Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&


Get step-by-step solutions to your math problems

Try Math Solver

Get step-by-step explanations
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language
Reset password New user? Sign up
Existing user? Log in
- Number Theory
- Probability
- Everyday Math
- Classical Mechanics
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Computer Science
- Quantitative Finance
Take a guided, problem-solving based approach to learning Algebra. These compilations provide unique perspectives and applications you won't find anywhere else.
Algebra through Puzzles
What's inside.
- Introduction
- Simplifying Shortcuts
- Arithmetic Logic and Magic
- Balancing Scales
- Rates and Ratios
- Equations and Unknowns
- Manipulating Exponents
- Algebra in Motion
- Common Misconceptions
- Function Fundamentals
- Transformations
- Powers and Radicals
- Polynomials
- Factoring Polynomials
Rational Functions
Piecewise functions, community wiki.
Browse through thousands of Algebra wikis written by our community of experts.
Expressions and Variables
- What Makes A Good Problem?
- Simplifying Expressions
- Distributive Property
- Zero Product Property
- Contest Math I
- Solving Equations
- Setting Up Equations
- Simple Equations
- Verifying Solutions
- Multi-step Equations
- Isolating a Variable
- Balance Puzzles
- System of Linear Equations (Simultaneous Equations)
- How are exponent towers evaluated?
- Does a square root have two values?
- Do Square Roots Always Multiply?
- Is 0.999... = 1?
- What is 0 to the power of 0?
- If AB=AC, does B=C?
- Is (a/b)/c = a/(b/c)?
- Does \(\sqrt{x^2+y^2}=x+y?\)
- Does cross multiply always work for inequalities?
- How does addition in the denominator work?
- List of Common Misconceptions
- Linear Equations
- Forms of Linear Equations
- Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
Systems of Linear Equations
- Solving Linear Systems Using Matrices
- Absolute Value
- Absolute Value Equations
- Absolute Value Inequalities
- Linear Inequalities
- Absolute Value Linear Inequalities
- System of Inequalities
- Linear Programming
Non-Linear Inequalities
- Polynomial Inequalities
- Classical Inequalities
- Absolute Value Inequalities - 1 Quadratic Term
- Exponential Inequalities
- Logarithmic Inequalities
Quadratic Equations (Parabolas)
- Factoring Quadratics
- Quadratic Equations
- Completing The Square
- Applications of Completing the Square
- Quadratic Discriminant
Square Roots (Radicals)
- Simplifying Radicals
- Radical Equations
- Square Roots
- Rationalizing Denominators
Arithmetic and Geometric Progressions
- Arithmetic Progressions
- Arithmetic Mean
- Harmonic Progression
- Harmonic Mean
- Geometric Progressions
- Geometric Mean
- Arithmetic and Geometric Progressions Problem Solving
- Arithmetic-Geometric Progression
- Evaluating Functions
- Function Composition
- Inverse Functions
- Function Terminology
- Graphs of Functions
- Transforming Graphs of Functions
- Functional Equations
- Multiplying Polynomials
- Polynomial Division
- Synthetic Division
- Solving Identity Equations
- Difference Of Squares
- Applying the Perfect Square Identity
- Applying the Perfect Cube Identity
- Factoring by Substitution
- Rational Expressions
- Simplifying Rational Expressions
- Factoring Compound Quadratics: \(\, ax^4 + bx^2 + c\)
- Factoring Cubic Polynomials
- Descartes' Rule of Signs
- Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
- Method of Undetermined Coefficients
- Remainder Factor Theorem
- Transforming Roots of Polynomials
- Intercepts of Rational Functions
- Rational Equations
- Graphing Rational Equations
- Partial Fractions - Linear Factors
- Partial Fractions - Cover Up Rule
- Partial Fractions - Irreducible Quadratics
