
Home » Tips for Teachers » 7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives

7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
In recent years, the question of why students should not have homework has become a topic of intense debate among educators, parents, and students themselves. This discussion stems from a growing body of research that challenges the traditional view of homework as an essential component of academic success. The notion that homework is an integral part of learning is being reevaluated in light of new findings about its effectiveness and impact on students’ overall well-being.

The push against homework is not just about the hours spent on completing assignments; it’s about rethinking the role of education in fostering the well-rounded development of young individuals. Critics argue that homework, particularly in excessive amounts, can lead to negative outcomes such as stress, burnout, and a diminished love for learning. Moreover, it often disproportionately affects students from disadvantaged backgrounds, exacerbating educational inequities. The debate also highlights the importance of allowing children to have enough free time for play, exploration, and family interaction, which are crucial for their social and emotional development.
Checking 13yo’s math homework & I have just one question. I can catch mistakes & help her correct. But what do kids do when their parent isn’t an Algebra teacher? Answer: They get frustrated. Quit. Get a bad grade. Think they aren’t good at math. How is homework fair??? — Jay Wamsted (@JayWamsted) March 24, 2022
As we delve into this discussion, we explore various facets of why reducing or even eliminating homework could be beneficial. We consider the research, weigh the pros and cons, and examine alternative approaches to traditional homework that can enhance learning without overburdening students.
Once you’ve finished this article, you’ll know:
- Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts →
- 7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework →
- Opposing Views on Homework Practices →
- Exploring Alternatives to Homework →
Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts: Diverse Perspectives on Homework
In the ongoing conversation about the role and impact of homework in education, the perspectives of those directly involved in the teaching process are invaluable. Teachers and education industry experts bring a wealth of experience and insights from the front lines of learning. Their viewpoints, shaped by years of interaction with students and a deep understanding of educational methodologies, offer a critical lens through which we can evaluate the effectiveness and necessity of homework in our current educational paradigm.
Check out this video featuring Courtney White, a high school language arts teacher who gained widespread attention for her explanation of why she chooses not to assign homework.
Here are the insights and opinions from various experts in the educational field on this topic:
“I teach 1st grade. I had parents ask for homework. I explained that I don’t give homework. Home time is family time. Time to play, cook, explore and spend time together. I do send books home, but there is no requirement or checklist for reading them. Read them, enjoy them, and return them when your child is ready for more. I explained that as a parent myself, I know they are busy—and what a waste of energy it is to sit and force their kids to do work at home—when they could use that time to form relationships and build a loving home. Something kids need more than a few math problems a week.” — Colleen S. , 1st grade teacher
“The lasting educational value of homework at that age is not proven. A kid says the times tables [at school] because he studied the times tables last night. But over a long period of time, a kid who is drilled on the times tables at school, rather than as homework, will also memorize their times tables. We are worried about young children and their social emotional learning. And that has to do with physical activity, it has to do with playing with peers, it has to do with family time. All of those are very important and can be removed by too much homework.” — David Bloomfield , education professor at Brooklyn College and the City University of New York graduate center
“Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?’” — John Hattie , professor
”Many kids are working as many hours as their overscheduled parents and it is taking a toll – psychologically and in many other ways too. We see kids getting up hours before school starts just to get their homework done from the night before… While homework may give kids one more responsibility, it ignores the fact that kids do not need to grow up and become adults at ages 10 or 12. With schools cutting recess time or eliminating playgrounds, kids absorb every single stress there is, only on an even higher level. Their brains and bodies need time to be curious, have fun, be creative and just be a kid.” — Pat Wayman, teacher and CEO of HowtoLearn.com
7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework
Let’s delve into the reasons against assigning homework to students. Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices.
1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences

The ongoing debate about homework often focuses on its educational value, but a vital aspect that cannot be overlooked is the significant stress and health consequences it brings to students. In the context of American life, where approximately 70% of people report moderate or extreme stress due to various factors like mass shootings, healthcare affordability, discrimination, racism, sexual harassment, climate change, presidential elections, and the need to stay informed, the additional burden of homework further exacerbates this stress, particularly among students.
Key findings and statistics reveal a worrying trend:
- Overwhelming Student Stress: A staggering 72% of students report being often or always stressed over schoolwork, with a concerning 82% experiencing physical symptoms due to this stress.
- Serious Health Issues: Symptoms linked to homework stress include sleep deprivation, headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems.
- Sleep Deprivation: Despite the National Sleep Foundation recommending 8.5 to 9.25 hours of sleep for healthy adolescent development, students average just 6.80 hours of sleep on school nights. About 68% of students stated that schoolwork often or always prevented them from getting enough sleep, which is critical for their physical and mental health.
- Turning to Unhealthy Coping Mechanisms: Alarmingly, the pressure from excessive homework has led some students to turn to alcohol and drugs as a way to cope with stress.
This data paints a concerning picture. Students, already navigating a world filled with various stressors, find themselves further burdened by homework demands. The direct correlation between excessive homework and health issues indicates a need for reevaluation. The goal should be to ensure that homework if assigned, adds value to students’ learning experiences without compromising their health and well-being.
By addressing the issue of homework-related stress and health consequences, we can take a significant step toward creating a more nurturing and effective educational environment. This environment would not only prioritize academic achievement but also the overall well-being and happiness of students, preparing them for a balanced and healthy life both inside and outside the classroom.
2. Inequitable Impact and Socioeconomic Disparities
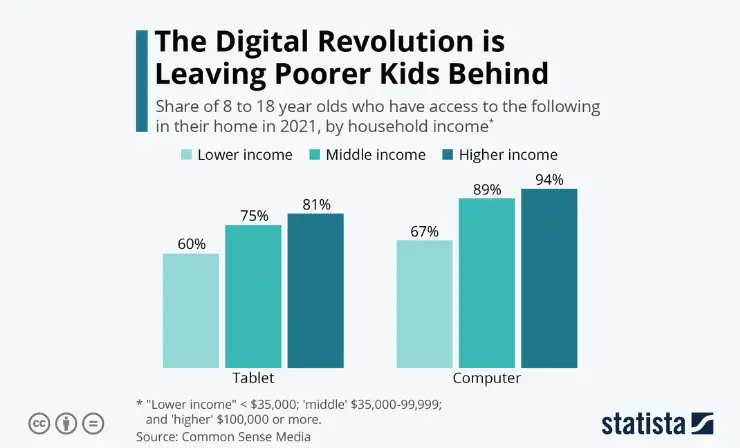
In the discourse surrounding educational equity, homework emerges as a factor exacerbating socioeconomic disparities, particularly affecting students from lower-income families and those with less supportive home environments. While homework is often justified as a means to raise academic standards and promote equity, its real-world impact tells a different story.
The inequitable burden of homework becomes starkly evident when considering the resources required to complete it, especially in the digital age. Homework today often necessitates a computer and internet access – resources not readily available to all students. This digital divide significantly disadvantages students from lower-income backgrounds, deepening the chasm between them and their more affluent peers.
Key points highlighting the disparities:
- Digital Inequity: Many students lack access to necessary technology for homework, with low-income families disproportionately affected.
- Impact of COVID-19: The pandemic exacerbated these disparities as education shifted online, revealing the extent of the digital divide.
- Educational Outcomes Tied to Income: A critical indicator of college success is linked more to family income levels than to rigorous academic preparation. Research indicates that while 77% of students from high-income families graduate from highly competitive colleges, only 9% from low-income families achieve the same . This disparity suggests that the pressure of heavy homework loads, rather than leveling the playing field, may actually hinder the chances of success for less affluent students.
Moreover, the approach to homework varies significantly across different types of schools. While some rigorous private and preparatory schools in both marginalized and affluent communities assign extreme levels of homework, many progressive schools focusing on holistic learning and self-actualization opt for no homework, yet achieve similar levels of college and career success. This contrast raises questions about the efficacy and necessity of heavy homework loads in achieving educational outcomes.
The issue of homework and its inequitable impact is not just an academic concern; it is a reflection of broader societal inequalities. By continuing practices that disproportionately burden students from less privileged backgrounds, the educational system inadvertently perpetuates the very disparities it seeks to overcome.
3. Negative Impact on Family Dynamics

Homework, a staple of the educational system, is often perceived as a necessary tool for academic reinforcement. However, its impact extends beyond the realm of academics, significantly affecting family dynamics. The negative repercussions of homework on the home environment have become increasingly evident, revealing a troubling pattern that can lead to conflict, mental health issues, and domestic friction.
A study conducted in 2015 involving 1,100 parents sheds light on the strain homework places on family relationships. The findings are telling:
- Increased Likelihood of Conflicts: Families where parents did not have a college degree were 200% more likely to experience fights over homework.
- Misinterpretations and Misunderstandings: Parents often misinterpret their children’s difficulties with homework as a lack of attention in school, leading to feelings of frustration and mistrust on both sides.
- Discriminatory Impact: The research concluded that the current approach to homework disproportionately affects children whose parents have lower educational backgrounds, speak English as a second language, or belong to lower-income groups.
The issue is not confined to specific demographics but is a widespread concern. Samantha Hulsman, a teacher featured in Education Week Teacher , shared her personal experience with the toll that homework can take on family time. She observed that a seemingly simple 30-minute assignment could escalate into a three-hour ordeal, causing stress and strife between parents and children. Hulsman’s insights challenge the traditional mindset about homework, highlighting a shift towards the need for skills such as collaboration and problem-solving over rote memorization of facts.
The need of the hour is to reassess the role and amount of homework assigned to students. It’s imperative to find a balance that facilitates learning and growth without compromising the well-being of the family unit. Such a reassessment would not only aid in reducing domestic conflicts but also contribute to a more supportive and nurturing environment for children’s overall development.
4. Consumption of Free Time

In recent years, a growing chorus of voices has raised concerns about the excessive burden of homework on students, emphasizing how it consumes their free time and impedes their overall well-being. The issue is not just the quantity of homework, but its encroachment on time that could be used for personal growth, relaxation, and family bonding.
Authors Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish , in their book “The Case Against Homework,” offer an insightful window into the lives of families grappling with the demands of excessive homework. They share stories from numerous interviews conducted in the mid-2000s, highlighting the universal struggle faced by families across different demographics. A poignant account from a parent in Menlo Park, California, describes nightly sessions extending until 11 p.m., filled with stress and frustration, leading to a soured attitude towards school in both the child and the parent. This narrative is not isolated, as about one-third of the families interviewed expressed feeling crushed by the overwhelming workload.
Key points of concern:
- Excessive Time Commitment: Students, on average, spend over 6 hours in school each day, and homework adds significantly to this time, leaving little room for other activities.
- Impact on Extracurricular Activities: Homework infringes upon time for sports, music, art, and other enriching experiences, which are as crucial as academic courses.
- Stifling Creativity and Self-Discovery: The constant pressure of homework limits opportunities for students to explore their interests and learn new skills independently.
The National Education Association (NEA) and the National PTA (NPTA) recommend a “10 minutes of homework per grade level” standard, suggesting a more balanced approach. However, the reality often far exceeds this guideline, particularly for older students. The impact of this overreach is profound, affecting not just academic performance but also students’ attitudes toward school, their self-confidence, social skills, and overall quality of life.
Furthermore, the intense homework routine’s effectiveness is doubtful, as it can overwhelm students and detract from the joy of learning. Effective learning builds on prior knowledge in an engaging way, but excessive homework in a home setting may be irrelevant and uninteresting. The key challenge is balancing homework to enhance learning without overburdening students, allowing time for holistic growth and activities beyond academics. It’s crucial to reassess homework policies to support well-rounded development.
5. Challenges for Students with Learning Disabilities
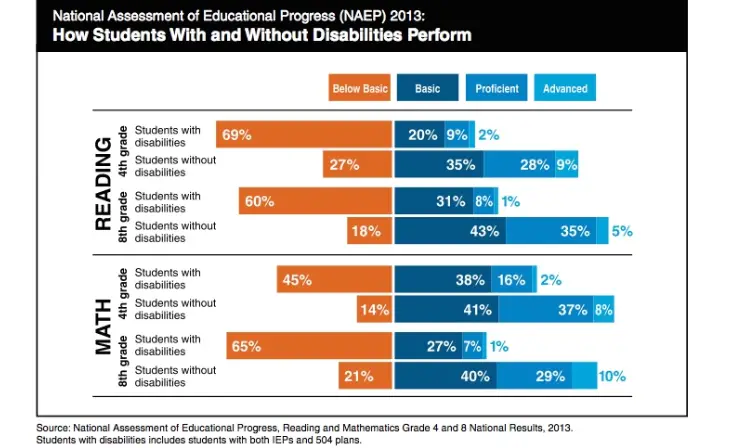
Homework, a standard educational tool, poses unique challenges for students with learning disabilities, often leading to a frustrating and disheartening experience. These challenges go beyond the typical struggles faced by most students and can significantly impede their educational progress and emotional well-being.
Child psychologist Kenneth Barish’s insights in Psychology Today shed light on the complex relationship between homework and students with learning disabilities:
- Homework as a Painful Endeavor: For students with learning disabilities, completing homework can be likened to “running with a sprained ankle.” It’s a task that, while doable, is fraught with difficulty and discomfort.
- Misconceptions about Laziness: Often, children who struggle with homework are perceived as lazy. However, Barish emphasizes that these students are more likely to be frustrated, discouraged, or anxious rather than unmotivated.
- Limited Improvement in School Performance: The battles over homework rarely translate into significant improvement in school for these children, challenging the conventional notion of homework as universally beneficial.
These points highlight the need for a tailored approach to homework for students with learning disabilities. It’s crucial to recognize that the traditional homework model may not be the most effective or appropriate method for facilitating their learning. Instead, alternative strategies that accommodate their unique needs and learning styles should be considered.
In conclusion, the conventional homework paradigm needs reevaluation, particularly concerning students with learning disabilities. By understanding and addressing their unique challenges, educators can create a more inclusive and supportive educational environment. This approach not only aids in their academic growth but also nurtures their confidence and overall development, ensuring that they receive an equitable and empathetic educational experience.
6. Critique of Underlying Assumptions about Learning
The longstanding belief in the educational sphere that more homework automatically translates to more learning is increasingly being challenged. Critics argue that this assumption is not only flawed but also unsupported by solid evidence, questioning the efficacy of homework as an effective learning tool.
Alfie Kohn , a prominent critic of homework, aptly compares students to vending machines in this context, suggesting that the expectation of inserting an assignment and automatically getting out of learning is misguided. Kohn goes further, labeling homework as the “greatest single extinguisher of children’s curiosity.” This critique highlights a fundamental issue: the potential of homework to stifle the natural inquisitiveness and love for learning in children.
The lack of concrete evidence supporting the effectiveness of homework is evident in various studies:
- Marginal Effectiveness of Homework: A study involving 28,051 high school seniors found that the effectiveness of homework was marginal, and in some cases, it was counterproductive, leading to more academic problems than solutions.
- No Correlation with Academic Achievement: Research in “ National Differences, Global Similarities ” showed no correlation between homework and academic achievement in elementary students, and any positive correlation in middle or high school diminished with increasing homework loads.
- Increased Academic Pressure: The Teachers College Record published findings that homework adds to academic pressure and societal stress, exacerbating performance gaps between students from different socioeconomic backgrounds.
These findings bring to light several critical points:
- Quality Over Quantity: According to a recent article in Monitor on Psychology , experts concur that the quality of homework assignments, along with the quality of instruction, student motivation, and inherent ability, is more crucial for academic success than the quantity of homework.
- Counterproductive Nature of Excessive Homework: Excessive homework can lead to more academic challenges, particularly for students already facing pressures from other aspects of their lives.
- Societal Stress and Performance Gaps: Homework can intensify societal stress and widen the academic performance divide.
The emerging consensus from these studies suggests that the traditional approach to homework needs rethinking. Rather than focusing on the quantity of assignments, educators should consider the quality and relevance of homework, ensuring it truly contributes to learning and development. This reassessment is crucial for fostering an educational environment that nurtures curiosity and a love for learning, rather than extinguishing it.
7. Issues with Homework Enforcement, Reliability, and Temptation to Cheat
In the academic realm, the enforcement of homework is a subject of ongoing debate, primarily due to its implications on student integrity and the true value of assignments. The challenges associated with homework enforcement often lead to unintended yet significant issues, such as cheating, copying, and a general undermining of educational values.
Key points highlighting enforcement challenges:
- Difficulty in Enforcing Completion: Ensuring that students complete their homework can be a complex task, and not completing homework does not always correlate with poor grades.
- Reliability of Homework Practice: The reliability of homework as a practice tool is undermined when students, either out of desperation or lack of understanding, choose shortcuts over genuine learning. This approach can lead to the opposite of the intended effect, especially when assignments are not well-aligned with the students’ learning levels or interests.
- Temptation to Cheat: The issue of cheating is particularly troubling. According to a report by The Chronicle of Higher Education , under the pressure of at-home assignments, many students turn to copying others’ work, plagiarizing, or using creative technological “hacks.” This tendency not only questions the integrity of the learning process but also reflects the extreme stress that homework can induce.
- Parental Involvement in Completion: As noted in The American Journal of Family Therapy , this raises concerns about the authenticity of the work submitted. When parents complete assignments for their children, it not only deprives the students of the opportunity to learn but also distorts the purpose of homework as a learning aid.
In conclusion, the challenges of homework enforcement present a complex problem that requires careful consideration. The focus should shift towards creating meaningful, manageable, and quality-driven assignments that encourage genuine learning and integrity, rather than overwhelming students and prompting counterproductive behaviors.
Addressing Opposing Views on Homework Practices
While opinions on homework policies are diverse, understanding different viewpoints is crucial. In the following sections, we will examine common arguments supporting homework assignments, along with counterarguments that offer alternative perspectives on this educational practice.
1. Improvement of Academic Performance

Homework is commonly perceived as a means to enhance academic performance, with the belief that it directly contributes to better grades and test scores. This view posits that through homework, students reinforce what they learn in class, leading to improved understanding and retention, which ultimately translates into higher academic achievement.
However, the question of why students should not have homework becomes pertinent when considering the complex relationship between homework and academic performance. Studies have indicated that excessive homework doesn’t necessarily equate to higher grades or test scores. Instead, too much homework can backfire, leading to stress and fatigue that adversely affect a student’s performance. Reuters highlights an intriguing correlation suggesting that physical activity may be more conducive to academic success than additional homework, underscoring the importance of a holistic approach to education that prioritizes both physical and mental well-being for enhanced academic outcomes.
2. Reinforcement of Learning

Homework is traditionally viewed as a tool to reinforce classroom learning, enabling students to practice and retain material. However, research suggests its effectiveness is ambiguous. In instances where homework is well-aligned with students’ abilities and classroom teachings, it can indeed be beneficial. Particularly for younger students , excessive homework can cause burnout and a loss of interest in learning, counteracting its intended purpose.
Furthermore, when homework surpasses a student’s capability, it may induce frustration and confusion rather than aid in learning. This challenges the notion that more homework invariably leads to better understanding and retention of educational content.
3. Development of Time Management Skills

Homework is often considered a crucial tool in helping students develop important life skills such as time management and organization. The idea is that by regularly completing assignments, students learn to allocate their time efficiently and organize their tasks effectively, skills that are invaluable in both academic and personal life.
However, the impact of homework on developing these skills is not always positive. For younger students, especially, an overwhelming amount of homework can be more of a hindrance than a help. Instead of fostering time management and organizational skills, an excessive workload often leads to stress and anxiety . These negative effects can impede the learning process and make it difficult for students to manage their time and tasks effectively, contradicting the original purpose of homework.
4. Preparation for Future Academic Challenges

Homework is often touted as a preparatory tool for future academic challenges that students will encounter in higher education and their professional lives. The argument is that by tackling homework, students build a foundation of knowledge and skills necessary for success in more advanced studies and in the workforce, fostering a sense of readiness and confidence.
Contrarily, an excessive homework load, especially from a young age, can have the opposite effect . It can instill a negative attitude towards education, dampening students’ enthusiasm and willingness to embrace future academic challenges. Overburdening students with homework risks disengagement and loss of interest, thereby defeating the purpose of preparing them for future challenges. Striking a balance in the amount and complexity of homework is crucial to maintaining student engagement and fostering a positive attitude towards ongoing learning.
5. Parental Involvement in Education

