Developing Critical Thinking
- Posted January 10, 2018
- By Iman Rastegari

In a time where deliberately false information is continually introduced into public discourse, and quickly spread through social media shares and likes, it is more important than ever for young people to develop their critical thinking. That skill, says Georgetown professor William T. Gormley, consists of three elements: a capacity to spot weakness in other arguments, a passion for good evidence, and a capacity to reflect on your own views and values with an eye to possibly change them. But are educators making the development of these skills a priority?
"Some teachers embrace critical thinking pedagogy with enthusiasm and they make it a high priority in their classrooms; other teachers do not," says Gormley, author of the recent Harvard Education Press release The Critical Advantage: Developing Critical Thinking Skills in School . "So if you are to assess the extent of critical-thinking instruction in U.S. classrooms, you’d find some very wide variations." Which is unfortunate, he says, since developing critical-thinking skills is vital not only to students' readiness for college and career, but to their civic readiness, as well.
"It's important to recognize that critical thinking is not just something that takes place in the classroom or in the workplace, it's something that takes place — and should take place — in our daily lives," says Gormley.
In this edition of the Harvard EdCast, Gormley looks at the value of teaching critical thinking, and explores how it can be an important solution to some of the problems that we face, including "fake news."

About the Harvard EdCast
The Harvard EdCast is a weekly series of podcasts, available on the Harvard University iT unes U page, that features a 15-20 minute conversation with thought leaders in the field of education from across the country and around the world. Hosted by Matt Weber and co-produced by Jill Anderson, the Harvard EdCast is a space for educational discourse and openness, focusing on the myriad issues and current events related to the field.

An education podcast that keeps the focus simple: what makes a difference for learners, educators, parents, and communities
Related Articles

The Wisdom of Data
Notes from ferguson, the case for homework.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Enter Today's Teacher Appreciation Giveaway!
What Is Critical Thinking and Why Do We Need To Teach It?
Question the world and sort out fact from opinion.
The world is full of information (and misinformation) from books, TV, magazines, newspapers, online articles, social media, and more. Everyone has their own opinions, and these opinions are frequently presented as facts. Making informed choices is more important than ever, and that takes strong critical thinking skills. But what exactly is critical thinking? Why should we teach it to our students? Read on to find out.
What is critical thinking?
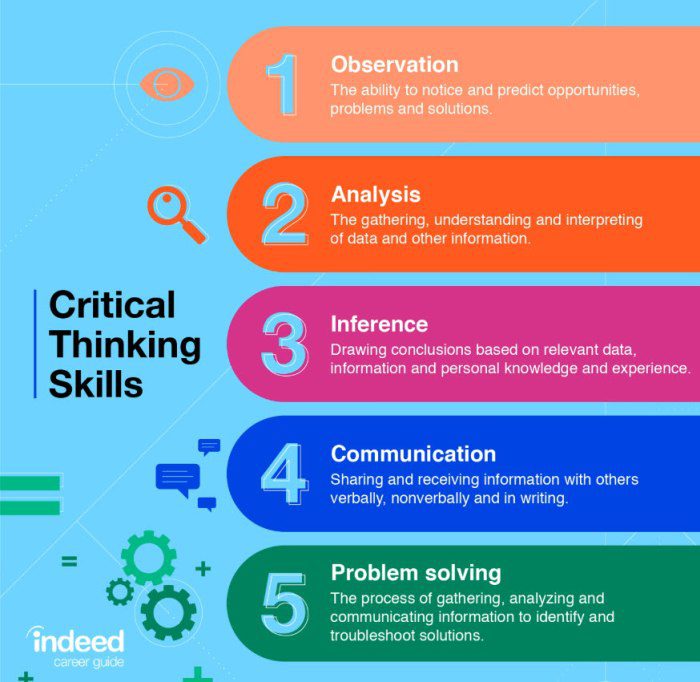
Source: Indeed
Critical thinking is the ability to examine a subject and develop an informed opinion about it. It’s about asking questions, then looking closely at the answers to form conclusions that are backed by provable facts, not just “gut feelings” and opinion. These skills allow us to confidently navigate a world full of persuasive advertisements, opinions presented as facts, and confusing and contradictory information.
The Foundation for Critical Thinking says, “Critical thinking can be seen as having two components: 1) a set of information and belief-generating and processing skills, and 2) the habit, based on intellectual commitment, of using those skills to guide behavior.”
In other words, good critical thinkers know how to analyze and evaluate information, breaking it down to separate fact from opinion. After a thorough analysis, they feel confident forming their own opinions on a subject. And what’s more, critical thinkers use these skills regularly in their daily lives. Rather than jumping to conclusions or being guided by initial reactions, they’ve formed the habit of applying their critical thinking skills to all new information and topics.
Why is critical thinking so important?
Imagine you’re shopping for a new car. It’s a big purchase, so you want to do your research thoroughly. There’s a lot of information out there, and it’s up to you to sort through it all.
- You’ve seen TV commercials for a couple of car models that look really cool and have features you like, such as good gas mileage. Plus, your favorite celebrity drives that car!
- The manufacturer’s website has a lot of information, like cost, MPG, and other details. It also mentions that this car has been ranked “best in its class.”
- Your neighbor down the street used to have this kind of car, but he tells you that he eventually got rid of it because he didn’t think it was comfortable to drive. Plus, he heard that brand of car isn’t as good as it used to be.
- Three independent organizations have done test-drives and published their findings online. They all agree that the car has good gas mileage and a sleek design. But they each have their own concerns or complaints about the car, including one that found it might not be safe in high winds.
So much information! It’s tempting to just go with your gut and buy the car that looks the coolest (or is the cheapest, or says it has the best gas mileage). Ultimately, though, you know you need to slow down and take your time, or you could wind up making a mistake that costs you thousands of dollars. You need to think critically to make an informed choice.
What does critical thinking look like?

Source: TeachThought
Let’s continue with the car analogy, and apply some critical thinking to the situation.
- Critical thinkers know they can’t trust TV commercials to help them make smart choices, since every single one wants you to think their car is the best option.
- The manufacturer’s website will have some details that are proven facts, but other statements that are hard to prove or clearly just opinions. Which information is factual, and even more important, relevant to your choice?
- A neighbor’s stories are anecdotal, so they may or may not be useful. They’re the opinions and experiences of just one person and might not be representative of a whole. Can you find other people with similar experiences that point to a pattern?
- The independent studies could be trustworthy, although it depends on who conducted them and why. Closer analysis might show that the most positive study was conducted by a company hired by the car manufacturer itself. Who conducted each study, and why?
Did you notice all the questions that started to pop up? That’s what critical thinking is about: asking the right questions, and knowing how to find and evaluate the answers to those questions.
Good critical thinkers do this sort of analysis every day, on all sorts of subjects. They seek out proven facts and trusted sources, weigh the options, and then make a choice and form their own opinions. It’s a process that becomes automatic over time; experienced critical thinkers question everything thoughtfully, with purpose. This helps them feel confident that their informed opinions and choices are the right ones for them.
Key Critical Thinking Skills
There’s no official list, but many people use Bloom’s Taxonomy to help lay out the skills kids should develop as they grow up.
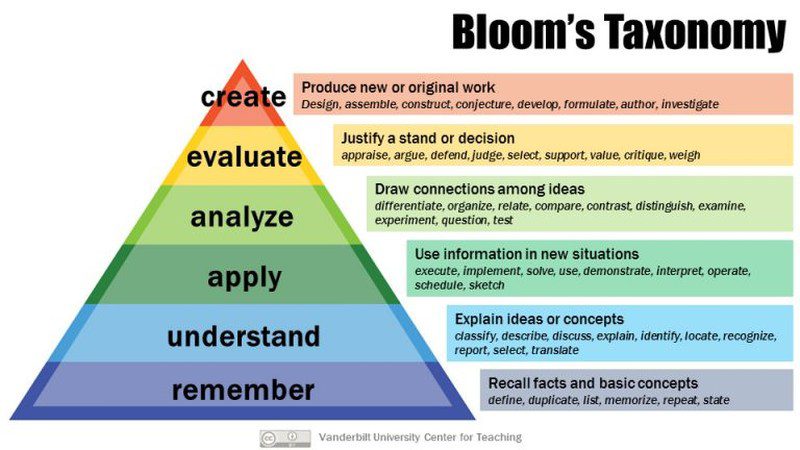
Source: Vanderbilt University
Bloom’s Taxonomy is laid out as a pyramid, with foundational skills at the bottom providing a base for more advanced skills higher up. The lowest phase, “Remember,” doesn’t require much critical thinking. These are skills like memorizing math facts, defining vocabulary words, or knowing the main characters and basic plot points of a story.
Higher skills on Bloom’s list incorporate more critical thinking.
True understanding is more than memorization or reciting facts. It’s the difference between a child reciting by rote “one times four is four, two times four is eight, three times four is twelve,” versus recognizing that multiplication is the same as adding a number to itself a certain number of times. When you understand a concept, you can explain how it works to someone else.
When you apply your knowledge, you take a concept you’ve already mastered and apply it to new situations. For instance, a student learning to read doesn’t need to memorize every word. Instead, they use their skills in sounding out letters to tackle each new word as they come across it.
When we analyze something, we don’t take it at face value. Analysis requires us to find facts that stand up to inquiry. We put aside personal feelings or beliefs, and instead identify and scrutinize primary sources for information. This is a complex skill, one we hone throughout our entire lives.
Evaluating means reflecting on analyzed information, selecting the most relevant and reliable facts to help us make choices or form opinions. True evaluation requires us to put aside our own biases and accept that there may be other valid points of view, even if we don’t necessarily agree with them.
Finally, critical thinkers are ready to create their own result. They can make a choice, form an opinion, cast a vote, write a thesis, debate a topic, and more. And they can do it with the confidence that comes from approaching the topic critically.
How do you teach critical thinking skills?
The best way to create a future generation of critical thinkers is to encourage them to ask lots of questions. Then, show them how to find the answers by choosing reliable primary sources. Require them to justify their opinions with provable facts, and help them identify bias in themselves and others. Try some of these resources to get started.
5 Critical Thinking Skills Every Kid Needs To Learn (And How To Teach Them)
- 100+ Critical Thinking Questions for Students To Ask About Anything
- 10 Tips for Teaching Kids To Be Awesome Critical Thinkers
- Free Critical Thinking Poster, Rubric, and Assessment Ideas
More Critical Thinking Resources
The answer to “What is critical thinking?” is a complex one. These resources can help you dig more deeply into the concept and hone your own skills.
- The Foundation for Critical Thinking
- Cultivating a Critical Thinking Mindset (PDF)
- Asking the Right Questions: A Guide to Critical Thinking (Browne/Keeley, 2014)
Have more questions about what critical thinking is or how to teach it in your classroom? Join the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook to ask for advice and share ideas!
Plus, 12 skills students can work on now to help them in careers later ..