- Partial Fractions - Repeated Factors
- Telescoping Series - Sum
- Floor Function
- Ceiling Function
- Trailing Number of Zeros
- Fractional Part Function
- Hermite's Identity
- Rules of Exponents
- Simplifying Exponents
Exponential Functions
- Rules of Exponents - Algebraic
- Solving Exponential Equations
- Graphs of Exponential Functions
- Exponential Functions - Problem Solving
- Interest Rate
- Leonhard Euler
- Solving Logarithmic Equations
- Polar Coordinates
- Converting Polar Coordinates to Cartesian
- Parametric Equations
- Complex Numbers
- Complex Conjugates
- Complex Numbers - Absolute Values
- Complex Plane
- Complex Numbers in Geometry
- Gaussian Integers
- Discrete Fourier Transform
- Euler's Formula
- De Moivre's Theorem
- Roots of Unity
Advanced Linear Algebra (Matrices)
- Linear Algebra
- Determinants
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
- Kernel (Nullspace)
- Vector Space
- Cayley-Hamilton Theorem
- Row And Column Spaces
- Spectral Theorem
- Fundamental Subspaces
- Change of Basis
- Rank-Nullity Theorem
- Linear Transformations
- Linear Independence
- Jordan Canonical Form
- Affine transformations
- Vieta Root Jumping
Advanced Polynomials
- Algebraic Manipulation
- Algebraic Manipulation Identities
- Sum of n, n², or n³
- Telescoping Series - Product
- Nested Functions
- Cardano's Method
- Cubic Discriminant
- Gauss: The Prince of Mathematics
- Srinivasa Ramanujan
- Binomial Coefficient
- Pascal's Triangle
- Binomial Theorem
- Negative Binomial Theorem
- Fractional Binomial Theorem
- Rational Root Theorem
- Vieta's Formula
- Newton's Identities
- Completing the Square - Multiple Variables
- Algebraic Identities
- Factorization of Polynomials
- Sophie Germain Identity
- Algebraic Number Theory
- Fermat's Last Theorem
- Eisenstein's Irreducibility Criterion
- Group Theory
- Lagrange's Theorem
- Schwartz-Zippel Lemma
- Polynomial Interpolation by Remainder Factor Theorem
- Lagrange Interpolation
- Method of Differences
- Primitive Roots of Unity
- Symmetric Polynomials
- The \(uvw\) Method
- Chebyshev Polynomials - Definition and Properties
Advanced Inequalities
- Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality
- Titu's Lemma
- Rearrangement Inequality
- Chebyshev's Inequality
- Jensen's Inequality
- Hölder's Inequality
- Young's Inequality
- Muirhead Inequality
- Reverse Rearrangement Inequality
- Arithmetic Mean - Geometric Mean
- Applying the Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Inequality
- Power Mean Inequality (QAGH)
- Quadratic Mean
- Triangle Inequality
- AIME Math Contest Preparation
- JEE Exam Preparation
- RMO Math Contest Preparation
- INMO Math Contest Preparation
- KVPY Exam Preparation
- BITSAT Exam Preparation
Problem Loading...
Note Loading...
Set Loading...
Math Solver
Geogebra math solver.
Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems, while enhancing your problem-solving skills!


- Mathematicians
- Math Lessons
- Square Roots
- Math Calculators
Simple Algebra Problems – Easy Exercises with Solutions for Beginners
JUMP TO TOPIC
Understanding Algebraic Expressions
Breaking down algebra problems, solving algebraic equations, tackling algebra word problems, types of algebraic equations, algebra for different grades.
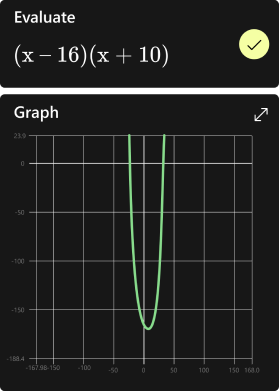
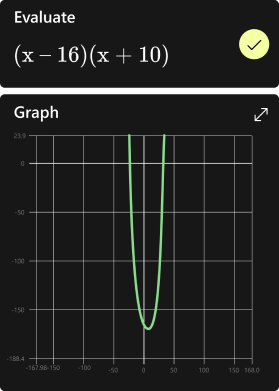
For instance, solving the equation (3x = 7) for (x) helps us understand how to isolate the variable to find its value.

I always find it fascinating how algebra serves as the foundation for more advanced topics in mathematics and science. Starting with basic problems such as ( $(x-1)^2 = [4\sqrt{(x-4)}]^2$ ) allows us to grasp key concepts and build the skills necessary for tackling more complex challenges.