Homework often acts as a vital link connecting parents to their child’s educational journey, offering insights into the school’s curriculum and their child’s learning process. This involvement is key in fostering a supportive home environment and encouraging a collaborative relationship between parents and the school. When parents understand and engage with what their children are learning, it can significantly enhance the educational experience for the child.
However, the line between involvement and over-involvement is thin. When parents excessively intervene by completing their child’s homework, it can have adverse effects . Such actions not only diminish the educational value of homework but also rob children of the opportunity to develop problem-solving skills and independence. This over-involvement, coupled with disparities in parental ability to assist due to variations in time, knowledge, or resources, may lead to unequal educational outcomes, underlining the importance of a balanced approach to parental participation in homework.
Exploring Alternatives to Homework and Finding a Middle Ground

In the ongoing debate about the role of homework in education, it’s essential to consider viable alternatives and strategies to minimize its burden. While completely eliminating homework may not be feasible for all educators, there are several effective methods to reduce its impact and offer more engaging, student-friendly approaches to learning.
Alternatives to Traditional Homework
- Project-Based Learning: This method focuses on hands-on, long-term projects where students explore real-world problems. It encourages creativity, critical thinking, and collaborative skills, offering a more engaging and practical learning experience than traditional homework. For creative ideas on school projects, especially related to the solar system, be sure to explore our dedicated article on solar system projects .
- Flipped Classrooms: Here, students are introduced to new content through videos or reading materials at home and then use class time for interactive activities. This approach allows for more personalized and active learning during school hours.
- Reading for Pleasure: Encouraging students to read books of their choice can foster a love for reading and improve literacy skills without the pressure of traditional homework assignments. This approach is exemplified by Marion County, Florida , where public schools implemented a no-homework policy for elementary students. Instead, they are encouraged to read nightly for 20 minutes . Superintendent Heidi Maier’s decision was influenced by research showing that while homework offers minimal benefit to young students, regular reading significantly boosts their learning. For book recommendations tailored to middle school students, take a look at our specially curated article .
Ideas for Minimizing Homework
- Limiting Homework Quantity: Adhering to guidelines like the “ 10-minute rule ” (10 minutes of homework per grade level per night) can help ensure that homework does not become overwhelming.
- Quality Over Quantity: Focus on assigning meaningful homework that is directly relevant to what is being taught in class, ensuring it adds value to students’ learning.
- Homework Menus: Offering students a choice of assignments can cater to diverse learning styles and interests, making homework more engaging and personalized.
- Integrating Technology: Utilizing educational apps and online platforms can make homework more interactive and enjoyable, while also providing immediate feedback to students. To gain deeper insights into the role of technology in learning environments, explore our articles discussing the benefits of incorporating technology in classrooms and a comprehensive list of educational VR apps . These resources will provide you with valuable information on how technology can enhance the educational experience.
For teachers who are not ready to fully eliminate homework, these strategies offer a compromise, ensuring that homework supports rather than hinders student learning. By focusing on quality, relevance, and student engagement, educators can transform homework from a chore into a meaningful component of education that genuinely contributes to students’ academic growth and personal development. In this way, we can move towards a more balanced and student-centric approach to learning, both in and out of the classroom.
Useful Resources
- Is homework a good idea or not? by BBC
- The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype
- Alternative Homework Ideas
The evidence and arguments presented in the discussion of why students should not have homework call for a significant shift in homework practices. It’s time for educators and policymakers to rethink and reformulate homework strategies, focusing on enhancing the quality, relevance, and balance of assignments. By doing so, we can create a more equitable, effective, and student-friendly educational environment that fosters learning, well-being, and holistic development.
- “Here’s what an education expert says about that viral ‘no-homework’ policy”, Insider
- “John Hattie on BBC Radio 4: Homework in primary school has an effect of zero”, Visible Learning
- HowtoLearn.com
- “Time Spent On Homework Statistics [Fresh Research]”, Gitnux
- “Stress in America”, American Psychological Association (APA)
- “Homework hurts high-achieving students, study says”, The Washington Post
- “National Sleep Foundation’s updated sleep duration recommendations: final report”, National Library of Medicine
- “A multi-method exploratory study of stress, coping, and substance use among high school youth in private schools”, Frontiers
- “The Digital Revolution is Leaving Poorer Kids Behind”, Statista
- “The digital divide has left millions of school kids behind”, CNET
- “The Digital Divide: What It Is, and What’s Being Done to Close It”, Investopedia
- “COVID-19 exposed the digital divide. Here’s how we can close it”, World Economic Forum
- “PBS NewsHour: Biggest Predictor of College Success is Family Income”, America’s Promise Alliance
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, Taylor & Francis Online
- “What Do You Mean My Kid Doesn’t Have Homework?”, EducationWeek
- “Excerpt From The Case Against Homework”, Penguin Random House Canada
- “How much homework is too much?”, neaToday
- “The Nation’s Report Card: A First Look: 2013 Mathematics and Reading”, National Center for Education Statistics
- “Battles Over Homework: Advice For Parents”, Psychology Today
- “How Homework Is Destroying Teens’ Health”, The Lion’s Roar
- “ Breaking the Homework Habit”, Education World
- “Testing a model of school learning: Direct and indirect effects on academic achievement”, ScienceDirect
- “National Differences, Global Similarities: World Culture and the Future of Schooling”, Stanford University Press
- “When school goes home: Some problems in the organization of homework”, APA PsycNet
- “Is homework a necessary evil?”, APA PsycNet
- “Epidemic of copying homework catalyzed by technology”, Redwood Bark
- “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame”, The Chronicle of Higher Education
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, ResearchGate
- “Kids who get moving may also get better grades”, Reuters
- “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Research, 1987–2003”, SageJournals
- “Is it time to get rid of homework?”, USAToday
- “Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework”, Stanford
- “Florida school district bans homework, replaces it with daily reading”, USAToday
- “Encouraging Students to Read: Tips for High School Teachers”, wgu.edu
- Recent Posts

Simona Johnes is the visionary being the creation of our project. Johnes spent much of her career in the classroom working with students. And, after many years in the classroom, Johnes became a principal.
- 28 Exciting Yarn Crafts for Preschool Kids: Igniting Creativity and Fine Motor Skills - April 29, 2024
- 16 Engaging and Educational Cause and Effect Activities for Preschoolers to Boost Cognitive Development - April 24, 2024
- 25 Innovative and Engaging Parts of Speech Activities for Middle School: Fun Grammar Games to Enhance Learning - April 14, 2024
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
Why I Think All Schools Should Abolish Homework

H ow long is your child’s workweek? Thirty hours? Forty? Would it surprise you to learn that some elementary school kids have workweeks comparable to adults’ schedules? For most children, mandatory homework assignments push their workweek far beyond the school day and deep into what any other laborers would consider overtime. Even without sports or music or other school-sponsored extracurriculars, the daily homework slog keeps many students on the clock as long as lawyers, teachers, medical residents, truck drivers and other overworked adults. Is it any wonder that,deprived of the labor protections that we provide adults, our kids are suffering an epidemic of disengagement, anxiety and depression ?
With my youngest child just months away from finishing high school, I’m remembering all the needless misery and missed opportunities all three of my kids suffered because of their endless assignments. When my daughters were in middle school, I would urge them into bed before midnight and then find them clandestinely studying under the covers with a flashlight. We cut back on their activities but still found ourselves stuck in a system on overdrive, returning home from hectic days at 6 p.m. only to face hours more of homework. Now, even as a senior with a moderate course load, my son, Zak, has spent many weekends studying, finding little time for the exercise and fresh air essential to his well-being. Week after week, and without any extracurriculars, Zak logs a lot more than the 40 hours adults traditionally work each week — and with no recognition from his “bosses” that it’s too much. I can’t count the number of shared evenings, weekend outings and dinners that our family has missed and will never get back.
How much after-school time should our schools really own?
In the midst of the madness last fall, Zak said to me, “I feel like I’m working towards my death. The constant demands on my time since 5th grade are just going to continue through graduation, into college, and then into my job. It’s like I’m on an endless treadmill with no time for living.”
My spirit crumbled along with his.
Like Zak, many people are now questioning the point of putting so much demand on children and teens that they become thinly stretched and overworked. Studies have long shown that there is no academic benefit to high school homework that consumes more than a modest number of hours each week. In a study of high schoolers conducted by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), researchers concluded that “after around four hours of homework per week, the additional time invested in homework has a negligible impact on performance.”
In elementary school, where we often assign overtime even to the youngest children, studies have shown there’s no academic benefit to any amount of homework at all.
Our unquestioned acceptance of homework also flies in the face of all we know about human health, brain function and learning. Brain scientists know that rest and exercise are essential to good health and real learning . Even top adult professionals in specialized fields take care to limit their work to concentrated periods of focus. A landmark study of how humans develop expertise found that elite musicians, scientists and athletes do their most productive work only about four hours per day .
Yet we continue to overwork our children, depriving them of the chance to cultivate health and learn deeply, burdening them with an imbalance of sedentary, academic tasks. American high school students , in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found.
It’s time for an uprising.
Already, small rebellions are starting. High schools in Ridgewood, N.J. , and Fairfax County, Va., among others, have banned homework over school breaks. The entire second grade at Taylor Elementary School in Arlington, Va., abolished homework this academic year. Burton Valley Elementary School in Lafayette, Calif., has eliminated homework in grades K through 4. Henry West Laboratory School , a public K-8 school in Coral Gables, Fla., eliminated mandatory, graded homework for optional assignments. One Lexington, Mass., elementary school is piloting a homework-free year, replacing it with reading for pleasure.
More from TIME
Across the Atlantic, students in Spain launched a national strike against excessive assignments in November. And a second-grade teacher in Texas, made headlines this fall when she quit sending home extra work , instead urging families to “spend your evenings doing things that are proven to correlate with student success. Eat dinner as a family, read together, play outside and get your child to bed early.”
It is time that we call loudly for a clear and simple change: a workweek limit for children, counting time on the clock before and after the final bell. Why should schools extend their authority far beyond the boundaries of campus, dictating activities in our homes in the hours that belong to families? An all-out ban on after-school assignments would be optimal. Short of that, we can at least sensibly agree on a cap limiting kids to a 40-hour workweek — and fewer hours for younger children.
Resistance even to this reasonable limit will be rife. Mike Miller, an English teacher at Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology in Alexandria, Va., found this out firsthand when he spearheaded a homework committee to rethink the usual approach. He had read the education research and found a forgotten policy on the county books limiting homework to two hours a night, total, including all classes. “I thought it would be a slam dunk” to put the two-hour cap firmly in place, Miller said.
But immediately, people started balking. “There was a lot of fear in the community,” Miller said. “It’s like jumping off a high dive with your kids’ future. If we reduce homework to two hours or less, is my kid really going to be okay?” In the end, the committee only agreed to a homework ban over school breaks.
Miller’s response is a great model for us all. He decided to limit assignments in his own class to 20 minutes a night (the most allowed for a student with six classes to hit the two-hour max). His students didn’t suddenly fail. Their test scores remained stable. And they started using their more breathable schedule to do more creative, thoughtful work.
That’s the way we will get to a sane work schedule for kids: by simultaneously pursuing changes big and small. Even as we collaboratively press for policy changes at the district or individual school level, all teachers can act now, as individuals, to ease the strain on overworked kids.
As parents and students, we can also organize to make homework the exception rather than the rule. We can insist that every family, teacher and student be allowed to opt out of assignments without penalty to make room for important activities, and we can seek changes that shift practice exercises and assignments into the actual school day.
We’ll know our work is done only when Zak and every other child can clock out, eat dinner, sleep well and stay healthy — the very things needed to engage and learn deeply. That’s the basic standard the law applies to working adults. Let’s do the same for our kids.
Vicki Abeles is the author of the bestseller Beyond Measure: Rescuing an Overscheduled, Overtested, Underestimated Generation, and director and producer of the documentaries “ Race to Nowhere ” and “ Beyond Measure. ”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- How Joe Biden Leads
- TIME100 Most Influential Companies 2024
- Javier Milei’s Radical Plan to Transform Argentina
- How Private Donors Shape Birth-Control Choices
- What Sealed Trump’s Fate : Column
- Are Walking Pads Worth It?
- 15 LGBTQ+ Books to Read for Pride
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
- Subscribe to BBC Science Focus Magazine
- Previous Issues
- Future tech
- Everyday science
- Planet Earth
- Newsletters
Should homework be banned?
Social media has sparked into life about whether children should be given homework - should students be freed from this daily chore? Dr Gerald Letendre, a professor of education at Pennsylvania State University, investigates.
We’ve all done it: pretended to leave an essay at home, or stayed up until 2am to finish a piece of coursework we’ve been ignoring for weeks. Homework, for some people, is seen as a chore that’s ‘wrecking kids’ or ‘killing parents’, while others think it is an essential part of a well-rounded education. The problem is far from new: public debates about homework have been raging since at least the early-1900s, and recently spilled over into a Twitter feud between Gary Lineker and Piers Morgan.
Ironically, the conversation surrounding homework often ignores the scientific ‘homework’ that researchers have carried out. Many detailed studies have been conducted, and can guide parents, teachers and administrators to make sensible decisions about how much work should be completed by students outside of the classroom.
So why does homework stir up such strong emotions? One reason is that, by its very nature, it is an intrusion of schoolwork into family life. I carried out a study in 2005, and found that the amount of time that children and adolescents spend in school, from nursery right up to the end of compulsory education, has greatly increased over the last century . This means that more of a child’s time is taken up with education, so family time is reduced. This increases pressure on the boundary between the family and the school.
Plus, the amount of homework that students receive appears to be increasing, especially in the early years when parents are keen for their children to play with friends and spend time with the family.
Finally, success in school has become increasingly important to success in life. Parents can use homework to promote, or exercise control over, their child’s academic trajectory, and hopefully ensure their future educational success. But this often leaves parents conflicted – they want their children to be successful in school, but they don’t want them to be stressed or upset because of an unmanageable workload.

However, the issue isn’t simply down to the opinions of parents, children and their teachers – governments also like to get involved. In the autumn of 2012, French president François Hollande hit world headlines after making a comment about banning homework, ostensibly because it promoted inequality. The Chinese government has also toyed with a ban, because of concerns about excessive academic pressure being put on children.
The problem is, some politicians and national administrators regard regulatory policy in education as a solution for a wide array of social, economic and political issues, perhaps without considering the consequences for students and parents.
Does homework work?
Homework seems to generally have a positive effect for high school students, according to an extensive range of empirical literature. For example, Duke University’s Prof Harris Cooper carried out a meta-analysis using data from US schools, covering a period from 1987 to 2003. He found that homework offered a general beneficial impact on test scores and improvements in attitude, with a greater effect seen in older students. But dig deeper into the issue and a complex set of factors quickly emerges, related to how much homework students do, and exactly how they feel about it.
In 2009, Prof Ulrich Trautwein and his team at the University of Tübingen found that in order to establish whether homework is having any effect, researchers must take into account the differences both between and within classes . For example, a teacher may assign a good deal of homework to a lower-level class, producing an association between more homework and lower levels of achievement. Yet, within the same class, individual students may vary significantly in how much homework improves their baseline performance. Plus, there is the fact that some students are simply more efficient at completing their homework than others, and it becomes quite difficult to pinpoint just what type of homework, and how much of it, will affect overall academic performance.
Over the last century, the amount of time that children and adolescents spend in school has greatly increased
Gender is also a major factor. For example, a study of US high school students carried out by Prof Gary Natriello in the 1980s revealed that girls devote more time to homework than boys, while a follow-up study found that US girls tend to spend more time on mathematics homework than boys. Another study, this time of African-American students in the US, found that eighth grade (ages 13-14) girls were more likely to successfully manage both their tasks and emotions around schoolwork, and were more likely to finish homework.
So why do girls seem to respond more positively to homework? One possible answer proposed by Eunsook Hong of the University of Nevada in 2011 is that teachers tend to rate girls’ habits and attitudes towards work more favourably than boys’. This perception could potentially set up a positive feedback loop between teacher expectations and the children’s capacity for academic work based on gender, resulting in girls outperforming boys. All of this makes it particularly difficult to determine the extent to which homework is helping, though it is clear that simply increasing the time spent on assignments does not directly correspond to a universal increase in learning.
Can homework cause damage?
The lack of empirical data supporting homework in the early years of education, along with an emerging trend to assign more work to this age range, appears to be fuelling parental concerns about potential negative effects. But, aside from anecdotes of increased tension in the household, is there any evidence of this? Can doing too much homework actually damage children?
Evidence suggests extreme amounts of homework can indeed have serious effects on students’ health and well-being. A Chinese study carried out in 2010 found a link between excessive homework and sleep disruption: children who had less homework had better routines and more stable sleep schedules. A Canadian study carried out in 2015 by Isabelle Michaud found that high levels of homework were associated with a greater risk of obesity among boys, if they were already feeling stressed about school in general.
For useful revision guides and video clips to assist with learning, visit BBC Bitesize . This is a free online study resource for UK students from early years up to GCSEs and Scottish Highers.
It is also worth noting that too much homework can create negative effects that may undermine any positives. These negative consequences may not only affect the child, but also could also pile on the stress for the whole family, according to a recent study by Robert Pressman of the New England Centre for Pediatric Psychology. Parents were particularly affected when their perception of their own capacity to assist their children decreased.
What then, is the tipping point, and when does homework simply become too much for parents and children? Guidelines typically suggest that children in the first grade (six years old) should have no more that 10 minutes per night, and that this amount should increase by 10 minutes per school year. However, cultural norms may greatly affect what constitutes too much.
A study of children aged between 8 and 10 in Quebec defined high levels of homework as more than 30 minutes a night, but a study in China of children aged 5 to 11 deemed that two or more hours per night was excessive. It is therefore difficult to create a clear standard for what constitutes as too much homework, because cultural differences, school-related stress, and negative emotions within the family all appear to interact with how homework affects children.
Should we stop setting homework?
In my opinion, even though there are potential risks of negative effects, homework should not be banned. Small amounts, assigned with specific learning goals in mind and with proper parental support, can help to improve students’ performance. While some studies have generally found little evidence that homework has a positive effect on young children overall, a 2008 study by Norwegian researcher Marte Rønning found that even some very young children do receive some benefit. So simply banning homework would mean that any particularly gifted or motivated pupils would not be able to benefit from increased study. However, at the earliest ages, very little homework should be assigned. The decisions about how much and what type are best left to teachers and parents.
As a parent, it is important to clarify what goals your child’s teacher has for homework assignments. Teachers can assign work for different reasons – as an academic drill to foster better study habits, and unfortunately, as a punishment. The goals for each assignment should be made clear, and should encourage positive engagement with academic routines.

Parents should inform the teachers of how long the homework is taking, as teachers often incorrectly estimate the amount of time needed to complete an assignment, and how it is affecting household routines. For young children, positive teacher support and feedback is critical in establishing a student’s positive perception of homework and other academic routines. Teachers and parents need to be vigilant and ensure that homework routines do not start to generate patterns of negative interaction that erode students’ motivation.
Likewise, any positive effects of homework are dependent on several complex interactive factors, including the child’s personal motivation, the type of assignment, parental support and teacher goals. Creating an overarching policy to address every single situation is not realistic, and so homework policies tend to be fixated on the time the homework takes to complete. But rather than focusing on this, everyone would be better off if schools worked on fostering stronger communication between parents, teachers and students, allowing them to respond more sensitively to the child’s emotional and academic needs.
- Five brilliant science books for kids
- Will e-learning replace teachers?
Follow Science Focus on Twitter , Facebook , Instagram and Flipboard
Share this article

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
- Code of conduct
- Magazine subscriptions
- Manage preferences
- Share full article
Advertisement
Subscriber-only Newsletter
Jay Caspian Kang
The movement to end homework is wrong.

