- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
🎉 Celebrate Small Business Month:
25% Off Annual Plans! SAVE NOW

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
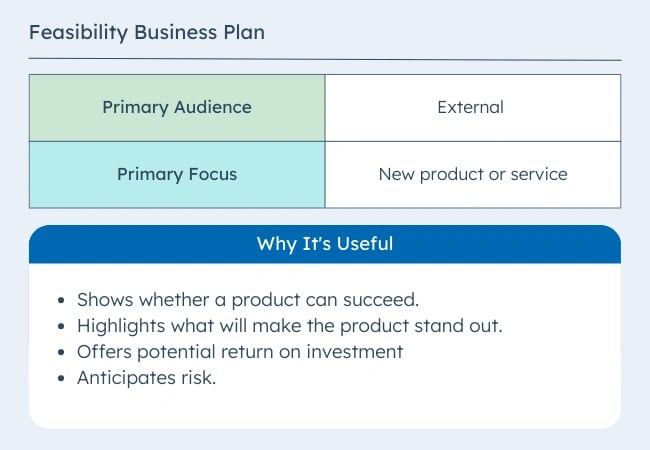
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
20 Free & Paid Small Business Tools for Any Budget

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![initial business plan definition How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![initial business plan definition 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![initial business plan definition The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
Elements of a Business Plan There are seven major sections of a business plan, and each one is a complex document. Read this selection from our business plan tutorial to fully understand these components.
Now that you understand why you need a business plan and you've spent some time doing your homework gathering the information you need to create one, it's time to roll up your sleeves and get everything down on paper. The following pages will describe in detail the seven essential sections of a business plan: what you should include, what you shouldn't include, how to work the numbers and additional resources you can turn to for help. With that in mind, jump right in.
Executive Summary
Within the overall outline of the business plan, the executive summary will follow the title page. The summary should tell the reader what you want. This is very important. All too often, what the business owner desires is buried on page eight. Clearly state what you're asking for in the summary.
The statement should be kept short and businesslike, probably no more than half a page. It could be longer, depending on how complicated the use of funds may be, but the summary of a business plan, like the summary of a loan application, is generally no longer than one page. Within that space, you'll need to provide a synopsis of your entire business plan. Key elements that should be included are:
- Business concept. Describes the business, its product and the market it will serve. It should point out just exactly what will be sold, to whom and why the business will hold a competitive advantage.
- Financial features. Highlights the important financial points of the business including sales, profits, cash flows and return on investment.
- Financial requirements. Clearly states the capital needed to start the business and to expand. It should detail how the capital will be used, and the equity, if any, that will be provided for funding. If the loan for initial capital will be based on security instead of equity, you should also specify the source of collateral.
- Current business position. Furnishes relevant information about the company, its legal form of operation, when it was formed, the principal owners and key personnel.
- Major achievements. Details any developments within the company that are essential to the success of the business. Major achievements include items like patents, prototypes, location of a facility, any crucial contracts that need to be in place for product development, or results from any test marketing that has been conducted.
When writing your statement of purpose, don't waste words. If the statement of purpose is eight pages, nobody's going to read it because it'll be very clear that the business, no matter what its merits, won't be a good investment because the principals are indecisive and don't really know what they want. Make it easy for the reader to realize at first glance both your needs and capabilities.
Business Description
Tell them all about it.
The business description usually begins with a short description of the industry. When describing the industry, discuss the present outlook as well as future possibilities. You should also provide information on all the various markets within the industry, including any new products or developments that will benefit or adversely affect your business. Base all of your observations on reliable data and be sure to footnote sources of information as appropriate. This is important if you're seeking funding; the investor will want to know just how dependable your information is, and won't risk money on assumptions or conjecture.
When describing your business, the first thing you need to concentrate on is its structure. By structure we mean the type of operation, i.e. wholesale, retail, food service, manufacturing or service-oriented. Also state whether the business is new or already established.
In addition to structure, legal form should be reiterated once again. Detail whether the business is a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation, who its principals are, and what they will bring to the business.
You should also mention who you will sell to, how the product will be distributed, and the business's support systems. Support may come in the form of advertising, promotions and customer service.
Once you've described the business, you need to describe the products or services you intend to market. The product description statement should be complete enough to give the reader a clear idea of your intentions. You may want to emphasize any unique features or variations from concepts that can typically be found in the industry.
Be specific in showing how you will give your business a competitive edge. For example, your business will be better because you will supply a full line of products; competitor A doesn't have a full line. You're going to provide service after the sale; competitor B doesn't support anything he sells. Your merchandise will be of higher quality. You'll give a money-back guarantee. Competitor C has the reputation for selling the best French fries in town; you're going to sell the best Thousand Island dressing.
How Will I Profit?
Now you must be a classic capitalist and ask yourself, "How can I turn a buck? And why do I think I can make a profit that way?" Answer that question for yourself, and then convey that answer to others in the business concept section. You don't have to write 25 pages on why your business will be profitable. Just explain the factors you think will make it successful, like the following: it's a well-organized business, it will have state-of-the-art equipment, its location is exceptional, the market is ready for it, and it's a dynamite product at a fair price.
If you're using your business plan as a document for financial purposes, explain why the added equity or debt money is going to make your business more profitable.
Show how you will expand your business or be able to create something by using that money.
Show why your business is going to be profitable. A potential lender is going to want to know how successful you're going to be in this particular business. Factors that support your claims for success can be mentioned briefly; they will be detailed later. Give the reader an idea of the experience of the other key people in the business. They'll want to know what suppliers or experts you've spoken to about your business and their response to your idea. They may even ask you to clarify your choice of location or reasons for selling this particular product.
The business description can be a few paragraphs in length to a few pages, depending on the complexity of your plan. If your plan isn't too complicated, keep your business description short, describing the industry in one paragraph, the product in another, and the business and its success factors in three or four paragraphs that will end the statement.
While you may need to have a lengthy business description in some cases, it's our opinion that a short statement conveys the required information in a much more effective manner. It doesn't attempt to hold the reader's attention for an extended period of time, and this is important if you're presenting to a potential investor who will have other plans he or she will need to read as well. If the business description is long and drawn-out, you'll lose the reader's attention, and possibly any chance of receiving the necessary funding for the project.
Market Strategies
Define your market.
Market strategies are the result of a meticulous market analysis. A market analysis forces the entrepreneur to become familiar with all aspects of the market so that the target market can be defined and the company can be positioned in order to garner its share of sales. A market analysis also enables the entrepreneur to establish pricing, distribution and promotional strategies that will allow the company to become profitable within a competitive environment. In addition, it provides an indication of the growth potential within the industry, and this will allow you to develop your own estimates for the future of your business.
Begin your market analysis by defining the market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends and sales potential.
The total aggregate sales of your competitors will provide you with a fairly accurate estimate of the total potential market. Once the size of the market has been determined, the next step is to define the target market. The target market narrows down the total market by concentrating on segmentation factors that will determine the total addressable market--the total number of users within the sphere of the business's influence. The segmentation factors can be geographic, customer attributes or product-oriented.
For instance, if the distribution of your product is confined to a specific geographic area, then you want to further define the target market to reflect the number of users or sales of that product within that geographic segment.
Once the target market has been detailed, it needs to be further defined to determine the total feasible market. This can be done in several ways, but most professional planners will delineate the feasible market by concentrating on product segmentation factors that may produce gaps within the market. In the case of a microbrewery that plans to brew a premium lager beer, the total feasible market could be defined by determining how many drinkers of premium pilsner beers there are in the target market.
It's important to understand that the total feasible market is the portion of the market that can be captured provided every condition within the environment is perfect and there is very little competition. In most industries this is simply not the case. There are other factors that will affect the share of the feasible market a business can reasonably obtain. These factors are usually tied to the structure of the industry, the impact of competition, strategies for market penetration and continued growth, and the amount of capital the business is willing to spend in order to increase its market share.
Projecting Market Share
Arriving at a projection of the market share for a business plan is very much a subjective estimate. It's based on not only an analysis of the market but on highly targeted and competitive distribution, pricing and promotional strategies. For instance, even though there may be a sizable number of premium pilsner drinkers to form the total feasible market, you need to be able to reach them through your distribution network at a price point that's competitive, and then you have to let them know it's available and where they can buy it. How effectively you can achieve your distribution, pricing and promotional goals determines the extent to which you will be able to garner market share.
For a business plan, you must be able to estimate market share for the time period the plan will cover. In order to project market share over the time frame of the business plan, you'll need to consider two factors:
- Industry growth which will increase the total number of users. Most projections utilize a minimum of two growth models by defining different industry sales scenarios. The industry sales scenarios should be based on leading indicators of industry sales, which will most likely include industry sales, industry segment sales, demographic data and historical precedence.
- Conversion of users from the total feasible market. This is based on a sales cycle similar to a product life cycle where you have five distinct stages: early pioneer users, early users, early majority users, late majority users and late users. Using conversion rates, market growth will continue to increase your market share during the period from early pioneers to early majority users, level off through late majority users, and decline with late users.
Defining the market is but one step in your analysis. With the information you've gained through market research, you need to develop strategies that will allow you to fulfill your objectives.
Positioning Your Business
When discussing market strategy, it's inevitable that positioning will be brought up. A company's positioning strategy is affected by a number of variables that are closely tied to the motivations and requirements of target customers within as well as the actions of primary competitors.
Before a product can be positioned, you need to answer several strategic questions such as:
- How are your competitors positioning themselves?
- What specific attributes does your product have that your competitors' don't?
- What customer needs does your product fulfill?
Once you've answered your strategic questions based on research of the market, you can then begin to develop your positioning strategy and illustrate that in your business plan. A positioning statement for a business plan doesn't have to be long or elaborate. It should merely point out exactly how you want your product perceived by both customers and the competition.
How you price your product is important because it will have a direct effect on the success of your business. Though pricing strategy and computations can be complex, the basic rules of pricing are straightforward:
- All prices must cover costs.
- The best and most effective way of lowering your sales prices is to lower costs.
- Your prices must reflect the dynamics of cost, demand, changes in the market and response to your competition.
- Prices must be established to assure sales. Don't price against a competitive operation alone. Rather, price to sell.
- Product utility, longevity, maintenance and end use must be judged continually, and target prices adjusted accordingly.
- Prices must be set to preserve order in the marketplace.
There are many methods of establishing prices available to you:
- Cost-plus pricing. Used mainly by manufacturers, cost-plus pricing assures that all costs, both fixed and variable, are covered and the desired profit percentage is attained.
- Demand pricing. Used by companies that sell their product through a variety of sources at differing prices based on demand.
- Competitive pricing. Used by companies that are entering a market where there is already an established price and it is difficult to differentiate one product from another.
- Markup pricing. Used mainly by retailers, markup pricing is calculated by adding your desired profit to the cost of the product. Each method listed above has its strengths and weaknesses.
- Distribution
Distribution includes the entire process of moving the product from the factory to the end user. The type of distribution network you choose will depend upon the industry and the size of the market. A good way to make your decision is to analyze your competitors to determine the channels they are using, then decide whether to use the same type of channel or an alternative that may provide you with a strategic advantage.
Some of the more common distribution channels include:
- Direct sales. The most effective distribution channel is to sell directly to the end-user.
- OEM (original equipment manufacturer) sales. When your product is sold to the OEM, it is incorporated into their finished product and it is distributed to the end user.
- Manufacturer's representatives. One of the best ways to distribute a product, manufacturer's reps, as they are known, are salespeople who operate out of agencies that handle an assortment of complementary products and divide their selling time among them.
- Wholesale distributors. Using this channel, a manufacturer sells to a wholesaler, who in turn sells it to a retailer or other agent for further distribution through the channel until it reaches the end user.
- Brokers. Third-party distributors who often buy directly from the distributor or wholesaler and sell to retailers or end users.
- Retail distributors. Distributing a product through this channel is important if the end user of your product is the general consuming public.
- Direct Mail. Selling to the end user using a direct mail campaign.
As we've mentioned already, the distribution strategy you choose for your product will be based on several factors that include the channels being used by your competition, your pricing strategy and your own internal resources.
Promotion Plan
With a distribution strategy formed, you must develop a promotion plan. The promotion strategy in its most basic form is the controlled distribution of communication designed to sell your product or service. In order to accomplish this, the promotion strategy encompasses every marketing tool utilized in the communication effort. This includes:
- Advertising. Includes the advertising budget, creative message(s), and at least the first quarter's media schedule.
- Packaging. Provides a description of the packaging strategy. If available, mockups of any labels, trademarks or service marks should be included.
- Public relations. A complete account of the publicity strategy including a list of media that will be approached as well as a schedule of planned events.
- Sales promotions. Establishes the strategies used to support the sales message. This includes a description of collateral marketing material as well as a schedule of planned promotional activities such as special sales, coupons, contests and premium awards.
- Personal sales. An outline of the sales strategy including pricing procedures, returns and adjustment rules, sales presentation methods, lead generation, customer service policies, salesperson compensation, and salesperson market responsibilities.
Sales Potential
Once the market has been researched and analyzed, conclusions need to be developed that will supply a quantitative outlook concerning the potential of the business. The first financial projection within the business plan must be formed utilizing the information drawn from defining the market, positioning the product, pricing, distribution, and strategies for sales. The sales or revenue model charts the potential for the product, as well as the business, over a set period of time. Most business plans will project revenue for up to three years, although five-year projections are becoming increasingly popular among lenders.
When developing the revenue model for the business plan, the equation used to project sales is fairly simple. It consists of the total number of customers and the average revenue from each customer. In the equation, "T" represents the total number of people, "A" represents the average revenue per customer, and "S" represents the sales projection. The equation for projecting sales is: (T)(A) = S
Using this equation, the annual sales for each year projected within the business plan can be developed. Of course, there are other factors that you'll need to evaluate from the revenue model. Since the revenue model is a table illustrating the source for all income, every segment of the target market that is treated differently must be accounted for. In order to determine any differences, the various strategies utilized in order to sell the product have to be considered. As we've already mentioned, those strategies include distribution, pricing and promotion.
Competitive Analysis
Identify and analyze your competition.
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy and how it relates to the competition. The purpose of the competitive analysis is to determine the strengths and weaknesses of the competitors within your market, strategies that will provide you with a distinct advantage, the barriers that can be developed in order to prevent competition from entering your market, and any weaknesses that can be exploited within the product development cycle.
The first step in a competitor analysis is to identify the current and potential competition. There are essentially two ways you can identify competitors. The first is to look at the market from the customer's viewpoint and group all your competitors by the degree to which they contend for the buyer's dollar. The second method is to group competitors according to their various competitive strategies so you understand what motivates them.
Once you've grouped your competitors, you can start to analyze their strategies and identify the areas where they're most vulnerable. This can be done through an examination of your competitors' weaknesses and strengths. A competitor's strengths and weaknesses are usually based on the presence and absence of key assets and skills needed to compete in the market.
To determine just what constitutes a key asset or skill within an industry, David A. Aaker in his book, Developing Business Strategies , suggests concentrating your efforts in four areas:
- The reasons behind successful as well as unsuccessful firms
- Prime customer motivators
- Major component costs
- Industry mobility barriers
According to theory, the performance of a company within a market is directly related to the possession of key assets and skills. Therefore, an analysis of strong performers should reveal the causes behind such a successful track record. This analysis, in conjunction with an examination of unsuccessful companies and the reasons behind their failure, should provide a good idea of just what key assets and skills are needed to be successful within a given industry and market segment.
Through your competitor analysis, you will also have to create a marketing strategy that will generate an asset or skill competitors don't have, which will provide you with a distinct and enduring competitive advantage. Since competitive advantages are developed from key assets and skills, you should sit down and put together a competitive strength grid. This is a scale that lists all your major competitors or strategic groups based upon their applicable assets and skills and how your own company fits on this scale.
Create a Competitive Strength Grid
To put together a competitive strength grid, list all the key assets and skills down the left margin of a piece of paper. Along the top, write down two column headers: "weakness" and "strength." In each asset or skill category, place all the competitors that have weaknesses in that particular category under the weakness column, and all those that have strengths in that specific category in the strength column. After you've finished, you'll be able to determine just where you stand in relation to the other firms competing in your industry.
Once you've established the key assets and skills necessary to succeed in this business and have defined your distinct competitive advantage, you need to communicate them in a strategic form that will attract market share as well as defend it. Competitive strategies usually fall into these five areas:
- Advertising
Many of the factors leading to the formation of a strategy should already have been highlighted in previous sections, specifically in marketing strategies. Strategies primarily revolve around establishing the point of entry in the product life cycle and an endurable competitive advantage. As we've already discussed, this involves defining the elements that will set your product or service apart from your competitors or strategic groups. You need to establish this competitive advantage clearly so the reader understands not only how you will accomplish your goals, but also why your strategy will work.
Design and Development Plan
What you'll cover in this section.
The purpose of the design and development plan section is to provide investors with a description of the product's design, chart its development within the context of production, marketing and the company itself, and create a development budget that will enable the company to reach its goals.
There are generally three areas you'll cover in the development plan section:
- Product development
- Market development
- Organizational development
Each of these elements needs to be examined from the funding of the plan to the point where the business begins to experience a continuous income. Although these elements will differ in nature concerning their content, each will be based on structure and goals.
The first step in the development process is setting goals for the overall development plan. From your analysis of the market and competition, most of the product, market and organizational development goals will be readily apparent. Each goal you define should have certain characteristics. Your goals should be quantifiable in order to set up time lines, directed so they relate to the success of the business, consequential so they have impact upon the company, and feasible so that they aren't beyond the bounds of actual completion.
Goals For Product Development
Goals for product development should center on the technical as well as the marketing aspects of the product so that you have a focused outline from which the development team can work. For example, a goal for product development of a microbrewed beer might be "Produce recipe for premium lager beer" or "Create packaging for premium lager beer." In terms of market development, a goal might be, "Develop collateral marketing material." Organizational goals would center on the acquisition of expertise in order to attain your product and market-development goals. This expertise usually needs to be present in areas of key assets that provide a competitive advantage. Without the necessary expertise, the chances of bringing a product successfully to market diminish.
With your goals set and expertise in place, you need to form a set of procedural tasks or work assignments for each area of the development plan. Procedures will have to be developed for product development, market development, and organization development. In some cases, product and organization can be combined if the list of procedures is short enough.
Procedures should include how resources will be allocated, who is in charge of accomplishing each goal, and how everything will interact. For example, to produce a recipe for a premium lager beer, you would need to do the following:
- Gather ingredients.
- Determine optimum malting process.
- Gauge mashing temperature.
- Boil wort and evaluate which hops provide the best flavor.
- Determine yeast amounts and fermentation period.
- Determine aging period.
- Carbonate the beer.
- Decide whether or not to pasteurize the beer.
The development of procedures provides a list of work assignments that need to be accomplished, but one thing it doesn't provide are the stages of development that coordinate the work assignments within the overall development plan. To do this, you first need to amend the work assignments created in the procedures section so that all the individual work elements are accounted for in the development plan. The next stage involves setting deliverable dates for components as well as the finished product for testing purposes. There are primarily three steps you need to go through before the product is ready for final delivery:
- Preliminary product review . All the product's features and specifications are checked.
