You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.

The Complete Guide to English Sentence Structure
By learning some easy English sentences, you are setting yourself up for understanding all English conversations .
Even the most complicated sentences start with a simple sentence structure . A sentence is created by combining a set of words to make a complete, grammatically correct communication.
Learn these basic English sentence structures, and you will be learning a valuable lesson —no matter your level of English.
How to Understand Any English Sentence
How to make your own english sentences, 18 easy formulas to build english sentences, making statements about the present, 1. describing something or someone., 2. stating the location of something or someone., 3. explaining what someone is doing., 4. stating what someone does for a living or a hobby., 5. expressing feelings., 6. making a suggestion., making statements about the past, 7. describing something or someone in the past., 8. stating the location of something or someone in the past., 9. explaining what someone did, or used to do in the past., making statements about the future, 10. stating what someone will do in the future., 11. stating when something will happen., making negative statements, 12. stating what someone is not, or not doing., 13. stating what someone did not do., 14. stating what someone will not do in the future., asking questions, 15. asking where someone is., 16. asking what someone is doing., 17. asking about when something will happen., 18. asking who is doing something., example sentences , mastering english introductions, everyday, conversational english phrases, talking about learning english, everyday english phrases for shopping, simple english sentences for your job, and one more thing....
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
To understand easy English sentences, you need to break them down into even smaller parts.
Sentences are made up of words. More specifically, they are made up of parts of speech . A part of speech defines what a word does in a sentence.
The parts of speech are:
- Noun : A noun is a person, place or thing. Examples: Cat, table, king.
- Pronoun : A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Examples: He, she, they.
- Verb : A verb is an action word. Examples: Swim, is, write.
- Adjective : An adjective word that modifies (changes) or describes a noun or another adjective. Examples: Beautiful, white, shiny.
- Adverb : An adverb is a word that modifies or describes a verb. (It shows how something is done.) Examples: Quickly, carefully, brightly.
- Preposition : A preposition is a word that describes the relationship to a noun. Examples: From, under, until.
- Conjunction : A conjunction is a connecting word. Examples: And, but, although.
These terms will be important later in this post, in your English studies and in whichever English situations you find yourself in, whether with friends, at school or at work!
Now you need to learn how to combine parts of speech to form your sentence. A sentence has a subject (the person, place or thing that the sentence is about) and an action (what the subject is doing). Together, they express a complete thought. Even the shortest complete sentence in the English language follows this rule:
“I am.” (“I” is the subject, “am” is the action!)
Here is another simple sentence:
“I ate.”
Once you have your subject and action, you can start to add more detail. You can add an object (whoever or whatever the action is being done to):
“I ate a hamburger .”
Or you can add a description:
“I ate a delicious hamburger.”
Sometimes you can even add more subjects and actions:
“I ate a delicious hamburger, but my friend only ate some fries.”
When you are trying to understand a sentence, you can use the above knowledge to break it into smaller pieces. You can also use this information to create the most basic sentences.
Take note of this basic form, as well as the sentence formulas below, when you’re reading, watching or listening to English content. Practice with movie clips, podcasts or any other content that you enjoy.
Pause English media and repeat the sentences. Be active in your learning! You can also use a language learning program to help you along, of course.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
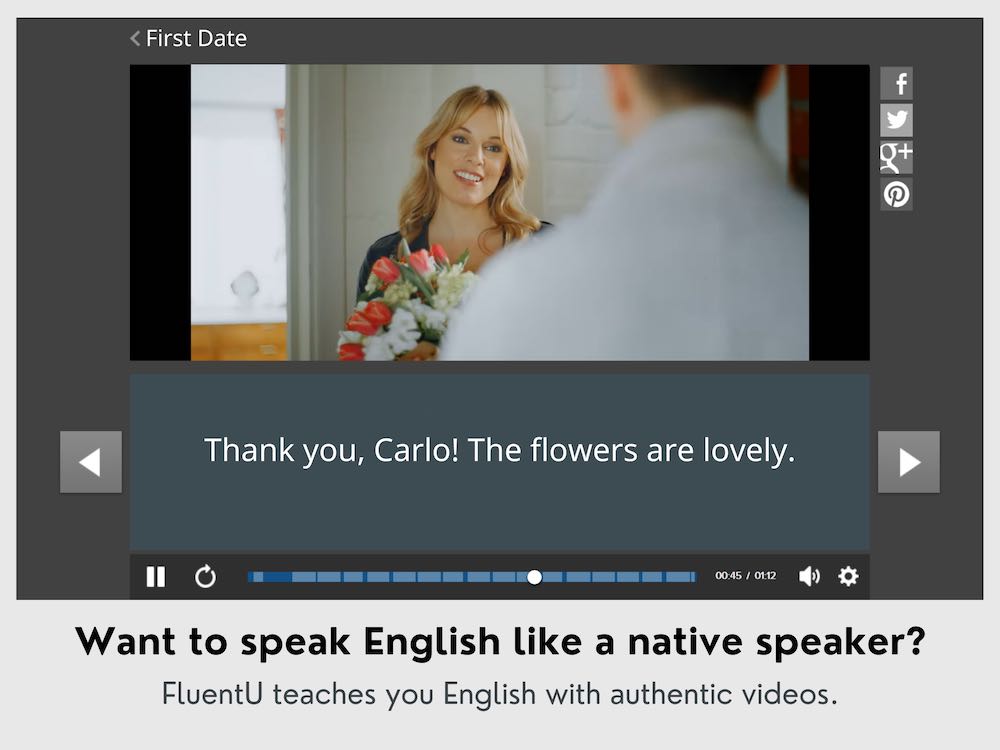
Try FluentU for FREE!
Before you begin, there are two things you should know about this guide:
1. Whenever we use [noun], you can replace it with a [pronoun]. For example, you can say “Sam is tired,” or you can say “He is tired.” Both are correct.
2. Whenever we use “is,” you will need to replace it with the correct form of “to be.” Choose the right form based on this list for the present tense:
- He / she / it is .
- You / they / we are .
And this list for the past tense:
- I / he / she / it was .
- You / they / we were .
That’s all! Now you are ready to begin.
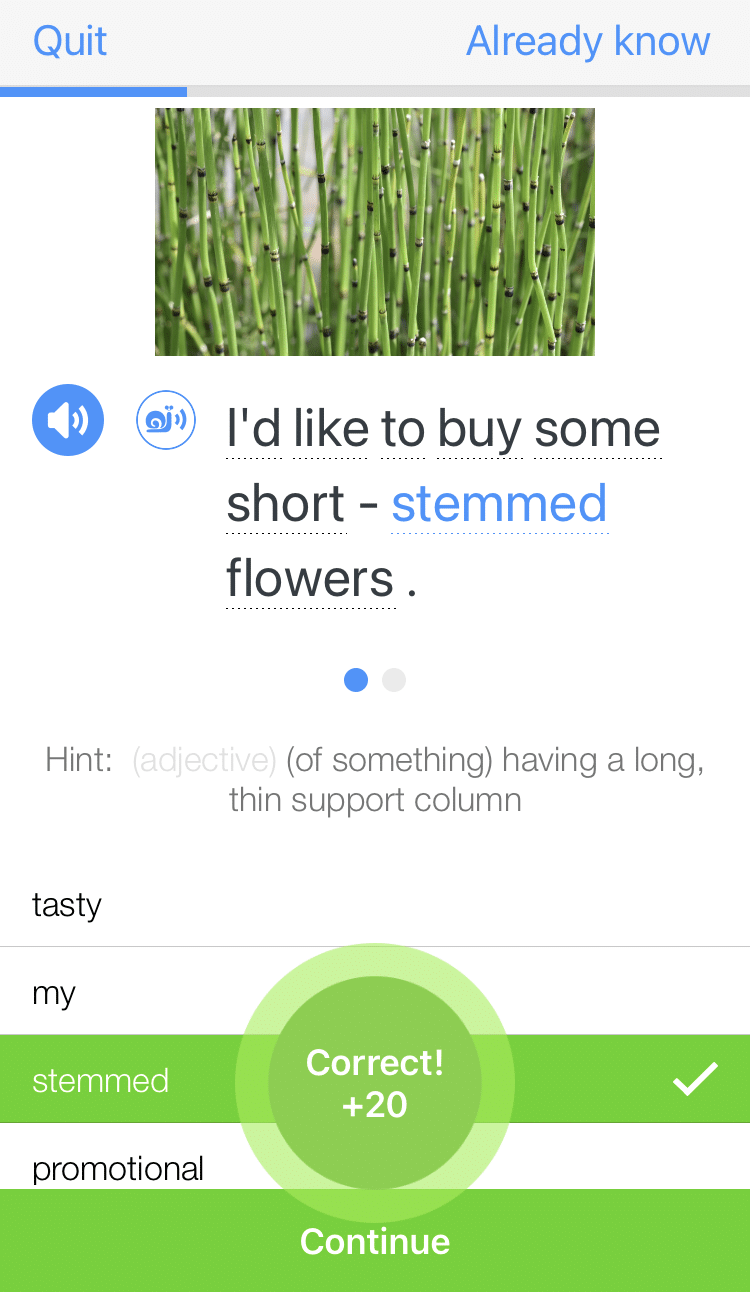
Form: [Noun] is [adjective].
Notes: If the noun you are using is not a pronoun (the name of a place or the name of a person), add the word “the” (or “this,” or “that”) before it.
- The flower is red.
- You are wonderful.
- The Empire State Building is tall.
Form: [Noun] is [preposition] [location].
Notes: To state the location of something or someone, a preposition is usually necessary. Choose the correct preposition to give the right information. You can also say someone was “here” or “over there.” Since these terms are relative (their meaning depends on your own location), you do not need to add the final “location.”
Once again, nouns that are not names of people or places get “the” added before them.
- The cat is under the bed.
- Charlie is next to Anne.
- He is on the train.
- The dog is here.
- The men are over there.
Form: [Noun] is [verb -ing].
Notes: The “-ing” form of a verb means an action is taking place right now. Use this form when talking about an action that has not ended yet.
- He is reading.
- The cat is napping.
- Kate is singing.
Form: [Noun] [verb -s].
Notes: Using this structure implies the subject of your sentence does the action regularly (like a hobby, or a job), even if they are not necessarily doing it right now.
- The cat naps.
- Kate sings.
Form: [Noun] [feeling verb -s] [noun]. / [Noun] [feeling verb -s] [to verb / verb -ing].
Notes: Feeling verbs include verbs like “love,” “like” or “hate.” You can love or hate an object, or an action. When you describe someone’s feelings about an action, you can use either the “to verb ” or “ verb -ing” forms. In most cases, both are correct!
You can also use this form to describe needs and wants, but remember that in that case, the “verb -ing” form cannot be used. For example, you don’t “need sleeping.” You “need to sleep,” or just “need sleep.”
- I love sunshine.
- The elephant likes painting.
- Tom hates his job.
- I need to eat.
- I want food.
- She wants to sleep.
- She needs sleep.
Form: Let’s [verb]. / Please [verb].
Notes: To suggest an action that you will also take part in, use the first structure. To politely ask someone to do something, use the second one.
- Let’s eat.
- Please eat.
- Please move. (Please note: This might be grammatically correct, but it is actually not very polite! The polite way to ask someone to move is to say “excuse me.”)
Form: [Noun] was [adjective].
Notes: You describe someone in the past tense almost the same exact way as in the present—just change the “is” to “was.” Using this structure suggests that either the description is no longer accurate, or that the description is for a specific moment.
- The flower was red. (…It is not red anymore.)
- You were wonderful. (…You played the violin so well in the concert.)
- The Empire State Building was tall. (…Until the giant apes tore it down.)
Form: [Noun] was [preposition] [location].
Notes: As with a description, describing a location in the past and the present is very similar. The rules remain the same; only the verb tense changes. Remember, again, that using this form means the location has changed, or that the statement was only true for a specific time period in the past.
- The cat was under the bed. (…But then it ran away.)
- Charlie was next to Anne. (…Then he went behind her.)
- He was on the train. (…That is how he knew the train was going to be late.)
- The dog was here. (…But then its owner took it away.)
- The men were over there. (…Until they finished their job and went home.)
Form: [Noun] was [verb -ing]. / [Noun] [verb -ed].
Notes: There is a slight difference between the “verb -ed” form of an action, and the “was verb -ing” form.
- Using the “verb -ed ” form describes something that has finished happening .
- Using the “ -ing ” form of a verb describes something that was happening during a specific period of time in the past .
Another form you can use is: [Noun] used [to verb]. This form is used for any kind of action that someone used to do in the past, but has since stopped doing.
All these forms can be used with feeling verbs, as well! Just add the “noun” or “verb -ing” after the feeling verb for a complete sentence.
- The cat napped. (…That’s why he is so happy now.)
- Kate sang. (…The concert was wonderful.)
- He was reading. (…That is why he did not hear the doorbell ring.)
- The Statue of Liberty used to shine. (…But being in the salty water all those years has made it green.)
- I used to love shrimp. (…But then I learned that I am allergic to it.)
- Sally hated swimming. (…She had to do it every day in school.)
Form: [Noun] is going to [verb]. / [Noun] will [verb].
Notes: The great thing about the future tense is that you don’t need to remember any verb forms! To turn a sentence into the future tense, just add the words “is going to” or “will” before the verb. Using this structure without any additional details means you will be doing the action very soon.
- I am going to dance.
- We are going to eat.
- The baby is going to sleep.
Form: [Noun] will [verb] [preposition] [time]. / [Noun] is going to [verb] [time adverb].
Notes: Use this structure to talk about things that will happen in the future. When you use a specific time, a preposition is needed.
- Use “ at ” when stating a clock time , and “ on ” when stating a day or date .
- Use “ in ” when stating a year , month or another time frame (like “a couple of years” or “two minutes”).
- When you use a time adverb like today, tomorrow or yesterday , you don’t need a preposition .
- The train will leave at 5:00 AM.
- I will visit my parents in October.
- Anthony is going to dance tomorrow.
Form: [Noun] is not [adjective / verb-ing].
Notes: Changing a sentence into a negative one is as easy as adding the word “not.”
- The flower is not red. (…It is white.)
- You are not wonderful. (…That’s not very nice!)
- The Empire State Building is not tall. (…We never said the sentence has to be true!)
- Kate is not singing. (…Why did she stop?)
Form: [Noun] did not [verb]. / [Noun] was not [verb -ing].
Notes: Remember the rules from before. Using the first form above puts the focus on the action (in this case, saying it did not happen at all). “Verb -ing” puts the focus on the time the action took place (saying it was not happening at a specific moment).
- I did not sleep. (…I stayed awake all night.)
- I was not sleeping. (…While the teacher gave her lesson.)
- The customer did not pay. (…At all. How terrible!)
Form: [Noun] is not going to [verb]. / [Noun] will not [verb].
Notes: Changing the future tense into a negative sentence is just as easy. Just add “not” before the verb.
- I am not going to eat. (…I will not eat green eggs and ham !)
- Sam will not dance. (…He has ants in his pants .)
- The cat will not nap. (…He is going to eat first.)
Form: Where is [noun]?
Notes: You can also use this form to ask about places, things and any other kind of noun you might be trying to find.
- Where is the dog?
- Where is George?
- Where is the bathroom?
Form: What is [noun] doing?
Notes: The noun in this case should be a living thing. (Generally, non-living objects don’t do much!)
- What is that dog doing?
- What is Sal doing?
- What is the baby doing?
Form: When will [noun] [verb]?
Notes: This is a useful sentence structure to know when you want to find out about events in the future.
- When will the train leave?
- When will Fran visit?
- When will your mom call?
Form: Who is [verb -ing]? / Who is [verb -ing] [noun]?
Notes: This structure is a bit different. It can be used to refer to the present, and to the near future tenses.
- Use it to find out who is doing a certain action— for example, if you hear a trumpet and want to know who is playing it).
- Or, you can use it to find out who will be doing an action in the near future —for example, if you are going on a trip and want to know who will drive the car.
If the action is being done to something, don’t forget to add that something in for a complete thought!
- Who is playing the trumpet?
- Who is driving?
- Who is cooking? (…It smells great!)
Here are some phrases for introducing yourself when you meet new people, and questions to learn more about them.
Hi! I am [Name]. (And you?)
Here is an informal greeting you can use when you meet new friends. If the person does not tell you their name, you can say your name first. Then ask, “And you?” or “And what is your name?”
Hi! I am Stephen. And you?
Nice to meet you.
After you learn each other’s names, it is polite to say this phrase.
A: Hi, Stephen, I am Chad.
B: Nice to meet you , Chad.
A: Nice to meet you , too.
Where are you from?
Ask this question to find out which country someone is from. You answer this question with “I am from _______.”
Can you answer this question in English? Say both the question and answer aloud right now.
A: Nice to meet you, Sergio. So, where are you from?
B: I am from Spain.
What do you do?
Most adults ask each other this question when they meet. It means what do you do for a living (what is your job).
I think this question is boring, so I ask other questions. But many people will probably ask you this, so it is important to know what it means.
A: What do you do , Cathleen?
B: I work at the university as a financial specialist.
What do you like to do (in your free time)?
Instead of asking for someone’s job title, I prefer to ask what they enjoy doing. The responses (answers) are usually much more interesting!
A: So, Cathleen, what do you like to do in your free time?
B: I love to read and to garden. I picked two buckets of tomatoes last week!
What is your phone number?
If you want to keep in contact with someone you just met, ask this question to find out their phone number. You can replace “phone number” with “email address” if you want to know their email address.
You might also hear people use the more casual, “ Can I get your phone number? “
It would be great to meet up again sometime. What is your phone number?
Do you have Facebook?
Many people keep in touch (contact) through Facebook . Use this question to find out if someone has a Facebook account. You might also ask, “Are you on Facebook?”
Let’s keep in touch! Do you have Facebook?
These eight phrases can be used in many different situations.
Thanks so much.
This is a simple sentence you can use to thank someone.
To add detail, say:
Thanks so much + for + [noun] / [-ing verb].
For example:
Thanks so much for the birthday money.
Thanks so much for driving me home.
I really appreciate…
You can also use this phrase to thank someone. For example, you might say:
I really appreciate your help.
Or you can combine this phrase with the last one:
Thanks so much for cooking dinner. I really appreciate it.
Thanks so much. I really appreciate your cooking dinner.
When you need to get through but there is someone blocking your way, say “Excuse me.”
You can also say this phrase to politely get someone’s attention. For example:
Excuse me , sir, you dropped your wallet.
Excuse me , do you know what time it is?
I am sorry.
Use this phrase to apologize, whether for something big or small. Use “for” to give more detail. For example:
I am sorry for being so late.
I was not expecting anyone today. I am sorry for the mess.
You can use “really” to show you are very sorry for something:
I am really sorry I did not invite you to the party.
In fact, I am sorry has many different uses in English and they are not always that obvious! Because of this, using native content when learning English expressions is very important to ensure you are learning them properly.
What do you think?
When you want to hear someone’s opinion on a topic, use this question.
I am not sure if we should paint the room yellow or blue. What do you think?
How does that sound?
If you suggest an idea or plan, use this phrase to find out what others think.
We could have dinner at 6, and then go to a movie. How does that sound?
Let’s hire a band to play music, and Brent can photograph the event. How does that sound?
That sounds great.
If you like an idea, you can respond to “How does that sound?” with this phrase. “Great” can be replaced with any synonym (similar word), such as “awesome,” “perfect,” “excellent” or “fantastic.”
A: My mom is baking cookies this afternoon. We could go to my house and eat some. How does that sound?
B: That sounds fantastic!
Oh, never mind.
Let’s say someone does not understand an idea you are trying to explain. If you have explained it over and over and want to stop, just say “oh, never mind.” You can now talk about something else!
You can also use “never mind” to mean “it does not matter” or “just forget it.” In these situations, say it with a smile and positive tone, though. When you say this phrase slowly with a falling, low tone, it can mean you are bothered or upset.
A: Are you going to the grocery store today?
B: No, I am not. But why—do you need something?
A: Oh, never mind! It is okay, I will go tomorrow.
As an English learner, you will likely want to tell others that English is not your first language. You will also need to ask native speakers to repeat phrases and words or to speak slower. The following phrases will be useful for these situations.
I am learning English.
This simple phrase tells people that English is not your native language. If you are a total beginner, you can add “just started” like this: “I just started learning English.”
My name is Sophie and I am learning English .
I do not understand.
Use this phrase when you do not understand what someone means.
Sorry, I do not understand. The U.S. Electoral College seems very confusing!
Could you repeat that please?
If you would like someone to say a word, question or phrase again, use this question. Since “to repeat” means “to say again,” you can also ask, “Could you say that again, please?”
We can say “please” either at the end of the question or right after “you,” like this:
Could you please repeat that?
Could you repeat that, please ?
Could you please talk slower?
Native speakers can talk very fast. Fast English is hard to understand! This is an easy way to ask someone to speak more slowly.
Note: This phrase is not grammatically correct. However, it is used often in every day (casual) speech. The grammatically correct question would be, “ Could you please talk more slowly ? “
That is because “slowly” is an adverb, so it describes verbs (like “talk”). “Slower” is a comparative adjective, which means it should be used to describe nouns (people, places or things), not verbs. (For example: My car is slower than yours.)
A: You can give us a call any weekday from 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. at five five five, two five zero eight, extension three three—
B: I am sorry, could you please talk slower?
Thank you. That helps a lot.
After someone starts speaking more slowly for you, thank them with this phrase.
You can use it in many other situations, too.
A: Ben, could you please make the font bigger? It is hard for me to read the words.
B: Sure! I will change it from size 10 to 16. How is this?
A: Thank you. That helps a lot.
What does _____ mean?
When you hear or see a new word, use this phrase to ask what it means.
A: What does “font” mean?
B: It is the style of letters, numbers and punctuation marks when you type. A common font in the USA is called Times New Roman.
How do you spell that?
English spelling can be tricky , so make sure to learn this question. You could also ask someone, “Could you spell that for me?”
A: My name is Robbertah Handkerchief.
B: How do you spell that?
What do you mean?
When you understand the words one by one, but not what they mean together, use this question. You can ask it whenever you are confused about what someone is telling you.
A: The Smiths do have a really nice house, but the grass is always greener on the other side.
B: What do you mean?
A: I mean that if we had the Smith’s house, we probably would not be happier. We always think that other people have better lives than us, but other people have problems, too.
Everyone needs to go shopping, whether it is for food, clothing or household items like furniture. These phrases will help you find what you want to buy and how much it costs.
Can you help me?
If you need help while you are shopping, this is a simple way to ask.
Can you help me? I canno t find what I want.
Excuse me, can you help me?
I am looking for…
If you cannot find what you want in a store, you can ask a salesperson to help you find it. Just add the name of what you want to buy after the phrase “I am looking for…”
Excuse me, I a m looking for a winter coat.
I a m looking for snow boots.
Do you have this [object] in a different color?
If you see something you like, but you do not like the color, you can ask if you can get it in a different color.
Another way to say this is “Does this come in a different color?”
You can also add the name of the object after “this.”
I do not like this shade of red. Do you have this in a different color?
Does this bowl come in a different color? This will not match my kitchen.
I do not know my size.
Sizes for clothing and other things differ from country to country, so you might have to look up the correct size for the country where you are shopping.
If you cannot figure out your correct size, it is perfectly fine to ask for help from the sales staff.
I do no t know my size. Can you help me?
I want to buy a shirt, but I do no t know my size.
I need this in a size ______.
This is a simple way to ask for a piece of clothing or a household item in the size you need—if you already happen to know the right size.
I need this in a size 10, please.
This is too large. I need this in a size 5.
Where can I find [item]?
Since every supermarket is set up (arranged) a little differently, we all can have trouble finding certain items.
You can ask someone at the store to help you find what you need with this simple phrase: “Where can I find…?” Just add the name of what you want after “find.”
The store clerk might answer you with a phrase like, “It is on aisle eight,” or, “It is in the Produce section, near the lettuce.”
Customer: Where can I find black olives?
Sales clerk: They a re on aisle ten, near the pickles.
Customer: Where can I find a bag of almonds?
Sales clerk : They a re in the baking section, on aisle seven.
How much does this/that cost?
If you are holding something you want to buy, or it is right near you, you can say “How much does this cost?” to find out (learn) the price.
You can also put the name of the object you want to buy after “this.”
How much does this shirt cost?
If you can see what you want to buy, but it is not right near you, you can point to it and say, “How much does that cost?” or “How much is that [item]?”
How much is that lamp over there ?
I do not need a bag.
Let us say you just bought something small. You can easily carry it. You might tell the sales clerk or cashier that you do not need a shopping bag.
You might also say this if you have a shopping bag with you and do not need to get one from the store.
No, thank you. I do no t need a bag. I can just carry it.
I do no t need a bag. I brought my own with me.
Can someone help me carry this out?
If you buy something really large and hard to carry, like a table or a huge order of groceries, you are going to need help.
Most stores that sell large and heavy items offer assistance (help) from a member of staff. The staff member can help you carry your purchase (what you have bought) out of the store. They might even help you place it in your vehicle.
This is too heavy for me. Can someone help me carry this out?
Can someone help me carry this out? I have eighteen bags of groceries here!
Can I have this delivered?
Sometimes, you need to buy something so large—and so heavy—that there is no way you could bring it home from the store yourself.
That is when you will want to ask, “Can I have this delivered?”
This refrigerator is perfect! Can I have this delivered?
Can I have this delivered next Tuesday?
Introducing yourself
“I just started working here. I’m the new [name of your job].” Tell people you’re new by using this sentence.
“I’m working in the [name] department. What do you do here?” Jobs fall under different departments , which are sections of the jobs that concentrate on one part of the job. For example, the IT (Information Technology) Department works with setting up and fixing the company’s computers. When you introduce yourself, tell the person which department you work for, and ask them for theirs.
Making “small talk”
Small talk is light, polite conversation. It can be about the weather, food , or anything that isn’t too serious. If you’re in the same room or in an elevator as someone else, or just standing near each other and you aren’t working, making small talk can open conversation. This saves you from uncomfortable silences but also forms connections and eventually friendships.
“I love your (shoes/necklace etc.). Where did you get it/them?” Complimenting someone (saying something nice about a person) makes them feel good, and asking a question afterwards starts a conversation.
“I can’t believe how hot/cold it is today!” The weather is always a safe topic and can be used for almost any kind of weather. If it’s a beautiful day, say “I can’t believe how nice it is today.”
Submitting reports and ideas
“If you have a moment, I would love your thoughts on this.” This is a polite way of asking your boss or coworker for input on something you wrote or did.
“I have the report/information you asked for.” This is just a simple way of saying you finished the job you had.
“Do you mind if I record this?” A good way to make sure you don’t miss anything important at a meeting is to record it so you can listen to it again later. Make sure to ask for permission first by using this sentence.
“Excuse me, can you please speak up?” This is a polite way to ask someone to speak louder if you can’t hear them.
“Do we still have that meeting after lunch?” Make sure you know when all the meetings are so you don’t miss them.
Asking for help/clarifications
“I’m having trouble with [something]. Do you know who can help me?” Before you ask someone for help, find out if they’re the right person for the type of problem you’re having.
“Do you have a minute?” Before you ask for help, this is a common way to politely make sure the person isn’t busy.
“Are there any rules I should know about?” Every job has its own rules and ways of doing things. Find out what they are so that you can follow them.
The easy sentences you learned above are just the beginning.
You have the first Legos in place.
Now go build a castle!
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials , as you can see here:
If you want to watch it, the FluentU app has probably got it.
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
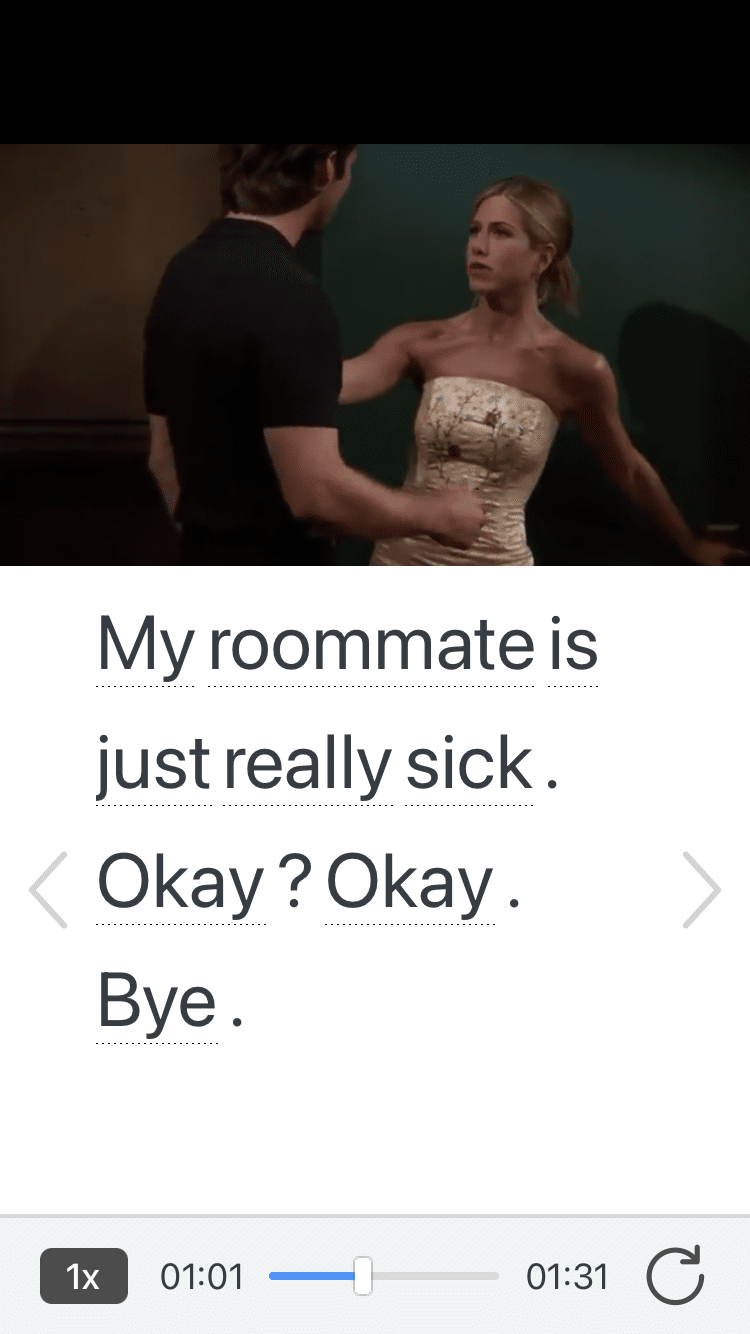
FluentU lets you learn engaging content with world famous celebrities.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
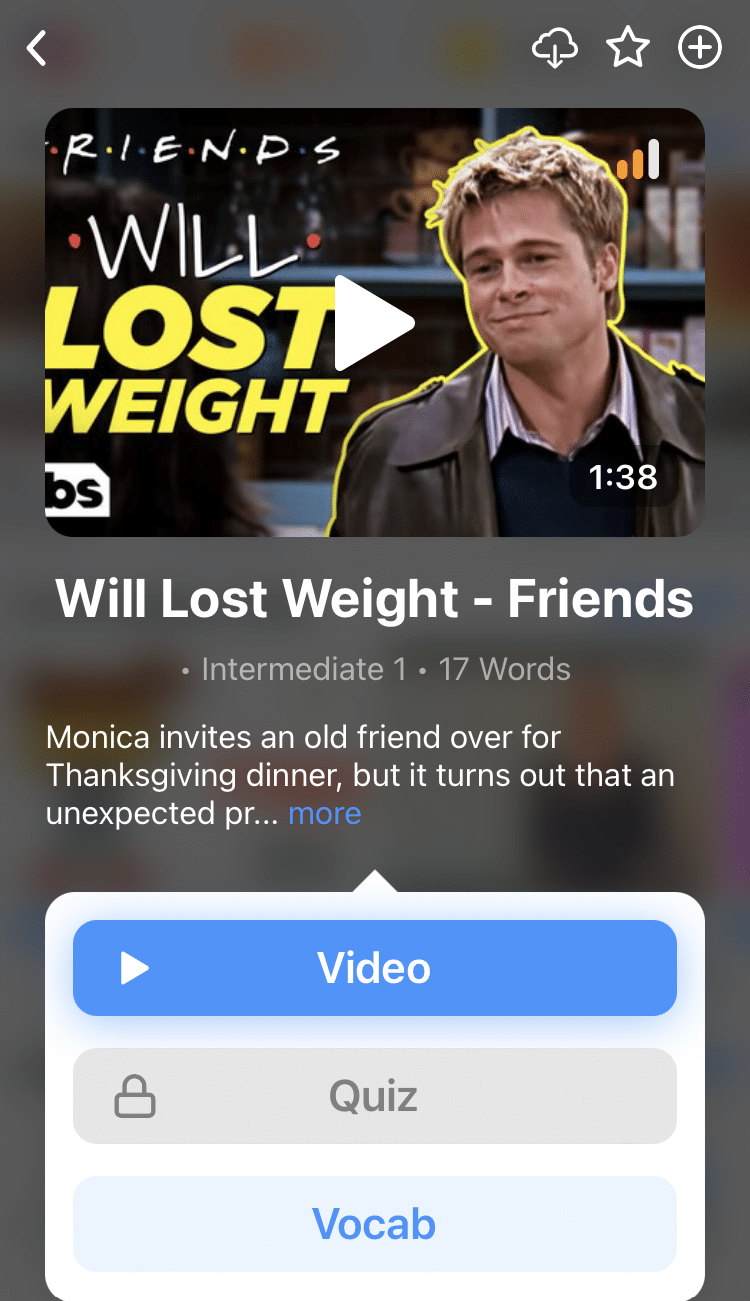
FluentU lets you tap to look up any word.
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe

The 9 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A part of speech is a term used in traditional grammar for one of the nine main categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences, such as nouns or verbs. Also known as word classes, these are the building blocks of grammar.
Every sentence you write or speak in English includes words that fall into some of the nine parts of speech. These include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. (Some sources include only eight parts of speech and leave interjections in their own category.)
Parts of Speech
- Word types can be divided into nine parts of speech:
- prepositions
- conjunctions
- articles/determiners
- interjections
- Some words can be considered more than one part of speech, depending on context and usage.
- Interjections can form complete sentences on their own.
Learning the names of the parts of speech probably won't make you witty, healthy, wealthy, or wise. In fact, learning just the names of the parts of speech won't even make you a better writer. However, you will gain a basic understanding of sentence structure and the English language by familiarizing yourself with these labels.
Open and Closed Word Classes
The parts of speech are commonly divided into open classes (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) and closed classes (pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections). Open classes can be altered and added to as language develops, and closed classes are pretty much set in stone. For example, new nouns are created every day, but conjunctions never change.
In contemporary linguistics , parts of speech are generally referred to as word classes or syntactic categories. The main difference is that word classes are classified according to more strict linguistic criteria. Within word classes, there is the lexical, or open class, and the function, or closed class.
The 9 Parts of Speech
Read about each part of speech below, and practice identifying each.
Nouns are a person, place, thing, or idea. They can take on a myriad of roles in a sentence, from the subject of it all to the object of an action. They are capitalized when they're the official name of something or someone, and they're called proper nouns in these cases. Examples: pirate, Caribbean, ship, freedom, Captain Jack Sparrow.
Pronouns stand in for nouns in a sentence . They are more generic versions of nouns that refer only to people. Examples: I, you, he, she, it, ours, them, who, which, anybody, ourselves.
Verbs are action words that tell what happens in a sentence. They can also show a sentence subject's state of being ( is , was ). Verbs change form based on tense (present, past) and count distinction (singular or plural). Examples: sing, dance, believes, seemed, finish, eat, drink, be, became.
Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns. They specify which one, how much, what kind, and more. Adjectives allow readers and listeners to use their senses to imagine something more clearly. Examples: hot, lazy, funny, unique, bright, beautiful, poor, smooth.
Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, and even other adverbs. They specify when, where, how, and why something happened and to what extent or how often. Many adjectives can be turned into adjectives by adding the suffix - ly . Examples: softly, quickly, lazily, often, only, hopefully, sometimes.
Preposition
Prepositions show spatial, temporal, and role relations between a noun or pronoun and the other words in a sentence. They come at the start of a prepositional phrase , which contains a preposition and its object. Examples: up, over, against, by, for, into, close to, out of, apart from.
Conjunction
Conjunctions join words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence. There are coordinating, subordinating, and correlative conjunctions. Examples: and, but, or, so, yet.
Articles and Determiners
Articles and determiners function like adjectives by modifying nouns, but they are different than adjectives in that they are necessary for a sentence to have proper syntax. Articles and determiners specify and identify nouns, and there are indefinite and definite articles. Examples of articles: a, an, the ; examples of determiners: these, that, those, enough, much, few, which, what.
Some traditional grammars have treated articles as a distinct part of speech. Modern grammars, however, more often include articles in the category of determiners , which identify or quantify a noun. Even though they modify nouns like adjectives, articles are different in that they are essential to the proper syntax of a sentence, just as determiners are necessary to convey the meaning of a sentence, while adjectives are optional.
Interjection
Interjections are expressions that can stand on their own or be contained within sentences. These words and phrases often carry strong emotions and convey reactions. Examples: ah, whoops, ouch, yabba dabba do!
How to Determine the Part of Speech
Only interjections ( Hooray! ) have a habit of standing alone; every other part of speech must be contained within a sentence and some are even required in sentences (nouns and verbs). Other parts of speech come in many varieties and may appear just about anywhere in a sentence.
To know for sure what part of speech a word falls into, look not only at the word itself but also at its meaning, position, and use in a sentence.
For example, in the first sentence below, work functions as a noun; in the second sentence, a verb; and in the third sentence, an adjective:
- Bosco showed up for work two hours late.
- The noun work is the thing Bosco shows up for.
- He will have to work until midnight.
- The verb work is the action he must perform.
- His work permit expires next month.
- The attributive noun (or converted adjective) work modifies the noun permit .
Learning the names and uses of the basic parts of speech is just one way to understand how sentences are constructed.
Dissecting Basic Sentences
To form a basic complete sentence, you only need two elements: a noun (or pronoun standing in for a noun) and a verb. The noun acts as a subject, and the verb, by telling what action the subject is taking, acts as the predicate.
In the short sentence above, birds is the noun and fly is the verb. The sentence makes sense and gets the point across.
You can have a sentence with just one word without breaking any sentence formation rules. The short sentence below is complete because it's a verb command with an understood "you" noun.
Here, the pronoun, standing in for a noun, is implied and acts as the subject. The sentence is really saying, "(You) go!"
Constructing More Complex Sentences
Use more parts of speech to add additional information about what's happening in a sentence to make it more complex. Take the first sentence from above, for example, and incorporate more information about how and why birds fly.
- Birds fly when migrating before winter.
Birds and fly remain the noun and the verb, but now there is more description.
When is an adverb that modifies the verb fly. The word before is a little tricky because it can be either a conjunction, preposition, or adverb depending on the context. In this case, it's a preposition because it's followed by a noun. This preposition begins an adverbial phrase of time ( before winter ) that answers the question of when the birds migrate . Before is not a conjunction because it does not connect two clauses.
- A List of Exclamations and Interjections in English
- Sentence Parts and Sentence Structures
- 100 Key Terms Used in the Study of Grammar
- Closed Class Words
- Word Class in English Grammar
- Prepositional Phrases in English Grammar
- Foundations of Grammar in Italian
- The Top 25 Grammatical Terms
- What Are the Parts of a Prepositional Phrase?
- Open Class Words in English Grammar
- What Is an Adverb in English Grammar?
- Definition and Examples of Function Words in English
- Telegraphic Speech
- Sentence Patterns
- Pronoun Definition and Examples
- Lesson Plan: Label Sentences with Parts of Speech