By Jay Caspian Kang
Opinion Writer
Do students really need to do their homework?
As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?”
I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.”
The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Put a bit more simply: The quality of students’ homework production is linked to their socioeconomic status. This alone doesn’t seem particularly controversial. As I’ve discussed in this newsletter, many measures of academic achievement wind up being linked to wealth. The authors go on to argue that since this is the case, teachers should “interpret differences in students’ homework production through a structural inequalities frame.” What they have found, however, is that teachers don’t think of homework this way. Instead, they tend to rely on the “myth of meritocracy” to explain “homework inequalities.”
Calarco, Horn and Chen are all respected scholars at top-tier universities. Their paper was published in Educational Researcher, a journal of the American Educational Research Association, one of the pre-eminent research organizations in the education space. Homework reduction, or abolition, is part of an emerging educational movement. And while the authors acknowledge that eliminating homework would be difficult in the short term, given how rooted it is in American pedagogy, I imagine that many public schools over the next decade or so will start to de-emphasize homework as these ideas start to make their way to school boards and curriculum writers.
Trying to assess the value of homework, reduce it or at least make less of it busywork might very well be a useful endeavor. But Calarco, Horn and Chen are questioning something much more fundamental to the American educational system than homework. Whether they intend to or not, they are, in effect, reframing the purpose of schooling itself. Is school a place where a select group of children can distinguish themselves from their peers through diligence, talent and the pursuit of upward mobility? Is it a place where everyone should have equal access to learning and opportunity, whatever that might mean? And are these two ideals mutually exclusive?
The authors of “You Need to Be More Responsible” are part of a movement that argues, sometimes convincingly, that a meritocratic vision impedes true equal opportunity. In regards to homework, what they are saying, in effect, is that the idea of responsibility itself — requiring students to be accountable for completing assignments — exacerbates inequality. And that rather than trying to run all students through a hierarchical educational system in the hopes that they will end up in the same place, it appears that the authors would rather de-emphasize anything that reinforces the idea that one student is better than another.
According to the authors, then, teachers should factor in students’ socioeconomic status when evaluating their homework. Teachers should acknowledge that, even with completed assignments, structural inequalities may be why students with access to fewer resources got more questions wrong than their better-resourced peers did. And if they want to help these hypothetical poor students, they shouldn’t appeal to messages of personal responsibility and individual agency because those concepts reinforce the myth of meritocracy.
This all sounds a bit abstract. Having taught at a variety of schools, I agree that students’ socioeconomic status will likely be a better predictor of how they do on their homework than any personal traits, but I still can’t quite imagine how a structural inequalities frame would operate in the classroom. How would you even talk to your students?
Teacher: Hey there. You got half the questions wrong on your homework.
Student: I’m sorry about that. What do you think I could do to improve my performance?
Teacher: Well, you could boost your socioeconomic status. Otherwise, the deck’s extremely stacked against you getting any of these questions right.
To help combat the myth of meritocracy, the authors suggest that teachers not assign overly challenging homework and stop rewarding or punishing students based on the quality of the homework they produce. They also suggest that some teachers, if so inclined, could go “a step further in attempting to reduce homework’s harm” and just get rid of it altogether. They write:
More research is needed to understand the consequences of these more “progressive” homework policies. Yet, we suspect that while optional and ungraded homework may reduce inequalities in homework-related rewards and punishments, it may not prevent teachers from judging those students (and their parents) who do not complete the optional or ungraded work. No-homework policies have greater potential for alleviating the kinds of unequal practices we observed in the schools in our study.
In short, teachers can’t even be trusted to give out optional homework because they’re too meritocracy-brained and will still judge the students based on the results. The easiest solution is to just stop giving homework altogether, so the wrong-thinking teachers don’t have as much of a platform upon which to prop up their meritocratic myths.
I want to be fair to the authors and acknowledge that even if I’m a bit skeptical about how their prescriptions could operate in a classroom, there might be other good reasons for doing away with homework.
Evidence about the effectiveness of homework is pretty scattered. There are studies and articles saying that homework helps students learn and that kids aren’t overly burdened with it. There are also studies and articles that say excessive homework shows diminishing returns and can be harmful to students’ mental health . Having read some of these studies, I think the fairest assessment right now would be to say that the evidence about the benefits of homework is pretty inconclusive because of the inherent difficulties in isolating one part of a student’s academic life and drawing huge conclusions about how it affects everything else.
From a theoretical standpoint, I mostly agree with Calarco, Horn and Chen’s diagnosis of the American educational system. It does largely function as a way to sort and stratify children into different socioeconomic bands, which, again, in theory, means that it would be helpful for teachers to approach their work with that in mind. Many richer kids go to private schools that feed into elite colleges that will more or less ensure their alumni will be on the glide path to staying rich. Many poorer kids go to poorer schools that provide them, in many cases, with fewer opportunities that might help them advance socioeconomically. Some portion of middle-class and working-class people, including a lot of immigrants and children of immigrants, pragmatically use the school system to achieve class mobility.
When you break it all down, the amount of class mobility our education system can grind out each year falls well short of what most people expect. The spoils of academic meritocracy, then, aren’t particularly widespread, which does bring up the question: If we all agree that everyone should go to school and if the class mobility part is working only for some families and not at all for others, why do we structure it in such a competitive way?
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility.
A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
Jay Caspian Kang ( @jaycaspiankang ), a writer for Opinion and The New York Times Magazine, is the author of “The Loneliest Americans.”
Have feedback? Send a note to [email protected] .
This is why we should stop giving homework
At Human Restoration Project, one of the core systemic changes we suggest is the elimination of homework. Throughout this piece, I will outline several research studies and reports that demonstrate how the negative impact of homework is so evident that any mandated homework, outside of some minor catching up or for incredibly niche cases, simply does more harm than good.
I’ll summarize four main reasons why homework just flat out doesn’t make sense.
- Achievement, whether that be measured through standardized tests or general academic knowledge, isn’t correlated to assigning or completing homework.
- Homework is an inequitable practice that harms certain individuals more than others, to the detriment of those with less resources and to minor, if any, improvement for those with resources.
- It contributes to negative impacts at home with one’s family, peer relationships, and just general school-life balance, which causes far more problems than homework is meant to solve.
- And finally, it highlights and exacerbates our obsession with ultra-competitive college admissions and job opportunities, and other detrimental faults of making everything about getting ahead .
Does Homework Make Us Learn More?
Homework is such a ubiquitous part of school that it’s considered radical to even suggest that lessening it could be good teaching. It’s completely normal for families to spend extra hours each night, even on weekends, completing projects, reports, and worksheets. On average, teenagers spend about an hour a day completing homework, which is up 30-45 minutes from decades past. Kindergartners, who are usually saved from completing a lot of after school work, average about 25 minutes of homework a night (which to note, is 25 minutes too much than is recommended by child development experts).
The “10-minute rule”, endorsed by the National Parent Teacher Association and National Education Association, is incorporated into most school policies: there’s 10 minutes of homework per day per grade level – as in 20 minutes a day in second grade or 2 hours a day in 12th grade.
It’s so normalized that it was odd, when seemingly out of nowhere the President of Ireland recently suggested that homework should be banned . (And many experts were shocked at this suggestion.)
Numerous studies on homework reflect inconsistent results on what it exactly achieves. Homework is rarely shown to have any impact on achievement, whether that be measured through standardized testing or otherwise. As I’ll talk about later, the amount of marginal gains homework may lead to aren’t worth its negative trade-offs.
Let’s look at a quick summary of various studies:
- First off, the book National Differences, Global Similarities: World Culture and the Future of Schooling by David P. Baker and Gerald K. LeTendre draws on a 4 year investigation of schools in 47 countries. It’s the largest study of its type: looking at how schools operate, their pedagogy, their procedures, and the like. They made a shocking discovery: countries that assigned the least amount of homework: Denmark and the Czech Republic, had much higher test scores than those who assigned the most amount of homework: Iran and Thailand. The same work indicated that there was no correlation between academic achievement and homework with elementary students, and any moderate positive correlation in middle or high school diminished as more and more homework was assigned.
- A study in Contemporary Educational Psychology of 28,051 high school seniors concluded that quality of instruction, motivation, and ability are all correlated to a student’s academic success. However, homework’s effectiveness was marginal or perhaps even counterproductive: leading to more academic problems than it hoped to solve.
- The Teachers College Record published that homework added academic pressure and societal stress to those already experiencing pressures from other forces at home. This caused a further divide in academic performance from those with more privileged backgrounds. We’ll talk about this more later.
- A study in the Journal of Educational Psychology examined 2,342 student attitudes toward homework in foreign language classes. They found that time spent on homework had a significant negative impact on grades and standardized test scores. The researchers concluded that this may be because participants had to spend their time completing worksheets rather than spend time practicing skills on their own time.
- Some studies are more positive. In fact, a meta-analysis of 32 homework studies in the Review of Educational Research found that most studies indicated a positive correlation between achievement and doing homework. However, the researchers noted that generally these studies made it hard to draw causal conclusions due to how they were set up and conducted. There was so much variance that it was difficult to make a claim one way or another, even though the net result seemed positive. This often cited report led by Dr. Harris Cooper at Duke University is the most commonly used by proponents of the practice. But popular education critic Alfie Kohn believes that this study fails to establish, ironically, causation among other factors.
- And that said in a later published study in The High School Journal , researchers concluded that in all homework assigned, there were only modest linkages to improved math and science standardized test scores, with no difference in other subjects between those who were assigned homework and those who were not. None of the homework assigned had any bearing on grades. The only difference was for a few points on those particular subject’s standardized test scores.
All in all, the data is relatively inconclusive. Some educational experts suggest that there should be hours of homework in high school, some homework in middle school, and none in elementary school. Some call for the 10-minute rule. Others say that homework doesn’t work at all. It’s still fairly unstudied how achievement is impacted as a result of homework. But as Alfie Kohn says , “The better the research, the less likely one is to find any benefits from homework.” That said, when we couple this data with the other negative impacts of assigning homework: how it impacts those at the margins, leads to anxiety and stress, and takes away from important family time – it really makes us question why this is such a ubiquitous practice.
Or as Etta Kralovec and John Buell write in The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning,
‘Extensive classroom research of ‘time on task’ and international comparisons of year-round time for study suggest that additional homework might promote U.S. students’ achievement.’ This written statement by some of the top professionals in the field of homework research raises some difficult questions. More homework might promote student achievement? Are all our blood, sweat, and tears at the kitchen table over homework based on something that merely might be true? Our belief in the value of homework is akin to faith. We assume that it fosters a love of learning, better study habits, improved attitudes toward school, and greater self-discipline; we believe that better teachers assign more homework and that one sign of a good school is a good, enforced homework policy.
Our obsession with homework is likely rooted in select studies that imply it leads to higher test scores. The authors continue by deciphering this phenomena:
“[this is] a problem that routinely bedevils all the sciences: the relationship between correlation and causality. If A and B happen simultaneously, we do not know whether A causes B or B causes A, or whether both phenomena occur casually together or are individually determined by another set of variables…Thus far, most studies in this area have amounted to little more than crude correlations that cannot justify the sweeping conclusions some have derived from them.”
Alfie Kohn adds that even the correlation between achievement and homework doesn’t really matter. Saying,
“If all you want is to cram kids’ heads with facts for tomorrow’s tests that they’re going to forget by next week, yeah, if you give them more time and make them do the cramming at night, that could raise the scores…But if you’re interested in kids who know how to think or enjoy learning, then homework isn’t merely ineffective, but counterproductive… The practice of homework assumes that only academic growth matters, to the point that having kids work on that most of the school day isn’t enough…”
Ramping Up Inequity
Many justify the practice of assigning homework with the well-intentioned belief that we’ll make a more equitable society through high standards. However, it seems to be that these practices actually add to inequity. “Rigorous” private and preparatory schools – whether they be “no excuses” charters in marginalized communities or “college ready” elite suburban institutions, are notorious for extreme levels of homework assignment. Yet, many progressive schools who focus on holistic learning and self-actualization assign no homework and achieve the same levels of college and career success.
Perhaps this is because the largest predictor of college success has nothing to do with rigorous preparation, and everything to do with family income levels. 77% of students from high income families graduated from a highly competitive college, whereas 9% of students from low income families did the same .
It seems like by loading students up with mountains of homework each night in an attempt to get them into these colleges, we actually make their chances of success worse .

When assigning homework, it is common practice to recommend that families provide a quiet, well-lit place for the child to study. After all, it’s often difficult to complete assignments after a long day. Having this space, time, and energy must always be considered in the context of the family’s education, income, available time, and job security. For many people, jobs have become less secure and less well paid over the course of the last two decades.
In a United States context, we work the longest hours of any nation . Individuals in 2006 worked 11 hours longer than their counterparts in 1979. In 2020, 70% of children lived in households where both parents work. We are the only country in the industrial world without guaranteed family leave. And the results are staggering: 90% of women and 95% of men report work-family conflict . According to the Center for American Progress , “the United States today has the most family-hostile public policy in the developed world due to a long-standing political impasse.”
As a result, parents have much less time to connect with their children. This is not a call to a return to traditional family roles or to have stay-at-home parents – rather, our occupation-oriented society is structured inadequately which causes problems with how homework is meant to function.
For those who work in entry level positions, such as customer service and cashiers, there is an average 240% turnover per year due to lack of pay, poor conditions, work-life balance, and mismanagement. Family incomes continue to decline for lower- and middle-class Americans, leaving more families to work increased hours or multiple jobs. In other words, families, especially poor families, have less opportunities to spend time with their children, let alone foster academic “gains” via homework.

Even for students with ample resources who attend “elite schools”, the amount of homework is stressful. In a 2013 study in The Journal of Experiential Education, researchers conducted a survey of 4,317 students in 10 high-performing upper middle class high schools. These students had an average of more than 3 hours of homework a night. In comparison to their peers, they had more academic stress, notable physical health problems, and spent a worrying amount of time focused entirely on school and nothing else. Competitive advantage came at the cost of well-being and just being a kid.
A similar study in Frontiers of Psychology found that students pressured in the competitive college admissions process , who attended schools assigning hours of homework each night and promoting college-level courses and resume building extracurriculars, felt extreme stress. Two-thirds of the surveyed students reported turning to alcohol and drugs to cope.
In fact, a paper published by Dr. Suniya Luthar and her colleagues concluded that upper middle-class youth are actually more likely to be troubled than their middle class peers . There is an extreme problem with academic stress, where young people are engaging in a rat race toward the best possible educational future as determined by Ivy League colleges and scholarships. To add fuel to the fire, schools continue to add more and more homework to have students get ahead – which has a massively negative impact on both ends of the economic spectrum.
A 2012 study by Dr. Jonathan Daw indicated that their results,
“...imply that increases in the amount of homework assigned may increase the socioeconomic achievement gap in math, science, and reading in secondary school.”
In an effort to increase engagement with homework, teachers have been encouraged to create interesting, creative assignments. In fact, most researchers seem to agree that the quality of assignments matters a whole lot . After all, maybe assigning all of this homework won’t matter as long as it’s interesting and relevant to students? Although this has good intentions, rigorous homework with increased complexity places more impetus on parents. As researcher and author Gary Natrillo, an initial proponent of creative homework , stated later:
…not only was homework being assigned as suggested by all the ‘experts,’ but the teacher was obviously taking the homework seriously, making it challenging instead of routine and checking it each day and giving feedback. We were enveloped by the nightmare of near total implementation of the reform recommendations pertaining to homework…More creative homework tasks are a mixed blessing on the receiving end. On the one hand, they, of course, lead to higher engagement and interest for children and their parents. On the other hand, they require one to be well rested, a special condition of mind not often available to working parents…
Time is a luxury to most people. With increased working hours, in conjunction with extreme levels of stress, many people don’t have the necessary mindset to adequately supply children with the attention to detail for complex homework. As Kralovec and Buell state,
To put it plainly, I have discovered that after a day at work, the commute home, dinner preparations, and the prospect of baths, goodnight stories, and my own work ahead, there comes a time beyond which I cannot sustain my enthusiasm for the math brain teaser or the creative story task.
Americans are some of the most stressed people in the world. Mass shootings, health care affordability, discrimination, racism, sexual harassment, climate change, the presidential elections, and literally: staying informed on current events have caused roughly 70% of people to report moderate or extreme stress , with increased rates for people of color, LGBTQIA Americans, and other discriminated groups. 90% of high schoolers and college students report moderate or higher stress, with half reporting depression and a lack of energy and motivation .

In 2015, 1,100 parents were surveyed on the impact of homework on family life. Fights over homework were 200% more likely in families where parents didn’t have a college degree. Generally, these families believed that if their children didn’t understand a homework assignment then they must have been not paying attention at school. This led to young people feeling dumb or upset, and parents feeling like their child was lying or goofing off. The lead researcher noted,
All of our results indicate that homework as it is now being assigned discriminates against children whose parents don’t have a college degree, against parents who have English as a second language, against, essentially, parents who are poor.
Schooling is so integrated into family life that a group of researchers noted that “...homework tended to recreate the problems of school, such as status degradation.” An online survey of over 2,000 students and families found that 90% of students reported additional stress from homework, and 40% of families saw it as nothing more than busy work. Authors Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish wrote the aptly titled The Case Against Homework which conducted interviews across the mid-2000s with families and children, citing just how many people are burdened with overscheduling homework featuring over-the-top assignments and constant work. One parent remarked,
I sit on Amy's bed until 11 p.m. quizzing her, knowing she's never going to use this later, and it feels like abuse," says Nina of Menlo Park, California, whose eleven-year-old goes to a Blue Ribbon public school and does at least three-and-a-half hours of homework each night. Nina also questions the amount of time spent on "creative" projects. "Amy had to visit the Mission in San Francisco and then make a model of it out of cardboard, penne pasta, and paint. But what was she supposed to be learning from this? All my daughter will remember is how tense we were in the garage making this thing. Then when she handed it in, the teacher dropped it and all the penne pasta flew off." These days, says Nina, "Amy's attitude about school has really soured." Nina's has, too. "Everything is an emergency and you feel like you're always at battle stations."
1/3rd of the families interviewed felt “crushed by the workload.” It didn’t matter if they lived in rural or suburban areas, or if they were rich or poor.
Learning this way is also simply ineffective because well, that’s just not how kids learn! Young people build upon prior knowledge. They use what they know to make what they’re currently doing easier. Adding more and more content to a student’s plate – having to connect the dots and build upon more information – especially with the distractions of home life is unrealistic. Plus, simply put…it’s just not fun! Why would I want to spend all of my free time on homework rather than hanging out with my friends or playing video games?
Even with all that said – if other countries demonstrate educational success on standardized testing with little to no assigned homework and limited school hours (nevermind the fact that this is measured through the questionable method of standardized testing), shouldn’t we take a step back and analyze the system as a whole, rather than figure out better homework policies? If other countries do this with limited to no homework , why can’t everyone else?
Investigating Systemic Problems
Perhaps the solution to academic achievement in America isn’t doubling down on increasing the work students do at home, but solving the underlying systemic inequities: the economic and discriminatory problems that plague our society. Yes, the United States tends to fall behind other countries on math and reading scores. Many countries impose increased workloads on students because they are afraid that they will fall behind economically with the standard of living to the rest of the world. But perhaps the problem with education doesn’t lie in not having enough “rigorous” methods, but with how easy it is for a family to simply live and be content.
Finland, frequently cited as a model education system which grew to prominence during the 2000s through popular scholars like Pasi Sahlberg, enjoys some of the highest standards of living in the world:
- Finland’s life expectancy is 81.8 years, compared to the US’ 78.7 years . Unlike Finland, there’s a notable difference between the richest and poorest Americans . The richest Americans are expected to live, on average, nearly 15 years longer than the poorest. Further, America’s life expectancy is declining, the only industrialized country with this statistic .
- Finland’s health care is rated best in the world and only spends $3,078 per capita, compared to $8,047 in the US.
- Finland has virtually no homelessness , compared to the 500,000 (and growing) homeless population in the United States .
- Finland has the lowest inequality levels in the EU , compared to the United States with one of the highest inequality levels in the world . Research has demonstrated that countries with lower inequality levels are happier and healthier .
These statistics reflect that potentially — instead of investing hundreds of millions of dollars in initiatives to increase national test scores , such as homework strategies, curriculum changes, and nationwide “raising the bar” initiatives — that we should invest in programs that improve our standard of living, such as universal healthcare and housing. The solution to test scores is rooted in solving underlying inequities in our societies — shining a light on our core issues — rather than making teachers solve all of our community’s problems.
This doesn’t mean that there’s no space for improving pedagogy, schooling, or curriculums, but at the end of the day the solution cannot solely be by improving education.