- Critical product review . All the key elements of the product are checked and gauged against the development schedule to make sure everything is going according to plan.
- Final product review . All elements of the product are checked against goals to assure the integrity of the prototype.
Scheduling and Costs
This is one of the most important elements in the development plan. Scheduling includes all of the key work elements as well as the stages the product must pass through before customer delivery. It should also be tied to the development budget so that expenses can be tracked. But its main purpose is to establish time frames for completion of all work assignments and juxtapose them within the stages through which the product must pass. When producing the schedule, provide a column for each procedural task, how long it takes, start date and stop date. If you want to provide a number for each task, include a column in the schedule for the task number.
Development Budget
That leads us into a discussion of the development budget. When forming your development budget, you need to take into account all the expenses required to design the product and to take it from prototype to production.
Costs that should be included in the development budget include:
- Material . All raw materials used in the development of the product.
- Direct labor . All labor costs associated with the development of the product.
- Overhead . All overhead expenses required to operate the business during the development phase such as taxes, rent, phone, utilities, office supplies, etc.
- G&A costs . The salaries of executive and administrative personnel along with any other office support functions.
- Marketing & sales . The salaries of marketing personnel required to develop pre-promotional materials and plan the marketing campaign that should begin prior to delivery of the product.
- Professional services . Those costs associated with the consultation of outside experts such as accountants, lawyers, and business consultants.
- Miscellaneous Costs . Costs that are related to product development.
- Capital equipment . To determine the capital requirements for the development budget, you first have to establish what type of equipment you will need, whether you will acquire the equipment or use outside contractors, and finally, if you decide to acquire the equipment, whether you will lease or purchase it.
As we mentioned already, the company has to have the proper expertise in key areas to succeed; however, not every company will start a business with the expertise required in every key area. Therefore, the proper personnel have to be recruited, integrated into the development process, and managed so that everyone forms a team focused on the achievement of the development goals.
Before you begin recruiting, however, you should determine which areas within the development process will require the addition of personnel. This can be done by reviewing the goals of your development plan to establish key areas that need attention. After you have an idea of the positions that need to be filled, you should produce a job description and job specification.
Once you've hired the proper personnel, you need to integrate them into the development process by assigning tasks from the work assignments you've developed. Finally, the whole team needs to know what their role is within the company and how each interrelates with every position within the development team. In order to do this, you should develop an organizational chart for your development team.
Assessing Risks
Finally, the risks involved in developing the product should be assessed and a plan developed to address each one. The risks during the development stage will usually center on technical development of the product, marketing, personnel requirements, and financial problems. By identifying and addressing each of the perceived risks during the development period, you will allay some of your major fears concerning the project and those of investors as well.
Operations & Management
The operations and management plan is designed to describe just how the business functions on a continuing basis. The operations plan will highlight the logistics of the organization such as the various responsibilities of the management team, the tasks assigned to each division within the company, and capital and expense requirements related to the operations of the business. In fact, within the operations plan you'll develop the next set of financial tables that will supply the foundation for the "Financial Components" section.
The financial tables that you'll develop within the operations plan include:
- The operating expense table
- The capital requirements table
- The cost of goods table
There are two areas that need to be accounted for when planning the operations of your company. The first area is the organizational structure of the company, and the second is the expense and capital requirements associated with its operation.
Organizational Structure
The organizational structure of the company is an essential element within a business plan because it provides a basis from which to project operating expenses. This is critical to the formation of financial statements, which are heavily scrutinized by investors; therefore, the organizational structure has to be well-defined and based within a realistic framework given the parameters of the business.
Although every company will differ in its organizational structure, most can be divided into several broad areas that include:
- Marketing and sales (includes customer relations and service)
- Production (including quality assurance)
- Research and development
- Administration
These are very broad classifications and it's important to keep in mind that not every business can be divided in this manner. In fact, every business is different, and each one must be structured according to its own requirements and goals.
The four stages for organizing a business are:
Calculate Your Personnel Numbers
Once you've structured your business, however, you need to consider your overall goals and the number of personnel required to reach those goals. In order to determine the number of employees you'll need to meet the goals you've set for your business, you'll need to apply the following equation to each department listed in your organizational structure: C / S = P
In this equation, C represents the total number of customers, S represents the total number of customers that can be served by each employee, and P represents the personnel requirements. For instance, if the number of customers for first year sales is projected at 10,110 and one marketing employee is required for every 200 customers, you would need 51 employees within the marketing department: 10,110 / 200 = 51
Once you calculate the number of employees that you'll need for your organization, you'll need to determine the labor expense. The factors that need to be considered when calculating labor expense (LE) are the personnel requirements (P) for each department multiplied by the employee salary level (SL). Therefore, the equation would be: P * SL = LE
Using the marketing example from above, the labor expense for that department would be: 51 * $40,000 = $2,040,000
Calculate Overhead Expenses
Once the organization's operations have been planned, the expenses associated with the operation of the business can be developed. These are usually referred to as overhead expenses. Overhead expenses refer to all non-labor expenses required to operate the business. Expenses can be divided into fixed (those that must be paid, usually at the same rate, regardless of the volume of business) and variable or semivariable (those which change according to the amount of business).
Overhead expenses usually include the following:
- Maintenance and repair
- Equipment leases
- Advertising & promotion
- Packaging & shipping
- Payroll taxes and benefits
- Uncollectible receivables
- Professional services
- Loan payments
- Depreciation
In order to develop the overhead expenses for the expense table used in this portion of the business plan, you need to multiply the number of employees by the expenses associated with each employee. Therefore, if NE represents the number of employees and EE is the expense per employee, the following equation can be used to calculate the sum of each overhead (OH) expense: OH = NE * EE
Develop a Capital Requirements Table
In addition to the expense table, you'll also need to develop a capital requirements table that depicts the amount of money necessary to purchase the equipment you'll use to establish and continue operations. It also illustrates the amount of depreciation your company will incur based on all equipment elements purchased with a lifetime of more than one year.
In order to generate the capital requirements table, you first have to establish the various elements within the business that will require capital investment. For service businesses, capital is usually tied to the various pieces of equipment used to service customers.
Capital for manufacturing companies, on the other hand, is based on the equipment required in order to produce the product. Manufacturing equipment usually falls into three categories: testing equipment, assembly equipment and packaging equipment.
With these capital elements in mind, you need to determine the number of units or customers, in terms of sales, that each equipment item can adequately handle. This is important because capital requirements are a product of income, which is produced through unit sales. In order to meet sales projections, a business usually has to invest money to increase production or supply better service. In the business plan, capital requirements are tied to projected sales as illustrated in the revenue model shown earlier in this chapter.
For instance, if the capital equipment required is capable of handling the needs of 10,000 customers at an average sale of $10 each, that would be $100,000 in sales, at which point additional capital will be required in order to purchase more equipment should the company grow beyond this point. This leads us to another factor within the capital requirements equation, and that is equipment cost.
If you multiply the cost of equipment by the number of customers it can support in terms of sales, it would result in the capital requirements for that particular equipment element. Therefore, you can use an equation in which capital requirements (CR) equals sales (S) divided by number of customers (NC) supported by each equipment element, multiplied by the average sale (AS), which is then multiplied by the capital cost (CC) of the equipment element. Given these parameters, your equation would look like the following: CR = [(S / NC) * AS] * CC
The capital requirements table is formed by adding all your equipment elements to generate the total new capital for that year. During the first year, total new capital is also the total capital required. For each successive year thereafter, total capital (TC) required is the sum of total new capital (NC) plus total capital (PC) from the previous year, less depreciation (D), once again, from the previous year. Therefore, your equation to arrive at total capital for each year portrayed in the capital requirements model would be: TC = NC + PC - D
Keep in mind that depreciation is an expense that shows the decrease in value of the equipment throughout its effective lifetime. For many businesses, depreciation is based upon schedules that are tied to the lifetime of the equipment. Be careful when choosing the schedule that best fits your business. Depreciation is also the basis for a tax deduction as well as the flow of money for new capital. You may need to seek consultation from an expert in this area.
Create a Cost of Goods Table
The last table that needs to be generated in the operations and management section of your business plan is the cost of goods table. This table is used only for businesses where the product is placed into inventory. For a retail or wholesale business, cost of goods sold --or cost of sales --refers to the purchase of products for resale, i.e. the inventory. The products that are sold are logged into cost of goods as an expense of the sale, while those that aren't sold remain in inventory.
For a manufacturing firm, cost of goods is the cost incurred by the company to manufacture its product. This usually consists of three elements:
As in retail, the merchandise that is sold is expensed as a cost of goods , while merchandise that isn't sold is placed in inventory. Cost of goods has to be accounted for in the operations of a business. It is an important yardstick for measuring the firm's profitability for the cash-flow statement and income statement.
In the income statement, the last stage of the manufacturing process is the item expensed as cost of goods, but it is important to document the inventory still in various stages of the manufacturing process because it represents assets to the company. This is important to determining cash flow and to generating the balance sheet.
That is what the cost of goods table does. It's one of the most complicated tables you'll have to develop for your business plan, but it's an integral part of portraying the flow of inventory through your operations, the placement of assets within the company, and the rate at which your inventory turns.
In order to generate the cost of goods table, you need a little more information in addition to what your labor and material cost is per unit. You also need to know the total number of units sold for the year, the percentage of units which will be fully assembled, the percentage which will be partially assembled, and the percentage which will be in unassembled inventory. Much of these figures will depend on the capacity of your equipment as well as on the inventory control system you develop. Along with these factors, you also need to know at what stage the majority of the labor is performed.
Financial Components
Financial statements to include.
Financial data is always at the back of the business plan, but that doesn't mean it's any less important than up-front material such as the business concept and the management team. Astute investors look carefully at the charts, tables, formulas and spreadsheets in the financial section, because they know that this information is like the pulse, respiration rate and blood pressure in a human--it shows whether the patient is alive and what the odds are for continued survival.
Financial statements, like bad news, come in threes. The news in financial statements isn't always bad, of course, but taken together it provides an accurate picture of a company's current value, plus its ability to pay its bills today and earn a profit going forward.
The three common statements are a cash flow statement, an income statement and a balance sheet. Most entrepreneurs should provide them and leave it at that. But not all do. But this is a case of the more, the less merry. As a rule, stick with the big three: income, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
These three statements are interlinked, with changes in one necessarily altering the others, but they measure quite different aspects of a company's financial health. It's hard to say that one of these is more important than another. But of the three, the income statement may be the best place to start.
Income Statement
The income statement is a simple and straightforward report on the proposed business's cash-generating ability. It's a score card on the financial performance of your business that reflects when sales are made and when expenses are incurred. It draws information from the various financial models developed earlier such as revenue, expenses, capital (in the form of depreciation), and cost of goods. By combining these elements, the income statement illustrates just how much your company makes or loses during the year by subtracting cost of goods and expenses from revenue to arrive at a net result--which is either a profit or a loss.
For a business plan, the income statement should be generated on a monthly basis during the first year, quarterly for the second, and annually for each year thereafter. It's formed by listing your financial projections in the following manner:
- Income . Includes all the income generated by the business and its sources.
- Cost of goods . Includes all the costs related to the sale of products in inventory.
- Gross profit margin . The difference between revenue and cost of goods. Gross profit margin can be expressed in dollars, as a percentage, or both. As a percentage, the GP margin is always stated as a percentage of revenue.
- Operating expenses . Includes all overhead and labor expenses associated with the operations of the business.
- Total expenses . The sum of all overhead and labor expenses required to operate the business.
- Net profit . The difference between gross profit margin and total expenses, the net income depicts the business's debt and capital capabilities.
- Depreciation . Reflects the decrease in value of capital assets used to generate income. Also used as the basis for a tax deduction and an indicator of the flow of money into new capital.
- Net profit before interest . The difference between net profit and depreciation.
- Interest . Includes all interest derived from debts, both short-term and long-term. Interest is determined by the amount of investment within the company.
- Net profit before taxes . The difference between net profit before interest and interest.
- Taxes . Includes all taxes on the business.
- Profit after taxes . The difference between net profit before taxes and the taxes accrued. Profit after taxes is the bottom line for any company.
Following the income statement is a short note analyzing the statement. The analysis statement should be very short, emphasizing key points within the income statement.
Cash Flow Statement
The cash-flow statement is one of the most critical information tools for your business, showing how much cash will be needed to meet obligations, when it is going to be required, and from where it will come. It shows a schedule of the money coming into the business and expenses that need to be paid. The result is the profit or loss at the end of the month or year. In a cash-flow statement, both profits and losses are carried over to the next column to show the cumulative amount. Keep in mind that if you run a loss on your cash-flow statement, it is a strong indicator that you will need additional cash in order to meet expenses.
Like the income statement, the cash-flow statement takes advantage of previous financial tables developed during the course of the business plan. The cash-flow statement begins with cash on hand and the revenue sources. The next item it lists is expenses, including those accumulated during the manufacture of a product. The capital requirements are then logged as a negative after expenses. The cash-flow statement ends with the net cash flow.
The cash-flow statement should be prepared on a monthly basis during the first year, on a quarterly basis during the second year, and on an annual basis thereafter. Items that you'll need to include in the cash-flow statement and the order in which they should appear are as follows:
- Cash sales . Income derived from sales paid for by cash.
- Receivables . Income derived from the collection of receivables.
- Other income . Income derived from investments, interest on loans that have been extended, and the liquidation of any assets.
- Total income . The sum of total cash, cash sales, receivables, and other income.
- Material/merchandise . The raw material used in the manufacture of a product (for manufacturing operations only), the cash outlay for merchandise inventory (for merchandisers such as wholesalers and retailers), or the supplies used in the performance of a service.
- Production labor . The labor required to manufacture a product (for manufacturing operations only) or to perform a service.
- Overhead . All fixed and variable expenses required for the production of the product and the operations of the business.
- Marketing/sales . All salaries, commissions, and other direct costs associated with the marketing and sales departments.
- R&D . All the labor expenses required to support the research and development operations of the business.
- G&A . All the labor expenses required to support the administrative functions of the business.
- Taxes . All taxes, except payroll, paid to the appropriate government institutions.
- Capital . The capital required to obtain any equipment elements that are needed for the generation of income.
- Loan payment . The total of all payments made to reduce any long-term debts.
- Total expenses . The sum of material, direct labor, overhead expenses, marketing, sales, G&A, taxes, capital and loan payments.
- Cash flow . The difference between total income and total expenses. This amount is carried over to the next period as beginning cash.
- Cumulative cash flow . The difference between current cash flow and cash flow from the previous period.
As with the income statement, you will need to analyze the cash-flow statement in a short summary in the business plan. Once again, the analysis statement doesn't have to be long and should cover only key points derived from the cash-flow statement.
The Balance Sheet
The last financial statement you'll need to develop is the balance sheet. Like the income and cash-flow statements, the balance sheet uses information from all of the financial models developed in earlier sections of the business plan; however, unlike the previous statements, the balance sheet is generated solely on an annual basis for the business plan and is, more or less, a summary of all the preceding financial information broken down into three areas:
To obtain financing for a new business, you may need to provide a projection of the balance sheet over the period of time the business plan covers. More importantly, you'll need to include a personal financial statement or balance sheet instead of one that describes the business. A personal balance sheet is generated in the same manner as one for a business.
As mentioned, the balance sheet is divided into three sections. The top portion of the balance sheet lists your company's assets. Assets are classified as current assets and long-term or fixed assets. Current assets are assets that will be converted to cash or will be used by the business in a year or less. Current assets include:
- Cash . The cash on hand at the time books are closed at the end of the fiscal year.
- Accounts receivable . The income derived from credit accounts. For the balance sheet, it's the total amount of income to be received that is logged into the books at the close of the fiscal year.
- Inventory . This is derived from the cost of goods table. It's the inventory of material used to manufacture a product not yet sold.
- Total current assets . The sum of cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and supplies.
Other assets that appear in the balance sheet are called long-term or fixed assets. They are called long-term because they are durable and will last more than one year. Examples of this type of asset include:
- Capital and plant . The book value of all capital equipment and property (if you own the land and building), less depreciation.
- Investment . All investments by the company that cannot be converted to cash in less than one year. For the most part, companies just starting out have not accumulated long-term investments.
- Miscellaneous assets . All other long-term assets that are not "capital and plant" or "investments."
- Total long-term assets . The sum of capital and plant, investments, and miscellaneous assets.
- Total assets . The sum of total current assets and total long-term assets.
After the assets are listed, you need to account for the liabilities of your business. Like assets, liabilities are classified as current or long-term. If the debts are due in one year or less, they are classified as a current liabilities. If they are due in more than one year, they are long-term liabilities. Examples of current liabilities are as follows:
- Accounts payable . All expenses derived from purchasing items from regular creditors on an open account, which are due and payable.
- Accrued liabilities . All expenses incurred by the business which are required for operation but have not been paid at the time the books are closed. These expenses are usually the company's overhead and salaries.
- Taxes . These are taxes that are still due and payable at the time the books are closed.
- Total current liabilities . The sum of accounts payable, accrued liabilities, and taxes.
Long-term liabilities include:
- Bonds payable . The total of all bonds at the end of the year that are due and payable over a period exceeding one year.
- Mortgage payable . Loans taken out for the purchase of real property that are repaid over a long-term period. The mortgage payable is that amount still due at the close of books for the year.
- Notes payable . The amount still owed on any long-term debts that will not be repaid during the current fiscal year.
- Total long-term liabilities . The sum of bonds payable, mortgage payable, and notes payable.
- Total liabilities . The sum of total current and long-term liabilities.
Once the liabilities have been listed, the final portion of the balance sheet-owner's equity-needs to be calculated. The amount attributed to owner's equity is the difference between total assets and total liabilities. The amount of equity the owner has in the business is an important yardstick used by investors when evaluating the company. Many times it determines the amount of capital they feel they can safely invest in the business.
In the business plan, you'll need to create an analysis statement for the balance sheet just as you need to do for the income and cash flow statements. The analysis of the balance sheet should be kept short and cover key points about the company.
Source: The Small Business Encyclopedia , Business Plans Made Easy, Start Your Own Business and Entrepreneur magazine.
Business Plan Guide
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- Lock 3 Things Your Business Idea Must Have to Succeed — as Proven By Famous Harvard Business School Startups
- This Couple Cashed in Their 401ks to Launch a Virtual Business — Here's How It Led to a 9-Figure Exit and Co-Owning 2 Professional Soccer Teams
- Lock The No. 1 State to Retire in Might Not Even Be on Your Radar, According to a New Report
- Lock 12 Books That Self-Made Millionaires Swear By
- Lock These Are the Highest-Paying Side Hustles for a Single Day of Work
- Use These 3 Steps to Find the Perfect Franchise Opportunity for You
Most Popular Red Arrow
Tiktok reportedly laid off a 'large percentage' of employees as the app's fate in the u.s. remains unclear.
Laid-off TikTok employees were notified Wednesday night through Thursday morning.
More People Are Exploring Entrepreneurship Because of This Unexpected Reason
More new business applications were filed in 2023 than in any other year so far.
Jack Dorsey Says 'the Closest Form of Global Consciousness' Used to Be Twitter — Now It's Something Else
Dorsey recently left Bluesky, an X rival he helped found.
Four Seasons Orlando Responds to Viral TikTok: 'There's Something Here For All Ages'
The video has amassed over 45.4 million views on TikTok.
63 Small Business Ideas to Start in 2024
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
8 Subtle Hints that People Don't Respect You — and How to Fix Them
While you have to earn respect, you don't have to deal with disrespect in the meantime.
Successfully copied link

