LaTeX – A document preparation system
LaTeX is a high-quality typesetting system; it includes features designed for the production of technical and scientific documentation. LaTeX is the de facto standard for the communication and publication of scientific documents. LaTeX is available as free software .
You don't have to pay for using LaTeX, i.e., there are no license fees, etc. But you are, of course, invited to support the maintenance and development efforts through a donation to the TeX Users Group (choose LaTeX Project contribution) if you are satisfied with LaTeX.
You can also sponsor the work of LaTeX team members through the GitHub sponsor program at the moment for Frank , David and Joseph . Your contribution goes without any reductions by GitHub to the developers in support of the project.
The volunteer efforts that provide you with LaTeX need financial support, so thanks for any contribution you are willing to make.

Recent News
- 24 April, 2024 Development releases for the L3 Programming Layer
- 27 March, 2024 ISO PDF/UA-2 standard released - Examples made by LaTeX
- 26 March, 2024 Accessibility talks at DEIMS 2024 conference in Tokyo
- 25 November, 2023 Talks from the TUG Conference 2023 in Bonn
- 4 November, 2023 LaTeX 2023-11-01 released and distributed
- 10 June, 2023 LaTeX 2023-06-01 released and distributed
- 27 May, 2023 Final pre-release of LaTeX 2023-06-01 is available for testing
LaTeX the product
The latex3 project, latex books.
List of books on LaTeX in English, French, German, and Spanish.
Documentation
The official LaTeX help and documentation section.
Learn more about the people behind the LaTeX project.

Formatting a Research Paper Using LaTeX in Overleaf

Introduction: Formatting a Research Paper Using LaTeX in Overleaf

Welcome to a guide suitable for novice or expierienced users on formatting a research paper using LaTeX. LaTeX is a typesetting language that gives users vast control on how they format their papers. Through these instructions you will find a clear and direct guide that will allow easy navigation through Overleaf and Latex.
Estimated time: 15-30 minutes depending on your familiarity with LaTeX.
Materials:
Access to Overleaf
Step 1: Optional Background Information
For a better understanding of LaTeX and Overleaf, consider following the link below for a thirty-minute tutorial on the basics of LaTeX.
https://www.overleaf.com/learn/latex/Learn_LaTeX_in_30_minutes
Step 2: Open Overleaf
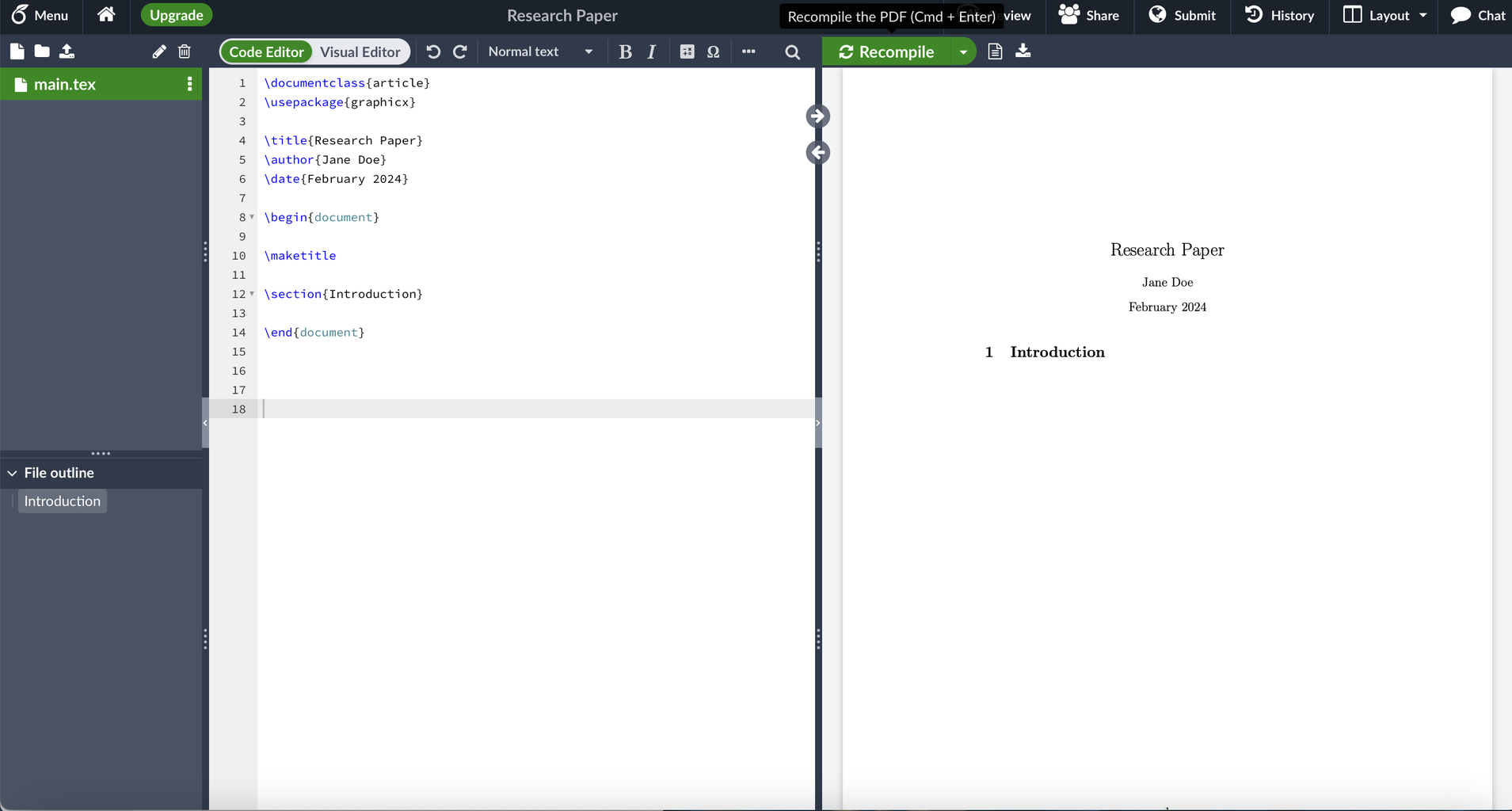
Open Overleaf, sign in, and press create a blank document. Above is what you should see.
Step 3: Change the Document Class and Import User Packages

Change the document class and import the following user packages shown below:
\usepackage{multirow} %allowed
\usepackage{listings} % allowed
\usepackage{amssymb} % allowed
\usepackage{natbib} % allowed
\usepackage{graphicx} % allowed
\usepackage{dirtytalk} % allowed
To the right of your code is what your document should look like so far after compiling.
Step 4: Include Author Information

Below the \author{} line, write the following lines to include additional details about the author:
\affiliation{%
\institution{University}
\streetaddress{123 Street}
\city{Chicago, IL}
\country{USA}
Replace the information inside the curly brackets with the information of your author. If you would like to include another author replicate this step again. If you would like to include your authors contact information, such as their email, under the affiliation block, write:
\email{[email protected]}
You can delete the \date{February 2024} line. Above is what your document should look like after compiling.
Step 5: Add Abstract

Below the \begin{document} block you can begin writing your abstract block by writing:
\begin{abstract}
On the line below, begin writing your abstract. After you finish writing your abstract, write \end{abstract} on the line below.
Above is what your document should look like after compiling.
Step 6: Add Keywords

Below the abstract block begin adding the keywords section by writing
\keywords{keyword, keyword2}
Replace the words inside the curly brackets with your keywords. Above is what your document should look like after compiling.
Step 7: Add Sections

Below the \maketitle section begin adding additional sections by using the \section{} command. Put your section title in between the curly brackets. You should already have an introduction section added, but for a research paper, I recommend adding a Related Work, Methodology, Results, and Conclusion section. After each section you can write the content you have for each section.
Above is what your document should look like after compiling.
Step 8: Add Subsections

To create subsections, use the \subsection{} command directly below the relevant \section{} line. Add the title of your subsection in between the curly brackets.
Step 9: Troubleshooting
It is very important to pay attention to case sensitivity. It is also important not to confuse \ with / in your document. Avoiding these syntax error will help your code run smoothly.
Congratulations! You have begun to format a research paper using LaTeX. Your document should look similar to the picture above, with your title, authors information, abtract, sections, and subsections neatly organized. You can now begin to further customize your document for your specific purpose.