Creating Future Workers
Education often equates learning with work. As a teacher, I had to stop myself from behaving like an economics analyst: telling students to quit “wasting time”, stating that the purpose of the lesson is useful for securing a high salary career, seeing everything as prep for college and career (and college’s purpose as just for more earnings in a career), and making blanket assumptions that those who aren’t motivated will ultimately never contribute to society, taking on “low levels” of work that “aren’t as important” as other positions.
A common argument exists that the pressure of homework mirrors the real world – that we should assign homework because that’s “just the way things are.” If we want kids to succeed in the “real world”, they need to have this pressure.
But this mentality is unhealthy and unjust. The purpose of education should be to develop purpose. People live happier and healthier lives as a result of pursuing and developing a core purpose. Some people’s purpose is related to their line of work, but there is not necessarily a connection. However, the primary goal for education stated by districts, states, and the national government is to make “productive members of society” – those who are “prepared for the future” through “college and career readiness.” When we double down on economic principles, rather than look to developmental psychology and holistic care, to raise young people, it’s no wonder we’re seeing such horrific statistics related to childhood .
Further, the consistent pressure to solely learn for future economic gain raises generations of young people to believe that wealth is a measurement of success, and that specific lines of work create happiness. Teachers and parents are told to make their children “work hard” for future success and develop “grit.” Although grit is an important indicator of overcoming obstacles , it is not developed by enforcing grit through authoritarian classrooms or meaningless, long tasks like homework. In fact, an argument could be made that many Americans accept their dramatically poor work-life balance and lack of access to needs such as affordable health care by being brought up in a society that rewards tasks of “working through it” to “eventually achieve happiness.”
Many families have shifted from having children participate in common household chores and activities to have them exclusively focus on their school work. Americans have more difficulty than ever raising children, with increasing demands of time and rising childcare costs . When teachers provide more and more homework, they take away from the parents’ ability to structure their household according to their needs. In fact, children with chores show completely positive universal growth across the board , from time management skills to responsibility to managing a healthy work-life balance.
Of course, this is not to say that it is all the teacher’s fault. Educators face immense pressure to carry out governmental/school policies that place test scores at the forefront. Plus, most families had homework themselves – so continuing the practice only makes sense. Many of these policies require homework, and an educator’s employment is centered on enacting these changes. Barbara Stengel , an education professor, noted that the reason why so much homework isn’t necessarily interesting or applicable to a student’s lived experience is because “some of the people who would really have pushed the limits of that are no longer in teaching.” The constant pressure on teachers to raise test scores while simultaneously being overworked and underpaid is making many leave the profession. Etta Kralovec and John Buell add:
As more academic demands are placed on teachers, homework can help lengthen the school day and thus ensure ‘coverage’ — that is, the completion of the full curriculum that each teacher is supposed to cover during the school year…This in itself places pressure on teachers to create meaningful homework and often to assign large amounts of it so that the students’ parents will think the teacher is rigorous and the school has high academic standards. Extensive homework is frequently linked in our minds to high standards.
Therefore, there’s a connection to be made between the school- or work-life balance of children and the people who are tasked with teaching them. 8% of the teacher workforce leaves every year , with one of the primary reasons being poor work-life balance . Perhaps teachers see an increased desire to “work” students in their class and at home due to the pressures they face in their own occupation?

The more we equate work with learning, and the more we accept that a school’s primary purpose is to prepare workers, the less we actually succeed at promoting academics. Instead, we bolster the neoliberal tendencies of the United States (and others like it) to work hard, yet comparably to other countries’ lifestyle gains, achieve little.
This is why so many families demand that their children have ample amounts of homework. In fact, the majority of parents believe their students have just the right amount. They’re afraid that their kids are going to fall behind, doomed to a life within an increasingly hostile and inequitable society. They want the best for their children, and taking the risk of not assigning homework means that someone else may take that top slot. The same could be said for many parts of the “tracks toward college and career readiness” that professor William Deresiewicz refers to as “zombication” – lurching through each stage of the rat race in competitive admissions: a lot of assignments, difficult courses, sports, clubs, forced volunteerism, internships, and other things to pack our schedules.
The United States must examine the underlying inequities of peoples’ lives, rather than focus on increasing schools’ workloads and lessening children’s free time for mythical academic gains that lead to little change. Teacher preparation programs and popular authors need to stop promoting “interesting and fun ways to teach ‘x’!” and propose systemic changes that radically change the way education is done, including systemic changes to society at large. Only then will the United States actually see improved livelihoods and a better education system for all.
And what could be done instead? Much of the research and writing on homework tends to conclude that we should find a “happy middle ground” to continue the practice of homework, just in case it does indeed work. However, based on the decades of studies we have on this issue…I’m not really sure. It seems the best practice, by far, is to eliminate homework altogether outside of incredibly niche and rare scenarios. If a student asks for more things to do at home because they want to explore something that interests them, great! But that doesn’t need to be mandated homework.
Human Restoration Project believes that the four recommendations of the late educator and scholar Ken Robinson allows young people to learn for themselves and make the most of their lives:
- Let children spend time with their families. The single strongest predictor of academic success and fewer behavioral problems for a child, 3-12 years old, is eating as a family. Make planned time during the day to catch up with children, talking to them about what they’re learning, and encouraging them to achieve.
- Give children time to play outside or create something, preferably not always with a screen. Let them dive into their passions and plan a trip to a library, park, or museum. Explore free online resources to discover new skills and interests.
- Give children opportunities to read by themselves or with their family. One of the best ways to learn about the world is developing a lifelong love of reading. Children who prioritize reading are more motivated to learn and see drastically improved academic outcomes.
- Let children sleep! Elementary students should sleep at least 10 hours each night and adolescents, 9 hours. Being awake and ready to tackle each day keeps us energized and healthy.
If you’re interested in learning more, see The Case Against Homework by Nancy Kalish and Sara Bennett, The Homework Myth by Alfie Kohn, The End of Homework by Etta Kralovec and John Muelle, or one of the many citations linked in the show notes.
You can also watch a modified video version of this piece on our YouTube channel:
Anderson, J. (2019, December 3). Finland has the most efficient education system in the world. Quartz . https://qz.com/1759598/finland-has-the-most-efficient-education-system-in-the-world
APA. (2019a). Stress in America . https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/stress/2019/stress-america-2019.pdf
APA. (2019b). Stress in America TM 2019: Interactive Graphics . https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/stress/2019/interactive-graphics
Baker, D., & LeTendre, G. K. (2005). National differences, global similarities: World culture and the future of schooling . Stanford University Press.
Balingit, M. (2022, September 13). Wanted: Teachers. No training necessary. The Washington Post . https://www.washingtonpost.com/education/2022/09/13/teacher-requirements-shortage-jobs/
Bennett, S., & Kalish, N. (2007). The Case Against Homework: How homework is hurting children and what parents can do about it . Harmony.
Byrnes, H. (2019a, April 11). U.S. leads among countries that spend the most on public health care. WLST . https://www.coloradoan.com/story/money/2019/04/11/countries-that-spend-the-most-on-public-health/39307147/
CDC. (2022, June 3). Data and statistics on children’s mental health . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/childrensmentalhealth/data.html
Chang, C. B., Wall, D., Tare, M., Golonka, E., & Vatz, K. (2014). Relationships of attitudes toward homework and time spent on homework to course outcomes: The case of foreign language learning. Journal of Educational Psychology , 106 (4), 1049–1065. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0036497
Chetty, R., Stepner, M., Abraham, S., Lin, S., Scuderi, B., Turner, N., Bergeron, A., & Cutler, D. (2016). The Association Between Income and Life Expectancy in the United States, 2001–2014: Association Between Income and Life Expectancy in the United States. JAMA , 315 (16). https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.4226
Chores and children . (2018). https://www.aacap.org/AACAP/Families_and_Youth/Facts_for_Families/FFF-Guide/Chores_and_Children-125.aspx
Cool, V. A., & Keith, T. Z. (1991). Testing a model of school learning: Direct and indirect effects on academic achievement. Contemporary Educational Psychology , 16 (1), 28–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-476x(91)90004-5
Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Review of Educational Research , 76 (1), 1–62. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543076001001
Costa, P. N. da. (2019, May 29). America’s humongous wealth gap is widening further. Forbes . https://www.forbes.com/sites/pedrodacosta/2019/05/29/americas-humungous-wealth-gap-is-widening-further/?sh=327f1ac342ee
Costley, K. (2013). Does Homework Really Improve Achievement? Arkansas Tech University .
Covington, N. (2020, January 31). A progressive response to “Ed. Reform’s Lost Decade.” Human Restoration Project . https://medium.com/human-restoration-project/a-progressive-response-to-ed-reforms-lost-decade-fb640c16d893
Daniels, E., & Steres, M. (2011). Examining the effects of a school-wide reading culture on the engagement of middle school students. RMLE Online , 35 (2), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/19404476.2011.11462085
Deresiewicz, W. (2015). Excellent sheep: The miseducation of the American elite and the way to a meaningful life . Simon and Schuster.
Dweck, C. S. (2006). Mindset: The new psychology of success . Random House.
Esdal, L. Teacher turnover: An overview of the problem and why it matters . (2019, February 28). Education Evolving. https://www.educationevolving.org/blog/2019/02/teacher-turnover-overview-of-problem-and-why-it-matters
Finland - WID - World inequality database . (2016, June 23). WID - Wealth and Income Database. https://wid.world/country/finland/
Galloway, M., Conner, J., & Pope, D. (2013). Nonacademic effects of homework in privileged, high-performing high schools. The Journal of Experimental Education , 81 (4), 490–510. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2012.745469
Henly, J. R., Shaefer, H. L., & Waxman, E. (2006). Nonstandard work schedules: Employer‐ and employee‐driven flexibility in retail jobs. Social Service Review , 80 (4), 609–634. https://doi.org/10.1086/508478
Hofferth, S. L., & Sandberg, J. F. (2001). How American children spend their time. Journal of Marriage and Family , 63 (2), 295–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-3737.2001.00295.x
Human Restoration Project. (n.d.). Research . Retrieved January 24, 2023, from https://www.humanrestorationproject.org/research
Indicators of Higher Education: Equity in the US . (2018). http://pellinstitute.org/downloads/publications-Indicators_of_Higher_Education_Equity_in_the_US_2018_Historical_Trend_Report.pdf&sa=D&source=docs&ust=1674598544982744&usg=AOvVaw3EdEhMRi9luOuJm0IKhMSF
Ken Robinson, TED. (2007). Do schools kill creativity? [Video]. In YouTube . https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iG9CE55wbtY
Kohn, A. (2007). The homework myth: Why our kids get too much of a bad thing . Da Capo Lifelong Books.
Kralovec, E., & Buell, J. (2001). The End of Homework: How homework disrupts families, overburdens children, and limits learning . Beacon Press.
Leonard, N. R., Gwadz, M. V., Ritchie, A., Linick, J. L., Cleland, C. M., Elliott, L., & Grethel, M. (2015). A multi-method exploratory study of stress, coping, and substance use among high school youth in private schools. Frontiers in Psychology , 6 . https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01028
Livingston, G. (2019, February 20). The way U.S. teens spend their time is changing, but differences between boys and girls persist. Pew Research Center . https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/02/20/the-way-u-s-teens-spend-their-time-is-changing-but-differences-between-boys-and-girls-persist/
Luthar, S. S., Barkin, S. H., & Crossman, E. J. (2013). “I can, therefore I must”: Fragility in the upper-middle classes. Development and Psychopathology , 25 (4pt2), 1529–1549. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579413000758
Lynch, R. The economic and fiscal consequences of improving U.S. educational outcomes - Equitable growth . (2015, February 2). Washington Center for Equitable Growth. https://equitablegrowth.org/achievement-gap/
Mcdermott, R. P., Goldman, S. V., & Varenne, H. (1984a). When school goes home: Some problems in the organization of homework. Teachers College Record: The Voice of Scholarship in Education , 85 (3), 391–409. https://doi.org/10.1177/016146818408500310
McGuire, J. (2023). The President Of Ireland Wants To Get Rid Of Homework & Honestly, He's Onto Something. Romper. https://www.romper.com/life/president-of-ireland-michael-d-higgins-homework
Miller, C. C. (2018, December 25). The relentlessness of modern parenting. The New York Times . https://www.nytimes.com/2018/12/25/upshot/the-relentlessness-of-modern-parenting.html
Natriello, G., & McDill, E. L. (1986). Performance standards, student effort on homework, and academic achievement. Sociology of Education , 59 (1), 18. https://doi.org/10.2307/2112483
PBS NewsHour : Biggest Predictor of College Success is Family Income . (2015). America’s Promise. https://web.archive.org/web/20220807230624/americaspromise.org/news/pbs-newshour-biggest-predictor-college-success-family-income
Plante, T. (2018, December 3). Americans are stressed out, and it is getting worse . Psychology Today. https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/do-the-right-thing/201812/americans-are-stressed-out-and-it-is-getting-worse
Pinsker, J. (2019, March 28). Does homework work? The Atlantic . https://www.theatlantic.com/education/archive/2019/03/homework-research-how-much/585889/
Pressman, R. M., Sugarman, D. B., Nemon, M. L., Desjarlais, J., Owens, J. A., & Schettini-Evans, A. (2015). Homework and family stress: With consideration of parents’ self confidence, educational level, and cultural background. The American Journal of Family Therapy , 43 (4), 297–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926187.2015.1061407
Sander, G. F. (2018). Finland’s homeless crisis nearly solved. How? By giving homes to all who need. The Christian Science Monitor . https://www.csmonitor.com/World/Europe/2018/0321/Finland-s-homeless-crisis-nearly-solved.-How-By-giving-homes-to-all-who-need
Smurthwaite, D. (2018, April 27). Why Overworking is Made in America and Work-Life Balance Lives in Europe . https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/why-overworking-made-america-work-life-balance-lives-dave-smurthwaite/
Taras, H., & Potts-Datema, W. (2005). Sleep and student performance at school. Journal of School Health , 75 (7), 248–254. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1746-1561.2005.00033.x
The State of Homelessness in America . (2019). https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/The-State-of-Homelessness-in-America.pdf
The three faces of work-family conflict . (2010, January 25). Center for American Progress. https://www.americanprogress.org/article/the-three-faces-of-work-family-conflict/
Walker, T. (2015). The great homework debate: What’s getting lost in the hype . NEA. https://www.nea.org/advocating-for-change/new-from-nea/great-homework-debate-whats-getting-lost-hype
Wallace, K. (2015, August 12). Kids have three times too much homework, study finds; what’s the cost? CNN . https://www.cnn.com/2015/08/12/health/homework-elementary-school-study/index.html
Weir, K. (2016). Is homework a necessary evil? https://www.apa.org/monitor/2016/03/homework
Wilkinson, R. G. (2002). Unhealthy societies: The afflictions of inequality . Routledge.
Wilkinson, R., & Pickett, K. (2020). The inner level: How more equal societies reduce stress, restore sanity and improve everyone’s well-being . Penguin.
Woolf, S. H. (2019). Life expectancy and mortality rates in the United States, 1959-2017. JAMA , 322 (20), 1996–2016. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.16932

read this next

take a listen

Join the Movement
Stay informed.
And I think another thing, in terms of academics in the classroom, the value of going into a class and walking out of it, maybe tired, like, "Oh, that was a lot of work." But feeling like you really took something from it, like an accomplishment, like you literally just built something in your brain, like a new piece of knowledge, it's like, "Oh, yes." It's satisfying. It's an achievement.
Where's this from?

School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students
The Pros and Cons of Homework
Updated: December 7, 2023
Published: January 23, 2020

Homework is a word that most students dread hearing. After hours upon hours of sitting in class , the last thing we want is more schoolwork over our precious weekends. While it’s known to be a staple of traditional schooling, homework has also become a rather divise topic. Some feel as though homework is a necessary part of school, while others believe that the time could be better invested. Should students have homework? Have a closer look into the arguments on both sides to decide for yourself.

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
Why should students have homework, 1. homework encourages practice.
Many people believe that one of the positive effects of homework is that it encourages the discipline of practice. While it may be time consuming and boring compared to other activities, repetition is needed to get better at skills. Homework helps make concepts more clear, and gives students more opportunities when starting their career .
2. Homework Gets Parents Involved
Homework can be something that gets parents involved in their children’s lives if the environment is a healthy one. A parent helping their child with homework makes them take part in their academic success, and allows for the parent to keep up with what the child is doing in school. It can also be a chance to connect together.
3. Homework Teaches Time Management
Homework is much more than just completing the assigned tasks. Homework can develop time management skills , forcing students to plan their time and make sure that all of their homework assignments are done on time. By learning to manage their time, students also practice their problem-solving skills and independent thinking. One of the positive effects of homework is that it forces decision making and compromises to be made.
4. Homework Opens A Bridge Of Communication
Homework creates a connection between the student, the teacher, the school, and the parents. It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student.
5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can’t see it in the moment.
6. Homework Reduces Screen Time
Many students in North America spend far too many hours watching TV. If they weren’t in school, these numbers would likely increase even more. Although homework is usually undesired, it encourages better study habits and discourages spending time in front of the TV. Homework can be seen as another extracurricular activity, and many families already invest a lot of time and money in different clubs and lessons to fill up their children’s extra time. Just like extracurricular activities, homework can be fit into one’s schedule.

The Other Side: Why Homework Is Bad
1. homework encourages a sedentary lifestyle.
Should students have homework? Well, that depends on where you stand. There are arguments both for the advantages and the disadvantages of homework.
While classroom time is important, playground time is just as important. If children are given too much homework, they won’t have enough playtime, which can impact their social development and learning. Studies have found that those who get more play get better grades in school , as it can help them pay closer attention in the classroom.
Children are already sitting long hours in the classroom, and homework assignments only add to these hours. Sedentary lifestyles can be dangerous and can cause health problems such as obesity. Homework takes away from time that could be spent investing in physical activity.
2. Homework Isn’t Healthy In Every Home
While many people that think homes are a beneficial environment for children to learn, not all homes provide a healthy environment, and there may be very little investment from parents. Some parents do not provide any kind of support or homework help, and even if they would like to, due to personal barriers, they sometimes cannot. Homework can create friction between children and their parents, which is one of the reasons why homework is bad .
3. Homework Adds To An Already Full-Time Job
School is already a full-time job for students, as they generally spend over 6 hours each day in class. Students also often have extracurricular activities such as sports, music, or art that are just as important as their traditional courses. Adding on extra hours to all of these demands is a lot for children to manage, and prevents students from having extra time to themselves for a variety of creative endeavors. Homework prevents self discovery and having the time to learn new skills outside of the school system. This is one of the main disadvantages of homework.
4. Homework Has Not Been Proven To Provide Results
Endless surveys have found that homework creates a negative attitude towards school, and homework has not been found to be linked to a higher level of academic success.
The positive effects of homework have not been backed up enough. While homework may help some students improve in specific subjects, if they have outside help there is no real proof that homework makes for improvements.
It can be a challenge to really enforce the completion of homework, and students can still get decent grades without doing their homework. Extra school time does not necessarily mean better grades — quality must always come before quantity.
Accurate practice when it comes to homework simply isn’t reliable. Homework could even cause opposite effects if misunderstood, especially since the reliance is placed on the student and their parents — one of the major reasons as to why homework is bad. Many students would rather cheat in class to avoid doing their homework at home, and children often just copy off of each other or from what they read on the internet.
5. Homework Assignments Are Overdone
The general agreement is that students should not be given more than 10 minutes a day per grade level. What this means is that a first grader should be given a maximum of 10 minutes of homework, while a second grader receives 20 minutes, etc. Many students are given a lot more homework than the recommended amount, however.
On average, college students spend as much as 3 hours per night on homework . By giving too much homework, it can increase stress levels and lead to burn out. This in turn provides an opposite effect when it comes to academic success.
The pros and cons of homework are both valid, and it seems as though the question of ‘‘should students have homework?’ is not a simple, straightforward one. Parents and teachers often are found to be clashing heads, while the student is left in the middle without much say.
It’s important to understand all the advantages and disadvantages of homework, taking both perspectives into conversation to find a common ground. At the end of the day, everyone’s goal is the success of the student.
Related Articles
- Choose your language

