Care Support Assignment Example, Ireland
The healthcare students preparing for Qqi Level courses often get confused with the task assigned by their professors. The students as a learner get a chance to provide care and support services to the elderly. However, it can be a daunting task to provide care support to someone and cure their physical and mental health. With efficient knowledge and an in-depth understanding of social care services, healthcare providers can help adults deal with illness and disability. Moreover, care support can take different forms including help while people live at home, hospital, or in a special care home. Whatever the task assigned to students, the main motive of care support assignment is to enhance their learning to work effectively in a care setting.

Get 100% Plagiarism-Free Care Support Assignment
Example of care support assignment for irish students.
Title : What is the need for care support planning? Aim of the study : Care support planning motivates healthcare providers to help anyone with needs and encourage social care staff to take part in the care providing process. It helps individuals to set their aims and then secures the care support required to achieve those goals. The students as a learner get a chance to work with professional care support provider and fulfill the health and care needs of adults. Introduction : People suffering from disability often consult professional care supporter who can be a doctor, social worker, or a nurse to get care support. The main motive of the healthcare supporters is to bring the new skills and knowledge among adults so that they can understand their disability and the choices for treatment. Care support workers help and assist people by providing excellent care to them and thus offer a valuable role in society. By working with vulnerable people, care support providers help individuals to overcome the illness and experience a crucial time while providing care to the elderly. Main body section: What are the Responsibilities of a Care Support Worker? The care support assistants can work from any type of environment that is suitable to provide help and care to individuals. Their responsibility is to work with disabled individuals struggling with illness and need help for performing day-to-day activities. Being a support worker, my primary duty was to enhance the lives of those individuals who require care support: By conducting different interviews with adults and their families, I was capable to assess the needs of people with special needs. Monitoring the medical conditions of individuals was my major concern. We have to submit the assessment report daily, thus I supposed to do a daily health checkup. Helping clients with general tasks like washing, dressing, drinking, eating, and many more are the responsibilities of healthcare supporters. Apart from all such activities, it is crucial to take participate in training to advance knowledge and maintain medical records. My mentor asked me to introduce clients with various recreational activities and help them to overcome their physical and mental illness effectively. What skills are required to become a care support worker? Interaction is one of the major skills that individuals must possess to become a care support worker. Whether it’s about providing care to children, adults, or the elderly, care support workers should know how to interact properly. Moreover, many people may have suffered from distressing time and thus require healthcare supporters to be patient and empathetic with them. Conclusion : Providing care supporter to people is a rewarding job. Healthcare supporters must remain patient and calm while providing care to the elderly. There are several responsibilities that individuals must take care of while providing care support and managing the needs of the elderly.
Try Care Support Assignment Writing For Free
Hire qqi assignment writers and get top-notch quality medical assignment help.
The professional writers of Irelandassignments.com know getting high marks in healthcare assignments is how much crucial for students. The students can hire expert assignment makers to fulfill their career goals successfully. Moreover, expert writers understand the value of meeting submission deadlines. Thus, they deliver high-quality assignment solutions before the final date of submission.
- Structures & Governance in Healthcare Assignment Sample Ireland
- RDGY10090 Healthcare Imaging and Information Systems UCD Assignment Sample Ireland
- SMGT10150 Health, Fitness and Nutrition UCD Assignment Sample Ireland
- MDSA40040 Repro Psych & Child Medicine UCD Assignment Sample Ireland
- AY104 Introduction to Financial Accounting NUIG assignment sample Ireland
- AR347 Palaeoecology – Reconstructing Past Environments NUIG assignment sample Ireland
- AN225 Human Gross Anatomy NUI assignment sample Ireland
- ACC20010 Financial Accounting 2 Assignment Sample Ireland
- ACC1071D An Introduction to Financial Accounting Information Assignment Sample Ireland
- BUU33530 Financial Accounting Assignment Example TCD Ireland
- AC4002 Managerial Accounting Assignment Example UL Ireland
- ACC40020 Management Accounting Assignment Example UCD Ireland
- Advancing Recovery in Ireland (ARI) Essay Example
- Pharmaceutical Analysis Essay Sample Ireland
- Impact of Covid-19 on Employment in Ireland Essay Example
Submit Your Assignment
How to Write a Nursing Care Plan
Nursing care plan components, nursing care plan fundamentals.

Knowing how to write a nursing care plan is essential for nursing students and nurses. Why? Because it gives you guidance on what the patient’s main nursing problem is, why the problem exists, and how to make it better or work towards a positive end goal. In this article, we'll dig into each component to show you exactly how to write a nursing care plan.
A nursing care plan has several key components including,
- Nursing diagnosis
- Expected outcome
- Nursing interventions and rationales
Each of the five main components is essential to the overall nursing process and care plan. A properly written care plan must include these sections otherwise, it won’t make sense!
- Nursing diagnosis - A clinical judgment that helps nurses determine the plan of care for their patients
- Expected outcome - The measurable action for a patient to be achieved in a specific time frame.
- Nursing interventions and rationales - Actions to be taken to achieve expected outcomes and reasoning behind them.
- Evaluation - Determines the effectiveness of the nursing interventions and determines if expected outcomes are met within the time set.
>> Related: What is the Nursing Process?
Get 10% OFF Nursing School Study Guides From nurseinthemaking.com ! Fill out the form to get your exclusive discount.
Before writing a nursing care plan, determine the most significant problems affecting the patient. Think about medical problems but also psychosocial problems. At times, a patient's psychosocial concerns might be more pressing or even holding up discharge instead of the actual medical issues.
After making a list of problems affecting the patient and corresponding nursing diagnosis, determine which are the most important. Generally, this is done by considering the ABCs (Airway, Breathing, Circulation). However, these will not ALWAYS be the most significant or even relevant for your patient.
Step 1: Assessment
The first step in writing an organized care plan includes gathering subjective and objective nursing data . Subjective data is what the patient tells us their symptoms are, including feelings, perceptions, and concerns. Objective data is observable and measurable.
This information can come from,
Verbal statements from the patient and family
Vital signs
Blood pressure
Respirations
Temperature
Oxygen Saturation
Physical complaints
Body conditions
Head-to-toe assessment findings
Medical history
Height and weight
Intake and output
Patient feelings, concerns, perceptions
Laboratory data
Diagnostic testing
Echocardiogram
Step 2: Diagnosis
Using the information and data collected in Step 1, a nursing diagnosis is chosen that best fits the patient, the goals, and the objectives for the patient’s hospitalization.
According to North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA), defines a nursing diagnosis as “a clinical judgment about the human response to health conditions/life processes, or a vulnerability for that response, by an individual, family, group or community.”
A nursing diagnosis is based on Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs pyramid and helps prioritize treatments. Based on the nursing diagnosis chosen, the goals to resolve the patient’s problems through nursing implementations are determined in the next step.
Get 5 FREE study guides from Simplenursing.com - fill out the form for instant access! 1. Fluid & Electrolytes study guide 2. EKG Rhythms study guide 3. Congestive Heart Failure study guide 4. Lab Values study guide 5. Metabolic Acidosis & Alkalosis study guide

By clicking download, you agree to receive email newsletters and special offers from Nurse.org & Simplenursing.com. You may unsubscribe at any time by using the unsubscribe link, found at the bottom of every email.
Your request has been received. Thanks!
There are 4 types of nursing diagnoses.
Problem-focused - Patient problem present during a nursing assessment is known as a problem-focused diagnosis
Risk - Risk factors require intervention from the nurse and healthcare team prior to a real problem developing
Health promotion - Improve the overall well-being of an individual, family, or community
Syndrome - A cluster of nursing diagnoses that occur in a pattern or can all be addressed through the same or similar nursing interventions
After determining which type of the four diagnoses you will use, start building out the nursing diagnosis statement.
The three main components of a nursing diagnosis are:
Problem and its definition - Patient’s current health problem and the nursing interventions needed to care for the patient.
Etiology or risk factors - Possible reasons for the problem or the conditions in which it developed
Defining characteristics or risk factors - Signs and symptoms that allow for applying a specific diagnostic label/used in the place of defining characteristics for risk nursing diagnosis
PROBLEM-FOCUSED DIAGNOSIS
Problem-Focused Diagnosis related to ______________________ (Related Factors) as evidenced by _________________________ (Defining Characteristics).
RISK DIAGNOSIS
The correct statement for a NANDA-I nursing diagnosis would be: Risk for _____________ as evidenced by __________________________ (Risk Factors).
Step 3: Outcomes and Planning
After determining the nursing diagnosis, it is time to create a SMART goal based on evidence-based practices. SMART is an acronym that stands for,
It is important to consider the patient’s medical diagnosis, overall condition, and all of the data collected. A medical diagnosis is made by a physician or advanced healthcare practitioner. It’s important to remember that a medical diagnosis does not change if the condition is resolved, and it remains part of the patient’s health history forever.
Examples of medical diagnosis include,
Chronic Lung Disease (CLD)
Alzheimer’s Disease
Endocarditis
Plagiocephaly
Congenital Torticollis
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
It is also during this time you will consider goals for the patient and outcomes for the short and long term. These goals must be realistic and desired by the patient. For example, if a goal is for the patient to seek counseling for alcohol dependency during the hospitalization but the patient is currently detoxing and having mental distress - this might not be a realistic goal.
Step 4: Implementation
Now that the goals have been set, you must put the actions into effect to help the patient achieve the goals. While some of the actions will show immediate results (ex. giving a patient with constipation a suppository to elicit a bowel movement) others might not be seen until later on in the hospitalization.
The implementation phase means performing the nursing interventions outlined in the care plan. Interventions are classified into seven categories:
Physiological
Complex physiological
Health system interventions
Some interventions will be patient or diagnosis-specific, but there are several that are completed each shift for every patient:
Pain assessment
Position changes
Fall prevention
Providing cluster care
Infection control
Step 5: Evaluation
The fifth and final step of the nursing care plan is the evaluation phase. This is when you evaluate if the desired outcome has been met during the shift. There are three possible outcomes,
Based on the evaluation, it can determine if the goals and interventions need to be altered. Ideally, by the time of discharge, all nursing care plans, including goals should be met. Unfortunately, this is not always the case - especially if a patient is being discharged to hospice, home care, or a long-term care facility. Initially, you will find that most care plans will have ongoing goals that might be met within a few days or may take weeks. It depends on the status of the patient as well as the desired goals.
Consider picking goals that are achievable and can be met by the patient. This will help the patient feel like they are making progress but also provide relief to the nurse because they can track the patient’s overall progress.
>> Show Me Online RN-to-BSN Programs
Nursing care plans contain information about a patient’s diagnosis, goals of treatment, specific nursing interventions, and an evaluation plan. The nursing plan is constantly updated with changes and new subjective and objective data.
Key aspects of the care plan include,
Outcome and Planning
Implementation
Through subjective and objective data, constantly assessing your patient’s physical and mental well-being, and the goals of the patient/family/healthcare team, a nursing care plan can be a helpful and powerful tool.
*This website is provided for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute providing medical advice or professional services. The information provided should not be used for diagnosing or treating a health problem or disease.

Kathleen Gaines (nee Colduvell) is a nationally published writer turned Pediatric ICU nurse from Philadelphia with over 13 years of ICU experience. She has an extensive ICU background having formerly worked in the CICU and NICU at several major hospitals in the Philadelphia region. After earning her MSN in Education from Loyola University of New Orleans, she currently also teaches for several prominent Universities making sure the next generation is ready for the bedside. As a certified breastfeeding counselor and trauma certified nurse, she is always ready for the next nursing challenge.

