

Understanding Case Study Method in Research: A Comprehensive Guide

Table of Contents
Have you ever wondered how researchers uncover the nuanced layers of individual experiences or the intricate workings of a particular event? One of the keys to unlocking these mysteries lies in the qualitative research focusing on a single subject in its real-life context.">case study method , a research strategy that might seem straightforward at first glance but is rich with complexity and insightful potential. Let’s dive into the world of case studies and discover why they are such a valuable tool in the arsenal of research methods.
What is a Case Study Method?
At its core, the case study method is a form of qualitative research that involves an in-depth, detailed examination of a single subject, such as an individual, group, organization, event, or phenomenon. It’s a method favored when the boundaries between phenomenon and context are not clearly evident, and where multiple sources of data are used to illuminate the case from various perspectives. This method’s strength lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case in its real-life context.
Historical Context and Evolution of Case Studies
Case studies have been around for centuries, with their roots in medical and psychological research. Over time, their application has spread to disciplines like sociology, anthropology, business, and education. The evolution of this method has been marked by a growing appreciation for qualitative data and the rich, contextual insights it can provide, which quantitative methods may overlook.
Characteristics of Case Study Research
What sets the case study method apart are its distinct characteristics:
- Intensive Examination: It provides a deep understanding of the case in question, considering the complexity and uniqueness of each case.
- Contextual Analysis: The researcher studies the case within its real-life context, recognizing that the context can significantly influence the phenomenon.
- Multiple Data Sources: Case studies often utilize various data sources like interviews, observations, documents, and reports, which provide multiple perspectives on the subject.
- Participant’s Perspective: This method often focuses on the perspectives of the participants within the case, giving voice to those directly involved.
Types of Case Studies
There are different types of case studies, each suited for specific research objectives:
- Exploratory: These are conducted before large-scale research projects to help identify questions, select measurement constructs, and develop hypotheses.
- Descriptive: These involve a detailed, in-depth description of the case, without attempting to determine cause and effect.
- Explanatory: These are used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships and understand underlying principles of certain phenomena.
- Intrinsic: This type is focused on the case itself because the case presents an unusual or unique issue.
- Instrumental: Here, the case is secondary to understanding a broader issue or phenomenon.
- Collective: These involve studying a group of cases collectively or comparably to understand a phenomenon, population, or general condition.
The Process of Conducting a Case Study
Conducting a case study involves several well-defined steps:
- Defining Your Case: What or who will you study? Define the case and ensure it aligns with your research objectives.
- Selecting Participants: If studying people, careful selection is crucial to ensure they fit the case criteria and can provide the necessary insights.
- Data Collection: Gather information through various methods like interviews, observations, and reviewing documents.
- Data Analysis: Analyze the collected data to identify patterns, themes, and insights related to your research question.
- Reporting Findings: Present your findings in a way that communicates the complexity and richness of the case study, often through narrative.
Case Studies in Practice: Real-world Examples
Case studies are not just academic exercises; they have practical applications in every field. For instance, in business, they can explore consumer behavior or organizational strategies. In psychology, they can provide detailed insight into individual behaviors or conditions. Education often uses case studies to explore teaching methods or learning difficulties.
Advantages of Case Study Research
While the case study method has its critics, it offers several undeniable advantages:
- Rich, Detailed Data: It captures data too complex for quantitative methods.
- Contextual Insights: It provides a better understanding of the phenomena in its natural setting.
- Contribution to Theory: It can generate and refine theory, offering a foundation for further research.
Limitations and Criticism
However, it’s important to acknowledge the limitations and criticisms:
- Generalizability : Findings from case studies may not be widely generalizable due to the focus on a single case.
- Subjectivity: The researcher’s perspective may influence the study, which requires careful reflection and transparency.
- Time-Consuming: They require a significant amount of time to conduct and analyze properly.
Concluding Thoughts on the Case Study Method
The case study method is a powerful tool that allows researchers to delve into the intricacies of a subject in its real-world environment. While not without its challenges, when executed correctly, the insights garnered can be incredibly valuable, offering depth and context that other methods may miss. Robert K\. Yin ’s advocacy for this method underscores its potential to illuminate and explain contemporary phenomena, making it an indispensable part of the researcher’s toolkit.
Reflecting on the case study method, how do you think its application could change with the advancements in technology and data analytics? Could such a traditional method be enhanced or even replaced in the future?
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
Research Methods in Psychology
1 Introduction to Psychological Research – Objectives and Goals, Problems, Hypothesis and Variables
- Nature of Psychological Research
- The Context of Discovery
- Context of Justification
- Characteristics of Psychological Research
- Goals and Objectives of Psychological Research
2 Introduction to Psychological Experiments and Tests
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Extraneous Variables
- Experimental and Control Groups
- Introduction of Test
- Types of Psychological Test
- Uses of Psychological Tests
3 Steps in Research
- Research Process
- Identification of the Problem
- Review of Literature
- Formulating a Hypothesis
- Identifying Manipulating and Controlling Variables
- Formulating a Research Design
- Constructing Devices for Observation and Measurement
- Sample Selection and Data Collection
- Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Hypothesis Testing
- Drawing Conclusion
4 Types of Research and Methods of Research
- Historical Research
- Descriptive Research
- Correlational Research
- Qualitative Research
- Ex-Post Facto Research
- True Experimental Research
- Quasi-Experimental Research
5 Definition and Description Research Design, Quality of Research Design
- Research Design
- Purpose of Research Design
- Design Selection
- Criteria of Research Design
- Qualities of Research Design
6 Experimental Design (Control Group Design and Two Factor Design)
- Experimental Design
- Control Group Design
- Two Factor Design
7 Survey Design
- Survey Research Designs
- Steps in Survey Design
- Structuring and Designing the Questionnaire
- Interviewing Methodology
- Data Analysis
- Final Report
8 Single Subject Design
- Single Subject Design: Definition and Meaning
- Phases Within Single Subject Design
- Requirements of Single Subject Design
- Characteristics of Single Subject Design
- Types of Single Subject Design
- Advantages of Single Subject Design
- Disadvantages of Single Subject Design
9 Observation Method
- Definition and Meaning of Observation
- Characteristics of Observation
- Types of Observation
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Observation
- Guides for Observation Method
10 Interview and Interviewing
- Definition of Interview
- Types of Interview
- Aspects of Qualitative Research Interviews
- Interview Questions
- Convergent Interviewing as Action Research
- Research Team
11 Questionnaire Method
- Definition and Description of Questionnaires
- Types of Questionnaires
- Purpose of Questionnaire Studies
- Designing Research Questionnaires
- The Methods to Make a Questionnaire Efficient
- The Types of Questionnaire to be Included in the Questionnaire
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Questionnaire
- When to Use a Questionnaire?
12 Case Study
- Definition and Description of Case Study Method
- Historical Account of Case Study Method
- Designing Case Study
- Requirements for Case Studies
- Guideline to Follow in Case Study Method
- Other Important Measures in Case Study Method
- Case Reports
13 Report Writing
- Purpose of a Report
- Writing Style of the Report
- Report Writing – the Do’s and the Don’ts
- Format for Report in Psychology Area
- Major Sections in a Report
14 Review of Literature
- Purposes of Review of Literature
- Sources of Review of Literature
- Types of Literature
- Writing Process of the Review of Literature
- Preparation of Index Card for Reviewing and Abstracting
15 Methodology
- Definition and Purpose of Methodology
- Participants (Sample)
- Apparatus and Materials
16 Result, Analysis and Discussion of the Data
- Definition and Description of Results
- Statistical Presentation
- Tables and Figures
17 Summary and Conclusion
- Summary Definition and Description
- Guidelines for Writing a Summary
- Writing the Summary and Choosing Words
- A Process for Paraphrasing and Summarising
- Summary of a Report
- Writing Conclusions
18 References in Research Report
- Reference List (the Format)
- References (Process of Writing)
- Reference List and Print Sources
- Electronic Sources
- Book on CD Tape and Movie
- Reference Specifications
- General Guidelines to Write References
Share on Mastodon

