, such as age, gender, offence, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status, were reported. The intervention data included the type of intervention used, setting, duration, and frequency, only when available.
Study risk of bias assessment
The Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) [ 52 ] is a comprehensive tool for critically evaluating various research methods. The methodological quality of each study and the potential risk of bias were assessed using the MMAT. The results of this assessment are presented in tabular form (Table 2 , ‘MMAT Quality Appraisal’, appendix).
Synthesis method
A narrative synthesis [ 53 ] was used for this review as a meta-analysis was not appropriate because of the significant heterogeneity between studies. The synthesis process began with a preliminary analysis, in which the data were extracted and presented in tabular form to provide a summary of the findings and to identify potential patterns within the data. A guided conceptual framework was constructed based on the narrative synthesis of the primary data. This framework aimed to assess both the similarities and differences between the included studies while exploring emerging thematic elements.
Study selection
The initial database search returned 2,551 results after removing duplicates, as shown in Fig. 1 of the PRISMA flow diagram, which depicts the flow of information at each stage of the systematic review search. Subsequent screening included an initial assessment of the titles and a subsequent assessment of the abstracts, which led to the exclusion of an additional 2,530 articles. To ensure accuracy, abstract screening was repeated one week later. Subsequent full-text eligibility screening excluded 14 additional studies. The reasons for exclusion included the following: (a) participants under 18 years of age ( n = 4), (b) lacked differentiation between the ID and ASD populations ( n = 4), (c) were differentiated but not described in the context of the results ( n = 2), (d) measurement of interventions for self-harm and suicide among offenders with ASD rather than for offending behaviour ( n = 1), and (e) removal of commentary papers ( n = 3). Consequently, the final number of included studies from the initial database search was seven ( n = 7).
Study characteristics
Among the seven studies identified, three were case reports ( n = 3), two were qualitative studies ( n = 2), and two were quantitative case series ( n = 2). These studies jointly assessed the effectiveness of the various interventions. The total sample size of all the studies was limited to 10; all the participants were men, and demographic information was limited. It is worth noting that despite the use of international terminology in the search criteria, all seven articles described studies conducted exclusively in southern England, United Kingdom (UK). In these studies, all participants, apart from one were held in secure hospital units under the provisions of the Mental Health Act 1983. The most prevalent types of offending behaviours observed were sexual offences ( n = 4), followed by manslaughter ( n = 3), and arson ( n = 3).
Table 1 ‘Summary of Findings’ provides a summary of each study included in the systematic review. The summary includes author information, available participant demographics, offence type, setting, detainment status (i.e., under the mental health act), intervention approach, study findings, intervention effectiveness, measurement used to assess effectiveness, and whether there was evidence to suggest that the core features of ASD impacted the effectiveness of forensic intervention(s). These are separated by impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI) and restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs).
Risk of bias in studies
The methodological quality of the studies was assessed using the MMAT [ 52 ] (Table 2 , ‘MMAT Quality Appraisal’, appendix). Each of the three case reports received a 3-star rating, indicating a moderate risk of bias and meeting 75% of the qualitative MMAT criteria [ 54 , 55 , 56 ].
The two quantitative case series were found to be at a higher risk of bias due to difficulties in distinguishing the treatment groups, recruitment difficulties, lack of a control group, and incomplete outcome data for the ASD group without co-occurring ID. They received a 2-star rating, meeting 50% of the MMAT quantitative criteria [ 58 ].
The second quantitative study [ 57 ], raised concerns about the validity and reliability of outcome measures, which were originally designed for the ID population but applied to the ASD group without co-occurring ID. This study also received a 2-star rating and met 50% of the MMAT’s quantitative criteria.
The remaining qualitative studies received a 3-star rating, meeting 75% of the MMAT criteria. The first evaluated intervention effectiveness from the perspective of the clinicians who delivered the therapeutic program [ 59 ]. The second assessed offenders’ views via self-report, which carry a potential risk of response bias [ 60 ].
Selection bias was observed in studies that combined ID and ASD populations. Overall, it was difficult to establish a causal relationship between the interventions and outcomes.
Notably, not all the studies reviewed explicitly documented obtaining informed consent from participants. The discrepancy in informed consent between studies, particularly in restrictive forensic settings, presents challenges extending beyond ethical considerations. Such discrepancies may compromise the validity of intervention comparisons, introduce biases in participant selection, and undermine the reliability of data.
