

A How-To Guide for Creating a Business Budget
Amanda Smith
Reviewed by
September 23, 2022
This article is Tax Professional approved
Most business owners know how important a business budget is when it comes to managing expenses and planning for the future—but in a challenging economic environment like the one we’ve been experiencing, your business budget takes on even greater significance.
With inflation running rampant and the possibility of a recession looming, business owners need to be able to forecast their cash flow, manage their expenses, and plan for the future. Creating a detailed business budget is the first step.
Whether you want to revamp your budgeting method, or you’ve never created a business budget before, this guide will walk you through the process.
I am the text that will be copied.
What is a business budget?
A budget is a detailed plan that outlines where you’ll spend your money monthly or annually.
You give every dollar a “job,” based on what you think is the best use of your business funds, and then go back and compare your plan with reality to see how you did.
A budget will help you:
- Forecast what money you expect to earn
- Plan where to spend that revenue
- See the difference between your plan and reality
What makes a good budget?
The best budgets are simple and flexible. If circumstances change (as they do), your budget can flex to give you a clear picture of where you stand at all times.
Every good budget should include seven components:
1. Your estimated revenue
This is the amount you expect to make from the sale of goods or services. It’s all of the cash you bring in the door, regardless of what you spent to get there. This is the first line on your budget. It can be based on last year’s numbers or (if you’re a startup ), based on industry averages.
2. Your fixed costs
These are all your regular, consistent costs that don’t change according to how much you make—things like rent, insurance, utilities, bank fees, accounting and legal services, and equipment leasing.
Further reading: Fixed Costs (Everything You Need to Know)
3. Your variable costs
These change according to production or sales volume and are closely related to “ costs of goods sold ,” i.e., anything related to the production or purchase of the product your business sells. Variable costs might include raw materials, inventory, production costs, packaging, or shipping. Other variable costs can include sales commission, credit card fees, and travel. A clear budget plan outlines what you expect to spend on all these costs.
The cost of salaries can fall under both fixed and variable costs. For example, your core in-house team is usually associated with fixed costs, while production or manufacturing teams—anything related to the production of goods—are treated as variable costs. Make sure you file your different salary costs in the correct area of your budget.
Further reading: Variable Costs (A Simple Guide)
4. Your one-off costs
One-off costs fall outside the usual work your business does. These are startup costs like moving offices, equipment, furniture, and software, as well as other costs related to launch and research.
5. Your cash flow
Cash flow is all money traveling into and out of a business. You have positive cash flow if there is more money coming into your business over a set period of time than going out. This is most easily calculated by subtracting the amount of money available at the beginning of a set period of time and at the end.
Since cash flow is the oxygen of every business, make sure you monitor this weekly, or at least monthly. You could be raking it in and still not have enough money on hand to pay your suppliers.
6. Your profit
Profit is what you take home after deducting your expenses from your revenue. Growing profits mean a growing business. Here you’ll plan out how much profit you plan to make based on your projected revenue, expenses, and cost of goods sold. If the difference between revenue and expenses (aka “ profit margins ”) aren’t where you’d like them to be, you need to rethink your cost of goods sold and consider raising prices .
Or, if you think you can’t squeeze any more profit margin out of your business, consider boosting the Advertising and Promotions line in your budget to increase total sales.
7. A budget calculator
A budget calculator can help you see exactly where you stand when it comes to your business budget planning. It might sound obvious, but getting all the numbers in your budget in one easy-to-read summary is really helpful.
In your spreadsheet, create a summary page with a row for each of the budget categories above. This is the framework of your basic budget. Then, next to each category, list the total amount you’ve budgeted. Finally, create another column to the right—when the time period ends, use it to record the actual amounts spent in each category. This gives you a snapshot of your budget that’s easy to find without diving into layers of crowded spreadsheets.
See the sample below.
Pro tip: link the totals on the summary page to the original sums in your other budget tabs . That way when you update any figures, your budget summary gets updated at the same time. The result: your very own budget calculator.
You can also check out this simple Startup Cost Calculator from CardConnect. It lays out some of the most common expenses that you might not have considered. From there, you can customize a rough budget for your own industry.
Small business budgets for different types of company
While every good budget has the same framework, you’ll need to think about the unique budgeting quirks of your industry and business type.
Seasonal businesses
If your business has a busy season and a slow season, budgeting is doubly important.
Because your business isn’t consistent each month, a budget gives you a good view of past and present data to predict future cash flow . Forecasting in this way helps you spot annual trends, see how much money you need to get you through the slow months, and look for opportunities to cut costs to offset the low season. You can use your slow season to plan for the next year, negotiate with vendors, and build customer loyalty through engagement.
Don’t assume the same thing will happen every year, though. Just like any budget, forecasting is a process that evolves. So start with what you know, and if you don’t know something—like what kind of unexpected costs might pop up next quarter— just give it your best guess . Better to set aside money for an emergency that doesn’t happen than to be blindsided.
Ecommerce businesses
The main budgeting factor for ecommerce is shipping. Shipping costs (and potential import duties) can have a huge impact.
Do you have space in your budget to cover shipping to customers? If not, do you have an alternative strategy that’s in line with your budget—like flat rate shipping or real-time shipping quotes for customers? Packaging can affect shipping rates, so factor that into your cost of goods sold too. While you’re at it, consider any international warehousing costs and duties.
You’ll also want to create the best online shopping experience for your customers, so make sure you include a good web hosting service, web design, product photography, advertising, blogging, and social media in your budget.
Inventory businesses
If you need to stock up on inventory to meet demand, factor this into your cost of goods sold. Use the previous year’s sales or industry benchmarks to take a best guess at the amount of inventory you need. A little upfront research will help ensure you’re getting the best prices from your vendors and shipping the right amount to satisfy need, mitigate shipping costs, and fit within your budget.
The volume of inventory might affect your pricing. For example, if you order more stock, your cost per unit will be lower, but your overall spend will be higher. Make sure this is factored into your budget and pricing, and that the volume ordered isn’t greater than actual product demand.
You may also need to include the cost of storage solutions or disposal of leftover stock.
Custom order businesses
When creating custom ordered goods, factor in labor time and cost of operations and materials. These vary from order to order, so make an average estimate.
Budgeting is tricky for startups—you rarely have an existing model to use. Do your due diligence by researching industry benchmarks for salaries, rent, and marketing costs. Ask your network what you can expect to pay for professional fees, benefits, and equipment. Set aside a portion of your budget for advisors—accountants, lawyers, that kind of thing. A few thousand dollars upfront could save you thousands more in legal fees and inefficiencies later on.
This is just scratching the surface, and there’s plenty more to consider when creating a budget for a startup. This business startup budget guide from The Balance is a great start.
Service businesses
If you don’t have a physical product, focus on projected sales, revenue, salaries, and consultant costs. Figures in these industries—whether accounting, legal services, creative, or insurance—can vary greatly, which means budgets need flexibility. These figures are reliant on the number of people required to provide the service, the cost of their time, and fluctuating customer demand.
Small business budgeting templates
A business budget template can be as simple as a table or as complex as a multi-page spreadsheet. Just make sure you’re creating something that you’ll actually use.
Create your budget yearly—a 12-month budget is standard fare—with quarterly or monthly updates and check-ins to ensure you’re on track.
Here are some of our favorite templates for you to plug into and get rolling.
- The Balance has a clear table template that lists every budget item, the budgeted amount, the actual amount, and the difference between the two. Use this one if you’re looking to keep it simple.
- Capterra has both monthly and annual breakdowns in their Excel download. It’s straightforward, thorough, and fairly foolproof.
- Google Sheets has plenty of budget templates hiding right under your nose. They’re easy to use, and they translate your figures into clear tables and charts on a concise, visual summary page.
- Smartsheet has multiple resources for small businesses, including 12-month budget spreadsheets, department budget templates, projection templates, project-by-project templates, and startup templates. These templates are ideal if you’re looking for a little more detail.
- Scott’s Marketplace is a blog for small businesses. Their budget template comes with step-by-step instructions that make it dead simple for anyone.
- Vertex42 focuses on Excel spreadsheets and offers templates for both product-based and service-based businesses, as well as a business startup costs template for anyone launching a new business.
Budgeting + bookkeeping = a match made in heaven
Making a budget is kind of like dreaming: it’s mostly pretend. But when you can start pulling on accurate historical financials to plan the upcoming year, and when you can check your budget against real numbers, that’s when budgets start to become useful.
The only way to get accurate financial data is through consistent bookkeeping.
Don’t have a regular bookkeeping process down pat? Check out our free guide, Bookkeeping Basics for Entrepreneurs . We’ll walk you through everything you need to know to get going yourself, for free.
If you need a bit more help, get in touch with us. Bookkeeping isn’t for everyone, especially when you’re also trying to stay on top of a growing business—but at Bench, bookkeeping is what we do best.
Related Posts
.png)
What Is Equity, and How Do You Calculate It?
How much of your business do you actually own? If you understand equity, you can answer that question.

The Basics of Small Business Accounting: A How-to
New to business? Learn the fundamentals of small business accounting, and set your financials up for success.

Quicken Alternatives: Your Top Six Options
Looking for a Quicken replacement? Here are your top six options.
Join over 140,000 fellow entrepreneurs who receive expert advice for their small business finances
Get a regular dose of educational guides and resources curated from the experts at Bench to help you confidently make the right decisions to grow your business. No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.

