- What is mixed methods research?
Last updated
20 February 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
By blending both quantitative and qualitative data, mixed methods research allows for a more thorough exploration of a research question. It can answer complex research queries that cannot be solved with either qualitative or quantitative research .

Analyze your mixed methods research
Dovetail streamlines analysis to help you uncover and share actionable insights
Mixed methods research combines the elements of two types of research: quantitative and qualitative.
Quantitative data is collected through the use of surveys and experiments, for example, containing numerical measures such as ages, scores, and percentages.
Qualitative data involves non-numerical measures like beliefs, motivations, attitudes, and experiences, often derived through interviews and focus group research to gain a deeper understanding of a research question or phenomenon.
Mixed methods research is often used in the behavioral, health, and social sciences, as it allows for the collection of numerical and non-numerical data.
- When to use mixed methods research
Mixed methods research is a great choice when quantitative or qualitative data alone will not sufficiently answer a research question. By collecting and analyzing both quantitative and qualitative data in the same study, you can draw more meaningful conclusions.
There are several reasons why mixed methods research can be beneficial, including generalizability, contextualization, and credibility.
For example, let's say you are conducting a survey about consumer preferences for a certain product. You could collect only quantitative data, such as how many people prefer each product and their demographics. Or you could supplement your quantitative data with qualitative data, such as interviews and focus groups , to get a better sense of why people prefer one product over another.
It is important to note that mixed methods research does not only mean collecting both types of data. Rather, it also requires carefully considering the relationship between the two and method flexibility.
You may find differing or even conflicting results by combining quantitative and qualitative data . It is up to the researcher to then carefully analyze the results and consider them in the context of the research question to draw meaningful conclusions.
When designing a mixed methods study, it is important to consider your research approach, research questions, and available data. Think about how you can use different techniques to integrate the data to provide an answer to your research question.
- Mixed methods research design
A mixed methods research design is an approach to collecting and analyzing both qualitative and quantitative data in a single study.
Mixed methods designs allow for method flexibility and can provide differing and even conflicting results. Examples of mixed methods research designs include convergent parallel, explanatory sequential, and exploratory sequential.
By integrating data from both quantitative and qualitative sources, researchers can gain valuable insights into their research topic . For example, a study looking into the impact of technology on learning could use surveys to measure quantitative data on students' use of technology in the classroom. At the same time, interviews or focus groups can provide qualitative data on students' experiences and opinions.
- Types of mixed method research designs
Researchers often struggle to put mixed methods research into practice, as it is challenging and can lead to research bias. Although mixed methods research can reveal differences or conflicting results between studies, it can also offer method flexibility.
Designing a mixed methods study can be broken down into four types: convergent parallel, embedded, explanatory sequential, and exploratory sequential.
Convergent parallel
The convergent parallel design is when data collection and analysis of both quantitative and qualitative data occur simultaneously and are analyzed separately. This design aims to create mutually exclusive sets of data that inform each other.
For example, you might interview people who live in a certain neighborhood while also conducting a survey of the same people to determine their satisfaction with the area.
Embedded design
The embedded design is when the quantitative and qualitative data are collected simultaneously, but the qualitative data is embedded within the quantitative data. This design is best used when you want to focus on the quantitative data but still need to understand how the qualitative data further explains it.
For instance, you may survey students about their opinions of an online learning platform and conduct individual interviews to gain further insight into their responses.
Explanatory sequential design
In an explanatory sequential design, quantitative data is collected first, followed by qualitative data. This design is used when you want to further explain a set of quantitative data with additional qualitative information.
An example of this would be if you surveyed employees at a company about their satisfaction with their job and then conducted interviews to gain more information about why they responded the way they did.
Exploratory sequential design
The exploratory sequential design collects qualitative data first, followed by quantitative data. This type of mixed methods research is used when the goal is to explore a topic before collecting any quantitative data.
An example of this could be studying how parents interact with their children by conducting interviews and then using a survey to further explore and measure these interactions.
Integrating data in mixed methods studies can be challenging, but it can be done successfully with careful planning.
No matter which type of design you choose, understanding and applying these principles can help you draw meaningful conclusions from your research.
- Strengths of mixed methods research
Mixed methods research designs combine the strengths of qualitative and quantitative data, deepening and enriching qualitative results with quantitative data and validating quantitative findings with qualitative data. This method offers more flexibility in designing research, combining theory generation and hypothesis testing, and being less tied to disciplines and established research paradigms.
Take the example of a study examining the impact of exercise on mental health. Mixed methods research would allow for a comprehensive look at the issue from different angles.
Researchers could begin by collecting quantitative data through surveys to get an overall view of the participants' levels of physical activity and mental health. Qualitative interviews would follow this to explore the underlying dynamics of participants' experiences of exercise, physical activity, and mental health in greater detail.
Through a mixed methods approach, researchers could more easily compare and contrast their results to better understand the phenomenon as a whole.
Additionally, mixed methods research is useful when there are conflicting or differing results in different studies. By combining both quantitative and qualitative data, mixed methods research can offer insights into why those differences exist.
For example, if a quantitative survey yields one result while a qualitative interview yields another, mixed methods research can help identify what factors influence these differences by integrating data from both sources.
Overall, mixed methods research designs offer a range of advantages for studying complex phenomena. They can provide insight into different elements of a phenomenon in ways that are not possible with either qualitative or quantitative data alone. Additionally, they allow researchers to integrate data from multiple sources to gain a deeper understanding of the phenomenon in question.
- Challenges of mixed methods research
Mixed methods research is labor-intensive and often requires interdisciplinary teams of researchers to collaborate. It also has the potential to cost more than conducting a stand alone qualitative or quantitative study .
Interpreting the results of mixed methods research can be tricky, as it can involve conflicting or differing results. Researchers must find ways to systematically compare the results from different sources and methods to avoid bias.
For example, imagine a situation where a team of researchers has employed an explanatory sequential design for their mixed methods study. After collecting data from both the quantitative and qualitative stages, the team finds that the two sets of data provide differing results. This could be challenging for the team, as they must now decide how to effectively integrate the two types of data in order to reach meaningful conclusions. The team would need to identify method flexibility and be strategic when integrating data in order to draw meaningful conclusions from the conflicting results.
- Advanced frameworks in mixed methods research
Mixed methods research offers powerful tools for investigating complex processes and systems, such as in health and healthcare.
Besides the three basic mixed method designs—exploratory sequential, explanatory sequential, and convergent parallel—you can use one of the four advanced frameworks to extend mixed methods research designs. These include multistage, intervention, case study , and participatory.
This framework mixes qualitative and quantitative data collection methods in stages to gather a more nuanced view of the research question. An example of this is a study that first has an online survey to collect initial data and is followed by in-depth interviews to gain further insights.
Intervention
This design involves collecting quantitative data and then taking action, usually in the form of an intervention or intervention program. An example of this could be a research team who collects data from a group of participants, evaluates it, and then implements an intervention program based on their findings .
This utilizes both qualitative and quantitative research methods to analyze a single case. The researcher will examine the specific case in detail to understand the factors influencing it. An example of this could be a study of a specific business organization to understand the organizational dynamics and culture within the organization.
Participatory
This type of research focuses on the involvement of participants in the research process. It involves the active participation of participants in formulating and developing research questions, data collection, and analysis.
An example of this could be a study that involves forming focus groups with participants who actively develop the research questions and then provide feedback during the data collection and analysis stages.
The flexibility of mixed methods research designs means that researchers can choose any combination of the four frameworks outlined above and other methodologies , such as convergent parallel, explanatory sequential, and exploratory sequential, to suit their particular needs.
Through this method's flexibility, researchers can gain multiple perspectives and uncover differing or even conflicting results when integrating data.
When it comes to integration at the methods level, there are four approaches.
Connecting involves collecting both qualitative and quantitative data during different phases of the research.
Building involves the collection of both quantitative and qualitative data within a single phase.
Merging involves the concurrent collection of both qualitative and quantitative data.
Embedding involves including qualitative data within a quantitative study or vice versa.
- Techniques for integrating data in mixed method studies
Integrating data is an important step in mixed methods research designs. It allows researchers to gain further understanding from their research and gives credibility to the integration process. There are three main techniques for integrating data in mixed methods studies: triangulation protocol, following a thread, and the mixed methods matrix.
Triangulation protocol
This integration method combines different methods with differing or conflicting results to generate one unified answer.
For example, if a researcher wanted to know what type of music teenagers enjoy listening to, they might employ a survey of 1,000 teenagers as well as five focus group interviews to investigate this. The results might differ; the survey may find that rap is the most popular genre, whereas the focus groups may suggest rock music is more widely listened to.
The researcher can then use the triangulation protocol to come up with a unified answer—such as that both rap and rock music are popular genres for teenage listeners.
Following a thread
This is another method of integration where the researcher follows the same theme or idea from one method of data collection to the next.
A research design that follows a thread starts by collecting quantitative data on a specific issue, followed by collecting qualitative data to explain the results. This allows whoever is conducting the research to detect any conflicting information and further look into the conflicting information to understand what is really going on.
For example, a researcher who used this research method might collect quantitative data about how satisfied employees are with their jobs at a certain company, followed by qualitative interviews to investigate why job satisfaction levels are low. They could then use the results to explore any conflicting or differing results, allowing them to gain a deeper understanding of job satisfaction at the company.
By following a thread, the researcher can explore various research topics related to the original issue and gain a more comprehensive view of the issue.
Mixed methods matrix
This technique is a visual representation of the different types of mixed methods research designs and the order in which they should be implemented. It enables researchers to quickly assess their research design and adjust it as needed.
The matrix consists of four boxes with four different types of mixed methods research designs: convergent parallel, explanatory sequential, exploratory sequential, and method flexibility.
For example, imagine a researcher who wanted to understand why people don't exercise regularly. To answer this question, they could use a convergent parallel design, collecting both quantitative (e.g., survey responses) and qualitative (e.g., interviews) data simultaneously.
If the researcher found conflicting results, they could switch to an explanatory sequential design and collect quantitative data first, then follow up with qualitative data if needed. This way, the researcher can make adjustments based on their findings and integrate their data more effectively.
Mixed methods research is a powerful tool for understanding complex research topics. Using qualitative and quantitative data in one study allows researchers to understand their subject more deeply.
Mixed methods research designs such as convergent parallel, explanatory sequential, and exploratory sequential provide method flexibility, enabling researchers to collect both types of data while avoiding the limitations of either approach alone.
However, it's important to remember that mixed methods research can produce differing or even conflicting results, so it's important to be aware of the potential pitfalls and take steps to ensure that data is being correctly integrated. If used effectively, mixed methods research can offer valuable insight into topics that would otherwise remain largely unexplored.
What is an example of mixed methods research?
An example of mixed methods research is a study that combines quantitative and qualitative data. This type of research uses surveys, interviews, and observations to collect data from multiple sources.
Which sampling method is best for mixed methods?
It depends on the research objectives, but a few methods are often used in mixed methods research designs. These include snowball sampling, convenience sampling, and purposive sampling. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages.
What is the difference between mixed methods and multiple methods?
Mixed methods research combines quantitative and qualitative data in a single study. Multiple methods involve collecting data from different sources, such as surveys and interviews, but not necessarily combining them into one analysis. Mixed methods offer greater flexibility but can lead to differing or conflicting results when integrating data.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Mixed methods research: what it is and what it could be
- Open access
- Published: 29 March 2019
- Volume 48 , pages 193–216, ( 2019 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Rob Timans 1 ,
- Paul Wouters 2 &
- Johan Heilbron 3
115k Accesses
92 Citations
13 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
A Correction to this article was published on 06 May 2019
This article has been updated
Combining methods in social scientific research has recently gained momentum through a research strand called Mixed Methods Research (MMR). This approach, which explicitly aims to offer a framework for combining methods, has rapidly spread through the social and behavioural sciences, and this article offers an analysis of the approach from a field theoretical perspective. After a brief outline of the MMR program, we ask how its recent rise can be understood. We then delve deeper into some of the specific elements that constitute the MMR approach, and we engage critically with the assumptions that underlay this particular conception of using multiple methods. We conclude by offering an alternative view regarding methods and method use.
Similar content being viewed by others

