- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

Understanding Case Study Method in Research: A Comprehensive Guide

Table of Contents
Have you ever wondered how researchers uncover the nuanced layers of individual experiences or the intricate workings of a particular event? One of the keys to unlocking these mysteries lies in the qualitative research focusing on a single subject in its real-life context.">case study method , a research strategy that might seem straightforward at first glance but is rich with complexity and insightful potential. Let’s dive into the world of case studies and discover why they are such a valuable tool in the arsenal of research methods.
What is a Case Study Method?
At its core, the case study method is a form of qualitative research that involves an in-depth, detailed examination of a single subject, such as an individual, group, organization, event, or phenomenon. It’s a method favored when the boundaries between phenomenon and context are not clearly evident, and where multiple sources of data are used to illuminate the case from various perspectives. This method’s strength lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case in its real-life context.
Historical Context and Evolution of Case Studies
Case studies have been around for centuries, with their roots in medical and psychological research. Over time, their application has spread to disciplines like sociology, anthropology, business, and education. The evolution of this method has been marked by a growing appreciation for qualitative data and the rich, contextual insights it can provide, which quantitative methods may overlook.
Characteristics of Case Study Research
What sets the case study method apart are its distinct characteristics:
- Intensive Examination: It provides a deep understanding of the case in question, considering the complexity and uniqueness of each case.
- Contextual Analysis: The researcher studies the case within its real-life context, recognizing that the context can significantly influence the phenomenon.
- Multiple Data Sources: Case studies often utilize various data sources like interviews, observations, documents, and reports, which provide multiple perspectives on the subject.
- Participant’s Perspective: This method often focuses on the perspectives of the participants within the case, giving voice to those directly involved.
Types of Case Studies
There are different types of case studies, each suited for specific research objectives:
- Exploratory: These are conducted before large-scale research projects to help identify questions, select measurement constructs, and develop hypotheses.
- Descriptive: These involve a detailed, in-depth description of the case, without attempting to determine cause and effect.
- Explanatory: These are used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships and understand underlying principles of certain phenomena.
- Intrinsic: This type is focused on the case itself because the case presents an unusual or unique issue.
- Instrumental: Here, the case is secondary to understanding a broader issue or phenomenon.
- Collective: These involve studying a group of cases collectively or comparably to understand a phenomenon, population, or general condition.
The Process of Conducting a Case Study
Conducting a case study involves several well-defined steps:
- Defining Your Case: What or who will you study? Define the case and ensure it aligns with your research objectives.
- Selecting Participants: If studying people, careful selection is crucial to ensure they fit the case criteria and can provide the necessary insights.
- Data Collection: Gather information through various methods like interviews, observations, and reviewing documents.
- Data Analysis: Analyze the collected data to identify patterns, themes, and insights related to your research question.
- Reporting Findings: Present your findings in a way that communicates the complexity and richness of the case study, often through narrative.
Case Studies in Practice: Real-world Examples
Case studies are not just academic exercises; they have practical applications in every field. For instance, in business, they can explore consumer behavior or organizational strategies. In psychology, they can provide detailed insight into individual behaviors or conditions. Education often uses case studies to explore teaching methods or learning difficulties.
Advantages of Case Study Research
While the case study method has its critics, it offers several undeniable advantages:
- Rich, Detailed Data: It captures data too complex for quantitative methods.
- Contextual Insights: It provides a better understanding of the phenomena in its natural setting.
- Contribution to Theory: It can generate and refine theory, offering a foundation for further research.
Limitations and Criticism
However, it’s important to acknowledge the limitations and criticisms:
- Generalizability : Findings from case studies may not be widely generalizable due to the focus on a single case.
- Subjectivity: The researcher’s perspective may influence the study, which requires careful reflection and transparency.
- Time-Consuming: They require a significant amount of time to conduct and analyze properly.
Concluding Thoughts on the Case Study Method
The case study method is a powerful tool that allows researchers to delve into the intricacies of a subject in its real-world environment. While not without its challenges, when executed correctly, the insights garnered can be incredibly valuable, offering depth and context that other methods may miss. Robert K\. Yin ’s advocacy for this method underscores its potential to illuminate and explain contemporary phenomena, making it an indispensable part of the researcher’s toolkit.
Reflecting on the case study method, how do you think its application could change with the advancements in technology and data analytics? Could such a traditional method be enhanced or even replaced in the future?
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
Research Methods in Psychology
1 Introduction to Psychological Research – Objectives and Goals, Problems, Hypothesis and Variables
- Nature of Psychological Research
- The Context of Discovery
- Context of Justification
- Characteristics of Psychological Research
- Goals and Objectives of Psychological Research
2 Introduction to Psychological Experiments and Tests
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Extraneous Variables
- Experimental and Control Groups
- Introduction of Test
- Types of Psychological Test
- Uses of Psychological Tests
3 Steps in Research
- Research Process
- Identification of the Problem
- Review of Literature
- Formulating a Hypothesis
- Identifying Manipulating and Controlling Variables
- Formulating a Research Design
- Constructing Devices for Observation and Measurement
- Sample Selection and Data Collection
- Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Hypothesis Testing
- Drawing Conclusion
4 Types of Research and Methods of Research
- Historical Research
- Descriptive Research
- Correlational Research
- Qualitative Research
- Ex-Post Facto Research
- True Experimental Research
- Quasi-Experimental Research
5 Definition and Description Research Design, Quality of Research Design
- Research Design
- Purpose of Research Design
- Design Selection
- Criteria of Research Design
- Qualities of Research Design
6 Experimental Design (Control Group Design and Two Factor Design)
- Experimental Design
- Control Group Design
- Two Factor Design
7 Survey Design
- Survey Research Designs
- Steps in Survey Design
- Structuring and Designing the Questionnaire
- Interviewing Methodology
- Data Analysis
- Final Report
8 Single Subject Design
- Single Subject Design: Definition and Meaning
- Phases Within Single Subject Design
- Requirements of Single Subject Design
- Characteristics of Single Subject Design
- Types of Single Subject Design
- Advantages of Single Subject Design
- Disadvantages of Single Subject Design
9 Observation Method
- Definition and Meaning of Observation
- Characteristics of Observation
- Types of Observation
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Observation
- Guides for Observation Method
10 Interview and Interviewing
- Definition of Interview
- Types of Interview
- Aspects of Qualitative Research Interviews
- Interview Questions
- Convergent Interviewing as Action Research
- Research Team
11 Questionnaire Method
- Definition and Description of Questionnaires
- Types of Questionnaires
- Purpose of Questionnaire Studies
- Designing Research Questionnaires
- The Methods to Make a Questionnaire Efficient
- The Types of Questionnaire to be Included in the Questionnaire
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Questionnaire
- When to Use a Questionnaire?
12 Case Study
- Definition and Description of Case Study Method
- Historical Account of Case Study Method
- Designing Case Study
- Requirements for Case Studies
- Guideline to Follow in Case Study Method
- Other Important Measures in Case Study Method
- Case Reports
13 Report Writing
- Purpose of a Report
- Writing Style of the Report
- Report Writing – the Do’s and the Don’ts
- Format for Report in Psychology Area
- Major Sections in a Report
14 Review of Literature
- Purposes of Review of Literature
- Sources of Review of Literature
- Types of Literature
- Writing Process of the Review of Literature
- Preparation of Index Card for Reviewing and Abstracting
15 Methodology
- Definition and Purpose of Methodology
- Participants (Sample)
- Apparatus and Materials
16 Result, Analysis and Discussion of the Data
- Definition and Description of Results
- Statistical Presentation
- Tables and Figures
17 Summary and Conclusion
- Summary Definition and Description
- Guidelines for Writing a Summary
- Writing the Summary and Choosing Words
- A Process for Paraphrasing and Summarising
- Summary of a Report
- Writing Conclusions
18 References in Research Report
- Reference List (the Format)
- References (Process of Writing)
- Reference List and Print Sources
- Electronic Sources
- Book on CD Tape and Movie
- Reference Specifications
- General Guidelines to Write References
Share on Mastodon

What Is a Case Study in Psychology?
Categories Research Methods
A case study is a research method used in psychology to investigate a particular individual, group, or situation in depth . It involves a detailed analysis of the subject, gathering information from various sources such as interviews, observations, and documents.
In a case study, researchers aim to understand the complexities and nuances of the subject under investigation. They explore the individual’s thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and experiences to gain insights into specific psychological phenomena.
This type of research can provide great detail regarding a particular case, allowing researchers to examine rare or unique situations that may not be easily replicated in a laboratory setting. They offer a holistic view of the subject, considering various factors influencing their behavior or mental processes.
By examining individual cases, researchers can generate hypotheses, develop theories, and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in psychology. Case studies are often utilized in clinical psychology, where they can provide valuable insights into the diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes of specific psychological disorders.
Case studies offer a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of complex psychological phenomena, providing researchers with valuable information to inform theory, practice, and future research.
Table of Contents
Examples of Case Studies in Psychology
Case studies in psychology provide real-life examples that illustrate psychological concepts and theories. They offer a detailed analysis of specific individuals, groups, or situations, allowing researchers to understand psychological phenomena better. Here are a few examples of case studies in psychology:
Phineas Gage
This famous case study explores the effects of a traumatic brain injury on personality and behavior. A railroad construction worker, Phineas Gage survived a severe brain injury that dramatically changed his personality.
This case study helped researchers understand the role of the frontal lobe in personality and social behavior.
Little Albert
Conducted by behaviorist John B. Watson, the Little Albert case study aimed to demonstrate classical conditioning. In this study, a young boy named Albert was conditioned to fear a white rat by pairing it with a loud noise.
This case study provided insights into the process of fear conditioning and the impact of early experiences on behavior.
Genie’s case study focused on a girl who experienced extreme social isolation and deprivation during her childhood. This study shed light on the critical period for language development and the effects of severe neglect on cognitive and social functioning.
These case studies highlight the value of in-depth analysis and provide researchers with valuable insights into various psychological phenomena. By examining specific cases, psychologists can uncover unique aspects of human behavior and contribute to the field’s knowledge and understanding.
Types of Case Studies in Psychology
Psychology case studies come in various forms, each serving a specific purpose in research and analysis. Understanding the different types of case studies can help researchers choose the most appropriate approach.
Descriptive Case Studies
These studies aim to describe a particular individual, group, or situation. Researchers use descriptive case studies to explore and document specific characteristics, behaviors, or experiences.
For example, a descriptive case study may examine the life and experiences of a person with a rare psychological disorder.
Exploratory Case Studies
Exploratory case studies are conducted when there is limited existing knowledge or understanding of a particular phenomenon. Researchers use these studies to gather preliminary information and generate hypotheses for further investigation.
Exploratory case studies often involve in-depth interviews, observations, and analysis of existing data.
Explanatory Case Studies
These studies aim to explain the causal relationship between variables or events. Researchers use these studies to understand why certain outcomes occur and to identify the underlying mechanisms or processes.
Explanatory case studies often involve comparing multiple cases to identify common patterns or factors.
Instrumental Case Studies
Instrumental case studies focus on using a particular case to gain insights into a broader issue or theory. Researchers select cases that are representative or critical in understanding the phenomenon of interest.
Instrumental case studies help researchers develop or refine theories and contribute to the general knowledge in the field.
By utilizing different types of case studies, psychologists can explore various aspects of human behavior and gain a deeper understanding of psychological phenomena. Each type of case study offers unique advantages and contributes to the overall body of knowledge in psychology.
How to Collect Data for a Case Study
There are a variety of ways that researchers gather the data they need for a case study. Some sources include:
- Directly observing the subject
- Collecting information from archival records
- Conducting interviews
- Examining artifacts related to the subject
- Examining documents that provide information about the subject
The way that this information is collected depends on the nature of the study itself
Prospective Research
In a prospective study, researchers observe the individual or group in question. These observations typically occur over a period of time and may be used to track the progress or progression of a phenomenon or treatment.
Retrospective Research
A retrospective case study involves looking back on a phenomenon. Researchers typically look at the outcome and then gather data to help them understand how the individual or group reached that point.
Benefits of a Case Study
Case studies offer several benefits in the field of psychology. They provide researchers with a unique opportunity to delve deep into specific individuals, groups, or situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena.
Case studies offer valuable insights that can inform theory development and practical applications by examining real-life examples.
Complex Data
One of the key benefits of case studies is their ability to provide complex and detailed data. Researchers can gather in-depth information through various methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of existing records.
This depth of data allows for a thorough exploration of the factors influencing behavior and the underlying mechanisms at play.
Unique Data
Additionally, case studies allow researchers to study rare or unique cases that may not be easily replicated in experimental settings. This enables the examination of phenomena that are difficult to study through other psychology research methods .
By focusing on specific cases, researchers can uncover patterns, identify causal relationships, and generate hypotheses for further investigation.
General Knowledge
Case studies can also contribute to the general knowledge of psychology by providing real-world examples that can be used to support or challenge existing theories. They offer a bridge between theory and practice, allowing researchers to apply theoretical concepts to real-life situations and vice versa.
Case studies offer a range of benefits in psychology, including providing rich and detailed data, studying unique cases, and contributing to theory development. These benefits make case studies valuable in understanding human behavior and psychological phenomena.
Limitations of a Case Study
While case studies offer numerous benefits in the field of psychology, they also have certain limitations that researchers need to consider. Understanding these limitations is crucial for interpreting the findings and generalizing the results.
Lack of Generalizability
One limitation of case studies is the issue of generalizability. Since case studies focus on specific individuals, groups, and situations, applying the findings to a larger population can be challenging. The unique characteristics and circumstances of the case may not be representative of the broader population, making it difficult to draw universal conclusions.
Researcher bias is another possible limitation. The researcher’s subjective interpretation and personal beliefs can influence the data collection, analysis, and interpretation process. This bias can affect the objectivity and reliability of the findings, raising questions about the study’s validity.
Case studies are often time-consuming and resource-intensive. They require extensive data collection, analysis, and interpretation, which can be lengthy. This can limit the number of cases that can be studied and may result in a smaller sample size, reducing the study’s statistical power.
Case studies are retrospective in nature, relying on past events and experiences. This reliance on memory and self-reporting can introduce recall bias and inaccuracies in the data. Participants may forget or misinterpret certain details, leading to incomplete or unreliable information.
