- Search by keyword
- Search by citation
Page 1 of 81

Transient anterior subcapsular vacuolar lens opacities after Tanito microhook trabeculotomy: report of six cases
To present six cases exhibiting transient anterior subcapsular vacuolar lens opacities following early postoperative Tanito microhook trabeculotomy (TMH) performed by the same surgeon.
- View Full Text
Prescribing patterns for hyperopia: an insight of the optometrist perspective and practice
To investigate the current prescribing patterns for correcting hyperopia among optometrists in clinical practice in Saudi Arabia and compare those to current international guidelines. And explore the factors t...
Bilateral optic nerve infiltration and leukemic retinopathy as initial signs of leukemia relapse with central nervous system involvement in an adult: a case report
We describe a case in which bilateral optic nerve infiltration and leukemic retinopathy were the initial signs of disease relapse in a patient with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia...
Progression of macular retinoschisis following intravitreal aflibercept injection for myopic macular neovascularization—a case report and review of literature
Macular retinoschisis (MRS) and myopic macular neovascularization (mMNV) are both potentially blinding complications of high myopia. In this case report, we highlight the progression of MRS after intravitreal ...
Correction: Efficacy of topical 0.05% cyclosporine A and 0.1% sodium hyaluronate in post-refractive surgery chronic dry eye patients with ocular pain
The original article was published in BMC Ophthalmology 2024 24 :28
Effect of 4-week preoperative prism adaptation in preventing postoperative residual esotropia
Preoperative prism adaptation (PPA) simulates postoperative status and possibly can predict postoperative undercorrection before surgery in esotropia. The present study aimed to assess the effect of 4-week PPA...
Impact of ophthalmic clinical service use in mitigating myopia onset and progression in preschool children: a retrospective cohort study
Although school screenings identify children with vision problems and issue referrals for medical treatment at an ophthalmic hospital, the effectiveness of this approach remains unverified.
Efficacy of supplemental oxygen in reducing the need for laser or intravitreal bevacizumab in preterm infants with stage 2 retinopathy of prematurity
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is a disease that affects preterm infants born younger than 30 weeks of gestation. The pathophysiology of ROP involves an initial vaso-obliterative phase followed by vaso-proli...
Decrease in electrolyte after vitrectomy surgery may affect the results of forensic investigations using vitreous humor
Vitreous humor (VH) is used for postmortem biochemical studies because it is well protected in an uncontaminated state even after death. The goal of this research was to investigate electrolyte concentrations ...
Pneumatic displacement with intravitreal tPA injection versus vitrectomy with sub retinal tPA injection in small and medium sub macular hemorrhages- a multicenter comparative study
Comparing between the visual outcomes and post operative complications of two surgical treatments for sub macular hemorrhage, pars plana vitrectomy with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) injection procedure, ...
Spiroplasma infection as a cause of severe congenital keratouveitis, cataract and glaucoma
Only seven cases of ocular Spiroplasma infection have been reported to date, all presenting as congenital cataracts with concomitant intraocular inflammation. We describe the first case of Spiroplasma infection i...
Multimodal imaging observation of primary vitreous cysts
Primary vitreous cyst is a clinical variant delineated by the existence of a vesicle within the vitreous cavity from birth. This particular disease tends to be uncommon, and the underlying mechanisms contribut...
Double-dose investigation of aflibercept in neovascular age-related macular degeneration (DIANA): a real-world study
To investigate the clinical effects of double-dose (4 mg) aflibercept treatment in neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD), compared with the standard-dose (2 mg) treatment.
Do not stumble over the same “stone” twice: a case series of endogenous endophthalmitis secondary to severe systemic diseases
Endogenous endophthalmitis (EE) is a rare but highly destructive eye emergency secondary to systemic infection. Acute endophthalmitis can lead to irreversible vision impairment or even loss of the whole eye, u...
Cerebral versus cortical visual impairment: eliminating the conflict and renewing the terminology
The inconsistency in terminology for Cortical Visual Impairment or Cerebral Visual Impairment presents challenges: (1) different levels of changes in visual pathway and other cerebral areas do not allow discri...
Comparison of macular changes and visual outcomes between femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery and conventional phacoemulsification surgery for high myopic cataract patients
To evaluate differences in log MAR best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) improvement and postoperative central foveal thickness (CFT) and choroidal thickness (CT) changes between conventional phacoemulsification...
Association of myopia and astigmatism with postoperative ocular high order aberration after small incision lenticule extraction
To investigate the correlation between higher-order aberrations (HOA) after small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) and the severity of myopia and astigmatism, along with the relevant factors. These findin...
Lens subluxation combined with parry-romberg syndrome: case report
Parry-Romberg syndrome (PRS) is a rare progressive degenerative disorder of unknown etiology. Here we report a rare case of PRS combined with lens subluxation in Eye and ENT hospital of Fudan University, Shang...
Associations of long-term fluctuation in blood pressure and ocular perfusion pressure with visual field progression in normal-tension glaucoma
The aim of this study was to investigate the associations between fluctuation in blood pressure (BP), ocular perfusion pressure (OPP) and visual field (VF) progression in normal-tension glaucoma (NTG).
Observation of structural and vascular features of retina and choroid in myopia using ultra-widefield SS-OCTA
To find the relationship between the changes of retinal and choriodal structure/ vascular densities (VD) and the myopia progress.
Refraction and ocular biometric parameters in 3-to 6-year-old preschool children : a large-scale population-based study in Chengdu, China
To understand the ocular biometric parameters characteristics and refractive errors in 3-to 6-year-old preschool children in Chengdu, China, and to investigate the prevalence of refractive errors.
Intraoperative quantitative crystalline lens nuclear opacities analysis based on crystalline lenSx platform
The main objective is to quantify the lens nuclear opacity using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) and to evaluate its association with Lens Opacities Classification System III (LOCS-III) s...
The outcomes of corneal sight rehabilitating surgery in Stevens-Johnson syndrome: case series
To summarize the outcomes of corneal sight rehabilitating surgery in Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS).
Does collagen cross linking have any effect on retinal circulation in patients with keratoconus? An optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) study
We aimed to employ Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography (OCTA) to comprehensively assess changes in the optic nerve head (ONH) and macular perfusion before and after the Corneal Collagen Cross-Linking (CCL...
Construction of oxidative phosphorylation-related prognostic risk score model in uveal melanoma
Uveal melanoma (UVM) is a malignant intraocular tumor in adults. Targeting genes related to oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) may play a role in anti-tumor therapy. However, the clinical significance of oxida...
Zonular instability-associated morphologic features in eyes with primary angle closure disease using the swept-source anterior segment – optical coherence tomography system
This study aims to investigate the morphologic features of the crystalline lens in Primary Angle Closure Disease (PACD) patients with zonular instability during cataract surgery using the swept-source CASIA 2 ...
Association between ambient air pollution and age-related macular degeneration: a meta-analysis
Several epidemiological studies have investigated the association between ambient air pollution and age-related macular degeneration (AMD). However, a consensus has not yet been reached. Our meta-analysis aime...
Central retinal artery occlusion after intravitreal brolucizumab injection for treatment-naïve neovascular age-related macular degeneration; a case report
To report a case of central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) after intravitreal injection of brolucizumab for a treatment-naïve neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) patient without comorbid cardi...
Choroidal manifestations of non-ocular sarcoidosis: an enhanced depth imaging OCT study
Although choroidal thickening was reported as a sign of active inflammation in ocular sarcoidosis, there has been no research on the choroidal changes in non-ocular sarcoidosis (defined as systemic sarcoidosis...
Comparatively analysing the postoperative optical performance of different intraocular lenses: a prospective observational study
Postoperative performance, including best corrected distance visual acuity (BCDVA) and optical metrics (from the OQAS and iTrace devices), was compared among 4 different intraocular lenses (IOLs).
Clinical features and comprehensive treatment of persistent corneal epithelial dysfunction after cataract surgery
Evaluation of clinical efficacy and safety of tobramycin/dexamethasone eye ointment in treating persistent corneal epithelial dysfunction (PED) after cataract surgery.
New-onset or relapse of uveitis after rapid spreading of COVID-19 infection in China and risk factor analysis for relapse
The aim of this study was to report the clinical profile of new-onset and relapse of uveitis following rapid spreading of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection due to change of anti-COVID-19 policies i...
Epidemiological variations and trends in glaucoma burden in the Belt and Road countries
Analyzing the glaucoma burden in "Belt and Road" (B&R) countries based on age, gender, and risk factors from 1990 to 2019 in order to provide evidence for future prevention strategies.
Swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography findings in a case of primary vitreoretinal lymphoma over a three-year follow-up
Vitreoretinal lymphoma (VRL) still represents a diagnostic challenge for retinal specialists. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for a better prognosis. Several diagnostic tools have proven helpful in ...
Optical coherence tomography biomarkers as outcome predictors to guide dexamethasone implant use in patients with iERM: a randomized controlled trial
We aimed to investigate the anatomical features of optical coherence tomography (OCT) and vitreous cytokine levels as predictors of outcomes of combined phacovitrectomy with intravitreal dexamethasone (DEX) im...
Isolated ectopia lentis with partial anterior dislocation and pupillary block: a case report
Ectopia lentis is the dislocation of the natural crystalline lens and usually presents in the setting of trauma or other systemic diseases. Herein, we describe a case of an otherwise healthy four-year-old boy ...
A retrospective study of cumulative absolute reduction in axial length after photobiomodulation therapy
To assess the age and timeline distribution of ocular axial length shortening among myopic children treated with photobiomodulation therapy in the real world situations.
Local resection via partial lamellar sclerouvectomy for ciliary body tumors — a case series
Ciliary body tumor is extremely rare and treatment is challenging. The aim of this study is to present our experience in treating this rare entity, especially large tumors with more than 5 clock hours of invol...
Comparison of short-term clinical outcomes of a diffractive trifocal intraocular lens with phacoemulsification and femtosecond laser assisted cataract surgery
To evaluate short-term visual and refractive outcomes after implantation of a diffractive trifocal intraocular lens (IOL) in cataract patients with phacoemulsification (PHACO) and femtosecond laser assisted ca...
Iris neovascularization and neurotrophic keratopathy following ultrasound cycloplasty in refractory glaucoma: case series
Ultrasound cycloplasty is a noninvasive surgery used to reduce intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma, with fewer severe complications. This report presents several cases of iris neovascularization and...
Relationship between lymphocytes and idiopathic macular hole
An idiopathic macular hole (IMH) is a full-thickness anatomic defect extending from the internal limiting membrane to the photoreceptor layer of the macula without any known cause. Recently, clinical laborator...
Macular hypoplasia and high myopia in 48, xxyy syndrome: a unique case of 48, xxyy syndrome that presents with high myopia and macular dysplasia
Among sex chromosome aneuploidies, 48, XXYY syndrome is a rare variant. This condition is marked by the existence of an additional X and Y chromosome in males, leading to a diverse range of physical, neurocogn...
Effect of intravitreal injections due to neovascular age-related macular degeneration on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and minimum rim width: a cross sectional study
The present study tested the hypothesis that repeated anti-VEGF injections are associated with reduced retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) and minimum rim width (MRW) of the optic nerve head.
Management of macula-on giant retinal tear detachments– outcome of pars-plana-vitrectomy with silicone oil versus gas tamponade
To compare the outcome of eyes with a macula-on giant retinal tear (GRT) detachment treated with pars-plana-vitrectomy (PPV) depending on the used endotamponade.
Extended depth of focus IOL in eyes with different axial myopia and targeted refraction
To evaluate the objective visual outcomes following implantation of extended depth of focus intraocular lens (EDOF IOL) in individuals with varying axial lengths (AL) and targeted refraction.
Repeatability assessment of anterior segment measurements in myopic patients using an anterior segment OCT with placido corneal topography and agreement with a swept-source OCT
The precision of anterior segment biometric measurements in eyes has become increasingly important in refractive surgery. The purpose of this study is to assess the repeatability of the automatic measurements ...
Prevalence, clinical characteristics, and independent predictors of uveitic macular edema in an Asian population: a retrospective cohort study
To determine the prevalence, clinical characteristics, and independent predictors of uveitic macular edema (UME) in patients with intermediate, posterior and panuveitis.
Non-surgical treatment of stage 4A retinopathy of prematurity
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is a major cause of visual impairment in premature infants, often requiring surgical interventions in advanced stages. This retrospective case series study investigates non-sur...
Comparison of photorefraction by Plusoptix A12 and cycloplegic autorefraction in children
Plusoptix photoscreeners are capable of measuring refractive errors of children from 1 meter distance, without cyloplegia. We aimed to compare refractive data obtained from the newest version of Plusoptix (mod...
Correction: Long-term real-life outcomes of the Clareon® hydrophobic intraocular lens: the Clarte study in 191 eyes
The original article was published in BMC Ophthalmology 2024 24 :133
Affiliated with