Accounting | How To
How To Create a Small Business Budget [+Free Template]
Published June 20, 2023
Published Jun 20, 2023
REVIEWED BY: Tim Yoder, Ph.D., CPA
WRITTEN BY: Eric Gerard Ruiz, CPA
This article is part of a larger series on Bookkeeping .
- 1. Create a Budget Process
- 2. Determine Key Assumptions in Budgeting
- 3. Create the Sales Budget
- 4. Create the Inventory and Purchases Budget
- 5. Create the COGS Budget
- 6. Create the Sales & Administrative Budget
- 7. Create the Capital Budget
- 8. Create the Cash Budget
- 9. Assemble Proforma Financial Statements
Common Problems in Budgeting
Bottom line.
Creating a business budget is an important step in planning. A small business budget starts with creating the budgeting process, the operating budgets, such as sales, inventory and purchases, cost of goods sold (COGS), and sales and administrative, and ends with the financial budgets, such as cash, capital, and proforma financial statements.
To help you get started, we’ve provided a very simplified version of a budget spreadsheet to illustrate how information from each area of your business is combined to form an annual budget. We’ll discuss how to use this spreadsheet throughout our article.
FILE TO DOWNLOAD OR INTEGRATE
FILE TO DOWNLOAD
Thank you for downloading!
Budgeting is an important subset of managerial accounting. Read our small business guide to managerial accounting and learn how managerial accounting concepts can be applied in a small business setup.
Step 1: Create a Budget Process
The budget process shows how the different departments of the business create a budget. Without a process, budgeting would be chaotic, and it would result in inefficiencies. In the budget process, you need to consider the following:
- Budget period: When are budgets created, reviewed, implemented, and evaluated against actual performance?
- Budgeting method: How are budgets created? Is it created from scratch (zero-based budgeting)? Is it based on actual results with adjustments (incremental budgeting)?
- Budget involvement: Who creates the budgets?
- Budget committee: Who oversees and approves the budgets?
- Budget manual: What are the guidelines for creating budgets?
Budget Period
The first thing to consider in the budget process is the budget period. How long should budgets be prepared? When will it be implemented? The budget period can be any time before the next business year begins. Hence, you can create next year’s budget three months prior to the end of the current year.
The crucial periods for budget planning are as follows:
- Budget preparation : The time at which managers and heads create a budget for their department.
- Budget review and approval : The time at which top management will review and approve all lower-level budgets.
- Budget implementation : The time at which all concerned parties will act upon planned activities stated in the budget. This phase runs until the effectiveness of the budget lasts.
- Budget accountability : The time at which top management will assess if the business is meeting its budgetary goals. This phase runs intermittently during the year, such as monthly, quarterly, or semiannually, especially during performance evaluation and review.
As a small business, you need not be particular about the phases. You can modify the phases depending on small business needs.
Budgeting Method
There are four different types of budgeting methods, but for small businesses, we picked only two, as they are the most appropriate for the setup:
- Zero-based budgeting : This is a budgeting technique that starts from scratch. It doesn’t use information from past budgets. Instead, departments and managers need to justify every dollar in the budget without referring to past performance or past budgeting practices.
- Incremental budgeting : This is a budgeting technique that uses actual figures from the past years and adjusts with a certain percentage. For example, if actual sales last year is $20,000, the incremental budgeted sales could be 10 percent more or $22,000.
Budget Involvement
Small businesses must consider what kind of involvement is needed during the budgeting process, given that budgets can be used to measure the performance of departments and managers. There are two kinds of budget involvement—for small businesses, authoritative budgeting is suitable if the small business owner is heavily involved in daily operations. Alternatively, participatory budgeting applies if the owner delegates decision-making to managers.
1. Authoritative budgeting
Also known as top-down budgeting, this budget involvement strategy only includes top management in the budgeting process, where operating personnel and lower-level employees have little to no say in the budget. It takes less time to create since there are fewer employees involved.
However, some operating personnel and lower-level employees may disagree with top management’s estimates in the budget. At the least, this strategy creates discord between top management and operating personnel due to conflicting views. But if prepared appropriately, authoritative budgeting reflects the business’ vision, mission, and goals better.
2. Participatory budgeting
This is also called bottom-up budgeting, and this budget involvement strategy includes operating personnel and lower-level employees in creating a budget. It is a budget co-created by everyone involved or affected by the budget being created.
It enhances the relationship between top management and operating personnel since everyone has a say in the budget. However, this strategy can take time since more employees are involved in the budgeting process. Also, some lower-level managers can use this opportunity to insert some budgetary slack so that they look good during performance.
Budget Committee
The budget committee is responsible for compiling all lower-level budgets and assembling them into one package called the master budget and reviewing and approving budgets from different departments. For small businesses, the composition of the budget committee can be the small business owners, chief executive officer (CEO), treasurer, budget coordinator, and chief accountant.
The role of the budget coordinator is to reach out to lower-level managers and communicate the wishes of the budget committee. If you’re a family-grown small business, family members, including the small business accountant or finance officer, can be committee members.
Budget Manual
The first order of business of the budget committee is to create a budget manual, which outlines the budgeting process. Lower-level managers and department heads will use the budget manual when creating lower-level budgets. The budget committee may also set specific budget formats and deadlines.
A budget manual standardizes the budgeting process—it ensures fairness and comparability among departments and managers. With this manual in place, you can prevent the instance of inserting unfamiliar line items in the budget or using different sources in forecasting budgeted figures.
The budget manual should include the following:
- Statements of budgetary purpose
- Budgetary activities, such as budget preparation, budget hearing and evaluation, budget approval, budget execution, and budget accountability
- Schedule of budgetary activities and deadlines
- Sample budgets
- Key assumptions used in budgeting
You can create a budget easily using QuickBooks Online. Its budgeting functions create budgets per account in the chart of accounts. Read our QuickBooks Online review for detailed information on our recommendation.
Step 2: Determine Key Assumptions in Budgeting
After performing the groundwork for budgeting, the next step is determining the key assumptions. These assumptions make it easy to prepare budgets since not all information is readily available until it happens. These assumptions are not arbitrary because they must be based on past experience and good business practices.
Examples of assumptions are:
- Sales forecast
- Selling price per unit
- Cost per unit
- Estimated discounts given to customers
- Estimated sales returns
- Desired ending inventory per month or quarter
- Number of raw materials used to produce one good unit
- Number of labor hours needed to produce one good unit
- Number of overhead hours (if any) needed to produce one good unit
- Inventory cost flow method used, such as first-in, first-out (FIFO), last-in, first-out (LIFO), or average cost
- Cash collection patterns
- Cash payments patterns
- Cash retention policies
Input your assumptions in the second tab of our downloadable spreadsheet. When done, all of the reports will automatically populate. It’s the quality of your assumptions that will determine if your budget is realistic. As you improve your budgeting process, you’ll come up with additional assumptions to include in the process.
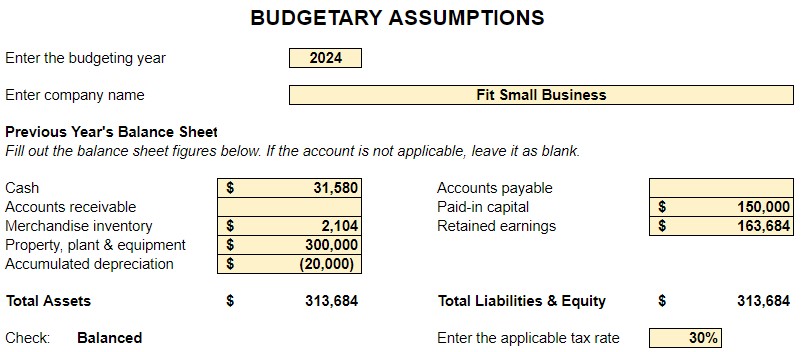
Step 3: Create the Sales Budget
The sales budget is the first budget that should be prepared because almost all budgets will depend on the information in it. It is the responsibility of the sales department to forecast and create the sales budget of the company, and it is crucial that the department forecast sales reasonably using the appropriate forecasting method. Our article about sales forecasting discusses the method of sales forecasting and shows how CRM software can help.
Below is an example of the sales budget taken from our small business master budget template.
Sales budget
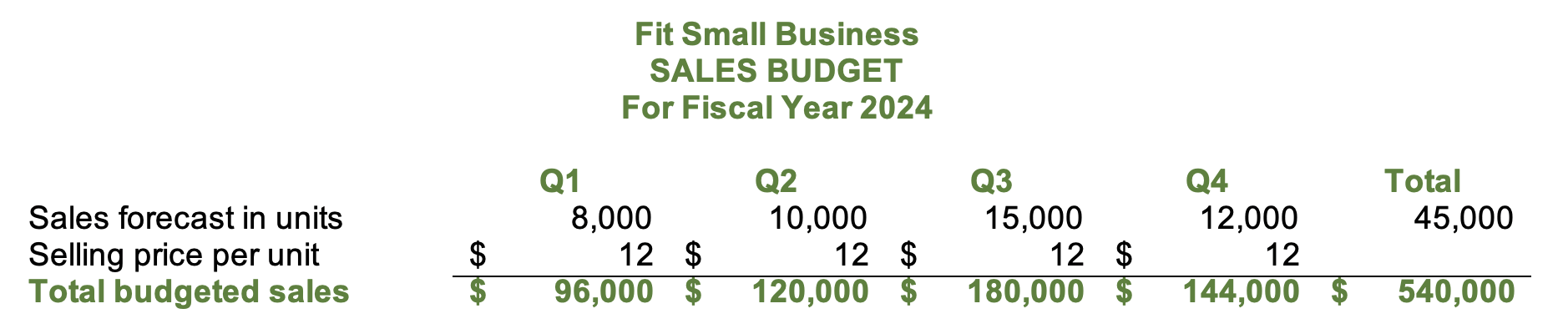
Step 4: Create the Inventory & Purchases Budget
There are two ways to call this budget: merchandising companies can call it inventory and purchases budget while manufacturing companies can call it production budget. However, the information shown in this budget remains the same. The inventory or production budget shows the number of units needed to meet the sales demand.
Inventory budget
The image above shows the sample inventory budget in our free template. One of our assumptions is that the business intends to keep 5% of next quarter’s sales forecast as current quarter’s ending inventory. In Q1, desired ending inventory is 500 units, which is 5% of 10,000 units of Q2’s sales forecast.
After determining the number of units needed, multiply them to the standard cost of inventory to get the total cost of inventory. The standard inventory cost is also the budgeted cost of inventory. Since some inventory prices fluctuate, setting standard costs makes it easy for us to budget.
When adding values in the total column, do not sum up the values in the beginning and desired ending inventory rows. Instead, the total beginning inventory in the total column should be the Q1 beginning inventory, while the total ending inventory should be the Q4 ending inventory.
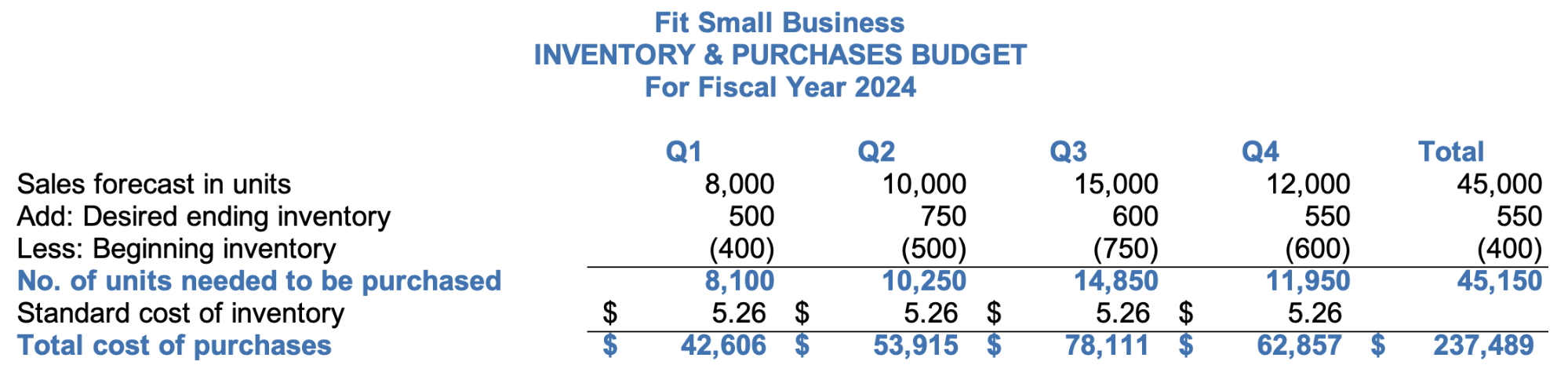
Step 5: Create the COGS Budget
The next logical step after budgeting inventory and purchases is to determine the COGS. Through the COGS budget, we can estimate the level of COGS per quarter. This budget is necessary for preparing the proforma income statement.
Below is the COGS budget from our small business budget template:
COGS budget
Step 6: Create the Sales & Administrative Budget
The sales and administrative (S&A) budget presents the budgeted costs for sales expenses, office expenses, and administrative expenses. This is necessary for budgeting the salaries of employees and other fixed expenses. The image below shows the sales and administrative budget from our template:
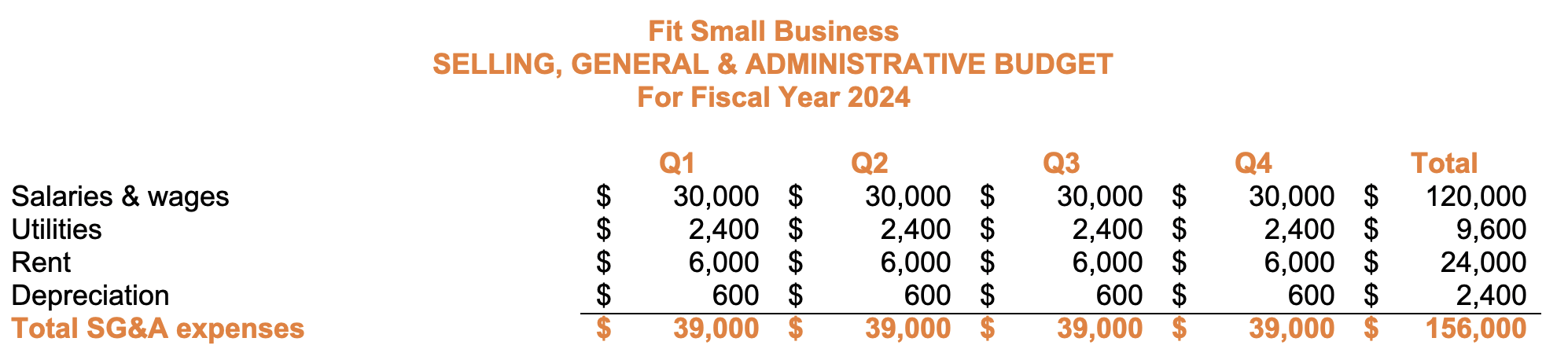
S&A budget
Most expenses in this budget are fixed costs. That’s why the amounts are the same for every quarter. Manufacturing companies may also call this budget a “fixed overhead budget.”
Step 7: Create the Capital Budget
A capital budget shows all the planned capital expenditures during the year. In our capital budget example below, there are no figures because the sample company didn’t plan any capital decisions for 2024. However, we’ve included common capital decisions for you to fill out when you use our template. For instance, a bank loan is a capital inflow while the purchase of equipment is a capital outflow.

