- Utility Menu

GA4 Tracking Code
fa51e2b1dc8cca8f7467da564e77b5ea
- Make a Gift
- Join Our Email List
Many students have had little experience working in groups in an academic setting. While there are many excellent books and articles describing group processes, this guide is intended to be short and simply written for students who are working in groups, but who may not be very interested in too much detail. It also provides teachers (and students) with tips on assigning group projects, ways to organize groups, and what to do when the process goes awry.
Some reasons to ask students to work in groups
Asking students to work in small groups allows students to learn interactively. Small groups are good for:
- generating a broad array of possible alternative points of view or solutions to a problem
- giving students a chance to work on a project that is too large or complex for an individual
- allowing students with different backgrounds to bring their special knowledge, experience, or skills to a project, and to explain their orientation to others
- giving students a chance to teach each other
- giving students a structured experience so they can practice skills applicable to professional situations
Some benefits of working in groups (even for short periods of time in class)
- Students who have difficulty talking in class may speak in a small group.
- More students, overall, have a chance to participate in class.
- Talking in groups can help overcome the anonymity and passivity of a large class or a class meeting in a poorly designed room.
- Students who expect to participate actively prepare better for class.
Caveat: If you ask students to work in groups, be clear about your purpose, and communicate it to them. Students who fear that group work is a potential waste of valuable time may benefit from considering the reasons and benefits above.
Large projects over a period of time
Faculty asking students to work in groups over a long period of time can do a few things to make it easy for the students to work:
- The biggest student complaint about group work is that it takes a lot of time and planning. Let students know about the project at the beginning of the term, so they can plan their time.
- At the outset, provide group guidelines and your expectations.
- Monitor the groups periodically to make sure they are functioning effectively.
- If the project is to be completed outside of class, it can be difficult to find common times to meet and to find a room. Some faculty members provide in-class time for groups to meet. Others help students find rooms to meet in.
Forming the group
- Forming the group. Should students form their own groups or should they be assigned? Most people prefer to choose whom they work with. However, many students say they welcome both kinds of group experiences, appreciating the value of hearing the perspective of another discipline, or another background.
- Size. Appropriate group size depends on the nature of the project. If the group is small and one person drops out, can the remaining people do the work? If the group is large, will more time be spent on organizing themselves and trying to make decisions than on productive work?
- Resources for students. Provide a complete class list, with current email addresses. (Students like having this anyway so they can work together even if group projects are not assigned.)
- Students that don't fit. You might anticipate your response to the one or two exceptions of a person who really has difficulty in the group. After trying various remedies, is there an out—can this person join another group? work on an independent project?
Organizing the work
Unless part of the goal is to give people experience in the process of goal-setting, assigning tasks, and so forth, the group will be able to work more efficiently if they are provided with some of the following:
- Clear goals. Why are they working together? What are they expected to accomplish?
- Ways to break down the task into smaller units
- Ways to allocate responsibility for different aspects of the work
- Ways to allocate organizational responsibility
- A sample time line with suggested check points for stages of work to be completed
Caveat: Setting up effective small group assignments can take a lot of faculty time and organization.
Getting Started
- Groups work best if people know each others' names and a bit of their background and experience, especially those parts that are related to the task at hand. Take time to introduce yourselves.
- Be sure to include everyone when considering ideas about how to proceed as a group. Some may never have participated in a small group in an academic setting. Others may have ideas about what works well. Allow time for people to express their inexperience and hesitations as well as their experience with group projects.
- Most groups select a leader early on, especially if the work is a long-term project. Other options for leadership in long-term projects include taking turns for different works or different phases of the work.
- Everyone needs to discuss and clarify the goals of the group's work. Go around the group and hear everyone's ideas (before discussing them) or encourage divergent thinking by brainstorming. If you miss this step, trouble may develop part way through the project. Even though time is scarce and you may have a big project ahead of you, groups may take some time to settle in to work. If you anticipate this, you may not be too impatient with the time it takes to get started.
Organizing the Work
- Break up big jobs into smaller pieces. Allocate responsibility for different parts of the group project to different individuals or teams. Do not forget to account for assembling pieces into final form.
- Develop a timeline, including who will do what, in what format, by when. Include time at the end for assembling pieces into final form. (This may take longer than you anticipate.) At the end of each meeting, individuals should review what work they expect to complete by the following session.
Understanding and Managing Group Processes
- Groups work best if everyone has a chance to make strong contributions to the discussion at meetings and to the work of the group project.
- At the beginning of each meeting, decide what you expect to have accomplished by the end of the meeting.
- Someone (probably not the leader) should write all ideas, as they are suggested, on the board, a collaborative document, or on large sheets of paper. Designate a recorder of the group's decisions. Allocate responsibility for group process (especially if you do not have a fixed leader) such as a time manager for meetings and someone who periodically says that it is time to see how things are going (see below).
- What leadership structure does the group want? One designated leader? rotating leaders? separately assigned roles?
- Are any more ground rules needed, such as starting meetings on time, kinds of interruptions allowed, and so forth?
- Is everyone contributing to discussions? Can discussions be managed differently so all can participate? Are people listening to each other and allowing for different kinds of contributions?
- Are all members accomplishing the work expected of them? Is there anything group members can do to help those experiencing difficulty?
- Are there disagreements or difficulties within the group that need to be addressed? (Is someone dominating? Is someone left out?)
- Is outside help needed to solve any problems?
- Is everyone enjoying the work?
Including Everyone and Their Ideas
Groups work best if everyone is included and everyone has a chance to contribute ideas. The group's task may seem overwhelming to some people, and they may have no idea how to go about accomplishing it. To others, the direction the project should take may seem obvious. The job of the group is to break down the work into chunks, and to allow everyone to contribute. The direction that seems obvious to some may turn out not to be so obvious after all. In any event, it will surely be improved as a result of some creative modification.
Encouraging Ideas
The goal is to produce as many ideas as possible in a short time without evaluating them. All ideas are carefully listened to but not commented on and are usually written on the board or large sheets of paper so everyone can see them, and so they don't get forgotten or lost. Take turns by going around the group—hear from everyone, one by one.
One specific method is to generate ideas through brainstorming. People mention ideas in any order (without others' commenting, disagreeing or asking too many questions). The advantage of brainstorming is that ideas do not become closely associated with the individuals who suggested them. This process encourages creative thinking, if it is not rushed and if all ideas are written down (and therefore, for the time-being, accepted). A disadvantage: when ideas are suggested quickly, it is more difficult for shy participants or for those who are not speaking their native language. One approach is to begin by brainstorming and then go around the group in a more structured way asking each person to add to the list.
Examples of what to say:
- Why don't we take a minute or two for each of us to present our views?
- Let's get all our ideas out before evaluating them. We'll clarify them before we organize or evaluate them.
- We'll discuss all these ideas after we hear what everyone thinks.
- You don't have to agree with her, but let her finish.
- Let's spend a few more minutes to see if there are any possibilities we haven't thought of, no matter how unlikely they seem.
Group Leadership
- The leader is responsible for seeing that the work is organized so that it will get done. The leader is also responsible for understanding and managing group interactions so that the atmosphere is positive.
- The leader must encourage everyone's contributions with an eye to accomplishing the work. To do this, the leader must observe how the group's process is working. (Is the group moving too quickly, leaving some people behind? Is it time to shift the focus to another aspect of the task?)
- The leader must encourage group interactions and maintain a positive atmosphere. To do this the leader must observe the way people are participating as well as be aware of feelings communicated non-verbally. (Are individuals' contributions listened to and appreciated by others? Are people arguing with other people, rather than disagreeing with their ideas? Are some people withdrawn or annoyed?)
- The leader must anticipate what information, materials or other resources the group needs as it works.
- The leader is responsible for beginning and ending on time. The leader must also organize practical support, such as the room, chalk, markers, food, breaks.
(Note: In addition to all this, the leader must take part in thc discussion and participate otherwise as a group member. At these times, the leader must be careful to step aside from the role of leader and signal participation as an equal, not a dominant voice.)
Concerns of Individuals That May Affect Their Participation
- How do I fit in? Will others listen to me? Am I the only one who doesn't know everyone else? How can I work with people with such different backgrounds and expericnce?
- Who will make the decisions? How much influence can I have?
- What do I have to offer to the group? Does everyone know more than I do? Does anyone know anything, or will I have to do most of the work myself?
Characteristics of a Group that is Performing Effectively
- All members have a chance to express themselves and to influence the group's decisions. All contributions are listened to carefully, and strong points acknowledged. Everyone realizes that the job could not be done without the cooperation and contribution of everyone else.
- Differences are dealt with directly with the person or people involved. The group identifies all disagreements, hears everyone's views and tries to come to an agreement that makes sense to everyone. Even when a group decision is not liked by someone, that person will follow through on it with the group.
- The group encourages everyone to take responsibility, and hard work is recognized. When things are not going well, everyone makes an effort to help each other. There is a shared sense of pride and accomplishment.
Focusing on a Direction
After a large number of ideas have been generated and listed (e.g. on the board), the group can categorize and examine them. Then the group should agree on a process for choosing from among the ideas. Advantages and disadvantages of different plans can be listed and then voted on. Some possibilities can be eliminated through a straw vote (each group member could have 2 or 3 votes). Or all group members could vote for their first, second, and third choices. Alternatively, criteria for a successful plan can be listed, and different alternatives can be voted on based on the criteria, one by one.
Categorizing and evaluating ideas
- We have about 20 ideas here. Can we sort them into a few general categories?
- When we evaluate each others' ideas, can we mention some positive aspects before expressing concerns?
- Could you give us an example of what you mean?
- Who has dealt with this kind of problem before?
- What are the pluses of that approach? The minuses?
- We have two basic choices. Let's brainstorm. First let's look at the advantages of the first choice, then the disadvantages.
- Let's try ranking these ideas in priority order. The group should try to come to an agreement that makes sense to everyone.
Making a decision
After everyone's views are heard and all points of agreement and disagreement are identified, the group should try to arrive at an agreement that makes sense to everyone.
- There seems to be some agreement here. Is there anyone who couldn't live with solution #2?
- Are there any objections to going that way?
- You still seem to have worries about this solution. Is there anything that could be added or taken away to make it more acceptable? We're doing fine. We've agreed on a great deal. Let's stay with this and see if we can work this last issue through.
- It looks as if there are still some major points of disagreement. Can we go back and define what those issues are and work on them rather than forcing a decision now.
How People Function in Groups
If a group is functioning well, work is getting done and constructive group processes are creating a positive atmosphere. In good groups the individuals may contribute differently at different times. They cooperate and human relationships are respected. This may happen automatically or individuals, at different times, can make it their job to maintain the atmospbere and human aspects of the group.
Roles That Contribute to the Work
Initiating —taking the initiative, at any time; for example, convening the group, suggesting procedures, changing direction, providing new energy and ideas. (How about if we.... What would happen if... ?)
Seeking information or opinions —requesting facts, preferences, suggestions and ideas. (Could you say a little more about... Would you say this is a more workable idea than that?)
Giving information or opinions —providing facts, data, information from research or experience. (ln my experience I have seen... May I tell you what I found out about...? )
Questioning —stepping back from what is happening and challenging the group or asking other specific questions about the task. (Are we assuming that... ? Would the consequence of this be... ?)
Clarifying —interpreting ideas or suggestions, clearing up confusions, defining terms or asking others to clarify. This role can relate different contributions from different people, and link up ideas that seem unconnected. (lt seems that you are saying... Doesn't this relate to what [name] was saying earlier?)
Summarizing —putting contributions into a pattern, while adding no new information. This role is important if a group gets stuck. Some groups officially appoint a summarizer for this potentially powerful and influential role. (If we take all these pieces and put them together... Here's what I think we have agreed upon so far... Here are our areas of disagreement...)
Roles That Contribute to the Atmosphere
Supporting —remembering others' remarks, being encouraging and responsive to others. Creating a warm, encouraging atmosphere, and making people feel they belong helps the group handle stresses and strains. People can gesture, smile, and make eye-contact without saying a word. Some silence can be supportive for people who are not native speakers of English by allowing them a chance to get into discussion. (I understand what you are getting at...As [name] was just saying...)
Observing —noticing the dynamics of the group and commenting. Asking if others agree or if they see things differently can be an effective way to identify problems as they arise. (We seem to be stuck... Maybe we are done for now, we are all worn out... As I see it, what happened just a minute ago.. Do you agree?)
Mediating —recognizing disagreements and figuring out what is behind the differences. When people focus on real differences, that may lead to striking a balance or devising ways to accommodate different values, views, and approaches. (I think the two of you are coming at this from completely different points of view... Wait a minute. This is how [name/ sees the problem. Can you see why she may see it differently?)
Reconciling —reconciling disagreements. Emphasizing shared views among members can reduce tension. (The goal of these two strategies is the same, only the means are different… Is there anything that these positions have in common?)
Compromising —yielding a position or modifying opinions. This can help move the group forward. (Everyone else seems to agree on this, so I'll go along with... I think if I give in on this, we could reach a decision.)
Making a personal comment —occasional personal comments, especially as they relate to the work. Statements about one's life are often discouraged in professional settings; this may be a mistake since personal comments can strengthen a group by making people feel human with a lot in common.
Humor —funny remarks or good-natured comments. Humor, if it is genuinely good-natured and not cutting, can be very effective in relieving tension or dealing with participants who dominate or put down others. Humor can be used constructively to make the work more acceptable by providing a welcome break from concentration. It may also bring people closer together, and make the work more fun.
All the positive roles turn the group into an energetic, productive enterprise. People who have not reflected on these roles may misunderstand the motives and actions of people working in a group. If someone other than the leader initiates ideas, some may view it as an attempt to take power from the leader. Asking questions may similarly be seen as defying authority or slowing down the work of the group. Personal anecdotes may be thought of as trivializing the discussion. Leaders who understand the importance of these many roles can allow and encourage them as positive contributions to group dynamics. Roles that contribute to the work give the group a sense of direction and achievement. Roles contributing to the human atmosphere give the group a sense of cooperation and goodwill.
Some Common Problems (and Some Solutions)
Floundering —While people are still figuring out the work and their role in the group, the group may experience false starts and circular discussions, and decisions may be postponed.
- Here's my understanding of what we are trying to accomplish... Do we all agree?
- What would help us move forward: data? resources?
- Let's take a few minutes to hear everyone's suggestions about how this process might work better and what we should do next.
Dominating or reluctant participants —Some people might take more than their share of the discussion by talking too often, asserting superiority, telling lengthy stories, or not letting others finish. Sometimes humor can be used to discourage people from dominating. Others may rarely speak because they have difficulty getting in the conversation. Sometimes looking at people who don't speak can be a non-verbal way to include them. Asking quiet participants for their thoughts outside the group may lead to their participation within the group.
- How would we state the general problem? Could we leave out the details for a moment? Could we structure this part of the discussion by taking turns and hearing what everyone has to say?
- Let's check in with each other about how the process is working: Is everyone contributing to discussions? Can discussions be managed differently so we can all participate? Are we all listening to each other?
Digressions and tangents —Too many interesting side stories can be obstacles to group progress. It may be time to take another look at the agenda and assign time estimates to items. Try to summarize where the discussion was before the digression. Or, consider whether there is something making the topic easy to avoid.
- Can we go back to where we were a few minutes ago and see what we were trying to do ?
- Is there something about the topic itself that makes it difficult to stick to?
Getting Stuck —Too little progress can get a group down. It may be time for a short break or a change in focus. However, occasionally when a group feels that it is not making progress, a solution emerges if people simply stay with the issue.
- What are the things that are helping us solve this problem? What's preventing us from solving this problem?
- I understand that some of you doubt whether anything new will happen if we work on this problem. Are we willing to give it a try for the next fifteen minutes?
Rush to work —Usually one person in the group is less patient and more action-oriented than the others. This person may reach a decision more quickly than the others and then pressure the group to move on before others are ready.
- Are we all ready-to make a decision on this?
- What needs to be done before we can move ahead?
- Let's go around and see where everyone stands on this.
Feuds —Occasionally a conflict (having nothing to do with the subject of the group) carries over into the group and impedes its work. It may be that feuding parties will not be able to focus until the viewpoint of each is heard. Then they must be encouraged to lay the issue aside.
- So, what you are saying is... And what you are saying is... How is that related to the work here?
- If we continue too long on this, we won't be able to get our work done. Can we agree on a time limit and then go on?
For more information...
James Lang, " Why Students Hate Group Projects (and How to Change That) ," The Chronicle of Higher Education (17 June 2022).
Hodges, Linda C. " Contemporary Issues in Group Learning in Undergraduate Science Classrooms: A Perspective from Student Engagement ," CBE—Life Sciences Education 17.2 (2018): es3.
- Designing Your Course
- A Teaching Timeline: From Pre-Term Planning to the Final Exam
- The First Day of Class
- Group Agreements
- Classroom Debate
- Flipped Classrooms
- Leading Discussions
- Polling & Clickers
- Problem Solving in STEM
- Teaching with Cases
- Engaged Scholarship
- Devices in the Classroom
- Beyond the Classroom
- On Professionalism
- Getting Feedback
- Equitable & Inclusive Teaching
- Advising and Mentoring
- Teaching and Your Career
- Teaching Remotely
- Tools and Platforms
- The Science of Learning
- Bok Publications
- Other Resources Around Campus
Center for Teaching
Group work: using cooperative learning groups effectively.
Many instructors from disciplines across the university use group work to enhance their students’ learning. Whether the goal is to increase student understanding of content, to build particular transferable skills, or some combination of the two, instructors often turn to small group work to capitalize on the benefits of peer-to-peer instruction. This type of group work is formally termed cooperative learning, and is defined as the instructional use of small groups to promote students working together to maximize their own and each other’s learning (Johnson, et al., 2008).
Cooperative learning is characterized by positive interdependence, where students perceive that better performance by individuals produces better performance by the entire group (Johnson, et al., 2014). It can be formal or informal, but often involves specific instructor intervention to maximize student interaction and learning. It is infinitely adaptable, working in small and large classes and across disciplines, and can be one of the most effective teaching approaches available to college instructors.
What can it look like?
What’s the theoretical underpinning, is there evidence that it works.
- What are approaches that can help make it effective?
Informal cooperative learning groups In informal cooperative learning, small, temporary, ad-hoc groups of two to four students work together for brief periods in a class, typically up to one class period, to answer questions or respond to prompts posed by the instructor.
Additional examples of ways to structure informal group work
Think-pair-share
The instructor asks a discussion question. Students are instructed to think or write about an answer to the question before turning to a peer to discuss their responses. Groups then share their responses with the class.

Peer Instruction
This modification of the think-pair-share involves personal responses devices (e.g. clickers). The question posted is typically a conceptually based multiple-choice question. Students think about their answer and vote on a response before turning to a neighbor to discuss. Students can change their answers after discussion, and “sharing” is accomplished by the instructor revealing the graph of student response and using this as a stimulus for large class discussion. This approach is particularly well-adapted for large classes.

In this approach, groups of students work in a team of four to become experts on one segment of new material, while other “expert teams” in the class work on other segments of new material. The class then rearranges, forming new groups that have one member from each expert team. The members of the new team then take turns teaching each other the material on which they are experts.

Formal cooperative learning groups
In formal cooperative learning students work together for one or more class periods to complete a joint task or assignment (Johnson et al., 2014). There are several features that can help these groups work well:
- The instructor defines the learning objectives for the activity and assigns students to groups.
- The groups are typically heterogeneous, with particular attention to the skills that are needed for success in the task.
- Within the groups, students may be assigned specific roles, with the instructor communicating the criteria for success and the types of social skills that will be needed.
- Importantly, the instructor continues to play an active role during the groups’ work, monitoring the work and evaluating group and individual performance.
- Instructors also encourage groups to reflect on their interactions to identify potential improvements for future group work.
This video shows an example of formal cooperative learning groups in David Matthes’ class at the University of Minnesota:
There are many more specific types of group work that fall under the general descriptions given here, including team-based learning , problem-based learning , and process-oriented guided inquiry learning .
The use of cooperative learning groups in instruction is based on the principle of constructivism, with particular attention to the contribution that social interaction can make. In essence, constructivism rests on the idea that individuals learn through building their own knowledge, connecting new ideas and experiences to existing knowledge and experiences to form new or enhanced understanding (Bransford, et al., 1999). The consideration of the role that groups can play in this process is based in social interdependence theory, which grew out of Kurt Koffka’s and Kurt Lewin’s identification of groups as dynamic entities that could exhibit varied interdependence among members, with group members motivated to achieve common goals. Morton Deutsch conceptualized varied types of interdependence, with positive correlation among group members’ goal achievements promoting cooperation.
Lev Vygotsky extended this work by examining the relationship between cognitive processes and social activities, developing the sociocultural theory of development. The sociocultural theory of development suggests that learning takes place when students solve problems beyond their current developmental level with the support of their instructor or their peers. Thus both the idea of a zone of proximal development, supported by positive group interdependence, is the basis of cooperative learning (Davidson and Major, 2014; Johnson, et al., 2014).
Cooperative learning follows this idea as groups work together to learn or solve a problem, with each individual responsible for understanding all aspects. The small groups are essential to this process because students are able to both be heard and to hear their peers, while in a traditional classroom setting students may spend more time listening to what the instructor says.
Cooperative learning uses both goal interdependence and resource interdependence to ensure interaction and communication among group members. Changing the role of the instructor from lecturing to facilitating the groups helps foster this social environment for students to learn through interaction.
David Johnson, Roger Johnson, and Karl Smith performed a meta-analysis of 168 studies comparing cooperative learning to competitive learning and individualistic learning in college students (Johnson et al., 2006). They found that cooperative learning produced greater academic achievement than both competitive learning and individualistic learning across the studies, exhibiting a mean weighted effect size of 0.54 when comparing cooperation and competition and 0.51 when comparing cooperation and individualistic learning. In essence, these results indicate that cooperative learning increases student academic performance by approximately one-half of a standard deviation when compared to non-cooperative learning models, an effect that is considered moderate. Importantly, the academic achievement measures were defined in each study, and ranged from lower-level cognitive tasks (e.g., knowledge acquisition and retention) to higher level cognitive activity (e.g., creative problem solving), and from verbal tasks to mathematical tasks to procedural tasks. The meta-analysis also showed substantial effects on other metrics, including self-esteem and positive attitudes about learning. George Kuh and colleagues also conclude that cooperative group learning promotes student engagement and academic performance (Kuh et al., 2007).
Springer, Stanne, and Donovan (1999) confirmed these results in their meta-analysis of 39 studies in university STEM classrooms. They found that students who participated in various types of small-group learning, ranging from extended formal interactions to brief informal interactions, had greater academic achievement, exhibited more favorable attitudes towards learning, and had increased persistence through STEM courses than students who did not participate in STEM small-group learning.
The box below summarizes three individual studies examining the effects of cooperative learning groups.