What Is a Case Study in Psychology?
Categories Research Methods
A case study is a research method used in psychology to investigate a particular individual, group, or situation in depth . It involves a detailed analysis of the subject, gathering information from various sources such as interviews, observations, and documents.
In a case study, researchers aim to understand the complexities and nuances of the subject under investigation. They explore the individual’s thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and experiences to gain insights into specific psychological phenomena.
This type of research can provide great detail regarding a particular case, allowing researchers to examine rare or unique situations that may not be easily replicated in a laboratory setting. They offer a holistic view of the subject, considering various factors influencing their behavior or mental processes.
By examining individual cases, researchers can generate hypotheses, develop theories, and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in psychology. Case studies are often utilized in clinical psychology, where they can provide valuable insights into the diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes of specific psychological disorders.
Case studies offer a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of complex psychological phenomena, providing researchers with valuable information to inform theory, practice, and future research.
Table of Contents
Examples of Case Studies in Psychology
Case studies in psychology provide real-life examples that illustrate psychological concepts and theories. They offer a detailed analysis of specific individuals, groups, or situations, allowing researchers to understand psychological phenomena better. Here are a few examples of case studies in psychology:
Phineas Gage
This famous case study explores the effects of a traumatic brain injury on personality and behavior. A railroad construction worker, Phineas Gage survived a severe brain injury that dramatically changed his personality.
This case study helped researchers understand the role of the frontal lobe in personality and social behavior.
Little Albert
Conducted by behaviorist John B. Watson, the Little Albert case study aimed to demonstrate classical conditioning. In this study, a young boy named Albert was conditioned to fear a white rat by pairing it with a loud noise.
This case study provided insights into the process of fear conditioning and the impact of early experiences on behavior.
Genie’s case study focused on a girl who experienced extreme social isolation and deprivation during her childhood. This study shed light on the critical period for language development and the effects of severe neglect on cognitive and social functioning.
These case studies highlight the value of in-depth analysis and provide researchers with valuable insights into various psychological phenomena. By examining specific cases, psychologists can uncover unique aspects of human behavior and contribute to the field’s knowledge and understanding.
Types of Case Studies in Psychology
Psychology case studies come in various forms, each serving a specific purpose in research and analysis. Understanding the different types of case studies can help researchers choose the most appropriate approach.
Descriptive Case Studies
These studies aim to describe a particular individual, group, or situation. Researchers use descriptive case studies to explore and document specific characteristics, behaviors, or experiences.
For example, a descriptive case study may examine the life and experiences of a person with a rare psychological disorder.
Exploratory Case Studies
Exploratory case studies are conducted when there is limited existing knowledge or understanding of a particular phenomenon. Researchers use these studies to gather preliminary information and generate hypotheses for further investigation.
Exploratory case studies often involve in-depth interviews, observations, and analysis of existing data.
Explanatory Case Studies
These studies aim to explain the causal relationship between variables or events. Researchers use these studies to understand why certain outcomes occur and to identify the underlying mechanisms or processes.
Explanatory case studies often involve comparing multiple cases to identify common patterns or factors.
Instrumental Case Studies
Instrumental case studies focus on using a particular case to gain insights into a broader issue or theory. Researchers select cases that are representative or critical in understanding the phenomenon of interest.
Instrumental case studies help researchers develop or refine theories and contribute to the general knowledge in the field.
By utilizing different types of case studies, psychologists can explore various aspects of human behavior and gain a deeper understanding of psychological phenomena. Each type of case study offers unique advantages and contributes to the overall body of knowledge in psychology.
How to Collect Data for a Case Study
There are a variety of ways that researchers gather the data they need for a case study. Some sources include:
- Directly observing the subject
- Collecting information from archival records
- Conducting interviews
- Examining artifacts related to the subject
- Examining documents that provide information about the subject
The way that this information is collected depends on the nature of the study itself
Prospective Research
In a prospective study, researchers observe the individual or group in question. These observations typically occur over a period of time and may be used to track the progress or progression of a phenomenon or treatment.
Retrospective Research
A retrospective case study involves looking back on a phenomenon. Researchers typically look at the outcome and then gather data to help them understand how the individual or group reached that point.
Benefits of a Case Study
Case studies offer several benefits in the field of psychology. They provide researchers with a unique opportunity to delve deep into specific individuals, groups, or situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena.
Case studies offer valuable insights that can inform theory development and practical applications by examining real-life examples.
Complex Data
One of the key benefits of case studies is their ability to provide complex and detailed data. Researchers can gather in-depth information through various methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of existing records.
This depth of data allows for a thorough exploration of the factors influencing behavior and the underlying mechanisms at play.
Unique Data
Additionally, case studies allow researchers to study rare or unique cases that may not be easily replicated in experimental settings. This enables the examination of phenomena that are difficult to study through other psychology research methods .
By focusing on specific cases, researchers can uncover patterns, identify causal relationships, and generate hypotheses for further investigation.
General Knowledge
Case studies can also contribute to the general knowledge of psychology by providing real-world examples that can be used to support or challenge existing theories. They offer a bridge between theory and practice, allowing researchers to apply theoretical concepts to real-life situations and vice versa.
Case studies offer a range of benefits in psychology, including providing rich and detailed data, studying unique cases, and contributing to theory development. These benefits make case studies valuable in understanding human behavior and psychological phenomena.
Limitations of a Case Study
While case studies offer numerous benefits in the field of psychology, they also have certain limitations that researchers need to consider. Understanding these limitations is crucial for interpreting the findings and generalizing the results.
Lack of Generalizability
One limitation of case studies is the issue of generalizability. Since case studies focus on specific individuals, groups, and situations, applying the findings to a larger population can be challenging. The unique characteristics and circumstances of the case may not be representative of the broader population, making it difficult to draw universal conclusions.
Researcher bias is another possible limitation. The researcher’s subjective interpretation and personal beliefs can influence the data collection, analysis, and interpretation process. This bias can affect the objectivity and reliability of the findings, raising questions about the study’s validity.
Case studies are often time-consuming and resource-intensive. They require extensive data collection, analysis, and interpretation, which can be lengthy. This can limit the number of cases that can be studied and may result in a smaller sample size, reducing the study’s statistical power.
Case studies are retrospective in nature, relying on past events and experiences. This reliance on memory and self-reporting can introduce recall bias and inaccuracies in the data. Participants may forget or misinterpret certain details, leading to incomplete or unreliable information.
Despite these limitations, case studies remain a valuable research tool in psychology. By acknowledging and addressing these limitations, researchers can enhance the validity and reliability of their findings, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of human behavior and psychological phenomena.
While case studies have limitations, they remain valuable when researchers acknowledge and address these concerns, leading to more reliable and valid findings in psychology.
Alpi, K. M., & Evans, J. J. (2019). Distinguishing case study as a research method from case reports as a publication type. Journal of the Medical Library Association , 107(1). https://doi.org/10.5195/jmla.2019.615
Crowe, S., Cresswell, K., Robertson, A., Huby, G., Avery, A., & Sheikh, A. (2011). The case study approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 11(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Paparini, S., Green, J., Papoutsi, C., Murdoch, J., Petticrew, M., Greenhalgh, T., Hanckel, B., & Shaw, S. (2020). Case study research for better evaluations of complex interventions: Rationale and challenges. BMC Medicine , 18(1), 301. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-020-01777-6
Willemsen, J. (2023). What is preventing psychotherapy case studies from having a greater impact on evidence-based practice, and how to address the challenges? Frontiers in Psychiatry , 13, 1101090. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1101090
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.

A case study is a research method that extensively explores a particular subject, situation, or individual through in-depth analysis, often to gain insights into real-world phenomena or complex issues. It involves the comprehensive examination of multiple data sources, such as interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, to provide a rich and holistic understanding of the subject under investigation.
Case studies are conducted to:
- Investigate a specific problem, event, or phenomenon
- Explore unique or atypical situations
- Examine the complexities and intricacies of a subject in its natural context
- Develop theories, propositions, or hypotheses for further research
- Gain practical insights for decision-making or problem-solving
A typical case study consists of the following components:
- Introduction: Provides a brief background and context for the study, including the purpose and research questions.
- Case Description: Describes the subject of the case study, including its relevant characteristics, settings, and participants.
- Data Collection: Details the methods used to gather data, such as interviews, observations, surveys, or document analysis.
- Data Analysis: Explains the techniques employed to analyze the collected data and derive meaningful insights.
- Findings: Presents the key discoveries and outcomes of the case study in a logical and organized manner.
- Discussion: Interprets the findings, relates them to existing theories or frameworks, discusses their implications, and addresses any limitations.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the main findings, highlights the significance of the research, and suggests potential avenues for future investigations.
Case studies offer several benefits, including:
- Providing a deep understanding of complex and context-dependent phenomena
- Generating detailed and rich qualitative data
- Allowing researchers to explore multiple perspectives and factors influencing the subject
- Offering practical insights for professionals and practitioners
- Allowing for the examination of rare or unique occurrences that cannot be replicated in experimental settings
What Is A Case Study In Psychology?
When people think about psychology studies, they are most likely to think about studies involving several participants split across a number of experimental and control groups. Studies like this are a good way to investigate the effect of a certain treatment or activity, but they are not always the best option. For example, if a scientist is interested in a specific rare disease, they cannot always find enough people with that disease to participate in a useful study. Similarly, one cannot give a group of participants a rare disease (for obvious reasons) and compare them to a group of participants without that disease. For situations like this, there are case studies.
What is a case study?
A case study is, as the name suggests, a study of a single case. For example, if someone has an extremely rare disease, a group of scientists might conduct a case study of that disease rather than attempting to set up an experimental study. In that case study, the researchers might test the effectiveness of a certain drug in treating that disease and carefully document the response of that participant over time.
Of course, the results seen in that one participant will not necessarily apply to all people with that rare disease. However, if the case study shows promising results, that treatment can then be tested in a larger experimental study. If it does not, it indicates that the treatment is not necessarily effective, at least in people that are similar to the original participant in the case study.
Why are case studies useful in psychology?
When people are still learning about psychology, they might think that group studies showing group effects are always better than individual studies showing individual effects. Of course, there is some truth to this notion, as results obtained from a large number of people are likely to be more generalizable than results obtained from a single person. However, this does not mean that we should discount the importance of individual effects.
Consider the following: In studies looking solely at group effects, individual effects can be masked. In other words, certain statistical quirks can lead to the appearance of a group effect despite the fact that no single individual showed that effect. While this is rare, it is possible. For this reason, it is important to consider individual effects. That is why, even in experimental studies examining groups, it can be useful to examine individual effects within that group. This underlines the value of case studies.
Wrapping up
At the end of the day, there are many good reasons that experimental studies examining groups are the most common types of psychological studies. However, case studies are also extremely valuable, particularly when group experiments are less feasible. Just as psychology is a large topic encompassing a wide variety of factors, both case studies and experimental group studies should be used in the larger overall strategy of psychology research.
- Author Details
Joaquín Selva
- Psychology Careers
- Psychology Explained
- Psychology Gear
- Psychology History
- Psychology In Pop Culture
- Psychology News
- Psychology Research
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples


Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Advertisement
A Case for the Case Study: How and Why They Matter
- Original Paper
- Published: 06 June 2017
- Volume 45 , pages 189–200, ( 2017 )
Cite this article

- Jeffrey Longhofer 1 ,
- Jerry Floersch 1 &
- Eric Hartmann 2
3931 Accesses
13 Citations
3 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
In this special issue we have asked the contributors to make a case for the case study. The guest editors, Jeffrey Longhofer, Jerry Floersch and Eric Hartmann, intergrate ideas from across the disciplines to explore the complexties of case study methods and theory. In education, Gary Thomas explores the importance of ethnographic case studies in understanding the relationships among schools, teachers, and students. Lance Dodes and Josh Dodes use the case study to articulate a psychoanalytic approach to addiction. In policy and generalist practice, Nancy Cartwright and Jeremy Hardie elaborate a model for a case-by-case approach to prediction and the swampy ground prediction serves up to practitioners. Christian Salas and Oliver Turnbull persuasively write about the role of the case study in neuro-psychoanalysis and illustrate it with a case vignette. In political science, Sanford Schram argues for a bottom up and ethnographic approach to studying policy implementation by describing a case of a home ownership program in Philadelphia. Eric Hartman queers the case study by articulating its role in deconstructing normative explanations of sexuality. In applied psychology, Daniel Fishman describes a comprehensive applied psychology perspective on the paradigmatic case study. Richard Miller and Miriam Jaffe offer us important ways of thinking about writing the case study and the use of multi-media. Each contributor brings a unique perspective to the use of the case study in their field, yet they share practical and philosophical assumptions.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Psychoanalysis, social science and the Tavistock tradition