You Might Also Like

Teach them to thoughtfully question the world around them. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Critical Thinking for Teachers
- First Online: 02 January 2023
Cite this chapter

- Diler Oner 3 &
- Yeliz Gunal Aggul 3
Part of the book series: Integrated Science ((IS,volume 13))
868 Accesses
2 Citations
Developing critical thinking is an important educational goal for all grade levels today. To foster their students’ critical thinking, future teachers themselves must become critical thinkers first. Thus, critical thinking should be an essential aspect of teacher training. However, despite its importance, critical thinking is not systematically incorporated into teacher education programs. There exist several conceptualizations of critical thinking in the literature, and these have different entailments regarding the guidelines and instructional strategies to teach critical thinking. In this paper, after examining the critical thinking literature, we suggested that critical thinking could be conceptualized in two distinct but complementary ways—as the acquisition of cognitive skills (instrumental perspective) and as identity development (situated perspective). We discussed the implications of these perspectives in teacher education. While the instrumental perspective allowed us to consider what to teach regarding critical thinking, the situated perspective enabled us to emphasize the broader social context where critical thinking skills and dispositions could be means of active participation in the culture of teaching.
Graphical Abstract/Art Performance

Critical thinking.
Everything we teach should be different from machines. If we do not change the way we teach, 30 years from now, we will be in trouble . Jack Ma
Jack Ma Co-founder of the Alibaba Group.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Burbules N-C, Berk R (1999) Critical thinking and critical pedagogy: relations, differences, and limits. In: Popkewitz T-S, Fendler L (eds) Critical theories in education. Routledge, New York, pp 45–65
Google Scholar
Hitchcock D (2018) Critical thinking. In: Zalta E-N (ed) The Stanford Encyclopedia of philosophy. https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/fall2018/entries/critical-thinking . Accessed 8 Aug 2020
Costa A-L (1985) Developing minds: preface to the revised edition. In: Costa A-L (ed) Developing minds: a resource book for teaching thinking. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development, Virginia, pp ix–x
National Education Association (2012) Preparing 21st-century students for a global society: an educator’s guide to “the four Cs.” http://www.nea.org/assets/docs/A-Guide-to-Four-Cs.pdf . Accessed 08 Aug 2020
Oner D (2019) Education 4.0: the skills needed for the future. In: Paper presented at the 5th Turkish-German frontiers of social science symposium (TUGFOSS) by Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, Stiftung Mercator, and Koç University, Leipzig, Germany, 24–27 Oct 2019
Elder L, Paul R (1994) Critical thinking: why we must transform our teaching. J Dev Educ 18(1):34–35
Williams R-L (2005) Targeting critical thinking within teacher education: the potential impact on society. Teach Educ Q 40(3):163–187
Holder J-J (1994) An epistemological foundation for thinking: a Deweyan approach. Stud Philos Educ 13:175–192
Article Google Scholar
Dewey J (1910) How we think. D.C. Heath and Company, Lexington
Bruner J (1966) Toward a theory of instruction. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Laanemets U, Kalamees-Ruubel K (2013) The Taba-Tyler rationales. J Am Assoc Advance Curriculum Stud 9:1–12
McTighe J, Schollenberger J (1985) Why teach thinking? A statement of rationale. In: Costa A-L (ed) Developing minds: a resource book for teaching thinking. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development, Alexandria, pp 2–5
Taba H (1962) The teaching of thinking. Element English 42(5):534–542
Pressesien B-Z (1985) Thinking skills: meanings and models revisited. In: Costa A-L (ed) Developing minds: a resource book for teaching thinking Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development, Alexandria, pp 56–62
Cohen J (1971) Thinking. Rand McNally, Chicago
Iowa Department of Education (1989) A guide to developing higher-order thinking across the curriculum. Department of Education, Des Moines (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED-306-550)
Jonassen D (1996) Computers as mindtools for schools: engaging critical thinking. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Ennis R-H (1996) Critical thinking dispositions: their nature and accessibility. Informal Logic 18:165–182
Facione P (1990) Critical thinking: a statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. California Academic Press, Millbrae
Paul R-W (1985) Goals for a critical thinking curriculum. In: Costa A-L (ed) Developing minds: a resource book for teaching thinking. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development, Alexandria, pp 77–84
Ennis R-H (1964) A definition of critical thinking. Read Teach 17(8):599–612
Ennis R-H (1985) Goals for a critical thinking curriculum. In: Costa A-L (ed) Developing minds: a resource book for teaching thinking. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development, Alexandria, pp 68–71
Ennis R-H (2015) Critical thinking: a streamlined conception. In: Davies M, Barnett R (eds) The Palgrave handbook of critical thinking in higher education. Palgrave Macmillan, New York, pp 31–47
Chapter Google Scholar
Davies M (2015) A model of critical thinking in higher education. In: Paulsen M (ed) Higher education: handbook of theory and research, vol 30. Springer, Cham, pp 41–92
Walters K-S (1994) Introduction: beyond logicism in critical thinking. In: Walters K-S (ed) Re-thinking reason: new perspectives in critical thinking. SUNY Press, Albany, pp 1–22
Barnett R (1997) Higher education: a critical business. Open University Press, Buckingham
Phelan A-M, Garrison J-W (1994) Toward a gender-sensitive ideal of critical thinking: a feminist poetic. Curric Inq 24(3):255–268
Kaplan L-D (1991) Teaching intellectual autonomy: the failure of the critical thinking movement. Educ Theory 41(4):361–370
McLaren P (1994) Critical pedagogy and predatory culture. Routledge, London
Giroux H-A (2010) Lessons from Paulo Freire. https://www.chronicle.com/article/lessons-from-paulo-freire/ . Accessed 8 Aug 2020
Freire P (2000) Pedagogy of the oppressed. Continuum, New York
Giroux H-A (2011) On critical pedagogy. The Continuum International Publishing Group, Auckland
Volman M, ten Dam G (2015) Critical thinking for educated citizenship. In: Davies M, Barnett R (eds) The Palgrave handbook of critical thinking in higher education. Palgrave Macmillan, New York, pp 593–603
Belenky M-F, Clinchy B-M, Goldberger N-R, Tarule J-M (1997) Women’s ways of knowing: the development of self, voice, and mind. Basic Books, New York
Warren K-J (1994) Critical thinking and feminism. In: Walters K-S (ed) Re-thinking reason: new perspectives in critical thinking. SUNY Press, Albany, pp 199–204
Thayer-Bacon B (2000) Transforming critical thinking. Teachers College Press, New York
Atkinson D (1997) A critical approach to critical thinking in TESOL. TESOL Q 31(1):71–94
ten Dam G, Volman M (2004) Critical thinking as a citizenship competence: teaching strategies. Learn Instr 14:359–379
Sfard A (1998) On two metaphors for learning and the dangers of choosing just one. Educ Res 27:4–13
Tsui L (1999) Courses and instruction affecting critical thinking. Res High Educ 40(2):185–200
Abrami P-C, Bernard R-M, Borokhovski E, Waddington D-I, Anne Wade C, Persson T (2015) Strategies for teaching students to think critically: a meta-analysis. Rev Educ Res 85(2):275–314
Mpofu N, Maphalala M-C (2017) Fostering critical thinking in initial teacher education curriculums: a comprehensive literature review. Gender Behav 15(2):9226–9236
Ennis R-H (1989) Critical thinking and subject specificity: clarification and needed research. Educ Res 18(3):4–10
Norris S-P (1985) The choice of standard conditions in defining critical thinking competence. Educ Theory 35(1):97–107
Paul R-W (1985) McPeck’s mistakes. Informal Logic 7(1):35–43
Siegel H (1991) The generalizability of critical thinking. Educ Philos Theory 23(1):18–30
McPeck J-E (1981) Critical thinking and education. St Martin’s Press, New York
McPeck J-E (1984) Stalking beasts, but swatting flies: the teaching of critical thinking. Can J Educ 9(1):28–44
McPeck J-E (1990) Critical thinking and subject-specificity: a reply to Ennis. Educ Res 19(4):10–12
Adler M (1986) Why critical thinking programs won’t work. Educ Week 6(2):28
Brown A (1997) Transforming schools into communities of thinking and learning about serious matters. Am Psychol 52(4):399–413
Article CAS Google Scholar
Oner D (2010) Öğretmenin bilgisi özel bir bilgi midir? Öğretmek için gereken bilgiye kuramsal bir bakış. Boğaziçi Üniversitesi Eğitim Dergisi 27(2):23–32
Shulman L-S (1987) Knowledge and teaching: foundations of the new reform. Harvard Educ Rev 57(1):61–77. https://doi.org/10.17763/haer.57.1.j463w79r56455411
Oner D, Adadan E (2011) Use of web-based portfolios as tools for reflection in preservice teacher education. J Teach Educ 62(5):477–492
Oner D, Adadan E (2016) Are integrated portfolio systems the answer? An evaluation of a web-based portfolio system to improve preservice teachers’ reflective thinking skills. J Comput High Educ 28(2):236–260
Lave J, Wenger E (1991) Situated learning: legitimate peripheral participation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Book Google Scholar
Brookfield S (2012) Teaching for critical thinking: tools and techniques to help students question their assumptions. Jossey-Bass, San Francisco
Korthagen F-A-J (2010) Situated learning theory and the pedagogy of teacher education: towards an integrative view of teacher behavior and teacher learning. Teach Teach Educ 26(1):98–106
Putnam R-T, Borko H (2000) What do new views of knowledge and thinking have to say about research on teacher learning? Educ Res 29(1):4–15
Brown J-S, Collins A, Duguid P (1989) Situated cognition and the culture of learning. Educ Res 18(1):32–42
Scardamalia M, Bereiter C (1991) Higher levels of agency for children in knowledge building: a challenge for the design of new knowledge media. J Learn Sci 1(1):37–68
Shaffer D-W (2005) Epistemic games. Innovate J Online Educ 1(6):Article 2
Oner D (2020) A virtual internship for developing technological pedagogical content knowledge. Australas J Educ Technol 36(2):27–42
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Bogazici University, Istanbul, Turkey
Diler Oner & Yeliz Gunal Aggul
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Diler Oner .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Universal Scientific Education and Research Network (USERN), Stockholm, Sweden
Nima Rezaei
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Oner, D., Aggul, Y.G. (2022). Critical Thinking for Teachers. In: Rezaei, N. (eds) Integrated Education and Learning. Integrated Science, vol 13. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15963-3_18
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15963-3_18
Published : 02 January 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-15962-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-15963-3
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students
Why Is Critical Thinking Important? A Survival Guide
Updated: December 7, 2023
Published: April 2, 2020