Interventions
The interventions examined across the reviewed studies were diverse, as presented in Table 3 , titled ‘Summary of Interventions’.
Three studies incorporated both pharmacological and psychological interventions. Specifically, antipsychotics were used to address co-occurring psychosis, contributing to instances of offending behaviour [ 55 ]. Antipsychotics were also used to manage stress-induced psychosis [ 56 ]. In the context of directly treating offending behaviours, two distinct medications were applied in cases of sexual offending, each with different mechanisms of action [ 54 ] (Table 3 ).
Four studies relied exclusively on psychological interventions [ 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 ]. Among these, two studies implemented adapted forms of CBT. Specific details regarding the non-standardised adaptations used in CBT were not provided by the study author, except that individual delivery was necessary due to difficulties encountered within group settings [ 54 , 56 ].
The third study that incorporated CBT included elements similar to those of the Adapted Sex Offender Treatment Program (A-SOTP) [ 58 ]. The effectiveness of the A-SOTP was described in two studies [ 59 , 60 ]. Furthermore, the Equipping Youth to Help One Another (EQUIP) was adapted and piloted for use with individuals with ID and developmental disabilities (DD) who had committed sexual offences [ 57 ]. Supplementary interventions included speech and language therapy to facilitate communication [ 55 ], occupational therapy to address impairments in executive functioning [ 55 , 56 ] and art therapy [ 54 ].
Table 3 visually depicts a summary of the diverse interventions extracted, reviewed, and categorised according to intervention type: pharmacological, psychological, and supplementary intervention approaches. In addition, the table includes the type of offence, studies using intervention, underlying mechanism of action or theory, evidence base supporting intervention, and measurements used to assess effectiveness.
Measurements
Numerous approaches were adopted to measure effectiveness across the studies. Two studies measured effectiveness by reduced recidivism and the need to repeat the intervention. Other studies utilised a range of standardised measurements to evaluate psychological interventions. For example, one study [ 54 ] employed the Behavioural Status Index (BSI) every six months as a measurement tool. In contrast, another [ 56 ] employed the State Trait Anger Expression Inventory (STAXII II) and the Millon Multiaxial Personality Inventory (MMPI), combined with standardised risk assessment, one-year postintervention.
Regarding pharmacological interventions, one case report used a combination of subjective and objective measurements. These included self-reports and the systematic monitoring of inappropriate glancing behaviours over time by staff members [ 54 ]. In another instance, the reduction in verbalised delusions served as a measure of the effectiveness of antipsychotic medication [ 55 , 56 ].
The effectiveness of interventions such as the A-SOTP was assessed differently across the two studies. In one study, effectiveness was evaluated through clinician views [ 59 ], while in the other, effectiveness was determined by the participants’ subjective experiences with the intervention [ 60 ].
In the case of CBT, which shares similarities with A-SOTP, standardised measures were applied both pre- and post-intervention. These measures consisted of sexual attitudes consistent with sexual offending (QACSO), sexual offenders’ self-appraisal scale (SOSAS), the sexual attitudes and knowledge scale (SAKS), and the victim empathy scale-adapted (VES-A) [ 58 ].
The EQIP study, which also focused on sexual offending [ 57 ], assessed effectiveness by examining improvements in baseline scores on standardised tests related to moral reasoning, cognitive distortions, problem-solving abilities, and anger. In addition, a move to a lower security level was considered an indicator of overall effectiveness. Furthermore, in a case study that included speech and language therapy, the clinician’s subjective view of improved communication within the secure unit served as a measure of the intervention’s effectiveness [ 55 ].
Among the seven studies reviewed, only one pertaining to an arson offence considered the intervention(s) effective. In this case, a pharmacological intervention was used to treat co-occurring alcohol-induced psychosis, and the unspecified antipsychotic proved successful in reducing delusions. Furthermore, speech and language therapy aimed at improving communication skills was also deemed to be effective [ 55 ].
However, the remaining six studies, which included a total of nine participants, concluded that the interventions were largely ineffective. One case report addressing sexual offending behaviours used pharmacological interventions. The first involved cyproterone acetate, a testosterone inhibitor, however, the outcome could not be conclusively determined owing to adherence and dosage issues [ 54 ]. In the second, the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) fluoxetine was deemed ineffective, as inappropriate behaviours did not significantly decrease [ 54 ]. It is worth noting that the evidence for both of these drugs has since been described as insufficient to guide clinical practice, with cyproterone acetate considered inadequate [ 61 ], and the evidence for fluoxetine has not been fully determined [ 62 ].