What are approaches that can help make group work effective?
Preparation
Articulate your goals for the group work, including both the academic objectives you want the students to achieve and the social skills you want them to develop.
Determine the group conformation that will help meet your goals.
- In informal group learning, groups often form ad hoc from near neighbors in a class.
- In formal group learning, it is helpful for the instructor to form groups that are heterogeneous with regard to particular skills or abilities relevant to group tasks. For example, groups may be heterogeneous with regard to academic skill in the discipline or with regard to other skills related to the group task (e.g., design capabilities, programming skills, writing skills, organizational skills) (Johnson et al, 2006).
- Groups from 2-6 are generally recommended, with groups that consist of three members exhibiting the best performance in some problem-solving tasks (Johnson et al., 2006; Heller and Hollabaugh, 1992).
- To avoid common problems in group work, such as dominance by a single student or conflict avoidance, it can be useful to assign roles to group members (e.g., manager, skeptic, educator, conciliator) and to rotate them on a regular basis (Heller and Hollabaugh, 1992). Assigning these roles is not necessary in well-functioning groups, but can be useful for students who are unfamiliar with or unskilled at group work.
Choose an assessment method that will promote positive group interdependence as well as individual accountability.
- In team-based learning, two approaches promote positive interdependence and individual accountability. First, students take an individual readiness assessment test, and then immediately take the same test again as a group. Their grade is a composite of the two scores. Second, students complete a group project together, and receive a group score on the project. They also, however, distribute points among their group partners, allowing student assessment of members’ contributions to contribute to the final score.
- Heller and Hollabaugh (1992) describe an approach in which they incorporated group problem-solving into a class. Students regularly solved problems in small groups, turning in a single solution. In addition, tests were structured such that 25% of the points derived from a group problem, where only those individuals who attended the group problem-solving sessions could participate in the group test problem. This approach can help prevent the “free rider” problem that can plague group work.
- The University of New South Wales describes a variety of ways to assess group work , ranging from shared group grades, to grades that are averages of individual grades, to strictly individual grades, to a combination of these. They also suggest ways to assess not only the product of the group work but also the process. Again, having a portion of a grade that derives from individual contribution helps combat the free rider problem.
Helping groups get started
Explain the group’s task, including your goals for their academic achievement and social interaction.
Explain how the task involves both positive interdependence and individual accountability, and how you will be assessing each.
Assign group roles or give groups prompts to help them articulate effective ways for interaction. The University of New South Wales provides a valuable set of tools to help groups establish good practices when first meeting. The site also provides some exercises for building group dynamics; these may be particularly valuable for groups that will be working on larger projects.
Monitoring group work
Regularly observe group interactions and progress , either by circulating during group work, collecting in-process documents, or both. When you observe problems, intervene to help students move forward on the task and work together effectively. The University of New South Wales provides handouts that instructors can use to promote effective group interactions, such as a handout to help students listen reflectively or give constructive feedback , or to help groups identify particular problems that they may be encountering.
Assessing and reflecting
In addition to providing feedback on group and individual performance (link to preparation section above), it is also useful to provide a structure for groups to reflect on what worked well in their group and what could be improved. Graham Gibbs (1994) suggests using the checklists shown below.

The University of New South Wales provides other reflective activities that may help students identify effective group practices and avoid ineffective practices in future cooperative learning experiences.
Bransford, J.D., Brown, A.L., and Cocking, R.R. (Eds.) (1999). How people learn: Brain, mind, experience, and school . Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press.
Bruffee, K. A. (1993). Collaborative learning: Higher education, interdependence, and the authority of knowledge. Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Cabrera, A. F., Crissman, J. L., Bernal, E. M., Nora, A., Terenzini, P. T., & Pascarella, E. T. (2002). Collaborative learning: Its impact on college students’ development and diversity. Journal of College Student Development, 43 (1), 20-34.
Davidson, N., & Major, C. H. (2014). Boundary crossing: Cooperative learning, collaborative learning, and problem-based learning. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching, 25 (3&4), 7-55.
Dees, R. L. (1991). The role of cooperative leaning in increasing problem-solving ability in a college remedial course. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 22 (5), 409-21.
Gokhale, A. A. (1995). Collaborative Learning enhances critical thinking. Journal of Technology Education, 7 (1).
Heller, P., and Hollabaugh, M. (1992) Teaching problem solving through cooperative grouping. Part 2: Designing problems and structuring groups. American Journal of Physics 60, 637-644.
Johnson, D.W., Johnson, R.T., and Smith, K.A. (2006). Active learning: Cooperation in the university classroom (3 rd edition). Edina, MN: Interaction.
Johnson, D.W., Johnson, R.T., and Holubec, E.J. (2008). Cooperation in the classroom (8 th edition). Edina, MN: Interaction.
Johnson, D.W., Johnson, R.T., and Smith, K.A. (2014). Cooperative learning: Improving university instruction by basing practice on validated theory. Journl on Excellence in College Teaching 25, 85-118.
Jones, D. J., & Brickner, D. (1996). Implementation of cooperative learning in a large-enrollment basic mechanics course. American Society for Engineering Education Annual Conference Proceedings.
Kuh, G.D., Kinzie, J., Buckley, J., Bridges, B., and Hayek, J.C. (2007). Piecing together the student success puzzle: Research, propositions, and recommendations (ASHE Higher Education Report, No. 32). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Love, A. G., Dietrich, A., Fitzgerald, J., & Gordon, D. (2014). Integrating collaborative learning inside and outside the classroom. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching, 25 (3&4), 177-196.
Smith, M. E., Hinckley, C. C., & Volk, G. L. (1991). Cooperative learning in the undergraduate laboratory. Journal of Chemical Education 68 (5), 413-415.
Springer, L., Stanne, M. E., & Donovan, S. S. (1999). Effects of small-group learning on undergraduates in science, mathematics, engineering, and technology: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 96 (1), 21-51.
Uribe, D., Klein, J. D., & Sullivan, H. (2003). The effect of computer-mediated collaborative learning on solving ill-defined problems. Educational Technology Research and Development, 51 (1), 5-19.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1962). Thought and Language. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.

Teaching Guides
- Online Course Development Resources
- Principles & Frameworks
- Pedagogies & Strategies
- Reflecting & Assessing
- Challenges & Opportunities
- Populations & Contexts
Quick Links
- Services for Departments and Schools
- Examples of Online Instructional Modules

Ideas for Great Group Work
Many students, particularly if they are new to college, don’t like group assignments and projects. They might say they “work better by themselves” and be wary of irresponsible members of their group dragging down their grade. Or they may feel group projects take too much time and slow down the progression of the class. This blog post by a student— 5 Reasons I Hate Group Projects —might sound familiar to many faculty assigning in-class group work and longer-term projects in their courses.
We all recognize that learning how to work effectively in groups is an essential skill that will be used by students in practically every career in the private sector or academia. But, with the hesitancy of students towards group work and how it might impact their grade, how do we make group in-class work, assignments, or long-term projects beneficial and even exciting to students?
The methods and ideas in this post have been compiled from Duke faculty who we have consulted with as part of our work in Learning Innovation or have participated in one of our programs. Also included are ideas from colleagues at other universities with whom we have talked at conferences and other venues about group work practices in their own classrooms.
Have clear goals and purpose
Students want to know why they are being assigned certain kinds of work – how it fits into the larger goals of the class and the overall assessment of their performance in the course. Make sure you explain your goals for assigning in-class group work or projects in the course. You may wish to share:
- Information on the importance of developing skills in group work and how this benefits the students in the topics presented in the course.
- Examples of how this type of group work will be used in the discipline outside of the classroom.
- How the assignment or project benefits from multiple perspectives or dividing the work among more than one person.
Some faculty give students the option to come to a consensus on the specifics of how group work will count in the course, within certain parameters. This can help students feel they have some control over their own learning process and and can put less emphasis on grades and more on the importance of learning the skills of working in groups.
Choose the right assignment
Some in-class activities, short assignments or projects are not suitable for working in groups. To ensure student success, choose the right class activity or assignment for groups.
- Would the workload of the project or activity require more than one person to finish it properly?
- Is this something where multiple perspectives create a greater whole?
- Does this draw on knowledge and skills that are spread out among the students?
- Will the group process used in the activity or project give students a tangible benefit to learning in and engagement with the course?
Help students learn the skills of working in groups
Students in your course may have never been asked to work in groups before. If they have worked in groups in previous courses, they may have had bad experiences that color their reaction to group work in your course. They may have never had the resources and support to make group assignments and projects a compelling experience.
One of the most important things you can do as an instructor is to consider all of the skills that go into working in groups and to design your activities and assignments with an eye towards developing those skills.
In a group assignment, students may be asked to break down a project into steps, plan strategy, organize their time, and coordinate efforts in the context of a group of people they may have never met before.
Consider these ideas to help your students learn group work skills in your course.
- Give a short survey to your class about their previous work in groups to gauge areas where they might need help: ask about what they liked best and least about group work, dynamics of groups they have worked in, time management, communication skills or other areas important in the assignment you are designing.
- Allow time in class for students in groups to get to know each other. This can be a simple as brief introductions, an in-class active learning activity or the drafting of a team charter.
- Based on the activity you are designing and the skills that would be involved in working as a group, assemble some links to web resources that students can draw on for more information, such as sites that explain how to delegate and share responsibilities, conflict resolution, or planning a project and time management. You can also address these issues in class with the students.
- Have a plan for clarifying questions or possible problems that may emerge with an assignment or project. Are there ways you can ask questions or get draft material to spot areas where students are having difficulty understanding the assignment or having difficulty with group dynamics that might impact the work later?
Designing the assignment or project
The actual design of the class activity or project can help the students transition into group work processes and gain confidence with the skills involved in group dynamics. When designing your assignment, consider these ideas.
- Break the assignment down into steps or stages to help students become familiar with the process of planning the project as a group.
- Suggest roles for participants in each group to encourage building expertise and expertise and to illustrate ways to divide responsibility for the work.
- Use interim drafts for longer projects to help students manage their time and goals and spot early problems with group projects.
- Limit their resources (such as giving them material to work with or certain subsets of information) to encourage more close cooperation.
- Encourage diversity in groups to spread experience and skill levels and to get students to work with colleagues in the course who they may not know.
Promote individual responsibility
Students always worry about how the performance of other students in a group project might impact their grade. A way to allay those fears is to build individual responsibility into both the course grade and the logistics of group work.
- Build “slack days” into the course. Allow a prearranged number of days when individuals can step away from group work to focus on other classes or campus events. Individual students claim “slack days” in advance, informing both the members of their group and the instructor. Encourage students to work out how the group members will deal with conflicting dates if more than one student in a group wants to claim the same dates.
- Combine a group grade with an individual grade for independent write-ups, journal entries, and reflections.
- Have students assess their fellow group members. Teammates is an online application that can automate this process.
- If you are having students assume roles in group class activities and projects, have them change roles in different parts of the class or project so that one student isn’t “stuck” doing one task for the group.
Gather feedback
To improve your group class activities and assignments, gather reflective feedback from students on what is and isn’t working. You can also share good feedback with future classes to help them understand the value of the activities they’re working on in groups.
- For in-class activities, have students jot down thoughts at the end of class on a notecard for you to review.
- At the end of a larger project, or at key points when you have them submit drafts, ask the students for an “assignment wrapper”—a short reflection on the assignment or short answers to a series of questions.
Further resources
Information for faculty
Best practices for designing group projects (Eberly Center, Carnegie Mellon)
Building Teamwork Process Skills in Students (Shannon Ciston, UC Berkeley)
Working with Student Teams (Bart Pursel, Penn State)
Barkley, E.F., Cross, K.P., and Major, C.H. (2005). Collaborative learning techniques: A handbook for college faculty. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Johnson, D.W., Johnson, R., & Smith, K. (1998). Active learning: Cooperation in the college classroom. Edina, MN: Interaction Book Company.
Thompson, L.L. (2004). Making the team: A guide for managers. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education Inc.
Information for students
10 tips for working effectively in groups (Vancouver Island University Learning Matters)
Teamwork skills: being an effective group member (University of Waterloo Centre for Teaching Excellence)
5 ways to survive a group project in college (HBCU Lifestyle)
Group project tips for online courses (Drexel Online)
Group Writing (Writing Center at UNC-Chapel Hill)
- Request a Consultation
- Workshops and Virtual Conversations
- Technical Support
- Course Design and Preparation
- Observation & Feedback
Teaching Resources
Using Roles in Group Work
Resource overview.
How using roles can improve group work in your class
While collaborative learning through group work has been proven to have the potential to produce stronger academic achievement than other kinds of learning environments (Johnson, Johnson, & Smith, 2006), it can be challenging to implement successfully because many students come to college without the tools they need to automatically succeed in collaborative learning contexts. One way of providing supportive structures to students in a collaborative learning environment is through assigning roles within group work.
Potential Benefits of Using Assigned Roles in Group Work
Assigning group roles can be a beneficial strategy for successful group work design for a number of reasons:
- Group roles offer an opportunity for high quality, focused interactions between group participants. Participants are more likely to stay on task and pay closer attention to the task at hand when their roles in the collaboration are clear and distinct.
- Group roles provide all students with a clear avenue for participation. Students are less likely to feel left out or unengaged when they have a particular duty that they are responsible for completing. Along the same lines, assigning group roles reduces the likelihood of one individual completing the task for the whole group, or “taking over,” to the detriment of others’ learning.
- Group roles encourage individual accountability. Group members are more likely to hold each other accountable for not completing work if a particular task is assigned to them.
- Group roles allow students to strengthen their communicative skills, especially in areas that they are less confident in volunteering for.
- Group roles can help disrupt stereotypical and gendered role assignments, which can be common in group learning. For example, Hirshfield and Chachra (2015) found that in first-year engineering courses, female students tended to undertake less technical roles and more communicative roles than their male colleagues. By assigning roles during group work, and by asking students to alternate these roles at different points in the semester, students can work past gendered assumptions about themselves and their groupmates.
POGIL: A Model for Role Assignments in Collaborative Learning
One small group learning methodology where the use of group roles is well-defined and researched is the Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning (POGIL) method . The POGIL method calls for groups of three or four students who work in a team on process-oriented guided inquiry activities in which students construct their knowledge through interactions with others. Traditional POGIL roles for group members are provided below (POGIL, 2016).
- Manager or Facilitator : Manages the group by helping to ensure that the group stays on task, is focused, and that there is room for everyone in the conversation.
- Recorder : Keeps a record of those who were in the group, and the roles that they play in the group. The recorder also records critical points from the small group’s discussion along with findings or answers.
- Spokesperson or Presenter : Presents the group’s ideas to the rest of the class. The Spokesperson should rely on the recorder’s notes to guide their report.
- Reflector or Strategy Analyst : Observes team dynamics and guides the consensus-building process (helps group members come to a common conclusion).
Other Highly Adaptable Roles to Consider
You can adapt roles for different kinds of group tasks. While the POGIL model is a useful place to start, you may find that the tasks associated with your discipline require other kinds of roles for effective group learning. Adding to or reframing POGIL roles can be beneficial in these contexts. Below are some suggestions for additional roles that might be valuable to a variety of learning situations.
- Encourager : Encourages group members to continue to think through their approaches and ideas. The Encourager uses probing questions to help facilitate deeper thinking, and group-wide consideration of ideas.
- Questioner : Pushes back when the team comes to consensus too quickly, without considering a number of options or points of view. The questioner makes sure that the group hears varied points of view, and that the group is not avoiding potentially rich areas of disagreement.
- Checker : Checks over work in problem-solving contexts before the group members finalize their answers.
Strategies for Effective Facilitation of Group Roles
The following suggestions are strategies for effective facilitation of group roles. These strategies are helpful in a wide variety of group work situations, but are essential for group work that will last beyond a single class period, or constitute a significant portion of student grades.
- Be transparent about why you are assigning group roles. This kind of transparency can increase student buy-in by helping them recognize the value in establishing group roles
- Provide students with a list of roles and brief definitions for each role at the beginning of the group work activity. Make it clear which tasks are associated with which roles.
- Alternatively, you may find it helpful, especially in advanced-level classes, to encourage students to develop their own roles in groups based on the tasks that they feel will be critical to the group’s success. This strategy provides the students with a larger level of autonomy in their learning, while also encouraging them to use proven structures that will help them be successful.
- Roles can be assigned randomly through a variety of strategies, from who has the next birthday to color-coded post-it notes, or a place card that points out roles based on where everyone is sitting.
- Circulate early in the class period to be sure that everyone has been assigned a role, and that everyone is clear about what their responsibilities include.
- Be willing to reinforce the given roles throughout the activity. For roles to work, students have to feel as though they will be held accountable for fulfilling those roles. Therefore, it is critical for you to step in if you see someone taking over someone else’s role or not fulfilling their assigned role. Often gentle reminders about who is supposed to be doing what can be useful interventions. For example, if someone is talking over everyone and not listening to their other groupmates, you might say something like “Remember, as a spokesperson, your job is to represent the ideas of everyone in the group.”
- Talk with students individually if their speech or conduct could be silencing, denigrating, or excluding others. Remember: your silence on this issue may be read as endorsement.
- Changing things up regularly is imperative. If you use group roles frequently, mixing up roles throughout the semester can help students develop communication skills in a variety of areas rather than relying on a single personal strength.
- If this is a long-term group assignment, be sure to provide structures for individual feedback for the instructor and other group member on group dynamics. This could be a formal or informal check in, but it’s critical for students to have a space to voice concerns related to group dynamics—especially if this assignment counts for a large portion of their final grade. This feedback might be provided through an anonymous survey in paper form or through a web-based tool like Qualtrics or a Google form. These check-ins can reduce student anxiety about the potential for uneven group participation.
Overall, using assigned roles in group work provides students with a supportive structure that promotes meaningful collaborative learning. While group learning can be challenging to implement effectively, using roles can mitigate some of the challenges associated with learning in groups, while offering students the opportunity to develop a variety of communication skills that will be critical to their success in college and their future careers.
Burke, Alison. (2011). Group work: How to use groups effectively. The Journal of Effective Teaching , 11(2), 87-95.
Beebe, S.A., & Masterson, J.T. (2003). Communicating in small groups . Boston, MA: Pearson Education.
Cheng, W. Y., Lam, S. F., & Chan, C. Y. (2008). When high achievers and low achievers work in the same group: The roles of group heterogeneity and processes in project‐based learning. British Journal of Educational Psychology , 78 (2), 205-221.
Eberlein, T., Kampmeier, J., Minderhout, V., Moog, R.S., Platt, T., Varma-Nelson, P., White, H.B. (2008). Pedagogies of engagement in science: A comparison of PBL, POGIL and PLTL. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education, 36 (4), 262-73.
Hale, D., & Mullen, L. G. (2009). Designing process-oriented guided-inquiry activities: A new innovation for marketing classes. Marketing Education Review , 19 (1), 73-80.
Hirshfield, L., & Chachra, D. (2015). Task choice, group dynamics and learning goals: Understanding student activities in teams. 2015 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference: Launching a New Vision in Engineering Education Proceedings, FIE 2015 , 1-5.
Johnson, C. (2011). Activities using process‐oriented guided inquiry learning (POGIL) in the foreign language classroom. Die Unterrichtspraxis/Teaching German , 44 (1), 30-38.
Johnson, D. W., Johnson, R. T., and Smith, K.A. (2006). Active learning: Cooperation in the university classroom . Edina, MN: Interaction.
Moog, R.S. (2014). Process oriented guided inquiry learning. In M.A. McDaniel, R. F. Frey, S.M. Fitzpatrick, & Roediger, H.L. (Eds.). Integrating cognitive science with innovative teaching in STEM disciplines (147-166). St. Louis: Washington University in St. Louis Libraries.
The POGIL Project. (2017). https://pogil.org/
Springer, L., Stanne, M.E., & Donovan, S.S. (1999). Effects of small-group learning on undergraduates in science, mathematics, engineering, and technology: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 96 (1), 21-51.
Have suggestions?
If you have suggestions of resources we might add to these pages, please contact us:
[email protected] (314) 935-6810 Mon - Fri, 8:30 a.m. - 5:00 p.m.
How Do I Facilitate Effective Group Work?