BMC Ophthalmology is associated with Cochrane Eyes and Vision
Important information
Editorial board
For authors
For editorial board members
For reviewers
- Manuscript editing services
Annual Journal Metrics
2022 Citation Impact 2.0 - 2-year Impact Factor 2.3 - 5-year Impact Factor 1.152 - SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper) 0.715 - SJR (SCImago Journal Rank)
2023 Speed 31 days submission to first editorial decision for all manuscripts (Median) 176 days submission to accept (Median)
2023 Usage 1,959,850 downloads 772 Altmetric mentions
- More about our metrics
Peer-review Terminology
The following summary describes the peer review process for this journal:
Identity transparency: Single anonymized
Reviewer interacts with: Editor
Review information published: Review reports. Reviewer Identities reviewer opt in. Author/reviewer communication
More information is available here
- Follow us on Twitter
BMC Ophthalmology
ISSN: 1471-2415
- General enquiries: [email protected]
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Med (Lausanne)
Hotspots and trends in ophthalmology in recent 5 years: Bibliometric analysis in 2017–2021
1 State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
2 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, Guangzhou, China
3 Guangdong Provincial Clinical Research Center for Ocular Diseases, Guangzhou, China
Weining Zhu
4 Zhongshan Medical School, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Yingshi Zou
Bowen zhang, guangming jin, zhenzhen liu, associated data.
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://www.webofscience.com/wos/alldb/basic-search .
The purpose of this study was to investigate the hotspots and research trends of ophthalmology research.
Ophthalmology research literature published between 2017 and 2021 was obtained in the Web of Science Core Collection database. The bibliometric analysis and network visualization were performed with the VOSviewer and CiteSpace. Publication-related information, including publication volume, citation counts, countries, journals, keywords, subject categories, and publication time, was analyzed.
A total of 10,469 included ophthalmology publications had been cited a total of 7,995 times during the past 5 years. The top countries and journals for the number of publications were the United States and the Ophthalmology. The top 25 global high-impact documents had been identified using the citation ranking. Keyword co-occurrence analysis showed that the hotspots in ophthalmology research were epidemiological characteristics and treatment modalities of ocular diseases, artificial intelligence and fundus imaging technology, COVID-19-related telemedicine, and screening and prevention of ocular diseases. Keyword burst analysis revealed that “neural network,” “pharmacokinetics,” “geographic atrophy,” “implementation,” “variability,” “adverse events,” “automated detection,” and “retinal images” were the research trends of research in the field of ophthalmology through 2021. The analysis of the subject categories demonstrated the close cooperation relationships that existed between different subject categories, and collaborations with non-ophthalmology-related subject categories were increasing over time in the field of ophthalmology research.
Conclusions
The hotspots in ophthalmology research were epidemiology, prevention, screening, and treatment of ocular diseases, as well as artificial intelligence and fundus imaging technology and telemedicine. Research trends in ophthalmology research were artificial intelligence, drug development, and fundus diseases. Knowledge from non-ophthalmology fields is likely to be more involved in ophthalmology research.
Introduction
More than 2.2 billion people worldwide were visually impaired or blind to date, with an annual economic burden of more than $269.4 billion ( 1 ). Development in ophthalmology is essential for the prevention and treatment of eye diseases, and relevant research is growing rapidly in breadth and depth and forming complex knowledge networks. Glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration, and some hereditary eye diseases were previously considered irreversible blindness-causing diseases, and progress had been made to cure or alleviate them by modulating new targets or using new technologies ( 2 – 4 ). Cataracts and posterior capsular opacification were previously thought to be treated only with surgery, but in the recent years, there had been new developments in research into drugs that inhibit cataract formation ( 5 , 6 ). With the advances in the field of ophthalmology, new hope has emerged in areas previously considered untreatable or treatable only through non-pharmaceutical interventions ( 7 – 10 ). However, it is not feasible to analyze the overall overview of the field of ophthalmology and to explore its research hotspots and trends with a traditional systematic review, which is not conducive to the development of the field.
Bibliometric analysis is the quantitative analysis of the universal scientific production data in a specific field ( 11 ). Bibliometric method obtains the history and current status of the research field development by analyzing the scientific research results and can make predictions of the research field ( 12 ). Previous studies have conducted bibliometric analysis on individual country contributions or focused only on randomized controlled studies in ophthalmology and citation patterns in ophthalmology journals ( 13 – 19 ). Unsolved questions still remain as to how to quantitatively evaluate the contribution of different global research forces (countries, journals) in ophthalmology and identify hotspots and future research trends in ophthalmology based on a wide range of research results in different subfields of ophthalmology.
This study was intended to quantitatively analyze and visualize the global ophthalmology publication from 2017 to 2021 using bibliometric methods to explore the global research forces (countries, journals), possible hotspots, and future trends of ophthalmology research and to provide insight for research development and public health policy formulation in the field of ophthalmology.
Data sources
All the data used in this study were obtained from the Web of Science Core Collection (Clarivate Analytics, Philadelphia, PA, USA). The search was conducted by searching the Topic Subject retrieval field using “ophthalmology” as the subject word. Articles published between 2017 and 2021 were included, with no restrictions on the language type or document type of the articles. Data were collected on 28 January 2022.
Data collection and processing
To describe the number of articles published per year, the number of annual citations of the articles, the number of country publications, and the number of journal publications in the field of ophthalmology, relevant data were downloaded in the Web of Science Core Collection. All ophthalmology-related articles with their corresponding references and all publication-related information were exported as plain text for country collaboration analysis, keyword co-occurrence analysis, keyword burst analysis, and subject category co-occurrence analysis. To make the results more informative, keywords that were not relevant or meaningful to the analysis were filtered and removed during the data processing.
Statistical and bibliometric analysis
Statistical descriptions of the number of annual publications, the number of annual citations, the number of country publications, and the number of journal publications were performed using Microsoft Excel 2019 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) and GraphPad Prism version 8.4.2 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA).
Bibliometric analysis was carried out using VOSviewer (Leiden University's Centre for Science and Technology Studies, Leiden, the Netherlands) to obtain country collaborations and research hotspots. Several clusters were formed based on the country cooperation analysis, with countries of the same color belonging to the same cluster. Countries within clusters cooperated relatively closely, whereas cooperation among countries between clusters was relatively weak. The research hotspots were obtained from the clusters formed by the co-occurrence analysis of high-frequency keywords. The common characteristics of high-frequency keywords within the same cluster revealed the research hotspots. The frequency of keyword occurrences was used to weight the size of the keywords. The larger the keyword, the higher the frequency of occurrence.
Furthermore, CiteSpace V version 5.8.R3 (Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, USA) was used for bibliometric analysis to obtain the burst keywords and subject category cooperation. The keyword burst analysis was performed to obtain temporal trends in keywords in the field of ophthalmology. The most recent burst keywords were defined as research frontier topics, indicating the potential for continued research breakthroughs in these topics. The co-occurrence of subject categories was analyzed to obtain the collaboration of subject categories. The number of occurrences of a subject category was used to weight the subject category. The more occurrences a subject category had, the larger it was. Temporal trends in subject category occurrences were represented by temporal rings of subject categories, the thickness of which represented the number of subject category occurrences in the corresponding year. Interdisciplinary cooperation was represented by the connecting line between subject categories. The thicker the connecting line, the closer the collaboration.
Global research output distribution
A total of 139 countries contributed to the publications related to ophthalmology research, with a total of 10,469 articles, which were cited 7,995 times. The number of publications had increased year by year, but there was an inflection point in citation counts. Citation counts increased year by year from 2017, reaching 2,650 citations in 2020, whereas citations in 2021 decreased compared to 2020 ( Figure 1A ). The analysis of countries showed that the United States had the highest number of publications, more than three to four times the number of other countries, followed by the United Kingdom, India, Germany, and China ( Figure 1B ). Country collaboration analysis yielded four clusters, with close cooperation between countries within each cluster ( Figure 1C ). Publications related to ophthalmology research were distributed in 1,876 journals, and the top 10 journals in terms of the number of articles published were the Ophthalmology ( n = 1,263, 12.06%), the Ophthalmology. Retina ( n = 580, 5.54%), the BMJ Case Reports ( n = 270, 2.58%), the Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology: the official journal of the North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society ( n = 260, 2.48%), the Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science ( n = 214, 2.04%), the Ophthalmology, Glaucoma ( n = 204, 1.95%), the Journal of Current Ophthalmology ( n = 200, 1.91%), the European Journal of Ophthalmology ( n = 191, 1.82%), the Indian Journal of Ophthalmology ( n = 173, 1.65%), and Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgery ( n = 171, 1.63%) ( Figure 1D ).