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

What is a business plan? Definition, Purpose, and Types
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies , and financial projections. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.
As a business plan writer and consultant , I’ve crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse range of businesses. In this article, I’ll be sharing my wealth of experience about what a business plan is, its purpose, and the step-by-step process of creating one. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how to develop a robust business plan that can drive your business to success.
What is a business plan?
Purposes of a business plan, what are the essential components of a business plan, executive summary, business description or overview, product and price, competitive analysis, target market, marketing plan, financial plan, funding requirements, types of business plan, lean startup business plans, traditional business plans, how often should a business plan be reviewed and revised, what are the key elements of a lean startup business plan.
- What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?
A business plan is a roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. It’s a living document that you can update as your business grows and changes.
Looking for someone to write a business plan?
Find professional business plan writers for your business success.
These are the following purpose of business plan:
- Attract investors and lenders: If you’re seeking funding for your business , a business plan is a must-have. Investors and lenders want to see that you have a clear plan for how you’ll use their money to grow your business and generate revenue.
- Get organized and stay on track: Writing a business plan forces you to think through all aspects of your business, from your target market to your marketing strategy. This can help you identify any potential challenges and opportunities early on, so you can develop a plan to address them.
- Make better decisions: A business plan can help you make better decisions about your business by providing you with a framework to evaluate different options. For example, if you’re considering launching a new product, your business plan can help you assess the potential market demand, costs, and profitability.

The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan, even though it’s the last one you’ll write. It’s the first section that potential investors or lenders will read, and it may be the only one they read. The executive summary sets the stage for the rest of the document by introducing your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
The business description section of your business plan should introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way. It should include your business name, years in operation, key offerings, positioning statement, and core values (if applicable). You may also want to include a short history of your company.
In this section, the company should describe its products or services , including pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other relevant information could include production and manufacturing processes, patents, and proprietary technology.
Every industry has competitors, even if your business is the first of its kind or has the majority of the market share. In the competitive analysis section of your business plan, you’ll objectively assess the industry landscape to understand your business’s competitive position. A SWOT analysis is a structured way to organize this section.
Your target market section explains the core customers of your business and why they are your ideal customers. It should include demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic information about your target market.
Marketing plan describes how the company will attract and retain customers, including any planned advertising and marketing campaigns . It also describes how the company will distribute its products or services to consumers.
After outlining your goals, validating your business opportunity, and assessing the industry landscape, the team section of your business plan identifies who will be responsible for achieving your goals. Even if you don’t have your full team in place yet, investors will be impressed by your clear understanding of the roles that need to be filled.
In the financial plan section,established businesses should provide financial statements , balance sheets , and other financial data. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years, and may also request funding.
Since one goal of a business plan is to secure funding from investors , you should include the amount of funding you need, why you need it, and how long you need it for.
- Tip: Use bullet points and numbered lists to make your plan easy to read and scannable.
Access specialized business plan writing service now!
Business plans can come in many different formats, but they are often divided into two main types: traditional and lean startup. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) says that the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
Lean startup business plans are short (as short as one page) and focus on the most important elements. They are easy to create, but companies may need to provide more information if requested by investors or lenders.
Traditional business plans are longer and more detailed than lean startup business plans, which makes them more time-consuming to create but more persuasive to potential investors. Lean startup business plans are shorter and less detailed, but companies should be prepared to provide more information if requested.
Need Guidance with Your Business Plan?
Access 14 free business plan samples!
A business plan should be reviewed and revised at least annually, or more often if the business is experiencing significant changes. This is because the business landscape is constantly changing, and your business plan needs to reflect those changes in order to remain relevant and effective.
Here are some specific situations in which you should review and revise your business plan:
- You have launched a new product or service line.
- You have entered a new market.
- You have experienced significant changes in your customer base or competitive landscape.
- You have made changes to your management team or organizational structure.
- You have raised new funding.
A lean startup business plan is a short and simple way for a company to explain its business, especially if it is new and does not have a lot of information yet. It can include sections on the company’s value proposition, major activities and advantages, resources, partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?

- Unrealistic assumptions: Business plans are often based on assumptions about the market, the competition, and the company’s own capabilities. If these assumptions are unrealistic, the plan is doomed to fail.
- Lack of focus: A good business plan should be focused on a specific goal and how the company will achieve it. If the plan is too broad or tries to do too much, it is unlikely to be successful.
- Poor execution: Even the best business plan is useless if it is not executed properly. This means having the right team in place, the necessary resources, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Unforeseen challenges: Every business faces challenges that could not be predicted or planned for. These challenges can be anything from a natural disaster to a new competitor to a change in government regulations.
What are the benefits of having a business plan?
- It helps you to clarify your business goals and strategies.
- It can help you to attract investors and lenders.
- It can serve as a roadmap for your business as it grows and changes.
- It can help you to make better business decisions.
How to write a business plan?
There are many different ways to write a business plan, but most follow the same basic structure. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Executive summary.
- Company description.
- Management and organization description.
- Financial projections.
How to write a business plan step by step?
Start with an executive summary, then describe your business, analyze the market, outline your products or services, detail your marketing and sales strategies, introduce your team, and provide financial projections.
Why do I need a business plan for my startup?
A business plan helps define your startup’s direction, attract investors, secure funding, and make informed decisions crucial for success.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Key components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, products or services, marketing and sales strategy, management and team, financial projections, and funding requirements.
Can a business plan help secure funding for my business?
Yes, a well-crafted business plan demonstrates your business’s viability, the use of investment, and potential returns, making it a valuable tool for attracting investors and lenders.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

- Scroll to top
- / Sign Up
- HOW WE HELP CLIENTS
- schedule your conversation
Business Plan Roadmap: Building Your Path to Business Success
Published: 31 December, 2023
Social Share:

Table of Contents
In today’s fast-paced entrepreneurial landscape, a meticulously crafted business plan functions as the guiding star for your venture’s journey toward success. Whether you’re an experienced entrepreneur or a budding startup creator, possessing a comprehensive business plan is indispensable, serving as the key to securing funding, making well-informed decisions, and effectively navigating the ever-evolving business environment.
Within the confines of this article, we will embark on a comprehensive exploration of the art of crafting an engaging and impactful business plan . We shall dissect critical components, including in-depth market research, meticulous financial projections, savvy marketing strategies, and effective operational blueprints. Additionally, we will unveil a plethora of tips and best practices designed to elevate your business plan above the competition, rendering it a value proposition for those seeking to invest in or collaborate with your enterprise.
What is a Business Plan
A business plan definition is a written document that outlines the goals, strategies, and detailed operational and financial plans of a business. It serves as a roadmap for the business, providing a clear direction for its growth and development. A typical business plan includes information about the company’s mission and vision, its products or services, market analysis, competition, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, organizational structure, financial projections, and funding requirements. Business plans are commonly used to secure funding from investors or lenders, guide the company’s operations, and communicate its vision and strategy to stakeholders.