Among the two studies that utilised the A-SOTP and a similar form of CBT for sexual offending, one participant repeated the intervention program six times and subsequently re-offended and a further two participants repeated the yearlong intervention program and reoffended [ 58 ]. These findings are consistent with the results of the study that assessed clinician views [ 59 ]. Even in the case of CBT, as used in two studies, the intervention was deemed ineffective despite adaptations made to accommodate individuals with ASD [ 54 , 56 ].
ASD core features and impact upon intervention effectiveness
The application of a narrative synthesis facilitated the identification and extraction of recurring patterns within the data. These patterns were evident across all the studies, highlighting the considerable challenges posed by impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI) and the presence of restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs) on the effectiveness of interventions, as depicted in Fig. 2 .
Impact of The Core Features of ASD upon Intervention Effectiveness. Note. This describes the core features of ASD, both ‘impairments to SCI’ and ‘presence of RRBs’, and their impact upon intervention effectiveness as extracted from studies
Additional factors impacting intervention effectiveness
In addition to the core features of ASD, this review sought to identify additional risk factors that may influence the effectiveness of the intervention(s). Potential risk factors highlighted by the authors of each study were collected, and through narrative synthesis, several recurring themes emerged from the data. Co-occurring personality disorders and psychosis [ 55 , 56 ], were identified as potential factors impacting intervention effectiveness, as described within the literature. Additionally, events such as childhood adversity, sexual abuse, trauma, and having a dysfunctional family life were described as potential contributors [ 58 ]. Late diagnosis of ASD was theorised to lead to maladaptive coping skills deriving from unmet needs, which were described in three of the studies [ 54 , 55 , 56 ].
An overarching theme identified across the majority of the seven studies was the insufficiency of service provision, staff expertise, and the evidence base.
The present systematic review identified seven studies with ten participants who underwent forensic interventions aimed at reducing offending behaviours in adults with ASD, particularly those without co-occurring ID. The principal aim of this review was to evaluate the effectiveness of these interventions. The secondary aim was to examine whether the core features of ASD have an impact on the effectiveness of these forensic interventions and to identify other variables that may impact the overall effectiveness of interventions.
Regarding the first aim, the evidence suggests that the interventions reviewed were inadequate. However, these findings should be treated with caution not only because of the small sample size but also because of limitations in the generalisability of the findings. Despite an extensive literature search, all the studies were conducted in southern England, UK, and included only male participants. In addition, all participants, with the exception of one individual living in the community, were detained within secure hospital settings under the provisions of the Mental Health Act (1983). This highlights the lack of data from prison and the probation service, which limits the scope of the review. Furthermore, this review highlights a critical lack of research within this domain. Even when the literature was identified, it was often of inadequate quality owing to various design limitations. The significant heterogeneity between studies, each utilising distinct intervention methods and tools for measuring intervention effectiveness, illustrates a notable lack of standardisation in both clinical and research methodologies within this field. This lack of consistency aligns with broader research on mental health in individuals with ASD [ 45 , 46 ]. Nonetheless, the forensic domain faces additional challenges, such as the lack of randomised control trials, which means that the effectiveness of interventions is difficult to fully determine. These challenges are exacerbated by unavoidable confounding variables, the risk of bias, and the ethical implications of a no-treatment group [ 66 ], all of which contribute to the lack of evidence.
The secondary aim was to examine the potential impact of the core features of ASD on the effectiveness of interventions designed to reduce recidivism. The data patterns identified through narrative synthesis consistently emerged across all studies, highlighting the significant challenges posed by impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI) and the presence of restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs). These challenges highlight the general inappropriateness of forensic interventions within this population.
The third and final aim was to identify factors, beyond the core features of ASD, that may influence the effectiveness of interventions. Throughout the studies, a recurring theme emerged, highlighting significant systemic factors impacting intervention effectiveness. These include issues such as a shortage of government funding leading to inadequate service provision, the question of whether ASD and ID services should be combined, and the substantial unmet needs throughout the lifespan of individuals with ASD, all of which affect the success of forensic interventions. While the core features of ASD are significant, they may not be the primary cause of intervention failure. Rather, they seem to be contributing factors within a broader and more complex array of variables that collectively impact the overall effectiveness of these forensic interventions.