- Books in English
- Other languages
- Infographics
- Hattie Ranking
- John Hattie
John Hattie on BBC Radio 4: “Homework in primary school has an effect of zero”
“Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero”, says Professor John Hattie. But what does really work in education, schools and classrooms around the world? Every week Sarah Montague interviews the people whose ideas are challenging the future of education, like Sugata Mitra, Sir Ken Robinson and the headmaster of Eton College Tony Little. In August John Hattie, Professor of Education at the University of Melbourne, was her guest at BBC Radio 4. You can listen to the whole interview with John Hattie following this link (28 mins). Here are some quick takeaways. If you want to read further about what works best in education you can order the books Visible Learning and Visible Learning for Teachers .
Visible Learning: Buy the book VL for Teachers: Buy the book
John Hattie about class size
“Well, the first thing is, reducing class size does enhance achievement. However, the magnitude of that effect is tiny. It’s about a hundred and fifth out of a hundred and thirty odd different effects out there and it’s just one of those enigmas and the only question to ask is why is that effect so small? Because it is small. And the reason, we’ve found out, that it’s so small is because teachers don’t change how they teach when they go from a class of thirty to fifteen and perhaps it’s not surprising.”
John Hattie about public vs private schools
“Here in England, if you take out the prior differences from going to a private school where they tend to get parents who choose, as oppose to them sent to the local school, they tend to get a brighter student, you take that out, there’s not much difference. In many places the government school would be better. So, it’s kind of ironic, in the last twenty years where we’ve pushed this notion that parents have choice, so they can choose the school that may not be in the best interest of their student.”
John Hattie about homework
“Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, “Is it really making a difference?” If you try and get rid of homework in primary schools many parents judge the quality of the school by the presence of homework. So, don’t get rid of it. Treat the zero as saying, “It’s probably not making much of a difference but let’s improve it”. Certainly I think we get over obsessed with homework. Five to ten minutes has the same effect of one hour to two hours. The worst thing you can do with homework is give kids projects. The best thing you can do is to reinforce something you’ve already learnt.”
John Hattie about streaming
“It doesn’t make a difference.” Sarah Montague: “But bright kids aren’t held back by less bright and less bright not suffering?” “No. No difference at all. No. Teachers think it’s easier for them and it may be but in terms of the effects of students, no. Now you’ve got to remember that a lot of students gain a tremendous amount of their learning from their other students in the class and variability is the way that you get more of that kind of learning from other students.”
Listen to the whole interview with John Hattie at BBC Radio 4 . If you want to read further you can order the books Visible Learning and Visible Learning for Teachers.
BBC Radio 4: The Educators . Sarah Montague interviews the people whose ideas are challenging the future of education. Episode 2: John Hattie Duration: 28 minutes First broadcast: 20 August 2014 Presenter: Sarah Montague Producer: Joel Moors.
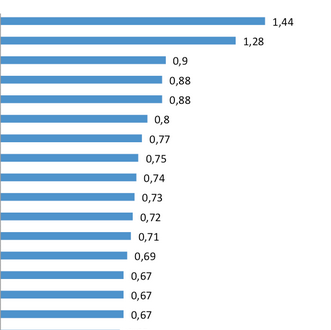
38 comments on “ John Hattie on BBC Radio 4: “Homework in primary school has an effect of zero” ”
John Hattie Homework I beg to differ, depends on what type ! E.g. Cook a meal with mum or day, explain today’s Math to a family member, read the last chapter of a book, make a touch cast report of your pet, use time laps photography with your iPad to show the growth of a seed into a plant, find Mars using an iPad app, create a billboard online that promotes one of the current issues ….
And I quote: So, don’t get rid of it. Treat the zero as saying, “It’s probably not making much of a difference but let’s improve it”.
I agree. What can we do to give it a greater effect? “Flipped” classrooms for example have a great effect on student learning as modern research shows.
Spot on.I work in Dubai and that’s how we plan homework. No rote but just enriching linkage to lessons learnt. Our kids enjoy these and are eager to share their experiences and learn tremendously from each other! !
All well and good if the parents can afford an iPad……….
Spot on John. Also, maybe let them chose from several options an activity which is of interest to them.
Why Is no one pointing out the fact of once these kids go to a higher grades the shock of how much of a load of homework will be a complete wreck them. My son was in 4th and he had homework and he hated doing it now he’s in 5th and the no homework rule is in place but once he hits 6th grade he will have it as again and i know sixth grade is always a shock for most kids. So I strongly disagree so we give him reading every night and review with him what he learned in class each day
Good revision routines prepare kids adequately
I use to be an advocate for streaming but I was wrong… kids learn best when there are varied abilities in the room. Class sizes don’t matter… quality instruction … minimal instruction .. maximum participation for students… and yes homework is over rated.
Based on what research? Im not saying you’re wrong, just curious what facts you’re using to support your opinion.
very simple data and anecdotal evidence.
Empirical research from over 800 meta-analysis — hardly “simple data” nor “anecdotal”. Evidence-based.
It’s John Hattie, are you a dinosaur? What current educational research sites don’t draw on his ongoing research?
These comments are reflecting what research the Sutton trust has accumulated. It shows that homework and class size make no difference and the thing that makes the most difference is noticing children’s responses and adjusting immediately according to them. In my head, this is obviously easier to do well with a smaller class. So if you want good teaching and not burn teachers out trying to individually respond to 32 children in each lesson, then reducing class size will make a difference. But class size in itself doesn’t. I also think that we have a large number of children who need nurturing not just teaching facts. So again a smaller class is beneficial to this end.
When a class size goes down to 5 then there are massive differences in learning. I was on a college course and for some reason, which I have forgotten, there were only 5 students on my engineering course. The teacher had a much better understanding of what we knew and on the effect of his teaching. We all got straight A’s.
It’s all about the quality of what is happening in the learning environment not the number students. A good teacher will have a good impact with 14 or 40 kids. You have to change what you do to meet the needs of the students.
I believe class size does make a difference. It certainly did with my daughter. Not from a teaching perspective, but from a learning perspective. The more students in a classroom, the more distractions and behavioral issues there are. My daughter is not a child who is easily distracted, but two years ago, she left public school and switched to online learning with a small amount of students in her class. She said there is a huge difference in the number of times the teacher has to stop the lesson in order to reprimand a student.
If students spent the first 3 years K-2 learning to get along in a classroom-how to work as a group and other social skills, there would be less disruptions in classrooms. Sone children at that you age are not neurologically developed enough to handle all of the reading, writing and math thrown at the lower grade levels. Throw some numbers and letters at them while building on their social skills and they will be much more successful students from 3rd grad and up.
The problem with Hattie’s research is that it is not primary school based but rather based across all schools from preschool to tertiary. Smaller classes make a huge difference especially in the junior school and it is covert teacher bashing to say that the teachers don’t change with smaller classes. They can and they do. They can’t with larger classes no matter how skilled they are. It’s the same with home work. If the homework is being encouraged to work with mum or dad in the kitchen or the garden por encouraging parents to read and act out stories with their children these will make massive differences to achievement.
I agree completely. Last year I was lucky enough to have a class of 18 for the best part of the year. I do believe the spring in my step made me a better teacher. A number of my D students became B’s. I believe in a normal class grouping I would have been lucky to get them to a C. I don’t think Prof. Hattie can measure my stress levels. There was so much joy in teaching my little group of children!
Jules, I completely agree with you. Hattie has, as far as I’m aware, never done research on the effect of larger/smaller class sizes on teacher stress levels and less/more time to think, prepare and spend more time with individual students. Of course, there are methods designed to maximise the learning of larger classes, but there is a huge time saving in marking a class of 18 essays to marking, say, 30. The time saved can be invested in lesson preparation, or even, time to just think! John Hattie was a maths teacher, though, so I guess he didn’t mark too many essays…
Jules you are so right! With the complexities of children’s personal lives having a smaller class enables us to have time to address their individual needs both personally and academically. We can then feel happier in our ability to fulfill each child’s needs which gives another avenue to help reduce our stress levels.
Not a fan of homework, except as a little revision, especially in primary school. My 5 children attended a state primary school, which had multi-age classrooms, which assisted children to learn at their own pace. It worked. It was also a Glasser school, which helped with socialisation. My eldest child is 27, and has Asperger’s Syndrome. The other 4 have all been accepted at tertiary institutions. All but one of those 4 were educated completely at state schools, with 1 attending a private school for her last 3 years of school, at her own request, for social (not academic) reasons. Perhaps children, especially boys, should begin school at a later age.
Having read and used Professor Hattie’s research in order to make positive impacts on student learning and outcomes, and having listened to many interviews, I can honestly say I have never felt that he covertly bashes teachers with his findings. The opposite in fact. I have always found Professor Hattie to speak positively of teachers. As a teacher, I wish more people in the public arena would validate what we do.
hang on. I remember like it was yesterday that when I was put down a group I immediately sank down to the equivalent level in that group. Ie in footballing terms, relegation zone in premiership led to relegation zone in championship. And how come nobody mentions the threat of being beaten up (let’s call it bullied) for doing well in the “second set” group? That was also a very real threat. You certainly didnt want to shine once you were relegated. Why does nobody mention this? Presumably this is a neutral site?
I agree as a parent i believe homework makes a difference….provided parent/s are involved. 1. I know what my child is learning in school. 2. I can pick up what my child needs extra attention to work on, help her with it and bring this to the teacher’s attention. 3. Show an interest in what my child is doing during her day. Only helps build on a stronger family unit.
Why is it, that never is there a word about student behaviour and the huge effect it has on learning, not just for the behaviour problem students, but for all children within that classroom! Unacceptable behaviour can keep a classroom in an upheaval . Also, the undesirable effects of hard drugs while in the womb…also alcohol! Then we have undernourishment and exhausted children. And we must not forget the trauma many are experiencing…separated parents, bickering parents, living in households where adults are smoking inside, eating a diet of processed foods, a parent or parents drinking to extremes on a daily basis, sexual abuse, seeing a parent being abused… and I could go on! All of these things and more are what many children are experiencing on a daily basis. Change will take place in the classroom and learning will take place when things change first in our homes and in our lives. It is the parents responsibility and we need to hand it back to them!
Couldn’t agree more with Elizabeth’s comments – but when you have an inspired and passionate teacher who can see beyond the behaviour and identify the effects of trauma in a youngster – the impact on that child, that class can be huge! Critical skills training can be invaluable – visible learning at worst can lead to children becoming statistics in the forensic analysis of data when actually they will gain more and teachers will have more of an impact with 5 minutes of care and concern and perhaps being the only person that has spent 5 minutes 1:1 with that child! Real relational trust takes time and genuine concern and interest in children developing and progressing – what is an assessment capable learner? Sounds like a robot!
Behavior is a big learning factor for the student with behaviors and those around them. Our son has a diagnoses with multiple co-morbids ADHD/Anxiety/OCD/Depresson/PTSD/Sensory disorder. The depression and PTSD was brought on in his therapist’s opinion by using peers to assist in helping other students, which doesn’t always have a positive impact and bullying at school.
It got to the point where he was taking 3 stimulants, a mood stabilizer and an anxiety med just to make it through the school day. And then he’d come home and have so much homework he never got to go outside to run off his excessive energy and then 3 more pills to bring him down so he could sleep. Not to mention the ill side effects of weight gain (he’s a 7th grader now 5’5 and weighs 200 pounds thats horrifying).
We pulled him out of mainstream school last year, weaned him off all meds and home school now. His self confidence is building, the weight is slowly coming off and he’ll be done early with the program we bought mainly because he can fly thru what interests him and he already has a wealth of information on and he can spend more time working on new information. We APPLY his lessons to his every day life.
All that being said maybe less pressure should be put on the child having homework and more time spent on educating parents about what their child is being taught and how to apply it to their every day life. As a daycare provider I know that not all parents will back a teacher up but I do think that they’d be surprised how many parents would.
Very interesting thoughts. To say it has zero effect seems a bit far fetched for all students. It depends on the quality of the school and quality of life at home. I work with low income students who seem to not have much education at home. The homework the teachers send helps us evaluate where the children are and help increase their education even if the parents are not involved in their education. Children with strong support systems probably benefit by helping around the house more and being a great part of the community.
Hattie’s work should be taken for what it is–superficial with blunders https://ollieorange2.wordpress.com/2014/09/24/half-of-the-statistics-in-visible-learning-are-wrong-part-2/
Yes I agree with Hattie when he says, “a lot of students gain a tremendous amount of their learning from their other students in the class.” Empirical evidence in my class has shown for those who are “not into” a particular subject, their influence (teaching) on others to fall behind, not engage in activities and not do the work is infectious. Make it more interesting people say, how interesting can you make a football game for those wanting to do ballet? Put them on the field and they will learn though, they will learn to avoid playing against the Alphas at all costs so the best solution, get into trouble to avoid having to integrate, cause trouble so the lessons gets dragged out. All of these theories I’m sure work, but it needs a tag line: They work “in the ideal world.” The fact is that we don’t live in one.
I’m not sure what you mean by integrate? Please forgive me if I’m wrong. I take your comment to say that if a child doesn’t itegrate into the classroom setting, they’ll fail at adulthood?
We have two older children with ADHD and they never truly integrated into the school system but outside school in their ongoing education and career’s they’ve chose career’s in fast paced, every changing fields one medical, one education and they’re excelling. Failure to integrate into a classroom setting does not automatically set a child up for failure in their adult life.
It’s parents who drive the homework. They think it’ll make their kids smarter. Teachers are under pressure to give kids extra work. A lot of teachers would rather not give homework. Reading with an adult is the best thing you can do for your child.
Teaching kids to be happy versus give them more work so they dont have time to find out for themselves or worse keeping them miserable
Homework that reinforces the application of skills and knowlegde already taught will prove to be purposeful. The time spent on homework must be in keeping with the concentration span of the child. It should not be an extension of the school day. 6 to 9 year olds learn best through play. Written tasks rob them of that opportunity to explore whilst developing valuable life skills.
When we know better, our moral obligation is to do better. Saying, “Yeah, I see this research. It just doesn’t fit with what I believe” is a profession of non-professionalism.
Hattie is a fraud. Unfortunately, many seem to have been taken in by his profoundly flawed research and his political motives.
11 other websites write about for "John Hattie on BBC Radio 4: “Homework in primary school has an effect of zero”"
[…] What really works in education, schools and classrooms around the world? Every week Sarah Montague interviews the people whose ideas are challenging the future of education, like Sugata Mitra, Sir Ken Robinson and the headmaster of Eton College Tony Little.…Read more › […]
[…] may be interested in John Hattie’s homework interview on the BBC recently. Professor Hattie is a leading and highly regarded educationalist and his […]
[…] What really works in education, schools and classrooms around the world? […]
[…] synest å seie at elevar med mykje lekser får dårlegare karakterar, medan velkjende John Hattie konkluderer med at “homework in primary school has an effect of […]
[…] John Hattie […]
[…] Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. John Hattie BBC interview. […]
[…] John Hattie, Professor of Education at the University of Melbourne, was her guest at BBC Radio 4. Read more or listen to the full […]
[…] educational researcher John Hattie interviewed on a few matters including Homework. Here’s the clip to listen […]
[…] prøver å være må vi ta inn over oss den forskning som er på lekser. Tradisjonelle lekser er verdiløse læringsinstrumenter i småskolen. Forskeren John Hattie (Det er han vi bruker for å fortelle at «forskning viser at […]
[…] First we explore our memories of homework as students, then our experiences as teachers, before introducing an outside source, in this episode,it’s ASCD’s article which quotes the The National PTA and the National Education Association “10-minute rule.” Also, check out John Hattie’s research on homework “effect size” here. […]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- شيخ روحاني on Hattie Ranking: 252 Influences And Effect Sizes Related To Student Achievement
- Pete Gabriella on Professor John Hattie
- Steve Capone on Video: John Hattie’s keynote at the Whole Education Annual Conference
- Phillip Cowell on Collective Teacher Efficacy (CTE) according to John Hattie
- simon on The Economist: John Hattie’s research and “Teaching the teachers”
- Susan Begin on Visible Learning World Conference 2019
- Anna on What is your experience?
- Rebekah Camp on Hattie Ranking: 252 Influences And Effect Sizes Related To Student Achievement
- Effective School Communications In The Summer | The Blogging Adviser on Hattie Ranking: 252 Influences And Effect Sizes Related To Student Achievement
- Sebastian Waack on Hattie Ranking: 252 Influences And Effect Sizes Related To Student Achievement
Request More Info
Fill out the form below and a member of our team will reach out right away!
" * " indicates required fields
Is Homework Necessary? Education Inequity and Its Impact on Students

The Problem with Homework: It Highlights Inequalities
How much homework is too much homework, when does homework actually help, negative effects of homework for students, how teachers can help.
Schools are getting rid of homework from Essex, Mass., to Los Angeles, Calif. Although the no-homework trend may sound alarming, especially to parents dreaming of their child’s acceptance to Harvard, Stanford or Yale, there is mounting evidence that eliminating homework in grade school may actually have great benefits , especially with regard to educational equity.
In fact, while the push to eliminate homework may come as a surprise to many adults, the debate is not new . Parents and educators have been talking about this subject for the last century, so that the educational pendulum continues to swing back and forth between the need for homework and the need to eliminate homework.
One of the most pressing talking points around homework is how it disproportionately affects students from less affluent families. The American Psychological Association (APA) explained:
“Kids from wealthier homes are more likely to have resources such as computers, internet connections, dedicated areas to do schoolwork and parents who tend to be more educated and more available to help them with tricky assignments. Kids from disadvantaged homes are more likely to work at afterschool jobs, or to be home without supervision in the evenings while their parents work multiple jobs.”
[RELATED] How to Advance Your Career: A Guide for Educators >>
While students growing up in more affluent areas are likely playing sports, participating in other recreational activities after school, or receiving additional tutoring, children in disadvantaged areas are more likely headed to work after school, taking care of siblings while their parents work or dealing with an unstable home life. Adding homework into the mix is one more thing to deal with — and if the student is struggling, the task of completing homework can be too much to consider at the end of an already long school day.
While all students may groan at the mention of homework, it may be more than just a nuisance for poor and disadvantaged children, instead becoming another burden to carry and contend with.
Beyond the logistical issues, homework can negatively impact physical health and stress — and once again this may be a more significant problem among economically disadvantaged youth who typically already have a higher stress level than peers from more financially stable families .
Yet, today, it is not just the disadvantaged who suffer from the stressors that homework inflicts. A 2014 CNN article, “Is Homework Making Your Child Sick?” , covered the issue of extreme pressure placed on children of the affluent. The article looked at the results of a study surveying more than 4,300 students from 10 high-performing public and private high schools in upper-middle-class California communities.
“Their findings were troubling: Research showed that excessive homework is associated with high stress levels, physical health problems and lack of balance in children’s lives; 56% of the students in the study cited homework as a primary stressor in their lives,” according to the CNN story. “That children growing up in poverty are at-risk for a number of ailments is both intuitive and well-supported by research. More difficult to believe is the growing consensus that children on the other end of the spectrum, children raised in affluence, may also be at risk.”
When it comes to health and stress it is clear that excessive homework, for children at both ends of the spectrum, can be damaging. Which begs the question, how much homework is too much?
The National Education Association and the National Parent Teacher Association recommend that students spend 10 minutes per grade level per night on homework . That means that first graders should spend 10 minutes on homework, second graders 20 minutes and so on. But a study published by The American Journal of Family Therapy found that students are getting much more than that.
While 10 minutes per day doesn’t sound like much, that quickly adds up to an hour per night by sixth grade. The National Center for Education Statistics found that high school students get an average of 6.8 hours of homework per week, a figure that is much too high according to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). It is also to be noted that this figure does not take into consideration the needs of underprivileged student populations.
In a study conducted by the OECD it was found that “after around four hours of homework per week, the additional time invested in homework has a negligible impact on performance .” That means that by asking our children to put in an hour or more per day of dedicated homework time, we are not only not helping them, but — according to the aforementioned studies — we are hurting them, both physically and emotionally.
What’s more is that homework is, as the name implies, to be completed at home, after a full day of learning that is typically six to seven hours long with breaks and lunch included. However, a study by the APA on how people develop expertise found that elite musicians, scientists and athletes do their most productive work for about only four hours per day. Similarly, companies like Tower Paddle Boards are experimenting with a five-hour workday, under the assumption that people are not able to be truly productive for much longer than that. CEO Stephan Aarstol told CNBC that he believes most Americans only get about two to three hours of work done in an eight-hour day.
In the scope of world history, homework is a fairly new construct in the U.S. Students of all ages have been receiving work to complete at home for centuries, but it was educational reformer Horace Mann who first brought the concept to America from Prussia.
Since then, homework’s popularity has ebbed and flowed in the court of public opinion. In the 1930s, it was considered child labor (as, ironically, it compromised children’s ability to do chores at home). Then, in the 1950s, implementing mandatory homework was hailed as a way to ensure America’s youth were always one step ahead of Soviet children during the Cold War. Homework was formally mandated as a tool for boosting educational quality in 1986 by the U.S. Department of Education, and has remained in common practice ever since.
School work assigned and completed outside of school hours is not without its benefits. Numerous studies have shown that regular homework has a hand in improving student performance and connecting students to their learning. When reviewing these studies, take them with a grain of salt; there are strong arguments for both sides, and only you will know which solution is best for your students or school.
Homework improves student achievement.
- Source: The High School Journal, “ When is Homework Worth the Time?: Evaluating the Association between Homework and Achievement in High School Science and Math ,” 2012.
- Source: IZA.org, “ Does High School Homework Increase Academic Achievement? ,” 2014. **Note: Study sample comprised only high school boys.
Homework helps reinforce classroom learning.
- Source: “ Debunk This: People Remember 10 Percent of What They Read ,” 2015.
Homework helps students develop good study habits and life skills.
- Sources: The Repository @ St. Cloud State, “ Types of Homework and Their Effect on Student Achievement ,” 2017; Journal of Advanced Academics, “ Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework ,” 2011.
- Source: Journal of Advanced Academics, “ Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework ,” 2011.
Homework allows parents to be involved with their children’s learning.
- Parents can see what their children are learning and working on in school every day.
- Parents can participate in their children’s learning by guiding them through homework assignments and reinforcing positive study and research habits.
- Homework observation and participation can help parents understand their children’s academic strengths and weaknesses, and even identify possible learning difficulties.
- Source: Phys.org, “ Sociologist Upends Notions about Parental Help with Homework ,” 2018.
While some amount of homework may help students connect to their learning and enhance their in-class performance, too much homework can have damaging effects.
Students with too much homework have elevated stress levels.
- Source: USA Today, “ Is It Time to Get Rid of Homework? Mental Health Experts Weigh In ,” 2021.
- Source: Stanford University, “ Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework ,” 2014.
Students with too much homework may be tempted to cheat.
- Source: The Chronicle of Higher Education, “ High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame ,” 2010.
- Source: The American Journal of Family Therapy, “ Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background ,” 2015.
Homework highlights digital inequity.
- Sources: NEAToday.org, “ The Homework Gap: The ‘Cruelest Part of the Digital Divide’ ,” 2016; CNET.com, “ The Digital Divide Has Left Millions of School Kids Behind ,” 2021.
- Source: Investopedia, “ Digital Divide ,” 2022; International Journal of Education and Social Science, “ Getting the Homework Done: Social Class and Parents’ Relationship to Homework ,” 2015.
- Source: World Economic Forum, “ COVID-19 exposed the digital divide. Here’s how we can close it ,” 2021.
Homework does not help younger students.
- Source: Review of Educational Research, “ Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Researcher, 1987-2003 ,” 2006.
To help students find the right balance and succeed, teachers and educators must start the homework conversation, both internally at their school and with parents. But in order to successfully advocate on behalf of students, teachers must be well educated on the subject, fully understanding the research and the outcomes that can be achieved by eliminating or reducing the homework burden. There is a plethora of research and writing on the subject for those interested in self-study.
For teachers looking for a more in-depth approach or for educators with a keen interest in educational equity, formal education may be the best route. If this latter option sounds appealing, there are now many reputable schools offering online master of education degree programs to help educators balance the demands of work and family life while furthering their education in the quest to help others.
YOU’RE INVITED! Watch Free Webinar on USD’s Online MEd Program >>
Be Sure To Share This Article
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Top 11 Reasons to get Your Master of Education Degree
Free 22-page Book