Despite these limitations, case studies remain a valuable research tool in psychology. By acknowledging and addressing these limitations, researchers can enhance the validity and reliability of their findings, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of human behavior and psychological phenomena.
While case studies have limitations, they remain valuable when researchers acknowledge and address these concerns, leading to more reliable and valid findings in psychology.
Alpi, K. M., & Evans, J. J. (2019). Distinguishing case study as a research method from case reports as a publication type. Journal of the Medical Library Association , 107(1). https://doi.org/10.5195/jmla.2019.615
Crowe, S., Cresswell, K., Robertson, A., Huby, G., Avery, A., & Sheikh, A. (2011). The case study approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 11(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Paparini, S., Green, J., Papoutsi, C., Murdoch, J., Petticrew, M., Greenhalgh, T., Hanckel, B., & Shaw, S. (2020). Case study research for better evaluations of complex interventions: Rationale and challenges. BMC Medicine , 18(1), 301. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-020-01777-6
Willemsen, J. (2023). What is preventing psychotherapy case studies from having a greater impact on evidence-based practice, and how to address the challenges? Frontiers in Psychiatry , 13, 1101090. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1101090
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
Research Methods In Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.

Hypotheses are statements about the prediction of the results, that can be verified or disproved by some investigation.
There are four types of hypotheses :
- Null Hypotheses (H0 ) – these predict that no difference will be found in the results between the conditions. Typically these are written ‘There will be no difference…’
- Alternative Hypotheses (Ha or H1) – these predict that there will be a significant difference in the results between the two conditions. This is also known as the experimental hypothesis.
- One-tailed (directional) hypotheses – these state the specific direction the researcher expects the results to move in, e.g. higher, lower, more, less. In a correlation study, the predicted direction of the correlation can be either positive or negative.
- Two-tailed (non-directional) hypotheses – these state that a difference will be found between the conditions of the independent variable but does not state the direction of a difference or relationship. Typically these are always written ‘There will be a difference ….’
All research has an alternative hypothesis (either a one-tailed or two-tailed) and a corresponding null hypothesis.
Once the research is conducted and results are found, psychologists must accept one hypothesis and reject the other.
So, if a difference is found, the Psychologist would accept the alternative hypothesis and reject the null. The opposite applies if no difference is found.
Sampling techniques
Sampling is the process of selecting a representative group from the population under study.
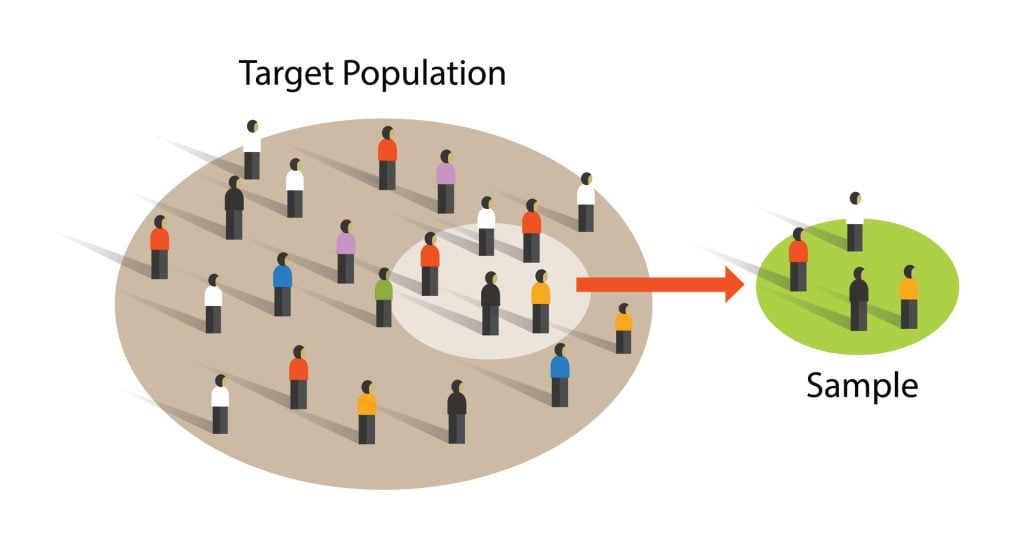
A sample is the participants you select from a target population (the group you are interested in) to make generalizations about.
Representative means the extent to which a sample mirrors a researcher’s target population and reflects its characteristics.
Generalisability means the extent to which their findings can be applied to the larger population of which their sample was a part.
- Volunteer sample : where participants pick themselves through newspaper adverts, noticeboards or online.
- Opportunity sampling : also known as convenience sampling , uses people who are available at the time the study is carried out and willing to take part. It is based on convenience.
- Random sampling : when every person in the target population has an equal chance of being selected. An example of random sampling would be picking names out of a hat.
- Systematic sampling : when a system is used to select participants. Picking every Nth person from all possible participants. N = the number of people in the research population / the number of people needed for the sample.
- Stratified sampling : when you identify the subgroups and select participants in proportion to their occurrences.
- Snowball sampling : when researchers find a few participants, and then ask them to find participants themselves and so on.
- Quota sampling : when researchers will be told to ensure the sample fits certain quotas, for example they might be told to find 90 participants, with 30 of them being unemployed.
Experiments always have an independent and dependent variable .
- The independent variable is the one the experimenter manipulates (the thing that changes between the conditions the participants are placed into). It is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable.
- The dependent variable is the thing being measured, or the results of the experiment.
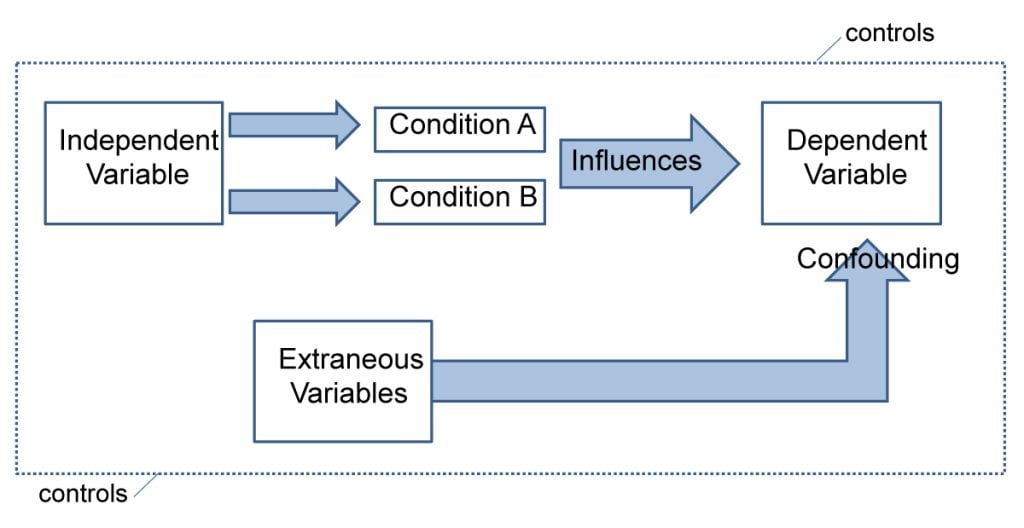
Operationalization of variables means making them measurable/quantifiable. We must use operationalization to ensure that variables are in a form that can be easily tested.
For instance, we can’t really measure ‘happiness’, but we can measure how many times a person smiles within a two-hour period.
By operationalizing variables, we make it easy for someone else to replicate our research. Remember, this is important because we can check if our findings are reliable.
Extraneous variables are all variables which are not independent variable but could affect the results of the experiment.
It can be a natural characteristic of the participant, such as intelligence levels, gender, or age for example, or it could be a situational feature of the environment such as lighting or noise.
Demand characteristics are a type of extraneous variable that occurs if the participants work out the aims of the research study, they may begin to behave in a certain way.
For example, in Milgram’s research , critics argued that participants worked out that the shocks were not real and they administered them as they thought this was what was required of them.
Extraneous variables must be controlled so that they do not affect (confound) the results.
Randomly allocating participants to their conditions or using a matched pairs experimental design can help to reduce participant variables.
Situational variables are controlled by using standardized procedures, ensuring every participant in a given condition is treated in the same way
Experimental Design
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to each condition of the independent variable, such as a control or experimental group.
- Independent design ( between-groups design ): each participant is selected for only one group. With the independent design, the most common way of deciding which participants go into which group is by means of randomization.
- Matched participants design : each participant is selected for only one group, but the participants in the two groups are matched for some relevant factor or factors (e.g. ability; sex; age).
- Repeated measures design ( within groups) : each participant appears in both groups, so that there are exactly the same participants in each group.
- The main problem with the repeated measures design is that there may well be order effects. Their experiences during the experiment may change the participants in various ways.
- They may perform better when they appear in the second group because they have gained useful information about the experiment or about the task. On the other hand, they may perform less well on the second occasion because of tiredness or boredom.
- Counterbalancing is the best way of preventing order effects from disrupting the findings of an experiment, and involves ensuring that each condition is equally likely to be used first and second by the participants.
If we wish to compare two groups with respect to a given independent variable, it is essential to make sure that the two groups do not differ in any other important way.
Experimental Methods
All experimental methods involve an iv (independent variable) and dv (dependent variable)..
- Field experiments are conducted in the everyday (natural) environment of the participants. The experimenter still manipulates the IV, but in a real-life setting. It may be possible to control extraneous variables, though such control is more difficult than in a lab experiment.
- Natural experiments are when a naturally occurring IV is investigated that isn’t deliberately manipulated, it exists anyway. Participants are not randomly allocated, and the natural event may only occur rarely.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. It uses information from a range of sources, such as from the person concerned and also from their family and friends.
Many techniques may be used such as interviews, psychological tests, observations and experiments. Case studies are generally longitudinal: in other words, they follow the individual or group over an extended period of time.
Case studies are widely used in psychology and among the best-known ones carried out were by Sigmund Freud . He conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
Case studies provide rich qualitative data and have high levels of ecological validity. However, it is difficult to generalize from individual cases as each one has unique characteristics.
Correlational Studies
Correlation means association; it is a measure of the extent to which two variables are related. One of the variables can be regarded as the predictor variable with the other one as the outcome variable.
Correlational studies typically involve obtaining two different measures from a group of participants, and then assessing the degree of association between the measures.
The predictor variable can be seen as occurring before the outcome variable in some sense. It is called the predictor variable, because it forms the basis for predicting the value of the outcome variable.
Relationships between variables can be displayed on a graph or as a numerical score called a correlation coefficient.
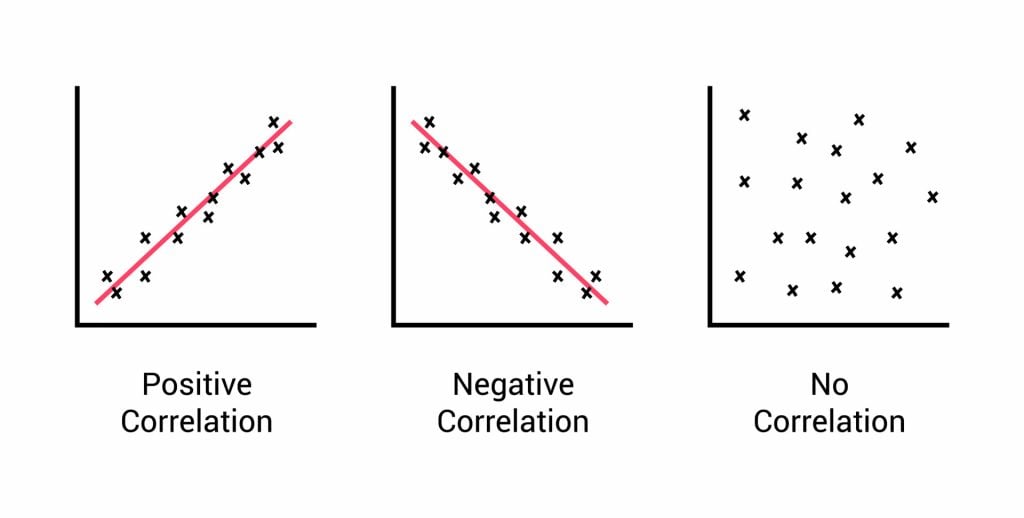
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with an increase in the other, then this is known as a positive correlation .
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with a decrease in the other, then this is known as a negative correlation .
- A zero correlation occurs when there is no relationship between variables.
After looking at the scattergraph, if we want to be sure that a significant relationship does exist between the two variables, a statistical test of correlation can be conducted, such as Spearman’s rho.
The test will give us a score, called a correlation coefficient . This is a value between 0 and 1, and the closer to 1 the score is, the stronger the relationship between the variables. This value can be both positive e.g. 0.63, or negative -0.63.