Global distribution of research output. (A) Annual publications and citations of ophthalmology research from 2017 to 2021. (B) Top 10 countries in terms of total publications. (C) Country cooperation networks. (D) Top 10 journals by total publication volume of ophthalmology research in a 5-year period.
Global high-impact documents
The top 25 high-impact articles in ophthalmology published between 2017 and 2021, ranked by total citations, are shown in Table 1 . All the articles had been cited more than 150 times, with the highest number of citations being 419. Of these articles, 10 were published in 2017, 12 in 2018, one in 2019, and two in 2020. In total, 12 of these articles were published in the Ophthalmology and three in the Progress in Retinal and Eye Research. According to the type of publication, there were 16 original research articles and 9 review articles. The keywords involved in the articles are listed in Table 1 , including 5 articles each on OCT and deep learning, 4 articles each on diabetes and macular degeneration, and other related research topics such as glaucoma, artificial intelligence, and drugs.
Top 25 most cited documents published between 2017 and 2021.
Research hotspots
Keyword co-occurrence analysis demonstrated that the three most frequent of all keywords were “glaucoma” ( n = 395), “retina” ( n = 321), and “optical coherence tomography” ( n = 230). In the past 5 years, 157 high-frequency keywords in the field of ophthalmology were identified by setting the minimum frequency of keyword occurrence at 20 times. These keywords formed four clusters: the “glaucoma” cluster (red; 86 items), the “retina” cluster (green; 47 items), the “COVID-19” cluster (blue; 13 items), and the “screening” cluster (yellow; 8 items) ( Figure 2 ). After summarizing the keyword clusters, four research hotspots were identified: epidemiological characteristics and treatment modalities of diseases such as glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy, artificial intelligence and fundus imaging technology, COVID-19-related telemedicine, and screening and prevention of eye diseases.

Ophthalmology research hotspots analysis. The keywords formed four clusters, which were differentiated by color in the diagram, with the same color being the same cluster. The keyword size indicated the number of occurrences of the keyword, whereas the thickness and distance of the connecting lines between the keywords indicated the frequency of co-occurrence between the two keywords.
Research trends
Keyword burst analysis showed that “neural network,” “pharmacokinetics,” “geographic atrophy,” “implementation,” “variability,” “adverse events,” “automated detection,” and “retinal images” were the hot topics of research in the field of ophthalmology through 2021 and displayed the potential to become the research frontiers to achieve breakthroughs shortly ( Figure 3A ).

Ophthalmology research trends analysis. (A) Keyword burst analysis. The red line indicates the year in which the burst of the corresponding keyword began and ended. (B) Subject category analysis. The larger subject categories indicate their greater frequency and importance, and the distance between subject categories indicates how closely they collaborate. The lines between subject categories indicate the collaboration between the subject categories at either end, with the color of the different lines representing the collaboration time in the different subject categories and the thickness representing the degree of collaboration closeness. The color of the temporal rings represents the occurrence of that subject category in different years, the thicker the corresponding temporal rings, the more frequently it occurs, with the time scale at the bottom right.
In terms of subject categories, the top three subject categories with the highest volume of ophthalmology-related research publications were medicine general internal ( n = 1,138, 10.87%), clinical neurology ( n = 482, 4.604%), and surgery ( n = 368, 3.515%) ( Table 2 ). The subject categories of ophthalmology research were divided into two types: one was the traditional ophthalmology-related subject categories, such as medicine general internal, clinical neurology, and surgery, and the other one was the non-ophthalmology-related subject categories, such as engineering, computer science, and chemistry. The analysis of subject category collaboration relationships indicated that over time more collaborative relationships had emerged between non-ophthalmology-related subject categories ( Figure 3B ).
Subject categories in ophthalmology from 2017 to 2021.
Research in the field of ophthalmology showed a year-on-year increase in the number of articles published in the last 5 years, with the most published country being the United States and the most prolific journal being the Ophthalmology. The top 25 high-impact articles worldwide were cited more than 150 times per article. A total of four research hotspots were identified: epidemiological characteristics and treatment modalities of diseases such as glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy, artificial intelligence and fundus imaging technology, COVID-19-related telemedicine, and screening and prevention of eye diseases. Cross-talk between different non-ophthalmology subject categories was also an important trend in ophthalmology.
The annual publication volume, country distribution, and journal distribution of the ophthalmology research articles revealed a global overview of research output in the field of ophthalmology. The output of ophthalmology research showed an increasing trend in the last 5 years, suggesting that the socioeconomic input and scientific output of the subject area were also developing ( 20 ). The individual contributions of some countries to ophthalmology research were previously reported, but there were limitations on the overall evaluation of all countries' contributions to ophthalmology research and of country collaboration ( 13 – 17 ). This study showed that the predominant countries in ophthalmology research included the United States, the United Kingdom, and India, and countries such as Germany, China, and Australia also played an important role in the contribution. Several stable collaborative networks have been formed between countries, which can facilitate cross-border research data sharing and the globalization of scientific research. The top five most published journals showed that ophthalmology research was mainly focused on clinical ophthalmology (Ophthalmology, BMJ Case Reports), basic ophthalmology research (Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science) and neuro-ophthalmology (Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology, Ophthalmology Retina).
The high-impact articles in ophthalmology indicated that researchers in the field of ophthalmology were primarily concerned with ophthalmological health or disease states, as well as ophthalmological technologies and applications. In terms of health or disease conditions, age-related macular degeneration ( 21 – 24 ), glaucomatous optic neuropathy ( 25 , 26 ), corneal blindness ( 27 ), and other blinding eye diseases occupied important research positions. Research directions such as screening for diabetic retinopathy ( 28 , 29 ), preventing myopia ( 30 ), optimizing visual outcomes, and controlling complications after IOL implantation following cataract surgery were dedicated to the active identification, management, and control of disease risk factors, making the eye disease controllable and manageable ( 31 , 32 ). In addition, researchers were also concerned with the management of Behcet's syndrome ( 33 ) and COVID-19 infection prevention in ophthalmology ( 34 ). In ophthalmology-related technologies, the frontiers were artificial intelligence algorithms ( 23 , 25 , 26 , 35 – 38 ), new pathways for drug delivery ( 39 , 40 ), and new materials for therapy ( 41 ). In ophthalmology-related applications, the pioneering applications were optical coherence tomography ( 23 , 24 , 35 , 42 – 44 ), stem cell therapy, and tissue repair ( 45 ).
After clustering the high-frequency keywords in the past 5 years, four research hotspots in the field of ophthalmology were obtained. First, the epidemiological characteristics and treatment modalities of diseases such as glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy were the hot topics of ophthalmology research. The emergence of these hot topics was consistent with the increasing prevalence of systemic chronic diseases such as diabetes in the last 5 years, and several studies have revealed associations and common biomarkers of ophthalmology and systemic diseases ( 46 – 49 ). More future work needs to further focus on the diagnosis and optimal treatment strategies for blinding diseases associated with systemic conditions ( 50 ). Moreover, deep learning algorithms that could rapidly and non-invasively identify pathological features of eye diseases joined ophthalmology research ( 23 ). Deep learning algorithms could classify age-related cataract types based on slit-lamp photographs, and fully automated AI-based screening systems had been approved for the use in diabetic retinopathy ( 37 , 51 ). Furthermore, the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic brought about an increase in the length of patient visits due to disease control and health-related problems associated with COVID-19 infections, which had a dramatic impact on ophthalmology health care. On the one hand, the close contacts physicians need when attending to patients could increase the risk of cross-infection between patients or between health care workers and patients, resulting in infection control to be optimized in ophthalmology practice. On the other hand, the need for timely intervention for patients was driving the development of telemedicine during the pandemic ( 34 , 52 ). Finally, the development of diagnostic technology has driven ophthalmology research toward early screening and disease prevention.
The keywords that were still bursting until 2021 were research trends. The keywords “neural networks,” “pharmacokinetics,” “automated detection,” and “retinal images” in this part of the keyword list were consistent with the hot research directions obtained by keyword clustering. Other keywords that had burst to 2021 could be newly emerging keywords that had not yet had time to be highly cited, were hotspots for research in ophthalmology, and were likely to continue to be of interest for some times to come. Concerning the disciplinary analysis, the analysis of this study revealed that there was extensive cross-collaboration in various basic areas of non-ophthalmology-related research. Knowledge from non-ophthalmology fields is likely to be more involved in ophthalmology research.
Strengths of the study include a global view of research forces in ophthalmology from a wide range of the literature. Additional study strengths include the revealing of highly cited documents in ophthalmology that provide useful information for researchers. Outcome measures addressed the global research force contributions, research hotspots, and research trends of ophthalmology research, providing an in-depth study of the field of ophthalmology.
Only data from the Web of Science Core Collection database were included in this study, but the Web of Science Core Collection database, as a citation database, already contained comprehensive data on the articles and corresponding citations, which was sufficient for capturing the overall development of the scientific field. In addition, the results of the analysis by the visualization software may include some repetitive and meaningless information. We tried to identify some of the hot topics that were influencing ophthalmology research, so the raw data had been further filtered to remove irrelevant or meaningless words.
In conclusion, this study provided a comprehensive analysis of ophthalmology-related research based on the Web of Science Core Collection database. The hotspots in ophthalmology research were epidemiology, prevention, screening, and treatment of ocular diseases, as well as artificial intelligence and fundus imaging technology and telemedicine. Research trends in ophthalmology research were artificial intelligence, drug development, and fundus diseases. There was an extensive cross-talk of ophthalmology-related research in various basic areas. Knowledge from non-ophthalmology fields is likely to be more involved in ophthalmology research.
Data availability statement
Author contributions.
ZL and GJ designed the study and provided a critical review for the manuscript. YT and WZ wrote the manuscript. YT, WZ, YZ, BZ, YY, and WL collected and analyzed the data. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81873675), the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2022A1515011181), the Teaching Reform Research Program of Sun Yat-sen University (JX3030604024), and the Youth Project of State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology (2021QN02).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Masks Strongly Recommended but Not Required in Maryland, Starting Immediately
Due to the downward trend in respiratory viruses in Maryland, masking is no longer required but remains strongly recommended in Johns Hopkins Medicine clinical locations in Maryland. Read more .
- Vaccines
- Masking Guidelines
- Visitor Guidelines
Wilmer Eye Institute
Research at the Wilmer Eye Institute
Our Research Teams
The center for nanomedicine.
A unique translational nanotechnology enterprise that brings engineers, scientists and clinicians together on the translation of novel drug and gene delivery technologies

The Center for Stem Cells and Ocular Regenerative Medicine (STORM)
A pioneering, collaborative research effort across Johns Hopkins to study and cure vision loss and blindness through regenerative medicine
Wilmer Core Research Centers
In support of a highly collaborative, interdisciplinary environment of research resource centers known as the Wilmer Core

Cornea, Cataract & External Disease
Aimed at improving the diagnosis, management and treatment of corneal and external disease problems
Dana Center for Preventive Ophthalmology
Focuses on national and international public health prevention of blinding eye diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, trachoma and glaucoma

Disability Research
Aims to improve the health of people with visual impairments and other types of disabilities

Microscopy at the Wilmer Eye Institute (MWEI)
MWEI comprises facilities for confocal and transmission microscopy, as well as imaging of tissue cultures and frozen sections that contribute to research into ocular disorders and allied health problems for those who access its facilities.