Recommendations

For the Home Contest

Green Future Student Design Challenge

Pets and Animals Contest

Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications
Tips for Writing a Research Paper using LaTeX
guanyingc/latex_paper_writing_tips
Folders and files, repository files navigation, table of contents, examples for table organization, examples for figure organization, latex templates for cvpr/iccv/neurips paper submission, sample latex conference posters (cvpr/iccv/eccv/neurips), latex files for my thesis (sysu b.eng. + hku phd.), simple python programs for figure creation, great resources shared by others, brief introduction.
LaTeX is a very powerful tool for documentation preparation, and is often used by researchers to prepare a manuscript for reviewing and publication. However, some new graduate students might not have experience in using LaTeX and thus have a difficult time in prepare their first papers.
In this article (PDF) , we will first provide some tips for paper writing. Then, we will showcase several working examples for the tables and figures, which have been used in our previous publications. The readers are encouraged to adapt those tables and figures to their purposes to save time when preparing their first papers.
Overleaf Link: https://www.overleaf.com/read/hypvpvnzjjwx

More Resources
- 💥 Main Paper + Supplementary for Conference Submission (NeurIPS) in Overleaf
- 💥 Main Paper + Rebuttal + Supplementary for Conference Submission (CVPR/ICCV) in Overleaf

Download or fork the overleaf project: click the menu at the top left, and select Source or Copy

- Rebuttal for Conference Submission (CVPR/ICCV)
- Supplementary Material for Conference Submission (CVPR/ICCV/ECCV)
- TOM-Net: Learning Transparent Object Matting from a Single Image (CVPR 2018)
- PS-FCN: A Flexible Learning Framework for Photometric Stereo (ECCV 2018)
- Self-calibrating Deep Photometric Stereo Networks (CVPR 2019)
- HDR Video Reconstruction: A Coarse-to-fine Network and A Real-world Benchmark Dataset (ICCV 2021)
- PS-NeRF: Neural Inverse Rendering for Multi-view Photometric Stereo (ECCV 2022)
- S^3-NeRF: Neural Reflectance Field from Shading and Shadow under a Single Viewpoint (NeurIPS 2022)

- Single View Analysis of Non-Lambertian Objects Based on Deep Learning (PhD Thesis, HKU CS)
- LaTex Template Files for Undergraduate Thesis (Sun Yat-sen University)
- A simple code for plotting figure, colorbar, and cropping with python
- Paper Writing Tips by MLNLP-World: https://github.com/MLNLP-World/Paper-Writing-Tips
- Paper Picture Writing Code by MLNLP-World: https://github.com/MLNLP-World/Paper-Picture-Writing-Code
- Makefile 0.4%

A Guide to Latex Editors for Academic Researchers
- Types of academic research abstracts
- What is the Differences between a Proofreader and a Copy Editor?