What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research
Reporting reliability, convergent and discriminant validity with structural equation modeling: a review and best-practice recommendations.
Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
The interest in combining methods in social scientific research has a long history. Terms such as “triangulation,” “combining methods,” and “multiple methods” have been around for quite a while to designate using different methods of data analysis in empirical studies. However, this practice has gained new momentum through a research strand that has recently emerged and that explicitly aims to offer a framework for combining methods. This approach, which goes by the name of Mixed Methods Research (MMR), has rapidly become popular in the social and behavioural sciences. This can be seen, for instance, in Fig. 1 , where the number of publications mentioning “mixed methods” in the title or abstract in the Thomson Reuters Web of Science is depicted. The number increased rapidly over the past ten years, especially after 2006. Footnote 1
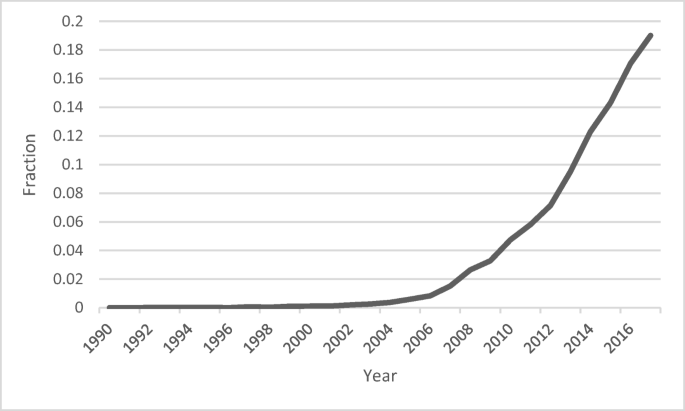
Fraction of the total of articles mentioning Mixed Method Research appearing in a given year, 1990–2017 (yearly values sum to 1). See footnote 1
The subject of mixed methods thus seems to have gained recognition among social scientists. The rapid rise of the number of articles mentioning the term raises various sociological questions. In this article, we address three of these questions. The first question concerns the degree to which the approach of MMR has become institutionalized within the field of the social sciences. Has MMR become a recognizable realm of knowledge production? Has its ascendance been accompanied by the production of textbooks, the founding of journals, and other indicators of institutionalization? The answer to this question provides an assessment of the current state of MMR. Once that is determined, the second question is how MMR’s rise can be understood. Where does the approach come from and how can its emergence and spread be understood? To answer this question, we use Pierre Bourdieu’s field analytical approach to science and academic institutions (Bourdieu 1975 , 1988 , 2004 , 2007 ; Bourdieu et al. 1991 ). We flesh out this approach in the next section. The third question concerns the substance of the MMR corpus seen in the light of the answers to the previous questions: how can we interpret the specific content of this approach in the context of its socio-historical genesis and institutionalization, and how can we understand its proposal for “mixing methods” in practice?
We proceed as follows. In the next section, we give an account of our theoretical approach. Then, in the third, we assess the degree of institutionalization of MMR, drawing on the indicators of academic institutionalization developed by Fleck et al. ( 2016 ). In the fourth section, we address the second question by examining the position of the academic entrepreneurs behind the rise of MMR. The aim is to understand these agents’ engagement in MMR, as well as its distinctive content as being informed by their position in this field. Viewing MMR as a position-taking of academic entrepreneurs, linked to their objective position in this field, allows us to reflect sociologically on the substance of the approach. We offer this reflection in the fifth section, where we indicate some problems with MMR. To get ahead of the discussion, these problems have to do with the framing of MMR as a distinct methodology and its specific conceptualization of data and methods of data analysis. We argue that these problems hinder fruitfully combining methods in a practical understanding of social scientific research. Finally, we conclude with some tentative proposals for an alternative view on combining methods.
A field approach
Our investigation of the rise and institutionalization of MMR relies on Bourdieu’s field approach. In general, field theory provides a model for the structural dimensions of practices. In fields, agents occupy a position relative to each other based on the differences in the volume and structure of their capital holdings. Capital can be seen as a resource that agents employ to exert power in the field. The distribution of the form of capital that is specific to the field serves as a principle of hierarchization in the field, differentiating those that hold more capital from those that hold less. This principle allows us to make a distinction between, respectively, the dominant and dominated factions in a field. However, in mature fields all agents—dominant and dominated—share an understanding of what is at stake in the field and tend to accept its principle of hierarchization. They are invested in the game, have an interest in it, and share the field’s illusio .
In the present case, we can interpret the various disciplines in the social sciences as more or less autonomous spaces that revolve around the shared stake in producing legitimate scientific knowledge by the standards of the field. What constitutes legitimate knowledge in these disciplinary fields, the production of which bestows scholars with prestige and an aura of competence, is in large part determined by the dominant agents in the field, who occupy positions in which most of the consecration of scientific work takes place. Scholars operating in a field are endowed with initial and accumulated field-specific capital, and are engaged in the struggle to gain additional capital (mainly scientific and intellectual prestige) in order to advance their position in the field. The main focus of these agents will generally be the disciplinary field in which they built their careers and invested their capital. These various disciplinary spaces are in turn part of a broader field of the social sciences in which the social status and prestige of the various disciplines is at stake. The ensuing disciplinary hierarchy is an important factor to take into account when analysing the circulation of new scientific products such as MMR. Furthermore, a distinction needs to be made between the academic and the scientific field. While the academic field revolves around universities and other degree-granting institutions, the stakes in the scientific field entail the production and valuation of knowledge. Of course, in modern science these fields are closely related, but they do not coincide (Gingras and Gemme 2006 ). For instance, part of the production of legitimate knowledge takes place outside of universities.
This framework makes it possible to contextualize the emergence of MMR in a socio-historical way. It also enables an assessment of some of the characteristics of MMR as a scientific product, since Bourdieu insists on the homology between the objective positions in a field and the position-takings of the agents who occupy these positions. As a new methodological approach, MMR is the result of the position-takings of its producers. The position-takings of the entrepreneurs at the core of MMR can therefore be seen as expressions in the struggles over the authority to define the proper methodology that underlies good scientific work regarding combining methods, and the potential rewards that come with being seen, by other agents, as authoritative on these matters. Possible rewards include a strengthened autonomy of the subfield of MMR and an improved position in the social-scientific field.
The role of these entrepreneurs or ‘intellectual leaders’ who can channel intellectual energy and can take the lead in institution building has been emphasised by sociologists of science as an important aspect of the production of knowledge that is visible and recognized as distinct in the larger scientific field (e.g., Mullins 1973 ; Collins 1998 ). According to Bourdieu, their position can, to a certain degree, explain the strategy they pursue and the options they perceive to be viable in the trade-off regarding the risks and potential rewards for their work.
We do not provide a full-fledged field analysis of MMR here. Rather, we use the concept as a heuristic device to account for the phenomenon of MMR in the social context in which it emerged and diffused. But first, we take stock of the current situation of MMR by focusing on the degree of institutionalization of MMR in the scientific field.
The institutionalization of mixed methods research
When discussing institutionalization, we have to be careful about what we mean by this term. More precisely, we need to be specific about the context and distinguish between institutionalization in the academic field and institutionalization within the scientific field (see Gingras and Gemme 2006 ; Sapiro et al. 2018 ). The first process refers to the establishment of degrees, curricula, faculties, etc., or to institutions tied to the academic bureaucracy and academic politics. The latter refers to the emergence of institutions that support the autonomization of scholarship such as scholarly associations and scientific journals. Since MMR is still a relatively young phenomenon and academic institutionalization tends to lag scientific institutionalization (e.g., for the case of sociology and psychology, see Sapiro et al. 2018 , p. 26), we mainly focus here on the latter dimension.
Drawing on criteria proposed by Fleck et al. ( 2016 ) for the institutionalization of academic disciplines, MMR seems to have achieved a significant degree of institutionalization within the scientific field. MMR quickly gained popularity in the first decade of the twenty-first century (e.g., Tashakkori and Teddlie 2010c , pp. 803–804). A distinct corpus of publications has been produced that aims to educate those interested in MMR and to function as a source of reference for researchers: there are a number of textbooks (e.g., Plowright 2010 ; Creswell and Plano Clark 2011 ; Teddlie and Tashakkori 2008 ); a handbook that is now in its second edition (Tashakkori and Teddlie 2003 , 2010a ); as well as a reader (Plano Clark and Creswell 2007 ). Furthermore, a journal (the Journal of Mixed Methods Research [ JMMR] ) was established in 2007. The JMMR was founded by the editors John Creswell and Abbas Tashakkori with the primary aim of “building an international and multidisciplinary community of mixed methods researchers.” Footnote 2 Contributions to the journal must “fit the definition of mixed methods research” Footnote 3 and explicitly integrate qualitative and quantitative aspects of research, either in an empirical study or in a more theoretical-methodologically oriented piece.
In addition, general textbooks on social research methods and methodology now increasingly devote sections to the issue of combining methods (e.g., Creswell 2008 ; Nagy Hesse-Biber and Leavy 2008 ; Bryman 2012 ), and MMR has been described as a “third paradigm” (Denscombe 2008 ), a “movement” (Bryman 2009 ), a “third methodology” (Tashakkori and Teddlie 2010b ), a “distinct approach” (Greene 2008 ) and an “emerging field” (Tashakkori and Teddlie 2011 ), defined by a common name (that sets it apart from other approaches to combining methods) and shared terminology (Tashakkori and Teddlie 2010b , p. 19). As a further indication of institutionalization, a research association (the Mixed Methods International Research Association—MMIRA) was founded in 2013 and its inaugural conference was held in 2014. Prior to this, there have been a number of conferences on MMR or occasions on which MMR was presented and discussed in other contexts. An example of the first is the conference on mixed method research design held in Basel in 2005. Starting also in 2005, the British Homerton School of Health Studies has organised a series of international conferences on mixed methods. Moreover, MMR was on the list of sessions in a number of conferences on qualitative research (see, e.g., Creswell 2012 ).
Another sign of institutionalization can be found in efforts to forge a common disciplinary identity by providing a narrative about its history. This involves the identification of precursors and pioneers as well as an interpretation of the process that gave rise to a distinctive set of ideas and practices. An explicit attempt to chart the early history of MMR is provided by Johnson and Gray ( 2010 ). They frame MMR as rooted in the philosophy of science, particularly as a way of thinking about science that has transcended some of the most salient historical oppositions in philosophy. Philosophers like Aristotle and Kant are portrayed as thinkers who sought to integrate opposing stances, forwarding “proto-mixed methods ideas” that exhibited the spirit of MMR (Johnson and Gray 2010 , p. 72, p. 86). In this capacity, they (as well as other philosophers like Vico and Montesquieu) are presented as part of MMR providing a philosophical validation of the project by presenting it as a continuation of ideas that have already been voiced by great thinkers in the past.
In the second edition of their textbook, Creswell and Plano Clark ( 2011 ) provide an overview of the history of MMR by identifying five historical stages: the first one being a precursor to the MMR approach, consisting of rather atomised attempts by different authors to combine methods in their research. For Creswell and Plano Clark, one of the earliest examples is Campbell and Fiske’s ( 1959 ) combination of quantitative methods to improve the validity of psychological scales that gave rise to the triangulation approach to research. However, they regard this and other studies that combined methods around that time, as “antecedents to (…) more systematic attempts to forge mixed methods into a complete research design” (Creswell and Plano Clark 2011 , p. 21), and hence label this stage as the “formative period” (ibid., p. 25). Their second stage consists of the emergence of MMR as an identifiable research strand, accompanied by a “paradigm debate” about the possibility of combining qualitative and quantitative data. They locate its beginnings in the late 1980s when researchers in various fields began to combine qualitative and quantitative methods (ibid., pp. 20–21). This provoked a discussion about the feasibility of combining data that were viewed as coming from very different philosophical points of view. The third stage, the “procedural development period,” saw an emphasis on developing more hands-on procedures for designing a mixed methods study, while stage four is identified as consisting of “advocacy and expansion” of MMR as a separate methodology, involving conferences, the establishment of a journal and the first edition of the aforementioned handbook (Tashakkori and Teddlie 2003 ). Finally, the fifth stage is seen as a “reflective period,” in which discussions about the unique philosophical underpinnings and the scientific position of MMR emerge.
Creswell and Plano Clark thus locate the emergence of “MMR proper” at the second stage, when researchers started to use both qualitative and quantitative methods within a single research effort. As reasons for the emergence of MMR at this stage they identify the growing complexity of research problems, the perception of qualitative research as a legitimate form of inquiry (also by quantitative researchers) and the increasing need qualitative researchers felt for generalising their findings. They therefore perceive the emergence of the practice of combining methods as a bottom up process that grew out of research practices, and at some point in time converged towards a more structural approach. Footnote 4 Historical accounts such as these add a cognitive dimension to the efforts to institutionalize MMR. They lay the groundwork for MMR as a separate subfield with its own identity, topics, problems and intellectual history. The use of terms such as “third paradigm” and “third methodology” also suggests that there is a tendency to perceive and promote MMR as a distinct and coherent way to do research.
In view of the brief exploration of the indicators of institutionalisation of MMR, it seems reasonable to conclude that MMR has become a recognizable and fairly institutionalized strand of research with its own identity and profile within the social scientific field. This can be seen both from the establishment of formal institutions (like associations and journals) and more informal ones that rely more on the tacit agreement between agents about “what MMR is” (an example of this, which we address later in the article, is the search for a common definition of MMR in order to fix the meaning of the term). The establishment of these institutions supports the autonomization of MMR and its emancipation from the field in which it originated, but in which it continues to be embedded. This way, it can be viewed as a semi-autonomous subfield within the larger field of the social sciences and as the result of a differentiation internal to this field (Steinmetz 2016 , p. 109). It is a space that is clearly embedded within this higher level field; for example, members of the subfield of MMR also qualify as members of the overarching field, and the allocation of the most valuable and current form of capital is determined there as well. Nevertheless, as a distinct subfield, it also has specific principles that govern the production of knowledge and the rewards of domination.
We return to the content and form of this specific knowledge later in the article. The next section addresses the question of the socio-genesis of MMR.
Where does mixed methods research come from?
The origins of the subfield of MMR lay in the broader field of social scientific disciplines. We interpret the positions of the scholars most involved in MMR (the “pioneers” or “scientific entrepreneurs”) as occupying particular positions within the larger academic and scientific field. Who, then, are the researchers at the heart of MMR? Leech ( 2010 ) interviewed 4 scholars (out of 6) that she identified as early developers of the field: Alan Bryman (UK; sociology), John Creswell (USA; educational psychology), Jennifer Greene (USA; educational psychology) and Janice Morse (USA; nursing and anthropology). Educated in the 1970s and early 1980s, all four of them indicated that they were initially trained in “quantitative methods” and later acquired skills in “qualitative methods.” For two of them (Bryman and Creswell) the impetus to learn qualitative methods was their involvement in writing on, and teaching of, research methods; for Greene and Morse the initial motivation was more instrumental and related to their concrete research activity at the time. Creswell describes himself as “a postpositivist in the 1970s, self-education as a constructivist through teaching qualitative courses in the 1980s, and advocacy for mixed methods (…) from the 1990s to the present” (Creswell 2011 , p. 269). Of this group, only Morse had the benefit of learning about qualitative methods as part of her educational training (in nursing and anthropology; Leech 2010 , p. 267). Independently, Creswell ( 2012 ) identified (in addition to Bryman, Greene and Morse) John Hunter, Allen Brewer (USA; Northwestern and Boston College) and Nigel Fielding (University of Surrey, UK) as important early movers in MMR.
The selections that Leech and Creswell make regarding the key actors are based on their close involvement with the “MMR movement.” It is corroborated by a simple analysis of the articles that appeared in the Journal of Mixed Methods Research ( JMMR ), founded in 2007 as an outlet for MMR.
Table 1 lists all the authors that have published in the issues of the journal since its first publication in 2007 and that have either received more than 14 (4%) of the citations allocated between the group of 343 authors (the TLCS score in Table 1 ), or have written more than 2 articles for the Journal (1.2% of all the articles that have appeared from 2007 until October 2013) together with their educational background (i.e., the discipline in which they completed their PhD).
All the members of Leech’s selection, except for Morse, and the members of Creswell’s selection (except Hunter, Brewer, and Fielding) are represented in the selection based on the entries in the JMMR . Footnote 5 The same holds for two of the three additional authors identified by Creswell. Hunter and Brewer have developed a somewhat different approach to combining methods that explicitly targets data gathering techniques and largely avoids epistemological discussions. In Brewer and Hunter ( 2006 ) they discuss the MMR approach very briefly and only include two references in their bibliography to the handbook of Tashakkori and Teddlie ( 2003 ), and at the end of 2013 they had not published in the JMMR . Fielding, meanwhile, has written two articles for the JMMR (Fielding and Cisneros-Puebla 2009 ; Fielding 2012 ). In general, it seems reasonable to assume that a publication in a journal that positions itself as part of a systematic attempt to build a research tradition, and can be viewed as part of a strategic effort to advance MMR as a distinct alternative to more “traditional” academic research—particularly in methods—at least signals a degree of adherence to the effort and acceptance of the rules of the game it lays out. This would locate Fielding closer to the MMR movement than the others.
The majority of the researchers listed in Table 1 have a background in psychology or social psychology (35%), and sociology (25%). Most of them work in the United States or are UK citizens, and the positions they occupied at the beginning of 2013 indicates that most of these are in applied research: educational research and educational psychology account for 50% of all the disciplinary occupations of the group that were still employed in academia. This is consistent with the view that MMR originated in applied disciplines and thematic studies like education and nursing, rather than “pure disciplines” like psychology and sociology (Tashakkori and Teddlie ( 2010b ), p. 32). Although most of the 20 individuals mentioned in Table 1 have taught methods courses in academic curricula (for 15 of them, we could determine that they were involved in the teaching of qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods), there are few individuals with a background in statistics or a neighbouring discipline: only Amy Dellinger did her PhD in “research methodology.” In addition, as far as we could determine, only three individuals held a position in a methodological department at some time: Dellinger, Tony Onwuegbuzie, and Nancy Leech.
The pre-eminence of applied fields in MMR is supported when we turn our attention to the circulation of MMR. To assess this we proceeded as follows. We selected 10 categories in the Web of Science that form a rough representation of the space of social science disciplines, taking care to include the most important so-called “studies.” These thematically orientated, interdisciplinary research areas have progressively expanded since they emerged at the end of the 1960s as a critique of the traditional disciplines (Heilbron et al. 2017 ). For each category, we selected the 10 journals with the highest 5-year impact factor in their category in the period 2007–2015. The lists were compiled bi-annually over this period, resulting in 5 top ten lists for the following Web of Science categories: Economics, Psychology, Sociology, Anthropology, Political Science, Nursing, Education & Educational Research, Business, Cultural Studies, and Family Studies. After removing multiple occurring journals, we obtained a list of 164 journals.
We searched the titles and abstracts of the articles appearing in these journals over the period 1992–2016 for occurrences of the terms “mixed method” or “multiple methods” and variants thereof. We chose this particular period and combination of search terms to see if a shift from a more general use of the term “multiple methods” to “mixed methods” occurred following the institutionalization of MMR. In total, we found 797 articles (out of a total of 241,521 articles that appeared in these journals during that time), published in 95 different journals. Table 2 lists the 20 journals that contain at least 1% (8 articles) of the total amount of articles.
As is clear from Table 2 , the largest number of articles in the sample were published in journals in the field of nursing: 332 articles (42%) appeared in journals that can be assigned to this category. The next largest category is Education & Educational Research, to which 224 (28 percentage) of the articles can be allocated. By contrast, classical social science disciples are barely represented. In Table 2 only the journal Field Methods (Anthropology) and the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry (Psychology) are related to classical disciplines. In Table 3 , the articles in the sample are categorized according to the disciplinary category of the journal in which they appeared. Overall, the traditional disciplines are clearly underrepresented: for the Economics category, for example, only the Journal of Economic Geography contains three articles that make a reference to mixed methods.
Focusing on the core MMR group, the top ten authors of the group together collect 458 citations from the 797 articles in the sample, locating them at the center of the citation network. Creswell is the most cited author (210 citations) and his work too receives most citations from journals in nursing and education studies.
The question whether a terminological shift has occurred from “multiple methods” to “mixed methods” must be answered affirmative for this sample. Prior to 2001 most articles (23 out of 31) refer to “multiple methods” or “multi-method” in their title or abstract, while the term “mixed methods” gains traction after 2001. This shift occurs first in journals in nursing studies, with journals in education studies following somewhat later. The same fields are also the first to cite the first textbooks and handbooks of MMR.
Taken together, these results corroborate the notion that MMR circulates mainly in nursing and education studies. How can this be understood from a field theoretical perspective? MMR can be seen as an innovation in the social scientific field, introducing a new methodology for combining existing methods in research. In general, innovation is a relatively risky strategy. Coming up with a truly rule-breaking innovation often involves a small probability of great success and a large probability of failure. However, it is important to add some nuance to this general observation. First, the risk an innovator faces depends on her position in the field. Agents occupying positions at the top of their field’s hierarchy are rich in specific capital and can more easily afford to undertake risky projects. In the scientific field, these are the agents richest in scientific capital. They have the knowledge, authority, and reputation (derived from recognition by their peers; Bourdieu 2004 , p. 34) that tends to decrease the risk they face and increase the chances of success. Moreover, the positions richest in scientific capital will, by definition, be the most consecrated ones. This consecration involves scientific rather than academic capital (cf. Wacquant 2013 , p. 20) and within disciplines these consecrated positions often are related to orthodox position-takings. This presents a paradox: although they have the capital to take more risks, they have also invested heavily in the orthodoxy of the field and will thus be reluctant to upset the status quo and risk destroying the value of their investment. This results in a tendency to take a more conservative stance, aimed at preserving the status quo in the field and defending their position. Footnote 6
For agents in dominated positions this logic is reversed. Possessing less scientific capital, they hold less consecrated positions and their chances of introducing successful innovations are much lower. This leaves them too with two possible strategies. One is to revert to a strategy of adaptation, accepting the established hierarchy in the field and embarking on a slow advancement to gain the necessary capital to make their mark from within the established order. However, Bourdieu notes that sometimes agents with a relatively marginal position in the field will engage in a “flight forward” and pursue higher risk strategies. Strategies promoting a heterodox approach challenge the orthodoxy and the principles of hierarchization of the field, and, if successful (which will be the case only with a small probability), can rake in significant profits by laying claim to a new orthodoxy (Bourdieu 1975 , p. 104; Bourdieu 1993 , pp. 116–117).
Thus, the coupling of innovative strategies to specific field positions based on the amount of scientific capital alone is not straightforward. It is therefore helpful to introduce a second differentiation in the field that, following Bourdieu ( 1975 , p. 103), is based on the differences between the expected profits from these strategies. Here a distinction can be made between an autonomous and a heteronomous pole of the field, i.e., between the purest, most “disinterested” positions and the most “temporal” positions that are more pervious to the heteronomous logic of social hierarchies outside the scientific field. Of course, this difference is a matter of degree, as even the works produced at the most heteronomous positions still have to adhere to the standards of the scientific field to be seen as legitimate. But within each discipline this dimension captures the difference between agents predominantly engaged in fundamental, scholarly work—“production solely for the producers”—and agents more involved in applied lines of research. The main component of the expected profit from innovation in the first case is scientific, whereas in the second case the balance tends to shift towards more temporal profits. This two-fold structuring of the field allows for a more nuanced conception of innovation than the dichotomy “conservative” versus “radical.” Holders of large amounts of scientific capital at the autonomous pole of the field are the producers and conservators of orthodoxy, producing and diffusing what can be called “orthodox innovations” through their control of relatively powerful networks of consecration and circulation. Innovations can be radical or revolutionary in a rational sense, but they tend to originate from questions raised by the orthodoxy of the field. Likewise, the strategy to innovate in this sense can be very risky in that success is in no way guaranteed, but the risk is mitigated by the assurance of peers that these are legitimate questions, tackled in a way that is consistent with orthodoxy and that does not threaten control of the consecration and circulation networks.
These producers are seen as intellectual leaders by most agents in the field, especially by those aspiring to become part of the specific networks of production and circulation they maintain. The exception are the agents located at the autonomous end of the field who possess less scientific capital and outright reject this orthodoxy produced by the field’s elite. Being strictly focused on the most autonomous principles of legitimacy, they are unable to accommodate and have no choice but to reject the orthodoxy. Their only hope is to engage in heterodox innovations that may one day become the new orthodoxy.
The issue is less antagonistic at the heteronomous side of the field, at least as far as the irreconcilable position-takings at the autonomous pole are concerned. The main battle here is also for scientific capital, but is complemented by the legitimacy it brings to gain access to those who are in power outside of the scientific field. At the dominant side, those with more scientific capital tend to have access to the field of power, agents who hold the most economic and cultural capital, for example by holding positions in policy advisory committees or company boards. The dominated groups at this side of the field will cater more to practitioners or professionals outside of the field of science.
Overall, there will be fewer innovations on this side. Moreover, innovative strategies will be less concerned with the intricacies of the pure discussions that prevail at the autonomous pole and be of a more practical nature, but pursued from different degrees of legitimacy according to the differences in scientific capital. This affects the form these more practical, process-orientated innovations take. At the dominant side of this pole, agents tend to accept the outcome of the struggles at the autonomous pole: they will accept the orthodoxy because mastery of this provides them with scientific capital and the legitimacy they need to gain access to those in power. In contrast, agents at the dominated side will be more interested in doing “what works,” neutralizing the points of conflict at the autonomous pole and deriving less value from strictly following the orthodoxy. This way, a four-fold classification of innovative strategies in the scientific field emerges (see Fig. 2 ) that helps to understand the context in which MMR was developed.
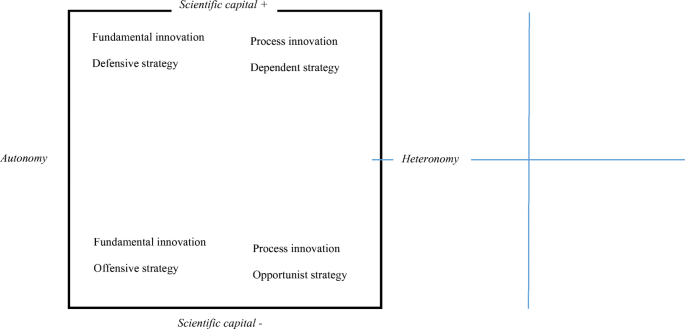
Scientific field and scientific innovation
In summary, the small group of researchers who have been identified as the core of MMR consist predominantly of users of methods, who were educated and have worked exclusively at US and British universities. The specific approach to combining methods that is proposed by MMR has been successful from an institutional point of view, achieving visibility through the foundation of a journal and association and a considerable output of core MMR scholars in terms of books, conference proceedings, and journal articles. Its origins and circulation in vocational studies rather than classical academic disciplines can be understood from the position these studies occupy in the scientific field and the kinds of position-taking and innovations these positions give rise to. This context allows a reflexive understanding of the content of MMR and the issues that are dominant in the approach. We turn to this in the next section.
Mixed methods research: Position-taking
The position of the subfield of MMR in the scientific field is related to the position-takings of agents that form the core of this subfield (Bourdieu 1993 , p. 35). The space of position takings, in turn, provides the framework to study the most salient issues that are debated within the subfield. Since we can consider MMR to be an emerging subfield, where positions and position takings are not as clearly defined as in more mature and settled fields, it comes as no surprise that there is a lively discussion of fundamental matters. Out of the various topics that are actively discussed, we have distilled three themes that are important for the way the subfield of MMR conveys its autonomy as a field and as a distinct approach to research. Footnote 7 In our view, these also represent the main problems with the way MMR approaches the issue of combining methods.
Methodology making and standardization
The first topic is that the approach is moving towards defining a unified MMR methodology. There are differences in opinion as to how this is best achieved, but there is widespread agreement that some kind of common methodological and conceptual foundation of MMR is needed. To this end, some propose a broad methodology that can serve as distinct marker of MMR research. For instance, in their introduction to the handbook, Tashakkori and Teddlie ( 2010b ) propose a definition of the methodology of mixed methods research as “the broad inquiry logic that guides the selection of specific methods and that is informed by conceptual positions common to mixed methods practitioners” (Tashakkori and Teddlie 2010b , p. 5). When they (later on in the text) provide two methodological principles that differentiate MMR from other communities of scholars, they state that they regard it as a “crucial mission” for the MMR community to generate distinct methodological principles (Tashakkori and Teddlie 2010b , pp. 16–17). They envision an MMR methodology that can function as a “guide” for selecting specific methods. Others are more in favour of finding a philosophical foundation that underlies MMR. For instance, Morgan ( 2007 ) and Hesse-Biber ( 2010 ) consider pragmatism as a philosophy that distinguishes MMR from qualitative (constructivism) and quantitative (positivist) research and that can provide a rationale for the paradigmatic pluralism typical of MMR.
Furthermore, there is wide agreement that some unified definition of MMR would be beneficial, but it is precisely here that there is a large variation in interpretations regarding the essentials of MMR. This can be seen in the plethora of definitions that have been proposed. Johnson et al. ( 2007 ) identified 19 alternative definitions of MMR at the time, out of which they condensed their own:
[MMR] is the type of research in which a researcher or team of researchers combines elements of qualitative and quantitative research approaches (e.g., use of qualitative and quantitative viewpoints, data collection, analysis, inference techniques) for the broad purpose of breath and depth of understanding and corroboration. Footnote 8
Four years later, the issue is not settled yet. Creswell and Plano Clark ( 2011 ) list a number of authors who have proposed a different definition of MMR, and conclude that there is a common trend in the content of these definitions over time. They take the view that earlier texts on mixing methods stressed a “disentanglement of methods and philosophy,” while later texts locate the practice of mixing methods in “all phases of the research process” (Creswell and Plano Clark 2011 , p. 2). It would seem, then, that according to these authors the definitions of MMR have become more abstract, further away from the practicality of “merely” combining methods. Specifically, researchers now seem to speak of mixing higher order concepts: some speak of mixing methodologies, others refer to mixing “research approaches,” or combining “types of research,” or engage in “multiple ways of seeing the social world” (Creswell and Plano Clark 2011 ).
This shift is in line with the direction in which MMR has developed and that emphasises practical ‘manuals’ and schemas for conducting research. A relatively large portion of the MMR literature is devoted to classifications of mixed methods designs. These classifications provide the basis for typologies that, in turn, provide guidelines to conduct MMR in a concrete research project. Tashakkori and Teddlie ( 2003 ) view these typologies as important elements of the organizational structure and legitimacy of the field. In addition, Leech and Onwuegbuzie ( 2009 ) see typologies as helpful guides for researchers and of pedagogical value (Leech and Onwuegbuzie 2009 , p. 272). Proposals for typologies can be found in textbooks, articles, and contributions to the handbook(s). For example, Creswell et al. ( 2003 , pp. 169-170) reviewed a number of studies and identified 8 different ways to classify MMR studies. This list was updated and extended by Creswell and Plano Clark ( 2011 , pp. 56-59) to 15 typologies. Leech and Onwuegbuzie ( 2009 ) identified 35 different research designs in the contributions to Teddlie and Tashakkori (2003) alone, and proposed their own three-dimensional typology that resulted in 8 different types of mixed methods studies. As another example of the ubiquity of these typologies, Nastasi et al. ( 2010 ) classified a large number of existing typologies in MMR into 7”meta-typologies” that each emphasize different aspects of the research process as important markers for MMR. According to the authors, these typologies have the same function in MMR as the more familiar names of “qualitative” or “quantitative” methods (e.g., “content analysis” or “structural equation modelling”) have: to signal readers of research what is going on, what procedures have been followed, how to interpret results, etc. (see also Creswell et al. 2003 , pp. 162–163). The criteria underlying these typologies mainly have to do with the degree of mixing (e.g., are methods mixed throughout the research project or not?), the timing (e.g., sequential or concurrent mixing of methods) and the emphasis (e.g., is one approach dominant, or do they have equal status?).
We find this strong drive to develop methodologies, definitions, and typologies of MMR as guides to valid mixed methods research problematic. What it amounts to in practice is a methodology that lays out the basic guidelines for doing MMR in a “proper way.” This entails the danger of straight-jacketing reflection about the use of methods, decoupling it from theoretical and empirical considerations, thus favouring the unreflexive use of a standard methodology. Researchers are asked to make a choice for a particular MMR design and adhere to the guidelines for a “proper” MMR study. Such methodological prescription diametrically opposes the initial critique of the mechanical and unreflexive use of methods. The insight offered by Bourdieu’s notion of reflexivity is, on the contrary, that the actual research practice is fundamentally open in terms of being guided by a logic of practice that cannot be captured by a preconceived and all-encompassing logic independent of that practice. Reflexivity in this view cannot be achieved by hiding behind the construct of a standardized methodology—of whatever signature—it can only be achieved by objectifying the process of objectification that goes on within the context of the field in which the researcher is embedded. This reflexivity, then, requires an analysis of the position of the researcher as a critical component of the research process, both as the embodiment of past choices that have consequences for the strategic position in the scientific field, and as predispositions regarding the choice for the subject and content of a research project. By adding the insight of STS researchers that the point of deconstructing science and technology is not so much to offer a new best way of doing science or technology, but to provide insights into the critical moments in research (for a take on such a debate, see, for example, Edge 1995 , pp. 16–20), this calls for a sociology of science that takes methods much more seriously as objects of study. Such a programme should be based on studying the process of codification and standardization of methods in their historical context of production, circulation, and use. It would provide a basis for a sociological understanding of methods that can illuminate the critical moments in research alluded to above, enabling a systematic reflection on the process of objectification. This, in turn, allows a more sophisticated validation of using—and combining—methods than relying on prescribed methodologies.
The role of epistemology
The second theme discussed in a large number of contributions is the role epistemology plays in MMR. In a sense, epistemology provides the lifeblood for MMR in that methods in MMR are mainly seen in epistemological terms. This interpretation of methods is at the core of the knowledge claim of MMR practitioners, i.e., that the mixing of methods means mixing broad, different ways of knowing, which leads to better knowledge of the research object. It is also part of the identity that MMR consciously assumes, and that serves to set it apart from previous, more practical attempts to combine methods. This can be seen in the historical overview that Creswell and Plano Clark ( 2011 ) presented and that was discussed above. This reading, in which combining methods has evolved from the rather unproblematic level (one could alternatively say “naïve” or “unaware”) of instrumental use of various tools and techniques into an act that requires deeper thinking on a methodological and epistemological level, provides the legitimacy of MMR.
At the core of the MMR approach we thus find that methods are seen as unproblematic representations of different epistemologies. But this leads to a paradox, since the epistemological frameworks need to be held flexible enough to allow researchers to integrate elements of each of them (in the shape of methods) into one MMR design. As a consequence, the issue becomes the following: methods need to be disengaged from too strict an interpretation of the epistemological context in which they were developed in order for them to be “mixable,”’, but, at the same time, they must keep the epistemology attributed to them firmly intact.
In the MMR discourse two epistemological positions are identified that matter most: a positivist approach that gives rise to quantitative methods and a constructivist approach that is home to qualitative methods. For MMR to be a feasible endeavour, the differences between both forms of research must be defined as reconcilable. This position necessitates an engagement with those who hold that the quantitative/qualitative dichotomy is unbridgeable. Within MMR an interesting way of doing so has emerged. In the first issue of the Journal of Mixed Methods Research, Morgan ( 2007 ) frames the debate about research methodology in the social sciences in terms of Kuhnian paradigms, and he argues that the pioneers of the emancipation of qualitative research methods used a particular interpretation of the paradigm-concept to state their case against the then dominant paradigm in the social sciences. According to Morgan, they interpreted a paradigm mainly in metaphysical terms, stressing the connections among the trinity of ontology, epistemology, and methodology as used in the philosophy of knowledge (Morgan 2007 , p. 57). This allowed these scholars to depict the line between research traditions in stark, contrasting terms, using Kuhn’s idea of “incommensurability” in the sense of its “early Kuhn” interpretation. This strategy fixed the contrast between the proposed alternative approach (a “constructivist paradigm”), and the traditional approach (constructed as “the positivist paradigm”) to research as a whole, and offered the alternative approach as a valid option rooted in the philosophy of knowledge. Morgan focuses especially on the work of Egon Guba and Yvonne Lincoln who developed what they initially termed a “naturalistic paradigm” as an alternative to their perception of positivism in the social sciences (e.g., Guba and Lincoln 1985 ). Footnote 9 MMR requires a more flexible or “a-paradigmatic stance” towards research, which would entail that “in real-world practice, methods can be separated from the epistemology out of which they emerged” (Patton 2002 , quoted in Tashakkori and Teddlie 2010b , p. 14).
This proposal of an ‘interpretative flexibility’ (Bijker 1987 , 1997 ) regarding paradigms is an interesting proposition. But it immediately raises the question: why stop there? Why not take a deeper look into the epistemological technology of methods themselves, to let the muted components speak up in order to look for alternative “mixing interfaces” that could potentially provide equally valid benefits in terms of the understanding of a research object? The answer, of course, was already seen above. It is that the MMR approach requires situating methods epistemologically in order to keep them intact as unproblematic mediators of specific epistemologies and, thus, make the methodological prescriptions work. There are several problems with this. First, seeing methods solely through an epistemological lens is problematic, but it would be less consequential if it were applied to multiple elements of methods separately. This would at least allow a look under the hood of a method, and new ways of mixing methods could be opened up that go beyond the crude “qualitative” versus “quantitative” dichotomy. Second, there is also the issue of the ontological dimension of methods that is disregarded in an exclusively epistemological framing of methods (e.g., Law 2004 ). Taking this ontological dimension seriously has at least two important facets. First, it draws attention to the ontological assumptions that are woven into methods in their respective fields of production and that are imported into fields of users. Second, it entails the ontological consequences of practising methods: using, applying, and referring to methods and the realities this produces. This latter facet brings the world-making and boundary-drawing capacities of methods to the fore. Both facets are ignored in MMR. We say more about the first facet in the next section. With regard to the second facet, a crucial element concerns the data that are generated, collected, and analysed in a research project. But rather than problematizing the link between the performativity of methods and the data that are enacted within the frame of a method, here too MMR relies on a dichotomy: that between quantitative and qualitative data. Methods are primarily viewed as ways of gathering data or as analytic techniques dealing with a specific kind of data. Methods and data are conceptualised intertwiningly: methods too are seen as either quantitative or qualitative (often written as QUANT and QUAL in the literature), and perform the role of linking epistemology and data. In the final analysis, the MMR approach is based on the epistemological legitimization of the dichotomy between qualitative and quantitative data in order to define and combine methods: data obtain epistemological currency through the supposed in-severable link to certain methods, and methods are reduced to the role of acting as neutral mediators between them.
In this way, methods are effectively reduced to, on the one hand, placeholders for epistemological paradigms and, on the other hand, mediators between one kind of data and the appropriate epistemology. To put it bluntly, the name “mixed methods research” is actually a misnomer, because what is mixed are paradigms or “approaches,” not methods. Thus, the act of mixing methods à la MMR has the paradoxical effect of encouraging a crude black box approach to methods. This is a third problematic characteristic of MMR, because it hinders a detailed study of methods that can lead to a much richer perspective on mixing methods.
Black boxed methods and how to open them
The third problem that we identified with the MMR approach, then, is that with the impetus to standardize the MMR methodology by fixing methods epistemologically, complemented by a dichotomous view of data, they are, in the words of philosopher Bruno Latour, “blackboxed.” This is a peculiar result of the prescription for mixing methods as proposed by MMR that thus not only denies practice and the ontological dimensions of methods and data, but also casts methods in the role of unyielding black boxes. Footnote 10 With this in mind, it will come as no surprise that most foundational contributions to the MMR literature do not explicitly define what a method is, nor that they do not provide an elaborative historical account of individual methods. The particular framing of methods in MMR results in a blind spot for the historical and social context of the production and circulation of methods as intellectual products. Instead it chooses to reify the boundaries that are drawn between “qualitative” and “quantitative” methods and reproduce them in the methodology it proposes. Footnote 11 This is an example of “circulation without context” (Bourdieu 2002 , p. 4): classifications that are constructed in the field of use or reception without taking the constellation within the field of production seriously.
Of course, this does not mean that the reality of the differences between quantitative and qualitative research must be denied. These labels are sticky and symbolically laden. They have come, in many ways, to represent “two cultures” (Goertz and Mahony 2012 ) of research, institutionalised in academia, and the effects of nominally “belonging” to (or being assigned to) one particular category have very real consequences in terms of, for instance, access to research grants and specific journals. However, if the goal of an approach such as MMR is to open up new pathways in social science research, (and why should that not be the case?) it is hard to see how that is accomplished by defining the act of combining methods solely in terms of reified differences between research using qualitative and quantitative data. In our view, methods are far richer and more interesting constructs than that, and a practice of combining methods in research should reflect that. Footnote 12
Addressing these problems entices a reflection on methods and using (multiple) methods that is missing in the MMR perspective. A fruitful way to open up the black boxes and take into account the epistemological and ontological facets of methods is to make them, and their use, the object of sociological-historical investigation. Methods are constituted through particular practices. In Bourdieusian terms, they are objectifications of the subjectively understood practices of scientists “in other fields.” Rather than basing a practice of combining methods on an uncritical acceptance of the historically grown classification of types of social research (and using these as the building stones of a methodology of mixing methods), we propose the development of a multifaceted approach that is based on a study of the different socio-historical contexts and practices in which methods developed and circulated.
A sociological understanding of methods based on these premises provides the tools to break with the dichotomously designed interface for combining methods in MMR. Instead, focusing on the historical and social contexts of production and use can reveal the traces that these contexts leave, both in the internal structure of methods, how they are perceived, how they are put into practice, and how this practice informs the ontological effects of methods. Seeing methods as complex technologies, with a history that entails the struggles among the different agents involved in their production, and use opens the way to identify multiple interfaces for combining them: the one-sided boxes become polyhedra. The critical study of methods as “objects of objectification” also entices analyses of the way in which methods intervene between subject (researcher) and object and the way in which different methods are employed in practice to draw this boundary differently. The reflexive position generated by such a systematic juxtaposition of methods is a fruitful basis to come to a richer perspective on combining methods.
We critically reviewed the emerging practice of combining methods under the label of MMR. MMR challenges the mono-method approaches that are still dominant in the social sciences, and this is both refreshing and important. Combining methods should indeed be taken much more seriously in the social sciences.
However, the direction that the practice of combining methods is taking under the MMR approach seems problematic to us. We identified three main concerns. First, MMR scholars seem to be committed to designing a standardized methodological framework for combining methods. This is unfortunate, since it amounts to enforcing an unnecessary codification of aspects of research practices that should not be formally standardized. Second, MMR constructs methods as unproblematic representations of an epistemology. Although methods must be separable from their native epistemology for MMR to work, at the same time they have to be nested within a qualitative or a quantitative research approach, which are characterized by the data they use. By this logic, combining quantitative methods with other quantitative methods, or qualitative methods with other qualitative methods, cannot offer the same benefits: they originate from the same way of viewing and knowing the world, so it would have the same effect as blending two gradations of the same colour paint. The importance attached to the epistemological grounding of methods and data in MMR also disregards the ontological aspects of methods. In this article, we are arguing that this one-sided perspective is problematic. Seeing combining methods as equivalent to combining epistemologies that are somehow pure and internally homogeneous because they can be placed in a qualitative or quantitative framework essentially amounts to reifying these categories.
It also leads to the third problem: the black boxing of methods as neutral mediators between these epistemologies and data. This not only constitutes a problem for trying to understand methods as intellectual products, but also for regarding the practice of combining methods, because it ignores the social-historical context of the development of individual methods and hinders a sociologically grounded notion of combining methods.
We proceed from a different perspective on methods. In our view, methods are complex constructions. They are world-making technologies that encapsulate different assumptions on causality, rely on different conceptual relations and categorizations, allow for different degrees of emergence, and employ different theories of the data that they internalise as objects of analysis. Even more importantly, their current form as intellectual products cannot be separated from the historical context of their production, circulation, and use.
A fully developed exposition of such an approach will have to await further work. Footnote 13 So far, the sociological study of methods has not (yet) developed into a consistent research programme, but important elements can be derived from existing contributions such as MacKenzie ( 1981 ), Chapoulie ( 1984 ), Platt ( 1996 ), Freeman ( 2004 ), and Desrosières ( 2008a , b ). The work on the “social life of methods” (e.g., Savage 2013 ) also contains important leads for the development of a systematic sociological approach to method production and circulation. Based on the discussion in this article and the contributions listed above, some tantalizing questions can be formulated. How are methods and their elements objectified? How are epistemology and ontology defined in different fields and how do those definitions feed into methods? How do they circulate and how are they translated and used in different contexts? What are the main controversies in fields of users and how are these related to the field of production? What are the homologies between these fields?
Setting out to answer these questions opens up the possibility of exploring other interesting combinations of methods that emerge from the combination of different practices, situated in different historical and epistemological contexts, and with their unique set of interpretations regarding their constituent elements. One of these must surely be the data-theoretical elements that different methods incorporate. The problematization of data has become all the more pressing now that the debate about the consequences of “big data” for social scientific practices has become prominent (Savage and Burrows 2007 ; Levallois et al. 2013 ; Burrows and Savage 2014 ). Whereas MMR emphasizes the dichotomy between qualitative and quantitative data, a historical analysis of the production and use of methods can explore the more subtle, different interpretations and enactments of the “same” data. These differences inform method construction, controversies surrounding methods and, hence, opportunities for combining methods. These could then be constructed based on alternative conceptualisations of data. Again, while in some contexts it might be enlightening to rely on the distinction between data as qualitative or quantitative, and to combine methods based on this categorization, it is an exciting possibility that in other research contexts other conceptualisations of data might be of more value to enhance a specific (contextual) form of knowledge.
Change history
06 may 2019.
Unfortunately, figure 2 was incorrectly published.
The search term used was “mixed method*” in the “topic” search field of SSCI, A&HCI, and CPCI-SSH as contained in the Web of Science. A Google NGram search (not shown) confirmed this pattern. The results of a search for “mixed methods” and “mixed methods research” showed a very steep increase after 1994: in the first case, the normalized share in the total corpus increased by 855% from 1994 till 2008. Also, Creswell ( 2012 ) reports an almost hundred-fold increase in the number of theses and dissertations with mixed methods’ in the citation and abstract (from 26 in 1990–1994 to 2524 in 2005–2009).
Retrieved from https://uk.sagepub.com/en-gb/eur/journal-of-mixed-methods-research/journal201775#aims-and-scope on 1/17/2019.
In terms of antecedents of mixed methods research, it is interesting to note that Bourdieu, whose sociology of science we draw on, was, from his earliest studies in Algeria onwards, a strong advocate of combining research methods. He made it into a central characteristic of his approach to social science in Bourdieu et al. ( 1991 [1968]). His approach, as we see below, was very different from the one now proposed under the banner of MMR. Significantly, there is no mention of Bourdieu’s take on combining methods in any of the sources we studied.
Morse’s example in particular warns us that restricting the analysis to the authors that have published in the JMMR runs the risk of missing some important contributors to the spread of MMR through the social sciences. On her website, Morse lists 11 publications (journal articles, book chapters, and books) that explicitly make reference to mixed methods (and a substantial number of other publications are about methodological aspects of research), so the fact that she has not (yet) published in the JMMR cannot, by itself, be taken as an indication of a lesser involvement with the practice of combining methods. See the website of Janice Morse at https://faculty.utah.edu/u0556920-Janice_Morse_RN,_PhD,_FAAN/hm/index.hml accessed 1/17/2019.
Bourdieu ( 1999 , p. 26) mentions that one has to be a scientific capitalist to be able to start a scientific revolution. But here he refers explicitly to the autonomy of the scientific field, making it virtually impossible for amateurs to stand up against the historically accumulated capital in the field and incite a revolution.
The themes summarize the key issues through which MMR as a group comes “into difference” (Bourdieu 1993 , p. 32). Of course, as in any (sub)field, the agents identified above often differ in their opinions on some of these key issues or disagree on the answer to the question if there should be a high degree of convergence of opinions at all. For instance, Bryman ( 2009 ) worried that MMR could become “a ghetto.” For him, the institutional landmarks of having a journal, conferences, and a handbook increase the risk of “not considering the whole range of possibilities.” He added: “I don’t regard it as a field, I kind of think of it as a way of thinking about how you go about research.” (Bryman, cited in Leech 2010 , p. 261). It is interesting to note that Bryman, like fellow sociologists Morgan and Denscombe, had published only one paper in the JMMR by the end of 2016 (Bryman passed away in June of 2017). Although these papers are among the most cited papers in the journal (see Table 1 ), this low number is consistent with the more eclectic approach that Bryman proposed.
Johnson, Onwuegbuzie, and Turner ( 2007 , p. 123).
Guba and Lincoln ( 1985 ) discuss the features of their version of a positivistic approach mainly in ontological and epistemological terms, but they are also careful to distinguish the opposition between naturalistic and positivist approaches from the difference between what they call the quantitative and the qualitative paradigms. Since they go on to state that, in principle, quantitative methods can be used within a naturalistic approach (although in practice, qualitative methods would be preferred by researchers embracing this paradigm), they seem to locate methods on a somewhat “lower,” i.e., less incommensurable level. However, in their later work (both together as well as with others or individually) and that of others in their wake, there seems to have been a shift towards a stricter interpretation of the qualitative/quantitative divide in metaphysical terms, enabling Teddlie and Tashakkori (2010b) to label this group “purists” (Tashakkori and Teddlie 2010b , p. 13).
See, for instance, Onwuegbuzie et al.’s ( 2011 ) classification of 58 qualitative data analysis techniques and 18 quantitative data analysis techniques.
This can also be seen in Morgan’s ( 2018 ) response to Sandelowski’s ( 2014 ) critique of the binary distinctions in MMR between qualitative and quantitative research approaches and methods. Morgan denounces the essentialist approach to categorizing qualitative and quantitative research in favor of a categorization based on “family resemblances,” in which he draws on Wittgenstein. However, this denies the fact that the essentialist way of categorizing is very common in the MMR corpus, particularly in textbooks and manuals (e.g., Plano Clark and Ivankova 2016 ). Moreover, and more importantly, he still does not extend this non-essentialist model of categorization to the level of methods, referring, for instance, to the different strengths of qualitative and quantitative methods in mixed methods studies (Morgan 2018 , p. 276).
While it goes beyond the scope of this article to delve into the history of the qualitative-quantitative divide in the social sciences, some broad observations can be made here. The history of method use in the social sciences can briefly be summarized as first, a rather fluid use of what can retrospectively be called different methods in large scale research projects—such as the Yankee City study of Lloyd Warner and his associates (see Platt 1996 , p. 102), the study on union democracy of Lipset et al. ( 1956 ), and the Marienthal study by Lazarsfeld and his associates (Jahoda et al. 1933 ); see Brewer and Hunter ( 2006 , p. xvi)—followed by an increasing emphasis on quantitative data and the objectification and standardization of methods. The rise of research using qualitative data can be understood as a reaction against this use and interpretation of method in the social sciences. However, out of the ensuing clash a new, still dominant classification of methods emerged, one that relies on the framing of methods as either “qualitative” or “quantitative.” Moreover, these labels have become synonymous with epistemological positions that are reproduced in MMR.
A proposal to come to such an approach can be found in Timans ( 2015 ).
Bijker, W. (1987). The social construction of bakelite: Toward a theory of invention. In W. Bijker, T. Hughes, T. Pinch, & D. Douglas (Eds.), The social construction of technological systems: New directions in the sociology and history of technology . Cambridge, MA: MIT press.
Google Scholar
Bijker, W. (1997). Of bicycles, bakelites, and bulbs: Toward a theory of sociotechnical change . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Bourdieu, P. (1975). La spécifité du champ scientifique et les conditions sociales du progrès de la raison. Sociologie et Sociétés, 7 (1), 91–118.
Article Google Scholar
Bourdieu, P. (1988). Homo academicus . Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Bourdieu, P. (1993). The field of cultural production . Cambridge, UK: Polity Press.
Bourdieu, P. (1999). Les historiens et la sociologie de Pierre Bourdieu. Le Bulletin de la Société d'Histoire Moderne et Contemporaine/SHMC, 1999 (3&4), 4–27.
Bourdieu, P. (2002). Les conditions sociales de la circulation internationale des idées. Actes de la Recherche en Sciences Sociales, 145 (5), 3–8.
Bourdieu, P. (2004). Science of science and reflexivity . Cambridge, UK: Polity.
Bourdieu, P. (2007). Sketch for a self-analysis . Cambridge, UK: Polity.
Bourdieu, P., Chamboredon, J., & Passeron, J. (1991). The craft of sociology: Epistemological preliminaries . Berlin, Germany: De Gruyter.
Book Google Scholar
Brewer, J., & Hunter, A. (2006). Multimethod research: A synthesis of styles . London, UK: Sage.
Bryman, A. (2009). Sage Methodspace: Alan Bryman on research methods. Retrieved from http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bHzM9RlO6j0 . Accessed 3/7/2019.
Bryman, A. (2012). Social research methods . Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Burrows, R., & Savage, M. (2014). After the crisis? Big data and the methodological challenges of empirical sociology. Big Data & Society, 1 (1), 1–6.
Campbell, D., & Fiske, D. (1959). Convergent and discriminant validation by the multitrait-multimethod matrix. Psychological Bulletin, 56 (2), 81–105.
Chapoulie, J. (1984). Everett C. Hughes et le développement du travail de terrain en sociologie. Revue Française de Sociologie, 25 (4), 582–608.
Collins, R. (1998). The sociology of philosophies: A global theory of intellectual change . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Creswell, J. (2008). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Creswell, J. (2011). Controversies in mixed methods research. In N. Denzin & Y. Lincoln (Eds.), The Sage handbook of qualitative research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Creswell, J. (2012). Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Creswell, J., & Plano Clark, V. (2011). Designing and conducting mixed methods research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Creswell, J., Plano Clark, V., Gutmann, M., & Hanson, W. (2003). Advanced mixed methods research designs. In A. Tashakkori & C. Teddlie (Eds.), Handbook of mixed methods in social and behavioral research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Denscombe, M. (2008). Communities of practice a research paradigm for the mixed methods approach. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 2 (3), 270–283.
Desrosières, A. (2008a). Pour une sociologie historique de la quantification - L’Argument statistique I . Paris, France: Presses des Mines.
Desrosières, A. (2008b). Gouverner par les nombres - L’Argument statistique II . Paris, France: Presses des Mines.
Edge, D. (1995). Reinventing the wheel. In D. Edge, S. Jasanof, G. Markle, J. Petersen, & T. Pinch (Eds.), Handbook of science and technology studies . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Fielding, N. (2012). Triangulation and mixed methods designs data integration with new research technologies. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 6 (2), 124–136.
Fielding, N., & Cisneros-Puebla, C. (2009). CAQDAS-GIS convergence: Toward a new integrated mixed method research practice? Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 3 (4), 349–370.
Fleck, C., Heilbron, J., Karady, V., & Sapiro, G. (2016). Handbook of indicators of institutionalization of academic disciplines in SSH. Serendipities, Journal for the Sociology and History of the Social Sciences, 1 (1) Retrieved from http://serendipities.uni-graz.at/index.php/serendipities/issue/view/1 . Accessed 10/10/2018.
Freeman, L. (2004). The development of social network analysis: A study in the sociology of science . Vancouver, Canada: Empirical Press.
Gingras, Y., & Gemme, B. (2006). L’Emprise du champ scientifique sur le champ universitaire et ses effets. Actes de la Recherche en Sciences Sociales, 164 , 51–60.
Goertz, G., & Mahony, J. (2012). A tale of two cultures: Qualitative and quantitative research in the social sciences . Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Greene, J. (2008). Is mixed methods social inquiry a distinctive methodology? Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 2 (1), 7–22.
Guba, E., & Lincoln, Y. (1985). Naturalistic inquiry . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Heilbron, J., Bedecarré, M., & Timans, R. (2017). European journals in the social sciences and humanities. Serendipities, Journal for the Sociology and History of the Social Sciences, 2 (1), 33–49 Retrieved from http://serendipities.uni-graz.at/index.php/serendipities/issue/view/5 . Accessed 10/10/2018.
Hesse-Biber, S. (2010). Mixed methods research: Merging theory with practice . New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Jahoda, M., Lazarsfeld, P., & Zeisel, H. (1933). Die Arbeitslosen von Marienthal. Psychologische Monographen, 5 .
Johnson, R., & Gray, R. (2010). A history of philosophical and theoretical issues for mixed methods research. In A. Tashakkori & C. Teddlie (Eds.), Handbook of mixed methods in social and behavioral research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Johnson, R., Onwuegbuzie, A., & Turner, L. (2007). Toward a definition of mixed methods research. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 1 (2), 112–133.
Law, J. (2004). After method: Mess in social science research . London, UK: Routledge.
Leech, N. (2010). Interviews with the early developers of mixed methods research. In A. Tashakkori & C. Teddlie (Eds.), Handbook of mixed methods in social and behavioral research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Leech, N., & Onwuegbuzie, T. (2009). A typology of mixed methods research designs. Quality & Quantity, 43 (2), 265–275.
Levallois, C., Steinmetz, S., & Wouters, P. (2013). Sloppy data floods or precise social science methodologies? In P. Wouters, A. Beaulieu, A. Scharnhorst, & S. Wyatt (Eds.), Virtual knowledge . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Lipset, S., Trow, M., & Coleman, J. (1956). Union democracy: The internal politics of the international typographical union . Glencoe, UK: Free Press.
MacKenzie, D. (1981). Statistics in Britain: 1865–1930: The social construction of scientific knowledge . Edinburgh, UK: Edinburgh University Press.
Morgan, D. (2007). Paradigms lost and pragmatism regained: Methodological implications of combining qualitative and quantitative methods. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 1 (1), 48–76.
Morgan, D. (2018). Living with blurry boundaries: The values of distinguishing between qualitative and quantitative research. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 12 (3), 268–276.
Mullins, N. (1973). Theories and theory groups in contemporary American sociology . New York, NY: Harper & Row.
Nagy Hesse-Biber, S., & Leavy, P. (Eds.). (2008). Handbook of emergent methods . New York, NY and London, UK: Guilford Press.
Nastasi, B., Hitchcock, J., & Brown, L. (2010). An inclusive framework for conceptualizing mixed method design typologies. In A. Tashakkori & C. Teddlie (Eds.), Handbook of mixed methods in social and behavioral research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Onwuegbuzie, A., Leech, N., & Collins, K. (2011). Toward a new era for conducting mixed analyses: The role of quantitative dominant and qualitative dominant crossover mixed analyses. In M. Williams & P. Vogt (Eds.), Handbook of innovation in social research methods . London, UK: Sage.
Patton, M. (2002). Qualitative research and evaluation methods (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Plano Clark, V., & Creswell, J. (Eds.). (2007). The mixed methods reader . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Plano Clark, V., & Ivankova, N. (2016). Mixed methods research: A guide to the field . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Platt, J. (1996). A history of sociological research methods in America: 1920–1960 . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Plowright, D. (2010). Using mixed methods – Frameworks for an integrated methodology . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Sandelowski, M. (2014). Unmixing mixed methods research. Research in Nursing & Health, 37 (1), 3–8.
Sapiro, G., Brun, E., & Fordant, C. (2018). The rise of the social sciences and humanities in France: Iinstitutionalization, professionalization and autonomization. In C. Fleck, M. Duller, & V. Karady (Eds.), Shaping human science disciplines: Institutional developments in Europe and beyond . Basingstoke, UK: Palgrave.
Savage, M. (2013). The ‘social life of methods’: A critical introduction. Theory, Culture and Society, 30 (4), 3–21.
Savage, M., & Burrows, R. (2007). The coming crisis of empirical sociology. Sociology, 41 (5), 885–899.
Steinmetz, G. (2016). Social fields, subfields and social spaces at the scale of empires: Explaining the colonial state and colonial sociology. The Sociological Review, 64(2_suppl). 98-123.
Tashakkori, A., & Teddlie, C. (Eds.). (2003). Handbook of mixed methods in social and behavioral research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Tashakkori, A., & Teddlie, C. (Eds.). (2010a). Handbook of mixed methods in social and behavioral research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Tashakkori, A., & Teddlie, C. (2010b). Overview of contemporary issues in mixed methods. In A. Tashakkori & C. Teddlie (Eds.), Handbook of mixed methods in social and behavioral research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Chapter Google Scholar
Tashakkori, A., & Teddlie, C. (2010c). Epilogue. In A. Tashakkori & C. Teddlie (Eds.), Handbook of mixed methods in social and behavioral research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Tashakkori, A., & Teddlie, C. (2011). Mixed methods research: Contemporary issues in an emerging field. In N. Denzin & Y. Lincoln (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of qualitative research (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Teddlie, C., & Tashakkori, A. (2008). Foundations of mixed methods research – Integrating quantitative and qualitative approaches in the social and behavioral sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Timans, R. (2015). Studying the Dutch business elite: Relational concepts and methods . Doctoral dissertation, Erasmus University Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
Wacquant, L. (2013). Bourdieu 1993: A case study in scientific consecration. Sociology, 47 (1), 15–29.
Download references
Acknowledgments
This research is part of the Interco-SSH project, funded by the European Union under the 7th Research Framework Programme (grant agreement no. 319974). Johan Heilbron would like to thank Louise and John Steffens, members of the Friends Founders’ Circle, who assisted his stay at the Princeton Institute for Advanced Study in 2017-18 during which he completed his part of the present article.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Erasmus Centre for Economic Sociology (ECES), Erasmus University Rotterdam, Rotterdam, Netherlands
Centre for Science and Technology Studies (CWTS), Leiden University, Leiden, Netherlands
Paul Wouters
Erasmus Centre for Economic Sociology (ECES), Rotterdam and Centre européen de sociologie et de science politique de la Sorbonne (CESSP-CNRS-EHESS), Paris, France
Johan Heilbron
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rob Timans .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Timans, R., Wouters, P. & Heilbron, J. Mixed methods research: what it is and what it could be. Theor Soc 48 , 193–216 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11186-019-09345-5
Download citation
Published : 29 March 2019
Issue Date : 01 April 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11186-019-09345-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Data, field analysis
- Mixed methods research
- Multiple methods
- Reflexivity
- Sociology of science
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 20, Issue 3
- Mixed methods research: expanding the evidence base
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Allison Shorten 1 ,
- Joanna Smith 2
- 1 School of Nursing , University of Alabama at Birmingham , USA
- 2 Children's Nursing, School of Healthcare , University of Leeds , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Allison Shorten, School of Nursing, University of Alabama at Birmingham, 1720 2nd Ave South, Birmingham, AL, 35294, USA; [email protected]; ashorten{at}uab.edu
https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2017-102699
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
‘Mixed methods’ is a research approach whereby researchers collect and analyse both quantitative and qualitative data within the same study. 1 2 Growth of mixed methods research in nursing and healthcare has occurred at a time of internationally increasing complexity in healthcare delivery. Mixed methods research draws on potential strengths of both qualitative and quantitative methods, 3 allowing researchers to explore diverse perspectives and uncover relationships that exist between the intricate layers of our multifaceted research questions. As providers and policy makers strive to ensure quality and safety for patients and families, researchers can use mixed methods to explore contemporary healthcare trends and practices across increasingly diverse practice settings.
What is mixed methods research?
Mixed methods research requires a purposeful mixing of methods in data collection, data analysis and interpretation of the evidence. The key word is ‘mixed’, as an essential step in the mixed methods approach is data linkage, or integration at an appropriate stage in the research process. 4 Purposeful data integration enables researchers to seek a more panoramic view of their research landscape, viewing phenomena from different viewpoints and through diverse research lenses. For example, in a randomised controlled trial (RCT) evaluating a decision aid for women making choices about birth after caesarean, quantitative data were collected to assess knowledge change, levels of decisional conflict, birth choices and outcomes. 5 Qualitative narrative data were collected to gain insight into women’s decision-making experiences and factors that influenced their choices for mode of birth. 5
In contrast, multimethod research uses a single research paradigm, either quantitative or qualitative. Data are collected and analysed using different methods within the same paradigm. 6 7 For example, in a multimethods qualitative study investigating parent–professional shared decision-making regarding diagnosis of suspected shunt malfunction in children, data collection included audio recordings of admission consultations and interviews 1 week post consultation, with interactions analysed using conversational analysis and the framework approach for the interview data. 8
What are the strengths and challenges in using mixed methods?
Selecting the right research method starts with identifying the research question and study aims. A mixed methods design is appropriate for answering research questions that neither quantitative nor qualitative methods could answer alone. 4 9–11 Mixed methods can be used to gain a better understanding of connections or contradictions between qualitative and quantitative data; they can provide opportunities for participants to have a strong voice and share their experiences across the research process, and they can facilitate different avenues of exploration that enrich the evidence and enable questions to be answered more deeply. 11 Mixed methods can facilitate greater scholarly interaction and enrich the experiences of researchers as different perspectives illuminate the issues being studied. 11
The process of mixing methods within one study, however, can add to the complexity of conducting research. It often requires more resources (time and personnel) and additional research training, as multidisciplinary research teams need to become conversant with alternative research paradigms and different approaches to sample selection, data collection, data analysis and data synthesis or integration. 11
What are the different types of mixed methods designs?
Mixed methods research comprises different types of design categories, including explanatory, exploratory, parallel and nested (embedded) designs. 2 Table 1 summarises the characteristics of each design, the process used and models of connecting or integrating data. For each type of research, an example was created to illustrate how each study design might be applied to address similar but different nursing research aims within the same general nursing research area.
- View inline
Types of mixed methods designs*
What should be considered when evaluating mixed methods research?
When reading mixed methods research or writing a proposal using mixed methods to answer a research question, the six questions below are a useful guide 12 :
Does the research question justify the use of mixed methods?
Is the method sequence clearly described, logical in flow and well aligned with study aims?
Is data collection and analysis clearly described and well aligned with study aims?
Does one method dominate the other or are they equally important?
Did the use of one method limit or confound the other method?
When, how and by whom is data integration (mixing) achieved?
For more detail of the evaluation guide, refer to the McMaster University Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool. 12 The quality checklist for appraising published mixed methods research could also be used as a design checklist when planning mixed methods studies.
- Elliot AE , et al
- Creswell JW ,
- Plano ClarkV L
- Greene JC ,
- Caracelli VJ ,
- Ivankova NV
- Shorten A ,
- Shorten B ,
- Halcomb E ,
- Cheater F ,
- Bekker H , et al
- Tashakkori A ,
- Creswell JW
- 12. ↵ National Collaborating Centre for Methods and Tools . Appraising qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods studies included in mixed studies reviews: the MMAT . Hamilton, ON : BMJ Publishing Group , 2015 . http://www.nccmt.ca/resources/search/232 (accessed May 2017) .
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
- News & Highlights
- Publications and Documents
- Postgraduate Education
- Browse Our Courses
- C/T Research Academy
- K12 Investigator Training
- Translational Innovator
- SMART IRB Reliance Request
- Biostatistics Consulting
- Regulatory Support
- Pilot Funding
- Informatics Program
- Community Engagement
- Diversity Inclusion
- Research Enrollment and Diversity
- Harvard Catalyst Profiles