paper-free learning
- conjunctions
- determiners
- interjections
- prepositions
- affect vs effect
- its vs it's
- your vs you're
- which vs that
- who vs whom
- who's vs whose
- averse vs adverse
- 250+ more...
- apostrophes
- quotation marks
- lots more...
- common writing errors
- FAQs by writers
- awkward plurals
- ESL vocabulary lists
- all our grammar videos
- idioms and proverbs
- Latin terms
- collective nouns for animals
- tattoo fails
- vocabulary categories
- most common verbs
- top 10 irregular verbs
- top 10 regular verbs
- top 10 spelling rules
- improve spelling
- common misspellings
- role-play scenarios
- favo(u)rite word lists
- multiple-choice test
- Tetris game
- grammar-themed memory game
- 100s more...
Parts of Speech
What are the parts of speech, a formal definition.
Table of Contents
The Part of Speech Is Determined by the Word's Function
Are there 8 or 9 parts of speech, the nine parts of speech, (1) adjective, (3) conjunction, (4) determiner, (5) interjection, (7) preposition, (8) pronoun, why the parts of speech are important, video lesson.

- You need to dig a well . (noun)
- You look well . (adjective)
- You dance well . (adverb)
- Well , I agree. (interjection)
- My eyes will well up. (verb)
- red, happy, enormous
- Ask the boy in the red jumper.
- I live in a happy place.
- I caught a fish this morning! I mean an enormous one.
- happily, loosely, often
- They skipped happily to the counter.
- Tie the knot loosely so they can escape.
- I often walk to work.
- It is an intriguingly magic setting.
- He plays the piano extremely well.
- and, or, but
- it is a large and important city.
- Shall we run to the hills or hide in the bushes?
- I know you are lying, but I cannot prove it.
- my, those, two, many
- My dog is fine with those cats.
- There are two dogs but many cats.
- ouch, oops, eek
- Ouch , that hurt.
- Oops , it's broken.
- Eek! A mouse just ran past my foot!
- leader, town, apple
- Take me to your leader .
- I will see you in town later.
- An apple fell on his head .
- in, near, on, with
- Sarah is hiding in the box.
- I live near the train station.
- Put your hands on your head.
- She yelled with enthusiasm.
- she, we, they, that
- Joanne is smart. She is also funny.
- Our team has studied the evidence. We know the truth.
- Jack and Jill went up the hill, but they never returned.
- That is clever!
- work, be, write, exist
- Tony works down the pit now. He was unemployed.
- I will write a song for you.
- I think aliens exist .
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .
Video for Each Part of Speech
The Most Important Writing Issues
The top issue related to adjectives, the top issue related to adverbs.
- Extremely annoyed, she stared menacingly at her rival.
- Infuriated, she glared at her rival.
The Top Issue Related to Conjunctions
- Burger, Fries, and a shake
- Fish, chips and peas
The Top Issue Related to Determiners
The Top Issue Related to Interjections
The top issue related to nouns, the top issue related to prepositions, the top issue related to pronouns, the top issue related to verbs.
- Crack the parts of speech to help with learning a foreign language or to take your writing to the next level.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
Learning Resources
more actions:
This test is printable and sendable
Help Us Improve Grammar Monster
- Do you disagree with something on this page?
- Did you spot a typo?
Find Us Quicker!
- When using a search engine (e.g., Google, Bing), you will find Grammar Monster quicker if you add #gm to your search term.
You might also like...
Share This Page

If you like Grammar Monster (or this page in particular), please link to it or share it with others. If you do, please tell us . It helps us a lot!
Create a QR Code

Use our handy widget to create a QR code for this page...or any page.
< previous lesson
next lesson >
Parts of Speech: A Guide to Learning English Grammar
By: Author English Study Online
Posted on Last updated: December 27, 2023
Sharing is caring!
In this page, we will break down each part of speech and provide examples to help you understand their usage. We will also discuss how to identify the different parts of speech in a sentence and provide tips on how to use them correctly. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced English learner, this article will provide valuable insights into the parts of speech and improve your language skills. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Overview of Parts of Speech
In this section, we will provide a brief overview of the eight parts of speech in English. Understanding the parts of speech is essential for anyone learning the English language, as it enables them to construct meaningful sentences and communicate effectively.
The eight parts of speech are:
Prepositions
Conjunctions, interjections.
Each part of speech has a specific function in a sentence. For example, nouns are used to name people, places, things, or ideas, while verbs are used to describe an action or state of being. Adjectives are used to describe nouns, while adverbs are used to describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
Pronouns are used to replace nouns in a sentence, while prepositions are used to indicate the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. Conjunctions are used to connect words, phrases, or clauses, while interjections are used to express emotions or feelings.

Nouns are words that represent people, places, things, or ideas. They are one of the most important parts of speech in English and are used in nearly every sentence. In this section, we will explore the different types of nouns and their functions.
Common Nouns
Common nouns are general names for people, places, or things. They are not capitalized unless they appear at the beginning of a sentence.
- Examples of common nouns include “book,” “city,” and “teacher.”
Proper Nouns
Proper nouns are specific names for people, places, or things. They are always capitalized.
- Examples of proper nouns include “Harry Potter,” “New York City,” and “Ms. Johnson.”
Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns are names for ideas, concepts, or emotions. They are intangible and cannot be seen, heard, or touched.
- Examples of abstract nouns include “love,” “happiness,” and “freedom.”
Collective Nouns
Collective nouns are names for groups of people or things. They can be singular or plural, depending on the context.
- Examples of collective nouns include “team,” “family,” and “herd.”
In this section, we will discuss the different types of pronouns used in English grammar. Pronouns are words that replace nouns in a sentence. They help to avoid repetition and make sentences more concise.
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns refer to specific people or things. They can be used as the subject or object of a sentence. Here are the personal pronouns in English:
Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns are used to point to specific people or things. They can be used to indicate distance or location. Here are the demonstrative pronouns in English:
Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. They are typically used at the beginning of a sentence. Here are the interrogative pronouns in English:
Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns refer to non-specific people or things. They can be used as the subject or object of a sentence. Here are the indefinite pronouns in English:
Verbs are one of the most important parts of speech in English. They are used to describe an action, state, or occurrence. In this section, we will cover the three types of verbs: action verbs, linking verbs, and helping verbs.
Action Verbs
Action verbs are used to describe an action that is being performed by the subject of the sentence. They can be used in the present, past, or future tense. Here are a few examples of action verbs:
Linking Verbs
Linking verbs are used to connect the subject of the sentence to a noun, pronoun, or adjective that describes it. They do not show action. Here are a few examples of linking verbs:
Helping Verbs
Helping verbs are used in conjunction with the main verb to express tense, voice, or mood. They do not have a meaning on their own. Here are a few examples of helping verbs:
In conclusion, verbs are an essential part of English grammar. Understanding the different types of verbs and how they are used in a sentence can help you communicate more effectively in both written and spoken English.
In this section, we will discuss adjectives, which are an important part of speech in English. Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns. They provide more information about the noun or pronoun, such as its size, shape, color, or quality.
Descriptive Adjectives
Descriptive adjectives are the most common type of adjectives. They describe the physical or observable characteristics of a noun or pronoun. For example, in the sentence “The red car is fast,” “red” is a descriptive adjective that describes the color of the car, and “fast” is another descriptive adjective that describes its speed.
Here are some examples of descriptive adjectives:
Quantitative Adjectives
Quantitative adjectives are used to describe the quantity or amount of a noun or pronoun. They answer the question “how much” or “how many.” For example, in the sentence “I have two apples,” “two” is a quantitative adjective that describes the number of apples.
Here are some examples of quantitative adjectives:
Demonstrative Adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives are used to point out or indicate a specific noun or pronoun. They answer the question “which one” or “whose.” For example, in the sentence “This book is mine,” “this” is a demonstrative adjective that indicates the specific book that belongs to the speaker.
Here are some examples of demonstrative adjectives:
In conclusion, adjectives are an important part of speech in English. They provide more information about nouns and pronouns, and they help to make our language more descriptive and precise. By understanding the different types of adjectives, we can use them effectively in our speaking and writing.
In this section, we will discuss adverbs, which are words that modify or describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Adverbs give more information about the action, manner, place, time, frequency, degree, or intensity of a verb.
Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of manner describe how an action is performed. They answer the question “how?” and usually end in “-ly”, but not always. Here are some examples:
- She sings beautifully.
- He speaks softly.
- They ran quickly.
- The dog barked loudly.
Adverbs of manner can also be formed by adding “-ly” to some adjectives. For example:
- She is a quick learner. (adjective: quick)
- He is a careful driver. (adjective: careful)
Adverbs of Place
Adverbs of place describe where an action takes place. They answer the question “where?” and usually come after the verb or object. Here are some examples:
- She looked everywhere.
- He lives nearby.
- They went outside.
- The cat hid underneath the bed.
Adverbs of Time
Adverbs of time describe when an action takes place. They answer the question “when?” and can come at the beginning, middle, or end of a sentence. Here are some examples:
- She wakes up early every day.
- He arrived yesterday.
- They will leave soon.
- The concert starts tonight.
Adverbs of time can also be used to show the duration of an action. For example:
- She studied for hours.
- He worked all day.
- They talked for a long time.
In this section, we will discuss prepositions and their usage in English. Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. They usually indicate the position or direction of the noun or pronoun in relation to other elements in the sentence.
Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time are used to indicate when an action took place. They include words such as “at,” “in,” and “on.”
- “At” is used for specific times, such as “at 2 pm” or “at midnight.”
- “In” is used for longer periods of time, such as “in the morning” or “in October.”
- “On” is used for dates, such as “on Monday” or “on July 4th.”
Prepositions of Place
Prepositions of place are used to indicate where something is located. They include words such as “in,” “on,” and “at.”
- “In” is used for enclosed spaces, such as “in the house” or “in the car.”
- “On” is used for surfaces, such as “on the table” or “on the floor.”
- “At” is used for specific locations, such as “at the park” or “at the beach.”
Prepositions of Direction
Prepositions of direction are used to indicate movement. They include words such as “to,” “from,” and “towards.”
- “To” is used to indicate movement towards a specific destination, such as “I am going to the store.”
- “From” is used to indicate movement away from a specific location, such as “I am coming from the park.”
- “Towards” is used to indicate movement in the direction of a specific location, such as “I am walking towards the museum.”
In this section, we will discuss the different types of conjunctions and their functions in English grammar. Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence. They are essential in creating complex sentences and conveying relationships between ideas.
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions join words, phrases, or clauses that are of equal importance. They are easy to remember using the mnemonic device FANBOYS: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so. Here are some examples:
- I like pizza and pasta.
- She is neither tall nor short.
- He wanted to go to the beach, but it was raining.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions connect dependent clauses to independent clauses and establish a relationship between them. They are used to show cause and effect, time, condition, and contrast. Some examples of subordinating conjunctions are:
Here are some examples:
- Because it was raining, we stayed inside.
- Although she was tired, she stayed up to finish her work.
- While I was studying, my roommate was watching TV.
Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions are pairs of words that work together to connect words, phrases, or clauses. They are used to show a relationship between two elements. Here are some examples:
- both…and
- either…or
- neither…nor
- not only…but also
- Both my sister and I like to read.
- Either you come with us or you stay here.
- Not only was he late, but he also forgot his homework.
In conclusion, conjunctions are important in creating complex sentences and conveying relationships between ideas. By understanding the different types of conjunctions and their functions, you can improve your writing and communication skills.
In English grammar, interjections are words or phrases that express strong emotions or feelings. They are also known as exclamations and are one of the eight parts of speech in English. Interjections are grammatically independent from the words around them, and they can often be removed from a sentence or context without affecting its basic meaning.
Interjections can be used to express a wide range of emotions, including surprise, joy, anger, frustration, and pain. Some common examples of interjections include “ wow ,” “ ouch ,” “ yay ,” “ oh no ,” and “ oops .” They can be used to add emphasis to a sentence or to convey a particular tone or mood.
It is important to note that interjections do not have any grammatical function in a sentence. They are not nouns, verbs, adjectives, or any other part of speech. Instead, they simply stand alone as a way to express emotion.
When using interjections in writing, it is important to consider the context in which they are being used. While they can be a useful tool for adding emphasis or conveying emotion, they can also be overused or misused, which can detract from the overall effectiveness of the writing.
Articles/Determiners
In English grammar, articles and determiners are words that are used with nouns to provide more information about them. They help us to understand the context and meaning of a sentence.
There are three articles in the English language: “ the ,” “ a, ” and “ an. ” “The” is known as the definite article because it refers to a specific noun that has already been mentioned or is known to the reader. For example, “The cat is sleeping on the sofa.” In this sentence, “the” refers to a specific cat that has already been mentioned or is known to the reader.
“A” and “an” are known as indefinite articles because they refer to any member of a group or class of nouns. “A” is used before words that begin with a consonant sound, while “an” is used before words that begin with a vowel sound. For example, “I need a pen” and “She ate an apple.”
Determiners
Determiners are words that come before a noun to provide more information about it. They can include articles, as well as words like “ this ,” “ that ,” “ these ,” and “ those .”
In addition to these, there are other types of determiners such as possessive determiners (e.g. “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their”), demonstrative determiners (e.g. “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those”), and quantifying determiners (e.g. “some,” “any,” “many,” “few,” “several,” etc.).
Determiners can also be used with adjectives to provide more information about a noun. For example, “She ate the delicious apple” and “I saw that beautiful sunset.”
Understanding articles and determiners is crucial for mastering English grammar. By using them correctly, you can convey your thoughts and ideas more clearly and effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 8 parts of speech in English?
In English, there are eight parts of speech: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Each part of speech serves a different function in a sentence and helps to convey meaning.
What are some examples of different parts of speech?
Here are a few examples of different parts of speech:
- Noun: dog, cat, book, table
- Pronoun: he, she, it, they
- Verb: run, jump, sing, dance
- Adjective: happy, sad, tall, short
- Adverb: quickly, slowly, loudly, softly
- Preposition: in, on, at, under
- Conjunction: and, but, or, so
- Interjection: wow, oh, ouch, hooray
What is the difference between a noun and a verb?
A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. A verb is a word that represents an action, occurrence, or state of being. In other words, a noun is a subject or object in a sentence, while a verb is the action or occurrence that takes place.
What are the different types of nouns?
There are several different types of nouns, including:
- Common nouns: refer to general, non-specific people, places, things, or ideas (e.g. dog, city, book)
- Proper nouns: refer to specific people, places, things, or ideas and are always capitalized (e.g. John, Paris, The Great Gatsby )
- Concrete nouns: refer to tangible, physical objects (e.g. table, chair, car)
- Abstract nouns: refer to intangible concepts or ideas (e.g. love, happiness, freedom)
- Recent Posts
- Juridical Process vs. Judicial Process: Understanding the Crucial Differences - December 14, 2023
- Compound Nouns: How to Use Them Effectively in English - November 9, 2023
- English Tenses: A Beginner’s Guide in English - November 6, 2023

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, understanding the 8 parts of speech: definitions and examples.
General Education
If you’re trying to learn the grammatical rules of English, you’ve probably been asked to learn the parts of speech. But what are parts of speech and how many are there? How do you know which words are classified in each part of speech?
The answers to these questions can be a bit complicated—English is a difficult language to learn and understand. Don’t fret, though! We’re going to answer each of these questions for you with a full guide to the parts of speech that explains the following:
- What the parts of speech are, including a comprehensive parts of speech list
- Parts of speech definitions for the individual parts of speech. (If you’re looking for information on a specific part of speech, you can search for it by pressing Command + F, then typing in the part of speech you’re interested in.)
- Parts of speech examples
- A ten question quiz covering parts of speech definitions and parts of speech examples
We’ve got a lot to cover, so let’s begin!
Feature Image: (Gavina S / Wikimedia Commons)

What Are Parts of Speech?
The parts of speech definitions in English can vary, but here’s a widely accepted one: a part of speech is a category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences.
To make that definition even simpler, a part of speech is just a category for similar types of words . All of the types of words included under a single part of speech function in similar ways when they’re used properly in sentences.
In the English language, it’s commonly accepted that there are 8 parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions, interjections, and prepositions. Each of these categories plays a different role in communicating meaning in the English language. Each of the eight parts of speech—which we might also call the “main classes” of speech—also have subclasses. In other words, we can think of each of the eight parts of speech as being general categories for different types within their part of speech . There are different types of nouns, different types of verbs, different types of adjectives, adverbs, pronouns...you get the idea.
And that’s an overview of what a part of speech is! Next, we’ll explain each of the 8 parts of speech—definitions and examples included for each category.