Neuro-Ophthalmology
Aims to advance the prevention and treatment of neuro-ophthalmic disorders through groundbreaking research.
Ocular Immunology
Focused on the causes and treatments of ocular inflammatory diseases, including uveitis, intraocular inflammation, scleritis and iritis.

Oculoplastics
Currently focused on structures around the eyes and their relation to ocular diseases and orbital trauma, as well as their treatments.
Pediatric Ophthalmology & Adult Stabismus
Focuses on detection, management and treatment of pediatric and adult forms of strabismus and amblyopia.

Includes projects and multiple labs engaged in groundbreaking discoveries aimed at transforming the study and treatment of retinal diseases.

Translational Tissue Engineering Center (TTEC)
A joint venture of Wilmer and the Department of Biomedical Engineering to establish focus in research, education, and industrial development in regenerative medicine
Ultra Low Vision
Focused on assessing and enhancing the functional visual abilities of individuals with ultra-low vision.
Vision Rehabilitation
Our research faculty are committed to discovering new and innovative ways to improving the lives of patients with low vision and to improving their vision rehabilitation outcomes.

Support Wilmer Research
Donate online to partner with us on our quest to find the next treatments and cures.

Over the Phone
Speak with someone about making a charitable gift to Wilmer. Please call 410-955-2020 .
Download our giving form to mail in your generous donation.

Research Topics
The Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences offers medical students and residents a variety of research opportunities. Please browse the basic science, translational and clinical research projects currently underway below.
Research Topic: Corneal endothelial health judged by endothelial image analysis
Description.
Endothelium is critical for dehydrating the cornea and keeping it clear. With loss of its barrier and pump function, the cornea swells and corneal transplantation may be needed.
Changes in the number, shape and size of the cells may predict loss of function.
Key Research Question/Hypothesis
Effect of drugs, surgery, devices, and preservation media on the endothelium.
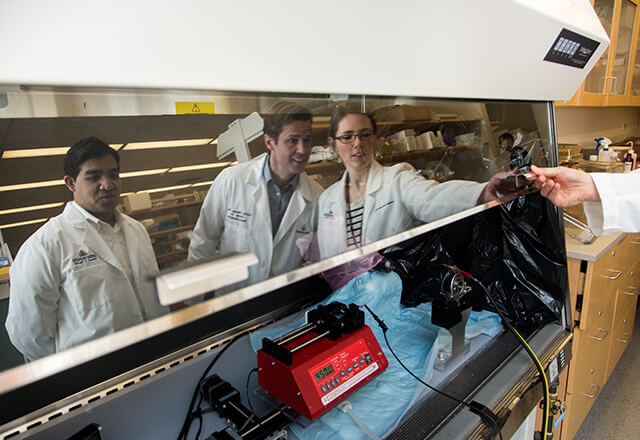
Images of the endothelium captured with either a specular or confocal microscope that can take repeated pictures of the endothelial cells non-invasively in patients. Once images are captured, they can be analyzed with special software in the Cornea Image Analysis Reading Center (CIARC) of the Department.
Student learn these techniques working with both patients and technicians, depending on the project.
Ongoing projects.
Status of IRB/IACUC approval
Image analysis studies in CIARC approved; ongoing projects have IRB approval. If launching a new project, IRB approval will need to be obtained.
Prospects for Publishing and Presenting
Excellent; we have a long track record of publications in major journals and presentations at national and international conferences.
Contact Information
Tanisha Rankins
Secretary to Dr. Jonathan Lass
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone: 216.983.5164
Research Topic: Retinopathy of Prematurity and other Pediatric Studies
Effect of low birth weight on the eye’s development.
Data analysis, chart review.
Several ongoing projects—long-term data collection.
Current study has IRB approval. Any new studies will need IRB approval.
Excellent; the data base study has been presented at ARVO and is in preparation for publication in a major pediatric journal.
Dr. Faruk Orge
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone: 440.684.1743
Research Topic: Cholesterol and function of the retina
Cholesterol is essential for life in mammal. Yet, if it is chronically in excess, it is a risk factor for cardiovascular and Alzheimer's disease and likely age-related macular degeneration.
To delineate the putative link between cholesterol and age-related macular degeneration.
Characterization of retinal function of mice deficient in different enzymes involved in cholesterol elimination. Animals are assessed by optical coherence tomography, electroretinography, fluorescein angiography and optomotor response.
Students learn these techniques working with post-doctoral researchers responsible for these projects.
All studies are approved by the IACUC.
Dr. Irina Pikuleva
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone: 216.368.3823
Research Topic: Contact Lens Related Complications
Ongoing clinical trials related to corneal infiltrative events associated with daily or extended wear of soft contact lenses. Fungal and bacterial biofilm-contact lens models and susceptibility to contact lens care products.
Assessment of sub-clinical corneal inflammation with confocal microscopy. Assessment of bacterial endotoxin and relationship to infiltrative events with soft lenses.
- Ocular and lens cultures for assessment of bioburden
- Reading/Assessment of stored confocal images
- Collection of worn lenses for biofilm formation
- Lab Assays (in conjunction with Dr. Pearlman’s lab) for endotoxin on lens surfaces or within solution
Active approved IRB protocols exist for current clinical trials on infiltrative events, biofilm studies, and assays of previously collected lenses, tears and images.
Excellent chance for authorship on investigator initiated studies of biofilm and endotoxin assays. Listing of authors will follow standard publishing guidelines.
Other corporate-funded work may or may not allow authorship.
Dr. Loretta Szcztoka-Flynn
- Email: [email protected]
Research Topic: Mechanisms of retinal degenerations
How do mutations in the light receptor rhodopsin cause retinal degenerations like retinitis pigmentosa? How does the retina protect against oxidative stresses that can lead to retinal degenerations such as retinitis pigmentosa and age-related macular degeneration?
A multi-disciplinary approach is employed that includes biochemistry, molecular biology, animal models and biophysics.
All animal studies have approved IACUC protocols.
Excellent with track record of publications in major journals and presentations at national and international conferences.
Information about the laboratory can be found by browsing the Park Lab webpage.

Retina Lasers in Ophthalmology
Clinical Insights and Advancements
- © 2023
- Andrzej Grzybowski 0 ,
- Jeffrey K. Luttrull 1 ,
- Igor Kozak 2
Institute for Research in Ophthalmology, Foundation for Ophthalmology Development, Poznan, Poland
You can also search for this editor in PubMed Google Scholar
Ventura County Retinal Vitreous Medical Group, Ventura, USA
Vitreoretinal surgeon and clinical lead, moorfields eye hospital, abu dhabi, united arab emirates.
- Examines the concepts, principles and applications of modern retina lasers
- Discusses the paradigm shifts toward retina laser surgery
- Written by world experts on the use of lasers for retinal diseases
5018 Accesses
3 Citations
1 Altmetric
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this book
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
Licence this eBook for your library
Institutional subscriptions
About this book
This book discusses the new era of modern retinal laser therapy and its clinical applications. While the photocoagulation era universally presupposed the therapeutic necessity of laser-induced retinal damage, the modern retinal laser therapy is equally opposed to this idea. The evidence for this sea-change in the understanding of retinal laser is well presented within this book, and the conceptual and clinical consequences are discussed with particular emphasis on the emergence of retinal laser therapy as the first reasonable preventive and restorative intervention for the most important retinal disorders. Finally, the future of modern retinal laser therapy is highlighted with respect to coming technological advances, remaining challenges, and the place of retinal laser in the management of retinal disease.
This book is an essential resource for all ophthalmic residents and clinicians seeking a clear and concise guide to modern retinal laser therapy in their everyday practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
Subthreshold laser treatment in retinal diseases: a mini review