Capital budget
The capital budget in our downloadable spreadsheet does not auto-populate from the assumptions tab. Instead, enter your budgeted loans and purchases directly in the report.
Step 8: Create the Cash Budget
The last budget that you need to prepare is the cash budget, which shows all the cash inflows and outflows from all budgets. Almost all budgets above affect cash flow. For example, the sales budget can show all cash inflows from cash sales and subsequent cash collections from credit sales.
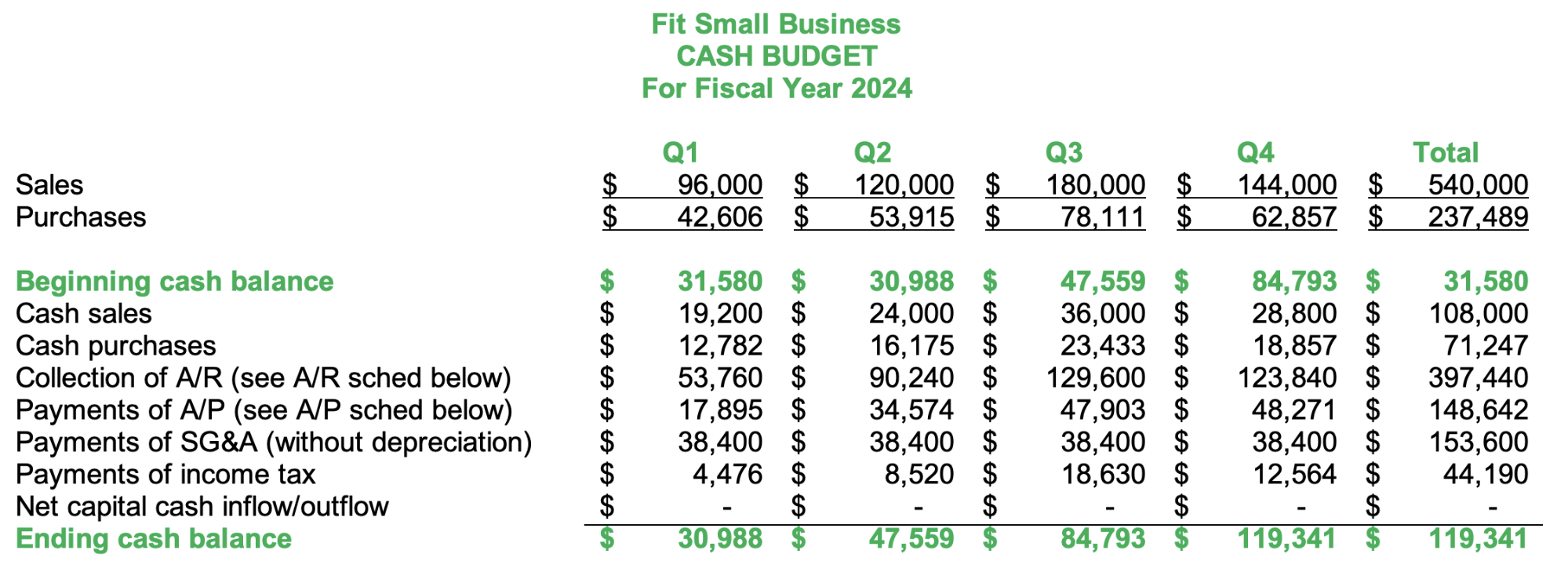
Cash budget
Accounts Receivable & Accounts Payable Schedule
Collections from accounts receivables (A/R) and payments of accounts payable (A/P) are integral parts of the cash budget. Creating the A/R and A/P schedules helps in computing the ending balance of A/R and A/P and the amount of cash collections and payments per quarter. Below are the supporting A/R and A/P schedules for our cash budget above:
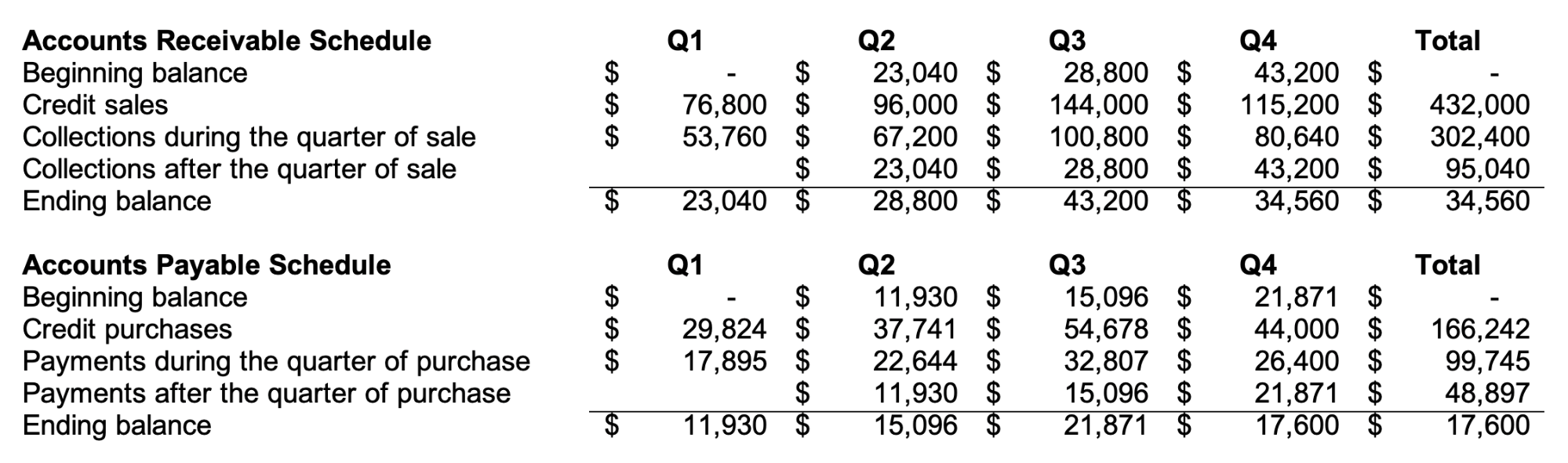
A/R and A/P schedules
Step 9: Assemble the Proforma Financial Statements Based on Budgeted Figures
The ultimate result of the budgeting process is the proforma financial statements, which are the budgeted or projected results of planned activities. If the budget goes as planned, the actual financial statements should be near the proforma financial statements. Below are the proforma income statement and balance sheet in our small business budget template.
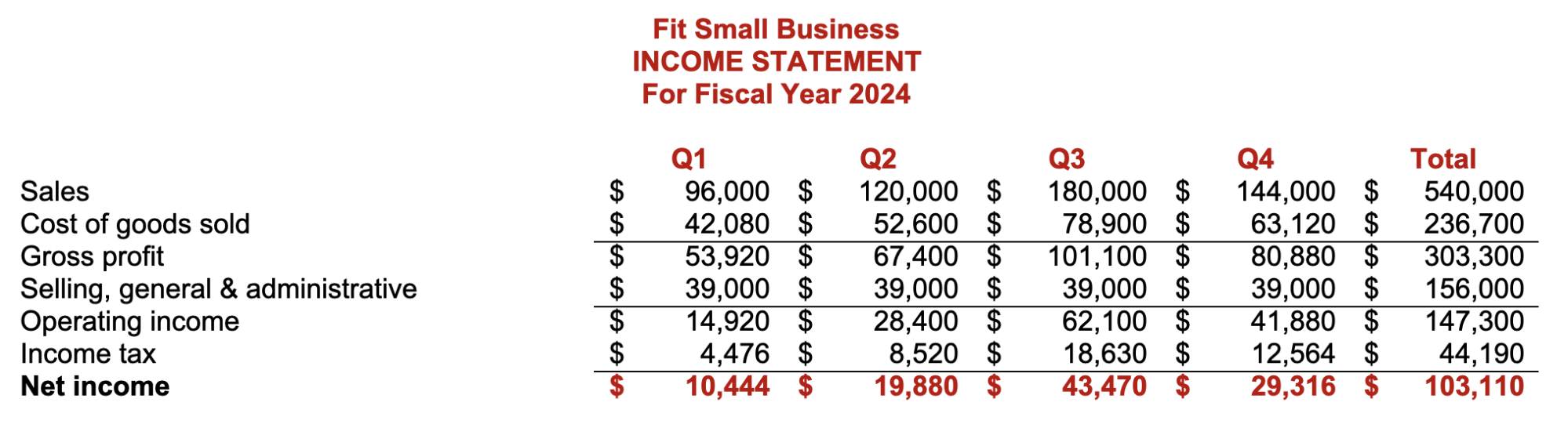
Proforma Income Statement
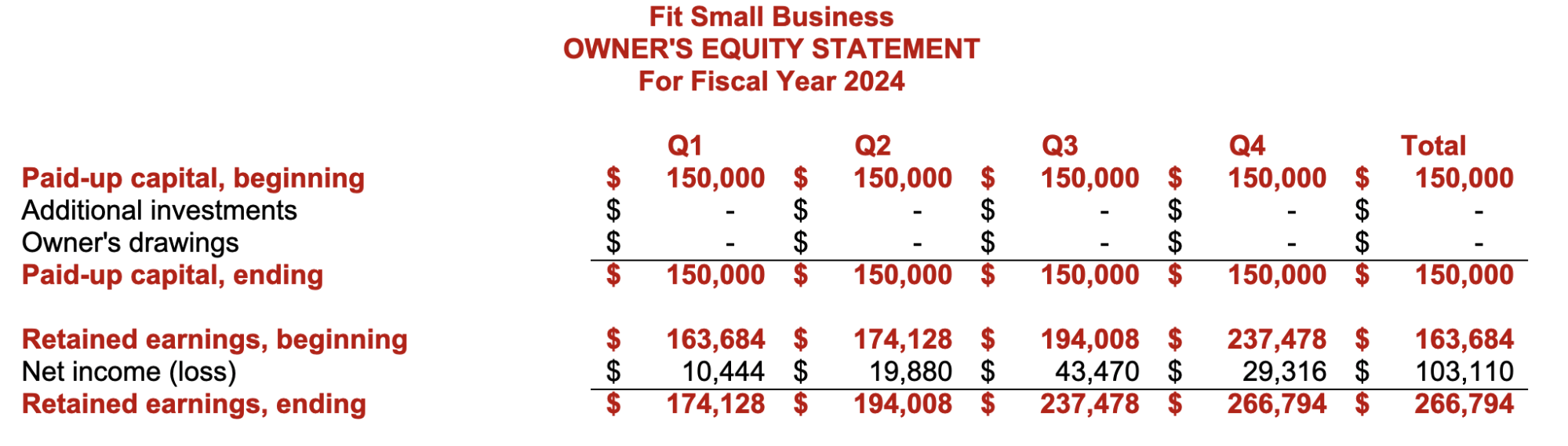
Proforma Owner’s Equity Statement
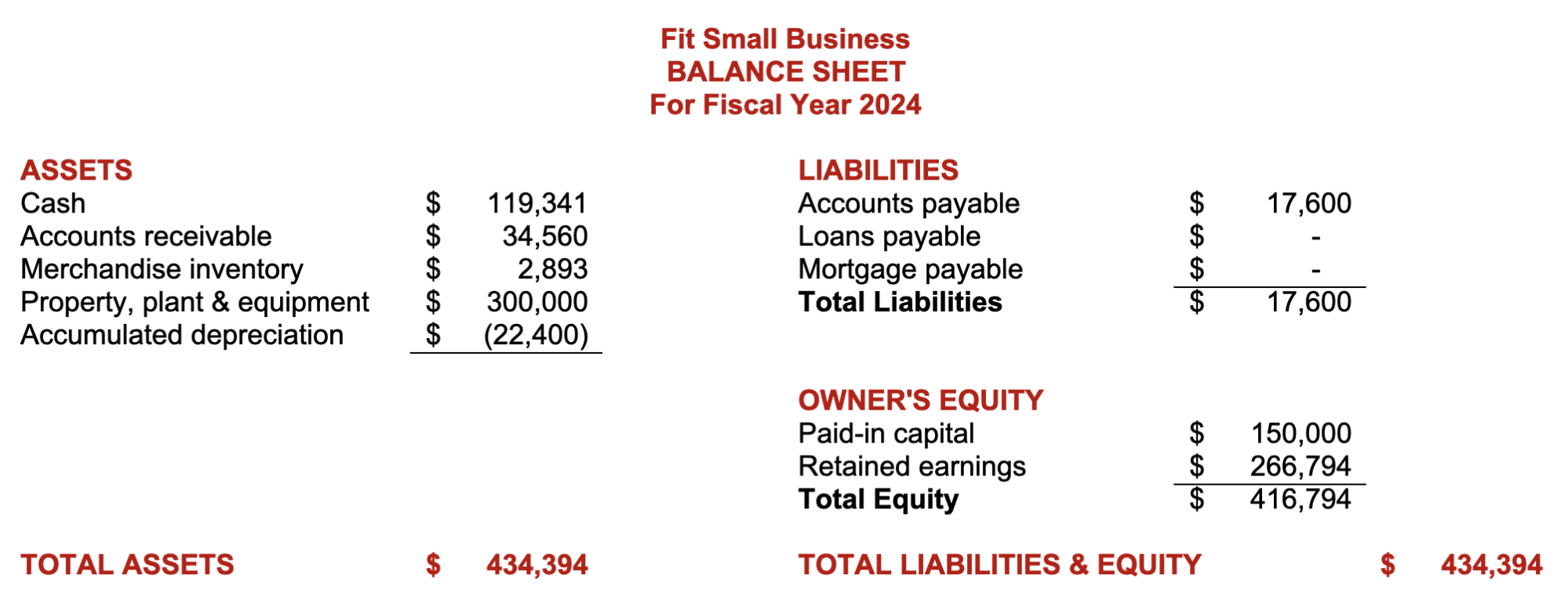
Proforma Balance Sheet
Budgeting helps businesses plan on future events and meet company goals. However, it is likely that you will experience difficulties and problems during the budgeting process. The four problems we’ll discuss are budgetary slack, goal incongruence, budget myopia, and standard setting.
Budgetary slack and goal incongruence occur when managers are not aligned with the business’s overall goals and objectives, while budget myopia happens when the business forgets to consider the impact of short-term decisions in the long run. Lastly, standard setting often poses a problem when standards are too high or ideal. Let’s discuss each of them in greater detail below.
Budgetary Slack
Sometimes, managers and heads can use budgets to preempt results to their favor. This unethical practice is called budgetary slack or budget padding. Budget slacks occur when managers underestimate revenue goals and overestimate expense goals and when the business follows the participatory budget involvement strategy.
When time for evaluation arrives, budget slacks will make the manager’s performance as exemplary. Managers tend to include budgetary slacks when top management is too strict and punitive whenever budgets aren’t met.
For example, the sales manager underestimates the sales forecast at $50,000 for the first quarter, knowing that they can achieve actual sales of $70,000. This example shows how budgetary slack can affect performance evaluation and create a false reflection of the company’s ability to generate revenue.
Goal Incongruence
Budgets are goals. When goals of management and employees don’t meet, the budget will not reflect the results that’s best for the business as a whole. Preventing goal incongruence enhances the quality of the budget. The goal of employees should be aligned with the business’s goals, and top management should provide opportunities for employees to pursue their career growth within the business.
Improper communication of business goals and ineffective leadership are the common causes of goal incongruence. As a small business owner or manager, you should show employees that you are committed to them with respect to their professional goals and that you expect them to align themselves with the business’s overall goals.
Budget Myopia
Budget myopia occurs when budgeting focuses only on short-term goals without considering how these goals will affect the company in the future. Managers become “myopic” in budgeting when they see budgets as measures for performance—they forget that the main objective of budgeting is to plan, organize, and manage the firm’s resources. As a result, budget realignments occur because there is a failure to plan future events.
Standard Setting
Another hurdle in budgeting is setting standards, which are tools for planning and controlling. If used inappropriately, they can cause problems in the budgeting process. It is important that you have to set your standards at a practical level.
Practical standards allow room for error or inefficiencies. It gives employees a chance to learn and improve their outputs without affecting performance. Unwise managers often impose ideal standards or standards that require optimum performance and perfection.
As a result, imposing ideal standards results in employee burnout, decreased productivity, and negative employee morale. Discouraged employees might also result in dysfunctional behavior that might be detrimental to the company.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is budgeting important.
Budgets help in planning and managing business resources. Since plans and goals require an outflow of resources, budgets help the business determine the right amount of resources needed to achieve the goal.
Who should have an active participation in the budgeting process for small businesses?
The small business owner should have an active role in helping managers and supervisors craft their budgets. As the owner, you should guide your employees to align their goals with the business’ overall goals.
With our small business budget guide and template, you can create a small business master budget. We hope that the template will help you understand why budgeting is crucial to the planning, organizing, and controlling business operations.
About the Author