Successful group work is characterized by trust, psychological safety, clarity of expectations, and good communication; being in the same location while working is not essential to group effectiveness (Duhigg, 2016; Kelly, 2008; Salmons, 2019). Below we offer strategies and examples that work for short-term collaborative group work (e.g., discussions in an online, hybrid/flexible, or in-person class) and long-term collaborative assignments (e.g., group projects), ending with additional considerations for long-term collaborative work.
STRATEGIES & EXAMPLES
Provide opportunities to develop connection and trust.
Engage students with community building activities. Groups work best when students feel connected and trust each other. Brief icebreaker activities are fun and allow students to get to know each other before delving into group work. If using a video conferencing platform such as Zoom or Echo360, ask students to type a word or emoji about how they are doing into the chat, or during in-person classes students can share this orally or via an audience response system. Let students practice group work in Moodle or Blackboard with some low-stakes group assignments.
Create group norms. In the first few weeks of class, create participation norms that all students agree upon as a class or within their small groups. Discuss with students how certain social identities (e.g., women in STEM, transgender students) can be unintentionally marginalized during group work as a justification for creating norms around respectful and inclusive communication (Oakley, Felder, Brent, & Elhajj, 2004). Vary the groupings of students so that students can meet other students and hear different perspectives, particularly in the first weeks of class. Refer back to the agreed-upon norms when conflict arises.
Proactively check in with groups. It’s important to pay attention to both process and the accomplished task. As you drop into groups during class time or consult with groups in office hours, note who does and does not speak; consider asking questions about process such as who is generating ideas and how they know everyone is on board with these ideas. Check in individually with quieter students. Remember, how you address group functioning models how they should interact with each other (Kelly, 2008).
(Over)communicate and Reinforce Expectations
Communicate the purpose. Communicate in writing and orally the skills students will develop by the end of their group work experience and why this is a valuable task or project to do in groups (as opposed to individually). You might ask students to connect skills they will learn to their personal goals and describe how they will know if they’ve developed these skills apart from your feedback.
Describe the tasks. In writing, describe the tasks in detail, including steps in the process with due dates/deadlines, resources needed, technology for communication, and expectations for group work. This means giving students clear topics, questions, deliverables, or goals for group work. Consider assigning rotating task roles such as discussion director, connector, summarizer, recorder, and reporter (Kennedy & Nilson, 2008). Create a space online for students to submit questions which are publicly answered for all to see; this can become an FAQ forum . At the end of group work, have groups submit something that demonstrates their engagement with the task for a small amount of points, such as group decisions, remaining questions, or discussion notes.
Clarify the criteria. Communicate specific details about how student work generated in groups will be assessed (i.e., rubrics, exemplars, grading scheme). Use positive, “do this” language rather than negative, “don’t do this” language when possible. Show examples that typify important or challenging aspects of the work with narrations (i.e., on video or in a commented document) of what makes the work exemplar.
Additional Tips for Long-term Collaborative Projects
Be sure students have a communication plan. This can be specified as part of their group norms and processes at the beginning of the project. In addition, be clear how and when groups should communicate with you, where and in what format they should submit materials, and what to do if they encounter a problem.
Break apart the project into phases or milestones with clear deliverables at each stage. Clearly specify how and where students should turn in work (i.e., online or in person), and use this format consistently for all deliverables.
Have students periodically check in about their group process and report back on their process. At the beginning of the project, ask students to identify how they want to work together, what their expectations are for each other, and what collaborative tools the group wants to use. Have them post their group norms in an online forum. Include a requirement for a "team effectiveness discussion" or evaluation (self or peer) after students have some time to work together (e.g., 2nd milestone; See Oakley et al. 2004 for a “Crisis Clinic” guide). Allow them to adjust norms and set goals for the next phase of group work.
Clearly connect homework, lectures, or other learning activities to the group project. For example, after learning new concepts, students might be asked to turn in a brief “Application memo” which connects course content to their group project. An online session might end with an “Integrate it” discussion among group members to integrate new learning into their project. Homework might be called “Project Prep.” Name activities by their purpose so that students see the relevance and utility of each activity more easily.
Foster cross-group peer review. Students will appreciate hearing what other groups are doing and can get ideas for their own projects. For example, have students share their milestones or group work with another group and have them record questions and feedback in a collaborative document. Review that document to provide feedback to the entire class, saving you from giving feedback to each group. Peer review can also be done as a workshop or group assignment activity in the LMS.
Please contact the CTL with any questions or for more details about the examples shared at [email protected] . For support with collaborative technology, email [email protected] .
For questions on your LMS, Google, and other educational technology contact IDEAS at [email protected]
Duhigg, C. (2016, February 25). What Google Learned From Its Quest to Build the Perfect Team . The New York Times.
Kelly, R. (2008, August 11). Creating trust in online education , Faculty Focus.
Kennedy, F. A., and Nilson, L. B. (2008). Successful strategies for teams. Team Member Handbook . Office of Teaching Effectiveness and Innovation, Clemson University.
Oakley, B., Felder, R. M., Brent, R., & Elhajj, I. (2004). Turning student groups into effective teams . Journal of Student Centered Learning, 2 (1), pp. 9-34.
Salmons, J. (2019). Learning to collaborate, collaborating to learn: Engaging students in the classroom and online . Sterling, VA: Stylus.
Image by Armin Rimoldi for Pexels.
RELATED TOPICS

How Do I Increase Student Engagement with Participation Agreements?
Students engage and participate when there is a class climate in which they feel safe, supported, and encouraged to express their thoughts, values, experiences, and perspectives.

How Do I Use Note Catchers to Support Group Work and Collaborative Note Taking?
Note catchers, shared collaborative documents accessed in real time, keep students focused and help you monitor online or in-person group work.

How Do I Navigate Hot Moments in the Classroom?
Strategies for navigating and managing yourself during hot moments during class discussions, and helping students process conflict.

How Do I Support Students with Compassion and Empathy?
Faculty can support student learning by designing courses to include compassion, communicating often, and connecting students to wellbeing resources on campus.
- Consultations
- MAP Program
- Departmental Administration of Forward FOCUS
- Forward FOCUS Frequently Asked Questions
- Implementing and Modifying Forward FOCUS
- Identifying and Responding to Pinch Points
- Using Forward FOCUS to Design Forward
- Alternative Grading
- Listen to Learn
- ChatGPT and Generative AI Discussion Group: Navigating the Future of Teaching and Learning
- Lilly Fellows Stories
- Lilly Fellowship Current Fellows
- Lilly Fellowship Past Fellows
- TIDE Ambassadors Fellowship Cohorts
- Contemplative Pedagogy Past Programming
- Contemplative Pedagogy Resources
- UMass Courses Taught with Contemplative Pedagogy
- SoTL Professional Development Award
- SoTL Working Group
- SoTL Conference Calendar
- SoTL Sprint
- How Do I...?
- Inclusive Syllabus Design
- Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
- Faculty Successes
- Building Belonging
- Talk Teaching
- Equity Action Plan Instructional Resources
- Teach Week 2024
- Gather to Grade
- Teaching with AI: A Practical Guide to a New Era of Human Learning
- 2021-2022 Highlights
- 2022-2023 Highlights
- Periodic Multi-Year Review (PMYR) Grant
- Previous DTA Winners
- DTA Frequently Asked Questions
- Tips for Writing a Teaching Statement
- Previous COTA Winners
- Step-by-Step Guide on How to Submit Materials for the Manning Prize 2023
- CTLs in Context
- A-Z Directory
- Campus Maps
- Faculties and Schools
- International
- People and Departments
- Become A Student
- Give to Memorial
- Faculty & Staff
- Online Learning
- Self Service
- Other MUN Login Services
- Academic Success Centre
- Learning skills resources
- Group work: Goals, roles, and ground rules
Group work: Goals, roles, & ground rules
You've been given your assignment and have your group members in place. Your next step is to set up your group's goals, roles, and ground rules to make the most of your time working together. Taking a few minutes at the start of your assignment to cover this will often proactively address any issues that may arise during group projects.
Let's look into each of these a bit more:
Ground Rules
Use our downloadable Group Work Roadmap [ .doc / .pdf ] to take the guesswork out of this process.
Group Goals
In this first step, you are ensuring everyone is on the same page regarding what mark you want for your project, what date you will submit your project, and determining your specific project topic or focus if given choice in your assignment.
Know from day one if your group is aiming for a final grade in the 70s, 80s, or 90s. Also, discuss if this mark is one you can comfortably achieve or if it is one you will strive for. This will help set both the tone for the group and the expectation for submissions.
As a group, collectively decide on a date for final review and submission. As you will have many people working on many parts try to build in time for group reviews of the final draft of a project well ahead of the required due date. This will allow time for additions or upgraded work ahead of the due date.
As a group, discuss the project's outline and be sure to come to a consensus about what is expected. Brainstorm and discuss topics if your professor allows self-selection. This will set your group up for drafting task assignments and ensuring everyone is working toward a common goal.
Group Roles
Now that your group has established the "what" of the project, you need to consider the "who" and the "when".
Each member should have an equal amount of tasks they will carry from the group's workload. This does not necessarily mean an equal number of tasks across all members as some tasks may be very large and others very small. As a group, look at your assignment and begin to break down the project into various tasks.
Once all tasks are written out, have each member indicate if there are any particular tasks they are best equipped for or are interested in doing. For tasks which remain after this initial selection process begin to delegate these out in an equitable fashion. This can be done through another round of self-selection, random draw, or any number of processes. Review again the overall workload being tasked to each member - does the amount of time and effort seem equal? Finally, collectively create a schedule of mini-deadlines each task must be drafted, reviewed, and submitted within the overall timeline of the project.
Another role to be considered is that of the draft reviewer. Each member's tasks should be shared with another member once a final draft has been created. This review period should allow time for feedback and for the draft creator to be able to implement any changes agreed upon.
Ground rules for groups cover the details which push your progress along and create fair communication & conflict expectations. Again, using our Group Work Roadmap resource will help navigate many of the ground rules needed to be covered. Considerations include meetings, attendance, communication, and conflict.
- Revisit the date chosen for the final draft submission review by the group and set a tentative date to all meet and discuss.
- Reviewing the mini-deadlines, or your own class schedules, establish meeting dates throughout the project's timeline to meet together as a group. This could be weekly, biweekly, or staggered dates throughout.
- Determine how long these meetings will be scheduled to last.
- Determine where meetings will take place; it doesn't have to be the same place every time. If meeting online, determine what tool you will use and try to pick one that everyone is comfortable with using.
- Determine the proper process for notifying the group if you will miss a meeting.
- Determine the plan of action if there is a member who continues to miss or be late for meetings.
- Determine how an emergency meeting will be requested/announced.
- Communication
- What will be the primary platform for asynchronous group communication? (e.g. email? an instant messaging system?)
- What will be the primary platform for asynchronous individual communication (e.g. sending drafts or reviews of drafts)?
- Review and agree to use healthy communication dynamics .
- Determine how information from meetings will be shared with members who were unavoidably absent.
- Discuss how the group will provide constructive feedback to members for absent, subpar, or low-effort submissions.
- Discuss the escalation process that will be followed in determining when to alert your instructor of a failing group member.
- Discuss how the group will respectfully get back on task when a group member(s) are off-topic, coopting too much time/energy of a meeting, or have become too fixated on an individual issue that is not impacting the group.
"Setting Expectations & Ground Rules" [Algonquin College Library; YouTube]
Whether big or small, using our Group Work Roadmap can help give a physical space for your group to document many of the choices made concerning goals, roles, and ground rules. Taking a couple of minutes to complete this at the start of your project will give everyone a clear path to navigate and clear expectations of them by the group. The more transparent these factors are, the less likely you are to encounter misunderstanding-based conflicts.
Algonquin College of Applied Arts & Technologies. (2021, June 3). Essential study skills: Group work . Algonquin College of Applied Arts & Technologies: Student Support Services. https://algonquincollege.libguides.com/studyskills/group-work
Carnegie Mellon University. (n.d.). Sample group project tools: team contract template . Carnegie Mellon University: Eberly Center. Retrieved March 9, 2022 from https://www.cmu.edu/teaching/designteach/teach/instructionalstrategies/groupprojects/tools/TeamContracts/teamcontracttemplate.docx
Carnegie Mellon University. (n.d.). What are the challenges of group work and how can I address them ? Carnegie Mellon University: Eberly Center. Retrieved March 9, 2022 from https://www.cmu.edu/teaching/designteach/teach/instructionalstrategies/groupprojects/challenges.html
Indeed Editorial Team. (2021, June 9). Four common types of team conflict and how to resolve them . Indeed. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/types-of-team-conflict
La Trobe University. (2020, September 18). Common types of group conflicts and how to resolve them . La Trobe University. https://www.latrobe.edu.au/mylatrobe/common-types-of-group-conflicts-and-how-to-resolve-them/
Levin, P., and Kent, I. (2001). Draft manual on teamwork tutoring: 28 questions and answers for academics on teamwork in universities .
Oregon State University. (n.d.). Team work makes the dream work: make your group project awesome like a blessing of unicorns. Oregon State University: Academic Success Center. Retrieved March 9, 2022 from https://success.oregonstate.edu/sites/success.oregonstate.edu/files/LearningCorner/Tools/4-page_twdw_-_fill_-_20.pdf
University of British Columbia. (n.d.). Resolving conflict. University of British Columbia: Chapman Learning Commons. Retrieved March 11, 2022 from https://learningcommons.ubc.ca/student-toolkits/working-in-groups/resolving-conflict/.
University of Waterloo. (n.d.). Teamwork skills: Being an effective group member . University of Waterloo: Centre for Teaching Excellence. Retrieved March 9, 2022 from https://uwaterloo.ca/centre-for-teaching-excellence/teaching-resources/teaching-tips/tips-students/being-part-team/teamwork-skills-being-effective-group-member
- Learning supports
- Peer-Assisted Learning
- Help centres
- Study spaces
- Graduate student supports
- Events and workshops
- Faculty & staff resources
Related Content
Common Group Work Challenges and Solutions