There are tons of nouns in this picture. Can you find them all?
Nouns are a class of words that refer, generally, to people and living creatures, objects, events, ideas, states of being, places, and actions. You’ve probably heard English nouns referred to as “persons, places, or things.” That definition is a little simplistic, though—while nouns do include people, places, and things, “things” is kind of a vague term. I t’s important to recognize that “things” can include physical things—like objects or belongings—and nonphysical, abstract things—like ideas, states of existence, and actions.
Since there are many different types of nouns, we’ll include several examples of nouns used in a sentence while we break down the subclasses of nouns next!
Subclasses of Nouns, Including Examples
As an open class of words, the category of “nouns” has a lot of subclasses. The most common and important subclasses of nouns are common nouns, proper nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, collective nouns, and count and mass nouns. Let’s break down each of these subclasses!
Common Nouns and Proper Nouns
Common nouns are generic nouns—they don’t name specific items. They refer to people (the man, the woman), living creatures (cat, bird), objects (pen, computer, car), events (party, work), ideas (culture, freedom), states of being (beauty, integrity), and places (home, neighborhood, country) in a general way.
Proper nouns are sort of the counterpart to common nouns. Proper nouns refer to specific people, places, events, or ideas. Names are the most obvious example of proper nouns, like in these two examples:
Common noun: What state are you from?
Proper noun: I’m from Arizona .
Whereas “state” is a common noun, Arizona is a proper noun since it refers to a specific state. Whereas “the election” is a common noun, “Election Day” is a proper noun. Another way to pick out proper nouns: the first letter is often capitalized. If you’d capitalize the word in a sentence, it’s almost always a proper noun.
Concrete Nouns and Abstract Nouns
Concrete nouns are nouns that can be identified through the five senses. Concrete nouns include people, living creatures, objects, and places, since these things can be sensed in the physical world. In contrast to concrete nouns, abstract nouns are nouns that identify ideas, qualities, concepts, experiences, or states of being. Abstract nouns cannot be detected by the five senses. Here’s an example of concrete and abstract nouns used in a sentence:
Concrete noun: Could you please fix the weedeater and mow the lawn ?
Abstract noun: Aliyah was delighted to have the freedom to enjoy the art show in peace .
See the difference? A weedeater and the lawn are physical objects or things, and freedom and peace are not physical objects, though they’re “things” people experience! Despite those differences, they all count as nouns.
Collective Nouns, Count Nouns, and Mass Nouns
Nouns are often categorized based on number and amount. Collective nouns are nouns that refer to a group of something—often groups of people or a type of animal. Team , crowd , and herd are all examples of collective nouns.
Count nouns are nouns that can appear in the singular or plural form, can be modified by numbers, and can be described by quantifying determiners (e.g. many, most, more, several). For example, “bug” is a count noun. It can occur in singular form if you say, “There is a bug in the kitchen,” but it can also occur in the plural form if you say, “There are many bugs in the kitchen.” (In the case of the latter, you’d call an exterminator...which is an example of a common noun!) Any noun that can accurately occur in one of these singular or plural forms is a count noun.
Mass nouns are another type of noun that involve numbers and amount. Mass nouns are nouns that usually can’t be pluralized, counted, or quantified and still make sense grammatically. “Charisma” is an example of a mass noun (and an abstract noun!). For example, you could say, “They’ve got charisma, ” which doesn’t imply a specific amount. You couldn’t say, “They’ve got six charismas, ” or, “They’ve got several charismas .” It just doesn’t make sense!

Verbs are all about action...just like these runners.
A verb is a part of speech that, when used in a sentence, communicates an action, an occurrence, or a state of being . In sentences, verbs are the most important part of the predicate, which explains or describes what the subject of the sentence is doing or how they are being. And, guess what? All sentences contain verbs!
There are many words in the English language that are classified as verbs. A few common verbs include the words run, sing, cook, talk, and clean. These words are all verbs because they communicate an action performed by a living being. We’ll look at more specific examples of verbs as we discuss the subclasses of verbs next!
Subclasses of Verbs, Including Examples
Like nouns, verbs have several subclasses. The subclasses of verbs include copular or linking verbs, intransitive verbs, transitive verbs, and ditransitive or double transitive verbs. Let’s dive into these subclasses of verbs!
Copular or Linking Verbs
Copular verbs, or linking verbs, are verbs that link a subject with its complement in a sentence. The most familiar linking verb is probably be. Here’s a list of other common copular verbs in English: act, be, become, feel, grow, seem, smell, and taste.
So how do copular verbs work? Well, in a sentence, if we said, “Michi is ,” and left it at that, it wouldn’t make any sense. “Michi,” the subject, needs to be connected to a complement by the copular verb “is.” Instead, we could say, “Michi is leaving.” In that instance, is links the subject of the sentence to its complement.
Transitive Verbs, Intransitive Verbs, and Ditransitive Verbs
Transitive verbs are verbs that affect or act upon an object. When unattached to an object in a sentence, a transitive verb does not make sense. Here’s an example of a transitive verb attached to (and appearing before) an object in a sentence:
Please take the clothes to the dry cleaners.
In this example, “take” is a transitive verb because it requires an object—”the clothes”—to make sense. “The clothes” are the objects being taken. “Please take” wouldn’t make sense by itself, would it? That’s because the transitive verb “take,” like all transitive verbs, transfers its action onto another being or object.
Conversely, intransitive verbs don’t require an object to act upon in order to make sense in a sentence. These verbs make sense all on their own! For instance, “They ran ,” “We arrived ,” and, “The car stopped ” are all examples of sentences that contain intransitive verbs.
Finally, ditransitive verbs, or double transitive verbs, are a bit more complicated. Ditransitive verbs are verbs that are followed by two objects in a sentence . One of the objects has the action of the ditransitive verb done to it, and the other object has the action of the ditransitive verb directed towards it. Here’s an example of what that means in a sentence:
I cooked Nathan a meal.
In this example, “cooked” is a ditransitive verb because it modifies two objects: Nathan and meal . The meal has the action of “cooked” done to it, and “Nathan” has the action of the verb directed towards him.

Adjectives are descriptors that help us better understand a sentence. A common adjective type is color.
#3: Adjectives
Here’s the simplest definition of adjectives: adjectives are words that describe other words . Specifically, adjectives modify nouns and noun phrases. In sentences, adjectives appear before nouns and pronouns (they have to appear before the words they describe!).
Adjectives give more detail to nouns and pronouns by describing how a noun looks, smells, tastes, sounds, or feels, or its state of being or existence. . For example, you could say, “The girl rode her bike.” That sentence doesn’t have any adjectives in it, but you could add an adjective before both of the nouns in the sentence—”girl” and “bike”—to give more detail to the sentence. It might read like this: “The young girl rode her red bike.” You can pick out adjectives in a sentence by asking the following questions:
- Which one?
- What kind?
- How many?
- Whose’s?
We’ll look at more examples of adjectives as we explore the subclasses of adjectives next!
Subclasses of Adjectives, Including Examples
Subclasses of adjectives include adjective phrases, comparative adjectives, superlative adjectives, and determiners (which include articles, possessive adjectives, and demonstratives).
Adjective Phrases
An adjective phrase is a group of words that describe a noun or noun phrase in a sentence. Adjective phrases can appear before the noun or noun phrase in a sentence, like in this example:
The extremely fragile vase somehow did not break during the move.
In this case, extremely fragile describes the vase. On the other hand, adjective phrases can appear after the noun or noun phrase in a sentence as well:
The museum was somewhat boring.
Again, the phrase somewhat boring describes the museum. The takeaway is this: adjective phrases describe the subject of a sentence with greater detail than an individual adjective.
Comparative Adjectives and Superlative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives are used in sentences where two nouns are compared. They function to compare the differences between the two nouns that they modify. In sentences, comparative adjectives often appear in this pattern and typically end with -er. If we were to describe how comparative adjectives function as a formula, it might look something like this:
Noun (subject) + verb + comparative adjective + than + noun (object).
Here’s an example of how a comparative adjective would work in that type of sentence:
The horse was faster than the dog.
The adjective faster compares the speed of the horse to the speed of the dog. Other common comparative adjectives include words that compare distance ( higher, lower, farther ), age ( younger, older ), size and dimensions ( bigger, smaller, wider, taller, shorter ), and quality or feeling ( better, cleaner, happier, angrier ).
Superlative adjectives are adjectives that describe the extremes of a quality that applies to a subject being compared to a group of objects . Put more simply, superlative adjectives help show how extreme something is. In sentences, superlative adjectives usually appear in this structure and end in -est :
Noun (subject) + verb + the + superlative adjective + noun (object).
Here’s an example of a superlative adjective that appears in that type of sentence:
Their story was the funniest story.
In this example, the subject— story —is being compared to a group of objects—other stories. The superlative adjective “funniest” implies that this particular story is the funniest out of all the stories ever, period. Other common superlative adjectives are best, worst, craziest, and happiest... though there are many more than that!
It’s also important to know that you can often omit the object from the end of the sentence when using superlative adjectives, like this: “Their story was the funniest.” We still know that “their story” is being compared to other stories without the object at the end of the sentence.
Determiners
The last subclass of adjectives we want to look at are determiners. Determiners are words that determine what kind of reference a noun or noun phrase makes. These words are placed in front of nouns to make it clear what the noun is referring to. Determiners are an example of a part of speech subclass that contains a lot of subclasses of its own. Here is a list of the different types of determiners:
- Definite article: the
- Indefinite articles : a, an
- Demonstratives: this, that, these, those
- Pronouns and possessive determiners: my, your, his, her, its, our, their
- Quantifiers : a little, a few, many, much, most, some, any, enough
- Numbers: one, twenty, fifty
- Distributives: all, both, half, either, neither, each, every
- Difference words : other, another
- Pre-determiners: such, what, rather, quite
Here are some examples of how determiners can be used in sentences:
Definite article: Get in the car.
Demonstrative: Could you hand me that magazine?
Possessive determiner: Please put away your clothes.
Distributive: He ate all of the pie.
Though some of the words above might not seem descriptive, they actually do describe the specificity and definiteness, relationship, and quantity or amount of a noun or noun phrase. For example, the definite article “the” (a type of determiner) indicates that a noun refers to a specific thing or entity. The indefinite article “an,” on the other hand, indicates that a noun refers to a nonspecific entity.
One quick note, since English is always more complicated than it seems: while articles are most commonly classified as adjectives, they can also function as adverbs in specific situations, too. Not only that, some people are taught that determiners are their own part of speech...which means that some people are taught there are 9 parts of speech instead of 8!
It can be a little confusing, which is why we have a whole article explaining how articles function as a part of speech to help clear things up .

Adverbs can be used to answer questions like "when?" and "how long?"
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives (including determiners), clauses, prepositions, and sentences. Adverbs typically answer the questions how?, in what way?, when?, where?, and to what extent? In answering these questions, adverbs function to express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty . Adverbs can answer these questions in the form of single words, or in the form of adverbial phrases or adverbial clauses.
Adverbs are commonly known for being words that end in -ly, but there’s actually a bit more to adverbs than that, which we’ll dive into while we look at the subclasses of adverbs!
Subclasses Of Adverbs, Including Examples
There are many types of adverbs, but the main subclasses we’ll look at are conjunctive adverbs, and adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency.
Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs look like coordinating conjunctions (which we’ll talk about later!), but they are actually their own category: conjunctive adverbs are words that connect independent clauses into a single sentence . These adverbs appear after a semicolon and before a comma in sentences, like in these two examples:
She was exhausted; nevertheless , she went for a five mile run.
They didn’t call; instead , they texted.
Though conjunctive adverbs are frequently used to create shorter sentences using a semicolon and comma, they can also appear at the beginning of sentences, like this:
He chopped the vegetables. Meanwhile, I boiled the pasta.
One thing to keep in mind is that conjunctive adverbs come with a comma. When you use them, be sure to include a comma afterward!
There are a lot of conjunctive adverbs, but some common ones include also, anyway, besides, finally, further, however, indeed, instead, meanwhile, nevertheless, next, nonetheless, now, otherwise, similarly, then, therefore, and thus.
Adverbs of Place, Time, Manner, Degree, and Frequency
There are also adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency. Each of these types of adverbs express a different kind of meaning.
Adverbs of place express where an action is done or where an event occurs. These are used after the verb, direct object, or at the end of a sentence. A sentence like “She walked outside to watch the sunset” uses outside as an adverb of place.
Adverbs of time explain when something happens. These adverbs are used at the beginning or at the end of sentences. In a sentence like “The game should be over soon,” soon functions as an adverb of time.
Adverbs of manner describe the way in which something is done or how something happens. These are the adverbs that usually end in the familiar -ly. If we were to write “She quickly finished her homework,” quickly is an adverb of manner.
Adverbs of degree tell us the extent to which something happens or occurs. If we were to say “The play was quite interesting,” quite tells us the extent of how interesting the play was. Thus, quite is an adverb of degree.
Finally, adverbs of frequency express how often something happens . In a sentence like “They never know what to do with themselves,” never is an adverb of frequency.
Five subclasses of adverbs is a lot, so we’ve organized the words that fall under each category in a nifty table for you here:
It’s important to know about these subclasses of adverbs because many of them don’t follow the old adage that adverbs end in -ly.
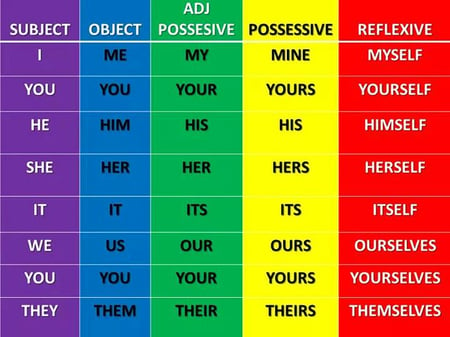
Here's a helpful list of pronouns. (Attanata / Flickr )
#5: Pronouns
Pronouns are words that can be substituted for a noun or noun phrase in a sentence . Pronouns function to make sentences less clunky by allowing people to avoid repeating nouns over and over. For example, if you were telling someone a story about your friend Destiny, you wouldn’t keep repeating their name over and over again every time you referred to them. Instead, you’d use a pronoun—like they or them—to refer to Destiny throughout the story.
Pronouns are typically short words, often only two or three letters long. The most familiar pronouns in the English language are they, she, and he. But these aren’t the only pronouns. There are many more pronouns in English that fall under different subclasses!
Subclasses of Pronouns, Including Examples
There are many subclasses of pronouns, but the most commonly used subclasses are personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, indefinite pronouns, and interrogative pronouns.
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are probably the most familiar type of pronoun. Personal pronouns include I, me, you, she, her, him, he, we, us, they, and them. These are called personal pronouns because they refer to a person! Personal pronouns can replace specific nouns in sentences, like a person’s name, or refer to specific groups of people, like in these examples:
Did you see Gia pole vault at the track meet? Her form was incredible!
The Cycling Club is meeting up at six. They said they would be at the park.
In both of the examples above, a pronoun stands in for a proper noun to avoid repetitiveness. Her replaces Gia in the first example, and they replaces the Cycling Club in the second example.
(It’s also worth noting that personal pronouns are one of the easiest ways to determine what point of view a writer is using.)
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are used to indicate that something belongs to or is the possession of someone. The possessive pronouns fall into two categories: limiting and absolute. In a sentence, absolute possessive pronouns can be substituted for the thing that belongs to a person, and limiting pronouns cannot.
The limiting pronouns are my, your, its, his, her, our, their, and whose, and the absolute pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs . Here are examples of a limiting possessive pronoun and absolute possessive pronoun used in a sentence:
Limiting possessive pronoun: Juan is fixing his car.
In the example above, the car belongs to Juan, and his is the limiting possessive pronoun that shows the car belongs to Juan. Now, here’s an example of an absolute pronoun in a sentence:
Absolute possessive pronoun: Did you buy your tickets ? We already bought ours .
In this example, the tickets belong to whoever we is, and in the second sentence, ours is the absolute possessive pronoun standing in for the thing that “we” possess—the tickets.
Demonstrative Pronouns, Interrogative Pronouns, and Indefinite Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns include the words that, this, these, and those. These pronouns stand in for a noun or noun phrase that has already been mentioned in a sentence or conversation. This and these are typically used to refer to objects or entities that are nearby distance-wise, and that and those usually refer to objects or entities that are farther away. Here’s an example of a demonstrative pronoun used in a sentence:
The books are stacked up in the garage. Can you put those away?
The books have already been mentioned, and those is the demonstrative pronoun that stands in to refer to them in the second sentence above. The use of those indicates that the books aren’t nearby—they’re out in the garage. Here’s another example:
Do you need shoes? Here...you can borrow these.
In this sentence, these refers to the noun shoes. Using the word these tells readers that the shoes are nearby...maybe even on the speaker’s feet!
Indefinite pronouns are used when it isn’t necessary to identify a specific person or thing . The indefinite pronouns are one, other, none, some, anybody, everybody, and no one. Here’s one example of an indefinite pronoun used in a sentence:
Promise you can keep a secret?
Of course. I won’t tell anyone.
In this example, the person speaking in the second two sentences isn’t referring to any particular people who they won’t tell the secret to. They’re saying that, in general, they won’t tell anyone . That doesn’t specify a specific number, type, or category of people who they won’t tell the secret to, which is what makes the pronoun indefinite.
Finally, interrogative pronouns are used in questions, and these pronouns include who, what, which, and whose. These pronouns are simply used to gather information about specific nouns—persons, places, and ideas. Let’s look at two examples of interrogative pronouns used in sentences:
Do you remember which glass was mine?
What time are they arriving?
In the first glass, the speaker wants to know more about which glass belongs to whom. In the second sentence, the speaker is asking for more clarity about a specific time.