So whether you’re refreshing your algebra skills or just beginning to explore this mathematical language, let’s dive into some examples and solutions to demystify the subject. Trust me, with a bit of practice, you’ll see algebra not just as a series of problems, but as a powerful tool that helps us solve everyday puzzles.
Simple Algebra Problems and Strategies
When I approach simple algebra problems, one of the first things I do is identify the variable.
The variable is like a placeholder for a number that I’m trying to find—a mystery I’m keen to solve. Typically represented by letters like ( x ) or ( y ), variables allow me to translate real-world situations into algebraic expressions and equations.
An algebraic expression is a mathematical phrase that can contain ordinary numbers, variables (like ( x ) or ( y )), and operators (like add, subtract, multiply, and divide). For example, ( 4x + 7 ) is an algebraic expression where ( x ) is the variable and the numbers ( 4 ) and ( 7 ) are terms. It’s important to manipulate these properly to maintain the equation’s balance.
Solving algebra problems often starts with simplifying expressions. Here’s a simple method to follow:
- Combine like terms : Terms that have the same variable can be combined. For instance, ( 3x + 4x = 7x ).
- Isolate the variable : Move the variable to one side of the equation. If the equation is ( 2x + 5 = 13 ), my job is to get ( x ) by itself by subtracting ( 5 ) from both sides, giving me ( 2x = 8 ).
With algebraic equations, the goal is to solve for the variable by performing the same operation on both sides. Here’s a table with an example:
Algebra word problems require translating sentences into equations. If a word problem says “I have six less than twice the number of apples than Bob,” and Bob has ( b ) apples, then I’d write the expression as ( 2b – 6 ).
Understanding these strategies helps me tackle basic algebra problems efficiently. Remember, practice makes perfect, and each problem is an opportunity to improve.
In algebra, we encounter a variety of equation types and each serves a unique role in problem-solving. Here, I’ll brief you about some typical forms.
Linear Equations : These are the simplest form, where the highest power of the variable is one. They take the general form ( ax + b = 0 ), where ( a ) and ( b ) are constants, and ( x ) is the variable. For example, ( 2x + 3 = 0 ) is a linear equation.
Polynomial Equations : Unlike for linear equations, polynomial equations can have variables raised to higher powers. The general form of a polynomial equation is ( $a_nx^n + a_{n-1}x^{n-1} + … + a_2x^2 + a_1x + a_0 = 0$ ). In this equation, ( n ) is the highest power, and ( $a_n$ ), ( $a_{n-1} $), …, ( $a_0$ ) represent the coefficients which can be any real number.
- Binomial Equations : They are a specific type of polynomial where there are exactly two terms. Like ($ x^2 – 4 $), which is also the difference of squares, a common format encountered in factoring.
To understand how equations can be solved by factoring, consider the quadratic equation ( $x^2$ – 5x + 6 = 0 ). I can factor this into ( (x-2)(x-3) = 0 ), which allows me to find the roots of the equation.
Here’s how some equations look when classified by degree:
Remember, identification and proper handling of these equations are essential in algebra as they form the basis for complex problem-solving.
In my experience with algebra, I’ve found that the journey begins as early as the 6th grade, where students get their first taste of this fascinating subject with the introduction of variables representing an unknown quantity.
I’ve created worksheets and activities aimed specifically at making this early transition engaging and educational.
6th Grade :
Moving forward, the complexity of algebraic problems increases:
7th and 8th Grades :
- Mastery of negative numbers: students practice operations like ( -3 – 4 ) or ( -5 $\times$ 2 ).
- Exploring the rules of basic arithmetic operations with negative numbers.
- Worksheets often contain numeric and literal expressions that help solidify their concepts.
Advanced topics like linear algebra are typically reserved for higher education. However, the solid foundation set in these early grades is crucial. I’ve developed materials to encourage students to understand and enjoy algebra’s logic and structure.
Remember, algebra is a tool that helps us quantify and solve problems, both numerical and abstract. My goal is to make learning these concepts, from numbers to numeric operations, as accessible as possible, while always maintaining a friendly approach to education.
I’ve walked through various simple algebra problems to help establish a foundational understanding of algebraic concepts. Through practice, you’ll find that these problems become more intuitive, allowing you to tackle more complex equations with confidence.