Find Eric Gerard On LinkedIn
Eric Gerard Ruiz, CPA
Eric is an accounting and bookkeeping expert for Fit Small Business. He has a CPA license in the Philippines and a BS in Accountancy graduate at Silliman University. Since joining FSB, Eric has used his expertise and authority in curating and writing content about small business accounting and bookkeeping, accounting software, financial accounting and reporting, managerial accounting, and financial management.
Join Fit Small Business
Sign up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. Select the newsletters you’re interested in below.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated May 7, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
The Best Free Business Budget Templates
Published: October 12, 2023
Business budgets are a source of truth for your income and expenses. That includes all the money you spend — from A/B testing your marketing campaigns to your monthly office rent.

While organizing the numbers may sound difficult, using a business budget template makes the process simple. Plus, there are thousands of business budget templates for you to choose from.

We’ll share seven budget templates that can help organize your finances. But first, you’ll learn about different types of business budgets and how to create one.
What is a Business Budget?
A business budget is a spending plan that estimates the revenue and expenses of a business for a period of time, typically monthly, quarterly, or yearly.
The business budget follows a set template, which you can fill in with estimated revenues, plus any recurring or expected business expenses.
For example, say your business is planning a website redesign. You'd need to break down the costs by category: software, content and design, testing, and more.
Having a clear breakdown will help you estimate how much each category will cost and compare it with the actual costs.
Image Source
Types of Budgets for a Business
Master budget, operating budget, cash budget, static budget, departmental budget, capital budget, labor budget, project budget.