Community Engagement Program
Supporting bi-directional community engagement to improve the relevance, quality, and impact of research.
- Getting Started
- Resources for Equity in Research
- Community-Engaged Student Practice Placement
- Maternal Health Equity
- Youth Mental Health
- Leadership and Membership
- Past Members
- Study Review Rubric
- Community Ambassador Initiative
- Implementation Science Working Group
- Past Webinars & Podcasts
- Policy Atlas
- Community Advisory Board
For more information:
Mixed methods research.
According to the National Institutes of Health , mixed methods strategically integrates or combines rigorous quantitative and qualitative research methods to draw on the strengths of each. Mixed method approaches allow researchers to use a diversity of methods, combining inductive and deductive thinking, and offsetting limitations of exclusively quantitative and qualitative research through a complementary approach that maximizes strengths of each data type and facilitates a more comprehensive understanding of health issues and potential resolutions.¹ Mixed methods may be employed to produce a robust description and interpretation of the data, make quantitative results more understandable, or understand broader applicability of small-sample qualitative findings.
Integration
This refers to the ways in which qualitative and quantitative research activities are brought together to achieve greater insight. Mixed methods is not simply having quantitative and qualitative data available or analyzing and presenting data findings separately. The integration process can occur during data collection, analysis, or in the presentation of results.
¹ NIH Office of Behavioral and Social Sciences Research: Best Practices for Mixed Methods Research in the Health Sciences
Basic Mixed Methods Research Designs
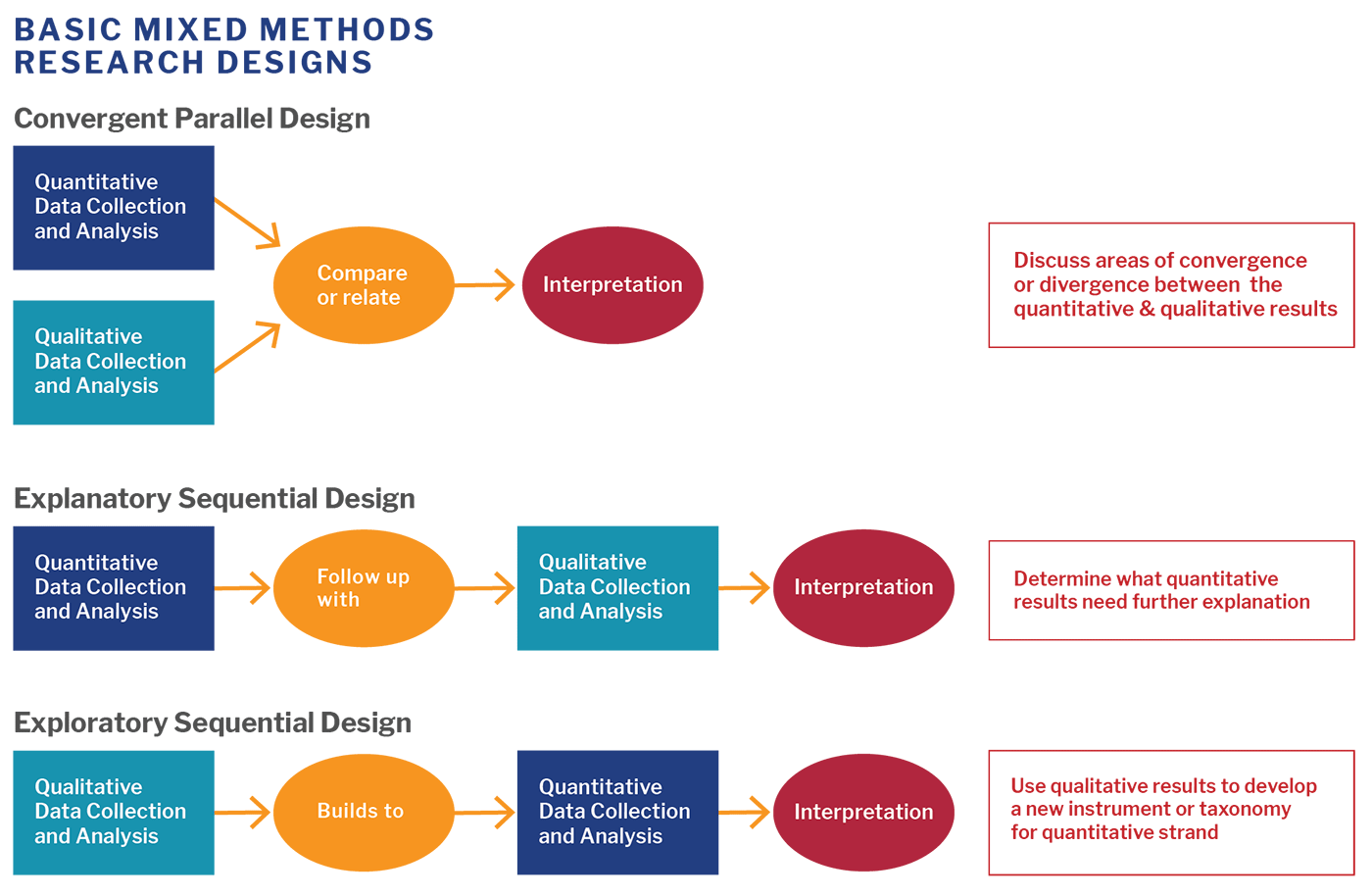
View image description .
Five Key Questions for Getting Started
- What do you want to know?
- What will be the detailed quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods research questions that you hope to address?
- What quantitative and qualitative data will you collect and analyze?
- Which rigorous methods will you use to collect data and/or engage stakeholders?
- How will you integrate the data in a way that allows you to address the first question?
Rationale for Using Mixed Methods
- Obtain different, multiple perspectives: validation
- Build comprehensive understanding
- Explain statistical results in more depth
- Have better contextualized measures
- Track the process of program or intervention
- Study patient-centered outcomes and stakeholder engagement
Sample Mixed Methods Research Study
The EQUALITY study used an exploratory sequential design to identify the optimal patient-centered approach to collect sexual orientation data in the emergency department.
Qualitative Data Collection and Analysis : Semi-structured interviews with patients of different sexual orientation, age, race/ethnicity, as well as healthcare professionals of different roles, age, and race/ethnicity.
Builds Into : Themes identified in the interviews were used to develop questions for the national survey.
Quantitative Data Collection and Analysis : Representative national survey of patients and healthcare professionals on the topic of reporting gender identity and sexual orientation in healthcare.
Other Resources:
Introduction to Mixed Methods Research : Harvard Catalyst’s eight-week online course offers an opportunity for investigators who want to understand and apply a mixed methods approach to their research.
Best Practices for Mixed Methods Research in the Health Sciences [PDF] : This guide provides a detailed overview of mixed methods designs, best practices, and application to various types of grants and projects.
Mixed Methods Research Training Program for the Health Sciences (MMRTP ): Selected scholars for this summer training program, hosted by Johns Hopkins’ Bloomberg School of Public Health, have access to webinars, resources, a retreat to discuss their research project with expert faculty, and are matched with mixed methods consultants for ongoing support.
Michigan Mixed Methods : University of Michigan Mixed Methods program offers a variety of resources, including short web videos and recommended reading.
To use a mixed methods approach, you may want to first brush up on your qualitative skills. Below are a few helpful resources specific to qualitative research:
- Qualitative Research Guidelines Project : A comprehensive guide for designing, writing, reviewing and reporting qualitative research.
- Fundamentals of Qualitative Research Methods – What is Qualitative Research : A six-module web video series covering essential topics in qualitative research, including what is qualitative research and how to use the most common methods, in-depth interviews, and focus groups.
View PDF of the above information.
- What Is Mixed Methods Research? Definition, Guide & Examples

As the world continues to evolve, we face increasingly complex problems, from climate change to global health disparities. These issues are becoming increasingly difficult to address through conventional research methods.
Mixed methods research offers a new way to tackle these challenges, by providing us with a deeper understanding of the underlying causes and effects of complex topics.
In this article, we’ll explore how mixed-method research works, and how it helps us solve real-world problems.