Jack D. Douglas
Toward an integral, professional-public sociology: the example of gordon w. allport.
Aastrup, J., & Halldórsson, Á (2008). Epistemological role of case studies in logistics: A critical realist perspective. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 38 (10), 746–763.
Article Google Scholar
Abbott, A. (1992). What do cases do? Some notes on activity in sociological analysis. In C. C. Ragin, & H. S. Becker (Eds.), What is a case?: Exploring the foundations of social inquiry (pp. 53–82). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Google Scholar
Ahbel-Rappe, K. (2009). “After a long pause”: How to read Dora as history. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 57 (3), 595–629.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Alfonso, C. A. (2002). Frontline—writing psychoanalytic case reports: Safeguarding privacy while preserving integrity. Journal of the American Academy of Psychoanalysis and Dynamic Psychiatry, 30 (2), 165–172.
Altstein, R. (2016). Finding words: How the process and products of psychoanalytic writing can channel the therapeutic action of the very treatment it sets out to describe. Psychoanalytic Perspectives, 13 (1), 51–70.
Anderson, W. (2013). The case of the archive. Critical Inquiry, 39 (3), 532–547.
Antommaria, A. (2004). Do as I say, not as I do: Why bioethicists should seek informed consent for some case studies. Hastings Center Report, 34 (3), 28–34.
Archer, M. S. (2010). Routine, reflexivity, and realism. Sociological Theory , 28 (3), 272–303.
Aron, L. (2000). Ethical considerations in the writing of psychoanalytic case histories. Psychoanalytic Dialogues, 10 (2), 231–245.
Aron, L. (2016). Ethical considerations in psychoanalytic writing revisited. Psychoanalytic Perspectives, 13 (3), 267–290.
Barth, M., & Thomas, I. (2012). Synthesising case-study research: Ready for the next step? Environmental Education Research, 18 (6), 751–764.
Benner, P. (1982). From novice to expert. The American Journal of Nursing, 82 (3), 402–407.
PubMed Google Scholar
Benner, P. (2000a). The wisdom of our practice. The American Journal of Nursing, 100 (10), 99–105.
Benner, P. (2000b). The roles of embodiment, emotion and lifeworld for rationality and agency in nursing practice. Nursing Philosophy, 1 (1), 5–19.
Benner, P. (2004). Using the Dreyfus model of skill acquisition to describe and interpret skill acquisition and clinical judgment in nursing practice and education. Bulletin of Science, Technology & Society, 24 (3), 188–199.
Bennett, A., & Elman, C. (2006). Qualitative research: Recent developments in case study methods. Annual Review of Political Science, 9 , 455–476.
Bennett, A., & Elman, C. (2007). Case study methods in the international relations subfield. Comparative Political Studies, 40 (2), 170–195.
Bergene, A. (2007). Towards a critical realist comparative methodology. Journal of Critical Realism, 3 (1), 5–27.
Berlant, L. (2007). On the case. Critical Inquiry, 33 (4), 663–672.
Bernstein, S. B. (2008a). Writing about the psychoanalytic process. Psychoanalytic Inquiry, 28 (4), 433–449.
Bernstein, S. B. (2008b). Writing, rewriting, and working through. Psychoanalytic Inquiry, 28 (4), 450–464.
Blechner, M. (2012). Confidentiality: Against disguise, for consent. Psychotherapy, 49 (1), 16–18.
Bornstein, R. F. (2007). Nomothetic psychoanalysis. Psychoanalytic Psychology, 24 (4), 590–602.
Bourdieu, P. (1990). The scholastic point of view. Cultural Anthropology, 5 (4), 380–391.
Bourdieu, P. (2000). Pascalian meditations . Stanford: Stanford University Press.
Boyce, N. (2015). Dora in the 21st century. Lancet, 386 (9997), 948–949.
Brandell, J., & Varkas, T. (2010). Narrative case studies. In B. Thyer (Ed.), The handbook of social work research methods (Chap. 20, pp. 375–396). Los Angeles: SAGE
Bunch, W. H., & Dvonch, V. M. (2000). Moral decisions regarding innovation: The case method. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 378 , 44–49.
Burawoy, M. (1998). The extended case method. Sociological theory, 16 (1), 4–33.
Campbell, D. T. (1975). “Degrees of freedom” and the case study. Comparative Political Studies, 8 (2), 178–193.
Carlson, J. (2010). Commentary: Writing about clients—ethical and professional issues in clinical case reports. Counseling and Values, 54 (2), 154–157.
Cartwright, N. (2007). Are RCTs the gold standard? BioSocieties, 2 (1), 11–20.
Cartwright, N. (2011). A philosopher’s view of the long road from RCTs to effectiveness. Lancet, 377 (9775), 1400–1401.
Charlton, B. G., & Walston, F. (1998). Individual case studies in clinical research. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice, 4 (2), 147–155.
Colombo, D., & Michels, R. (2007). Can (should) case reports be written for research use? Psychoanalytic Inquiry, 27 (5), 640–649.
Damousi, J., Lang, B., & Sutton, K. (Eds.) (2015). Case studies and the dissemination of knowledge . London: Routledge Press.
Desmet, M., Meganck, R., Seybert, C., Willemsen, J., Geerardyn, F., Declercq, F., & Schindler, I. (2012). Psychoanalytic single cases published in ISI-ranked journals: The construction of an online archive. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, 82 (2), 120–121.
Dobson, P. J. (2001). Longitudinal case research: A critical realist perspective. Systemic Practice and Action Research, 14 (3), 283–296.
Dreyfus, H. L. (2008). On the internet . London: Routledge Press.
Dreyfus, H. L., & Dreyfus, S. E. (2005). Peripheral vision expertise in real world contexts. Organization Studies, 26 (5), 779–792.
Easton, G. (2010). Critical realism in case study research. Industrial Marketing Management, 39 (1), 118–128.
Edelson, M. (1985). The hermeneutic turn and the single case study in psychoanalysis. Psychoanalysis & Contemporary Thought, 8 , 567–614.
Feagin, J. R., Orum, A. M., & Sjoberg, G. (Eds.) (1991). A case for the case study . Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
Ferguson, H. (2016). Researching social work practice close up: Using ethnographic and mobile methods to understand encounters between social workers, children and families. British Journal of Social Work, 46 (1), 153–168.
Fisher, M. A. (2013). The ethics of conditional confidentiality: A practice model for mental health professionals . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Fleischman, J. (2002). Phineas Gage: A gruesome but true story about brain science . New York: Houghton Mifflin.
Floersch, J. (2000). Reading the case record: The oral and written narratives of social workers. Social Service Review, 74 (2), 169–192.
Floersch, J. (2002). Meds, money, and manners: The case management of severe mental illness . Columbia: Columbia University Press.
Floersch, J., & Longhofer, J. (2016). Social work and the scholastic fallacy. Investigacao Em Trabalho Social, 3 , 71–91. https://www.isssp.pt/si/web_base.gera_pagina?p_pagina=21798 .
Florek, A. G., & Dellavalle, R. P. (2016). Case reports in medical education: A platform for training medical students, residents, and fellows in scientific writing and critical thinking. Journal of Medical Case Reports, 10 (1), 1.
Flyvbjerg, B. (2001). Making social science matter: Why social inquiry fails and how it can succeed again . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Flyvbjerg, B. (2006). Five misunderstandings about case-study research. Qualitative Inquiry, 12 (2), 219–245.
Flyvbjerg, B., Landman, T., & Schram, S. (Eds.). (2012). Real social science: Applied phronesis . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Forrester, J. (1996). If p, then what? Thinking in cases. History of the Human Sciences, 9 (3), 1–25.
Forrester, J. (2007). On Kuhn’s case: Psychoanalysis and the paradigm. Critical Inquiry, 33 (4), 782–819.
Foucault, M. (1994). The birth of the clinic: An archaeology of medical perception . London: Routledge Press.
Freeman, W. J. (2000). How brains make up their minds . New York: Columbia University Press.
Freud, S. (1905). Fragment of an analysis of a case of hysteria. Standard Edition , 7 , 7–122.
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia in a five-year-old boy. Standard Edition , 10 , 5–147.
Freud, S. (1909b). Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis. Standard Edition , 10 , 151–318.
Freud, S. (1911). Psycho-analytic notes on an autobiographical account of a case of paranoia (dementia paranoides). Standard Edition , 12 , 9–79.
Freud, S. (1918). From the history of an infantile neurosis. Standard Edition , 17 , 7–122.
George, A. L. & Bennett, A. (2004). Case studies and theory development in the social sciences. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Gerring, J. (2004). What is a case study and what is it good for? American Political Science Review, 98 (02), 341–354.
Gerring, J. (2007a). Case study research: Principles and practices . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Gerring, J. (2007b). Is there a (viable) crucial-case method? Comparative Political Studies, 40 (3), 231–253.
Gilgun, J. F. (1994). A case for case studies in social work research. Social Work, 39 , 371–380.
Gottdiener, W. H., & Suh, J. J. (2012). Expanding the single-case study: A proposed psychoanalytic research program. The Psychoanalytic Review, 99 (1), 81–102.
Gupta, M. (2007). Does evidence-based medicine apply to psychiatry? Theoretical Medicine and Bioethics, 28 (2), 103–120.
Gupta, M. (2014). Is evidence-based psychiatry ethical? Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Gwande, A. (2014). Being mortal: Medicine and what matters most in the end . New York: Metropolitan Books.
Haas, L. (2001). Phineas Gage and the science of brain localisation. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 71 (6), 761.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hacking, I. (1999). The social construction of what? Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Haggis, T. (2008). ‘Knowledge must be contextual’: Some possible implications of complexity and dynamic systems theories for educational research. Educational Philosophy and Theory, 40 (1), 158–176.
Hare-Mustin, R. T. (1983). An appraisal of the relationship between women and psychotherapy: 80 years after the case of Dora. American Psychologist, 38 (5), 593–601.
Held, B. S. (2009). The logic of case-study methodology. Pragmatic Case Studies in Psychotherapy, 5 (3), 90–100.
Hoffman, I. Z. (2009). Doublethinking our way to “scientific” legitimacy: The desiccation of human experience. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 57 (5), 1043–1069.
Hollan, D., & Throop, C. J. (2008). Whatever happened to empathy?: Introduction. Ethos, 36 (4), 385–401.
Hurwitz, B. (2011). Clinical cases and case reports: Boundaries and porosities. The Case and the Canon. Anomalies, Discontinuities, Metaphors Between Science and Literature , 45–57.
Ioannidis, J. P., Haidich, A. B., & Lau, J. (2001). Any casualties in the clash of randomized and observational evidence? British Medical Journal, 322 , 879–880.
Iosifides, T. (2012). Migration research between positivistic scientism and relativism: A critical realist way out. In C. Vargas-Silva (Ed.), Handbook of research methods in migration (pp. 26–49). Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Kächele, H., Schachter, J., & Thomä, H. (2011). From psychoanalytic narrative to empirical single case research: Implications for psychoanalytic practice (vol. 30). New York: Taylor & Francis.