Business budgets aren’t one size fits all. In fact, there are many different types of budgets that serve various purposes. Let’s dive into some commonly used budgets:
Think of a master budget as the superhero of budgets — it brings together all the individual budgets from different parts of your company into one big, consolidated plan. It covers everything from sales and production to marketing and finances.
It includes details like projected revenues, expenses, and profitability for each department or business unit. It also considers important financial aspects like cash flow, capital expenditures, and even creates a budgeted balance sheet to show the organization's financial position.
The master budget acts as a guide for decision-making, helps with strategic planning, and gives a clear picture of the overall financial health and performance of your company. It's like the master plan that ties everything together and helps the organization move in the right direction.
Your operating budget helps your company figure out how much money it expects to make and spend during a specific period, usually a year. It not only predicts the revenue your business will bring in, but also outlines expenses it will need to cover, like salaries, rent, bills, and other operational costs.
By comparing your actual expenses and revenue to the budgeted amounts, your company can see how it's performing and make adjustments if needed. It helps keep things in check, allowing your business to make wise financial decisions and stay on track with its goals.
.png)
Free Business Budget Templates
Manage your business, personal, and program spend on an annual, quarterly, and monthly basis.
- Personal Budget Template
- Annual Budget Template
- Program Budget Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A cash budget estimates the cash inflows and outflows of your business over a specific period, typically a month, quarter, or year. It provides a detailed projection of cash sources and uses, including revenue, expenses, and financing activities.
The cash budget helps you effectively manage your cash flow, plan for cash shortages or surpluses, evaluate the need for external financing, and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
By utilizing a cash budget, your business can ensure it has enough cash on hand to meet its financial obligations, navigate fluctuations, and seize growth opportunities.
A static budget is a financial plan that remains unchanged, regardless of actual sales or production volumes.
It’s typically created at the beginning of a budget period and doesn’t account for any fluctuations or changes in business conditions. It also assumes that all variables, such as sales, expenses, and production levels, will remain the same throughout the budget period.
While a static budget provides a baseline for comparison, it may not be realistic for businesses with fluctuating sales volumes or variable expenses.
A departmental budget focuses on the financial aspects of a specific department within your company, such as sales, marketing or human resources.
When creating a departmental budget, you may look at revenue sources like departmental sales, grants, and other sources of income. On the expense side, you consider costs such as salaries, supplies, equipment, and any other expenses unique to that department.
The goal of a departmental budget is to help the department manage its finances wisely. It acts as a guide for making decisions and allocating resources effectively. By comparing the actual numbers to the budgeted amounts, department heads can see if they're on track or if adjustments need to be made.
A capital budget is all about planning for big investments in the long term. It focuses on deciding where to spend money on things like upgrading equipment, maintaining facilities, developing new products, and hiring new employees.
The budget looks at the costs of buying new stuff, upgrading existing things, and even considers depreciation, which is when something loses value over time. It also considers the return on investment, like how much money these investments might bring in or how they could save costs in the future.
The budget also looks at different ways to finance these investments, whether it's through loans, leases, or other options. It's all about making smart decisions for the future, evaluating cash flow, and choosing investments that will help the company grow and succeed.
A labor budget helps you plan and manage the costs related to your employees. It involves figuring out how much your business will spend on wages, salaries, benefits, and other labor-related expenses.
To create a labor budget, you'll need to consider factors like how much work needs to be done, how many folks you'll need to get it done, and how much it'll all cost. This can help your business forecast and control labor-related expenses and ensure adequate staffing levels.
By having a labor budget in place, your business can monitor and analyze your labor costs to make informed decisions and optimize your resources effectively.
A project budget is the financial plan for a specific project.
Let's say you have an exciting new project you want to tackle. A project budget helps you figure out how much money you'll need and how it will be allocated. It covers everything from personnel to equipment and materials — basically, anything you'll need to make the project happen.
By creating a project budget, you can make sure the project is doable from a financial standpoint. It helps you keep track of how much you planned to spend versus how much you actually spend as you go along. That way, you have a clear idea of whether you're staying on track or if there are any financial challenges that need attention.
How to Create a Business Budget
While creating a business budget can be straightforward, the process may be more complex for larger companies with multiple revenue streams and expenses.
No matter the size of your business, here are the basic steps to creating a business budget.
1. Gather financial data.
Before you create a business budget, it’s important to gather insights from your past financial data. By looking at things like income statements, expense reports, and sales data, you can spot trends, learn from past experiences, and see where you can make improvements.
Going through your financial history helps you paint a true picture of your income and expenses. So, when you start creating your budget, you can set achievable targets and make sure your estimates match what's actually been happening in your business.
2. Find a template, or make a spreadsheet.
There are many free or paid budget templates online. You can start with an already existing budget template. We list a few helpful templates below.
You may also opt to make a spreadsheet with custom rows and columns based on your business.
3. Fill in revenues.
Once you have your template, start by listing all the sources of your business’ income. With a budget, you’re planning for the future, so you’ll also need to forecast revenue streams based on previous months or years. For a new small business budget, you’ll rely on your market research to estimate early revenue for your company.
When you estimate your revenue , you're essentially figuring out how much money you have to work with. This helps you decide where to allocate your resources and which expenses you can fund.
4. Subtract fixed costs for the time period.
Fixed costs are the recurring costs you have during each month, quarter, or year. Examples include insurance, rent for office space, website hosting, and internet.
The key thing to remember about fixed costs is that they stay relatively stable, regardless of changes in business activity. Even if your sales decrease or production slows down, these costs remain the same.
However, it's important to note that fixed costs can still change over the long term, such as when renegotiating lease agreements or adjusting employee salaries.
5. Consider variable costs.
Variable costs will change from time to time. Unlike fixed costs, variable costs increase or decrease as the level of production or sales changes.
Examples include raw materials needed to manufacture your products, packaging and shipping costs, utility bills, advertising costs, office supplies, and new software or technology.
You may always need to pay some variable costs, like utility bills. However, you can shift how much you spend toward other expenses, like advertising costs, when you have a lower-than-average estimated income.
6. Set aside time for business budget planning.
Unexpected expenses might come up, or you might want to save to expand your business. Either way, review your budget after including all expenses, fixed costs, and variable costs. Once completed, you can determine how much money you can save. It’s wise to create multiple savings accounts. One should be used for emergencies. The other holds money that can be spent on the business to drive growth.
Fill out the form to get the free templates.
How to manage a business budget.
There are a few key components to managing a healthy business budget.
Budget Preparation
The process all starts with properly preparing and planning the budget at the beginning of each month, quarter, or year. You can also create multiple budgets, some short-term and some long-term. During this stage, you will also set spending limits and create a system to regularly monitor the budget.
Budget Monitoring
In larger businesses, you might delegate budget tracking to multiple supervisors. But even if you’re a one-person show, keep a close eye on your budget. That means setting a time in your schedule each day or week to review the budget and track actual income and expenses. Be sure to compare the actual numbers to the estimates.
Budget Forecasting
With regular budget tracking, you always know how your business is doing. Check in regularly to determine how you are doing in terms of revenue and where you have losses. Find where you can minimize expenses and how you can move more money into savings.
Why is a Budget Important for a Business?
A budget is crucial for businesses. Without one, you could easily be drowning in expenses or unexpected costs.
The business budget helps with several operations. You can use a business budget to keep track of your finances, save money to help you grow the business or pay bonuses in the future, and prepare for unexpected expenses or emergencies.
You can also review your budget to determine when to take the next leap for your business. For example, you might be dreaming of a larger office building or the latest software, but you want to make sure you have a healthy net revenue before you make the purchase.
Best Free Business Budget Templates
1. marketing budget template.
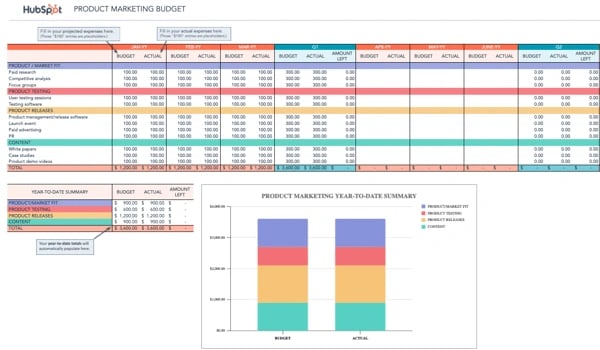
Knowing how to manage a marketing budget can be a challenge, but with helpful free templates like this marketing budget template bundle , you can track everything from advertising expenses to events and more.
This free bundle includes eight different templates, so you can create multiple budgets to help you determine how much money to put toward marketing, plus the return on your investment.
2. Small Business Budget Template
For small businesses, it can be hard to find the time to draw up a budget, but it’s crucial to help keep the business in good health.
Capterra offers a budget template specifically for small businesses. Plus, this template works with Excel. Start by inputting projections for the year. Then, the spreadsheet will project the month-to-month budget. You can input your actual revenue and expenses to compare, making profits and losses easy to spot.
3. Startup Budget Template
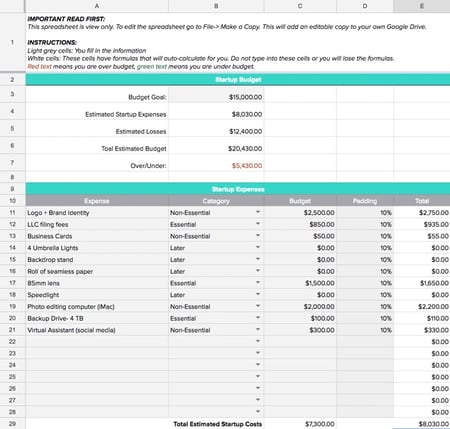
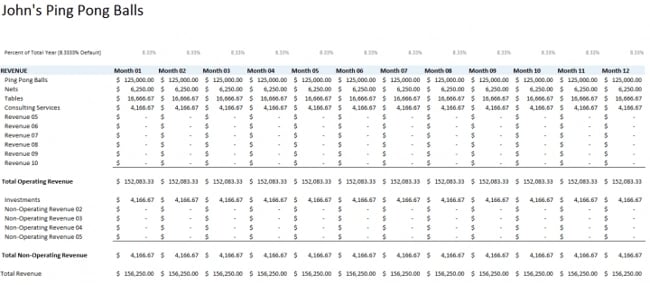
What if you don’t have any previous numbers to rely on to create profit and expense estimates? If you are a startup, this Gusto budget template will help you draw up a budget before your business is officially in the market. This will help you track all the expenses you need to get your business up and running, estimate your first revenues, and determine where to pinch pennies.
4. Free Business Budget Template
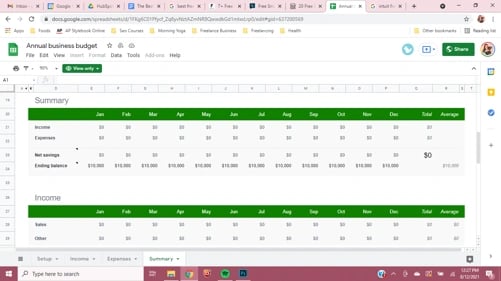
You might be familiar with Intuit. Many companies, big and small, rely on Intuit’s services like Quickbooks and TurboTax. Even if you don’t use the company’s paid financial services, you can take advantage of Intuit’s free budget template , which works in Google Sheets or Excel.
It features multiple spreadsheet tabs and simple instructions. You enter your revenue in one specific tab and expenses in another. You can also add additional tabs as needed. Then, like magic, the spreadsheet uses the data in the income and expense tabs to summarize the information. This template can even determine net savings and the ending balance.
5. Department Budget Sheet
A mid- to large-size company will have multiple departments, all with different budgetary needs. These budgets will all be consolidated into a massive, company-wide budget sheet. Having a specific template for each department can help teams keep track of spending and plan for growth.
This free template from Template.net works in either document or spreadsheet formats. This budget template can help different departments keep track of their income and spending.
6. Project Budget Template
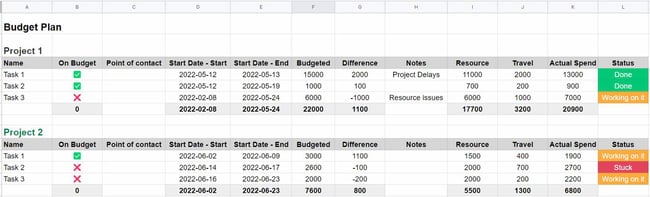
Every new project comes with expenses. This free budget template from Monday will help your team estimate costs before undertaking a project. You can easily spot if you're going over budget midway through a project so you can adjust.
This template is especially useful for small companies that are reporting budgets to clients and for in-house teams getting buy-in for complex projects.
7. Company Budget Template
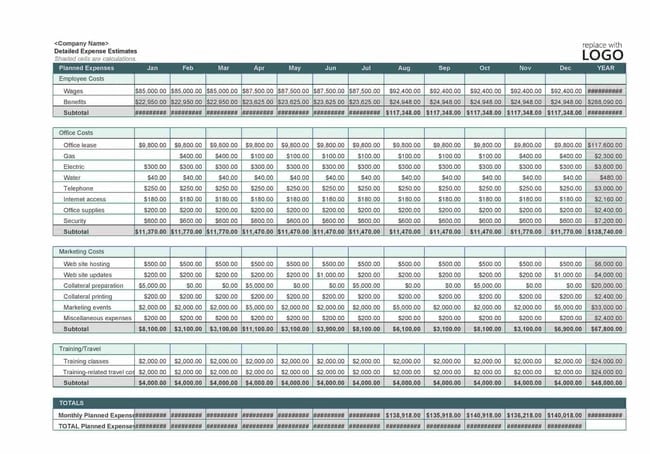
Want to keep track of every penny? Use this template from TemplateLab to draw up a detailed budget. The list of expenses includes fixed costs, employee costs, and variable costs. This business template can be especially useful for small businesses that want to keep track of expenses in one, comprehensive document.
Create a Business Budget to Help Your Company Grow
Making your first business budget can be daunting, especially if you have several revenue streams and expenses. Using a budget template can make getting started easy. And, once you get it set up, these templates are simple to replicate.
With little planning and regular monitoring, you can plan for the future of your business.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in September 2021 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![budget of your business plan Marketing Budget: How Much Should Your Team Spend in 2024? [By Industry]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how%20to%20spend%20your%20marketing%20budget_featured.webp)
Marketing Budget: How Much Should Your Team Spend in 2024? [By Industry]
![budget of your business plan How Marketing Leaders are Navigating Recession [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how%20marketing%20leaders%20are%20navigating%20recession.webp)
How Marketing Leaders are Navigating Recession [New Data]
![budget of your business plan 3 Ways Marketers are Already Navigating Potential Recession [Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-marketers-are-navigating-recession.jpg)
3 Ways Marketers are Already Navigating Potential Recession [Data]
![budget of your business plan Marketing Without a Budget? Use These 10 Tactics [Expert Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketing%20without%20budget.jpg)
Marketing Without a Budget? Use These 10 Tactics [Expert Tips]

24 Ways to Spend Your Marketing Budget Next Quarter

Startup Marketing Budget: How to Write an Incredible Budget for 2023
![budget of your business plan How to Manage Your Entire Marketing Budget [Free Budget Planner Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/free-marketing-budget-templates_5.webp)
How to Manage Your Entire Marketing Budget [Free Budget Planner Templates]

10 Best Free Project Management Budget Templates for Marketers

What Marketing Leaders Are Investing in This Year

The Best Free Business Budget Worksheets
6 templates to manage your business, personal, and program spend on an annual, quarterly, and monthly basis.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Building Your Site
- Promote Your Site
- Entrepreneurship
- Design & Inspiration
- Tips & Tricks
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Business Budget Plan
A well-structured business budget plan is crucial for success. It serves as a financial stability and growth roadmap, allowing companies to allocate resources wisely and make informed decisions. Understanding the basics of business budgeting is essential for any entrepreneur or business owner looking to create a solid financial plan to help them achieve their goals.
The Importance of Business Budget Planning
Business budget planning is not just about crunching numbers; it's about setting clear financial goals and outlining strategies to achieve them. It provides a framework for managing expenses, maximizing revenue , and ensuring the long-term sustainability of a company. Without a well-thought-out budget plan, businesses may struggle to stay afloat in today's competitive market.
Understanding the Basics of Business Budget
At its core, a business budget is an estimate of future income and expenses based on historical data and current trends. It involves identifying all sources of revenue and categorizing various types of expenses, including fixed costs (rent, salaries) and variable costs (utilities, marketing). Understanding these fundamental concepts is essential for creating an effective budget plan.
Benefits of Creating a Business Budget Plan
The benefits of creating a business budget plan are manifold. It clarifies where money is being spent and helps identify areas where costs can be reduced or investments can be made to drive growth. Additionally, having a well-structured budget plan can instill confidence in stakeholders, such as investors or lenders who want to see evidence of sound financial management .
Now that we've laid the groundwork for understanding the importance of business budget planning and its basics, let's delve deeper into the process by assessing your financial situation and setting achievable goals.
Assessing Your Financial Situation

