- Number Charts
- Multiplication
- Long division
- Basic operations
- Telling time
- Place value
- Roman numerals
- Fractions & related
- Add, subtract, multiply, and divide fractions
- Mixed numbers vs. fractions
- Equivalent fractions
- Prime factorization & factors
- Fraction Calculator
- Decimals & Percent
- Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals
- Fractions to decimals
- Percents to decimals
- Percentage of a number
- Percent word problems
- Classify triangles
- Classify quadrilaterals
- Circle worksheets
- Area & perimeter of rectangles
- Area of triangles & polygons
- Coordinate grid, including moves & reflections
- Volume & surface area
- Pre-algebra
- Square Roots
- Order of operations
- Scientific notation
- Proportions
- Ratio word problems
- Write expressions
- Evaluate expressions
- Simplify expressions
- Linear equations
- Linear inequalities
- Graphing & slope
- Equation calculator
- Equation editor
- Elementary Math Games
- Addition and subtraction
- Math facts practice
- The four operations
- Factoring and number theory
- Geometry topics
- Middle/High School
- Statistics & Graphs
- Probability
- Trigonometry
- Logic and proof
- For all levels
- Favorite math puzzles
- Favorite challenging puzzles
- Math in real world
- Problem solving & projects
- For gifted children
- Math history
- Math games and fun websites
- Interactive math tutorials
- Math help & online tutoring
- Assessment, review & test prep
- Online math curricula
Curriculum / Math / 8th Grade / Unit 7: Pythagorean Theorem and Volume / Lesson 6

Pythagorean Theorem and Volume
Lesson 6 of 16
Criteria for Success
Tips for teachers, anchor problems, problem set, target task, additional practice.
Understand the Pythagorean Theorem as a relationship between the side lengths in a right triangle.
Common Core Standards
Core standards.
The core standards covered in this lesson
8.G.B.6 — Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse.
The essential concepts students need to demonstrate or understand to achieve the lesson objective
- Understand the relationship between the legs and the hypotenuse of right triangles, named the Pythagorean Theorem : $${a^2+b^2=c^2}$$ .
- Use the Pythagorean Theorem to verify the relationship between the legs and hypotenuse of right triangles.
- Understand that the hypotenuse of a right triangle is the longest side of the triangle located across from the right angle.
Suggestions for teachers to help them teach this lesson
In this lesson, students are introduced to the famous relationship that exists between the side lengths of right triangles. In the next lesson, students will investigate informal proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem, followed by lessons where students will apply the theorem in various problems.
Lesson Materials
- Graph Paper (1 sheet per student)
Unlock features to optimize your prep time, plan engaging lessons, and monitor student progress.
Problems designed to teach key points of the lesson and guiding questions to help draw out student understanding
Several right triangles are shown below (not drawn to scale). In a right triangle, the two side lengths that form the right angle are called legs, and the side length opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse.

Use the triangles to investigate the question: What relationship do you see between the measures of the legs and the measure of the hypotenuse?
Guiding Questions
Use the Pythagorean Theorem to show the relationship between the sides of the right triangles shown below.
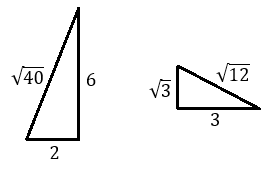
A right triangle has side lengths $$6$$ units, $$4$$ units, and $${\sqrt{20}}$$ units.
Which side length represents the hypotenuse?
A set of suggested resources or problem types that teachers can turn into a problem set
Give your students more opportunities to practice the skills in this lesson with a downloadable problem set aligned to the daily objective.
A task that represents the peak thinking of the lesson - mastery will indicate whether or not objective was achieved
Lee tried to use the Pythagorean Theorem on the triangle shown below and found that the relationship did not hold true.

Explain why the Pythagorean Theorem did not show a true relationship in Lee’s triangle.
Which three measures could be the side lengths of a right triangle? Explain or show your reasoning.
$$5$$ $$2$$ $$7$$ $$\sqrt{24}$$
Student Response
An example response to the Target Task at the level of detail expected of the students.
The following resources include problems and activities aligned to the objective of the lesson that can be used for additional practice or to create your own problem set.
- Include problems where students use given side lengths or identify side lengths from a group for a right triangle and verify the relationship using the Pythagorean Theorem.
- Open Up Resources Grade 8 Unit 8 Practice Problems — Lesson 6 #2-3
- Open Middle Pythagorean Theorem 2 — Challenge
- Open Middle Pythagorean Theorem 1
Topic A: Irrational Numbers and Square Roots
Define, evaluate, and estimate square roots.