Laser/Light Applications in Ophthalmology: Posterior Segment Applications

Laser Therapies for Glaucoma
- Neuroprotection
- Vitreous Floaters
- Chorioretinopathy
- Vascular Occlusion
- Laser Applications
- Diabetic Retinopathy
Table of contents (19 chapters)
Front matter, book introduction.
- Andrzej Grzybowski, Jeffrey K. Luttrull, Igor Kozak
History of Lasers in Ophthalmology
Andrzej Grzybowski
Basics of Laser Use in Ophthalmology
- Maram E. A. Abdalla Elsayed, Igor Kozak
Retinal Laser Treatment for Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Jeffrey K. Luttrull
Lasers in Diabetic Retinopathy
- Maciej Gawęcki, Jeffrey K. Luttrull, Andrzej Grzybowski
Lasers in the Treatment of Central Serous Chorioretinopathy
- Maciej Gawęcki, Andrzej Grzybowski
Laser for Retinal Vascular Occlusions
- Sathy V. Bhavan, Jeffrey K. Luttrull
Laser Treatment in Intraocular Tumors
- Korol A. R., Nasinnyk I. O.
Laser Treatment in Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment
- Jana Stefaničková, Igor Kozak
Laser Treatment of Vitreous Floaters
Ischemic peripheral retinopathies, laser treatment of retinopathy of prematurity.
- Katsan Sergey, Adakhovska Anastasiia, Igor Kozak
Laser Use for Hyaloidotomy
The mechanism of retinal laser and its end result: neuroprotecion, laser in treatment of retinal artery occlusions.
- Stanislav Saksonov, Lyubomyr Lytvynchuk, Goran Petrovski, Andrzej Grzybowski
Laser Treatment of Submacular Hemorrhages
- Lyubomyr Lytvynchuk, Stanislav Saksonov, Goran Petrovski, Andrzej Grzybowski
Retinal Laser Telephotocoagulation and Teleeducation
Diabetes mellitus associated progressive neurovascular retinal injury.
- Stephen H. Sinclair
The Future for Retinal Laser Treatment. Is There One?
Editors and affiliations, about the editors.
Dr. Luttrull is a life member of the American Academy of Ophthalmology; an “Honor Award” recipient of the American Society of Retinal Specialists; founder of the Ventura County Ophthalmology Society; the founder and executive director of LIGHT: The International Retinal Laser Society; and the founder and chief medical officer of the Vision Protection Institutes.
Igor Kozak MD, PhD is a consultant ophthalmic surgeon and clinical lead at Moorfields Eye Hospital Centre, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Dr Kozak is a graduate of Pavol Jozef Šafárik University in Slovakia and is a fellowship-trained retina and uveitis specialist from the University of California San Diego Shiley Eye Institute, where he served on the retina faculty. He is currently a consultant ophthalmic surgeon and a clinical lead at the Moorfields Eye Hospital Centre in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, where he attends to patients with retinal and inflammatory problems and performs vitreoretinal surgery on adults and children.
Dr. Kozak’s academic interests include clinical research, ocular imaging, drug delivery, and pharmacology. He has participated in numerous clinical trials and has been principal investigator in some. He has published extensively in premier ophthalmic and scientific journals and has edited 6 ophthalmic books internationally. He serves as a scientific reviewer for more than 50 ophthalmology journals and is an editorial board member for 4 journals.
Bibliographic Information
Book Title : Retina Lasers in Ophthalmology
Book Subtitle : Clinical Insights and Advancements
Editors : Andrzej Grzybowski, Jeffrey K. Luttrull, Igor Kozak
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25779-7
Publisher : Springer Cham
eBook Packages : Medicine , Medicine (R0)
Copyright Information : The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2023
Hardcover ISBN : 978-3-031-25778-0 Published: 27 May 2023
Softcover ISBN : 978-3-031-25781-0 Published: 28 May 2024
eBook ISBN : 978-3-031-25779-7 Published: 26 May 2023
Edition Number : 1
Number of Pages : X, 356
Number of Illustrations : 29 b/w illustrations, 57 illustrations in colour
Topics : Ophthalmology
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Eye diseases articles from across Nature Portfolio
Related subjects.
- Conjunctival diseases
- Corneal diseases
- Eye abnormalities
- Eyelid diseases
- Hereditary eye disease
- Lacrimal apparatus diseases
- Lens diseases
- Macular degeneration
- Ocular hypertension
- Ocular ischemic syndrome
- Ocular motility disorders
- Optic nerve diseases
- Pupil disorders
- Refractive errors
- Retinal diseases
- Scleral diseases
- Uveal diseases
- Vision disorders
- Vitreous detachment
Latest Research and Reviews
ROBIN: a randomised, double-masked, placebo-controlled Phase IIa study of the AOC3 inhibitor BI 1467335 in diabetic retinopathy
- Quan Dong Nguyen
- Justis P. Ehlers
- Sunil Patel
A fundus image dataset for intelligent retinopathy of prematurity system
- Shaobin Chen
- Guoming Zhang
Variability of relationship between inner-retinal structural changes and visual dysfunction in optic neuropathy
- Hye Jun Joo
- Jae Ho Jung
Age-related changes of intraocular pressure in Dutch belted rabbits
- Young In Shin
- Young Kook Kim
Trimebutine prevents corneal inflammation in a rat alkali burn model
- Hitoshi Goto
- Takeshi Arima
- Fumiki Okamoto
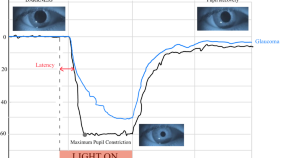
Basics, benefits, and pitfalls of pupillometers assessing visual function
- Manon Philibert
News and Comment
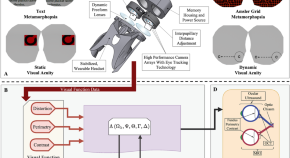
XR-SANS: a multi-modal framework for analyzing visual changes with extended reality (XR) in Spaceflight Associated Neuro-Ocular Syndrome (SANS)
- Ritu Sampige
- Andrew G. Lee
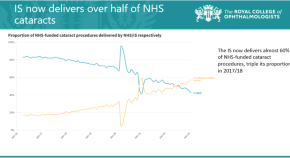
Independent sector cataract training
- Sarah Maling
Sleep and optic disc edema in spaceflight associated neuro-ocular syndrome (SANS)
- Tuan Nguyen
In vivo gene editing for inherited vision loss
An early-phase trial suggests safety and improvements in vision after treatment with the CRISPR-based therapy EDIT-101, providing proof of concept for in vivo retinal gene editing.
- Karen O’Leary
Refractive shifts in astronauts during spaceflight: mechanisms, countermeasures, and future directions for in-flight measurements
- Kelsey Vineyard
Disease latency bias and the protective effect of metformin against age-related macular degeneration
- Nicholas Beare
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Innovative 3D printing could revolutionize treatment for cataracts and other eye conditions
University of East Anglia researchers have made a significant breakthrough in ocular device technology with the introduction of a novel resin for 3D printing intraocular devices. This innovation has potential to enhance the manufacture of eye implants universally used in cataract and refractive surgeries.
An artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is primarily required for people with cataracts, a condition where the eye's natural lens becomes cloudy, obscuring vision.
They can also be also used to correct refractive errors such as myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness) and presbyopia (when eyes gradually lose the ability to see things clearly up close, as a normal part of aging).
Lead author Dr Aram Saeed, Associate Professor in Healthcare Technologies at UEA's School of Pharmacy, said: "For the first time, we have developed a resin that can be used to print ocular devices directly.
"While still in the early stages, the ability to 3D print these lenses could significantly enhance eye care for patients by offering unprecedented levels of customisation and design precision, potentially leading to better clinical outcomes."
Historically, IOLs have been made from a variety of materials, including glass and silicone, although more recently the industry has significantly evolved to predominantly use acrylic materials.
Currently hydrophilic and hydrophobic acrylic are the most commonly used materials due to their excellent optical clarity, flexibility, biocompatibility with the body and for their stability and safety within the eye.
Current methods of making IOLs use lathing and moulding techniques. While these methods offer the production of well-engineered and high-optical quality devices, they also come with inherent limitations, particularly in terms of design complexity and customisation.
Dr Aram Saeed said: "3D printing could significantly enhance the production of ocular devices, not only improving speed and precision in manufacturing but also enabling greater complexity and customisation in design.
"Our proof-of-concept paper is the first in a series that will detail our developments in this area and set the stage for transforming eye care practices globally.
"Our work combines material science with healthcare technology and requires extensive know-how in developing these types of ocular devices.
"As we continue to publish our findings and share our advancements, we aim to be at the forefront of the industry, working with industrial partners and researchers worldwide to refine and enhance the technology."
Although still in the early stages of development, the innovation could potentially have several advantages:
Tailored Lenses : 3D printing could create lenses customised to each patient's eye shape and vision needs, potentially improving vision correction and comfort.
Faster Production : Compared to traditional methods, 3D printing has the potential to enable quicker design, testing, and manufacturing of lenses. This speed could reduce the time between diagnosis and surgery, providing faster care to patients.
Complex Designs : 3D printing makes it possible to create intricate lens shapes that were previously difficult to manufacture. These designs could better address a wider range of vision problems.
Cost Reduction : By using 3D printing, the production cost of custom or high-quality lenses may decrease, making them more affordable for more patients, particularly in economically disadvantaged regions. This could lead to better overall public health outcomes.
Compatibility with Imaging : The researchers hope that combining 3D printing with advanced imaging technologies in the future could help produce lenses that fit individual patients' eyes optimally, reducing the need for adjustments or complications after surgery.
Material Innovation : 3D printing allows for the development of new materials with improved optical performance. This could result in lenses that not only correct vision but also enhance it.
The study found that the 3D printed lenses have good optical clarity, can be folded, and implanted into a human capsular bag.
Co-author Michael Wormstone, Emeritus Professor at UEA's School of Biological Sciences, said: "If successful in further developments, this new technology could transform the industry by enabling portable manufacturing solutions, especially beneficial in remote and economically disadvantaged areas.
"It also has the potential to support the production of premium, customised lenses that could enhance surgical outcomes in more advanced healthcare settings."
The team's efforts have been recognised with the awarding of a United States patent, assigned to UEA Enterprise Limited, a business entity of the university focused on fostering innovation and commercialising research.
The UEA researchers continue to work closely with industry partners to refine the technology.
For example, further work has been underway to ensure the process works accurately on a larger scale and to increase the printing resolution to improve the dimensional accuracy.
It is hoped that clinical trials could start in the next few years.
Dr Saeed and Prof Wormstone have a strong partnership with the ophthalmology department at Norwich and Norfolk University Hospital (NNUH), which brings valuable clinical insights and visionary approaches to their work, with both UEA and the hospital members of the pioneering Norwich Research Park.
Mr Anas Injarie, a leading consultant ophthalmologist at NNUH with more than 20 years of experience, said: "This innovation has the potential to enable the production of lenses that match patient specifications in design and optical performance.
"For premium markets, it represents an exciting possibility to provide tailored treatments that could enhance patient satisfaction and surgical success."
The research was funded by the University of East Anglia through the Innovation Development Fund and Proof-Of-Concept grants; the Humane Research Trust; and the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).
Further funding was provided by UEA's Impact Acceleration Account (IAA) funding from the Medical Research Council (MRC).
'Stereolithographic Rapid Prototyping of Clear, Foldable, Non-refractive Intraocular Lens Designs: A Proof-of-Concept Study' is published in the journal Current Eye Research .
- Today's Healthcare
- Patient Education and Counseling
- Diseases and Conditions
- 3-D Printing
- Medical Technology
- Engineering and Construction
- Contact lens
- Dominant eye in vision
- Refractive surgery
- Eye examination
- Visual acuity
- Formaldehyde
Story Source:
Materials provided by University of East Anglia . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Veronica Hidalgo-Alvarez, Noelia D. Falcon, Julie Eldred, Michael Wormstone, Aram Saeed. Stereolithographic Rapid Prototyping of Clear, Foldable, Non-Refractive Intraocular Lens Designs: A Proof-of-Concept Study . Current Eye Research , 2024; 1 DOI: 10.1080/02713683.2024.2344164
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Extinct Saber-Toothed Cat On Texas Coast
- Some Black Holes Survive in Globular Clusters
- People Altering Decomposition in Waterways
- Historic Iceberg Surges
- Food Groups Based On Level of Processing
- Computer Vision, Machine Learning Aid Driving
- Most Distant Known Galaxy
- A New Dinosaur from Zimbabwe
- The Case of the Missing Black Holes
- Menstrual Periods Arriving Earlier
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
- Introduction
- Conclusions
- Article Information
- References:
LGBTQ indicates lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer.
eTable. Characteristics of Included Studies
- From Research to Action—Implementing Initiatives to Address Ophthalmologic Health Disparities JAMA Ophthalmology Invited Commentary January 1, 2023 Janice C. Law, MD; Michael A. Puente, MD
See More About
Select your interests.
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
Others Also Liked
- Download PDF
- X Facebook More LinkedIn
Hemmerich C , Jones G , Staggs J , Anderson RM , Bacani R , Vassar M. Inequities and Research Gaps in Ophthalmology : A Scoping Review . JAMA Ophthalmol. 2023;141(1):63–70. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2022.5237
Manage citations:
© 2024
- Permissions
Inequities and Research Gaps in Ophthalmology : A Scoping Review
- 1 Office of Medical Student Research, Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences, Tulsa
- 2 Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences, Tulsa
- Invited Commentary From Research to Action—Implementing Initiatives to Address Ophthalmologic Health Disparities Janice C. Law, MD; Michael A. Puente, MD JAMA Ophthalmology
Question What patient inequities have been assessed and how has research on these inequities differed from 2016 to 2021 within the field of ophthalmology?
Findings This scoping review of 75 publications revealed substantial research gaps regarding health inequities associated with the lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) community, race and ethnicity—namely, American Indian and Alaska Native, Asian, and Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander individuals—and the role of telemedicine for rural and underresourced areas.
Meaning This review suggests future ophthalmology studies (1) examine barriers to clinical study and medical trainee recruitment as well as patient values and preference studies and (2) investigate the implementation of telemedicine in underresourced areas.
Importance Deficient ophthalmologic care is costly to patients, making the identification of groups not receiving adequate care of vital importance. The current landscape of equity in ophthalmic care has yet to be thoroughly investigated and is important to ensure inclusivity and patient-centered care.
Objective To perform a scoping review of the literature pertaining to health care inequities in the field of ophthalmology.
Evidence Review A comprehensive database search using MEDLINE (via PubMed) and Ovid Embase was done in July 2022. English-language articles published from 2016 to 2021 were included and encompassed all article types except commentaries or correspondence. The search modeled the National Institutes of Health list of designated US health inequity populations, which includes income, education level, occupational status, rural and underresourced area, sex and gender, lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) identity, and race and ethnicity. A total of 8170 abstracts and titles were screened by 2 independent investigators, and 189 studies were assessed in full text for eligibility. For inclusion, articles needed to be an ophthalmic study discussing health inequities. In a masked, duplicate fashion, 2 independent investigators screened 75 full-text studies for data extraction using a pilot-tested form. Data extraction included general publication characteristics and health inequity data based on the National Institutes of Health’s defined inequity groups.
Findings A total of 75 publications were included. Notable inequities were found among Black and Hispanic patients associated with negative ophthalmic outcomes and mixed associations regarding sex or gender. Overall, lower-income patients were more likely to have vision impairment, use eye care services less, and have lower adherence to eye examinations. No articles within our sample examined LGBTQ inequities among ophthalmology patients since the 2016 National Institutes of Health classification of sexual and gender minority populations. Substantial research gaps were observed within the ophthalmic literature pertaining to the LGBTQ community, race and ethnicity, and rural and underresourced areas.
Conclusions and Relevance This scoping review found substantial findings associated with the LGBTQ community, race and ethnicity, and the role of telemedicine in rural and underresourced areas. Because of the importance of ophthalmic care in overall patient health, it is vital to understand the various inequities present and strive to improve the current gaps in the literature. Future studies should (1) examine barriers to clinical study and medical trainee recruitment as well as patient values and preference studies and (2) investigate the implementation of telemedicine in underresourced areas.
Despite increased attention and improvements toward health care equity, inequities are still pervasive throughout the US. 1 In nearly every state in the US, Black individuals are more likely than White individuals to die early from preventable causes. 2 , 3 Areas in which health care inequities are common include race, ethnicity, lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) identity, and socioeconomic status. 4 Although considerable attention has been given to racial and economic inequities, there are several obstacles preventing adequate research regarding health inequities. For example, Black researchers are significantly less likely to receive National Institutes of Health R01 grants than White researchers. 5 Such an obstacle has the potential to affect health inequity research, as Black investigators are more likely to suggest study designs that address health inequities. 6 An additional obstacle may be the cultural competency of researchers, who often take on the cultural perspective of the majority. 7 By holding the dominant cultural perspective, researchers may be less likely to investigate certain minority groups. These barriers can hinder identifying historically marginalized populations in need of improved care, thus leaving the societal and economical implications of unequal health care unresolved.
Ophthalmology is a field in which understanding health inequities is especially important. Visual impairment can be severely debilitating, affecting many aspects of one’s life, including mobility, mental health, feelings of independence, 8 , 9 and ability to carry out activities of daily living. 9 , 10 Furthermore, visual impairment has an annual cost of more than $5.4 billion in the US. 11 Cases of age-related causes of vision loss (eg, glaucoma) in the US are expected to rise due to an increasingly aging population. 12 Chronic conditions like diabetes are also increasing in prevalence within the US, creating a growing population that is at increased risk of eye diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy. 13 Taken together, there is an expectation of increased future demand in ophthalmic care, which could exacerbate current inequities if they are not identified and addressed effectively.
The aim of our scoping review is to evaluate health care inequities within ophthalmology to illuminate gaps in the current literature. Deficient ophthalmologic care is costly to society and individuals, making the identification of groups not receiving adequate care of vital importance. 8 - 10 The current landscape of equity in ophthalmic care has yet to be thoroughly investigated. With this present study, we will assess published ophthalmology literature for the purpose of identifying gaps surrounding health inequities.