Sarah Horsman Template from Strikingly
Now that you understand the importance of business budget planning, it's time to assess your financial situation. This involves analyzing your current revenue and expenses, identifying fixed and variable costs, and projecting future income and expenses.
Analyzing Current Revenue and Expenses
You must clearly understand your current revenue and expenses to create a business budget plan that works for your company . This involves looking at your sales figures, incoming cash flow, and all the money going out of your business. By analyzing these numbers, you can gain valuable insights into where your money is coming from and where it's going.
Identifying Fixed and Variable Costs
When creating a business budget plan, it's crucial to distinguish between fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs, such as rent or salaries, remain constant regardless of your level of production or sales. Variable costs, like raw materials or shipping expenses, fluctuate with production levels or sales volume. Identifying these costs will help you make more accurate financial projections.
Projecting Future Income and Expenses
Looking ahead is an essential part of business budget planning. You can anticipate potential financial challenges or opportunities by projecting future income and expenses based on historical data and market trends. This will enable you to make informed decisions about resource allocation and strategic investments.
Remember that creating a business budget plan is not just about crunching numbers; it's about setting the stage for sustainable growth and success in the long run.
Setting Financial Goals
Now that you understand the basics of business budget planning, it's time to set your financial goals . Establishing short-term and long-term objectives can create a roadmap for your business's financial success. Whether increasing revenue or reducing expenses, having clear goals will guide your budgeting decisions.
Establishing Short-term and Long-term Objectives
To effectively create a business budget plan, it's crucial to establish both short-term and long-term financial objectives. Short-term goals could include reducing overhead costs by a certain percentage within six months, while long-term goals might involve doubling your annual revenue within three years. These objectives provide direction for allocating funds and making strategic financial decisions.
Allocating Funds for Growth and Expansion
One of the key benefits of creating a business budget plan is the ability to allocate funds for growth and expansion. Whether you're looking to invest in new equipment, expand your product line, or open additional locations, setting aside funds in your budget allows you to pursue these opportunities without compromising your financial stability .
Planning for Contingencies and Emergencies
In business, unexpected events can have a significant impact on your finances. Planning for contingencies and emergencies is essential when creating a business budget plan. You can protect your business from potential financial hardships by setting aside a portion of your budget for unforeseen circumstances, such as economic downturns or equipment breakdowns.
Creating the Budget Plan
Now that you understand the importance of business budget planning, it's time to create a solid business budget plan. When choosing the right budgeting method, consider your company's size, industry, and financial goals. Whether it's zero- or activity-based budgeting, select a method that aligns with your business objectives and ensures accurate financial management .
Choosing the Right Budgeting Method
Selecting the right budgeting method is crucial for effective business budget planning. Zero-based budgeting involves justifying every expense from scratch, while activity-based budgeting focuses on cost allocation based on activities. Whichever method you choose, ensure it aligns with your company's financial objectives and provides a clear resource allocation roadmap.
Allocating Funds to Different Departments
When creating a business budget plan, allocating funds to different departments is essential based on their specific needs and priorities. Consider departmental goals, operational requirements, and revenue generation potential when distributing financial resources. This approach ensures each department has the necessary funds to function effectively within the business framework.
Monitoring and Adjusting the Budget as Needed
Once you've allocated funds to different departments in your business budget plan, monitoring and adjusting the budget as needed is essential. Regularly review your financial performance against the set targets and adjust based on changing market conditions or internal dynamics. Flexibility ensures that your business remains agile and responsive to evolving economic landscapes.
By carefully choosing the right budgeting method, allocating funds to different departments thoughtfully, and monitoring and adjusting the budget as needed, you can create a robust business budget plan that sets your company up for long-term success in managing its finances effectively.
Implementing the Budget Plan

Quantum Template from Strikingly
Now that you have created a solid business budget plan, it's time to implement it. This step involves communicating the budget to key stakeholders, training employees on budgetary guidelines, and integrating the budget into daily operations.
Communicating the Budget to Key Stakeholders
It is crucial to inform all relevant stakeholders about the business budget plan. This includes shareholders, managers, and other decision-makers who must know the financial goals and constraints. Clear communication will ensure everyone is on the same page and can work towards common objectives.
Training Employees on Budgetary Guidelines
Employees play a vital role in adhering to the budget plan. Providing them with comprehensive training on budgetary guidelines will help them understand their responsibilities in managing costs and staying within allocated funds. This will empower them to make informed decisions that align with the company's financial objectives.
Integrating the Budget into Daily Operations
Incorporating the business budget plan into daily operations requires a strategic approach. It involves aligning all activities with the financial goals outlined in the budget, ensuring that resources are utilized efficiently, and making adjustments as needed to stay within budgetary limits. This integration fosters a culture of financial responsibility throughout the organization.
By effectively implementing your business budget plan through clear communication, employee training, and seamless integration into daily operations, you can set your company up for financial success while achieving your long-term objectives.
Tracking and Evaluating Performance

Monitoring Budget Variance and Deviations
Once you have implemented your business budget plan, it's crucial to regularly monitor the budget variance and identify any deviations from the projected expenses and revenue. This will help you understand where adjustments need to be made and where you may exceed or fall short of your financial goals.
Conducting Regular Financial Reviews
Regular financial reviews are essential for evaluating the performance of your business budget plan. By conducting these reviews, you can assess whether your actual income and expenses align with what was projected in the budget. This will allow you to make informed decisions on where to allocate funds or where to cut back to stay on track with your financial objectives.
Making Informed Decisions Based on Budget Analysis
Analyzing the data from your business budget plan is key to making informed decisions for your company's future. By understanding how well your budget is performing, you can strategically plan for growth, expansion, and any potential contingencies or emergencies that may arise.
Continuously tracking and evaluating the performance of your business budget plan is vital for maintaining financial stability and achieving long-term success. By closely monitoring variance, conducting regular reviews, and making informed decisions based on budget analysis, you can ensure that your business stays on track toward its financial goals.
Tips for Successfully Implementing Your Business Budget Plan: Striking a Balance Between Dreams and Dollars
Every business owner knows the importance of a budget—it's the roadmap to financial stability and growth. But crafting a brilliant budget is only half the battle. The real test lies in implementation. How do you translate those meticulously planned numbers into tangible results? Here are some key tips to ensure your business budget plan becomes a reality, not just a document gathering dust on a shelf:
1. Set SMART Goals
Your budget shouldn't exist in a vacuum. It should be tightly woven into your business goals. But instead of vague aspirations, set SMART goals: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound . This clarity provides a clear direction for allocating resources and tracking progress.
2. Foster Collaboration
Budgeting isn't a solo act. Involve key stakeholders in the process, from department heads to team members. This collaborative approach fosters buy-in, ensures everyone understands their role in achieving financial goals, and harnesses diverse perspectives for smarter decision-making.
3. Embrace Transparency
Open communication is crucial. Share the budget with relevant team members, not just financial experts. This transparency builds trust, empowers employees to make informed decisions, and encourages a culture of financial responsibility.
4. Track and Monitor
Don't let your budget become a static document. Regularly track actual spending against the planned figures. Identify any discrepancies, analyze the causes, and make adjustments as needed. This active monitoring allows you to course-correct before small deviations snowball into major issues.
5. Leverage Technology

Strikingly Landing Page
- Easy to use. Strikingly is a user-friendly platform that is easy to use, even for those without experience in website design .
- Affordable. Strikingly offers a variety of affordable plans to fit any budget.
- Mobile-friendly. Strikingly's websites are mobile-friendly, so you can reach your customers wherever they are.

Strikingly Website on a Mobile Device
- SEO-friendly. Strikingly's websites are SEO-friendly so that you can improve your website's ranking in search results.
Strikingly is a valuable tool to help businesses create and manage their online presence . Strikingly's features can also be helpful for businesses when creating a business budget plan.
6. Review and Adapt
The business landscape is dynamic. Be prepared to adapt your budget as circumstances change. Regularly review your plan, considering market shifts, new opportunities, and unforeseen challenges. A flexible approach ensures your budget remains relevant and responsive to the ever-evolving environment.
7. Celebrate Successes
Don't forget to celebrate your wins! Recognizing positive financial milestones and acknowledging the collective effort motivates everyone and reinforces the importance of adhering to the budget plan.
8. Build a Culture of Accountability
Create a culture where all share financial responsibility. Hold yourself and your team accountable for staying within budget limits. This fosters a sense of ownership and promotes responsible financial behavior across the organization.
9. Communicate Effectively
Regularly communicate budget updates, performance metrics, and any necessary adjustments to the team. This transparency keeps everyone informed, engaged, and empowered to contribute to the business's financial success.
10. Continuously Improve
Never stop learning and evolving. Regularly evaluate your budgeting process, identify areas for improvement, and implement new strategies to optimize your financial management. Remember, a successful budget is a living document, constantly adapting and growing alongside your business.
By following these tips and embracing tools like Strikingly , you can transform your business budget plan from a theoretical framework into a powerful tool for driving growth and achieving your financial aspirations. Remember, successful budgeting is a journey, not a destination. It requires ongoing commitment, collaboration, and a continuous focus on improvement. So, embark on your financial journey confidently and watch your business reach new heights of success.
A well-structured business budget plan can lead to long-term financial stability and growth. It helps identify areas for cost savings, allocate funds for expansion, and plan for contingencies, ultimately leading to improved profitability and sustainability for your business.
Remember that creating a well-structured business budget plan is crucial for the success and sustainability of your business. By following these steps and incorporating these tips into your planning process, you can ensure that your business is on the path to financial success and growth.
Trusted by millions of entrepreneurs & creatives.
How to Create a Small Business Budget in 5 Simple Steps
Want to protect the financial health of your small business? You need a business budget. Here's how to create one.

When you build a business, there are a lot of things to stay on top of, from marketing and finding new clients to building a website and establishing your digital presence. But there’s one element that you want to stay on top of from the very beginning—and that’s your business budget.
Having a detailed and accurate budget is a must if you want to build a thriving, sustainable business. But how, exactly, do you create one? What are the steps for business budget planning?
As a small business owner, let’s take a look at how to create a business budget in five simple, straightforward steps.
What’s a Business Budget—and Why Is It Important?
Before we jump into creating a business budget, let’s quickly cover what a business budget is—and why it’s so important for small businesses.
A business budget is an overview of your business funds. It outlines key information on both the current state of your finances (including income and expenses) and your long-term financial goals. Because your budget will play a key role in making sound financial decisions for your business, it should be one of the first tasks you tackle to improve business success.
And, as a financially savvy owners, you’ll also want to have a budget in place to help you:
- Make sound financial decisions. In many ways, your business budgets are like a financial road map. It helps you evaluate where your business finances currently stand—and what you need to do to hit your financial goals in the future for business growth.
- Identify where to cut spending or grow revenue. Your business budgets can help you identify areas to decrease your spending or increase your revenue, which will increase your profitability in the process, outline unexpected costs, and help your sustain your business goals.
- Land funding to grow your business. If you’re planning to apply for a business loan or raise funding from investors, you’ll need to provide a detailed budget that outlines your income and expenses.
Now that you understand why budget creation is so important to your business decisions, let’s jump into how to do it.
Business Budget Step 1: Tally Your Income Sources

First things first. When building a small business budget, you need to figure out how much money your business is bringing in each month and where that money is coming from – this will hep create an operating budget based on your business income.
Your sales figures (which you can access using the Profit & Loss report function in FreshBooks) are a great place to start. From there, you can add any other sources of income for your business throughout the month.
Your total number of income sources will depend on your business model.
For example, if you run a freelance writing business, you might have multiple sources of income from:
- Freelance writing projects
- A writing course you sell on your website
- Consulting with other writers who are starting small businesses
Or, if you run a brick-and-mortar retail business, you may only have one source of income from your store sales.
However many income sources you have, make sure to account for any and all income that’s flowing into your business—then tally all those sources to get a clear picture of your total monthly income to build your master business budget template.
Business Budget Step 2: Determine Fixed Costs
Once you’ve got a handle on your income, it’s time to get a handle of your costs—starting with fixed costs.
Your fixed costs are any expenses that stay the same from month to month. This can include expenses like rent, certain utilities (like internet or phone plans), website hosting, and payroll costs.
Review your expenses (either via your bank statements or through your FreshBooks reports) and see which costs have stayed the same from month to month. These are the expenses you’re going to categorize as fixed costs.
Once these costs are determined, add them together to get your total fixed and variable costs expense for the month.
TIP: If you’re just starting your business and don’t have financial data to review, make sure to use projected costs. For example, if you’ve signed a lease for office space, use the monthly rent you will pay moving forward.
Business Budget Step 3: Include Variable Expenses
Related articles.