Implications
The inadequate provision of forensic services carries significant implications, especially when prolonged detainment becomes necessary due to the shortcomings of forensic interventions. Such deficiencies may subject individuals with ASD to non-evidence-based interventions, often repeatedly [ 56 , 58 ]. This then increases the likelihood of these individuals being labelled as ‘unrehabilitated,’ potentially leading to extended periods of detainment. Consequently, this creates a counterproductive cycle that not only exacerbates the economic burden but also raises serious concerns about human rights and the potential legal consequences of prolonged confinement.
These issues underscore fundamental questions about the fairness and adequacy of the legal system. Therefore, addressing these knowledge gaps and the lack of evidence-based approaches are crucial to ensuring a more equitable criminal justice system for individuals with ASD.
Future research
This review identifies several key areas for future research in this field. Developing evidence-based interventions tailored to the unique needs of individuals with ASD is crucial. Establishing a consensus on the measurements used for assessing the effectiveness of these interventions, as well as a clear definition of what constitutes effectiveness, would significantly enhance research quality.
Moreover, due to the bias towards studies conducted in southern England, the consistency of interventions for treating offending behaviours in adults with ASD in England remains unclear, especially considering the persistent regional health disparities between the North and South of England [ 67 , 68 ].
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Association AP. DSM-5 classification. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2015.
Masi A, DeMayo MM, Glozier N, Guastella AJ. An overview of Autism Spectrum Disorder, Heterogeneity and Treatment options. Neurosci Bull. 2017;33(2):183–93.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Berry K, Russell K, Frost K. Restricted and repetitive behaviors in Autism Spectrum Disorder: a review of Associated features and presentation across clinical populations. Curr Dev Disorders Rep. 2018;5(2):108–15.
Article Google Scholar
Geurts HM, Corbett B, Solomon M. The paradox of cognitive flexibility in autism. Trends Cogn Sci. 2009;13(2):74–82.
Chaplin E, McCarthy J, Allely CS, Forrester A, Underwood L, Hayward H, et al. Self-harm and Mental Health Characteristics of Prisoners with elevated rates of autistic traits. Res Dev Disabil. 2021;114:103987.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Hirvikoski T, Boman M, Chen Q, D’Onofrio BM, Mittendorfer-Rutz E, Lichtenstein P, et al. Individual risk and familial liability for suicide attempt and suicide in autism: a population-based study. Psychol Med. 2019;50(9):1463–74.
Kim SH, Lord C. The Behavioral Manifestations of Autism Spectrum Disorders. In: The Neuroscience of Autism Spectrum Disorders [Internet]. Elsevier; 2013 [cited 2024 Jan 7]. pp. 25–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-391924-3.00002-8 .
Jensen CM, Steinhausen HC, Lauritsen MB. Time trends over 16 years in incidence-rates of Autism Spectrum Disorders across the Lifespan Based on Nationwide Danish Register Data. J Autism Dev Disord. 2014;44(8):1808–18.
Roman-Urrestarazu A, van Kessel R, Allison C, Matthews FE, Brayne C, Baron-Cohen S. Association of Race/Ethnicity and Social Disadvantage with Autism Prevalence in 7 million School Children in England. JAMA Pediatr. 2021;175(6):e210054.
Haas K, Gibbs V. Does a person’s autism play a role in their interactions with police: the perceptions of autistic adults and Parent/Carers. J Autism Dev Disord. 2020;51(5):1628–40.
Murphy D. Interviewing individuals with an autism spectrum disorder in forensic settings. Int J Forensic Mental Health. 2018;17(4):310–20.
Allely CS, Cooper P, Jurors’. and Judges’ evaluation of defendants with autism and the impact on sentencing: a systematic Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) review of Autism Spectrum Disorder in the courtroom. J Law Med. 2017;25(1).
Allely CS. Experiences of prison inmates with autism spectrum disorders and the knowledge and understanding of the spectrum amongst prison staff: a review. J Intellect Disabil Offending Behav. 2015;6(2):55–67.
King C, Murphy GH. A systematic review of people with Autism Spectrum Disorder and the Criminal Justice System. J Autism Dev Disord. 2014;44(11):2717–33.
Maras K, Mulcahy S, Crane L. Is autism linked to criminality? Autism. 2015;19(5):515–6.
Robertson CE, McGillivray JA. Autism behind bars: a review of the research literature and discussion of key issues. J Forensic Psychiatr Psychol. 2015;26(6):719–36.