Group work necessitates emotional intelligence and other skills such as communication, time management, conflict resolution, and recognition of team member differences. A successful group project will provide a framework to ensure students are properly equipped with these skills.
Scheduling Conflicts
Scheduling conflicts often create roadblocks to getting started or continuing with projects. Group members may feel others aren’t compromising or taking each other’s situations into consideration. Use the suggestions below to help students communicate effectively and avoid scheduling conflicts.
- Pre-project scheduling solutions
- Mid-project scheduling solutions
- Request students share their availability prior to group formation so that students with similar schedules can be grouped together.
- Provide access to virtual meeting spaces through a web conferencing platform (e.g., MS Teams, Webex, Zoom).
- Require that students take turns picking the venue and time of the meeting.
- Encourage students to be understanding of others’ schedules and responsibilities.
- Point students to online collaboration tools that facilitate working asynchronously.
Group Conflict
Conflict is natural and sometimes necessary for effective group work. Sometimes it may escalate and make it difficult for members to focus on the project. Use the solutions below to help avoid and resolve conflict during group activities.
- Pre-project conflict solutions
- Mid-project conflict solutions
- Provide the time and opportunities for students to build communication, time management, and conflict resolution skills within the classroom setting.
- Help students to stay focused on the work to be accomplished and to not let personal feelings impact their work in the group by ensuring expectations are clearly defined at the beginning of the project.
- Use office hours to help students find common ground between two ideas to reach reconciliation.
- Encourage students to address conflicts directly and respectfully.
- There are instances that, for the well-being of the students, you may need to reform groups.
Uneven Contributions (Loafing/Overachieving)
Uneven student contribution occurs when some group members don’t (or aren’t perceived to) contribute equally to the group project. Often, this results in tension within the group and feels unfair to group members. There are multiple methods of managing an uneven work distribution, as described below.
- Pre-project contribution solutions
- Mid-project contribution solutions
- Set clear guidelines and work expectations at the beginning of the group project.
- Clearly define and assign the group roles and responsibilities so that each person will contribute equally.
- Increase individual accountability by combining group assessments with individual assessments.
- Provide a mechanism for teams to dismiss a member. Be sure to have a contingency plan for a dismissed student.
- Encourage students to speak directly, but respectfully, to the person who is contributing unequally.
- Ask students to do an anonymous mid-project evaluation of each other’s contributions and performance to assess the group process and monitor dynamics. This can be facilitated through an anonymous peer review using rubrics .
- Provide multiple in-class “checkpoints” to assess group processes and monitor dynamics.
Conflicting Expectations
Conflicting expectations arise when group activities are loosely defined. For example, some group members may strive for perfection, while others simply want to pass. Other opportunities for discord arise when discussing deadlines. Some people begin projects in well advance, while others procrastinate. Both examples create tension because the group isn’t working toward the same goal or deadline. The opportunities below will help you frame the group work to ensure a cohesive experience.
- Pre-project expectations solutions
- Mid-project expectations solutions
- Early communication is key to ensure everyone agrees on common goals. Require teams to determine how they will communicate (e.g., Canvas Inbox, MS Teams).
- Help students to keep goals realistic by breaking the project down into smaller tasks.
- In class, give students the opportunity to create a timeline so the group can keep to an agreed-upon plan for completing the project.
- Ask students to complete a Plus/Delta survey to assess what’s going well and what changes could be made to help the group align their expectations.
- Rotate responsibilities to provide all group members the opportunity to excel.
Getting Stuck
All the challenges thus far have focused on conflict. What happens when the group is cohesive but still unable to make progress? Sometimes they get stuck or hit a mental roadblock. This lack of progress can be discouraging and lead to procrastination or avoidance. Read the techniques below to help students find the path forward.
- Pre-project solutions for getting stuck
- Mid-project solutions for getting stuck
- Precede group brainstorming with a period of individual brainstorming.
- Create structured opportunities at the halfway point of projects to allow students to reevaluate and revise their strategies and approaches.
- Assign roles to reduce conformity (devil’s advocate, doubter, the fool)
- Require group members to reflect on and highlight their contributions in a self-evaluation.
- Build in mechanisms for students to work through projects analytically using the groups’ combined and diverse knowledge and experience.
As groups navigate the many types of conflict, some students may begin to feel frustrated or unheard. In these instances, there is a tendency for individuals to agree with others to avoid conflict. This is especially problematic as it stifles creativity and constructive evaluation of alternative ideas. Fortunately, groupthink can be prevented through a little intentionality.
- Pre-project groupthink solutions
- Mid-project groupthink solutions
- Provide an archive of past projects for students to browse. Be sure to follow FERPA guidelines by removing all identifying information such as names and pictures, and deleting author metadata from the document.
- Break the project down into smaller pieces to prevent overwhelming students.
- Share sources of inspiration for the project.
- What is our next task?
- Who should do it?
- Review the assignment expectations and goals during class
- Hold a whole-class or group-specific brainstorming session where ideas are discussed.
- Demonstrate how to create a mind map to link common ideas and trains of thought.
- Provide time during student office hours to guide groups that may be stuck.
Isolation of a Group Member
The last challenge we’ll look at can start as an effort to increase the diversity of each group, minimizing the likelihood of students falling into the groupthink mentality. However, research and experience tell us that being the “only” in a group can be isolating. Consider the pre-project solutions below to avoid the isolation of a group member and use the mid-project corrections if a student comes to you with a concern.
- Pre-project isolation solutions
- Mid-project isolation solutions
- If there are a limited number of visibly diverse students, try to keep these underrepresented students together to limit isolation (Bailey, 2020).
- Establish expectations that require equal contribution and interaction.
- Ask the class to take a few minutes to write about what helps and hinders their group work experience. Review their comments, share the findings with the class, and provide strategies to address their concerns.
- Re-assign the student to another group.
- Review the roles, responsibilities, and expectations with the class.
Instructor's Guide: Facilitating Group Work When done correctly, group projects can facilitate the development of communication, time management, collaboration, and conflict resolution skills that are vital in the professional world. Set the Stage for Success in Group Projects There are steps you can take as the instructor of the course to help set the stage for student success when assigning group work. Grading Methods for Group Work Once you have the group activity established, you should consider the different methods and tools available for grading group work. References
- Bailey, E. G., et.al. (2020). Female in-class participation and performance increase with more female peers and/or a female instructor in a life sciences course . CBE – Life Sciences Education , 19 (3). https://www.lifescied.org/action/cookieAbsent
- Huang, L. (2018, September 20). Students riding on coattails during group work? Five simple ideas to try. Retrieved from https://www.facultyfocus.com/articles/effective-teaching-strategies/students-riding-coattails-group-work-five-simple-ideas-try/
Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, how can i assess group work.
All of the principles of assessment that apply to individual work apply to group work as well. Assessing group work has added challenges, however.
First, depending on the objectives of the assignment, the instructor might want to assess the team’s final product (e.g., design, report, presentation), their group processes (e.g., ability to meet deadlines, contribute fairly, communicate effectively), or both. Second, group performance must be translated into individual grades – which raises issues of fairness and equity. Complicating both these issues is the fact that neither group processes nor individual contribution are necessarily apparent in the final product.
Thus, in addition to evaluating the group’s output, instructors may need to find ways to determine how groups functioned and the extent to which individuals contributed to the effort. This isn’t always easy, but these general principles can guide you, and the Eberly Center for Teaching Excellence can help you find and implement the right approach for your goals and context.
Assess individual, as well as group, learning and performance.
Assess process as well as product..
- Make your assessment criteria and grading scheme clear .
Find samples of group project assessment tools here...
Diligent students can be profoundly demotivated by group projects if they feel that their own success is dependent on team members who don’t do their share. One way to counteract the motivational hazards of group projects is to assess individual students’ learning and performance in addition to the group’s output. This strategy gives diligent students a greater sense of fairness and control and discourages free ridership.
Individual learning and performance can be assessed in any number of ways. Some instructors add an individual component to group projects (e.g., a short essay, journal entries); some combine a group project with an individual test or quiz. Both group and individual performance are then reflected in the total project grade (e.g., some faculty members make the group grade worth 50% and the individual grade worth 50%; others split it 80%/20%. There’s no perfect breakdown, but the grading scheme should (a) reflect your goals for student learning and (b) seek to motivate the kind of work you want to see.)
Professor Solomon asks student groups to research a famous anthropological controversy, and give an oral presentation analyzing the issues, positions, and people involved. She assigns a group grade for the presentation, but also requires all the team members to write a short, individual paper summarizing what they learned from the assignment and what they contributed to the team. If the individual piece demonstrates a poor understanding of the material or a low level of participation in the group, she reserves the right to lower the individual’s grade by a full letter grade. If it is particularly informed, thorough, or demonstrates an exceptionally high contribution to the team, she raises the individual’s grade by a full letter grade.
If developing teamwork skills is one of your learning objectives for the course, it’s important to assess students’ progress toward that goal. In other words, you should assess process (how students work) as well as product (the work they produce).
Process can be assessed according to a number of dimensions, such as the ability to generate a range of ideas, listen respectfully to disparate perspectives, distribute work fairly, resolve differences, and communicate effectively. Since instructors don’t always have a direct window into the dynamics of student groups, they often rely on teams to self-report via:
- team evaluations: each member of the team evaluates the dynamics of the team as a whole.
- peer evaluations: each team member evaluates the contributions of his/her teammates.
- self-evaluations: each team member documents and evaluates his own contributions to the team.
- Find samples of evaluations here...
These assessments can be quantitative or qualitative. They can be done as reflective writing assignments or as questionnaires targeting specific dimensions of teamwork. Think about which tools suit your purpose and context. Also give some thought to when you’ll use them (in the middle of the semester? at the end? both?), who should see them (just you? other team members?), and whether or not they should be anonymous. The Eberly Center can help you find, adapt, or create the right tool and determine how to use it to best effect.
Remember, too, that process assessments are subjective and students are not always straightforward when evaluating one another or themselves. However, in combination with product assessments and individual assessments, they can offer valuable glimpses into how teams function and alert you to major problems (e.g., particularly problematic team members or serious conflict), which can help to inform your feedback and grading.
Professor Montoya assigns a multi-stage information systems project where students work together in teams over much of the semester. Over the course of the semester, he periodically asks students to evaluate both the dynamics of the team as a whole and their own contributions, and to reflect on ways to improve both as the project continues. At the end of the project, he asks students to complete a peer evaluation for every member of their team, indicating each member’s contribution to the group. Professor Montoya’s total grade for the project combines a group grade (75%) and an individual grade (25%). The individual grade is based, in equal parts, on how each student’s teammates evaluated his contribution to the group and on the quality of the feedback he provided to them.
Make your assessment criteria and grading scheme clear.
It’s always important to articulate your performance criteria so students understand your expectations and standards. This is especially true if you are emphasizing skills that are not usually assessed, such as the ability to resolve conflict, delegate tasks, etc. Criteria for evaluating both product and process can be communicated by giving students a group work rubric ( pdf ) before they begin their work and then using it to provide meaningful feedback during and at the end of the project.
It’s also important to think about how you will weigh the various components of group projects in your grading scheme. Some questions to consider include:
- What percentage of the student’s total project grade will be based on the group’s performance vs. individual components?
- What percentage will be based on assessments of product vs. assessments of process?
- How much weight will you give to peer evaluations or self-evaluations?
- Will feedback from external clients also be incorporated into your assessment of the group’s work? If so, what sorts of feedback will you solicit: feedback on product (e.g., Does it work? Is it a good solution/design?), feedback on process (e.g., Did the group communicate effectively with the client? Did it meet deadlines?), or both?
A number of dimensions of group work can factor, either formally or informally, into a student’s grade. What’s important is to think about what dimensions of student performance matter to you and how your grading criteria and the weighting of assessment components can help motivate the behaviors you want to see. Finally, it’s critical to clearly communicate your grading scheme to students.
Center for Teaching Innovation
Ideas for group & collaborative assignments, why collaborative learning.
Collaborative learning can help
- students develop higher-level thinking, communication, self-management, and leadership skills
- explore a broad range of perspectives and provide opportunities for student voices/expression
- promote teamwork skills & ethics
- prepare students for real life social and employment situations
- increase student retention, self-esteem, and responsibility
Collaborative activities & tools
Group brainstorming & investigation in shared documents.
Have students work together to investigate or brainstorm a question in a shared document (e.g., structured Google doc, Google slide, or sheet) or an online whiteboard, and report their findings back to the class.
- Immediate view of contributions
- Synchronous & asynchronous group work
- Students can come back to the shared document to revise, re-use, or add information
- Google workspace (Google Docs, Sheets, Forms, & Slides)
- Microsoft 365 (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Teams)
- Cornell Box (document storage)
- Whiteboarding tools ( Zoom , JamBoard , Miro , Mural , etc.)
Considerations
- Sharing settings
- Global access
- Accessibility
Group discussions with video conferencing and chat
Ask students to post an answer to a question or share their thoughts about class content in the Zoom chat window (best for smaller classes). For large classes, ask students in Zoom breakout rooms to choose a group notetaker to post group discussion notes in the chat window after returning to the main class session.
You can also use a discussion board for asynchronous group work.
- Students can post their reflections in real time and read/share responses
- If group work is organized asynchronously, students can come back to the discussion board at their own time
Synchronous group work:
- Zoom Breakout rooms
- Microsoft Teams
- Canvas Conferences
- Canvas Group Discussions
- Ed Discussion
- Stable access to WiFi and its bandwidth
- Clear expectations about participation and pace for asynchronous discussion boards
- Monitoring discussion boards
Group projects: creation
Students retrieve and synthesize information by collaborating with their peers to create something new: a written piece, an infographic, a piece of code, or students collectively respond to sample test questions.
- Group projects may benefit from features offered by shared online space (ability to chat, do video conferencing, share files and links, post announcements and discussion threads, and build content)
- Canvas groups with all available tools
Setting up groups and group projects for success may require the following steps:
- Introduce group or peer work early in the semester
- Establishing ground rules for participation
- Plan for each step of group work
- Explain how groups will function and the grading
Peer learning, critiquing, giving feedback
Students submit their first draft of an essay, research proposal, or a design, and the submitted work is distributed for peer review. If students work on a project in teams, they can check in with each other through a group member evaluation activity. Students can also build on each other’s knowledge and understanding of the topic in Zoom breakout room discussions or by sharing and responding in an online discussion board.
When providing feedback and critiquing, students have to apply their knowledge, problem-solving skills, and develop feedback literacy. Students also engage more deeply with the assignment requirements and/or the rubric.
- FeedbackFruits Peer Review and Group Member Evaluation
- Canvas Peer Review
- Turnitin PeerMark
- Zoom breakout rooms
- Canvas discussions, and other discussion tools
- Peer review is a multistep activity and may require careful design and consideration of requirements to help students achieve the learning outcomes. The assignment requirements will inform which platform is best to use and the best settings for the assignment
- We advise making the first peer review activity a low-stakes assignment for the students to get used to the platform and the flow.
- A carefully written rubric helps guide students through the process of giving feedback and yields more constructive feedback.
- It helps when the timing for the activity is generous, so students have enough time to first submit their work and then give feedback.
Group reflection & social annotation activities
Students can annotate, highlight, discuss, and collaborate on text documents, images, video, audio, and websites. Instructors can post guiding questions for students to respond to, and allow students to post their own questions to be answered by peers. This is a great reading activity leading up to an inperson discussion.
- Posing discussion topics and/or questions for students to answer as they read a paper
- Students can collaboratively read and annotate synchronously and asynchronously
- Collaborative annotation helps students to acknowledge some parts of reading that they could have neglected otherwise
- Annotating in small groups
- FeedbackFruits
- Interactive Media (annotations on document, video, and audio)
- Providing students with thorough instructions
- These are all third-party tools, so the settings should be selected thoughtfully
- Accessibility (Perusall)
Group learning with polling and team competitions
Instructors can poll students while they are in breakout rooms using Poll Everywhere. This activity is great for checking understanding and peer learning activities, as students will be able to discuss solutions.
- Students can share screen in a breakout room and/or answer questions together
- This activity can be facilitated as a competition among teams
- Poll Everywhere competitions, surveys, and polls facilitated in breakout rooms
- Careful construction of questions for students
- Students may need to be taught how to answer online questions
- It requires appropriate internet connection and can experience delays in response summaries.
More information
- Group work & collaborative learning
- Collaboration tools
- Active learning
- Active learning in online teaching
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- CBE Life Sci Educ
- v.17(3); Fall 2018
When Group Work Doesn’t Work: Insights from Students
Yunjeong chang.
† Department of Instructional Technology, University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602
Peggy Brickman
§ Department of Plant Biology, University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602
Associated Data
Introducing group work in college science classrooms can lead to noticeable gains in student achievement, reasoning ability, and motivation. To realize these gains, students must all contribute. Strategies like assigning roles, group contracts, anonymous peer evaluations, and peer ratings all encourage student participation. In a class using these strategies, we conducted in-depth interviews to uncover student perceptions of group work in general and the utility of these support strategies. Students in both high- and low-performance groups still complained of unequal contributions while praising the social support provided by groups. Students who scored highly on tests were more likely to recognize the benefits of group work, regardless of their groups’ overall performance levels, while lower-scoring students perceived group work as time-consuming “busy work” with little cognitive benefit. Comments from anonymous peer evaluations differed only subtly between high- and low-performance groups. Numerical ratings on these evaluations did correlate with overall group performance. However, students in lower-performance groups assigned harsh ratings to their low-scoring members, while students in higher-performance groups were more generous in their ratings for low-scoring members. We discuss implications of relying on support strategies for promoting productive group work.
INTRODUCTION
Science education policy ( Handelsman et al. , 2004 ; American Association for the Advancement of Science, 2010 ; Couch et al. , 2015 ; National Research Council, 2015 ) advocates for including peer interactions (referred to as “group work” hereafter) in college courses because they provide opportunities for students to practice scientific reasoning, critical-thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills that have been shown to result in greater gains in achievement ( Slavin, 1991 ; Springer et al. , 1999 ; Johnson et al. , 2000 ; Armstrong et al. , 2007 ; Preszler, 2009 ; Freeman et al. , 2014 ; Batz et al. , 2015 ). Group-work pedagogies with demonstrated evidence of effectiveness include collaborative learning ( Phelps and Damon, 1989 ), cooperative learning ( Slavin, 1991 ), team-based learning ( Michaelsen et al. , 2014 ), peer instruction ( Crouch and Mazur, 2001 ), SCALE-UP (Student-Centered Activities for Large Enrollment Undergraduate Programs project) in physics ( Beichner et al. , 2007 ), and POGIL (process-oriented guided-inquiry learning) in chemistry ( Moog and Spencer, 2008 ). All of these group-work pedagogies encourage students to construct their own understanding of scientific concepts through a process of negotiation and consensus building with their peers ( Solomon, 1987 ; Latour and Woolgar, 2013 ). Group work also provides a basis for social comparison, social learning, and social cognition ( Solomon et al. , 2010 ), and students working in small groups may make gains in terms of achievement, motivation, and self-efficacy as a result of this comparison ( Bandura, 2000 ; Hernandez et al. , 2013 ).
Several integrated theoretical frameworks have been espoused within educational psychology to explain the different constructs (motivational, social, and cognitive) that influence the achievement effects of group work ( Sweet and Michaelsen, 2007 ; Slavin, 2014 ). Social interdependence theory ( Johnson and Johnson, 2009 ) is a particularly helpful theoretical framework, because it describes five major variables that mediate the effects of cooperation, including motivational, social, and cognitive aspects. The first variable described in social interdependence theory is positive interdependence: individuals’ perception that they can reach their goals if and only if the other individuals with whom they cooperate also reach their goals and, therefore, promote one another’s efforts to achieve the goals. The second variable is individual accountability: the responsibility to complete one’s own share of the work and also facilitate others’ work. The third variable is promotive interactions: individuals motivating and facilitating the work of others through sharing resources, providing help to one another, challenging reasoning and conclusions provided by group members, and taking varying points of view into account. The fourth variable is the appropriate use of social skills: skills in which individuals get to know and trust one another, communicate, support one another, and resolve conflicts that arise. Finally, group work should provide a mechanism for group processing and reflection: encouraging students to set collective goals, assess positive and negative group interactions, and provide feedback to group members. Instructors play a major role in promoting the variables required for these aspects of social interdependence during group work, and students express greater satisfaction with group work when their instructors include support strategies to assess and foster group collaboration ( Chapman and Van Auken, 2001 ).
Recommended support strategies to foster effective collaboration include assigning roles, group contracts, peer evaluations, and peer ratings that measure differences in contributions.
Role Assignment
Assigning tasks or roles for students to assume while completing tasks is recommended as a way to promote individual accountability and ensure that instructors can monitor contributions ( Chapman and Van Auken, 2001 ; Davies, 2009 ). Group work pedagogies like POGIL ( Moog and Spencer, 2008 ) and SCALE-UP ( Beichner et al. , 2007 ) recommend assigning specific roles to promote critical discussion and to prevent students from either dominating discussions or avoiding conflict by accepting the quickest answer during problem-solving tasks ( Heller and Hollabaugh, 1992 ). Role assignment has been shown to promote greater learning gains ( Bailey et al. , 2012 ) and student satisfaction ( Brown, 2010 ). The caveat remains that supervision is required so that students cycle through the cognitive acts of listening and recalling that are necessary for greater exchange of ideas and thus learning ( O’Donnell, 2006 ).
Group Contracts
Groups that discuss expectations before group work begins and draft group contracts that spell out consequences for failure to meet expectations foster appropriate use of social skills ( Chapman and Van Auken, 2001 ; Oakley et al. , 2004 ). Feelings of interdependence, cohesion, psychological safety, and confidence all strengthen the belief that investment in group activities will pay off and thus encourage students to engage in cognitive processes key to learning ( Van den Bossche et al. , 2006 ).

Peer Evaluations
Anonymous peer evaluations in which students reflect on their own and others’ contributions and group dynamics and have the ability to inform the instructor of problems within the group help promote reflection, group processing, and individual accountability ( Harkins and Jackson, 1985 ; Strong and Anderson, 1990 ; Brooks and Ammons, 2003 ; Oakley et al. , 2004 ; Aggarwal and O’Brien, 2008 ). Evaluations also help reduce social loafing, a situation in which students in a group commit less effort to a group project, because they believe their lack of effort will not be identified, and free riding, a situation in which students knowingly allow others to complete their work for them ( Aggarwal and O’Brien, 2008 ). In Strong and Anderson’s (1990) study of student opinions about group work, students indicated that they believed that peer evaluations do reduce free riding, but they rated other factors—including group cohesiveness, small team size, the option to “divorce” a team member, or the option to leave a team—as having a stronger effect on reducing free riding. Students also rated the divorcing option as more effective at motivating team members than end-of-semester evaluations, which have been shown to be negatively associated with good team experiences ( Bacon et al. , 1999 ). This suggests that peer evaluations may encourage students to tolerate bad behavior, knowing they can exact retribution at the end of the semester. In addition, researchers have found that students may be unlikely to provide honest evaluations of their peers and are unlikely to directly confront free riders ( Strong and Anderson, 1990 ).
Peer Ratings
There are challenges to determining the effort and achievement level of individual students during group tasks. On typical group tasks, all group members work together without being evaluated individually on the final product by the instructor, and all group members receive the same grade for the final product. If the level of contribution differs among group members, then the single group grade may not accurately reflect individual effort or performance. One solution is to collect information on the contributions of each group member using quantitative ratings and to adjust the final scores to reflect lack of effort ( Latane et al. , 1979 ; Bartlett, 1995 ). Students should be aware of the contributions of each member, and if they can be trusted to provide accurate ratings, the ratings could be used to derive a numerical weighting factor to adjust group grades accordingly. Researchers have recommended administering both holistic rubrics in which students are given points that they must divide between the group members to gauge contributions ( Lejk and Wyvill, 2001 ; Johnston and Miles, 2004 ) and analytical rubrics with multiple indicators such as attendance, cooperativeness, and academic contributions to gauge contributions ( Kaufman et al. , 2000 ; Stefanou et al. , 2001 ; Kilic and Cakan, 2006 ). Holistic rubrics have been found to be more effective at identifying very good and very weak contributors to the group, whereas analytic assessments are able to identify small differences in group contributions and may be more effective for providing formative feedback ( Falchikov and Goldfinch, 2000 ; Lejk and Wyvill, 2001 ). Holistic rubrics, however, need to be adjusted by calculating an individual’s contribution to maximize the correlation between actual group scores and true levels of a student’s contribution ( Zhang and Ohland, 2009 ).
Faculty members have reported concern about providing sufficient support to ensure that students are interacting productively during group work in large-enrollment classes ( Pundak and Rozner, 2008 ; Freeman and Greenacre, 2011 ; Barkley et al. , 2014 ). And many faculty attest to difficulties they have encountered implementing group work in their classes and have reported frustration with dysfunctional groups that require a great deal of supervision to ensure equitable student participation and reward productive social interactions ( Kreijns et al. , 2003 ; Davies, 2009 ; Svinicki and Schallert, 2016 ).
In an attempt to improve student learning through group work, we implemented many of these recommended strategies for supporting group dynamics in a very large enrollment introductory biology course that was often linked to poor student learning, attitudes, and retention ( Seymour and Hewitt, 1997 ; Barr et al. , 2008 ; Chang et al. , 2011 ; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, 2016 ). In a preliminary study, we were able to demonstrate that group activities benefited students at diverse performance levels, but the students also reported persistent social loafing ( Chang and Hannafin, 2015 ).
Managing group dynamics for successful implementation of group work is time intensive for instructors. We hypothesized that exploring students’ perceptions of group work might provide insights into which time-consuming support strategies (e.g., role assignment, group contracts, peer evaluations at the midpoint and endpoint of the semester, and summative peer ratings) students were using effectively. We also hoped that the perceptions of students in high-performance groups could provide insight into critical features to be nurtured and enhanced in all groups. Because this was a primarily observational study aimed at characterizing student perceptions of group work and use of support strategies designed to monitor and improve group interactions in a large-enrollment college classroom, we employed a concurrent mixed-methods design ( Creswell, 2009 ). We characterized student perceptions of group work using qualitative interviews and written comments submitted on peer-evaluation surveys. We also compared the interviews, comments, and numeric peer-evaluation ratings given by and from students at different achievement levels, which we determined using quantitative data from course assessments ( Teddlie and Tashakkori, 2003 ). Table 1 outlines our major research questions and the data sources used to address each question.
Overview of research questions and data sources
Instructional Setting
We examined learning performance and group work for 246 students enrolled in an introductory biology course for non–science majors at a large public university in the southeastern United States. The course included two 75-minute classes per week and comprised five different content units. Class time was devoted to providing core content through instructor minilectures and daily individual and group activities that required students to apply the content to specific situations ( Brickman et al. , 2012 ). Individual assignments included clicker questions, preclass written assignments to prepare for group work, practice tests, and a final unit test composed of multiple-choice questions. Group work included completing in-class worksheets to structure or organize content knowledge (e.g., drawing a diagram, finding relevant resources from websites) as well as outside-class group projects that required students to apply their knowledge ( Brickman et al. , 2012 ). In addition, after completing unit tests individually, group members collaboratively answered the same test items again to earn a group test score. Group activities were designed to build social interaction and interdependence through deadlines that required individual work be submitted before beginning group work, initial activities that built rapport, and grading that emphasized attaining common goals ( Deutsch, 1949 ). All group members received the same score for work from their group. All activities and test scores were weighted to compute each student’s final course grade: individual test scores: 36%; clicker questioning: 12%; individual assignments to prepare for group work: 12%; group assignments and projects: 28%; and group tests: 12%.
Group Formation and Support Strategies
During the second week of the semester, the instructor asked students to organize themselves into groups of four or five members, resulting in 65 groups that completed group assignments and tests together throughout the rest of the semester. Owing to a 5% withdrawal rate, no five-member groups were present at the midpoint. The instructor did not dictate group composition because of a lack of clear consensus from the literature on the most effective characteristics to use when forming groups and because autonomous group composition minimized logistical and practical problems in course administration (i.e., tackling individual group requests) and students’ resistance (i.e., request for changing groups or sitting near the front of the auditorium). Individuals assigned themselves to different roles within their groups for daily activities: manager/spokesperson, researcher, recorder, and whiteboard writer. The manager/spokesperson supported group processes during discussions (i.e., time management, soliciting ideas from all, speaking for the group); researchers gathered additional ideas for the group from class notes and the Internet; recorders summarized discussions and submitted group worksheets; and whiteboard writers created diagrams and figures on worksheets. At the beginning and during the semester, the instructor gave mini-lessons to remind groups to rotate roles in an attempt to balance participation by each group member ( Johnson et al. , 1998 ). The instructor also created a section in the group worksheets where the assigned roles of each student in the group could be recorded.
Throughout the semester, groups were given opportunities to promote productive interactions and mediate conflict. At the beginning of the semester, groups created a contract in which they established expectations, set ground rules (e.g., penalties for failure to participate), and established communication channels. At the midpoint of the semester, groups were encouraged to revise and resubmit their contracts if necessary and to complete an anonymous online peer-evaluation survey to provide midcourse feedback to one another. Students also completed an online, end-of-course peer-evaluation survey to assess each group member’s contribution. These surveys included eight numeric questions that asked students to evaluate individual group members’ preparation, participation, collaboration, attitude, and performance during group work. For example, “Did this person participate in group discussions during class? This could include sitting with the group during class, attending regularly, etc.” Students ranked each team member on a four-point scale for each question (1 = unacceptable performance, I would fire this person; 2 = improvement needed; 3 = good, met or exceeded all expectations; 4 = outstanding, a rare individual). Text for each question in the survey can be viewed in Appendix A in the Supplemental Material. Each group member was finally asked to respond to one open-ended question: “Please provide written comments about each of your team members so they can learn how you viewed their contributions to the team. After all evaluations are submitted they will be able to read these comments but not tell who they came from. You and they can use this feedback to improve your future performance.” Students were also asked to rate the quality of each group mate’s contributions to the group on a scale of 0–100, similar to earning a grade in a class. Students were told that their group scores would be adjusted based on the average rating that they received. The Opensource online platform that we used (Simple Team Experience Assessment Measure—STEAM) used the expected-contribution method ( Lejk et al. , 1996 ), which is based on adjusting the group grade by adding a deviance from the expected contribution. If you have a group of four members, each member is expected to contribute 25% of the work. If a group member’s average score indicates that he or she completed only 20% of the work, then the assigned group score is adjusted by subtracting 5% of the group score. Group members were able to view the scores and comments from their peers after all group members had submitted their responses.
Quantitative Data Collection and Analysis
Three different measures were used to compare individual students and groups. First, we calculated group performance levels based on the rank-ordered group assignment scores and averaged group scores on a series of group tests. We were interested in how groups performed relative to one another, so we rank ordered assignments within each unique unit, because topics differed and the variance of scores differed between units ( Kruskal and Wallis, 1952 ). To have an adequate number of groups for statistical analysis, we ranked groups based on the median group score. Groups ranked above the median score were classified as high-performance groups ( n = 32), while groups that scored lower than the median were categorized as lower-performance groups ( n = 33). Categorizing groups into high-performance groups and low-performance groups allowed us to select balanced numbers of interviewees and compare the perceptions of students within those groups (more details about the distribution of the interviewers are described in the Qualitative Data Collection and Analysis section).
Second, we used final course grades to divide students into higher-, mid-, and lower-scorer categories. Students ranked in the highest 33% using ranked final course grades were categorized as higher scorers ( n = 82), those in the middle 33% as midscorers ( n = 79), and those in the lowest 33% as lower scorers ( n = 84). This allowed us to quickly identify students to interview to address question 1, which compared perceptions of higher- and lower-scoring students within groups, and question 2, which addressed the use of group-based support strategies before the end of the course. A breakdown of the distribution of students at high-, mid-, and low-scoring levels is outlined in Figure 1 . Eighty-seven percent of the groups contained a mixture of students of different scoring levels (heterogeneous), rather than containing students of similar scoring levels (homogeneous). All of the high-performance groups included at least one higher-scoring student, while only 10 of the 33 low-performance groups included at least one or two more higher-scoring students in their groups.