Kantrowitz, J. L. (2004). Writing about patients: I. Ways of protecting confidentiality and analysts’ conflicts over choice of method. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 52 (1), 69–99.
Ketokivi, M., & Choi, T. (2014). Renaissance of case research as a scientific method. Journal of Operations Management, 32 (5), 232–240.
Kitchin, R. (2014a). Big data, new epistemologies and paradigm shifts. Big Data & Society, 1 (1), 1–12.
Kitchin, R. (2014b). The data revolution: Big data, open data, data infrastructures and their consequences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Press.
Kitchin, R., & Lauriault, T. P. (2015). Small data in the era of big data. GeoJournal, 80 (4), 463–475.
Koenig, G. (2009). Realistic evaluation and case studies stretching the potential. Evaluation, 15 (1), 9–30.
Lahire, B. (2011). The plural actor . Cambridge: Polity.
Leong, S. M. (1985). Metatheory and metamethodology in marketing, a lakatosian reconstruction. Journal of Marketing, 49 (4), 23–40.
Levy, J. S. (2008). Case studies: Types, designs, and logics of inference. Conflict Management and Peace Science, 25 (1), 1–18.
Longhofer, J., & Floersch, J. (2012). The coming crisis in social work: Some thoughts on social work and science. Research on Social Work Practice, 22 (5), 499–519.
Longhofer, J., & Floersch, J. (2014). Values in a science of social work: Values-informed research and research-informed values. Research on Social Work Practice, 24 (5), 527–534.
Longhofer, J., Floersch, J., & Hoy, J. (2013). Qualitative methods for practice research. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Luyten, P., Corveleyn, J., & Blatt, S. J. (2006). Minding the gap between positivism and hermeneutics in psychoanalytic research. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 54 (2), 571–610.
Macmillan, M. (2000). Restoring phineas gage: A 150th retrospective. Journal of the History of the Neurosciences, 9 (1), 46–66.
Mahoney, J., Kimball, E., & Koivu, K. L. (2009). The logic of historical explanation in the social sciences. Comparative Political Studies, 42 (1), 114–146.
Marchal, B., Westhorp, G., Wong, G., Van Belle, S., Greenhalgh, T., Kegels, G., & Pawson, R. (2013). Realist RCTs of complex interventions: An oxymoron. Social Science & Medicine, 94 (12), 124–128.
Maroglin, L. (1997). Under the cover of kindness. The invention of social work . Charlottesville: University Press of Virginia.
McKeown, A. (2015). Critical realism and empirical bioethics: A methodological exposition. Health Care Analysis, 1–21. doi: 10.1007/s10728-015-0290-2 .
McLeod, J. (2010). Case study research in counseling and psychotherapy . Thousand Oaks, LA: Sage Publications.
McLeod, J. (2015). Reading case studies to inform therapeutic practice. In Psychotherapie forum (vol. 20, No. 1–2, pp. 3–9). Vienna: Springer.
McLeod, J., & Balamoutsou, S. (1996). Representing narrative process in therapy: Qualitative analysis of a single case. Counseling Psychology Quarterly, 9 (1), 61–76.
Mearsheimer, J. J., & Walt, S. M. (2013). Leaving theory behind: Why simplistic hypothesis testing is bad for international relations. European Journal of International Relations, 19 (3), 427–457.
Michels, R. (2000). The case history. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 48 (2), 355–375.
Miller, E. (2009). Writing about patients: What clinical and literary writers share. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 57 (5), 1097–1120.
Mingers, J. (2004). Realizing information systems: Critical realism as an underpinning philosophy for information systems. Information and Organization, 14 (2), 87–103.
Mishna, F. (2004). A qualitative study of bullying from multiple perspectives. Children & Schools, 26 (4), 234–247.
Mittelstadt, B. D., Allo, P., Taddeo, M., Wachter, S., & Floridi, L. (2016). The ethics of algorithms: Mapping the debate. Big Data & Society , 3(2), 2053951716679679
Morgan, M. S. (2012). Case studies: One observation or many? Justification or discovery? Philosophy of Science, 79 (5), 667–677.
Naiburg, S. (2015). Structure and spontaneity in clinical prose: A writer’s guide for psychoanalysts and psychotherapists . London: Routledge Press.
Nissen, T., & Wynn, R. (2014a). The clinical case report: A review of its merits and limitations. BMC Research Notes, 7 (1), 1–7.
Nissen, T., & Wynn, R. (2014b). The history of the case report: A selective review. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Open, 5 (4), 1–5. doi: 10.1177/2054270414523410 .
O’Neil, C. (2016). Weapons of math destruction: How big data increases inequality and threatens democracy . New York: Crown Publishing Group.
Payne, S., Field, D., Rolls, L., Hawker, S., & Kerr, C. (2007). Case study research methods in end-of-life care: Reflections on three studies. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 58 (3), 236–245.
Perry, C. (1998). Processes of a case study methodology for postgraduate research in marketing. European Journal of Marketing, 32 (9/10), 785–802.
Pinter, H. (1982). A kind of alaska: A premier . Retrieved from http://www.haroldpinter.org/plays/plays_alaska.shtml .
Probst, B. (2015). The eye regards itself: Benefits and challenges of reflexivity in qualitative social work research. Social Work Research Social Work Research , 39 (1), 37–48.
Romano, C. (2015). Freud and the Dora case: A promise betrayed . London: Karnac Books.
Ruddin, L. P. (2006). You can generalize stupid! Social scientists, Bent Flyvbjerg, and case study methodology. Qualitative Inquiry, 12 (4), 797–812.
Sacks, O. (1970). The man who mistook his wife for a hat . New York: Touchstone.
Sacks, O. (1995). An anthropologist on mars: Seven paradoxical tales . New York: Alfred A. Knopf.
Sacks, O. (2015). On the move: A life . New York: Alfred A. Knopf.
Safran, J. D. (2009). Clinical and empirical issues: Disagreements and agreements. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 57 (5), 1043–1069.
Sampson, R. J. (2010). Gold standard myths: Observations on the experimental turn in quantitative criminology. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 26 (4), 489–500.
Sayer, A. (2011). Why things matter to people: Social science, values and ethical life . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Shaw, E. (2013). Sacred cows and sleeping dogs: Confidentiality: Not as straightforward as we would have thought. Psychotherapy in Australia, 19 (4), 65–66.
Sieck, B. C. (2012). Obtaining clinical writing informed consent versus using client disguise and recommendations for practice. Psychotherapy, 49 (1), 3–11.
Siggelkow, N. (2007). Persuasion with case studies. Academy of Management Journal, 50 (1), 20–24.
Skocpol, T., & Sommers, M. (1980). The uses of comparative theory in macrosocial inquiry. Comparative Studies in Society and History, 22 (2), 174–197.
Smith, C. (2011). What is a person?: Rethinking humanity, social life, and the moral good from the personup . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Sperry, L., & Pies, R. (2010). Writing about clients: Ethical considerations and options. Counseling and Values, 54 (2), 88–102.
Steinmetz, G. (2004). Odious comparisons: Incommensurability, the case study, and “small N’s” in sociology. Sociological Theory, 22 (3), 371–400.
Steinmetz, G. (2005). The politics of method in the human. In G. Steinmetz (Ed.), Sciences . Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
Sutherland, E. (2016). The case study in telecommunications policy research. Info, 18 (1), 16–30.
Taylor, C., & White, S. (2001). Knowledge, truth and reflexivity: The problem of judgement in social work. Journal of social work , 1 (1), 37–59.
Taylor, C., & White, S. (2006). Knowledge and reasoning in social work: Educating for humane judgement. British Journal of Social Work , 36 (6), 937–954.
Thacher, D. (2006). The Normative Case Study 1. American journal of sociology , 111 (6), 1631–1676.
Tice, K. W. (1998). Tales of wayward girls and immoral women: Case records and the professionalization of social work . Chicago: University of Illinois Press.
Tsang, E. W. (2014). Case studies and generalization in information systems research: A critical realist perspective. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 23 (2), 174–186.
Tsang, E. W. (2014). Generalizing from research findings: The merits of case studies. International Journal of Management Reviews, 16 (4), 369–383.
Tufekci, Z. (2015). Algorithmic harms beyond Facebook and Google: Emergent challenges of computational agency. Journal on Telecommunication, 13 , 203–218.
Van de Ven, A. H. (2007). Engaged scholarship: A guide for organizational and social research: A guide for organizational and social research . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Van Haselen, R. A. (2015). Towards improving the reporting quality of clinical case reports in complementary medicine: Assessing and illustrating the need for guideline development. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 23 (2), 141–148.
Welch, C., Piekkari, R., Plakoyiannaki, E., & Paavilainen-Mäntymäki, E. (2011). Theorising from case studies: Towards a pluralist future for international business research. Journal of International Business Studies, 42 (5), 740–762.
Wilgus, J., & Wilgus, B. (2009). Face to face with Phineas Gage. Journal of the History of the Neurosciences, 18 (3), 340–345.
Willemsen, J., Cornelis, S., Geerardyn, F. M., Desmet, M., Meganck, R., Inslegers, R., & Cauwe, J. M. (2015). Theoretical pluralism in psychoanalytic case studies. Frontiers in Psychology, 6 , 1466
Willemsen, J., Della Rosa, E., & Kegerreis, S. (2017). Clinical case studies in psychoanalytic and psychodynamic treatment. Frontiers in Psychology, 8 , 1–7. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00108 .
Winship, G. (2007). The ethics of reflective research in single case study inquiry. Perspectives in Psychiatric Care, 43 (4), 174–182.
Wolpert, L., & Fonagy, P. (2009). There is no place for the psychoanalytic case report in the British Journal of Psychiatry. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 195 , 483–487.
Woolcock, M. (2013). Using case studies to explore the external validity of ‘complex’ development interventions. Evaluation, 19 (3), 229–248.
Wynn, D. Jr., & Williams, C. K. (2012). Principles for conducting critical realist case study research in information systems. Mis Quarterly, 36 (3), 787–810.
Yang, D. D. (2006). Empirical social inquiry and models of causal inference. The New England Journal of Political Science, 2 (1), 51–88.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Rutgers School of Social Work, New Brunswick, USA
Jeffrey Longhofer & Jerry Floersch
DSW Program, Rutgers School of Social Work, New Brunswick, USA
Eric Hartmann
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jeffrey Longhofer .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Longhofer, J., Floersch, J. & Hartmann, E. A Case for the Case Study: How and Why They Matter. Clin Soc Work J 45 , 189–200 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10615-017-0631-8
Download citation
Published : 06 June 2017
Issue Date : September 2017
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10615-017-0631-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Case study research
- Critical realism
- Psychoanaltyic case study
- Social work clinical research
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