The Foundation of Mixed Methods Research
Mixed methods research is an effective approach to understanding complex phenomena. It combines the strengths of quantitative and qualitative methods to provide a more comprehensive and nuanced perspective.
Here is a breakdown of the pioneers of mixed-method research and how it has evolved over the years:
A. Historical Development of Mixed Methods
Mixed methods research dates back to the early 1900s , but it didn’t become widely adopted until the late 1980s. Before that, people thought that quantitative and qualitative methods were two different concepts.
Quantitative research focuses on numbers and facts, while qualitative research focuses on people’s experiences and meanings. Combining these two using mixed-method research gives you a more accurate understanding of complex concepts.
Today, Mixed methods research is widely used across different industries, such as education, health science, social science, business, etc. This is because it gives a holistic view of research findings, making them easily reproducible and accurate.
Ensure clear and accurate clinical communication with our comprehensive Clinical Report Form Template.
B. Key Figures and Contributions in the Field
- Abbas Tashakkori
Tashakkori is one of the leading experts in mixed-methods research with his work has provided a valuable framework for understanding and conducting mixed-methods research.
He has published several books and papers on mixed methods research, including the “Foundation of mixed methods” and “Mixed Methodology: combining quantitative and qualitative research approaches.”
- John W. Creswell
Creswell has established himself as a leading authority on mixed methods research. He has published several books and papers on the subject, including the groundbreaking textbook “Qualitative Inquiry: Choosing Between Five Traditions”.
Creswell’s work has contributed to the legitimization of mixed-method research as a robust and scientifically sound research approach.
- Charles Teddlie
Another big name in mixed methods research is Charles Teddlie. He’s co-authored several books and journals about mixed methods, including the textbook, “Foundations of Mixed Methods Research: Integrating Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches in the Social and Behavioral Sciences.” His work has helped make mixed methods research better understood and practiced across different fields.
C. Paradigms and Philosophies Underlying Mixed Methods Research
Mixed methods research is grounded in several paradigms and philosophies, each of which offers unique insights into why mixed methods should be adopted for research processes.
Some of the most common paradigms and philosophies underlying mixed methods research include:
- Pragmatism
Pragmatism on the practical implications of things. This approach focuses on researching concepts to see how they help solve real-world problems.
Mixed methods research is compatible with pragmatism because it gives researchers the freedom to use different methods so they can determine the most effective way to solve research problems.
- Triangulation
Triangulation uses multiple techniques to collect data on the same subject to improve the validity and robustness of the research results. Mixed methods research frequently uses triangulation to gather and analyze data from quantitative and qualitative sources.
- Integration
Integration is the process of combining quantitative and qualitative data to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a phenomenon.
The purpose of mixed methods research is to bring quantitative and qualitative information together in a meaningful manner, rather than just combining them. Integration methods such as data transformation, mixed methods convergence analysis, and mixed methods modeling help you do this seamlessly.

Understanding the Components of Mixed Methods Research
The following are the key elements that make up mixed-method research:
- Quantitative Research
Quantitative research focuses on collecting and analyzing numerical data. It helps you to collect numerical data test hypotheses, identify patterns and trends, and make predictions.
It’s like taking a photograph of a crowd: you can see who’s there and how many are there, but you can’t see what they’re thinking or how they feel.
You can perform quantitative research using surveys, questionnaires, experiments, and observations. The most common methods of analyzing quantitative analysis findings are statistical analysis, regression analysis, and factor analysis.
- Qualitative Research
Qualitative research focuses on gathering and analyzing non-structural data, such as text, pictures, and audio. It looks at complex phenomena by focusing on people’s experiences and opinions.
Think of qualitative research as talking to the people in a crowd. It allows you to capture their individual experiences and points of view.
The most common methods for collecting qualitative data collection methods include interviews, focus groups, ethnography, and document analysis. You can analyze your findings using thematic analysis, discourse analysis, and grounded theory.

The Advantages of Mixed Methods Research
A. comprehensive understanding of research questions.
Quantitative research is good at identifying patterns and trends, while qualitative research is good at providing depth and understanding. Mixed method research combines these features to gain a more complete understanding of the research topic.
For example, a mixed-method study on the impact of a new teaching approach on student learning outcomes would use quantitative methods (academic performance) to measure student improvement. It would also use qualitative data (interviews and questionnaires) to gain insight into why a teaching approach is doing well or poorly.
B. Increased Validity and Reliability
Mixed methods research often employs triangulation which uses multiple methods to collect data on the same phenomenon. This reduces the risk of bias and ensures that the research findings are accurate and reliable.
For example, a mixed-method study on the challenges people with chronic illnesses face would track symptoms and interview their caregivers to get a better idea of what they’re going through and what they’re facing.
C. Enhanced Triangulation
Mixed methods research provides several opportunities for triangulation by combining multiple techniques, sources, and viewpoints to collect and analyze data. This helps improve the accuracy and completeness of research results.
For example, in a study about student performance you can triangulate quantitative and qualitative data, data from different sources (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations), and data from different perspectives (e.g., students, teachers, parents).
D. Addressing Research Bias
Research bias is a potential problem in all types of research, but it can be particularly challenging to address in qualitative research. Mixed methods research can help to address research bias by combining quantitative and qualitative data.
For example, you can use a survey to gather data on demographic factors prone to bias, like race, gender, and income. Then, you for control bias by analyzing the data using qualitative data such as focus groups and interviews.
E. Opportunities for Exploration and Discovery
Mixed-method research allows you to collect and analyze data from various perspectives and methods. This allows you to gain new insights and understandings that would not be possible with either quantitative or qualitative research alone.
For instance, a mixed-method study on the school experience of students with disabilities could collect quantitative data on student performance such as grades, standardized test results, and school attendance. Combining this data with qualitative data from the students, their teachers, and their parents would give you a deeper understanding of the unique challenges and experiences of students with disabilities in school.

Designing a Mixed Methods Study
You need a proper design to successfully execute your mixed-method research. Here is the list of steps that will get you there:
A. Research Questions and Hypotheses
Start by clearly defining your research questions and hypotheses. This will help you to choose the appropriate research design and data collection methods.
Also, ensure the research questions are specific, measurable, and relevant to your research goals.
B. Choosing the Appropriate Research Design
There are three main types of mixed methods research designs: concurrent, sequential, and exploratory.
- Concurrent designs collect and analyze quantitative and qualitative data simultaneously. This helps you explore complex phenomena in detail and to develop new theories.
- Sequential design is all about collecting and analyzing data one after the other, not simultaneously like concurrent design. It’s usually used to test hypotheses and build on existing studies.
- Exploratory design is the process of coming up with new concepts and ideas. This is the most suitable research method if you are working on a new topic that there’s little to no understanding of.
C. Sampling Strategies
Sampling is the process of selecting a subset of a population to represent the entire population. When designing a mixed methods study, you have to sample both quantitatively and qualitatively.
In qualitative sampling, participants are selected based on their likelihood of providing high-quality and meaningful data. However, in quantitative sampling, participants are randomly selected or stratified to ensure that the sample is representative of the population.
D. Data Collection and Instrumentation
You have to choose your data collection instruments; these are the tools that allow you to collect research data. Quantitative research typically uses surveys, questionnaires, and tests, while qualitative uses interviews, focus groups, and observation guides to collect data.
E. Data Analysis
Data analysis is the process of organizing, summarizing, and interpreting data.
Statistical and regression analysis are the most common ways of analyzing quantitative data. Qualitative research uses different analysis methods including, thematic analysis, discourse analysis, and grounded theories.
F, Integration of Findings
Integration of findings is the final step in the mixed methods research process. This involves combining the quantitative and qualitative findings in a meaningful way to answer the research questions and hypotheses.
Here are the most common methods of integrating findings in mixed-method research:
- Triangulation matrix : it uses a table to compare and contrast the quantitative and qualitative findings.
- Convergence analysis : this is a statistical analysis method that helps you determine the relationship between quantitative and qualitative results, by looking at their similarities and differences.

Real-World Applications of Mixed Methods Research
Mixed methods research allows you to gain better insights into complex topics across different industries including:
- Education : You can use mixed methods research to study a variety of topics in education, such as the effectiveness of new teaching methods, the impact of school policies on student achievement, or determining the optimal courseload for students.
- Healthcare : Mixed methods also allow you to effectively investigate healthcare topics, such as the effectiveness of new medical treatments, the impact of public health interventions on population health, etc.
- Social sciences: Mixed methods research helps you to explore social science topics like what influences crime rate in different regions, how policies affect social well-being, etc.
- Business and marketing : You can also use mixed-method research to determine the effectiveness of new marketing campaigns, the impact of customer satisfaction on business performance, etc.
Improve your teaching and classroom environment with valuable student feedback using our Student Perception Survey Template.
B. Impact of Mixed Methods Research on Policy Development and Decision-Making
Mixed methods research helps policymakers develop more effective policies and programs by giving them a deeper understanding of different topics.
For example, the findings of the mixed methods study on the effectiveness of the public health intervention on childhood obesity could be used to inform the development of other public health interventions to reduce obesity rates.

Challenges and Limitations of Mixed Methods Research
While mixed-method research is an effective approach to solving complex problems, it’s not without its limitations. Here are common mixed-method research limitations and challenges:
A. Integration Challenges
One of the most difficult aspects of mixed methods research is the integration of qualitative and quantitative data. This is because qualitative and quantitative data are very different in content and format.
You can integrate by using data transformation to convert qualitative data into quantitative data. You could also use convergence analysis to identify patterns and trends in both the quantitative and qualitative data.
B. Resource-Intensive Nature
Mixed methods studies involve collecting and analyzing both quantitative and qualitative data. This requires significant time, money, and personnel resources.
You can overcome this challenge by carefully planning the mixed methods studies by ensuring you have all the resources you need. You could also look for funding from outside sources, like the government or private foundations.
C. Potential for Researcher Bias
All types of research are susceptible to researcher bias, but this can be a particular challenge in mixed-methods research. This is because mixed methods research often involves collecting and analyzing data from multiple perspectives.
You can use strategies such as triangulation, peer review, and member checking to pinpoint your biases and mitigate them.
D. Complexity in Data Interpretation
Mixed methods studies often produce a large amount of data from multiple sources, making it difficult to interpret.
One of the simplest ways to mitigate this difficulty is to use data visualization techniques such as graphs, maps, charts, and more. This makes it easier for you to identify trends and patterns in the data.

Best Practices for Conducting Mixed Methods Research
Here are some best practices to ensure you have an effective mixed-method research:
A. Establishing a Clear Research Plan
Start your research by outlining your research questions, hypotheses, research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and integration strategies.
Also, ensure you are very specific in your research plan. This will help you to stay on track throughout the research process and to ensure that your study is rigorous and well-structured.
B. Collaborative Research Teams
Mixed method research is a very rigorous and resource-intensive research method, so having a team of researchers on board makes sure you’re collecting and analyzing data thoroughly without the same amount of stress if you were doing it alone. Having a collaborative research team also helps reduce researcher bias and generate stronger results.
C. Ongoing Reflexivity and Transparency
Being reflexive means being aware of your own biases and limitations, while transparency means honestly reporting your research methods and findings.
One way to be more reflexive and transparent is to keep a research journal. This allows you to document your thoughts and feelings about the research process, as well as any challenges or obstacles that you encounter.
You can also seek feedback from others on your research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and integration strategies.
D. Reporting Mixed Methods Research Findings
Clearly and honestly document your research by providing detailed descriptions of your data collection methods, data analysis methods, and integration strategies.
You can do this by using a mixed-methods research reporting template. This ensures you have a structure for reporting your results and avoid leaving out important information.
Dive into Experimental Research Designs: Exploring Types, Examples, and Methods
Mixed method research enables you to get a better grasp on topics that would be hard to understand using just one research method. This allows you to make accurate data-driven decisions, and it works across different fields.
However, like any other research method, mixed-method research is not without its challenges and limitations. Ensure you use the best practices in this guide to get quality data and achieve your mixed-method research goals.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- Mixed Methods Research
- qualitative research
- quantitative research
- research design
- Research Plan
- Sampling Strategies
- Moradeke Owa

You may also like:
Desk Research: Definition, Types, Application, Pros & Cons
If you are looking for a way to conduct a research study while optimizing your resources, desk research is a great option. Desk research...

What is Field Research: Meaning, Examples, Pros & Cons
Introduction Field research is a method of research that deals with understanding and interpreting the social interactions of groups of...
Statistical Analysis Software: A Guide For Social Researchers
Introduction Social research is a complex endeavor. It takes a lot of time, energy, and resources to gather data, analyze and present...
How to Write An Abstract For Research Papers: Tips & Examples
In this article, we will share some tips for writing an effective abstract, plus samples you can learn from.
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Introduction
What is a mixed methods design?
Triangulation in mixed methods research, types of mixed methods research designs, using atlas.ti for mixed methods research.
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
- Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
- Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Case studies
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
What is mixed methods research?
When starting the research process, researchers sometimes think they have to decide whether qualitative research or quantitative research is more appropriate for their research design. However, the more important question is whether the methods they employ in data collection and analysis sufficiently capture the phenomenon they want to study. In some cases, answering this question requires using multiple methods of research.
Mixed methods research is a research paradigm that involves collecting qualitative data and quantitative data on the same object of inquiry. Researchers who employ mixed methods research synthesize qualitative findings with quantitative findings to achieve a better understanding.
Let's look at the established research paradigms, then mixed methods research, why it's useful, and which research methods complement each other. Then we'll examine how ATLAS.ti can help you execute a mixed methods design.
Mixed methods research is followed out of the need to understand concepts or phenomena at a deep level. A standalone quantitative study or qualitative study can provide great insight. Still, one method alone may not be able to capture all knowledge necessary to fully understand a topic or issue.
Those who conduct mixed methods research acknowledge the importance of pursuing both qualitative and quantitative research to achieve more complete results. However, this is not simply an issue of collecting more data just for its own sake. Mixed methods design is purposeful in carefully crafting research questions and employing appropriate research methods to essentially fill in the gaps of knowledge surrounding a particular research inquiry.
To determine which methods and data can address particular research needs, let's look at the capabilities of and differences between qualitative and quantitative data collection .
Qualitative and quantitative data
Researchers are often quick to make conclusions about whether qualitative research is better than quantitative research or vice versa. The reality is that quantitative and qualitative data can both look at the world in different ways that are useful at various points of a research inquiry. Qualitative and quantitative research are established research paradigms precisely because they provide relevant insights with the appropriate research design, data collection, and analysis.
One of the main goals of qualitative research is to generate a description of a social phenomenon. When something is difficult to quantify, it needs to be broken down into more constituent elements that are, by themselves, easier to perceive. In educational evaluation, for example, it is difficult to evaluate good academic writing with just a single score alone. Writing teachers employ a rubric to measure writing by a number of aspects which may include argumentation, organization, and cohesion.
Qualitative methods of research tend to collect data for an analysis that is capable of generating frameworks of constituent elements. Such a framework can then be used in subsequent research, evaluation, or decision-making processes. Researchers can collect qualitative data from observations , interviews , or records searches. Qualitative data analysis then aims to identify patterns and themes frequently appearing in the collected data.
The efficacy of experimental drugs in clinical trials, for example, is seldom easy to measure through quantitative methods alone. Qualitative research methods are often employed to determine a research participant's well-being, emotional state of mind, and other factors to help researchers decide the overall success of their clinical trials.
Quantitative research
If qualitative methods describe a concept or phenomenon, quantitative methods employ the resulting framework to measure that concept or phenomenon. Quantitative research methodology takes the theories generated from qualitative findings to collect quantitative data that can be used to measure a concept or phenomenon at scale.
Ultimately, numbers and values inform decision-making processes in many contexts. Quantitative results are useful in research areas where precision is valued or required. Still, they are also used in social and behavioral research to numerically describe phenomena that may not appear to be naturally quantifiable.
Mixing methods
Quantitative and qualitative strands of research are often pitted against each other for various reasons. Researchers might shun qualitative data collection as it is often time-consuming. In contrast, quantitative data collection is often critiqued for its reductive power (i.e., reducing ambiguous concepts into simplistic numerical values). Many scholarly disciplines, as a result, tend to prefer one research paradigm over the other (e.g., chemistry tends toward quantitative data collection, while anthropology tends toward qualitative data collection).
In the long run of any sufficiently complex research inquiry, however, it is seldom necessary to remain confined to one research approach. The main objective of scientific research is to organize knowledge through theories about the world around us. As a result, researchers employ mixed methods to combine theory generation in qualitative research with confirmatory testing in quantitative research to ultimately produce a robust theory and new knowledge.
However, research studies that combine qualitative and quantitative methods for the sake of having multiple methods of data collection and analysis are not as persuasive or impactful as true mixed methods studies where research methods are purposefully chosen to achieve a better understanding.
An example of mixed methods research
The objective of mixed methods research designs is to employ different inquiry components under one larger study. However, it might be easier to think of mixed methods research designs as having at least one qualitative study and one quantitative study, each with related but ultimately separate research questions . Examining a mixed methods research design in this way might make it easier to understand the need for pursuing multiple methods in certain cases.
- Consider the following example:
Remote work performance and job satisfaction
- RQ1: How have work outputs at XYZ Company changed since the shift to fully remote work?
- RQ2: What perceptions do remote workers at XYZ Company have about the shift to fully remote work?
In general terms, the goal of the study is to examine the efficacy of remote work in comparison to traditional, in-office work at one company. Actually determining this efficacy requires looking at the phenomenon of remote work through different methods.

As a result, one possible mixed methods study might look at the performance metrics of the company. Research question 1 (RQ1) is posed to conduct a quantitative research study that collects data on possibly quantifiable concepts related to work (e.g., amount of sales generated, number of new clients acquired). In this case, the researchers collect quantitative data to compare post-remote work performance to pre-remote work performance and determine if productivity has changed over time.
While this is a useful angle to examine remote work, it does not tell the whole story. After all, if people at Company XYZ are more or less productive than before, what are the reasons that explain this change? To address research question 2 (RQ2), researchers collect qualitative data on the level of satisfaction employees have with their jobs. Qualitative data from interviews with employees can be used to determine which aspects of their job they find satisfying or not.
With all the data collected, mixed methods researchers can combine the initial quantitative results and the initial qualitative results to form a deeper understanding of their topic of inquiry. In this case, if the quantitative data shows that worker productivity has suffered since the switch to remote work, the qualitative data might illuminate the aspects of remote work that employees don't like.
Other mixed methods research examples
While there are many different forms of mixed-methods research, the research approach is generally the same across mixed-methods research designs. A mixed methods research design is likely to require researchers to collect quantitative and qualitative data relevant to an overarching topic that necessitates examination from different methods. A couple of examples are:
Literacy development among children
RQ1: What is the rate of literacy development among children at ABC School based on scores from a standardized reading test?
RQ2: What are the instructional practices common in classrooms with high-performing students on standardized reading tests?
Market research for a new computer model
RQ1: How much time does it take to complete a series of tasks on an experimental computer model compared to a comparable computer model?
RQ2: What factors do potential customers take into consideration when buying a new computer?
Notice that qualitative and quantitative data pursue related but ultimately different aspects of the phenomena under study. As a result, the discrete inquiries in a mixed methods study will most likely employ different methods to collect data.
Conduct research from conception to analysis with ATLAS.ti.
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to see how our software can aid you in the research process.
Researchers do not employ mixed methods research just for the sake of having different methods in one research inquiry. The objective behind mixing methods is to generate new knowledge and strengthen understanding of that knowledge by examining it from different angles. This is a concept in research called triangulation, which refers to affirming a given location based on measures taken from different points. The equivalent notion in research is that viewing the same object of inquiry from multiple angles will provide a more reliable understanding of that object.
To further understand the utility of a mixed methods approach, imagine you and your friends are looking at a merry-go-round. You can only see one part of it at any one time, while other parts are obscured from your view. On the other hand, if your friends are positioned to see the merry-go-round from different angles, your combined observations can capture a more complete picture of the object you are studying.

Mixed methods research relies on multiple research methods, data sets, or theoretical approaches to assemble a more comprehensive picture of a concept or phenomenon. Especially in qualitative research or social science research, any set of findings can be considered more credible if they are supported with evidentiary data that comes from different perspectives.
Method triangulation
Method triangulation involves combining qualitative and quantitative methods together to study different but related aspects. In this respect, quantitative and qualitative research study the same phenomenon to lend support to each method's findings. Note that the goal of triangulated mixed methods research is not to simply use multiple methods to arrive at the same answer but to generate a better understanding of a phenomenon that one method alone cannot sufficiently capture.
In this case, method triangulation is a useful concept for a mixed methods researcher because it requires them to acknowledge the strengths and weaknesses of each particular research method. At scale, quantitative methods cannot capture concepts that are unquantifiable (e.g., beauty, convenience). In contrast, qualitative methods often do not conduct data collection at scales necessary to make generalizations about phenomena. Integrating quantitative and qualitative research components under the same mixed methods design ensures a comprehensive examination of a phenomenon that one method alone cannot accomplish.
Ethnography provides ample opportunities to pursue method triangulation. Data collection in ethnographic research often involves collecting qualitative data through observations and interviews . In contrast, data analysis can assess quantitative data by identifying patterns in behavior and perspectives and determining their frequencies.
Another example is a mixed methods study that examines patient outcomes at a hospital. Initial qualitative results might come from field notes from observations of doctors and nurses and interview data with patients. The quantitative findings might come from conducting a statistical analysis of the money and resources used for each patient observed or interviewed to determine whether the expenditure is commensurate with the patient outcomes achieved.
A standalone quantitative study might look only at the financial aspects of health care, while a qualitative study might do better at examining the social and emotional aspects. Conducting both of these studies in tandem can help researchers determine actionable insights for streamlining health care services while maintaining satisfactory standards of care.
Data triangulation
Mixed methods research usually depends on method triangulation, but it's important to identify other forms of triangulation that can strengthen the findings in any research. A study that relies on data triangulation looks at different sets of data. For example, an educational researcher might examine student outcomes at different schools or at the same school but at different times. Data triangulation is useful in affirming that the findings in one context are applicable across other contexts.
Theory triangulation
Another kind of triangulation less commonly associated with mixed methods research deals with analyzing data using different theories. A sequential research design, for example, may use the initial quantitative results from a survey study to generate a conceptual framework for the analysis of a subsequent qualitative study. At the same time, existing theories may also be employed in that analysis to compare and contrasts the kinds of insights and outcomes that each may produce.
Theory generation in mixed methods research
Many forms of research seek to generate or develop a theoretical framework to understand the object of inquiry. There are two common forms of theory generation, and both can manifest in the research questions that are posed in any study.
Research questions can either be exploratory, which try to define or gain a greater understanding of a phenomenon, or confirmatory, which try to test a theory or hypothesis regarding that phenomenon. With some exceptions, exploratory research questions call for collecting qualitative data , while confirmatory research questions require quantitative data .
In that respect, common mixed methods designs combine qualitative and quantitative components to generate a theory and either strengthen or challenge that theory, respectively. To understand what that theory generation looks like when employing mixed methods, we need to examine some of the different kinds of mixed methods research designs.
Look at your data from all angles with ATLAS.ti.
Analyze your data quickly and efficiently with ATLAS.ti. Click here for a free trial.
Data collection and analysis in mixed methods research depends on the research design you adopt. Ultimately, it might be easy to think about the different research designs in terms of the timing of the discrete inquiries within a mixed methods inquiry.
Concurrent triangulation design
A study that collects quantitative and qualitative data simultaneously is a common form of mixed methods design to achieve triangulation. The goal of a concurrent triangulation design is to observe the object of inquiry from multiple methods.
For example, imagine an educational researcher who wants to examine the efficacy of an after-school reading program. The researcher can then pursue two concurrent studies, one that qualitatively observes the reading program in action between educators and students and another that quantitatively tests students' reading comprehension. Over time, the researcher can draw correlations between improvements in test scores and any observations of the students in the program.
Exploratory sequential design
Another way to look at mixed methods research is with the idea that data collection and analysis are cyclical and evolve as new knowledge is generated. Researchers might undertake an exploratory sequential design if they don't yet know the aspects of a concept or phenomenon they want to test. In short, they need to conduct a qualitative study first in order to generate a conceptual framework to apply in a subsequent quantitative study.
Exploratory sequential design is useful in market research, for example, to identify the potential needs and preferences of prospective customers. Focus group research with a group of target customers can inquire about what they are looking for when choosing from a line of products. The researcher can take the initial qualitative findings to inform the design of a subsequent survey study that can confirm the extent to which the preferences of the focus group are reflected in the larger market.
Researchers can also conduct a quantitative study to preface observations in a qualitative study. Imagine that an educational researcher is adopting mixed methods approaches when examining learning outcomes among schools within a given geographical area. They might start by examining test scores published by these schools, using the initial quantitative results to determine where students are struggling and might need intervention. The resulting qualitative study might conduct observations in struggling schools to determine potential shortcomings in teaching and learning.
Concurrent nested design
This research design involves conducting multiple inquiries at the same time for the purpose of using one inquiry to strengthen the other. In a mixed methods approach, concurrent nested design places one research paradigm within another (e.g., a quantitative study within a qualitative study).
Sequential transformative design
This is a mixed methods research design with a critical or social justice orientation, meaning that the research is ultimately conducted to challenge the understanding of existing theory or produce meaningful social change, respectively. In either case, a sequential mixed methods research design can have a transformative effect by employing one study to create the rationale for a second critical or social justice research inquiry.
As you employ multiple research methods for a single mixed methods research design, you might find that your data collection will involve large sets of data, presenting a challenge in managing all that information in an orderly manner. Whether you are conducting research through qualitative data collection, quantitative data collection, or both, ATLAS.ti can help you organize and analyze your data. A robust mixed methods approach requires systematic organization of your data collection to ensure efficient and insightful analysis.
Document groups
Data in ATLAS.ti is stored in documents, which can be classified by the data type they contain. ATLAS.ti allows you to analyze text, images, video, audio , and more, and each document's data type is marked in the Document Manager for easy organization.
However, you may also need to divide your documents by type of study or method employed. In that case, you can use Document Groups in ATLAS.ti to label your documents so your project has categories for quantitative and qualitative data, interviews and focus groups, observations and test scores. Documents can belong to multiple document groups, allowing for easy organization of documents into multiple categories.
Once you have fully coded your data , it might be a challenge to narrow down your analysis to the relevant data you're looking for. If you have to sift through large numbers of documents, the Query Tool can help you look for the most relevant quotations based on the codes you have applied to your data.
Global filters
Studies that employ mixed methods research can accumulate such vast amounts of qualitative and quantitative data that it might become cumbersome for the human eye to keep track of it all manually. Even the most organized project in ATLAS.ti can have thousands of documents or hundreds of codes, making it a challenge to find the right data.
In ATLAS.ti, you can set a global filter using any of the elements of your project. For example, if you have a document group labeled " interviews ," you can set a global filter for that document group, which will lead ATLAS.ti to only show the documents in that group.
Working with both qualitative and quantitative software
ATLAS.ti has a number of tools that provide visualizations to help illustrate quantitative findings. However, you may find that other software, such as Microsoft Excel or SPSS, can help you further analyze and visualize the quantitative research components in your study. As a result, ATLAS.ti allows you to export your analysis into a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. The Code Co-Occurrence Analysis and Code-Document Analysis tools, for example, can export their resulting tables into Microsoft Excel, which includes tools for deeper statistical analysis or for creating other kinds of data visualizations.
ATLAS.ti projects can also be exported as syntax files that can be imported into other statistical analysis software such as SPSS and R. These files convert qualitative data into quantitative data for further statistical analyses, regressions, and quantitative visualizations. Researchers can fully realize the convergence between qualitative and quantitative research when using multiple software platforms to conduct their analysis.