Table of Contents
What is LaTex?
LaTeX (pronounced Lay-tek) is a markup-level text editing tool that separates the process of word formatting from the task of content entry. LaTeX, which is quite comparable to HTML in terms of formatting, is one of the most widely used text editors in academia. For those who work with scientific papers and publishing, particularly those who work with a lot of mathematical equations, LaTeX text editors are pretty much the industry standard.
LaTeX is a free software package developed in 1985 as an extension to the TeX typesetting system by American computer scientist Leslie Lamport. LaTeX was designed to make it easier for TeX users to create general-purpose books and articles. Since LaTeX is an extension to the TeX typesetting system, it inherits TeX’s ability to typeset complex mathematical equations. This feature helped to establish LaTeX’s popularity among scientists and engineers.
The process of creating a LaTeX manuscript begins with a text file containing content that has been tagged with special LaTeX codes that specify how the text will be styled. When a LaTeX processor is used to process the file, typeset pages are generated. Due to the fact that LaTeX typesetting involves wrapping text in complex computer rules (markup code), it has a relatively steep learning curve. Although there are presently software programs that assist in automating the creation of LaTeX documents, this type of typesetting still requires a working knowledge of LaTeX.
LaTeX was among the first typesetting programs to support the generation of complex mathematical equations. It has been used to typeset numerous science, mathematics, and engineering journals and publications over the years. The American Mathematical Society (AMS) even has its own set of extensions, renamed AMS-LaTeX, which contributors use to create articles for its journal. Today, it is also used in fields such as physics, engineering, computer science, linguistics, and economics.
Why you Should Learn to Use LaTex for Manuscript Preparation
LaTex is a markup language that is specifically designed for the needs of academic, technical and scientific texts. The LaTex markup language enables you to create complex mathematical formulas, constants, and symbols in your document. It also allows you to control the layout of your text with very high precision, as opposed to used conventional word processors such as Microsoft Word. This comes in handy when adjusting the format of your paper according to the journal’s style guide.
If you are not familiar with LaTex or have little experience with it, it might be difficult to get started on your own without any help from someone who has already mastered it. This is where LaTex Format Templates come in handy! They provide a pre-made structure for the content so that all you have to do is fill in the blanks. The templates will also give you access to professional-quality graphics for use in your documents.
LaTex can help in preparing your manuscript’s format according to a predefined journal style guide. The journal would commonly have a readily available LaTex template which you can use to add your content to. Using a template would be easier than writing up the LaTex markup from scratch. The advantages of LaTeX are that it can be edited with any text editor and there are no glitches caused by problems with different graphics cards setup or different printers setting.
How do LaTex Documents Work?
LaTeX is a document preparation system. It is the most widely used one, especially in the field of computer science, engineering and mathematical publications. It uses a free-form language for writing mathematical formulas. The LaTeX compiler then generates other formats like PDF or PS from the original markup language. LaTeX was designed to resemble American Typewriter fonts, but it does not have any other dependencies on the computer system used to view it.
Best LaTex Editor Software for Researchers
LaTeX packages provide a great way to make your writing more attractive and fancy. They enable you to produce high-quality graphics, equations, and tables without having to go through the hassle of learning how to use a tool like Inkscape or Illustrator. Packages offer a means for editing LaTex documents and the more advanced ones come in different price ranges.
Each LaTeX program has its own features that make it better for one task or another. If you are looking for a good LaTex Editor software package, there are several popular ones available for researchers. Five of the prominent and widely-used editors are presented hereafter.
If you enjoy working with open-source software, TeXmaker is a popular open-source, cross-platform solution for LaTeX editing. This application is available on all major platforms and has a number of features that make it a compelling alternative to any LaTeX text editor. To get started using TeXmaker, its configuration window enables users to configure all of the document’s essential settings before beginning work on it.
Additionally, TeXmaker’s ‘Quick start’ box enables users to configure spell-checking and other document layout parameters. The ‘Structure View’ feature enables users to segment their documents into distinct sections, identifying each one as they go. Inserting tables, mathematical formulas, cross-references, and images is rather simple with TeXmaker.
After establishing the foundation for your document’s layout with TeXmaker, the document can be compiled to obtain it in the PDF, HTML, or ODF file format. Another critical element of TeXmaker is the way it enables users to trace compilation problems.
All warnings and faults are provided to allow the user to take appropriate action. TeXmaker enables you to effortlessly fold/unfold sections/parts of your papers. Additionally, this tool is excellent for structuring the Bibliography portion of your manuscript. TeXmaker has a plethora of keyboard shortcuts, which makes the whole experience with this program rather beneficial. TeXmaker is, in general, one of the best LaTeX editors available for Linux, Mac, and Windows.
Some of the benefits of using TeXmaker:
- Simple to operate and adjust. The code can be collapsed (code folding). Compile the code effortlessly. There are almost 370 mathematical symbols available. It has a wizard for quickly creating a document. This Mac LaTeX editor software can find warnings and problems automatically. You can perform a text search within a folder and its subfolders. Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux are all supported operating systems.
LyX is one of the most popular LaTeX editors available today, thanks to its support for a variety of modern and innovative features. It is an open-source editor that runs on a variety of operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. It stresses the WYSIWYM writing style and features a straightforward graphical user interface. The program creates LateX documents effortlessly by utilizing numerous configurable capabilities such as an integrated equation editor and reference indexing.
While many choose LyX for mathematical documents, you may also use its extensive markup features to construct a structured novel or script. Additionally, you get support for referencing academic articles, link overlay, and the ability to compose a master thesis utilizing branched out nodes.
Additionally, you can author scientific articles complete with references and citations. Automatic index construction is a one-of-a-kind function available only in LyX. With its sophisticated mathematical tools, you may visually drag and drop equations and alter them directly on the screen.
Additionally, you get access to a large number of methods, theorems, and equation arrays. Having said that, what I enjoy most about it is how simple it is to write LaTeX documents without having to worry about formatting or design attributes. Simply said, if you are new to LaTeX word processing and wish to generate scientific documents, choose LyX. It is an excellent LaTeX editor that runs on Ubuntu, Windows, and Mac.
Some of the benefits of using LyX
- It supports tables and floating point numbers well.
- The document can be exported as a PDF.
- This LaTeX editor for Windows includes functionality for tables and captions.
- You are capable of writing documents in multiple languages.
- It provides text completion automatically.
- You can compare the document’s multiple versions.
- This application enables you to keep track of changes.
- The same ease is available on Windows, Mac, and Linux.
The Overleaf LaTex editor is a web-based LaTex exporter for Microsoft Word documents that is available for free. Additionally, Overleaf includes an undo/redo feature that enables you to alter a previously printed page. This is an excellent option if you wish to edit multiple papers concurrently (for example, numerous documents on a single subject).
Additionally, if you need to make tiny modifications to a document, such as placing a space between words, you will be able to do it immediately – no need to save and waste time searching for the relevant keystroke.
Some of the benefits of using Overleaf
- Overleaf offers a wide range of templates.
- It makes writing, editing, and publishing documents quicker.
- This application offers a real-time preview of code.
- Share with other people effortlessly.
- You can switch to LaTeX and Rich Text mode.
- Find LaTeX error in less time.
- You can track changes and comments in real-time.
TeXstudio is another prominent open-source and cross-platform LaTeX editor in academics. This tool is built on the previously discussed open-source TeXmaker. TeXstudio is essentially an expansion of the previously stated program, adding additional functionality and capabilities.
While the UI is very similar to TeXmaker, extra functions such as Document Word count, frequency count analysis, and more have turned it into a stand-alone full-featured LaTeX editing tool.
Among its notable features are syntax highlighting, reference checking, multi-cursor support, and over 1000 mathematical formulas. Citations are a significant component of scientific writings, and TeXstudio’s support for Link overlay assists significantly in this. TeXstudio’s Assistant feature enables anyone without extensive understanding of LaTeX editors to easily build up a file and insert blocks of pictures or tables wherever in the page.
Drag and drop images into this editor, and the Table Auto-formatter takes care of properly formatting your newly produced tables. These are the additional capabilities available in TeXstudio, in addition to the standard Structure viewing, Code folding, Spell checking, Auto-corrections, Syntax highlighting, and all other TeXmaker features.
Some of the benefits of using TeXstudio
- This tool has almost a thousand mathematical symbols.
- You can use bookmarks to keep track of key passages in your work.
- When you press control and click, references and filenames are turned to links.
- With a single mouse click, you may copy, paste, and insert table columns.
- It enables drag-and-drop picture loading into the editor.
TeXnicCenter
TeXnicCenter is another excellent LaTeX editor that was designed exclusively for the Windows operating system. TeXnicCenter operates on Windows and takes use of Microsoft’s MiKTeX typesetting package, which simplifies the processing of LaTeX texts in Microsoft Word. Additionally, TeXnicCenter is a free and open-source LaTeX editor, which is wonderful. In terms of features, it includes practically everything you might desire in a LaTeX editor.
You have a robust graphical user interface editor with auto-completion and support for hundreds of UTF-8 character encodings. Additionally, TeXnicCenter uses a master-branch navigator to assist users in navigating LaTeX documents.
TeXnicCenter includes all of the standard syntax highlighting, bracket matching, and spell checking functions. To summarize, if you are a Windows user, TeXnicCenter is one of the best LaTeX editors available in 2021.
Some of the benefits of using TeXnicCenter
- TeXnicCenter includes an easy-to-use setup wizard.
- The interface is simple to use, including toolbars and menus.
- It is possible to customize tools.
- It comes equipped with syntax highlighting.
- This editor is UTF-8 compatible (Unicode Transformation Format).
- Matches the parentheses automatically.
- It is a free and open-source application.
- Compatible with Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Leave a reply Click here to cancel the reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
4.8 4.8 out of 5 stars (based on 16 reviews) Excellent 81% Very good 19% Average 0% Poor 0% Terrible 0%
See More Reviews


- Future Students
- Parents and Families
College of Engineering
- Research and Facilities
- Departments
Guide to Writing Your Thesis in LaTeX
Step 1: install latex and a latex aware editor.
LaTeX is not a word processor, it is a document preparation system for high-quality typesetting. It is most often used for medium-to-large technical or scientific documents, but it can be used for almost any form of publishing. LaTeX encourages authors not to worry too much about the appearance of their documents but to concentrate on getting the content right.
Because LaTeX source files are just ordinary text files, any text editor can be used to edit them, but it is important to have a LaTeX aware editor. A LaTeX aware editor can do things like syntax highlighting, spell checking, and automatic formatting. It can also run LaTeX on the source files, update the bibliography, then update the document in a viewer all at the click of a button.
Below are links to what you need to get started on various operating systems. Check out the LaTeX Project website for more information.
Your system distribution or vendor has probably provided a LaTeX system. If not, check your usual software source for the texlive package, or otherwise install texlive directly. All of the Linux systems in the ELE Department already have a complete LaTeX system installed.
Two good editors for Linux are Texmaker and TeXstudio .
MacTeX is a full LaTeX system for MacOS which includes an editor.
The editors Texmaker and TeXstudio can also be used.
Microsoft Windows
proTeXt is a full LaTeX system for Windows, which includes MikTeX and an editor. You can also install MikTeX directly with the editor of your choice.
There are numerous good editors for Windows, some of which are TeXnicCenter , Texmaker and TeXstudio .
- About the author