A conventional business plan typically divides into two primary segments:
- The Explanatory Segment: This portion encompasses written content that serves the business purpose of providing a detailed description of the business idea and/or the company. It covers elements such as the executive summary, company overview, market analysis, product or service particulars, marketing and sales strategies, organizational structure, operational blueprints, and funding needs.
- The Financial Segment: Within this section, you’ll discover financial data and projections, encompassing income statements, balance sheets, cash flow forecasts, and detailed information regarding financing prerequisites and potential sources. This segment offers a quantitative view of the business’s financial situation and future expectations.
Components of a Business Plan: What is Included in a Business Plan
Crafting a thorough and compelling business plan is a fundamental step for entrepreneurs and business leaders seeking to chart a successful course for their ventures. A well-structured business plan not only serves as a roadmap for your business’s growth but also communicates your vision, strategy, and potential to investors, partners, and stakeholders. The key components of a business plan make up a robust business plan, offering valuable insights and practical tips to help you create a document that inspires confidence and aligns your team with a shared vision. Each key element plays a critical role in constructing a business plan that not only secures financial support but also guides your organization toward sustainable success. Let’s delve deeper into these components, adding depth and clarity to your business plan ‘s narrative.
- Executive Summary: This should succinctly encapsulate the essence of your business plan . It should briefly touch on the market opportunity, your unique value proposition, revenue projections, funding requirements, and the overarching goals of the business.
- Company Description: Elaborate on your company’s history, including significant milestones and achievements. Clearly define your mission, vision, and values, providing insight into what drives the company’s culture and decisions.
- Market Analysis: Delve into the market’s nuances by discussing not only its size but also its growth rate, trends, and dynamics. Highlight specific target market segments, customer personas, and pain points that your business aims to address. Include a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis to showcase your understanding of the competitive landscape.
- Products or Services: Offer a detailed explanation of your offerings, emphasizing their key features and benefits. Describe how these offerings fulfill specific customer needs or solve problems, and explain any proprietary technology or intellectual property.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: Provide a comprehensive overview of your marketing and sales plans. Discuss your pricing strategy in depth, outlining how it aligns with market dynamics. Explain your distribution channels and marketing tactics, including digital and traditional methods.
- Organizational Structure: Present bios of key team members, underscoring their relevant experience, expertise, and roles within the organization. Include an organizational chart to illustrate reporting relationships and the structure’s scalability.
- Operational Plan: Go into detail about your daily operations, covering everything from production processes and supply chain management to facility requirements and technology utilization. Discuss quality control measures and scalability strategies.
- Financial Projections: Provide a thorough breakdown of financial forecasts, including monthly or quarterly projections for at least three to five years. Explain the assumptions behind these numbers, including factors such as market growth rates and pricing strategies. Highlight critical financial metrics like burn rate, customer acquisition costs, and return on investment.
- Funding Requirements: Specify the exact amount of capital you’re seeking, the purpose of the funds, and how the investment will be utilized to achieve specific milestones. Outline potential sources of funding, such as equity investment, loans, or grants. Clarify the expected terms and conditions.
- Appendix: In the appendix, include supplementary materials that reinforce your business plan’s credibility and depth. This can encompass market research reports, letters of intent, prototypes, patents, legal contracts, and any other relevant documentation that adds value to your case.
Your download is now available!
You can now access the complete Business Model Canvas Package, including a full presentation, related models and instructions for use.
The UNITE Business Model Canvas
Creating a business plan essential steps.
Creating a business plan is a crucial step in launching or growing a business. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you create an effective business plan :
1- Draft an Executive Summary:
- Write a concise overview of your business, including the mission, vision, and goals.
- Summarize the business concept, target market, and unique value proposition.
- Keep it brief but compelling to grab the reader’s attention.
2- Compose a Business Description:
- Provide detailed information about your business, industry, and the problem or need your product/service addresses.
- Explain your mission, vision, and core values.
- Describe the legal structure of your business (e.g., sole proprietorship, LLC, corporation).
3- Conduct a Market Analysis:
- Conduct thorough market research to understand your industry, target market, and competitors.
- Define your target audience and demonstrate a clear understanding of market trends.
- Conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats).
4- Outline Organization and Management:
- Outline the organizational structure of your business.
- Introduce key team members and their roles, highlighting their relevant experience.
- Provide an overview of your advisory board or external support.
5- Detail the Product or Service Line:
- Describe your products or services in detail.
- Highlight the features, benefits, and unique selling points.
- Explain how your offerings meet the needs of your target market.
6- Develop a Marketing and Sales Strategy:
- Develop a comprehensive marketing strategy to reach your target audience.
- Outline your sales process, distribution channels , and pricing strategy.
- Include a sales forecast and customer acquisition plan.
7- Specify Funding Request (if applicable):
- Specify the amount of funding you are seeking (if any) and how you plan to use it.
- Justify the funding request with clear financial projections and a solid business case.
8- Prepare Financial Projections:
- Prepare detailed financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Provide assumptions and methodologies used for financial forecasts.
- Demonstrate your business’s profitability and financial viability.
9- Include an Appendix:
- Include supplementary materials such as resumes, permits, contracts, market research, or any other relevant documents.
- Keep this section optional but use it to provide additional context.
10- Review and Revise:
- Review your business plan thoroughly for clarity, consistency, and completeness.
- Seek feedback from mentors, advisors, or potential investors.
- Revise the plan based on feedback and ensure it aligns with your business goals.
Remember, a business plan is a dynamic document that should be revisited and updated regularly to reflect changes in your business environment. It serves as a roadmap for your business and a valuable tool for communicating your vision to others.
Types of Business Plans
Startup business plan:.
A comprehensive document crafted by entrepreneurs to outline the vision, mission, target market, competition analysis, financial projections, and strategies for launching and operating a new business.
Feasibility Business Plan:
A plan designed to assess the viability of a business idea or project by analyzing market demand, potential challenges, financial feasibility, and overall sustainability before committing resources.

One-Page Business Plan:
A condensed version of a traditional business plan, focusing on key elements such as the business concept, target market, value proposition, marketing strategy, and financial projections—all presented on a single page.
What-If Business Plan:
A flexible and dynamic plan that explores various scenarios and outcomes based on changing factors or assumptions. It helps businesses anticipate challenges and adjust strategies accordingly.
Growth Business Plan:
Tailored for businesses aiming to expand, this plan outlines strategies for scaling operations, entering new markets, launching products or services, and includes financial projections to support growth initiatives.
Operations Business Plan:
Geared towards day-to-day activities, this plan details operational procedures, resource allocation, supply chain management, and other aspects essential for the smooth functioning of the business.
Strategic Business Plan:
A long-term plan outlining the organization’s mission, vision, core values, and strategic initiatives. It guides decision-making, sets priorities, and aligns the company toward achieving overarching objectives.
The purpose of a business plan
A business plan is not a static document with a limited shelf life; rather, it evolves alongside the company it represents. It serves as a dynamic tool that adapts to changing market conditions, emerging opportunities, and evolving strategic priorities. Here’s a closer look at its continuous relevance:
- Guiding the Business ( Business Concept/Business Idea and Strategy ) : A business plan serves as an internal guide that helps entrepreneurs and management teams set clear objectives, develop business strategies, and make informed decisions. It provides a framework for prioritizing tasks, allocating resources, and monitoring progress toward achieving business goals.
- Securing Financing: One of the primary reasons for creating a business plan is to secure financing from lenders, investors, or banks. A well-prepared plan presents a compelling case for why the business is a viable and profitable investment. It includes financial projections, market research, and a clear explanation of how the funds will be used to achieve growth.
- Attracting Investors: For startups and early-stage companies, attracting equity investors is often crucial for rapid growth. A comprehensive business plan not only showcases the business opportunity but also outlines how investors can potentially realize significant returns on their investment. It highlights the company’s unique value proposition and competitive advantage.
- Setting Goals and Objectives: Business plan s articulate both short-term and long-term objectives for the company. Specific, measurable, and time-bound goals are essential for motivating employees, aligning efforts, and tracking progress. Objectives can encompass revenue targets, market share goals, expansion plans, and more.
- Managing Operations: Business plans include detailed operational plans, covering aspects such as production processes, supply chain management, inventory control, quality assurance, and logistics. These operational details ensure that the business runs smoothly and efficiently.
- Market Analysis: Comprehensive market research within the business plan helps the company understand its target market, customer demographics, and competitive landscape. This knowledge enables the business to adapt to changing market conditions and identify opportunities for growth, product development, or market expansion.
- Communicating the Vision: A well-crafted business plan communicates the company’s mission, vision, and values to both internal and external stakeholders. This clarity fosters a shared sense of purpose among employees and resonates with customers and partners.
- Risk Management: Business plans identify potential risks and challenges that the company may encounter. By acknowledging these risks upfront, the plan can outline strategies for risk mitigation or contingency plans. This proactive approach helps the business better navigate unforeseen challenges.
- Measuring Progress: A business plan serves as a benchmark for assessing the company’s performance and growth. By comparing actual results to the plan’s projections, the business can identify areas where it is excelling and areas that require adjustment. Regularly measuring progress is crucial for making data-driven decisions.
- Exit Strategy: In some cases, especially for entrepreneurs and investors, a business plan includes an exit strategy. This strategy outlines how the business owners plan to realize their investment, whether through selling the company, going public, or transitioning leadership to others.
- Competitive Adaptation: In the face of a constantly changing competitive landscape, a well-maintained business plan allows a company to regularly assess its competitive position. It aids in identifying emerging competitors, market shifts, and areas where the business can gain a competitive edge.
- Performance Measurement: By providing a baseline for projected financials and key performance indicators (KPIs), a business plan becomes a tool for measuring actual performance against expectations. This ongoing evaluation enables the organization to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
- Resource Allocation: As a company grows, it often requires additional resources such as capital, personnel, or technology. The business plan assists in rationalizing and justifying resource allocation decisions to support expansion or address operational challenges.
- Innovation and Adaptation: In today’s rapidly changing business environment, adaptation and innovation are essential. A business plan encourages a culture of adaptability by fostering discussions on new opportunities and strategies for staying ahead of industry trends.
- External Engagement: Externally, the business plan remains a valuable tool for engaging with investors, partners, lenders, and other stakeholders. It provides a transparent and comprehensive view of the company’s past performance and future potential.
Important External Tasks of a Business Plan
A business plan holds significance beyond its internal utility, as it acts as the company’s calling card in external contexts. Primarily, it serves as a persuasive tool for potential investors, bolstering the chances of securing essential financing, whether during startup or later stages for marketing initiatives or product development. Additionally, a well-crafted business plan proves valuable in negotiation discussions with potential key partners and regulatory bodies, enhancing the stability of current and future business relationships with customers and suppliers alike.
Here are some significant external tasks associated with a business plan:
- Securing Financial Support: One of the primary external objectives of a business plan is to attract external financing from investors or lenders. A well-prepared plan should clearly communicate the company’s financial requirements and how those funds will be utilized to achieve its objectives.
- Presenting to Investors: If you are seeking investment from angel investors, venture capitalists, or private equity firms, you must effectively present your business plan . This entails pitching your business to potential investors, highlighting key aspects of your plan, and addressing their inquiries and concerns.
- Applying for Financing or Grants: If you intend to secure loans or grants to fund your business, your business plan will be a crucial component of your application. It should demonstrate your capacity to repay loans or meet grant criteria, as well as how the funds will drive growth.
- Negotiating Partnerships and Collaborations: When pursuing partnerships, joint ventures, or alliances with other businesses, a business plan can outline the strategic advantages and potential outcomes of the collaboration. This is vital for persuading potential partners of the value of working together.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: Depending on your industry and location, you may need to submit your business plan to regulatory agencies for approval or compliance. This is particularly common in sectors like healthcare, finance, and energy.
- Obtaining Licenses and Permits: If your business requires specific licenses or permits to operate, your business plan may be requested during the application process to demonstrate your readiness and compliance with regulations.
- Facilitating Mergers and Acquisitions: In mergers or acquisitions, both the acquiring and target companies may need to provide business plans to potential investors or lenders involved in the transaction. This aids in evaluating the financial viability and strategic fit of the merger or acquisition.
- Attracting Strategic Partners: In addition to traditional investors, you may seek to attract strategic partners who can offer resources, expertise, or distribution channels. You r business plan should compellingly illustrate why potential partners should collaborate with your company.
- Preparing for an IPO (Initial Public Offering): If your long-term strategy includes taking your company public, a comprehensive business plan is essential to attract public market investors. It must provide a detailed view of your company’s financial health, growth potential, and market position.
- Undergoing Due Diligence: When external parties consider investing in or partnering with your company, they often conduct due diligence. Your business plan should be precise and comprehensive to withstand scrutiny during this process.
When is a Business Plan Needed
When starting a new business, it makes sense to write a business plan . A strong business concept helps you find investors and convince big business figures, investors, or banks of your business idea.
In addition, a business plan forces a start-up to confront the strengths but also weaknesses of its business idea. However, an already existing company can equally benefit from a business plan. Many companies often lack a clearly recognizable strategy or guidelines against which success can be measured.
A business plan also leads to more transparency in entrepreneurial decisions and is necessary for an already existing company when raising outside capital and investors. An increasing number of investors and capital providers demand the submission of such a plan, thus making a strong business concept so important.
- Startup Phase : A business plan is essential when starting a new venture as it helps define your business concept, target market, and competitive strategy. It outlines your initial funding requirements, revenue projections, and expected milestones, providing a roadmap for the early stages of your business.
- Securing Financing : Whether you’re seeking a bank loan, angel investment, venture capital, or crowdfunding, a detailed business plan is a prerequisite. It should include financial forecasts, an analysis of your industry and competitors, and a clear description of how the funds will be used to grow the business.
- Strategic Planning : Regularly updating your business plan is crucial for strategic planning . It allows you to assess your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis) and adjust your strategies accordingly. It provides a long-term vision and helps align the organization’s efforts toward common goals.
- New Product or Service Launch : Before launching a new offering, a business plan helps you research the market, understand underserved customer needs, and determine the product’s unique selling points. It outlines your marketing and sales strategy, pricing structure, and expected return on investment.
- Mergers and Acquisitions : In mergers and acquisitions (M&A) transactions, a business plan is used to evaluate the financial viability and strategic fit of the deal. It provides insights into the target company’s operations, revenue streams , and potential synergies with the acquiring company.
- Partnerships and Alliances : When exploring collaborations with other businesses, a business plan outlines the mutual benefits and objectives of the partnership. It clarifies roles and responsibilities, risk-sharing arrangements, and how the partnership aligns with each party’s strategic goals.
- Regulatory Compliance : Certain industries, like healthcare, finance, and energy, require businesses to submit comprehensive business plans to regulatory authorities. These plans demonstrate compliance with industry-specific regulations and provide transparency in operations.
- Licensing and Permits : When applying for licenses or permits, particularly in regulated industries such as food service, healthcare, or construction, a business plan may be necessary to prove that your operations meet safety, health, and environmental standards.
- IPO (Initial Public Offering) : Making a company public is a complex process. A thorough business plan is crucial to attract public investors. It should provide historical financial performance, future growth prospects, and a clear value proposition for potential shareholders.
- Crisis Management : In times of financial distress or operational challenges, businesses may develop a crisis management or turnaround plan. This specialized business plan outlines the steps needed to stabilize the company’s finances, restructure operations, and restore profitability.
Example of Business Plan Structure
Generally, there are no fixed guidelines as to how a business plan should be structured. Business concepts heavily depend on the recipient of the business plan and the orientation and structure of the company. The following bullet points are therefore only to be understood as basic building blocks that must be adapted to the individual situation.
1. Business Concept/Business Idea and Strategy:
- Illustrate your business concept, including the idea and methods for successful implementation.
- Include a timeline for implementing the concept.
- Optionally, provide information about your company and headquarters.
2. Company Description:
- Provide detailed information about your company, including its name, location, legal structure, and history.
- Explain your business’s purpose and the problems it aims to solve.
- Describe your target market and your business’s role within it.
3. Target Market:
- Market volume and potential.
- Growth potential.
- Barriers to entry and market restrictions.
- Supplier positioning.
- Relevant laws and regulations.
- Competitor analysis (strengths, weaknesses, product range).
- Identifying potential customers.
4- Operational Plan:
- Describe your business’s day-to-day operations, including location, facilities, equipment, and technology.
- Explain your supply chain, production processes, and quality control.
- Address any regulatory or compliance requirements.
5. Products and Services:
- Describe your products or services, highlighting how they differentiate from competitors.
- Unique Selling Proposition.
- Customer Benefits.
- Competitive Advantages.
- Innovation or optimization of existing products.
- Patent or property rights.
6. Marketing and Sales Planning:
- Outline your marketing strategy and timetable.
- Specify market entry plans.
- Set company goals related to market leadership, market share, revenue, and brand awareness.
- Discuss sales policy, pricing policy, and communication policy & advertising.
- Address sales methods, future developments, and pricing strategy justification.
7. Management, Employees, and Organization:
- Highlight management skills, qualifications, and key team members.
- Emphasize industry knowledge, social skills, previous successes, and professional experience.
- Mention personnel development strategies.
- Describe the organizational structure , focusing on procurement, development, production, sales, and administration.
8. Opportunities and Risks:
- In the ‘Opportunities’ section, showcase the potential of your business idea and the conditions for exploiting that potential.
- Address risks comprehensively, demonstrating a detailed and critical approach.
- Include potential risk scenarios and proposed solutions.
9. Financial Planning:
- Present concrete financial figures derived from previous analyses and plans.
- Profit Planning: Include a profit and loss statement (P&L).
- Balance Sheet: Provide an overview of assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Liquidity Plan: Compare expenditures with available funds.
10. Appendix:
- Include necessary documents like commercial register excerpts, business registrations, shareholder agreements, and legal forms.
- Attach CVs and references of key team members.
- Include relevant financial spreadsheets, patents, permits, licenses, brochures, leaflets, and organizational charts or graphs.
Reasons for Business Plan Failures
- Lack of Market Research: Failing to thoroughly understand the target market and its needs can lead to products or services that don’t resonate with customers.
- Inflexibility: A rigid plan that doesn’t adapt to changing market conditions or feedback from customers can become obsolete quickly.
- Overly Optimistic Projections: Unrealistic financial projections can mislead investors and hinder the business’s ability to meet expectations.
- Poor Execution: Even the best plan will fail without proper execution. A lack of skilled team members, resources, or a clear execution strategy can doom a business.
- Ignoring Competition: Ignoring or underestimating competitors can lead to a business being unprepared for market competition.
- Insufficient Funding: Underestimating the capital required to launch and sustain the business can lead to financial troubles.
- Inadequate Marketing: Without effective marketing, even great products or services may go unnoticed by potential customers.
- Ignoring Customer Feedback: Not listening to customer feedback and adjusting the business accordingly can result in products or services that don’t meet market needs.
Connecting The Dots: Importance of Business Model Canvas in Business Plan
Integrating the Business Model Canvas (BMC) into a traditional business plan is a pivotal process in crafting a comprehensive and highly effective business strategy . The Business Model Canvas , with its visual and succinct approach, offers a distinctive viewpoint on your business model. It functions as a complementary tool to the in-depth components of a traditional plan, strengthening your strategic capabilities. You can download it now.
The synergy between these two strategic instruments not only facilitates communication but also empowers you to analyze and adjust your business strategy with precision, ultimately fostering a pathway to success. In the following discussion, we delve into the significance of bridging the gap between these two potent tools within the domain of business planning. Here’s why the Business Model Canvas is essential within the context of a business plan:
- Visual Representation: The Business Model Canvas provides a visual framework that allows you to quickly grasp and convey the fundamental elements of your business model. This visual clarity is especially valuable when presenting your business concept to potential investors, partners, or team members.
- Concise Overview: While a traditional business plan can be lengthy and detailed, the BMC offers a concise summary of key components, including customer segments, value propositions, channels, revenue streams, and cost structures . It distills complex business concepts into a simplified format, making it easier to communicate and understand.
- Iterative Planning: The BMC encourages an iterative approach to business strategic planning . It enables you to experiment with different business model hypotheses and make adjustments as you gather feedback and insights. This agility is vital, especially for startups and businesses in rapidly evolving markets.
- Focus on Value: The Business Model Canvas places a strong emphasis on understanding customer needs and value creation . It prompts you to identify your unique value propositions and how they address customer pain points, aligning your strategy with customer-centric principles.
- Holistic View: By using the BMC, you’re prompted to consider all aspects of your business model, from customer acquisition to revenue generation and cost management. This holistic perspective helps identify potential gaps, dependencies, and opportunities that might be overlooked in a traditional plan.
- Alignment and Coordination: The BMC fosters alignment among team members and stakeholders. It’s a collaborative tool that encourages discussions about the business model, ensuring that everyone shares a common understanding and vision. This alignment is critical for execution.
- Integration with Traditional Plan: While the BMC is an excellent starting point, it can be seamlessly integrated into a traditional business plan. The insights and clarity gained from the BMC can inform and enrich the sections of the plan related to products/services, target market, marketing strategy, and financial projections.
- Efficiency: The BMC saves time and resources, particularly in the early stages of planning when you’re exploring different business model scenarios. It allows you to focus on the most critical aspects of your strategy before diving into the details.
- Adaptability: In a rapidly changing business environment, having a flexible and adaptable business model is essential. The BMC’s modular structure makes it easier to pivot or adapt your strategy in response to market shifts, competitive pressures, or emerging opportunities.
In summary, a business plan is a multifaceted and indispensable tool for businesses at every stage of their journey. It serves as a compass, guiding strategic decisions, securing essential financing, and attracting potential investors. Its ongoing relevance is a testament to its adaptability, enabling businesses to measure performance, allocate resources, and manage risks effectively. Beyond its practical utility, a business plan is a communication tool, conveying a company’s vision and objectives to both internal teams and external stakeholders. It is a dynamic and ever-evolving document that empowers businesses to navigate uncertainties, foster innovation, and drive sustainable growth, making it an indispensable companion in the pursuit of business success.
Frequently Asked Questions
1- how does a business plan relate to business strategy.
A business plan is closely intertwined with a company’s business strategy. The plan lays out the specific actions and tactics required to achieve the strategic goals of the business. It provides a roadmap for implementing the chosen strategy, outlining how resources will be allocated, what markets will be targeted, and how the business will position itself in the competitive landscape.
2- Is a business plan necessary if I already have a solid business strategy?
Yes, a business plan is still essential, even if you have a well-defined strategy. It serves as the detailed execution plan for your strategy, providing clarity on how you will achieve your strategic objectives. It also helps you anticipate challenges, manage risks, and secure financing or investments by demonstrating the viability of your strategy.
3- Can I use the Business Model Canvas in place of a business plan for a startup?
While the Business Model Canvas is an excellent tool for conceptualizing and validating your business model, it is often not a substitute for a comprehensive business plan , especially when seeking financing or investments. Startups may begin with Canvas to clarify their model but should eventually develop a full business plan to provide in-depth financial projections, market analysis, and operational details.
4- How often should I update my business plan to align with my evolving strategy?
It’s advisable to review and update your business plan regularly, typically at least once a year. However, major changes in your business environment, such as shifts in market conditions or strategic pivots, may require more frequent updates. Keeping your plan current ensures it remains a relevant and effective tool for guiding your business.
Related Posts
Business level strategy: examples & types for business strategy success.
In strategic management, businesses use a variety of approaches to craft a1
50 Innovation Examples: Exciting Innovative Ideas in Business
In the Business environment, strategic innovation has taken centre stage as a1
Innovation Strategy: Developing Innovative Strategies in Business
Innovation has become an imperative for organizations worldwide, yet the multitude of1
Minimum Viable Product (MVP) Examples and Definition
The MVP or Minimum Viable Product approach is an idea that was1
Recent Posts