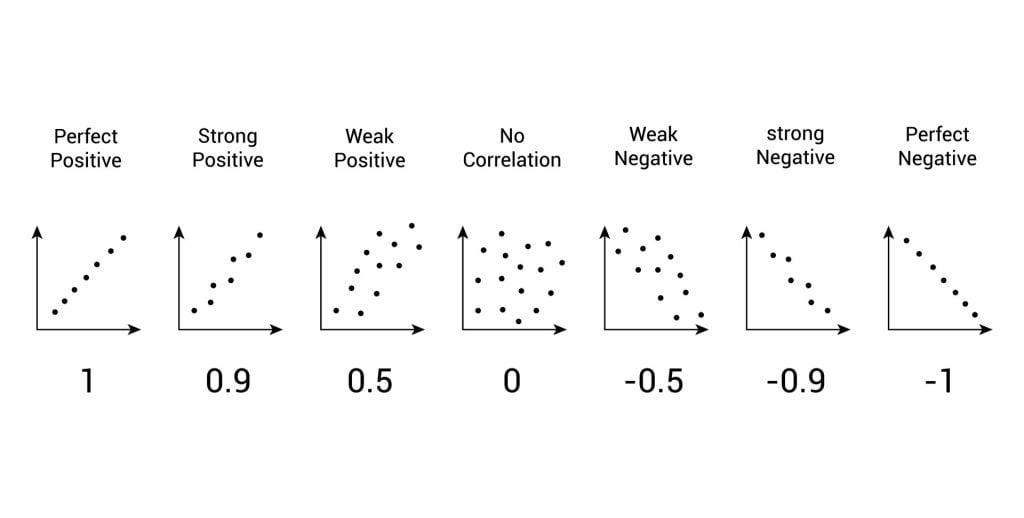
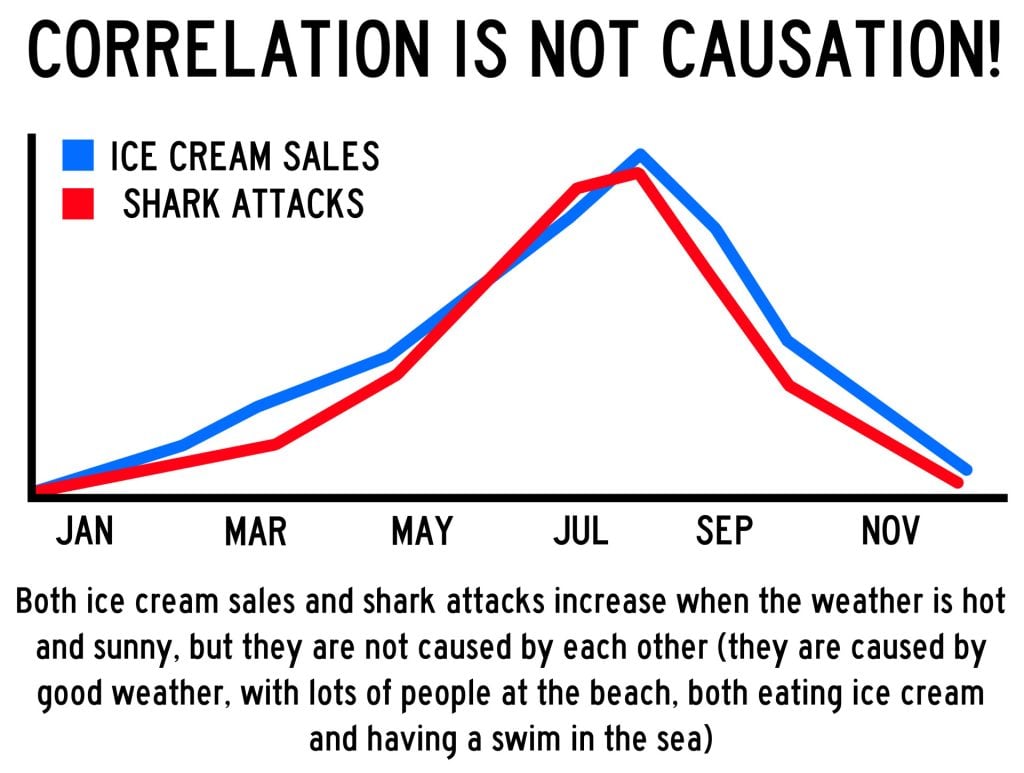
A correlation between variables, however, does not automatically mean that the change in one variable is the cause of the change in the values of the other variable. A correlation only shows if there is a relationship between variables.
Correlation does not always prove causation, as a third variable may be involved.

Interview Methods
Interviews are commonly divided into two types: structured and unstructured.
A fixed, predetermined set of questions is put to every participant in the same order and in the same way.
Responses are recorded on a questionnaire, and the researcher presets the order and wording of questions, and sometimes the range of alternative answers.
The interviewer stays within their role and maintains social distance from the interviewee.
There are no set questions, and the participant can raise whatever topics he/she feels are relevant and ask them in their own way. Questions are posed about participants’ answers to the subject
Unstructured interviews are most useful in qualitative research to analyze attitudes and values.
Though they rarely provide a valid basis for generalization, their main advantage is that they enable the researcher to probe social actors’ subjective point of view.
Questionnaire Method
Questionnaires can be thought of as a kind of written interview. They can be carried out face to face, by telephone, or post.
The choice of questions is important because of the need to avoid bias or ambiguity in the questions, ‘leading’ the respondent or causing offense.
- Open questions are designed to encourage a full, meaningful answer using the subject’s own knowledge and feelings. They provide insights into feelings, opinions, and understanding. Example: “How do you feel about that situation?”
- Closed questions can be answered with a simple “yes” or “no” or specific information, limiting the depth of response. They are useful for gathering specific facts or confirming details. Example: “Do you feel anxious in crowds?”
Its other practical advantages are that it is cheaper than face-to-face interviews and can be used to contact many respondents scattered over a wide area relatively quickly.
Observations
There are different types of observation methods :
- Covert observation is where the researcher doesn’t tell the participants they are being observed until after the study is complete. There could be ethical problems or deception and consent with this particular observation method.
- Overt observation is where a researcher tells the participants they are being observed and what they are being observed for.
- Controlled : behavior is observed under controlled laboratory conditions (e.g., Bandura’s Bobo doll study).
- Natural : Here, spontaneous behavior is recorded in a natural setting.
- Participant : Here, the observer has direct contact with the group of people they are observing. The researcher becomes a member of the group they are researching.
- Non-participant (aka “fly on the wall): The researcher does not have direct contact with the people being observed. The observation of participants’ behavior is from a distance
Pilot Study
A pilot study is a small scale preliminary study conducted in order to evaluate the feasibility of the key s teps in a future, full-scale project.
A pilot study is an initial run-through of the procedures to be used in an investigation; it involves selecting a few people and trying out the study on them. It is possible to save time, and in some cases, money, by identifying any flaws in the procedures designed by the researcher.
A pilot study can help the researcher spot any ambiguities (i.e. unusual things) or confusion in the information given to participants or problems with the task devised.
Sometimes the task is too hard, and the researcher may get a floor effect, because none of the participants can score at all or can complete the task – all performances are low.
The opposite effect is a ceiling effect, when the task is so easy that all achieve virtually full marks or top performances and are “hitting the ceiling”.
Research Design
In cross-sectional research , a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at the same time
Sometimes, we want to see how people change over time, as in studies of human development and lifespan. Longitudinal research is a research design in which data-gathering is administered repeatedly over an extended period of time.
In cohort studies , the participants must share a common factor or characteristic such as age, demographic, or occupation. A cohort study is a type of longitudinal study in which researchers monitor and observe a chosen population over an extended period.
Triangulation means using more than one research method to improve the study’s validity.
Reliability
Reliability is a measure of consistency, if a particular measurement is repeated and the same result is obtained then it is described as being reliable.
- Test-retest reliability : assessing the same person on two different occasions which shows the extent to which the test produces the same answers.
- Inter-observer reliability : the extent to which there is an agreement between two or more observers.
Meta-Analysis
A meta-analysis is a systematic review that involves identifying an aim and then searching for research studies that have addressed similar aims/hypotheses.
This is done by looking through various databases, and then decisions are made about what studies are to be included/excluded.
Strengths: Increases the conclusions’ validity as they’re based on a wider range.
Weaknesses: Research designs in studies can vary, so they are not truly comparable.
Peer Review
A researcher submits an article to a journal. The choice of the journal may be determined by the journal’s audience or prestige.
The journal selects two or more appropriate experts (psychologists working in a similar field) to peer review the article without payment. The peer reviewers assess: the methods and designs used, originality of the findings, the validity of the original research findings and its content, structure and language.
Feedback from the reviewer determines whether the article is accepted. The article may be: Accepted as it is, accepted with revisions, sent back to the author to revise and re-submit or rejected without the possibility of submission.
The editor makes the final decision whether to accept or reject the research report based on the reviewers comments/ recommendations.
Peer review is important because it prevent faulty data from entering the public domain, it provides a way of checking the validity of findings and the quality of the methodology and is used to assess the research rating of university departments.
Peer reviews may be an ideal, whereas in practice there are lots of problems. For example, it slows publication down and may prevent unusual, new work being published. Some reviewers might use it as an opportunity to prevent competing researchers from publishing work.
Some people doubt whether peer review can really prevent the publication of fraudulent research.
The advent of the internet means that a lot of research and academic comment is being published without official peer reviews than before, though systems are evolving on the internet where everyone really has a chance to offer their opinions and police the quality of research.
Types of Data
- Quantitative data is numerical data e.g. reaction time or number of mistakes. It represents how much or how long, how many there are of something. A tally of behavioral categories and closed questions in a questionnaire collect quantitative data.
- Qualitative data is virtually any type of information that can be observed and recorded that is not numerical in nature and can be in the form of written or verbal communication. Open questions in questionnaires and accounts from observational studies collect qualitative data.
- Primary data is first-hand data collected for the purpose of the investigation.
- Secondary data is information that has been collected by someone other than the person who is conducting the research e.g. taken from journals, books or articles.
Validity means how well a piece of research actually measures what it sets out to, or how well it reflects the reality it claims to represent.
Validity is whether the observed effect is genuine and represents what is actually out there in the world.
- Concurrent validity is the extent to which a psychological measure relates to an existing similar measure and obtains close results. For example, a new intelligence test compared to an established test.
- Face validity : does the test measure what it’s supposed to measure ‘on the face of it’. This is done by ‘eyeballing’ the measuring or by passing it to an expert to check.
- Ecological validit y is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other settings / real life.
- Temporal validity is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other historical times.
Features of Science
- Paradigm – A set of shared assumptions and agreed methods within a scientific discipline.
- Paradigm shift – The result of the scientific revolution: a significant change in the dominant unifying theory within a scientific discipline.
- Objectivity – When all sources of personal bias are minimised so not to distort or influence the research process.
- Empirical method – Scientific approaches that are based on the gathering of evidence through direct observation and experience.
- Replicability – The extent to which scientific procedures and findings can be repeated by other researchers.
- Falsifiability – The principle that a theory cannot be considered scientific unless it admits the possibility of being proved untrue.
Statistical Testing
A significant result is one where there is a low probability that chance factors were responsible for any observed difference, correlation, or association in the variables tested.
If our test is significant, we can reject our null hypothesis and accept our alternative hypothesis.
If our test is not significant, we can accept our null hypothesis and reject our alternative hypothesis. A null hypothesis is a statement of no effect.
In Psychology, we use p < 0.05 (as it strikes a balance between making a type I and II error) but p < 0.01 is used in tests that could cause harm like introducing a new drug.
A type I error is when the null hypothesis is rejected when it should have been accepted (happens when a lenient significance level is used, an error of optimism).
A type II error is when the null hypothesis is accepted when it should have been rejected (happens when a stringent significance level is used, an error of pessimism).
Ethical Issues
- Informed consent is when participants are able to make an informed judgment about whether to take part. It causes them to guess the aims of the study and change their behavior.
- To deal with it, we can gain presumptive consent or ask them to formally indicate their agreement to participate but it may invalidate the purpose of the study and it is not guaranteed that the participants would understand.
- Deception should only be used when it is approved by an ethics committee, as it involves deliberately misleading or withholding information. Participants should be fully debriefed after the study but debriefing can’t turn the clock back.
- All participants should be informed at the beginning that they have the right to withdraw if they ever feel distressed or uncomfortable.
- It causes bias as the ones that stayed are obedient and some may not withdraw as they may have been given incentives or feel like they’re spoiling the study. Researchers can offer the right to withdraw data after participation.
- Participants should all have protection from harm . The researcher should avoid risks greater than those experienced in everyday life and they should stop the study if any harm is suspected. However, the harm may not be apparent at the time of the study.
- Confidentiality concerns the communication of personal information. The researchers should not record any names but use numbers or false names though it may not be possible as it is sometimes possible to work out who the researchers were.
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

A-Level Psychology
A-level Psychology AQA Revision Notes

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Psychological Research
Descriptive Research
Learning objectives.
- Differentiate between descriptive, experimental, and correlational research
- Explain the strengths and weaknesses of case studies, naturalistic observation, and surveys
There are many research methods available to psychologists in their efforts to understand, describe, and explain behavior and the cognitive and biological processes that underlie it. Some methods rely on observational techniques. Other approaches involve interactions between the researcher and the individuals who are being studied—ranging from a series of simple questions to extensive, in-depth interviews—to well-controlled experiments.
The three main categories of psychological research are descriptive, correlational, and experimental research. Research studies that do not test specific relationships between variables are called descriptive, or qualitative, studies . These studies are used to describe general or specific behaviors and attributes that are observed and measured. In the early stages of research it might be difficult to form a hypothesis, especially when there is not any existing literature in the area. In these situations designing an experiment would be premature, as the question of interest is not yet clearly defined as a hypothesis. Often a researcher will begin with a non-experimental approach, such as a descriptive study, to gather more information about the topic before designing an experiment or correlational study to address a specific hypothesis. Descriptive research is distinct from correlational research , in which psychologists formally test whether a relationship exists between two or more variables. Experimental research goes a step further beyond descriptive and correlational research and randomly assigns people to different conditions, using hypothesis testing to make inferences about how these conditions affect behavior. It aims to determine if one variable directly impacts and causes another. Correlational and experimental research both typically use hypothesis testing, whereas descriptive research does not.
Each of these research methods has unique strengths and weaknesses, and each method may only be appropriate for certain types of research questions. For example, studies that rely primarily on observation produce incredible amounts of information, but the ability to apply this information to the larger population is somewhat limited because of small sample sizes. Survey research, on the other hand, allows researchers to easily collect data from relatively large samples. While this allows for results to be generalized to the larger population more easily, the information that can be collected on any given survey is somewhat limited and subject to problems associated with any type of self-reported data. Some researchers conduct archival research by using existing records. While this can be a fairly inexpensive way to collect data that can provide insight into a number of research questions, researchers using this approach have no control on how or what kind of data was collected.
Correlational research can find a relationship between two variables, but the only way a researcher can claim that the relationship between the variables is cause and effect is to perform an experiment. In experimental research, which will be discussed later in the text, there is a tremendous amount of control over variables of interest. While this is a powerful approach, experiments are often conducted in very artificial settings. This calls into question the validity of experimental findings with regard to how they would apply in real-world settings. In addition, many of the questions that psychologists would like to answer cannot be pursued through experimental research because of ethical concerns.
The three main types of descriptive studies are case studies, naturalistic observation, and surveys.