Using LaTeX for writing research papers
Many researchers are using Microsoft Word for writing research papers . However, Microsoft Word has several problems or limitations. In this blog post, I will discuss the use of LaTeX as an alternative to Microsoft Word for writing research papers .
What is LaTeX?
LaTeX is a document preparation system, proposed in the 1980s. It is used to create documents such as research papers , books, or even slides for presentations.
The key difference between LaTeX and software like Microsoft Word is that Microsoft Word let you directly edit your document and immediately see the result, while using LaTeX is a bit like programming. To write a research paper using LaTeX , you have to write a text file with the .tex extension using a formatting language to roughly indicate how your paper should look like. Then, you can run the LaTeX engine to generate a PDF file of your research paper. The following figure illustrate this process:
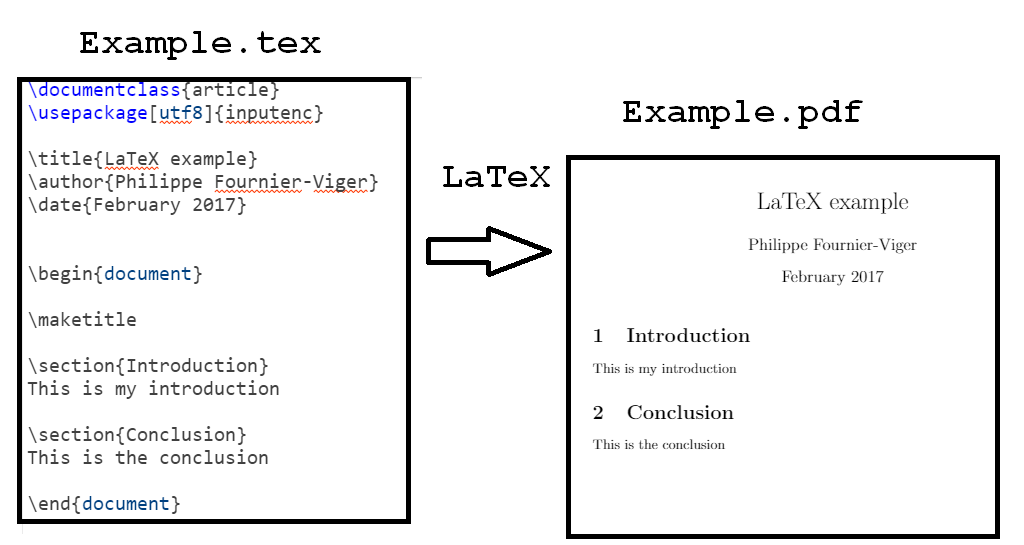
In the above example, I have created a very simple LaTeX document ( Example.tex ) and then I have generated the corresponding PDF for visualization ( Example.pdf ).
Why using LaTeX?
There are several reasons why many researchers prefer LaTeX to Microsoft Word for writing research papers . I will explain some of them, and then I will discuss also some problems about using LaTeX .
Reason 1: LaTeX papers generally look better
LaTeX papers often look better than papers written using Microsoft Word. This is especially true for fields like computer science, mathematics and engineering where mathematical equations are used. To illustrate this point, I will show you some screenshots of a paper that I have written for the ADMA 2012 conference a few years ago. For this paper, I had made two versions: one using the Springer LNCS LaTeX template and the other one using the Springer LNCS Microsoft Word template.
This is the first page of the paper.

The first page is quite similar. The main difference is the font being used, which is different using LaTeX . Personally, I prefer the default LaTeX font. Now let’s compare how the mathematical equations appears in Latex and Word.

Here, we can see that mathematical symbols are more beautiful using LaTeX . For example, the set union and the subset inclusion operators are in my opinion quite ugly in Microsoft Word. The set union operator of Word looks too much like the letter “U”. In this example, the mathematical equations are quite simple. But LaTeX really shines when displaying more complex mathematical equations, for example using matrices.
Now let’s look at another paragraph of text from the paper to further compare the appearance of Word and LaTeX papers :

In the above picture, it can be argued that both LaTeX and Word papers look quite similar. For me, the big difference is again in the font being used. In the Springer Word template, the Times New Roman font, while LaTeX has its own default font. I prefer the LaTeX font. Also, I think that the URLs look better in LaTeX using the url package.
Reason 2: LaTeX is available for all platforms
The LaTeX system is free and available for most operating systems, and documents will look the same on all operating systems.
To install LaTeX on your computer you need to install a LaTeX distribution such as MikTeK ( https://miktex.org/ ). After installing LaTeX , you can start working on LaTeX documents using a text editor such as Notepad. However, it is more convenient to also install an editor such as TexWorks or WinShell. Personally, I use TexWorks. This is a screenshot of my working environment using TexWorks:
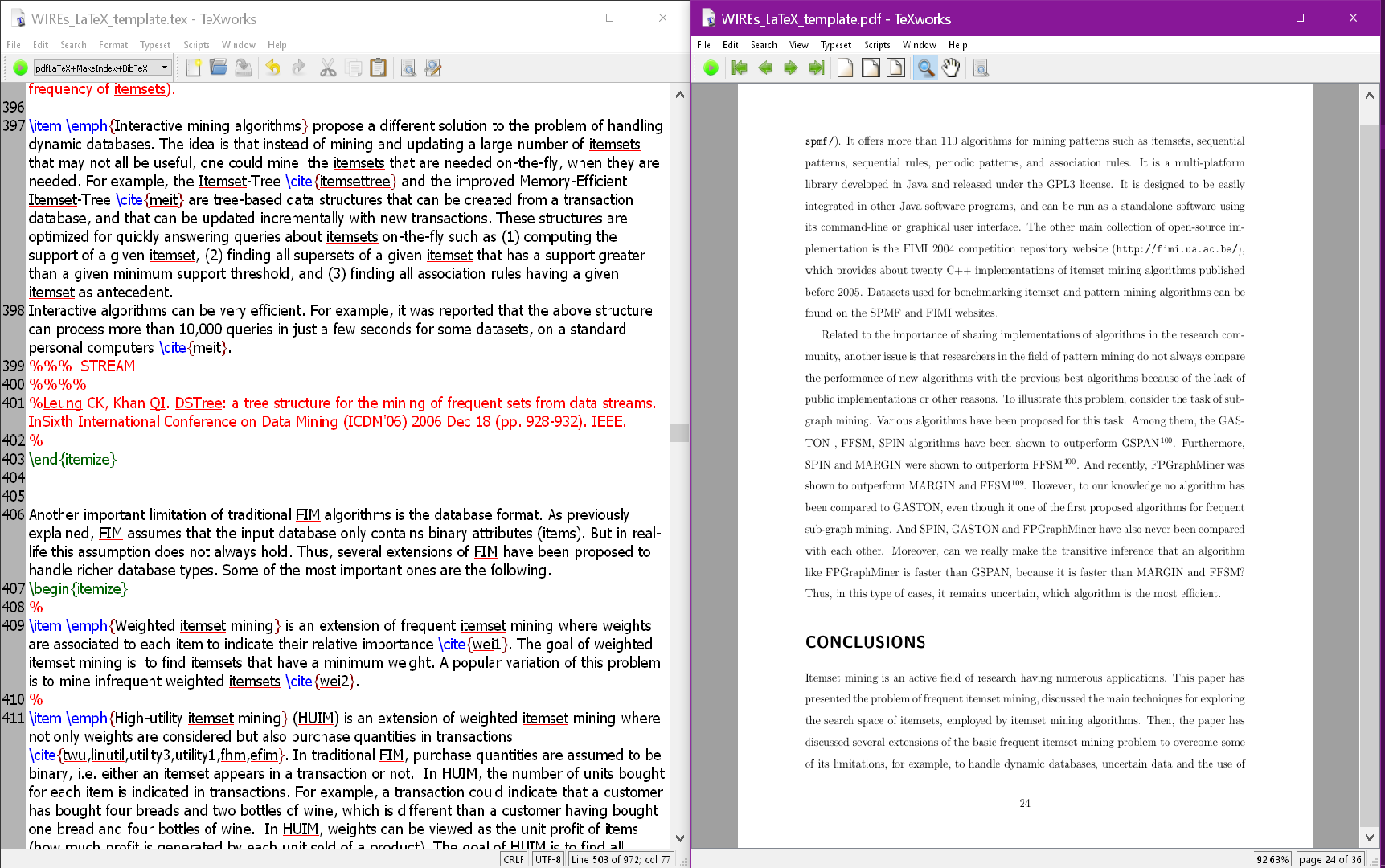
I will open my LaTeX document on the left window. Then, the right window will display the PDF generated by LaTeX . Thus, I can work on the LaTeX code of my documents on the left and see the result on the right.
If you want to try LaTeX without installing it on your computer, you can use an online LaTeX editor such as ShareLatex (http://www.sharelatex.org ) or OverLeaf. Using these editors, it is not necessary to install LaTeX on your computer. I personally sometimes use ShareLatex as it also has some function for collaboration (history, chat, etc.), which is very useful when working on a research paper with other people.
Reason 3: LaTeX offers many packages
Besides the basic functionalities of LaTeX , you can install hundreds of packages to add more features to LaTeX . If you use MikTek for example, there is a tool called the “MikTek package manager” that let you choose and install packages. There are packages for about everything from packages to display algorithms to packages for displaying chessboards. For example, here is some algorithm pseudocode that I have written in one of my recent paper using a LaTeX package called algorithm2e :
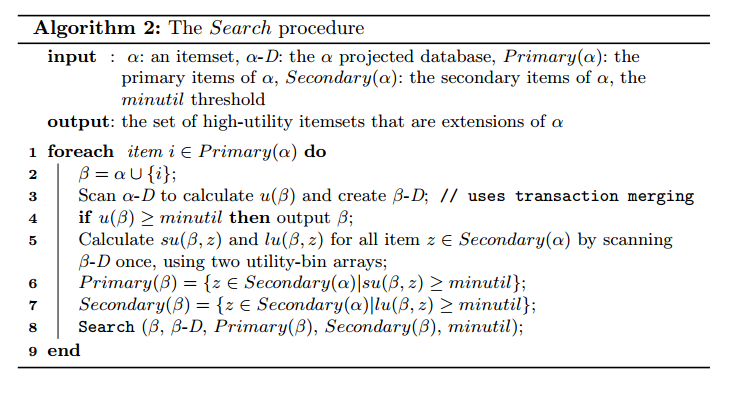
As you can see the presentation of the algorithm is quite nice. Doing the same using Word would be very difficult. For example, it would be quite difficult to add a vertical line for the “for” loop using Microsoft Word.
Reason 4: You don’t need to worry about how your document will look like
When writing a LaTeX document, you don’t need to worry about how your final document will look like. For example, you don’t need to worry about where the figures and tables will appear in your document or where the page breaks will be. All of this is handled by the LaTeX engine during the compilation of your document. When writing document, you only need to use some basic formatting instructions such as indicating when a new section starts in your document. This let you focus on writing .
Reason 5: LaTeX can generate and update your bibliography automatically
Another reason for using LaTeX is that it can generate the bibliography of a document automatically. There are different ways of writing a bibliography using LaTeX . One of the most common way is to use a .bib file. A .bib file provide a list of references that can be used in your document. Then, you can use these references in your .tex document using the \cite{} command and the bibliography will be automatically generated.
I will illustrate this with an example:

A), I have created a Latex document (a . tex file) where I cite a paper called “efim” using the LaTeX command \cite{efim} .
B) I have created a corresponding LaTeX bib file that provides bibliographical information about the “efim” paper.
C) I have generated the PDF file using the .tex file and the .bib file. As you can see, the \cite{} command has been replaced by 25, and the corresponding entry 25 has been automatically generated in the correct format for this paper and added to the bibliography.
The function for generating a bibliography using LaTeX can save a lot of time to researchers especially for documents containing many references such as thesis, books, and journal papers .
Moreover, once you have created a .bib file, you can reuse it in many different papers . And it is also very easy to change the style of your bibliography. For example, if you want to change from the APA style to the IEEE style, it can be done almost automatically, which saves lot of time.
In Microsoft Word, there is some basic tool for generating a bibliography but it provides much less features than LaTeX .
Reason 6: LaTeX works very well for large documents
LaTeX also provides many features that are useful for large documents such as Ph.D thesis and books . These features include generating tables of contents, tables of figures, and dividing a document into several files. Some of these features are also provided in Microsoft Word but are not as flexible as in LaTeX . I have personally written both my M.Sc. and Ph.D. thesis using LaTeX and I have saved a lot of time by doing this. I have simply downloaded the LaTeX style file from my university and then used it in my LaTeX document, and after that all my thesis was properly formatted according to the university style, without too much effort.
Problems of LaTeX
Now, let’s talk about the disadvantage or problems faced using LaTeX . The first problem is that there is a somewhat steep learning curve . LaTeX is actually not so difficult to learn but it is more difficult than using Word. It is necessary to learn various commands for preparing LaTeX documents. Moreover, some errors are not so easy to debug. However, the good news is that there exist some good places to ask questions and obtain answers when encountering problems with LaTeX such as Tex.StackExchange ( http://tex.stackexchange.com/ ). There also exist some free books such as the Not So Short Introduction To LaTeX that are quite good for learning LaTeX , and that I use as reference. Actually, although, there is a steep learning curve, I think that it is an excellent investment to learn to use LaTeX for researchers. Moreover, some journals in academia actually only accept LaTeX papers .
The second problem with LaTeX is that it is actually not necessary to use LaTeX for writing simple documents. LaTeX is best used for large documents or documents with complex layouts or for special needs such as displaying mathematical equations and algorithms. I personally use LaTeX only for writing research papers . For other things, I use Microsoft Word. Some people also use LaTeX for preparing slides using packages such as beamer , instead of using Powerpoint. This can be useful for preparing a presentation with lot of mathematical equations.
In this blog post, I have discussed the use of LaTeX for writing research papers . I hope that you have enjoyed this blog post.
— Philippe Fournier-Viger is a professor of Computer Science and also the founder of the open-source data mining software SPMF, offering more than 120 data mining algorithms.
Related posts:
One response to using latex for writing research papers.
Pingback: Comparing Two LaTeX documents with Latexdiff | The Data Mining Blog
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Search for:
- Academia (85)
- artificial intelligence (34)
- Big data (82)
- Bioinformatics (3)
- Chinese posts (1)
- Conference (74)
- Data Mining (183)
- Data science (102)
- Database (2)
- General (43)
- Industry (2)
- Machine Learning (20)
- Mathematics (2)
- open-source (37)
- Pattern Mining (86)
- Plagiarism (1)
- Programming (17)
- Research (109)
- Time series (3)
- Uncategorized (23)
- Utility Mining (23)
- Website (3)
Recent Posts
- Two new shopping datasets with taxonomy
- How to deal with unethical reviewers? The good example of the EAAI journal
- CSRankings: still a biased ranking
- The story of the most influential paper award of PAKDD 2024
- A brief report about PAKDD 2024
- Report on the UDML 2024 workshop @ PAKDD 2024
- Upcoming SPMF features for v.2.62 – More Dataset Stats Tools
- UDML 2024 Workshop program @ PAKDD 2024
- SPMF: bug fix about screen resolution
- SPMF 2.60 is released!
Recent Comments
- K. P. Birla on About the author
- Philippe Fournier-Viger on About the author
- The story of the most influential paper award of PAKDD 2024 | The Data Blog on An introduction to frequent pattern mining
- The story of the most influential paper award of PAKDD 2024 | The Data Blog on Report of the PAKDD 2014 conference (part 1)
- CSRankings: still a biased ranking | The Data Blog on Some shortcomings of CSRankings