From data collection to data analysis, rely on ATLAS.ti.
Start with a free trial of our software to conduct your mixed methods research.

- Student Notebook
Mixed Methods Research
- Experimental Psychology
- Quantitative
- Statistical Analysis
Traditionally, there are three branches of methodology: quantitative (numeric data), qualitative (observational or interview data), and mixed methods (using both types of data). Psychology relies heavily on quantitative-based data analyses but could benefit from incorporating the advantages of both quantitative and qualitative methodologies into one cohesive framework. Mixed Methods (MM) ideally includes the benefits of both methods (Johnson, Onwuegbuzie, & Turner, 2007): Quantitative analyses employ descriptive and inferential statistics, whereas qualitative analyses produce expressive data that provide descriptive details (often in narrative form) to examine the study’s research objectives. Whereas quantitative data may be collected via measures such as self-reports and physiological tests, qualitative data are collected via focus groups, structured or semistructured interviews, and other forms (Creswell, 2013).
MM hypotheses differ in comparison with solely quantitative or qualitative research questions. Not only must the quantitative and qualitative data be integrated, but the hypotheses also must be integrated. MM practitioners promote the development of a theory-based set of three hypotheses. Hypotheses should be conducted a priori and be both logical and sequential research questions (for more information, see Onwuegbuzie & Leech, 2006). Specialists encourage researchers to construct three separate types of hypotheses for an MM research project. There can be more than three hypotheses but there must be at least one of each type. The first hypothesis should be quantitative and the second should be qualitative. The third hypothesis will be an MM hypothesis.
Integration of these data is often complex, even when there is a strong theoretical rationale for doing so. Data integration occurs when quantitative and qualitative are combined in a data set. There are multiple ways for this to occur, including triangulation, following a thread, and the mixed methods matrix (see O’Cathain, Murphy, & Nicholl, 2010, for a brief review). Yet understanding the overall reasoning for using MM and how to best combine the approaches in practice can help lessen the challenge of MM data integration (Bryman, 2006).

Types of MM Research
- There are dozens of MM designs, but for the purpose of this article, six MM designs will be presented:
- The sequential explanatory method employs two different data-collection time points; the quantitative data are collected first and the qualitative collected last.
- The sequential exploratory design is best for testing emergent theory because both types of data are interpreted during the data integration phase.
- The sequential transformative approach has no preference for sequencing of data collection and emphasizes theory.
- Concurrent triangulation is the ideal method for cross-validation studies and has only one point of data collection.
- The concurrent nested design is best used to gain perspectives on understudied phenomena.
- The concurrent transformative approach is theory driven and allows the researcher to examine phenomena on several different levels.
Strengths and Challenges of MM Research
An MM approach is helpful in that one is able to conduct in-depth research and, when using complementary MM, provide for a more meaningful interpretation of the data and phenomenon being examined (Teddlie & Tashakkori, 2003). Another strength of MM is the dynamic between the qualitative and quantitative portions of the study. If the design is planned appropriately, each type of data can mirror the other’s findings, so the methodology can benefit many types of research. However, interpreting data using the MM framework can be complicated and time intensive given that the data and interpretations are often abstract. Additionally, conducting MM research requires training and mastery of the methodology, so there can be a learning curve for researchers who traditionally use only quantitative or qualitative methods. Sticking to the theory-based and evidence-based designs will aid in your understanding and interpretation of the data.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative coding is a multistep process that includes different types of analyses depending on the nature of your data. Codebooks are important before, during, and after qualitative coding due to the detailed nature of the qualitative data. It is also important to know your expected codes and themes in order to promote interrater reliability (Hruschka et al., 2004). Expected codes are based on the theoretical foundation of your project. I suggest including the expected codes and themes in your codebooks. As previously mentioned, research designs involving this type of data can vary greatly, but in general, the following is a framework of how to conduct a thematic data analysis: Know your data inside and out, generate codes, search for themes, and review themes with a research team (Braun & Clarke, 2006). For more detailed instructions on conducting a qualitative analysis, please refer to last month’s Student Notebook article (Heydarian, 2016).
Lessons Learned
From the start, the researcher or research team must have a clear idea of their resources and the pros and cons of each method. Researchers also must be flexible. I am interested in examining the factors that compose seeking health information online. To investigate this topic, I developed an online, two-part study. Information obtained from qualitative prompts was used to inform the development of a scale measuring health-information-seeking behavior online. The first study used MM, and the data collection occurred on Amazon Mechanical Turk, a marketplace where researchers can post their available studies. Potential participants are paid a small fee, and data collection usually is completed in less than a week. I expected to conduct magnitude coding — a type of qualitative coding that evaluates the emphasis of content — but instead I had to choose a more appropriate type of coding because the participants provided extremely brief responses.
In closing, the design of your study (quantitative, qualitative, or MM) should align with your training and your research objectives. MM has the potential to bring your research to the next level by combining the strengths of quantitative and qualitative methodologies.
Suggestions for Conducting MM Research
Be proficient in MM research by keeping up to date with the latest techniques, software, textbooks, and manuals.
Think “outside the box” and consider other data-analytic approaches that are not used in your field.
Choose the research design that best fits the hypotheses, and know the assumptions and limitations of that design.
Incorporate figures and tables into your qualitative codebook to deepen the conceptualizations for the coders and provide a few examples of already coded data in order to provide thorough instructions.
Create and use summary statements for each participant to help with the abstract portion of the analyses. Summary statements should be a few sentences that describe the participant’s statement and provide an overall gist of the available qualitative information.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 3 , 77–101. doi:10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Bryman, A. (2006). Integrating quantitative and qualitative research: How is it done? Qualitative Research, 6 , 97–113. doi:10.1177/1468794106058877
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Heydarian, N. (2016). Developing theory with the grounded-theory approach and thematic analysis. Observer, 29(4) , 38–39.
Hruschka, D. J., Schwartz, D., John, D. C. S., Picone-Decaro, E., Jenkins, R. A., & Carey, J. W. (2004). Reliability in coding open-ended data: Lessons learned from HIV behavioral research. Field Methods, 16 , 307–331. doi:10.1177/1525822X04266540
Johnson, R. B., Onwuegbuzie, A. J., & Turner, L. A. (2007). Toward a definition of mixed methods research. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 1 , 112–133. doi:10.1177/1558689806298224
O’Cathain, A., Murphy, E., & Nicholl, J. (2010). Three techniques for integrating data in mixed methods studies. BMJ, 341 , c4587. doi:10.1136/bmj.c4587
Onwuegbuzie, A. J., & Leech, N. L. (2006). Linking research questions to mixed methods data analysis procedures 1. The Qualitative Report, 11 , 474–498.
Teddlie, C., & Tashakkori, A. (2003). Major issues and controversies in the use of mixed methods in the social and behavioral sciences. In A. Tashakkori & C. Teddlie (Eds.), Handbook of mixed methods in social & behavioral research (pp. 3–50). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
VERY RELEVANT AND COMPREHENSIVE TEXT ON MM ETHODS
The analysis of mixed methods is fairly comprehensive and educative especially for scholars and/researchers who are used to the traditional Qualitative and Quantitatve research as a stand alone methodologies. I feel like looking for a workshop sponsor so that I can share these ideas to our colleagues in African universities generally and Kenya in particular. Our postgraduate students have not yet embrased the use of mixed methods. Four of my own supervised doctoral students have successfully used th MMR.We should do much more!
I am currently pursuing my PhD and using mixed method. I am interested in this combination of research methods.
I have gained much from the source which clearly spells out the strengths of MM and its applicability in research.
Iam conducting a sequential explanatory mixed methods study in PhD Management and I have benefited a lot from combining quantitative and qualitative research approaches operating with what works best per given research probem.
APS regularly opens certain online articles for discussion on our website. Effective February 2021, you must be a logged-in APS member to post comments. By posting a comment, you agree to our Community Guidelines and the display of your profile information, including your name and affiliation. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations present in article comments are those of the writers and do not necessarily reflect the views of APS or the article’s author. For more information, please see our Community Guidelines .
Please login with your APS account to comment.
About the Author
Allyson S. Hughes is a Health Psychology doctoral student at The University of Texas at El Paso. Her research examines judgment and decision-making concerning health decisions using Internet resources. She can be reached at [email protected] .

Research Briefs
Recent highlights from APS journals articles on learning about working memory, psychological measurement, patterns of implicit and explicit attitudes, and much more.

Careers Up Close: Jolynn Pek on Quantifying Uncertainty
Pek analyzes sources of uncertainty in statistical results and develops new approaches to practicing replicable psychological science.

Speaking Evidence to Policy
The Commission on Evidence-Based Policymaking has issued a report that points to significant new opportunities in research and leadership for psychological scientists with expertise in areas including judgment and decision making, analysis and research design, data privacy and ethics issues, and more.
Privacy Overview

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Mixed Methods Research – Different Types & Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Researchers often conduct various types of research in the same study to investigate the different variables in a research project.
Mixed method research is a crucial aspect of research methodology as it combines qualitative and quantitative research approaches, thereby providing a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena through numerical data and nuanced contextual insights.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Mixed methods research – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition – Mixed methods research
- 3 When to use mixed methods research
- 4 Types of mixed methods research designs
- 5 Advantages of mixed methods research
- 6 Disadvantages of mixed methods research
Mixed methods research – In a Nutshell
- Mixed methods research is a hybrid of quantitative research and qualitative research methodology.
- Researchers use the mixed approach to leverage the benefits of each research method.
- Mixed methods often yield more detailed findings, although they are limited by timelines and inadequate resources.
Definition – Mixed methods research
Mixed methods research incorporates qualitative and quantitative research elements to propose a solution for a research problem . When used together, quantitative and qualitative methods provide more comprehensive findings than the use of each method alone.
Qualitative methods are used to study natural phenomena using observations, interviews, and analysis of text data. Quantitative research involves numerical analysis of quantifiable variables. Mixed methods research is often used in research cases with various variables and data sets such as social and behavioral sciences.
When to use mixed methods research
Mixed methods research is best used when your research displays variables with both qualitative and quantitative characteristics. You can use mixed methods research to formulate generalizable findings, often limited by a standalone quantitative approach.
In addition, using mixed methods research lends credibility to your research findings. By showing how you applied different research methods, your work can hold up under scrutiny since you have covered several aspects. Highlight how your research question will deploy quantitative and qualitative techniques and why it is necessary to use both through mixed methods research.
- ✓ Post a picture on Instagram
- ✓ Get the most likes on your picture
- ✓ Receive up to $300 cash back
Research example
Maybe you want to study road safety on a particular road. You can take a purely quantitative approach if your main metric is the daily average number of road accidents and in which sections they happen. For a qualitative study, you can interview drivers on their thoughts on driving in certain road sections.
A mixed methods research approach seems like the most appropriate way to answer both questions to uncover deeper insights. It can find cause and effect relationships between qualitative and quantitative variables in a detailed study.
For this research problem, a mixed methods research framework may explore whether the sections drivers deem to be more hazardous report more accidents. Note that mixed methods research doesn’t just imply qualitative and quantitative data collection. Both methods should complement each other to answer a common research problem.
Types of mixed methods research designs
There are various mixed methods research designs. The appropriate mixed methods research design choice depends on the research objective, the duration of data collection, and other factors.
We will discuss some designs of mixed methods research. They are used in different contexts to answer different kinds of research problems.
Explanatory sequential
In this type of mixed research, you first collect and analyze quantitative data. This is followed by gathering and analyzing qualitative data. This approach best applies to a research problem where researchers believe the qualitative data will explain the quantitative analysis.
You can estimate the average number of accidents and determine which areas are classified as high risk. From these conclusions, you can interview drivers in these areas and analyze their responses in a qualitative framework.
Based on your qualitative data, you can give possible explanations for why accidents happen in some sections and investigate specific causes.
Exploratory sequential
In this inverse approach, researchers examine qualitative data points and then collect and analyze quantitative data sets.
This approach can be used to formulate research problems and hypotheses. After developing a valid hypothesis, quantitative methods are used to test or validate the qualitative conclusions.
You can begin by talking to drivers or handing out questionnaires to discover hazardous road sections. This is followed by looking at the number of accidents in these sections to compare the statistics with the general drivers’ sentiments.
In a parallel approach, researchers collect both quantitative and qualitative data simultaneously. The findings are analyzed separately, then their respective conclusions are compared to give a general conclusion.
In the analysis of road safety, you can carry out both quantitative and qualitative research as follows:
Qualitative research – You can look at the driver’s comments and issues raised on online platforms such as Twitter.
Quantitative research – You can analyze traffic police reports on the frequency of accidents in various road sections.
The nested approach is also known as the embedded method. In this design, both qualitative and quantitative data are collected concurrently. However, one type of data takes precedence over the other.
Researchers usually adopt a nested approach when there are time restrictions or scarce resources. The nested design is used to support the findings of the main research design.
In the quantitative test, you can investigate if the frequency of the drivers’ concerns about a particular road section corresponds with the frequency of accidents in that section. You can include some qualitative questionnaires to support your quantitative findings.
Advantages of mixed methods research
A win-win scenario – Using both qualitative and quantitative methods takes advantage of the benefits of both research methods. A mixed approach ensures in-depth and generalizable findings.
Versatility in research – Mixed research methods offer more flexibility when formulating research problems. They let researchers break down a research problem into its constituent qualitative and quantitative elements for more comprehensive conclusions.
Expanding the scope of the study – Researchers can expand the subject matter of a research problem using a mixed framework. This often leads to more discoveries beyond the initial research problem.
Disadvantages of mixed methods research
Mismatch of conclusions – Some research designs, such as the parallel design, may yield contrasting results. This poses the problem of generalization as the findings have no similarities.
Lack of sufficient resources – Most research undertakings rely on external funding. Collecting and analyzing both qualitative and quantitative data may consume a lot of time and resources.
Skill gaps – A mixed approach requires skilled qualitative and quantitative analysts. The quantitative field currently has a shortage of skilled personnel due to the complex nature of the quantitative methods available.
What are the key aspects of mixed methods research?
Mixed methods research involves qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods. There are different designs under this approach for various research problems.
When should I use a mixed approach in research?
A mixed approach delivers the best results when the research problem has qualitative and quantitative aspects. Using both methods offers more granular-level insights.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative research?
Qualitative is a text analysis of data collected from observation and questionnaires. Quantitative research is a numerical method of collecting and analyzing figures associated with certain research variables.
Which are the 4 mixed research designs?
The main forms of mixed research designs are embedded, parallel, explanatory sequential, and exploratory sequential. They are used in different research proposals to answer research problems.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint

Mixed Methods
- Research Design
6 Types of Mixed Methods Designs
Sequential explanatory design, sequential exploratory design, sequential transformative design, concurrent triangulation design.
- Mixed Methods References
Sequential Explanatory Design *
Sequential Exploratory Design *
Concurrent Embedded Design **
Concurrent Transformative Design **
*most common
** least common and not discussed
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . Sage Publications, Incorporated
Two phase project
(1) Quantitative Data Collection and Analysis
(2) Qualitative Data Collection and Analysis
Larger focus on quantitative data
Example: Survey data informs interviews
(1) Qualitative Data Collection and Analysis
(2) Quantitative Data Collection and Analysis
Larger focus on qualitative data
Example: Focus group shapes survey questions
Four phase project (two data collection series)
Qualitative Data Collection and Analysis x2
Quantitative Data Collection and Analysis x2
Collect qualitative and quantitative data at the same time
Compare results from qualitative data to results from quantitative data
Analysis for quantitative and qualitattive is completed separately
- << Previous: Research Design
- Next: Mixed Methods References >>
- Last Updated: Mar 30, 2023 12:46 PM
- URL: https://research.library.gsu.edu/c.php?g=1050115

Mixed Method Research: What It Is & Why You Should Use It

This article will give an overview of Mixed Method Research, its types, pros and cons of using mixed method.
Mixed method research is a methodological approach that combines different research methods to gain a more holistic understanding of a problem or issue. Mixed method techniques can be used to study human behavior, attitudes, and preferences, as well as social and environmental issues.
Mixed methods research can help researchers avoid the biases that are often associated with specific research methods. Mixed method research is also useful for generating new insights and knowledge about complex topics.
Mixed methods research is a hybrid approach to research that incorporates both qualitative and quantitative methods. Mixed methods research can provide more accurate and comprehensive data because it allows researchers to explore different aspects of a problem or issue from different angles.
Mixed methods research also allows researchers to better understand the participants’ perspectives and experiences.
- Table of Contents
What is Mixed Method?
Mixed methods research seeks to answer research issues that cannot be answered by “qualitative” or “quantitative” methods alone.
The goal of mixed methods research is to gather, analyze, and combine quantitative and qualitative data in a single study or series of studies.
A mixed methodologies approach to business research is becoming more popular. This technique is appealing because it allows researchers to combine Inductive and deductive reasoning, using more than one research approach to handle the research problem and solving it with multiple types of data.
A mixed methods approach, on the other hand, complicates the study design and hence necessitates clear presentation to allow the reader to sort out its various components.
Example of Mixed Method
The company’s CEO interviewed managers to learn more about the nature of management work. Based on his interview data analysis, he developed theories on managerial roles, the nature and forms of managerial activities, and so on. These have been evaluated in a variety of situations, including interviews and questionnaire surveys.
Types Mixed Method Design
Mixed methods research designs are classified into several sorts. The distinctions between them are related to the purpose of the research, the timing of data collection, and the weight given to each data type.
- Convergent Parallel Design
In a convergent parallel design, quantitative and qualitative data are collected together and analyzed separately. When both analyses are finished, compare your results to reach broad conclusions.
Convergent design is employed when it is necessary to compare statistical data with qualitative findings in order to better comprehend the study challenge. This hybrid qualitative and quantitative research methods design is also used by researchers to validate and highlight qualitative findings with quantitative results.
- Embedded Design
If you are short on time or resources, this is a great method to adopt. An embedded design can be used to strengthen or supplement the primary type of research design’s conclusions.
In an embedded design, both forms of data are collected and analyzed at the same time, but within the context of a wider quantitative or qualitative design. One form of data is subordinate to another.
- Exploratory Sequential Design
Qualitative data gathering and analysis come first in an exploratory sequential design, followed by quantitative data collection and analysis.
This design can be used to generate first questions and hypotheses. The quantitative data can then be used to test or verify your qualitative finding.
- Explanatory Sequential Design
In an explanatory sequential design, quantitative data is collected and analysed first, then qualitative data is collected and analyzed.
This design should be used if you believe your qualitative data will explain and contextualize your quantitative findings.
Research Questions in Mixed Method
Most researchers consider the research questions and/or hypotheses to be critical in determining the type of research approach to use. When both qualitative and quantitative data are needed to answer a question, a mixed method research design should be used.
Suppose a researcher conducted a study on the successful leadership strategies of Pakistani school principals. His research questions were as follows:
1. What types of leadership strategies do successful school principals in Pakistan employ? 2. Is there any overlap in the leadership styles of these schools’ principals? 3. Is there a difference in view about leadership methods between headteachers and their subordinates?
Researcher obviously wanted a broad profile, so his design included a survey with demographic, Likert-scaled, and open-ended questions; nevertheless, he also needed opinions, which are subjective and best handled by qualitative approaches.
Quantitative methods may be better suited to investigating frequency questions, whereas qualitative methods may be better suited to investigating perception and opinion.
Mixed techniques are likely to be preferred if the questions address both of these. It is also possible that the investigator wishes to delve deeper into a subset of a population, maybe following a larger survey.
Purpose of Conducting Mixed Method Research
There are five key reasons for performing mixed methods research:
Expansion entails broadening the scope and scope of the research by employing diverse approaches for different lines of inquiry.
- Triangulation
Triangulation is the process of confirming results using multiple approaches.
the discovery of fresh insights that lead to the generation of new research questions.
Complementarity
Complementarity occurs when the results of one approach are utilized to enrich, elaborate, or clarify the conclusions of another method.
Pros of Mixed Method Research
1- The fundamental advantage of conducting mixed methods research is that you can use both qualitative and quantitative research approaches.
2- This method lets you to use the strength of one data type to compensate for the weakness of another.
3- Because mixed qualitative and quantitative research approaches are less bound by traditional research paradigms, they are more adaptable.
4- It enables to investigate a wide range of research problems. This is due to the fact that you are not restricted to a single study method.
5- This method assists researchers in gathering more evidence to support their findings.
6- It provides researchers with a comprehensive understanding of the topic or phenomenon under investigation.
Cons of Mixed Method Research
1- Mixed methods research necessitates the collection and analysis of two types of data, making it time-consuming and labor-intensive.
2- If the findings of two data formats in mixed method provide distinct outcomes, research can be difficult to comprehend.
3- Understanding numerous methodologies and how to combine them appropriately is required for mixed methods research.
Steps to conduct Mixed Method Research
There is no set procedure for performing a mixed-methods study. You can, however, perform mixed methods research by following the steps outlined below:
Determine whether mixed methods research is appropriate in your research.
The first stage is to decide whether mixed methods research will answer your research questions and provide the greatest type of evidence for your research topic.
Determine purpose of study.
Determine the purpose of study by employing a mixed methods study approach.
Is it to test, verify, develop, or supplement the results of one data type?
Choose the most suitable design.
Choose the best design from the four types of mixed methods research designs.
Gather qualitative and quantitative data.
Gather the qualitative and quantitative data that will be analyzed.
Data Analysis
Analyze the data you’ve gathered by using statistical tools.
Write research paper
After conducting data analysis you can validate, interpret, and write your research paper.
FAQs about Mixed Methods
How can you choose the right mixed methods research question.
When choosing the right mixed methods research question, it is important to consider the research question’s purpose and goals.
- The purpose of the study should be clear from the outset, and should guide both the selection of methods and analysis of data.
- Goals of the study should also be considered, as they will help determine what questions are most relevant to answering the research question.
Once a clear goal for the study is established, other factors to consider include whether or not a single method or set of methods will provide enough information to answer the question. If more than one approach is needed, it is important to select which one will provide the most reliable data.
Additionally, it is important to choose a method that will allow for an accurate assessment of participant’s experiences and opinions.
After selecting a method, it is necessary to develop a research design that will allow for collection of useful data.
How do you ensure that your findings from a mixed methods study are generalizable?
The goal of any research study is to generate valid and reliable findings that can be applied to the general population.
To do this, it is important to ensure that the findings from a mixed methods study are generalizable.
There are a number of ways to do this, but some key considerations include:
- Ensuring that the study design is appropriate for the research question being asked.
- Ensuring that the data collection procedures are standardized and fair.
- Considering whether the findings from the study can be generalized to other contexts or populations.
- It is also important to consider how specific factors, such as participant characteristics or researcher biases, might have influenced the results of a mixed methods study.
Ultimately, following these steps will help ensure that the findings from a mixed methods study are useful and applicable in multiple contexts.
How can you report the results of a mixed methods study effectively and efficiently?
When conducting a mixed methods study, it is important to be clear about the goals of each study component and how they will impact the overall results.
The following tips can help you report the results of your study effectively and efficiently:
1. Clearly outline the goals of each study component. This will help ensure that data from each component is used appropriately and that conclusions reached are consistent with the overall purpose of the study.
2. Label all data accurately. Tag all interview transcripts, observation logs, and survey responses with appropriate labels so that analysts can easily track information throughout the research process.
3. Make sure all data is properly archived. Researchers must always keep track of their data in order to reproduce findings or build upon previous work. Archiving data allows for future use in analysis, as well as provides evidence for academic publications or other presentations about the research project.
How do you deal with bias when conducting a mixed methods study?
When conducting a mixed methods study, it is important to be aware of the potential for bias.
There are a few ways to deal with bias in a study:
- First, try to ensure that all participants are treated equally.
- Second, try to use a variety of methodological strategies (e.g., qualitative and quantitative methods)
- Third, try to collect data from as many participants as possible.
There are a few things you can do to help reduce the chances of bias creeping into your research.
Before starting any study, be sure to discuss with your team what measures you will take to avoid bias.
Once you have started your study, it is important to keep track of how biased you are feeling and how this might be affecting the data collection and analysis.
Be honest with yourself and others about how you are behaving; if something is interfering with our ability to be unbiased, we need to address it.
Finally, once you have completed your study, make sure to share it with all the people who were involved in its production. This will help them understand how bias may have affected the results and help them develop ways to avoid it in their own work.
Mixed Methods research is a type of research that uses multiple methods to gather data. This approach can help researchers identify hidden patterns and insights that would not be apparent from just one method. Mixed Methods research can be helpful when studying complex topics or when data from different sources is needed. Additionally, using multiple methods can increase the reliability of the research findings. This article have given an overview of Mixed Method Research, its types, pros and cons of using mixed method.
Other articles
Please read through some of our other articles with examples and explanations if you’d like to learn more about research methodology.
- PLS-SEM model
- Principal Components Analysis
- Multivariate Analysis
- Friedman Test
- Chi-Square Test (Χ²)
- Effect Size
Methodology
- Research Methods
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Case Study Research
- Survey Research
- Conclusive Research
- Descriptive Research
- Cross-Sectional Research
- Theoretical Framework
- Conceptual Framework
- Grounded Theory
- Quasi-Experimental Design
- Mixed Method
- Correlational Research
- Randomized Controlled Trial
- Stratified Sampling
- Ethnography
- Ghost Authorship
- Secondary Data Collection
- Primary Data Collection
- Ex-Post-Facto
- Dissertation Topic
- Thesis Statement
- Research Proposal
- Research Questions
- Research Problem
- Research Gap
- Types of Research Gaps
- Operationalization of Variables
- Literature Review
- Research Hypothesis
- Questionnaire
- Reliability
- Measurement of Scale
- Sampling Techniques
- Acknowledgements
Related Posts
Peer review | types of peer review, ethics in research: safeguarding integrity and credibility, advantages and disadvantages of snowball sampling, exploring qualitative researcher skills: what they are and how to develop them, difference between quota sampling and stratified sampling, how effective laboratory design impacts health, safety, and productivity, why is laboratory safety important in research, what is purposive sampling | examples, quota sampling in research, top ai tools for literature review .
I would like to know your bibliography, thank you! great job.
Lovely just what I was looking for.Thanks to the author for taking his clock time on this one.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Acta Inform Med
- v.30(1); 2022 Mar
Mixed Methodology of Scientific Research in Healthcare
Emina smajic.
1 Agram Polyclinic, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Dijana Avdic
2 Faculty of Health Studies, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Aleksandra Pasic
3 Clinical Biochemistry with Immunology, Sarajevo, Clinical Center University of Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Alden Prcic
4 General Hospital “Prim dr. Abdulah Nakas”, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Maja Stancic
Background:.
Scientific research is usually classified as quantitative or qualitative. However, methodologists are increasingly emphasizing the integration of qualitative and quantitative data as the center of mixed methods (mix methodologies). Mixed research method implies the use of different research methods, ie. quantitative and qualitative methods in one study.
The aim of this review paper is to present the purpose of using a mixed methodology in health research.
The relevant articles were searched from online data sources including PubMed and Google Scholar.
This approach to the use of mixed methods creates opportunities for a deeper study of various problems. The purpose of using mixed research methods is to obtain valid answers to research questions, however the researcher may still have different reasons or purposes for which he wants to strengthen the research study and its conclusions by applying mixed methods. The use of mixed scientific methodology is widely used in the field of health outcomes and should not be limited to a closed list of possible methodological options.
Conclusion:
Recently, there has been an increase in the number of scientific studies in healthcare that use mixed research methods. The advantage of applying this scientific method is that through the triangulation of data obtained by different (quantitative / qualitative) approaches, we get a deeper and more complete picture of the phenomenon in health care that we observe.
1. BACKGROUND
In health science research, there is a priority to develop new methodologies to improve the quality and scientific strength of data leading to an extraordinary increase in methodological diversity. This diversity reflects the nature of public health problems, such as differences between populations, age groups, ethnic groups and cultures, poor adherence to treatments considered effective, behavioral factors contributing to disability and health, and translational needs for health research. Diversity also signals a growing acceptance of qualitative and social science research, the formation of interdisciplinary research teams, and the use of multilevel approaches to research complex health issues such as patient attitudes and cultural and social models of disease and health (1) .
2. OBJECTIVE
The retrieved articles were reviewed by the authors and the results are presented along with the relevant discussion
4.1. MIXED METHODOLOGY
Scientific research is usually classified as quantitative or qualitative. However, methodologists are increasingly emphasizing the integration of qualitative and quantitative data as the center of mixed methods (mix methodologies). Integration is a deliberate process by which the researcher combines quantitative and qualitative approaches in the study. Quantitative and qualitative data then become interdependent in solving questions and hypotheses. Mixed research method implies the use of different research methods, quantitative and qualitative methods in one study ( 2 , 3 ). Research on mixed methods should be distinguished from multi-method research (method-combination) in which either multiple qualitative approaches or only multiple quantitative approaches are combined (4) .