Remember, the key steps in solving any algebra problem include:
- Identifying variables and what they represent.
- Setting up the equation that reflects the problem statement.
- Applying algebraic rules such as the distributive property ($a(b + c) = ab + ac$), combining like terms, and inverse operations.
- Checking your solutions by substituting them back into the original equations to ensure they work.
As you continue to engage with algebra, consistently revisiting these steps will deepen your understanding and increase your proficiency. Don’t get discouraged by mistakes; they’re an important part of the learning process.
I hope that the straightforward problems I’ve presented have made algebra feel more manageable and a little less daunting. Happy solving!
- Pre Calculus
- Probability
- Sets & Set Theory
- Trigonometry

Game Central

Get step-by-step explanations
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language
- Solve equations and inequalities
- Simplify expressions
- Factor polynomials
- Graph equations and inequalities
- Advanced solvers
- All solvers
- Arithmetics
- Determinant
- Percentages
- Scientific Notation
- Inequalities
What can QuickMath do?
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students.
- The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and cancelling common factors within a fraction.
- The equations section lets you solve an equation or system of equations. You can usually find the exact answer or, if necessary, a numerical answer to almost any accuracy you require.
- The inequalities section lets you solve an inequality or a system of inequalities for a single variable. You can also plot inequalities in two variables.
- The calculus section will carry out differentiation as well as definite and indefinite integration.
- The matrices section contains commands for the arithmetic manipulation of matrices.
- The graphs section contains commands for plotting equations and inequalities.
- The numbers section has a percentages command for explaining the most common types of percentage problems and a section for dealing with scientific notation.

Math Topics
More solvers.
- Add Fractions
- Simplify Fractions
- Math Article
Algebra Problems
Algebra problems are not only based on algebraic expressions but also on various types of equations in Maths where a quantity or variable is unknown to us. Many of us are familiar with the word problem, but are we aware of the fact and problems related to variables and constants? When we say 5 it means a number but what if we say x=5 or 5y or something like that?
This is where algebra came into existence algebra is that branch of mathematics which not only deals with numbers but also variable and alphabets. The versatility of Algebra is very deep and very conceptual, all the non-numeric character represents variable and numeric as constants. Let us solve some problems based algebra with solutions which will cover the syllabus for class 6, 7, 8. Below are some of the examples of algebraic expressions .
For example.
Algebra Word Problems deal with real-time situations and solutions which can be solved using algebra.
Basic Algebra Identities
- (a + b) 2 = a 2 + b 2 + 2ab
- (a – b) 2 = a 2 + b 2 – 2ab
- a 2 – b 2 = (a + b)(a – b)
- a 2 + b 2 = (a + b) 2 – 2ab = (a – b) 2 + 2ab
- a 3 + b 3 = (a + b)(a 2 – ab + b 2 )
- a 3 – b 3 = (a – b)(a 2 + ab + b 2 )
- (a + b) 3 = a 3 + 3ab(a + b) + b 3
- (a – b) 3 = a 3 – 3ab(a – b) – b 3
Algebra problems With Solutions
Example 1: Solve, (x-1) 2 = [4√(x-4)] 2 Solution: x 2 -2x+1 = 16(x-4)
x 2 -2x+1 = 16x-64
x 2 -18x+65 = 0
(x-13) (x-5) = 0
Hence, x = 13 and x = 5.
Algebra Problems for Class 6
In class 6, students will be introduced with an algebra concept. Here, you will learn how the unknown values are represented in terms of variables. The given expression can be solved only if we know the value of unknown variable. Let us see some examples.
Example: Solve, 4x + 5 when, x = 3.
Solution: Given, 4x + 5
Now putting the value of x=3, we get;
4 (3) + 5 = 12 + 5 = 17.
Example: Give expressions for the following cases:
(i) 12 added to 2x
(ii) 6 multiplied by y
(iii) 25 subtracted from z
(iv) 17 times of m
(i) 12 + 2x
Algebra Problems for Class 7
In class 7, students will deal with algebraic expressions like x+y, xy, 32x 2 -12y 2 , etc. There are different kinds of the terminology used in case algebraic equations such as;
- Coefficient
Let us understand these terms with an example. Suppose 4x + 5y is an algebraic expression, then 4x and 5y are the terms. Since here the variables used are x and y, therefore, x and y are the factors of 4x + 5y. And the numerical factor attached to the variables are the coefficient such as 4 and 5 are the coefficient of x and y in the given expression.