Understand that some numbers, including $${\sqrt{2}}$$ , are irrational. Approximate the value of irrational numbers.
8.NS.A.1 8.NS.A.2
Locate irrational values approximately on a number line. Compare values of irrational numbers.
Represent rational numbers as decimal expansions.
Represent decimal expansions as rational numbers in fraction form.
Create a free account to access thousands of lesson plans.
Already have an account? Sign In
Topic B: Understanding and Applying the Pythagorean Theorem
Understand a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem.
Use the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if a triangle is a right triangle.
Find missing side lengths involving right triangles and apply to area and perimeter problems.
Solve real-world and mathematical problems using the Pythagorean Theorem (Part I).
Solve real-world and mathematical problems using the Pythagorean Theorem (Part II).
Find the distance between points in the coordinate plane using the Pythagorean Theorem.
Topic C: Volume and Cube Roots
Define and evaluate cube roots. Solve equations in the form $${x^2=p}$$ and $${x^3=p}$$ .
8.EE.A.2 8.NS.A.2
Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the volume of cylinders and cones.
Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the volume of spheres.
Solve real-world problems involving multiple three-dimensional shapes, in particular, cylinders, cones, and spheres.
Request a Demo
See all of the features of Fishtank in action and begin the conversation about adoption.
Learn more about Fishtank Learning School Adoption.
Contact Information
School information, what courses are you interested in, are you interested in onboarding professional learning for your teachers and instructional leaders, any other information you would like to provide about your school.

Effective Instruction Made Easy
Access rigorous, relevant, and adaptable math lesson plans for free
- → Resources
- → 8th Grade
The Pythagorean Theorem Lesson Plan
Get the lesson materials.

The Pythagorean Theorem Guided Notes with Doodles Legs Hypotenuse Right Triangle
Ever wondered how to teach the Pythagorean Theorem in an engaging way to your 8th grade students?
In this lesson plan, students will learn about the Pythagorean Theorem proofs, legs and hypotenuse, right triangles, and their real-life applications. Through artistic, interactive guided notes, check for understanding, a color by code activity, and a real-life application example, students will gain a comprehensive understanding of the Pythagorean Theorem.
The lesson culminates with an exploration of baseball diamond highlighting the importance of understanding the Pythagorean Theorem in real-world scenarios.
- Type : Lesson Plans
- Grade : 8th Grade
- Standard : CCSS 8.G.B.7
Learning Objectives
After this lesson, students will be able to:
Identify the hypotenuse and legs of a right triangle
Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of a missing side in a right triangle
Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to solve real-life problems
Prerequisites
Before this lesson, students should be familiar with:
Basic understanding of triangles (including how to identify right triangles) and their properties, such as side lengths and angle measures
Basic algebra skills, including solving for unknown variables and simplifying equations
Familiarity with squaring and square roots
Colored pencils or markers
Pythagorean Theorem
Guided Notes
Key Vocabulary
Right triangle
Square Roots

Introduction
As a hook, ask students why the Pythagorean Theorem is important in real life, such as finding the dimensions of a baseball diamond. Use the guided notes to introduce the Pythagorean Theorem.
Walk through the key points of the topic of the guided notes to teach. Refer to the FAQs for a walk-through on this, as well as ideas on how to respond to common student questions.
For Page 1 of the guided notes, introduce the Pythagorean Theorem with the worked example "what do you notice."
For Page 2 of the guided notes, explain how to know which side is a, b, or c, and check for understanding. Based on student responses, reteach concepts that students need extra help with.
Have students practice using the Pythagorean Theorem with the Maze activity. Walk around to answer student questions.
Fast finishers can dive into the Doodle Math activity for extra practice. You can assign it as homework for the remainder of the class.
Real-Life Application
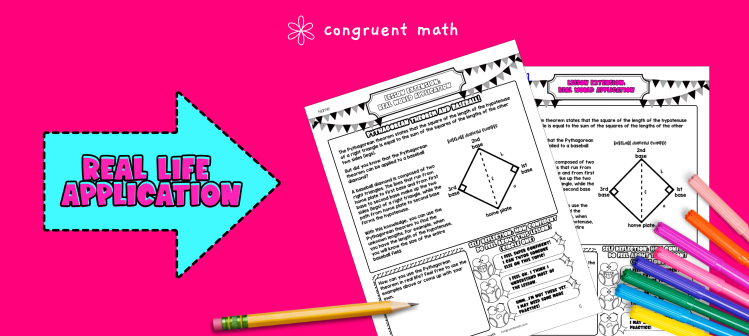
Bring the class back together, and introduce the concept of using the Pythagorean Theorem to determine the dimensions of a baseball diamond. Explain that the Pythagorean Theorem can be used to find the distance between any two points, even if they are not directly next to each other. In the case of a baseball diamond, the distance from home plate to first base, home plate to second base, and so on can be found by using the Pythagorean Theorem. Refer to the FAQ for more ideas on how to teach it!