Case Studies
In 2011, the New York Times published a feature story on Krista and Tatiana Hogan, Canadian twin girls. These particular twins are unique because Krista and Tatiana are conjoined twins, connected at the head. There is evidence that the two girls are connected in a part of the brain called the thalamus, which is a major sensory relay center. Most incoming sensory information is sent through the thalamus before reaching higher regions of the cerebral cortex for processing.
Link to Learning
To learn more about Krista and Tatiana, watch this video about their lives as conjoined twins.
The implications of this potential connection mean that it might be possible for one twin to experience the sensations of the other twin. For instance, if Krista is watching a particularly funny television program, Tatiana might smile or laugh even if she is not watching the program. This particular possibility has piqued the interest of many neuroscientists who seek to understand how the brain uses sensory information.
These twins represent an enormous resource in the study of the brain, and since their condition is very rare, it is likely that as long as their family agrees, scientists will follow these girls very closely throughout their lives to gain as much information as possible (Dominus, 2011).
In observational research, scientists are conducting a clinical or case study when they focus on one person or just a few individuals. Indeed, some scientists spend their entire careers studying just 10–20 individuals. Why would they do this? Obviously, when they focus their attention on a very small number of people, they can gain a tremendous amount of insight into those cases. The richness of information that is collected in clinical or case studies is unmatched by any other single research method. This allows the researcher to have a very deep understanding of the individuals and the particular phenomenon being studied.
If clinical or case studies provide so much information, why are they not more frequent among researchers? As it turns out, the major benefit of this particular approach is also a weakness. As mentioned earlier, this approach is often used when studying individuals who are interesting to researchers because they have a rare characteristic. Therefore, the individuals who serve as the focus of case studies are not like most other people. If scientists ultimately want to explain all behavior, focusing attention on such a special group of people can make it difficult to generalize any observations to the larger population as a whole. Generalizing refers to the ability to apply the findings of a particular research project to larger segments of society. Again, case studies provide enormous amounts of information, but since the cases are so specific, the potential to apply what’s learned to the average person may be very limited.
Naturalistic Observation
If you want to understand how behavior occurs, one of the best ways to gain information is to simply observe the behavior in its natural context. However, people might change their behavior in unexpected ways if they know they are being observed. How do researchers obtain accurate information when people tend to hide their natural behavior? As an example, imagine that your professor asks everyone in your class to raise their hand if they always wash their hands after using the restroom. Chances are that almost everyone in the classroom will raise their hand, but do you think hand washing after every trip to the restroom is really that universal?
This is very similar to the phenomenon mentioned earlier in this module: many individuals do not feel comfortable answering a question honestly. But if we are committed to finding out the facts about hand washing, we have other options available to us.
Suppose we send a classmate into the restroom to actually watch whether everyone washes their hands after using the restroom. Will our observer blend into the restroom environment by wearing a white lab coat, sitting with a clipboard, and staring at the sinks? We want our researcher to be inconspicuous—perhaps standing at one of the sinks pretending to put in contact lenses while secretly recording the relevant information. This type of observational study is called naturalistic observation : observing behavior in its natural setting. To better understand peer exclusion, Suzanne Fanger collaborated with colleagues at the University of Texas to observe the behavior of preschool children on a playground. How did the observers remain inconspicuous over the duration of the study? They equipped a few of the children with wireless microphones (which the children quickly forgot about) and observed while taking notes from a distance. Also, the children in that particular preschool (a “laboratory preschool”) were accustomed to having observers on the playground (Fanger, Frankel, & Hazen, 2012).

It is critical that the observer be as unobtrusive and as inconspicuous as possible: when people know they are being watched, they are less likely to behave naturally. If you have any doubt about this, ask yourself how your driving behavior might differ in two situations: In the first situation, you are driving down a deserted highway during the middle of the day; in the second situation, you are being followed by a police car down the same deserted highway (Figure 1).
It should be pointed out that naturalistic observation is not limited to research involving humans. Indeed, some of the best-known examples of naturalistic observation involve researchers going into the field to observe various kinds of animals in their own environments. As with human studies, the researchers maintain their distance and avoid interfering with the animal subjects so as not to influence their natural behaviors. Scientists have used this technique to study social hierarchies and interactions among animals ranging from ground squirrels to gorillas. The information provided by these studies is invaluable in understanding how those animals organize socially and communicate with one another. The anthropologist Jane Goodall, for example, spent nearly five decades observing the behavior of chimpanzees in Africa (Figure 2). As an illustration of the types of concerns that a researcher might encounter in naturalistic observation, some scientists criticized Goodall for giving the chimps names instead of referring to them by numbers—using names was thought to undermine the emotional detachment required for the objectivity of the study (McKie, 2010).

The greatest benefit of naturalistic observation is the validity, or accuracy, of information collected unobtrusively in a natural setting. Having individuals behave as they normally would in a given situation means that we have a higher degree of ecological validity, or realism, than we might achieve with other research approaches. Therefore, our ability to generalize the findings of the research to real-world situations is enhanced. If done correctly, we need not worry about people or animals modifying their behavior simply because they are being observed. Sometimes, people may assume that reality programs give us a glimpse into authentic human behavior. However, the principle of inconspicuous observation is violated as reality stars are followed by camera crews and are interviewed on camera for personal confessionals. Given that environment, we must doubt how natural and realistic their behaviors are.
The major downside of naturalistic observation is that they are often difficult to set up and control. In our restroom study, what if you stood in the restroom all day prepared to record people’s hand washing behavior and no one came in? Or, what if you have been closely observing a troop of gorillas for weeks only to find that they migrated to a new place while you were sleeping in your tent? The benefit of realistic data comes at a cost. As a researcher you have no control of when (or if) you have behavior to observe. In addition, this type of observational research often requires significant investments of time, money, and a good dose of luck.
Sometimes studies involve structured observation. In these cases, people are observed while engaging in set, specific tasks. An excellent example of structured observation comes from Strange Situation by Mary Ainsworth (you will read more about this in the module on lifespan development). The Strange Situation is a procedure used to evaluate attachment styles that exist between an infant and caregiver. In this scenario, caregivers bring their infants into a room filled with toys. The Strange Situation involves a number of phases, including a stranger coming into the room, the caregiver leaving the room, and the caregiver’s return to the room. The infant’s behavior is closely monitored at each phase, but it is the behavior of the infant upon being reunited with the caregiver that is most telling in terms of characterizing the infant’s attachment style with the caregiver.
Another potential problem in observational research is observer bias . Generally, people who act as observers are closely involved in the research project and may unconsciously skew their observations to fit their research goals or expectations. To protect against this type of bias, researchers should have clear criteria established for the types of behaviors recorded and how those behaviors should be classified. In addition, researchers often compare observations of the same event by multiple observers, in order to test inter-rater reliability : a measure of reliability that assesses the consistency of observations by different observers.
Often, psychologists develop surveys as a means of gathering data. Surveys are lists of questions to be answered by research participants, and can be delivered as paper-and-pencil questionnaires, administered electronically, or conducted verbally (Figure 3). Generally, the survey itself can be completed in a short time, and the ease of administering a survey makes it easy to collect data from a large number of people.
Surveys allow researchers to gather data from larger samples than may be afforded by other research methods . A sample is a subset of individuals selected from a population , which is the overall group of individuals that the researchers are interested in. Researchers study the sample and seek to generalize their findings to the population.

There is both strength and weakness of the survey in comparison to case studies. By using surveys, we can collect information from a larger sample of people. A larger sample is better able to reflect the actual diversity of the population, thus allowing better generalizability. Therefore, if our sample is sufficiently large and diverse, we can assume that the data we collect from the survey can be generalized to the larger population with more certainty than the information collected through a case study. However, given the greater number of people involved, we are not able to collect the same depth of information on each person that would be collected in a case study.
Another potential weakness of surveys is something we touched on earlier in this module: people don’t always give accurate responses. They may lie, misremember, or answer questions in a way that they think makes them look good. For example, people may report drinking less alcohol than is actually the case.
Any number of research questions can be answered through the use of surveys. One real-world example is the research conducted by Jenkins, Ruppel, Kizer, Yehl, and Griffin (2012) about the backlash against the US Arab-American community following the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001. Jenkins and colleagues wanted to determine to what extent these negative attitudes toward Arab-Americans still existed nearly a decade after the attacks occurred. In one study, 140 research participants filled out a survey with 10 questions, including questions asking directly about the participant’s overt prejudicial attitudes toward people of various ethnicities. The survey also asked indirect questions about how likely the participant would be to interact with a person of a given ethnicity in a variety of settings (such as, “How likely do you think it is that you would introduce yourself to a person of Arab-American descent?”). The results of the research suggested that participants were unwilling to report prejudicial attitudes toward any ethnic group. However, there were significant differences between their pattern of responses to questions about social interaction with Arab-Americans compared to other ethnic groups: they indicated less willingness for social interaction with Arab-Americans compared to the other ethnic groups. This suggested that the participants harbored subtle forms of prejudice against Arab-Americans, despite their assertions that this was not the case (Jenkins et al., 2012).
Think It Over
A friend of yours is working part-time in a local pet store. Your friend has become increasingly interested in how dogs normally communicate and interact with each other, and is thinking of visiting a local veterinary clinic to see how dogs interact in the waiting room. After reading this section, do you think this is the best way to better understand such interactions? Do you have any suggestions that might result in more valid data?
CC licensed content, Original
- Modification and adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Approaches to Research. Authored by : OpenStax College. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/2-2-approaches-to-research . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction.
- Descriptive Research. Provided by : Boundless. Located at : https://www.boundless.com/psychology/textbooks/boundless-psychology-textbook/researching-psychology-2/types-of-research-studies-27/descriptive-research-124-12659/ . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
research studies that do not test specific relationships between variables; they are used to describe general or specific behaviors and attributes that are observed and measured
tests whether a relationship exists between two or more variables
tests a hypothesis to determine cause and effect relationships
observational research study focusing on one or a few people
observation of behavior in its natural setting
inferring that the results for a sample apply to the larger population
when observations may be skewed to align with observer expectations
measure of agreement among observers on how they record and classify a particular event
list of questions to be answered by research participants—given as paper-and-pencil questionnaires, administered electronically, or conducted verbally—allowing researchers to collect data from a large number of people
the collection of individuals on which we collect data.
a larger collection of individuals that we would like to generalize our results to.
General Psychology Copyright © by OpenStax and Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Res Notes

The clinical case report: a review of its merits and limitations
Trygve nissen.
1 Department of Clinical Medicine, University of Tromsø, N-9038 Tromsø, Norway
2 Division of General Psychiatry, University Hospital of North Norway, N-9291 Tromsø, Norway
3 Division of Addictions and Specialized Psychiatry, University Hospital of North Norway, N-9291 Tromsø, Norway
The clinical case report has a long-standing tradition in the medical literature. While its scientific significance has become smaller as more advanced research methods have gained ground, case reports are still presented in many medical journals. Some scholars point to its limited value for medical progress, while others assert that the genre is undervalued. We aimed to present the various points of view regarding the merits and limitations of the case report genre. We searched Google Scholar, PubMed and select textbooks on epidemiology and medical research for articles and book-chapters discussing the merits and limitations of clinical case reports and case series.
The major merits of case reporting were these: Detecting novelties, generating hypotheses, pharmacovigilance, high applicability when other research designs are not possible to carry out, allowing emphasis on the narrative aspect (in-depth understanding), and educational value. The major limitations were: Lack of ability to generalize, no possibility to establish cause-effect relationship, danger of over-interpretation, publication bias, retrospective design, and distraction of reader when focusing on the unusual.
Conclusions
Despite having lost its central role in medical literature in the 20th century, the genre still appears popular. It is a valuable part of the various research methods, especially since it complements other approaches. Furthermore, it also contributes in areas of medicine that are not specifically research-related, e.g. as an educational tool. Revision of the case report genre has been attempted in order to integrate the biomedical model with the narrative approach, but without significant success. The future prospects of the case report could possibly be in new applications of the genre, i.e. exclusive case report databases available online, and open access for clinicians and researchers.
Throughout history the clinical case report and case report series have been integral components of medical literature [ 1 ]. The case report genre held a strong position until it was sidelined in the second half of the 20 th century [ 2 , 3 ]. New methodologies for research articles paved the way for evidence-based medicine. Editors had to make space for these research articles and at the same time signaled less enthusiasm for publishing case reports [ 4 ]. This spurred some heated debates in medical journals as readers were worried that the traditional case report was in jeopardy [ 5 , 6 ]. Those who welcomed the new trend with fewer case reports being published pointed mainly to their low quality and inclination to emphasize mere curiosa [ 7 - 9 ]. Some of the proponents of the genre claimed that the case report had been and still was indispensible for furthering medical knowledge and that it was unique in taking care of the detailed study of the individual patient as opposed to the new research methods with their “…nomothetic approach [taking] precedence…” [ 5 ]. Still, the case report got a low ranking on the evidence hierarchy. After a decline in popularity a new interest for the case report emerged, probably beginning in the late 1990s [ 2 ]. A peer-reviewed ‘Case reports’ section was introduced in the Lancet in 1995 [ 10 ]. In 2007, the first international, Pubmed-listed medical journal publishing only case reports was established [ 11 , 12 ]. In the following years, several similar journals, for the most part online and open-access, have been launched.
The present debate is not so much focused on whether case reporting is obsolete or not. Some of the discussions after the turn of the century have been about adapting the case report genre to new challenges. One example is the suggestion of incorporating the narrative, i.e. “… stressing the patient’s story”, in the case report [ 13 ]. The authors termed their initiative “The storied case report”. Their endeavor was not met with success. In analyzing the causes for this, they wondered if “… junior trainees find it too hard to determine what is relevant and senior trainees find it too hard to change their habits” [ 13 ]. A similar attempt was done when the editors of the Journal of Medical Case Reports in 2012 encouraged authors to include the patients’ perspectives by letting patients describe their own experiences [ 14 ].
Notwithstanding, we feel there is much to be gained from having an ongoing discussion highlighting the indications and contraindications for producing case reports. This can to some degree be facilitated by getting an understanding of the merits and limitations of the genre. The objective of this article is to present the merits and limitations of case reports and case series reports.
