
- Richard G. Trefry Library
- Writing & Citing

Q. What is the difference between a thesis statement and a hypothesis statement?

- Course-Specific
- Textbooks & Course Materials
- Tutoring & Classroom Help
- 1 Artificial Intelligence
- 43 Formatting
- 5 Information Literacy
- 13 Plagiarism
- 23 Thesis/Capstone/Dissertation
Answered By: APUS Librarians Last Updated: Apr 15, 2022 Views: 127600
Both the hypothesis statement and the thesis statement answer a research question.
- A hypothesis is a statement that can be proved or disproved. It is typically used in quantitative research and predicts the relationship between variables.
- A thesis statement is a short, direct sentence that summarizes the main point or claim of an essay or research paper. It is seen in quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods research. A thesis statement is developed, supported, and explained in the body of the essay or research report by means of examples and evidence.
Every research study should contain a concise and well-written thesis statement. If the intent of the study is to prove/disprove something, that research report will also contain a hypothesis statement.
NOTE: In some disciplines, the hypothesis is referred to as a thesis statement! This is not accurate but within those disciplines it is understood that "a short, direct sentence that summarizes the main point" will be included.
For more information, see The Research Question and Hypothesis (PDF file from the English Language Support, Department of Student Services, Ryerson University).
How do I write a good thesis statement?
How do I write a good hypothesis statement?
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 115 No 63
writing tutor
Related topics.
Need personalized help? Librarians are available 365 days/nights per year! See our schedule.

Learn more about how librarians can help you succeed.
Thesis Vs Hypothesis: Understanding The Basis And The Key Differences
Hypothesis vs. thesis: They sound similar and seem to discuss the same thing. However, these terms have vastly different meanings and purposes. You may have encountered these concepts in school or research, but understanding them is key to executing quality work.
As an inexperienced writer, the thought of differentiating between hypotheses and theses might seem like an insurmountable task. Fortunately, I am here to help.
In this article, I’ll discuss hypothesis vs. thesis, break down their differences, and show you how to apply this knowledge to create quality written works. Let’s get to it!
Thesis vs. Hypothesis: Understanding the Basis
The power of a thesis.
A thesis is a foundational element in academic writing and research. It also serves as the linchpin of your argument, encapsulating the central idea or point you aim to prove or disprove throughout your work.
A thesis statement is typically found at the end of the introduction in an essay or research paper, succinctly summarizing the overarching theme.
Crafting a strong thesis
- Understand the research: Begin by thoroughly comprehending the requirements and objectives of your research. Having a clear understanding of the topic you are arguing or analyzing is crucial.
- Choose a clear topic: Choose one that interests you and aligns with the research’s scope. Clarity and focus are essential in crafting a strong thesis.
- Conduct research: Gather relevant information and sources to develop a deep understanding of your topic. This research will provide the evidence and context for your thesis.
- Identify your position: Determine your stance or position on the topic. Your thesis should express a clear opinion or argument you intend to support throughout your work.
- Narrow down your focus: Refine your topic and thesis more precisely. Avoid broad, generalized statements. Instead, aim for a concise and specific thesis that addresses a particular aspect of the topic.
- Test for validity: Ensuring that you can argue and provide evidence to support your thesis is crucial. It should not be a self-evident or universally accepted fact.
- Write and revise: Craft your thesis statement as a clear, concise sentence summarizing your main argument. Revise and refine it as needed to improve its clarity and strength.
Remember that a strong thesis serves as the foundation for your entire piece of writing, guiding your readers and keeping your work focused and organized.
Hypothesis: The scientific proposition
In contrast, a hypothesis is a tentative proposition or educated guess. It is the initial step in the scientific method, where researchers formulate a hunch to test their assumptions and theories.
A hypothesis is an assertion that can be proven or disproven through experimentation and observation.
Formulating a hypothesis
- Identify the research question: Identify the research question or problem you want to investigate. Clearly define the scope and boundaries of your inquiry.
- Review existing knowledge: Conduct a literature review to gather information about the topic. Understand the existing body of knowledge and literature in the field.
- Formulate a tentative explanation: Based on your research and understanding of the topic, create a tentative explanation or educated guess about the phenomenon you are studying. This should be a statement that can be falsifiable through experimentation or observation.
- Make it testable: Ensure that your hypothesis is testable and falsifiable. In other words, designing experiments or gathering data supporting or refuting your hypothesis should be possible.
- Specify variables and predictions: Clearly define the variables involved in your hypothesis and make predictions about how changes in these variables will affect the outcome. It also helps in designing experiments and collecting data to test your hypothesis.
Formulating a hypothesis is a crucial step in the scientific method since it directs research and guides efforts to validate theories or uncover new knowledge.
Key Differences Between Thesis vs. Hypothesis

1. Nature of statement
- Thesis: A thesis presents a clear and definitive statement or argument that summarizes the main point of a research paper or essay.
- Hypothesis: A hypothesis is a tentative and testable proposition or educated guess that suggests a possible outcome of an experiment or research study.
- Thesis: The primary purpose of a thesis is to provide a central focus and roadmap for the entire piece of academic writing.
- Hypothesis: The main purpose of a hypothesis is to guide scientific research by proposing a specific prediction that can be tested and validated.
3. Testability
- Thesis: A thesis is not typically subjected to experimentation but serves as a point of argumentation and discussion.
- Hypothesis: A hypothesis, on the other hand, is explicitly designed for testing through experimentation or observation, making it a fundamental part of the scientific method.
4. Research stage
- Thesis: A thesis is usually formulated after extensive research and analysis as a conclusion or summary of findings.
- Hypothesis: A hypothesis is formulated at the beginning of a research project to establish a basis for experimentation and data collection.
- Thesis: A thesis typically encompasses the entire research paper or essay, providing an overarching theme throughout the work.
- Hypothesis: A hypothesis addresses a specific aspect of a research question or problem, guiding the focus of experiments or investigations.
6. Examples
- Thesis: Example of a thesis statement: “The impact of climate change on marine ecosystems is irreversible.”
- Hypothesis: Example of a hypothesis: “If increased temperatures continue, coral reefs will experience bleaching events.”
- Thesis: The thesis represents a conclusion or a well-supported argument and does not aim to be proven or disproven.
- Hypothesis: On the other hand, a hypothesis aims to be tested and validated through empirical evidence. Besides, it can be proven true or false based on the results of experiments or observations.
These differences highlight the distinct roles that the thesis and hypothesis play in academic writing and scientific research, with one providing a point of argumentation and the other guiding the scientific inquiry process.
Can a hypothesis become a thesis?
Yes. A hypothesis can develop into a thesis as it accumulates substantial evidence through research.
Do all research papers require a thesis?
Not necessarily. While most academic papers benefit from a clear thesis, some, like purely descriptive papers, may follow a different structure.
Can a thesis be proven wrong?
Yes. The purpose of a thesis is not only to prove but also to encourage critical analysis. It can be proven wrong with compelling counterarguments and evidence.
How long should a thesis statement be?
A thesis statement should be concise and to the point, typically one or two sentences.
Is a hypothesis only used in scientific research?
Although hypotheses are typically linked to scientific research, they can also be used to verify assumptions and theories in other areas.
Can a hypothesis be vague?
No. When creating a hypothesis, it’s important to make it clear and able to be tested. Developing experiments and making conclusions based on the results can be difficult if the hypothesis needs clarification.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding the differences between a hypothesis and a thesis is vital to crafting successful research projects and academic papers. While they may seem interchangeable at first glance, these two concepts serve distinct purposes in the research process.
A hypothesis serves as a testable prediction or explanation, whereas a thesis is the central argument of a paper or project. Your work can lack clarity and purpose without understanding the difference.
So, the next time you embark on a research project, take the time to ensure that you understand the fundamental difference between a hypothesis and a thesis. Doing so can lead to more focused, meaningful research that advances knowledge and understanding in your field.
You can also learn more about how long a thesis statement should be .
Thanks for reading.
You may also like:
- Discover Where Thesis Statement Is Located In An Essay
- Master’s Thesis Length: How Long Should A Master’s Thesis Be?
- How Long Is A Thesis Paper: Factors Involved & Formatting Tips
- Moral Argument – Examples And Benefits
- Examples of Work Ethic: Everyone Loves a Good Employee
People Also Read:

Why Do Waiters Get Paid So Little [+ How To Make More Money]

Navigating Workplace Norms: Can You Email A Resignation Letter?

Difference Between Roles And Responsibilities

Does Suspension Mean Termination?

Moral Claim: Definition, Significance, Contemporary Issues, & Challenges

Why Can’t You Flush The Toilet After A Drug Test?


Home » Education » Difference Between Thesis and Hypothesis
Difference Between Thesis and Hypothesis
Main difference – thesis vs hypothesis .
Thesis and hypothesis are two common terms that are often found in research studies. Hypothesis is a logical proposition that is based on existing knowledge that serves as the starting point of an investigation. A thesis is a statement that is put forward as a premise to be maintained or proved. The main difference between thesis and hypothesis is that thesis is found in all research studies whereas a hypothesis is mainly found in experimental quantitative research studies.
This article explains,
1. What is a Thesis? – Definition, Features, Function
2. What is a Hypothesis? – Definition, Features, Function

What is a Thesis
The word thesis has two meanings in a research study. Thesis can either refer to a dissertation or a thesis statement. Thesis or dissertation is the long essay or document that consists of the research study. Thesis can also refer to a theory or statement that is used as a premise to be maintained or proved.
The thesis statement in a research article is a sentence found at the beginning of the paper that presents the main argument of the paper. The rest of the document will gather, organize and present evidence to support this argument. The thesis statement will basically present the topic of the paper and indicate what position the researcher is going to take in relation to this topic. A thesis statement can generally be found at the end of the first paragraph (introductory paragraph) of the paper.

What is a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a logical assumption based on available evidence. Hypothesis is defined as “a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation” in the Oxford dictionary and as “an idea or theory that is not proven but that leads to further study or discussion” in the Merriam-Webster dictionary. In simple words, it is an educated guess that is not proven with concrete scientific evidence. Once it is scientifically tested and proven, it becomes a theory. However, it is important to note that a hypothesis can be accurate or inaccurate.
Hypotheses are mostly used in experiments and research studies. However, hypotheses are not used in every research study. They are mostly used in quantitative research studies that deal with experiments. Hypotheses are often used to test a specific model or theory . They can be used only when the researcher has sufficient knowledge about the subject since hypothesis are always based on the existing knowledge. Once the hypothesis is built, the researcher can find and analyze data and use them to prove or disprove the hypothesis.

Thesis: A thesis is a “statement or theory that is put forward as a premise to be maintained or proved” or a “long essay or dissertation involving personal research, written by a candidate for a university degree” (Oxford dictionary).
Hypothesis: A hypothesis is “a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation” (Oxford dictionary).
Thesis: Thesis statement can be found in all research papers.
Hypothesis: Hypotheses are usually found in experimental quantitative research studies.
Thesis: Thesis statement may explain the hypothesis and how the researcher intends to support it.
Hypothesis: Hypothesis is an educated guess based on the existing knowledge.
Image Courtesy:
“Master’s Thesis” by Henri Sivonen (CC BY 2.0) via Flickr
“Colonial Flagellate Hypothesis” By Katelynp1 – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
About the Author: Hasa
Hasanthi is a seasoned content writer and editor with over 8 years of experience. Armed with a BA degree in English and a knack for digital marketing, she explores her passions for literature, history, culture, and food through her engaging and informative writing.
You May Also Like These
Leave a reply cancel reply.

The Real Differences Between Thesis and Hypothesis (With table)
A thesis and a hypothesis are two very different things, but they are often confused with one another. In this blog post, we will explain the differences between these two terms, and help you understand when to use which one in a research project.
As a whole, the main difference between a thesis and a hypothesis is that a thesis is an assertion that can be proven or disproven, while a hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research.
We probably need to expand a bit on this topic to make things clearer for you, let’s start with definitions and examples.
Definitions
As always, let’s start with the definition of each term before going further.