Hands-on project
A fun, no-prep way for students to practice is my Pythagorean Spiral project . Students will use a square to draw successive triangles and create a spiral. They will then measure the spiral and solve for the length of the hypotenuse for every triangle in their Pythagorean spiral. At the end of the activity, students can turn their Pythagorean spiral into an art project.
Additional self-checking digital practice
If you’re looking for digital practice for the Pythagorean theorem, try my Pixel Art activities in Google Sheets. Every answer is automatically checked, and correct answers unlock parts of a mystery picture. It’s incredibly fun, and a powerful tool for differentiation.
There’s two version depending on the focus with your students:
Finding the hypotenuse and leg
. It’s available with fall , winter , Valentine’s Day , and St. Patrick’s Day themed images.
Challenge: Finding the distance between two points
. It’s available with Valentine’s Day and St. Patrick’s Day
themed images.
What is the Pythagorean theorem? Open
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. In equation form, it can be written as a^2 + b^2 = c^2, where c is the length of the hypotenuse and a and b are the lengths of the other two sides.
How do you use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of a missing side in a right triangle? Open
To use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of a missing side in a right triangle, follow these steps:
Identify the two sides of the right triangle that are known.
Assign one of the sides as "a" and the other as "b."
Identify the hypotenuse of the right triangle
, which is the side opposite the right angle. Assign the hypotenuse as "c."
Plug the known values into the Pythagorean theorem
, which states that a^2 + b^2 = c^2. Solve for the unknown side by isolating it on one side of the equation and taking the square root of both sides.
For example, if the length of side a is 3 and the length of side b is 4, and you want to find the length of the hypotenuse (c), you would use the equation 3^2 + 4^2 = c^2. Simplifying, you get 9 + 16 = c^2, or 25 = c^2. Taking the square root of both sides gives you c = 5. Therefore, the length of the hypotenuse (c) is 5.
What is a hypotenuse? Open
A hypotenuse is the longest side of a right triangle and is opposite the right angle. It is the side that connects the two legs of the triangle.
What are the legs of a right triangle? Open
The legs of a right triangle are the two sides that form the right angle. They are usually labeled as 'a' and 'b'.
How do you identify a right triangle? Open
To identify a right triangle, you need to look for a triangle with one angle that measures 90 degrees, also known as a right angle. This means that one side of the triangle will be perpendicular to another side, forming the right angle.
What are some real-life applications of the Pythagorean theorem? Open
The Pythagorean theorem has a wide range of applications in real life. Some examples include:
Architecture:
Architects use the Pythagorean theorem to make sure that building corners are square, and to calculate the length of sloping roofs.
Navigation:
The Pythagorean theorem is used in navigation to determine distances between two points. This is particularly useful in aviation and marine navigation.
In sports, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to calculate the distance between bases on a baseball diamond, or to determine the length of a shot in basketball.
Surveyors use the Pythagorean theorem to measure distances between points on the earth's surface, and to calculate elevations.
In the classroom, students can apply the Pythagorean theorem to real-world problems, such as finding the distance between two points on a map or the height of a building. One particularly fun application is to use the Pythagorean theorem to find the dimensions of a baseball diamond, which involves using the theorem to calculate the distance between bases.
How do you find the dimensions of a baseball diamond using the Pythagorean theorem? Open
To find the dimensions of a baseball diamond using the Pythagorean theorem, you need to calculate the distance between the bases. Here's how:
Identify the two bases you want to calculate the distance between.
Draw a right triangle connecting the two bases and home plate, with the two bases forming the legs and the distance between them forming the hypotenuse.
Measure the distance between the bases and record it as one leg of the triangle.
Measure the distance from the starting base to home plate and record it as the other leg of the triangle.
Use the Pythagorean theorem (a^2 + b^2 = c^2) to solve for the hypotenuse, which represents the distance between the two bases.
Want more ideas and freebies?