Most student groups, either high-performance (A) or low-performance (B), were composed of a mixture of high-, mid-, and low-scoring members and classified as heterogeneous (top row), 57/65 total groups. A much smaller number of groups (8/57) were homogeneous (bottom row) and were composed of either all high- (three groups), all mid- (one group), or all low-scoring students (four groups).
To test our research question 4, whether numeric peer-evaluation ratings served as a quantitative measure of students’ perceptions of their group members, we used the average ratings that students received to compare average ratings between high- and low-performance groups as well as high- and low-scoring students within those groups. To investigate the effects of group performance, we used a random effects model that can control for the variance associated with random factors that may occur during the interaction between students and groups ( Judd et al. , 2012 ). By using random effects for students in different groups, we controlled for the influence of different student interactions associated with group variables. In our model, we used the score gap between group and individual scores as a dependent variable and group performance levels as the fixed effects. To determine whether a relationship existed between peer-evaluation scores and individual test scores, we used a paired t test. A student’s peer-evaluation rating score was used as an independent variable, and individual test scores as a dependent variable.
Qualitative Data Collection and Analysis
We conducted in-depth interviews ( Esterberg, 2002 ) to explore the range of students’ perceptions, attitudes, and participation in group work in order to gain better insight into the briefer comments made on the peer evaluations. Appendix B in the Supplemental Material contains our interview protocol and question items. We recruited interviewees at the beginning of the last unit (unit 5). The first author (Y.C.) verbally recruited interviewees by announcing the interview in front of the class and sending out an email. The verbal and email announcements included information of the purposes and the foci of the study and the interview. From among 27 volunteers, the authors purposefully selected 15 interviewees to ensure that we had seven higher-scoring students and eight lower-scoring students based on their test scores. Among the seven higher scorers whom we interviewed, five were from high-performance groups and two were from low-performance groups. Among the eight lower scorers whom we interviewed, three were from high-performance groups and five were from low-performance groups. The number of high and low scorers selected for interviews was related to the proportion of these students in the respective groups (see Figure 2 for the group score distribution of the interviewers and Figure 1 for breakdown of student distribution in groups). Thirteen groups were represented in our student interviewees; three were homogeneous groups (composed of all lower scorers), while 10 were heterogeneous groups (with a mix of high, mid-, and low scorers). Interviewee profiles with pseudonyms to maintain students’ confidentiality are provided in Table 2 . Emerged themes and quotes are summarized in Table 3 .

Performance levels of high- and low-performance groups. To select a balanced numbers of high- and low-performance groups, we divided groups into higher (> 175) and low-performance groups (< 175) using the median (175). Equal numbers of interviewees were selected (dark blue) from both types of groups.
Interviewee profiles
H = Higher scorer, L = Lower scorer, HG = Higher-performing group, LG = Lower-performing group.
Excerpts per theme from in-depth interviews
Interview data were recorded, transcribed verbatim, and coded through multiple transcript readings by both authors. Specifically, we employed thematic analysis of the student interviews using ATLAS.ti v. 7.1 software. One researcher created a codebook related to how students perceived the group work and how it influenced their learning. Then the researchers worked together to refine the codebook and identify and characterize themes represented by the codes ( Braun and Clarke, 2006 ).
We were interested in determining how statements made during interviews might be represented in comments on student evaluations of their peers, and we also believed these comments could provide insight into how students gave feedback to their group members to answer research question 3. Triangulating data from various sources provided a mechanism to verify and support the breadth and overall representation of our understanding of what students meant in their comments ( Morse et al. , 2002 ). Students from 65 groups provided a total of 1341 entries on the midsemester and end-of-semester peer evaluations. We excluded 120 blank entries without text from further analysis. Of 26 students who failed to leave comments, seven were high-scoring students, nine were lower-scoring students, and 10 were midscorers. Most of the students (20) were from high-performance groups, and only three were from low-performance groups. We analyzed the remaining 1221 comments to provide insight into what students told their peers to help them improve group dynamics.
Because these comments could help determine whether or not students were taking advantage of this as a vehicle to express positive as well as negative perceptions, we began with categorizing a priori codes into three categories: positive, neutral, and negative indicators/experiences. We then added more a priori codes elicited from theoretical models of collaborative or cooperative learning that focused on explaining student motivation and engagement. For example, social interdependence theory ( Johnson and Johnson, 2009 ) was considered, because the analysis aimed to examine how student perceptions of group work could derive from both interactions between individual students and group-level attributes that support effective group work. A priori codes that reflected students’ perceptions of group work in peer-evaluation comments and interviews are represented in Appendix C in the Supplemental Material. We initiated the coding of peer-evaluation comments by using these codes and added emerging codes as necessary. The first author (Y.C.) initiated the analysis and then the second author (P.B.) reviewed the analysis. Initially, 21 codes, including 11 codes for positive perspectives and 10 codes for negative perspectives on collaborative learning, were used to analyze peer-evaluation comments. After the second author (P.B.) reviewed the codes, the codebook was modified and clarified through discussion. Two codes were merged in both the positive and negative perspectives, and three more codes were added. Finally, both authors reviewed the coding together, discussing and merging codes through consensus, and adding emergent codes as needed. Interrater reliability ( Cohen, 1968 ) between the two authors was achieved at 0.85, considered as very good strength of agreement ( Altman, 1991 ). Among all codes, 18 codes (10 positive, six negative, and two neutral) finally emerged from the analysis of peer-evaluation comments (Appendix C in the Supplemental Material).
Students in Both High- and Low-Performance Groups Valued the Social and Cognitive Support Provided by Groups.
Seven interviewees (four from high-performance groups and three from low-performance groups) mentioned the social and cognitive benefits of group work. Among four students in higher-performance groups, two were higher scorers and the other two were lower scorers. Ruth, like other students (even those in lower-performance groups), exhibited positive perceptions about the benefits of group work, saying, “Our group got along a lot better with just interacting with each other. I’ve definitely learned better in a group because I had the opportunity to kind of answer some of their questions which helps me understand it more.” Amy, a lower scorer in a higher-performance group, also described group work as “a nice little support system” that helped her to feel like she was “not alone in the class.” Ethan, another lower scorer in a higher-performance group, mentioned that having group members helped him to understand course concepts, as they “elaborated on the concept and went into a little deeper context with me and tried to explain in it my terms in a way that the teacher couldn’t because there is just so many people.” Higher scorers in higher-performance groups also acknowledged benefits of group work, as it allowed them to “have friends in the class who can discuss things with typical lectures” (Beth) and “study together to prepare for the exam” (Chen). (See Table 3 for additional interview excerpts for each theme.)
Students Assigned Roles Depending on Circumstances and Ignored Group Contracts.
We were interested in determining students’ perceptions of the support strategies (e.g., role assignment and creating and revising group contracts) used to increase individual accountability and appropriate use of social skills. In general, students did not perceive the support strategies as beneficial. Regarding assigning or rotating roles, roles were naturally assigned “with respect and making it fair” (Amy) and rotated. One interviewee mentioned, “ We always rotated who would actually compile all of the finished work and put it into a document and submit it to the class” (Jenn). None of the interviewees used role assignments consistently, citing a variety of reasons. Some groups felt they were unnecessary. “Our group didn’t really do the role assignments, it was just kind of ‘You get it this time, I’ll get it next time’” (Jenn). Others reported grappling with disorganized or absent students. “If you’re not communicating as well … you don’t get to do the part that you want to do” (Emma). “Even though we assign each other the role, not everybody follows it in a way and they usually forget about it, it’s not something they are used to having to do” (Min). Finally, some students expressed anxiety about assuming certain roles. “You were supposed to assign someone each of those jobs but I found it kind of limiting sometimes because … I got put as manager except I don’t like raising my hand and talking in front of people and this other guy in my group did and he knew a lot of the answers” (Beth). Another interviewee commented that with such a large class they “never really had to use that role because we weren’t really asked questions like in class about stuff” (Zoe).
In terms of the group contract, students described it as “another assignment that we had to do so we could leave” (Karen). Although some groups set punishment rules, such as “treat a coffee for all in the group if you missed a class without communication with group members” (Chen), group members reported that they rarely abided by the rules from their contracts. In fact, most of the groups (59 out of 65 groups) simply resubmitted their original contracts without revision at the midpoint of the semester, with only seven groups revising their contracts to provide better feedback to one another. One group revised their contract following discussion about lack of compliance with the initial contract. However, the group members still did not comply: “They all said, ‘Sure’ and then they don’t do it” (Min). We also found peer pressure was significant when it came to opting not to follow through on punishments or criticize group member’s behaviors. “I’d never tell these guys, because I didn’t want them to say something about me” (Ethan).
We did find that students perceived the group contract as useful when it came to setting up communication methods. For example, “we all got our phone numbers and everything” (Min) and “when missing a class, text to all” (Beth). However, in well-functioning groups, the group contract was not needed. Six interviewees, five from high-performance groups and one from a low-performance group, mentioned that their groups did not need to use the group contract, because they encountered few challenges. For example, members from high-performance groups agreed that “we know we would follow through when we had stuff and we never really had to use the group contract” (Brian). As one of the interviewees mentioned, “I think if there had been problems in our group, the contract would’ve been a bigger role” (Nora).
Students in Both High- and Low-Performance Groups Reported Social Loafing.
Regardless of group performance, most of the interviewees reported social loafing issues during group work that resulted in them having to assume responsibility for submitting work for others. Min, a higher-scoring student in a high-performance group, stated, “[My group members] just sent me all copy and paste. They didn’t do any research and follow any APA format. But they simply sent me the link of the resources and said, ‘here is the link.’ So I have to go back to the website that they’d found and had to summarize them.” Lower-scorer Ruth, who was in a low-performance group, commented that “it’s more difficult to get all the members to contribute equally especially if someone is … doing all the work and then other people feel like they can relax. You’re doing all the work and I can just sit back and get a hundred sort of like the prisoner effect.”
Student remarks differed when they described the same situation, one in which they had to take over and perform work to make up for noncontributing students. Min, a high-scoring student in a high-performance group, criticized other group members’ inadequate participation, even though her group achieved higher scores on group work. “Normally they don’t do the pre-quiz because it’s not for a grade. But like I do it just for my good, but they don’t. It feels like they don’t care and know I’ll do it anyway” (Min). While Ruth, a lower scorer in a lower-performance group described her experience as “getting sucked into all of the group work.” Hard-working students reported experiencing the “sucker effect,” in which they began to pull back on the amount of work they contributed to force noncontributing members to work: “We were like ‘We’ll say we don’t understand this part so she can do it’ and then she like didn’t know and just held it until the end of the class and was like, ‘I don’t get it’… and so my friend got kind of bothered and she snatched it from her and did it” (Monica).
Perceptions of the Value of Group Activities Differed between High- and Low-Scoring Students.
We found that three of the seven higher-scoring students interviewed, two from high-performance groups and one from a low-performance group, remarked that they found group activities were critical for their learning and that they provided an opportunity to apply what they learned from lecture to their real life. For example, Beth, who was a higher scorer, reported that group work was “more real-life situations which I found interesting because it was more relatable and like scientific theories that would apply to you … based on how it would affect something in real life.” Six of the seven lower scorers interviewed, in both high- and low-performance groups, tended to perceive group activities as time-consuming. For example, Jenn asked, “Why do that and spend an hour going through all of that stuff when I could just finish it in ten minutes?” She felt, “It was like a stumbling around so that didn’t really help with the learning.” Zoe, another lower scorer, echoed this sentiment, describing group work as “something [that] doesn’t seem very important and sound[s] silly,” and said, “I don’t see any relationship with my real life.”
High- and Low-Performance Groups Left Very Similar Comments on Peer Evaluations.
We compared patterns observed between the overall frequency of peer-evaluation comments (positive or negative, as well as those expressing specific ideas) between students in high- and low-performance groups. We calculated the frequency of the code by total number of submitted comments. We found that there was no statistically significant association between group performance levels and the trends on the positive or negative comments; x 2 (34) = 30.78, p = 0.626. In addition, regardless of group performance levels, three categories of ideas were commonly expressed (appearing in more than 10% of all comments) in both groups in both the first and second peer-evaluation surveys ( Figure 3 ). A fourth and fifth category did differ in its frequency between groups of different performance levels, which we will describe later. No distinctive patterns were found in the comments categorized as no responses or not applicable.

Frequency comparison for the top four ideas provided as anonymous comments on peer evaluations. Student groups were categorized as higher-performing ( n = 32) and lower-performing ( n = 33) based on the rank-ordered group assignment scores and averaged group test scores. A total of 1221 comments on peer evaluations were coded using 21 a priori categories. Each number (%) in the figure is calculated as the frequency of the code/total numbers of submitted comments.
The most common idea mentioned (>55% of all codes present) in peer evaluations involved individual accountability. Individual accountability involves students completing their own work (personal accountability) and facilitating other students completing their work (accountability to the group; Johnson et al. , 2014 ). Students mentioned aspects that reflected positively on their peers: “always doing her part,” “completing assigned works in a timely and efficient manner,” and “pulls his weight and helps with all group work.” See Appendix C in the Supplemental Material for additional codes, summaries of ideas represented in those codes, and example quotes. We found that comments about individual accountability were equally predominant in high- and low-performance groups and at the midpoint and endpoint of the semester (χ 2 = 4, p = 0.261).
The second most prevalent idea that emerged in peer-evaluation comments concerned the cognitive learning supports provided by peers (22–31% of comments contained this idea). Students seemed to appreciate aspects of the promotive interactions mentioned by Johnson et al. (2014) that enhanced social constructivism, such as engaging in a dialogue with their peers to ask and answer questions, share reasoning, and build upon each other’s understanding until they reach mutual agreement ( Phelps and Damon, 1989 ; Slavin, 1991 ). Student evaluation comments mentioned students “explaining difficult concepts” or a peer “helps us understand” or “takes the time to learn the material so she can teach others.” The degree to which students mentioned learning supports appeared to differ between higher- and low-performance groups when comparing the midpoint to endpoint survey, but these differences were not significant (χ 2 = 3, p = 0.223).
The third most frequent idea that emerged in the peer-evaluation comments concerned students providing procedural support. This idea was present in more than 17% of all comments. However, there was no statistical difference between high- and low-performance groups mentioning procedural support (χ 2 = 4, p = 0.261). Procedural support involved helping to complete steps to finalize a task that were not connected to cognitive activities but aided in making decisions and completing assignments in a timely manner. Examples of comments that were coded for procedural support mentioned their peers helping to “keep everyone focused and turn in our papers at the end of class” or being “very organized and keeps the group on track, schedules group meetings.”
The fourth most frequent idea that was mentioned differed depending on the time of the semester the evaluation was given and the performance level of the group. At the midpoint of the semester, the fourth most frequent idea mentioned in high-performance groups involved social/interpersonal communication skills (10.3% of comments). This idea included the ability to get along with group members and communicate effectively, for example, “displays a positive attitude and is very encouraging,” “easy to talk to and easy to get along,” and “very flexible and open to everyone’s contributions and a fun person to have in the group.” Social perceptiveness has emerged as a major factor in predicting group performance ( Woolley et al. , 2015 ). Interestingly, social/interpersonal communication was not a frequent idea mentioned in low-performance groups until the end of the semester. In those groups, the fourth most frequent type of comment left at the midpoint was to not leave any comment at all (13% of comments left in low-performance groups were left intentionally blank). By the end of the semester, social/interpersonal skills rose in its frequency to become the fourth most frequent code mentioned in evaluations from students in low-performance groups (10.3% in the end-of-semester peer evaluations).
Students in high- and low-performance groups also differed in the degree to which they mentioned that their peers provided positive interdependence, with promoting the group’s success by working together seen as a fifth frequent idea. Calculating the percentage of frequency of the positive interdependence code by the total number of submitted comments, students in high-performance groups mentioned positive interdependence in 12% of all comments on the final peer evaluation, up from only 6% on the midsemester evaluation. Lower-performance groups mentioned positive interdependence on the midsemester evaluations (7% of comments); however, this level dropped to less than 2% of the final evaluation.
When comparing comments between heterogeneous groups of either higher- or lower-performance levels, we found that students in heterogeneous groups leave more comments with a negative perspective (31.25% on midpoint evaluation and 28.57% on final evaluation) compared with homogeneous groups (nothing on mid and 18.18% on final), regardless of the timing of the evaluation.
Influence of Group Work on Individual Learning Achievement within Groups.
We compared the mean score differences between group and individual test scores in units 1 and 4 to understand the influence of group work on individual learning. The random intercepts model results show that group performance levels influenced score differences between individual and group tests from unit 1 and unit 4. As shown in Table 4 , both high- and low-performance groups actually decreased the mean score differences between group and individual test scores from unit 1, F (1, 122) = 19.83, p < 0.005, to unit 4, F (1, 100.72) = 20.29, p < 0.005. In unit 1, the main effect of group performance levels on mean score differences between individual and group test scores are significant ( p < 0.005), estimating that the mean score differences of high-performance groups are 12.92 (SE = 2.68) higher than those of low-performance groups. In unit 4, the estimated mean score differences of high-performance groups are 11.85 (SE = 2.9) higher than those of low-performance groups.
Estimates of fixed effects of score gap between group and individual scores in units 1 and 4
Within groups, high-performance group score differences decreased significantly from unit 1 (M = −12.04, SE = 1.83) to unit 4 (M = −6.78, SE = 1.70), p < 0.005. Low-performance groups also decreased from unit 1 (M = 24.96, SE = 2.26) to unit 4 (M = 18.63, SE = 2.10). However, high-performance groups demonstrated a greater reduction (43.7%) in the learning gap between group members compared with low-performance groups (25.3%).
Peer-Evaluation Ratings: Indicative of Performance but Possibly Biased
We found that, when students were asked to provide quantitative ratings of their peers, the ratings differed based on their groups’ level of performance, F (1, 164) = 12.97, p < 0.001. In groups ranked as higher performing, students gave higher mean peer ratings to group members (M = 102.63, SD = 5.83) than students in low-performance groups (M = 92.32, SD = 19.15). As shown in Figure 4 , in terms of individual differences between group members, t tests revealed statistically significant differences, t (166) = −20.21, p < 0.001, r = 0.32. Students who earned lower test scores received higher mean peer-evaluation ratings when they were in high-performance groups (M = 101.21, SD = 1.99) rather than in low-performance groups (M = 86.96, SD = 25.63). Higher scorers received relatively similar peer-evaluation ratings from both high-performance groups (M = 101.78, SD = 5.96) and low-performance groups (M = 97.35, SD = 7.04). This resulted in greater mean score differences between higher and lower scorers in low-performance groups (mean score differences = 14.25) than between higher and lower scorers in high-performance groups (mean score differences = 5.53). In other words, students in low-performance groups were holding lower-scoring students to a greater degree of accountability on peer ratings than lower scorers in high-performance groups.