n. an in-depth assessment and investigation conducted on a target individual, family unit, or social group. It requires a researcher to collect multiple types of data that would prove to be useful in creating a complete biographical, psychological, physiological, and environmental background on the case.
What is a case study in psychology?
In psychology, a case study is a comprehensive, qualitative research of a single person or occasion that offers in-depth knowledge and insight into the subject's behavior, experiences, and thought processes. Observation, interviews, and the investigation of records, papers, and other artifacts are frequently used in case studies.
What is the purpose of a case study?
A case study in psychology is designed to produce rich, comprehensive data that can be utilized to comprehend a specific phenomenon or person in deeper detail. Researchers can use case studies to investigate the complexity of human behavior and mental processes, spot trends and themes, and develop hypotheses for more study. They are a useful tool for psychology teaching and learning because they may be used to demonstrate concepts or theories in a practical setting.
Types of psychology case studies
A case study is a method used in psychology to gather comprehensive data that would help researchers better understand a particular occurrence or individual. Case studies are a useful tool for researchers because they let them explore the complexity of human thought and behavior, identify patterns and themes, and provide hypotheses for further investigation. Because they can be used to demonstrate ideas or theories in a real-world situation, they are a helpful tool for psychology teaching and learning.
The following are the five main types of case studies in psychology:
- Exploratory case studies: These case studies are designed to investigate new or under-researched areas within the field of psychology. The primary purpose of exploratory case studies is to generate hypotheses or initial theories, which can then be tested using more rigorous research methods .
- Descriptive case studies: Descriptive case studies aim to provide a comprehensive account of a specific individual, event, or phenomenon.
- Explanatory case studies: Explanatory case studies seek to identify the underlying causes or mechanisms responsible for a particular outcome or behavior. They often involve the analysis of relationships between various factors, with the goal of uncovering causal connections. These case studies may employ quantitative methods, such as statistical analyses or experiments, in addition to qualitative data collection techniques.
- Intrinsic case studies: Intrinsic case studies focus on a unique, rare, or unusual case that is of particular interest to the researcher. The primary goal of this type of case study is to gain a deep understanding of the specific individual or event, rather than generalizing the findings to a broader population.
- Instrumental case studies: Instrumental case studies use a specific case as a means to gain insight into a broader issue or to support or challenge a theory. In this type of case study, the focus is not on the individual case itself, but on the wider implications it has for understanding psychological phenomena.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad construction worker who survived a catastrophic brain injury in 1848 and is a well-known case study in the history of psychology. His example has been utilized to examine the connection between brain make-up and personality as well as the function of the frontal lobes in social cognition and judgment.
- Little Hans: Little Hans, a 5-year-old boy, was the subject of a psychoanalytic case study by Sigmund Freud in the early 20th century. The study aimed to explore the development of anxiety and phobias in children and provided support for some of Freud's theories on psychosexual development and the Oedipus complex.
- Genie: Genie was a young girl who was discovered in 1970 after being locked in isolation for most of her life. Her case has been used to study the effects of extreme social isolation on cognitive and linguistic development, as well as the critical period hypothesis in language acquisition .
References:
Baxter, P., & Jack, S. (2008). Qualitative Case Study Methodology: Study Design and Implementation for Novice Researchers. The Qualitative Report, 13(4), 544-559. https://doi.org/10.46743/2160-3715/2008.1573
Creswell, J.W. and Poth, C.N. (2018) Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design Choosing among Five Approaches. 4th Edition, SAGE Publications, Inc., Thousand Oaks. https://www.scirp.org/(S(lz5mqp453edsnp55rrgjct55))/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=2155979
Hollweck, T. (2016). Robert K. Yin. (2014). Case Study Research Design and Methods (5th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. 282 pages. The Canadian Journal of Program Evaluation , 30, 108. https://doi.org/10.3138/cjpe.30.1.108

Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Latest Posts

The Future Of Education: Can You Earn A Psychology Degree Online?

Insomnia & Mental Illness: What is the Correlation?

Stop Guessing: Here Are 3 Steps to Data-Driven Psychological Decisions

Getting Help with Grief: Understanding Therapy & How It Can Help

Exploring the Psychology of Risk and Reward

Understanding ADHD in Women: Symptoms, Treatment & Support

Meeting the Milestones: A Guide to Piaget's Child Developmental Stages

Counseling, Therapy, and Psychology: What Is The Difference?

The Psychology of Metaphysical Belief Systems

4 Key Considerations When Supporting a Loved One Through a Legal Battle for Justice

Finding Balance: The Psychological Benefits of Staying Active

The Psychology of Winning: Case Studies and Analysis from the World of Sports
Popular psychology terms, medical model, hypermnesia, affirmation, brainwashing, backup reinforcer, message-learning approach, affiliative behavior, gross motor, behavioral modeling, approach motivation.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
Research Methods In Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.

Hypotheses are statements about the prediction of the results, that can be verified or disproved by some investigation.
There are four types of hypotheses :
- Null Hypotheses (H0 ) – these predict that no difference will be found in the results between the conditions. Typically these are written ‘There will be no difference…’
- Alternative Hypotheses (Ha or H1) – these predict that there will be a significant difference in the results between the two conditions. This is also known as the experimental hypothesis.
- One-tailed (directional) hypotheses – these state the specific direction the researcher expects the results to move in, e.g. higher, lower, more, less. In a correlation study, the predicted direction of the correlation can be either positive or negative.
- Two-tailed (non-directional) hypotheses – these state that a difference will be found between the conditions of the independent variable but does not state the direction of a difference or relationship. Typically these are always written ‘There will be a difference ….’
All research has an alternative hypothesis (either a one-tailed or two-tailed) and a corresponding null hypothesis.
Once the research is conducted and results are found, psychologists must accept one hypothesis and reject the other.
So, if a difference is found, the Psychologist would accept the alternative hypothesis and reject the null. The opposite applies if no difference is found.
Sampling techniques
Sampling is the process of selecting a representative group from the population under study.
A sample is the participants you select from a target population (the group you are interested in) to make generalizations about.
Representative means the extent to which a sample mirrors a researcher’s target population and reflects its characteristics.
Generalisability means the extent to which their findings can be applied to the larger population of which their sample was a part.
- Volunteer sample : where participants pick themselves through newspaper adverts, noticeboards or online.
- Opportunity sampling : also known as convenience sampling , uses people who are available at the time the study is carried out and willing to take part. It is based on convenience.
- Random sampling : when every person in the target population has an equal chance of being selected. An example of random sampling would be picking names out of a hat.
- Systematic sampling : when a system is used to select participants. Picking every Nth person from all possible participants. N = the number of people in the research population / the number of people needed for the sample.
- Stratified sampling : when you identify the subgroups and select participants in proportion to their occurrences.
- Snowball sampling : when researchers find a few participants, and then ask them to find participants themselves and so on.
- Quota sampling : when researchers will be told to ensure the sample fits certain quotas, for example they might be told to find 90 participants, with 30 of them being unemployed.
Experiments always have an independent and dependent variable .
- The independent variable is the one the experimenter manipulates (the thing that changes between the conditions the participants are placed into). It is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable.
- The dependent variable is the thing being measured, or the results of the experiment.
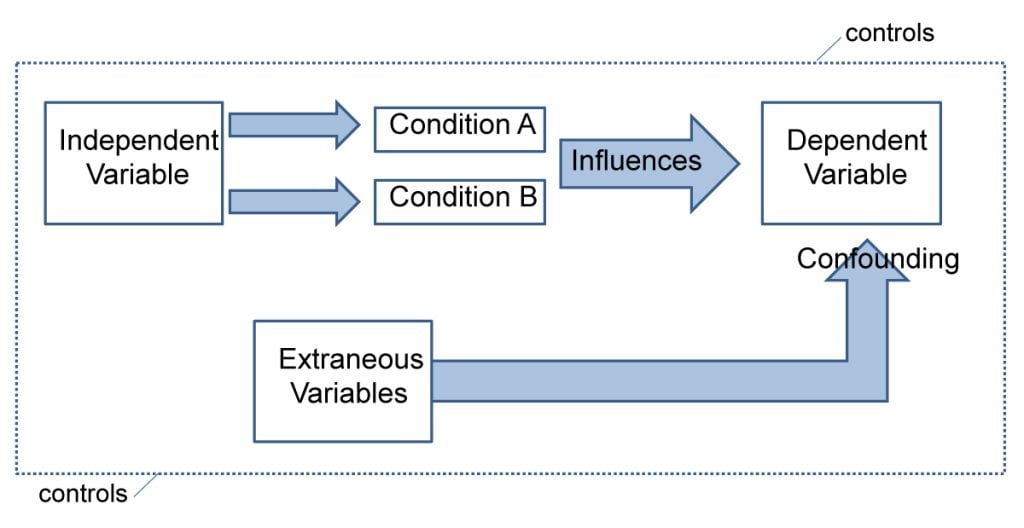
Operationalization of variables means making them measurable/quantifiable. We must use operationalization to ensure that variables are in a form that can be easily tested.
For instance, we can’t really measure ‘happiness’, but we can measure how many times a person smiles within a two-hour period.
By operationalizing variables, we make it easy for someone else to replicate our research. Remember, this is important because we can check if our findings are reliable.
Extraneous variables are all variables which are not independent variable but could affect the results of the experiment.
It can be a natural characteristic of the participant, such as intelligence levels, gender, or age for example, or it could be a situational feature of the environment such as lighting or noise.
Demand characteristics are a type of extraneous variable that occurs if the participants work out the aims of the research study, they may begin to behave in a certain way.
For example, in Milgram’s research , critics argued that participants worked out that the shocks were not real and they administered them as they thought this was what was required of them.
Extraneous variables must be controlled so that they do not affect (confound) the results.
Randomly allocating participants to their conditions or using a matched pairs experimental design can help to reduce participant variables.
Situational variables are controlled by using standardized procedures, ensuring every participant in a given condition is treated in the same way
Experimental Design
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to each condition of the independent variable, such as a control or experimental group.
- Independent design ( between-groups design ): each participant is selected for only one group. With the independent design, the most common way of deciding which participants go into which group is by means of randomization.
- Matched participants design : each participant is selected for only one group, but the participants in the two groups are matched for some relevant factor or factors (e.g. ability; sex; age).
- Repeated measures design ( within groups) : each participant appears in both groups, so that there are exactly the same participants in each group.
- The main problem with the repeated measures design is that there may well be order effects. Their experiences during the experiment may change the participants in various ways.
- They may perform better when they appear in the second group because they have gained useful information about the experiment or about the task. On the other hand, they may perform less well on the second occasion because of tiredness or boredom.
- Counterbalancing is the best way of preventing order effects from disrupting the findings of an experiment, and involves ensuring that each condition is equally likely to be used first and second by the participants.
If we wish to compare two groups with respect to a given independent variable, it is essential to make sure that the two groups do not differ in any other important way.
Experimental Methods
All experimental methods involve an iv (independent variable) and dv (dependent variable)..
- Field experiments are conducted in the everyday (natural) environment of the participants. The experimenter still manipulates the IV, but in a real-life setting. It may be possible to control extraneous variables, though such control is more difficult than in a lab experiment.
- Natural experiments are when a naturally occurring IV is investigated that isn’t deliberately manipulated, it exists anyway. Participants are not randomly allocated, and the natural event may only occur rarely.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. It uses information from a range of sources, such as from the person concerned and also from their family and friends.
Many techniques may be used such as interviews, psychological tests, observations and experiments. Case studies are generally longitudinal: in other words, they follow the individual or group over an extended period of time.
Case studies are widely used in psychology and among the best-known ones carried out were by Sigmund Freud . He conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
Case studies provide rich qualitative data and have high levels of ecological validity. However, it is difficult to generalize from individual cases as each one has unique characteristics.
Correlational Studies
Correlation means association; it is a measure of the extent to which two variables are related. One of the variables can be regarded as the predictor variable with the other one as the outcome variable.
Correlational studies typically involve obtaining two different measures from a group of participants, and then assessing the degree of association between the measures.
The predictor variable can be seen as occurring before the outcome variable in some sense. It is called the predictor variable, because it forms the basis for predicting the value of the outcome variable.
Relationships between variables can be displayed on a graph or as a numerical score called a correlation coefficient.
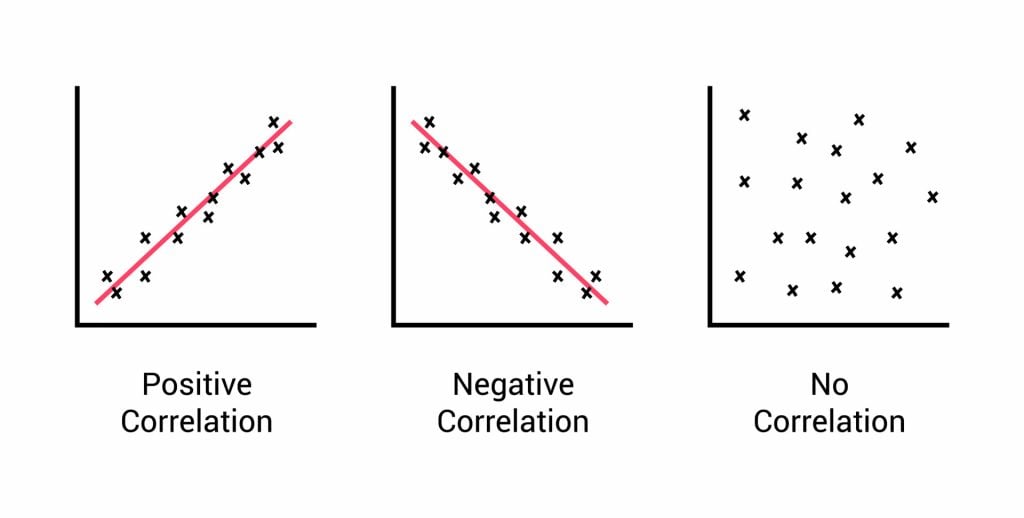
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with an increase in the other, then this is known as a positive correlation .
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with a decrease in the other, then this is known as a negative correlation .
- A zero correlation occurs when there is no relationship between variables.
After looking at the scattergraph, if we want to be sure that a significant relationship does exist between the two variables, a statistical test of correlation can be conducted, such as Spearman’s rho.
The test will give us a score, called a correlation coefficient . This is a value between 0 and 1, and the closer to 1 the score is, the stronger the relationship between the variables. This value can be both positive e.g. 0.63, or negative -0.63.
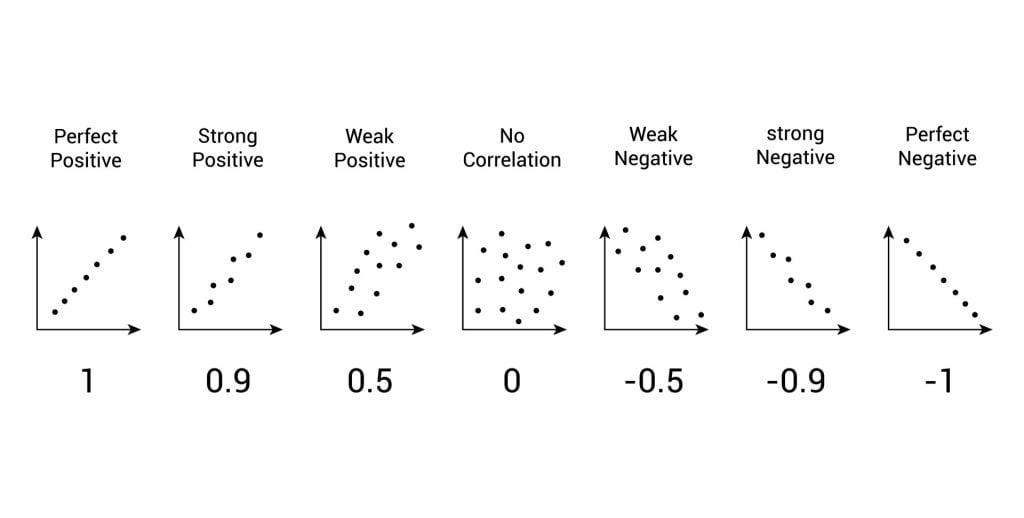
A correlation between variables, however, does not automatically mean that the change in one variable is the cause of the change in the values of the other variable. A correlation only shows if there is a relationship between variables.
Correlation does not always prove causation, as a third variable may be involved.
Interview Methods
Interviews are commonly divided into two types: structured and unstructured.
A fixed, predetermined set of questions is put to every participant in the same order and in the same way.
Responses are recorded on a questionnaire, and the researcher presets the order and wording of questions, and sometimes the range of alternative answers.
The interviewer stays within their role and maintains social distance from the interviewee.
There are no set questions, and the participant can raise whatever topics he/she feels are relevant and ask them in their own way. Questions are posed about participants’ answers to the subject
Unstructured interviews are most useful in qualitative research to analyze attitudes and values.
Though they rarely provide a valid basis for generalization, their main advantage is that they enable the researcher to probe social actors’ subjective point of view.
Questionnaire Method
Questionnaires can be thought of as a kind of written interview. They can be carried out face to face, by telephone, or post.
The choice of questions is important because of the need to avoid bias or ambiguity in the questions, ‘leading’ the respondent or causing offense.
- Open questions are designed to encourage a full, meaningful answer using the subject’s own knowledge and feelings. They provide insights into feelings, opinions, and understanding. Example: “How do you feel about that situation?”
- Closed questions can be answered with a simple “yes” or “no” or specific information, limiting the depth of response. They are useful for gathering specific facts or confirming details. Example: “Do you feel anxious in crowds?”
Its other practical advantages are that it is cheaper than face-to-face interviews and can be used to contact many respondents scattered over a wide area relatively quickly.
Observations
There are different types of observation methods :
- Covert observation is where the researcher doesn’t tell the participants they are being observed until after the study is complete. There could be ethical problems or deception and consent with this particular observation method.
- Overt observation is where a researcher tells the participants they are being observed and what they are being observed for.
- Controlled : behavior is observed under controlled laboratory conditions (e.g., Bandura’s Bobo doll study).
- Natural : Here, spontaneous behavior is recorded in a natural setting.
- Participant : Here, the observer has direct contact with the group of people they are observing. The researcher becomes a member of the group they are researching.
- Non-participant (aka “fly on the wall): The researcher does not have direct contact with the people being observed. The observation of participants’ behavior is from a distance
Pilot Study
A pilot study is a small scale preliminary study conducted in order to evaluate the feasibility of the key s teps in a future, full-scale project.
A pilot study is an initial run-through of the procedures to be used in an investigation; it involves selecting a few people and trying out the study on them. It is possible to save time, and in some cases, money, by identifying any flaws in the procedures designed by the researcher.
A pilot study can help the researcher spot any ambiguities (i.e. unusual things) or confusion in the information given to participants or problems with the task devised.