- artificial intelligence
- association rule
- data mining
- data science
- high utility itemset mining
- itemset mining
- machine learning
- open-source
- open source
- pattern mining
- periodic pattern
- sequential pattern
- utility mining
Number of visitors:

Why Should I Use LaTeX over Word for Writing My Research? | Orvium
Researchers have long been split on whether to use Word or LaTex for their academic papers. The fact is, you can achieve results with both, and considering the latter is more complex, most don’t understand why LaTeX is so good.
Today, let’s look at the differences between the two and present LaTeX in an objective view, taking into account the benefits it presents as well as the things that aren't so great - such as the big issue with learning LaTeX.
What Is LaTeX?
LaTeX (/ˈlɑːtɛx/, often pronounced lay-tech) is a writing software centered around document creation, allowing users to input commands and add unformatted text. The UI is split between an Edit window, where users can write text and code, and a Typeset Window, which appears after the first save, allowing users to see the results of their work and how the document will look in real-time.
Compared to Word or Word-like document processors, LaTeX is fairly complex. The coding element can be a big hurdle for most researchers or students who are used to the simplicity of opening a document and simply starting to write. However, this issue can be easily overcome through an instructional video:
Benefits of LaTeX over Word for Research
1. Professional typesetting
LaTeX is specifically designed to produce high-quality typesetting, which makes your documents look professional and polished. This is especially important for academic writing, where the appearance of your document can affect how seriously your work is taken.
LaTeX is great because it’s not simply a word processor but rather a typesetting application designed for ultimate freedom when creating documents.
In academic writing, the aspect of your final document matters a lot. And since you’re essentially writing code, you can meticulously fine-tune your document to look exactly the way you want it or in accordance with the highly specific requirements some journals have.
Example: LaTeX automatically generates consistent and visually pleasing formatting for sections, equations, figures, and citations.
2. Efficient handling of large documents
Unlike Word and Google Docs, which lags up when editing large documents, LaTeX is optimized for minimal resource utilization. This allows researchers to work more efficiently on large documents with many equations, figures, images, and cross-references (think dissertations, books, or studies).
LaTeX also generates a table of contents, a list of figures, and a complete list of references which you can manually edit in code. I’m sure you know trying to edit and correct your references in Word is a buggy nightmare, and just the thought of it is enough to raise your levels of anxiety.
Another cool feature for large documents is the autosave option. That way, there is close to 0 risk of losing your work due to crashes or faulty equipment. Once you save your initial file, TeXShop, one of the tools in the LaTeX suite, automatically saves your work regularly.
Example: In LaTeX, the \input and \include commands allow you to split up sources in a controlled way, effectively making large documents into smaller files that can be managed separately.
3. Easy version control
Since LaTeX operates with plain text files, the level of control you have as a user is beyond what traditional word processors can offer. This can prove very handy when collaborating with multiple authors on a big project, as it allows you to use tools like Git or SVN to implement version control and track changes.
4. Wide range of packages and templates
LaTeX comes pre-equipped with multiple packages and templates that allow researchers to work on different types of projects, such as multiple kinds of math papers, articles, letters, memoirs, and more.
Furthermore, you can use online repositories such as the Comprehensive TeX Archive to find more packages and templates specifically made for diagrams, coding, tables, and more.
Example: The "tikz" package in LaTeX allows you to create professional-looking diagrams and illustrations.
5. Portable and platform-independent
Don’t you hate it when there's an issue with old versions of word documents? Or when you’re trying to edit a Word doc on a Mac and it doesn’t initially work? LaTeX removes all those headaches with compatibility.
The plain text docs you work on in LaTeX are portable and platform-independent. This makes sharing documents a breeze, regardless of the operating system or software setup. And it’s especially useful if you need to collaborate with colleagues or co-authors who use different systems.
Comparison Table: LaTeX vs Word
Who benefits most from using latex.
To sum up, LaTeX is better than Word for:
- Scientific researchers - from math to physics to chemistry and beyond. Anything that prominently features equations, tables, figures, or other designs is best completed via LaTeX.
- Academic dissertations and doctoral theses - from the reference system to the automatic and efficient table of contents, LaTeX makes working on gigantic projects such as these very easy. By comparison, researchers using Word frequently save chapters in separate documents to keep the software from lagging up or crashing and thereby losing their work.
- Textbook writing and editing - if you’re authoring math, physics, or other scientific textbooks, your best chance is with LaTeX, and students will thank you as the equations alone will look miles ahead of what Word can accomplish.
- Any other book authors and editors - for general authors, LaTeX might be a bit complex but worth the learning curve. Editors, however, tend to need a more professional tool to polish the final document for printing, so LaTeX is the better, more logical choice.
- Journalistic investigations - once again, the reference system in LaTeX can easily help journalists keep track of their sources, but it might be too complex on the go.
Overall, LaTeX frequently has a steeper learning curve compared to Word - which is also its biggest disadvantage. However, it offers many benefits that can make research writing more efficient, professional-looking, collaborative, and highly scalable due to its many templates.
If you’re looking to publish your research via Orvium, you should know that our platform is compatible with the LaTeX documents thanks to our integration with Overleaf. But if you want to suggest even more features we should implement in the future, don’t hesitate to reach out.
Learn more about our initiatives and stay up-to-date with the latest news and product features by following us on Twitter , Facebook , Linkedin , or Instagram .
- Academic Resources
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest posts delivered right to your inbox.

Now check your inbox and click the link to confirm your subscription.
Please enter a valid email address
Oops! There was an error sending the email, please try later.
Antonio Romero
Led several big-data and ML projects for the R&D between CERN and multiple ICT market-leaders. His work accelerating predictive-maintenance and machine-learning solutions at CERN
Recommended for you

How to Write a Research Funding Application | Orvium

Increasing Representation and Diversity in Research with Open Science | Orvium

Your Guide to Open Access Week 2023

Wait, fellow math enthusiast!
To find out more about why you should hire a math tutor, just click on the "Read More" button at the right!
What Is LaTeX Software Used For? (7 Things To Know)
LaTeX is widely used in academia, but outside of that realm, it is less commonly seen. Still, it is useful to know how to use LaTeX, at least at a basic level.
So, what is LaTeX software used for? LaTeX is free software used to create formatted documents (such as PDF or DVI files) for technical writing (such as scientific research papers). When using LaTeX, you create a plain text file with markup tags for things like text in bold or italic, as well as symbols (such as π and √).
Of course, LaTeX uses the TeX typesetting program as the basis for creating formatted files.
In this article, we’ll talk about LaTeX and what it is used for. We’ll also answer some common questions about LaTeX and some ways you can get started or find help with document creation.
Let’s get started.
What Is LaTeX Software Used For?
LaTeX is used for typesetting in technical writing (such as academic papers or textbooks) to publish in fields like:
- Computer Science
- Mathematics
- & others

LaTeX makes it easy for anyone in academia or industry to create a nicely formatted technical document, with “source code” (a LaTeX file) that can be edited easily to change things like:
- Chapters & Sections
- Graphs, Charts, & Tables

LaTeX separates the appearance (layout, spacing, font, etc.) of a document from the content.
Is LaTeX Software Free?
LaTeX software is free, since you do not need to pay for a license or software download. However, you should include a copyright notice i n y o u r w o r k , as seen here .
You can find the LaTeX Project Public License (LPPL) as a text file here.
Free LaTeX Editors
There are several free versions of LaTeX available, including:
- TeX Live – Unix, MacOSX, Windows
- MacTeX – MacOSX
- MiKTeX – Windows
If you have any trouble, you can get help with LaTeX here .
You can find a list of additional TeX resources here.
Is LaTeX Software Safe?
LaTeX software is generally safe, as long as you download it from one of the “official” sources listed above. However, there is the potential for viruses in malicious LaTeX files, as detailed here.
So, make sure that you only accept LaTeX files from people you know and trust, or write your own files from scratch (or modify files you wrote yourself in the past).
Is LaTeX A Programming Language?
LaTeX is a programming language , but it is also considered a document preparation system for the TeX typesetting program. However, LaTeX is also a macro language and a markup language, which uses tags.