Why is critical thinking important? The decisions that you make affect your quality of life. And if you want to ensure that you live your best, most successful and happy life, you’re going to want to make conscious choices. That can be done with a simple thing known as critical thinking. Here’s how to improve your critical thinking skills and make decisions that you won’t regret.
What Is Critical Thinking?
You’ve surely heard of critical thinking, but you might not be entirely sure what it really means, and that’s because there are many definitions. For the most part, however, we think of critical thinking as the process of analyzing facts in order to form a judgment. Basically, it’s thinking about thinking.
How Has The Definition Evolved Over Time?
The first time critical thinking was documented is believed to be in the teachings of Socrates , recorded by Plato. But throughout history, the definition has changed.
Today it is best understood by philosophers and psychologists and it’s believed to be a highly complex concept. Some insightful modern-day critical thinking definitions include :
- “Reasonable, reflective thinking that is focused on deciding what to believe or do.”
- “Deciding what’s true and what you should do.”
The Importance Of Critical Thinking
Why is critical thinking important? Good question! Here are a few undeniable reasons why it’s crucial to have these skills.
1. Critical Thinking Is Universal
Critical thinking is a domain-general thinking skill. What does this mean? It means that no matter what path or profession you pursue, these skills will always be relevant and will always be beneficial to your success. They are not specific to any field.
2. Crucial For The Economy
Our future depends on technology, information, and innovation. Critical thinking is needed for our fast-growing economies, to solve problems as quickly and as effectively as possible.
3. Improves Language & Presentation Skills
In order to best express ourselves, we need to know how to think clearly and systematically — meaning practice critical thinking! Critical thinking also means knowing how to break down texts, and in turn, improve our ability to comprehend.
4. Promotes Creativity
By practicing critical thinking, we are allowing ourselves not only to solve problems but also to come up with new and creative ideas to do so. Critical thinking allows us to analyze these ideas and adjust them accordingly.
5. Important For Self-Reflection
Without critical thinking, how can we really live a meaningful life? We need this skill to self-reflect and justify our ways of life and opinions. Critical thinking provides us with the tools to evaluate ourselves in the way that we need to.

6. The Basis Of Science & Democracy
In order to have a democracy and to prove scientific facts, we need critical thinking in the world. Theories must be backed up with knowledge. In order for a society to effectively function, its citizens need to establish opinions about what’s right and wrong (by using critical thinking!).
Benefits Of Critical Thinking
We know that critical thinking is good for society as a whole, but what are some benefits of critical thinking on an individual level? Why is critical thinking important for us?
1. Key For Career Success
Critical thinking is crucial for many career paths. Not just for scientists, but lawyers , doctors, reporters, engineers , accountants, and analysts (among many others) all have to use critical thinking in their positions. In fact, according to the World Economic Forum, critical thinking is one of the most desirable skills to have in the workforce, as it helps analyze information, think outside the box, solve problems with innovative solutions, and plan systematically.
2. Better Decision Making
There’s no doubt about it — critical thinkers make the best choices. Critical thinking helps us deal with everyday problems as they come our way, and very often this thought process is even done subconsciously. It helps us think independently and trust our gut feeling.
3. Can Make You Happier!
While this often goes unnoticed, being in touch with yourself and having a deep understanding of why you think the way you think can really make you happier. Critical thinking can help you better understand yourself, and in turn, help you avoid any kind of negative or limiting beliefs, and focus more on your strengths. Being able to share your thoughts can increase your quality of life.
4. Form Well-Informed Opinions
There is no shortage of information coming at us from all angles. And that’s exactly why we need to use our critical thinking skills and decide for ourselves what to believe. Critical thinking allows us to ensure that our opinions are based on the facts, and help us sort through all that extra noise.
5. Better Citizens
One of the most inspiring critical thinking quotes is by former US president Thomas Jefferson: “An educated citizenry is a vital requisite for our survival as a free people.” What Jefferson is stressing to us here is that critical thinkers make better citizens, as they are able to see the entire picture without getting sucked into biases and propaganda.
6. Improves Relationships
While you may be convinced that being a critical thinker is bound to cause you problems in relationships, this really couldn’t be less true! Being a critical thinker can allow you to better understand the perspective of others, and can help you become more open-minded towards different views.
7. Promotes Curiosity
Critical thinkers are constantly curious about all kinds of things in life, and tend to have a wide range of interests. Critical thinking means constantly asking questions and wanting to know more, about why, what, who, where, when, and everything else that can help them make sense of a situation or concept, never taking anything at face value.
8. Allows For Creativity
Critical thinkers are also highly creative thinkers, and see themselves as limitless when it comes to possibilities. They are constantly looking to take things further, which is crucial in the workforce.
9. Enhances Problem Solving Skills
Those with critical thinking skills tend to solve problems as part of their natural instinct. Critical thinkers are patient and committed to solving the problem, similar to Albert Einstein, one of the best critical thinking examples, who said “It’s not that I’m so smart; it’s just that I stay with problems longer.” Critical thinkers’ enhanced problem-solving skills makes them better at their jobs and better at solving the world’s biggest problems. Like Einstein, they have the potential to literally change the world.
10. An Activity For The Mind
Just like our muscles, in order for them to be strong, our mind also needs to be exercised and challenged. It’s safe to say that critical thinking is almost like an activity for the mind — and it needs to be practiced. Critical thinking encourages the development of many crucial skills such as logical thinking, decision making, and open-mindness.
11. Creates Independence
When we think critically, we think on our own as we trust ourselves more. Critical thinking is key to creating independence, and encouraging students to make their own decisions and form their own opinions.
12. Crucial Life Skill
Critical thinking is crucial not just for learning, but for life overall! Education isn’t just a way to prepare ourselves for life, but it’s pretty much life itself. Learning is a lifelong process that we go through each and every day.
How to Think Critically
Now that you know the benefits of thinking critically, how do you actually do it?
How To Improve Your Critical Thinking
- Define Your Question: When it comes to critical thinking, it’s important to always keep your goal in mind. Know what you’re trying to achieve, and then figure out how to best get there.
- Gather Reliable Information: Make sure that you’re using sources you can trust — biases aside. That’s how a real critical thinker operates!
- Ask The Right Questions: We all know the importance of questions, but be sure that you’re asking the right questions that are going to get you to your answer.
- Look Short & Long Term: When coming up with solutions, think about both the short- and long-term consequences. Both of them are significant in the equation.
- Explore All Sides: There is never just one simple answer, and nothing is black or white. Explore all options and think outside of the box before you come to any conclusions.
How Is Critical Thinking Developed At School?
Critical thinking is developed in nearly everything we do. However, much of this important skill is encouraged to be practiced at school, and rightfully so! Critical thinking goes beyond just thinking clearly — it’s also about thinking for yourself.
When a teacher asks a question in class, students are given the chance to answer for themselves and think critically about what they learned and what they believe to be accurate. When students work in groups and are forced to engage in discussion, this is also a great chance to expand their thinking and use their critical thinking skills.
How Does Critical Thinking Apply To Your Career?
Once you’ve finished school and entered the workforce, your critical thinking journey only expands and grows from here!
Impress Your Employer
Employers value employees who are critical thinkers, ask questions, offer creative ideas, and are always ready to offer innovation against the competition. No matter what your position or role in a company may be, critical thinking will always give you the power to stand out and make a difference.
Careers That Require Critical Thinking
Some of many examples of careers that require critical thinking include:
- Human resources specialist
- Marketing associate
- Business analyst
Truth be told however, it’s probably harder to come up with a professional field that doesn’t require any critical thinking!
Photo by Oladimeji Ajegbile from Pexels
What is someone with critical thinking skills capable of doing.
Someone with critical thinking skills is able to think rationally and clearly about what they should or not believe. They are capable of engaging in their own thoughts, and doing some reflection in order to come to a well-informed conclusion.
A critical thinker understands the connections between ideas, and is able to construct arguments based on facts, as well as find mistakes in reasoning.
The Process Of Critical Thinking
The process of critical thinking is highly systematic.
What Are Your Goals?
Critical thinking starts by defining your goals, and knowing what you are ultimately trying to achieve.
Once you know what you are trying to conclude, you can foresee your solution to the problem and play it out in your head from all perspectives.
What Does The Future Of Critical Thinking Hold?
The future of critical thinking is the equivalent of the future of jobs. In 2020, critical thinking was ranked as the 2nd top skill (following complex problem solving) by the World Economic Forum .
We are dealing with constant unprecedented changes, and what success is today, might not be considered success tomorrow — making critical thinking a key skill for the future workforce.
Why Is Critical Thinking So Important?
Why is critical thinking important? Critical thinking is more than just important! It’s one of the most crucial cognitive skills one can develop.
By practicing well-thought-out thinking, both your thoughts and decisions can make a positive change in your life, on both a professional and personal level. You can hugely improve your life by working on your critical thinking skills as often as you can.
Related Articles

- Effective Teaching
The Importance of Critical Thinking in the Classroom: Strategies for Teachers

Critical thinking is a crucial skill for students to develop in school. It is the ability to think deeply, logically, and independently about a topic, problem, or situation. The importance of critical thinking in education cannot be overstated, as it empowers students to become more effective learners, thinkers, and problem-solvers.
5 Reasons Why Critical Thinking Is So Important To Teach in School:
1. it prepares students for the real world..
In today’s fast-paced and constantly changing world, critical thinking is essential for success. The ability to analyze information, evaluate arguments, and make informed decisions is crucial in any career or life situation.
2. Enhances problem-solving skills.
Critical thinking skills help students approach problems from different angles and develop creative solutions. They learn to ask questions, challenge assumptions, and make informed decisions based on evidence.
3. Encourages intellectual curiosity.
Critical thinking encourages students to be curious about the world around them. They learn to seek out new information, consider multiple perspectives, and evaluate the credibility of sources.
4. Improves academic performance.
The ability to think critically can help students excel in their academic pursuits. They learn to read and analyze texts more effectively, write more persuasive arguments, and participate more meaningfully in class discussions.
5. Fosters independent thinking.
Thinking critically encourages students to think for themselves, rather than simply accepting what they are told. They learn to question authority, challenge conventional wisdom, and form their own opinions based on evidence.