A thesis is a statement or theory that is put forward as a premise to be maintained or proved. A thesis statement is usually one sentence, and it states your position on the topic at hand.
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. A hypothesis is usually based on observations, and it seeks to explain how these observations fit together.
You may also like:
- Differences between Hardcover and Paperback
- Differences between Average and Median
- Differences between Embassy and Consulate
The best way to understand the slight difference between those terms, is to give you an example for each of them.
If you are writing a paper about the effects of climate change on the environment, your thesis might be “Climate change is causing irreparable damage to our planet, and we must take action to prevent further damage”.
If you observe that the leaves on a tree are turning yellow, your hypothesis might be “The tree is sick”. It’s the starting point of experimental research: what can you do then to prove if your hypothesis is right or wrong?
If your hypothesis is correct, then further research should be able to confirm it. However, if your hypothesis is incorrect, research will disprove it. Either way, a hypothesis is an important part of the scientific process.
Taking a look at the etymology of words can help you to remember which one to use is each case.
The word “thesis” comes from the Greek θέσις, meaning “something put forth”, and refers to an intellectual proposition.
The word “hypothesis” comes from the Greek words “hupo,” meaning “under”, and “thesis” that we just explained.
This reflects the fact that a hypothesis is an educated guess, based on observations.
Argumentation vs idea
Hypothesis are generally base on simple observation, while thesis imply that more work has been done on the topic.
A thesis is usually the result of extensive research and contemplation, and seeks to prove a point or theory.
A hypothesis is only a statement that need to be tested by observation or experimentation.
5 mains differences between thesis and hypothesis
Thesis and hypothesis are different in several ways, here are the 5 keys differences between those terms:
- A thesis is a statement that can be argued, while a hypothesis cannot be argued.
- A thesis is usually longer than a hypothesis.
- A thesis is more detailed than a hypothesis.
- A thesis is based on research, while a hypothesis may or may not be based on research.
- A thesis must be proven, while a hypothesis need not be proven.
So, in short, a thesis is an argument, while a hypothesis is a prediction. A thesis is more detailed and longer than a hypothesis, and it is based on research. Finally, a thesis must be proven, while a hypothesis does not need to be proven.
Is there a difference between a thesis and a claim?
Yes, there is a difference between a thesis and a claim. A thesis statement is usually one sentence that states your main argument, while a claim is a more general statement that can be supported by evidence.
Is a hypothesis a prediction?
No, a hypothesis is not a prediction. A prediction is a statement about what you think will happen in the future, whereas a hypothesis is a statement about what you think is causing a particular phenomenon.
What’s the difference between thesis and dissertation?
A thesis is usually shorter and more focused than a dissertation, and it is typically achieved in order to earn a bachelor’s degree. A dissertation is usually longer and more comprehensive, and it is typically completed in order to earn a master’s or doctorate degree.
What is a good thesis statement?
A good thesis statement is specific, debatable, and supports the main point of the paper. It should be clear what the researcher position is, and what evidence they will use to support it.
Thanks for reading! I hope this post helped clear up the differences between thesis and hypothesis. Like that kind of comparison? These other articles might be interesting for you:
- What is the Difference between Mandate and Law?
- The 6 Differences Between Space And Universe
- What’s the Difference Between Cosmology and Astrology?
I am very curious and I love to learn about all types of subjects. Thanks to my experience on the web, I share my discoveries with you on this site :)
Similar Posts

The True Differences Between a Monarchy and an Empire
We learn this in school, but we teach us so many things in a short period of time and with so little experience of the real world (especially in politics), that it quickly becomes overwhelming. The differences between monarchy and empire weren’t clear for me, so I did the research and can now share what…
5 Crucial Differences Between Prefecture and Province
Ever been puzzled by the distinction between a prefecture and a province? If so, you’ve come to the right spot. Understanding these terms is vital for a deeper comprehension of worldwide administrative divisions. In this article, I’ll cover everything I know about the subject. The primary distinction between a prefecture and a province lies in…

Centaurs vs Satyrs: What’s the Real Difference?
Centaurs and Satyrs have fascinated people for centuries, sparking curiosity about their mythical origins and meanings. If you’ve ever wondered what sets these two creatures apart, you’re in the right place! I’m here to tell you about their unique characteristics and cultural significance. Centaurs are half human, half horse and are known for their dual…

Missile Vs Artillery: What’s the exact difference? (Table)
What’s the difference between an artillery shell and a missile? This is a question that often confuses people. The two weapons systems are very similar, but there are some key differences. In this blog post, we will discuss the differences between artillery and missiles, and explain which one is better for your needs. The key…

What’s the Difference Between Embassy and Consulate?
Are you looking for a visa to visit a foreign country? Do you know where to get such services between an embassy and a consulate? Have you had issues directing a fellow citizen on where to report a crisis in a foreign country between a consulate and an embassy? Like in any other field, these…

What’s the Difference between Rap and Poetry Slam?
Although the messages communicated may be similar, rap and poetry slam have little in common.These are two very distinct forms of expression. What is the difference between rap and slam?Rap is a musical genre, in which vocal expression is essential, respecting rhymes and a very rhythmic diction.Slam is closer to reading a poem, rhymes and…
Thesis vs. Hypothesis: What's the Difference?
Key Differences
Comparison chart, verification, thesis and hypothesis definitions, is a thesis subjective, can a thesis be a question, who verifies a hypothesis, who writes a thesis, can a hypothesis be proven, does a thesis require research, what's a thesis statement, what forms a good hypothesis, is a hypothesis always true, can a thesis change during research, how broad can a hypothesis be, is defending a thesis challenging, is every thesis published, how long is a thesis, what if research contradicts my hypothesis, why is a thesis important, are hypotheses guaranteed to progress science, is there risk in a hypothesis, can a hypothesis lead to a theory, what's a null hypothesis.

Trending Comparisons

Popular Comparisons

New Comparisons

What Is A Research (Scientific) Hypothesis? A plain-language explainer + examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
If you’re new to the world of research, or it’s your first time writing a dissertation or thesis, you’re probably noticing that the words “research hypothesis” and “scientific hypothesis” are used quite a bit, and you’re wondering what they mean in a research context .
“Hypothesis” is one of those words that people use loosely, thinking they understand what it means. However, it has a very specific meaning within academic research. So, it’s important to understand the exact meaning before you start hypothesizing.
Research Hypothesis 101
- What is a hypothesis ?
- What is a research hypothesis (scientific hypothesis)?
- Requirements for a research hypothesis
- Definition of a research hypothesis
- The null hypothesis
What is a hypothesis?
Let’s start with the general definition of a hypothesis (not a research hypothesis or scientific hypothesis), according to the Cambridge Dictionary:
Hypothesis: an idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved.
In other words, it’s a statement that provides an explanation for why or how something works, based on facts (or some reasonable assumptions), but that has not yet been specifically tested . For example, a hypothesis might look something like this:
Hypothesis: sleep impacts academic performance.
This statement predicts that academic performance will be influenced by the amount and/or quality of sleep a student engages in – sounds reasonable, right? It’s based on reasonable assumptions , underpinned by what we currently know about sleep and health (from the existing literature). So, loosely speaking, we could call it a hypothesis, at least by the dictionary definition.
But that’s not good enough…
Unfortunately, that’s not quite sophisticated enough to describe a research hypothesis (also sometimes called a scientific hypothesis), and it wouldn’t be acceptable in a dissertation, thesis or research paper . In the world of academic research, a statement needs a few more criteria to constitute a true research hypothesis .
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes – specificity , clarity and testability .
Let’s take a look at these more closely.
Need a helping hand?
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
A good research hypothesis needs to be extremely clear and articulate about both what’ s being assessed (who or what variables are involved ) and the expected outcome (for example, a difference between groups, a relationship between variables, etc.).
Let’s stick with our sleepy students example and look at how this statement could be more specific and clear.
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
As you can see, the statement is very specific as it identifies the variables involved (sleep hours and test grades), the parties involved (two groups of students), as well as the predicted relationship type (a positive relationship). There’s no ambiguity or uncertainty about who or what is involved in the statement, and the expected outcome is clear.
Contrast that to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – and you can see the difference. “Sleep” and “academic performance” are both comparatively vague , and there’s no indication of what the expected relationship direction is (more sleep or less sleep). As you can see, specificity and clarity are key.

Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
A statement must be testable to qualify as a research hypothesis. In other words, there needs to be a way to prove (or disprove) the statement. If it’s not testable, it’s not a hypothesis – simple as that.
For example, consider the hypothesis we mentioned earlier:
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
We could test this statement by undertaking a quantitative study involving two groups of students, one that gets 8 or more hours of sleep per night for a fixed period, and one that gets less. We could then compare the standardised test results for both groups to see if there’s a statistically significant difference.
Again, if you compare this to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – you can see that it would be quite difficult to test that statement, primarily because it isn’t specific enough. How much sleep? By who? What type of academic performance?
So, remember the mantra – if you can’t test it, it’s not a hypothesis 🙂

Defining A Research Hypothesis
You’re still with us? Great! Let’s recap and pin down a clear definition of a hypothesis.
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable.
So, when you write up hypotheses for your dissertation or thesis, make sure that they meet all these criteria. If you do, you’ll not only have rock-solid hypotheses but you’ll also ensure a clear focus for your entire research project.
What about the null hypothesis?
You may have also heard the terms null hypothesis , alternative hypothesis, or H-zero thrown around. At a simple level, the null hypothesis is the counter-proposal to the original hypothesis.
For example, if the hypothesis predicts that there is a relationship between two variables (for example, sleep and academic performance), the null hypothesis would predict that there is no relationship between those variables.
At a more technical level, the null hypothesis proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations and that any differences are due to chance alone.
And there you have it – hypotheses in a nutshell.
If you have any questions, be sure to leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to help you. If you need hands-on help developing and testing your hypotheses, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

16 Comments
Very useful information. I benefit more from getting more information in this regard.
Very great insight,educative and informative. Please give meet deep critics on many research data of public international Law like human rights, environment, natural resources, law of the sea etc
In a book I read a distinction is made between null, research, and alternative hypothesis. As far as I understand, alternative and research hypotheses are the same. Can you please elaborate? Best Afshin
This is a self explanatory, easy going site. I will recommend this to my friends and colleagues.
Very good definition. How can I cite your definition in my thesis? Thank you. Is nul hypothesis compulsory in a research?
It’s a counter-proposal to be proven as a rejection
Please what is the difference between alternate hypothesis and research hypothesis?
It is a very good explanation. However, it limits hypotheses to statistically tasteable ideas. What about for qualitative researches or other researches that involve quantitative data that don’t need statistical tests?
In qualitative research, one typically uses propositions, not hypotheses.
could you please elaborate it more
I’ve benefited greatly from these notes, thank you.
This is very helpful
well articulated ideas are presented here, thank you for being reliable sources of information
Excellent. Thanks for being clear and sound about the research methodology and hypothesis (quantitative research)
I have only a simple question regarding the null hypothesis. – Is the null hypothesis (Ho) known as the reversible hypothesis of the alternative hypothesis (H1? – How to test it in academic research?
this is very important note help me much more
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is Research Methodology? Simple Definition (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and objectives are confirmatory in nature. For example,…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