Variable costs don’t come with a fixed price tag—and will vary each month based on your business performance and activity. These can include things like usage-based utilities (like electricity or gas), shipping costs, sales commissions, or travel costs.
Variable expenses will, by definition, change from month to month. When your profits are higher than expected, you can spend more on the variables that will help your business scale faster. But when your profits are lower than expected, consider cutting these variable costs until you can get your profits up.
At the end of each month, tally these expenses. Over time, you’ll get a sense of how these expenses fluctuate with your business performance or during certain months, which can help you make more accurate financial projections and budget accordingly.
Business Budget Step 4: Predict One-Time Spends
Many of your business expenses will be regular expenses that you pay for each month, whether they’re fixed or variable costs. But there are also costs that will happen far less frequently. Just don’t forget to factor those expenses when you create a budget as well.
If you know you have one-time spends on the horizon (for example, an upcoming business course or a new laptop), adding them to your budget can help you set aside the financial resources necessary to cover those expenses—and protect your business from unexpected costs in the form of a sudden or large financial burden.
On top of adding planned one-time spends to your budget, you should also add a buffer to cover any unplanned purchases or expenses, like fixing a damaged cell phone or hiring an IT consultant to deal with a security breach. That way, when an unexpected expense pops up (and they always do), you’re prepared!
Business Budget Step 5: Pull It All Together
You’ve gathered all of your income sources and all of your revenue and expenses. What’s next? Pulling it all together to get a comprehensive view of your financial standing for the month.
On your businesses master budget, you’ll want to tally your total income and your total expenses (i.e., adding your total fixed costs, variable expenses, cost of goods, and one-time spends)—then compare cash flow in (income) to cash flow out (expenses) to determine your overall profitability.
Having a hard time visualizing what a business budget looks like in action? Here’s an operating budget example to give you an idea of what your new business budget might look like each month:
A Client Hourly Earnings: $5,000 B Client Hourly Earnings: $4,500 C Client Hourly Earnings: $6,000 Product Sales: $1,500 Loans: $1,000 Savings: $1,000 Investment Income: $500
Total Income: $19,500
Fixed Costs
Rent: $1,000 Internet: $50 Payroll costs: $5,000 Website hosting: $50 Insurance: $50 Government and bank fees: $25 Cell phone: $50 Accounting services : $100 Legal services: $100
Total Fixed Costs: $6,425
Variable Expenses
Sales commissions: $2,000 Contractor wages: $500 Electricity bill: $125 Gas bill: $75 Water bill: $125 Printing services: $300 Raw materials: $200 Digital advertising costs: $750 Travel and events: $0 Transportation: $50
Total Variable Expenses: $4,125
One-Time Spends
Office furniture: $450 Office supplies for new location: $300 December business retreat: $1,000 New time tracking software: $500 Client gifts : $100
One-Time Spends: $2,350
Expenses: $12,900
Total Income ($19,500) – Total Expenses ($12,900) = Total Net Income ($6,600)
Above all, once you have a clear sense of your profitability for the month, you can use it to make the right financial decisions for your small business moving forward.

For example, if you realize you’re in the red and spending more than you earn, you might cut your spending and focus on finding new clients . Alternatively, if your income is significantly higher than your expenses, you might consider investing your profits back into your business (like investing in new software or equipment).
Use Your Business Budget to Stay on Track
Putting in the work to create a budget for your small business may seem like a hassle. But while it takes a bit of time and energy, it’s worth the extra effort. Thorough business budgeting gives you the financial insights you need to make the right decisions for your business to grow, scale, and prosper in the future.
This post was updated in October 2023

Written by Deanna deBara , Freelance Contributor
Posted on June 20, 2017
Freshly picked for you

Thanks for subscribing to the FreshBooks Blog Newsletter.
Expect the first one to arrive in your inbox in the next two weeks. Happy reading!
Business growth
Business tips
7 free small business budget templates for future-proofing your finances