The most accepted definition of a mixed research method is that it is a research in which a researcher or team of researchers combines elements of a qualitative and quantitative approach to research (use of qualitative and quantitative perspectives, data collection, analysis, inference techniques) to understand and support research. As we see in the definition, the use of both quantitative and qualitative methods in a single study (or series of related studies) is crucial, unlike the use of combined methods that combine two or more quantitative or two or more qualitative research methods ( 2 , 4 ).
The basic premise of using mixed research methods is that some research issues can be addressed more comprehensively than using either quantitative or qualitative methods. The issues that benefit most from the design of mixed methods tend to be broad and complex, with multiple aspects that each can have. Mixed research methods can exploit the strengths and weaknesses of both approaches and can be particularly useful when addressing complex, multifaceted issues such as health service interventions and living with chronic diseases (2) . This approach to the use of mixed methods creates opportunities for a deeper study of various problems (5) .
4.2. PURPOSE OF USING MIXED RESEARCH
The purpose of using mixed research methods is to obtain valid answers to research questions, however the researcher may still have different reasons or purposes for which he wants to strengthen the research study and its conclusions by applying mixed methods. The purpose classification of mixed research methods was first introduced in 1989 by Greene, Caracelli, and Graham, based on an analysis of published studies of mixed methods. This classification is still used and we have a total of five “purposes” for why a mixed methodology is used in research (4) . Classification of the purpose of using mixed methodology:
- Complementarity. Using data obtained from one method to illustrate the results of another method.
- Development. Using the results of one method to develop or inform about the use of another method.
- Initiation. We can use the results of different methods to search for areas of non-compliance in certain areas in order to create new insights.
- Expansion. Examining different aspects of a research question, with each aspect justifying different methods.
- Triangulation. Use of data obtained by both methods to support the findings (2) .
In the last 28 years, this classification has been supplemented by several other authors. So in 2006 Bryman compiled a list of more specific rationales for the use or purpose of mixed research methods. Bryman’s classification decomposes the categorization of Greene et al. on several aspects and adds a number of additional aspects (3) .