PSC 352: Introduction to Comparative Politics
- Getting Started
- Comparative Politics Overview
- Current World/Political News Feeds
- Choose a country
What is the difference between a thesis & a hypothesis?
- Find Books/eBooks
- Find Articles, Reports & Documents
- Find Statistics
- Find Poll & Survey Results
- Evaluate Your Sources
- Cite Your Sources
B oth the hypothesis statement and the thesis statement answer the research question of the study. When the statement is one that can be proved or disproved, it is an hypothesis statement. If, instead, the statement specifically shows the intentions/objectives/position of the researcher, it is a thesis statement.
A hypothesis is a statement that can be proved or disproved. It is typically used in quantitative research and predicts the relationship between variables.
A thesis statement is a short, direct sentence that summarizes the main point or claim of an essay or research paper. It is seen in quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods research. A thesis statement is developed, supported, and explained in the body of the essay or research report by means of examples and evidence.
Every research study should contain a concise and well-written thesis statement. If the intent of the study is to prove/disprove something, that research report will also contain an hypothesis statement.
Jablonski , Judith. What is the difference between a thesis statement and an hypothesis statement? Online Library. American Public University System. Jun 16, 2014. Web. http://apus.libanswers.com/faq/2374
Let’s say you are interested in the conflict in Darfur, and you conclude that the issues you wish to address include the nature, causes, and effects of the conflict, and the international response. While you could address the issue of international response first, it makes the most sense to start with a description of the conflict, followed by an exploration of the causes, effects, and then to discuss the international response and what more could/should be done.
This hypothetical example may lead to the following title, introduction, and statement of questions:
Conflict in Darfur: Causes, Consequences, and International Response This paper examines the conflict in Darfur, Sudan. It is organized around the following questions: (1) What is the nature of the conflict in Darfur? (2) What are the causes and effects of the conflict? (3) What has the international community done to address it, and what more could/should it do?
Following the section that presents your questions and background, you will offer a set of responses/answers/(hypo)theses. They should follow the order of the questions. This might look something like this, “The paper argues/contends/ maintains/seeks to develop the position that...etc.” The most important thing you can do in this section is to present as clearly as possible your best thinking on the subject matter guided by course material and research. As you proceed through the research process, your thinking about the issues/questions will become more nuanced, complex, and refined. The statement of your theses will reflect this as you move forward in the research process.
So, looking to our hypothetical example on Darfur:
The current conflict in Darfur goes back more than a decade and consists of fighting between government-supported troops and residents of Darfur. The causes of the conflict include x, y, and z. The effects of the conflict have been a, b, and c. The international community has done 0, and it should do 1, 2, and 3.
Once you have setup your thesis you will be ready to begin amassing supporting evidence for you claims. This is a very important part of the research paper, as you will provide the substance to defend your thesis.
- << Previous: Choose a country
- Next: Find Books/eBooks >>
- Last Updated: Feb 28, 2024 3:19 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mssu.edu/PSC352
This site is maintained by the librarians of George A. Spiva Library . If you have a question or comment about the Library's LibGuides, please contact the site administrator .
Research Hypothesis In Psychology: Types, & Examples
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A research hypothesis, in its plural form “hypotheses,” is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method .
Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding
Some key points about hypotheses:
- A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
- It is stated in clear, precise terms before any data collection or analysis occurs. This makes the hypothesis testable.
- A hypothesis must be falsifiable. It should be possible, even if unlikely in practice, to collect data that disconfirms rather than supports the hypothesis.
- Hypotheses guide research. Scientists design studies to explicitly evaluate hypotheses about how nature works.
- For a hypothesis to be valid, it must be testable against empirical evidence. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
- Hypotheses are informed by background knowledge and observation, but go beyond what is already known to propose an explanation of how or why something occurs.
Predictions typically arise from a thorough knowledge of the research literature, curiosity about real-world problems or implications, and integrating this to advance theory. They build on existing literature while providing new insight.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Alternative hypothesis.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative or experimental hypothesis in experimental research.
It typically suggests a potential relationship between two key variables: the independent variable, which the researcher manipulates, and the dependent variable, which is measured based on those changes.
The alternative hypothesis states a relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable affects the other).
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses:
- Important hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested empirically. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
In summary, a hypothesis is a precise, testable statement of what researchers expect to happen in a study and why. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and are significant in supporting the theory being investigated.
The alternative hypothesis can be directional, indicating a specific direction of the effect, or non-directional, suggesting a difference without specifying its nature. It’s what researchers aim to support or demonstrate through their study.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable.
It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The null hypothesis, positing no effect or relationship, is a foundational contrast to the research hypothesis in scientific inquiry. It establishes a baseline for statistical testing, promoting objectivity by initiating research from a neutral stance.
Many statistical methods are tailored to test the null hypothesis, determining the likelihood of observed results if no true effect exists.
This dual-hypothesis approach provides clarity, ensuring that research intentions are explicit, and fosters consistency across scientific studies, enhancing the standardization and interpretability of research outcomes.
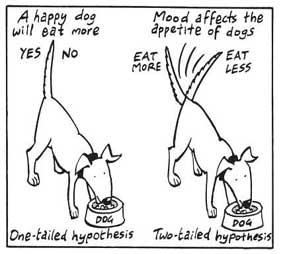
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of this relationship.
It merely indicates that a change or effect will occur without predicting which group will have higher or lower values.
For example, “There is a difference in performance between Group A and Group B” is a non-directional hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional (one-tailed) hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It predicts in which direction the change will take place. (i.e., greater, smaller, less, more)
It specifies whether one variable is greater, lesser, or different from another, rather than just indicating that there’s a difference without specifying its nature.
For example, “Exercise increases weight loss” is a directional hypothesis.
Falsifiability
The Falsification Principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory or hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable and irrefutable.
Falsifiability emphasizes that scientific claims shouldn’t just be confirmable but should also have the potential to be proven wrong.
It means that there should exist some potential evidence or experiment that could prove the proposition false.
However many confirming instances exist for a theory, it only takes one counter observation to falsify it. For example, the hypothesis that “all swans are white,” can be falsified by observing a black swan.
For Popper, science should attempt to disprove a theory rather than attempt to continually provide evidence to support a research hypothesis.
Can a Hypothesis be Proven?
Hypotheses make probabilistic predictions. They state the expected outcome if a particular relationship exists. However, a study result supporting a hypothesis does not definitively prove it is true.
All studies have limitations. There may be unknown confounding factors or issues that limit the certainty of conclusions. Additional studies may yield different results.
In science, hypotheses can realistically only be supported with some degree of confidence, not proven. The process of science is to incrementally accumulate evidence for and against hypothesized relationships in an ongoing pursuit of better models and explanations that best fit the empirical data. But hypotheses remain open to revision and rejection if that is where the evidence leads.
- Disproving a hypothesis is definitive. Solid disconfirmatory evidence will falsify a hypothesis and require altering or discarding it based on the evidence.
- However, confirming evidence is always open to revision. Other explanations may account for the same results, and additional or contradictory evidence may emerge over time.
We can never 100% prove the alternative hypothesis. Instead, we see if we can disprove, or reject the null hypothesis.
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct but does support the alternative/experimental hypothesis.
Upon analysis of the results, an alternative hypothesis can be rejected or supported, but it can never be proven to be correct. We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist which could refute a theory.
How to Write a Hypothesis
- Identify variables . The researcher manipulates the independent variable and the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
- Operationalized the variables being investigated . Operationalization of a hypothesis refers to the process of making the variables physically measurable or testable, e.g. if you are about to study aggression, you might count the number of punches given by participants.
- Decide on a direction for your prediction . If there is evidence in the literature to support a specific effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a directional (one-tailed) hypothesis. If there are limited or ambiguous findings in the literature regarding the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.
- Make it Testable : Ensure your hypothesis can be tested through experimentation or observation. It should be possible to prove it false (principle of falsifiability).
- Clear & concise language . A strong hypothesis is concise (typically one to two sentences long), and formulated using clear and straightforward language, ensuring it’s easily understood and testable.
Consider a hypothesis many teachers might subscribe to: students work better on Monday morning than on Friday afternoon (IV=Day, DV= Standard of work).
Now, if we decide to study this by giving the same group of students a lesson on a Monday morning and a Friday afternoon and then measuring their immediate recall of the material covered in each session, we would end up with the following:
- The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
- The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors.
More Examples
- Memory : Participants exposed to classical music during study sessions will recall more items from a list than those who studied in silence.
- Social Psychology : Individuals who frequently engage in social media use will report higher levels of perceived social isolation compared to those who use it infrequently.
- Developmental Psychology : Children who engage in regular imaginative play have better problem-solving skills than those who don’t.
- Clinical Psychology : Cognitive-behavioral therapy will be more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety over a 6-month period compared to traditional talk therapy.
- Cognitive Psychology : Individuals who multitask between various electronic devices will have shorter attention spans on focused tasks than those who single-task.
- Health Psychology : Patients who practice mindfulness meditation will experience lower levels of chronic pain compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Organizational Psychology : Employees in open-plan offices will report higher levels of stress than those in private offices.
- Behavioral Psychology : Rats rewarded with food after pressing a lever will press it more frequently than rats who receive no reward.
Related Articles

Research Methodology
What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
Convergent Validity: Definition and Examples
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization

Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
What Is the Difference Between a Thesis Statement & a Research Question?
Meagan roper.