Peer-evaluation ratings and group performance. The average numerical ratings (out of 100) that students wrote on peer evaluations differed for high- and low-performance groups. The average rating for all students in high-performance groups (M = 102.63, SD = 5.83) was higher than students in low-performance groups (M = 92.32, SD = 19.15). Lower-scoring students received higher mean peer-evaluation ratings when they were in high-performance groups (M = 101.21, SD = 1.99) than in low-performance groups (M = 86.96, SD = 25.63). Higher scorers received relatively similar peer-evaluation ratings from both high-performance groups (M = 101.78, SD = 5.96) and low-performance groups (M = 97.35, SD = 7.04), t (166) = −20.21, p < 0.001, r = 0.32).
To understand group work in a real-world classroom setting, we conducted our study in a classroom that allowed students to self-assemble into groups. We conducted a mixed-methods analysis to investigate how students’ personal scoring in the course and their groups’ levels of performance on group tasks affected their perception of group activities. Much of a student’s individual performance was calculated after group work occurred. Group and individual performance, though, may not be completely independent of each other, because students who score highly on individual tests could have an increased effect on their groups’ scores on assignments and tests, and groups that worked well together could have had a positive effect on individual grades. Collection of an initial independent measure of a student’s abilities (e.g., grade point average [GPA] or pretest scores) or analysis of discourse practices during group work would be needed to further elucidate the relationship between individual ability on group performance. We also interviewed students on their use of strategies such as role assignment and group contracts, and we compared the comments and ratings from anonymous peer evaluations to determine what differences could be observed between high- and low-performance groups. We found that, regardless of group performance levels, salient elements that might affect students’ perceptions of the group work emerged. We did find differences in perceptions of group work, some comments on peer evaluations, and ratings between individuals. Our hope was to uncover factors that could explain why groups might not be working effectively and to provide faculty with a better mechanism to identify and solve group problems. However, we did not conduct empirical tests for these observations, so we will use our results to suggest future research to expand on our findings.
Without Supervision, Students Fail to Use Role Assignment and Group Contracts to Their Fullest
In our study, students were asked to self-assign to specific roles and rotate the roles within the group activities in a very large classroom without supervision (either from undergraduate peers or graduate students). It has been reported that structured discussion with role assignment enhances students’ engagement in interactive information sharing ( Mesmer-Magnus and DeChurch, 2009 ), knowledge construction, knowledge transfer ( Kane et al. , 2002 ), and equitable participation ( Savadori et al. , 2001 ). In the in-depth interviews, however, students did not report engaging in what Chan (2001) described as detailed “problem-centered” discourse that involved recognition of the problem, formulation of questions, and construction of explanations. Instead, they reported that they felt that they did not need official roles. Some students struggled assigning roles to absent or inactive members, and other students commented that certain roles were never used because of the number of groups and the difficulty hearing ideas from all groups during class discussion. Instead, they reported using roles to subdivide labor, merging individual contributions to a final document without critically evaluating members’ submissions, failing to communicate, and completing a task at the very last minute so that it could not be reviewed by all group members (see comments in Students in Both High- and Low-Performance Groups Reported Social Loafing ). All these obstructions to the collaboration process erode the sense of trust needed for the social interactions required for social interdependence. Students in our groups were only provided with brief descriptions of what group roles entailed and were not explicitly trained to use roles effectively. Several research groups have attempted to test the effect of providing scripts to enhance students’ use of cognitive prompts during group work ( O’Donnell, 1996 ; Gillies, 2003 ; Brewer and Klein, 2006 ). It would be interesting to determine whether these scripts can be useful in the very large lecture settings we encountered.
Group contracts provide a mechanism to initiate discussion of expectations and reservations, to strengthen social skills, and to build interpersonal relationships critical to effective group work ( Oakley et al. , 2004 ; Davies, 2009 ; Shimazoe and Aldrich, 2010 ). It is clear from our interviews, however, that students did not view the completion of a group contract as a significant vehicle to strengthening interdependence or other key social skills. They felt the assignment was cursory, just something to be completed without depth of thought. Student teams become progressively more collaborative and productive over time ( Hong et al. , 2014 ), with successful teams demonstrating constant levels of socioemotional and procedural support ( Kwon et al. , 2014 ). So, rather than assigning a simple contract at the beginning of the course, instructors may need to provide more opportunities for deeper interactions that build trust and a sense of belonging ( Kreijns et al. , 2003 ), to be conscious of the fact that trust can be easily eroded when members lower their individual participation and commitment toward quality work ( Kreijns et al. , 2003 ), and to provide greater opportunities for identifying and resolving conflict ( Brooks and Ammons, 2003 ). We found that students were not relying on group contracts to set punishments for lack of participation and that other mechanisms need to be employed to help groups resolve conflicts (see Peer Ratings May Be Biased against Low-Scoring Students in Low-Performance Groups ). An alternative assignment with more utility might be to engage in an initial team-building activity in which students share contact information to begin to build socioemotional interactions like getting to know one another by sharing hobbies, interests, and experiences ( Oakley et al. , 2004 ). Researchers could test the efficacy of such an assignment using measures like the Team Interdependence ( Van der Vegt et al. , 2001 ), Team Cohesiveness ( Carless and De Paola, 2000 ), or Psychological Safety ( Edmondson, 1999 ) surveys.
Peer-Evaluation Comments Are Not Useful for Identifying Group Dysfunction
Anonymous peer evaluations have been suggested as a method for identifying inequity and other problematic group issues ( Wenzel, 2007 ; Aggarwal and O’Brien, 2008 ). Peer evaluations have been shown to reduce the incidence of free riding and to improve student attitudes toward groups and group projects if they are done early and frequently ( Feichtner and Davis, 1984 ; Brooks and Ammons, 2003 ). Using performance on group assessments to identify high- and low-performance groups, we asked whether performance could be differentiated using responses to students’ peer-evaluation comments and numerical ratings. We also used students’ responses to in-depth interviews to provide context and explanations for our observations. Several assumptions may limit our findings: We must assume that students were willing to communicate honestly about problems that were occurring during group work. We also must rely on students’ ability to recognize what constitutes effective group functioning. Also, we assume that, because a group is performing well on assignments, they are functioning better than a group that is not earning high scores on group assignments and tests. It is possible that high-performance groups do better on assignments because one high-scoring student has taken on more of the responsibility. However, it is clear from our analysis of how the score gap between individual and group tests is minimized in high-performance groups ( Table 4 ) that learning as measured by the level of scoring on individual tests improves for low-scoring members of these groups. This study does not clarify the reason for this improvement, but high-performance groups had a higher percentage of high-scoring students, so access to these students could be one important variable. With this in mind, we were surprised that comments on anonymous peer evaluations do not adequately distinguish between high- and low-performance groups, considering that the major comment codes were similar in both these groups at the middle and end of the semester, with only a few subtle differences. The data did, however, spur us to hypothesize that one of the major differences between high- and low-performance groups may derive from student attitudes and appreciation of the value of group work to their learning overall.
We found that all groups, regardless of their success, clearly viewed individual accountability as their basic responsibility as a group member. This constituted the most frequent comment in peer evaluations from both high- and low-performance groups at both the midpoint and end of the semester. Individual accountability, although critical and mentioned as the primary comment in peer-evaluation comments, should be seen as a minimal requirement for effective group work. In well-designed group work, task assessments and grading for individual contribution play a greater role in promoting and enforcing individual accountability than self-regulation from group members. From a cognitive learning perspective, consensus building and coconstruction of knowledge ( Solomon, 1987 ; Latour and Woolgar, 2013 ) constitute a more effective method for enhancing learning during group work than promoting completion of tasks by divvying up the work. Students bring misconceptions about their fellow students’ attitudes and abilities to group work that prevent them from distinguishing peers who were deliberately failing to contribute from peers who were struggling academically and contributing to the best of their abilities ( Freeman and Greenacre, 2011 ). Without some clarity, peer evaluations can reinforce these attitudes. Providing students with a more careful evaluation of cognitive behaviors (e.g., asking to list individual efforts toward completing group activities such as editing, writing portions, finding references) and creating task structures that ensure that students provide explanations or elaborations could help produce more turn-taking, productive discourse, and appreciation that students bring varying levels of expertise and contributions to understanding. Student groups that exhibit networks of communication with frequent interpersonal interactions exhibit higher cognitive complexity and performance overall ( Curs¸eu et al. , 2012 ).
It is interesting that peer-evaluation comments related to communicating effectively were less frequently observed in lower-performance groups. Students in lower-performance groups do eventually mention this, but not until later in the semester. In addition to communication, students in high- and low-performance groups expressed an appreciation for the value and importance of positive interdependence in comments on midsemester evaluations. However, students in low-performance groups were less likely to mention positive interdependence in the end-of-semester evaluations. Reliance on group members to achieve common goals has been consistently identified as a critical factor in increasing collaboration, and its effect on achievement ( Slavin, 1991 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ; Johnson et al. , 2007 ; Scager et al. , 2016 ). High-performance groups may work better because they perceive the value of group work from the beginning of the course and recognize their group members for providing features of learning support, communication, and positive interdependence ( Kwon et al. , 2014 ). The absence of comments about positive interdependence in low-performance groups at the end-of-semester evaluations is not unexpected: they were not performing effectively on assignments. However, in considering the implications for instructors, these are not the comments that are showing up most frequently, so it would be hard to identify dysfunctional groups using this feature.
There are several limitations to our findings, and additional research is needed to corroborate the correlations we observed between these self-report measures and academic performance. Our finding that lower-scoring students are critical of group work comes from interview data. It would be interesting to extend our work by surveying an entire course with a group-work satisfaction survey to determine whether our findings extend to all students within the course. We did not ask students to provide detailed self-reports on their own contributions to each assignment. These may prove useful for further studies that could compare individual self-reports (self-evaluations) with anonymous peer evaluations to correlate with individual and group performance measures. Interview and reflection journals may also prove important in determining the extent to which self-report indicators can be employed with either individual or consensus self-assessment measures. Instructors could then provide adaptive scaffolding to support students’ monitoring and reflection on their learning depending on the progress of group work. For example, when groups perform poorly, instructors would be able to provide extra procedural support (e.g., providing a checklist, suggesting using track-changes options to record individual contributions) or strategic support (e.g., providing summary notes or extra review sessions).
In addition to their ineffectiveness at identifying group dysfunction, peer evaluations may negatively impact how students interact with one another. During the interviews, students reported that they were concerned about the possibility of their identities being revealed in their peer-evaluation comments and that this would negatively affect their group relationships. It is obvious that students experienced peer pressure even with an online peer-evaluation system designed with a confidential log-in system to ensure anonymity.
As Bacon et al. ’s (1999) study indicated, use of evaluations can be negatively associated with good team experiences. Strong and Anderson (1990) observed that students preferred other factors—including group cohesiveness, small team size, the option to divorce a team member, or the option to leave a team—as stronger countermeasures for reducing free riding.
Peer Ratings May Be Biased against Low-Scoring Students in Low-Performance Groups
We also examined the numerical ratings that students provided for one another as a summative assessment of their effort on group work throughout the semester. This reward or punishment system is designed to deter social loafing, to motivate individual students to enhance their performances, and to account for inequities in students’ contributions. Students’ most common complaints about group work involve uneven contributions from group members ( Livingstone and Lynch, 2000 ; Aggarwal and O’Brien, 2008 ; Pauli et al. , 2008 ; Shimazoe and Aldrich, 2010 ; Hall and Buzwell, 2012 ). However, there are several problems with using peer ratings to evaluate contributions. First, students have expressed discomfort using ratings that they view as criticizing their friends ( Williams, 1992 ). Student raters may not have the ability to distinguish between high and low contributions, and their ratings may be influenced by their own experiences and norms within their groups ( Loughry et al. , 2007 ). Underperforming students tend to over- or underrate their individual progress, need for support, and understanding ( Winne and Jamieson-Noel, 2002 ). Students often resort to giving all students equal marks on a holistic evaluation compared with a categorical evaluation that queries about individual skills ( Lejk and Wyvill, 2001 ), and unadjusted ratings that students receive from their peers do not correlate with course grades ( Zhang and Ohland, 2009 ). Finally, students within a group may intentionally inflate or reduce the contribution of members due to friendship ( Zhang et al. , 2008 ).
We found that the ratings students gave their peers did correlate with group performance: high-performance groups gave higher ratings to their members compared with low-performance groups. So, groups were clearly using ratings in a small way to indicate poor performance, but their use may only be accurate for high-scoring students who received high ratings in both higher- and low-performance groups. Ratings may not provide an unbiased measure of individual effort or accountability for lower-scoring students, who were more likely to receive lower peer ratings in low-performance groups relative to lower-scoring students in high-performance groups. In the successful student groups that Scager and colleagues (2016) interviewed, students expressed a sense of empathy for their peers who contributed less, noting that it may have been “beyond (their) capabilities at that point.” This may echo what we have seen in our analysis of peer ratings. High-scoring students in high-performance groups may recognize that their lower-scoring peers are simply contributing to the level of their ability. It was clear from their peer-evaluation comments that students in high-performance groups value communication and the sense of communal effort that is afforded by positive interdependence to a greater degree than students in low-performance groups. It is also possible that lower-scoring students in low-performance groups actually participate less than those in high-performance groups and actually earn those lower scores. Considering that students in both high- and low-performance groups complained of social loafing and free riding in interviews and that there are discrepancies within ratings for low-scoring students, there are clearly problems with using peer ratings to evaluate contributions to group work.
Alternative measures may be required to ensure equitable assignment of group contributions to account for biases in peer ratings. We used the expected contributions adjustment to modify group scores based on peer ratings. However, Zhang and Ohland (2009) found this to have higher absolute error and low correlation with true contribution to the team as measured by Monte Carlo simulations or actual class data. They recommend using a between-group difference adjustment that compares students to other students in matched performance groups, explaining that “as peer and self ratings are related to the quality of group work, ratings from groups with different group scores are not directly comparable” ( Zhang and Ohland, 2009, p. 295 ). This is only a partial solution to the problems mentioned earlier. It may also be useful to ask students to specify the cognitive and functional efforts contributed by each group member on each assignment (e.g., an acknowledgments section in which they select from a list of tasks, including conducting a literature search, writing, creating figures, and editing). This could be very effective if students are also asked to reflect qualitatively on the social support (motivation, response to criticism, adaptability, creativity, and attitude) provided by members of their group.
For instructors with extremely limited time, there are also several scales specifically developed to identify conflict ( Jehn and Mannix, 2001 ) or satisfaction ( Van der Vegt et al. , 2001 ) in student teams. These may be a quick way to identify problems in the early stages of group work. Organizations can provide resources for managing team conflict ( Manktelow et al. , 2017 ), and there is evidence that conflict management can improve team performance, even in student teams ( Tekleab et al. , 2009 ). Assigning group members descriptions of group dysfunction and asking students to identify strategies for solving the problem as a way to mediate their own conflicts ( Lerner, 1995 ) or training students in reflexivity ( O’Neill et al. , 2017 ) could provide mechanisms for groups to resolve conflicts before they result in dysfunction.
Are Time-Consuming Strategies That Facilitate Group Work Worth All the Effort?
In this study, we discovered that students of all abilities valued group work for various reasons in addition to how it benefited their learning. In student interviews, we observed that only about one out of seven lower-scoring students perceived group work and instructional facilitating activities to be beneficial for their learning performance (compared with three of seven high-scoring students). Lower-scoring students commented that they found group work to be beneficial primarily as a comfort zone or the incentive for them to go to class because they have friends to talk with. Motivation and social cognition are important mediators of group work ( Slavin, 2014 ). Researchers have suggested that the quality of interactions between group members may be more predictive of learning gains than ability grouping and have recommended that an individual student’s attitude, motivation, or personality traits may provide a better predictor of group success than cognitive ability alone ( Webb et al. , 2002 ; Woolley et al. , 2010 ). In laboratory simulations of group work in which students are tasked with solving visual puzzles, brainstorming, making collective moral judgments, and negotiating limited resources, Woolley and colleagues (2010) have identified a single latent factor they call general collective intelligence—supported by strong interitem correlation on different tasks—that strongly predicts the groups’ ability to solve tasks. Collective intelligence appears to depend both on the composition of the group (e.g., average member intelligence and, more importantly, social sensitivity) and how group members interact when they are assembled (e.g., their conversational turn-taking behavior). Groups in which a few people dominated the conversation were less collectively intelligent than those with a more equal distribution of conversational turn-taking ( Woolley et al. , 2010 ). This was substantiated recently in a study that demonstrated that students who indicate higher levels of comfort with their group members achieve higher learning gains, whereas lower learning gains occur in groups with a reported conversation dominator ( Theobald et al. , 2017 ). Because we allowed students to self-select in this study, it is possible that purposeful group composition may yield different results, as peer relationship can be used as a predictor of student performance within a group ( Klein and Mulvey, 1995 ; Chung et al. , 2018 ). It would be interesting to examine the role of social sensitivity, beliefs about learning, friendship, and social skills such as conversational turn-taking as predictors of group performance in the college science, technology, engineering, and mathematics classroom. Also, as one of the goals of this study is to understand the effectiveness of group work in an uncontrolled classroom, we did not measure students’ prior knowledge levels (e.g., Scholastic Aptitude Test scores, college GPA, pretest). To further investigate the influence of the specific group-based activity, we recommend administering pre- and posttests.
We found that, regardless of group composition or group performance level, students were likely to report positive experiences with group members. When group members function interdependently, collective efficacy beliefs have been shown to provide a greater impact on performance: groups with higher self-efficacy beliefs were more likely to encourage group members to use resources more effectively ( Bandura, 2001 ) and to engage in higher-quality discussions ( Wang and Lin, 2007 ). Thus, the establishment of collective group efficacy may be well worth the effort to promote group-learning performance ( Gully et al. , 2002 ).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments.
We acknowledge continuing support and feedback from the University of Georgia SEER (Scientists Engaged in Education Research) Center. Permission to survey and audio-record students was obtained from the University of Georgia Institutional Review Board (STUDY2013104060 and MOD00000647).
- Aggarwal P., O’Brien C. L. (2008). Social loafing on group projects: Structural antecedents and effect on student satisfaction . Journal of Marketing Education , ( 3 ), 255–264. [ Google Scholar ]
- Altman D. G. (1991). Practical statistics for medical research . London: Chapman and Hall. [ Google Scholar ]
- American Association for the Advancement of Science. (2010). Vision and change: A call to action . Washington, DC: Retrieved August 24, 2018, from www.visionandchange.org/VC_report.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Armstrong N., Chang S.-M., Brickman M. (2007). Cooperative learning in industrial-sized biology classes . CBE—Life Sciences Education , ( 2 ), 163–171. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bacon D. R., Stewart K. A., Silver W. S. (1999). Lessons from the best and worst student team experiences: How a teacher can make the difference . Journal of Management Education , ( 5 ), 467–488. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bailey C. P., Minderhout V., Loertscher J. (2012). Learning transferable skills in large lecture halls: Implementing a POGIL approach in biochemistry . Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education , ( 1 ), 1–7. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura A. (2000). Exercise of human agency through collective efficacy . Current Directions in Psychological Science , ( 3 ), 75–78. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura A. (2001). Social cognitive theory: An agentic perspective . Annual Review of Psychology , , 1–26. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barkley E. F., Cross K. P., Major C. H. (2014). Collaborative learning techniques: A handbook for college faculty . Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barr D. A., Gonzalez M. E., Wanat S. F. (2008). The leaky pipeline: Factors associated with early decline in interest in premedical studies among underrepresented minority undergraduate students . Academic Medicine , ( 5 ), 503–511. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bartlett R. L. (1995). A flip of the coin—a roll of the die: An answer to the free-rider problem in economic instruction . Journal of Economic Education , ( 2 ), 131–139. [ Google Scholar ]
- Batz Z., Olsen B. J., Dumont J., Dastoor F., Smith M. K. (2015). Helping struggling students in introductory biology: A peer-tutoring approach that improves performance, perception, and retention . CBE—Life Sciences Education , ( 2 ), ar16. 10.1187/cbe.14-08-0120 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beichner R. J., Saul J. M., Abbott D. S., Morse J. J., Deardorff D., Allain R. J., Risley J. S. (2007). The student-centered activities for large enrollment undergraduate programs (SCALE-UP) project . Research-Based Reform of University Physics , ( 1 ), 2–39. [ Google Scholar ]
- Braun V., Clarke V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology . Qualitative Research in Psychology , , 77–101. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brewer S., Klein J. D. (2006). Type of positive interdependence and affiliation motive in an asynchronous, collaborative learning environment . Educational Technology Research and Development , ( 4 ), 331–354. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brickman P., Gormally C., Francom G., Jardelezz S. E., Schutte V. G. W., Jordan C., Kanizay L. (2012). Media-savvy scientific literacy: Developing critical evaluation skills by investigating scientific claims . American Biology Teacher , ( 6 ), 374–379. 10.1525/Abt.2012.74.6.4 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brooks C. M., Ammons J. L. (2003). Free riding in group projects and the effects of timing, frequency, and specificity of criteria in peer assessments . Journal of Education for Business , ( 5 ), 268–272. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown P. J. (2010). Process-oriented guided-inquiry learning in an introductory anatomy and physiology course with a diverse student population . Advances in Physiology Education , ( 3 ), 150–155. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carless S. A., De Paola C. (2000). The measurement of cohesion in work teams . Small Group Research , ( 1 ), 71–88. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chan C. K. K. (2001). Peer collaboration and discourse patterns in learning from incompatible information . Instructional Science , ( 6 ), 443–479. 10.1023/A:1012099909179 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chang M. J., Eagan M. K., Lin M. H., Hurtado S. (2011). Considering the impact of racial stigmas and science identity: Persistence among biomedical and behavioral science aspirants . Journal of Higher Education , ( 5 ), 564–596. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chang Y., Hannafin M. J. (2015). The uses (and misuses) of collaborative distance education technologies . Quarterly Review of Distance Education , ( 2 ), 77–92. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chapman K. J., Van Auken S. (2001). Creating positive group project experiences: An examination of the role of the instructor on students’ perceptions of group projects . Journal of Marketing Education , ( 2 ), 117–127. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chung S., Lount R. B., Jr., Park H. M., Park E. S. (2018). Friends with performance benefits: A meta-analysis on the relationship between friendship and group performance . Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , ( 1 ), 63–79. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen J. (1968). Weighted kappa: Nominal scale agreement with provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit . Psychological Bulletin , , 213–220. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Couch B., Brown T., Schelpat T. J., Graham M. J., Knight J. K. (2015). Scientific teaching: Defining a taxonomy of observable practices . CBE—Life Sciences Education , ( 1 ), ar9. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell J. W. (2009). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research . Los Angeles: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Crouch C. H., Mazur E. (2001). Peer instruction: Ten years of experience and results . American Journal of Physics , ( 9 ), 970–977. [ Google Scholar ]
- Curşeu P. L., Janssen S. E., Raab J. (2012). Connecting the dots: Social network structure, conflict, and group cognitive complexity . Higher Education , ( 5 ), 621–629. [ Google Scholar ]
- Davies W. M. (2009). Groupwork as a form of assessment: Common problems and recommended solutions . Higher Education , ( 4 ), 563–584. [ Google Scholar ]
- Deutsch M. (1949). A theory of cooperation and competition . Human Relations , , 129–152. [ Google Scholar ]
- Edmondson A. (1999). Psychological safety and learning behavior in work teams . Administrative Science Quarterly , ( 2 ), 350–383. [ Google Scholar ]
- Esterberg K. G. (2002). Qualitative methods in social research . Boston: McGraw-Hill. [ Google Scholar ]
- Falchikov N., Goldfinch J. (2000). Student peer assessment in higher education: A meta-analysis comparing peer and teacher marks . Review of Educational Research , ( 3 ), 287–322. [ Google Scholar ]
- Feichtner S. B., Davis E. A. (1984). Why some groups fail: A survey of students’ experiences with learning groups . Journal of Management Education , ( 4 ), 58–73. [ Google Scholar ]
- Freeman L., Greenacre L. (2011). An examination of socially destructive behaviors in group work . Journal of Marketing Education , ( 1 ), 5–17. [ Google Scholar ]
- Freeman S., Eddy S. L., McDonough M., Smith M. K., Okoroafor N., Jordt H., Wenderoth M. P. (2014). Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA , ( 23 ), 8410–8415. 10.1073/pnas.1319030111 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gillies R. M. (2003). Structuring Cooperative Group Work in Classrooms . International Journal of Educational Research , ( 1–2 ), 35–49. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gully S. M., Incalcaterra K. A., Joshi A., Beaubien J. M. (2002). A meta-analysis of team-efficacy, potency, and performance: Interdependence and level of analysis as moderators of observed relationships . Journal of Applied Psychology , ( 5 ), 819–832. 10.1037/0021-9010.87.5.819 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hall D., Buzwell S. (2012). The problem of free-riding in group projects: Looking beyond social loafing as reason for non-contribution . Active Learning in Higher Education , , 37–49. [ Google Scholar ]
- Handelsman J., Ebert-May D., Beichner R., Bruns P., Chang A., DeHaan R., Wood W. B. (2004). Scientific teaching . Science , ( 5670 ), 521–522. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harkins S. G., Jackson J. M. (1985). The role of evaluation in eliminating social loafing . Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , ( 4 ), 457–465. 10.1177/0146167285114011 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Heller P., Hollabaugh M. (1992). Teaching problem solving through cooperative grouping. Part 2: Designing problems and structuring groups . American Journal of Physics , ( 7 ), 637–644. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hernandez P. R., Schultz P. W., Estrada M., Woodcock A., Chance R. C. (2013). Sustaining optimal motivation: A longitudinal analysis of interventions to broaden participation of underrepresented students in STEM . Journal of Educational Psychology , ( 1 ), 89–107. 10.1037/A0029691 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hong H. Y., Chang Y. H., Chai C. S. (2014). Fostering a collaborative and creative climate in a college class through idea-centered knowledge-building . Instructional Science , ( 3 ), 389–407. 10.1007/s11251-013-9289-y [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jehn K. A., Mannix E. A. (2001). The dynamic nature of conflict: A longitudinal study of intragroup conflict and group performance . Academy of Management Journal , ( 2 ), 238–251. [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson D. W., Johnson R. T. (2009). An educational psychology success story: Social interdependence theory and cooperative learning . Educational Researcher , ( 5 ), 365–379. [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson D. W., Johnson R. T., Smith K. (2007). The state of cooperative learning in postsecondary and professional settings . Educational Psychology Review , ( 1 ), 15–29. [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson D. W., Johnson R. T., Smith K. A. (1998). Cooperative learning returns to college: What evidence is there that it works ? Change , ( 4 ), 26–35. [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson D. W., Johnson R. T., Smith K. A. (2000). Constructive controversy: The educative power of intellectual conflict . Change , ( 1 ), 28–37. [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson D. W., Johnson R. T., Smith K. A. (2014). Cooperative learning: Improving university instruction by basing practice on validated theory . Journal on Excellence in University Teaching , ( 4 ), 1–26. [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnston L., Miles L. (2004). Assessing contributions to group assignments . Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , ( 6 ), 751–768. [ Google Scholar ]
- Judd C. M., Westfall J., Kenny D. A. (2012). Treating stimuli as a random factor in social psychology: A new and comprehensive solution to a pervasive but largely ignored problem . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , ( 1 ), 54–69. 10.1037/a0028347 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kane A., Argote L., Levine J. M. (2002). Social identity and knowledge transfer between groups . In Annual Meeting of the Academy of Management, Denver, CO . [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaufman D. B., Felder R. M., Fuller H. (2000). Accounting for individual effort in cooperative learning teams . Journal of Engineering Education , ( 2 ), 133–140. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kilic G. B., Cakan M. (2006). The analysis of the impact of individual weighting factor on individual scores . Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , ( 6 ), 639–654. [ Google Scholar ]
- Klein H. J.,, Mulvey P. W. (1995). Two investigations of the relationships among group goals, goal commitment, cohesion, and performance . Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes , ( 1 ), 44–53. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kreijns K., Kirschner P. A., Jochems W. (2003). Identifying the pitfalls for social interaction in computer-supported collaborative learning environments: A review of the research . Computers in Human Behavior , ( 3 ), 335–353. PIi S0747-5632(02)00057-2 Doi 10.1016/S0747-5632(02)00057-2 [ Google Scholar ]
- Kruskal W. H.,, Wallis W. A. (1952). Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis . Journal of the American Statistical Association , ( 260 ), 583–621. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kwon K., Liu Y.-H., Johnson L. P. (2014). Group regulation and social-emotional interactions observed in computer supported collaborative learning: Comparison between good vs. poor collaborators . Computers & Education , , 185–200. [ Google Scholar ]
- Latane B., Williams K., Harkins S. (1979). Many hands make light the work—causes and consequences of social loafing . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , ( 6 ), 822–832. 10.1037//0022-3514.37.6.822 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Latour B. M. D., Woolgar J. (2013). Laboratory life: The construction of scientific facts . Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lejk M., Wyvill M. (2001). Peer assessment of contributions to a group project: A comparison of holistic and category-based approaches . Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , ( 1 ), 61–72. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lejk M., Wyvill M., Farrow S. (1996). A survey of methods of deriving individual grades from group assessments . Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , ( 3 ), 267–280. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lerner L. D. (1995). Making student groups work . Journal of Management Education , ( 1 ), 123–125. [ Google Scholar ]
- Livingstone D., Lynch K. (2000). Group project work and student-centred active learning: Two different experiences . Studies in Higher Education , ( 3 ), 325–345. [ Google Scholar ]
- Loughry M. L., Ohland M. W., Moore D. D. (2007). Development of a theory-based assessment of team member effectiveness . Educational and Psychological Measurement , ( 3 ), 505–524. [ Google Scholar ]
- Manktelow J., Jackson K., Edwards S., Pearcey E., Eyre E., Cook L., Moss I. (2017). Resolving team conflict: Building stronger teams by facing your differences . MindTools. Retrieved August 24, 2018, from www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMM_79.htm
- Mesmer-Magnus J. R.,, DeChurch L. A. (2009). Information sharing and team performance: A meta-analysis . Journal of Applied Psychology , ( 2 ), 535. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Michaelsen L. K., Davidson N., Major C. H. (2014). Team-based learning practices and principles in comparison with cooperative learning and problem-based learning . Journal on Excellence in College Teaching , ( 3–4 ), 57–84. [ Google Scholar ]
- Moog R. S., Spencer J. N. (2008). Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning (POGIL) , American Chemical Society Symposium Series, Vol. 994 , 1–13. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morse J. M., Barrett M., Mayan M., Olson K., Spiers J. (2002). Verification strategies for establishing reliability and validity in qualitative research . International Journal of Qualitative Methods , ( 2 ), 13–22. [ Google Scholar ]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. (2016). Barriers and opportunities for 2-Year and 4-Year STEM degrees: Systemic change to support students’ diverse pathways . Washington, DC: National Academies Press. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- National Research Council. (2015). Reaching students: What research says about effective instruction in undergraduate science and engineering . Washington, DC: National Academies Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Oakley B., Felder R. M., Brent R., Elhajj I. (2004). Turning student groups into effective teams . Journal of Student Centered Learning , ( 1 ), 9–34. [ Google Scholar ]
- O’Donnell A. (2006). The role of peers and group learning . In Alexander P., Winne P. (Eds.), Handbook of educational psychology (pp. 781–802). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum. [ Google Scholar ]
- O’Donnell A. M. (1996). Effects of explicit incentives on scripted and unscripted cooperation . Journal of Educational Psychology , , 74–86. [ Google Scholar ]
- O’Neill T. A., Hoffart G. C., McLarnon M. M., Woodley H. J., Eggermont M., Rosehart W., Brennan R. (2017). Constructive controversy and reflexivity training promotes effective conflict profiles and team functioning in student learning teams . Academy of Management Learning & Education , ( 2 ), 257–276. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pauli R., Mohiyeddini C., Bray D., Michie F., Street B. (2008). Individual differences in negative group work experiences in collaborative student learning . Educational Psychology , ( 1 ), 47–58. 10.1080/01443410701413746 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Phelps E., Damon W. (1989). Problem-solving with equals—peer collaboration as a context for learning mathematics and spatial concepts . Journal of Educational Psychology , ( 4 ), 639–646. 10.1037//0022-0663.81.4.639 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Preszler R. W. (2009). Replacing lecture with peer-led workshops improves student learning . CBE—Life Sciences Education , ( 3 ), 182–192. 10.1187/cbe.09-01-0002 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pundak D., Rozner S. (2008). Empowering engineering college staff to adopt active learning methods . Journal of Science Education and Technology , ( 2 ), 152–163. 10.1007/s10956-007-9057-3 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Savadori L., Van Swol L. M., Sniezek J. A. (2001). Information sampling and confidence within groups and judge advisor systems . Communication Research , ( 6 ), 737–771. [ Google Scholar ]
- Scager K., Boonstra J., Peeters T., Vulperhorst J., Wiegant F. (2016). Collaborative learning in higher education: Evoking positive interdependence . CBE—Life Sciences Education , ( 4 ), ar69. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Seymour E., Hewitt N. (1997). Talking about leaving: Why undergraduates leave the sciences . Boulder, CO: Westview. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shimazoe J., Aldrich H. (2010). Group work can be gratifying: Understanding and overcoming resistance to cooperative learning . College Teaching , ( 2 ), 52–57. [ Google Scholar ]
- Slavin R. E. (1991). Synthesis of research of cooperative learning . Educational Leadership , ( 5 ), 71–82. [ Google Scholar ]
- Slavin R. E. (2014). Cooperative learning and academic achievement: Why does groupwork work ? Anales de Psicología/Annals of Psychology , ( 3 ), 785–791. [ Google Scholar ]
- Solomon J. (1987). Social influences on the construction of pupil’s understanding of science . Studies in Science Education , , 63–82. [ Google Scholar ]
- Solomon Y., Croft T., Lawson D. (2010). Safety in numbers: Mathematics support centres and their derivatives as social learning spaces . Studies in Higher Education , ( 4 ), 421–431. [ Google Scholar ]
- Springer L., Donovan S. S., Stanne M. E. (1999). Effects of small-group learning on undergraduates in science, mathematics, engineering, and technology: A meta-analysis . Review of Educational Research , ( 1 ), 21–51. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stefanou S. E., Hood L. F., Stefanou C. R. (2001). Feedback and change: Assessment of individual contributions within collaborative activities in the higher education classroom . Journal on Excellence in College Teaching , ( 2 ), 77–91. [ Google Scholar ]
- Strong J. T., Anderson R. E. (1990). Free-riding in group projects: Control mechanisms and preliminary data . Journal of Marketing Education , , 61–67. [ Google Scholar ]
- Svinicki M. D., Schallert D. L. (2016). Learning through group work in the college classroom: Evaluating the evidence from an instructional goal perspective . In Paulsen M. B. (Ed.), Higher education: Handbook of theory and research (Vol. 31 , pp. 513–538). Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sweet M., Michaelsen L. K. (2007). How group dynamics research can inform the theory and practice of postsecondary small group learning . Educational Psychology Review , ( 1 ), 31–47. [ Google Scholar ]
- Teddlie C.,, Tashakkori A. (2003). Major issues and controveries in the use of mixed methods in the social and behvioral sciences . In Handbook of mixed methods in social & behavioral research , 3–50. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tekleab A. G., Quigley N. R., Tesluk P. E. (2009). A longitudinal study of team conflict, conflict management, cohesion, and team effectiveness . Group & Organization Management , ( 2 ), 170–205. [ Google Scholar ]
- Theobald E., Eddy S., Grunspan D., Wiggins B., Crowe A. (2017). Student perception of group dynamics predicts individual performance: Comfort and equity matter . PLoS ONE , ( 7 ), e0181336. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Van den Bossche P., Gijselaers W. H., Segers M., Kirschner P. A. (2006). Social and cognitive factors driving teamwork in collaborative learning environments: Team learning beliefs and behaviors . Small Group Research , ( 5 ), 490–521. [ Google Scholar ]
- Van der Vegt G. S., Emans B. J., Van der Liert E. (2001). Patterns of interdependence in work teams: A two-level investigation of the relations with job and team satisfaction . Personnel Psychology , ( 1 ), 51–69. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang S.-L., Lin S. S. (2007). The effects of group composition of self-efficacy and collective efficacy on computer-supported collaborative learning . Computers in Human Behavior , ( 5 ), 2256–2268. [ Google Scholar ]
- Webb N. M., Nemer K. M., Zuniga S. (2002). Short circuits or superconductors? Effects of group composition on high-achieving students’ science assessment performance . American Educational Research Journal , ( 4 ), 943–989. [ Google Scholar ]
- Webb N. M., Palincsar A. S. (1996). Group processes in the classroom . In Calfee D. B. R. (Ed.), Handbook of educational psychology (pp. 841–873). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wenzel T. J. (2007). Evaluation tools to guide students’ peer-assessment and self-assessment in group activities for the lab and classroom . Journal of Chemical Education , ( 1 ), 182. [ Google Scholar ]
- Williams E. (1992). Student attitudes towards approaches to learning and assessment . Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , ( 1 ), 45–58. [ Google Scholar ]
- Winne P. H., Jamieson-Noel D. (2002). Exploring students’ calibration of self reports about study tactics and achievement . Contemporary Educational Psychology , ( 4 ), 551–572. https//.org/10.1016/S0361-476x(02)00006-1 [ Google Scholar ]
- Woolley A. W., Aggarwal I., Malone T. W. (2015). Collective intelligence and group performance . Current Directions in Psychological Science , ( 6 ), 420–424. 10.1177/0963721415599543 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Woolley A. W., Chabris C. F., Pentland A., Hashmi N., Malone T. W. (2010). Evidence for a collective intelligence factor in the performance of human groups . Science , ( 6004 ), 686–688. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang B., Johnston L., Kilic G. B. (2008). Assessing the reliability of self- and peer rating in student group work . Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , ( 3 ), 329–340. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang B., Ohland M. W. (2009). How to assign individualized scores on a group project: An empirical evaluation . Applied Measurement in Education , ( 3 ), 290–308. [ Google Scholar ]