Plus, get exclusive access to discounts for nurses, stay informed on the latest nurse news, and learn how to take the next steps in your career.
By clicking “Join Now”, you agree to receive email newsletters and special offers from Nurse.org. We will not sell or distribute your email address to any third party, and you may unsubscribe at any time by using the unsubscribe link, found at the bottom of every email.
Nursing Care Plans (NCP) Ultimate Guide and List

Writing the best nursing care plan requires a step-by-step approach to complete the parts needed for a care plan correctly. This tutorial will walk you through developing a care plan. This guide has the ultimate database and list of nursing care plans (NCP) and nursing diagnosis samples for our student nurses and professional nurses to use—all for free! Care plan components, examples, objectives, and purposes are included with a detailed guide on writing an excellent nursing care plan or a template for your unit.
Table of Contents
Standardized care plans, individualized care plans, purposes of a nursing care plan, three-column format, four-column format, student care plans, step 1: data collection or assessment, step 2: data analysis and organization, step 3: formulating your nursing diagnoses, step 4: setting priorities, short-term and long-term goals, components of goals and desired outcomes, types of nursing interventions, step 7: providing rationale, step 8: evaluation, step 9: putting it on paper, basic nursing and general care plans, surgery and perioperative care plans, cardiac care plans, endocrine and metabolic care plans, gastrointestinal, hematologic and lymphatic, infectious diseases, integumentary, maternal and newborn care plans, mental health and psychiatric, musculoskeletal, neurological, pediatric nursing care plans, reproductive, respiratory, recommended resources, references and sources, what is a nursing care plan.
A nursing care plan (NCP) is a formal process that correctly identifies existing needs and recognizes a client’s potential needs or risks. Care plans provide a way of communication among nurses, their patients, and other healthcare providers to achieve healthcare outcomes. Without the nursing care planning process, the quality and consistency of patient care would be lost.
Nursing care planning begins when the client is admitted to the agency and is continuously updated throughout in response to the client’s changes in condition and evaluation of goal achievement. Planning and delivering individualized or patient-centered care is the basis for excellence in nursing practice.
Types of Nursing Care Plans
Care plans can be informal or formal: An informal nursing care plan is a strategy of action that exists in the nurse ‘s mind. A formal nursing care plan is a written or computerized guide that organizes the client’s care information.
Formal care plans are further subdivided into standardized care plans and individualized care plans: Standardized care plans specify the nursing care for groups of clients with everyday needs. Individualized care plans are tailored to meet a specific client’s unique needs or needs that are not addressed by the standardized care plan.
Standardized care plans are pre-developed guides by the nursing staff and health care agencies to ensure that patients with a particular condition receive consistent care. These care plans are used to ensure that minimally acceptable criteria are met and to promote the efficient use of the nurse’s time by removing the need to develop common activities that are done repeatedly for many of the clients on a nursing unit.
Standardized care plans are not tailored to a patient’s specific needs and goals and can provide a starting point for developing an individualized care plan .
Care plans listed in this guide are standard care plans which can serve as a framework or direction to develop an individualized care plan.
An individualized care plan care plan involves tailoring a standardized care plan to meet the specific needs and goals of the individual client and use approaches shown to be effective for a particular client. This approach allows more personalized and holistic care better suited to the client’s unique needs, strengths, and goals.
Additionally, individualized care plans can improve patient satisfaction . When patients feel that their care is tailored to their specific needs, they are more likely to feel heard and valued, leading to increased satisfaction with their care. This is particularly important in today’s healthcare environment, where patient satisfaction is increasingly used as a quality measure.
Tips on how to individualize a nursing care plan:
- Perform a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s health, history, health status, and desired goals.
- Involve the patient in the care planning process by asking them about their health goals and preferences. By involving the client, nurses can ensure that the care plan is aligned with the patient’s goals and preferences which can improve patient engagement and compliance with the care plan.
- Perform an ongoing assessment and evaluation as the patient’s health and goals can change. Adjust the care plan accordingly.
The following are the goals and objectives of writing a nursing care plan:
- Promote evidence-based nursing care and render pleasant and familiar conditions in hospitals or health centers.
- Support holistic care, which involves the whole person, including physical, psychological, social, and spiritual, with the management and prevention of the disease.
- Establish programs such as care pathways and care bundles. Care pathways involve a team effort to reach a consensus regarding standards of care and expected outcomes. In contrast, care bundles are related to best practices concerning care for a specific disease.
- Identify and distinguish goals and expected outcomes.
- Review communication and documentation of the care plan.
- Measure nursing care.
The following are the purposes and importance of writing a nursing care plan:
- Defines nurse’s role. Care plans help identify nurses’ unique and independent role in attending to clients’ overall health and well-being without relying entirely on a physician’s orders or interventions.