Knowing the right time to use either a thesis statement or a research question can make the difference between inspiring your readers and confusing them. Both thesis statements and research questions are used in academic writing to provide purpose and direction to the work. However, each writing situation calls for different kinds of direction-giving.
Explore this article
- Thesis Statements
- Research Questions
- Differences
- Similarities
1 Thesis Statements
Most good, well-organized writing will contain a thesis statement near the beginning of the essay or paper and will repeat it at the end of the work. The thesis statement tells your audience what you plan to talk about or prove, serving as a preview to the rest of your work. Thesis statements take a position on a debatable topic or make a statement of information, and then the rest of the paper proves the position or provides more detailed information.
2 Research Questions
While most quality writing will naturally contain a thesis statement, only certain kinds of writing will contain one or more research questions. Research studies, like the kind that appear in academic journals and scientific research publications, usually seek to discover new information about a little known topic. The purpose of the research question is to tell your reader what you are after as you dive into your investigation. A research question must be debatable but should be an open question rather than one that takes a position.
3 Differences
The two types of direction-giving at the beginning and end of academic writing differ in their purpose. A thesis statement delivers a positional statement about information. A research question, on the other hand, asks an open-ended question about a topic to be investigated. For example, a research question might ask "How does competitive soccer affect adolescent girls?" while a thesis statement on the same topic might state "Competitive soccer provides many benefits to adolescent girls, such as exercise, but may also have negative effects, such as increased risk of concussion."
4 Similarities
Both thesis statements and research questions can be used to provide direction for academic journal articles, research papers, reports of research studies and qualitative investigations of events or text. Both must be carefully crafted by the writer to give the reader a clear understanding of the purpose of the work. In order to be clear and effective, research questions and thesis statements must be specific, concise and purposeful.
- 1 Kean University: What is a thesis?
- 2 Purdue Online Writing Lab: Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements
About the Author
Meagan Roper has worked in public relations, journalism and the publishing industry. She has a bachelor's degree in public relations and advertising, and a master's degree in interpersonal and organizational communication, both from Liberty University. Roper also has several years of experience teaching college communication courses, and working in information technology and web design.
Related Articles

What Can You Do With a Master's Degree in Criminal...

The Difference Between Discursive & Argumentative Essays

How to Write a Negative Debate Speech

How to Make Group Discussions & Interactions Work in...

Correctional Officer Testing

How to Calculate a Monthly Salary to Hourly

How to Write Assumptions for a Thesis

Target Pharmacy Technician Training

How to Pass a Police Psychological Evaluation

How to Make Observations Using the Scientific Method

Define Primary & Secondary Data

What Is a Quasi Experimental Study?

How to Make an Introduction Paragraph for a Debate

Difference Between a PhD & a PsyD

How to Write an Informative Essay

How to Write a Thesis Statement in High School Essays

What Criteria Should Be Used to Evaluate the Credibility...

How to Write a Critique Essay

How to Write an Argumentative Speech

The Best Bra for a One-Shoulder Dress
Regardless of how old we are, we never stop learning. Classroom is the educational resource for people of all ages. Whether you’re studying times tables or applying to college, Classroom has the answers.
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Manage Preferences
© 2020 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved. Based on the Word Net lexical database for the English Language. See disclaimer .
Thesis and Purpose Statements
Use the guidelines below to learn the differences between thesis and purpose statements.
In the first stages of writing, thesis or purpose statements are usually rough or ill-formed and are useful primarily as planning tools.
A thesis statement or purpose statement will emerge as you think and write about a topic. The statement can be restricted or clarified and eventually worked into an introduction.
As you revise your paper, try to phrase your thesis or purpose statement in a precise way so that it matches the content and organization of your paper.
Thesis statements
A thesis statement is a sentence that makes an assertion about a topic and predicts how the topic will be developed. It does not simply announce a topic: it says something about the topic.
Good: X has made a significant impact on the teenage population due to its . . . Bad: In this paper, I will discuss X.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic.
A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire paragraph.
A thesis statement is focused and specific enough to be proven within the boundaries of the paper. Key words (nouns and verbs) should be specific, accurate, and indicative of the range of research, thrust of the argument or analysis, and the organization of supporting information.
Purpose statements
A purpose statement announces the purpose, scope, and direction of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect in a paper and what the specific focus will be.
Common beginnings include:
“This paper examines . . .,” “The aim of this paper is to . . .,” and “The purpose of this essay is to . . .”
A purpose statement makes a promise to the reader about the development of the argument but does not preview the particular conclusions that the writer has drawn.
A purpose statement usually appears toward the end of the introduction. The purpose statement may be expressed in several sentences or even an entire paragraph.
A purpose statement is specific enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. Purpose statements are common in research papers in some academic disciplines, while in other disciplines they are considered too blunt or direct. If you are unsure about using a purpose statement, ask your instructor.
This paper will examine the ecological destruction of the Sahel preceding the drought and the causes of this disintegration of the land. The focus will be on the economic, political, and social relationships which brought about the environmental problems in the Sahel.
Sample purpose and thesis statements
The following example combines a purpose statement and a thesis statement (bold).
The goal of this paper is to examine the effects of Chile’s agrarian reform on the lives of rural peasants. The nature of the topic dictates the use of both a chronological and a comparative analysis of peasant lives at various points during the reform period. . . The Chilean reform example provides evidence that land distribution is an essential component of both the improvement of peasant conditions and the development of a democratic society. More extensive and enduring reforms would likely have allowed Chile the opportunity to further expand these horizons.
For more tips about writing thesis statements, take a look at our new handout on Developing a Thesis Statement.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Developing a Thesis Statement
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
- Visit the University of Nebraska–Lincoln
- Apply to the University of Nebraska–Lincoln
- Give to the University of Nebraska–Lincoln
Search Form
Research question, purpose statement, hypothesis(es).
Here’s a good example of how to narrow your topic into a good research question:
- Too broad — Rural America
- Narrowed topic — Role of women in rural America?
- Research question — What is the central role of women in today’s farming communities?
If you’re asked to write a proposal before you begin your actual research, the proposal will contain a purpose statement that states in some detail what you want to learn about in your research project; it looks something like this:
- Ex.: “This study will examine the…”
Your purpose statement leads you to write a more refined thesis statement or hypothesis(es), an assertion that you can defend and support with evidence gathered in your literature review and research. Here are some examples:
- Ex.: “In the United States, government regulation plays an important role in the fight against air pollution.” Or, conversely,
- Ex.: “United States government regulation has little effect in the fight against air pollution.”
The type of design selected for your study depends on your research question(s), hypothesis(es), or problem.
You’ll use evidence you’ve gathered in your research to confirm — or reject — your hypothesis.
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

Thesis vs Hypothesis vs Theory: the Differences and examples

thesis hypothesis and theory
Many students may have a hard time understanding the differences between a thesis, a hypothesis, and a theory. It is important to understand their differences. Such an understanding will be instrumental.
More so, when writing complex research papers that require a thesis that has a hypothesis and utilizes theories. We have gathered from responses of our college writing service that the difference between the three is confusing.