Any expression with one or more terms is called a polynomial. Specifically, a one-term expression is called a monomial; a two-term expression is called a binomial, and a three-term expression is called a trinomial.
Terms which have the same algebraic factors are like terms . Terms which have different algebraic factors are unlike terms . Thus, terms 4xy and – 3xy are like terms; but terms 4xy and – 3x are not like terms.
Example: Add 3x + 5x
Solution: Since 3x and 5x have the same algebraic factors, hence, they are like terms and can be added by their coefficient.
3x + 5x = 8x
Example: Collect like terms and simplify the expression: 12x 2 – 9x + 5x – 4x 2 – 7x + 10.
Solution: 12x 2 – 9x + 5x – 4x 2 – 7x + 10
= (12 – 4)x 2 – 9x + 5x – 7x + 10
= 8x 2 – 11x + 10
Algebra Problems for Class 8
Here, students will deal with algebraic identities. See the examples.
Example: Solve (2x+y) 2
Solution: Using the identity: (a+b) 2 = a 2 + b 2 + 2 ab, we get;
(2x+y) = (2x) 2 + y 2 + 2.2x.y = 4x 2 + y 2 + 4xy
Example: Solve (99) 2 using algebraic identity.
Solution: We can write, 99 = 100 -1
Therefore, (100 – 1 ) 2
= 100 2 + 1 2 – 2 x 100 x 1 [By identity: (a -b) 2 = a 2 + b 2 – 2ab
= 10000 + 1 – 200
Algebra Word Problems
Question 1: There are 47 boys in the class. This is three more than four times the number of girls. How many girls are there in the class?
Solution: Let the number of girls be x
As per the given statement,
4 x + 3 = 47
4x = 47 – 3
Question 2: The sum of two consecutive numbers is 41. What are the numbers?
Solution: Let one of the numbers be x.
Then the other number will x+1
Now, as per the given questions,
x + x + 1 = 41
2x + 1 = 41
So, the first number is 20 and second number is 20+1 = 21
Linear Algebra Problems
There are various methods For Solving the Linear Equations
- Cross multiplication method
- Replacement method or Substitution method
- Hit and trial method
There are Variety of different Algebra problem present and are solved depending upon their functionality and state. For example, a linear equation problem can’t be solved using a quadratic equation formula and vice verse for, e.g., x+x/2=7 then solve for x is an equation in one variable for x which can be satisfied by only one value of x. Whereas x 2 +5x+6 is a quadratic equation which is satisfied for two values of x the domain of algebra is huge and vast so for more information. Visit BYJU’S. where different techniques are explained different algebra problem.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu
Khan Academy Blog
Free Math Worksheets — Over 100k free practice problems on Khan Academy
Looking for free math worksheets.
You’ve found something even better!
That’s because Khan Academy has over 100,000 free practice questions. And they’re even better than traditional math worksheets – more instantaneous, more interactive, and more fun!
Just choose your grade level or topic to get access to 100% free practice questions:
Kindergarten, basic geometry, pre-algebra, algebra basics, high school geometry.
- Trigonometry
Statistics and probability
High school statistics, ap®︎/college statistics, precalculus, differential calculus, integral calculus, ap®︎/college calculus ab, ap®︎/college calculus bc, multivariable calculus, differential equations, linear algebra.