McQuaid GA, Pelphrey KA, Bookheimer SY, Dapretto M, Webb SJ, Bernier RA, et al. The gap between IQ and adaptive functioning in autism spectrum disorder: disentangling diagnostic and sex differences. Autism. 2021;25(6):1565–79.
Dein K, Hassiotis A, Woodbury-Smith M, Roychowdhury A, Squires R, Freestone M. Prevalence of autism within medium secure units: a feasibility study. J Forensic Psychiatr Psychol. 2021;32(6):861–78.
Murphy D, Allely C. Autism spectrum disorders in high secure psychiatric care: a review of literature, future research and clinical directions. Adv Autism. 2019;6(1):17–34.
Davoren M, Byrne O, O’Connell P, O’Neill H, O’Reilly K, Kennedy HG. Factors affecting length of stay in forensic hospital setting: need for therapeutic security and course of admission. BMC Psychiatry. 2015;15(1).
Lewis A, Pritchett R, Hughes C, Turner K. Development and implementation of autism standards for prisons. J Intellect Disabil Offending Behav. 2015;6(2):68–80.
Criminal justice joint inspectorate. Neurodiversity in the criminal justice system: a review of evidence. 2021.
Allely CS. A systematic PRISMA review of individuals with autism spectrum disorder in secure psychiatric care: prevalence, treatment, risk assessment and other clinical considerations. J Criminal Psychol. 2018;8(1):58–79.
Howlin P. Outcome in adult life for more able individuals with autism or Asperger Syndrome. Autism. 2000;4(1):63–83.
Newman SS, Ghaziuddin M. Violent crime in Asperger Syndrome: the Role of Psychiatric Comorbidity. J Autism Dev Disord. 2008;38(10):1848–52.
Allely CS, Minnis H, Thompson L, Wilson P, Gillberg C. Neurodevelopmental and psychosocial risk factors in serial killers and mass murderers. Aggress Violent Beh. 2014;19(3):288–301.
Newman BN, Crowell KA. The intersectionality of criminality and substance use self-stigmas. Stigma Health. 2023;8(2):212–22.
Schofield PW, Malacova E, Preen DB, D’Este C, Tate R, Reekie J, et al. Does traumatic Brain Injury lead to criminality? A Whole-Population Retrospective Cohort Study using Linked Data. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(7):e0132558.
Benevides TW, Carretta HJ, Lane SJ. Unmet need for Therapy among children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: results from the 2005–2006 and 2009–2010 National Survey of children with Special Health Care needs. Matern Child Health J. 2015;20(4):878–88.
Płatos M, Pisula E. Service use, unmet needs, and barriers to services among adolescents and young adults with autism spectrum disorder in Poland. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1).
Green RM, Travers AM, Howe Y, McDougle CJ. Women and Autism Spectrum Disorder: diagnosis and implications for treatment of adolescents and adults. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019;21(4).
Gupta M, Chaudhary R. Diagnostic challenges of High-Functioning Autism Spectrum disorder in females. Cureus. 2021 Jan 30.
Durkin MS, Maenner MJ, Meaney FJ, Levy SE, DiGuiseppi C, Nicholas JS, et al. Socioeconomic inequality in the prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder: evidence from a U.S. cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(7):e11551.
Crane L, Hearst C, Ashworth M, Davies J, Hill EL. Supporting newly identified or diagnosed autistic adults: an initial evaluation of an autistic-led Programme. J Autism Dev Disord. 2020;51(3):892–905.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kelly B, Williams S, Collins S, Mushtaq F, Mon-Williams M, Wright B, et al. The association between socioeconomic status and autism diagnosis in the United Kingdom for children aged 5–8 years of age: findings from the born in Bradford cohort. Autism. 2017;23(1):131–40.
Ministry of Justice. Offending behaviour programmes and interventions [Internet]. GOV.UK. 2018 [cited 2021 Dec 13]. https://www.gov.uk/guidance/offending-behaviour-programmes-and-interventions#accreditation .
Lipsey MW, Landenberger NA. Cognitive-Behavioral Interventions. In: Preventing Crime [Internet]. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 2006. pp. 57–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-4244-2_4 .
Henwood KS, Chou S, Browne KD. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the effectiveness of CBT informed anger management. Aggress Violent Beh. 2015;25:280–92.
Wilson DB, Bouffard LA, Mackenzie DL. A quantitative review of structured, Group-Oriented, cognitive-behavioral programs for offenders. Criminal Justice Behav. 2005;32(2):172–204.