So how can educators foster critical thinking in the classroom? Here are some strategies:
1. ask open-ended questions..
Instead of asking questions with simple answers, ask questions that require students to think deeply and develop their own answers. Encourage them to support their answers with evidence and to consider alternative viewpoints. You can use tools such as Bloom’s Taxonomy or Webb’s Depths of Knowledge to help you ask deeper questions. Check out these FREE Bloom’s question stem slips that you can print out. Cut them up and stick them in a jar. Each time you’re trying to think of a question to ask, just pull out a question stem from the jar.

2. Encourage reflection.
Have students reflect on their own thinking processes and decision-making strategies. This can help them become more aware of their own biases and assumptions. I’ve got a set of exit tickets that include a lot of reflection questions. They can be used for any subject.

3. Use problem-based learning.
Engage students in real-world problems that require them to think critically and apply what they have learned. This can help them develop their problem-solving and critical thinking skills.
4. Teach information literacy.
Help students learn how to evaluate sources and analyze information effectively. Teach them to identify bias, recognize propaganda, and use critical thinking to assess the credibility of sources.
5. Promote debate and discussion.
Encourage students to engage in respectful debates and discussions about complex topics. This can help them develop their thinking, communication, and collaboration skills.
6. Model critical thinking.
As an educator, model critical thinking by asking thoughtful questions, challenging assumptions, and encouraging students to think for themselves. This can help students learn to think critically and independently.
By implementing these strategies, teachers can help students develop critical thinking skills that will serve them well throughout their academic and professional careers. Thinking critically is a crucial skill for success in today’s world, and it is up to educators to help students develop this essential skill.
Check out these other posts:


Explained: Importance of critical thinking, problem-solving skills in curriculum
F uture careers are no longer about domain expertise or technical skills. Rather, critical thinking and problem-solving skills in employees are on the wish list of every big organization today. Even curriculums and pedagogies across the globe and within India are now requiring skilled workers who are able to think critically and are analytical.
The reason for this shift in perspective is very simple.
These skills provide a staunch foundation for comprehensive learning that extends beyond books or the four walls of the classroom. In a nutshell, critical thinking and problem-solving skills are a part of '21st Century Skills' that can help unlock valuable learning for life.
Over the years, the education system has been moving away from the system of rote and other conventional teaching and learning parameters.
They are aligning their curriculums to the changing scenario which is becoming more tech-driven and demands a fusion of critical skills, life skills, values, and domain expertise. There's no set formula for success.
Rather, there's a defined need for humans to be more creative, innovative, adaptive, agile, risk-taking, and have a problem-solving mindset.
In today's scenario, critical thinking and problem-solving skills have become more important because they open the human mind to multiple possibilities, solutions, and a mindset that is interdisciplinary in nature.
Therefore, many schools and educational institutions are deploying AI and immersive learning experiences via gaming, and AR-VR technologies to give a more realistic and hands-on learning experience to their students that hone these abilities and help them overcome any doubt or fear.
ADVANTAGES OF CRITICAL THINKING AND PROBLEM-SOLVING IN CURRICULUM
Ability to relate to the real world: Instead of theoretical knowledge, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills encourage students to look at their immediate and extended environment through a spirit of questioning, curiosity, and learning. When the curriculum presents students with real-world problems, the learning is immense.
Confidence, agility & collaboration : Critical thinking and problem-solving skills boost self-belief and confidence as students examine, re-examine, and sometimes fail or succeed while attempting to do something.
They are able to understand where they may have gone wrong, attempt new approaches, ask their peers for feedback and even seek their opinion, work together as a team, and learn to face any challenge by responding to it.
Willingness to try new things: When problem-solving skills and critical thinking are encouraged by teachers, they set a robust foundation for young learners to experiment, think out of the box, and be more innovative and creative besides looking for new ways to upskill.
It's important to understand that merely introducing these skills into the curriculum is not enough. Schools and educational institutions must have upskilling workshops and conduct special training for teachers so as to ensure that they are skilled and familiarized with new teaching and learning techniques and new-age concepts that can be used in the classrooms via assignments and projects.
Critical thinking and problem-solving skills are two of the most sought-after skills. Hence, schools should emphasise the upskilling of students as a part of the academic curriculum.
The article is authored by Dr Tassos Anastasiades, Principal- IB, Genesis Global School, Noida.
Watch Live TV in English
Watch Live TV in Hindi

- Our Mission

4 Strategies for Sparking Critical Thinking in Young Students
Fostering investigative conversation in grades K–2 isn’t easy, but it can be a great vehicle to promote critical thinking.
In the middle of class, a kindergartner spotted an ant and asked the teacher, “Why do ants come into the classroom?” Fairly quickly, educational consultant Cecilia Cabrera Martirena writes , students started sharing their theories: Maybe the ants were cold, or looking for food, or lonely.
Their teacher started a KWL chart to organize what students already knew, what they wanted to know, and, later, what they had learned. “As many of the learners didn’t read or write yet, the KWL was created with drawings and one or two words,” Cabrera Martirena writes. “Then, as a group, they decided how they could gather information to answer that first question, and some possible research routes were designed.”
As early elementary teachers know, young learners are able to engage in critical thinking and participate in nuanced conversations, with appropriate supports. What can teachers do to foster these discussions? Elementary teacher Jennifer Orr considered a few ideas in an article for ASCD .
“An interesting question and the discussion that follows can open up paths of critical thinking for students at any age,” Orr says. “With a few thoughtful prompts and a lot of noticing and modeling, we as educators can help young students engage in these types of academic conversations in ways that deepen their learning and develop their critical thinking skills.”
While this may not be an “easy process,” Orr writes—for the kids or the teacher—the payoff is students who from a young age are able to communicate new ideas and questions; listen and truly hear the thoughts of others; respectfully agree, disagree, or build off of their peers’ opinions; and revise their thinking.
4 Strategies for Kick-Starting Powerful Conversations
1. Encourage Friendly Debate: For many elementary-aged children, it doesn’t take much provoking for them to share their opinions, especially if they disagree with each other. Working with open-ended prompts that “engage their interest and pique their curiosity” is one key to sparking organic engagement, Orr writes. Look for prompts that allow them to take a stance, arguing for or against something they feel strongly about.
For example, Orr says, you could try telling first graders that a square is a rectangle to start a debate. Early childhood educator Sarah Griffin proposes some great math talk questions that can yield similar results:
- How many crayons can fit in a box?
- Which takes more snow to build: one igloo or 20 snowballs?
- Estimate how many tissues are in a box.
- How many books can you fit in your backpack?
- Which would take less time: cleaning your room or reading a book?
- Which would you rather use to measure a Christmas tree: a roll of ribbon or a candy cane? Why?
Using pictures can inspire interesting math discussions as well, writes K–6 math coach Kristen Acosta . Explore counting, addition, and subtraction by introducing kids to pictures “that have missing pieces or spaces” or “pictures where the objects are scattered.” For example, try showing students a photo of a carton of eggs with a few eggs missing. Ask questions like, “what do you notice?” and “what do you wonder?” and see how opinions differ.
2. Put Your Students in the Question: Centering students’ viewpoints in a question or discussion prompt can foster deeper thinking, Orr writes. During a unit in which kids learned about ladybugs, she asked her third graders, “What are four living and four nonliving things you would need and want if you were designing your own ecosystem?” This not only required students to analyze the components of an ecosystem but also made the lesson personal by inviting them to dream one up from scratch.
Educator Todd Finley has a list of interesting writing prompts for different grades that can instead be used to kick off classroom discussions. Examples for early elementary students include:
- Which is better, giant muscles or incredible speed? Why?
- What’s the most beautiful person, place, or thing you’ve ever seen? Share what makes that person, place, or thing so special.
- What TV or movie characters do you wish were real? Why?
- Describe a routine that you often or always do (in the morning, when you get home, Friday nights, before a game, etc.).
- What are examples of things you want versus things you need?
3. Open Several Doors: While some students take to classroom discussions like a duck to water, others may prefer to stay on dry land. Offering low-stakes opportunities for students to dip a toe into the conversation can be a great way to ensure that everyone in the room can be heard. Try introducing hand signals that indicate agreement, disagreement, and more. Since everyone can indicate their opinion silently, this supports students who are reluctant to speak, and can help get the conversation started.
Similarly, elementary school teacher Raquel Linares uses participation cards —a set of different colored index cards, each labeled with a phrase like “I agree,” “I disagree,” or “I don’t know how to respond.” “We use them to assess students’ understanding, but we also use them to give students a voice,” Linares says. “We obviously cannot have 24 scholars speaking at the same time, but we want everyone to feel their ideas matter. Even if I am very shy and I don’t feel comfortable, my voice is still heard.” Once the students have held up the appropriate card, the discussion gets going.
4. Provide Discussion Sentence Starters: Young students often want to add their contribution without connecting it to what their peers have said, writes district-level literacy leader Gwen Blumberg . Keeping an ear out for what students are saying to each other is an important starting point when trying to “lift the level of talk” in your classroom. Are kids “putting thoughts into words and able to keep a conversation going?” she asks.
Introducing sentence starters like “I agree…” or “I feel differently…” can help demonstrate for students how they can connect what their classmate is saying to what they would like to say, which grows the conversation, Blumberg says. Phrases like “I’d like to add…” help students “build a bridge from someone else’s idea to their own.”
Additionally, “noticing and naming the positive things students are doing, both in their conversation skills and in the thinking they are demonstrating,” Orr writes, can shine a light for the class on what success looks like. Celebrating when students use these sentence stems correctly, for example, helps reinforce these behaviors.
“Students’ ability to clearly communicate with others in conversation is a critical literacy skill,” Blumberg writes, and teachers in grades K–2 can get students started on the path to developing this skill by harnessing their natural curiosity and modeling conversation moves.