- Addition and subtraction
- Place value (tens and hundreds)
- Addition and subtraction within 20
- Addition and subtraction within 100
- Addition and subtraction within 1000
- Measurement and data
- Counting and place value
- Measurement and geometry
- Place value
- Measurement, data, and geometry
- Add and subtract within 20
- Add and subtract within 100
- Add and subtract within 1,000
- Money and time
- Measurement
- Intro to multiplication
- 1-digit multiplication
- Addition, subtraction, and estimation
- Intro to division
- Understand fractions
- Equivalent fractions and comparing fractions
- More with multiplication and division
- Arithmetic patterns and problem solving
- Quadrilaterals
- Represent and interpret data
- Multiply by 1-digit numbers
- Multiply by 2-digit numbers
- Factors, multiples and patterns
- Add and subtract fractions
- Multiply fractions
- Understand decimals
- Plane figures
- Measuring angles
- Area and perimeter
- Units of measurement
- Decimal place value
- Add decimals
- Subtract decimals
- Multi-digit multiplication and division
- Divide fractions
- Multiply decimals
- Divide decimals
- Powers of ten
- Coordinate plane
- Algebraic thinking
- Converting units of measure
- Properties of shapes
- Ratios, rates, & percentages
- Arithmetic operations
- Negative numbers
- Properties of numbers
- Variables & expressions
- Equations & inequalities introduction
- Data and statistics
- Negative numbers: addition and subtraction
- Negative numbers: multiplication and division
- Fractions, decimals, & percentages
- Rates & proportional relationships
- Expressions, equations, & inequalities
- Numbers and operations
- Solving equations with one unknown
- Linear equations and functions
- Systems of equations
- Geometric transformations
- Data and modeling
- Volume and surface area
- Pythagorean theorem
- Transformations, congruence, and similarity
- Arithmetic properties
- Factors and multiples
- Reading and interpreting data
- Negative numbers and coordinate plane
- Ratios, rates, proportions
- Equations, expressions, and inequalities
- Exponents, radicals, and scientific notation
- Foundations
- Algebraic expressions
- Linear equations and inequalities
- Graphing lines and slope
- Expressions with exponents
- Quadratics and polynomials
- Equations and geometry
- Algebra foundations
- Solving equations & inequalities
- Working with units
- Linear equations & graphs
- Forms of linear equations
- Inequalities (systems & graphs)
- Absolute value & piecewise functions
- Exponents & radicals
- Exponential growth & decay
- Quadratics: Multiplying & factoring
- Quadratic functions & equations
- Irrational numbers
- Performing transformations
- Transformation properties and proofs
- Right triangles & trigonometry
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry (Advanced)
- Analytic geometry
- Conic sections
- Solid geometry
- Polynomial arithmetic
- Complex numbers
- Polynomial factorization
- Polynomial division
- Polynomial graphs
- Rational exponents and radicals
- Exponential models
- Transformations of functions
- Rational functions
- Trigonometric functions
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry
- Trigonometric equations and identities
- Analyzing categorical data
- Displaying and comparing quantitative data
- Summarizing quantitative data
- Modeling data distributions
- Exploring bivariate numerical data
- Study design
- Probability
- Counting, permutations, and combinations
- Random variables
- Sampling distributions
- Confidence intervals
- Significance tests (hypothesis testing)
- Two-sample inference for the difference between groups
- Inference for categorical data (chi-square tests)
- Advanced regression (inference and transforming)
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- Scatterplots
- Data distributions
- Two-way tables
- Binomial probability
- Normal distributions
- Displaying and describing quantitative data
- Inference comparing two groups or populations
- Chi-square tests for categorical data
- More on regression
- Prepare for the 2020 AP®︎ Statistics Exam
- AP®︎ Statistics Standards mappings
- Polynomials
- Composite functions
- Probability and combinatorics
- Limits and continuity
- Derivatives: definition and basic rules
- Derivatives: chain rule and other advanced topics
- Applications of derivatives
- Analyzing functions
- Parametric equations, polar coordinates, and vector-valued functions
- Applications of integrals
- Differentiation: definition and basic derivative rules
- Differentiation: composite, implicit, and inverse functions
- Contextual applications of differentiation
- Applying derivatives to analyze functions
- Integration and accumulation of change
- Applications of integration
- AP Calculus AB solved free response questions from past exams
- AP®︎ Calculus AB Standards mappings
- Infinite sequences and series
- AP Calculus BC solved exams
- AP®︎ Calculus BC Standards mappings
- Integrals review
- Integration techniques
- Thinking about multivariable functions
- Derivatives of multivariable functions
- Applications of multivariable derivatives
- Integrating multivariable functions
- Green’s, Stokes’, and the divergence theorems
- First order differential equations
- Second order linear equations
- Laplace transform
- Vectors and spaces
- Matrix transformations
- Alternate coordinate systems (bases)
Frequently Asked Questions about Khan Academy and Math Worksheets
Why is khan academy even better than traditional math worksheets.