- Provides direction for individualized care of the client. It serves as a roadmap for the care that will be provided to the patient and allows the nurse to think critically in developing interventions directly tailored to the individual.
- Continuity of care. Nurses from different shifts or departments can use the data to render the same quality and type of interventions to care for clients, therefore allowing clients to receive the most benefit from treatment.
- Coordinate care. Ensures that all members of the healthcare team are aware of the patient’s care needs and the actions that need to be taken to meet those needs preventing gaps in care.
- Documentation. It should accurately outline which observations to make, what nursing actions to carry out, and what instructions the client or family members require. If nursing care is not documented correctly in the care plan, there is no evidence the care was provided.
- Serves as a guide for assigning a specific staff to a specific client. There are instances when a client’s care needs to be assigned to staff with particular and precise skills.
- Monitor progress. To help track the patient’s progress and make necessary adjustments to the care plan as the patient’s health status and goals change.
- Serves as a guide for reimbursement. The insurance companies use the medical record to determine what they will pay concerning the hospital care received by the client.
- Defines client’s goals. It benefits nurses and clients by involving them in their treatment and care.
A nursing care plan (NCP) usually includes nursing diagnoses, client problems, expected outcomes, nursing interventions, and rationales. These components are elaborated on below:
- Client health assessment , medical results, and diagnostic reports are the first steps to developing a care plan. In particular, client assessment relates to the following areas and abilities: physical, emotional, sexual, psychosocial, cultural, spiritual/transpersonal, cognitive, functional, age-related, economic, and environmental. Information in this area can be subjective and objective.
- Nursing diagnosis . A nursing diagnosis is a statement that describes the patient’s health issue or concern. It is based on the information gathered about the patient’s health status during the assessment.
- Expected client outcomes. These are specific goals that will be achieved through nursing interventions. These may be long and short-term.
- Nursing interventions . These are specific actions that will be taken to address the nursing diagnosis and achieve expected outcomes . They should be based on best practices and evidence-based guidelines.
- Rationales. These are evidence-based explanations for the nursing interventions specified.
- Evaluation . These includes plans for monitoring and evaluating a patient’s progress and making necessary adjustments to the care plan as the patient’s health status and goals change.
Care Plan Formats
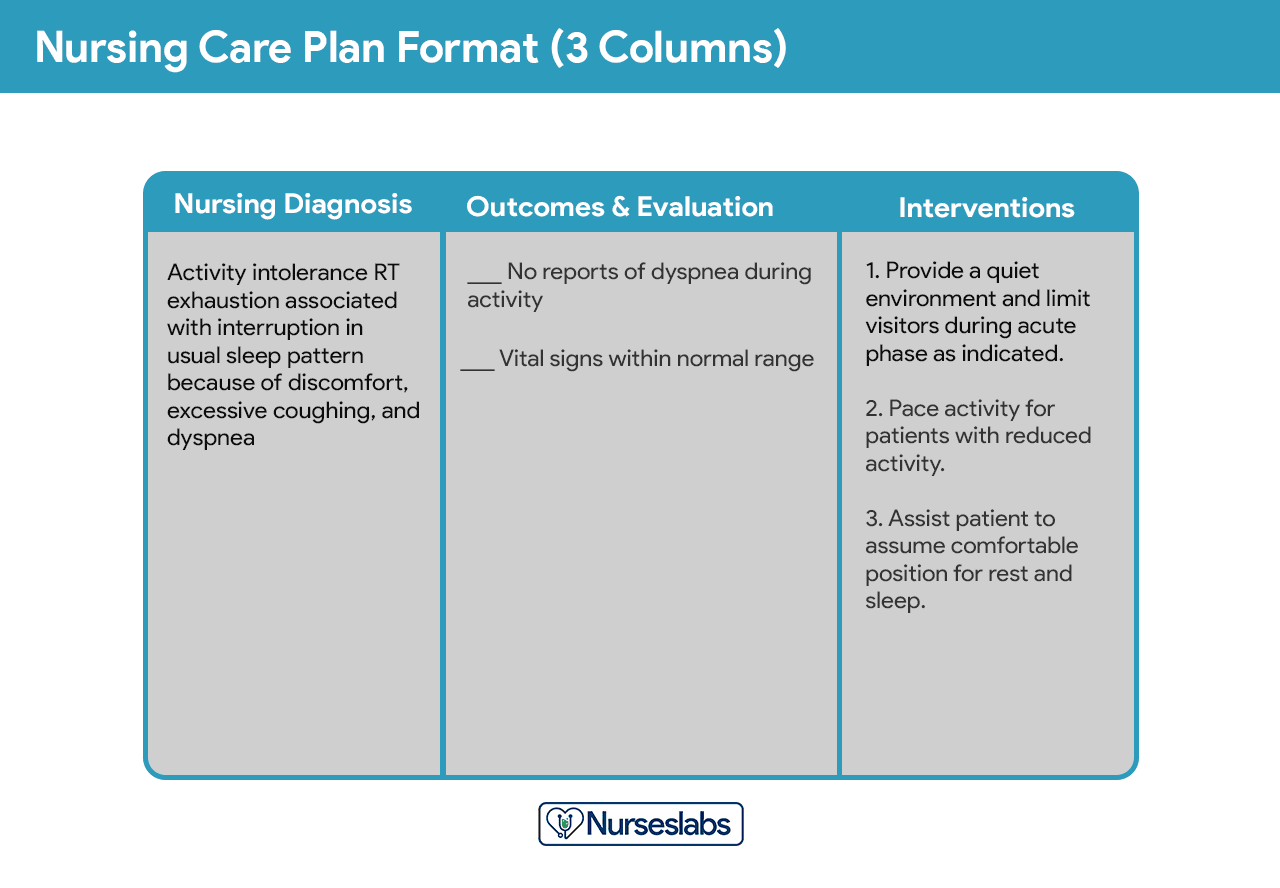
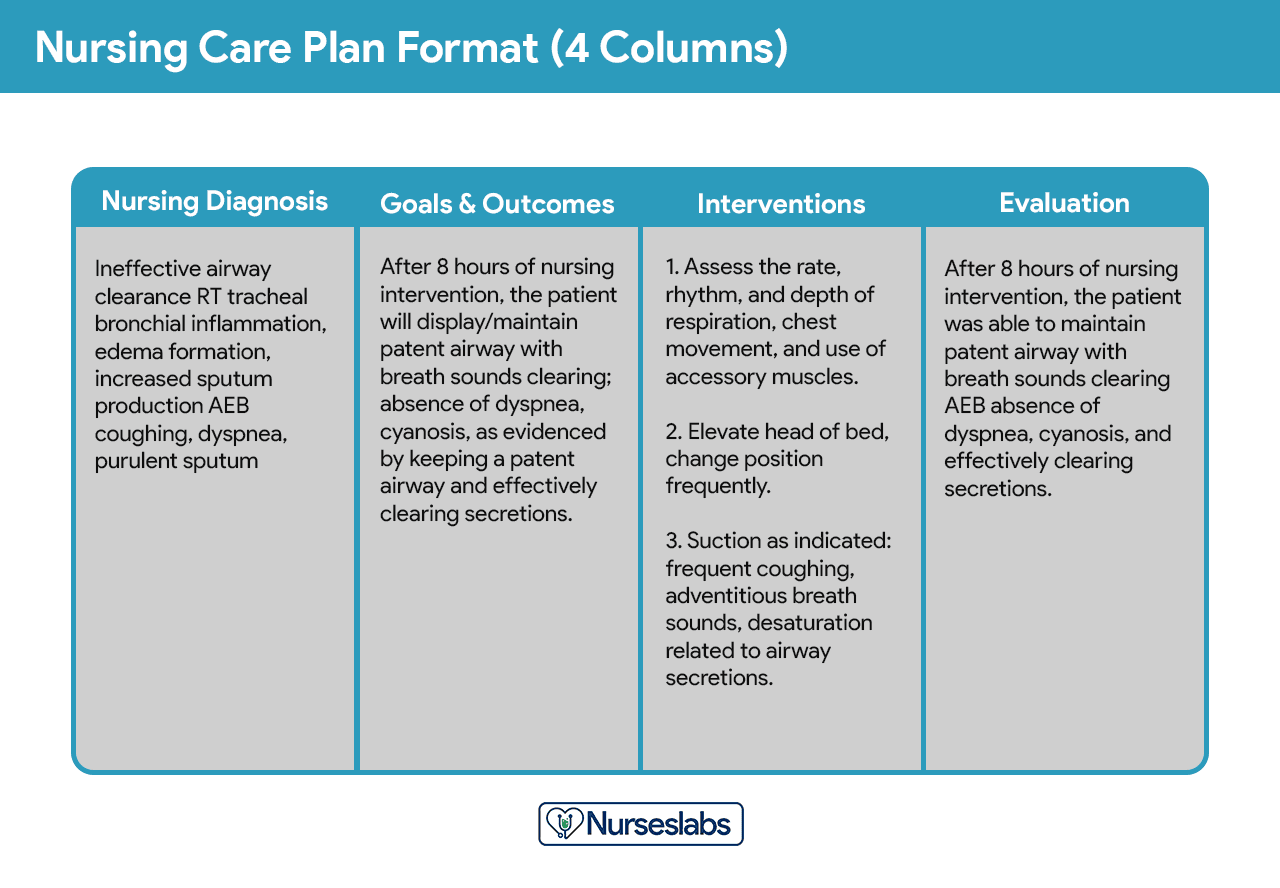
Nursing care plan formats are usually categorized or organized into four columns: (1) nursing diagnoses, (2) desired outcomes and goals, (3) nursing interventions, and (4) evaluation. Some agencies use a three-column plan where goals and evaluation are in the same column. Other agencies have a five-column plan that includes a column for assessment cues.
The three-column plan has a column for nursing diagnosis, outcomes and evaluation, and interventions.
This format includes columns for nursing diagnosis, goals and outcomes, interventions, and evaluation.
Below is a document containing sample templates for the different nursing care plan formats. Please feel free to edit, modify, and share the template.
Download: Printable Nursing Care Plan Templates and Formats
Student care plans are more lengthy and detailed than care plans used by working nurses because they serve as a learning activity for the student nurse.
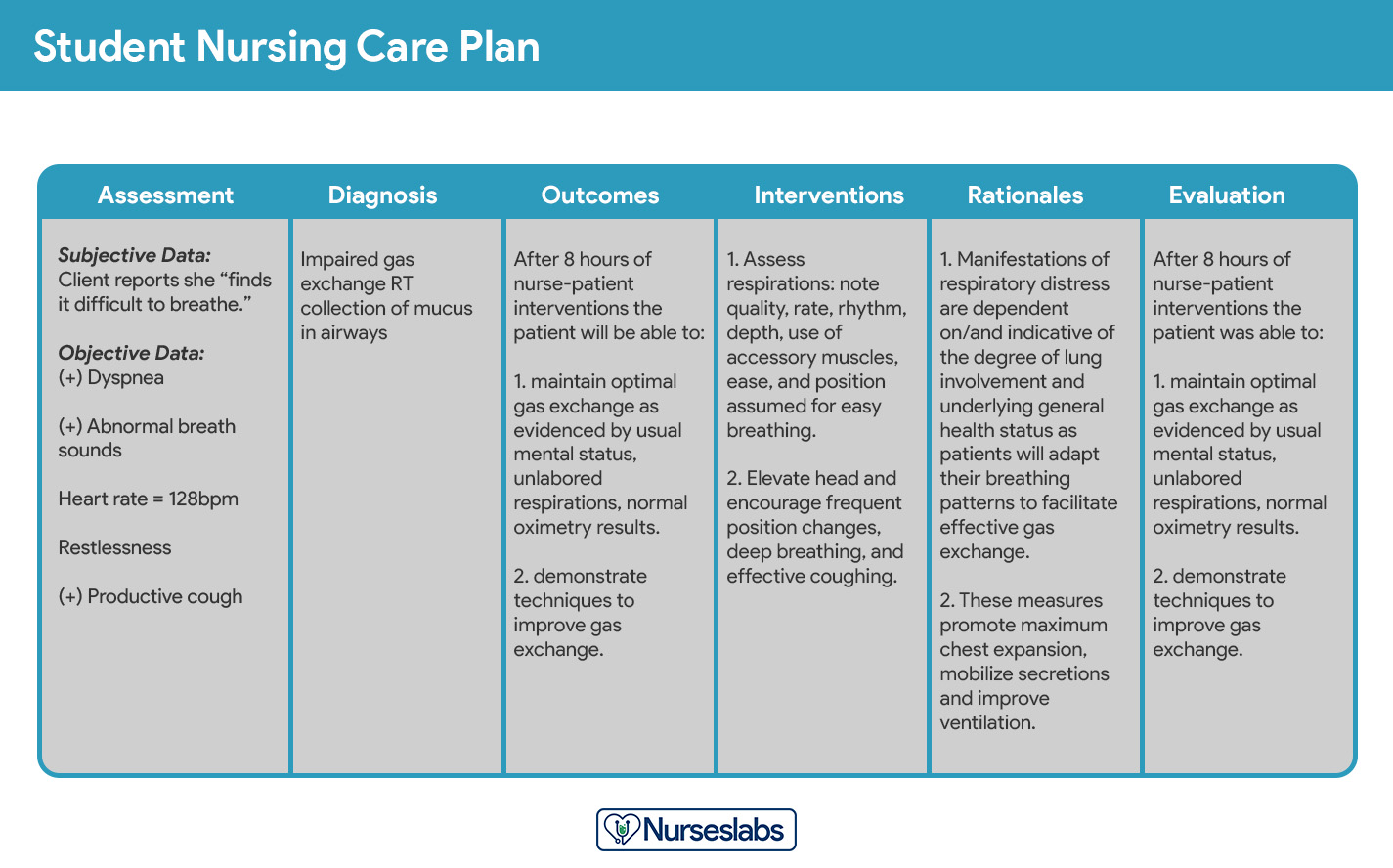
Care plans by student nurses are usually required to be handwritten and have an additional column for “Rationale” or “Scientific Explanation” after the nursing interventions column. Rationales are scientific principles that explain the reasons for selecting a particular nursing intervention.
Writing a Nursing Care Plan
How do you write a nursing care plan (NCP)? Just follow the steps below to develop a care plan for your client.
The first step in writing a nursing care plan is to create a client database using assessment techniques and data collection methods (physical assessment, health history, interview, medical records review, and diagnostic studies). A client database includes all the health information gathered . In this step, the nurse can identify the related or risk factors and defining characteristics that can be used to formulate a nursing diagnosis. Some agencies or nursing schools have specific assessment formats you can use.
Critical thinking is key in patient assessment, integrating knowledge across sciences and professional guidelines to inform evaluations. This process, crucial for complex clinical decision-making, aims to identify patients’ healthcare needs effectively, leveraging a supportive environment and reliable information
Now that you have information about the client’s health, analyze, cluster, and organize the data to formulate your nursing diagnosis, priorities, and desired outcomes.
Nursing diagnoses are a uniform way of identifying, focusing on and dealing with specific client needs and responses to actual and high-risk problems. Actual or potential health problems that can be prevented or resolved by independent nursing intervention are termed nursing diagnoses.
We’ve detailed the steps on how to formulate your nursing diagnoses in this guide: Nursing Diagnosis (NDx): Complete Guide and List .
Setting priorities involves establishing a preferential sequence for addressing nursing diagnoses and interventions. In this step, the nurse and the client begin planning which of the identified problems requires attention first. Diagnoses can be ranked and grouped as having a high, medium, or low priority. Life-threatening problems should be given high priority.
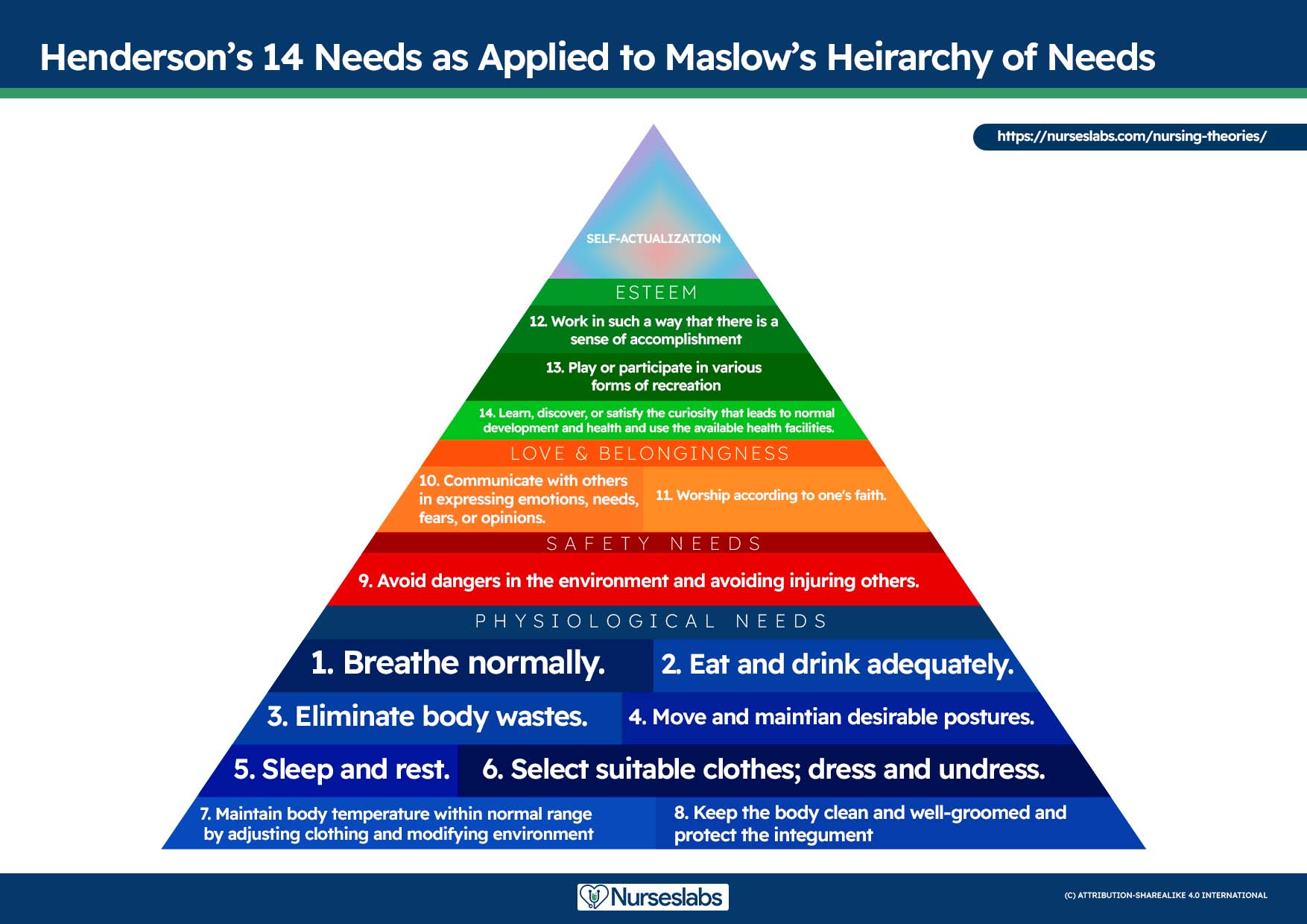