Conjunctions hook phrases and clauses together so they fit like pieces of a puzzle.
#6: Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that are used to connect words, phrases, clauses, and sentences in the English language. This function allows conjunctions to connect actions, ideas, and thoughts as well. Conjunctions are also used to make lists within sentences. (Conjunctions are also probably the most famous part of speech, since they were immortalized in the famous “Conjunction Junction” song from Schoolhouse Rock .)
You’re probably familiar with and, but, and or as conjunctions, but let’s look into some subclasses of conjunctions so you can learn about the array of conjunctions that are out there!
Subclasses of Conjunctions, Including Examples
Coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions are three subclasses of conjunctions. Each of these types of conjunctions functions in a different way in sentences!
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions are probably the most familiar type of conjunction. These conjunctions include the words for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so (people often recommend using the acronym FANBOYS to remember the seven coordinating conjunctions!).
Coordinating conjunctions are responsible for connecting two independent clauses in sentences, but can also be used to connect two words in a sentence. Here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two independent clauses in a sentence:
He wanted to go to the movies, but he couldn’t find his car keys.
They put on sunscreen, and they went to the beach.
Next, here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two words:
Would you like to cook or order in for dinner?
The storm was loud yet refreshing.
The two examples above show that coordinating conjunctions can connect different types of words as well. In the first example, the coordinating conjunction “or” connects two verbs; in the second example, the coordinating conjunction “yet” connects two adjectives.
But wait! Why does the first set of sentences have commas while the second set of sentences doesn’t? When using a coordinating conjunction, put a comma before the conjunction when it’s connecting two complete sentences . Otherwise, there’s no comma necessary.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are used to link an independent clause to a dependent clause in a sentence. This type of conjunction always appears at the beginning of a dependent clause, which means that subordinating conjunctions can appear at the beginning of a sentence or in the middle of a sentence following an independent clause. (If you’re unsure about what independent and dependent clauses are, be sure to check out our guide to compound sentences.)
Here is an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears at the beginning of a sentence:
Because we were hungry, we ordered way too much food.
Now, here’s an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears in the middle of a sentence, following an independent clause and a comma:
Rakim was scared after the power went out.
See? In the example above, the subordinating conjunction after connects the independent clause Rakim was scared to the dependent clause after the power went out. Subordinating conjunctions include (but are not limited to!) the following words: after, as, because, before, even though, one, since, unless, until, whenever, and while.
Correlative Conjunctions
Finally, correlative conjunctions are conjunctions that come in pairs, like both/and, either/or, and neither/nor. The two correlative conjunctions that come in a pair must appear in different parts of a sentence to make sense— they correlate the meaning in one part of the sentence with the meaning in another part of the sentence . Makes sense, right?
Here are two examples of correlative conjunctions used in a sentence:
We’re either going to the Farmer’s Market or the Natural Grocer’s for our shopping today.
They’re going to have to get dog treats for both Piper and Fudge.
Other pairs of correlative conjunctions include as many/as, not/but, not only/but also, rather/than, such/that, and whether/or.

Interjections are single words that express emotions that end in an exclamation point. Cool!
#7: Interjections
Interjections are words that often appear at the beginning of sentences or between sentences to express emotions or sentiments such as excitement, surprise, joy, disgust, anger, or even pain. Commonly used interjections include wow!, yikes!, ouch!, or ugh! One clue that an interjection is being used is when an exclamation point appears after a single word (but interjections don’t have to be followed by an exclamation point). And, since interjections usually express emotion or feeling, they’re often referred to as being exclamatory. Wow!
Interjections don’t come together with other parts of speech to form bigger grammatical units, like phrases or clauses. There also aren’t strict rules about where interjections should appear in relation to other sentences . While it’s common for interjections to appear before sentences that describe an action or event that the interjection helps explain, interjections can appear after sentences that contain the action they’re describing as well.
Subclasses of Interjections, Including Examples
There are two main subclasses of interjections: primary interjections and secondary interjections. Let’s take a look at these two types of interjections!
Primary Interjections
Primary interjections are single words, like oh!, wow!, or ouch! that don’t enter into the actual structure of a sentence but add to the meaning of a sentence. Here’s an example of how a primary interjection can be used before a sentence to add to the meaning of the sentence that follows it:
Ouch ! I just burned myself on that pan!
While someone who hears, I just burned myself on that pan might assume that the person who said that is now in pain, the interjection Ouch! makes it clear that burning oneself on the pan definitely was painful.
Secondary Interjections
Secondary interjections are words that have other meanings but have evolved to be used like interjections in the English language and are often exclamatory. Secondary interjections can be mixed with greetings, oaths, or swear words. In many cases, the use of secondary interjections negates the original meaning of the word that is being used as an interjection. Let’s look at a couple of examples of secondary interjections here:
Well , look what the cat dragged in!
Heck, I’d help if I could, but I’ve got to get to work.
You probably know that the words well and heck weren’t originally used as interjections in the English language. Well originally meant that something was done in a good or satisfactory way, or that a person was in good health. Over time and through repeated usage, it’s come to be used as a way to express emotion, such as surprise, anger, relief, or resignation, like in the example above.

This is a handy list of common prepositional phrases. (attanatta / Flickr)
#8: Prepositions
The last part of speech we’re going to define is the preposition. Prepositions are words that are used to connect other words in a sentence—typically nouns and verbs—and show the relationship between those words. Prepositions convey concepts such as comparison, position, place, direction, movement, time, possession, and how an action is completed.
Subclasses of Prepositions, Including Examples
The subclasses of prepositions are simple prepositions, double prepositions, participle prepositions, and prepositional phrases.
Simple Prepositions
Simple prepositions appear before and between nouns, adjectives, or adverbs in sentences to convey relationships between people, living creatures, things, or places . Here are a couple of examples of simple prepositions used in sentences:
I’ll order more ink before we run out.
Your phone was beside your wallet.
In the first example, the preposition before appears between the noun ink and the personal pronoun we to convey a relationship. In the second example, the preposition beside appears between the verb was and the possessive pronoun your.
In both examples, though, the prepositions help us understand how elements in the sentence are related to one another. In the first sentence, we know that the speaker currently has ink but needs more before it’s gone. In the second sentence, the preposition beside helps us understand how the wallet and the phone are positioned relative to one another!
Double Prepositions
Double prepositions are exactly what they sound like: two prepositions joined together into one unit to connect phrases, nouns, and pronouns with other words in a sentence. Common examples of double prepositions include outside of, because of, according to, next to, across from, and on top of. Here is an example of a double preposition in a sentence:
I thought you were sitting across from me.
You see? Across and from both function as prepositions individually. When combined together in a sentence, they create a double preposition. (Also note that the prepositions help us understand how two people— you and I— are positioned with one another through spacial relationship.)
Prepositional Phrases
Finally, prepositional phrases are groups of words that include a preposition and a noun or pronoun. Typically, the noun or pronoun that appears after the preposition in a prepositional phrase is called the object of the preposition. The object always appears at the end of the prepositional phrase. Additionally, prepositional phrases never include a verb or a subject. Here are two examples of prepositional phrases:
The cat sat under the chair .
In the example above, “under” is the preposition, and “the chair” is the noun, which functions as the object of the preposition. Here’s one more example:
We walked through the overgrown field .
Now, this example demonstrates one more thing you need to know about prepositional phrases: they can include an adjective before the object. In this example, “through” is the preposition, and “field” is the object. “Overgrown” is an adjective that modifies “the field,” and it’s quite common for adjectives to appear in prepositional phrases like the one above.
While that might sound confusing, don’t worry: the key is identifying the preposition in the first place! Once you can find the preposition, you can start looking at the words around it to see if it forms a compound preposition, a double preposition of a prepositional phrase.

10 Question Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples
Since we’ve covered a lot of material about the 8 parts of speech with examples ( a lot of them!), we want to give you an opportunity to review and see what you’ve learned! While it might seem easier to just use a parts of speech finder instead of learning all this stuff, our parts of speech quiz can help you continue building your knowledge of the 8 parts of speech and master each one.
Are you ready? Here we go:
1) What are the 8 parts of speech?
a) Noun, article, adverb, antecedent, verb, adjective, conjunction, interjection b) Noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, determiner, clause, adjective, preposition c) Noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, conjunction, interjection, preposition
2) Which parts of speech have subclasses?
a) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs b) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, and prepositions c) All of them! There are many types of words within each part of speech.
3) What is the difference between common nouns and proper nouns?
a) Common nouns don’t refer to specific people, places, or entities, but proper nouns do refer to specific people, places, or entities. b) Common nouns refer to regular, everyday people, places, or entities, but proper nouns refer to famous people, places, or entities. c) Common nouns refer to physical entities, like people, places, and objects, but proper nouns refer to nonphysical entities, like feelings, ideas, and experiences.
4) In which of the following sentences is the emboldened word a verb?
a) He was frightened by the horror film . b) He adjusted his expectations after the first plan fell through. c) She walked briskly to get there on time.
5) Which of the following is a correct definition of adjectives, and what other part of speech do adjectives modify?
a) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns and noun phrases. b) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify verbs and adverbs. c) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns, verbs, and adverbs.
6) Which of the following describes the function of adverbs in sentences?
a) Adverbs express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty. b) Adverbs express an action performed by a subject. c) Adverbs describe nouns and noun phrases.
7) Which of the following answers contains a list of personal pronouns?
a) This, that, these, those b) I, you, me, we, he, she, him, her, they, them c) Who, what, which, whose
8) Where do interjections typically appear in a sentence?
a) Interjections can appear at the beginning of or in between sentences. b) Interjections appear at the end of sentences. c) Interjections appear in prepositional phrases.
9) Which of the following sentences contains a prepositional phrase?
a) The dog happily wagged his tail. b) The cow jumped over the moon. c) She glared, angry that he forgot the flowers.
10) Which of the following is an accurate definition of a “part of speech”?
a) A category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences. b) A category of words that are of similar length and spelling. c) A category of words that mean the same thing.
So, how did you do? If you got 1C, 2C, 3A, 4B, 5A, 6A, 7B, 8A, 9B, and 10A, you came out on top! There’s a lot to remember where the parts of speech are concerned, and if you’re looking for more practice like our quiz, try looking around for parts of speech games or parts of speech worksheets online!

What’s Next?
You might be brushing up on your grammar so you can ace the verbal portions of the SAT or ACT. Be sure you check out our guides to the grammar you need to know before you tackle those tests! Here’s our expert guide to the grammar rules you need to know for the SAT , and this article teaches you the 14 grammar rules you’ll definitely see on the ACT.
When you have a good handle on parts of speech, it can make writing essays tons easier. Learn how knowing parts of speech can help you get a perfect 12 on the ACT Essay (or an 8/8/8 on the SAT Essay ).
While we’re on the topic of grammar: keep in mind that knowing grammar rules is only part of the battle when it comes to the verbal and written portions of the SAT and ACT. Having a good vocabulary is also important to making the perfect score ! Here are 262 vocabulary words you need to know before you tackle your standardized tests.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

- Language , Speechwriting
Powerful Sentence Structure for Your Speech
Mannerofspeaking.
- May 26, 2016

Powerful sentence structure is fundamental to captivating writing or speaking. Here is a little gem of advice from writer Gary Provost . (The highlighting is mine.)
Vary Sentence Length This sentence has five words. Here are five more words. Five-word sentences are fine. But several together become monotonous. Listen to what is happening. The writing is getting boring. The sound of it drones. It’s like a stuck record. The ear demands some variety. Now listen. I vary the sentence length, and I create music. Music. The writing sings. It has a pleasant rhythm, a lilt, a harmony. I use short sentences. And I use sentences of medium length. And sometimes when I am certain the reader is rested, I will engage him with a sentence of considerable length, a sentence that burns with energy and builds with all the impetus of a crescendo, the roll of the drums, the crash of the cymbals—sounds that say listen to this, it is important. So write with a combination of short, medium, and long sentences. Create a sound that pleases the reader’s ear. Don’t just write words. Write music.
The difference in sentence structure between the first paragraph and the second and third paragraphs is stark. To get the full effect, read them aloud.
This advice is not just useful for novelists; it is also important when it comes to writing a speech. You want to vary the sentences so that there is a dynamic flow to your words. When the sentences contrast, the words come alive.
For example, take the sentence structure in Barack Obama’s speech after the 2008 New Hampshire Primary:
It was a creed written into the founding documents that declared the destiny of a nation. Yes, we can. It was whispered by slaves and abolitionists as they blazed a trail towards freedom through the darkest of nights. Yes, we can. It was sung by immigrants as they struck out from distant shores and pioneers who pushed westward against an unforgiving wilderness. Yes, we can. It was the call of workers who organized, women who reached for the ballot, a president who chose the moon as our new frontier, and a king who took us to the mountaintop and pointed the way to the promised land. Yes, we can, to justice and equality.
Two other thoughts when it comes to adding punch to your sentences.
The first is to write your speech as something to be heard, not to be read. Yes, the words may look nice on paper, but people are going to be listening, not reading. So write the way you would speak. Practice your speech out loud and record yourself. If a sentence sounds robotic, that is usually a sign that it needs to be revised.
The second is something about which I have written before , but it is worth repeating; namely, that you should write your speech out, not in paragraphs, but rather as a poem. This will allow you to get a sense for the rhythm of the words, the cadence, where to pause, where to place the emphasis. Even if you do not read your speech, crafting it this way will help you formulate your ideas, choose the right words and deliver them well.
By way of example, here is the second paragraph of Gary Provost’s advice above, rewritten as a poem:
Now listen. I vary the sentence length, and I create music. Music. The writing sings. It has a pleasant rhythm, a lilt, a harmony. I use short sentences. And I use sentences of medium length. And sometimes when I am certain the reader is rested, I will engage him with a sentence of considerable length, a sentence that burns with energy and builds with all the impetus of a crescendo, the roll of the drums, the crash of the cymbals— sounds that say listen to this, it is important.
Notice how each line ends with a powerful word. Notice, also how I have sometimes split a single sentence into multiple stanzas. Doing so makes the pauses and points of emphasis more obvious.
For more information about speechwriting—and a free speechwriting course—check out Global Speechwriter , the website of my friend, Brent Kerrigan. Brent has a wealth of speechwriting experience and knows his stuff.
Like this article?
I love speaking for a large public. In the past, I did theater as a hobby.
Thanks for the comment, Sophie. We share the same passion. Whether I am giving a speech or doing improv theatre, there is a real rush to being in front of an audience!
I agree…I love it too!
Interesting. I have been doing this intuitively. It must be because I have sang in choirs all my life and I am also a professional dancer. Or was, anyway. Music is an intrinsic part of life. It is intertwined in my DNA.
Completely agree about the significance of music in our lives. Thanks for the comment.
Thanks John for sharing and spreading more good public speaking ideas & pointers.
I particularly appreciate your final point of not writing out a “final or reading script” in paragraphs but as a poem. It is surprising how infrequently this approach is actually used.
I find this approach has an additional benefit. It is a good way to make a final reading script when I do not have the luxury of memorizing the speech. Each line is a “snap-shot” or “chunk”. This makes “never-read-and-speak-at-the-same-time” more achievable. I have described it in more detail in a recent answer to a QUORA question: Point 3. May be of interest to your readers: https://www.quora.com/How-do-I-remember-so-many-informations-for-presentation-or-speech/answer/Rashid-Kapadia?srid=HrGm&share=2875c063
Good Luck … Rashid
Thank you, Rashid. And a terrific answer on Quora! In fact, I use the “memory palace” to remember lists of things. I learned it years ago from a cassette tape that my father played for me on battery-operated tape recorder during a long-distance car trip. I was fascinated by the concept. In my case, I use 20 different parts of a car to remember lists of 20 and more things.
Very good to note that you appreciate the value of “memory palace” approach. I cannot recommend “Moonwalking with Einstein” highly enough. I think it is specially important to expose children to this technique. After all “our lives are the sum of our memories”.
That’s a great example from Gary, so thanks for sharing it.
If your mind’s at all like mine, you’ll have specific sentence lengths in mind for each highlight colour you use. I’m curious what those numbers were!
What a fantastic tip about writing out a speech as a poem. Currently I tend to use bold text to show where I’ll stress a word, but sometimes I end up with too many of those and it sounds unnatural. So I’ll have to try your “stanza” method.
P.S. The photo of a stone wall really reminds of a picture of multicoloured tiles that I used in my post called “How consistent should you make your slides?” My answer to that rhetorical question is “Go for cohesion instead.” Just like samey sentences sound soporific, what I call “cookie-cutter consistency” on your slides puts people to sleep, too!
Thanks, Craig. When I saw the writing example from Gary, I knew that I had to write about it. Of course, we speak differently than we write, but the principle of varying the length of our sentence or phrases is the same.
Writing speeches out like a poem is something I started doing a long time ago. I remember reading somewhere that when Winston Churchill reviewed his speeches that he had had typed up for him, he would insist that each line had to end with a word that could be emphasized. Ending a line with a “the” or an “an” was not acceptable!
This approach could work for reading too. Anything to energise an email. Cut though the clutter.
Absolutely, Bridgit. In fact, the inspiration comes from an article on writing and reading.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Please enter an answer in digits: 5 + nineteen =

Testimonials

John delivered a keynote address about the importance of public speaking to 80 senior members of Gore’s Medical Device Europe team at an important sales event. He was informative, engaging and inspirational. Everyone was motivated to improve their public speaking skills. Following his keynote, John has led public speaking workshops for Gore in Barcelona and Munich. He is an outstanding speaker who thinks carefully about the needs of his audience well before he steps on stage.
Karsta Goetze
TA Leader, Gore and Associates

I first got in touch with John while preparing to speak at TED Global about my work on ProtonMail. John helped me to sharpen the presentation and get on point faster, making the talk more focused and impactful. My speech was very well received, has since reached almost 1.8 million people and was successful in explaining a complex subject (email encryption) to a general audience.
CEO, Proton Technologies

John gave the opening keynote on the second day of our unit’s recent offsite in Geneva, addressing an audience of 100+ attendees with a wealth of tips and techniques to deliver powerful, memorable presentations. I applied some of these techniques the very next week in an internal presentation, and I’ve been asked to give that presentation again to senior management, which has NEVER happened before. John is one of the greatest speakers I know and I can recommend his services without reservation.
David Lindelöf
Senior Data Scientist, Expedia Group

After a morning of team building activities using improvisation as the conduit, John came on stage to close the staff event which was organised in Chamonix, France. His energy and presence were immediately felt by all the members of staff. The work put into the preparation of his speech was evident and by sharing some his own stories, he was able to conduct a closing inspirational speech which was relevant, powerful and impactful for all at IRU. The whole team left feeling engaged and motivated to tackle the 2019 objectives ahead. Thank you, John.
Umberto de Pretto
Secretary General, World Road Transport Organization

I was expecting a few speaking tips and tricks and a few fun exercises, but you went above and beyond – and sideways. You taught me to stand tall. You taught me to anchor myself. You taught me to breathe. You taught me to open up. You taught me to look people in the eye. You taught me to tell the truth. You taught me to walk a mile in someone else’s shoes. I got more than I bargained for in the best possible way.
Thuy Khoc-Bilon
World Cancer Day Campaign Manager, Union for International Cancer Control

John gave a brilliant presentation on public speaking during the UN EMERGE programme in Geneva (a two days workshop on leadership development for a group of female staff members working in the UN organizations in Geneva). His talk was inspirational and practical, thanks to the many techniques and tips he shared with the audience. His teaching can dramatically change our public speaking performance and enable us as presenters to have a real and powerful impact. Thank you, John, for your great contribution!
HR Specialist, World Health Organization