Bryman’s addition to the classification of Greene et al.
Credibility. It refers to suggestions that the application of both methodological approaches improves the integrity of the results.
Context. Refers to cases where the combination is justified in terms of qualitative research that provides contextual understanding, along with generalized, externally valid results, or broad relationships between the variables identified by the survey.
Illustration. It refers to the use of qualitative data to illustrate quantitative findings, often referred to as putting “meat on the bone” “dry” quantitative findings.
Usefulness or improvement of usefulness of results. It refers to the suggestion, which is more likely to be highlighted among articles with an applied focus, that combining the two approaches will be more useful for practitioners.
Confirmation and discovery. It involves the use of qualitative data to generate hypotheses and the use of quantitative research to test them within a single project.
Diversity of views. This includes two slightly different explanations–namely, combining the perspective of researchers and participants through quantitative and qualitative research, and discovering the relationship between variables through quantitative research, while revealing meanings among research participants through qualitative research (3) .
4.3. RESEARCH DESIGN
Research designs are procedures for collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and reporting data in research studies. They represent different models for doing research, and these models have distinct names and procedures associated with them (6) .
The four major types of mixed methods designs are the Triangulation Design, the Embedded Design, the Explanatory Design, and the Exploratory Design (6) .
4.4. HEALTH APPLICATION
There is a wide range of methods used to collect both quantitative and qualitative data. And the research question and the necessary data are the main determinants of the methods used. To a lesser extent, the choice of methods may be influenced by feasibility. Method priority refers to the emphasis on each method in the study. For example, a study may be predominantly quantitative with a small qualitative component or vice versa. Alternatively, both quantitative and qualitative methods and data may be equally weighted. The emphasis on each methodological component of the study will be driven mainly by the research question, research team skills and feasibility. Finally, researchers must decide when each method will be used in research (2) . By analyzing the research methods and research designs used, Bryman suggests that on the quantitative side, structured interview and questionnaire research within cross-sectional design predominates, while on the qualitative side, semi-structured interviews within cross-sectional design predominate (7) . A key feature of mixed-method research is its methodological pluralism, which often results in research that provides broader perspectives than those offered by monomethodal designs (8) .
The use of mixed scientific methodology is widely used in the field of health outcomes and should not be limited to a closed list of possible methodological options, but should be seen as a framework for a specific research issue to be addressed using quantitative and qualitative components (data and / or methods) , when quantitative and qualitative components are articulated intentionally and prospectively in a well-defined, pre-specified research design and as a framework for meta-inference (9) .
The importance of applying mixed research methods can be reflected in the trend of “measuring / analysing what is important” for patients and the treatment outcomes reported by patients are increasingly used in clinical care and research. However, a recent review of studies documenting the development of outcome measures reported by patients highlights that only 11% of them were developed actually asking patients which outcomes are important to them. This emphasizes the importance of applying mixed qualitative and quantitative methods in health research to ensure a focus on the priorities identified by the patient, scientific rigor, and improved patient outcomes (9) . Mixed methods are also an increasingly accepted approach used to investigate organizational phenomena in health care (10) .
The application of the mix methodology is considered a significant contribution to health science. By combining quantitative and qualitative data in the same study, health researchers can reap the benefits of each approach while minimizing their disadvantages. In practice, this endeavor facilitates research by health science researchers on the complex and multifactorial nature of human health and disease. Researchers using the mixed method approach for the first time can easily feel overwhelmed by uncertainty about the philosophical foundations of the method, as well as the multitude of typologies of mixed method research. Although further research and debate are warranted, health researchers seeking solutions to real problems are increasingly embracing pragmatism as a paradigm of choice (11) .
Author’s contribution:
All authors were involved in preparation of this article. Final proofreading was made by first author.
Financial support and sponsorship:
Conflicts of interest:.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Quantitative, Qualitative, and Mixed-Methods Research: Home
Quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods research.
Depending on the philosophy of the researcher, the nature of the data, and how it is collected, behavioral science can be classified into qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods research. Below are descriptions of each method.
Quantitative Research
Collects numerical data, such as frequencies or scores to focus on cause-and-effect relationships among variables
Variables and research methodologies are defined in advance by theories and hypotheses derived from other theories. These remain unchanged throughout the research process.
The researcher tries to achieve objectivity by distancing himself or herself from the research, not allowing himself or herself to be emotionally involved.
The researcher mostly studies research in artificial or less than its natural setting, and manipulates behavior as opposed to studying the behavior in its natural context.
The researcher tries to maintain internal validity and focuses on average behavior or thoughts of people in a population
Qualitative Research
Where researchers collect non-numerical information, such as descriptions of behavioral phenomena, how people experience or interpret events, and/or answers to participants' open-ended responses.
The researcher's variables andmethods used come from the researcher's experiences and can be modified as the research progresses.
The researcher is involved and his or her experiences are valuable as well as the participants' experiences.
The researcher studies behavior as it naturally happens in the natural context.
The researcher tries to maximize ecological validity.
The researcher focuses on similarities and differences in experiences and how people interpret them.
Mixed-Methods Research
Involves both quantitative and qualitative components.
The researcher specifies in advance the types of information necessary to accomplish the study's goals.
The researcher needs to carefully consider the order in which the data types will be collected and the selection criteria for participants in the various parts of the study (e.g., which people will participate in the qualitative assessment if a sub-selection of participants will be involved).
Involves development (where the researcher uses one method to inform data collection or analysis with another method) initiation (where unexpected results change protocol in the other method), corroboration (where consistency is evaluated and compared between methods), and elaboration (where one method is used to expand on the results of the other method).
Whitley, B. E. & Kite, M. E. (2013). Principles of research in behavioral science (3rd ed.). Routledge.
- Last Updated: Sep 2, 2020 12:29 PM
- URL: https://library.divinemercy.edu/research-types
- Open access
- Published: 19 April 2024
A scoping review of continuous quality improvement in healthcare system: conceptualization, models and tools, barriers and facilitators, and impact
- Aklilu Endalamaw 1 , 2 ,
- Resham B Khatri 1 , 3 ,
- Tesfaye Setegn Mengistu 1 , 2 ,
- Daniel Erku 1 , 4 , 5 ,
- Eskinder Wolka 6 ,
- Anteneh Zewdie 6 &
- Yibeltal Assefa 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 487 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
785 Accesses
Metrics details
The growing adoption of continuous quality improvement (CQI) initiatives in healthcare has generated a surge in research interest to gain a deeper understanding of CQI. However, comprehensive evidence regarding the diverse facets of CQI in healthcare has been limited. Our review sought to comprehensively grasp the conceptualization and principles of CQI, explore existing models and tools, analyze barriers and facilitators, and investigate its overall impacts.
This qualitative scoping review was conducted using Arksey and O’Malley’s methodological framework. We searched articles in PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and EMBASE databases. In addition, we accessed articles from Google Scholar. We used mixed-method analysis, including qualitative content analysis and quantitative descriptive for quantitative findings to summarize findings and PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR) framework to report the overall works.
A total of 87 articles, which covered 14 CQI models, were included in the review. While 19 tools were used for CQI models and initiatives, Plan-Do-Study/Check-Act cycle was the commonly employed model to understand the CQI implementation process. The main reported purposes of using CQI, as its positive impact, are to improve the structure of the health system (e.g., leadership, health workforce, health technology use, supplies, and costs), enhance healthcare delivery processes and outputs (e.g., care coordination and linkages, satisfaction, accessibility, continuity of care, safety, and efficiency), and improve treatment outcome (reduce morbidity and mortality). The implementation of CQI is not without challenges. There are cultural (i.e., resistance/reluctance to quality-focused culture and fear of blame or punishment), technical, structural (related to organizational structure, processes, and systems), and strategic (inadequate planning and inappropriate goals) related barriers that were commonly reported during the implementation of CQI.
Conclusions
Implementing CQI initiatives necessitates thoroughly comprehending key principles such as teamwork and timeline. To effectively address challenges, it’s crucial to identify obstacles and implement optimal interventions proactively. Healthcare professionals and leaders need to be mentally equipped and cognizant of the significant role CQI initiatives play in achieving purposes for quality of care.
Peer Review reports
Continuous quality improvement (CQI) initiative is a crucial initiative aimed at enhancing quality in the health system that has gradually been adopted in the healthcare industry. In the early 20th century, Shewhart laid the foundation for quality improvement by describing three essential steps for process improvement: specification, production, and inspection [ 1 , 2 ]. Then, Deming expanded Shewhart’s three-step model into ‘plan, do, study/check, and act’ (PDSA or PDCA) cycle, which was applied to management practices in Japan in the 1950s [ 3 ] and was gradually translated into the health system. In 1991, Kuperman applied a CQI approach to healthcare, comprising selecting a process to be improved, assembling a team of expert clinicians that understands the process and the outcomes, determining key steps in the process and expected outcomes, collecting data that measure the key process steps and outcomes, and providing data feedback to the practitioners [ 4 ]. These philosophies have served as the baseline for the foundation of principles for continuous improvement [ 5 ].
Continuous quality improvement fosters a culture of continuous learning, innovation, and improvement. It encourages proactive identification and resolution of problems, promotes employee engagement and empowerment, encourages trust and respect, and aims for better quality of care [ 6 , 7 ]. These characteristics drive the interaction of CQI with other quality improvement projects, such as quality assurance and total quality management [ 8 ]. Quality assurance primarily focuses on identifying deviations or errors through inspections, audits, and formal reviews, often settling for what is considered ‘good enough’, rather than pursuing the highest possible standards [ 9 , 10 ], while total quality management is implemented as the management philosophy and system to improve all aspects of an organization continuously [ 11 ].
Continuous quality improvement has been implemented to provide quality care. However, providing effective healthcare is a complicated and complex task in achieving the desired health outcomes and the overall well-being of individuals and populations. It necessitates tackling issues, including access, patient safety, medical advances, care coordination, patient-centered care, and quality monitoring [ 12 , 13 ], rooted long ago. It is assumed that the history of quality improvement in healthcare started in 1854 when Florence Nightingale introduced quality improvement documentation [ 14 ]. Over the passing decades, Donabedian introduced structure, processes, and outcomes as quality of care components in 1966 [ 15 ]. More comprehensively, the Institute of Medicine in the United States of America (USA) has identified effectiveness, efficiency, equity, patient-centredness, safety, and timeliness as the components of quality of care [ 16 ]. Moreover, quality of care has recently been considered an integral part of universal health coverage (UHC) [ 17 ], which requires initiatives to mobilise essential inputs [ 18 ].
While the overall objective of CQI in health system is to enhance the quality of care, it is important to note that the purposes and principles of CQI can vary across different contexts [ 19 , 20 ]. This variation has sparked growing research interest. For instance, a review of CQI approaches for capacity building addressed its role in health workforce development [ 21 ]. Another systematic review, based on random-controlled design studies, assessed the effectiveness of CQI using training as an intervention and the PDSA model [ 22 ]. As a research gap, the former review was not directly related to the comprehensive elements of quality of care, while the latter focused solely on the impact of training using the PDSA model, among other potential models. Additionally, a review conducted in 2015 aimed to identify barriers and facilitators of CQI in Canadian contexts [ 23 ]. However, all these reviews presented different perspectives and investigated distinct outcomes. This suggests that there is still much to explore in terms of comprehensively understanding the various aspects of CQI initiatives in healthcare.
As a result, we conducted a scoping review to address several aspects of CQI. Scoping reviews serve as a valuable tool for systematically mapping the existing literature on a specific topic. They are instrumental when dealing with heterogeneous or complex bodies of research. Scoping reviews provide a comprehensive overview by summarizing and disseminating findings across multiple studies, even when evidence varies significantly [ 24 ]. In our specific scoping review, we included various types of literature, including systematic reviews, to enhance our understanding of CQI.
This scoping review examined how CQI is conceptualized and measured and investigated models and tools for its application while identifying implementation challenges and facilitators. It also analyzed the purposes and impact of CQI on the health systems, providing valuable insights for enhancing healthcare quality.
Protocol registration and results reporting
Protocol registration for this scoping review was not conducted. Arksey and O’Malley’s methodological framework was utilized to conduct this scoping review [ 25 ]. The scoping review procedures start by defining the research questions, identifying relevant literature, selecting articles, extracting data, and summarizing the results. The review findings are reported using the PRISMA extension for a scoping review (PRISMA-ScR) [ 26 ]. McGowan and colleagues also advised researchers to report findings from scoping reviews using PRISMA-ScR [ 27 ].
Defining the research problems
This review aims to comprehensively explore the conceptualization, models, tools, barriers, facilitators, and impacts of CQI within the healthcare system worldwide. Specifically, we address the following research questions: (1) How has CQI been defined across various contexts? (2) What are the diverse approaches to implementing CQI in healthcare settings? (3) Which tools are commonly employed for CQI implementation ? (4) What barriers hinder and facilitators support successful CQI initiatives? and (5) What effects CQI initiatives have on the overall care quality?
Information source and search strategy
We conducted the search in PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and EMBASE databases, and the Google Scholar search engine. The search terms were selected based on three main distinct concepts. One group was CQI-related terms. The second group included terms related to the purpose for which CQI has been implemented, and the third group included processes and impact. These terms were selected based on the Donabedian framework of structure, process, and outcome [ 28 ]. Additionally, the detailed keywords were recruited from the primary health framework, which has described lists of dimensions under process, output, outcome, and health system goals of any intervention for health [ 29 ]. The detailed search strategy is presented in the Supplementary file 1 (Search strategy). The search for articles was initiated on August 12, 2023, and the last search was conducted on September 01, 2023.
Eligibility criteria and article selection
Based on the scoping review’s population, concept, and context frameworks [ 30 ], the population included any patients or clients. Additionally, the concepts explored in the review encompassed definitions, implementation, models, tools, barriers, facilitators, and impacts of CQI. Furthermore, the review considered contexts at any level of health systems. We included articles if they reported results of qualitative or quantitative empirical study, case studies, analytic or descriptive synthesis, any review, and other written documents, were published in peer-reviewed journals, and were designed to address at least one of the identified research questions or one of the identified implementation outcomes or their synonymous taxonomy as described in the search strategy. Based on additional contexts, we included articles published in English without geographic and time limitations. We excluded articles with abstracts only, conference abstracts, letters to editors, commentators, and corrections.
We exported all citations to EndNote x20 to remove duplicates and screen relevant articles. The article selection process includes automatic duplicate removal by using EndNote x20, unmatched title and abstract removal, citation and abstract-only materials removal, and full-text assessment. The article selection process was mainly conducted by the first author (AE) and reported to the team during the weekly meetings. The first author encountered papers that caused confusion regarding whether to include or exclude them and discussed them with the last author (YA). Then, decisions were ultimately made. Whenever disagreements happened, they were resolved by discussion and reconsideration of the review questions in relation to the written documents of the article. Further statistical analysis, such as calculating Kappa, was not performed to determine article inclusion or exclusion.
Data extraction and data items
We extracted first author, publication year, country, settings, health problem, the purpose of the study, study design, types of intervention if applicable, CQI approaches/steps if applicable, CQI tools and procedures if applicable, and main findings using a customized Microsoft Excel form.
Summarizing and reporting the results
The main findings were summarized and described based on the main themes, including concepts under conceptualizing, principles, teams, timelines, models, tools, barriers, facilitators, and impacts of CQI. Results-based convergent synthesis, achieved through mixed-method analysis, involved content analysis to identify the thematic presentation of findings. Additionally, a narrative description was used for quantitative findings, aligning them with the appropriate theme. The authors meticulously reviewed the primary findings from each included material and contextualized these findings concerning the main themes1. This approach provides a comprehensive understanding of complex interventions and health systems, acknowledging quantitative and qualitative evidence.
Search results
A total of 11,251 documents were identified from various databases: SCOPUS ( n = 4,339), PubMed ( n = 2,893), Web of Science ( n = 225), EMBASE ( n = 3,651), and Google Scholar ( n = 143). After removing duplicates ( n = 5,061), 6,190 articles were evaluated by title and abstract. Subsequently, 208 articles were assessed for full-text eligibility. Following the eligibility criteria, 121 articles were excluded, leaving 87 included in the current review (Fig. 1 ).
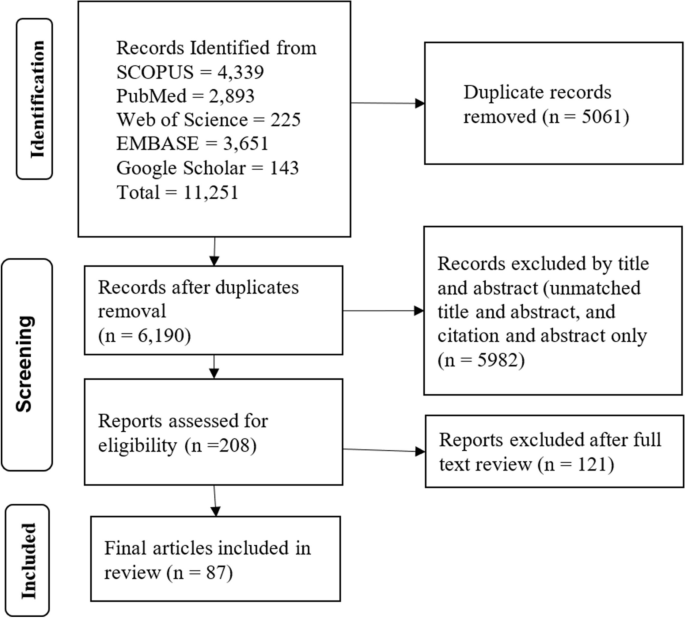
Article selection process
Operationalizing continuous quality improvement
Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI) is operationalized as a cyclic process that requires commitment to implementation, teamwork, time allocation, and celebrating successes and failures.
CQI is a cyclic ongoing process that is followed reflexive, analytical and iterative steps, including identifying gaps, generating data, developing and implementing action plans, evaluating performance, providing feedback to implementers and leaders, and proposing necessary adjustments [ 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 ].
CQI requires committing to the philosophy, involving continuous improvement [ 19 , 38 ], establishing a mission statement [ 37 ], and understanding quality definition [ 19 ].
CQI involves a wide range of patient-oriented measures and performance indicators, specifically satisfying internal and external customers, developing quality assurance, adopting common quality measures, and selecting process measures [ 8 , 19 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 39 , 40 ].
CQI requires celebrating success and failure without personalization, leading each team member to develop error-free attitudes [ 19 ]. Success and failure are related to underlying organizational processes and systems as causes of failure rather than blaming individuals [ 8 ] because CQI is process-focused based on collaborative, data-driven, responsive, rigorous and problem-solving statistical analysis [ 8 , 19 , 38 ]. Furthermore, a gap or failure opens another opportunity for establishing a data-driven learning organization [ 41 ].
CQI cannot be implemented without a CQI team [ 8 , 19 , 37 , 39 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 ]. A CQI team comprises individuals from various disciplines, often comprising a team leader, a subject matter expert (physician or other healthcare provider), a data analyst, a facilitator, frontline staff, and stakeholders [ 39 , 43 , 47 , 48 , 49 ]. It is also important to note that inviting stakeholders or partners as part of the CQI support intervention is crucial [ 19 , 38 , 48 ].
The timeline is another distinct feature of CQI because the results of CQI vary based on the implementation duration of each cycle [ 35 ]. There is no specific time limit for CQI implementation, although there is a general consensus that a cycle of CQI should be relatively short [ 35 ]. For instance, a CQI implementation took 2 months [ 42 ], 4 months [ 50 ], 9 months [ 51 , 52 ], 12 months [ 53 , 54 , 55 ], and one year and 5 months [ 49 ] duration to achieve the desired positive outcome, while bi-weekly [ 47 ] and monthly data reviews and analyses [ 44 , 48 , 56 ], and activities over 3 months [ 57 ] have also resulted in a positive outcome.
Continuous quality improvement models and tools
There have been several models are utilized. The Plan-Do-Study/Check-Act cycle is a stepwise process involving project initiation, situation analysis, root cause identification, solution generation and selection, implementation, result evaluation, standardization, and future planning [ 7 , 36 , 37 , 45 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 53 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 ]. The FOCUS-PDCA cycle enhances the PDCA process by adding steps to find and improve a process (F), organize a knowledgeable team (O), clarify the process (C), understand variations (U), and select improvements (S) [ 55 , 71 , 72 , 73 ]. The FADE cycle involves identifying a problem (Focus), understanding it through data analysis (Analyze), devising solutions (Develop), and implementing the plan (Execute) [ 74 ]. The Logic Framework involves brainstorming to identify improvement areas, conducting root cause analysis to develop a problem tree, logically reasoning to create an objective tree, formulating the framework, and executing improvement projects [ 75 ]. Breakthrough series approach requires CQI teams to meet in quarterly collaborative learning sessions, share learning experiences, and continue discussion by telephone and cross-site visits to strengthen learning and idea exchange [ 47 ]. Another CQI model is the Lean approach, which has been conducted with Kaizen principles [ 52 ], 5 S principles, and the Six Sigma model. The 5 S (Sort, Set/Straighten, Shine, Standardize, Sustain) systematically organises and improves the workplace, focusing on sorting, setting order, shining, standardizing, and sustaining the improvement [ 54 , 76 ]. Kaizen principles guide CQI by advocating for continuous improvement, valuing all ideas, solving problems, focusing on practical, low-cost improvements, using data to drive change, acknowledging process defects, reducing variability and waste, recognizing every interaction as a customer-supplier relationship, empowering workers, responding to all ideas, and maintaining a disciplined workplace [ 77 ]. Lean Six Sigma, a CQI model, applies the DMAIC methodology, which involves defining (D) and measuring the problem (M), analyzing root causes (A), improving by finding solutions (I), and controlling by assessing process stability (C) [ 78 , 79 ]. The 5 C-cyclic model (consultation, collection, consideration, collaboration, and celebration), the first CQI framework for volunteer dental services in Aboriginal communities, ensures quality care based on community needs [ 80 ]. One study used meetings involving activities such as reviewing objectives, assigning roles, discussing the agenda, completing tasks, retaining key outputs, planning future steps, and evaluating the meeting’s effectiveness [ 81 ].
Various tools are involved in the implementation or evaluation of CQI initiatives: checklists [ 53 , 82 ], flowcharts [ 81 , 82 , 83 ], cause-and-effect diagrams (fishbone or Ishikawa diagrams) [ 60 , 62 , 79 , 81 , 82 ], fuzzy Pareto diagram [ 82 ], process maps [ 60 ], time series charts [ 48 ], why-why analysis [ 79 ], affinity diagrams and multivoting [ 81 ], and run chart [ 47 , 48 , 51 , 60 , 84 ], and others mentioned in the table (Table 1 ).
Barriers and facilitators of continuous quality improvement implementation
Implementing CQI initiatives is determined by various barriers and facilitators, which can be thematized into four dimensions. These dimensions are cultural, technical, structural, and strategic dimensions.
Continuous quality improvement initiatives face various cultural, strategic, technical, and structural barriers. Cultural dimension barriers involve resistance to change (e.g., not accepting online technology), lack of quality-focused culture, staff reporting apprehensiveness, and fear of blame or punishment [ 36 , 41 , 85 , 86 ]. The technical dimension barriers of CQI can include various factors that hinder the effective implementation and execution of CQI processes [ 36 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 ]. Structural dimension barriers of CQI arise from the organization structure, process, and systems that can impede the effective implementation and sustainability of CQI [ 36 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 ]. Strategic dimension barriers are, for example, the inability to select proper CQI goals and failure to integrate CQI into organizational planning and goals [ 36 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 90 ].
Facilitators are also grouped to cultural, structural, technical, and strategic dimensions to provide solutions to CQI barriers. Cultural challenges were addressed by developing a group culture to CQI and other rewards [ 39 , 41 , 80 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 90 , 91 , 92 ]. Technical facilitators are pivotal to improving technical barriers [ 39 , 42 , 53 , 69 , 86 , 90 , 91 ]. Structural-related facilitators are related to improving communication, infrastructure, and systems [ 86 , 92 , 93 ]. Strategic dimension facilitators include strengthening leadership and improving decision-making skills [ 43 , 53 , 67 , 86 , 87 , 92 , 94 , 95 ] (Table 2 ).
Impact of continuous quality improvement
Continuous quality improvement initiatives can significantly impact the quality of healthcare in a wide range of health areas, focusing on improving structure, the health service delivery process and improving client wellbeing and reducing mortality.
Structure components
These are health leadership, financing, workforce, technology, and equipment and supplies. CQI has improved planning, monitoring and evaluation [ 48 , 53 ], and leadership and planning [ 48 ], indicating improvement in leadership perspectives. Implementing CQI in primary health care (PHC) settings has shown potential for maintaining or reducing operation costs [ 67 ]. Findings from another study indicate that the costs associated with implementing CQI interventions per facility ranged from approximately $2,000 to $10,500 per year, with an average cost of approximately $10 to $60 per admitted client [ 57 ]. However, based on model predictions, the average cost savings after implementing CQI were estimated to be $5430 [ 31 ]. CQI can also be applied to health workforce development [ 32 ]. CQI in the institutional system improved medical education [ 66 , 96 , 97 ], human resources management [ 53 ], motivated staffs [ 76 ], and increased staff health awareness [ 69 ], while concerns raised about CQI impartiality, independence, and public accountability [ 96 ]. Regarding health technology, CQI also improved registration and documentation [ 48 , 53 , 98 ]. Furthermore, the CQI initiatives increased cleanliness [ 54 ] and improved logistics, supplies, and equipment [ 48 , 53 , 68 ].
Process and output components
The process component focuses on the activities and actions involved in delivering healthcare services.
Service delivery
CQI interventions improved service delivery [ 53 , 56 , 99 ], particularly a significant 18% increase in the overall quality of service performance [ 48 ], improved patient counselling, adherence to appropriate procedures, and infection prevention [ 48 , 68 ], and optimised workflow [ 52 ].
Coordination and collaboration
CQI initiatives improved coordination and collaboration through collecting and analysing data, onsite technical support, training, supportive supervision [ 53 ] and facilitating linkages between work processes and a quality control group [ 65 ].
Patient satisfaction
The CQI initiatives increased patient satisfaction and improved quality of life by optimizing care quality management, improving the quality of clinical nursing, reducing nursing defects and enhancing the wellbeing of clients [ 54 , 76 , 100 ], although CQI was not associated with changes in adolescent and young adults’ satisfaction [ 51 ].
CQI initiatives reduced medication error reports from 16 to 6 [ 101 ], and it significantly reduced the administration of inappropriate prophylactic antibiotics [ 44 ], decreased errors in inpatient care [ 52 ], decreased the overall episiotomy rate from 44.5 to 33.3% [ 83 ], reduced the overall incidence of unplanned endotracheal extubation [ 102 ], improving appropriate use of computed tomography angiography [ 103 ], and appropriate diagnosis and treatment selection [ 47 ].
Continuity of care
CQI initiatives effectively improve continuity of care by improving client and physician interaction. For instance, provider continuity levels showed a 64% increase [ 55 ]. Modifying electronic medical record templates, scheduling, staff and parental education, standardization of work processes, and birth to 1-year age-specific incentives in post-natal follow-up care increased continuity of care to 74% in 2018 compared to baseline 13% in 2012 [ 84 ].
The CQI initiative yielded enhanced efficiency in the cardiac catheterization laboratory, as evidenced by improved punctuality in procedure starts and increased efficiency in manual sheath-pulls inside [ 78 ].
Accessibility
CQI initiatives were effective in improving accessibility in terms of increasing service coverage and utilization rate. For instance, screening for cigarettes, nutrition counselling, folate prescription, maternal care, immunization coverage [ 53 , 81 , 104 , 105 ], reducing the percentage of non-attending patients to surgery to 0.9% from the baseline 3.9% [ 43 ], increasing Chlamydia screening rates from 29 to 60% [ 45 ], increasing HIV care continuum coverage [ 51 , 59 , 60 ], increasing in the uptake of postpartum long-acting reversible contraceptive use from 6.9% at the baseline to 25.4% [ 42 ], increasing post-caesarean section prophylaxis from 36 to 89% [ 62 ], a 31% increase of kangaroo care practice [ 50 ], and increased follow-up [ 65 ]. Similarly, the QI intervention increased the quality of antenatal care by 29.3%, correct partograph use by 51.7%, and correct active third-stage labour management, a 19.6% improvement from the baseline, but not significantly associated with improvement in contraceptive service uptake [ 61 ].
Timely access
CQI interventions improved the time care provision [ 52 ], and reduced waiting time [ 62 , 74 , 76 , 106 ]. For instance, the discharge process waiting time in the emergency department decreased from 76 min to 22 min [ 79 ]. It also reduced mean postprocedural length of stay from 2.8 days to 2.0 days [ 31 ].
Acceptability
Acceptability of CQI by healthcare providers was satisfactory. For instance, 88% of the faculty, 64% of the residents, and 82% of the staff believed CQI to be useful in the healthcare clinic [ 107 ].
Outcome components
Morbidity and mortality.
CQI efforts have demonstrated better management outcomes among diabetic patients [ 40 ], patients with oral mucositis [ 71 ], and anaemic patients [ 72 ]. It has also reduced infection rate in post-caesarean Sect. [ 62 ], reduced post-peritoneal dialysis peritonitis [ 49 , 108 ], and prevented pressure ulcers [ 70 ]. It is explained by peritonitis incidence from once every 40.1 patient months at baseline to once every 70.8 patient months after CQI [ 49 ] and a 63% reduction in pressure ulcer prevalence within 2 years from 2008 to 2010 [ 70 ]. Furthermore, CQI initiatives significantly reduced in-hospital deaths [ 31 ] and increased patient survival rates [ 108 ]. Figure 2 displays the overall process of the CQI implementations.
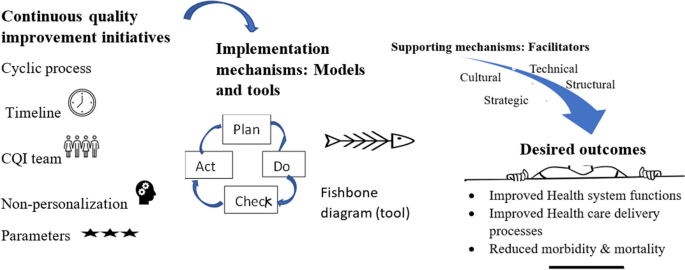
The overall mechanisms of continuous quality improvement implementation
In this review, we examined the fundamental concepts and principles underlying CQI, the factors that either hinder or assist in its successful application and implementation, and the purpose of CQI in enhancing quality of care across various health issues.
Our findings have brought attention to the application and implementation of CQI, emphasizing its underlying concepts and principles, as evident in the existing literature [ 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 39 , 40 , 43 , 45 , 46 ]. Continuous quality improvement has shared with the principles of continuous improvement, such as a customer-driven focus, effective leadership, active participation of individuals, a process-oriented approach, systematic implementation, emphasis on design improvement and prevention, evidence-based decision-making, and fostering partnership [ 5 ]. Moreover, Deming’s 14 principles laid the foundation for CQI principles [ 109 ]. These principles have been adapted and put into practice in various ways: ten [ 19 ] and five [ 38 ] principles in hospitals, five principles for capacity building [ 38 ], and two principles for medication error prevention [ 41 ]. As a principle, the application of CQI can be process-focused [ 8 , 19 ] or impact-focused [ 38 ]. Impact-focused CQI focuses on achieving specific outcomes or impacts, whereas process-focused CQI prioritizes and improves the underlying processes and systems. These principles complement each other and can be utilized based on the objectives of quality improvement initiatives in healthcare settings. Overall, CQI is an ongoing educational process that requires top management’s involvement, demands coordination across departments, encourages the incorporation of views beyond clinical area, and provides non-judgemental evidence based on objective data [ 110 ].
The current review recognized that it was not easy to implement CQI. It requires reasonable utilization of various models and tools. The application of each tool can be varied based on the studied health problem and the purpose of CQI initiative [ 111 ], varied in context, content, structure, and usability [ 112 ]. Additionally, overcoming the cultural, technical, structural, and strategic-related barriers. These barriers have emerged from clinical staff, managers, and health systems perspectives. Of the cultural obstacles, staff non-involvement, resistance to change, and reluctance to report error were staff-related. In contrast, others, such as the absence of celebration for success and hierarchical and rational culture, may require staff and manager involvement. Staff members may exhibit reluctance in reporting errors due to various cultural factors, including lack of trust, hierarchical structures, fear of retribution, and a blame-oriented culture. These challenges pose obstacles to implementing standardized CQI practices, as observed, for instance, in community pharmacy settings [ 85 ]. The hierarchical culture, characterized by clearly defined levels of power, authority, and decision-making, posed challenges to implementing CQI initiatives in public health [ 41 , 86 ]. Although rational culture, a type of organizational culture, emphasizes logical thinking and rational decision-making, it can also create challenges for CQI implementation [ 41 , 86 ] because hierarchical and rational cultures, which emphasize bureaucratic norms and narrow definitions of achievement, were found to act as barriers to the implementation of CQI [ 86 ]. These could be solved by developing a shared mindset and collective commitment, establishing a shared purpose, developing group norms, and cultivating psychological preparedness among staff, managers, and clients to implement and sustain CQI initiatives. Furthermore, reversing cultural-related barriers necessitates cultural-related solutions: development of a culture and group culture to CQI [ 41 , 86 ], positive comprehensive perception [ 91 ], commitment [ 85 ], involving patients, families, leaders, and staff [ 39 , 92 ], collaborating for a common goal [ 80 , 86 ], effective teamwork [ 86 , 87 ], and rewarding and celebrating successes [ 80 , 90 ].
The technical dimension barriers of CQI can include inadequate capitalization of a project and insufficient support for CQI facilitators and data entry managers [ 36 ], immature electronic medical records or poor information systems [ 36 , 86 ], and the lack of training and skills [ 86 , 87 , 88 ]. These challenges may cause the CQI team to rely on outdated information and technologies. The presence of barriers on the technical dimension may challenge the solid foundation of CQI expertise among staff, the ability to recognize opportunities for improvement, a comprehensive understanding of how services are produced and delivered, and routine use of expertise in daily work. Addressing these technical barriers requires knowledge creation activities (training, seminar, and education) [ 39 , 42 , 53 , 69 , 86 , 90 , 91 ], availability of quality data [ 86 ], reliable information [ 92 ], and a manual-online hybrid reporting system [ 85 ].
Structural dimension barriers of CQI include inadequate communication channels and lack of standardized process, specifically weak physician-to-physician synergies [ 36 ], lack of mechanisms for disseminating knowledge and limited use of communication mechanisms [ 86 ]. Lack of communication mechanism endangers sharing ideas and feedback among CQI teams, leading to misunderstandings, limited participation and misinterpretations, and a lack of learning [ 113 ]. Knowledge translation facilitates the co-production of research, subsequent diffusion of knowledge, and the developing stakeholder’s capacity and skills [ 114 ]. Thus, the absence of a knowledge translation mechanism may cause missed opportunities for learning, inefficient problem-solving, and limited creativity. To overcome these challenges, organizations should establish effective communication and information systems [ 86 , 93 ] and learning systems [ 92 ]. Though CQI and knowledge translation have interacted with each other, it is essential to recognize that they are distinct. CQI focuses on process improvement within health care systems, aiming to optimize existing processes, reduce errors, and enhance efficiency.
In contrast, knowledge translation bridges the gap between research evidence and clinical practice, translating research findings into actionable knowledge for practitioners. While both CQI and knowledge translation aim to enhance health care quality and patient outcomes, they employ different strategies: CQI utilizes tools like Plan-Do-Study-Act cycles and statistical process control, while knowledge translation involves knowledge synthesis and dissemination. Additionally, knowledge translation can also serve as a strategy to enhance CQI. Both concepts share the same principle: continuous improvement is essential for both. Therefore, effective strategies on the structural dimension may build efficient and effective steering councils, information systems, and structures to diffuse learning throughout the organization.
Strategic factors, such as goals, planning, funds, and resources, determine the overall purpose of CQI initiatives. Specific barriers were improper goals and poor planning [ 36 , 86 , 88 ], fragmentation of quality assurance policies [ 87 ], inadequate reinforcement to staff [ 36 , 90 ], time constraints [ 85 , 86 ], resource inadequacy [ 86 ], and work overload [ 86 ]. These barriers can be addressed through strengthening leadership [ 86 , 87 ], CQI-based mentoring [ 94 ], periodic monitoring, supportive supervision and coaching [ 43 , 53 , 87 , 92 , 95 ], participation, empowerment, and accountability [ 67 ], involving all stakeholders in decision-making [ 86 , 87 ], a provider-payer partnership [ 64 ], and compensating staff for after-hours meetings on CQI [ 85 ]. The strategic dimension, characterized by a strategic plan and integrated CQI efforts, is devoted to processes that are central to achieving strategic priorities. Roles and responsibilities are defined in terms of integrated strategic and quality-related goals [ 115 ].
The utmost goal of CQI has been to improve the quality of care, which is usually revealed by structure, process, and outcome. After resolving challenges and effectively using tools and running models, the goal of CQI reflects the ultimate reason and purpose of its implementation. First, effectively implemented CQI initiatives can improve leadership, health financing, health workforce development, health information technology, and availability of supplies as the building blocks of a health system [ 31 , 48 , 53 , 68 , 98 ]. Second, effectively implemented CQI initiatives improved care delivery process (counselling, adherence with standards, coordination, collaboration, and linkages) [ 48 , 53 , 65 , 68 ]. Third, the CQI can improve outputs of healthcare delivery, such as satisfaction, accessibility (timely access, utilization), continuity of care, safety, efficiency, and acceptability [ 52 , 54 , 55 , 76 , 78 ]. Finally, the effectiveness of the CQI initiatives has been tested in enhancing responses related to key aspects of the HIV response, maternal and child health, non-communicable disease control, and others (e.g., surgery and peritonitis). However, it is worth noting that CQI initiative has not always been effective. For instance, CQI using a two- to nine-times audit cycle model through systems assessment tools did not bring significant change to increase syphilis testing performance [ 116 ]. This study was conducted within the context of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people’s primary health care settings. Notably, ‘the clinics may not have consistently prioritized syphilis testing performance in their improvement strategies, as facilitated by the CQI program’ [ 116 ]. Additionally, by applying CQI-based mentoring, uptake of facility-based interventions was not significantly improved, though it was effective in increasing community health worker visits during pregnancy and the postnatal period, knowledge about maternal and child health and exclusive breastfeeding practice, and HIV disclosure status [ 117 ]. The study conducted in South Africa revealed no significant association between the coverage of facility-based interventions and Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI) implementation. This lack of association was attributed to the already high antenatal and postnatal attendance rates in both control and intervention groups at baseline, leaving little room for improvement. Additionally, the coverage of HIV interventions remained consistently high throughout the study period [ 117 ].
Regarding health care and policy implications, CQI has played a vital role in advancing PHC and fostering the realization of UHC goals worldwide. The indicators found in Donabedian’s framework that are positively influenced by CQI efforts are comparable to those included in the PHC performance initiative’s conceptual framework [ 29 , 118 , 119 ]. It is clearly explained that PHC serves as the roadmap to realizing the vision of UHC [ 120 , 121 ]. Given these circumstances, implementing CQI can contribute to the achievement of PHC principles and the objectives of UHC. For instance, by implementing CQI methods, countries have enhanced the accessibility, affordability, and quality of PHC services, leading to better health outcomes for their populations. CQI has facilitated identifying and resolving healthcare gaps and inefficiencies, enabling countries to optimize resource allocation and deliver more effective and patient-centered care. However, it is crucial to recognize that the successful implementation of Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI) necessitates optimizing the duration of each cycle, understanding challenges and barriers that extend beyond the health system and settings, and acknowledging that its effectiveness may be compromised if these challenges are not adequately addressed.
Despite abundant literature, there are still gaps regarding the relationship between CQI and other dimensions within the healthcare system. No studies have examined the impact of CQI initiatives on catastrophic health expenditure, effective service coverage, patient-centredness, comprehensiveness, equity, health security, and responsiveness.
Limitations
In conducting this review, it has some limitations to consider. Firstly, only articles published in English were included, which may introduce the exclusion of relevant non-English articles. Additionally, as this review follows a scoping methodology, the focus is on synthesising available evidence rather than critically evaluating or scoring the quality of the included articles.
Continuous quality improvement is investigated as a continuous and ongoing intervention, where the implementation time can vary across different cycles. The CQI team and implementation timelines were critical elements of CQI in different models. Among the commonly used approaches, the PDSA or PDCA is frequently employed. In most CQI models, a wide range of tools, nineteen tools, are commonly utilized to support the improvement process. Cultural, technical, structural, and strategic barriers and facilitators are significant in implementing CQI initiatives. Implementing the CQI initiative aims to improve health system blocks, enhance health service delivery process and output, and ultimately prevent morbidity and reduce mortality. For future researchers, considering that CQI is context-dependent approach, conducting scale-up implementation research about catastrophic health expenditure, effective service coverage, patient-centredness, comprehensiveness, equity, health security, and responsiveness across various settings and health issues would be valuable.
Availability of data and materials
The data used and/or analyzed during the current study are available in this manuscript and/or the supplementary file.
Shewhart WA, Deming WE. Memoriam: Walter A. Shewhart, 1891–1967. Am Stat. 1967;21(2):39–40.
Article Google Scholar
Shewhart WA. Statistical method from the viewpoint of quality control. New York: Dover; 1986. ISBN 978-0486652320. OCLC 13822053. Reprint. Originally published: Washington, DC: Graduate School of the Department of Agriculture, 1939.
Moen R, editor Foundation and History of the PDSA Cycle. Asian network for quality conference Tokyo. https://www.deming.org/sites/default/files/pdf/2015/PDSA_History_Ron_MoenPdf . 2009.
Kuperman G, James B, Jacobsen J, Gardner RM. Continuous quality improvement applied to medical care: experiences at LDS hospital. Med Decis Making. 1991;11(4suppl):S60–65.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Singh J, Singh H. Continuous improvement philosophy–literature review and directions. Benchmarking: An International Journal. 2015;22(1):75–119.
Goldstone J. Presidential address: Sony, Porsche, and vascular surgery in the 21st century. J Vasc Surg. 1997;25(2):201–10.
Radawski D. Continuous quality improvement: origins, concepts, problems, and applications. J Physician Assistant Educ. 1999;10(1):12–6.
Shortell SM, O’Brien JL, Carman JM, Foster RW, Hughes E, Boerstler H, et al. Assessing the impact of continuous quality improvement/total quality management: concept versus implementation. Health Serv Res. 1995;30(2):377.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lohr K. Quality of health care: an introduction to critical definitions, concepts, principles, and practicalities. Striving for quality in health care. 1991.
Berwick DM. The clinical process and the quality process. Qual Manage Healthc. 1992;1(1):1–8.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Gift B. On the road to TQM. Food Manage. 1992;27(4):88–9.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Greiner A, Knebel E. The core competencies needed for health care professionals. health professions education: A bridge to quality. 2003:45–73.
McCalman J, Bailie R, Bainbridge R, McPhail-Bell K, Percival N, Askew D et al. Continuous quality improvement and comprehensive primary health care: a systems framework to improve service quality and health outcomes. Front Public Health. 2018:6 (76):1–6.
Sheingold BH, Hahn JA. The history of healthcare quality: the first 100 years 1860–1960. Int J Afr Nurs Sci. 2014;1:18–22.
Google Scholar
Donabedian A. Evaluating the quality of medical care. Milbank Q. 1966;44(3):166–206.
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America. Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US). 2001. 2, Improving the 21st-century Health Care System. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK222265/ .
Rubinstein A, Barani M, Lopez AS. Quality first for effective universal health coverage in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet Global Health. 2018;6(11):e1142–1143.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Agency for Healthcare Reserach and Quality. Quality Improvement and monitoring at your fingertips USA,: Agency for Healthcare Reserach and Quality. 2022. Available from: https://qualityindicators.ahrq.gov/ .
Anderson CA, Cassidy B, Rivenburgh P. Implementing continuous quality improvement (CQI) in hospitals: lessons learned from the International Quality Study. Qual Assur Health Care. 1991;3(3):141–6.
Gardner K, Mazza D. Quality in general practice - definitions and frameworks. Aust Fam Physician. 2012;41(3):151–4.
PubMed Google Scholar
Loper AC, Jensen TM, Farley AB, Morgan JD, Metz AJ. A systematic review of approaches for continuous quality improvement capacity-building. J Public Health Manage Pract. 2022;28(2):E354.
Hill JE, Stephani A-M, Sapple P, Clegg AJ. The effectiveness of continuous quality improvement for developing professional practice and improving health care outcomes: a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2020;15(1):1–14.
Candas B, Jobin G, Dubé C, Tousignant M, Abdeljelil AB, Grenier S, et al. Barriers and facilitators to implementing continuous quality improvement programs in colonoscopy services: a mixed methods systematic review. Endoscopy Int Open. 2016;4(02):E118–133.
Peters MD, Marnie C, Colquhoun H, Garritty CM, Hempel S, Horsley T, et al. Scoping reviews: reinforcing and advancing the methodology and application. Syst Reviews. 2021;10(1):1–6.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
McGowan J, Straus S, Moher D, Langlois EV, O’Brien KK, Horsley T, et al. Reporting scoping reviews—PRISMA ScR extension. J Clin Epidemiol. 2020;123:177–9.
Donabedian A. Explorations in quality assessment and monitoring: the definition of quality and approaches to its assessment. Health Administration Press, Ann Arbor. 1980;1.
World Health Organization. Operational framework for primary health care: transforming vision into action. Geneva: World Health Organization and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF); 2020 [updated 14 December 2020; cited 2023 Nov Oct 17]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240017832 .
The Joanna Briggs Institute. The Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewers’ Manual :2014 edition. Australia: The Joanna Briggs Institute. 2014:88–91.
Rihal CS, Kamath CC, Holmes DR Jr, Reller MK, Anderson SS, McMurtry EK, et al. Economic and clinical outcomes of a physician-led continuous quality improvement intervention in the delivery of percutaneous coronary intervention. Am J Manag Care. 2006;12(8):445–52.
Ade-Oshifogun JB, Dufelmeier T. Prevention and Management of Do not return notices: a quality improvement process for Supplemental staffing nursing agencies. Nurs Forum. 2012;47(2):106–12.
Rubenstein L, Khodyakov D, Hempel S, Danz M, Salem-Schatz S, Foy R, et al. How can we recognize continuous quality improvement? Int J Qual Health Care. 2014;26(1):6–15.
O’Neill SM, Hempel S, Lim YW, Danz MS, Foy R, Suttorp MJ, et al. Identifying continuous quality improvement publications: what makes an improvement intervention ‘CQI’? BMJ Qual Saf. 2011;20(12):1011–9.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sibthorpe B, Gardner K, McAullay D. Furthering the quality agenda in Aboriginal community controlled health services: understanding the relationship between accreditation, continuous quality improvement and national key performance indicator reporting. Aust J Prim Health. 2016;22(4):270–5.
Bennett CL, Crane JM. Quality improvement efforts in oncology: are we ready to begin? Cancer Invest. 2001;19(1):86–95.
VanValkenburgh DA. Implementing continuous quality improvement at the facility level. Adv Ren Replace Ther. 2001;8(2):104–13.
Loper AC, Jensen TM, Farley AB, Morgan JD, Metz AJ. A systematic review of approaches for continuous quality improvement capacity-building. J Public Health Manage Practice. 2022;28(2):E354–361.
Ryan M. Achieving and sustaining quality in healthcare. Front Health Serv Manag. 2004;20(3):3–11.
Nicolucci A, Allotta G, Allegra G, Cordaro G, D’Agati F, Di Benedetto A, et al. Five-year impact of a continuous quality improvement effort implemented by a network of diabetes outpatient clinics. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(1):57–62.
Wakefield BJ, Blegen MA, Uden-Holman T, Vaughn T, Chrischilles E, Wakefield DS. Organizational culture, continuous quality improvement, and medication administration error reporting. Am J Med Qual. 2001;16(4):128–34.
Sori DA, Debelew GT, Degefa LS, Asefa Z. Continuous quality improvement strategy for increasing immediate postpartum long-acting reversible contraceptive use at Jimma University Medical Center, Jimma, Ethiopia. BMJ Open Qual. 2023;12(1):e002051.
Roche B, Robin C, Deleaval PJ, Marti MC. Continuous quality improvement in ambulatory surgery: the non-attending patient. Ambul Surg. 1998;6(2):97–100.
O’Connor JB, Sondhi SS, Mullen KD, McCullough AJ. A continuous quality improvement initiative reduces inappropriate prescribing of prophylactic antibiotics for endoscopic procedures. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94(8):2115–21.
Ursu A, Greenberg G, McKee M. Continuous quality improvement methodology: a case study on multidisciplinary collaboration to improve chlamydia screening. Fam Med Community Health. 2019;7(2):e000085.
Quick B, Nordstrom S, Johnson K. Using continuous quality improvement to implement evidence-based medicine. Lippincotts Case Manag. 2006;11(6):305–15 ( quiz 16 – 7 ).
Oyeledun B, Phillips A, Oronsaye F, Alo OD, Shaffer N, Osibo B, et al. The effect of a continuous quality improvement intervention on retention-in-care at 6 months postpartum in a PMTCT Program in Northern Nigeria: results of a cluster randomized controlled study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017;75(Suppl 2):S156–164.
Nyengerai T, Phohole M, Iqaba N, Kinge CW, Gori E, Moyo K, et al. Quality of service and continuous quality improvement in voluntary medical male circumcision programme across four provinces in South Africa: longitudinal and cross-sectional programme data. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(8):e0254850.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wang J, Zhang H, Liu J, Zhang K, Yi B, Liu Y, et al. Implementation of a continuous quality improvement program reduces the occurrence of peritonitis in PD. Ren Fail. 2014;36(7):1029–32.
Stikes R, Barbier D. Applying the plan-do-study-act model to increase the use of kangaroo care. J Nurs Manag. 2013;21(1):70–8.
Wagner AD, Mugo C, Bluemer-Miroite S, Mutiti PM, Wamalwa DC, Bukusi D, et al. Continuous quality improvement intervention for adolescent and young adult HIV testing services in Kenya improves HIV knowledge. AIDS. 2017;31(Suppl 3):S243–252.
Le RD, Melanson SE, Santos KS, Paredes JD, Baum JM, Goonan EM, et al. Using lean principles to optimise inpatient phlebotomy services. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67(8):724–30.
Manyazewal T, Mekonnen A, Demelew T, Mengestu S, Abdu Y, Mammo D, et al. Improving immunization capacity in Ethiopia through continuous quality improvement interventions: a prospective quasi-experimental study. Infect Dis Poverty. 2018;7:7.
Kamiya Y, Ishijma H, Hagiwara A, Takahashi S, Ngonyani HAM, Samky E. Evaluating the impact of continuous quality improvement methods at hospitals in Tanzania: a cluster-randomized trial. Int J Qual Health Care. 2017;29(1):32–9.
Kibbe DC, Bentz E, McLaughlin CP. Continuous quality improvement for continuity of care. J Fam Pract. 1993;36(3):304–8.
Adrawa N, Ongiro S, Lotee K, Seret J, Adeke M, Izudi J. Use of a context-specific package to increase sputum smear monitoring among people with pulmonary tuberculosis in Uganda: a quality improvement study. BMJ Open Qual. 2023;12(3):1–6.
Hunt P, Hunter SB, Levan D. Continuous quality improvement in substance abuse treatment facilities: how much does it cost? J Subst Abuse Treat. 2017;77:133–40.
Azadeh A, Ameli M, Alisoltani N, Motevali Haghighi S. A unique fuzzy multi-control approach for continuous quality improvement in a radio therapy department. Qual Quantity. 2016;50(6):2469–93.
Memiah P, Tlale J, Shimabale M, Nzyoka S, Komba P, Sebeza J, et al. Continuous quality improvement (CQI) institutionalization to reach 95:95:95 HIV targets: a multicountry experience from the Global South. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):711.
Yapa HM, De Neve JW, Chetty T, Herbst C, Post FA, Jiamsakul A, et al. The impact of continuous quality improvement on coverage of antenatal HIV care tests in rural South Africa: results of a stepped-wedge cluster-randomised controlled implementation trial. PLoS Med. 2020;17(10):e1003150.
Dadi TL, Abebo TA, Yeshitla A, Abera Y, Tadesse D, Tsegaye S, et al. Impact of quality improvement interventions on facility readiness, quality and uptake of maternal and child health services in developing regions of Ethiopia: a secondary analysis of programme data. BMJ Open Qual. 2023;12(4):e002140.
Weinberg M, Fuentes JM, Ruiz AI, Lozano FW, Angel E, Gaitan H, et al. Reducing infections among women undergoing cesarean section in Colombia by means of continuous quality improvement methods. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(19):2357–65.
Andreoni V, Bilak Y, Bukumira M, Halfer D, Lynch-Stapleton P, Perez C. Project management: putting continuous quality improvement theory into practice. J Nurs Care Qual. 1995;9(3):29–37.
Balfour ME, Zinn TE, Cason K, Fox J, Morales M, Berdeja C, et al. Provider-payer partnerships as an engine for continuous quality improvement. Psychiatric Serv. 2018;69(6):623–5.
Agurto I, Sandoval J, De La Rosa M, Guardado ME. Improving cervical cancer prevention in a developing country. Int J Qual Health Care. 2006;18(2):81–6.
Anderson CI, Basson MD, Ali M, Davis AT, Osmer RL, McLeod MK, et al. Comprehensive multicenter graduate surgical education initiative incorporating entrustable professional activities, continuous quality improvement cycles, and a web-based platform to enhance teaching and learning. J Am Coll Surg. 2018;227(1):64–76.
Benjamin S, Seaman M. Applying continuous quality improvement and human performance technology to primary health care in Bahrain. Health Care Superv. 1998;17(1):62–71.
Byabagambi J, Marks P, Megere H, Karamagi E, Byakika S, Opio A, et al. Improving the quality of voluntary medical male circumcision through use of the continuous quality improvement approach: a pilot in 30 PEPFAR-Supported sites in Uganda. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(7):e0133369.
Hogg S, Roe Y, Mills R. Implementing evidence-based continuous quality improvement strategies in an urban Aboriginal Community Controlled Health Service in South East Queensland: a best practice implementation pilot. JBI Database Syst Rev Implement Rep. 2017;15(1):178–87.
Hopper MB, Morgan S. Continuous quality improvement initiative for pressure ulcer prevention. J Wound Ostomy Cont Nurs. 2014;41(2):178–80.
Ji J, Jiang DD, Xu Z, Yang YQ, Qian KY, Zhang MX. Continuous quality improvement of nutrition management during radiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nurs Open. 2021;8(6):3261–70.
Chen M, Deng JH, Zhou FD, Wang M, Wang HY. Improving the management of anemia in hemodialysis patients by implementing the continuous quality improvement program. Blood Purif. 2006;24(3):282–6.
Reeves S, Matney K, Crane V. Continuous quality improvement as an ideal in hospital practice. Health Care Superv. 1995;13(4):1–12.
Barton AJ, Danek G, Johns P, Coons M. Improving patient outcomes through CQI: vascular access planning. J Nurs Care Qual. 1998;13(2):77–85.
Buttigieg SC, Gauci D, Dey P. Continuous quality improvement in a Maltese hospital using logical framework analysis. J Health Organ Manag. 2016;30(7):1026–46.
Take N, Byakika S, Tasei H, Yoshikawa T. The effect of 5S-continuous quality improvement-total quality management approach on staff motivation, patients’ waiting time and patient satisfaction with services at hospitals in Uganda. J Public Health Afr. 2015;6(1):486.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Jacobson GH, McCoin NS, Lescallette R, Russ S, Slovis CM. Kaizen: a method of process improvement in the emergency department. Acad Emerg Med. 2009;16(12):1341–9.
Agarwal S, Gallo J, Parashar A, Agarwal K, Ellis S, Khot U, et al. Impact of lean six sigma process improvement methodology on cardiac catheterization laboratory efficiency. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;85:S119.
Rahul G, Samanta AK, Varaprasad G A Lean Six Sigma approach to reduce overcrowding of patients and improving the discharge process in a super-specialty hospital. In 2020 International Conference on System, Computation, Automation and Networking (ICSCAN) 2020 July 3 (pp. 1-6). IEEE
Patel J, Nattabi B, Long R, Durey A, Naoum S, Kruger E, et al. The 5 C model: A proposed continuous quality improvement framework for volunteer dental services in remote Australian Aboriginal communities. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2023;51(6):1150–8.
Van Acker B, McIntosh G, Gudes M. Continuous quality improvement techniques enhance HMO members’ immunization rates. J Healthc Qual. 1998;20(2):36–41.
Horine PD, Pohjala ED, Luecke RW. Healthcare financial managers and CQI. Healthc Financ Manage. 1993;47(9):34.
Reynolds JL. Reducing the frequency of episiotomies through a continuous quality improvement program. CMAJ. 1995;153(3):275–82.
Bunik M, Galloway K, Maughlin M, Hyman D. First five quality improvement program increases adherence and continuity with well-child care. Pediatr Qual Saf. 2021;6(6):e484.
Boyle TA, MacKinnon NJ, Mahaffey T, Duggan K, Dow N. Challenges of standardized continuous quality improvement programs in community pharmacies: the case of SafetyNET-Rx. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2012;8(6):499–508.
Price A, Schwartz R, Cohen J, Manson H, Scott F. Assessing continuous quality improvement in public health: adapting lessons from healthcare. Healthc Policy. 2017;12(3):34–49.
Gage AD, Gotsadze T, Seid E, Mutasa R, Friedman J. The influence of continuous quality improvement on healthcare quality: a mixed-methods study from Zimbabwe. Soc Sci Med. 2022;298:114831.
Chan YC, Ho SJ. Continuous quality improvement: a survey of American and Canadian healthcare executives. Hosp Health Serv Adm. 1997;42(4):525–44.
Balas EA, Puryear J, Mitchell JA, Barter B. How to structure clinical practice guidelines for continuous quality improvement? J Med Syst. 1994;18(5):289–97.
ElChamaa R, Seely AJE, Jeong D, Kitto S. Barriers and facilitators to the implementation and adoption of a continuous quality improvement program in surgery: a case study. J Contin Educ Health Prof. 2022;42(4):227–35.
Candas B, Jobin G, Dubé C, Tousignant M, Abdeljelil A, Grenier S, et al. Barriers and facilitators to implementing continuous quality improvement programs in colonoscopy services: a mixed methods systematic review. Endoscopy Int Open. 2016;4(2):E118–133.
Brandrud AS, Schreiner A, Hjortdahl P, Helljesen GS, Nyen B, Nelson EC. Three success factors for continual improvement in healthcare: an analysis of the reports of improvement team members. BMJ Qual Saf. 2011;20(3):251–9.
Lee S, Choi KS, Kang HY, Cho W, Chae YM. Assessing the factors influencing continuous quality improvement implementation: experience in Korean hospitals. Int J Qual Health Care. 2002;14(5):383–91.
Horwood C, Butler L, Barker P, Phakathi S, Haskins L, Grant M, et al. A continuous quality improvement intervention to improve the effectiveness of community health workers providing care to mothers and children: a cluster randomised controlled trial in South Africa. Hum Resour Health. 2017;15(1):39.
Hyrkäs K, Lehti K. Continuous quality improvement through team supervision supported by continuous self-monitoring of work and systematic patient feedback. J Nurs Manag. 2003;11(3):177–88.
Akdemir N, Peterson LN, Campbell CM, Scheele F. Evaluation of continuous quality improvement in accreditation for medical education. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20(Suppl 1):308.
Barzansky B, Hunt D, Moineau G, Ahn D, Lai CW, Humphrey H, et al. Continuous quality improvement in an accreditation system for undergraduate medical education: benefits and challenges. Med Teach. 2015;37(11):1032–8.
Gaylis F, Nasseri R, Salmasi A, Anderson C, Mohedin S, Prime R, et al. Implementing continuous quality improvement in an integrated community urology practice: lessons learned. Urology. 2021;153:139–46.
Gaga S, Mqoqi N, Chimatira R, Moko S, Igumbor JO. Continuous quality improvement in HIV and TB services at selected healthcare facilities in South Africa. South Afr J HIV Med. 2021;22(1):1202.
Wang F, Yao D. Application effect of continuous quality improvement measures on patient satisfaction and quality of life in gynecological nursing. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(6):6391–8.
Lee SB, Lee LL, Yeung RS, Chan J. A continuous quality improvement project to reduce medication error in the emergency department. World J Emerg Med. 2013;4(3):179–82.
Chiang AA, Lee KC, Lee JC, Wei CH. Effectiveness of a continuous quality improvement program aiming to reduce unplanned extubation: a prospective study. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22(11):1269–71.
Chinnaiyan K, Al-Mallah M, Goraya T, Patel S, Kazerooni E, Poopat C, et al. Impact of a continuous quality improvement initiative on appropriate use of coronary CT angiography: results from a multicenter, statewide registry, the advanced cardiovascular imaging consortium (ACIC). J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2011;5(4):S29–30.
Gibson-Helm M, Rumbold A, Teede H, Ranasinha S, Bailie R, Boyle J. A continuous quality improvement initiative: improving the provision of pregnancy care for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander women. BJOG: Int J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;122:400–1.
Bennett IM, Coco A, Anderson J, Horst M, Gambler AS, Barr WB, et al. Improving maternal care with a continuous quality improvement strategy: a report from the interventions to minimize preterm and low birth weight infants through continuous improvement techniques (IMPLICIT) network. J Am Board Fam Med. 2009;22(4):380–6.
Krall SP, Iv CLR, Donahue L. Effect of continuous quality improvement methods on reducing triage to thrombolytic interval for Acute myocardial infarction. Acad Emerg Med. 1995;2(7):603–9.
Swanson TK, Eilers GM. Physician and staff acceptance of continuous quality improvement. Fam Med. 1994;26(9):583–6.
Yu Y, Zhou Y, Wang H, Zhou T, Li Q, Li T, et al. Impact of continuous quality improvement initiatives on clinical outcomes in peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int. 2014;34(Suppl 2):S43–48.
Schiff GD, Goldfield NI. Deming meets Braverman: toward a progressive analysis of the continuous quality improvement paradigm. Int J Health Serv. 1994;24(4):655–73.
American Hospital Association Division of Quality Resources Chicago, IL: The role of hospital leadership in the continuous improvement of patient care quality. American Hospital Association. J Healthc Qual. 1992;14(5):8–14,22.
Scriven M. The Logic and Methodology of checklists [dissertation]. Western Michigan University; 2000.
Hales B, Terblanche M, Fowler R, Sibbald W. Development of medical checklists for improved quality of patient care. Int J Qual Health Care. 2008;20(1):22–30.
Vermeir P, Vandijck D, Degroote S, Peleman R, Verhaeghe R, Mortier E, et al. Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. Int J Clin Pract. 2015;69(11):1257–67.
Eljiz K, Greenfield D, Hogden A, Taylor R, Siddiqui N, Agaliotis M, et al. Improving knowledge translation for increased engagement and impact in healthcare. BMJ open Qual. 2020;9(3):e000983.
O’Brien JL, Shortell SM, Hughes EF, Foster RW, Carman JM, Boerstler H, et al. An integrative model for organization-wide quality improvement: lessons from the field. Qual Manage Healthc. 1995;3(4):19–30.
Adily A, Girgis S, D’Este C, Matthews V, Ward JE. Syphilis testing performance in Aboriginal primary health care: exploring impact of continuous quality improvement over time. Aust J Prim Health. 2020;26(2):178–83.
Horwood C, Butler L, Barker P, Phakathi S, Haskins L, Grant M, et al. A continuous quality improvement intervention to improve the effectiveness of community health workers providing care to mothers and children: a cluster randomised controlled trial in South Africa. Hum Resour Health. 2017;15:1–11.
Veillard J, Cowling K, Bitton A, Ratcliffe H, Kimball M, Barkley S, et al. Better measurement for performance improvement in low- and middle-income countries: the primary Health Care Performance Initiative (PHCPI) experience of conceptual framework development and indicator selection. Milbank Q. 2017;95(4):836–83.
Barbazza E, Kringos D, Kruse I, Klazinga NS, Tello JE. Creating performance intelligence for primary health care strengthening in Europe. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):1006.
Assefa Y, Hill PS, Gilks CF, Admassu M, Tesfaye D, Van Damme W. Primary health care contributions to universal health coverage. Ethiopia Bull World Health Organ. 2020;98(12):894.
Van Weel C, Kidd MR. Why strengthening primary health care is essential to achieving universal health coverage. CMAJ. 2018;190(15):E463–466.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
The authors received no fund.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Public Health, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
Aklilu Endalamaw, Resham B Khatri, Tesfaye Setegn Mengistu, Daniel Erku & Yibeltal Assefa
College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Bahir Dar University, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia
Aklilu Endalamaw & Tesfaye Setegn Mengistu
Health Social Science and Development Research Institute, Kathmandu, Nepal
Resham B Khatri
Centre for Applied Health Economics, School of Medicine, Grifth University, Brisbane, Australia
Daniel Erku
Menzies Health Institute Queensland, Grifth University, Brisbane, Australia
International Institute for Primary Health Care in Ethiopia, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Eskinder Wolka & Anteneh Zewdie
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
AE conceptualized the study, developed the first draft of the manuscript, and managing feedbacks from co-authors. YA conceptualized the study, provided feedback, and supervised the whole processes. RBK provided feedback throughout. TSM provided feedback throughout. DE provided feedback throughout. EW provided feedback throughout. AZ provided feedback throughout. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Aklilu Endalamaw .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable because this research is based on publicly available articles.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Endalamaw, A., Khatri, R.B., Mengistu, T.S. et al. A scoping review of continuous quality improvement in healthcare system: conceptualization, models and tools, barriers and facilitators, and impact. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 487 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10828-0
Download citation
Received : 27 December 2023
Accepted : 05 March 2024
Published : 19 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10828-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Continuous quality improvement
- Quality of Care
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
U.S. Surveys
Pew Research Center has deep roots in U.S. public opinion research. Launched initially as a project focused primarily on U.S. policy and politics in the early 1990s, the Center has grown over time to study a wide range of topics vital to explaining America to itself and to the world. Our hallmarks: a rigorous approach to methodological quality, complete transparency as to our methods, and a commitment to exploring and evaluating ongoing developments in data collection. Learn more about how we conduct our domestic surveys here .
The American Trends Panel