Online Students
For All Online Programs
International Students
On Campus, need or have Visa
Campus Students
For All Campus Programs
The Importance of Critical Thinking, For Students and Ourselves

Critical thinking is a vital skill, yet it’s often neglected. In higher education, we know the importance of learning objectives that let us measure learner success. Starting with a clear definition of critical thinking allows us to identify the associated skills that we want to imbue in our students and ourselves.
Defining Critical Thinking
According to the Oxford Languages dictionary , critical thinking is “the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgment.” It sounds relatively simple, yet we often form judgments without that all-important objective analysis/evaluation piece.
Employers on the Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU) Social Sciences Advisory Board tell us that they want to hire people with critical thinking skills, but applicants often lack this ability. According to Professor of Science Dr. Norman Herr , critical thinking skills can be boiled down to the following key sequential elements:
- Identification of premises and conclusions — Break arguments down into logical statements
- Clarification of arguments — Identify ambiguity in these stated assertions
- Establishment of facts — Search for contradictions to determine if an argument or theory is complete and reasonable
- Evaluation of logic — Use inductive or deductive reasoning to decide if conclusions drawn are adequately supported
- Final evaluation — Weigh the arguments against the evidence presented
As educators, we must teach our students those critical thinking skills and practice them ourselves to objectively analyze an onslaught of information. Ideas, especially plausible-sounding philosophies, should be challenged and pass the credibility litmus test.
Red Flag Alert
The School Library Journal lists four types of information that should raise red flags when we’re watching the news, reading social media, or at any point in our everyday lives when we are confronted with something purported to be “fact:”
- Fake news, which refers to purported news that is demonstrably untrue.
- Misinformation, which is spread by those who don’t realize that it’s false or only partially true.
- Disinformation, which is deliberately spread by people who know that it’s not accurate and who want to spread a false message.
- Propaganda, which is information that is spread with a specific agenda. It may or may not be false, but it’s intended to get an emotional reaction.
Get With the Times
SNHU, and other colleges and universities across the U.S., must use updated tools to help their students think critically about the information they consume. Currently, many institutions of higher learning fail to teach students how to identify misinformation sources. Sam Wineburg and Nadiv Ziv , professors of education at Stanford University, argue that many colleges offer guides to evaluating website trustworthiness, but far too many of them base their advice on a 1998 report on assessing websites. They warn that it makes no sense for colleges to share 20-year-old advice on dealing with the rapidly-changing online landscape, where two decades feels like a century.
Further, as educators in institutions of higher education, we must afford learners as many opportunities as possible to hone their critical thinking skills when interacting with instructors and fellow students. Greg Lukianoff and Johnathan Haidt , authors of The Coddling of the American Mind , contend that “one of the most brilliant features of universities is that, when they are working properly, they are communities of scholars who cancel out one another’s confirmation biases .” Without exploring opposing viewpoints, students may fall prey to confirmation bias, further cementing ideas that they already believe to be true. Being inclusive when it comes to viewpoint diversity is indispensable for avoiding these echo chambers that circumvent having one’s ideas challenged.
Separating Wheat from Chaff: Critical Thinking Examples
As we teach our students the importance of critical thinking, how do we equip them to sift through the onslaught of information they encounter every day, both personally and in their educational pursuits? And how do we do the same for ourselves?
Here are four critical thinking examples that anyone can apply when evaluating information:
- Consider whether the person who wrote or is sharing the information has any vested interest in doing so. For example, a writer may have a degree and professional experience that gives them expertise to write an article on specific communication techniques. Be aware that the writer’s credibility can be affected by outside interests. These include being paid to write a book with a certain viewpoint, giving paid seminars, affiliation with certain organizations or anything else that creates a financial or personal interest in promoting a specific perspective.
- Consider the venue in which the person is sharing the information. Newscasts and newspapers once were slanted more toward neutrality, although there was never an era when bias was completely absent. The 19th century even had its own version of “clickbait” in the form of yellow journalism . Today, it’s getting more difficult for those with critical thinking skills to find unbiased sources. Websites like Towards Data Science publish lists rating major sites on their leanings; check these lists to view content on biased sites through a more skeptical lens, verifying their claims for yourself.
- Read beyond clickbait headlines. Websites create headlines to generate traffic and ad revenue, not to support critical thinking or give accurate information. Too many people go by what the headline says without reading more deeply, even though media misrepresentation of studies is rampant . Often, the information contained within the article is not accurately represented in the headline. Sometimes there’s even a direct contradiction, or the publication is focusing on one single study that may mean nothing because other studies have contradictory results.
- Use Snopes , Fact Check , and other fact-checking websites. Ironically, Snopes itself has been the victim of misinformation campaigns designed to discredit its efforts to promote the importance of critical thinking.
Anyone in a teaching position should point their students toward reliable references. For example, at SNHU, instructors can point their students towards the Shapiro Library for their assignments. No matter where you teach, the main objective is to give them opportunities to apply critical thinking skills by evaluating material that they encounter in everyday life. Another way to do this at SNHU or in any online classroom is by incorporating elements of the four points into your announcements, discussion posts and feedback. For example, you might post two articles with differing viewpoints on the week’s material. For each, break down the publication’s possible slant, the way in which any research-based material is presented and the author’s credentials. Hypothetically, ask students whether those factors might be playing into the opinions expressed.
Misinformation Morphs into Disinformation
Misinformation, if not addressed, easily turns into disinformation when it is readily shared by students, individuals and groups that may know it is wrong. They may continue to intentionally spread it to cast doubt or stir divisiveness. Students listen to their peers, and the more critical thinking is addressed in a course, the more we prepare students not to fall into the misinformation trap.
Courtney Brown and Sherrish Holland , of the Center for the Professional Education of Teachers, argue that for educators, the challenge is now far more about how they need to inform their students to interpret and assess the information they come across and not simply how to gain access to it. The term “fake news” is used to discredit anyone trying to clarify fact from fiction. Fake news is a cover for some people when they are being deliberately deceptive. As educators become clearer about the distinction, it can be better communicated to students.
Anyone Can Promote Critical Thinking
Even if you don’t teach, use those points in conversations to help others hone their critical thinking skills, along with a dose of emotional intelligence. If someone shares misinformation with you, don’t be combative. Instead, use probing statements and questions designed to spark their critical thinking.
Here are some examples:
“That’s very interesting. Do you think the person they’re quoting might be letting his business interests color what he’s saying?”
“I know that sometimes the media oversimplifies research. I wonder who funded that study and if that’s influencing what they’re saying.”
Of course, you need to adapt to the situation and to make what you say sound organic and conversational, but the core idea remains the same. Inspire the other person to use critical thinking skills. Give them reasons to look more deeply into the topic instead of blindly accepting information. Course activities that stimulate interaction and a deep dive into course-related ideas will encourage perspective-taking and foster new avenues of thought along the path to life-long learning. As American cultural anthropologist Margaret Mead said, “Children must be taught how to think, not what to think.” While Mead was referring to younger children, this statement is apropos for learners in higher education who are tasked with dissecting volumes of information.
It’s crucial to teach our students to question what they read and hear. Jerry Baldasty , provost at the University of Washington, believes that democracies live and die by the ability of their people to access information and engage in robust discussions based upon facts. It is the facts that are being attacked by misinformation. The result is a growing distrust of our core societal institution. People have lost confidence in religious organizations, higher education, government and the media as they believe deliberately deceptive information they come across.
Baldasty argues, “this is why it is crucial that we educate our students how to think critically, access and analyze data, and, above all, question the answers.” Students need critical thinking skills for much more than their self-enlightenment. They will become our leaders, politicians, teachers, researchers, advocates, authors, business owners and perhaps most importantly, voters. The more we can imbue them with critical thinking skills, the better.

Explore more content like this article

Time Management Strategies: 8 Tips for Balancing College and Life

What is a Terminal Degree?

What is an MEd Degree?
About southern new hampshire university.