John is a genuine communication innovator. His seminars on gamification of public speaking learning and his interactive Rhetoric game at our conference set the tone for change and improvement in our organisation. The quality of his input, the impact he made with his audience and his effortlessly engaging style made it easy to get on board with his core messages and won over some delegates who were extremely skeptical as to the efficacy of games for learning. I simply cannot recommend him highly enough.
Thomas Scott
National Education Director, Association of Speakers Clubs UK

John joined our Global Sales Meeting in Segovia, Spain and we all participated in his "Improv(e) your Work!" session. I say “all” because it really was all interactive, participatory, learning and enjoyable. The session surprised everybody and was a fresh-air activity that brought a lot of self-reflection and insights to improve trust and confidence in each other inside our team. It´s all about communication and a good manner of speaking!"
General Manager Europe, Hayward Industries

Thank you very much for the excellent presentation skills session. The feedback I received was very positive. Everyone enjoyed the good mix of listening to your speech, co-developing a concrete take-away and the personal learning experience. We all feel more devoted to the task ahead, more able to succeed and an elevated team spirit. Delivering this in a short time, both in session and in preparation, is outstanding!
Henning Dehler
CFO European Dairy Supply Chain & Operations, Danone

Thanks to John’s excellent workshop, I have learned many important tips and techniques to become an effective public speaker. John is a fantastic speaker and teacher, with extensive knowledge of the field. His workshop was a great experience and has proven extremely useful for me in my professional and personal life.
Eric Thuillard
Senior Sales Manager, Sunrise Communications

John’s presentation skills training was a terrific investment of my time. I increased my skills in this important area and feel more comfortable when speaking to an audience. John provided the right mix between theory and practice.
Diego Brait
Director of the Jura Region, BKW Energie AG

Be BOLD. Those two words got stuck in my head and in the heads of all those ADP leaders and associates that had the privilege to see John on stage. He was our keynote speaker at our annual convention in Barcelona, and his message still remains! John puts his heart in every word. Few speakers are so credible, humble and yet super strong with large audiences!
Guadalupe Garcia
Senior Director and Talent Partner, ADP International

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Grammar: Sentence Structure and Types of Sentences
Definitions and examples of basic sentence elements.
The Mastering the Mechanics webinar series also describes required sentence elements and varying sentence types. Please see these archived webinars for more information.
Key: Yellow, bold = subject; green underline = verb, blue, italics = object, pink, regular font = prepositional phrase
Independent clause : An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence. It contains a subject and a verb and is a complete idea.
- I like spaghetti .
- He reads many books .
Dependent clause : A dependent clause is not a complete sentence. It must be attached to an independent clause to become complete. This is also known as a subordinate clause.
- Although I like spaghetti,…
- Because he reads many books,…
Subject : A person, animal, place, thing, or concept that does an action. Determine the subject in a sentence by asking the question “Who or what?”
- I like spaghetti.
- He reads many books.
Verb : Expresses what the person, animal, place, thing, or concept does. Determine the verb in a sentence by asking the question “What was the action or what happened?”
- The movie is good. (The be verb is also sometimes referred to as a copula or a linking verb. It links the subject, in this case "the movie," to the complement or the predicate of the sentence, in this case, "good.")
Object : A person, animal, place, thing, or concept that receives the action. Determine the object in a sentence by asking the question “The subject did what?” or “To whom?/For whom?”
Prepositional Phrase : A phrase that begins with a preposition (i.e., in, at for, behind, until, after, of, during) and modifies a word in the sentence. A prepositional phrase answers one of many questions. Here are a few examples: “Where? When? In what way?”
- I like spaghetti for dinner .
- He reads many books in the library .
English Sentence Structure
The following statements are true about sentences in English:
- H e obtained his degree.
- He obtained his degree .
- Smith he obtained his degree.
- He obtained his degree.
- He (subject) obtained (verb) his degree (object).
Simple Sentences
A simple sentence contains a subject and a verb, and it may also have an object and modifiers. However, it contains only one independent clause.
Key: Yellow, bold = subject; green underline = verb, blue, italics = object, pink, regular font =prepositional phrase
Here are a few examples:
- She wrote .
- She completed her literature review .
- He organized his sources by theme .
- They studied APA rules for many hours .
Compound Sentences
A compound sentence contains at least two independent clauses. These two independent clauses can be combined with a comma and a coordinating conjunction or with a semicolon .
Key: independent clause = yellow, bold ; comma or semicolon = pink, regular font ; coordinating conjunction = green, underlined
- She completed her literature review , and she created her reference list .
- He organized his sources by theme ; then, he updated his reference list .
- They studied APA rules for many hours , but they realized there was still much to learn .
Using some compound sentences in writing allows for more sentence variety .
Complex Sentences
A complex sentence contains at least one independent clause and at least one dependent clause. Dependent clauses can refer to the subject (who, which) the sequence/time (since, while), or the causal elements (because, if) of the independent clause.
If a sentence begins with a dependent clause, note the comma after this clause. If, on the other hand, the sentence begins with an independent clause, there is not a comma separating the two clauses.
Key: independent clause = yellow, bold ; comma = pink, regular font ; dependent clause = blue, italics
- Note the comma in this sentence because it begins with a dependent clause.
- Note that there is no comma in this sentence because it begins with an independent clause.
- Using some complex sentences in writing allows for more sentence variety .
Compound-Complex Sentences
Sentence types can also be combined. A compound-complex sentence contains at least two independent clauses and at least one dependent clause.
Key: independent clause = yellow, bold ; comma or semicolon = pink, regular font ; coordinating conjunction = green, underlined ; dependent clause = blue, italics
- She completed her literature review , but she still needs to work on her methods section even though she finished her methods course last semester .
- Although he organized his sources by theme , he decided to arrange them chronologically , and he carefully followed the MEAL plan for organization .
- T hey studied APA rules for many hours , and they decided that writing in APA made sense because it was clear, concise, and objective .
- Using some complex-compound sentences in writing allows for more sentence variety .
- Pay close attention to comma usage in complex-compound sentences so that the reader is easily able to follow the intended meaning.
Sentence Structure Video Playlist
Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.
- Structuring Sentences: Types of Sentences (video transcript)
- Structuring Sentences: Simple Sentences (video transcript)
- Structuring Sentences: Compound Sentences (video transcript)
- Structuring Sentences: Complex Sentences (video transcript)
- Structuring Sentences: Combining Sentences (video transcript)
- Common Error: Unclear Subjects (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Punctuation as Symbols (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Commas (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Periods (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Semicolons (video transcript)
Related Resources
Knowledge Check: Sentence Structure and Types of Sentences
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Main Parts of Speech
- Next Page: Run-On Sentences and Sentence Fragments
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
How do you write direct speech in English? - Easy Learning Grammar
- The comma comes inside the quotation marks, unless the reporting verb is positioned inside a reported sentence that itself does not require a comma.
- Typical reporting verbs are: agree, answer, ask, inquire, explain, say, tell, and wonder.
- The words spoken are enclosed in inverted commas (single or double quotation marks).
- Single quotation marks are often used to draw attention to a word that is being mentioned for a particular purpose.
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

Pasco-Hernando State College
Parts of a Sentence
- Punctuation
- Parts of Speech
- Sentence Variety
- Problems with Sentences
Related Pages
- Sentence Structure
What is a Sentence?
A sentence must contain a subject and a predicate . The subject must contain a noun or nominal word, and the predicate must contain a verb. A sentence can be as simple as a noun and a verb.
- Example: Birds fly.
The subject can contain more than a noun, and the predicate can contain more than a verb.
- Example: Migratory birds fly to Florida.
In the above example, the subject contains an adjective ( migratory ) and a noun ( birds ), and the predicate contains a verb ( fly ), a preposition ( to ), and a direct object ( Florida ).
In this section we will examine the different parts of a sentence including: subject, predicate, object, complement, phrase, and clause.
- Printer-friendly version

EnglishGrammarSoft

The Parts of Speech Examples (127 Mixed Sentences)
What are parts of speech.
Parts of speech are the building blocks or components of a sentence. All words belong to one part of speech or another; there are eight parts of speech in all. Knowing what they are will help you choose your words wisely and use them correctly in your writing.
Parts of Speech Examples
Nouns sentences.
- The cat is fat.
- My dog likes to lick people’s faces.
- A house can be a place for living or an investment property.
- Spain has many different types of cheese , such as Manchego and Idiazabal.
- I need some apples for my lunch today.
- My parents live in North America.
- I like to eat bananas for breakfast.
- I like to put jam on toast .
- Fruits are my favorite dessert.
- We were ordered to carry sacks of rice across the river .
- The best way to start a business is to know what you need before beginning.
- Always look at the big picture when creating a product .
- I recently met your brother ’s girlfriend .
- The newly elected president was sworn in on January 12th, 2019.
- He quickly walked out of the room .
Pronouns Sentences
- I went to the store yesterday
- They are my favorite animal
- She is so nice.
- He lives in this house next door.
- I have my own car.
- She may go to Hawaii next month.
- The man who helped us is my brother.
- They are here somewhere.
- He played for years before he became famous.
- Did you like the film?
- He plays the guitar.
- You are an important part of this project.
- His dog is cute.
- I love the new dress you bought.
- You are always helping me with my work, thanks!
You may also like: Parts of Speech Free Posters
Verb Sentences
- She puts the entire responsibility on him.
- I went to the mall.
- He decided to pursue his dream to become a drummer on its own.
- She spoke for an hour.
- They suggested an alternative.
- We showed them around.
- The match made it three on the bounce.
- You were told to hold tight, but you leant back on the rope and fell over.
- They finally agreed on a price with their business partner, after several months of negotiation.
- Did he order a lobster or a steak?
- I like to workout at home.
- She decided to start running.
- I would like to take a vacation.
- They wanted to go camping.
- You should work on your Spanish.
- It’s important to learn how to cook basic meals.
- I like to look at the stars and plan my day tomorrow.
- My first job out of college was as an assistant manager at Starbucks and I loved it.
- Furthermore, I would work hard on my new business and close the gap between my income and how much I was spending.
- She founded her first business as a result of moving to a new town, where she needed a way to meet new people.
Adverb Sentences
- Steve will always say what he thinks.
- I am waiting patiently for my pay rise.
- She left very quickly .
- The bill was paid promptly .
- I will definitely complete it soon.
- And they did it immediately .
- Lisa presently earns more money.
- It is finally finished.
- The medicine only works temporarily.
- She was totally exhausted after the ordeal.
- She immediately cancelled her membership.
- We eventually found a solution.
- Their voices were gradually fading away.
- I will gladly help you whenever you need it.
- She hasn’t been very consistent at sleeping lately .
Adjectives Sentences
- She is the kindest person in the class.
- I need a new dress for the party.
- This is the coldest winter we have ever had.
- The tree was full of green leaves.
- You are the most beautiful person ever!
- The fox was funny with its big bushy tail!
- The large conference table was perfectly suited for the big conference room.
- The small desk was perfectly suited for the small office.
- The purple chair was perfectly suited for the pink room.
- The long conference table was not suited for the short conference room.
- The blue chair was not suited for the yellow room.
- The wooden desk was not suited for the carpeted floor.
- The big table is perfect for the big meeting room.
- Sometimes drastic measures are necessary to turn a company around.
- The government needs to understand the gravity of the economic crisis.
Preposition Sentences
- The book is lying on the table.
- I’m going to put a piece of paper below this book.
- He went to the hospital.
- I have to work on Saturday.
- The world champion spoke with the President of Brazil about corruption in sport.
- The stove burst open with a bang.
- She didn’t want to do so without her brother.
- The dog seemed very happy to meet you.
- She came out the door crying.
- On average, people sleep for 8 hours each night.
- Your flight leaves in 20 minutes.
- She presided over the meeting.
- We are behind schedule.
- We are running late for work.
- It’s in front of the house.
- It’s located in front of our home.
- This is a project about leadership.
- One way to get there is by setting goals.
- That’s the purpose of this site.
Conjunction Sentences
- I went to the cinema, but I didn’t enjoy it.
- I was really tired during the day, so I woke up later than usual. And when I woke up, I had no time to get ready for school.
- He waited a long time, but his parents did not come back home.
- Choose a number from 1-10 and write its name in the box.
- I love this dress, but there are no sleeves.
- These tacos are tasty but they are spicy.
- She is a top actress as well as a social worker.
- She walked in with her friends, but left alone the moment she saw the crowd waiting for autographs at the entrance of the theatre.
- It is also important that the media covers all sides of the story.
- Finally, economy will diminish because many companies will go bankrupt if they are not able to remain competitive.
- Writers are supposed to be excited about what they are writing about.
Interjection Sentences
- Wow! I can’t believe I won!
- Yay, it’s the weekend!
- Aww, you’re so sweet.
- Yikes, that’s a lot of work.
- Oops, I forgot my wallet!
- Wow! I can’t believe I hit the jackpot!
- Be careful! You might fall off that ladder!
- It’s amazing! We won the lottery!
- Yay! We have a better looking lawn than our neighbors.
- How fun! We have been randomly selected to win two free tickets to a rock concert.
- Aww, poor little one, did you hurt yourself?
- Wow! I can’t believe I got an “A” on my math test!
- Oh how exciting! Prize money awaits!
- Yippee! We’ve hit the jackpot!
- Thanks for your help! I’m having so much fun up here.
- Oh, man! I can’t wait for the weekend!
- Yay, I’m so excited!

Further Reading
- 8 Parts of Speech with Examples | An Easy Guide for you
- Parts of Speech Exercises [Worksheet] with Answers
- Parts of Speech Lesson Plans
- Nouns | What are 11 Types of Nouns? Explain with Examples | Useful Guide
- Pronoun | What does pronoun mean? Different Types of Pronouns with 60+ Perfect Examples
- How do you describe adjectives? 13 Types of Adjectives with Examples
- What does adverb mean? 11 Types of Adverb with Examples
What is a preposition? Types of Preposition According to Function
What are the verbs in english | types of verbs and examples.
- What are the 4 types of conjunctions? | Conjunction rules with examples
- Adjectives Exercises with Answers
Preposition Usage and Examples
- Interjections Definition and Examples | Interjections Anchor Chart
Similar Posts

Conjunction Sentences (50 Examples)
50 Conjunction Sentences We have narrated conjunction sentences. You will find here examples of all types of conjunctions. Let’s start! 1 – Coordinating Conjunction:- 1.1…

What are the verbs in English? The verb is concerned with doing and being. Its function is to make a statement, to ask questions, and…

In this post, we are covering preposition, its types with examples and rules. Following points will be covered. What is a preposition? List of Prepositions…

Sentences of Adjectives (50 Examples)
Sentences of Adjectives Sentences of Adjectives of Quality Brutus was an ideal man of Rome. I have a white cow. I am black. Rita is an ideal wife. Tom is…

A preposition is used to show the relation of one thing to another. It connects a noun or a pronoun with a verb, adjective, pronoun…

Parts of Speech Posters (Free Printables)
Parts of speech posters are a great way to reinforce language arts skills in your classroom. Students can use these posters to help them identify…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