A scoping review was performed to investigate current gaps within health inequity research pertaining to ophthalmology. This study adhered to the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) methodology for developing scoping reviews as well as the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) checklist. 14 , 15 We conducted this study according to a prespecified protocol, which is available on Open Science Framework—along with search strings, data files, and extraction forms—to provide transparency and reproducibility. 16
Study eligibility criteria were derived from the JBI Manual’s methodology on included population, concept, and context. 15 The following study designs were eligible for inclusion: systematic reviews, meta-analyses, clinical trials, case-control studies, cohort studies, cross-sectional analyses, retrospective database reviews, scoping reviews, and literature reviews. Literature related to ophthalmology was included as the population of focus. Regarding the concept of this review, only literature focused on health inequities was included. Lastly, to fulfill this review’s context, inequities meeting inclusion criteria were limited to income, education level, occupational status, rural or underresourced populations, sex and/or gender, LGBTQ identity, race, and ethnicity. These specific inequities were included based on the National Institute of Health’s list of health inequity population and thus align with the initial search strategy. 17 To enhance the quality of data extraction, only studies written in English were included. 18 , 19 Based on the National Institute of Health’s addition of the sexual and gender minority classification in 2016, we only included literature published between 2016 and 2021. 17 Since sexual and gender minority as a group was not acknowledged as a health inequity population until 2016, a scoping review is merited to encompass literature starting from that point in time. There is ambiguity within inequity terminology across different countries; thus, only literature conducted within the US was included. For example, what one country may define as race may be considered ethnicity in another. 20
Exclusion criteria were met if a study was (1) published before 2016 or after 2021, (2) written in a language other than English, (3) conducted outside of the US, (4) not related to ophthalmology, (5) focused on ophthalmology training, (6) failed to report a health inequity as an outcome, or (7) was a commentary or correspondence. Each step of the screening process was performed independently by 2 masked investigators (C. H. and G. J.). Incongruities between selections were resolved through discussion, with a third investigator available for reconciliation (J. S.). Literature search and screening results were recorded along with exclusion justification, found within the PRISMA flow diagram.
Stata version 17.0 (StataCorp) software was used to summarize data using descriptive statistics, including (1) frequencies and percentages of studies assessing each inequity, (2) study designs that were included in our scoping review, and (3) the settings under which the included articles were conducted (eg, single institution or multiple institution). In addition, longitudinal changes of the individual inequities researched were investigated as a function of time. The longitudinal figures were limited to the top 4 most prevalent inequities to illustrate the most relevant inequities being researched over time.
Our literature search yielded 10 496 records. Duplicate removal excluded 2144 records. Of the remaining articles, 8170 were excluded on title and abstract screening. The remaining 182 articles underwent full-text screening, and 75 were included in our final sample for data extraction. An outline of our article selection is illustrated by the PRISMA flow diagram in Figure 1 , along with exclusion justifications. The Table displays the frequencies of inequities along with study characteristics of the included sample. The most commonly assessed factors were race and ethnicity (70 of 75 [93%]) and sex and/or gender (40 of 75 [53%]). The least commonly assessed factors were LGBTQ identity (0 of 75) and occupational status (4 of 75 [5%]). Detailed findings of each article were summarized and demonstrated in the eTable in the Supplement . Figure 2 demonstrates the frequency of inequities analyzed. Figure 3 shows the frequency of the 4 most common inequities examined over the 2016 to 2021 range.
An association between race and ethnicity inequities and ophthalmology was reported by 70 included studies (93%). There was conflicting evidence over follow-up appointment adherence being associated with race and ethnicity. Six studies found that White patients were more likely to follow up with an ophthalmologist than American Indian and Alaska Native, Asian, Black, Hispanic, and Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander patients and patients of unreported race 21 - 26 ; conversely, 3 studies found no significant association between race and ethnicity and follow-up adherence. 27 - 29 Pineles et al 30 reported that White patients were more likely to be diagnosed with eye diseases than patients of other races. Several studies found that Hispanic individuals were more likely to develop chalazion, 31 cataracts, 32 myopia, 33 diabetic retinopathy, 34 and visual impairments 35 , 36 than White individuals; however, Hispanic individuals were less likely to adhere to annual eye examinations compared with other races. 37 , 38 Regarding Black race, some studies found Black individuals were more likely to develop glaucoma than White patients. 39 , 40 However, several studies found that Black individuals were less likely to access ophthalmic care compared with other races. 35 , 41 , 42 Taubenslag and Kammer 43 found that Black patients had decreased surgical success rates following trabeculectomy than other races. Conversely, Chou et al 44 found that residents were more likely to have had an eye examination in the last year if they lived in a county with a higher percentage of Black residents. Asian individuals were more susceptible to developing myopia compared with White individuals. 33 , 45 Additional findings of racial and ethnic inequities can be found in the eTable in the Supplement .
A total of 40 studies (53%) examined sex and/or gender inequities relating to ophthalmology. There were mixed findings for the associations observed over sex and/or gender. Several studies demonstrated that men had decreased odds of having ever received a dilated eye examination, 46 higher postsurgical complications, 47 - 49 and were more likely to develop certain eye conditions, including primary open-angle glaucoma, 39 ocular hypertension, 36 and fovea-off rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. 50 Conversely, Wang et al 42 found that men had greater odds of an ophthalmology consultation than women, and Uhr et al 51 reported male sex was associated with decreased risk of vision impairment. Two studies reported that women were more likely to be compliant and/or follow up with care 52 and were also found to have higher glaucoma medication adherence. 53 In contrast, Tam et al 54 found that women had higher eye screening failure rates. Women were less likely to undergo certain ophthalmic surgical procedures. 55 , 56 In contrast, 11 studies found no association between sex and/or gender and ophthalmic conditions, 30 , 34 , 57 - 60 follow-up adherence, 23 , 27 - 29 or access to eye care. 37 Further findings can be found in the eTable in the Supplement .
Among the studies analyzed, income was the third most frequent health care inequity observed (26 of 75 studies [35%]). Six studies demonstrated that patients with lower income were more likely to have vision impairment, 48 , 50 , 51 have worse postsurgical outcomes, 61 and/or use eye care services less. 35 , 41 Seven studies reported that lower-income patients had lower adherence to both eye examinations and glaucoma medication use, 22 , 38 , 62 , 63 received fewer anti–vascular endothelial growth factor injections, 64 and were more likely to report having glaucoma 65 or diabetic retinopathy. 66 Regarding patients with higher income, studies found that higher income was associated with lower prevalence of myopia, 45 glaucoma, 65 and diabetic retinopathy 66 as well as an increased likelihood of receiving an eye examination. 38 , 46 , 67 However, 2 studies found no association between income and follow-up adherence, 23 , 28 and 1 conflicting study found no association regarding income and diabetic retinopathy. 59 Additional findings can be found in the eTable in the Supplement .
Rural and underresourced inequities were evaluated in 21 studies (28%). One study by Chiam et al 22 found that increased drive time to an ophthalmology clinic was associated with no-show appointment status, and Mikolajczyk et al 23 reported that decreased distance from an ophthalmology clinic was associated with follow-up adherence. However, Wang et al 42 found that patients living greater distances from a medical center were more likely to receive an ophthalmology consultation. With regard to regional differences across the US, New Mexico, the District of Columbia, and Texas were found to have the highest levels of vision impairment. 68 Another study conducted by Pineles et al 30 found that children in the northeastern US were more likely to be diagnosed with eye disease than any other region. Further reporting can be found in the eTable in the Supplement .
Education level was evaluated in 17 studies (23%). Research regarding patient education was conflicting. Salman et al 63 found that patients with less education demonstrated lower adherence to glaucoma medications. Lower educational attainment was found to be associated with poor adherence to annual eye examinations, 38 decreased use of eye care, 35 and higher rates of visual impairment. 48 , 51 Additionally, lower education was positively correlated with self-reported diabetic retinopathy 34 , 66 and self-reported glaucoma, 65 while higher education was negatively correlated with these ophthalmologic conditions. 34 , 65 , 66 Higher educational attainment demonstrated a greater likelihood of visiting an ophthalmologist 41 and receiving a dilated eye examination. 46 In contrast, other studies found that education was not associated with diabetic retinopathy awareness 69 or with follow-up adherence for ophthalmic care. 27 , 28 Additional information can be found in the eTable in the Supplement .
Four studies (5%) reported on ophthalmology inequities associated with occupational status. Lu et al 70 found that those who were employed were more likely to report lack of time as a barrier to diabetic retinopathy screening. Nathan and Joos 36 found that unemployment was a risk factor for the diagnosis of ocular hypertension, while Silverberg et al 34 found that unemployment was associated with having diabetic retinopathy.
Since the 2016 National Institutes of Health classification of sexual and gender minority as a health disparity population, 0 studies have investigated inequities within LGBTQ groups.
The ophthalmology literature is deficient in health inequities research among historically marginalized populations—namely, by occupational status and LGBTQ identity. Specifically, no studies assessed inequities among the LGBTQ community, making this group the least examined of all demographic groups analyzed. Only 4 articles evaluated occupational status, whereas race and ethnicity was assessed by 70 of 75 studies included in our review. The frequency of studies investigating each of the 4 most common health inequities in our sample increased substantially by the end of the study period. The surge in frequency of health care inequity research suggests improvements and may foreshadow the future of health care equity research. However, at the current stage, literature published within the field of ophthalmology appears to lack data into health inequity groups, which can limit the ability to identify and resolve inequities. Our review highlights those groups most in need for further investigation, ensuring that equal access and quality care is not reserved for particular groups. In the following discussion, we illuminate gaps within the existing literature, discuss inequities with the greatest need for improvement, and provide recommendations for future research.
Our study found a lack of research and funding for the LGBTQ community. Coulter et al 17 found that only 0.5% of all National Institutes of Health–funded research projects concerned LGBTQ health. Further ophthalmology research within the LGBTQ community may lead to important advancements in health outcomes and equity, as has been demonstrated in other areas of medicine. Chum et al 71 evaluated 1703 LGBTQ individuals from the UK Household Longitudinal Study, observing that family support improved sleep outcomes. Additionally, a lack of health equity exists in this community owing to potential root causes, like slurs, microaggressions, sexual harassment, violence, and harassment regarding bathroom use which contribute to patients not seeking care. 72 Thus, these factors must be studied, identified, and corrected through interventional efforts. Existing literature regarding transgender patients in ophthalmology is largely limited to case reports. 73 Thus, more research is needed to examine facilitators and barriers to clinical study recruitment and participation among the transgender population. Moreover, oculoplastic surgeons must make special considerations for transgender patients undergoing oculoplastic feminization surgery to ensure alignment with patient desires for facial appearance. Hollar et al 73 reported that the greatest barrier patients and clinicians experience in this area is clear communication around the patients’ expectations and the feasibility of surgical outcomes, making studies regarding patient values and preferences warranted. Such barriers to ophthalmic care of LGBTQ individuals may also benefit from initiatives that focus on recruiting medical trainees representing this community to enhance the patient-clinician relationship and make LGBTQ health a research focus in ophthalmology.
Our review found substantial racial and ethnic inequities between Black and White patients and between Hispanic and non-Hispanic patients, yet many articles failed to thoroughly investigate other historically marginalized groups. Specifically, only 27% of studies focusing on race and ethnicity inequities included American Indian and Alaska Native, Asian, and Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander patients. However, this finding is not limited to our study; 3 additional studies reported inadequate data and research existing in these populations. 74 - 76 Blindness is one of the top public health concerns, and the gap in existing research has consequences on patient outcomes. 77 For example, Woodward et al 78 found American Indian and Alaska Native patients to disproportionately have higher rates of blindness, low vision, refractive errors, diabetic eye conditions, and ophthalmic surgical complications while having lower treatment rates compared with White patients. Despite efforts to increase historically marginalized group participation in clinical research, such as the US Food and Drug Administration Race and Ethnicity Guidance, a recent study of clinical trials performed in the last 2 decades found little improvement in racial and ethnic diversity. 79 Current limitations to increasing diversity in clinical trials include insufficient reporting of race and ethnicity, particularly among historically marginalized groups. 76 Thus, more research is needed to better understand the recruitment and retention of these groups into clinical studies.
Our review found associations between greater distances to clinics and decreased follow-up adherence and increased numbers of no-show appointments. 22 Although prior studies have investigated the efficacy of telemedicine in ophthalmology, research regarding implementation has been fairly limited. A systematic review examining barriers to implementation of telemedicine worldwide found significant barriers for both the patient and clinician, such as challenges to training of staff, resistance to change, and lack of internet access for patients in underresourced areas. 80 Another limitation to further research in this area is cost, as clinicians struggled to justify the upfront cost of training and technology needed to implement telemedicine into their practices. 81 Although there has been increased uptake and successful adoption of telemedicine, Zanaboni and Wootton 82 found that there has not been large-scale implementation. Additional programming and research funding are needed to address the problem with implementation. Research is also needed to determine contextual and sociopolitical factors influencing implementations of telehealth into rural and underresourced areas. As eye care is very limited in rural communities, additional modalities of care delivery should be developed and tested in rural communities. Recommendations to address this issue include public policy initiatives to fund and support health care staff to increase access for underresourced and rural areas.
Our study had several strengths, including the use of a protocol that was developed a priori and posted on Open Science Framework 16 for transparency and reproducibility, multiple investigators in the screening and data extraction process, and the JBI Manual and PRISMA-ScR when conducting and reporting this investigation. Our limitations include restrictions imposed on our sample, including language, geography, and time, which may have resulted in bias; failure of our search strategy to identify relevant studies for inclusion; and possibilities for data extraction errors.
Our scoping review found noteworthy findings associated with LGBTQ identity, race and ethnicity—namely, American Indian and Alaska Native, Asian, and Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander race—and the role of telemedicine for rural and underresourced areas. The recent increases in frequency of published research for common health inequities suggests a positive trend in ophthalmic research. Because of the importance of ophthalmic care in overall patient health, it is vital to understand the various inequities present and strive to improve the current gaps in the literature. We hope our findings will provide guidance for future research into health inequities. We recommend future studies examine barriers to clinical study and medical trainee recruitment as well as patient values and preference studies and investigate the implementation of telemedicine in underresourced areas.
Accepted for Publication: October 15, 2022.
Published Online: December 8, 2022. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2022.5237
Corresponding Author: Christian Hemmerich, BS, Office of Medical Student Research, Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences, 1111 W 17th St, Tulsa, OK 74107 ( [email protected] ).
Author Contributions: Messrs Hemmerich and Jones had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Study concept and design : Staggs, Anderson, Bacani, Vassar.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data : All authors.
Drafting of the manuscript : All authors.
Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content : Hemmerich, Jones, Staggs, Anderson, Bacani.
Statistical analysis : Jones, Anderson.
Administrative, technical, or material support : Staggs, Bacani.
Study supervision : Staggs, Anderson, Bacani, Vassar.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: Dr Vassar has received funding from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the US Office of Research Integrity, Oklahoma Center for Advancement of Science and Technology, and internal grants from Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Additional Contributions: We are grateful to the Oklahoma State University medical library for their procurement of relevant literature.
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts
- Alzheimer's disease & dementia
- Arthritis & Rheumatism
- Attention deficit disorders
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Biomedical technology
- Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Gastroenterology
- Gerontology & Geriatrics
- Health informatics
- Inflammatory disorders
- Medical economics
- Medical research
- Medications
- Neuroscience
- Obstetrics & gynaecology
- Oncology & Cancer
- Ophthalmology
- Overweight & Obesity
- Parkinson's & Movement disorders
- Psychology & Psychiatry
- Radiology & Imaging
- Sleep disorders
- Sports medicine & Kinesiology
- Vaccination
- Breast cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Colon cancer
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Lung cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Ovarian cancer
- Post traumatic stress disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Skin cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Full List »
share this!
May 29, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
Is stress worsening your dry eye?
by CU Anschutz Medical Campus