A nursing diagnosis encompasses Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and helps to prioritize and plan care based on patient-centered outcomes. In 1943, Abraham Maslow developed a hierarchy based on basic fundamental needs innate to all individuals. Basic physiological needs/goals must be met before higher needs/goals can be achieved, such as self-esteem and self-actualization. Physiological and safety needs are the basis for implementing nursing care and interventions. Thus, they are at the base of Maslow’s pyramid, laying the foundation for physical and emotional health.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
- Basic Physiological Needs: Nutrition (water and food), elimination (Toileting), airway (suction)-breathing (oxygen)-circulation (pulse, cardiac monitor, blood pressure) (ABCs), sleep , sex, shelter, and exercise.
- Safety and Security: Injury prevention ( side rails , call lights, hand hygiene , isolation , suicide precautions, fall precautions, car seats, helmets, seat belts), fostering a climate of trust and safety ( therapeutic relationship ), patient education (modifiable risk factors for stroke , heart disease).
- Love and Belonging: Foster supportive relationships, methods to avoid social isolation ( bullying ), employ active listening techniques, therapeutic communication , and sexual intimacy.
- Self-Esteem: Acceptance in the community, workforce, personal achievement, sense of control or empowerment, accepting one’s physical appearance or body habitus.
- Self-Actualization: Empowering environment, spiritual growth, ability to recognize the point of view of others, reaching one’s maximum potential.
The client’s health values and beliefs, priorities, resources available, and urgency are factors the nurse must consider when assigning priorities. Involve the client in the process to enhance cooperation.
Step 5: Establishing Client Goals and Desired Outcomes
After assigning priorities for your nursing diagnosis, the nurse and the client set goals for each determined priority. Goals or desired outcomes describe what the nurse hopes to achieve by implementing the nursing interventions derived from the client’s nursing diagnoses. Goals provide direction for planning interventions, serve as criteria for evaluating client progress, enable the client and nurse to determine which problems have been resolved, and help motivate the client and nurse by providing a sense of achievement.
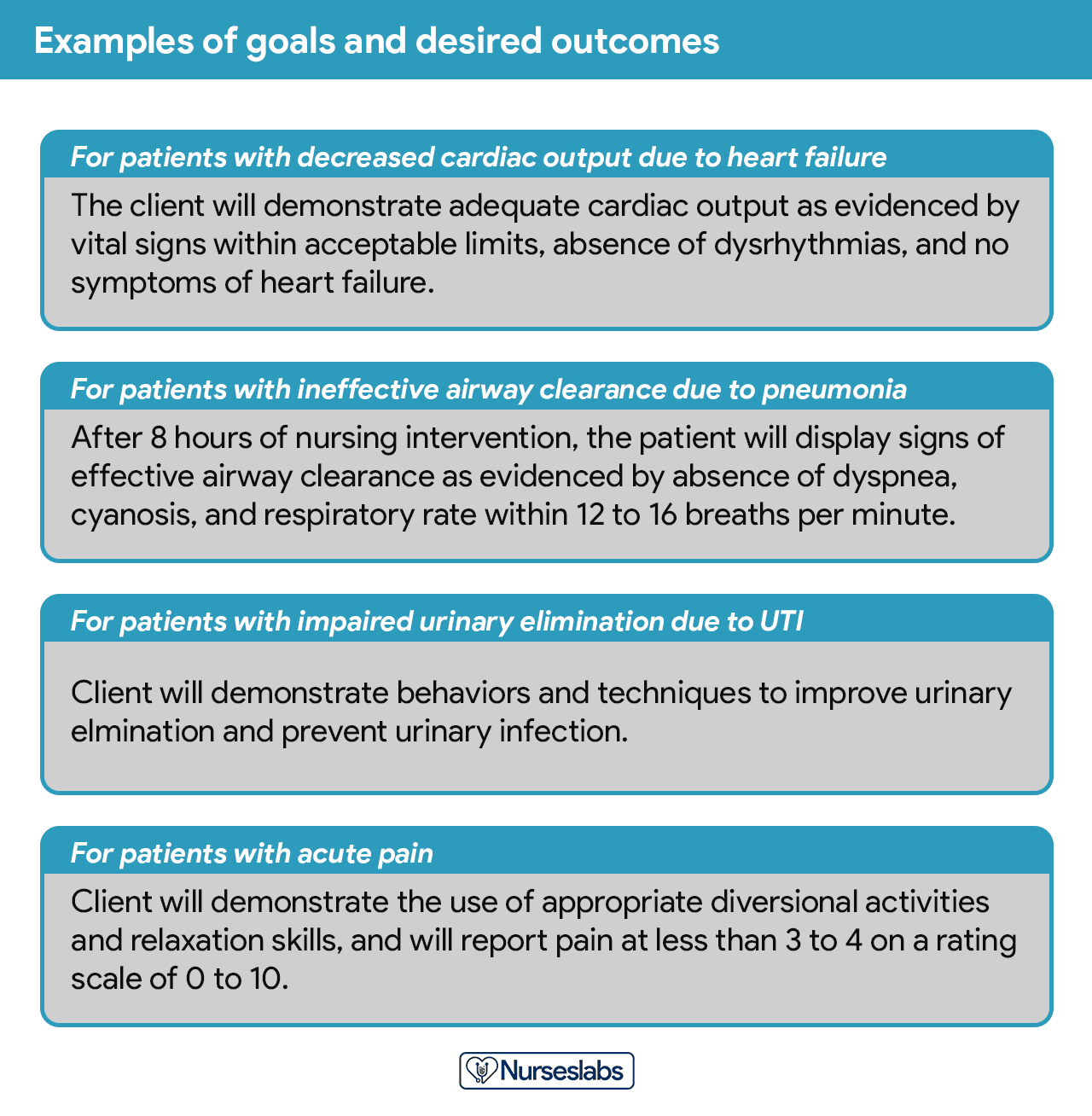
One overall goal is determined for each nursing diagnosis. The terms “ goal outcomes “ and “expected outcome s” are often used interchangeably.
According to Hamilton and Price (2013), goals should be SMART . SMART stands for specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-oriented goals.
- Specific. It should be clear, significant, and sensible for a goal to be effective.
- Measurable or Meaningful. Making sure a goal is measurable makes it easier to monitor progress and know when it reaches the desired result.
- Attainable or Action-Oriented. Goals should be flexible but remain possible.
- Realistic or Results-Oriented. This is important to look forward to effective and successful outcomes by keeping in mind the available resources at hand.
- Timely or Time-Oriented. Every goal needs a designated time parameter, a deadline to focus on, and something to work toward.
Hogston (2011) suggests using the REEPIG standards to ensure that care is of the highest standards. By this means, nursing care plans should be:
- Realistic. Given available resources.
- Explicitly stated. Be clear about precisely what must be done, so there is no room for misinterpretation of instructions.
- Evidence-based. That there is research that supports what is being proposed.
- Prioritized. The most urgent problems are being dealt with first.
- Involve. Involve both the patient and other members of the multidisciplinary team who are going to be involved in implementing the care.
- Goal-centered. That the care planned will meet and achieve the goal set.
Goals and expected outcomes must be measurable and client-centered. Goals are constructed by focusing on problem prevention, resolution, and rehabilitation. Goals can be short-term or long-term . Most goals are short-term in an acute care setting since much of the nurse’s time is spent on the client’s immediate needs. Long-term goals are often used for clients who have chronic health problems or live at home, in nursing homes, or in extended-care facilities.
- Short-term goal . A statement distinguishing a shift in behavior that can be completed immediately, usually within a few hours or days.
- Long-term goal . Indicates an objective to be completed over a longer period, usually weeks or months.
- Discharge planning . Involves naming long-term goals, therefore promoting continued restorative care and problem resolution through home health, physical therapy, or various other referral sources.
Goals or desired outcome statements usually have four components: a subject, a verb, conditions or modifiers, and a criterion of desired performance.
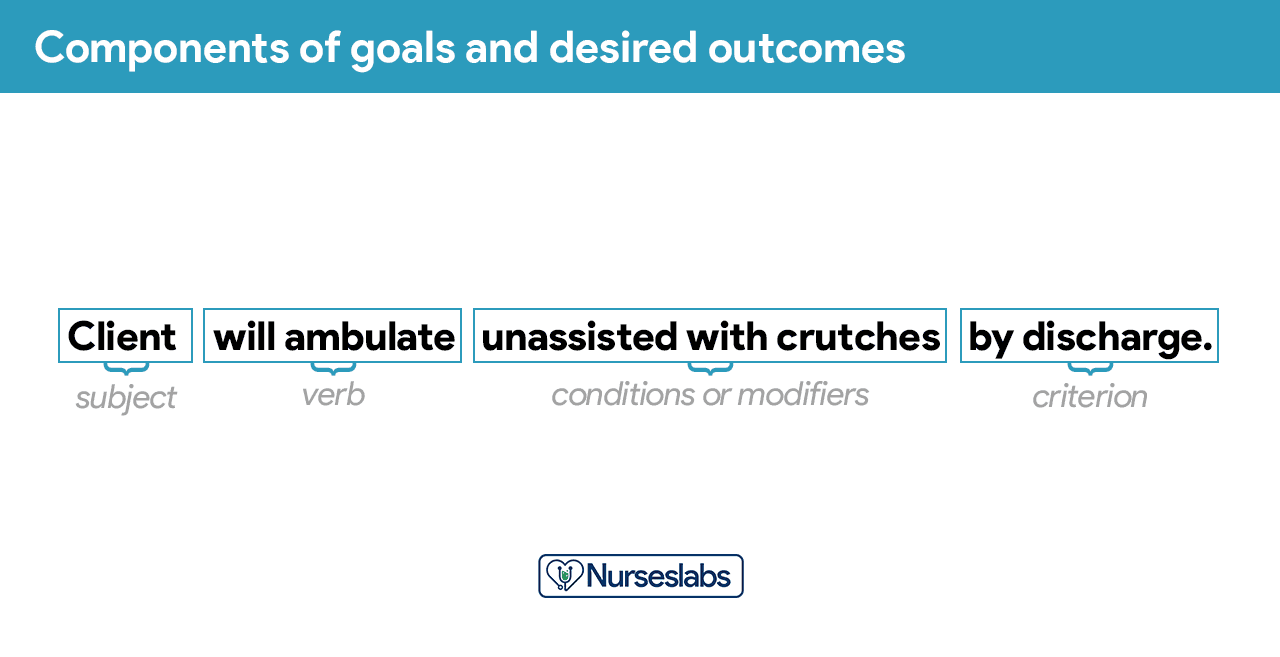
- Subject. The subject is the client, any part of the client, or some attribute of the client (i.e., pulse, temperature, urinary output). That subject is often omitted in writing goals because it is assumed that the subject is the client unless indicated otherwise (family, significant other ).
- Verb. The verb specifies an action the client is to perform, for example, what the client is to do, learn, or experience.
- Conditions or modifiers. These are the “what, when, where, or how” that are added to the verb to explain the circumstances under which the behavior is to be performed.
- Criterion of desired performance. The criterion indicates the standard by which a performance is evaluated or the level at which the client will perform the specified behavior. These are optional.
When writing goals and desired outcomes, the nurse should follow these tips:
- Write goals and outcomes in terms of client responses and not as activities of the nurse. Begin each goal with “Client will […]” help focus the goal on client behavior and responses.
- Avoid writing goals on what the nurse hopes to accomplish, and focus on what the client will do.
- Use observable, measurable terms for outcomes. Avoid using vague words that require interpretation or judgment of the observer.