Try our email course on polling
Want to know more about polling? Take your knowledge to the next level with a short email mini-course from Pew Research Center. Sign up now .
From the 1980s until relatively recently, most national polling organizations conducted surveys by telephone, relying on live interviewers to call randomly selected Americans across the country. Then came the internet. While it took survey researchers some time to adapt to the idea of online surveys, a quick look at the public polls on an issue like presidential approval reveals a landscape now dominated by online polls rather than phone polls.
Most of our U.S. surveys are conducted on the American Trends Panel (ATP), Pew Research Center’s national survey panel of over 10,000 randomly selected U.S. adults. ATP participants are recruited offline using random sampling from the U.S. Postal Service’s residential address file. Survey length is capped at 15 minutes, and respondents are reimbursed for their time. Respondents complete the surveys online using smartphones, tablets or desktop devices. We provide tablets and data plans to adults without home internet. Learn more about how people in the U.S. take Pew Research Center surveys.

Methods 101
Our video series helps explain the fundamental concepts of survey research including random sampling , question wording , mode effects , non probability surveys and how polling is done around. the world.
The Center also conducts custom surveys of special populations (e.g., Muslim Americans , Jewish Americans , Black Americans , Hispanic Americans , teenagers ) that are not readily studied using national, general population sampling. The Center’s survey research is sometimes paired with demographic or organic data to provide new insights. In addition to our U.S. survey research, you can also read more details on our international survey research , our demographic research and our data science methods.
Our survey researchers are committed to contributing to the larger community of survey research professionals, and are active in AAPOR and is a charter member of the American Association of Public Opinion Research (AAPOR) Transparency Initiative .
Frequently asked questions about surveys
- Why am I never asked to take a poll?
- Can I volunteer to be polled?
- Why should I participate in surveys?
- What good are polls?
- Do pollsters have a code of ethics? If so, what is in the code?
- How are your surveys different from market research?
- Do you survey Asian Americans?
- How are people selected for your polls?
- Do people lie to pollsters?
- Do people really have opinions on all of those questions?
- How can I tell a high-quality poll from a lower-quality one?
Reports on the state of polling
- Key Things to Know about Election Polling in the United States
- A Field Guide to Polling: 2020 Edition
- Confronting 2016 and 2020 Polling Limitations
- What 2020’s Election Poll Errors Tell Us About the Accuracy of Issue Polling
- Q&A: After misses in 2016 and 2020, does polling need to be fixed again? What our survey experts say
- Understanding how 2020 election polls performed and what it might mean for other kinds of survey work
- Can We Still Trust Polls?
- Political Polls and the 2016 Election
- Flashpoints in Polling: 2016
Sign up for our Methods newsletter
The latest on survey methods, data science and more, delivered quarterly.
OTHER RESEARCH METHODS
Sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

COMMENTS
Mixed methods research designs. There are different types of mixed methods research designs. The differences between them relate to the aim of the research, the timing of the data collection, and the importance given to each data type. As you design your mixed methods study, also keep in mind: Your research approach (inductive vs deductive)
Mixed Methods Research. Mixed methods research is an approach to research that combines both quantitative and qualitative research methods in a single study or research project. It is a methodological approach that involves collecting and analyzing both numerical (quantitative) and narrative (qualitative) data to gain a more comprehensive understanding of a research problem.
Mixed methods research combines the elements of two types of research: quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative data is collected through the use of surveys and experiments, for example, containing numerical measures such as ages, scores, and percentages.. Qualitative data involves non-numerical measures like beliefs, motivations, attitudes, and experiences, often derived through interviews ...
Mixed methods research is the type of research in which a researcher or team of researchers combines elements of qualitative and quantitative research approaches (e. g., use of qualitative and quantitative viewpoints, data collection, analysis, inference techniques) for the broad purposes of breadth and depth of understanding and corroboration. ...
Combining methods in social scientific research has recently gained momentum through a research strand called Mixed Methods Research (MMR). This approach, which explicitly aims to offer a framework for combining methods, has rapidly spread through the social and behavioural sciences, and this article offers an analysis of the approach from a field theoretical perspective. After a brief outline ...
Mixed methods approaches allows researchers to use a diversity of methods, combining inductive and deductive thinking, and offsetting limitations of exclusively quantitative and qualitative research through a complementary approach that maximizes strengths of each data type and facilitates a more comprehensive understanding of health issues and ...
Mixed methods research begins with the assumption that investigators, in understanding the social and health worlds, gather evidence based on the nature of the question ... (e.g., observations and interviews) or multiple types of quantitative evidence (e.g., surveys and diagnostic tests). It involves the intentional collection of .
What are the different types of mixed methods designs? Mixed methods research comprises different types of design categories, including explanatory, exploratory, parallel and nested (embedded) designs.2 Table 1 summarises the characteristics of each design, the process used and models of connecting or integrating data. For each type of research, an example was created to illustrate how each ...
Type of mixed‐methods study design Example; Sequential exploratory : Fisher and colleagues designed a mixed‐methods study to explore the prescribing activities of hospital pharmacists.9 The study had a sequential exploratory design: first, in a qualitative phase, 27 people were interviewed individually or in a focus group and the data were analysed, with the results grouped into themes.
Mixed method approaches allow researchers to use a diversity of methods, combining inductive and deductive thinking, and offsetting limitations of exclusively quantitative and qualitative research through a complementary approach that maximizes strengths of each data type and facilitates a more comprehensive understanding of health issues and ...
• an introduction to mixed methods research • the process involved in designing and conducting this form of inquiry, and • within this process, a focus on four types of mixed methods designs Two key elements form the central features of this book: the phases in the process of mixed methods research and four specific mixed methods designs.
Mixed methods research is an effective approach to understanding complex phenomena. It combines the strengths of quantitative and qualitative methods to provide a more comprehensive and nuanced perspective. Here is a breakdown of the pioneers of mixed-method research and how it has evolved over the years:
The relevance of mixed-methods in health research. The overall goal of the mixed-methods research design is to provide a better and deeper understanding, by providing a fuller picture that can enhance description and understanding of the phenomena [].Mixed-methods research has become popular because it uses quantitative and qualitative data in one single study which provides stronger inference ...
These are four of the most common mixed methods designs: Convergent parallel: Quantitative and qualitative data are collected at the same time and analyzed separately. After both analyses are complete, compare your results to draw overall conclusions. Embedded: Quantitative and qualitative data are collected at the same time, but within a ...
Mixed-methods research can be thought of as looking at a merry-go-round from different angles or with different methods. Photo by Jordan Ling. Mixed methods research relies on multiple research methods, data sets, or theoretical approaches to assemble a more comprehensive picture of a concept or phenomenon.
should be aware of the range of mixed methods design types, as well as the discipline-based discussions of mixed methods designs. Methodologists writing about mixed methods research have devoted a great deal of attention to classifying the different types of mixed methods designs. In the final chapter of the Handbook of Mixed Methods in Social
A description of mixed methods as a research design is presented below. 3. Mixed Methods as a Research Methodology A mixed-methods approach is a research methodology in its own right. As stated by Creswell and Plano Clark (2011), a mixed-methods research design is a research design that has its own philosophical assumptions and methods of inquiry.
"Mixed methods research is the type of research in which a researcher or team of researchers combines elements of qualitative and quantitative research approaches (e.g., use of qualitative and quantitative viewpoints, data collection, analysis, inference techniques) for the broad purposes of breadth and depth of understanding and ...
Traditionally, there are three branches of methodology: quantitative (numeric data), qualitative (observational or interview data), and mixed methods (using both types of data). Psychology relies heavily on quantitative-based data analyses but could benefit from incorporating the advantages of both quantitative and qualitative methodologies ...
You can also create a mixed methods research design that has elements of both. Descriptive research vs experimental research. Descriptive research gathers data without controlling any variables, while experimental research manipulates and controls variables to determine cause and effect.
Mixed methods research - In a Nutshell. Mixed methods research is a hybrid of quantitative research and qualitative research methodology. Researchers use the mixed approach to leverage the benefits of each research method. Mixed methods often yield more detailed findings, although they are limited by timelines and inadequate resources.
6 Types of Mixed Methods Designs. Sequential Explanatory Design *. Sequential Exploratory Design *. Sequential Transformative Design. Concurrent Triangulation Design. Concurrent Embedded Design **. Concurrent Transformative Design **. *most common. ** least common and not discussed.
Mixed Methods research is a type of research that uses multiple methods to gather data. This approach can help researchers identify hidden patterns and insights that would not be apparent from just one method. Mixed Methods research can be helpful when studying complex topics or when data from different sources is needed. Additionally, using ...
Mixed research method implies the use of different research methods, quantitative and qualitative methods in one study (2,3). Research on mixed methods should be distinguished from multi-method ... The four major types of mixed methods designs are the Triangulation Design, the Embedded Design, the Explanatory Design, and the Exploratory Design ...
Mixed methods research. Known as the third methodological movement, mixed methods research can be defined as empirical research that "combines elements of qualitative and quantitative research approaches (e.g., use of qualitative and quantitative viewpoints, data collection, analysis, inference techniques) for the broad purpose of breadth and depth of understanding and corroboration ...
Our research team will conduct a mixed-methods study to investigate the implementation and early effects of the two aforementioned policy changes on pregnancy and infant health equity. Our research aims are to: (1) evaluate implementation and early effects of the equity incentive payment program prenatal and early childhood healthcare outcomes ...
Qualitative Research. Where researchers collect non-numerical information, such as descriptions of behavioral phenomena, how people experience or interpret events, and/or answers to participants' open-ended responses. The researcher's variables andmethods used come from the researcher's experiences and can be modified as the research progresses.
The growing adoption of continuous quality improvement (CQI) initiatives in healthcare has generated a surge in research interest to gain a deeper understanding of CQI. However, comprehensive evidence regarding the diverse facets of CQI in healthcare has been limited. Our review sought to comprehensively grasp the conceptualization and principles of CQI, explore existing models and tools ...
Through an empirical mixed-methods synthesis three themes were developed 1) The importance of social connections on self-identity; 2) Self-views and quality of life; 3) Sport and the establishment of a new self. ... Future research exploring disabled veterans' identities should consider gender differences, disability type, and severity, to ...
Pew Research Center has deep roots in U.S. public opinion research. Launched initially as a project focused primarily on U.S. policy and politics in the early 1990s, the Center has grown over time to study a wide range of topics vital to explaining America to itself and to the world.Our hallmarks: a rigorous approach to methodological quality, complete transparency as to our methods, and a ...