We adopted Taber’s Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary’s definition of the case report : “A formal summary of a unique patient and his or her illness, including the presenting signs and symptoms, diagnostic studies, treatment course and outcome” [ 15 ]. A case report consists of one or two cases, most often only one. The case series or case series report usually consists of three to ten cases [ 16 ]. (In the following we use the term case report to denote both case reports and case series report). Case reports are most often naturalistic and descriptive. Sometimes, however, they can be prospective and experimental.
As literature specifically dealing with the case report genre seemed harder to elicit from the databases than the vast amount of particular case reports, we performed iterative searches. We searched Google Scholar and PubMed using the search terms ‘case report(s)’, ‘case series’, ‘case series report(s)’, ‘case reporting’ in various combinations with ‘clinical’, ‘medical’, ‘anecdotal’, ‘methodology’, ‘review’, ‘overview’, ‘strengths’, ‘weaknesses’, ‘merits’, and ‘limitations’. Further references were identified by examining the literature found in the electronic searches. We also consulted major textbooks on epidemiology [ 17 , 18 ], some scholars of medical genres [ 19 , 20 ] and a monograph on case reporting by the epidemiologist M. Jenicek [ 16 ]. We delimited our review to the retrospective, naturalistic, and descriptive case report, also labeled the “traditional” or “classic” case report, and case series including such reports. Thus we excluded other types, such as the planned, qualitative case study approach [ 21 ] and simulated cases [ 22 - 24 ]. Finally, we extracted the relevant data and grouped the merits and limitations items in rank order with the items we judged to be the most important first.
New observations
The major advantage of case reporting is probably its ability to detect novelties [ 16 ]. It is the only way to present unusual, uncontrolled observations regarding symptoms, clinical findings, course of illness, complications of interventions, associations of diseases, side effects of drugs, etc. In short, anything that is rare or has never been observed previously might be important for the medical community and ought to be published. A case report might sensitize readers and thus facilitate detection of similar or identical cases.
Generating hypotheses
From a single, or preferably several single case reports or a case series, new hypotheses could be formulated. These could then be tested with formal research methods that are designed to refute or confirm the hypotheses, i.e. comparative (observational and experimental) studies.
There are numerous examples of new discoveries or major advancements in medicine that started with a case report or, in some cases, as humbly as a letter to the editor. The first concern from the medical community about the devastating side effect of thalidomide, i.e. the congenital abnormalities, appeared as a letter to the editor in the Lancet in 1961 [ 25 ]. Soon thereafter, several case reports and case series reports were published in various journals. Case reporting is thus indispensable in drug safety surveillance (pharmacovigilance) [ 26 ].
Sometimes significant advancements in knowledge have come not from what researchers were pursuing, but from “accidental discoveries”, i.e. by serendipity. The story of Alexander Fleming’s discovery of penicillin in 1928 is well known in the medical field [ 27 ]. Psychiatry has profited to a large degree from this mode of advancing medical science as many of the drugs used for mental disorders have been discovered serendipitously [ 27 ]. One notable example is the discovery of the effect of lithium on manic episodes in patients with manic-depressive disorder [ 28 ]. A more recent discovery is the successful treatment of infantile hemangiomas with systemic propranolol. This discovery was published, as a case series report, in the correspondence section in New England Journal of Medicine [ 29 ]. However, the evidence for the effect of this treatment is still preliminary, and several randomized trials are under way [ 30 , 31 ].
Clear and operational entities are prerequisites for doing medical research. Descriptions must come before understanding. Clinical observations that lead to new disorders being described are well suited for case reporting. The medical literature is replete with case-based articles describing new diseases and syndromes. One notable example is the first description of neurasthenia by G. Beard in Boston Medical and Surgical Journal in 1869 [ 32 ].
Researching rare disorders
For rare disorders randomized controlled trials (RCTs) can be impossible to run due to lack of patients to be enrolled. Research on drug treatment and other kinds of interventions must therefore be based on less rigorous methodologies, among them case series and case reports. This would be in accordance with the European Commission’s recommendation to its members to improve health care for those with rare disorders [ 33 ].
Solving ethical constraints
Case reporting can be valuable when ethical constraints prohibit experimental research. Take as an example the challenge of how to manage the side effects of accidental extravasation of cytotoxic drugs. As RCTs on humans seem unethical in this clinical situation the current guidelines rest on small observational studies, case reports and animal studies [ 34 ]. Or another example: Physical restraint is sometimes associated with sudden, unexpected death. The cause or causes for this are to some degree enigmatic, and it is hard to conceive of a controlled study that could be ethical [ 35 , 36 ]. Case reports and case series being “natural experiments” might be the only evidence available for guiding clinical practice.
In-depth narrative case studies
Case reporting can be a way of presenting research with an idiographic emphasis. As contrasted to nomothetic research, an idiographic approach aims at in-depth understanding of human phenomena, especially in the field of psychology and psychiatry. The objective is not generalizable knowledge, but an understanding of meaning and intentionality for an individual or individuals. Sigmund Freud’s case studies are relevant examples. This usage of case reports borders on qualitative research. Qualitative studies, although developed in the social sciences, have become a welcome contribution within health sciences in the last two decades.
Educational value
Clinical medical learning is to a large degree case-based. Typical case histories and vignettes are often presented in textbooks, in lectures, etc. Unusual observations presented as published case reports are important as part of doctors’ continuing medical education, especially as they demonstrate the diversity of manifestations both within and between medical diseases and syndromes [ 37 , 38 ]. Among the various medical texts, the case report is the only one that presents day-to-day clinical practice, clinicians’ diagnostic reasoning, disease management, and follow-up. We believe that some case reports that are written with the aim of contributing to medical knowledge turn out to be of most value educationally because the phenomena have already been described elsewhere. Other case reports are clearly primarily written for educational value [ 37 ]. Some journals have regular sections dedicated to educational case reports, e.g. The Case Records of the Massachusetts General Hospital in the New England Journal of Medicine and the Clinical Case Conference found in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
The cost of doing a case report is low compared to planned, formal studies. Most often the necessary work is probably done in the clinical setting without specific funding. Larger studies, for instance RCTs, will usually need an academic setting.
Fast publication
The time span from observation to publication can be much shorter than for other kinds of studies. This is obviously a great advantage as a case report can be an important alert to the medical community about a serious event. The unexpected side effects of the sedative-antinauseant thalidomide on newborn babies is a telling story. The drug had been prescribed during pregnancy to the babies’ mothers. After the first published observation of severe abnormalities in babies appeared as a letter to the editor of the Lancet in December 16 th , 1961 [ 25 ], several case reports and series followed [ 39 , 40 ]. It should be mentioned though that the drug company had announced on December 2 nd , 1961, i.e. two weeks before the letter from McBride [ 25 ], that it would withdraw the drug form the market immediately [ 41 ].
Flexible structure
Riaz Agha, editor of the International Journal of Surgery Case Reports suggests that the case report, with its less rigid structure is useful as it “… allows the surgeon(s) to discuss their diagnostic approach, the context, background, decision-making, reasoning and outcomes” [ 42 ]. Although the editor is commenting on the surgical case report, the argument can be applied for the whole field of clinical medicine. It should be mentioned though, that other commentators have argued for a more standardized, in effect more rigid, structure [ 43 ].
Clinical practice can be changed
Case reporting can lead to or contribute to a change in clinical practice. A drug might be withdrawn from the market. Or a relabeling might change the attitude to and treatment of a condition. During Word War I the shell shock syndrome was labeled and described thoroughly in several articles in the Lancet , the first of them appearing in February 1915 [ 44 ]. The author was the British captain and military doctor Charles S. Myers. Before his efforts to bring good care and treatment to afflicted soldiers there had been a common misconception that many of these dysfunctional soldiers were malingerers or cowards.
Exercise for novice researchers
The case report format is well suited for young doctors not yet trained as researchers. It can be an opportunity for a first exercise in authoring an article and a preparation for a scientific career [ 37 , 45 , 46 ].
Communication between the clinical and academic fields
Articles authored by clinicians can promote communication between practicing clinicians and academic researchers. Observations published can generate ideas and be a trigger for further studies. For instance, a case series consisting of several similar cases in a short period can make up the case-group for a case–control study [ 47 ]. Clinicians could do the observation and publish the case series while the case–control study could be left to the academics.
Entertainment
Some commentators find reading case reports fun. Although a rather weak argument in favor of case reporting, the value of being entertained should not be dismissed altogether. It might inspire physicians to spend more time browsing and reading scientific literature [ 48 ].
Studying the history of medicine
Finally, we present a note on a different and unintended aspect of the genre. The accumulated case reports from past eras are a rich resource for researching and understanding medical history [ 49 , 50 ]. A close study of old case reports can provide valuable information about how medicine has been practiced through the centuries [ 50 , 51 ].
Limitations
No epidemiological quantities.
As case reports are not chosen from representative population samples they cannot generate information on rates, ratios, incidences or prevalences. The case or cases being the numerator in the equation, has no denominator. However, if a case series report consists of a cluster of cases, it can signal an important and possibly causal association, e.g. an epidemic or a side effect of a newly marketed drug.
Causal inference not possible
Causality cannot be inferred from an uncontrolled observation. An association does not imply a cause-effect relationship. The observation or event in question could be a mere coincidence. This is a limitation shared by all the descriptive studies [ 47 ]. Take the thalidomide tragedy already mentioned as an example; Unusual events such as congenital malformations in some of the children born to mothers having taken a specific drug during pregnancy does not prove that the drug is the culprit. It is a mere hypothesis until further studies have either rejected or confirmed it. Cause-effect relationships require planned studies including control groups that to the extent possible control for chance, bias and confounders [ 52 ].
Generalization not possible
From the argument above, it follows that findings from case reports cannot be generalized. In order to generalize we need both a cause-effect relationship and a representative population for which the findings are valid. A single case report has neither. A case series, on the other hand, e.g. many “thalidomide babies” in a short time period, could strengthen the suspicion of a causal relationship, demanding further surveillance and research.
Publication bias could be a limiting factor. Journals in general favor positive-outcome findings [ 53 ]. One group of investigators studying case reports published in the Lancet found that only 5% of case reports and 10% of case series reported treatment failures [ 54 ]. A study of 435 case reports from the field of dentistry found that in 99.1%, the reports “…clearly [had] a positive outcome and the intervention was considered and described as successful by the authors” [ 55 ].
Overinterpretation
Overinterpretation or misinterpretation is the tendency or temptation to generalize when there is no justification for it. It has also been labeled “the anecdotal fallacy” [ 56 ]. This is not a shortcoming intrinsic to the method itself. Overinterpretation may be due to the phenomenon of case reports often having an emotional appeal on readers. The story implicitly makes a claim to truth. The reader might conclude prematurely that there is a causal connection. The phenomenon might be more clearly illustrated by the impact of the clinician’s load of personal cases on his or her practice. Here exemplified by a young doctor’s confession: “I often tell residents and medical students, ‘The only thing that actually changes practice is adverse anecdote.’” [ 57 ].
Emphasis on the rare
As case reporting often deals with the rare and atypical, it might divert the readers’ attention from common diseases and problems [ 58 ].
Confidentiality
Journals today require written informed consent from patients before publishing case reports. Both authors and publishers are responsible for securing confidentiality. A guarantee for full confidentiality is not always possible. Despite all possible measures taken to preserve confidentiality, sometimes the patient will be recognized by someone. This information should be given to the patient. An adequately informed patient might not consent to publication. In 1995 in an Editorial in the British Journal of Psychiatry one commentator, Isaac Marks, feared that written consent would discourage case reports being written [ 59 ]. Fortunately, judged form the large number of reports being published today, it seems unlikely that the demand for consent has impeded their publication.
Other methodological limitations
Case reports and series are written after the relevant event, i.e. the observation. Thus, the reports are produced retrospectively. The medical record might not contain all relevant data. Recall bias might prevent us from getting the necessary information from the patient or other informants such as family members and health professionals.
It has also been held against case reporting that it is subjective. The observer’s subjectivity might bias the quality and interpretation of the observation (i.e. information bias).
Finally, the falsification criterion within science, which is tested by repeating an experiment, cannot be applied for case reports. We cannot design another identical and uncontrolled observation. However, unplanned similar “experiments” of nature can be repeated. Several such observations can constitute a case series that represents stronger indicative evidence than the single case report.
The major advantages of case reporting are the ability to make new observations, generate hypotheses, accumulate scientific data about rare disorders, do in-depth narrative studies, and serve as a major educational tool. The method is deficient mainly in being unable to deliver quantitative data. Nor can it prove cause-effect relationship or allow generalizations. Furthermore, there is a risk of overinterpretation and publication bias.
The traditional case report does not fit easily into the qualitative-quantitative dichotomy of research methods. It certainly shares some characteristics with qualitative research [ 16 ], especially with regard to the idiographic, narrative perspective – the patient’s “interior world” [ 60 ] – that sometimes is attended to. Apart from “The storied case report” mentioned in the Background-section, other innovative modifications of the traditional case report have been tried: the “evidence-based case report” [ 61 ], the “interactive case report” [ 62 ] and the “integrated narrative and evidence based case report” [ 63 ]. These modifications of the format have not made a lasting impact on the way case reports in general are written today.
The method of case reporting is briefly dealt with in some textbooks on epidemiology [ 17 , 18 ]. Journals that welcome case reports often put more emphasis on style and design than on content in their ‘instruction to authors’ section [ 64 ]. As a consequence, Sorinola and coworkers argue for more consensus and more consistent guidance on writing case reports [ 64 ]. We feel that a satisfactory amount of guidance concerning both style and content now exists [ 12 , 16 , 65 , 66 ]. The latest contribution, “The CARE guidelines”, is an ambitious endeavor to improve completeness and transparency of reports [ 66 ]. These guidelines have included the “Patient perspective” as an item, apparently a bit half-heartedly as this item is placed after the Discussion section, thus not allowing this perspective to influence the Discussion and/or Conclusion section. We assume this is symptomatic of medicine’s problem with integrating the biomedical model with “narrative-based medicine”.