You must write LaTeX code (in a document) and compile it to create a formatted document that you can read. This is similar to how a programming language (such as C or C++) must be compiled before you can create a program you can run.
A program like pdflatex can create a PDF file from a LaTeX document.
Is LaTeX Similar To HTML?
LaTeX is similar to HTML in that both use tags to begin and end elements (such as a document in LaTeX or a heading in HTML):
However, there are also many differences between LaTeX and HTML. For example, LaTeX is used for typesetting to create static documents (PDF, etc.) while HTML (with CSS) is used for dynamic web pages.
Both file types can be edited at a later time to change the appearance of the resulting PDF, web page, etc.
Why Learn LaTeX?
It is a good idea to learn LaTeX for several reasons.
In academia (teaching and research), LaTeX is useful to create well-formatted versions of:
- Class presentations
- Lecture notes
- Scientific papers
- Theses or dissertations
Being able to use LaTeX to create or edit documents means that you will be able to communicate within academia in a format that is widely used and accepted.

A LaTeX file is also able to produce the same output (e.g. a PDF) on different machines running different operating systems and versions.
Is LaTeX Difficult To Learn?
LaTeX is a little bit difficult to learn, especially if you have no experience with markup languages like HTML. One of the best ways to learn LaTeX is to start by examining a simple document to make sure that you understand what each of the tags is doing.
Then, try to modify the document slightly (for example, change an equation slightly). Then, add a new element (equation, header/section, etc.) and then change the style to suit your needs. One thing at a time!
You can also learn by copying the code for objects (like tables) from existing documents or online sources. Then, you can modify them slightly to get what you want (instead of starting from scratch each time you write a paper).
Also, there are lots of online tutorials available to help you learn LaTeX as you get started.
LaTeX-tutorial has a tutorial series where you can learn about documents, sections, packages, tables of contents, and so forth.
There is also a LaTeX help series on Overleaf .
YouTube has plenty of tutorials if you would rather watch and learn for a while – including this one :
In the short run, using a program like Microsoft Word is easier than LaTeX, due to the “what you see is what you get” nature of Word and the learning curve for LaTeX.
In the long run, you might be able to type up a document faster in LaTeX than in Word, especially if you are using lots of uncommon symbols that are hard to find in Word’s equation editor (or if you don’t have all of the keyboard shortcuts for symbols memorized in Word).
If you are plan to be in academia for a while (or if you plan on publishing scientific papers), then it is probably worthwhile to learn LaTeX.
Is LaTeX Better Than Word?
LaTeX is better than Word for scientific publishing or technical writing. Once you get used to writing in LaTeX, you will likely be able to create nicely formatted documents with equations faster than if you used Word.
However, Word is probably a better choice if you just want to write a simple essay, since no special typesetting is required (no equations, formulas, tables, etc.)
Should I Write My Thesis, Dissertation, or Resume In LaTeX?
It is probably a good idea to write your thesis or dissertation in LaTeX, especially if you will be making extensive use of equations, tables, and so forth.
A thesis or dissertation in Mathematics, Computer Science, and other equation-heavy fields will benefit from use of LaTeX for typesetting.
If you want a nice-looking paper resume to print out, creating a LaTeX file will work great. However, just be aware that a PDF resume created from a LaTeX document may cause problems in your online job search.
A resume created with LaTeX looks good on paper, but an online ATS (applicant tracking system) may not be able to read the PDF version.
This could lead to your application being automatically rejected. When applying to a job online, make sure you create a resume that an ATS can read easily.
LaTeX Alternatives
There are several LaTeX alternatives, including:
You can learn more about LaTeX alternatives here .
Now you know what LaTeX software is, what it is used for, and why you might want to learn it. You also know the answers to some common questions about LaTeX, along with some of its advantages and limitations.
I hope you found this article helpful. If so, please share it with someone who can use the information.

Don’t forget to subscribe to our YouTube channel & get updates on new math videos!
JDM Educational Staff
Recent Posts
The New Digital SAT (3 Changes To Know About)
Have you heard the news? The SAT is changing in 2024. Yes, it’s true. The College Board, the creators of the SAT, are revamping the entire exam for spring of 2024. PSAT test takers will see the...
Percents (9 Examples Of Percents & Their Uses)
Percents are used all the time in everyday life to find the size of an increase or decrease and to calculate discounts in stores. You’ve probably used percentages before. “I got a 94% on the...

Main Navigation
- Contact NeurIPS
- Code of Ethics
- Code of Conduct
- Create Profile
- Journal To Conference Track
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Proceedings
- Future Meetings
- Exhibitor Information
- Privacy Policy
Call for High School Projects
Machine learning for social impact .
The Thirty-Eighth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2024) is an interdisciplinary conference that brings together researchers in machine learning, neuroscience, statistics, optimization, computer vision, natural language processing, life sciences, natural sciences, social sciences, and other adjacent fields.
This year, we invite high school students to submit research papers on the topic of machine learning for social impact. A subset of finalists will be selected to present their projects virtually and will have their work spotlighted on the NeurIPS homepage. In addition, the leading authors of up to five winning projects will be invited to attend an award ceremony at NeurIPS 2024 in Vancouver.
Each submission must describe independent work wholly performed by the high school student authors. We expect each submission to highlight either demonstrated positive social impact or the potential for positive social impact using machine learning. Application areas may include but are not limited to the following:
- Agriculture
- Climate change
- Homelessness
- Food security
- Mental health
- Water quality
Authors will be asked to confirm that their submissions accord with the NeurIPS code of conduct and the NeurIPS code of ethics .
Submission deadline: All submissions must be made by June 27th, 4pm EDT. The system will close after this time, and no further submissions will be possible.
We are using OpenReview to manage submissions. Papers should be submitted here . Submission will open June 1st. Submissions under review will be visible only to their assigned program committee. We will not be soliciting comments from the general public during the reviewing process. Anyone who plans to submit a paper as an author or a co-author will need to create (or update) their OpenReview profile by the full paper submission deadline.
Formatting instructions: All submissions must be in PDF format. Submissions are limited to four content pages , including all figures and tables; additional pages containing only references are allowed. You must format your submission using the NeurIPS 2024 LaTeX style file using the “preprint” option for non-anonymous submission. The maximum file size for submissions is 50MB. Submissions that violate the NeurIPS style (e.g., by decreasing margins or font sizes) or page limits may be rejected without further review. Papers may be rejected without consideration of their merits if they fail to meet the submission requirements, as described in this document.
Mentorship and collaboration: The submitted research can be a component of a larger research endeavor involving external collaborators, but the submission should describe only the authors’ contributions. The authors can also have external mentors but must disclose the nature of the mentorship. At the time of submission, the authors will be asked to describe the involvement of any mentors or external collaborators and to distinguish mentor and collaborator contributions from those of the authors. In addition, the authors may (optionally) include an acknowledgements section acknowledging the contributions of others following the content sections of the submission. The acknowledgements section will not count toward the submission page limit.
Proof of high school attendance: Submitting authors will also be asked to upload a signed letter, on school letterhead, from each author’s high school confirming that the author was enrolled in high school during the 2023-2024 academic year.
Supplementary artifacts: In their submission, authors may link to supplementary artifacts including videos, working demonstrations, digital posters, websites, or source code. Please do not link to additional text. All such supplementary material should be wholly created by the authors and should directly support the submission content.
Review process: Each submission will be reviewed by anonymous referees. The authors, however, should not be anonymous. No written feedback will be provided to the authors.
Use of Large Language Models (LLMs): We welcome authors to use any tool that is suitable for preparing high-quality papers and research. However, we ask authors to keep in mind two important criteria. First, we expect papers to fully describe their methodology. Any tool that is important to that methodology, including the use of LLMs, should be described also. For example, authors should mention tools (including LLMs) that were used for data processing or filtering, visualization, facilitating or running experiments, or proving theorems. It may also be advisable to describe the use of LLMs in implementing the method (if this corresponds to an important, original, or non-standard component of the approach). Second, authors are responsible for the entire content of the paper, including all text and figures, so while authors are welcome to use any tool they wish for writing the paper, they must ensure that all text is correct and original.
Dual submissions: Submissions that are substantially similar to papers that the authors have previously published or submitted in parallel to other peer-reviewed venues with proceedings or journals may not be submitted to NeurIPS. Papers previously presented at workshops or science fairs are permitted, so long as they did not appear in a conference proceedings (e.g., CVPRW proceedings), a journal, or a book. However, submissions will not be published in formal proceedings, so work submitted to this call may be published elsewhere in the future. Plagiarism is prohibited by the NeurIPS Code of Conduct .
Paper checklist: In order to improve the rigor and transparency of research submitted to and published at NeurIPS, authors are required to complete a paper checklist . The paper checklist is intended to help authors reflect on a wide variety of issues relating to responsible machine learning research, including reproducibility, transparency, research ethics, and societal impact. The checklist does not count towards the page limit and will be entered in OpenReview.
Contact: [email protected]
Research template
Research Article Template for submission to the journal Research