Examples and Types of Effective Functional Level Strategy for Business Support
A key objective of any business strategy is to improve operational efficiencies...

The Three Levels of Strategy: Corporate Strategy, Business Strategy, and Functional Strategy
Understanding the intricate levels of strategy is crucial for any organization aiming...

Register For Your FREEE Innovation Show Seat Now!
Learn how to overcome the 90% failure rate in innovation from a master innovator and best-selling author.

Expert tactics to boost your innovation odds.
Insights on capturing customer needs for innovation.
Tools that turn your ideas into triumphs.
First name *
Last name *
Professional E-mail *
I want to be kept up-to-date and accept the privacy statement *
By signing up, you agree to receive news and accept the privacy statement (mandatory)
Already have an account? Log in
- FREE LIVE TRAINING
How To Overcome The 90% Failure Rate in Innovation
Learn the winning formula from over 80+ successful innovation projects
SAVE MY FREE SPOT NOW

Learn how to overcome the 90% failure rate in innovation from a master innovator & bestselling author!
Your e-mail address: * Your first name: *

One Last Step..
Help us better understand the UNITE community
Free guide to improve your innovation success rate*
Our 35-page comprehensive innovation guide covers the key areas why innovation fails. While it cannot cover all the solutions (that would take books to fill), it provides you with a convenient starting point for your analysis and provides further resources and links to the corresponding UNITE models, ultimately allowing you to work towards a doubling and tripling your chances of success.

Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the entire Internet!
LOG IN VIA E-MAIL
Forgot password?
New to Digital Leadership? Create your account
Get access to the UNITE Models now!
Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the internet!
Choose Your Password *
Confirm Your Password *
Verify your e-mail address now by entering the 6-digit code we’ve just sent to your inbox
Don't receive Code? Resend code
Country * Please Select Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin (Dahomey) Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Brunswick and Lüneburg Bhutan Bulgaria Burkina Faso (Upper Volta) Burundi Cabo Verde Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cayman Islands Central African Republic Central American Federation Chad Chile China Colombia Comoros Congo Free State Costa Rica Cote d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast) Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czechia Democratic Republic of the Congo Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Eswatini Ethiopia Fiji Finland France Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Grand Duchy of Tuscany Greece Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Holy See Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nassau Nauru Nepal Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria North Macedonia Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papal States Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Piedmont-Sardinia Poland Portugal Qatar Republic of Congo Republic of Korea (South Korea) Republic of the Congo Romania Russia Rwanda Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Schaumburg-Lippe Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Sweden Switzerland State of Palestine Syria Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United States United Arab Emirates United Kingdom Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vietnam Württemberg Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe Industry * Please Select Automotive, mobilty & transport Financial Services Chemical & agriculture Construction & Real Estate Consulting Education Energy Banking, insurance & FS FMCG Food Gov / Public Industry Health & lifestyle Logistics, Aero & Shipping Media & Entertainment Natural resources & mining Pharma & Biotech Retail & trade Tech & E-Commerce Telco Tourism design Information technology & services Management consulting Retail Pharmaceuticals International trade & development Professional training & coaching luxury goods & jewelry Automotive Insurance Mechanical or industrial engineering Company Size * XS - 1-10 S - 10-100 M - 100-1000 L - 1000-5000 XL - > 5000
Seniority * Please Select Junior Consultant Senior Consultant Manager Senior Manager Director VP SVP Partner CXO Board Member
Areas of interest * Innovation Digital Transformation Culture & Organization IT Strategy & Bus. Alignment Customer Experience
Editable UNITE models (PowerPoint) included
Most of our models and canvases are designed to be applied!
To help you personalize them to your exact business requirements, you can download fully editable versions of the UNITE models available (PowerPoint format)!
They are straightforward to work with, and you can directly incorporate them into your presentations as you need…thus saving countless hours of replication!
PS: did you know that you are also getting hi-res print-ready versions for your workshops?
Monthly live webinars
Each month we host our exclusive, invitation-only webinar series where one of our industry-leading experts updates our members on the latest news, progress and concepts around business strategy, innovation and digital transformation, as well as other related topics.
You will receive the book in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
Bi-weekly live group Q&A sessions
These sessions are your opportunity to bring any questions or challenges you’re facing and receive expert guidance on the spot.
Come and be a part of engaging discussions where your unique concerns are heard and addressed.
1x personal coaching session / month
If you are occasionally looking for a sparring partner or you need limited support, then this option will be ideal for you. Coaching sessions are 1-2 hours where we can discuss any challenge or opportunity you are currently facing.
If you need a few more hours outside of this provision, then these could be billed transparently.
Unlimited video call support! – it’s like always making the right decision!
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. Because we typically find that the occasional hour just doesn’t cut it – particularly if you and your team are in the midst of a large and complex project.
Your time with Stefan is therefore unlimited (fair usage applies) – in his function as coach and sparring partner. That does mean that you will still have to do the work – we cannot take that off you, unless you hire us as consultants. But you will get valuable strategic insight and direction to make sure you are always focusing your efforts where they will lead to the best results.
One personal coaching session / month + unlimited support via e-mail & WhatsApp
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. If you generally know what you are doing but want a sparring partner to frequently raise questions to, this is the perfect choice!
In addition to your monthly 1-1 live coaching sessions with Stefan, you will also get unlimited support from him via email and WhatsApp messaging (fair usage applies). This not only allows you to get valuable strategic direction in your calls, but also gives you instant access to expert help as you work through your plans each month.
The fact that support is text-based means that we can speed up our responses to you while keeping the overall cost of support down.
Welcome gift of our book “How to Create Innovation” (digital + physical editions)*
As a welcome gift, you will receive the both the digital and physical version of our book “How to Create Innovation”, which covers numerous relevant resources and provides additional deep dives into our UNITE models and concepts.
The print version will be shipped out to you on sign-up. The digital version will be emailed to you, and comes in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
1x major workshop or 2x smaller workshops / month
1x major or 2x smaller workshops based on the UNITE models.
- Topics covered: almost any challenge under the header of #strategy, #innovation or #transformation, leveraging the UNITE models.
- Hands-On Learning: solve your challenges while learning the practical application of the UNITE models and walk away with concrete plans and tools to take your next steps.
- Industry thought leadership: facilitated by Stefan, the founder of Digital Leadership and the main author of the UNITE models, ensuring top-tier guidance and knowledge sharing.
- Collaborative approach: engage in interactive sessions that foster collaboration, idea exchange, and real-time problem-solving among peers and industry leaders.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular workshops ensure ongoing development in your organization staying ahead of industry trends and customer needs.
Access all of our UNITE models, (incl. editable & print versions)
All of our Professional plans offer full access to the following:
- 6x UNITE model package downloads are included per month, if you need something in addition to these however, please let us know!
- Hi-res, print-ready versions you can use in your workshops
- Fully editable PowerPoint versions where applicable – personalize to your needs.
- Exclusive access to our vault of never-before-published strategic materials. We have much more to share – a lot of our concepts have never been published!
Exclusive access to our private UNITE community (upcoming)
We are currently in the process of launching our brand new community., we are designing our community to specifically help you:.
- Get answers to questions (“How do I …”)
- Share leading practices & knowledge
- Jointly develop new models
- Network amongst a highly qualified group of peers
Please, select the reason
Cancelling your plan will deactivate your plan after the current billing period ends. You will not be charged further, but also won’t be able to access [exclusive features/services].
- Cost-related issues
- Unsatisfied with the service
- Features I need are missing
- Switching to a different service
- Other (Please specify)
Book Your Initial Blueprint Session Now
Simply fill out the below form and book in a time for our initial session that works for you. This initial session is free, no strings attached, and is where we can discuss your Blueprint needs more in-depth before moving forward.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher
Founder of digital leadership.
Adam D. Wisniewski
Partner for it strategy & business alignment.

Get in touch with Digital Leadership
Speak to our team today to find the best solution for your business to grow and scale.
We are here to support you across the entire lifecycle in all topics related to #digital, #innovation, #transformation and #marketing!