In recent years the medical community has taken an increased interest in case reports [ 2 ], especially after the surge of online, exclusive case report journals started in 2007 with the Journal of Medical Case Reports (which was the first international, Pubmed-listed medical journal publishing only case reports) as the first of this new brand. The climate of skepticism has been replaced by enthusiasm and demand for more case reports. A registry for case reports, Cases Database, was founded in 2012 [ 67 ]. On the condition that it succeeds in becoming a large, international database it could serve as a register being useful for clinicians at work as well as for medical research on various clinical issues. Assuming Pamela P. Powell’s assertion that “[a]lmost all practicing physicians eventually will encounter a case worthy of being reported” [ 60 ] is valid, there should be no shortage of potential cases waiting to be reported and filed in various databases, preferably online and open access.
Limitations of this review
There are several limitations to this study. It is a weakness that we have not been able to review all the relevant literature. The number of publications in some way related to case reports and case report series is enormous, and although we have attempted to identify those publications relevant for our purpose (i.e. those that describe the merits and limitations of the case report genre), we might have missed some. It was difficult to find good search terms for our objective. Still, after repeated electronic searches supplemented with manual searches in reference lists, we had a corpus of literature where essentially no new merits or limitations emerged.
As we point out above, the ranking of merits and limitations represents our subjective opinion and we acknowledge that others might rank the importance of the items differently.
The perspective on merits and limitations of case reporting has been strictly medical. As a consequence we have not analyzed or discussed the various non-medical factors affecting the publication of case reports in different medical journals [ 2 ]. For instance, case reports are cited less often than other kinds of medical research articles [ 68 ]. Thus they can lower a journal’s impact factor, potentially making the journal less attractive. This might lead some high-impact journals to publish few or no case reports, while other journals have chosen to specialize in this genre.
Before deciding on producing a case report or case series based on a particular patient or patients at hand, the observant clinician has to determine if the case report method is the appropriate article type. This review could hopefully assist in that judgment and perhaps be a stimulus to the continuing debate in the medical community on the value of case reporting.
Competing interests
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
TN contributed to the conception, drafting, and revision of the article. RW contributed to the conception, drafting, and revision of the article. Both authors approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
There was no specific funding for this study.
- Cabán-Martinez AJ, Beltrán WF. Advancing medicine one note at a time: the educational value in clinical case reports. BMC Res Notes. 2012; 5 :293. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-293. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nissen T, Wynn R. The recent history of the clinical case report: a narrative review. JRSM Sh Rep. 2012; 3 :87. doi: 10.1258/shorts.2012.012046. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nissen T, Wynn R. The history of the case report: a selective review. JRSM Open. 2014; 5 :4. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilkinson G. Fare the well – the Editor’s last words. Br J Psychiatry. 2003; 182 :465–466. doi: 10.1192/bjp.182.6.465. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Williams DDR. In defence of case of the case report (Letter) Br J Psychiatry. 2004; 184 :84. doi: 10.1192/bjp.184.1.84. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Enoch MD. Case reports (Letter) Br J Psychiatry. 2005; 185 :169. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nahum AM. The clinical case report: “Pot boiler” or scientific literature? Head Neck Surg. 1979; 1 :291–292. doi: 10.1002/hed.2890010402. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Doherty M. What value case reports? (Editorial) Ann Rheum Dis. 1994; 53 :1–2. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.1.1. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Procopio M. Publication of case reports. Br J Psychiatry. 2005; 187 :91. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bignall J, Horton R. Learning from stories – Lancet’s case reports. Lancet. 1995; 346 :1256. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kidd M, Hubbard C. Introducing Journal of Medical Case Reports. J Med Case Rep. 2007; 1 :1. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-1-1. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rison RA. A guide to writing case reports for the Journal of Medical Case Reports and BioMed Central Research Notes. J Med Case Reports. 2013; 7 :239. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-7-239. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bayoumi AM, Kopplin PA. The storied case report. CMAJ. 2004; 171 :569–570. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.1031503. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kidd MR, Saltman D. Case reports at the vanguard of the 21 st century medicine (Editorial) J Med Case Rep. 2012; 6 :156. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-6-156. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Venes D. Taber’s Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary. 21. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis Company; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jenicek M. Clinical case reporting in evidence-based medicine. Oxford: Butterworth Heinemann; 1999. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fletcher RH, Fletcher SW. Clinical epidemiology: The essentials. 4. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sackett DL, Brian Haynes R, Tugwell P. Clinical epidemiology. Boston: Little, Brown and Company; 1985. [ Google Scholar ]
- Berkencotter C. Patient tales. Case histories and the uses of narrative in psychiatry. Columbia: University of South Carolina Press; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hunter KM. Doctors’ stories. The narrative structure of medical knowledge. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1991. [ Google Scholar ]
- Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2011; 11 :100. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-11-100. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wynn R, Kvalvik AM, Hynnekleiv T. Attitudes to coercion at two Norwegian psychiatric units. Nord J Psychiatry. 2011; 65 :133–137. doi: 10.3109/08039488.2010.513068. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wynn R, Myklebust LH, Bratlid T. Psychologists and coercion: decisions regarding involuntary psychiatric admission and treatment in a group of Norwegian psychologists. Nord J Psychiatry. 2007; 61 :433–437. doi: 10.1080/08039480701773139. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aaker E, Knudsen A, Wynn R, Lund A. General practitioners’ reactions to non-compliant patients. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2001; 19 :103–106. doi: 10.1080/028134301750235330. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McBride WG. Thalidomide and congenital abnormalities. (Letter) Lancet. 1961; 278 :1358. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chakra CAN, Pariente A, Pinet M, Nkeng L, Moore N, Moride Y. Case series in drug safety. A review to determine characteristics and quality. Drug Saf. 2010; 33 :1081–1088. doi: 10.2165/11539300-000000000-00000. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ban TA. The role of serendipity in drug discovery. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2006; 8 :335–344. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cade JFJ. Lithium salts in the treatment of psychotic excitement. Med J Aust. 1949; 2 :349–352. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Léauté-Labrèze C, de la Roque Dumas E, Hubiche T, Boralevi F. Propranolol for severe hemangiomas of infancy. (Letter to the editor) N Engl J Med. 2008; 358 :2649–2651. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc0708819. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fretheim A. Godt nok dokumentert? (Sufficiently documented?) (Editorial) Tidsskr Nor Legeforen. 2010; 130 :1806. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- U.S. National Institutes of Health. Studies found for the search 'propanolol and hemangiomas' in the ClinicalTrials.gov database. Accessed on 22 April, 2014 at: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=propanolol+and+hemangiomas&Search=Search .
- Beard G. Neurasthenia, or nervous exhaustion. Boston Med Surg J. 1869; 80 :217–221. doi: 10.1056/NEJM186904290801301. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Taylor DM. Developing a strategy for the management of rare disorders. BMJ. 2012; 344 :e2417. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e2417. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bjånes TK. Lokale bivirkninger ved parenteral administrering av legemidler. (Localized side effects caused by parenteral administration of drugs) Tidsskr Nor Legeforen. 2011; 131 :472–474. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nissen T, Rørvik P, Haugslett L, Wynn R. Physical restraint and near death of a psychiatric patient. J Forensic Sci. 2013; 58 :259–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1556-4029.2012.02290.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wynn R. Coercion in psychiatric care: clinical, legal, and ethical controversies. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2006; 10 :247–251. doi: 10.1080/13651500600650026. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lundh A, Christensen M, Jørgensen AW. International or national publication of case reports. Dan Med Bul. 2011; 58 :A4242. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Grønli O, Wynn R. Normocalcemic hyperparathyroidism and treatment resistant depression. Psychosomatics. 2013; 54 :493–497. doi: 10.1016/j.psym.2012.10.008. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ward SP. Thalidomide and congenital abnormalities. BMJ. 1962; 2 (5305):646–647. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5305.646. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Coodin FJ, Uchida CM, Murphy CH. Phocomelia: report of three cases. CMAJ. 1962; 87 :735–739. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Heyman DJ. Managing director of the Destillers Company Ltd. (Letter) Lancet. 1961; 278 :1262. [ Google Scholar ]
- Agha R, Rosin RD. Time for a new approach to case reports. (Editorial) Int J Surg Case Rep. 2010; 1 :1–3. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2010.04.001. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2010.04.001. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aronson JA. Anecdotes as evidence. (Editorial) BMJ. 2003; 326 :1346. doi: 10.1136/bmj.326.7403.1346. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Myers CS. A contribution to the study of the shell shock. Being an account of three cases of loss of memory, vision, smell and taste, admitted into the Duchess of Westminster’s War Hospital, Le Touquet. Lancet. 1915; 185 :316–320. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)52916-X. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morris BA. The importance of case reports. (Letter to the Editor) CMAJ. 1989; 141 :875–876. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rison RA. Neurology case reports: a call for all. J Med Case Rep. 2011; 5 :113. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-5-113. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Grimes DA, Schulz KF. Descriptive studies: what they can and cannot do. Lancet. 2002; 359 :145–149. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07373-7. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kang S. Anecdotes in medicine - 15 years of Lancet case reports. Lancet. 2010; 376 :1448–1449. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60624-1. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rose JC, Corn M. Dr. E. and other patients: new lessons from old case reports. J Hist Med Allied Sci. 1984; 39 :3–32. doi: 10.1093/jhmas/39.1.3. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Álvarez Millán C. Practice versus theory: tenth-century case histories from Islamic Middle East. Soc Hist Med. 2000; 13 :293–306. doi: 10.1093/shm/13.2.293. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Álvarez Millán C. The case history in Medieval Islamic medical literature: Tajarib and Mujarrabat as source. Med Hist. 2010; 54 :195–214. doi: 10.1017/S0025727300006712. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hulley SB, Cummings SR, Browner WS, Grady DG, Newman TB. Designing clinical research. 3. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Easterbrook PJ, Gopalan R, Berlin JA, Matthews DR. Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet. 1991; 337 :867–872. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90201-Y. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Albrecht J, Meves A, Bigby M. Case reports and case series from the Lancet had significant impact on medical literature. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005; 58 :1227–1232. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.04.003. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Oliveira GJ, Leles CR. Critical appraisal and positive outcome bias in case reports published in Brazilian dental journals. J Dent Educ. 2006; 70 :869–874. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Charlton BG, Walston F. Individual case studies in clinical research. J Eval Clin Practice. 1998; 4 :147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.1998.tb00081.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stuebe AM. Level IV evidence – adverse anecdote and clinical practice. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365 :8–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1102632. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hoffman JR. Rethinking case reports. West J Med. 1999; 170 :253–254. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilkinson G, Fahy T, Russell G, Healy D, Marks I, Tantam D, Dimond B. Case reports and confidentiality. (Editorial) Br J Psychiatry. 1995; 166 :555–558. doi: 10.1192/bjp.166.5.555. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Powell PP. The single-case report in medical literature: the ‘Elephant man’ serves as an exellent example. J Am Med Writers Assoc. 1990; 5 :9–12. [ Google Scholar ]
- Glasziou P. Evidence based case report: twenty year cough in a non-smoker. BMJ. 1998; 316 :1660–1661. doi: 10.1136/bmj.316.7145.1660. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harker N, Montgomery A, Fahey T. Interactive case report. Treating nausea and vomiting during pregnancy: case outcome. BMJ. 2004; 328 :276. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7434.276. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reis S, Hermoni D, Livingstone P, Borkan J. Integrated narrative and evidence based case report: case report of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and anticoagulation. BMJ. 2002; 325 :1018–1020. doi: 10.1136/bmj.325.7371.1018. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sorinola O, Olufowobi O, Coomarasamy A, Khan KS. Instructions to authors for case reporting are limited: a review of a core journal list. BMC Med Educ. 2004; 4 :4. doi: 10.1186/1472-6920-4-4. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rossor MN. In: How to write a paper. 4. Hall GM, editor. London: Blackwell Publishing; 2008. How to write a case report; pp. 71–75. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gagnier JJ, Kienle G, Altman DG, Moher D, Sox H, Riley D. CARE group. The CARE guidelines: consensus-based clinical case reporting guideline development. J Med Case Rep. 2013; 7 :223. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-7-223. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- BioMed Central. Cases Database. Accessed on 22 April, 2014 at: http://www.casesdatabase.com .
- Mason RA. The case report – an endangered species? (Editorial) Anesthesia. 2001; 56 :99–102. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2044.2001.01919.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Policy & Compliance
- Clinical Trials
NIH Definition of Clinical Trial Case Studies
The case studies provided below are designed to help you identify whether your study would be considered by NIH to be a clinical trial. Expect the case studies and related guidance to evolve over the upcoming year. For continuity and ease of reference, case studies will retain their original numbering and will not be renumbered if cases are revised or removed.
The simplified case studies apply the following four questions to determine whether NIH would consider the research study to be a clinical trial:
- Does the study involve human participants?
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention?
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants?
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome?
If the answer to all four questions is “yes,” then the clinical study would be considered a clinical trial according to the NIH definition.
See this page for more information about the NIH definition of a clinical trial.
General Case Studies
Institute or center specific case studies.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants who are randomized to receive one of two approved drugs. It is designed to compare the effects of the drugs on the blood level of a protein.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, the study involves human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, one of two drugs.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the drugs on the level of the protein in the participants’ blood.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, the level of a protein, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with condition Y to receive a drug that has been approved for another indication. It is designed to measure the drug’s effects on the level of a biomarker associated with the severity of condition Y.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, the approved drug.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the drug’s effect on the level of the biomarker.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, the level of a biomarker, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with condition X to receive investigational compound A. It is designed to assess the pharmacokinetic properties of compound A.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, compound A.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate how the body interacts with compound A
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, pharmacokinetic properties, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X to receive an investigational drug. It is designed to assess safety and determine the maximum tolerated dose of the drug.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, the investigational drug.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to assess safety and determine the maximum tolerated dose of the investigational drug.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, safety and maximum tolerated dose, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X to receive a chronic disease management program. It is designed to assess usability and to determine the maximum tolerated dose of the chronic disease program (e.g., how many in-person and telemedicine visits with adequate adherence).