- Master of Education
Related Posts

Enter the username on file and we'll send you a code to reset your password.
A verification code has been emailed to
Is homework actually necessary?

Log in to share your opinion with MPR News and add it to your profile.
Thanks for liking this story! We have added it to a list of your favorite stories.
The start of the school year means the return of daily homework for many students. But is all that homework really necessary ?
Some educators and parents say that there isn’t much evidence that some types of homework actually help students learn. Too much homework might have the opposite effect on young students and can negatively impact their lives outside the classroom.
But the momentum to get rid of homework is being met by others who say it’s a tool to instill responsibility, time management, practice, and eliminating it would be wrong . MPR News host Angela Davis talks with educators about the evolution of homework and the value it holds in today’s curriculum.
Miranda Featherstone is a writer and a school social worker who has worked with children and families from preschool to high school. She is based in Rhode Island.
David Heistad spent 25 years as head of research, evaluation and assessment for the public school districts in Minneapolis and Bloomington. He has a Ph.D. in special education and a master’s in statistics.
Subscribe to the MPR News with Angela Davis podcast on: Apple Podcasts , Google Podcasts , Spotify or RSS .
Use the audio player above to listen to the full conversation.
Create a More Connected Minnesota
MPR News is your trusted resource for the news you need. With your support, MPR News brings accessible, courageous journalism and authentic conversation to everyone - free of paywalls and barriers. Your gift makes a difference.
Fostering and supporting mental health, focusing on empowerment, well-being and suicide prevention
Is it time to get rid of homework mental health experts weigh in, august 17 , 2021.
It’s no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Are You Down With or Done With Homework?
- Posted January 17, 2012
- By Lory Hough

The debate over how much schoolwork students should be doing at home has flared again, with one side saying it's too much, the other side saying in our competitive world, it's just not enough.
It was a move that doesn't happen very often in American public schools: The principal got rid of homework.
This past September, Stephanie Brant, principal of Gaithersburg Elementary School in Gaithersburg, Md., decided that instead of teachers sending kids home with math worksheets and spelling flash cards, students would instead go home and read. Every day for 30 minutes, more if they had time or the inclination, with parents or on their own.
"I knew this would be a big shift for my community," she says. But she also strongly believed it was a necessary one. Twenty-first-century learners, especially those in elementary school, need to think critically and understand their own learning — not spend night after night doing rote homework drills.
Brant's move may not be common, but she isn't alone in her questioning. The value of doing schoolwork at home has gone in and out of fashion in the United States among educators, policymakers, the media, and, more recently, parents. As far back as the late 1800s, with the rise of the Progressive Era, doctors such as Joseph Mayer Rice began pushing for a limit on what he called "mechanical homework," saying it caused childhood nervous conditions and eyestrain. Around that time, the then-influential Ladies Home Journal began publishing a series of anti-homework articles, stating that five hours of brain work a day was "the most we should ask of our children," and that homework was an intrusion on family life. In response, states like California passed laws abolishing homework for students under a certain age.
But, as is often the case with education, the tide eventually turned. After the Russians launched the Sputnik satellite in 1957, a space race emerged, and, writes Brian Gill in the journal Theory Into Practice, "The homework problem was reconceived as part of a national crisis; the U.S. was losing the Cold War because Russian children were smarter." Many earlier laws limiting homework were abolished, and the longterm trend toward less homework came to an end.
The debate re-emerged a decade later when parents of the late '60s and '70s argued that children should be free to play and explore — similar anti-homework wellness arguments echoed nearly a century earlier. By the early-1980s, however, the pendulum swung again with the publication of A Nation at Risk , which blamed poor education for a "rising tide of mediocrity." Students needed to work harder, the report said, and one way to do this was more homework.
For the most part, this pro-homework sentiment is still going strong today, in part because of mandatory testing and continued economic concerns about the nation's competitiveness. Many believe that today's students are falling behind their peers in places like Korea and Finland and are paying more attention to Angry Birds than to ancient Babylonia.
But there are also a growing number of Stephanie Brants out there, educators and parents who believe that students are stressed and missing out on valuable family time. Students, they say, particularly younger students who have seen a rise in the amount of take-home work and already put in a six- to nine-hour "work" day, need less, not more homework.
Who is right? Are students not working hard enough or is homework not working for them? Here's where the story gets a little tricky: It depends on whom you ask and what research you're looking at. As Cathy Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework , points out, "Homework has generated enough research so that a study can be found to support almost any position, as long as conflicting studies are ignored." Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth and a strong believer in eliminating all homework, writes that, "The fact that there isn't anything close to unanimity among experts belies the widespread assumption that homework helps." At best, he says, homework shows only an association, not a causal relationship, with academic achievement. In other words, it's hard to tease out how homework is really affecting test scores and grades. Did one teacher give better homework than another? Was one teacher more effective in the classroom? Do certain students test better or just try harder?
"It is difficult to separate where the effect of classroom teaching ends," Vatterott writes, "and the effect of homework begins."
Putting research aside, however, much of the current debate over homework is focused less on how homework affects academic achievement and more on time. Parents in particular have been saying that the amount of time children spend in school, especially with afterschool programs, combined with the amount of homework given — as early as kindergarten — is leaving students with little time to run around, eat dinner with their families, or even get enough sleep.
Certainly, for some parents, homework is a way to stay connected to their children's learning. But for others, homework creates a tug-of-war between parents and children, says Liz Goodenough, M.A.T.'71, creator of a documentary called Where Do the Children Play?
"Ideally homework should be about taking something home, spending a few curious and interesting moments in which children might engage with parents, and then getting that project back to school — an organizational triumph," she says. "A nag-free activity could engage family time: Ask a parent about his or her own childhood. Interview siblings."

Instead, as the authors of The Case Against Homework write, "Homework overload is turning many of us into the types of parents we never wanted to be: nags, bribers, and taskmasters."
Leslie Butchko saw it happen a few years ago when her son started sixth grade in the Santa Monica-Malibu (Calif.) United School District. She remembers him getting two to four hours of homework a night, plus weekend and vacation projects. He was overwhelmed and struggled to finish assignments, especially on nights when he also had an extracurricular activity.
"Ultimately, we felt compelled to have Bobby quit karate — he's a black belt — to allow more time for homework," she says. And then, with all of their attention focused on Bobby's homework, she and her husband started sending their youngest to his room so that Bobby could focus. "One day, my younger son gave us 15-minute coupons as a present for us to use to send him to play in the back room. … It was then that we realized there had to be something wrong with the amount of homework we were facing."
Butchko joined forces with another mother who was having similar struggles and ultimately helped get the homework policy in her district changed, limiting homework on weekends and holidays, setting time guidelines for daily homework, and broadening the definition of homework to include projects and studying for tests. As she told the school board at one meeting when the policy was first being discussed, "In closing, I just want to say that I had more free time at Harvard Law School than my son has in middle school, and that is not in the best interests of our children."
One barrier that Butchko had to overcome initially was convincing many teachers and parents that more homework doesn't necessarily equal rigor.
"Most of the parents that were against the homework policy felt that students need a large quantity of homework to prepare them for the rigorous AP classes in high school and to get them into Harvard," she says.
Stephanie Conklin, Ed.M.'06, sees this at Another Course to College, the Boston pilot school where she teaches math. "When a student is not completing [his or her] homework, parents usually are frustrated by this and agree with me that homework is an important part of their child's learning," she says.
As Timothy Jarman, Ed.M.'10, a ninth-grade English teacher at Eugene Ashley High School in Wilmington, N.C., says, "Parents think it is strange when their children are not assigned a substantial amount of homework."
That's because, writes Vatterott, in her chapter, "The Cult(ure) of Homework," the concept of homework "has become so engrained in U.S. culture that the word homework is part of the common vernacular."
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn.
"Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of time that children will have to do something every night (or several times a week). … This commitment to the idea of homework in the abstract is accepted by the overwhelming majority of schools — public and private, elementary and secondary."
Brant had to confront this when she cut homework at Gaithersburg Elementary.
"A lot of my parents have this idea that homework is part of life. This is what I had to do when I was young," she says, and so, too, will our kids. "So I had to shift their thinking." She did this slowly, first by asking her teachers last year to really think about what they were sending home. And this year, in addition to forming a parent advisory group around the issue, she also holds events to answer questions.
Still, not everyone is convinced that homework as a given is a bad thing. "Any pursuit of excellence, be it in sports, the arts, or academics, requires hard work. That our culture finds it okay for kids to spend hours a day in a sport but not equal time on academics is part of the problem," wrote one pro-homework parent on the blog for the documentary Race to Nowhere , which looks at the stress American students are under. "Homework has always been an issue for parents and children. It is now and it was 20 years ago. I think when people decide to have children that it is their responsibility to educate them," wrote another.
And part of educating them, some believe, is helping them develop skills they will eventually need in adulthood. "Homework can help students develop study skills that will be of value even after they leave school," reads a publication on the U.S. Department of Education website called Homework Tips for Parents. "It can teach them that learning takes place anywhere, not just in the classroom. … It can foster positive character traits such as independence and responsibility. Homework can teach children how to manage time."
Annie Brown, Ed.M.'01, feels this is particularly critical at less affluent schools like the ones she has worked at in Boston, Cambridge, Mass., and Los Angeles as a literacy coach.
"It feels important that my students do homework because they will ultimately be competing for college placement and jobs with students who have done homework and have developed a work ethic," she says. "Also it will get them ready for independently taking responsibility for their learning, which will need to happen for them to go to college."
The problem with this thinking, writes Vatterott, is that homework becomes a way to practice being a worker.
"Which begs the question," she writes. "Is our job as educators to produce learners or workers?"
Slate magazine editor Emily Bazelon, in a piece about homework, says this makes no sense for younger kids.
"Why should we think that practicing homework in first grade will make you better at doing it in middle school?" she writes. "Doesn't the opposite seem equally plausible: that it's counterproductive to ask children to sit down and work at night before they're developmentally ready because you'll just make them tired and cross?"
Kohn writes in the American School Board Journal that this "premature exposure" to practices like homework (and sit-and-listen lessons and tests) "are clearly a bad match for younger children and of questionable value at any age." He calls it BGUTI: Better Get Used to It. "The logic here is that we have to prepare you for the bad things that are going to be done to you later … by doing them to you now."
According to a recent University of Michigan study, daily homework for six- to eight-year-olds increased on average from about 8 minutes in 1981 to 22 minutes in 2003. A review of research by Duke University Professor Harris Cooper found that for elementary school students, "the average correlation between time spent on homework and achievement … hovered around zero."
So should homework be eliminated? Of course not, say many Ed School graduates who are teaching. Not only would students not have time for essays and long projects, but also teachers would not be able to get all students to grade level or to cover critical material, says Brett Pangburn, Ed.M.'06, a sixth-grade English teacher at Excel Academy Charter School in Boston. Still, he says, homework has to be relevant.
"Kids need to practice the skills being taught in class, especially where, like the kids I teach at Excel, they are behind and need to catch up," he says. "Our results at Excel have demonstrated that kids can catch up and view themselves as in control of their academic futures, but this requires hard work, and homework is a part of it."
Ed School Professor Howard Gardner basically agrees.
"America and Americans lurch between too little homework in many of our schools to an excess of homework in our most competitive environments — Li'l Abner vs. Tiger Mother," he says. "Neither approach makes sense. Homework should build on what happens in class, consolidating skills and helping students to answer new questions."
So how can schools come to a happy medium, a way that allows teachers to cover everything they need while not overwhelming students? Conklin says she often gives online math assignments that act as labs and students have two or three days to complete them, including some in-class time. Students at Pangburn's school have a 50-minute silent period during regular school hours where homework can be started, and where teachers pull individual or small groups of students aside for tutoring, often on that night's homework. Afterschool homework clubs can help.
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.) Other schools offer an extended day that allows teachers to cover more material in school, in turn requiring fewer take-home assignments. And for others, like Stephanie Brant's elementary school in Maryland, more reading with a few targeted project assignments has been the answer.
"The routine of reading is so much more important than the routine of homework," she says. "Let's have kids reflect. You can still have the routine and you can still have your workspace, but now it's for reading. I often say to parents, if we can put a man on the moon, we can put a man or woman on Mars and that person is now a second-grader. We don't know what skills that person will need. At the end of the day, we have to feel confident that we're giving them something they can use on Mars."
Read a January 2014 update.
Homework Policy Still Going Strong
Ed. Magazine
The magazine of the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Commencement Marshal Sarah Fiarman: The Principal of the Matter


Making Math “Almost Fun”
Alum develops curriculum to entice reluctant math learners

Reshaping Teacher Licensure: Lessons from the Pandemic
Olivia Chi, Ed.M.'17, Ph.D.'20, discusses the ongoing efforts to ensure the quality and stability of the teaching workforce
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Study Skills
- Homework Skills
11 Ways to Deal With Homework Overload
Last Updated: May 22, 2024 Fact Checked
Making a Plan
Staying motivated, starting good homework habits, expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Jennifer Kaifesh . Jennifer Kaifesh is the Founder of Great Expectations College Prep, a tutoring and counseling service based in Southern California. Jennifer has over 15 years of experience managing and facilitating academic tutoring and standardized test prep as it relates to the college application process. She takes a personal approach to her tutoring, and focuses on working with students to find their specific mix of pursuits that they both enjoy and excel at. She is a graduate of Northwestern University. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 254,144 times.
A pile of homework can seem daunting, but it’s doable if you make a plan. Make a list of everything you need to do, and work your way through, starting with the most difficult assignments. Focus on your homework and tune out distractions, and you’ll get through things more efficiently. Giving yourself breaks and other rewards will help you stay motivated along the way. Don’t be afraid to ask for help if you get stuck! Hang in there, and you’ll knock the homework out before you know it.
Things You Should Know
- Create a checklist of everything you have to do, making sure to include deadlines and which assignments are a top priority.
- Take a 15-minute break for every 2 hours of studying. This can give your mind a break and help you feel more focused.
- Make a schedule of when you plan on doing your homework and try to stick to it. This way, you won’t feel too overwhelmed as the assignments roll in.

- Make a plan to go through your work bit by bit, saving the easiest tasks for last.

- Put phones and any other distractions away. If you have to do your homework on a computer, avoid checking your email or social media while you are trying to work.
- Consider letting your family (or at least your parents) know where and when you plan to do homework, so they'll know to be considerate and only interrupt if necessary.

- If you have the option to do your homework in a study hall, library, or other place where there might be tutors, go for it. That way, there will be help around if you need it. You'll also likely wind up with more free time if you can get work done in school.

- To take a break, get up and move away from your workspace. Walk around a bit, and get a drink or snack.
- Moving around will recharge you mentally, physically, and spiritually, so you’re ready to tackle the next part of your homework.

- For instance, you might write “I need to do this chemistry homework because I want a good average in the class. That will raise my GPA and help me stay eligible for the basketball team and get my diploma.”
- Your goals might also look something like “I’m going to write this history paper because I want to get better as a writer. Knowing how to write well and make a good argument will help me when I’m trying to enter law school, and then down the road when I hope to become a successful attorney.”

- Try doing your homework as soon as possible after it is assigned. Say you have one set of classes on Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays, and another on Tuesdays and Thursdays. Do the Monday homework on Monday, instead of putting it off until Tuesday.
- That way, the class will still be fresh in your mind, making the homework easier.
- This also gives you time to ask for help if there’s something you don’t understand.

- If you want to keep everyone accountable, write a pact for everyone in your study group to sign, like “I agree to spend 2 hours on Monday and Wednesday afternoons with my study group. I will use that time just for working, and won’t give in to distractions or playing around.”
- Once everyone’s gotten through the homework, there’s no problem with hanging out.

- Most teachers are willing to listen if you’re trying and legitimately have trouble keeping up. They might even adjust the homework assignments to make them more manageable.

Reader Videos
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.understood.org/en/articles/homework-strategies
- ↑ https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/homework.html
- ↑ https://kidshelpline.com.au/kids/tips/dealing-with-homework
- ↑ https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/focused.html
- ↑ http://www.aiuniv.edu/blog/august-2014/tips-for-fighting-homework-fatigue
- ↑ http://kidshealth.org/en/parents/homework.html
- ↑ https://learningcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/study-partners/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Daniella Dunbar
Oct 28, 2016
Did this article help you?
Dec 2, 2023
Anamika Gupta
Oct 16, 2020
Mar 8, 2016
Jorien Yolantha
May 8, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Breaking News
Letters to the Editor: Schools teach kids not to slack off. How would no more homework help?