- Desired outcomes should be realistic for the client’s resources, capabilities, limitations, and on the designated time span of care.
- Ensure that goals are compatible with the therapies of other professionals.
- Ensure that each goal is derived from only one nursing diagnosis. Keeping it this way facilitates evaluation of care by ensuring that planned nursing interventions are clearly related to the diagnosis set.
- Lastly, make sure that the client considers the goals important and values them to ensure cooperation.
Step 6: Selecting Nursing Interventions
Nursing interventions are activities or actions that a nurse performs to achieve client goals. Interventions chosen should focus on eliminating or reducing the etiology of the priority nursing problem or diagnosis. As for risk nursing problems, interventions should focus on reducing the client’s risk factors. In this step, nursing interventions are identified and written during the planning step of the nursing process ; however, they are actually performed during the implementation step.
Nursing interventions can be independent, dependent, or collaborative:
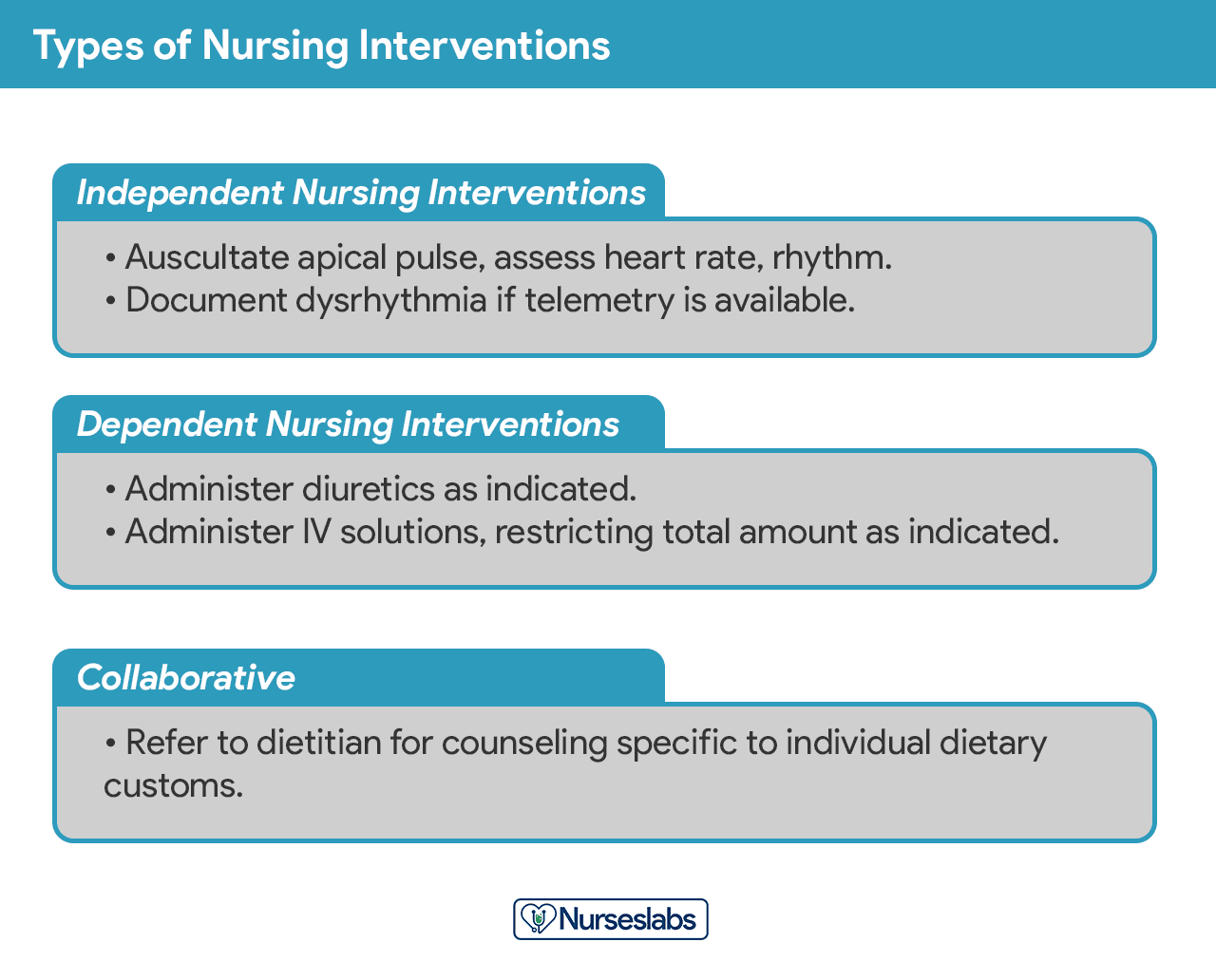
- Independent nursing interventions are activities that nurses are licensed to initiate based on their sound judgement and skills. Includes: ongoing assessment, emotional support, providing comfort, teaching, physical care, and making referrals to other health care professionals.
- Dependent nursing interventions are activities carried out under the physician’s orders or supervision. Includes orders to direct the nurse to provide medications, intravenous therapy , diagnostic tests, treatments, diet, and activity or rest. Assessment and providing explanation while administering medical orders are also part of the dependent nursing interventions.
- Collaborative interventions are actions that the nurse carries out in collaboration with other health team members, such as physicians, social workers, dietitians, and therapists. These actions are developed in consultation with other health care professionals to gain their professional viewpoint.
Nursing interventions should be:
- Safe and appropriate for the client’s age, health, and condition.
- Achievable with the resources and time available.
- Inline with the client’s values, culture, and beliefs.
- Inline with other therapies.
- Based on nursing knowledge and experience or knowledge from relevant sciences.
When writing nursing interventions, follow these tips:
- Write the date and sign the plan. The date the plan is written is essential for evaluation, review, and future planning. The nurse’s signature demonstrates accountability.
- Nursing interventions should be specific and clearly stated, beginning with an action verb indicating what the nurse is expected to do. Action verb starts the intervention and must be precise. Qualifiers of how, when, where, time, frequency, and amount provide the content of the planned activity. For example: “ Educate parents on how to take temperature and notify of any changes,” or “ Assess urine for color, amount, odor, and turbidity.”
- Use only abbreviations accepted by the institution.
Rationales, also known as scientific explanations, explain why the nursing intervention was chosen for the NCP.
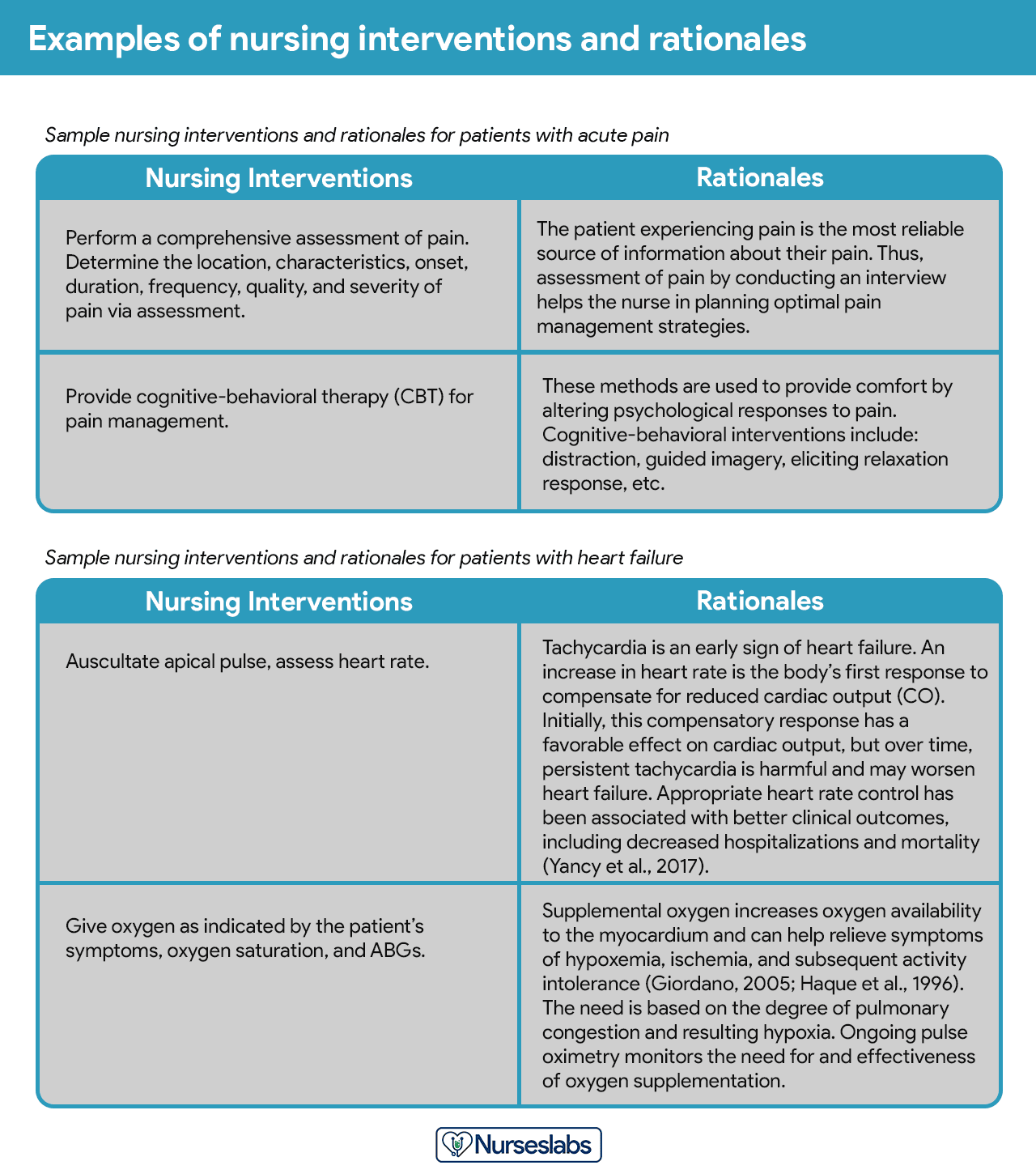
Rationales do not appear in regular care plans. They are included to assist nursing students in associating the pathophysiological and psychological principles with the selected nursing intervention.
Evaluation is a planned, ongoing, purposeful activity in which the client’s progress towards achieving goals or desired outcomes is assessed, and the effectiveness of the nursing care plan (NCP). Evaluation is an essential aspect of the nursing process because the conclusions drawn from this step determine whether the nursing intervention should be terminated, continued, or changed.
The client’s care plan is documented according to hospital policy and becomes part of the client’s permanent medical record, which may be reviewed by the oncoming nurse. Different nursing programs have different care plan formats. Most are designed so that the student systematically proceeds through the interrelated steps of the nursing process , and many use a five-column format.
Nursing Care Plan List
This section lists the sample nursing care plans (NCP) and nursing diagnoses for various diseases and health conditions. They are segmented into categories:
Miscellaneous nursing care plans examples that don’t fit other categories:
Care plans that involve surgical intervention.
Nursing care plans about the different diseases of the cardiovascular system :
Nursing care plans (NCP) related to the endocrine system and metabolism:
Care plans (NCP) covering the disorders of the gastrointestinal and digestive system :
Care plans related to the hematologic and lymphatic system :
NCPs for communicable and infectious diseases:
All about disorders and conditions affecting the integumentary system :
Nursing care plans about the care of the pregnant mother and her infant. See care plans for maternity and obstetric nursing:
Care plans for mental health and psychiatric nursing:
Care plans related to the musculoskeletal system:
Nursing care plans (NCP) for related to nervous system disorders:
Care plans relating to eye disorders:
Nursing care plans (NCP) for pediatric conditions and diseases:
Care plans related to the reproductive and sexual function disorders:
Care plans for respiratory system disorders:
Care plans related to the kidney and urinary system disorders:
Recommended nursing diagnosis and nursing care plan books and resources.
Disclosure: Included below are affiliate links from Amazon at no additional cost from you. We may earn a small commission from your purchase. For more information, check out our privacy policy .
Ackley and Ladwig’s Nursing Diagnosis Handbook: An Evidence-Based Guide to Planning Care We love this book because of its evidence-based approach to nursing interventions. This care plan handbook uses an easy, three-step system to guide you through client assessment, nursing diagnosis, and care planning. Includes step-by-step instructions showing how to implement care and evaluate outcomes, and help you build skills in diagnostic reasoning and critical thinking.