Get in touch
Have you checked our knowledge base ?
Message sent! Our team will review it and reply by email.
Email:

COMMENTS
LaTeX is a high-quality typesetting system; it includes features designed for the production of technical and scientific documentation. LaTeX is the de facto standard for the communication and publication of scientific documents. LaTeX is available as free software. You don't have to pay for using LaTeX, i.e., there are no license fees, etc.
LaTeX is a typesetting software used as a document preparation system, very often used by academicians, researchers, scientists, mathematicians, and other professionals. ... While writing research papers it is mandatory to include the abstract and the keywords before the main section of the body. The LaTeX engine bears pre-defined commands that ...
However, you don't need to learn LaTeX to use our tool. Our editor looks like a word processor on steroids, specifically built to cater to the research writing industry. SciSpace helps authors write, collaborate, and convert their thesis/research papers into your pre-set journal or conference formats in just a few clicks.
HenriquesLab bioRxiv template Official. This is a gorgeous template for bioRxiv pre-prints. An example manuscript using it can be found here. Ricardo Henriques. Produce beautiful documents starting from our gallery of LaTeX templates for journals, conferences, theses, reports, CVs and much more.
The preamble. In this example, the main.tex file is the root document and is the .tex file that will draw the whole document together. The first thing we need to choose is a document class. The article class isn't designed for writing long documents (such as a thesis) so we'll choose the report class, but we could also choose the book class.. We can also change the font size by adding square ...
Step 7: Add Sections. Below the \maketitle section begin adding additional sections by using the \section {} command. Put your section title in between the curly brackets. You should already have an introduction section added, but for a research paper, I recommend adding a Related Work, Methodology, Results, and Conclusion section.
Edit your research notes from any computer, or even on a tablet when mobile. When writing a scientific paper, refer to past entries, and just paste the LaTeX into your paper. Share your research notes with other members in your group, or with your research supervisor. Save the compiled PDFs and print them before meetings with your supervisor ...
However, some new graduate students might not have experience in using LaTeX and thus have a difficult time in prepare their first papers. In this article (PDF), we will first provide some tips for paper writing. Then, we will showcase several working examples for the tables and figures, which have been used in our previous publications.
LaTeX is a free software package developed in 1985 as an extension to the TeX typesetting system by American computer scientist Leslie Lamport. LaTeX was designed to make it easier for TeX users to create general-purpose books and articles. ... Master's theses and dissertations, research proposals, scientific journal papers, as well as other ...
2.Read through at least one full paper in your target journal, to get a sense of the content and writing style. 3.To clarify in your own head the purpose of your paper, start by drafting your abstract [2]. 4.Before you tackle the body of the paper, sketch block outlines of the gures. Decide what images and plots you will put in the paper, and ...
With L ATEX, you just tell it to start a new section. With a word processor, changing the formatting means you have to change each instance individually. With L ATEX, you just rede ne the relevant commands. With a word processor, you have to carefully match any provided templates. With L ATEX, you can be sure you've t the template, and switch ...
Step 1: Install LaTeX and a LaTeX Aware Editor. LaTeX is not a word processor, it is a document preparation system for high-quality typesetting. It is most often used for medium-to-large technical or scientific documents, but it can be used for almost any form of publishing. LaTeX encourages authors not to worry too much about the appearance of ...
In this video, I'll provide a step-by-step tutorial on how you can write a research article online on the Overleaf platform. Briefly, Overleaf is an online L...
LaTeX is a document preparation system for high-quality typesetting. Often used for technical or scientific documents, it can be used for almost any form of ...
LaTeX is a document preparation system, proposed in the 1980s. It is used to create documents such as research papers, books, or even slides for presentations. The key difference between LaTeX and software like Microsoft Word is that Microsoft Word let you directly edit your document and immediately see the result, while using LaTeX is a bit ...
2. Efficient handling of large documents. Unlike Word and Google Docs, which lags up when editing large documents, LaTeX is optimized for minimal resource utilization. This allows researchers to work more efficiently on large documents with many equations, figures, images, and cross-references (think dissertations, books, or studies).
Other (as stated in the work) Abstract. Here we present a standard format for academic papers, using a two column layout. This example lets you get started right away, and includes some sample text and formulae to help learn how to write LaTeX. Click below to get started.
I am mostly happy with it. I am a Windows user so it works well with Windows 10. Thanks very much 😊. I would recommend TeXworks. Another editor is TeXnicCenter, but TeXworks is better. See also ...
Superficially, one of the advantages of LaTeX over other more traditional systems (e.g. Word or OpenOffice) is the high typographical quality of the documents that you'll be able to produce. This is particularly true for documents that are heavy on mathematics, but documents for any other area could also take advantage of these qualities.
LaTeX is free software used to create formatted documents (such as PDF or DVI files) for technical writing (such as scientific research papers). When using LaTeX, you create a plain text file with markup tags for things like text in bold or italic, as well as symbols (such as π and √).
Papers may be rejected without consideration of their merits if they fail to meet the submission requirements, as described in this document. Mentorship and collaboration: The submitted research can be a component of a larger research endeavor involving external collaborators, but the submission should describe only the authors' contributions ...
The biggest hit has come to Wiley, a 217-year-old publisher based in Hoboken, N.J., which Tuesday will announce that it is closing 19 journals, some of which were infected by large-scale research ...
An online LaTeX editor that's easy to use. No installation, real-time collaboration, version control, hundreds of LaTeX templates, and more. ... The manuscript should start with a brief introduction that lays out the problem addressed by the research and describes the paper's importance. The scientific question being investigated should be ...