Sometimes the task is too hard, and the researcher may get a floor effect, because none of the participants can score at all or can complete the task – all performances are low.
The opposite effect is a ceiling effect, when the task is so easy that all achieve virtually full marks or top performances and are “hitting the ceiling”.
Research Design
In cross-sectional research , a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at the same time
Sometimes, we want to see how people change over time, as in studies of human development and lifespan. Longitudinal research is a research design in which data-gathering is administered repeatedly over an extended period of time.
In cohort studies , the participants must share a common factor or characteristic such as age, demographic, or occupation. A cohort study is a type of longitudinal study in which researchers monitor and observe a chosen population over an extended period.
Triangulation means using more than one research method to improve the study’s validity.
Reliability
Reliability is a measure of consistency, if a particular measurement is repeated and the same result is obtained then it is described as being reliable.
- Test-retest reliability : assessing the same person on two different occasions which shows the extent to which the test produces the same answers.
- Inter-observer reliability : the extent to which there is an agreement between two or more observers.
Meta-Analysis
A meta-analysis is a systematic review that involves identifying an aim and then searching for research studies that have addressed similar aims/hypotheses.
This is done by looking through various databases, and then decisions are made about what studies are to be included/excluded.
Strengths: Increases the conclusions’ validity as they’re based on a wider range.
Weaknesses: Research designs in studies can vary, so they are not truly comparable.
Peer Review
A researcher submits an article to a journal. The choice of the journal may be determined by the journal’s audience or prestige.
The journal selects two or more appropriate experts (psychologists working in a similar field) to peer review the article without payment. The peer reviewers assess: the methods and designs used, originality of the findings, the validity of the original research findings and its content, structure and language.
Feedback from the reviewer determines whether the article is accepted. The article may be: Accepted as it is, accepted with revisions, sent back to the author to revise and re-submit or rejected without the possibility of submission.
The editor makes the final decision whether to accept or reject the research report based on the reviewers comments/ recommendations.
Peer review is important because it prevent faulty data from entering the public domain, it provides a way of checking the validity of findings and the quality of the methodology and is used to assess the research rating of university departments.
Peer reviews may be an ideal, whereas in practice there are lots of problems. For example, it slows publication down and may prevent unusual, new work being published. Some reviewers might use it as an opportunity to prevent competing researchers from publishing work.
Some people doubt whether peer review can really prevent the publication of fraudulent research.
The advent of the internet means that a lot of research and academic comment is being published without official peer reviews than before, though systems are evolving on the internet where everyone really has a chance to offer their opinions and police the quality of research.
Types of Data
- Quantitative data is numerical data e.g. reaction time or number of mistakes. It represents how much or how long, how many there are of something. A tally of behavioral categories and closed questions in a questionnaire collect quantitative data.
- Qualitative data is virtually any type of information that can be observed and recorded that is not numerical in nature and can be in the form of written or verbal communication. Open questions in questionnaires and accounts from observational studies collect qualitative data.
- Primary data is first-hand data collected for the purpose of the investigation.
- Secondary data is information that has been collected by someone other than the person who is conducting the research e.g. taken from journals, books or articles.
Validity means how well a piece of research actually measures what it sets out to, or how well it reflects the reality it claims to represent.
Validity is whether the observed effect is genuine and represents what is actually out there in the world.
- Concurrent validity is the extent to which a psychological measure relates to an existing similar measure and obtains close results. For example, a new intelligence test compared to an established test.
- Face validity : does the test measure what it’s supposed to measure ‘on the face of it’. This is done by ‘eyeballing’ the measuring or by passing it to an expert to check.
- Ecological validit y is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other settings / real life.
- Temporal validity is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other historical times.
Features of Science
- Paradigm – A set of shared assumptions and agreed methods within a scientific discipline.
- Paradigm shift – The result of the scientific revolution: a significant change in the dominant unifying theory within a scientific discipline.
- Objectivity – When all sources of personal bias are minimised so not to distort or influence the research process.
- Empirical method – Scientific approaches that are based on the gathering of evidence through direct observation and experience.
- Replicability – The extent to which scientific procedures and findings can be repeated by other researchers.
- Falsifiability – The principle that a theory cannot be considered scientific unless it admits the possibility of being proved untrue.
Statistical Testing
A significant result is one where there is a low probability that chance factors were responsible for any observed difference, correlation, or association in the variables tested.
If our test is significant, we can reject our null hypothesis and accept our alternative hypothesis.
If our test is not significant, we can accept our null hypothesis and reject our alternative hypothesis. A null hypothesis is a statement of no effect.
In Psychology, we use p < 0.05 (as it strikes a balance between making a type I and II error) but p < 0.01 is used in tests that could cause harm like introducing a new drug.
A type I error is when the null hypothesis is rejected when it should have been accepted (happens when a lenient significance level is used, an error of optimism).
A type II error is when the null hypothesis is accepted when it should have been rejected (happens when a stringent significance level is used, an error of pessimism).
Ethical Issues
- Informed consent is when participants are able to make an informed judgment about whether to take part. It causes them to guess the aims of the study and change their behavior.
- To deal with it, we can gain presumptive consent or ask them to formally indicate their agreement to participate but it may invalidate the purpose of the study and it is not guaranteed that the participants would understand.
- Deception should only be used when it is approved by an ethics committee, as it involves deliberately misleading or withholding information. Participants should be fully debriefed after the study but debriefing can’t turn the clock back.
- All participants should be informed at the beginning that they have the right to withdraw if they ever feel distressed or uncomfortable.
- It causes bias as the ones that stayed are obedient and some may not withdraw as they may have been given incentives or feel like they’re spoiling the study. Researchers can offer the right to withdraw data after participation.
- Participants should all have protection from harm . The researcher should avoid risks greater than those experienced in everyday life and they should stop the study if any harm is suspected. However, the harm may not be apparent at the time of the study.
- Confidentiality concerns the communication of personal information. The researchers should not record any names but use numbers or false names though it may not be possible as it is sometimes possible to work out who the researchers were.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews). The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient's personal history). In psychology, case studies are ...
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The case study method is an in-depth research strategy focusing on the detailed examination of a specific subject, situation, or group over time. It's employed across various disciplines to narrow broad research fields into manageable topics, enabling researchers to conduct detailed investigations in real-world contexts. This method is characterized by its intensive examination of individual ...
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
The purpose of case study research is twofold: (1) to provide descriptive information and (2) to suggest theoretical relevance. Rich description enables an in-depth or sharpened understanding of the case. It is unique given one characteristic: case studies draw from more than one data source. Case studies are inherently multimodal or mixed ...
A case study is a research method used in psychology to investigate a particular individual, group, or situation in depth. It involves a detailed analysis of the subject, gathering information from various sources such as interviews, observations, and documents. In a case study, researchers aim to understand the complexities and nuances of the ...
Case studies are conducted to: Investigate a specific problem, event, or phenomenon. Explore unique or atypical situations. Examine the complexities and intricacies of a subject in its natural context. Develop theories, propositions, or hypotheses for further research. Gain practical insights for decision-making or problem-solving.
First, a case study allows a researcher to illustrate or test a specific theory. Many psychologists use case studies as exploratory research to develop treatments and confirm diagnoses. Third, the data gathered provides empirical research for others to study and expand on their theories and hypotheses.
Case study in psychology refers to the use of a descriptive research approach to obtain an in-depth analysis of a person, group, or phenomenon. A variety of techniques may be employed including personal interviews, direct-observation, psychometric tests, and archival records.In psychology case studies are most often used in clinical research to describe rare events and conditions, which ...
A case study is, as the name suggests, a study of a single case. For example, if someone has an extremely rare disease, a group of scientists might conduct a case study of that disease rather than attempting to set up an experimental study. In that case study, the researchers might test the effectiveness of a certain drug in treating that ...
Defnition: A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
As you read case studies across the disciplines, you will find that patterns emerge in the framing and production of cases. The paradigmatic approach in social work and psychology connects a specific clinical theory—e.g., psychodynamic, family systems, cognitive-behavioral—to specific client contexts or outcomes. The humanistic approach offers first-person practitioner accounts of ...
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
A case study is a method used in psychology to gather comprehensive data that would help researchers better understand a particular occurrence or individual. Case studies are a useful tool for researchers because they let them explore the complexity of human thought and behavior, identify patterns and themes, and provide hypotheses for further ...
Résumé. Case study is a common methodology in the social sciences (management, psychology, science of education, political science, sociology). A lot of methodological papers have been dedicated to case study but, paradoxically, the question "what is a case?" has been less studied.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc. Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.
to use a case study in our research, this does not mean the selection of a method, but rather a selection of what will be explored (ibid., p. 301). An individual case
Researchers, economists, and others frequently use case studies to answer questions across a wide spectrum of disciplines, from analyzing decades of climate data for conservation efforts to developing new theoretical frameworks in psychology. Learn about the different types of case studies, their benefits, and examples of successful case studies.
an in-depth investigation of a single individual, family, event, or other entity. Multiple types of data (psychological, physiological, biographical, environmental) are assembled, for example, to understand an individual's background, relationships, and behavior. Although case studies allow for intensive analysis of an issue, they are limited ...
Descriptive Case Study Research . A descriptive approach to a case study is akin to a biography of a person, honing in on the experiences of a small group to extrapolate to larger themes. We most commonly see descriptive case studies when those in the psychology field are using past clients as an example to illustrate a point.
A case study is a detailed description and assessment of a specific situation in the real world, often for the purpose of deriving generalizations and other insights about the subject of the case study. Case studies can be about an individual, a group of people, an organization, or an event, and they are used in multiple fields, including business, health care, anthropology, political science ...
A case study is an in-depth, detailed examination of a particular case (or cases) within a real-world context. For example, case studies in medicine may focus on an individual patient or ailment; case studies in business might cover a particular firm's strategy or a broader market; similarly, case studies in politics can range from a narrow happening over time like the operations of a specific ...