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher Founder of Digital Leadership
Contact Us!
Contact form, contact details, book a call.
Title, first name & last name * Email address * Phone number Please let us know how we can best support you! *
By clicking “Send”, I agree to Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
Let’s have a conversation!
“Please be invited to reach out! We are happy to help and look forward to a first meeting!”
+41 (0) 44 562 42 24
Schedule Your Call With Our Team
Find a time on our calender that best suits you !

Founder and CEO of Digital Leadership
SCHEDULE YOUR INITIAL CALL
A Quick Survey!
What is the main challenge you're currently facing in your business?
You Want To Drive Change?
Let’s find the best solution for your business to grow and scale sustainably!
Let’s kick start it!
We will uncover your current business situation and goals and provide you with a bespoke solution that helps you drastically grow your business working with us.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, M.B.A.
Feedback about our consulting that we are proud of
Read the reviews and make sure that this is not a waste of time, but a super effective tool.
You want to drive change?
Schedule your free business assessment call with our founder.
On this call, we will uncover your current business situation and goals and talk about how to drive change and solve your need.
Choose the meeting type that applies to your needs and schedule a time to meet with someone from our team. We look forward to speaking with you soon!
Thanks, We’ve Received Your Updated Details

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment Call With Adam D. Wisniewski
Welcome to our scheduling page.

Let’s Design your Customer Experience Blueprint !
In a uniquely designed 60 or 90 minute session* , we will …
- > identify where to start with near-certainty
- > define what approach it takes to create success in your organization
Based on the Blueprinting session, you will receive a tailored blueprint that aligns with your objectives, vision and goals, ensuring that your initiative is a success from start to finish.

In this session, you will be working together with Patrick Zimmermann, Associate Partner for Customer Experience

Let’s Design your Culture & Org-Change Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Dr. Andreas Rein, Partner at Digital Leadership for Culture & Org Change
Let’s Design your Innovation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Sascha Martini, Partner at Digital Leadership for Innovation and Digital Transformation
Let’s Design your Transformation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, Founder of Digital Leadership Stefan is a global thought leader in the innovation space
Let’s Design your IT Strategy & Business Alignment Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Adam D. Wisniewski, Partner for IT Strategy & Business Alignment

Patrick Zimmermann

Sascha Martini

Dr. Andreas Rein
Write a personalized review! Log in
Create Review


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.4: Chapter 4 – Initial Business Plan Draft
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 21278

- Lee A. Swanson
- University of Saskatchewan
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to
- Develop a comprehensive business plan draft
This chapter describes an approach to writing your draft business plan. It also outlines the elements of a comprehensive business plan that can be used as a template for starting your business plan.

Figure 7 – Initial Business Plan Draft (Illustration by Lee A. Swanson)
Effective Business Plans
Effective business plans
- Provide statements that are backed by evidence or data
- Include context and references with every table, figure, or illustration
- Include relevant, clear, concise tables and financial information, and exclude unnecessary material
- Present timelines for distinct purposes
- Use clear sections customized to the particular business or its environment rather than generic sections
Writing the Draft Business Plan
Although there are various ways to approach the task of writing a draft business plan, one effective approach is to do the following:
- This will provide you with a template for the information needed for your plan.
- You can copy and paste the results of your essential initial research into the sections of your business plan template where you believe that they can be used to support or justify the strategies and other decisions you will later describe in those sections. Of course, you can later move those parts of your environmental scan as needed as you develop your plan. In general, this strategy results in a stronger business plan .
- Completing this step will give you the satisfaction of seeing some of your work so far taking shape in the form of a business plan.
- Also, inserting the results from your environmental scan into the relevant sections of your plan should later provide you with the stimulus and support you will need to develop solid, realistic, evidence-based strategies and decisions for those sections.
- Incorporate your business model into your new business plan template. As there is no section in a business plan in which you specifically describe your business model, you will need to incorporate your business model elements into appropriate sections of your plan.
- You will normally include both information that you got from particular sources and information based on an assumption you made (and that you might intend to replace later with more accurate information from valid sources).
Follow these practices as you develop your plan:
- When you do this, you help establish your credibility as a business plan writer, and your business plan’s credibility. It also might save you time later when you discover that you need to add a similar item along with its cost to your list.
- Note: Do not reinvent the wheel by “inventing” your own method to reference your sources and do not use multiple methods. Use one (and only one) proper and well-established referencing method, like APA. This will improve the degree of professionalism of your plan.
- Note: if you are an expert source on something—maybe you are a construction expert that business plan readers will trust to do estimates on building costs—you should establish your credentials and clearly indicate when some of the information in your plan is based on your own expert knowledge.
- When you flag your assumptions in this way, you can quickly and easily see what information needs to be replaced with sourced information before you finalize your business plan.
- Projecting realistic sales can be difficult, but setting up a method for doing so early gives business plan writers a significant start toward completing their business plan. A well-developed sales model that takes advantage of the powers of electronic spreadsheets gives business plan writers the opportunity to relatively quickly and easily make necessary changes to their assumptions and overall estimates when needed.
- When you use the schedules provided on the spreadsheet templates, and any others that you add, you will be well on your way to developing the financial component of your business plan.
General Business Plan Format
Letter of transmittal.
A letter of transmittal is similar to the cover letter of a resume. The letter of transmittal should be tailored to the reader, clearly identifying the customized ask of the potential investor or lender. It should be short and succinct, delineating the ask (i.e. funding, specialized recruiting, purchasing a product or service, obtaining advice, etc.) within a few paragraphs. It should not summarize the business plan, as that is the job of the executive summary.
- Includes nice, catchy, professional, appropriate graphics to make it appealing for targeted readers
Executive Summary
- Can be longer than normal executive summaries—up to three pages
- Written after remainder of plan is complete
- Includes information relevant to targeted readers as this is the place where they are most likely to form their first impressions of the business idea and decide whether they wish to read the rest of the plan
Table of Contents
List of tables.
- References every table, figure, and appendix within the text of the plan so the relevance of each of these elements is clear.
List of Figures
Introduction.
- Indicates the purpose for the plan
- Appeals to targeted readers
Business Idea
- May include description of history behind the idea and the evolution of the business concept if relevant
Value Proposition
- Explains how your business idea solves a problem for your expected customers or otherwise should make them want to purchase your product or service instead of a competitor’s
- Outlines what you intend for the venture to be
- Inspires all members of the organization
- Helps stakeholders aspire to achieve greater things through the venture because of the general direction provided through the vision statement
After articulating a good vision, the business plan writer should consider what achieving the vision looks like. Many business plan writers write their vision and leave it at that. The problem with this approach is that they often then do not take the necessary steps to illustrate how the strategies they outline in their plan will move them toward achieving their vision. If they make this mistake, their strategies might indicate that they are fulfilling their current mission, but are not taking steps to move beyond that.
Vision statements should be clear with context throughout the business plan. For example, if the goal is to be the premier business operating in that industry in Saskatchewan, does that mean you have one location and are considered the best at what you do it even though you only have a small corner of the market, or does it mean that you have many locations across the province and enjoy a large market share?
- Should be very brief—a few sentences or a short paragraph
- Indicates what your organization does and why it exists—may describe the business strategy and philosophy
- Consists of five to ten short statements indicating the important values that will guide everything the business will do
- Outlines the personal commitments members of the organization must make, and what they should consider to be important
- Defines how people behave and interact with each other
- Should be reflected in all of the decisions outlined in the business plan, from hiring to promotions to location choices
- Helps the reader understand the type of culture and operating environment this business intends to develop
Major Goals
- Describes the major organizational goals
- Specific, Measurable, Action oriented, Realistic, and Timely [SMART]
- Realistic, Understandable, Measureable, Believable, and Achievable [RUMBA]
- Aligns with everything in plan
- Written, or re-written as the second last thing you do before finalizing your business plan by proofreading, polishing, and printing it (writing the Executive Summary is the final thing you should write)
Operating Environment
Trend analysis.
- However, consider whether this is the right place for this analysis: it may be better positioned, for example, in the Financial Plan section to provide context to the analysis of the critical success factors, or in the Marketing Plan to help the reader understand the basis for the sales projections.
Industry Analysis
- Includes an analysis of the industry in which this business will operate
- As above, consider whether this is the right place for this analysis: it may be better placed, for example, in the Marketing Plan to enhance the competitor analysis, or in the Financial plan to provide context to the industry standard ratios in the Investment Analysis section.
Of course, your trend analysis will also include a market-level analysis (using a set of questions, like those listed in Chapter 2) and a firm-level analysis (using tools like a SWOT Analysis / TOWS Matrix, various forms of financial analyses, a founder fit analysis, and so on), but those analyses are usually best placed in other sections of your plan to support the strategies and decisions you present there. The market-level analysis will inevitably fit in the Marketing Plan section, but the firm-level analysis might be spread across some or all of the Operating Plan, Human Resources Plan, Marketing Plan, and Financial Plan sections.
Operations Plan
- Given these constraints, what is your operating capacity (in terms of production, sales, etc.)?
- What is the work flow plan for your operation?
- What work will your company do and what work will you outsource?
Operations Timeline
- When will you make the preparations, such as registering the business name and purchasing equipment, to start the venture?
- When will you begin operations and make your first sales?
- When will other milestone events occur such as moving operations to a larger facility, offering a new product line, hiring new key employees, and beginning to sell products internationally?
- Sometimes it is useful to include a graphical timeline showing when these milestone events have occurred and are expected to occur.
Business Structure and other Set-up Elements
- Sole Proprietorship
- Partnership
- Limited Partnership
- Corporation
- Cooperative
Note: Your financial statements, risk management strategy, and other elements of your plan are affected by the type of legal structure you choose for your business. For example, all partnerships should have a clear agreement outlining the duties, expectations, and compensation of all partners as well as the process of dissolution. Spreadsheet templates are formatted for corporations and will need to be formatted for other forms of businesses.
- Zoning, equipment prices, suppliers, etc.
- Leasing terms, leasehold improvements, signage, pay deposits, etc.
- Getting business license, permits, etc.
- Setting up banking arrangements
- Setting up legal and accounting systems (or professionals)
- Ordering equipment, locks and keys, furniture, etc.
- Recruiting employees, setting up the payroll system and benefit programs, etc.
- Training employees
- Testing the products/services that will be offered
- Testing the systems for supply, sales, delivery, and other functions
- Creating graphics, logos, promotional methods, etc.
- Ordering business cards, letter head, etc.
- Setting up supplier agreements and outlining why those sellers are preferred
- Buying inventory, insurance, etc.
- Revising business plan
- And many more things, including, when possible, attracting purchased orders in advance of start-up through personal selling (by the owner, a paid sales force, independent representatives, or by selling through brokers wholesalers, catalogue houses, retailers), a promotional campaign, or other means
Note: As part of your business set-up, you need to determine what kinds of control systems you should have in place, establish necessary relationships with suppliers prior to your start-up, and generally deal with a list of issues like those mentioned above.
- What is required to start-up your business including the purchases and activities that must occur before you make your first sale?
- When identifying capital requirements for start-up, a distinction should be made between fixed capital requirements and working capital requirements.
Fixed Capital Requirements
- What fixed assets, including equipment and machinery, must be purchased so your venture can conduct its business?
- May also show the financing required, often in the form of longer-term loans
Working Capital Requirements
- What money is needed to operate the business (separately from the money needed to purchase fixed assets) including the money needed to purchase inventory and pay initial expenses?
- May also show the financing required. Working capital is usually financed with operating loans, trade credit, credit card debt, or other forms of shorter-term loans
Risk Management Strategies
- Enterprise – liability exposure for things like when someone accuses your employees or products you sell of injuring them
- Financial – securing loans when needed and otherwise having the right amount of money when you need it
- Operational – securing needed inventories, recruiting needed employees in tight labour markets, operating when customers you counted on not purchasing product as you had anticipated, managing theft, arson, and natural disasters like fires and floods, etc.
- Avoid – choose to avoid doing something, outsource, etc.
- Reduce – through training, assuming specific operational strategies, etc.
- Transfer – insure against, outsource, etc.
- Assume – self-insure, accept, etc.

Figure 8 – Risk Management Strategies (Illustration by Lee A. Swanson)
Operating Processes
- What operating processes will you apply?
- How will you ensure your cash is managed effectively?
- How will you schedule your employees?
- How will you manage your inventories?
- If you will have a workforce, how will you manage them?
- How will you bill out your employee time?
- How will you schedule work on your contracts?
- How you will manufacture your product (process flow, job shop, etc.?)
- How will you maintain quality?
- How will you institute and manage effective financial monitoring and control systems that provide needed information in a timely manner?
- How will you manage expansion?
- May include planned layouts for facilities
- What are your facility plans?
- Expressed as a set physical location
- Expressed as a set of requirements and characteristics
- How large will your facility be and why must it be this size?
- How much will it cost to buy or lease your facility?
- What utility, parking, and other costs must you pay for this facility?
- What expansion plans must be factored into the facility requirements?
- What transportation and storage issues must be addressed by facility decisions?
- What zoning and other legal issues must you deal with?
- What will be the layout for your facility and how will this best accommodate customer and employee requirements?
Organizational Structure
- May include information on Advisory Boards or Board of Directors from which the company will seek advice or guidance or direction
- May include an organizational chart
- Can be a nice lead-in to the Human Resources Plan
Human Resources Plan
- How do you describe your desired corporate culture?
- What are the key positions within your organization?
- How many employees will you have?
- What characteristics define your desired employees?
- What is your recruitment strategy? What processes will you apply to hire the employees you require?
- What is your leadership strategy and why have you chosen this approach?
- What performance appraisal and employee development methods will you use?
- What is your organizational structure and why is this the best way for your company to be organized?
- How will you pay each employee (wage, salary, commission, etc.)? How much will you pay each employee?
- What are your payroll costs, including benefits?
- What work will be outsourced and what work will be completed in-house?
- Have you shown and described an organizational chart?
Recruitment and Retention Strategies
- Includes how many employees are required at what times
- Estimates time required to recruit needed employees
- Employment advertisements
- Contracts with employment agency or search firms
- Travel and accommodations for potential employees to come for interviews
- Travel and accommodations for interviewers
- Facility, food, lost time, and other interviewing costs
- Relocation allowances for those hired including flights, moving companies, housing allowances, spousal employment assistance, etc.
- May include a schedule showing the costs of initial recruitment that then flows into your start-up expense schedules
Leadership and Management Strategies
- Outlines your leadership philosophy
- Explains why it is the most appropriate leadership approach for this venture
- What training is required because of existing rules and regulations?
- How will you ensure your employees are as capable as required?
- Health and safety (legislation, WHMIS, first aid, defibulators, etc.)
- Initial workplace orientation
- Financial systems
- Product features
Performance Appraisals
- Identifies how you will manage your performance appraisal systems
Health and Safety
- Notes any legal requirements (and also legal requirements for other issues that may be included in other parts of the plan)
- Identifies accreditation you might pursue, such as ISO 9000, and if so, evaluates the costs, benefits, and time frame
- Outlines training for employees, such as WHMIS training or machinery handling training
Compensation
- Always justifies your planned employee compensation methods and amounts
- Always includes all components of the compensation (CPP, EI, holiday pay, etc.)
- Identifies how you will ensure both internal and external equity in your pay systems
- Describes any incentive-based pay or profit sharing systems planned
- May include a schedule that shows the financial implications of your compensation strategy and supports the cash flow and income statements shown later
Key Personnel
- May include brief biographies of the key organizational people
Marketing Plan
- You must show evidence of having done proper research, both primary and secondary. If you make a statement of fact, you must back it up with properly referenced supporting evidence. If you indicate a claim is based on your own assumptions, you must back this up with a description as to how you came to the conclusion.
- It is a given that you must provide some assessment of the economic situation as it relates to your business. For example, you might conclude that the current economic crisis will reduce the potential to export your product and it may make it more difficult to acquire credit with which to operate your business. Of course, conclusions such as these should be matched with your assessment as to how your business will make the necessary adjustments to ensure it will thrive despite these challenges, or how it will take advantage of any opportunities your assessment uncovers.
- If you apply the Five Forces Model, do so in the way in which it was meant to be used to avoid significantly reducing its usefulness while also harming the viability of your industry analysis. This model is meant to be used to consider the entire industry, not a subcomponent of it (and it usually cannot be used to analyze a single organization).
- Your competitor analysis might fit within your assessment of the industry, or it might be best as a section within your marketing plan. Usually a fairly detailed description of your competitors is required, including an analysis of their strengths and weaknesses. In some cases, your business may have direct and indirect competitors to consider. Maintain credibility by demonstrating that you fully understand the competitive environment.
- Assessments of the economic conditions and the state of the industry appear incomplete without accompanying appraisals outlining the strategies the organization can/should employ to take advantage of these economic and industry situations. So, depending upon how you have organized your work, it is usually important to couple your appraisal of the economic and industry conditions with accompanying strategies for your venture. This shows the reader that you not only understand the operating environment, but that you have figured out how best to operate your business within that situation.
- Outlines an effective analysis of your venture (see the Organizational Analysis section below)
Market Analysis
- Usually contains customer profiles, constructed through primary and secondary research, for each market targeted
- Contains detailed information on the major product benefits you will deliver to the markets targeted
- Describes the methodology used and the relevant results from the primary market research completed
- If there was little primary research completed, justifies why it is acceptable to have done little of this kind of research and/or indicate what will be done and by when
- Includes a complete description of the secondary research conducted and the conclusions reached
- Define your target market in terms of identifiable entities sharing common characteristics. For example, it is not meaningful to indicate you are targeting Canadian universities. It is, however, useful to define your target market as Canadian university students between the ages of 18 and 25, or as information technology managers at Canadian universities, or as student leaders at Canadian universities. Your targeted customer should generally be able to make or significantly influence the buying decision.
- You must usually define your target market prior to describing your marketing mix, including your proposed product line. Sometimes the product descriptions in business plans seem to be at odds with the described target market characteristics. Ensure your defined target market aligns completely with your marketing mix (including product/service description, distribution channels, promotional methods, and pricing). For example, if the target market is defined as Canadian university students between the ages of 18 and 25, the product component of the marketing mix should clearly be something that appeals to this target market.
- Carefully choose how you will target potential customers. Should you target them based on their demographic characteristics, psychographic characteristics, or geographic location?
- You will need to access research to answer this question. Based on what you discover, you will need to figure out the optimum mix of pricing, distribution, promotions, and product decisions to best appeal to how your targeted customers make their buying decisions.
Competition
- However, this information might fit instead under the market analysis section.
- Describes all your direct competitors
- Describes all your indirect competitors
- If you include a competitor positioning map, insure that the x-axis and y-axis are meaningful. Often, competitor maps include quality and price as axes. Unless you can clearly articulate the distinction between high quality and low quality, it may be more valuable to have more meaningful axes or describe your value proposition relative to your competitors in the absence of a positioning map.