SNHU is a nonprofit, accredited university with a mission to make high-quality education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Founded in 1932, and online since 1995, we’ve helped countless students reach their goals with flexible, career-focused programs . Our 300-acre campus in Manchester, NH is home to over 3,000 students, and we serve over 135,000 students online. Visit our about SNHU page to learn more about our mission, accreditations, leadership team, national recognitions and awards.
Rahul Education
- 1800 210 1002
- [email protected]
- Alumni Association
- Get Scholarship
- get in touch
- Parents login

THE IMPORTANCE OF CRITICAL THINKING IN EDUCATION
Being a student in 2021 is quite different from being one is 2011. In a span of 10 years, the world of education has witnessed a sea change. As the world keeps facing new challenges, especially due to COVID-19, younger generations, and the education system they are a part of, has also become dynamic. However, there are certain foundations to any education system that has stood the test of time. One key element that has always been stressed upon and practiced by educators in the liberal education spectrum is imparting Critical Thinking skills.
Enhancing a student’s critical thinking skills is particularly essential in a liberal education model, which believes in teaching students how to think and not what to think.
Here are some of the reasons why students need critical thinking skills in today’s age-
Enhancing creativity and curiosity:
A student who is encouraged to be a critical thinker invariably develops a sense of curiosity of happenings around him/her. A strong and genuine sense of curiosity leads to students wanting to analyse and assimilate information and events. In the process, they form their own informed ideas, mostly out-of-the-box ones, that in turn improves their creativity. Creativity is a skill that all critical thinkers will dally with in their professional and personal life. In the process of finding answers in a logical and rational manner, they will usually be able to get their creative juices flowing.
Promoting self-assertion and self-reflection:
Critical thinking is essentially self-disciplined, self-monitored, and self-corrective thinking. When one thinks critically, it is done is a self-directed manner. There is an internalization of the issue at hand and a deep understanding of it in an objective fashion. Critical thinking is at the forefront of learning, as it aids a student reflect and understand their points of views. This skill helps a student figure out how to make sense of the world, based on personal observation and understanding. It makes learners self-assertive and confident as they know that the outcome is the result of a thought process that yields results. Students also gain confidence and the ability to learn from mistakes both of which are crucial in their personal and professional lives.
Boosting career prospects:
Critical thinking is not confined to the classroom. In the aftermath of COVID-19, the new economy places a lot of demand on a flexible workforce and employee’s ability to analyse information from various sources and come up with ingenuous solutions towards the same. An employee with strong critical thinking skills will be valued in a fast-changing workplace.
Nurturing problem-solvers and innovators:
One of the by-products of critical thinking skills is the ability to analyse and look at problems in a creative and constructive method. Critical thinkers are invariably good problem solvers. A good critical thinker will be able to separate facts from opinions and fiction and examine the issue from all angles before making rational decisions towards solving a problem. They will also be able to produce bias free solutions to problems, a fact that is crucial to note in the employment arena. As universal challenges like global warming, pollution, pandemics, continue to plague the world, youngsters of today – who will become the leaders of tomorrow – will be expected to take the mantle of finding effective solutions. Critical thinkers will engineer creative and lasting solutions.
Fostering allied life skills:
Critical thinking fosters allied life skills such as organisational skills, planning, open-mindedness, communication skills among others. Being a life skill by itself, critical thinking enables you to take on challenges in the personal and professional world with ease. It encourages confidence and independence, thereby shaping successful lives. As a critical thinker, one will learn from their mistakes, thereby notching up their productivity in all spheres of life.
As education takes different forms in a world hit by a pandemic, it is extremely crucial for students to possess skills like critical thinking, that will prepare them for tomorrow. After all, children of today are the leaders of tomorrow. Thinking critically boost creativity and enhance the way we use and manage our time and critical thinking not only describes the ability to think in accordance with the rules of logic and probability, but also the ability to apply these skills to real-life problems, which are not content-independent. . Critical thinking can provide you with a more insightful understanding of yourself. It will offer you an opportunity to be objective, less emotional, and more open-minded as you appreciate others’ views and opinions. By thinking ahead, you will gain the confidence to present fresh perspectives and new insights into burden some concerns.
Critical thinking occurs when students are analyzing, evaluating, interpreting, or synthesizing information and applying creative thought to form an argument, solve a problem, or reach a conclusion. The aim of Critical Thinking is to promote independent thinking, personal autonomy and reasoned judgment in thought and action. This involves two related dimensions:
- The ability to reason well and
- The disposition to do so.
Critical thinking involves logic as well as creativity. It may involve inductive and deductive reasoning, analysis and problem-solving as well as creative, innovative and complex approaches to the resolution of issues and challenges. One of the significant aims of education is to produce learners who are well informed, that is to say, learners should understand ideas that are important, useful, beautiful and powerful. Another is to create learners who have the appetite to think analytically and critically, to use what they know to enhance their own lives and also to contribute to their society, culture and civilization. Every pupil should have an effective skill of critical thinking, and they must not accept anything for granted It’s the ability of the child to think about anything and everything. An ability of critical thinking
Critical thinking should be encouraged. Traditional concepts of learning are loosing its charm. Text based passive learning is giving way to active thinking and learning process. The vital goal of education is to promote critical thinking in students, not making them reflect like a parrot. EYFS and KHDA are new terms that aim at improving the quality in education.
It’s really important to instil the ability of critical thinking in children through education. Early Years Foundation Stage is providing better guidance for children at a very tender age, they believe in individual abilities of children. There are Government bodies such as the KHDA in Dubai who takes the responsibility of the growth and quality of private education institutions.
As far as 21st century learning is concerned, critical thinking is an important factor. Spoon-feeding system in education has changed for better. It’s an era of better education.

Dr. Mamta Singh
B.A | B.Ed | M.A | Persuing M.Ed School Principal at Rahul Education, Queen Mary’s High School
WhatsApp us
States Have Restricted Teaching on Social Justice. Is Teacher Preparation Next?

- Share article
When Andrew Spar first started teaching music to elementary students at Turie T. Small Elementary School in Daytona Beach, Fla., he assumed they all would know to be gentle with instruments.
Spar, now president of the Florida Education Association (FEA) and a vice president of the American Federation of Teachers (AFT), quickly learned the importance of understanding the differences between his upbringing and that of the students he served.
He grew up in a middle-class neighborhood in the suburbs of New York City, and was a trained violinist from an early age. But Spar was teaching in a school where he said a majority of students lived in poverty, he said, and his students hadn’t had the same opportunities to play instruments like he had.
The concept of preparing teachers to understand their students’ backgrounds—and how systemic racism and sexism impact those backgrounds—has been a growing feature of many teacher-preparation programs, some of which pride themselves on integrating social justice themes into their coursework.
Now, that’s being called into question as more state legislatures take aim at how those issues can be taught in teacher preparation. The efforts have left educators and advocates concerned it will encompass culturally responsive teaching methods, and fearing it will ultimately negatively impact student learning.
Earlier this month, Florida Republican Gov. Ron DeSantis signed into law a measure prohibiting teacher training and education preparation programs from delving into “identity politics,” and teaching that “systemic racism, sexism, oppression, and privilege are inherent in the institutions of the United States and were created to maintain social, political, and economic inequities.”
The measure was part of an effort to “fight back against indoctrination in education and the workplace,” DeSantis said in a news release. It appears to build on the state’s other similar efforts, including a law that restricts what teachers can say about LGBTQ+ individuals in their classrooms.
(DeSantis’ office did not respond to a request for comment before publication.)
Republican Florida Rep. Berny Jacques, a sponsor of the legislation, said in an email to EdWeek that the legislation addressed concerns lawmakers have about teaching about race and oppression.
“This legislation will allow students to be taught by teachers focused on delivering exceptional education,” he said.
The recent Florida law is part of a larger, years-long effort to restrict discussions of racism or sexism in schools, taking particular aim at educator preparation. Broadly, at least nine states have enacted legislation in the last three years to prohibit mandatory professional development or training of public school teachers on topics such as racism or sexism, according to data from the National Conference of State Legislatures. Legislation is pending in at least four others.
Several states have introduced similar bills or taken other steps that would limit how teachers can discuss racism and sexism in the classroom . Those efforts have faced legal challenges in some states, even as some social studies groups have started training teachers to navigate these so-called “divisive concepts” laws . However, momentum has largely been slowing for measures targeting “divisive concepts,” and research has found most lessons are kept politically neutral.
Spar said he had to learn to adapt to his students’ backgrounds to effectively teach them early in his teaching career. (The FEA, a major political opponent of DeSantis, criticized the Florida legislation as harmful.)
“I think it’s just so important, and it required me to really open my horizons and open my view of the world so that I could better interact and support the students I was teaching,” he said. “It’s something you have to be able to do if you’re going to truly connect with the kids, and it doesn’t happen unless we’re deliberately having that discussion.”
Educators worry the legislation will impact student learning
Dr. Kai Mathews, the director of the California Educator Diversity Project at the University of California, Los Angeles’ Center for the Transformation of Schools, says it’s taken time for teacher-preparation courses to begin embedding culturally responsive teaching. The 2020 racial reckoning following the public killing of George Floyd and protests of injustices against Black people nationwide fueled that work, she said.
“It’s not just for the historical knowledge and facts. It is also when we’re including students from a diverse background, to see themselves in the making up, and in the composite of, history and of society, and we’re bringing it into the classroom,” Mathews said. “There’s a relatability that then comes with the content that we’re teaching. It’s not just math for math’s sake.”
With schools facing a student chronic absenteeism crisis and competing with student apathy , connecting students to their education is even more vital, she said.
“I don’t know how many more ways students need to show us that disengagement is attached to our inability to make our education relevant and meaningful,” she said.
Dr. Omiunota N. Ukpokodu, a professor of education at the University of Missouri, Kansas City, said so often she hears from student teachers that their classes are struggling academically, with many testing two grades below their level. She pointed to the 2023 results of the National Assessment of Educational Progress, which showed a significant decrease in 8th grade students’ civics scores.
There’s a gap caused by teachers being afraid to teach critically about racism in the wake of laws restricting class discussions, she said. That’s troubling when the U.S. is multicultural and multiracial, and the world is becoming more and more interdependent, she said.
“How are they being prepared to take this responsibility of preparing the young for the world that we live in, that they will be part of in a workforce that is diverse? How can they learn to become participatory citizens when they don’t have the critical thinking skills that they need to engage?” she said.
Sign Up for The Savvy Principal
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Why writing by hand beats typing for thinking and learning
Jonathan Lambert

If you're like many digitally savvy Americans, it has likely been a while since you've spent much time writing by hand.
The laborious process of tracing out our thoughts, letter by letter, on the page is becoming a relic of the past in our screen-dominated world, where text messages and thumb-typed grocery lists have replaced handwritten letters and sticky notes. Electronic keyboards offer obvious efficiency benefits that have undoubtedly boosted our productivity — imagine having to write all your emails longhand.
To keep up, many schools are introducing computers as early as preschool, meaning some kids may learn the basics of typing before writing by hand.
But giving up this slower, more tactile way of expressing ourselves may come at a significant cost, according to a growing body of research that's uncovering the surprising cognitive benefits of taking pen to paper, or even stylus to iPad — for both children and adults.
Is this some kind of joke? A school facing shortages starts teaching standup comedy
In kids, studies show that tracing out ABCs, as opposed to typing them, leads to better and longer-lasting recognition and understanding of letters. Writing by hand also improves memory and recall of words, laying down the foundations of literacy and learning. In adults, taking notes by hand during a lecture, instead of typing, can lead to better conceptual understanding of material.
"There's actually some very important things going on during the embodied experience of writing by hand," says Ramesh Balasubramaniam , a neuroscientist at the University of California, Merced. "It has important cognitive benefits."
While those benefits have long been recognized by some (for instance, many authors, including Jennifer Egan and Neil Gaiman , draft their stories by hand to stoke creativity), scientists have only recently started investigating why writing by hand has these effects.
A slew of recent brain imaging research suggests handwriting's power stems from the relative complexity of the process and how it forces different brain systems to work together to reproduce the shapes of letters in our heads onto the page.
Your brain on handwriting
Both handwriting and typing involve moving our hands and fingers to create words on a page. But handwriting, it turns out, requires a lot more fine-tuned coordination between the motor and visual systems. This seems to more deeply engage the brain in ways that support learning.