Nursing Care Plans – Nursing Diagnosis & Intervention (10th Edition) Includes over two hundred care plans that reflect the most recent evidence-based guidelines. New to this edition are ICNP diagnoses, care plans on LGBTQ health issues, and on electrolytes and acid-base balance.

Nurse’s Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Prioritized Interventions, and Rationales Quick-reference tool includes all you need to identify the correct diagnoses for efficient patient care planning. The sixteenth edition includes the most recent nursing diagnoses and interventions and an alphabetized listing of nursing diagnoses covering more than 400 disorders.

Nursing Diagnosis Manual: Planning, Individualizing, and Documenting Client Care Identify interventions to plan, individualize, and document care for more than 800 diseases and disorders. Only in the Nursing Diagnosis Manual will you find for each diagnosis subjectively and objectively – sample clinical applications, prioritized action/interventions with rationales – a documentation section, and much more!

All-in-One Nursing Care Planning Resource – E-Book: Medical-Surgical, Pediatric, Maternity, and Psychiatric-Mental Health Includes over 100 care plans for medical-surgical, maternity/OB, pediatrics, and psychiatric and mental health. Interprofessional “patient problems” focus familiarizes you with how to speak to patients.

Recommended reading materials and sources for this NCP guide:
- Björvell, C., Thorell-Ekstrand, I., & Wredling, R. (2000). Development of an audit instrument for nursing care plans in the patient record. BMJ Quality & Safety , 9 (1), 6-13. [ Link ]
- DeLaune, S. C., & Ladner, P. K. (2011). Fundamentals of nursing: Standards and practice . Cengage learning.
- Freitas, F. A., & Leonard, L. J. (2011). Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and student academic success . Teaching and learning in Nursing , 6 (1), 9-13.
- Hamilton, P., & Price, T. (2007). The nursing process, holistic. Foundations of Nursing Practice E-Book: Fundamentals of Holistic Care , 349.
- Lee, T. T. (2004). Evaluation of computerized nursing care plan: instrument development . Journal of Professional Nursing , 20 (4), 230-238.
- Lee, T. T. (2006). Nurses’ perceptions of their documentation experiences in a computerized nursing care planning system . Journal of Clinical Nursing , 15 (11), 1376-1382.
- Rn, B. O. C., Rn, H. M., Rn, D. T., & Rn, F. E. (2000). Documenting and communicating patient care: Are nursing care plans redundant?. International Journal of Nursing Practice , 6 (5), 276-280.
- Stonehouse, D. (2017). Understanding the nursing process . British Journal of Healthcare Assistants , 11 (8), 388-391.
- Yildirim, B., & Ozkahraman, S. (2011). Critical thinking in nursing process and education . International journal of humanities and social science , 1 (13), 257-262.
66 thoughts on “Nursing Care Plans (NCP) Ultimate Guide and List”
This page is helpful!
Thank you! Hope we’ve helped you write better nursing care plans!
Will definitely use this site to help write care plans. How should I cite this link when using APA format. Thank You
HI Can some one help me to do assignment on Impaired renal perfusion. 1.Goal 2.Related Action 3.Rational 4.Evaluate outcome
Wow God bless plenty Nurseslabs really relieve my burdens 😊😊
Thank you for all this useful info! I have been looking for something like this online.
You’re welcome! :)
Quite educative thank you
The notes were indeed useful
I hope to learn more and improve my skills towards nursing
Thank you so so much! This website is of great assistance to me. God bless you.
It’s so great for nursing student
Very beautiful ,Good work keep it up
Nice work. Well done
Very helpful
Great job,thank you
Thanks so much , it’s of much support for students .
Risk for ineffective thermoregulation would be a good one for you to do next for newborn.
Hi, i have learnt a lot THANK YOU. i would kindly like to learn more on paper 1 since am yet to sit for my nursing council exams and feel challenged on the paper.please do assist me thank you.
This site is a total lifesaver!
What is a nursing care plan a mother in second stage of labour?
Please see: 36 Labor Stages, Induced and Augmented Labor Nursing Care Plans
What is the nursing care plan for pulmonary oedema?
I m interest in receiving a blank nursing care plan template for my students to type on. I was wondering if it was available and if so can you please direct me on where to find it?
Hi! You can download it here: Nursing Care Plan Template
I love this website!!! Is there a textbook version of the Nurseslabs that I can purchase??
Thank you Nurseslabs. This is a wonderful note you’ve prepared for all nurses. I would like a pdf of this. Thanks.
I wish I had had this resource when i was in nursing school 2008!!
Yeah! It’s nice
Thanks for this information!
God bless you sis…Thank you for all this useful info!
This is the kind of step-by-step guidance that I needed. Thank you!
Thank you. I have learned a lot!
Wow! This is a hidden treasure!
Thanks a lot for this, it is really helpful!
Hi Matt! I would like to purchase a textbook of your nursing care plan. Where I can purchase pls help!
Hi Criselda,
Sorry, we don’t have a textbook. All of our resources are here on the website and free to use.
Good day, I would like to know how can I use your website to help students with care plans.
Sincerely, Oscar A. Acosta DNP, RN
Oh I love your works. Your explanations
I’m glad I’ve met your website. It helps me a lot. Thank you
I love this, so helpful.
These care plans are great for using as a template. I don’t have to reinvent the wheel, and the information you provided will ensure that I include the important data without leaving things out. Thanks a million!
Hi, I have learnt a lot, this is a wonderful note you’ve prepared for all nurses thank you.
Matt, this page is very informative and I especially appreciate seeing care plans for patients with neurological disorders. I notice, though, that traumatic brain injury is not on your list. Might you add a care plan page for this?
Thanks alot I had gained much since these are detailed notes 🙏🙏
OMG, this is amazing!
Wow very helpful.thank you very much🙏🙏
Hi, is there a downloadable version of this, pdf or other files maybe this is awesome!
Hi Paul, on your browser go to File > Print > Save as PDF. Hope that helps and thanks for visiting Nurseslabs!
Matt, I’m a nursing instructor looking for tools to teach this. I am interested in where we can find “rules” for establishing “related to” sections…for example –not able to utilize medical diagnosis as a “related to” etc. Also, resources for nursing rationale.
Hello, please check out our guide on how to write nursing diagnoses here: https://nurseslabs.com/nursing-diagnosis/
Nursing care plan is very amazing
Thanks for your time. Nursing Care Plan looks great and helpful!
complete knowledge i get from here
great resource. puts it all together. Thank for making it free for all
Hello Ujunwa, Thanks a lot for the positive vibes! 🌟 It’s super important to us that everyone has access to quality resources. Just wondering, is there any specific topic or area you’d love to see more about? We’re always looking to improve and add value!
Great work.
Hi Abbas, Thank you so much! Really glad to hear you found the nursing care plans guide useful. If there’s a specific area or topic you’re keen on exploring more, or if you have any suggestions for improvement, feel free to share. Always aiming to make our resources as helpful as possible!
It has been good time me to use these nursing guides.
What is ncp for acute pain
For everything you need to know about managing acute pain, including a detailed nursing care plan (NCP), definitely check out our acute pain nursing care plan guide . It’s packed with insights on assessment, interventions, and patient education to effectively manage and alleviate acute pain.
Good morning. I love this website
what is working knowledge on nursing standard, and Basic Life Support documentation?
Leave a Comment Cancel reply

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Assignment: Supporting Clients with Dementia or a Mental Health Disorder
Assignment outline.
The purpose of this assignment is to explore best practices for communicating with clients with dementia or mental health disorders.
Working in small groups, students will research a cognitive or mental health disorder of their choice. After completing the research, the groups will prepare an 8–10 minute presentation, with visual materials (e.g., a PowerPoint presentation or poster) and a short written handout to give to the class, addressing the following components:
- Briefly describe the type of dementia or mental health disorder (causes, signs, and symptoms).
- Describe how communication between a client with this diagnosis and an HCA may be impacted. Consider the elements of interpersonal communication (sender, receiver, message, feedback).
- Demonstrate and/or describe a minimum of three communication strategies/techniques (verbal and non-verbal) that can be used by the HCA to enhance communication while providing care to the client.
You will be marked using the following criteria:
- The ability of the team to thoroughly address the required components of the assignment (Total possible marks: 15/15).
- The ability of the team to present the information in a thorough and engaging presentation (Total possible marks: 10/10). *Each group member will receive an individual mark based on delivery of a portion of the presentation.
- The ability of the team to develop visual and written materials to support the presentation (Total possible marks: 5/5).
Online Resources
- Alzheimer Society of B.C.
- Canadian Mental Health Association, B.C. Division
- HealthLinkBC
Rubric: Supporting Clients with Dementia or a Mental Health Disorder
Note : This sample tool has been included to align with Suggested Course Assessment 3 for the Healing 2: Caring for Individuals Experiencing Cognitive or Mental Challenges .
Download Rubric: Supporting Clients with Dementia or a Mental Health Disorder [PDF] .
- For any assignment requiring referencing of resources, it would be expected that the program would indicate the referencing style (e.g., APA) to be used and provide the necessary instruction and supporting materials for students to be successful in this criterion of the assignment. It would also be expected that referencing resources would be included as a criteria in the marking rubric, with placement depending on the parameters of the assignment. criteria of the assignment. It would also be expected that referencing resources would be included as a criteria in the marking rubric, with placement depending on the parameters of the assignment. ↵
Health Care Assistant Program Supplement to the Provincial Curriculum Guide (2015) - Third Edition Copyright © 2022 by Province of British Columbia is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Care Plan Templates: Examples of Person-Centred Care

In this post, you'll discover the best examples of person centred care plans templates .
Not sure where to start with care planning? Looking for a guide or example care plan to help you get started?
There’s a wealth of information available to support you through every aspect of care planning, (for example here at Birdie we’ve created our own guide to care planning and a blog that outlines the basics of care planning software, plus tips on having the right conversations ). But when it comes to a real care plan example that you can follow, the available options are a little limited. That's because there is no one-size-fits-all, standardised template for care planning.
Where can I find a care plan example template?
Care plans must be created individually to suit the needs of the people you’re caring for. A care plan for an individual with dementia would be vastly different to a care plan for a young adult who needs support due a disability.
That’s why, when it comes to finding an example care plan template for your home care agency, you might find it difficult to find one you can download or replicate. We've included a printable example of a care plan template , based on the questions we use on the Birdie system, at the bottom of this article. It covers the personal information and preferences section of a care plan, and is a great starting point for setting goals and assigning tasks. If you need help with goal setting, you can download a free SMART template from Birdie too.
To help you, the next few steps in this article will walk you through the basics of a person centred care plan and show you how you can use the principles to create your own care plans. You can download and print a care plan example template at the end.

Elements to include in a care plan template
Here are a few elements to includes in your person-centred care plan template :
- Personal information
- Medical history
- Mental health
- Social support
- Environmental risks
- Nutrition requirements
- Interests and activities
- Communication
Of course, there are many, many more you could focus on and each element may have multiple sub-elements inside, but not all areas will be required for every person.
Each area of the care plan template should include :
- The area you’re focusing on (for example, communication or personal care)
- The person’s desired outcomes in this area
- How you will support them with their outcomes/how they would like support
You'll also like: Domiciliary care - Complete guide
Do I need to create every care plan from scratch?
You don’t always need to create a care plan from scratch . The elements inside each care plan should be different for each client, but you could start with a basic care plan framework for each client and personalise accordingly. That’s exactly how we create care plans at Birdie. Our care planning software allows you to choose the areas that need more information and you can fill out the relevant sections, without having to create a new document every time.
Get a demo now of our care management software and create the perfect care plan for your agency.
- Best care agency software
- How Birdie can help you with care management
How we create person centred care plans that are in-line with CQC requirements at Birdie

Within each category you can add objectives and tasks, and personalise these alongside your clients. For example:
If the person in your care has recently been discharged from hospital after a fall, they may have a goal to be able to resume an activity (for example; walking in the garden) once again.
By making a note of this goal with them, you can devise a plan to support them, using all of the elements above. Walking in the garden may require:
- A risk assessment of the garden
- The medical history of the person (how long until their injuries heal, for example)
- Social support from outside (how can occupational therapists and families help progress this goal?)
- A waterlow assessment to inform decisions on how often this person should be encouraged to move/change positions if they are currently immobile
As this goal (and every goal) is very specific, it’s difficult to provide a one-size-fits-all framework for a care plan that can be adapted to suit everyone’s requirements, however...
Read also: How to setup a care agency
If you’re not using care planning software like Birdie, you could create a Word document with appropriate tables that summarise the points above. Here’s an example excerpt that focuses on personal care:

This is of course, just one example area. You can see a full care plan example, here (from Devon County Council).
One really important area in every care plan is the personal details section, where you can list a person's preferences, needs and any external social and economic factors that may influence their care needs. Click below for a free template from Birdie for you to download and print.
Read also: Everything you need to know about advanced care planning

A quick note on digital vs paper care planning
Using a word document that’s printed in a client’s house and distributed to family members and others involved in their care can be a time consuming process - and takes a long time to update when changes are made. If you’re interested in digitising your care plans, you can read all about the difference between paper and digital care planning software here . Find out more about person centred care planning, here or get a free SMART care plan template, here .
We hope this overview of some care plan examples helps you with your person centred care planning. If you’re interested in digitising your care planning process with care planning software , get in touch with our team - they’ll be happy to walk you through the available options and help you decide on the right digital plan for you.
Birdie CEO Max recently visited Michael, who has been receiving care from the brilliant Alina Homecare . Find out what he thinks of homecare (and Birdie!) here :
Discover our care management software
Related posts

8 Benefits of International Recruitment for Homecare
International recruitment within the health and social care sector has been a necessity in the UK - and without it, it could pose huge workforce issues for businesses within the industry. This article explores the multifaceted advantages of international recruitment, delving into how it not only enhances staff diversity but also addresses the myriad challenges faced by the sector.
.jpg)
What's new at Birdie: April 2024
Not feeling too springlike? Ignore the cold winds outside, here at Birdie we’ve got plenty of exciting new features that will be sure to warm your cockles and put a smile on your face. Read on to see what the team have been working on!