Figure 9 – Competitor Positioning Map (Illustration by Lee A. Swanson)
- You must clearly communicate the answers to these questions in your business plan in order to attract the needed support for your business. One caution is that it may sound appealing to claim you will provide a superior service to the existing competitors, but the only meaningful judge of your success in this regard will be customers. Although it is possible some of your competitors might be complacent in their current way of doing things, it is very unlikely that all your competitors provide an inferior service to that which you will be able to provide.
Marketing Strategy
- Covers all aspects of the marketing mix: your promotional decisions, product decisions, distribution decisions, and pricing decisions
- Outlines how you plan to influence your targeted customers to buy from you (your optimum marketing mix, and why is this one better than the alternatives)
Organizational Analysis
- Leads in to your marketing strategy or is positioned elsewhere depending upon how your business plan is best structured
- If doing so, ALWAYS ensure this analysis results in more than a simple list of internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. A SWOT analysis should always prove to the reader that there are organizational strategies in place to address each of the weaknesses and threats identified and to leverage each of the strengths and opportunities identified.
- An effective way to ensure an effective outcome to your SWOT Analysis is to apply a TOWS Matrix approach to develop strategies to take advantage of the identified strengths and opportunities while mitigating the weaknesses and threats. A TOWS Matrix evaluates each of the identified threats along with each of the weaknesses and then each of the strengths. It does the same with each of the identified opportunities. In this way strategies are developed by considering pairs of factors.
- The TOWS Matrix is a framework with which to help you organize your thoughts into strategies. Most often you would not label a section of your business plan as a TOWS Matrix because this would not add value for the reader. Instead, you should describe the resultant strategies—perhaps while indicating how they were derived from your assessment of the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. For example, you could indicate that certain strategies were developed by considering how internal strengths could be employed toward mitigating external threats faced by the business.
Product Strategy
- If your product or service is standardized, you will need to compete on the basis of something else—like a more appealing price, having a superior location, better branding, or improved service. If you can differentiate your product or service, you might be able to compete on the basis of better quality, more features, appealing style, or something else. When describing your product, you should demonstrate that you understand this.
Pricing Strategy
- If you intend to accept payment by credit card (which is probably a necessity for most companies), you should be aware of the fee you are charged as a percentage of the value of each transaction. If you don’t account for this you risk overstating your actual revenues by perhaps one percent or more.
- Sales forecasts must be done on at least a monthly basis if you are using a projected cash flow statement. These must be accompanied by explanations designed to establish their credibility for readers of your business plan. Remember that many readers will initially assume your planned time frames are too long, your revenues are overstated, and you have underestimated your expenses. Well crafted explanations for all of these numbers will help establish credibility.
Distribution Strategy
- If you plan to use e-commerce, you should include all the costs associated with maintaining a website and accepting payments over the Internet.
Promotions Strategy
- As a new entrant into the market, must you attract your customers away from your competitors they currently buy from or will you be creating new customers for your product or service (i.e. not attracting customers away from your competitors)?
- If you are attracting customers away from competitors, how will these rivals respond to the threat you pose to them?
- If you intend to create new customers, how will you convince them to reallocate their dollars toward your product or service (and away from other things they want to purchase)?
- In what ways will you communicate with your targeted customers? When will you communicate with them? What specific messages do you plan to convey to them? How much will this promotions plan cost?
- If your entry into the market will not be a threat to direct competitors, it is likely you must convince potential customers to spend their money with you rather than on what they had previously earmarked those dollars toward. In your business plan you must demonstrate an awareness of these issues.
- Consider listing the promotional methods in rows on a spreadsheet with the columns representing weeks or months over probably about 18 months from the time of your first promotional expenditure. This can end up being a schedule that feeds the costs into your projected cash flow statement and from there into your projected income statements.
- If you phone or visit newspapers, radio stations, or television stations seeking advertising costs, you must go only after you have figured out details like on which days you would like to advertise, at what times on those days, whether you want your print advertisements in color, and what size of print advertisements you want.
- Carefully consider which promotional methods you will use. While using a medium like television may initially sound appealing, it is very expensive unless your ad runs during the non-prime times. If you think this type of medium might work for you, do a serious cost-benefit analysis to be sure.
- Some promotional plans are developed around newspaper ads, promotional pamphlets, printing business cards, and other more obvious mediums of promotion. Be certain to, include the costs of advertising in telephone directories, sponsoring a little league soccer team, producing personalized pens and other promotional client give-always, donating items to charity auctions, printing and mailing client Christmas cards, and doing the many things businesses find they do on-the-fly. Many businesses find it to be useful to join the local chamber of commerce and relevant trade organizations with which to network. Some find that setting a booth up at a trade fair helps launch their business.
- If you are concerned you might have missed some of these promotional expenses, or if you want to have a buffer in place in case you feel some of these opportunities are worthwhile when they arise, you should add some discretionary money to your promotional budget. A problem some companies get into is planning out their promotions in advance only to reallocate some of their newspaper advertisement money, for example, toward some of these other surprise purposes resulting in less newspaper advertising than had been intended.
Financial Plan
- Contains financial statements
- Various funding options and exit strategies for potential investors
- Business valuation (be cautious not to over value your business)
- Break-even analysis
Business Valuation
There are a multitude of sophisticated business valuation methodologies. A rule of thumb for business valuations is a multiple of its earnings. For example, if the chosen multiple is five and the business’ earnings before taxes are $55M, the business’ valuation would be approximately $275M.
Break-Even Analysis
Break-Even Point = FC/(P-VC)
- FC = Fixed Costs
- P = Unit Price
- VC = Variable Cost
Example: If the business’ total fixed costs are $1,000,000.00, it costs $5.00 to produce the widget, and the business sells the widget for $7.00, the break-even point is 500,000 widgets.
- You will most certainly need to make monthly cash flow projections from business inception to possibly three years out. Your projections will show the months in which the activities shown on your fixed capital and working capital schedules will occur. This is nearly the only way to clearly estimate your working capital needs and, specifically, important things like the times when you will need to draw on or can pay down your operating loans and the months when you will need to take out longer-term loans with which to purchase your fixed assets. Without a tool like this you will be severely handicapped when talking with bankers about your expected needs. They will want to know how large of a line of credit you will need and when you anticipate needing to borrow longer-term money. It is only through doing cash flow projections that you will be able to answer these questions. This information is also needed to determine things like the changes to your required loan payments and when you can take owner draws or pay dividends.
- Your projected cash flows are also used to develop your projected income statements and balance sheets.
Pro forma Cash Flow Statements
Pro forma income statements, pro forma balance sheets, investment analysis, projected financial ratios and industry standard ratios, critical success factors (sensitivity analysis), list of items a business may need to purchase.
- Business license
- Registration for name, etc.
- Domain name registration
- Initial product inventory
- All the little things like curtains/blinds, decorations, microwave for staff room, etc.
- All the things needed to run the business from day #1 (like cutlery, plates, cooking pots, table settings etc. for restaurants; like towels, soap, etc. for gyms; like equipment and so on for manufacturing and service places)
- Set-up and testing of new facilities—new factories and offices do not operate at peak efficiency for some time after start-up because it takes time for the new systems to kick into high gear
- Professional services needed
- Lawyer’s fees to make sure agreements are solid
- Graphic designer or design company needed to develop visuals
- Accounting firm needed to set up initial systems
- Insurance—maybe not a direct cost to this one to account for
- Accounting system software
- Computer, printer, other things needed like scanner
- Office furniture
- Initial office supplies—paper, pens, etc.
- Internet/wifi
- Microwave and coffee maker and similar supplies for staff room or coffee room
- Bank fees—business banking is normally not free—might also need to have business cheques
Customer Interaction
- Cash register
- Loyalty cards/system
Production/Operations
- Safety equipment (fire extinguishers, AED)
- Security systems
- Equipment maintenance
- Janitorial services and cleaning supplies
- Bathroom supplies—toilet paper, soap, towels
- Membership costs for various associations, including the local chamber of commerce, any professional associations for the relevant industry, etc.
- Subscriptions for things like important trade publications, etc.
- Shelving and storage systems
- Even when not full restaurant, operations like coffee shops still require equipment like dishwasher
- Safety—prior to start-up and ongoing and for new employees
- Ads, travel expenses—flights, hotels, taxi rides, meal allowances, etc.—to recruit people through interviews, meeting meals, set up with real estate agents, etc.
- Website development
- Costs for setting up and managing social media (can take a lot of an employee’s time)
- Grand opening costs
- If buying, include property taxes and all utilities in cash flows and income statement and include building maintenance and maybe build up a reserve fund to pay for things like future roof repairs and needed renovations and upgrades
- If renting/leasing, include rental/least cost and whatever utilities are not included in rental/lease payment
Renovations
- Construction
- Utility hookups
- Inspections
- Interior signage
- Fencing, parking lot, exterior lighting, other exterior things
Risk Management
- Insurance (need to choose the types needed)
- Training costs
- Things like snow removal, de-icing sidewalks, etc.
Chapter Summary
This chapter described the basic elements of a comprehensive business plan.

The Business Planning Process: 6 Steps To Creating a New Plan
In this article, we will define and explain the basic business planning process to help your business move in the right direction.
What is Business Planning?
Business planning is the process whereby an organization’s leaders figure out the best roadmap for growth and document their plan for success.
The business planning process includes diagnosing the company’s internal strengths and weaknesses, improving its efficiency, working out how it will compete against rival firms in the future, and setting milestones for progress so they can be measured.
The process includes writing a new business plan. What is a business plan? It is a written document that provides an outline and resources needed to achieve success. Whether you are writing your plan from scratch, from a simple business plan template , or working with an experienced business plan consultant or writer, business planning for startups, small businesses, and existing companies is the same.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
The best business planning process is to use our business plan template to streamline the creation of your plan: Download Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template and finish your business plan & financial model in hours.
The Better Business Planning Process
The business plan process includes 6 steps as follows:
- Do Your Research
- Calculate Your Financial Forecast
- Draft Your Plan
- Revise & Proofread
- Nail the Business Plan Presentation
We’ve provided more detail for each of these key business plan steps below.
1. Do Your Research
Conduct detailed research into the industry, target market, existing customer base, competitors, and costs of the business begins the process. Consider each new step a new project that requires project planning and execution. You may ask yourself the following questions:
- What are your business goals?
- What is the current state of your business?
- What are the current industry trends?
- What is your competition doing?
There are a variety of resources needed, ranging from databases and articles to direct interviews with other entrepreneurs, potential customers, or industry experts. The information gathered during this process should be documented and organized carefully, including the source as there is a need to cite sources within your business plan.
You may also want to complete a SWOT Analysis for your own business to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and potential risks as this will help you develop your strategies to highlight your competitive advantage.
2. Strategize
Now, you will use the research to determine the best strategy for your business. You may choose to develop new strategies or refine existing strategies that have demonstrated success in the industry. Pulling the best practices of the industry provides a foundation, but then you should expand on the different activities that focus on your competitive advantage.
This step of the planning process may include formulating a vision for the company’s future, which can be done by conducting intensive customer interviews and understanding their motivations for purchasing goods and services of interest. Dig deeper into decisions on an appropriate marketing plan, operational processes to execute your plan, and human resources required for the first five years of the company’s life.
3. Calculate Your Financial Forecast
All of the activities you choose for your strategy come at some cost and, hopefully, lead to some revenues. Sketch out the financial situation by looking at whether you can expect revenues to cover all costs and leave room for profit in the long run.
Begin to insert your financial assumptions and startup costs into a financial model which can produce a first-year cash flow statement for you, giving you the best sense of the cash you will need on hand to fund your early operations.
A full set of financial statements provides the details about the company’s operations and performance, including its expenses and profits by accounting period (quarterly or year-to-date). Financial statements also provide a snapshot of the company’s current financial position, including its assets and liabilities.
This is one of the most valued aspects of any business plan as it provides a straightforward summary of what a company does with its money, or how it grows from initial investment to become profitable.
4. Draft Your Plan
With financials more or less settled and a strategy decided, it is time to draft through the narrative of each component of your business plan . With the background work you have completed, the drafting itself should be a relatively painless process.
If you have trouble writing convincing prose, this is a time to seek the help of an experienced business plan writer who can put together the plan from this point.
5. Revise & Proofread
Revisit the entire plan to look for any ideas or wording that may be confusing, redundant, or irrelevant to the points you are making within the plan. You may want to work with other management team members in your business who are familiar with the company’s operations or marketing plan in order to fine-tune the plan.
Finally, proofread thoroughly for spelling, grammar, and formatting, enlisting the help of others to act as additional sets of eyes. You may begin to experience burnout from working on the plan for so long and have a need to set it aside for a bit to look at it again with fresh eyes.
6. Nail the Business Plan Presentation
The presentation of the business plan should succinctly highlight the key points outlined above and include additional material that would be helpful to potential investors such as financial information, resumes of key employees, or samples of marketing materials. It can also be beneficial to provide a report on past sales or financial performance and what the business has done to bring it back into positive territory.
Business Planning Process Conclusion
Every entrepreneur dreams of the day their business becomes wildly successful.
But what does that really mean? How do you know whether your idea is worth pursuing?
And how do you stay motivated when things are not going as planned? The answers to these questions can be found in your business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs make better decisions and avoid common pitfalls along the way.
Business plans are dynamic documents that can be revised and presented to different audiences throughout the course of a company’s life. For example, a business may have one plan for its initial investment proposal, another which focuses more on milestones and objectives for the first several years in existence, and yet one more which is used specifically when raising funds.
Business plans are a critical first step for any company looking to attract investors or receive grant money, as they allow a new organization to better convey its potential and business goals to those able to provide financial resources.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink business plan consultants can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