15 Powerful Speech Opening Lines (And How to Create Your Own)
Hrideep barot.
- Public Speaking , Speech Writing

Powerful speech opening lines set the tone and mood of your speech. It’s what grips the audience to want to know more about the rest of your talk.
The first few seconds are critical. It’s when you have maximum attention of the audience. And you must capitalize on that!
Instead of starting off with something plain and obvious such as a ‘Thank you’ or ‘Good Morning’, there’s so much more you can do for a powerful speech opening (here’s a great article we wrote a while ago on how you should NOT start your speech ).
To help you with this, I’ve compiled some of my favourite openings from various speakers. These speakers have gone on to deliver TED talks , win international Toastmaster competitions or are just noteworthy people who have mastered the art of communication.
After each speaker’s opening line, I have added how you can include their style of opening into your own speech. Understanding how these great speakers do it will certainly give you an idea to create your own speech opening line which will grip the audience from the outset!
Alright! Let’s dive into the 15 powerful speech openings…
Note: Want to take your communications skills to the next level? Book a complimentary consultation with one of our expert communication coaches. We’ll look under the hood of your hurdles and pick two to three growth opportunities so you can speak with impact!
1. Ric Elias
Opening: “Imagine a big explosion as you climb through 3,000 ft. Imagine a plane full of smoke. Imagine an engine going clack, clack, clack. It sounds scary. Well I had a unique seat that day. I was sitting in 1D.”
How to use the power of imagination to open your speech?
Putting your audience in a state of imagination can work extremely well to captivate them for the remainder of your talk.
It really helps to bring your audience in a certain mood that preps them for what’s about to come next. Speakers have used this with high effectiveness by transporting their audience into an imaginary land to help prove their point.
When Ric Elias opened his speech, the detail he used (3000 ft, sound of the engine going clack-clack-clack) made me feel that I too was in the plane. He was trying to make the audience experience what he was feeling – and, at least in my opinion, he did.
When using the imagination opening for speeches, the key is – detail. While we want the audience to wander into imagination, we want them to wander off to the image that we want to create for them. So, detail out your scenario if you’re going to use this technique.
Make your audience feel like they too are in the same circumstance as you were when you were in that particular situation.
2. Barack Obama
Opening: “You can’t say it, but you know it’s true.”
3. Seth MacFarlane
Opening: “There’s nowhere I would rather be on a day like this than around all this electoral equipment.” (It was raining)
How to use humour to open your speech?
When you use humour in a manner that suits your personality, it can set you up for a great speech. Why? Because getting a laugh in the first 30 seconds or so is a great way to quickly get the audience to like you.
And when they like you, they are much more likely to listen to and believe in your ideas.
Obama effortlessly uses his opening line to entice laughter among the audience. He brilliantly used the setting (the context of Trump becoming President) and said a line that completely matched his style of speaking.
Saying a joke without really saying a joke and getting people to laugh requires you to be completely comfortable in your own skin. And that’s not easy for many people (me being one of them).
If the joke doesn’t land as expected, it could lead to a rocky start.
Keep in mind the following when attempting to deliver a funny introduction:
- Know your audience: Make sure your audience gets the context of the joke (if it’s an inside joke among the members you’re speaking to, that’s even better!). You can read this article we wrote where we give you tips on how you can actually get to know your audience better to ensure maximum impact with your speech openings
- The joke should suit your natural personality. Don’t make it look forced or it won’t elicit the desired response
- Test the opening out on a few people who match your real audience. Analyze their response and tweak the joke accordingly if necessary
- Starting your speech with humour means your setting the tone of your speech. It would make sense to have a few more jokes sprinkled around the rest of the speech as well as the audience might be expecting the same from you
4. Mohammed Qahtani
Opening: Puts a cigarette on his lips, lights a lighter, stops just before lighting the cigarette. Looks at audience, “What?”
5. Darren Tay
Opening: Puts a white pair of briefs over his pants.
How to use props to begin your speech?
The reason props work so well in a talk is because in most cases the audience is not expecting anything more than just talking. So when a speaker pulls out an object that is unusual, everyone’s attention goes right to it.
It makes you wonder why that prop is being used in this particular speech.
The key word here is unusual . To grip the audience’s attention at the beginning of the speech, the prop being used should be something that the audience would never expect. Otherwise, it just becomes something that is common. And common = boring!
What Mohammed Qahtani and Darren Tay did superbly well in their talks was that they used props that nobody expected them to.
By pulling out a cigarette and lighter or a white pair of underwear, the audience can’t help but be gripped by what the speaker is about to do next. And that makes for a powerful speech opening.
6. Simon Sinek
Opening: “How do you explain when things don’t go as we assume? Or better, how do you explain when others are able to achieve things that seem to defy all of the assumptions?”
7. Julian Treasure
Opening: “The human voice. It’s the instrument we all play. It’s the most powerful sound in the world. Probably the only one that can start a war or say “I love you.” And yet many people have the experience that when they speak people don’t listen to them. Why is that? How can we speak powerfully to make change in the world?”
How to use questions to open a speech?
I use this method often. Starting off with a question is the simplest way to start your speech in a manner that immediately engages the audience.
But we should keep our questions compelling as opposed to something that is fairly obvious.
I’ve heard many speakers start their speeches with questions like “How many of us want to be successful?”
No one is going to say ‘no’ to that and frankly, I just feel silly raising my hand at such questions.
Simon Sinek and Jullian Treasure used questions in a manner that really made the audience think and make them curious to find out what the answer to that question is.
What Jullian Treasure did even better was the use of a few statements which built up to his question. This made the question even more compelling and set the theme for what the rest of his talk would be about.
So think of what question you can ask in your speech that will:
- Set the theme for the remainder of your speech
- Not be something that is fairly obvious
- Be compelling enough so that the audience will actually want to know what the answer to that question will be
8. Aaron Beverley
Opening: Long pause (after an absurdly long introduction of a 57-word speech title). “Be honest. You enjoyed that, didn’t you?”
How to use silence for speech openings?
The reason this speech opening stands out is because of the fact that the title itself is 57 words long. The audience was already hilariously intrigued by what was going to come next.
But what’s so gripping here is the way Aaron holds the crowd’s suspense by…doing nothing. For about 10 to 12 seconds he did nothing but stand and look at the audience. Everyone quietened down. He then broke this silence by a humorous remark that brought the audience laughing down again.
When going on to open your speech, besides focusing on building a killer opening sentence, how about just being silent?
It’s important to keep in mind that the point of having a strong opening is so that the audience’s attention is all on you and are intrigued enough to want to listen to the rest of your speech.
Silence is a great way to do that. When you get on the stage, just pause for a few seconds (about 3 to 5 seconds) and just look at the crowd. Let the audience and yourself settle in to the fact that the spotlight is now on you.
I can’t put my finger on it, but there is something about starting the speech off with a pure pause that just makes the beginning so much more powerful. It adds credibility to you as a speaker as well, making you look more comfortable and confident on stage.
If you want to know more about the power of pausing in public speaking , check out this post we wrote. It will give you a deeper insight into the importance of pausing and how you can harness it for your own speeches. You can also check out this video to know more about Pausing for Public Speaking:
9. Dan Pink
Opening: “I need to make a confession at the outset here. Little over 20 years ago, I did something that I regret. Something that I’m not particularly proud of. Something that in many ways I wish no one would ever know but that here I feel kind of obliged to reveal.”
10. Kelly McGonigal
Opening: “I have a confession to make. But first I want you to make a little confession to me.”
How to use a build-up to open your speech?
When there are so many amazing ways to start a speech and grip an audience from the outset, why would you ever choose to begin your speech with a ‘Good morning?’.
That’s what I love about build-ups. They set the mood for something awesome that’s about to come in that the audience will feel like they just have to know about.
Instead of starting a speech as it is, see if you can add some build-up to your beginning itself. For instance, in Kelly McGonigal’s speech, she could have started off with the question of stress itself (which she eventually moves on to in her speech). It’s not a bad way to start the speech.
But by adding the statement of “I have a confession to make” and then not revealing the confession for a little bit, the audience is gripped to know what she’s about to do next and find out what indeed is her confession.
11. Tim Urban
Opening: “So in college, I was a government major. Which means that I had to write a lot of papers. Now when a normal student writes a paper, they might spread the work out a little like this.”
12. Scott Dinsmore
Opening: “8 years ago, I got the worst career advice of my life.”
How to use storytelling as a speech opening?
“The most powerful person in the world is the storyteller.” Steve Jobs
Storytelling is the foundation of good speeches. Starting your speech with a story is a great way to grip the audience’s attention. It makes them yearn to want to know how the rest of the story is going to pan out.
Tim Urban starts off his speech with a story dating back to his college days. His use of slides is masterful and something we all can learn from. But while his story sounds simple, it does the job of intriguing the audience to want to know more.
As soon as I heard the opening lines, I thought to myself “If normal students write their paper in a certain manner, how does Tim write his papers?”
Combine such a simple yet intriguing opening with comedic slides, and you’ve got yourself a pretty gripping speech.
Scott Dismore’s statement has a similar impact. However, just a side note, Scott Dismore actually started his speech with “Wow, what an honour.”
I would advise to not start your talk with something such as that. It’s way too common and does not do the job an opening must, which is to grip your audience and set the tone for what’s coming.
13. Larry Smith
Opening: “I want to discuss with you this afternoon why you’re going to fail to have a great career.”
14. Jane McGonigal
Opening: “You will live 7.5 minutes longer than you would have otherwise, just because you watched this talk.”
How to use provocative statements to start your speech?
Making a provocative statement creates a keen desire among the audience to want to know more about what you have to say. It immediately brings everyone into attention.
Larry Smith did just that by making his opening statement surprising, lightly humorous, and above all – fearful. These elements lead to an opening statement which creates so much curiosity among the audience that they need to know how your speech pans out.
This one time, I remember seeing a speaker start a speech with, “Last week, my best friend committed suicide.” The entire crowd was gripped. Everyone could feel the tension in the room.
They were just waiting for the speaker to continue to know where this speech will go.
That’s what a hard-hitting statement does, it intrigues your audience so much that they can’t wait to hear more! Just a tip, if you do start off with a provocative, hard-hitting statement, make sure you pause for a moment after saying it.
Silence after an impactful statement will allow your message to really sink in with the audience.
Related article: 5 Ways to Grab Your Audience’s Attention When You’re Losing it!
15. Ramona J Smith
Opening: In a boxing stance, “Life would sometimes feel like a fight. The punches, jabs and hooks will come in the form of challenges, obstacles and failures. Yet if you stay in the ring and learn from those past fights, at the end of each round, you’ll be still standing.”
How to use your full body to grip the audience at the beginning of your speech?
In a talk, the audience is expecting you to do just that – talk. But when you enter the stage and start putting your full body into use in a way that the audience does not expect, it grabs their attention.
Body language is critical when it comes to public speaking. Hand gestures, stage movement, facial expressions are all things that need to be paid attention to while you’re speaking on stage. But that’s not I’m talking about here.
Here, I’m referring to a unique use of the body that grips the audience, like how Ramona did. By using her body to get into a boxing stance, imitating punches, jabs and hooks with her arms while talking – that’s what got the audience’s attention.
The reason I say this is so powerful is because if you take Ramona’s speech and remove the body usage from her opening, the entire magic of the opening falls flat.
While the content is definitely strong, without those movements, she would not have captured the audience’s attention as beautifully as she did with the use of her body.
So if you have a speech opening that seems slightly dull, see if you can add some body movement to it.
If your speech starts with a story of someone running, actually act out the running. If your speech starts with a story of someone reading, actually act out the reading.
It will make your speech opening that much more impactful.
Related article: 5 Body Language Tips to Command the Stage
Level up your public speaking in 15 minutes!
Get the exclusive Masterclass video delivered to your inbox to see immediate speaking results.
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Final Words
So there it is! 15 speech openings from some of my favourite speeches. Hopefully, these will act as a guide for you to create your own opening which is super impactful and sets you off on the path to becoming a powerful public speaker!
But remember, while a speech opening is super important, it’s just part of an overall structure.
If you’re serious about not just creating a great speech opening but to improve your public speaking at an overall level, I would highly recommend you to check out this course: Acumen Presents: Chris Anderson on Public Speaking on Udemy. Not only does it have specific lectures on starting and ending a speech, but it also offers an in-depth guide into all the nuances of public speaking.
Being the founder of TED Talks, Chris Anderson provides numerous examples of the best TED speakers to give us a very practical way of overcoming stage fear and delivering a speech that people will remember. His course has helped me personally and I would definitely recommend it to anyone looking to learn public speaking.
No one is ever “done” learning public speaking. It’s a continuous process and you can always get better. Keep learning, keep conquering and keep being awesome!
Lastly, if you want to know how you should NOT open your speech, we’ve got a video for you:
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

Lost Voice? Here’s How to Recover Sore Throat and Speak Again

7 Keys to Emcee Like a Pro: Unlock Your Hosting Potential

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.


“Speech” in a Sentence (with Audio)
Examples of how to use the word “speech” in a sentence. How to connect “speech” with other words to make correct English sentences.
speech (n): the ability to talk, the activity of talking, or a piece of spoken language
Use “speech” in a sentence
Related lessons.
“Why” in a Sentence (with Audio)
“Who” in a Sentence (with Audio)
“Whether” in a Sentence (with Audio)
“Where” in a Sentence (with Audio)
“When” in a Sentence (with Audio)
“What” in a Sentence (with Audio)
“Washing” in a Sentence (with Audio)
“Wash” in a Sentence (with Audio)
Leave a Reply:
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
trending now in US News

English teacher at posh $61K-per-year NYC school resigns after...

Knife-wielding madman attacks 4 girls at movie theater, 2 others...

NYC straphanger who was set on fire blocked fiancée from...

Hillary Clinton praises 'tremendously impressive' GOP tactics,...

At least 11 killed as powerful tornadoes devastate Texas town,...

Seattle museum shut down by staffers who walk off job to protest...

Tennessee adults, children brawl during chaotic kindergarten...

Former Red Lobster execs describe 'miserable' work environment,...
White house makes nine brutal corrections to biden’s naacp detroit speech.
- View Author Archive
- Get author RSS feed
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
They went the whole nine yards with this one.
White House officials went into cleanup mode after President Biden delivered a gaffe-riddled speech to the NAACP in Detroit Sunday — making a whopping nine corrections to the formal transcript.
The changes fixed both trips of Biden’s tongue — such as calling Capitol rioters “irrectionists” — and flagrant retellings of history, like claiming he was still vice president during the COVID-19 pandemic .

The official transcript, released Monday, made no bones about the errors, with strikethroughs of Biden’s mistakes and the corrected comments included in brackets.
The 81-year-old’s address to the 69th annual Fight for Freedom Fund Dinner was part of an outreach effort to black Americans as polls show support for him softening in the demographic.
Here are the nine adjustments that were made in the official transcript :
Vice president during the pandemic
During his opening, Biden conveyed his “love” for Detroit, before slipping up and suggesting he was the vice president during the outbreak of COVID-19.
“And when I was vice president, things were kind of bad during the pandemic [recession], and what happened was Barack said to me, ‘Go to Detroit and help fix it,'” the transcript said.
Honored to receive this organization
Part of the impetus for Biden’s speech was to accept a lifetime achievement award from the Detroit branch of the NAACP, but he mangled that part during his acceptance.

“Folks, I’m humbled to receive this organization [award], which defines the character and consequence of what we do,” Biden said.
‘Truly inspiresing’
Biden’s swing through Detroit came on the heels of his commencement address at Atlanta’s Morehouse College, an all-male historically black institution that bestowed an honorary degree on him.
“It was truly inspiresing [inspiring]: over 400 young Black men who will do extraordinary things,” the transcript said.
$800,000 in health care premium savings
Back when Democrats had control of Congress, Biden was able to push through an expansion of subsidies in the Affordable Care Act. The administration estimates that can save families up to $800 annually, but Biden mangled it and said $800,000.
“I protected and expanded the Affordable Care Act, saving millions of families $800,000 in prem- — $8,000 [$800] in — a year in premiums,” the president said.
Fighting landlords who keep rents down
While touting efforts to lower the cost of living, the president inadvertently claimed to be fighting unscrupulous landlords who are trying to keep rents down.
“We’re cracking down on corporate landlords who [to] keep rents down,” Biden said.
Black women ‘have nearly three times more likely to die’
In another verbal flub, Biden swapped in the word “have” when he meant to say “are.”
“He [Trump] not only denies reproductive freedom but worsens the mortality rate for Black moms, who have [are] nearly three times more likely to die from pregnancy complications than a white woman,” the president declared.

‘Irrectionists’
Some politicians have mangled the word “insurrection ” (which Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer once called an “erection”), but Biden had a unique fumble on that front.
“He [Trump] calls the irrectionists [insurrectionists] who stormed Capitol Hill ‘patriots.’ He says, if re-elected, he wants, quote, ‘every’ one of them pardoned,” the transcript noted.
‘Bloodshed’
Back in March, former President Donald Trump warned there would be a “bloodbath” in the auto industry if he loses the 2024 election. Biden misquoted him as saying “bloodshed.”
Get opinions and commentary from our columnists
Subscribe to our daily Post Opinion newsletter!
Thanks for signing up!
Please provide a valid email address.
By clicking above you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Never miss a story.
“But that’s not Donald Trump. Donald Trump has said, if he loses again in November, there will be, quote, ‘bloodshed ‘ [‘bloodbath’]. What in God’s name are we talking about here?” Biden said, according to the transcript.
And to cap things off, Biden butchered the very name of the organization to which he was speaking.
“Earlier this month, I posthumously awarded Medgar Evers the Presidential Medal of Freedom, our nation’s highest civilian honor. His spirit endures. The NAAC [NAACP] spirit endures,” the transcript said.

The commander-in-chief, who has been open about growing up with a stutter, has been no stranger to rhetorical doozies during some of his public outings.
Between the start of the year and late last month, the White House made at least 148 adjustments to transcripts of his remarks, according to an analysis by the Daily Caller.
Ahead of Biden’s Nov. 5 rematch with Trump, the issue of age has loomed large. Biden is already the oldest president in US history and would be 86 at the end of a second four-year term.
Trump and Biden are slated to square off in a CNN-hosted debate on June 27 in Atlanta.
Share this article:

Advertisement
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
Remarks by President Biden at the Morehouse College Class of 2024 Commencement Address | Atlanta, GA
Morehouse College Atlanta, Georgia
10:29 A.M. EDT
THE PRESIDENT: Thank you. (Applause.) Thank you, thank you, thank you, President Thomas, faculty, staff, alumni. And a special thanks — I’ll ask all the folks who helped you get here — your mothers, fathers, grandmothers, grandfathers — all those who got you here, all the way in the back, please, parents, grandparents, all who helped, stand up, because we owe you a debt of gratitude. (Applause.) To all the family. And that is not hyperbole. A lot of you, like my family, had to make significant sacrifices to get your kids to school. It mattered. This mattered a lot. And the friends of Morehouse and the Morehouse men of the Class of 2024. I got more Morehouse men in the White House telling me what to do than I know what to do. (Laughter.) You all think I’m kidding, don’t you? (Laughs.) You know I’m not. And it’s the best thing that’s happened to me.
Scripture says, “The prayers of a righteous man availeth much.” In Augusta, Georgia, a righteous man once enslaved set foot for freedom. The story goes he feared no evil; he walked through the valley of the shadow of death on his way north to free soil in Philadelphia. A Baptist minister, he walked with faith in his soul, powering the steps of his feet to glory. But after the Union won the war, he knew his prayers availed him freedom that was not his alone. And so, this righteous man, Richard Coulter, returned home, his feet wary, his spirit in no ways tired. A hundred and fifty-seven years ago — you all know the story, but the rest of the world doesn’t, and it should — in the basement of a Baptist church in Augusta, he and two other ministers, William Jefferson White and Edmund Turney, planted the seeds of something revolutionary — and it was at the time — a school — a school to help formerly enslaved men enter the ministry, where education would be the great equalizer from slavery to freedom — an institution of higher learning that would become Morehouse College.
I don’t know any other college in America that has that tradition and that consequence. To the Class of 2024, you join, as you know, a sacred tradition. An education makes you free. And Morehouse education makes you fearless. (Applause.) I mean it. Visionary. Exceptional. Congratulations. You are Morehouse men. God love you. (Applause.)
And, again, I thank your families and your friends who helped you get here, because they made sacrifices for you as well. This graduation day is a day for generations, a day of joy, a day earned, not given.
We gather on this Sunday morning because — if we were in church, perhaps there would be this reflection. There would be a reflection about resurrection and redemption. Remember, Jesus was buried on Friday, and it was Sunday — on Sunday he rose again. But — but we don’t talk enough about Saturday, when the discip- — his disciples felt all hope was lost. In our lives and the lives of the nation, we have those Saturdays — to bear witness the day before glory, seeing people’s pain and not looking away. But what work is done on Saturday to move pain to purpose? How can faith get a man, get a nation through what was to come?
Here’s what my faith has taught me.
I was the first Biden to ever graduate from college, taking out loans with my dad and my — all through school to get me there. My junior year spring break, I fell in love at first sight, literally, with a woman I adored. I graduated from law school in her hometown, and I got married and took a job at a law firm in my hometown, Wilmington, Delaware. But then everything changed.
One of my heroes — and he was my hero — a Baptist minister, a Morehouse man, Dr. Martin Luther King — in April of my law school graduation year, he was murdered.
My city of Wilmington — and we were a — to our great shame, a slave state, and we were segregated. Delaware erupted into flames when he was assassinated, literally.
We’re the only city in America where the National Guard patrolled every street corner for nine full months with drawn bayonets, the longest stretch in any American city since the Civil War. Dr. le- — Dr. King’s legacy had a profound impact on me and my generation, whether you’re Black or white. I left the fancy law firm I had just joined and decided to become a public defender and then a county councilman, working to change our state’s politics to embrace the cause of civil rights. The Democratic Party in Delaware was a Southern Democratic Party at the time. We wanted to change it to become a Northeastern Democratic Party.
Then, we were trying to get someone to run for the United States Senate the year Nixon ran. I was 29 years of age. I had no notion of running — I love reading about everybody knew I was going to run; I didn’t know I was going to run — (laughter) — when a group of senior members of the Democratic Party came to me. They couldn’t find anybody to run and said, “You should run.” Nixon won my state by 60 percent of the vote. We won by 3,100 votes. We won by the thinnest of margins but with a broad coalition, including students from the best HBCU in America, Delaware State University. You guys are good, but — (laughter) — they got me elected. And you all — you all think I’m kidding. (Laughter.) I’m not kidding. But by Christmas, I was a newly elected senator hiring staff in Washington, D.C., when I got a call from the first responders, my fire department in my hometown, that forever altered my life. They put a young woman first responder on the line to say, “There was an automobile accident. A tractor-trailer hit your wife’s car while she was Christmas shopping with your three children.” And she — poor woman, she just blurted out. She said, “Your wife and daughter are killed” — my 13-month-old daughter — “they’re dead, and your almost three-year-old and four-year-old sons are badly injured. We’re not sure they’re going to make it, either.” I rushed from Washington to their bedside. I wanted to pray, but I was so angry. I was angry at God. I was angry at the world.
I had the same pain 43 years later when that four-year-old boy who survived was a grown man and a father himself, laying in another hospital bed at Walter Reed hospital having contracted stage four glioblastoma because he was a year in Iraq as a major — he won the Bronze Star — living next to a burn pit. Cancer took his last breath. On this walk of life, you can understand — you come to understand that we don’t know where or what fate will bring you or when. But we also know we don’t walk alone. When you’ve been a beneficiary of the compassion of your family, your friends, even strangers, you know how much the compassion matters. I’ve learned there is no easy optimism, but by faith — by faith, we can find redemption.
I was a single father for five years —
No man deserves one great love, let alone two. My youngest brother, who was a hell of an athlete, did a great thing. He introduced me to a classmate of his and said, “You’ll love her; she doesn’t like politics.” (Laughter.) But all kidding aside, until I met Jill, who healed — who healed the family in all the broken places. Our family became my redemption. Many of you have gone through similar or worse — and even worse things. But you lean on others, they lean on you, and together, you keep the faith in a better day tomorrow. But it’s not easy.
I know four years ago, as some of your speakers have already mentioned, it felt like one of those Saturdays.
The pandemic robbed you of so much. Some of you lost loved ones — mothers, fathers, brothers, sisters, who were — aren’t able to be here to celebrate with you today — today. You missed your high school graduation. You started college just as George Floyd was murdered and there was a reckoning on race.
It’s natural to wonder if democracy you hear about actually works for you.
What is democracy if Black men are being killed in the street?
What is democracy if a trail of broken promises still leave Black — Black communities behind?
What is democracy if you have to be 10 times better than anyone else to get a fair shot?
And most of all, what does it mean, as we’ve heard before, to be a Black man who loves his country even if it doesn’t love him back in equal measure? (Applause.)
When I sit behind the Resolute Desk in the Oval Office, in front of the fireplace across from my — my desk, I have two busts: one of Dr. King and one of Bobby Kennedy. I often find myself looking at those busts and making decisions. I ask myself: Are we living up to what we say we are as a nation, to end racism and poverty, to deliver jobs and justice, to restore our leadership in the world? Then I look down and see the rosary on my wrist that was out of — my late son, he had on him when he w- — died at Walter Reed and I was with him. And I ask myself: What would he say? I know the answer because he told me in his last days.
My son knew the days were numbered. The last conversation was, “Dad, I’m not afraid, but I’m worried. I’m worried you’re going to give up when I go. You’re going to give up.” We have an expression in the Biden family. When you want someone to know — give you their word, you say, “Look at me.” He was lying to me — he said, “Look at me, Dad. Look at me.”
He said, “Give me your word. Give me your word as my father that you will not quit, that you will stay engaged. Promise me, Dad. Stay engaged. Promise me. Promise me.” I wrote a book called “Promise Me, Dad,” not for the public at large, although a lot of people would end up buying it. It’s for my grandchildren and great-grandchildren to know who Beau Biden was.
The rosary on the — my wrist, the bust in my office remind me that faith asks you to hold on to hope, to move heaven and earth to make better days. Well, that’s my commitment to you: to show you democracy, democracy, democracy is still the way.
If Black men are being killed on the streets, we bear witness. For me, that means to call out the poison of white supremacy, to root out systemic racism.
I stood up for George — with George Floyd’s family to help create a country where you don’t need to have that talk with your son or grandson as they get pulled over.
Instead of a trail of broken promises, we’re investing more money than ever in Black families and Black communities. We’re reconnecting Black neighborhoods cut off by old highways and decades of disinvestment where no one cared about the community.
We’ve delivered checks in pockets to reduce child — Black child poverty to the lowest rate in history. We’re removing every lead pipe in America so every child can drink clean water without fear of brain damage, and then can’t afford to remove the lead pipes themselves.
We’re delivering affordable high-speed Internet so no child has to sit in their parents’ car or do their homework in a parking lot outside of McDonald’s.
Instead of forcing you to prove you’re 10 times better, we’re breaking down doors so you have 100 times more opportunities: good-paying jobs you can raise a family on in your neighborhood — (applause); capital to start small business and loans to buy homes; health insurance, prescriptions drugs, housing that’s more affordable and accessible.
I’ve walked the picket line and defended the rights of workers. I’m relieving the burden of student debt — many of you have already had the benefit of it — (applause) — so I [you] can chase your dreams and grow the economy. When the Supreme Court told me I couldn’t, I found two other ways to do it. (Applause.) And we were able to do it, because it grows the economy. And I — in addition to the original $7 billion investment in HBCUs, I’m investing 16 billion more dollars — (applause) — more in our history, because you’re vital to our nation. Most HBCUs don’t have the endowments. The jobs of the future require sophisticated laboratories, sophisticated oppor- — opportunity on campus. We’re opening doors so you can walk into a life of generational wealth, to be providers and leaders for your families and communities. Today, record numbers of Black Americans have jobs, health insurance, and more [wealth] than ever.
Democracy is also about hearing and heeding your generation’s call to a community free of gun violence and a planet free of climate crisis and showing your power to change the world.
But I also know some of you ask: What is democracy if we can’t stop wars that break out and break our hearts?
In a democracy, we debate and dissent about America’s role in the world.
I want to say this very clearly. I support peaceful, nonviolent protest. Your voices should be heard, and I promise you I hear them. I determined to make my c- — my administration look like America. I have more African Americans in high places, including on the Court, than any president in American history — (applause) — because I need the input. What’s happening in Gaza and Israel is heartbreaking. Hamas’s vicious attack on Israel, killing innocent lives and holding people hostage. I was there nine days after, s- — pictures of tying a mother and a daughter with a rope, pouring kerosene on them, burning them and watching as they died. Innocent Palestinians caught in the middle of all this: men, women, and children killed or displaced in despite — in desperate need of water, food, and medicine. It’s a humanitarian crisis in Gaza. That’s why I’ve called for an immediate ceasefire — an immediate ceasefire to stop the fighting — (applause) — bring the hostages home. And I’ve been working on a deal as we speak, working around the clock to lead an international effort to get more aid into Gaza, rebuild Gaza. I’m also working around the clock for more than just one ceasefire. I’m working to bring the region together. I’m working to build a lasting, durable peace. Because the question is, as you see what’s going on in Israel today: What after? What after Hamas? What happens then? What happens in Gaza? What rights do the Palestinian people have? I’m working to make sure we finally get a two-state solution — the only solution — (applause) — for two people to live in peace, security, and dignity. This is one of the hardest, most complicated problems in the world. And there’s nothing easy about it. I know it angered and frustrates many of you, including my family. But most of all, I know it breaks your heart. It breaks mine as well. Leadership is about fighting through the most intractable problems. It’s about challenging anger, frustration, and heartbreak to find a solution. It’s about doing what you believe is right, even when it’s hard and lonely. You’re all future leaders, every one of you graduating today. And that’s not hyperbole. You’re future leaders, all of you. You’ll face complicated, tough moments. In these moments, you’ll listen to others, but you’ll have to decide, guided by knowledge, conviction, principle, and your own moral compass.
And the desire to know what freedom is, what it can be is the heart and soul of why this college was founded in the first place, proving that a free nation is born in the hearts of men spellbound by freedom. But the — that’s the magic of Morehouse. That’s the magic of America.
But let’s be clear what happens to you and your family when old ghosts in new garments seize power, extremists come for the freedoms you thought belonged to you and everyone.
Today in Georgia, they won’t allow water to be available to you while you wait in line to vote in an election. What in the hell is that all about? (Applause.) I’m serious. Think about it. And then the constant attacks on Black election workers who count your vote.
Insurrectionists who storm the Capitol with Confederate flags are called “patriots” by some. Not in my house. (Applause.) Black police officers, Black veterans protecting the Capitol were called another word, as you’ll recall.
They also say out loud, these other groups, immigrants “poison the blood” of our country, like the Grand Wizard and fascists said in the past. But you know and I know we all bleed the same color. In America, we’re all created equal. (Applause.)
Extremists close the doors of opportunity; strike down affirmative action; attack the values of diversity, equality, and inclusion.
I never thought when I was graduating in 1968 — as your honoree just was — we talked about — I never thought I’d be in — present in a time when there’s a national effort to ban books — not to write history but to erase history. They don’t see you in the future of America. But they’re wrong. To me, we make history, not erase it. We know Black history is American history. (Applause.) Many of you graduates don’t know me, but check my record, you’ll know what I’m saying I mean from my gut.
And we know Black men are going to help us, lead us to the future — Black men from this class, in this university. (Applause.)
But, graduates, this is what we’re up against: extremist forces aligned against the meaning and message of Morehouse. And they peddle a fiction, a caricature what being a man is about — tough talk, abusing power, bigotry. Their idea of being a man is toxic. I ran into them all the time when I was younger. They got — all right, I don’t want to get started. (Laughter.) But that’s not you. It’s not us. You all know and demonstrate what it really means to be a man. Being a man is about the strength of respect and dignity. It’s about showing up because it’s too late if you have to ask. It’s about giving hate no safe harbor and leaving no one behind and defending freedoms. It’s about standing up to the abuse of power, whether physical, economic, or psychological. It’s about knowing faith without works is dead. (Applause.)
Look — and you’re doing the work. Today, I look out at all you graduates and I see the next generation of Morehouse men who are doctors and researchers curing cancer; artists shaping our culture; fearless journalists and intellectuals challenging convention. I see preachers and advocates who might even join another Morehouse man in the United States Senate. You can clap for him. He’s a good man. (Applause.)
As I said, I’m proud to have the most diverse administration in history to tap into the full talents of our nation. I’m also proud of putting the first Black woman on the United States Supreme Court. (Applause.) And I have no doubt, one day a Morehouse man will be on that Court as well. (Applause.) You know it.
I’ve been vice president to the first Black president and become my close friend and president to the first woman vice president. (Applause.) Wh- — I have no idea — no doubt that a Morehouse man will be president one day, just after an AKA from Howard. (Laughter and applause.) She’s tough, guys. (Laughter.)
Look, let me close with this. I know I don’t look like I’ve been around very long. (Laughter.) (The President makes the sign of the cross.) But in my career, for the first 30 years, I was told, “You’re too young, kid.” They used to stop me from getting on the Senate elevator when I first got there, for real. Now, I’m too old. Whether you’re young or old, I know what endures: The strength and wisdom of faith endures. And I hope — my hope for you is — my challenge to you is that you still keep the faith so long as you can. That cap on your head proves you’ve earned your crown. The question is now, 25 years from now, 50 years from now, when you’re asked to stand and address the next generation of Morehouse men, what will you say you did with that power you’ve earned? What will you say you’ve done for your family, for your community, your country when it mattered most? I know what we can do. Together, we’re capable of building a democracy worthy of our dreams; a future where every — even more of your brothers and sisters can follow their dreams; a boundless future where your legacies lift us up t- — so those who follow; a bigger, brighter future that proves the American Dream is big enough for everyone to succeed.
Class of 2024, four years ago, it felt probably like Saturday. Four years later, you made it to Sunday, to commencement, to the beginning. And with faith and determination, you can push the sun above the horizon once more. You can reveal a light hope — and that’s not — I’m not kidding — for yourself and for your nation. “The prayers of a righteous man availeth much.” A righteous man. A good man. A Morehouse man. God bless you all. We’re expecting a lot from you. Thank you. (Applause.)
10:55 A.M. EDT
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
- My View My View
- Following Following
- Saved Saved
After backlash, Trump pulls social media post with reference to 'unified Reich'
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Nathan Layne in Wilton, Connecticut; Additional reporting by Steve Holland, Jarrett Renshaw and Andy Sullivan; Editing by Ross Colvin, Daniel Wallis, Jonathan Oatis and Christopher Cushing
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

The tornado left trucks overturned, homes damaged and nearly 250,000 households without power, the report said.

World Chevron
North Korea has notified Japan of its plan to launch a rocket carrying a space satellite towards the Yellow Sea and east of Luzon Island between May 27 and June 4, the Japan Coast Guard said on Monday.

Ten people died and 39 others were injured in southern Turkey on Sunday when an intercity bus collided with three other vehicles on a main highway, Interior Minister Ali Yerlikaya said.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Just like y is sometimes a vowel and sometimes a consonant, there are words that are sometimes one part of speech and other times another. Here are a few examples: "I went to work " (noun). "I work in the garden" (verb). "She paints very well " (adverb). "They are finally well now, after weeks of illness" (adjective).
How to Understand Any English Sentence. To understand easy English sentences, you need to break them down into even smaller parts. Sentences are made up of words. More specifically, they are made up of parts of speech. A part of speech defines what a word does in a sentence. The parts of speech are: Noun : A noun is a person, place or thing.
Step 3: Edit and polish what you've written until you have a cohesive first draft of your speech. Step 4: Practice, practice, practice. The more you practice your speech the more you'll discover which sections need reworked, which transitions should be improved, and which sentences are hard to say. You'll also find out how you're doing ...
The parts of speech in English are extensive. There's a lot to cover in each category—much more than we can in this blog post. The information below is simply a brief overview of the basics of the parts of speech. Nevertheless, the concise explanations and accompanying example sentences will help you gain an understanding of how to use them ...
A verb is one of the most important parts of speech and is a word that is used to describe an action. There are three main types of verbs which are detailed below. Examples: Walk, is, seem, realize, run, see, swim, stand, go, have, get, promise, invite, listen, sing, sit, laugh, walk…. Verb example sentences:
A part of speech (also called a word class) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence.Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing. The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs ...
Also known as word classes, these are the building blocks of grammar. Every sentence you write or speak in English includes words that fall into some of the nine parts of speech. These include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. (Some sources include only eight parts ...
The 9 parts of speech are adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, determiners, interjections, nouns, prepositions, pronouns, and verbs. (These are also known as "word classes.") A Formal Definition. A "part of speech" is a category to which a word is assigned in accordance with its syntactic functions. In English, the main parts of speech are noun ...
This comes before a noun or a noun phrase and links it to other parts of the sentence. These are usually single words (e.g., on, at, by ,…) but can be up to four words (e.g., as far as, in addition to, as a result of, …). I chose to interview teachers in the district closest to me. The recorder was placed next to the interviewee.
EnglishClub: Learn English: Grammar: Parts of Speech Parts of Speech. What is a Part of Speech? We can categorize English words into 9 basic types called "parts of speech" or "word classes". It's quite important to recognize parts of speech. This helps you to analyze sentences and understand them. It also helps you to construct good sentences.
Overview of Parts of Speech. In this section, we will provide a brief overview of the eight parts of speech in English. Understanding the parts of speech is essential for anyone learning the English language, as it enables them to construct meaningful sentences and communicate effectively. The eight parts of speech are: Nouns. Verbs.
Knowing the different parts of speech is essential for good grammar. Become an expert at knowing when and what parts of speech to use with these examples.
The parts of speech definitions in English can vary, but here's a widely accepted one: a part of speech is a category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences. To make that definition even simpler, a part of speech is just a category for similar types of words. All of the types of words included under a single part of ...
Sentence structure is the order of all the parts in a sentence: subject, predicate, objects, phrases, punctuation, etc. It deals a lot with independent and dependent clauses and how they combine (explained below), the placement of words and phrases next to what they modify, as well as the use of proper grammar.
So write with a combination of short, medium, and long sentences. Create a sound that pleases the reader's ear. Don't just write words. Write music. The difference in sentence structure between the first paragraph and the second and third paragraphs is stark. To get the full effect, read them aloud.
A simple sentence contains a subject and a verb, and it may also have an object and modifiers. However, it contains only one independent clause. Key: Yellow, bold = subject; green underline = verb, blue, italics = object, pink, regular font =prepositional phrase. Here are a few examples: She wrote.
Typical reporting verbs are: agree, answer, ask, inquire, explain, say, tell, and wonder. The subject and the reporting verb are sometimes reversed. 'There is nothing we can do about it,' said Monica. The actual words spoken always begin with a capital letter, unless the reporting verb comes within a sentence.
In the above example, the subject contains an adjective ( migratory) and a noun ( birds ), and the predicate contains a verb ( fly ), a preposition ( to ), and a direct object ( Florida ). In this section we will examine the different parts of a sentence including: subject, predicate, object, complement, phrase, and clause. Printer-friendly ...
When planning, remember to: Underline key words from the question and blurb. Underline the audience you will be delivering your speech to. Decide on your "voice" and point of view. Write a one-sentence statement that summarises your point of view. Note down the points you can develop to support your point of view.
Further Reading. The Parts of Speech Examples (127 Mixed Sentences): arts of speech are the building blocks or components of a sentence. All words belong to one part of speech or another; there are eight parts of speech in all. Knowing what they are will help you choose your words wisely and use them correctly in your writing.
Each common English phrase includes real audios and scripts which help you learn sentence structures better, and make sentences in English much more easily. If you master just one common English phrase or sentence pattern, you can make hundreds of correct sentences. This is the easiest way to make sentences in English.
Analyze their response and tweak the joke accordingly if necessary. Starting your speech with humour means your setting the tone of your speech. It would make sense to have a few more jokes sprinkled around the rest of the speech as well as the audience might be expecting the same from you. 4. Mohammed Qahtani.
How to connect 'speech' with other words to make correct English sentences. speech (n): the ability to talk, the activity of talking, or a piece of spoken language Use 'speech' in a sentence His speech captured our attention. The ceremony began with his speech. The audience clapped loudly after his speech. I entered a speech contest. He gave an ...
4. The White House made nine corrections to the official transcript of the president's speech over the weekend. REUTERS. The official transcript, released Monday, made no bones about the errors ...
In the official transcript of the speech, released after Mr. Biden's remarks, the White House crossed out 10 words where the president made factual and pronunciation errors.
Morehouse CollegeAtlanta, Georgia 10:29 A.M. EDT THE PRESIDENT: Thank you. (Applause.) Thank you, thank you, thank you, President Thomas, faculty, staff, alumni. And a special thanks — I'll ...
Preparatory for Early College Graduation 2024 at Joe R. Sanchez Stadium
Donald Trump deleted a video posted to his Truth Social account that included reference to a "unified Reich" after President Joe Biden's campaign and others criticized the use of language often ...