Birdie Voices: How we hire engineers humanely at Birdie
The hiring process at Birdie is deeply rooted in first recognising each candidate's unique values and potential. Unlike traditional hiring methods, which can focus narrowly on technical abilities or past achievements, we strive to understand the whole person. This approach is inspired by the insights shared by Daniel Coyle in "The Culture Code," where the emphasis is on creating environments that foster successful collaboration and growth.
Let us show you how birdie can help
You're the expert. You deserve home healthcare technology that motivates your team and helps you grow.
Join our mailing list
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Care Planning

Related Papers
In I. Needham, K. McKenna, M. Kingma, N. Oud (Ed.), Third International Conference on Violence in the Health Sector
Ameil Joseph
Dianne Rekow
Critical Care Nursing Clinics of North America
James Krinsley
Jonathan Silcock
Daniele Arcoria
Journal of Nursing Education and Practice
Sara Eriksen
Sonya Albury
www.jetir.org - ISSN-2349-5162
Dr. Hari Prasad. N
Post employability awareness and skill development of safety & security is an earned aptitude with copious enthusiasm at the workstation. Exhibiting skills during the day to day operations with combination and permutation of hard and soft skills can be easily defined as performing uninterrupted employability. Edification of skills elates the performance of an employee in safety and security arena. The ongoing research is an extending a step further to outstanding study and practices suggested by National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH), on safety and security aspects. By considering major recommendations, present cram wholly focuses on four important dimensions of skills such as safety and security, post employability skills, fire safety, and service standards. The worldwide trade body NASSCOM strongly recommends that employability skills are the key element to conquer and uphold the advanced aspirations of the ever-changing corporate world. The gentle blend of the service standards and service excellence can be a way out to answer the umpteen questions pertaining to experience economies in health care sectors i.e. for Multi-Specialty Hospitals intended for signs of Hospitality.
CCHS-1 Manual
T. Langdon Hill
Gian Domenico Giusti
Lateral hostilities are a variety of “nasty, unkind, aggressive behavior between colleagues working at comparable organizational levels” and are widely diffused phenomena documented by international literature especially in the United States and England. When this type of prevalently not physical aggression develops within nurse settings, the consequences may become serious up to the point of causing, at arious professional levels, psychosomatic types of symptoms and even pushing individuals to also leave work definitively. Furthermore, if the abuses characterizing this phenomenon are perpetrated constantly, at least once a week for six consecutive months, a true and proper type of horizontal mobbing can be envisaged. Midway between the end of 2011and the start of 2012, Aniarti promoted among its members and nonmembers, an online survey that used a previously drawn up questionnaire, as a validation study that could quantify and estimate the phenomenon of horizontal hostility within ...
RELATED PAPERS
Colleen Maykut , Lisa Adams
Sílvia Roura
Nurses’ and Medical Officers’ Knowledge, Attitude, and Preparedness Toward Potential Bioterrorism Attacks
Confidence Alorse Atakro
Catherine Ebenezer
José Vasconcelos-Raposo
BMC Public Health
Health Services and Delivery Research
Glenn Robert
dwi adiyanto
Dr.Bayap Reddy
Marcel Popa
Dragutin Petrić
Derek Thomson
NEERAJ ARORA
Andrew Lovell Dr
Nicolae Steiner
Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences
Marianne Wallis
Vikrant Kumar
Rajib Khanal , Mitz Serofia
Nebil Achour , Andrew Price
Dixon Thomas
Happy Malama
Guillaume Alinier , Colin Harwood , Krishna Ruparelia
Marsha Gold
Journal of Clinical Psychology
Alexander Blount
Ferdinando Fornara
Alaa Khalil
Mahama Dauda
Prof. Dr. Sabine Junginger
Turk psikiyatri dergisi = Turkish journal of psychiatry
amin saburi
Zakirul Islam
Nursing standard (Royal College of Nursing (Great Britain) : 1987)
annie topping , Jason Alcorn
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Palliative Care Support Assignment
Comprehensive account of working and interacting with others In the area of palliative care. The author of this essay is a Health Care Assistant for three years and works as a member of a Hospice Home Care Team. For the purpose of this assignment the author will outline a selection of evidence of their work and interaction with their Palliative Care Clients and the Palliative Care Team. For the privacy and dignity of the client we will refer to the client as John (an alias) and me as the author or HCI (Health Care Assistant).
John is a 78 year old single man who has retired from farming. John has a nephew, Tom (name changed to protect his identity) who works at the farm everyday although he lives a few miles away. John is a very happy and Independent person; he has many good neighbors who stop in regularly to visit. John was diagnosed with stage 3 Prostate Cancer 4 years ago. The client has undergone treatment however the cancer has spread and tumors have developed in the groin area. John underwent surgery to remove the tumors and contracted MRS. while recovering in hospital.
Don’t waste your time! Order your assignment!
The MRS. has prevented the surgical area from healing completely and as John’s HCI it Is my responsibility to change his dressings overall times per week. The client Is terminal and Is currently receiving Palliative Care in his home. The Palliative care team consists of John’s nephew Tom, the local GPO, oncologist consultant, Palliative Care Nurse and the HCI. The nephew, Tom, is largely responsible for ensuring that John makes it to his medical appointments and caring for his daily needs. Tom is very busy with farm work and as John’s health has deteriorated he is becoming more reliant on certain members of the Palliative Care Team.
Although John’s local GPO and Oncologist Consultant are members of the Care Team, they are not involved In the daily care of him. The Palliative Care Nurse Is calling in on John once a week and more if necessary. The nurse communicates with the HCI regarding John’s daily care. The HCI is the one member of the team that has daily contact with John and Tom. The HCI keeps a close eye on John’s physical and emotional health. John has been suffering from depression lately and the HCI has communicated her concern to the Palliative Care Nurse.
As part of her daily care of John, the HCI has made It a priority to actively listen to John and his sadness over his diminishing ability to care for himself. I make It a point to sit facing John and making ye contact with him, when he becomes very upset I lightly touch his hand and ask what I can do for him. An important aspect of caring for the dying is to Listen. (Kibble Ross, 1969) Clear Awareness of need to treat others with respect and sensitivity. As HCI, I have communicated my concerns about John’s depression to the Palliative Care Nurse and have stressed how much his personality has changed.
By actively listening to John and his feelings of helplessness, I never diddles John’s feelings but rather encourage John to complete personal tasks which he is capable of completing. John can no longer stand without the assistance of his walking frame, this makes shaving in the morning difficult and John is quite particular about his appearance. John feels better about himself when he is clean shaven and dressed for the day, ensuring that John’s dignity remains Intact is extremely Important. I have discussed an alternative to shaving at the bathroom sink with John.
John has a desk have the desk in his bedroom and everything necessary for him to shave at his desk with a mirror stand. John’s feelings of inadequacy about caring for himself have been improved and he feels more independent. The HCI empowered John to make his decision and thereby improving his emotional self worth. Effective reflection on personal interaction/communication with dying person and family. During John’s care, especially as his health deteriorated, there was a concern from both and John and his extended family that John is kept comfortable and his pain minimized.
John was fearful of the pain associated with dying from Cancer. These feelings were communicated to me the HCI in a conversation one day while John was being assisted with his dressing. His sister had died of Lung Cancer 30 years before. At the time of her death, pain management and hospice care were not s evolved as today. I listened to John and reassured him that Palliative Care both at home or in a hospice had changed immensely over the past 30 years and that his comfort and needs would be fully met.
Tom was also concerned that his uncle was becoming more agitated and upset about being in unbearable pain. The HCI communicated both in writing and in a meeting with the Palliative Care Nurse and GPO about these concerns. We talked about John’s failing physical health and how this was affecting his emotional state. After consulting with Tom it was decided that the HCI would stay with John from 10:00 pm until 8:00 am and a family member would e there to spend the morning and afternoon with John. Tom explained to the Nurse and HCI that John was most agitated and uncomfortable during the night.
It was suggested by Tom that if John didn’t feel that he was alone during the night he may feel more secure and his fears might be lessened. It was agreed that we would discuss the situation after 4 nights and reflect on John’s response to the additional care. Out of respect for John the plan was discussed and he was happy to have a career there at night and that if he was experiencing any discomfort there would be a professional there to ensure he was kept comfortable. The Palliative Care Nurse after consulting with John’s GPO spoke to John about using a Morphine Patch in addition to the pain medication he was taking orally.
It was explained that this would provide a consistent flow of Morphine into John’s body and thus keeping any discomfort or pain too minimum. John could take additional pain medication when the need arose. During John’s last week of life he was surrounded by family and friends, nieces and nephews took turns staying at John’s house at night in addition to the HCI. While tending to John’s personal hygiene I would speak to John about what ties I was performing, respecting him and protecting his dignity at all times.
As HCI, I had cared for John for several months and was aware of his fear of being alone; during his final week I made my presence known to him during the night when he would become agitated. Sitting holding his hand and speaking softly to him, reassuring him that I was there, that he was not alone, brought comfort to John. I also encouraged the family members to sit quietly with John either holding his hand or wiping his brow with a cool damp face cloth. One member of John’s family, a niece had a tendency to speak in front of John about his deterioration.
In a very thoughtful and respectful manner I spoke quietly to the niece explaining to her that although John appeared to be unconscious we should refrain from speaking about him in his comforted by their presence. The family was very caring and the niece was very fond of her uncle. Her concern for his care made her actions understandable but it was important that John’s room remain peaceful and calm. The last 24 hours of John’s life were very peaceful. The nieces and nephews of John were present during those last hours and two nephews were with him when he died.
The family was very close knit ND extremely appreciative of all the support that had received from the Palliative Care Team. Reflecting back on John’s final days, I felt that John’s greatest fear of being alone and his pain management were handled extremely well. By working with Tom and other family members, the Palliative Care Team was able to care for John in a caring and supportive manner. With attentive listening the HCI, who spent the most time with John, became aware of John’s fears and worked with the Palliative team and John’s family to improve the quality of John’s life and keep communication open and focused on John’s care.
Clear awareness of role of other members of the healthcare team. The healthcare team consists of the client’s local GPO, Specialist Consultant, Palliative Care Nurse, Health Care Assistant and the client’s family. The local GPO is the diagnostician, provider of prescriptions, and the person who initializes the clients care within the healthcare system. The GPO will refer a client too specialist consultant for further tests and treatments. The consultant will offer treatments and communicate the findings with the local GPO.
A Healthcare Assistant works under the direction and guidance of the Palliative Care Nurse. The Nurse can administer the medications that doctors prescribe and offer guidance and help with solutions to difficulties encountered in the care of clients. The HCI and Palliative Care Nurse work closely together and communication between the two is vitally important. The Family of the client is the most important participant in the client’s care; their assistance in caring for the client is crucial.
It is important to include the family in the care plan of the client, respect their emotional needs and above all else respect their right to privacy. The Nurse and pharmacist are the main sources for information regarding dedications prescribed and how they may interact with one another. Family members with questions regarding medications should be referred to the GPO, Nurse or Pharmacist. Communicated/Supported family after their loved one has died. Having known John for several months I attended his wake and funeral. I had become fond of John and his friendly nature.
I have stopped in to say hello to Tom and his family in the weeks after John’s death to see how they were doing. I always have leaflets and contact numbers for Bereavement services and counseling in the event that I feel they might be useful for the family. Tom seems to be getting on fine and although he mentions how quiet the house feels now that John is gone and he misses the great banter the two had every morning, he appears to be handling his grief well and I let him know that if we can offer any assistance to please call. Conclusion.
This assignment has been beneficial to my learning by providing me with an opportunity to reflect on a series of events while caring for a client during his final 3 months of life. I understand that by paying close attention to the client and by listening to their concerns I can make important decisions about the care of my achieved this by using active listening skills and taking the time to engage on a personal level with my client. The Hospice movement plays an important role in the community, caring for the terminally ill. The Hospice movement believes in the idea of the patient as a family unit and not as an individual.