7 Strategies for Taking Group Projects by Storm
It’s day one of the new semester, and you see it…staring ominously from the syllabus, it lurks in eager waiting…haunting unlit corners of your lecture hall, the beast inches closer every class until one day, it strikes — sinking its teeth in. No silver tokens or wooden stakes will save you now. It’s time for mandatory group projects.
For even the most scholarly students, the mere suggestion of a group project can send shivers down the spine. These projects plague the mind with many questions. What if I get stuck with someone who does nothing? Will communication break down into a chaotic mess of emojis? And, sometimes, above all else, why do I have to do this?
So, fellow Purple Knights, let’s turn that stress into success — equip yourself with these 7 strategies to help you make the most of group assignments.
1. Acknowledge your anxiety and self-assess
Let’s take a moment to commemorate the ghosts of group projects past. Remember that paper from history class? The one on the American Revolution? Your whole team was supposed to write it, yet your group dedicated more time to scrolling through TikTok than typing. Oh, and how about that PowerPoint presentation for your accounting class? You know, the one nobody pulled their weight on, shaving a few precious points off your final grade?
Although you should never begin a group project with the attitude that failure is inevitable, being honest with yourself about any anxiety you feel helps repurpose the stress of past projects into lessons with future applicability.
So, when you see a group assignment on your syllabus, don’t panic. Instead, ask yourself a few questions, such as:
- What were some issues I encountered during previous group projects?
- How could these issues have been avoided or addressed?
- Did I give the project my all and contribute to the best of my ability?
- What did I learn about the subject I was studying?
- What did I learn about working with a group?
- More specifically, what did I learn about how I work with others?
If this self-assessment only serves to raise more questions, consider talking to your instructor or visiting the Academic Success Center . Expressing your concern about group work, and consulting with supportive and experienced professionals, can help you kickstart your collaboration with confidence.
2. Assemble your A-Team
Now that your head is in the game, it’s time to assemble the A-Team! Whether your group is self-selected or pre-assigned, first things first — for a cohesive collaboration, every teammate must cooperate.
Think of it like building a boat. Each crewmate takes on a different, albeit pivotal, role to ensure the ship will stay afloat. While some people lay floor plans and foundations, others gather materials, create sails, or complete safety assessments. Although every team member has their own purview, everyone must cooperate to achieve a common goal. If one person drops the ball, the vessel might not be seaworthy. The same goes for your group project — without joint effort, your crew may flounder in the face of challenges.
To take the helm, create team roles with the project’s guidelines in mind. Weigh the academic expectations with the skills and strengths of your teammates. Does one partner have a head for facts and figures? Group Researcher , reporting for duty! How about the group member with an eye for design? PowerPoint Coordinator may be the perfect fit!
Scenario snapshot
You and your best friend want to be in the same group for an English presentation. They’re a stand-up pal and astute problem-solver, but they often slack off on assignments. Let’s turn procrastination into collaboration. How can you help establish a healthy group dynamic without boxing out your bestie?
3. Planning is power
Collaborating on an assignment isn’t as simple as casting roles for each group member. You will also need a plan of attack outlining what must be done (and when).
During your initial group meeting, roll up your sleeves to brainstorm ideas and generate timelines for the different components of your project. To keep all the most vital information in an accessible location, utilize project management tools like Google Docs or Trello — providing a clear, shared resource teammates can refer to when working independently.
What would you do?
It’s been two weeks, and one of your group mates still hasn’t opened the shared document outlining their role and the project schedule. They were attentive when your team first met to discuss the presentation, but you’re concerned the assignment has fallen from their radar. How can you address your concerns?
At University of Bridgeport, your personal and professional success is our priority. Learn more about our comprehensive support services today!
4. keep up communication.
Determining guidelines for group check-ins is essential to success. Whether you’re meeting in person or virtually, it’s critical to establish when, where, and how your team will update one another.
You may even consider setting parameters for your group pow-wows. How long should each check-in last? Should one teammate have the floor during each meeting, or will everyone provide updates? Agreeing on these expectations can facilitate smooth sailing ahead.
Your four-person biology group includes a pair of close friends. Each time your team meets to discuss the project, the duo brings little to the table, filling most of the hour with fits of giggly gossip.
The last group check-in was the biggest bust yet — extending an hour longer than the agreed-upon time due to constant distractions and derailments. The following afternoon, your third partner privately messaged you, expressing the same frustrations you’re feeling. How can you and your partner constructively address this issue with your other teammates?
5. Be fair and flexible…
When collaborating with classmates, it’s crucial to remember that is difficult. With academic, personal, and professional demands competing for space, everybody has more than one ball in the air. If someone on your team needs an extension for their part of an assignment, show grace and understanding — most people are doing their best to meet all the expectations tossed their way, and a little leniency can go a long way.
6. …but remember to set boundaries
Flexibility may be paramount, but have you ever flexed too far? If you’re always happy to go with the flow, your willingness to bend could cause your group to break. If you and your teammates are always cleaning up after one partner, burnout will ensue — potentially leading to an underwhelming final project.
If you have a teammate who isn’t pulling their weight, it’s time to set boundaries and reiterate your group’s agreed-upon expectations. If you’re uncomfortable breaching the topic, consult with your professor. Even if they expect you to start the conversation on your own, they can offer support and strategies for addressing conflicts in your group. Moreover, communicating these concerns keeps your instructor in the loop about your team’s progress.
Last month, you were randomly assigned to group for your nursing project. You were pleasantly surprised by how well it was going — at least, at first. Over the past few weeks, one of your partners has missed every meeting due to a personal problem. While they didn’t disclose the specifics, they’ve missed three deadlines and have been completely incommunicado.
With the deadline quickly approaching, you and your other teammates are starting to sweat. What could you do to help your team overcome this challenge?
7. Celebrate success
Group projects are full of peaks and valleys alike. When you hit “submit” and the game is over, take some time to acknowledge your dedicated team. Collaborative assignments can present an invaluable opportunity to connect with classmates, learn from each other, and create something truly impressive.
While the anxiety of an impending group project can be overwhelming, don’t let it overshadow the fact that these ventures can be rewarding and, dare we say, enjoyable experiences. Furthermore, in our increasingly interconnected world, nurturing your collaborative aptitude provides you with a career-ready skill — sought after by employers across all industries.
At University of Bridgeport, #UBelong. Begin your UB journey today — learn more about becoming a Purple Knight !

Create group assignments or assign to individual students
Create an assignment in Microsoft Teams for Education and assign it to individual or small groups of students in a class. Groups turn in one copy of the assignment that can be graded separately or together.
Create a new assignment
Navigate to your desired class team and select Assignments .
Select Create > Assignment .
Create a group assignment
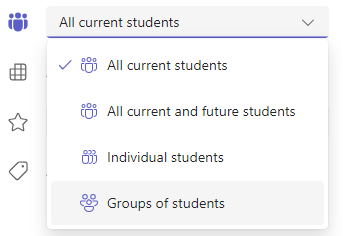
If you chose Randomly group students:
Enter number of groups, then select Create groups .
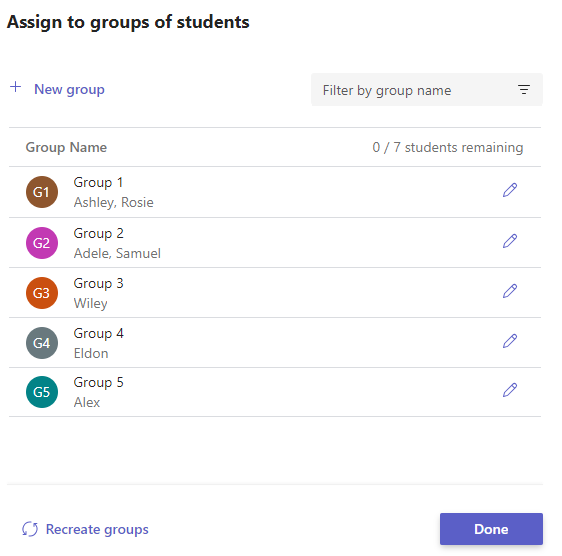
When everything looks good, select Done . If you decide you need more edits, select Groups of students again.
Finish adding details to your assignment, then select Assign . Note that once an assignment has been distributed to students, you can no longer edit groups.