Get my free resource library with digital & print activities—plus tips over email.
- Kindergarten
- Greater Than Less Than
- Measurement
- Multiplication
- Place Value
- Subtraction
- Punctuation
- 1st Grade Reading
- 2nd Grade Reading
- 3rd Grade Reading
- Cursive Writing
Lesson 5 Homework Practice The Pythagorean Theorem
Lesson 5 Homework Practice The Pythagorean Theorem - Displaying top 8 worksheets found for this concept.
Some of the worksheets for this concept are 8 the pythagorean theorem and its converse, Lesson 3 using the pythagorean theorem, Lesson 1 the pythagorean theorem, Chapter 9 the pythagorean theorem, Dg4psa 894 106 134 pm 59 lesson the, The pythagorean theorem date period, Lesson 2 pythagorean theorem, Using the pythagorean theorem.
Found worksheet you are looking for? To download/print, click on pop-out icon or print icon to worksheet to print or download. Worksheet will open in a new window. You can & download or print using the browser document reader options.
1. 8-The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse
2. lesson 3: using the pythagorean theorem, 3. lesson 1: the pythagorean theorem, 4. chapter 9 the pythagorean theorem, 5. dg4psa 894 09.qxd 11/1/06 1:34 pm page 59 lesson 9.1 the ..., 6. the pythagorean theorem date period, 7. lesson 2: pythagorean theorem -, 8. 6.5 using the pythagorean theorem.
Chapter 3, Lesson 6: Using the Pythagorean Theorem
- Extra Examples
- Group Activity Cards
- Personal Tutor
- Self-Check Quizzes
The resource you requested requires you to enter a username and password below:
Please read our Terms of Use and Privacy Notice before you explore our Web site. To report a technical problem with this Web site, please contact the site producer .


COMMENTS
Course 3 • Chapter 5 Triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem 85 Lesson 6 Homework Practice Use The Pythagorean Theorem Write an equation that can be used to answer the question. Then solve. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. 1. How far is the ship from 2. How long is the wire 3. How far above the water is the
WS_5.6_HP - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Learn. Test your understanding of Pythagorean theorem with these NaN questions. The Pythagorean theorem describes a special relationship between the sides of a right triangle. Even the ancients knew of this relationship. In this topic, we'll figure out how to use the Pythagorean theorem and prove why it works.
Pythagorean Theorem. a²+b²=c² where a and b represent the legs of a right triangle and c represents the hypotenuse. right angle. An angle that measures 90°. Right angles are often marked with a special square symbol. Perpendicular lines form right angles. right cone. A cone whose vertex is directly over the center of its circular base.
Here are eight (8) Pythagorean Theorem problems for you to solve. You might need to find either the leg or the hypotenuse of the right triangle. ... Pythagorean Theorem Practice Problems with Answers. There are eight (8) problems here about the Pythagorean Theorem for you to work on. When you do something a lot, you get better at it. Let's ...
Standardized Test Practice Vocabulary Review Lesson Resources ... Hotmath Homework Help Math Review Math Tools Multilingual eGlossary Visual Vocabulary Cards Online Calculators Study to Go. Mathematics. Home > Chapter 3 > Lesson 6. Math Connects: Concepts, Skills, and Problem Solving, Course 3. Chapter 3, Lesson 6: Using the Pythagorean Theorem ...
A collection of quality worksheets with variable problems for grades 3-8. Topics include angle relationships, triangles, quadrilaterals, congruency, similar figures, constructions, area, volume, and the Pythagorean Theorem. Price: $9.00 download. See the free samples!
Test Practice Lesson Resources Extra Examples Personal Tutor Self-Check Quizzes Concepts in Motion. Hotmath Homework Help Math Review Multilingual Glossary Virtual Manipulatives. Mathematics. Home > Chapter 6 > Lesson 6. Geometry: Concepts and Applications. Chapter 6, Lesson 6: The Pythagorean Theorem. Extra Examples; Personal Tutor; Self-Check ...
You can use the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to test whether a triangle is a right triangle. 258 Chapter 6 More About Triangles Example Carpentry Link 3 Theorem 6-10 Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem If c is the measure of the longest side of a triangle,a and b are the lengths of the other two sides, and c2 a2 b2, then the triangle ...