The hospice movement is deeply rooted in holistic care; the spiritual, physical, psychological and social care. A Hospice provides expert medical care, highly skilled and confident nursing care with an emphasis on experienced use of drugs. In Ireland, a hospice is considered a centre of excellence for palliative care. The act of dying is a personal and unique experience; therefore the caring for those dying should be unique and personal. Holistic care is patient centered and is all about the needs of the patient and their family.
Tending to their spiritual and social needs, getting to know the patient as a whole rather than Just providing for the physical needs improves the quality of care. (Luke, Austin, Caress & Halest, April 2000) Ronald of Advanced Nursing, Volume 31, Issue 4 pages 775-782 April 2000) The Importance of “knowing the patient”: community nurses constructions of quality in providing palliative care. In order to meet the client’s needs and maintain a high standard of care it is essential that all members of the palliative care team communicate with one another.
More importantly it is essential that communication be open and honest with the client and their family, making sure to actively listen to their needs and concerns and act in their best interest. Working in Palliative Care can be very draining emotionally and you need to be secure in your own emotional self regarding death and dying. When caring for other people in their hour of need it is crucial that as a career I am taking mime to mind myself both physically and emotionally.
Working in Palliative Care, while it can be draining is also very fulfilling. I take great satisfaction in caring for a person up until life ceases and hopefully somehow ensuring that they have had a peaceful death. Although it can be sad, caring for someone dying is a privilege. In the future I would like to be more knowledgeable about how you can offer comfort to someone. Communicating with a person who is dying and responding to their difficult questions I believe is an area where I could greatly improve.
How to cite this assignment
Related assignments:.
- Suffering Nursing Assignment
- Conflict resolution inlong term care Assignment
- Surgical Nursing Care Assignment
- Acute Care: Care Implementation and Evaluation. Assignment
Haven't Found The Paper You Want?
For Only $13.90/page
- Search entire site
- Search for a course
- Browse study areas
Analytics and Data Science
- Data Science and Innovation
- Postgraduate Research Courses
- Business Research Programs
- Undergraduate Business Programs
- Entrepreneurship
- MBA Programs
- Postgraduate Business Programs
Communication
- Animation Production
- Business Consulting and Technology Implementation
- Digital and Social Media
- Media Arts and Production
- Media Business
- Media Practice and Industry
- Music and Sound Design
- Social and Political Sciences
- Strategic Communication
- Writing and Publishing
- Postgraduate Communication Research Degrees
Design, Architecture and Building
- Architecture
- Built Environment
- DAB Research
- Public Policy and Governance
- Secondary Education
- Education (Learning and Leadership)
- Learning Design
- Postgraduate Education Research Degrees
- Primary Education
Engineering
- Civil and Environmental
- Computer Systems and Software
- Engineering Management
- Mechanical and Mechatronic
- Systems and Operations
- Telecommunications
- Postgraduate Engineering courses
- Undergraduate Engineering courses
- Sport and Exercise
- Palliative Care
- Public Health
- Nursing (Undergraduate)
- Nursing (Postgraduate)
- Health (Postgraduate)
- Research and Honours
- Health Services Management
- Child and Family Health
- Women's and Children's Health
Health (GEM)
- Coursework Degrees
- Clinical Psychology
- Genetic Counselling
- Good Manufacturing Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Speech Pathology
- Research Degrees
Information Technology
- Business Analysis and Information Systems
- Computer Science, Data Analytics/Mining
- Games, Graphics and Multimedia
- IT Management and Leadership
- Networking and Security
- Software Development and Programming
- Systems Design and Analysis
- Web and Cloud Computing
- Postgraduate IT courses
- Postgraduate IT online courses
- Undergraduate Information Technology courses
- International Studies
- Criminology
- International Relations
- Postgraduate International Studies Research Degrees
- Sustainability and Environment
- Practical Legal Training
- Commercial and Business Law
- Juris Doctor
- Legal Studies
- Master of Laws
- Intellectual Property
- Migration Law and Practice
- Overseas Qualified Lawyers
- Postgraduate Law Programs
- Postgraduate Law Research
- Undergraduate Law Programs
- Life Sciences
- Mathematical and Physical Sciences
- Postgraduate Science Programs
- Science Research Programs
- Undergraduate Science Programs
Transdisciplinary Innovation
- Creative Intelligence and Innovation
- Diploma in Innovation
- Transdisciplinary Learning
- Postgraduate Research Degree
Sample written assignments
Look at sample assignments to help you develop and enhance your academic writing skills.
How to use this page
This page features authentic sample assignments that you can view or download to help you develop and enhance your academic writing skills.
PLEASE NOTE: Comments included in these sample written assignments are intended as an educational guide only. Always check with academic staff which referencing convention you should follow. All sample assignments have been submitted using Turnitin® (anti-plagiarism software). Under no circumstances should you copy from these or any other texts.
Annotated bibliography
Annotated Bibliography: Traditional Chinese Medicine (PDF, 103KB)
Essay: Business - "Culture is a Tool Used by Management" (PDF, 496KB)
Essay: Business - "Integrating Business Perspectives - Wicked Problem" (PDF, 660KB)
Essay: Business - "Overconsumption and Sustainability" (PDF, 762KB)
Essay: Business - "Post bureaucracy vs Bureaucracy" (PDF, 609KB)
Essay: Design, Architecture & Building - "Ideas in History - Postmodernism" (PDF, 545KB)
Essay: Design, Architecture & Building - "The Context of Visual Communication Design Research Project" (PDF, 798KB)
Essay: Design, Architecture & Building - "Ideas in History - The Nurses Walk and Postmodernism" (PDF, 558KB)
Essay: Health (Childhood Obesity ) (PDF, 159KB)
Essay: Health (Improving Quality and Safety in Healthcare) (PDF, 277KB)
Essay: Health (Organisational Management in Healthcare) (PDF, 229KB)
UTS HELPS annotated Law essay
(PDF, 250KB)
Essay: Science (Traditional Chinese Medicine) (PDF, 153KB)
Literature review
Literature Review: Education (Critical Pedagogy) (PDF, 165KB)
Reflective writing
Reflective Essay: Business (Simulation Project) (PDF, 119KB)
Reflective Essay: Nursing (Professionalism in Context) (PDF, 134KB)
Report: Business (Management Decisions and Control) (PDF, 244KB)
Report: Education (Digital Storytelling) (PDF, 145KB)
Report: Education (Scholarly Practice) (PDF, 261KB)
Report: Engineering Communication (Flood Mitigation & Water Storage) (PDF, 1MB)
UTS acknowledges the Gadigal people of the Eora Nation, the Boorooberongal people of the Dharug Nation, the Bidiagal people and the Gamaygal people, upon whose ancestral lands our university stands. We would also like to pay respect to the Elders both past and present, acknowledging them as the traditional custodians of knowledge for these lands.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Example of Care Support Assignment for Irish Students Title: What is the need for care support planning?. Aim of the study: Care support planning motivates healthcare providers to help anyone with needs and encourage social care staff to take part in the care providing process.It helps individuals to set their aims and then secures the care support required to achieve those goals.
Here is the list of the foremost topics most the Irish students ask for assignment help for: -. Examine Swanson's Theory of caring. Incorporate the meta paradigm of nursing with the theory of caring. Explain the theory of self-care. Describe Dr Jane Watson's theory of human caring. Explain Jane Watson's theory of caring.
IrelandAssignmentHelp.com is a reputable online platform that offers comprehensive assignment help in Ireland, catering to students pursuing the 5N0758 Care Support course. With a team of expert Irish writers, the website ensures top-notch academic assistance to learners across Ireland. Our platform provides a wide range of services, including ...
So, you now know how to write a care support learner record. You are also informed about various techniques guidelines and needed skills required to write an assignment or assessment of care support learner record sample. This care support example task is widely done by the students of Ireland who are pursuing health care and nursing courses ...
Unit 17 Caring for Individuals with dementia Assignment 1; Unit 11 Genetic and Genetic Engineering Assignment 1 ... Introduction: This assignment will examine principles, values and skills, which underpin meeting the care and support needs of individuals. ... For example, in a care home a social worker approaches a patient in a friendly manner ...
Unit 7 Principles of Safe Practice Mini Assignment P1; AC1.5 Media REP - Ac1. 5 course work; UNIT 12 - SUPPORTING INDIVIDUALS WITH ADDITIONAL NEEDS ... and two different professionals may be provided, an example is a care worker, and consultant (stroke medicine) might work together to discuss and maintain and provide her with the right need and ...
care, new nurse orientation, patient requests and sat-isfaction, staff well-being, fairness, equal distribution of the workload, nurse development, and workload completion. Make the assignments Grab your writing instrument and pencil in that first nurse's name. This first match should satisfy your highest priority. For example, if
Nursing team collaboration. Writing a care plan allows a team of nurses (as well as physicians, assistants, and other care providers) to access the same information, share opinions, and collaborate to provide the best possible care for the patient. Documentation and compliance. A well-written care plan allows nurses to measure the effectiveness ...
Understanding the skill level and even personality of fellow nurses will allow you to create a safe and effective care assignment. Let's look at some examples: Carrie is a brand new nurse who has ...
The example care plan you see here is very brief. 4:10: Many care plans will be significantly more extensive than this, but each should be carefully tailored to the patient's actual needs. 4:17: Notice that the care plan is "you" focused, meaning that the language tells the patient exactly what he or she should do and expect. Displayed on ...
Step 1: Assessment. The first step in writing an organized care plan includes gathering subjective and objective nursing data. Subjective data is what the patient tells us their symptoms are, including feelings, perceptions, and concerns. Objective data is observable and measurable. This information can come from,
Includes: ongoing assessment, emotional support, providing comfort, teaching, physical care, and making referrals to other health care professionals. ... This section lists the sample nursing care plans (NCP) ... HI Can some one help me to do assignment on Impaired renal perfusion. 1.Goal 2.Related Action 3.Rational 4.Evaluate outcome. Reply.
The ability of the team to develop visual and written materials to support the presentation (Total possible marks: 5/5). Online Resources. Alzheimer Society of B.C. Canadian Mental Health Association, B.C. Division; HealthLinkBC; Heretohelp; Rubric: Supporting Clients with Dementia or a Mental Health Disorder
NIFAST Care Skills and Care Support 6 March.indd 5 06/03/2013 17:09. 6 Care Skills and Care Support There may be a crisis situation where there is a need to break client confidentiality, but this is rare. For example, there may be occasions when client-carer trust may cause a problem because of a revelation − a depressed
Care Skills FETAC Level 5 Example. FETAC Level 5 course consists of care support, care skills, safety & health at work, experience, behaviour management, care of people with mental illness, etc. Here we are providing you with a list of care skills FETAC level 5 assignments. During the Care skill course, students have to write essays and skill ...
Effective Care and Support Quality Assessment and Improvement: Specialist Palliative Care Services, May 2014 4 2. EFFECTIVE CARE AND SUPPORT WHAT A SERVICE USER CAN EXPECT OR EXPERIENCE WHEN A SPECIALIST PALLIATIVE CARE SERVICE IS MEETING THIS STANDARD. SPC provided will be based on the best available evidence to maximise your health benefit.
We've included a printable example of a care plan template, based on the questions we use on the Birdie system, at the bottom of this article. It covers the personal information and preferences section of a care plan, and is a great starting point for setting goals and assigning tasks. If you need help with goal setting, you can download a free ...
Develop a client profile and carry out an assessment of the individual client need. Determine the level of assistance required to complete the activities of daily living. Maintain the clients' safe environment. Promote the clients' involvement in social events and therapies. Mobility including falls and pressure area care.
Buy Properly Written Care Support Learner Record. The services offered by the team of Ireland Assignment Help are the topmost plus trustworthy. Almost every student of Ireland prefers to take the care support module assignment help from a group of expert writers.. The work offered by the group of professional writers is original and unique. It helps the students to enhance their knowledge plus ...
The modified nursing process consists of five different stages such as assessment, systematic nursing diagnosis, planning, implementation, recheck and evaluation. The ASPIRE framework of nursing process provides humanistic, person centric, dynamic, planned and collaborative approach for care planning in nursing (Taylor, 2011).
The author of this essay is a Health Care Assistant for three years and works as a member of a Hospice Home Care Team. For the purpose of this assignment the author will outline a selection of evidence of their work and interaction with their Palliative Care Clients and the Palliative Care Team. For the privacy and dignity of the client we will ...
This page features authentic sample assignments that you can view or download to help you develop and enhance your academic writing skills. PLEASE NOTE: Comments included in these sample written assignments are intended as an educational guide only. Always check with academic staff which referencing convention you should follow. All sample ...