That being said, this article is meant to explain the differences between a thesis, a hypothesis, and a theory.
Difference between Hypothesis and Thesis
There are major differences between hypothesis and thesis. While they seem to be related on the face, their differences are huge both in concept and practice.
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation of something or a phenomenon. A scientific hypothesis uses a scientific method that requires any hypothesis to be tested. As such, scientists and researchers base their hypothesis on observations that have been previously made and that which cannot be explained by the available or prevailing scientific theories.
From the definition of a hypothesis, you can see that theories must be included in any scientific method. This is the reason why this article tries to differentiate a thesis, a hypothesis, and a theory.
Moving forward, a thesis can be defined as a written piece of academic work that is submitted by students to attain a university degree. However, on a smaller scale, there is something that is referred to as a thesis statement.
This is written at the introduction of a research paper or essay that is supported by a credible argument. The link between a hypothesis and thesis is that a thesis is a distinction or an affirmation of the hypothesis.
What this means is that whenever a research paper contains a hypothesis, there should be a thesis that validates it.
People Also Read: Is using an Essay Writing Service Cheating? Is it Ethical?
What is a Hypothesis?
A hypothesis can be defined as the proposed or suggested explanation for an occurrence, something, or a phenomenon. It should be testable through scientific methods. The reason why scholarly works should have a hypothesis is that the observed phenomena could not be explained using the prevailing scientific theories hence the reason why it should be tested.
Testing the hypothesis may result in the development of new or improved scientific theories that are beneficial to the discipline and society in general.
What is a Thesis?
A thesis is a written piece of academic work that is submitted by students to attain a university degree. When a thesis is used as a stand-alone word, it denotes academic papers written by university students. It is mostly written by those pursuing postgraduate degrees, at the end of their courses. They demonstrate their proficiency in their disciplines and the topics they have selected for research.
However, when a thesis is used to refer to a statement, it denotes the statement that is written at the introduction of a research paper or essay. A thesis is supported by a credible argument.
Every research paper must have a thesis statement that acts as a guide to what the research will be all about. It is possible to receive very poor grades or even score a zero if your research paper lacks the thesis statement.
What is a Theory?
A theory can be defined as a rational form of abstract perspectives or thinking concerning the results of such thinking or a phenomenon. The process of rational and contemplative thinking is mostly associated with processes such as research or observational study.
As such, a theory can be considered to belong to both scientific and non-scientific disciplines. Theories can also belong to no discipline.
From a modernistic scientific approach, a theory can mean scientific theories that have been well confirmed to explain nature and that are created in such a way that they are consistent with the standard scientific method. A theory should fulfill all the criteria required by modern-day science.
A theory should be described in a way that scientific tests that have been conducted can provide empirical support or contradiction to the theory.
Because of the nature by which scientific theories are developed, they tend to be the most rigorous, reliable, and comprehensive when it comes to describing and supporting scientific knowledge.
The connection between a theory and a hypothesis is that when a theory has not yet been proven, it can be referred to as a hypothesis.
The thing about theories is that they are not meant to help the scientist or researcher reach a particular goal. Rather, a theory is meant to guide the process of finding facts about a phenomenon or an observation.
People Also Read: How to Use Personal Experience in Research Paper or Essay
Difference between a Theory and Thesis
A theory is a rational form of abstract perspectives or thinking concerning the results of such thinking or a phenomenon. The process of rational and contemplative thinking is mostly associated with processes such as research or observational study. On the other hand, a thesis is a written piece of academic work that is submitted by students to attain a university degree.
It denotes academic papers that are written by students in the university, especially those pursuing postgraduate degrees, at the end of their courses to demonstrate their proficiency in their disciplines and the topics they have selected for research.
To understand the application of these, read our guide on the difference between a research paper and a thesis proposal to get a wider view.
How to write a Good Hypothesis
1. asking a question.
Asking a question is the first step in the scientific method and the question should be based on who, what, where, when, why, and how . The question should be focused, specific, and researchable.
2. Gathering preliminary research
This is the process of collecting relevant data. It can be done by researching academic journals, conducting case studies, observing phenomena, and conducting experiments.
3. Formulating an answer
When the research is completed, you should think of how best to answer the question and defend your position. The answer to your question should be objective.
4. Writing the hypothesis
When your answer is ready, you can move to the next step of formulating the hypothesis. A good hypothesis should contain relevant variables, predicted outcomes, and a study group that can include non-human things. The hypothesis should not be a question but a complete statement.
5. Refining the hypothesis
Though you may skip this step, it is advisable to include it because your study may involve two groups or be a correlational study. Refining the hypothesis will ensure that you have stated the difference or relationship you expect to find.
6. Creating a null and alternative hypotheses
A null hypothesis (H0) will postulate that there is no evidence to support the difference. On the other hand, an alternative hypothesis (H1) posits that there is evidence in support of the difference.
People Also Read: Research Paper Graph: How to insert Graphs, Tables & Figures
Frequently Asked Questions
Difference between thesis and hypothesis example.
Thesis: High levels of alcohol consumption have detrimental effects on your health, such as weight gain, heart disease, and liver complications.
Hypothesis: The people who consume high levels of alcohol experience detrimental effects on their health such as weight gain, heart disease, and liver complications.
What is the difference between a summary and a thesis statement?
A summary is a brief account or statement of the main points from the researches. A thesis statement is a statement that is written at the end of the introduction of a research paper or essay that summarizes the main claims of the paper.
Difference between hypothesis and statement of the problem
A hypothesis can be defined as the proposed or suggested explanation for an occurrence, something, or a phenomenon. The same should be testable through scientific methods. Conversely, a statement of a problem is a concise description of the issue to be addressed on how it can be improved.

When not handling complex essays and academic writing tasks, Josh is busy advising students on how to pass assignments. In spare time, he loves playing football or walking with his dog around the park.
Related posts