MacInnes D, Masino S. Psychological and psychosocial interventions offered to forensic mental health inpatients: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2019;9(3):e024351.
Spain D, Blainey SH. Group social skills interventions for adults with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review. Autism. 2015;19(7):874–86.
Spain D, Happé F. How to optimise cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) for people with Autism Spectrum disorders (ASD): a Delphi Study. J Rational-Emot Cognitive-Behav Ther. 2019;38(2):184–208.
Parr JR, Brice S, Welsh P, Ingham B, Le Couteur A, Evans G et al. Treating anxiety in autistic adults: study protocol for the personalised anxiety treatment–autism (PAT-A©) pilot randomised controlled feasibility trial. Trials. 2020;21(1).
Gantman A, Kapp SK, Orenski K, Laugeson EA. Social Skills Training for Young Adults with high-functioning Autism Spectrum disorders: a Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. J Autism Dev Disord. 2011;42(6):1094–103.
Chambers JC, Yiend J, Barrett B, Burns T, Doll H, Fazel S, et al. Outcome measures used in forensic mental health research: a structured review. Criminal Behav Mental Health. 2009;19(1):9–27.
Fitzpatrick R, Chambers J, Burns T, Doll H, Fazel S, Jenkinson C et al. A systematic review of outcome measures used in forensic mental health research with consensus panel opinion. Health Technol Assess. 2010;14(18).
Weston L, Hodgekins J, Langdon PE. Effectiveness of cognitive behavioural therapy with people who have autistic spectrum disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev. 2016;49:41–54.
Higgs T, Carter AJ. Autism spectrum disorder and sexual offending: Responsivity in forensic interventions. Aggress Violent Beh. 2015;22:112–9.
Melvin CL, Langdon PE, Murphy GH. Treatment effectiveness for offenders with autism spectrum conditions: a systematic review. Psychol Crime Law. 2017;23(8):748–76.
Shuster JJ, Review. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews for interventions, Version 5.1.0, published 3/2011. Julian P.T. Higgins and Sally Green, editors. Res Synthesis Methods. 2011;2(2):126–30.
Völlm B, Braun P. Long-Term Forensic Psychiatric Care: clinical, ethical and legal challenges. Springer; 2019.
Hong QN, Fàbregues S, Bartlett G, Boardman F, Cargo M, Dagenais P, et al. The mixed methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) version 2018 for information professionals and researchers. Educ Inform. 2018;34(4):285–91.
Campbell M, McKenzie JE, Sowden A, Katikireddi SV, Brennan SE, Ellis S et al. Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: reporting guideline. BMJ. 2020;l6890.
Milton J, Duggan C, Latham A, Egan V, Tantam D. Case History of Co-morbid Asperger’s syndrome and paraphilic behaviour. Med Sci Law. 2002;42(3):237–44.
Radley J, Shaherbano Z. Asperger syndrome and arson: a case study. Adv Mental Health Intellect Disabil. 2011;5(6):32–6.
Murphy D. Extreme violence in a man with an autistic spectrum disorder: assessment and treatment within high-security psychiatric care. J Forensic Psychiatry Psychol. 2010;21(3):462–77.
Langdon PE, Murphy GH, Clare ICH, Palmer EJ, Rees J. An evaluation of the EQUIP Treatment Programme with men who have intellectual or other Developmental Disabilities. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2012;26(2):167–80.
Murphy G, Powell S, Guzman A, Hays S. Cognitive-behavioural treatment for men with intellectual disabilities and sexually abusive behaviour: a pilot study. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2007;51(11):902–12.
Melvin CL, Langdon PE, Murphy GH. They’re the hardest group to treat, that changes the least. Adapted sex offender treatment programmes for individuals with Autism Spectrum disorders: clinician views and experiences. Res Dev Disabil. 2020;105:103721.
Melvin CL, Langdon PE, Murphy GH. I feel that if I didn’t come to it anymore, maybe I would go back to my old ways, and I don’t want that to happen: adapted sex offender treatment programmes: views of service users with autism spectrum disorders. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2019;33(4):739–56.
Khan O, Ferriter M, Huband N, Powney MJ, Dennis JA, Duggan C. Pharmacological interventions for those who have sexually offended or are at risk of offending. Cochrane Database Syst Reviews. 2015 Feb 18.
National Institute for Health. And Care Excellence (NICE). Hypersexuality: fluoxetine; 2015.