Include problems where students use given side lengths or identify side lengths from a group for a right triangle and verify the relationship using the Pythagorean Theorem. Open Up Resources Grade 8 Unit 8 Practice Problems — Lesson 6 #2-3; Open Middle Pythagorean Theorem 2 — Challenge; Open Middle Pythagorean Theorem 1
Scanned by CamScanner. NAME Lesson 5 Homework Practice The Pythagorean Theorem DATE PERIOD Write an equation you could use to find the length of the missing side -—of eachxight-triangle. the missing Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. 18 cm 26 in. a in. 8fi IOft b ft c cm 182 + 152 cm 64 m 24 in. a2+ 242 = 262. c mm 50 mm 50 mm 502 + 502 ...
Unit 2 Dilations, similarity, and introducing slope. Unit 3 Linear relationships. Unit 4 Linear equations and linear systems. Unit 5 Functions and volume. Unit 6 Associations in data. Unit 7 Exponents and scientific notation. Unit 8 Pythagorean theorem and irrational numbers. Course challenge. Test your knowledge of the skills in this course.
86 Course 3 • Chapter 5 Triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem ... Lesson 6 Skills Practice Use the Pythagorean Theorem Write an equation that can be used to answer the question. Then ... 192 + 412 = c2; 45.2 mi d2 + 202 = 602; 56.6 yd 302 + h2 = 402; 26.5 in. 752 + 902 = d2; 117.2 m
Explanation: The question relates to using the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse or a leg in a right-angled triangle. This theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse ( c) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides ( a and b ). This can be mathematically represented as a² + b² ...
Practice B 6-3 The Pythagorean Theorem LESSON Find the length of the hypotenuse in each triangle. 1. 2. 3. Solve for the unknown side in each right triangle. Round the ... 6.3 c B C 12 5 c Holt Pre-Algebra. Title: practiceb.pdf Author: 15654 Created Date: 2/7/2013 12:04:30 PM ...
Standardized Test Practice Vocabulary Review Lesson Resources ... Personal Tutor Self-Check Quizzes. Hotmath Homework Help Math Review Math Tools Multilingual eGlossary Visual Vocabulary Cards ... Skills, and Problem Solving, Course 3. Chapter 3, Lesson 6: Using the Pythagorean Theorem. Extra Examples; Group Activity Cards; Personal Tutor; Self ...
The Pythagorean Theorem Lesson Plan. Get the Lesson Materials. ... Fast finishers can dive into the Doodle Math activity for extra practice. You can assign it as homework for the remainder of the class. Real-Life Application. ... Use the Pythagorean theorem (a^2 + b^2 = c^2) to solve for the hypotenuse, which represents the distance between the ...
California Standards Practice (STP) Vocabulary Review Lesson Resources Extra Examples Group Activity Cards Personal Tutor Self-Check Quizzes. Hotmath Homework Help Math Review Math Tools Multilingual Glossary ... Concepts, Skills, and Problem Solving, Grade 7. Chapter 3, Lesson 6: Using the Pythagorean Theorem. Extra Examples; Group Activity ...
Section 5-6: Use the Pythagorean Theorem. Section 5-7: Distance on the Coordinate Plane. Page 441: Vocabulary Check. Page 442: ... Section 7-6: Sole and Similar Triangles. Section 7-7: Area and Perimeter of Similar Figures. Page 579: ... With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and ...
In this lesson we review, but do not prove, the Pythagorean Theorem. We use the theorem to solve for missing sides of a right triangle in integer, simplest r...
Lesson 5 Homework Practice The Pythagorean Theorem - Displaying top 8 worksheets found for this concept.. Some of the worksheets for this concept are 8 the pythagorean theorem and its converse, Lesson 3 using the pythagorean theorem, Lesson 1 the pythagorean theorem, Chapter 9 the pythagorean theorem, Dg4psa 894 106 134 pm 59 lesson the, The pythagorean theorem date period, Lesson 2 ...
TAKS Test Practice Vocabulary Review Lesson Resources Extra Examples Group Activity Cards ... Hotmath Homework Help Math Review Multilingual Glossary Online Calculators Study to Go. Mathematics. Home > Chapter 3 > Lesson 6. ... Chapter 3, Lesson 6: Using the Pythagorean Theorem. Extra Examples; Group Activity Cards; Personal Tutor; Self-Check ...
Standardized Test Practice Vocabulary Review Lesson Resources ... Hotmath Homework Help Math Review Math Tools Multilingual eGlossary Visual Vocabulary Cards Online Calculators Study to Go. Mathematics. Home > Chapter 3 > Lesson 6. Oklahoma Math Connects Concepts, Skills, and Problem Solving Course 3. Chapter 3, Lesson 6: Using the Pythagorean ...