What is a Business Plan?
Home › Business Management › What is a Business Plan?
Definition: A business plan is a detailed written steps and goals defined to guide a business’ course of action from its initial stages. A business plan provides a complete description and projection of the company as well as its core strategies and expected results.
- What Does Business Plan Mean?
The creation of a new organization or a new business requires coherent actions in order to achieve the desired outcomes. Following a business plan allows to link actions and resources to objectives and measurable goals. This plan can be used internally like a roadmap for the owner but also can be a requirement when looking for funding or partners.
A business plan is generally a precise, short document that commonly contains the following sections: executive summary, business description with its products or services, marketing plan, operational plan and financial plan with its forecasted financial statements for the first years of operation, often five to ten years. The initial business plan is later substituted by annual or bi-annual strategic plans.
Mark Tilson is a young professional that wants to start a new business. He has the idea of providing an innovative maintenance service to medium-size manufacturing companies but he needs funds to implement it. Mr. Tilson therefore decided to write a business plan to present the idea to some potential capital partners. He though that the ideas were already clear but soon realized that more analysis and pre-launching work was required.
How many employees the company will have? How the company will market its services? How much money the initial investment requires? How much profit the company is expected to generate at the end of the fifth year of operation? These and other questions must be answered and coherently written in the business plan. Finally, Mr. Tilson improved his ideas, presented the plan and found the required partner.

Accounting & CPA Exam Expert
Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career.
Search 2,000+ accounting terms and topics.
- Basic Accounting Course
- Financial Accounting Basics
- Accounting Principles
- Accounting Cycle
- Financial Statements
- Financial Ratio
Do This One Thing Before You Write Your Business Plan

Noah Parsons
6 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024
So, you’ve been asked to write a business plan. It’s likely that your mind is filled with images of long documents, bad memories of writing term papers, and worries about doing market research and creating financial forecasts.
Take a deep breath.
It doesn’t have to be that way. Today, I’m going to walk you through an easier way to get your business plan started, and show you how to develop a winning strategy.
Start with why you’re writing a business plan
But first, let’s talk about why you’re writing a business plan .
There are a lot of reasons why writing a business plan is important . Most businesses start the planning process because they are applying for a loan or seeking funding from investors .
But, beyond needing to develop a plan that will impress the bank or your investors, you want to build a solid company. You want to develop a sound strategy that will help your business grow and be successful.
Unfortunately, while traditional business plans will help you develop strategy, they have several drawbacks.
Traditional business plans take too long to write, they’re rarely updated, and they are time-consuming to read.
Now, there may be a point in your business career that you will need to deliver a formal business plan to a bank, investors, or other business partners. But, until that point, I recommend that you start your planning with a simpler process— a one-page plan —that will help you develop your business strategy.
Building a one-page plan takes less than 20 minutes . You can even build several of them in an afternoon to try out different business ideas.
A Lean Plan forces you to distill your ideas for your business into the core of your strategy. As planning expert Tim Berry says, “a good strategy is about what you’re not doing.”
And, once you have nailed down your business strategy, you can expand on it with a longer business plan document that fleshes out the details of your plan.
What to include:
Your one-page plan is a very high-level overview of your business. Each section should only be a few bullet points, so you should be able to complete an initial draft of your plan in 20 minutes or less.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- 1. Your identity
What sets your business apart from others? What’s your focus? For example, a bike shop’s identity might be, “High-quality biking gear for families and regular people, not just for gearheads.” With this identity, this bike shop has focus. It describes who they are and what they are trying to do. Ideally, you should be able to describe your identity in one or two short sentences.
- 2. The problem you are solving
How are you helping your customers? What problem will they go to you to solve? Don’t think that your business doesn’t solve a problem; for example, a new restaurant would fill a need for a particular type of cuisine or a certain atmosphere that is not currently available in a certain neighborhood.
- 3. Your solution to the problem
How does your business solve a customer’s problem? What is your product or service? Make sure your product or service is addressing your customer’s needs.
- 4. Your customer
Who is your ideal customer? A great exercise is to create a buyer persona, but you can just jot down some notes at this stage about who your customer is. Focus on a specific type of customer or certain groups. Focusing on “everyone” is not a sound business strategy.
- 5. The competition
Who is your competition , and what sets you apart? How are you better or different than other options available to your customers?
- 6. Sales channels
How will you reach your target customers ? Do you have a single storefront? Are you selling online? Do you rely on distributors to get your products onto store shelves?
- 7. Marketing activities
How will you let your customers know about your product or service? Do you need to go to trade shows? Will you buy online advertising?
- 8. Your team
Probably the single key to a successful business is a great group of people to turn an idea into reality. Do you have the right people? If you need additional key team members to help you build the business, identify them here.
- 9. Your business model
“ Business model ” sounds like a confusing term, but really it’s just a fancy way of talking about how you will make money. In the early stages of fleshing out your business idea, you can just write down a few bullet points about how you will make money and what your key expenses will be.
As you refine your business idea, you will want to turn these initial notes into a sales forecast and an expense budget . But for your initial 20-minute plan, just write down a short list of the things you will charge for and the important expenses that you will have as you run the business.
- 10. Milestones
Ideas are nothing without execution—you need to turn your idea into a real business. Use the “ Milestones ” section of your one-page plan to list the critical things that need to be accomplished to start your business. Do you need to find a location? Maybe you need to get FDA approval for a new medical device. List the key milestones you need to accomplish here. Ideally, add approximate dates and list who will accomplish each task.
- 11. Partners and resources
If you need to work with other companies or business partners to get your idea off the ground, list those partners and resources here. Do you need a manufacturer or supplier for your products? Do you need a distributor to get your product on store shelves?
That’s it! A first pass at creating a one-page plan should only take 20 minutes or so. Set a timer and jump right in. Just getting everything down on paper is a great first step. The beauty of the one-page format is that you can come back and revise as you go.
- How to use your one-page plan
Now that you have the first draft of your Lean Plan, or maybe even several different mini-plans, you need to put it to use.
First, you’ll want to use your plan to identify the key assumptions about your business. Typically, those assumptions are around what famous entrepreneur and investor Marc Andreessen calls “product/market fit.” What that really means is that you’ve found a group of potential customers who have the problem you say they have, and who are willing to spend money on your solution.
Your Lean Plan includes assumptions about who your customer is, what problem they have, and what kind of solution they want.
As a next step, you’ll want to go out and talk to potential customers and verify that they do indeed have the problem you’ve assumed they have and that they’re willing to spend money on your solution.
As you gather feedback from potential customers, you’ll refine your plan . This is where you’ll be glad that you started with a one-page plan instead of a detailed business plan. It’s easy to update and revise as you go. You can quickly update it with new information as needed.
Now, if you don’t need to present a plan to outsiders, this may be all the business plan that you need. But, if you do need to create that formal business plan document, you can use your one-page plan as the key outline for that document. The business plan may also document more details about your marketing plan, product plan, or hiring plans, but ultimately, your business plan will just expand on and provide additional detail for each section of your one-page plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

14 Min. Read
15 Ways to Use and Get Incredible Value From a Business Plan

8 Min. Read
How to Write a Business Plan in One Day [2024 Guide]

1 Min. Read
10 Questions to Ask Before Hiring a Business Plan Writer

3 Min. Read
Celebrate National Write a Business Plan Month in December
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Entrepreneurs
- Investor pitch
- Small business

Business Plan Definition
Let’s define what “business plan” means and explore why and how you should prepare one.
Definition of a Business Plan
A business plan is a document that outlines the goals, resources, and strategies of a business. The plan articulates the entity’s vision, setting out history, strategic direction, and steps to be taken going forward, such as funding, product development, and marketing.
A business plan is a written document that describes the goals, strategies, and financial projections of a business. It is a roadmap that outlines the steps needed to achieve the desired results and helps to guide the decision-making and actions of the business. A business plan is typically used to secure funding, attract investors, and to set the direction of the business.
Elements of a Detailed Plan
Here are the common elements of a business plan. Each element should be considered, though you may want to ultimately include only the parts that are most helpful.
- Executive summary : Brief summary of the entire business plan, highlighting the key points.
- Company description : Overview of the company, including its history, mission, and values.
- Market analysis : Examination of the target market, including industry trends and competition.
- Product or service offering : Descriptions of the products or services that the business will offer.
- Marketing and sales strategy : Outline of the marketing and sales efforts that will be used to reach target customers.
- Operations : Outline of the day-to-day operations of the business, including production and supply chain management.
- Management team : Introduction to key members of the management team, including qualifications and responsibilities.
- Financial plan : Financial projections, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
A business plan is a dynamic document that should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that it remains relevant and accurate.
Why Prepare a Business Plan?

If you’re planning to start a new business or expand your activities, preparing a business plan is an obligation, not an option. This position seems somewhat radical, but maybe you’ll agree with me if you see the business plan not as a formal document to convince investors, but as a roadmap for growth .
A formal and complete plan should only be done when you are seeking investors for your business. In this situation, the plan should be structured and detailed and, in some cases, you should even hire a consultant to help you in its development.
Nevertheless, not every business plan must have all the parts that the “guides” say. If you face the plan as your database of ideas and strategies for your actions, the form will not be as important as the content.
The main importance of the plan is to define which steps you have to take to reach business success. From the moment you define what success really means to you, and document the strategy to get there, you set a baseline for two important issues:
- Not getting yourself too involved with daily activities and keeping the plan in focus.
- Comparing the real performance to what was planned and taking corrective actions to get back on the right track.
The plan doesn’t have to be 100% ready before starting your activities. You can begin with something very basic, which gives a general view of the business. From this basic document, new ideas will be developed and added as the work advances.
This progressive elaboration is the best track for those who still have doubts or do not feel comfortable with business plans. Preparing the document little by little using professional business writing . This will help give you the flexibility, mental tranquillity and clarity you need to start your project.
Marketing Strategy

A marketing strategy is a key component of business plans. It outlines the actions that will be taken to reach target customers and achieve marketing and sales goals. The strategy should be based on a good understanding of the target market, the business’s unique value proposition, and the competition.
The strategic plan for marketing should include:
- Target market: Who are the business’s ideal customers?
- Marketing goals: What does the business hope to achieve from its marketing efforts?
- Marketing mix: What products or services will the business offer, at what price, through which channels, and using what promotions?
- Marketing tactics: How will the business reach target customers? This may include advertising, social media marketing, content marketing, email marketing, and more.
- Measuring success: How will you track the success of marketing campaigns and make adjustments as needed?
Marketing plans should align with the overall goals and objectives of the business, and integrated with other functional areas, such as operations, finance, and human resources.
Develop the Plan With Incremental Gains
What’s interesting is that when you document your plan, you automatically find blanks in your ideas, which must be filled. Suppose you have an idea in your head of how to reach your target audience. When you create a simple marketing plan, you may notice that you hadn’t thought of many obstacles and the plan must be adapted.
Ideas normally have to be worked on and improved. Understand that your first vision will not always be implemented without changes; it evolves .
In summary, don’t feel intimidated by the “work” of preparing a business plan. Take gradual steps, and know that it is a tool that will increase your probability of success.
Business plans always change, so no need to get carried away with them. Good planning is essential, but a great document is only important when pitching to investors or otherwise trying to impress people.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections. Executive summary. Briefly tell your reader what your company is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your company's leadership team, employees, and location.
It's the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you'll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and ...
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you'll write, it's the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company's mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals. 3.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Startups is the world's largest startup platform, helping over 1 million startup companies find customers, funding, mentors, and world-class education. An introductory guide to explain what a business plan is, why you need it (and how it helps), key components, how long it should be, how to write it, who needs to see it, and much more.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business. But the reality can be more nuanced - it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written. Ideal times to write a business plan include: When you have an idea for a ...
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing. A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all ...
Business Plan Definition: A written document describing the nature of the business, the sales and marketing strategy, and the financial background, and containing a projected profit and loss ...
A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. ... Venture capitalists are primarily concerned about initial investment, feasibility, and exit valuation.
The sum of capital and plant, investments, and miscellaneous assets. Total assets. The sum of total current assets and total long-term assets. After the assets are listed, you need to account for ...
This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections. Whether you're starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool. As a business plan writer and consultant, I've crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse ...
What is a Business Plan. A business plan definition is a written document that outlines the goals, strategies, and detailed operational and financial plans of a business. It serves as a roadmap for the business, providing a clear direction for its growth and development. ... IPO (Initial Public Offering): Making a company public is a complex ...
This page titled 1.4: Chapter 4 - Initial Business Plan Draft is shared under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Lee A. Swanson via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request.
The Better Business Planning Process. The business plan process includes 6 steps as follows: Do Your Research. Strategize. Calculate Your Financial Forecast. Draft Your Plan. Revise & Proofread. Nail the Business Plan Presentation. We've provided more detail for each of these key business plan steps below.
business plan: A business plan is a document demonstrating the feasibility of a prospective new business and providing a roadmap for its first several years of operation.
Definition: A business plan is a detailed written steps and goals defined to guide a business' course of action from its initial stages. A business plan provides a complete description and projection of the company as well as its core strategies and expected results.
But for your initial 20-minute plan, just write down a short list of the things you will charge for and the important expenses that you will have as you run the business. 10. Milestones. Ideas are nothing without execution—you need to turn your idea into a real business.
Calculate your business startup costs before you launch. The key to a successful business is preparation. Before your business opens its doors, you'll have bills to pay. Understanding your expenses will help you launch successfully. Calculating startup costs helps you: Estimate profits. Conduct a break-even analysis.
Definition of a Business Plan. A business plan is a document that outlines the goals, resources, and strategies of a business. The plan articulates the entity's vision, setting out history, strategic direction, and steps to be taken going forward, such as funding, product development, and marketing. A business plan is a written document that ...
Examples of Initial Business Plan in a sentence. The Initial Business Plan is attached to this Agreement as Schedule 6 (Initial Business Plan).. Such investment shall be made in accordance with the Initial Business Plan and subsequent Business Plans, which shall include staffing, retail and wholesale shop construction, marketing and public relations, and all other significant details necessary ...