Khan Academy’s 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don’t need to be graded, and don’t require a printer.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets look like?
Here’s an example:
What are teachers saying about Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets?
“My students love Khan Academy because they can immediately learn from their mistakes, unlike traditional worksheets.”
Is Khan Academy free?
Khan Academy’s practice questions are 100% free—with no ads or subscriptions.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets cover?
Our 100,000+ practice questions cover every math topic from arithmetic to calculus, as well as ELA, Science, Social Studies, and more.
Is Khan Academy a company?
Khan Academy is a nonprofit with a mission to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere.
Want to get even more out of Khan Academy?
Then be sure to check out our teacher tools . They’ll help you assign the perfect practice for each student from our full math curriculum and track your students’ progress across the year. Plus, they’re also 100% free — with no subscriptions and no ads.
Praxis Core Math
Course: praxis core math > unit 1.
- Algebraic properties | Lesson
- Algebraic properties | Worked example
- Solution procedures | Lesson
- Solution procedures | Worked example
- Equivalent expressions | Lesson
- Equivalent expressions | Worked example
- Creating expressions and equations | Lesson
- Creating expressions and equations | Worked example
Algebraic word problems | Lesson
- Algebraic word problems | Worked example
- Linear equations | Lesson
- Linear equations | Worked example
- Quadratic equations | Lesson
- Quadratic equations | Worked example
What are algebraic word problems?
What skills are needed.
- Translating sentences to equations
- Solving linear equations with one variable
- Evaluating algebraic expressions
- Solving problems using Venn diagrams
How do we solve algebraic word problems?
- Define a variable.
- Write an equation using the variable.
- Solve the equation.
- If the variable is not the answer to the word problem, use the variable to calculate the answer.
What's a Venn diagram?
- 7 + 10 − 13 = 4 brought both food and drinks.
- 7 − 4 = 3 brought only food.
- 10 − 4 = 6 brought only drinks.
- Your answer should be
- an integer, like 6
- a simplified proper fraction, like 3 / 5
- a simplified improper fraction, like 7 / 4
- a mixed number, like 1 3 / 4
- an exact decimal, like 0.75
- a multiple of pi, like 12 pi or 2 / 3 pi
- (Choice A) $ 4 A $ 4
- (Choice B) $ 5 B $ 5
- (Choice C) $ 9 C $ 9
- (Choice D) $ 14 D $ 14
- (Choice E) $ 20 E $ 20
- (Choice A) 10 A 10
- (Choice B) 12 B 12
- (Choice C) 24 C 24
- (Choice D) 30 D 30
- (Choice E) 32 E 32
- (Choice A) 4 A 4
- (Choice B) 10 B 10
- (Choice C) 14 C 14
- (Choice D) 18 D 18
- (Choice E) 22 E 22
Things to remember
Want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations.
Algebra (all content) 20 units · 412 skills. Unit 1 Introduction to algebra. Unit 2 Solving basic equations & inequalities (one variable, linear) Unit 3 Linear equations, functions, & graphs. Unit 4 Sequences. Unit 5 System of equations. Unit 6 Two-variable inequalities. Unit 7 Functions. Unit 8 Absolute value equations, functions, & inequalities.
Get math help in your language. Works in Spanish, Hindi, German, and more. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
Unit test. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 1,100 Mastery points! Start Unit test. There are lots of strategies we can use to solve equations. Let's explore some different ways to solve equations and inequalities. We'll also see what it takes for an equation to have no solution, or infinite solutions.
Live Online Course. In this online class, students proactively engage with the fundamental concepts of algebra. Part of our introductory math series, Introduction to Algebra A builds on the foundations of both Prealgebra 1 and Prealgebra 2. This advanced math course is offered in two formats: a live online course or a self-paced course.
Free Pre-Algebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators step-by-step ... define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem. Show more; en. Related Symbolab blog posts. Practice, practice, practice. Math can be an intimidating subject. Each new topic we learn has symbols and problems we ...