Google Scholar
Masood B, Lepping P, Romanov D, Poole R. Treatment of Alcohol-Induced psychotic disorder (alcoholic Hallucinosis)—A systematic review. Alcohol Alcohol. 2017;53(3):259–67.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Rehabilitation for adults with complex psychosis. 2020.
Patterson C. Does the adapted sex offender treatment programme reduce cognitive distortions? A meta-analysis. J Intellect Disabil Offending Behav. 2018;9(1):9–21.
Robertson MD, Walter G. Many faces of the dual-role Dilemma in Psychiatric Ethics. Australian New Z J Psychiatry. 2008;42(3):228–35.
Bambra C, Barr B, Milne E. North and South: addressing the English health divide. J Public Health. 2014;36(2):183–6.
Whitehead M, Doran T. The north-south health divide. BMJ. 2011;342(feb15 2):d584–584.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Forensic and Neurodevelopmental Sciences, Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience, King’s College London, London, UK
Jody Salter & Sarah Blainey
School of Health and Society, University of Salford, Greater Manchester, UK
Jody Salter
Central and North West London NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK
Sarah Blainey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JS was responsible for writing the manuscript, including the creation of figures and tables. SB provided supervision and editorial input throughout the manuscript’s development.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jody Salter .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The systematic review did not involve original data collection; therefore, no ethical statement is required.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Salter, J., Blainey, S. The effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviours in adults with autism spectrum disorders (ASD): a systematic PRISMA review. BMC Psychol 12 , 316 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01770-1
Download citation
Received : 15 January 2024
Accepted : 07 May 2024
Published : 30 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01770-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Offending behaviour
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Forensic psychology
- Intervention
- Criminal justice system
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Narrative reviews have many strengths. They are flexible and practical, and ideally provide a readable, relevant synthesis of a diverse literature. Narrative reviews are often helpful for teaching or learning about a topic because they deliver a general overview. They are also useful for setting the stage for future research, as they offer an ...
The main objective of a systematic review is to formulate a well-defined research question and use qualitative and quantitative methods to analyze all the available evidence attempting to answer the question. In contrast, narrative reviews can address one or more questions with a much broader scope.
A narrative review is the "older" format of the two, presenting a (non-systematic) summation and analysis of available literature on a specific topic of interest. Interestingly, probably because the "approach" is non-systematic, there are no acknowledged formal guidelines for writing narrative reviews.
A narrative or traditional literature review is a comprehensive, critical and objective analysis of the current knowledge on a topic. They are an essential part of the research process and help to establish a theoretical framework and focus or context for your research. A literature review will help you to identify patterns and trends in the ...
A narrative literature review is an integrated analysis of the existing literature used to summarize a body of literature, draw conclusions about a topic, and identify research gaps. By understanding the current state of the literature, you can show how new research fits into the larger research landscape.
A narrative literature review is an integrated analysis of the existing literature used to summarize a body of literature, draw conclusions about a topic, and identify research gaps. By understanding the current state of the literature, you can show how new research fits into the larger research landscape.
Narrative literature reviews serve a vital scientific function, but few resources help people learn to write them. As compared with empirical reports, literature reviews can tackle broader and more abstract questions, can engage in more post hoc theorizing without the danger of capitalizing on chance, can make a stronger case for a null-hypothesis conclusion, and can appreciate and use ...
1. The two standard types of reviews are (a) sys-. tematic (SR) and (b) non-systema tic or narrative. review (NR). NRs are aimed at identifying and. summarizing what has been previously published ...
Our goal with this paper is to conduct a narrative review of the literature about systematic reviews and outline the essential elements of a systematic review along with the limitations of such a review. Keywords: systematic reviews, meta-analysis, narrative literature review, prisma checklist. A literature review provides an important insight ...
Background. A systematic review, as its name suggests, is a systematic way of collecting, evaluating, integrating, and presenting findings from several studies on a specific question or topic.[] A systematic review is a research that, by identifying and combining evidence, is tailored to and answers the research question, based on an assessment of all relevant studies.[2,3] To identify assess ...
Narrative literature reviews serve a vital scientific function, but few resources help people learn to write them. As compared with empirical reports, literature reviews can tackle broader and more abstract questions, can engage in more post hoc theorizing without the danger of capitalizing on chance, can make a stronger case for a ...
Most literature reviews are narrative reviews. Umbrella Review. Umbrella reviews are, essentially, systematic reviews of systematic reviews. These compile evidence from multiple review studies into one usable document. Adapted from. Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. "A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated ...