If you chose Manually group students:
Select Create groups .
Edit the default group name, if desired.
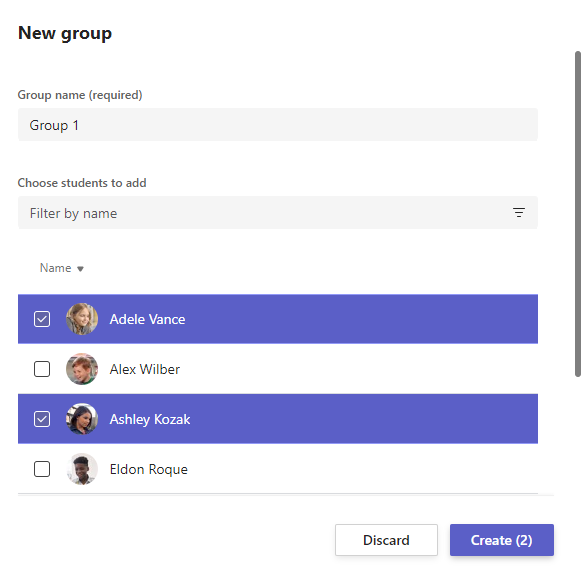
Select Create .
When you're done, select + New group and repeat Steps 2 and 3 until all students have been assigned to a group.
Finish adding details to your assignment, then select Assign . Note that once an assignment has been distributed to students, you can no longer edit groups.
Assign to individual students
Select the student dropdown under Assign to . By default, All Students will be selected. Select student names or type to search for a student.
Note: You can only assign work to individual students in one class at a time.
Once you've selected the students, finish adding details to your assignment.
Select Assign . The students you chose will be notified of their new assignment.
Create an assignment
Grade an assignment
Edit an assignment
Additional resources for educators
Ask the community

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.

LX / Design a group assignment
Design a group assignment
This resource offers suggestions for designing group assignments which students will finding motivating. We’ll explore how to make the assignment meaningful, easily allocated into sub-tasks, relevant to learning outcomes and achievable.
One of the most crucial aspects of group work is the task set for the group. If students engage in their task, they will be more likely to be motivated to be an active participant in group work and develop new skills. Unfortunately, many students find their tasks to be inappropriate or too difficult for group work and thus lack motivation to work collectively on the assignment. In fact, many students view their assignments as little more than an individual assessment task applied to a group of students to reduce marking.
Develop a motivating group assignment
To develop a motivating group assignment, first you need to understand what students look for in a collaborative assessment task. Understanding students’ expectations is important because it allows you to see where your task can be aligned with their expectations. It also allows you to identify where alignment may not be possible. These differences can then be discussed with the students so they understand your reasons. Students will always work better when they understand why they are being assessed in a particular way.
There are four important factors which students look for in a group assignment.
1. A meaningful assignment
Students are not only motivated by the mark they will receive for their assignment. They are also motivated by the work they will produce.
Students often report that their most motivating group assignments are those which are “client-based”. These are assignments where the groups enact the role of consultant and work on an issue which has been identified by the client (in most instances, an organisation). Groups usually produce some form of written report (or in some disciplines a product) which is assessed by the lecturer. Occasionally, the client is also invited to assess the group’s output. Students are particularly motivated when they know that the client will be viewing and assessing the work.
Designing “client-based” group assignments are becoming increasingly popular in university settings. Many organisations are interested in participating in such projects because of the insights and perspectives generated by the project groups. Non-profit organisations, with their limited resources, are often keen to become clients and students are particularly motivated to help such organisations.
Some lecturers are even beginning to view the university as a client and are designing group assignments which address particular concerns faced by students and staff.
2. Easily allocated into sub-tasks
Student groups almost always divide up their task and allocate different sections to each member. Even if you do not want the assignment to be broken up, they probably will (or at least attempt to do so).
Students argue that this is the only strategy to use when they are members of 3 or 4 other groups. Unfortunately, most groups struggle when they attempt to divide up the task because it has not been designed to be broken up. It has been designed to be completed collectively. The rationale behind this strategy is that students learn group skills by closely working together on every aspect of the task.
While this strategy can be effective, it usually takes much longer than one semester for it to work. Furthermore, it usually requires that members work together full-time on the one task. With students working part-time, on more than one task, in more than one group, it is in many ways an unrealistic strategy. There is just not enough time for students to work together on every issue.
Knowing that students divide up their group task, many lecturers are beginning to devise group assignments with this in mind. In these assignments, each group member is required to do a piece of work. These individual pieces are then combined together to form a completed group product (there is usually an introduction and conclusion which the group write together to bring the individual sections together).
Students are motivated by these types of assignments because:
- they are less dependent on each other
- they don’t have to make joint decisions on each and every issue,
- there are fewer disagreements
- they have the opportunity to ‘shine’ as well as contribute to the group
Lecturers also benefit greatly from the task design due to:
- fewer complaints about free-riding (because each member’s work is identifiable)
- greater enthusiasm for group work
- less conflict in groups
- greater peer support
As with any innovation, there are of course critics to the approach. The main criticism is that students are not working in ‘fully fledged’ groups and, as such, fail to develop a broad range of skills. While this may be true, proponents argue that it is far better to learn some skills well than many at only a shallow level. This approach works on the rationale that students should not be expected to learn too many skills in a semester, but rather focus on a number of key skills (eg. coordination, peer support, accountability).
Proponents also argue that the notion of the fully fledged group rarely exists in industry and that their approach more accurately mirrors the “real world”. In many organisations, team members often work independently on individual pieces and bring them together to form the product (or the collection of group products). The aim of their approach is to reflect this style of team work and to teach students how to operate under such a system.
It is understandable that many group assignments must be collaborative and result in a single product. For these assignments, it is important to remember that students will try to split the task up. If the task can be logically divided, it may be advisable to help them do so – this will save the group valuable time. If the task cannot be broken apart, this should be clearly explained to students before they try to do so.
3. Relevant to learning outcomes
As mentioned earlier, many students are sceptical about collaborative assessment tasks and often view them merely as a way of reducing marking. For students to be motivated to participate in group assignments, they often need to see the tangible benefits of doing so. This is best achieved by designing group assignments which are closely aligned to the learning objectives of the subject.
When designing collaborative assignments, it is important to consider what knowledge, skills and abilities you want your students to learn through group work. While there will be a generic set applicable to most group assignments (eg. learning to communicate and cooperate with peers), there will also be a specific set which need to be geared to the assignment. For example, what type of interpersonal communication skills do you want your students to learn? Do you want them to learn to communicate face-to-face or also to learn computer mediated communication? If the latter is important, then establishing an “on-line” group task (eg. an on-line debate or discussion group) would be appropriate.
All too often, lectures design group assignments with little reference to the learning objectives and this can create confusion for students. For example, students often fail to see how requirements such as communicating “on-line” or making a group presentation are relevant to their learning outcomes. Whilst the objective may be clear to the lecturer, students often have little idea. It is therefore important that the objectives of the group assignment are explicitly made known to students. This is best achieved through a well structured subject outline that breaks down the group assignment into its sub-components and links each component to a key learning objective.
4. An achievable assignment
When designing an appropriate group assignment, it is also important to set a task which can realistically be achieved by students within the specified time frame. Whilst the task may be meaningful and challenging, it can become too time consuming and overwhelming for students. This is particularly the case when students are doing equally challenging group assignments in their other subjects. Students often complain that many of their difficulties arise from the multiple group assignments they are forced to do each semester and how many lecturers are either insensitive or oblivious to this fact. T
he unfortunate result is that students become disillusioned with their group assignments and tend to apply themselves less. This usually results in a decrease in learning, motivation and output quality and an increase in group related problems such as conflict and the withdrawal of effort. To help design a realistically achievable task, it may therefore be worth ‘standing back’ and viewing the group assignment from the student’s perspective.
Things to consider
- Invite the client to a class or classes throughout the semester
- Restrict students from contacting the clients whenever they choose
- Provide samples of work completed by groups in previous years.
- Discuss how groups, particularly those who have done well in previous years, have gone about completing their assignment
- If you are having difficulties finding a real client, design your group assignment around a mock client (eg. a hypothetical client or a client from a previous year)
Still need help?
Get in touch with the LX.lab team by logging a ticket via ServiceConnect. We'll be in touch shortly.
Want to provide feedback on this resource? Please log in first via the top nav menu.
Marking in Canvas | 22 August
- Thursday, 22 August, 2024 11:00 am-12:00 pm
Assignments in Canvas | 11 July
- Thursday, 11 July, 2024 10:00 am-11:30 am

Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning

Inclusive group assignments: Fostering teamwork among diverse identities
A survey conducted by Peter D. Hart Research Associates on behalf of the Association of American Colleges and Universities found that employers believe undergraduate programs do not sufficiently prepare students for teamwork and intercultural skills. As educators, we have the power to rise to this challenge and teach inclusive leadership through high-quality group assignments that foster teamwork among diverse identities.
A wealth of evidence indicates that our collective intelligence, when working together in teams, outperforms even the highest-achieving individual intelligence. We witnessed the powerful results of collective intelligence when the world came together to address the COVID-19 pandemic. However, effectively cultivating teams’ intelligence requires intention and preparation. Leading diverse teams in the age of AI is even more complex. Despite the challenges, diverse teams enhance creativity and innovation, improve decision-making, and provide students and instructors with better learning and teaching experiences.
Designing effective group assignments
Well-thought-out team assignments are essential for effective student teamwork. By ensuring that team assignments have a clear purpose and that the grading criteria are aligned with the course outcomes, we can foster individual accountability while promoting positive interdependence, leading to successful teamwork.
Designing effective student groups
When assigning group projects, it’s crucial to consider how to create effective student teams. Factors to consider include team size and heterogeneousness. Smaller teams promote individual accountability and flexibility, while larger teams offer more resources and diverse perspectives. Generally, teams of three to five students work best, with smaller teams for short-term tasks and larger teams for long-term projects.
Guiding teams to improve interpersonal skills
Team members’ ability to work effectively together can improve over time as they acquire interpersonal skills, but they need guidance to get there. It’s essential to explain to students that they need to learn practical and character skills, including a commitment to the common goal and the well-being of other team members. Encourage students to be aware of how gender, cultural backgrounds, socio-economic status, and life experiences could affect their team members’ performance.
Provide time and guidance for teams to examine how they work together
Consider asking questions that allow students to reflect on their own and their peers’ contributions to the team and distributing peer evaluations at multiple points during the term so students can improve their performance. At the end of the term, the instructor can factor the students’ ratings into the overall grade to reflect their team contributions. A group grade doesn’t indicate whether individuals have mastered the standards. To be fair and have students’ grades reflect their learning, individual grades should be assigned for group work.
Further reading
- 10 Benefits of Diversity in the Workplace (Washington State University Carson College of Business)
- Benefits of Group Work (Washington U. in St. Louis Center for Teaching and Learning)
- The Benefits of Inclusion and Diversity in the Classroom (American University School of Education)
- Diverse Teams Feel Less Comfortable — and That’s Why They Perform Better (Harvard Business Review)
- Getting Serious About Diversity: Enough Already with the Business Case (Harvard Business Review)
- How Diversity Makes Us Smarter (Scientific American)
- Team Creativity/Innovation in Culturally Diverse Teams: A Meta‐Analysis (Journal of Organizational Behavior)
- Using Group Projects Effectively (Carnegie Mellon Eberly Center for Teaching Excellence and Innovation)
- Why Diverse Teams Outperform Homogeneous Teams (Psychology Today)

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

You're signed out
Sign in to ask questions, follow content, and engage with the Community
- Canvas Question Forum
Group Assignments
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Report Inappropriate Content
Instructional Designer
- All forum topics
- Previous Topic

Can I restore deleted data from a course
Observer accounts and pairing codes, program learning outcomes, external tools ideas for course designed for submi..., badge verification fails due to redirecting error, swap classes, grades from two classes (co-requisite) in a single..., instuctor question, community help, view our top guides and resources:.
To participate in the Instructurer Community, you need to sign up or log in:
- Arch Capital Group LtdShs-stock
- News for Arch Capital Group LtdShs
Pershing Square Holdings Approves Deemed Assignment Of Its Investment Management Agreement
(RTTNews) - Pershing Square Holdings said it noted that Pershing Square Capital Management, which serves as PSH's investment manager, announced a sale to strategic investors of a 10% common equity interest in Pershing Square Holdco, L.P., a newly formed limited partnership that owns 100% of Pershing Square Capital Management. The sale is for a purchase price of $1.05 billion and is to a consortium of strategic investors including Arch Capital Group Ltd. (ACGL), BTG Pactual, Consulta Limited, ICONIQ Investment Management, Menora Mivtachim Holdings, an international group of family offices, and other investors.
In connection with the deal, Pershing Square Capital Management is completing an internal reorganization of its ownership structure which will result in the voting securities of Pershing Square Holdco being indirectly owned by a limited liability company, an entity which will be controlled by senior management of Pershing Square Holdco including Bill Ackman who is the largest shareholder of the LLC. Ben Hakim has been appointed as President of PSCM.
In connection with the reorganization, each of PSCM's funds, including Pershing Square Holdings, approved the deemed assignment of its Investment Management Agreement.
Related Stocks

Rep. Stefanik files misconduct complaint against Judge Juan Merchan over ‘random’ assignment to Trump’s NYC trial
R ep. Elise Stefanik (R-NY) filed a misconduct complaint Tuesday against the judge overseeing Donald Trump’s Manhattan hush money trial, alleging that his selection to handle the former president’s case — and others involving his allies — is “not random at all.”
The House Republican Conference chairwoman’s complaint with the inspector general of the New York State Unified Court System called for an investigation into Justice Juan Merchan “to determine whether the required random selection process was in fact followed.”
“The potential misconduct pertains to the repeated assignment of Acting Justice Juan Merchan, a Democrat Party donor, to criminal cases related to President Donald J. Trump and his allies,” Stefanik wrote.
“Acting Justice Merchan currently presides over the criminal case against President Trump brought by Manhattan District Attorney Alvin Bragg,” she said.
“Acting Justice Merchan also presided over the criminal trial against the Trump Organization and will be presiding over the criminal trial of Steve Bannon, a senior advisor in President Trump’s White House and a prominent advocate for President Trump,” Stefanik continued, noting that there were at least two dozen sitting justices eligible to oversee the cases but Merchan – an acting jurist – was selected for all three related to the presumptive 2024 GOP nominee for president and his allies.
“If justices were indeed being randomly assigned in the Criminal Term, the probability of two specific criminal cases being assigned to the same justice is quite low, and the probability of three specific criminal cases being assigned to the same justice is infinitesimally small. And yet, we see Acting Justice Merchan on all three cases,” Stefanik argued.
The congresswoman also highlighted the judge’s political donations, for which he was cleared of misconduct last July by the New York State Commission on Judicial Conduct.
Merchan contributed $15 earmarked for the “Biden for President” campaign on July 26, 2020, and then the following day made $10 contributions to the Progressive Turnout Project and Stop Republicans each, Federal Election Commission records show
The donations were made through ActBlue, the Democratic Party’s preferred online fundraising platform.
The Progressive Turnout Project’s stated mission is to “rally Democrats to vote,” according to the group’s website.
Stop Republicans is a subsidiary of the Progressive Turnout Project and describes itself as “a grassroots-funded effort dedicated to resisting the Republican Party and Donald Trump’s radical right-wing legacy.”
The judge’s daughter, Loren Merchan, is more involved in Democratic politics – through her work as head of the consulting firm Authentic Campaigns — and Stefanik argued in her missive that Loren Merchan’s “firm stands to profit greatly if Donald Trump is convicted.”
“One cannot help but suspect that the ‘random selection’ at work in the assignment of Acting Justice Merchan, a Democrat Party donor, to these cases involving prominent Republicans, is in fact not random at all,” the New York Republican lawmaker wrote.
Stefanik demanded an investigation into the “anomaly” and asked that anyone found to be involved in any sort of “scheme” to get Merchan on the three cases face discipline.

Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications You must be signed in to change notification settings

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Group work also introduces more unpredictability in teaching, since groups may approach tasks and solve problems in novel, interesting ways. This can be refreshing for instructors. Additionally, group assignments can be useful when there are a limited number of viable project topics to distribute among students.
Group Leadership. The leader is responsible for seeing that the work is organized so that it will get done. The leader is also responsible for understanding and managing group interactions so that the atmosphere is positive. The leader must encourage everyone's contributions with an eye to accomplishing the work.
Group assignments are a near-universal feature of classrooms around the world. They are broadly viewed as more effective than passive forms of learning and are assumed to position students for success in fields that demand high levels of interpersonal communication, like public affairs. But does research support that view?
Regularly observe group interactions and progress, either by circulating during group work, collecting in-process documents, or both. When you observe problems, intervene to help students move forward on the task and work together effectively.
Here are some other considerations for creating effective group work activities: Break a larger assignment into smaller pieces and set multiple deadlines to ensure that students work toward reaching milestones throughout the process rather than pulling it all together at the last minute. Incorporate peer assessments at each milestone to ...
Ideas for Great Group Work. Many students, particularly if they are new to college, don't like group assignments and projects. They might say they "work better by themselves" and be wary of irresponsible members of their group dragging down their grade. Or they may feel group projects take too much time and slow down the progression of ...
Group roles allow students to strengthen their communicative skills, especially in areas that they are less confident in volunteering for. Group roles can help disrupt stereotypical and gendered role assignments, which can be common in group learning.
However, if coordination costs are excessive or are not factored into the structure of group assignments, groups tend to miss deadlines, their work is poorly integrated, motivation suffers, and creativity declines.
Below we offer strategies and examples that work for short-term collaborative group work (e.g., discussions in an online, hybrid/flexible, or in-person class) and long-term collaborative assignments (e.g., group projects), ending with additional considerations for long-term collaborative work.
You've been given your assignment and have your group members in place. Your next step is to set up your group's goals, roles, and ground rules to make the most of your time working together. Taking a few minutes at the start of your assignment to cover this will often proactively address any issues that may arise during group projects.
Group work necessitates emotional intelligence and other skills such as communication, time management, conflict resolution, and recognition of team member differences. A successful group project will provide a framework to ensure students are properly equipped with these skills.
Group work is used as a means for learning at all levels in educational systems. There is strong scientific support for the benefits of having students learning and working in groups. Nevertheless, studies about what occurs in groups during group work and which factors actually influence the students' ability to learn is still lacking.
First, depending on the objectives of the assignment, the instructor might want to assess the team's final product (e.g., design, report, presentation), their group processes (e.g., ability to meet deadlines, contribute fairly, communicate effectively), or both. Second, group performance must be translated into individual grades - which raises issues of fairness and equity. Complicating ...
Collaborative learning can help. students develop higher-level thinking, communication, self-management, and leadership skills. explore a broad range of perspectives and provide opportunities for student voices/expression. promote teamwork skills & ethics. prepare students for real life social and employment situations.
Create a group assignment. On the New Assignment page, select the Settings icon to open the Assignment Settings panel. Provide a due date and select the settings you want to apply to the group assignment: You can allow class conversations for a group assignment.
Introducing group work in college science classrooms can lead to noticeable gains in student achievement, reasoning ability, and motivation. To realize these gains, students must all contribute. Strategies like assigning roles, group contracts, anonymous peer evaluations, and peer ratings all encourage student participation.
How do you effectively manage a group project? Explore these seven strategies for success in helping you make the most of group assignments.
Create an assignment in Microsoft Teams for Education and assign it to individual or small groups of students in a class. Groups turn in one copy of the assignment that can be graded separately or together.
Design a group assignment. This resource offers suggestions for designing group assignments which students will finding motivating. We'll explore how to make the assignment meaningful, easily allocated into sub-tasks, relevant to learning outcomes and achievable. One of the most crucial aspects of group work is the task set for the group. If ...
You can create a group assignment by using the Group Assignment checkbox. Canvas uses group sets to assign group assignments, and each group within the group set that is assigned to the assignment is required to complete the assignment. When creating or editing a group assignment, you can assign an ...
A group assignment is a way for instructors to allow students to work together on an assignment and submit it as a group. Only one group member needs to submit the assignment on behalf of the group. Any attachments added as part of a graded assignment submission are also copied to your group files b...
The Group assignment allows teachers to set an assignment which a group can work on collaboratively, and receive a common grade and feedback. Before adding a group assignment in your course, you have to split the students into different groups. Once you have created the groups, add the assignment by clicking on Add an activity or resource and ...
Well-thought-out team assignments are essential for effective student teamwork. By ensuring that team assignments have a clear purpose and that the grading criteria are aligned with the course outcomes, we can foster individual accountability while promoting positive interdependence, leading to successful teamwork.
Instuctor question. Group Assignments. using data fields in Canvas. Program Learning Outcomes. View All. View All. Is there a way to create group assignments so that everyone can see the grades and the feedback provided on an assignment? - 605278.
In connection with the reorganization, each of PSCM's funds, including Pershing Square Holdings, approved the deemed assignment of its Investment Management Agreement.
Rep. Elise Stefanik (R-NY) filed a misconduct complaint Tuesday against the judge overseeing Donald Trump's Manhattan hush money trial, alleging that his selection to handle the former president ...
A programming framework for agentic AI. Discord: https://aka.ms/autogen-dc. Roadmap: https://aka.ms/autogen-roadmap - microsoft/autogen
CST8276 - Advanced Database Topics Group Assignment Spring 2024 Group Assignment The group assignment will be completed in groups of 4 to 6 students. You will be creating a demonstration to show the class on a database topic of your own choice.
CMPT641 - Group Assignment University Canada West 2024 Reproduction, distribution and/or publication of this material or any substantial part of it without the permission from the course instructor is prohibited. Knowledge Management Consultation NOTE: THIS IS A GROUP WORK. Individual Submissions will not be accepted/marked.