Shots - Health News
Feeling artsy here's how making art helps your brain.
"Handwriting is probably among the most complex motor skills that the brain is capable of," says Marieke Longcamp , a cognitive neuroscientist at Aix-Marseille Université.
Gripping a pen nimbly enough to write is a complicated task, as it requires your brain to continuously monitor the pressure that each finger exerts on the pen. Then, your motor system has to delicately modify that pressure to re-create each letter of the words in your head on the page.
"Your fingers have to each do something different to produce a recognizable letter," says Sophia Vinci-Booher , an educational neuroscientist at Vanderbilt University. Adding to the complexity, your visual system must continuously process that letter as it's formed. With each stroke, your brain compares the unfolding script with mental models of the letters and words, making adjustments to fingers in real time to create the letters' shapes, says Vinci-Booher.
That's not true for typing.
To type "tap" your fingers don't have to trace out the form of the letters — they just make three relatively simple and uniform movements. In comparison, it takes a lot more brainpower, as well as cross-talk between brain areas, to write than type.
Recent brain imaging studies bolster this idea. A study published in January found that when students write by hand, brain areas involved in motor and visual information processing " sync up " with areas crucial to memory formation, firing at frequencies associated with learning.
"We don't see that [synchronized activity] in typewriting at all," says Audrey van der Meer , a psychologist and study co-author at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. She suggests that writing by hand is a neurobiologically richer process and that this richness may confer some cognitive benefits.
Other experts agree. "There seems to be something fundamental about engaging your body to produce these shapes," says Robert Wiley , a cognitive psychologist at the University of North Carolina, Greensboro. "It lets you make associations between your body and what you're seeing and hearing," he says, which might give the mind more footholds for accessing a given concept or idea.
Those extra footholds are especially important for learning in kids, but they may give adults a leg up too. Wiley and others worry that ditching handwriting for typing could have serious consequences for how we all learn and think.
What might be lost as handwriting wanes
The clearest consequence of screens and keyboards replacing pen and paper might be on kids' ability to learn the building blocks of literacy — letters.
"Letter recognition in early childhood is actually one of the best predictors of later reading and math attainment," says Vinci-Booher. Her work suggests the process of learning to write letters by hand is crucial for learning to read them.
"When kids write letters, they're just messy," she says. As kids practice writing "A," each iteration is different, and that variability helps solidify their conceptual understanding of the letter.
Research suggests kids learn to recognize letters better when seeing variable handwritten examples, compared with uniform typed examples.
This helps develop areas of the brain used during reading in older children and adults, Vinci-Booher found.
"This could be one of the ways that early experiences actually translate to long-term life outcomes," she says. "These visually demanding, fine motor actions bake in neural communication patterns that are really important for learning later on."
Ditching handwriting instruction could mean that those skills don't get developed as well, which could impair kids' ability to learn down the road.
"If young children are not receiving any handwriting training, which is very good brain stimulation, then their brains simply won't reach their full potential," says van der Meer. "It's scary to think of the potential consequences."
Many states are trying to avoid these risks by mandating cursive instruction. This year, California started requiring elementary school students to learn cursive , and similar bills are moving through state legislatures in several states, including Indiana, Kentucky, South Carolina and Wisconsin. (So far, evidence suggests that it's the writing by hand that matters, not whether it's print or cursive.)
Slowing down and processing information
For adults, one of the main benefits of writing by hand is that it simply forces us to slow down.
During a meeting or lecture, it's possible to type what you're hearing verbatim. But often, "you're not actually processing that information — you're just typing in the blind," says van der Meer. "If you take notes by hand, you can't write everything down," she says.
The relative slowness of the medium forces you to process the information, writing key words or phrases and using drawing or arrows to work through ideas, she says. "You make the information your own," she says, which helps it stick in the brain.
Such connections and integration are still possible when typing, but they need to be made more intentionally. And sometimes, efficiency wins out. "When you're writing a long essay, it's obviously much more practical to use a keyboard," says van der Meer.
Still, given our long history of using our hands to mark meaning in the world, some scientists worry about the more diffuse consequences of offloading our thinking to computers.
"We're foisting a lot of our knowledge, extending our cognition, to other devices, so it's only natural that we've started using these other agents to do our writing for us," says Balasubramaniam.
It's possible that this might free up our minds to do other kinds of hard thinking, he says. Or we might be sacrificing a fundamental process that's crucial for the kinds of immersive cognitive experiences that enable us to learn and think at our full potential.
Balasubramaniam stresses, however, that we don't have to ditch digital tools to harness the power of handwriting. So far, research suggests that scribbling with a stylus on a screen activates the same brain pathways as etching ink on paper. It's the movement that counts, he says, not its final form.
Jonathan Lambert is a Washington, D.C.-based freelance journalist who covers science, health and policy.
- handwriting
K-12 Resources By Teachers, For Teachers Provided by the K-12 Teachers Alliance
- Teaching Strategies
- Classroom Activities
- Classroom Management
- Technology in the Classroom
- Professional Development
- Lesson Plans
- Writing Prompts
- Graduate Programs
The Importance of Art Class
Janelle cox.
- May 24, 2024

In today’s technology-driven classrooms , art remains an important component of student development. Despite often being the first to be cut from the curriculum in some schools, dismissed as a luxury, or merely a source of fridge-worthy projects, art education holds profound benefits.
From fostering cognitive abilities and emotional resilience to enhancing academic performance and learning lifelong skills, art class provides much more than just a creative outlet. Here, we’ll explore why art class is so essential and how to make it more accessible to all students.
Cognitive Skills
Art classes play a critical role in developing a student’s cognitive skills. They encourage creativity, allowing students to express themselves in a different way other than writing. This freedom promotes innovative thinking. It also helps to develop students’ critical thinking skills.
As students look at their work and that of their classmates, they learn to observe, analyze, and make judgments, which are all valuable skills students will use in all aspects of their lives. Art classes can also enhance students’ visual-spatial skills. When students are drawing, painting, or creating sculptures they need to understand space and perspective which are skills they need if they ever go into fields like architecture or engineering.
Social-Emotional Learning
Art class extends beyond a student’s cognitive development, it can also impact their social- emotional learning . Artistic activities can tap into students’ feelings so if they have a hard time vocalizing their feelings, they may be better able to express themselves through art.
This can feel therapeutic and help to build their self-confidence. It can also release any anxiety and stress they may be feeling. Art can also promote empathy. When students explore different art forms and learn different cultural and personal perspectives, they have a better understanding of other people’s experiences.
Academic Achievement
Various studies conducted over the years have shown a correlation between art education and academic achievement. Reports from organizations like the Arts Education Partnership and the National Endowment for the Arts in the United States suggest that the arts are linked to improved test scores, enhanced reading and language skills, and higher rates of going to and completing college. Additional findings show artistic activities enhance memory and attention to detail. Integrating art with other subjects, referred to now as STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics) can help make learning more relatable and deepen students’ understanding and retention.
Lifelong Skills
The skills learned in art class extend far beyond the classroom. In today’s job market creativity is valued. Employers are seeking individuals who are innovative, creative, and who think outside of the box. This need for creative thinking is ranked as a top skill for future professionals. Additionally, art class teaches risk-taking and resilience. By continually taking creative risks students are developing resilience which can help them with any challenges they may face in the future.
Cultural Awareness and Appreciation
When students are engaged with art forms from different cultures , they gain a deeper understanding of global cultures. They learn to respect and value different viewpoints and traditions. By creating and discussing art from various backgrounds, students dispel stereotypes and prejudices, promoting a society that is more inclusive and empathetic to others.
Making Art Class Accessible
Art classes are not always accessible to all students. This may be driven by socioeconomic status, school funding, or geographic location. Ensuring that every student has access to art education is crucial for a student’s well-rounded academic experience. Here are a few approaches to achieve this goal.
Invest in Art
One way to make art classes universally accessible is to invest in art programs. Allocate funds for basic supplies and materials that will inspire students to create as well as invest in professional development for teachers. Teachers who have a background in art education will help foster a greater appreciation for the arts among students.
Integrate Art
Art can be integrated into the core curriculum to ensure all students have access to art education. STEAM education combining art with other core curricula can become fundamental to every child’s educational experience.
Utilize Technology
Art education can be made more accessible through technology. Digital tools can bring art classes to children across the globe. Virtual classes mean students can learn, create, and share their work with anyone worldwide.
Form Partnerships within the Community
Partnerships with local art galleries and artists can provide schools with additional resources. These partnerships might involve professional artists working with students, or collaborations with local museums that offer field trips or workshops. Community involvement enhances the school’s art program and strengthens the community culture.
Art class is a vital part of a child’s educational experience. It nurtures cognitive, social, and emotional skills, boosts academic achievements, makes them more culturally aware, and prepares students with skills they will use throughout their lives. Making art education accessible for all students should be a priority for all leaders and administrators .
- #ArtClass , #Classroom Management
More in Classroom Management

Beyond Monkey Bars: The Vital Role of Recess in Child Development
Do students need recess? This question has been discussed for years among parents and educators….