Delta math hacks
How to get Delta Math Answers: Top Hacks to Cheat Delta Math

How to Show Paraphrasing
How to Show Paraphrasing: Ways to Cite a Paraphrase

How to Write an Ethnography Essay
How to Write an Ethnography Essay or Research Paper
Assumption vs. Hypothesis
What's the difference.
Assumption and hypothesis are both concepts used in research and reasoning, but they differ in their nature and purpose. An assumption is a belief or statement that is taken for granted or accepted as true without any evidence or proof. It is often used as a starting point or a premise in an argument or analysis. On the other hand, a hypothesis is a tentative explanation or prediction that is based on limited evidence or prior knowledge. It is formulated to be tested and verified through empirical research or experimentation. While assumptions are often subjective and can be biased, hypotheses are more objective and aim to provide a basis for scientific investigation.
Further Detail
Introduction.
Assumptions and hypotheses are fundamental concepts in the fields of logic, science, and research. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct attributes that set them apart. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of assumptions and hypotheses, their roles in different contexts, and how they contribute to the process of knowledge acquisition and problem-solving.
Assumptions
An assumption is a belief or statement that is taken for granted or accepted as true without any proof or evidence. It serves as a starting point for reasoning or argumentation. Assumptions can be based on personal experiences, cultural norms, or generalizations. They are often used to fill in gaps in knowledge or to simplify complex situations.
One key attribute of assumptions is that they are not necessarily true or proven. They are subjective and can vary from person to person. Assumptions can be implicit, meaning they are not explicitly stated, or explicit, where they are clearly expressed. They can also be conscious or unconscious, depending on whether we are aware of them or not.
Assumptions play a crucial role in everyday life, decision-making, and problem-solving. They help us make sense of the world and navigate through uncertain situations. However, it is important to recognize that assumptions can introduce biases and limit our understanding if they are not critically examined or challenged.
A hypothesis, on the other hand, is a tentative explanation or prediction that is based on limited evidence or prior knowledge. It is formulated as a testable statement that can be supported or refuted through empirical observation or experimentation. Hypotheses are commonly used in scientific research to guide investigations and generate new knowledge.
Unlike assumptions, hypotheses are grounded in evidence and are subject to verification. They are formulated based on existing theories, observations, or logical reasoning. Hypotheses are often stated in the form of "if-then" statements, where the independent variable (the "if" part) is manipulated or observed to determine its effect on the dependent variable (the "then" part).
Hypotheses are essential in the scientific method, as they provide a framework for conducting experiments and gathering data. They allow researchers to make predictions and draw conclusions based on empirical evidence. If a hypothesis is supported by the data, it can lead to the development of theories or further research. If it is refuted, it may prompt the formulation of new hypotheses or the revision of existing ones.
Comparison of Attributes
While assumptions and hypotheses share the commonality of being statements or beliefs, they differ in several key attributes:
Assumptions are often based on personal beliefs, experiences, or cultural norms. They can be influenced by subjective factors and may not have a solid foundation in evidence or logic. In contrast, hypotheses are grounded in existing knowledge, theories, or observations. They are formulated based on logical reasoning and are subject to empirical testing.
2. Verifiability
Assumptions are not easily verifiable since they are often subjective or based on incomplete information. They are accepted as true without rigorous testing or evidence. On the other hand, hypotheses are formulated to be testable and verifiable. They can be supported or refuted through empirical observation or experimentation.
Assumptions are primarily used to simplify complex situations, fill in gaps in knowledge, or provide a starting point for reasoning. They are often employed in everyday life, decision-making, and problem-solving. Hypotheses, on the other hand, serve the purpose of generating new knowledge, guiding scientific research, and making predictions about the relationship between variables.
4. Role in Knowledge Acquisition
Assumptions can limit knowledge acquisition if they are not critically examined or challenged. They can introduce biases and prevent us from exploring alternative explanations or perspectives. Hypotheses, on the other hand, contribute to knowledge acquisition by providing a structured approach to testing and refining ideas. They encourage critical thinking, data collection, and analysis.
5. Testability
Assumptions are often difficult to test since they are not formulated as specific statements or predictions. They are more subjective in nature and may not lend themselves to empirical verification. Hypotheses, on the other hand, are designed to be testable. They are formulated as specific statements that can be supported or refuted through observation or experimentation.
Assumptions and hypotheses are both important concepts in reasoning, problem-solving, and scientific research. While assumptions provide a starting point for reasoning and decision-making, hypotheses offer a structured approach to generating new knowledge and making predictions. Understanding the attributes and differences between assumptions and hypotheses is crucial for critical thinking, avoiding biases, and advancing our understanding of the world.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
A hypothesis is a statement that can be proved or disproved. It is typically used in quantitative research and predicts the relationship between variables. A thesis statement is a short, direct sentence that summarizes the main point or claim of an essay or research paper. It is seen in quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods research.
1. Nature of statement. Thesis: A thesis presents a clear and definitive statement or argument that summarizes the main point of a research paper or essay. Hypothesis: A hypothesis is a tentative and testable proposition or educated guess that suggests a possible outcome of an experiment or research study. 2.
A thesis is a statement that is put forward as a premise to be maintained or proved. The main difference between thesis and hypothesis is that thesis is found in all research studies whereas a hypothesis is mainly found in experimental quantitative research studies. This article explains, 1. What is a Thesis? - Definition, Features, Function. 2.
Thesis and hypothesis are different in several ways, here are the 5 keys differences between those terms: A thesis is a statement that can be argued, while a hypothesis cannot be argued. A thesis is usually longer than a hypothesis. A thesis is more detailed than a hypothesis. A thesis is based on research, while a hypothesis may or may not be ...
After delving into the differences between thesis and hypothesis, it is clear that these terms have distinct meanings and applications in the academic world. A thesis is a statement or argument that is supported by evidence and presented in a written work, while a hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon that is based on limited ...
A "thesis" is a statement or theory that is put forward as a premise to be maintained or proved, typically a position a student proposes to defend in a thesis (long essay/dissertation). Conversely, a "hypothesis" is a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation. A ...
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable. So, when you write up hypotheses for your dissertation or thesis, make sure that they meet all these criteria. If you do, you'll not only have rock-solid ...
What is the difference between a thesis & a hypothesis? B oth the hypothesis statement and the thesis statement answer the research question of the study. When the statement is one that can be proved or disproved, it is an hypothesis statement. If, instead, the statement specifically shows the intentions/objectives/position of the researcher ...
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses: A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process. Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test ...
Hypotheses. A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a precise, testable statement of what the researchers predict will be the outcome of the study. This usually involves proposing a possible relationship between two variables: the independent variable (what the researcher changes) and the dependant variable (what the research measures).
It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis. 7.
Knowing the right time to use either a thesis statement or a research question can make the difference between inspiring your readers and confusing them. Both thesis statements and research questions are used in academic writing to provide purpose and direction to the work. However, each writing situation calls for ...
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic. A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire ...
The Hypothesis statement comes in different format but with the intent to help prove or disprove a phenomenon. The hypothesis can help defend, support, explain or disprove, argue against the thesis statement.Usually the hypothesis measures specific issues or variables-two or more and therefore should be testable.
If you're asked to write a proposal before you begin your actual research, the proposal will contain a purpose statement that states in some detail what you want to learn about in your research project; it looks something like this: Ex.: "This study will examine the…". Your purpose statement leads you to write a more refined thesis ...
However, on a smaller scale, there is something that is referred to as a thesis statement. This is written at the introduction of a research paper or essay that is supported by a credible argument. The link between a hypothesis and thesis is that a thesis is a distinction or an affirmation of the hypothesis.
Theory vs. Hypothesis: Basics of the Scientific Method. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 2 min read. Though you may hear the terms "theory" and "hypothesis" used interchangeably, these two scientific terms have drastically different meanings in the world of science.
An assumption is a belief or statement that is taken for granted or accepted as true without any evidence or proof. It is often used as a starting point or a premise in an argument or analysis. On the other hand, a hypothesis is a tentative explanation or prediction that is based on limited evidence or prior knowledge.
One of the entry mechanisms of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus into host cells involves endosomal acidification. It has been proposed that under acidic conditions the Fusion Peptide Proximal Region (FPPR) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein acts as a pH-dependent switch, modulating immune response accessibility by influencing the positioning of the Receptor Binding Domain (RBD). This would provide ...