Most reviews fall into the following types: literature review, narrative review, integrative review, evidenced based review, meta-analysis and systematic review. This LibGuide will provide you a general overview of the specific review, offer starting points, and outline the reporting process.
Narrative or traditional literature reviews can take many shapes and forms. They do not need to follow any specific guideline or standard. A narrative literature view may be assigned as part of your coursework or capstone. A narrative literature review can be a first step to building on other research in the field.
(AKA Literature Reviews) Narrative Reviews involve looking at literature across a specific topic and synthesizing what you have learned. You can either look at one specific database, or across multiple databases. You aren't expected to become a subject expert, but you should have a pretty good concept of the topic once the review is completed.
Narrative Literature Reviews are works in which the author reviews a body of literature on a topic and synthesizes the information into a clear narrative that demonstrates the general context of the field. They can also be called a Traditional Literature Review. Compared to Systematic and Scoping reviews, Narrative literature reviews do not use ...
Writing a narrative literature review requires careful planning. This chapter summarizes some key steps in reviewing the literature. First, a team needs to be formed. Second, a topic needs to be chosen. This needs to be relevant to the author's research/teaching interests and a well-defined issue.
The labels Narrative Review and Literature Review are often describing the same type of review. For scientific purposes, the term Literature Review is the one used most often. ... Traditional Narrative Reviews: Review question formulation: Start with clear question to be answered or hypothesis to be tested. Specific: the populations ...
A literature review, or lit review, is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. Often, a lit review is embedded as part of a larger essay or thesis or dissertation or it may stand on its own.
According to those in the know, "A narrative literature review is fairly broad, as it involves gathering, critiquing and summarizing journal articles and textbooks about a particular topic.". In other words, you enter general search terms into a search engine and sift through the yielded articles. Essentially, a narrative literature review ...
As the size of the published scientific literature has increased exponentially over the past 30 years, review articles play an increasingly important role in helping researchers to make sense of original research results. Literature reviews can be broadly classified as either "systematic" or "narrative". Narrative reviews may be broader in scope than systematic reviews, but have been ...
Dissecting Literature Review Format. There are 6 main sections to make a note of while writing a literature review. Those are: The Introduction Section. Topic Background. Conceptual Framework. Synthesis and Evaluation in Literature Reviews. Conclusion for Your Literature Review. Reference List in Your Literature Review.
There are many types of literature reviews. The purposes of a literature review will vary, and the sources used in one will depend on the discipline and the review's topic. ... Topical or narrative: by subject or theme of documents included in the review. Chronological: by when the included documents were published. Geographical: by regions ...
Types of reviews and examples. Definition: "A term used to describe a conventional overview of the literature, particularly when contrasted with a systematic review (Booth et al., 2012, p. 265). Characteristics: Example: Mitchell, L. E., & Zajchowski, C. A. (2022). The history of air quality in Utah: A narrative review.
An initial scoping search on masks and masking in respiratory infections identified thousands of studies and more than 100 reviews. In view of this, our chosen review design was an in-depth narrative review in the hermeneutic tradition, whose primary aim was to make sense of this vast literature . We sought to summarize previous reviews and ...
3.1 Literature Search. The systematic literature review method, based on the PRISMA 2020 guidelines [], is used to guide the selection, evaluation and synthetization of existing literature in a reproducible process to address the research question [].This method has been used to, for example, review user trust in AI-enabled systems from an HCI perspective [] and evaluate the theories and ...
Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade - PMC. Journal List. J Chiropr Med. v.5 (3); Fall 2006. PMC2647067. As a library, NLM provides access to scientific literature. Inclusion in an NLM database does not imply endorsement of, or agreement with, the contents by NLM or the National Institutes of Health.
The goal of this narrative literature review is to discuss current evidence and propose preliminary guidelines regarding the application of HRV in strength and conditioning. A literature review was conducted searching for HRV and strength and conditioning, aiming to focus on studies with time-domain measurements. ...
AMA Style. Kostrakiewicz-Gierałt K. Plant-Based Proteins, Peptides and Amino Acids in Food Products Dedicated for Sportspeople—A Narrative Review of the Literature.
Study selection. The initial database search returned 2,551 results after removing duplicates, as shown in Fig. 1 of the PRISMA flow diagram, which depicts the flow of information at each stage of the systematic review search. Subsequent screening included an initial assessment of the titles and a subsequent assessment of the abstracts, which led to the exclusion of an additional 2,530 articles.