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, the chronic disease management program.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to determine the maximum tolerated dose of the program to obtain adequate adherence.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, tolerable intensity and adequate adherence of the intervention, is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X to receive either an investigational drug or a placebo. It is designed to evaluate the efficacy of the investigational drug to relieve disease symptoms.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, the investigational drug or placebo.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the investigational drug on the participants’ symptoms.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, relief of symptoms, is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X to receive an investigational drug. It is designed to assess whether there is a change in disease progression compared to baseline. There is no concurrent control used in this study.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the investigational drug on the subject’s disease progression.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, disease progression, is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X to test an investigational in vitro diagnostic device (IVD). It is designed to evaluate the ability of the device to measure the level of an antibody in blood.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, in this context the IVD would not be considered an intervention. The IVD is being used to test its ability to measure antibody levels, but not to test its effects on any health-related biomedical or behavioral outcomes.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X to be evaluated with an investigational in vitro diagnostic device (IVD). The study is designed to evaluate how knowledge of certain antibody levels impacts clinical management of disease.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to an intervention, measurement of an antibody level, with the idea that knowledge of that antibody level might affect clinical management.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate how knowledge of the level of an antibody might inform treatment.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being measured, how blood antibody levels inform treatment, is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of healthy volunteers who will be randomized to different durations of sleep deprivation (including no sleep deprivation as a control) and who will have stress hormone levels measured. It is designed to determine whether the levels of stress hormones in blood rise in response to different durations of sleep deprivation.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, the healthy volunteers are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to an intervention, different durations of sleep deprivation followed by a blood draw.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to measure the effect of different durations of sleep deprivation on stress hormone levels.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, stress hormone levels, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
The study involves the analysis of de-identified, stored blood samples and de-identified medical records of patients with disease X who were treated with an approved drug. The study is designed to evaluate the level of a protein in the blood of patients that is associated with therapeutic effects of the drug.
- Does the study involve human participants? No, the study does not involve human participants because only de-identified samples and information are used.
The study involves the analysis of identifiable, stored blood samples and identified medical records of patients with disease X who were treated with an approved drug. The study is designed to evaluate the level of a protein in the blood of patients that is associated with therapeutic effects of the drug.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, patients are human participants because the blood and information are identifiable.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, secondary research with biospecimens or health information is not a clinical trial.
The study involves the recruitment of a healthy volunteers whose blood is drawn for genomic analysis. It is designed to identify the prevalence of a genetic mutation in the cohort and evaluate potential association between the presence of the mutation and the risk of developing a genetic disorder.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, sample collection (blood draw) is not an intervention in this context.
Physicians report that some patients being treated with drug A for disease X are also experiencing some improvement in a second condition, condition Y. The study involves the recruitment of research participants who have disease X and condition Y and are being treated with drug A. The participants are surveyed to ascertain whether they are experiencing an improvement in condition Y.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, participants are not prospectively assigned to receive an intervention as they are receiving drugs as part of their clinical care. The surveys are being used for measurement, not to modify a biomedical or behavioral outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of patients with disease X who are receiving one of three standard therapies as part of their clinical care. It is designed to assess the relative effectiveness of the three therapies by monitoring survival rates using medical records over a few years.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, there is no intervention. The therapies are prescribed as part of clinical care; they are not prospectively assigned for the purpose of the study. The study is observational.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X vs. healthy controls and comparing these participants on a range of health processes and outcomes including genomics, biospecimens, self-report measures, etc. to explore differences that may be relevant to the development of disease X.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, the measures needed to assess the outcomes are not interventions in this context, as the study is not intended to determine whether the measures modify a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of healthy volunteers for a respiratory challenge study; participants are randomized to receive different combinations of allergens. The study evaluates the severity and mechanism of the immune response to different combinations of allergens introduced via inhalation.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, healthy volunteers are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, healthy volunteers are prospectively assigned to randomly selected combinations of allergens.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is evaluating the effects of different combinations of allergens on the immune response in healthy individuals.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the study evaluates the severity and mechanism of the immune reaction to allergens, which are health-related biomedical outcomes.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) to evaluate the effects of an investigational drug on memory, and retention and recall of information.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, participants are prospectively assigned to receive the investigational drug.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is evaluating the effects of the drug on participants’ memory.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the study evaluates memory, and retention and recall of information in the context of AD.
The study involves the recruitment of individuals to receive a new behavioral intervention for sedentary behavior. It is designed to measure the effect of the intervention on hypothesized differential mediators of behavior change.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, participants are prospectively assigned to receive a behavioral intervention.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is evaluating the effects of the intervetion on mediators of behavior change.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, mediators of behavior change, are behavioral outcomes relevant to health.
The study involves the recruitment of patients with disease X to be evaluated with a new visual acuity task. It is designed to evaluate the ability of the new task to measure visual acuity as compared with the gold standard Snellen Test
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to an intervention, the new visual acuity test.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? No, the study is designed to evaluate the ability of the new visual acuity test to measure visual acuity as compared to the gold standard Snellen Test, but not to modify visual acuity.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with CHF who were hospitalized before or after implementation of the Medicare incentives to reduce re-hospitalizations. Morbidity, mortality, and quality of life of these participants are evaluated to compare the effects of these Medicare incentives on these outcomes.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, the intervention (incentives to reduce re-hospitalization) were assigned by Medicare, not by the research study.
The study involves the recruitment of healthcare providers to assess the extent to which being provided with genomic sequence information about their patients informs their treatment of those patients towards improved outcomes.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, both the physicians and the patients are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, physicians are prospectively assigned to receive genomic sequence information, which is the intervention.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of intervening with physicians, on the treatment they provide to their patients.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related, biomedical, or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, the extent to which providing specific information to physicians informs the treatment of patients, is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with a behavioral condition to receive either an investigational behavioral intervention or a behavioral intervention in clinical use. It is designed to evaluate the effectiveness of the investigational intervention compared to the intervention in clinical use in reducing the severity of the obsessive compulsive disorder.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to an intervention, either the investigational intervention or an intervention in clinical use.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate whether the investigational intervention is as effective as the standard intervention, at changing behavior.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related, biomedical, or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, the interventions’ effectiveness in reducing the severity of the condition, is a health-related behavioral outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of physicians who will be randomly assigned to use a new app or an existing app, which cues directed interviewing techniques. The study is designed to determine whether the new app is better than the existing app at assisting physicians in identifying families in need of social service support. The number of community service referrals will be measured.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, both the physicians and the families are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, physicians are prospectively assigned to use one of two apps, which are the interventions.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of intervening with physicians, on social service support referral for families.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related, biomedical, or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, the number of referrals, is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of parents to participate in focus groups to discuss topics related to parental self-efficacy and positive parenting behaviors. It is designed to gather information needed to develop an intervention to promote parental self-efficacy and positive parenting behaviors.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, the parents are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, a focus group is not an intervention.
The study involves the recruitment of healthy volunteers to test a new behavioral intervention. It is designed to evaluate the effect of a meditation intervention on adherence to exercise regimens and quality of life to inform the design of a subsequent, fully-powered trial.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, study participants are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to a behavioral intervention.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on adherence, and quality of life.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, adherence and quality of life are health-related outcomes.
A study will test the feasibility a mobile phone app designed to increase physical activity. A group of sedentary individuals will use the app for a week while their interactions with the app are monitored. The number of interactions with the app will be measured, as well as any software issues. Participants will also complete a survey indicating their satisfaction with and willingness to use the app, as well as any feedback for improvement. The app’s effect on physical activity, weight, or cardiovascular fitness will not be evaluated.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, sedentary individuals will be enrolled.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? The participants will interact with the app for a week.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? No. While the participants’ interactions are monitored (steps or heart rate may be recorded in this process), the study is NOT measuring the effect of using the app ON the participant. The study is only measuring the usability and acceptability of the app, and testing for bugs in the software. The effect on physical activity is NOT being measured.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? N/A
The study involves the recruitment of healthy family members of patients hospitalized for disease X to test two CPR training strategies. Participants will receive one of two training strategies. The outcome is improved CPR skills retention.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, family members of patients are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to one of two CPR educational strategies.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of educational strategies on CPR skills.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, retention of CPR skills is a health-related behavioral outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants in three different communities (clusters) to test three CPR training strategies. The rate of out-of- hospital cardiac arrest survival will be compared.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive one of three types of CPR training, which is the intervention.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of different CPR training strategies on patient survival rates post cardiac arrest.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, out-of-hospital cardiac arrest survival is a health-related outcome.
A study involves the recruitment of school children to evaluate two different tools for monitoring food intake. Food consumption behavior will be measured by asking children to activate a pocket camera during meals and to use a diary to record consumed food. The accuracy of the two food monitoring methods in measuring energy intake will be assessed.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, children are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, in this context the monitoring methods would not be considered an intervention. The study is designed to test the accuracy of two monitoring methods, but not to test the effect on any health-related biomedical or behavioral outcomes.
A study involves the recruitment of school children to evaluate two different tools for monitoring food intake. Food consumption behavior will be measured by asking children to activate a pocket camera during meals and to use a diary to record consumed food. Changes to eating behavior will be assessed.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to two food monitoring methods.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to determine whether using the monitoring methods changes eating behavior.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, eating behavior is a health-related outcome.
A study involves the recruitment of children at two schools to monitor eating behavior. Children’s food choices will be monitored using a remote food photography method. Food consumption and the accuracy of food monitoring methods will be assessed.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, the children participating in this study are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, not in this context. The study involves observing and measuring eating behavior, but not modifying it. This is an observational study.
A study involves the recruitment of children at two schools to evaluate their preferences for graphics and colors used in healthy food advertisements. Children will be presented with multiple health advertisements and their preferences for graphics and colors will be assessed.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to see different advertisements.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the advertisements.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? No, preferences are not health-related biomedical or behavioral outcomes.
The study involves ambulatory patients who have new-onset stable angina and who are recruited from community practices. They are randomized to undergo CT angiography or an exercise stress test of the doctor’s choice. To keep the trial pragmatic, the investigators do not prescribe a protocol for how physicians should respond to test results. The study is designed to determine whether the initial test (CT angiography or stress test) affects long-term rates of premature death, stroke, or myocardial infarctions.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are randomized to undergo CT angiography or an exercise stress test.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to determine whether the initial test done affects long-term rates of certain clinical events.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, premature death, stroke, and myocardial infarction are health-related biomedical outcomes.
The study involves patients who present with stable angina to community practices. As part of their routine care some of their physicians refer them for CT angiography, while others refer them for exercise stress tests. The study is designed to see whether or not there's an association between the type of test that is chosen and long-term risk of death, stroke, or myocardial infarction.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, the intervention is not prospectively assigned by the investigators. Rather, the intervention, in this case diagnostic study, occurs as part of routine clinical care.
The investigators conduct a longitudinal study of patients with schizophrenia. Their physicians, as part of their standard clinical care, prescribe antipsychotic medication. The investigators conduct an imaging session before starting treatment; they repeat imaging 4-6 weeks later.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, not in this context. Antipsychotic medications are given as part of clinical care, not as part of a prospective, approved research protocol.
The investigators conduct a longitudinal study of patients with schizophrenia. Their physicians, as part of their standard clinical care, prescribe antipsychotic medication. As part of the research protocol, all participants will be prescribed the same dose of the antipsychotic medication. The investigators conduct an imaging session before starting treatment; they repeat imaging 4-6 weeks later.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, although participants are all receiving antipsychotic medication as part of their standard medical care, the dose of the antipsychotic medication is determined by the research protocol, rather than individual clinical need.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of a dose of antipsychotic medication on brain function.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome ? Yes, brain function measured by imaging is a health-related outcome.
The study involves recruitment of healthy volunteers who will wear a thermal compression device around their legs. This pilot study is designed to examine preliminary performance and safety of a thermal compression device worn during surgery. Investigators will measure core temperature, comfort, and presence of skin injury in 15-minute intervals.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, participants are assigned to wear a thermal compression device.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the thermal compression device on participant core temperature, comfort, and presence of skin injury.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome ? Yes, participant core temperature, comfort, and presence of skin injury are health-related biomedical outcomes.
The study involves collection of data on hospitalizations for various acute illnesses among people who live close to a border between two states that have recently implemented different laws related to public health (e.g. smoking regulations, soda taxes). The investigators want to take advantage of this “natural experiment” to assess the health impact of the laws.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, the study involves human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, the interventions were assigned by state laws and state of residence, not by the research study.
The study involves recruitment of healthy volunteers to engage in working memory tasks while undergoing transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to induce competing local neuronal activity. The study is measuring task performance to investigate the neural underpinnings of working memory storage and processing.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, healthy volunteers are prospectively assigned to receive TMS stimulation protocols during a working memory task.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is evaluating the effects of local TMS stimulation on working memory performance and oscillatory brain activity in healthy individuals.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the study evaluates working memory processes, which are health-related biomedical outcomes.
The study involves recruitment of healthy volunteers to engage in a social valuation task while dopamine tone in the brain is manipulated using tolcapone, an FDA-approved medication. The study aims to understand the role of dopamine in social decision-making and to search for neural correlates of this valuation using fMRI.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, healthy volunteers are prospectively assigned to receive tolcapone during a social valuation task.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is evaluating the effects of modulating dopamine tone on social decision-making. Although this study uses an FDA-approved drug to modulate dopamine tone, the goal of this intervention is to understand the role of dopamine in a fundamental phenomenon (social valuation), and not to study the mechanism of action of the drug or its clinical effects.
The career development candidate proposes to independently lead a study to test a new drug A on patients with disease X. Patients will be randomized to a test and control group, with the test group receiving one dose of drug A per week for 12 months and controls receiving placebo. To assess presence, number, and type of any polyps, a colonoscopy will be performed. To assess biomarkers of precancerous lesions, colon mucosal biopsies will be collected. Complete blood count will be measured, and plasma will be stored for potential biomarker evaluation.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, drug A or placebo.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of drug A and placebo on the presence and type of polyps.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, the presence and type of polyps, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
Ancillary Study to Case Study #42b: Some types of drug A being evaluated in Case Study #42a have been reported to impact renal function. An internal medicine fellow performs an ancillary study where stored plasma from Case Study #42a will be evaluated for multiple biomarkers of renal function.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, patients are human participants because the plasma and information are identifiable.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, because the assignment of participants to an intervention occurs as part of an existing, separately funded clinical trial. This proposal would be considered an ancillary study that is not an independent clinical trial.