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
To the editor: Reading your editorial favoring a school grading system that deemphasizes homework and task completion , I though what great news this might mean to journalists. Just turn your articles in whenever, no consequences, and don’t worry about work outside your official hours.
Advertisers, turn in your ad copy whenever. Delivery folks, take your time, because deadlines don’t matter. Custodians, clean the toilets whenever you feel like it.
Now, to real life: There are very few tests given once we are adults, but there are many daily chores that must be done and deadlines that must be met. My job as a teacher is not only to educate my students, but also to turn them into employable and responsible adults.
That means daily practice with a routine that becomes ingrained. Completing homework teaches a student organization and planning; it also improves academic skills and reinforces knowledge.
Kathleen McCarthy, Torrance
To the editor: After raising a family of seven quite successful students and teaching public school for 10 years, I agree with your editorial about homework and grading.
I graduated from Reed College in Oregon, a school that deemphasizes grades and is renowned for sending many alumni to graduate school. As students we got many comments on the margins of our papers and tests followed by a conference with the professor or our advisor.
I was also influenced by a book I read early in my career pointing out that if you gave a test on the first day of school, some children would ace it, others would have mixed results, and some would fail. If you did a good job, by the end of the term, everyone should do fairly well on the test, even those who initially failed. The grade should reflect the knowledge gained.
I did my best to follow this advice, and I am encouraged that people are once again considering what education is really all about — and it certainly should not be about averaging test scores.
Sharon Toji, Irvine
To the editor: Letter writers brought up important issues on homework and education . Missing, however, was the fact that students are different, with different interests and talents. The human race depends on this diversity.
As the late psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi pointed out: “If we were all more or less alike, humans would grow into narrowly specialized organisms. It would be difficult for us to adapt to changing conditions.”
An important function of school is to help students discover and develop their interests and pursue their strengths. Overemphasizing “requirements” not only leads to boredom, it also doesn’t result in as much learning as encouraging students to engage in tasks they find natural and interesting.
Plato understood this: “Bodily exercise, when compulsory, does no harm to the body; but knowledge which is acquired under compulsion obtains no hold on the mind.”
Stephen Krashen, Los Angeles
The writer is a professor emeritus of education at USC.
More to Read

Commentary: Here’s how to actually show appreciation for teachers
May 25, 2024

Letters to the Editor: Learning cursive can be torture. Why force something so obsolete on kids?
Jan. 18, 2024
Column: Don’t force kids to learn cursive. Mine is terrible, and I’m doing just fine
Jan. 11, 2024
Letters to the Editor
Readers show off their cursive skills, and then sound off about handwriting
Jan. 8, 2024

Granderson: ChatGPT hasn’t fueled cheating in schools. Do teens know something adults don’t?
Dec. 21, 2023

Letters to the Editor: It’s OK to pay kids for good grades. Just know when to stop
Nov. 19, 2023

Abcarian: Is your kid getting bad grades in math? I found a simple, questionable tactic that works
Nov. 15, 2023

Editorial: We know how to turn students into better readers. Why doesn’t California do it?
Nov. 3, 2023

Letters to the Editor: Why calls to restore discipline in the classroom are troubling
Aug. 12, 2023
A cure for the common opinion
Get thought-provoking perspectives with our weekly newsletter.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Editorial: Lawmakers, quit trying to evade your constituents
June 4, 2024

Opinion: Could the guilty verdict cost Donald Trump the election? Sure it could

Opinion: Mexico’s election of Claudia Sheinbaum is historic. But should we be celebrating it?

Letters to the Editor: Trump wasn’t on trial for sex, and other things his followers refuse to understand
Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .
UConn Today
- School and College News
- Arts & Culture
- Community Impact
- Entrepreneurship
- Health & Well-Being
- Research & Discovery
- UConn Health
- University Life
- UConn Voices
- University News
June 3, 2024 | Mike Enright '88 (CLAS), University Communications
Invasive Plants Hurt the Connecticut Ecosystem in Many Ways. See Why We Need to Get Rid of Them.
Recent articles.

June 4, 2024
Dr. George Kuchel to Serve on Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Advisory Committee
Read the article

Favarh’s Project SEARCH Graduates 3 More at UConn Health

Game On: UConn 4-H Introduces Youth to Biotechnology
'ZDNET Recommends': What exactly does it mean?
ZDNET's recommendations are based on many hours of testing, research, and comparison shopping. We gather data from the best available sources, including vendor and retailer listings as well as other relevant and independent reviews sites. And we pore over customer reviews to find out what matters to real people who already own and use the products and services we’re assessing.
When you click through from our site to a retailer and buy a product or service, we may earn affiliate commissions. This helps support our work, but does not affect what we cover or how, and it does not affect the price you pay. Neither ZDNET nor the author are compensated for these independent reviews. Indeed, we follow strict guidelines that ensure our editorial content is never influenced by advertisers.
ZDNET's editorial team writes on behalf of you, our reader. Our goal is to deliver the most accurate information and the most knowledgeable advice possible in order to help you make smarter buying decisions on tech gear and a wide array of products and services. Our editors thoroughly review and fact-check every article to ensure that our content meets the highest standards. If we have made an error or published misleading information, we will correct or clarify the article. If you see inaccuracies in our content, please report the mistake via this form .
What is a VPN and why do you need one? All your virtual private network questions answered

Whether you work from a traditional office, home office, your iPhone , or on the road, a VPN is one of the best ways to protect yourself from data breaches on the internet, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks.
Also: The best VPN services of 2024: Expert tested and reviewed
This begs more questions. How effective are VPNs, and what's the best VPN for you? What are the downsides to using a VPN? Our VPN guide will answer all your VPN-related questions -- including a few you probably haven't thought to ask.
What is a VPN?
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network.
The purpose of a VPN is to provide you with security and privacy as you communicate over the internet.
Here's the problem with the internet: it's inherently insecure. When the internet was first designed, the priority was to be able to send packets (chunks of data) as reliably as possible. Networking across the country and the world was relatively new, and nodes often went down. Most of the internet's core protocols (communication methods) were designed to route around failure, rather than secure data.
Also: The best mobile VPNs of 2024
The applications you're accustomed to using, such as email, web, messaging, and Facebook, are all built on top of that Internet Protocol (IP) core. While some standards have developed, not all internet apps are secure. Many still send their information without any security or privacy protection whatsoever.
This leaves any internet user vulnerable to criminals who might steal your banking or credit card information, governments who might want to eavesdrop on their citizens, and other internet users who might want to spy on you for a whole range of nefarious reasons.
A VPN creates a private tunnel over the open internet. The idea is that everything you send is encapsulated in this private communications channel and encrypted so -- even if your packets are intercepted -- they can't be deciphered. VPNs are powerful and important tools to protect you and your data , but they have limitations.
How does a VPN work?
Let's start with the basic idea of internet communication. Suppose you're at your desk and you want to access a website like ZDNET. To do this, your computer initiates a request by sending some packets. If you're in an office, those packets often travel through switches and routers on your LAN before they are transferred to the public internet through a router.
Once on the public internet, those packets travel through a bunch of computers. A separate request is made to a series of name servers to translate the DNS name ZDNET.com to an IP address. That information is sent back to your browser, which then sends the request again through many computers on the public internet. Eventually, it reaches the ZDNET infrastructure, which also routes those packets, grabs a web page (which is a bunch of separate elements), and sends all that back to you.
Also: The best VPN for streaming in 2024
Each internet request usually results in a whole series of communication events between multiple points. The way a VPN works is by encrypting those packets at the originating point, often hiding the data and the information about your originating IP address. The VPN software on your end then sends those packets to the VPN server at some destination point, decrypting that information.
One of the most important issues in understanding the limits of VPNs is understanding where the endpoint of the VPN server resides. We'll talk about that next.
What are the two main types of VPNs?
Most of us are familiar with the concept of a LAN, or a local area network. That's the private network inside one physical location -- be it a home, a corporate building, or a campus. Many businesses use more than one LAN since they don't run out of one location -- they have branch offices, departments, and divisions that are geographically dispersed.
In many cases, each of these offices have LANs. For some very specialized solutions, companies lease private lines to connect their offices. That can be very expensive so most companies opt to connect separated private LANs over the public internet geographically. To protect their data, they set up VPNs between offices, encrypting the data as it traverses the public internet.
Also: How to check if your VPN is working (and what to do if your VPN won't connect)
This is a corporate or enterprise VPN, and it's characterized by the same organization controlling both endpoints of the VPN. If your company controls the originating point (say a sales office) and the endpoint (like a VPN server at your corporate HQ), you can be assured ( unless there's a bug ) that your data is securely transmitted.
The second type of VPN is a consumer VPN. This is for those of you who compute in hotels or at coffee shops and connect to web applications like social networks, email, banks, or shopping sites. Consumer VPN services help ensure that those communications are protected.
What does a consumer VPN service do?
A consumer VPN service is, fundamentally, a software-as-a-service (SaaS) offering . The VPN service provides a secure tunnel between your computing device (whether laptop, phone, or tablet) and the provider's data center.
This feature is important to understand. Consumer VPN services protect your transmission from your location to their location, not from your location to the destination application you're using. If you think about it, this approach makes sense -- a consumer VPN service is operated by a completely different company than, for example, Facebook or your bank.
Also: The best VPN services for iPhone and iPad in 2024
The VPN service gives you an app that you run on your local device, which encrypts your data, and it travels in its encrypted form through a tunnel to the VPN service provider's infrastructure. At that point, the data is decrypted and sent on its way.
Two things happen here. First, if you're using an HTTPS connection, your data is encrypted by your browser and then by your VPN app. Your data is decrypted only once at the VPN data center, leaving the original encryption provided by the browser intact. That encrypted data then goes on to the destination application, such as your bank.
The second thing that happens is that the web application you're talking to does not get to see your IP address. Instead, it sees an IP address owned by the VPN service. This approach allows you some level of anonymous networking. This IP spoofing is also used to trick applications into thinking you're located in a different region or even a different country than you are located in. There are reasons (both illegal and legal) to do this. We'll discuss that in a bit.
When should I use a VPN?
We've already discussed the use of a VPN when connecting offices. Any time you have two LANs that need to link over the public internet, you should consider using VPN technology or an equivalent method of enterprise protection. In this case, the VPN software will probably run in a router, a server, or a dedicated VPN server hardware appliance.
We talked about two use cases above for consumer VPN services: protecting your data and spoofing your location. We'll talk more about location spoofing later, so let's focus on data protection for now.
Also: The best travel VPNs of 2024
When you're away from home or the office, and you connect to the internet, you'll most often be doing so via Wi-Fi provided by your hotel or the restaurant, library, or coffee shop you're working out of at that moment. Sometimes, the Wi-Fi network requires a password. Other times, it will be completely open. In either case, you have no idea who else is accessing that network. Therefore, you have no idea who might be snooping on your internet traffic, browsing history, or online activity.
I recommend always using a VPN when using someone else's Wi-Fi network. Here's a good rule of thumb: if you're away from the office or home, and you're using someone else's Wi-Fi (even that of a family member or a friend, because you never know if they've been compromised), use a VPN. It's particularly important if you're accessing a service that has personally identifying information. Remember, a lot goes on behind the scenes, and you never really know if one or more of your apps are authenticating in the background and putting your information at risk.
Another reason you might choose to use a VPN is if you have something to hide, which isn't just about folks doing things they shouldn't do. Sometimes people really need to hide information. Take, for example, the person who is worried an employer might discriminate against them because of their sexual orientation or medical condition. Another example is a person who needs to go online, but is concerned about revealing location information to a person in their life who might be a threat.
And then, of course, there are those people in restrictive countries who need to hide their activity merely to gain access to the internet without potentially grave penalties.
Are the free VPN services any good?
There are some good free VPN services , but I avoid all free VPNs .
Why? It costs a lot to provide the infrastructure to operate a VPN service, from the network pipes to the servers. That infrastructure has to be paid for somehow. If user fees do not pay for it, advertising, data gathering, or some nastier reason are likely picking up the slack.
Here's another reason not to use a free service, and this one is a lot scarier. Malware providers and criminal organizations have set up free VPN services that not only don't protect you but actively harvest personal data, and either use it or sell it to the highest bidder. Instead of being protected, you're being plundered.
What's the best way to choose a VPN service?
To be fair, not all paid VPN services are legitimate, either. It's important to be careful about which you choose. We've put together an always up-to-date directory of quality VPN providers. Some are better than others (and that's reflected in their ratings), but all are legitimate companies that provide quality service.
Also: 3 security gadgets I never leave home without
Beyond our directory, it's always good practice to Google a company or product name and read the user reviews. If you see a huge number of old complaints or new complaints suddenly start showing up, it might be that there's been a change of management or policies. When I'm looking for a service, I always base my decision partially on professional reviews and partially based on the tone of user reviews.
Finally, be sure to choose a service with the capabilities that meet your needs . You may need one or more features only provided by certain services. So, think through your needs as you make a decision.
Can a VPN guarantee my privacy?
Oh, heck no . A VPN can help ensure you're not snooped on when connecting between your computer and a website. That said, the website itself is quite capable of some serious privacy violations. For example, a VPN can't protect you against a website setting a tracking cookie that will tell other websites about you. A VPN can't protect you against a website recording information about products you're interested in. A VPN can't protect you against a website that sells your email address to list brokers. And so on and so on.
Also: The best VPN deals right now
A VPN does help protect you in the situations we've discussed in previous sections, but don't expect a VPN to be a magical privacy shield that will keep everything you do private and confidential. There are many, many ways your privacy can be compromised, and a VPN is only partially helpful .
Will VPN software slow down my computer?
Maybe. Back in the day, the process of encrypting and decrypting packets would take a toll on CPU performance. Most current CPUs are now fast enough that most crypto algorithms can run without much of an impact on processor performance.
Also: The best cheap VPNs of 2024
However, network performance is another thing entirely. First, keep in mind that if you're using a VPN, you're probably using it at a public location. That public Wi-Fi service is likely to range in performance somewhere between "meh" and unusable. So, just the fact that you're remotely working on a mediocre network will reduce performance. Additionally, if you connect to a VPN in a different country, the connection between countries is also likely to degrade network performance. Server locations matter.
My rule of thumb is to use a domestic VPN and connect to servers as close to my location as possible. That said, I have had good nights and bad nights getting online. On a recent trip, I found most hotel networks become unusable after about 9pm. My theory is that many of the guests are watching Netflix at that time, completely clogging the hotels' pipes.
Do VPN service providers limit usage and how?
Some do. Some don't. Look at that directory I mentioned earlier because that's one of the factors where a service might lose some points.
Some VPN services limit the total amount of data you can send and receive, either in one connection session or over a month. Other VPN services limit the speed of the data, effectively sharing less of their pipe with you than might be optimal. That could slow your browsing experience to a crawl or completely prevent you from watching videos through streaming services.
Also: Five easy steps to keep your smartphone safe from hackers
Usually, it's the free services that throttle your usage in these ways. Some paid services offer a trial, where you can transmit up to a certain data cap before being asked to sign up as a paying customer. That's actually pretty cool because it gives you a chance to try out the performance of their service before paying, but it also gives the vendor a chance to make the money necessary to operate the service.
Many VPN services claim that they'll provide you with unlimited data transmission if you pay their fee and won't throttle your speeds. Generally, this is true, but I'll give you my standard "unlimited bandwidth" warning: it's been my experience that when a vendor says something is "unlimited," it's almost always limited. There will be a note somewhere in the fine print or terms of service that allows the vendor to limit you in some way. It pays to read those agreements.
How private are VPNs? Do they log everything I do?
In our VPN directory , we track two types of logging. The first is whether providers log traffic, DNS requests, and IP addresses. This is pretty nasty stuff. If a VPN service logs this, they would have the information you might choose to hide, like sites you visit, your physical locations, and possibly even information you might be sending.
Also: 7 hacking tools that look harmless but can do real damage
Although the use of these services will still protect you from Wi-Fi spies in your hotel or restaurant, I can't recommend signing up for any service that does DNS, traffic, or IP logging. There are better, more private options.
The second type of logging is more benign. VPN services that log bandwidth usage and connection timestamp data usually do so either to tune their own systems or manage any abuse of their services.
I have less of a concern with services that just monitor bandwidth usage, as long as they don't store any specifics. That said, we gave top marks to those services that don't do any logging. When I choose a VPN service, I avoid all logging.
Is it legal to use a VPN?
That depends. VPN use is legal in most countries, but, according to VPN provider CyberGhost , VPN use is illegal in the United Arab Emirates, Turkey, China, Iran, North Korea, Saudi Arabia, and Russia . Vladimir Putin has recently banned VPN use in Russia. Also, be aware that the so-called proxy server alternative to VPNs is also illegal in many countries, which consider any form of IP spoofing to be illegal, not just those services labeled as VPNs.
Also: The best security keys you can buy
Restrictions vary, as do penalties. China allows certain approved VPNs . In the UAE, if you use a VPN, you could go to jail or be fined a minimum of more than the equivalent of $100,000.
Definitely research these laws before you visit a country. Many travelers mistakenly believe that just because they're not citizens, and all they're doing is linking back to a corporate system, they should be able to have unrestricted use of VPN software. This is a mistake.
The bottom line is to check the laws of the country you're in before connecting. It's also a good idea to check with your VPN provider, both for insight into whether it knows if there are issues, and whether it'll support connectivity from the country you're visiting.
Do I need to use a VPN if my hotel has a wired internet connection?
Yes. It is almost totally unlikely that each room is on a dedicated subnet, so that means packets are traveling across a network shared by other guests. In addition, you never know whether someone in the front office has set up a packet sniffer for the express purpose of mining guest information.
So, yes, use a VPN, even if there's a hard-wired connection.
Will a VPN service help me connect securely to my office network?
If you're trying to connect to your on-premises corporate network, you'll most likely be assigned a VPN application by your IT department. This will allow you to establish a point-to-point connection between your local device and a server owned and operated by your company.
Also: 6 simple cybersecurity rules to live by
If your company is cloud-based, however, and you're connecting to SaaS applications like Salesforce or Google, you should probably use a VPN service since you're not actually connecting to your company but instead to a public cloud application.
If your IT department does not specifically identify a VPN service you should use for accessing their public cloud applications, definitely look at our VPN directory and choose one of the higher-rated service providers.
Can I get away with a VPN app, or do I need to bring my own router/bridge/dongle?
Let's talk about what happens when you use a VPN app on your computer or mobile device. Any VPN app will require an existing network connection to be able to connect to the VPN service provider. This approach means that even if you set your VPN app to automatically launch when your device boots, there will be a period when your computer is connected to the internet directly, not through your VPN.
Also: 9 top mobile security threats and how you can avoid them
Some background services can send information across that initial, unsecured connection before the VPN loads. To be fair, the risk is relatively minor for most usage profiles. If you're establishing a connection automatically to your corporate server, you will want to check with your IT team about how they want you to set things up.
If you are interested in an added level of protection, consider adding a travel router like the TP-Link AC750 . This device can be configured in a variety of modes, so you can configure it to be sure your computer's communication is always blocked before it calls out to the internet.
Should I use a VPN on my phone or tablet?
Both Android and iOS come with basic VPN capabilities to allow you to connect to your corporate networks securely. Your IT organization will generally advise you when to use this feature, but as we've discussed, you should do so whenever you're away from your home or office, and especially if you're using an open, public Wi-Fi connection.
If you're connecting to web applications, like email or Facebook, you should consider using a VPN service -- particularly if you're connecting via an open Wi-Fi network. Most good VPN services offer both iOS and Android clients.
Do I need a VPN if I'm connecting my phone via LTE?
That depends. Once again, your corporate IT department will let you know their policy for connecting directly to their corporate network. Usually, you'll use the VPN client built into your device's operating system for this.
The connection also depends on how much you trust your carrier, where you're located in the world, and how secure you want to be. The carriers ( net neutrality notwithstanding ) can generally be relied upon to provide a secure connection from your phone to their network in the US.
That said, it is possible to compromise wireless phone services with a man-in-the-middle attack . This situation occurs when a malevolent actor places a device designed to confuse your phone, and cause your phone to connect to what it thinks is the phone network, but is, in fact, a device designed for spying.
Outside the US, the requirement for a VPN depends on what country you're in. If you are really concerned about security, simply avoid bringing any devices into a foreign nation that you intend to use after your trip. Those devices can be compromised in the country or during customs inspections.
Likewise, if you're connecting via a nation's local carrier, that carrier may be intercepting your traffic, particularly if you're a non-native of that nation. In that situation, if you must connect back to applications and services at home, using a VPN is quite literally the least you can do. Also, keep in mind that if you use your phone's hotspot to connect your computer to the internet, you'll want to use a VPN on your computer as well.
Finally, as we covered earlier in this guide, it's worth reminding you that some countries consider VPN use illegal. If you're planning on traveling, be sure to research local laws.
What happens if a VPN connection fails while I'm on a remote connection?
A lot depends on what VPN you're using, how it's set up, and where you're connecting. That said, let's look at the most likely scenario.
Recall that when you're online and connected to an internet application through a VPN, a few things are happening. Your data from your computer to the VPN service is encrypted by the VPN. Your data from the VPN service to the internet application may or may not be encrypted via HTTPS, but the VPN service just spoofs your IP address and does not encrypt the connection. The online application sees the IP address of the VPN service, not of your laptop.
Also: How to find and remove spyware from your phone
When a VPN connection drops, you might just lose your connection. Because the internet is very good at routing around failures, what is more likely to happen is your computer will reconnect to the internet application, simply bypassing the VPN service. That means that -- on failure -- your local IP address may "leak out" and be logged by the internet application, and your data may be open to local Wi-Fi hackers at your hotel or wherever you're doing your computing.
There is a reasonably robust solution to that problem, and that's next.
What does a VPN kill switch do?
Put simply, a VPN kill switch kills your internet connection if it detects that your VPN's connection has failed. There are generally two types of VPN kill switches.
The first runs in the VPN client app on your computer, so if the VPN connection fails while the VPN client app is running, that VPN client app can turn off the computer or mobile device's internet connection. Unfortunately, if your VPN connection fails because the VPN client app itself crashed, then the kill switch may not work, and your IP and data may leak onto the internet.
Also: 8 habits of highly secure remote workers
The second type of VPN kill switch is at the operating system level. These switches are usually driver-level systems that run regardless of whether the VPN application is running. As such, they provide a bit more protection for your surfing activities.
Given that so many VPN products we reviewed in our directory support a kill switch, we recommend choosing a client with this feature. There may be a slight annoyance if you lose your connection, but that's more than made up for in the added security.
What do all those protocol names mean and which one should I choose?
If you've been shopping for a VPN service, you've undoubtedly come across a bunch of terms like SSL, OpenVPN, SSTP, L2TP/IPSec, PPP, PPTP, IKEv2/IPSec, SOCKS5, and more. These are all communication protocols. They are, essentially, the name of the method by which your communication is encrypted and packaged for tunneling to the VPN provider.
Also: How to stay safe on public Wi-Fi: 5 tips you need to know
There is a lot of debate among security purists about which VPN protocol is better. Some protocols (like PPP and its tunneling variant, PPTP) are old and compromised. Others, like SSTP, are proprietary to one company or another.
My recommendation -- and the protocol I most often choose to use -- is OpenVPN. OpenVPN is a non-proprietary, open-source implementation of a VPN communication layer protocol. It's well-understood, well-regarded, generally quite secure, and robust. Also, it has the benefit of communicating over port 443, which is the standard port for HTTPS communication, which means almost all firewalls will allow OpenVPN traffic -- and most won't even be able to detect that a VPN is being used.
Yes, there are certainly other protocol choices, even some that might be more appropriate than OpenVPN in certain situations. But if that's the case, either you've already made that decision, or your IT organization has specified a protocol you should use. If, however, you're not sure what to look for, look for OpenVPN.
What does it mean when a VPN service talks about simultaneous connections?
The term "simultaneous connections" generally refers to the number of devices that can be connected to a VPN service and that can talk to the internet at once. For example, when I was driving across the country and working in my hotel room at night, I often had both my MacBook Pro and iPad connected to the internet.
Also: The best password managers to help you easily maintain all your logins
I used the MacBook Pro for writing and kept the iPad open to do searches and find supporting information. Both of these were connected to the internet at once. This was possible because the VPN service I was using allowed up to three simultaneous connections.
This form of connectivity is also a good way to provide support for more than one family member on a single subscription. Generally, there's no good reason for a VPN provider to allow less than two or three connections. If your provider only allows one, find another vendor. We gave extra points in our VPN directory to the vendors that allowed three or more connections.
If I'm using an XR headset, do I need a VPN?
Since one of the most popular uses of XR headsets is when traveling, you might want to consider using one. It may not be all that easy, but we have found that some VPNs install neatly on the Apple Vision Pro .
VPNs do not seem to install as easily on the Meta Quest, and if you want a VPN on that device, you'll have to side-load it from an Android app provider. I'm guessing that Meta will eventually add support for VPNs.
Also: Why you'll need a VPN for the Vision Pro (and other XR headsets)
When should I choose either dynamic or static IP?
Every device connected to the public internet is assigned an IP address. It's like a phone number for each device. To be able to connect to the internet, each device needs such an address.
The term "dynamic IP address" means that when a device connects to the internet, it's given an IP address taken from a pool of available addresses. While it's possible to get the same IP address on multiple connections, generally, each time you connect, you'll get a different address.
If you want to hide your address from the web applications you're connecting to, you'll want a VPN service that provides dynamic IP addresses. In our directory, we list the number of IP addresses each service offers . By using a service with more available IP addresses, the chances of you getting a repeated IP are quite small.
There are some minor disadvantages to using a dynamic IP. If someone who previously had the IP address you've been assigned did something nefarious on a service you use, the IP address might be banned. Usually, VPN providers are cautious about checking their IP addresses against blacklists, so the chances of this being a problem for you are slim.
By contrast, a static IP address is an address that's assigned to you and only you. Most often, this is needed if you're running a server. Usually, static IP addresses are used in corporate situations and are generally not practical for general remote access, like from a hotel or a coffee shop.
Unless you have a specific application that you know needs a static IP, you'll want to be assigned a new dynamic IP address for each VPN session you initiate.
What does it mean when a VPN service talks about server switching?
As we mentioned in the previous section, you're usually assigned a dynamic IP address from a pool of addresses when you connect to a VPN service. Those addresses are attached to servers located, usually, around the world.
Most VPN services allow you to connect to server locations in many different countries. In our VPN directory, we list both the number of servers the service maintains and the number of countries . By default, you'll usually be assigned a server located in your home country. Still, if you want to obfuscate your location, you may want to connect to a server located in a different country.
Also: The best VPN routers of 2024
Server switching is a feature -- offered by most VPN service providers -- that allows you to change what region or country you're going to connect to. Most providers allow you to switch as often as you'd like (although you usually have to disconnect, then change your configuration, and reconnect). This may be useful if you're trying to hide your location or if you're running into some communications glitches on the server you're currently using.
Can I use a VPN to spoof my location or country of origin?
Because the VPN server you're connected to presents its IP address to whatever web application you're using, by choosing a server located in a different country, you can represent your connection as if you're in a different country. This may be illegal in certain regions, so use caution when doing this.
In my testing, some VPN providers could successfully hide their originating country or the fact that they were VPNs, but others could not. You'll probably want to do some testing. Of the services where I did my testing, NordVPN and Hotspot Shield could successfully hide their VPN origins, while StrongVPN and CyberGhost could not.
Can I use a VPN to watch a blacked-out program or video?
Sometimes it is possible to watch a blacked-out sporting event or other show, although we certainly can't advise you to do so. Spoofing your location to bypass broadcast restrictions may get you in hot water.
Also: What is the dark web? Here's everything to know before you access it
Also, be aware that some broadcasters have developed increasingly sophisticated methods to determine whether the IP address you represent is the IP address where you're located. The VPN may be able to protect your original IP address from being seen, but there are characteristics of proxy communications (like a slightly longer time to transfer packets) that can be used to identify whether you are trying to bypass watching restrictions.
Is it true that a VPN is completely unhackable?
No. No. Did I mention... no. Nothing is unhackable .
In January 2018, Cisco Systems (a very highly respected maker of internet communications hardware) revealed that a critical bug was found in its ASA (Adaptive Security Appliance) software that could allow hackers to execute code remotely.
This is a bug in enterprise-level VPN systems used by corporations, so it's severe. Fortunately, responsible IT administrators could patch their systems to fix the bug. However, the incident goes to show how no system can be truly deemed absolutely secure.
Another example was a bug in Hotspot Shield , a popular VPN service. This bug allowed a hacker to expose private information, including originating IP addresses. Hotspot Shield issued an update, which gives us an excuse to remind you that you should always install updates, especially on your VPN client software.
Who are the key players?
We've done in-depth reviews of the following VPN services. If you're considering a VPN, you might want to read these articles first:
NordVPN review: Sincere about security and privacy
StrongVPN Review: A clear and easy-to-use VPN ideal for coffee shop use
Hotspot Shield review: Here's a VPN that actually lives up to its hype
CyberGhost VPN review: More than just VPN, an all-in-one security kit
IPVanish review: VPN delivers a wealth of options and browsing controls
While there are a tremendous number of VPN vendors out there, we think the following are some of the best:
- ExpressVPN : Detailed FAQ, good refund policy, Bitcoin
- Surfshark : Unlimited device support, whitelisting feature
- NordVPN : 30-day refund, lots of simultaneous connections
- Private Internet Access : Lowest yearly price, most servers
- Proton VPN : Privacy-conscious, many add-ons available
You can follow my day-to-day project updates on social media. Be sure to subscribe to my weekly update newsletter , and follow me on Twitter/X at @DavidGewirtz , on Facebook at Facebook.com/DavidGewirtz , on Instagram at Instagram.com/DavidGewirtz , and on YouTube at YouTube.com/DavidGewirtzTV .
ZDNET Recommends
The best vpns for iphone and ipad: expert tested, the best vpn for windows: expert tested, the best vpn services: expert tested.