Long work hours, little sleep, a full inbox; balancing work and a social life: Stress can pile up and have notable physical effects on the body, including the eyes. Ocular symptoms such as burning, redness, irritation, watery eyes, and blurred vision may signify the presence of dry eye disease, which affects as much as 8% of the U.S. population . These symptoms can intensify in troubling times.
"Stress can certainly exacerbate dry eye problems in a variety of ways," says Darren Gregory, MD, professor of ophthalmology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine.
"The body experiences elevated levels of inflammation when you're feeling stressed, and inflammation is a factor in dry eyes," he explains. "In inflammation, white blood cells are recruited to the surface of the eye where they start releasing the inflammatory chemicals they produce, and this can make symptoms worse."
Gregory explains why stress seems to impact dry eye and how patients can help alleviate some of the symptoms.
Intensifying stress and symptoms
Stress can increase sensitivity to pain all over the body.
"Our perception of pain is heightened, so the discomfort a person may feel in their eyes can be amplified," Gregory explains.
There are other factors at play, too. Lack of sleep, coupled with medications used to treat behavioral conditions like anxiety, depression, and insomnia may also contribute to worsening dry eye symptoms.
"We may have difficulty sleeping or sleep less because of various demands, whether it's work or family or whatever else is going on," Gregory says. "This may decrease the quality and the quantity of our sleep. Just like our brains need some time to recover from the stresses of the day, so do our eyes."
Additionally, many medications that are used to help induce sleep can intensify eye discomfort.
"We often see that these medications can cause dry mouth and dry eyes," he says. "When I see a new patient who's coming to the Sue Anschutz-Rodgers Eye Center with dry eye troubles, one of the first things I look at with them is their medication list, which might help explain why they're having these worsening symptoms."
It might not be feasible to stop those medications, Gregory adds, but it can provide some peace of mind to at least understand why the dry eye symptoms are happening.
Finding relief for dry eye symptoms
Dry eye disease can be a frustrating condition for patients because it can be difficult to manage, but being mindful of the environment and taking precautionary measures, especially when stress is elevated, may help.
"A lot of what I do is explain to patients that it's important to take breaks from staring at the computer, use moisturizing eye drops as part of a daily routine, and make environmental adjustments to minimize the wind stress on the eyes," Gregory says.
Actions such as remembering to stay hydrated, turning off vents or fans that may further dry eyes , and using eye drops preventively can help alleviate and prevent bothersome symptoms.
"Don't wait until your eyes are burning to use moisturizing drops," Gregory explains. "That's sort of like waiting until your lips are chapped and cracked to start using lip balm. If you do a little bit of treatment more often and develop a routine, you may find that the dry eye symptoms are not as bad."
Gregory also recommends using a warm eye compress for about five to 10 minutes and then gently massaging the eye lids or taking a few big, firm blinks. This can help disperse natural oils needed to keep the eye properly lubricated.
Finally, finding some time to destress and relax is important for ocular health.
"Our modern world is not very kind to eyes," Gregory explains. "Taking time to prioritize your health is important. Whether it's yoga or limiting screen time , these little improvements can make a difference and potentially help those bothersome symptoms that act up when we're stressed."
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Tobacco firms invest billions in medical products: Call for journals to ban research by the firms, their subsidiaries
6 hours ago