The Algebra 1 course, often taught in the 9th grade, covers Linear equations, inequalities, functions, and graphs; Systems of equations and inequalities; Extension of the concept of a function; Exponential models; and Quadratic equations, functions, and graphs. Khan Academy's Algebra 1 course is built to deliver a comprehensive, illuminating, engaging, and Common Core aligned experience!
Factoring by Substitution. Rational Expressions. Simplifying Rational Expressions. Factoring Compound Quadratics: a x 4 + b x 2 + c. \, ax^4 + bx^2 + c ax4 +bx2 + c. Factoring Cubic Polynomials. Descartes' Rule of Signs. Fundamental Theorem of Algebra.
Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems with the free GeoGebra Math Solver. Enhance your problem-solving skills while learning how to solve equations on your own. Try it now!
Solving algebra problems often starts with simplifying expressions. Here's a simple method to follow: Combine like terms: Terms that have the same variable can be combined. For instance, ( 3x + 4x = 7x ). Isolate the variable: Move the variable to one side of the equation. If the equation is ( 2x + 5 = 13 ), my job is to get ( x ) by itself ...
Get math help in your language. Works in Spanish, Hindi, German, and more. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students. The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and ...
Intro to equations with variables on both sides. (Opens a modal) Equations with variables on both sides: 20-7x=6x-6. (Opens a modal) Equation with variables on both sides: fractions. (Opens a modal) Equation with the variable in the denominator. (Opens a modal) Figuring out missing algebraic step.
We offer hundreds of free videos featuring AoPS founder Richard Rusczyk. Below are videos aligned to our Prealgebra text, the first half of our Introduction to Algebra text, and our Introduction to Counting & Probability text.. We also regularly produce MATHCOUNTS Minis featuring problems from State-level MATHCOUNTS competitions, as well as videos for select AMC 10, AMC 12, and AIME problems.
A thorough introduction for students in grades 6-9 to algebra topics such as linear equations, ratios, quadratic equations, special factorizations, complex numbers, graphing linear and quadratic equations, linear and quadratic inequalities, functions, polynomials, exponents and logarithms, absolute value, sequences and series, and more!
Algebra Calculator - get free step-by-step solutions for your algebra math problems ... Solving simultaneous equations is one small algebra step further on from simple equations. Symbolab math solutions... Enter a problem.
There are Variety of different Algebra problem present and are solved depending upon their functionality and state. For example, a linear equation problem can't be solved using a quadratic equation formula and vice verse for, e.g., x+x/2=7 then solve for x is an equation in one variable for x which can be satisfied by only one value of x.
Step 1: Multiply the denominators (x/3) Step 2: Cross multiply the numerators and denominators (2x1 and 3x1) Step 3: Add the two products together (2x1=2, 3x1=3 therefore, add 2+3). WITHOUT touching the denominator! Step 4: 5/3b + 5 = 20. Subtract 5 from both sides of the equation to cancel out 5. Step 5. divide 5/3 to 15.
Khan Academy's 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don't need to be graded, and don't require a printer. Math Worksheets. Khan Academy. Math worksheets take forever to hunt down across the internet. Khan Academy is your one-stop-shop for practice from arithmetic to calculus. Math worksheets can vary in quality from ...
Solving an equation for a variable. The perimeter of a rectangle is equal to 2 times the length plus 2 times the width. We can solve for the length by isolating it on one side of the equation. We do this by subtracting 2 times the width from both sides, and then dividing both sides by 2. This gives us the formula for the length.
Art of Problem Solving offers two other multifaceted programs. Beast Academy is our comic-based online math curriculum for students ages 6-13. And AoPS Academy brings our methodology to students grades 2-12 through small, in-person classes at local campuses. ... Alcumus is aligned to our Introductory Math, Intermediate Algebra, and ...
Popular Calculators. Fractions Radical Equation Factoring Inverse Quadratic Simplify Slope Domain Antiderivatives Polynomial Equation Log Equation Cross Product Partial Derivative Implicit Derivative Tangent Complex Numbers. Symbolab: equation search and math solver - solves algebra, trigonometry and calculus problems step by step.
Solving algebraic word problems requires us to combine our ability to create equations and solve them. To solve an algebraic word problem: Define a variable. Write an equation using the variable. Solve the equation. If the variable is not the answer to the word problem, use the variable to calculate the answer.