What to get rid of for a minimalist bedroom – 9 essentials we need to ditch, according to pros
E ven those of us who love decorating with color and pattern in our living spaces can appreciate a more calm and minimalist approach to the bedroom.
Of course, minimalist bedrooms don't have to be stark white with only a bed and a dresser, but there are a few bedroom decluttering rules worth bearing in mind if you want to create a soothing sleep space.
Especially if you are rethinking your bedroom to help sleep better . Here, professional home organizers and designers have shared the nine things to get rid of for a more minimalist bedroom.
What to get rid of for a minimalist bedroom
Simple bedrooms have a whole host of benefits for our health and well-being and are worth considering if you have been finding it difficult to relax at night, begins Victor Cheung , Feng Shui expert, designer, and founder of Feng Shui Nexus.
Not only does a visually uncluttered space remove distractions to promote restful sleep, but the calmness and simplicity of a minimalist environment enhance relaxation. ‘Additionally, minimizing the presence of dust and promoting better air quality contributes to a healthier sleeping environment,’ he adds.
‘Moreover, a minimalist approach to your bedroom fosters mindfulness and intentionality. By intentionally curating your space and keeping only what is essential and meaningful you cultivate a sense of gratitude and contentment.’
With that in mind, here is what the experts wish we left at the bedroom door.
1. Electronics
If you have ever dreamed of recreating one of the many aesthetic bedrooms from Instagram or Pinterest, you may have noticed the lack of any electronics, from cords to TVs.
Stephanie Calderon , principal designer and founder of Stephanie Calderon Interiors believes that TVs have no place in the bedroom, admitting that it may be a touchy subject. ‘Aside from its potential to negatively impact sleep quality, it can draw attention away from other design elements or focal points and make a space feel more cluttered,’ she shares. ‘We prefer to design without TVs in the bedroom if we are allowed the option. If not, we try to find somewhere where we can close the TV away when it is not being used, such as a closet or cabinet to reduce its impact.’
2. Furniture that doesn't have storage
When decorating a minimalist space, it is important to be able to hide your clutter – unless you are planning on adopting a true minimalist way of life and cutting back on everything you own.
To make this easier, Amy Berryhill , founder and chief organizer at Spiffy Chicks suggests getting rid of any furniture that does not offer additional storage.
‘If you just have a flat surface, items can pile up over time. A wide nightstand with drawers is my favorite item of bedroom storage , so you can put most items away and only have a few decorative items on top. A calm, relaxing environment has also been shown to improve your quality of sleep – and who doesn't want that?’
That being said, keeping absolutely everything hidden away with storage capabilities can overwhelm the space too, tipping the scale too far the other way, as Victor Cheung points out. He recommends ditching ‘excessive storage containers or bins that don't serve a specific purpose or do not fit in existing furniture.’
Round Storage Ottoman | Was $273.99,
Now $159.99 at Ashley
3. Paper clutter
Bedrooms may not be the first place you take your mail to read, but they can become littered with magazines and receipts that we pull from our purses after a shopping trip. Getting rid of paper clutter is an ongoing task to keep on top of, as it builds up quickly.
‘I encourage my clients to deposit all catalogs and junk mail into a recycling bin before entering their homes,' comments Amy Bloomer, professional organizer and organizational psychologist, and founder of Let Your Space Bloom.
'Place magazines where you will read them (on a bedside table) and commit to recycling them immediately after reading them. If there is any information that you want to save, take a picture of it and move on.’
4. Excess blankets and pillows
In an effort to make a bedroom cozy, we have all been guilty of overspending on blankets and pillows to layer up and style our bed like a five-star hotel . After a while, these throws end up in a pile unused when the novelty of making the bed with them all every single day wears off.
Amy Bloomer suggests ditching the worn-out pillows and blankets, either taking them to a fabric recycling point or donating them if they are not in bad condition. ‘Bring old towels, blankets, and pillows that can be taken to your local animal shelter or zoo, where the animals will be able to make good use of them,’ she adds.
Be realistic about what you will have time and energy to fluff and arrange every morning and edit down your collection.
5. Excess decor that doesn’t hold significance
Our bedrooms need a little decor to add personality and warmth, but that doesn't mean that we need to hold on to every little trinket we have ever been given, Victor Cheung, Feng Shui expert and designer advises. For a minimalist space, we should really be keeping everything that isn't essential off of our surfaces.
‘Having too many wall art pieces, decorative items, or unnecessary furniture can create visual chaos and disrupt the overall harmony. By simplifying the visual space, we can establish a clean and uncluttered atmosphere that fosters a peaceful ambiance.’
6. Overflowing bookshelves
There is nothing as relaxing as reading a good book before bed, but overflowing bookshelves are the epitome of chaos (especially when you haven't read half the tomes on there.)
One of the best steps you can take to create a minimalist bedroom is to declutter your books , or even move your shelves elsewhere, suggests Amy Bloomer, professional organizer. ‘Keep your favorites and donate the balance of the books to your local library, school (where appropriate), or charitable thrift store.’
7. Everything on your nightstand
Bedroom nightstands are magnets for clutter, even though they are, arguably, the most important place to keep clean in your room, says Stephanie Calderon, designer.
‘Really you shouldn't have any decor on your nightstand at all, keeping it clear so that you can pop down the essentials, such as a drink, a book, and some glasses if you need them,’ she advises. ‘For those who have additional bedside necessities, we always suggest nightstands with drawers to hide the excess clutter.’
8. Clothes you no longer wear
You are probably tired of hearing it by now, but decluttering clothes is essential for a minimalist space – even if you are not looking to have a minimalist capsule closet.
The clothing you no longer like or wear is an obvious target for this, but anything that doesn't fit into the closet or dressers needs to go too, Victor Cheung, feng shui expert, and designer cautions.
‘Keeping a minimal and organized collection of clothing avoids a cluttered environment and contributes to a sense of calmness and order, and having excess garments strewn around your room is detracting from that.’
If you have space in your home, it is a good idea to consider moving your clothing out of your bedroom entirely and opting for a separate dressing room instead. This can help to separate the chaos of the day from the sleep space and make for a truly relaxing environment.
9. Highly saturated colors
When designing a bedroom , you should really aim to pick the most relaxing colors when putting together a palette, as this can help to achieve that sleek minimalist aesthetic, suggests Courtney Finley , professional organizer, and designer and owner of Organized Designs.
‘You can paint your walls a soothing calming color such as a creamy white or even a pastel color – it doesn't have to be bleak,’ she advises. ‘Greens, blues, and purples are common for this, but you could get adventurous and opt for limewashing , a painting technique proven to aid relaxation,’ she adds.
What should a minimalist bedroom have?
An extremely minimalist bedroom should have at least a bed, a storage unit for clothing, nightstands, and a light source to allow for reading in the evening. From there, you may choose to add in a few personal mementos, playing with different degrees of minimalism to create a space that makes you feel safe and cozy, as well as relaxed.
What is the 90 rule in minimalism?
The 90-day rule in minimalism dictates that when decluttering, you should only keep hold of things that you have used in the past 90 days, or will use in the next 90. This allows you to keep hold of seasonal items while singling out those that you promised yourself you would use but never touched. It can be a hard but useful exercise to try if you are finding it difficult to let go of items you are worried you will need again in the future. If you haven't used it by now and have no plan to, you likely don’t need it.
As well as considering what to remove, think about what you are bringing in. Before purchasing a new nightstand or chest of drawers, for instance, measure carefully, and consider exactly where it will go and how it will be used. If you cannot think of an exact spot for it, don't bring it through your front door.
Given how quickly our kitchens can become cluttered, it's worth getting rid of items for a minimalist kitchen , too.


COMMENTS
Should we get rid of homework? In ... Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly ...
"Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it's larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It's one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, 'Is it really making a difference?'" — John Hattie, professor
Homework negatively affects students' health. Download Article. Homework takes a toll physically. Recent studies have demonstrated that too much homework can disrupt a student's sleep cycle, and cause stress headaches, stomach problems, and depression. [3] 3.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night. "Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's ...
American high school students, in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found. It's time for an uprising. Already, small rebellions ...
Getting rid of homework is a relatively simple way to combat this high-stakes problem. ... author of "The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing." "After all, we adults need ...
But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether. Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students ...
From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. []While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word "homework" dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home.
Ultimately, minimizing homework or getting rid of it entirely denies children autonomy and prevents them from discovering what they are capable of. As we work to repair the academic damage from the last two-plus years, I encourage educators to focus not on the quantity of homework, but instead on its quality—and on using it effectively in class.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
Homework is a controversial topic in education, but what does the science say? Explore the pros and cons of homework and its impact on students' well-being in this article from BBC Science Focus Magazine.
The authors of "You Need to Be More Responsible" are part of a movement that argues, sometimes convincingly, that a meritocratic vision impedes true equal opportunity. In regards to homework ...
A common argument exists that the pressure of homework mirrors the real world - that we should assign homework because that's "just the way things are." If we want kids to succeed in the "real world", they need to have this pressure. But this mentality is unhealthy and unjust. The purpose of education should be to develop purpose.
It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student. 5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time.
If you try and get rid of homework in primary schools many parents judge the quality of the school by the presence of homework. So, don't get rid of it. Treat the zero as saying, "It's probably not making much of a difference but let's improve it". Certainly I think we get over obsessed with homework. Five to ten minutes has the same ...
Negative Effects of Homework for Students. While some amount of homework may help students connect to their learning and enhance their in-class performance, too much homework can have damaging effects. Students with too much homework have elevated stress levels. Students regularly report that homework is their primary source of stress.
Too much homework might have the opposite effect on young students and can negatively impact their lives outside the classroom. But the momentum to get rid of homework is being met by others who ...
August 17, 2021. Anxiety Children Covid-19 Mental Health Depression Mental Health. It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
An article on Newsday.com says that since 1981, time spent on homework is up 51 per cent. Author Bennett agrees that too much homework hurts the whole family. "It takes away from family time, puts parents in an adversarial role with kids and interferes with the child's ability to play and have other after-school activities.".
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn. "Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of ...
However, the truth is it's hard to know. Professor Hallam explains that part of the problem is that it is difficult to accurately work out how useful homework is. The Homework Debate: Adults face ...
1. Take a break now and then. You might think that tearing through all of your homework tasks from start to finish is the fastest way to do it. If you have a ton of homework, however, you'll probably get burnt out if you don't take a break every now and then. At least every two hours, take a 15 minute breather.
Completing homework teaches a student organization and planning; it also improves academic skills and reinforces knowledge. Kathleen McCarthy, Torrance. .. To the editor: After raising a family of ...
See Why We Need to Get Rid of Them. View Article. Recent Articles. June 3, 2024. Connecticut Manufacturing Simulation Center Offers Technical Advising to Small Businesses. Read the article. June 3, 2024. Ten Students Earn Awards From Gilman Foundation. Read the article. May 31, 2024.
Another invasive plant, tree of heaven, attracts the. Japanese lantern fly. , an invasive insect that has been spreading into Connecticut and destroying trees and crops. "And after that it'll ...
The VPN service gives you an app that you run on your local device, which encrypts your data, and it travels in its encrypted form through a tunnel to the VPN service provider's infrastructure. At ...
4. Excess blankets and pillows. In an effort to. make a bedroom cozy, we have all been guilty of overspending on blankets and pillows to layer up and. style our bed like a five-star hotel. After a ...