New avenues to developing personalized treatments for schizophrenia
7 hours ago
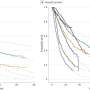
Study: Access to targeted lung cancer drug is cost-prohibitive globally
Researchers identify factors that heighten risk for catheter-associated urinary tract infections and sepsis
'Sticky and strain-gradient artificial epineurium' can heal severed nerves in only one minute, study claims
8 hours ago

Could ultra-processed foods be associated with your insomnia?
Tiny worm helps uncover long-lasting prenatal effects from amphetamines

PTSD, anxiety is rising among college students

Study confirms effectiveness of 'watch-and-wait' approach to prostate cancer
9 hours ago
Cause of common type of heart failure may be different for women and men
Related stories.

Expert explains pink eye
May 8, 2024
Causes, symptoms and treatments for dry eyes
Mar 3, 2023

Spotting the silent symptoms of stress
May 6, 2024

Mayo Clinic Q and A: Relief for dry eyes
Mar 17, 2022

How to prevent and treat eye allergies
Jan 31, 2019
Research reveals how COVID-19 affects the eyes
Dec 8, 2020
Recommended for you

Study finds even low lead levels in US water are linked to lead poisoning among susceptible people
11 hours ago

Snapping photos of our food could be good for us, study suggests
12 hours ago

Study shows N95 masks near-perfect at blocking escape of airborne COVID-19

Survey on trust and equity in emergency departments aims to improve system for all patients
14 hours ago
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
WEB51 Research Topics. Submission open. Thyroid eye diseases. Alon Kahana. Raymond Cho. Tarjani Dave. 140 views. Submission open. Ocular Surface Disorders- An Insight. Shweta Agarwal. Hon Shing Ong. Alfonso Vasquez-Perez. Submission open. Myopia in Childhood and Adolescence. Lei Wan. Sheila Gillard Crewther. 198 views. Submission …
An exciting new journal which advances our knowledge of the mechanisms underlying eye diseases and disorders, to aid in diagnosis and best management, thereby aiming to prevent visual loss. ... 51 Research Topics Guest edit your own article collection Suggest a topic. Submission. null. Submission All; Submission open; Submission closed ...
Quantification and Predictors of Visual Field Variability in Healthy, Glaucoma Suspect, and Glaucomatous Eyes Using SITA-Faster. Jeremy C.K. Tan, Ashish Agar, Michael Kalloniatis, Jack Phu. Published online: December 16, 2023. p658-666. Full-Text HTML. PDF.
Evaluation of clinical efficacy and safety of tobramycin/dexamethasone eye ointment in treating persistent corneal epithelial dysfunction (PED) after cataract surgery. Xianwen Xiao, Yuan Lin, Xie Fang, Zhiwen Xie, Shunrong Luo and Huping Wu. BMC Ophthalmology 2024 24 :197. Research Published on: 26 April 2024.
Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology, the journal of the American Academy of Ophthalmology, serves society by publishing clinical research and other relevant manuscripts that relate to the sense of sight. Excellence is pursued through unbiased peer-review, the advancement of innovation and discovery, and the promotion of lifelong learning. More.
H. VanDolah and R. TungN Engl J Med 2023;389:1510-1510. A 44-year-old man presented with a 2-week history of pain and blurry vision in the left eye, fevers, and back pain. The left eye had ...
ROBIN: a randomised, double-masked, placebo-controlled Phase IIa study of the AOC3 inhibitor BI 1467335 in diabetic retinopathy. Quan Dong Nguyen. Justis P. Ehlers. Sunil Patel. Article Open ...
Ophthalmology is a rapidly growing research area in the UK recruiting on average more than 15,000 patients into clinical research trials annually with most National Health Service (NHS) trusts ...
Harvard Ophthalmology research contributions have resulted in major advancements in medical science and ophthalmic practice. Discoveries made in various fields—including genetics, immunology and ocular biology—have reshaped the foundations of ophthalmology and formed many new paradigms for the repair, regeneration, and rehabilitation of countless disorders.
Ophthalmology has been at the forefront of many innovations in basic science and clinical research. The randomized prospective multicenter clinical trial, comparative clinical trials, the bench to beside development of diagnostic and therapeutic devices, the powerful combination of biostatistics and epidemiology, gene therapy, cell-based therapy, stem cell therapy, regenerative medicine ...
Home-Monitoring Vision Tests to Detect Active Neovascular AMD. 2,005Views. Efficacy and Safety of 0.01% and 0.02% Atropine for the Treatment of Pediatric Myopia Progression Over 3 Years. View more. Explore the latest in vision science including causes & treatment of cataract, glaucoma, retinal disorders, & more. Formerly Archives of Ophthalmology.
Efficacy and Safety of 8 Atropine Concentrations for Myopia Control in Children: A Network Meta-Analysis. Ahnul Ha, Seong Joon Kim, Sung Ryul Shim, Young Kook Kim, Jae Ho Jung. March 2022. Pages 322-333. View PDF.
Current Opinion in Ophthalmology is an indispensable resource featuring key up-to-date and important advances in the field from around the world. With renowned guest editors for each section, every bimonthly issue of Current Opinion in Ophthalmology delivers a fresh insight into topics such as glaucoma, refractive surgery and corneal and external disorders.
Table 2 Journals of top 100 most cited articles on ophthalmic trauma. Among research institutions that have published multiple T100 papers, Wilmer Eye Institute, Johns Hopkins University, had the ...
The top 25 high-impact articles in ophthalmology published between 2017 and 2021, ranked by total citations, are shown in Table 1. All the articles had been cited more than 150 times, with the highest number of citations being 419. Of these articles, 10 were published in 2017, 12 in 2018, one in 2019, and two in 2020.
The Wilmer Eye Institute is the largest department of ophthalmology in the United States and is an internationally-recognized research enterprise. Wilmer receives more funding from the National Eye Institute than any other university system, and is a leading recipient of research funding in the nation. Wilmer is a thriving place for basic ...
The Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences offers medical students and residents a variety of research opportunities. Please browse the basic science, translational and clinical research projects currently underway below. Research Topic: Corneal endothelial health judged by endothelial image analysis Description.
Andrzej Grzybowski, M.D., Ph.D., MBA, MAE is a Professor of Ophthalmology and Chair of the Department of Ophthalmology, University of Warmia and Mazury, Olsztyn, Poland; Head of Institute for Research in Ophthalmology, Foundation for Ophthalmology Development, Poznan, Poland.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Pioneering research by the UAB Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences into retinal disorders, specifically age-related macular degeneration, has led to major scientific breakthroughs. Age-related macular degeneration is one of the most common ocular disorders in the U.S., and there is no cure.
Ophthalmology Topics. AMD and Retinal Disease. Cataract and Refractive Surgery. Cornea and External Disease. Diabetic Microvascular Complications. Glaucoma. Pediatric Ophthalmology. Residents.
Latest Research and Reviews. ROBIN: a randomised, double-masked, placebo-controlled Phase IIa study of the AOC3 inhibitor BI 1467335 in diabetic retinopathy ... Comments & Opinion 27 May 2024 Eye ...
Abstract. This series continues to present basic research topics to the ophthalmic community. Some of the chapters are difficult reading for anyone not well grounded in biochemistry or molecular biology. The article most pertinent to clinical ophthalmology is by Ronald A. Laing of Boston University on specular microscopy of the cornea.
'Stereolithographic Rapid Prototyping of Clear, Foldable, Non-refractive Intraocular Lens Designs: A Proof-of-Concept Study' is published in the journal Current Eye Research. RELATED TOPICS Health ...
Key Points. Question What patient inequities have been assessed and how has research on these inequities differed from 2016 to 2021 within the field of ophthalmology?. Findings This scoping review of 75 publications revealed substantial research gaps regarding health inequities associated with the lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) community, race and ethnicity—namely ...
Feedback to editors. Long work hours, little sleep, a full inbox; balancing work and a social life: Stress can pile up and have notable physical effects on the body, including the eyes. Ocular ...
Dr. Kendall designed metal quail feeders that will be sold under the name QuailSafe, and the design affords the birds protection from predators while they consume the inoculated feed. Once the ...
A new study led by UC Davis researchers finds widespread differences in brain development between autistic boys and girls ages 2-13. The study, published recently in Molecular Psychiatry, found sex-specific changes in the thickness of the outer layer of the brain, called the cortex. Brain regions associated with autism showed different rates of ...