Brain Breaks: The Science Behind it and the Benefits
The Science Behind Brain Breaks Most educators experience students’ glazed eyes, heads down,…

Classroom Attention-Getters to Use for Engaging Students
For many teachers, classroom management is a challenge. Without various strategies in your…

Unmute the Classroom: Unleashing the Power of Student Participation
The silence of unengaged students who are hesitant to raise their hands or…
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Handwashing
- Hand Hygiene as a Family Activity
- Hand Hygiene FAQs
- Handwashing Facts
- Publications, Data, & Statistics
- Health Promotion Materials
- Global Handwashing Day
- Clean Hands and Spaces: Handwashing and Cleaning in Educational Facilities
- Life is Better with Clean Hands Campaign
- Clinical Safety
- Healthcare Training
- Clean Hands Count Materials
About Handwashing
- Many diseases and conditions are spread by not washing hands with soap and clean, running water.
- Handwashing with soap is one of the best ways to stay healthy.
- If soap and water are not readily available, use a hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol to clean your hands.

Why it's important
Washing hands can keep you healthy and prevent the spread of respiratory and diarrheal infections. Germs can spread from person to person or from surfaces to people when you:
- Touch your eyes, nose, and mouth with unwashed hands
- Prepare or eat food and drinks with unwashed hands
- Touch surfaces or objects that have germs on them
- Blow your nose, cough, or sneeze into hands and then touch other people's hands or common objects
Key times to wash hands
You can help yourself and your loved ones stay healthy by washing your hands often, especially during these key times when you are likely to get and spread germs:
- Before, during, and after preparing food
- Before and after eating food
- Before and after caring for someone at home who is sick with vomiting or diarrhea
- Before and after treating a cut or wound
- After using the toilet
- After changing diapers or cleaning up a child who has used the toilet
- After blowing your nose, coughing, or sneezing
- After touching an animal, animal feed, or animal waste
- After handling pet food or pet treats
- After touching garbage
How it works
Washing your hands is easy, and it’s one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of germs. Follow these five steps every time.
- Wet your hands with clean, running water (warm or cold), turn off the tap, and apply soap.
- Lather your hands by rubbing them together with the soap. Lather the backs of your hands, between your fingers, and under your nails.
- Scrub your hands for at least 20 seconds . Need a timer? Hum the “Happy Birthday” song from beginning to end twice.
- Rinse your hands well under clean, running water.
- Dry your hands using a clean towel or an air dryer.
Use hand sanitizer when you can't use soap and water
Washing hands with soap and water is the best way to get rid of germs in most situations. If soap and water are not readily available, you can use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer that contains at least 60% alcohol. You can tell if the sanitizer contains at least 60% alcohol by looking at the product label.
What you can do
CDC has health promotion materials to encourage kids and adults to make handwashing part of their everyday lives.
- Share social media graphics and messages.
- Print stickers and place clings on bathroom mirrors.
- Promote handwashing on or around Global Handwashing Day , celebrated each year on October 15.
- Distribute fact sheets to share information about hand hygiene for specific audiences.
- Frequent Questions About Hand Hygiene
- Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Settings
- The Life is Better with Clean Hands Campaign
Clean Hands
Having clean hands is one of the best ways to avoid getting sick and prevent the spread of germs to others.
For Everyone
Health care providers.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A complete guide to teaching Critical Thinking. This 180 page e-book is an excellent resource for teachers looking to implement critical thinking in the classroom. It is packed full of great content whether you are just starting out, or looking to go further. It makes relevant connections to technology, STEM, and critical and creative thinking.
In a time where deliberately false information is continually introduced into public discourse, and quickly spread through social media shares and likes, it is more important than ever for young people to develop their critical thinking. That skill, says Georgetown professor William T. Gormley, consists of three elements: a capacity to spot ...
Critical thinking is a key skill that goes far beyond the four walls of a classroom. It equips students to better understand and interact with the world around them. Here are some reasons why fostering critical thinking is important: Making Informed Decisions: Critical thinking enables students to evaluate the pros and cons of a situation ...
The Foundation for Critical Thinking says, "Critical thinking can be seen as having two components: 1) a set of information and belief-generating and processing skills, and 2) the habit, based on intellectual commitment, of using those skills to guide behavior.". In other words, good critical thinkers know how to analyze and evaluate ...
Developing critical thinking is an important educational goal for all grade levels today. As the hallmark of the Western tradition of schooling originating from the Greeks to the Scholastics [], critical thinking is related to the idea of rationality, which is regarded as a significant aim of modern education.While earlier definitions of critical thinking go back to as early as the beginning ...
Critical thinking blasts through the surface level of a topic. It reaches beyond the who and the what and launches students on a learning journey that ultimately unlocks a deeper level of ...
Teach Reasoning Skills. Reasoning skills are another key component of critical thinking, involving the abilities to think logically, evaluate evidence, identify assumptions, and analyze arguments. Students who learn how to use reasoning skills will be better equipped to make informed decisions, form and defend opinions, and solve problems.
Equally, the importance of teachers thinking critically is well established. Dewey (Citation 1910) regarded critical thinking as a vital element of teachers' work: 'Only by taking a hand in the making of knowledge, by transferring guess and opinion into the belief authorised by inquiry, does one ever get a knowledge of the method of knowing'.
Since teachers tend to replicate the educational models they have experienced as students, new references are needed. In order to address these concerns, we present an interdisciplinary intervention in initial teacher education and analyse its impact on teachers' critical thinking and awareness of the importance to promote it.
Teacher education as a powerful mediator in CT instruction. Based on the above review and discussion, we, as teacher educators and CT researchers, hold a firm belief that teacher education can serve as a powerful mediator that can bridge the theory-practice divide and provide a full-fledged CT experience that benefits our students' academic development and life-long learning.
Students grappled with ideas and their beliefs and employed deep critical-thinking skills to develop arguments for their claims. Embedding critical-thinking skills in curriculum that students care ...
1. Introduction. Different education systems have highlighted the importance of citizens acquiring the necessary skills to participate in an ever-changing and increasingly-complex world (Pellegrino & Hilton, 2012).This includes critical thinking, which is thought to strengthen democracies and allow citizens to actively participate in an economy that requires increasing levels of preparation ...
Critical thinking can help you better understand yourself, and in turn, help you avoid any kind of negative or limiting beliefs, and focus more on your strengths. Being able to share your thoughts can increase your quality of life. 4. Form Well-Informed Opinions.
1. Identifying a problem and asking questions about that problem. 2. Selecting information to respond to the problem and evaluating it. 3. Drawing conclusions from the evidence. Critical thinking can be developed through focussed learning activities. Students not only need to receive information but also benefit from being encouraged to think ...
Decades of cognitive research point to a disappointing answer: not really. People who have sought to teach critical thinking have assumed that it is a skill, like riding a bicycle, and that, like other skills, once you learn it, you can apply it in any situation. Research from cognitive science shows that thinking is not that sort of skill.
It makes you a well-rounded individual, one who has looked at all of their options and possible solutions before making a choice. According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [ 1 ]: Universal. Crucial for the economy. Essential for improving language and presentation skills.
educating good critical thinkers of " a rational and democratic society " [19, p. 3]. In addition to. this definition, the experts developed a taxonomy including six core cognitive skills, namely ...
Critical thinking is a crucial skill for students to develop in school. It is the ability to think deeply, logically, and independently about a topic, problem, or situation. The importance of critical thinking in education cannot be overstated, as it empowers students to become more effective learners, thinkers, and problem-solvers. 5 Reasons Why Critical Thinking
In this post, we share five strategies for teaching critical thinking - or higher order thinking skills - in your classroom. ... 4 reasons why critical thinking skills are important. 1. Learners with better critical thinking are more prepared for the workforce. 2. Critical thinking skills can predict academic success in university.
In a nutshell, critical thinking and problem-solving skills are a part of '21st Century Skills' that can help unlock valuable learning for life. Over the years, the education system has been ...
Teachers can foster critical thinking in the early elementary grades by guiding students to develop their conversation skills. ... a kindergartner spotted an ant and asked the teacher, "Why do ants come into the classroom?" ... Keeping an ear out for what students are saying to each other is an important starting point when trying to ...
Critical thinking occurs when students are. analyzing, evaluating, in terpreting, or synthesizing information and applying. creative thought to form an argument, solve a problem, or reach a ...
According to the Oxford Languages dictionary, critical thinking is "the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgment.". It sounds relatively simple, yet we often form judgments without that all-important objective analysis/evaluation piece. Employers on the Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU) Social ...
Critical thinking occurs when students are analyzing, evaluating, interpreting, or synthesizing information and applying creative thought to form an argument, solve a problem, or reach a conclusion. The aim of Critical Thinking is to promote independent thinking, personal autonomy and reasoned judgment in thought and action.
There's a gap caused by teachers being afraid to teach critically about racism in the wake of laws restricting class discussions, she said. That's troubling when the U.S. is multicultural and ...
As schools reconsider cursive, research homes in on handwriting's brain benefits : Shots - Health News Researchers are learning that handwriting engages the brain in ways typing can't match ...
Art classes play a critical role in developing a student's cognitive skills. They encourage creativity, allowing students to express themselves in a different way other than writing. This freedom promotes innovative thinking. It also helps to develop students' critical thinking skills. As students look at their work and that of their ...
Drowning is the process of experiencing respiratory impairment from submersion or immersion in liquid. Drowning happens when a person's nose and mouth are under water for too long, making it impossible to breath. Drowning is not always fatal. Fatal drowning happens when the drowning results in death. Nonfatal drowning happens when a person ...
Why it's important. Washing hands can keep you healthy and prevent the spread of respiratory and diarrheal infections. Germs can spread from person to person or from surfaces to people when you: Touch your eyes, nose, and mouth with unwashed hands. Prepare or eat food and drinks with unwashed hands. Touch surfaces or objects that have germs on them