Ancillary Study to Case Study #42a: An internal medicine fellow designs an independent ancillary trial where a subset of patients from the parent trial in Case Study #42a will also receive drug B, based on the assumption that a two-drug combination will work significantly better than a single drug at both improving renal function and reducing polyps. The test subjects will be evaluated for renal function via plasma clearance rates at 6 and 12 months after initiation of drugs A and B.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, drugs A and B.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of drugs A and B on renal function.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, renal function, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
A group of healthy young adults will perform a Go/No-Go task while undergoing fMRI scans. The purpose of the study is to characterize the pattern of neural activation in the frontal cortex during response inhibition, and the ability of the participant to correctly withhold a response on no-go
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, healthy young adults will be enrolled in this study.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants will be prospectively assigned to perform a Go/No-Go task, which involves different levels of inhibitory control.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the Go/No-Go task on neural activation in the frontal cortex. The study will measure inhibitory control and the neural systems being engaged. In this study, the Go/No-Go task is the independent variable, and behavioral performance and the associated fMRI activations are the dependent variables.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the neural correlates of inhibitory control and behavioral performance are health-related biomedical outcomes.
A group of adolescents will participate in a longitudinal study examining changes in executive function over the course of a normal school year. Color naming performance on the standard version of the Stroop test will be obtained. All measures will be compared at multiple time points during the school year to examine changes in executive function. The purpose is to observe changes in executive function and to observe if differences exist in the Stroop effect over the course of the school year for these adolescents.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, adolescents will be enrolled in this study.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, there is no intervention in this study and no independent variable manipulated. The adolescents are not prospectively assigned to an intervention, but instead the investigator will examine variables of interest (including the Stroop test) over time. The Stroop effect is used as a measurement of point-in-time data.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? No, there is no intervention. Performance on the Stroop test is a well-established measure of executive function and the test is not providing an independent variable of interest here. It is not being used to manipulate the participants or their environment. The purpose is simply to obtain a measure of executive function in adolescents over the course of the school year.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? N/A. No effect of an intervention is being evaluated.
A group of participants with social anxiety will perform an experimentally manipulated Stroop test. In this variant of the Stroop test, the stimuli presented are varied to include emotional and neutral facial expressions presented in different colors. Participants are instructed to name the colors of the faces presented, with the expectation that they will be slower to name the color of the emotional face than the neutral face. The purpose of the study is to examine the degree to which participants with social anxiety will be slower to process emotional faces than neutral faces.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, participants with social anxiety will be enrolled in this study.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants will be prospectively assigned to perform a modified Stroop test using different colored emotional/neutral faces to explore emotional processing in people with social anxiety. Note that the independent variable is the presentation of emotional vs neutral faces.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to measure the effect of emotional valence (i.e. emotional faces) on participant response time to name the color. The purpose is to determine whether the response time to emotional faces is exaggerated for people with social anxiety as compared to neutral faces. Note that the response time to name the colors is the dependent variable in this study.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the processing of emotional information is a health-related biomedical outcome.
The study involves healthy volunteers and compares temporal SNR obtained with a new fMRI pulse sequence with that from another sequence.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, in this context the different pulse sequences would not be considered an intervention. The pulse sequences are not being used to modify any biomedical or behavioral outcome; rather the investigator is comparing performance characteristics of the two pulse sequences.
The study is designed to demonstrate that a new imaging technology (e.g. MRI, PET, ultrasound technologies, or image processing algorithm) is equivalent to, or has better sensitivity/specificity than a standard of care imaging technology. Aim one will use the new imaging technology and the gold standard in ten healthy volunteers. Aim Two will use the new imaging technology and the gold standard before and after a standard care procedure in ten patients. In both aims the performance of the new technology will be compared to the gold standard. No clinical care decisions will be made based on the use of the device in this study.
- Does the study involve human participants? YES. Aim one will study ten healthy volunteers, and aim two will study ten patient volunteers.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, participants will be prospectively assigned to be evaluated with a new imaging technology and the gold standard technology.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? No, the study is not measuring the effect of the technologies ON the human subjects. The study is determining if the new technology is equivalent or better than the gold standard technology. No effect on the participant is being measured.
An investigator proposes to add secondary outcomes to an already funded clinical trial of a nutritional intervention. The trial is supported by other funding, but the investigator is interested in obtaining NIH funding for studying oral health outcomes. Participants in the existing trial would be assessed for oral health outcomes at baseline and at additional time points during a multi-week dietary intervention. The oral health outcomes would include measures of gingivitis and responses to oral health related quality of life questionnaires. Oral fluids would be collected for analysis of inflammatory markers and microbiome components.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, because the assignment of participants to an intervention (and the administration of the intervention) occur as part of an existing, separately funded clinical trial. This proposal would be considered an ancillary study that leverages an already existing clinical trial.
The goal of the project is to use functional neuroimaging to distinguish patients with temporomandibular disorders (TMD) who experience TMD pain through centralized pain processes from those with TMD related to peripheral pain. Pain processing in a study cohort of TMD patients and healthy controls will be measured through functional magnetic resonance neuroimaging (fMRI) following transient stimulation of pain pathways through multimodal automated quantitative sensory testing (MAST QST). TMD patients will receive study questionnaires to better correlate the extent to which TMD pain centralization influences TMD prognosis and response to standard of care peripherally targeted treatment (prescribed by physicians, independently of the study).
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, not in this context. The transient stimulation of pain pathways and the fMRI are being performed to measure and describe brain activity, but not to modify it.
An investigator proposes to perform a study of induced gingivitis in healthy humans, to study microbial colonization and inflammation under conditions of health and disease. During a 3-week gingivitis induction period, each study participant will use a stent to cover the teeth in one quadrant during teeth brushing. A contralateral uncovered quadrant will be exposed to the individual's usual oral hygiene procedures, to serve as a control. Standard clinical assessments for gingivitis will be made and biospecimens will be collected at the point of maximal induced gingivitis, and again after normal oral hygiene is resumed. Biospecimens will be assessed for microbial composition and levels of inflammation-associated chemokines.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to an intervention, abstaining from normal oral hygiene for a portion of the mouth, to induce gingivitis.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the induced gingivitis on microbial composition and levels of inflammatory chemokines in oral samples.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the microbial composition and chemokine levels in oral samples are health-related biomedical outcomes.
The study will enroll older adults with hearing loss, comparing the effectiveness of enhanced hearing health care (HHC) to usual HHC. In addition to routine hearing-aid consultation and fitting, participants randomized to enhanced HCC will be provided patient-centered information and education about a full range of hearing assistive technologies and services. Study outcomes include the utilization of technology or services, quality of life, communication abilities, and cognitive function.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, the study enrolls older adults with hearing loss.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, participants are randomized to receive enhanced HCC or usual HCC interventions.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study will evaluate enhanced HCC’s effectiveness in modifying participant behavior and biomedical outcomes.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, rate of technology/service utilization is a behavioral outcome and quality of life, communications, and cognition are biomedical outcomes that may be impacted by the interventions.
The study involves the recruitment of obese individuals who will undergo a muscle biopsy before and after either exercise training or diet-induced weight loss. Sarcolemmal 1,2-disaturated DAG and C18:0 ceramide species and mitochondrial function will be measured. Levels will be correlated with insulin sensitivity.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are assigned to either exercise training or a diet.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to compare the effects of the interventions on muscle metabolism.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, muscle metabolism/signaling is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of participants with type 2 diabetes who will undergo a muscle biopsy before and after a fast to measure acetylation on lysine 23 of the mitochondrial solute carrier adenine nucleotide translocase 1 (ANT1). Levels will be related to rates of fat oxidation.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are assigned to undergo a fast.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to compare the effects of the fast on molecular parameters of metabolism.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, metabolism is a health-related outcome.
Insulin-resistant and insulin-sensitive nondiabetic adults who have a parent with type 2 diabetes will be followed over time to understand the role of mitochondrial dysfunction in the development of diabetes. Oral glucose tolerance tests will be performed annually to measure insulin sensitivity and glycemic status. Participants will also undergo a brief bout of exercise, and mitochondrial ATP synthesis rates will be measured by assessing the rate of recovery of phosphocreatine in the leg muscle, using 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, the participants are not assigned to an intervention; the OGTT and 31P MRS are measures.
Participants with chronic kidney disease will be recruited to receive one of two drug agents. After 6 weeks of therapy, subjects will undergo vascular function testing and have measures of oxidative stress evaluated in their plasma and urine. Results of the function testing and the oxidative stress biomarkers will be related to drug treatment.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are assigned to receive two different drugs.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to compare the effects of the drugs on vascular function.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, vascular function is a health-related outcome.
Participants with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease will be recruited to receive an oral curcumin therapy or placebo and the participants will undergo vascular function testing, renal imaging to assess kidney size, and assessment of oxidative stress biomarkers in urine and plasma after an ascorbic acid challenge. Changes in these outcomes will be related to oral therapy.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are assigned to receive medication or placebo.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to compare the effects of the drugs on vascular function and kidney size.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, vascular function and kidney size are health-related outcomes.
Kidney transplant recipients will be recruited to undergo an experimental imaging procedure at several timepoints up to 4 months post-transplantation. Output from the images will be related to pathological assessments of the transplant as well as clinical measures of renal function.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, the participants are not assigned to receive an intervention. They undergo transplantation as part of their routine clinical care. The imaging procedure is a measure and not an intervention.
The study proposes the development of a novel probe to assess clearance of a nutritional metabolite in a given disease state. The probe is a GMP grade, deuterated, intravenously administered tracer and clearance is assessed by mass spectrometry analysis of serial blood draws. Participants will either receive a micronutrient supplement or will receive no supplementation. The clearance rate of the probe will be compared in the two groups, to understand the performance of the probe.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are assigned to receive either a micronutrient supplement or nothing.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? No, the intervention is being used to assess the performance of the probe and is not looking at an effect on the participant.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are assigned to receive a controlled diet for three days.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? No, the intervention (controlled diet) is being used to minimize exogenous dietary sources of oxalate in the participants prior to the labeled tracer infusion. The study will not be evaluating the effect of the diet on the participants.
This page last updated on: April 28, 2021
- Bookmark & Share
- E-mail Updates
- Help Downloading Files
- Privacy Notice
- Accessibility
- National Institutes of Health (NIH), 9000 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, Maryland 20892
- NIH... Turning Discovery Into Health

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews). The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient's personal history). In psychology, case studies are ...
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The Methodology index offers clinical and non-clinical entries. "Clinical Case Study" is defined as "case reports that include disorder, diagnosis, and clinical treatment for individuals with mental or medical illnesses," whereas "Non-clinical Case Study" is a "document consisting of non-clinical or organizational case examples of ...
an in-depth investigation of a single individual, family, event, or other entity. Multiple types of data (psychological, physiological, biographical, environmental) are assembled, for example, to understand an individual's background, relationships, and behavior. Although case studies allow for intensive analysis of an issue, they are limited ...
Case formulation, or case conceptualization, is regarded as a core competency in many helping professions, including psychology. The origins of case formulation in professional practice can be traced back as far as Hippocrates and Galen in Ancient Greece. And yet anecdotally it is interesting that many psychologists find it difficult to express what exactly is case formulation. I remember ...
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
The case study method is an in-depth research strategy focusing on the detailed examination of a specific subject, situation, or group over time. It's employed across various disciplines to narrow broad research fields into manageable topics, enabling researchers to conduct detailed investigations in real-world contexts. This method is characterized by its intensive examination of individual ...
A case study is a research method used in psychology to investigate a particular individual, group, or situation in depth. It involves a detailed analysis of the subject, gathering information from various sources such as interviews, observations, and documents. In a case study, researchers aim to understand the complexities and nuances of the ...
In clinical psychology, the term case study as a research approach is traditionally defined as the "intensive investigation of the individual client" (Kazdin, 1981, p. 184), be the client "an individual, group, organization, community, or even a society" (Fishman, 1999, p. 10). What is distinctive in the case study is that the client is a single unit that is studied as a whole. Within ...
Case study in psychology refers to the use of a descriptive research approach to obtain an in-depth analysis of a person, group, or phenomenon. A variety of techniques may be employed including personal interviews, direct-observation, psychometric tests, and archival records.In psychology case studies are most often used in clinical research to describe rare events and conditions, which ...
Résumé. Case study is a common methodology in the social sciences (management, psychology, science of education, political science, sociology). A lot of methodological papers have been dedicated to case study but, paradoxically, the question "what is a case?" has been less studied.
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table.
A case report is a detailed report of the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports usually describe an unusual or novel occurrence and as such, remain one of the cornerstones of medical progress and provide many new ideas in medicine. Some reports contain an extensive review of the relevant ...
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc. Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Evidence-based case study guidelines. The clinical case study may be defined as a detailed analysis of the therapy conducted with a couple or family that will be instructive, may be exemplary or cautionary, and stresses factors contributing to either success or failure of the treatment. Because evidence-based clinical case studies can be ...
Case Studies. In 2011, the New York Times published a feature story on Krista and Tatiana Hogan, Canadian twin girls. These particular twins are unique because Krista and Tatiana are conjoined twins, connected at the head. There is evidence that the two girls are connected in a part of the brain called the thalamus, which is a major sensory relay center.
The place of Case Formulation in the field of psychotherapy is conceptualized as a necessary bridge between diagnostic systems and clinical practice. The common aspects of the five approaches included in the issue, as well as of the cases to which they were applied, are discussed to explore their possible cross-theoretical nature, especially in ...
A case study psychology example could be that a researcher wants to study the onset of severe anxiety by a teenager following a natural disaster. The three most common types of case studies are ...
Relative frequencies (%) of case studies with reference to all publications on all ICD-10 chapters and with reference to the specific chapters on mental disorders, diseases of the skin and ...
Observations published can generate ideas and be a trigger for further studies. For instance, a case series consisting of several similar cases in a short period can make up the case-group for a case-control study . Clinicians could do the observation and publish the case series while the case-control study could be left to the academics.
The study involves the recruitment of patients with disease X who are receiving one of three standard therapies as part of their clinical care. It is designed to assess the relative effectiveness of the three therapies by monitoring survival rates using medical records over a few years. Case #13b.
Clinical psychologists provide psychological treatment, research, or work with specific patients, patient groups, disorders, or conditions. Work settings range from hospitals, private practices ...