As a small business owner, you're likely balling with a lot more than your personal checking account. If you don't properly manage your business finances, there's more on the line than an overdraft fee—you now have an entire organization to account for.
Small business budgets are necessary to balance revenue, estimate how much you'll spend, and project financial forecasts, so you can stay out of the red and keep your business afloat.
But creating a small business budget template isn't a small task. Since I don't have a business to run, I did the heavy lifting for you—check out these free, downloadable templates for your small business budgeting.
Table of contents:
1. Static budget template
Best for: Multiple departments or revenue streams; Industries with complex operations
A static budget combines all the function-specific budgets a business uses into one. Typically, a static budget includes the following items (plus any other budgets your business might use):
Cash flow projections: Estimations of how much money will flow into and out of your business. They also help you decide when, how, and what you should spend money on.
Total expected spending: All estimated expenses, including labor and administrative costs.
By integrating all of your budgets and projections, the static budget provides a full picture of your business's estimated expenses and financial strategy for the upcoming fiscal year.
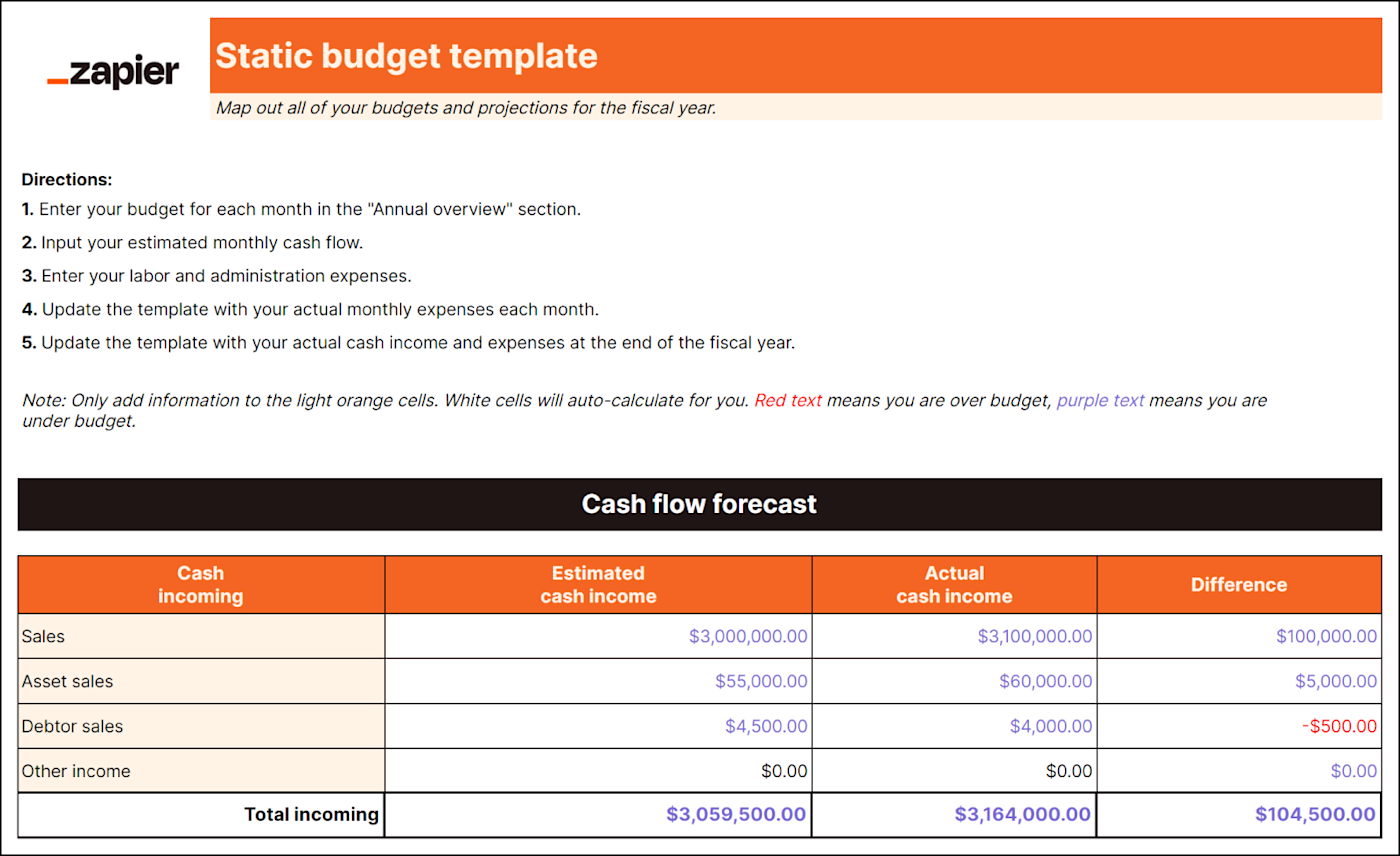
2. Overhead budget template
Best for: Service-based businesses
It's easy to forget about expenses that aren't directly tied to production, like delivery charges or utilities. But these costs exist (and can add up quickly), so you need an overhead budget. A detailed overhead budget template will include:
Administration expenses
It compares your budgeted amount to actual figures (warning: it may be a rude awakening) and can help improve accuracy for future financial planning.
Predicting overhead spending helps you plan how to use other funds more practically too—if you know how much you'll spend on overhead, you can make better business decisions. For example, you'd know whether you can afford to invest money into other initiatives like adding a delivery service or upgrading equipment.
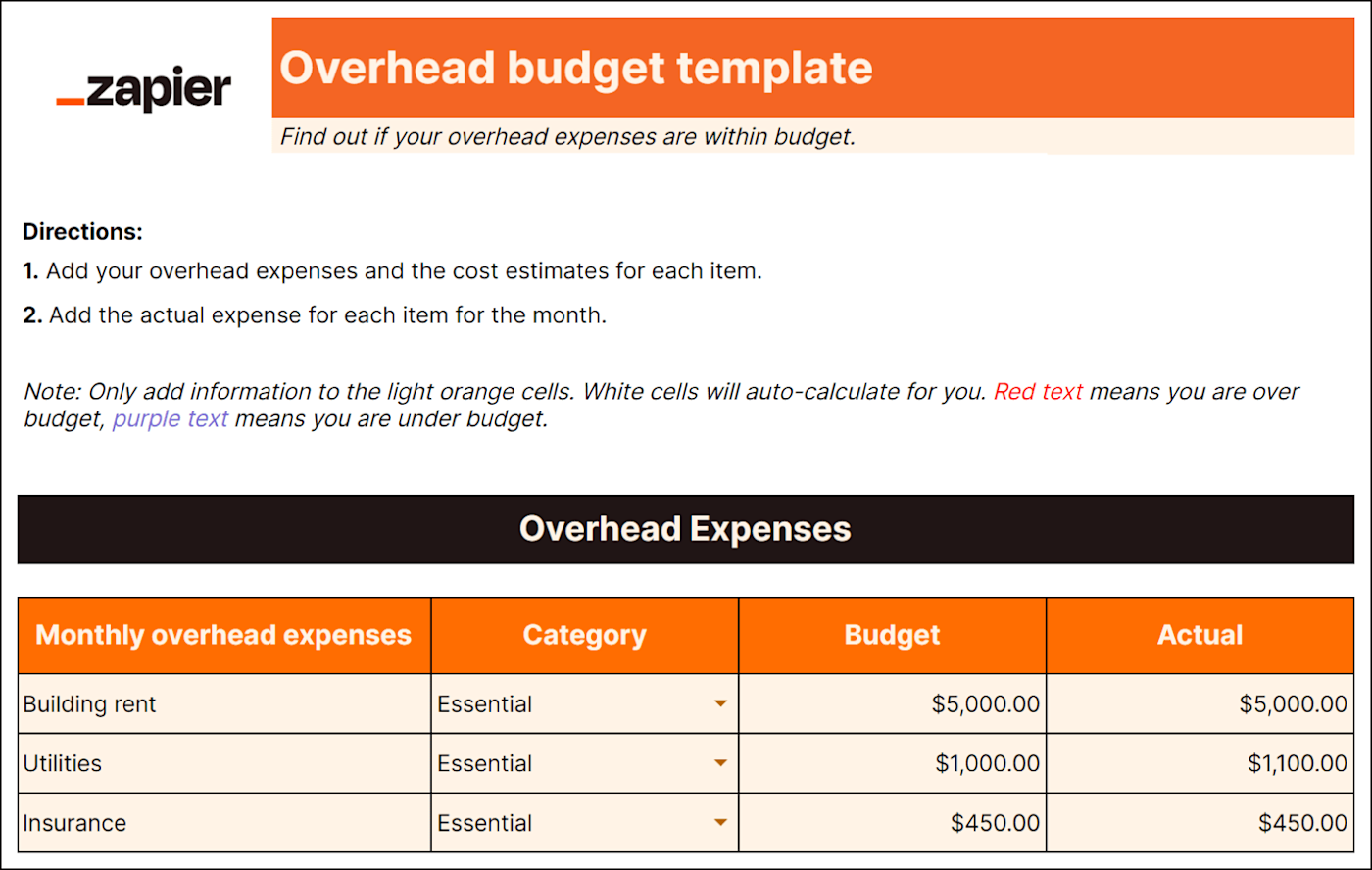
3. Multiple-project budget template
Best for: Project-based industries
Product-by-product COGS (cost of goods sold)
Labor costs
Equipment and resource costs
Indirect project expenses like travel
A multiple-projects budget establishes estimates for everything you need to get projects across the finish line. It also lets you track costs to ensure you're not spending more than you accounted for in the budget.
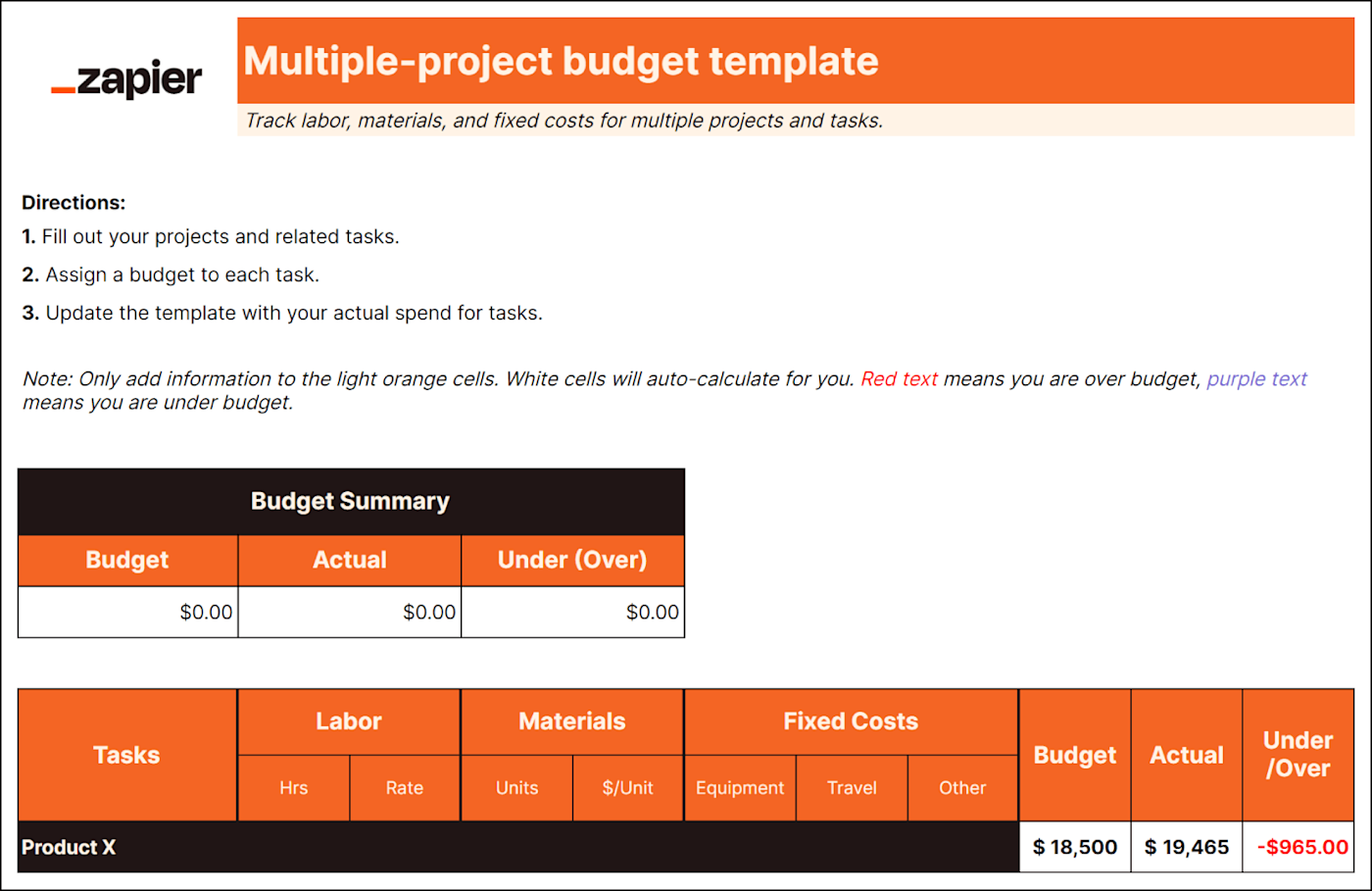
4. Startup budget template
Best for: New small businesses and startups
But unlike established small businesses, you don't have past financial data to base expenses on. That's why you need a startup budget to focus on expenses for your first year of business, including items like:
Funding from investors and loans
Licensing and permits
Logo and website design
Website domain
Business software
Security installation
Overhead expenses
Capital expenses
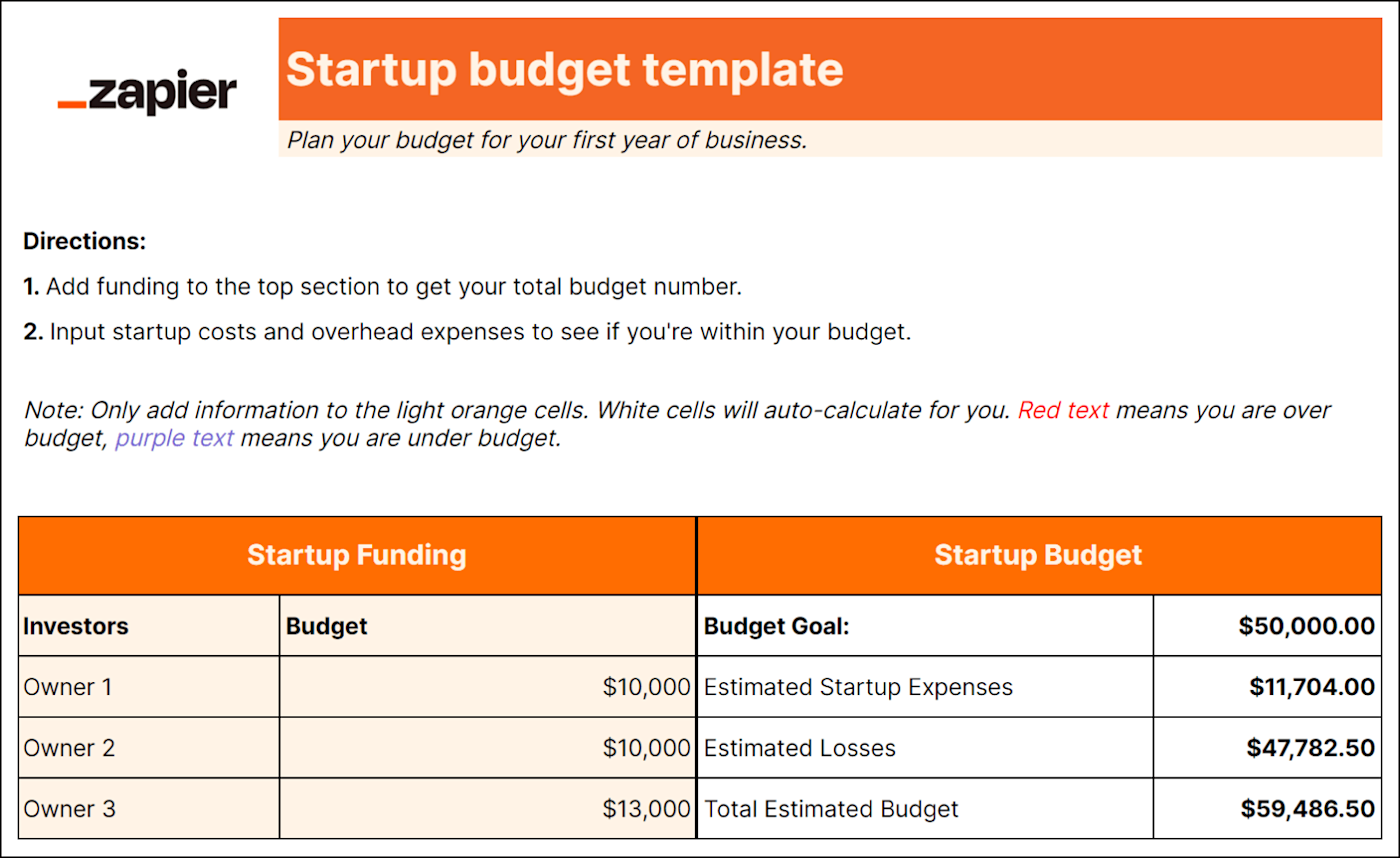
5. Labor budget template
Best for: Larger businesses with lots of employees
Unless you're a one-person show, you'll need a labor budget. And even if you are a one-person show, it's good to know if you can afford to pay yourself. A labor budget breaks down all employee-related costs like:
Payroll taxes
Contract labor
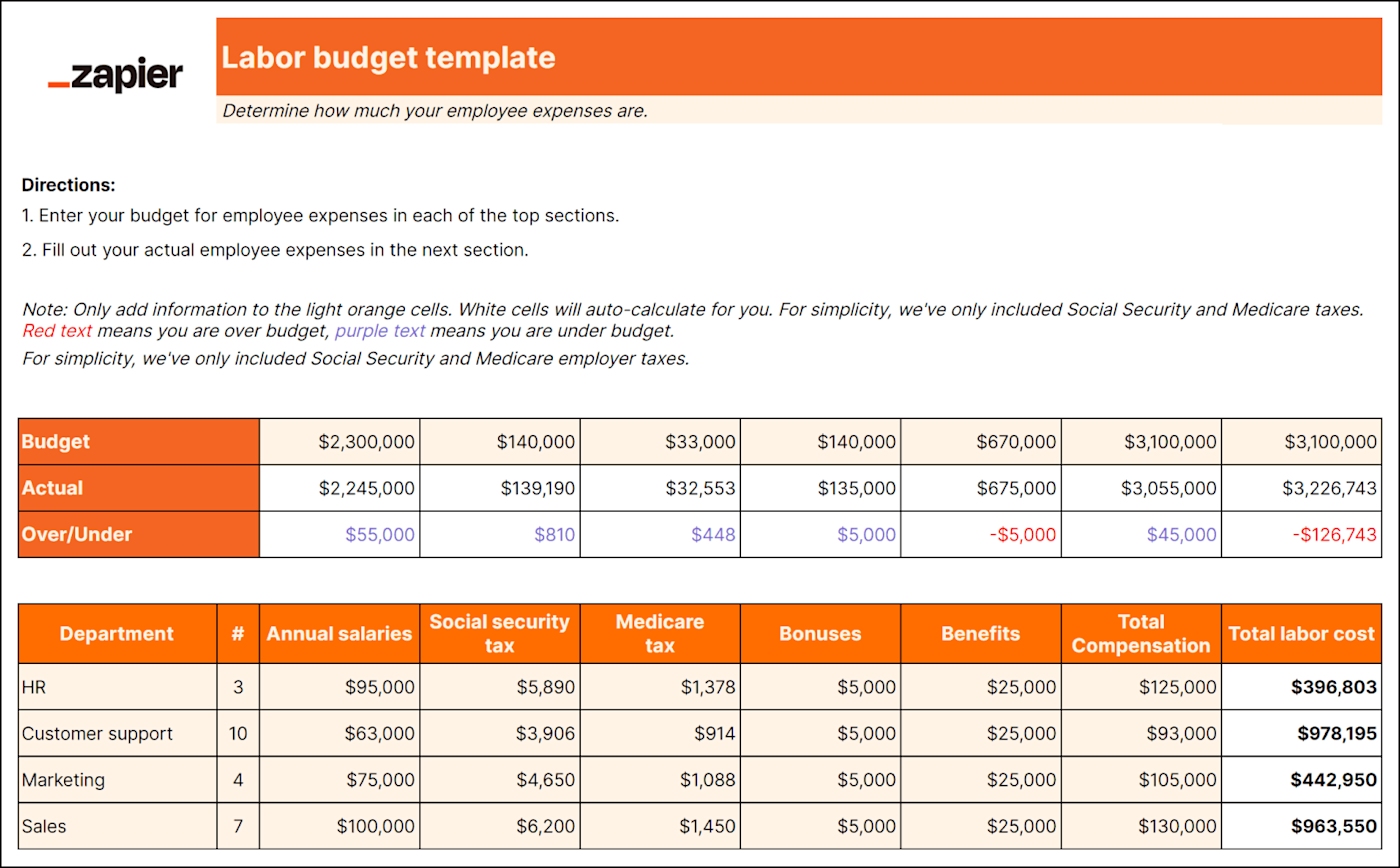
Break down employee costs into direct, indirect, fixed, and variable categories to clarify how your company allocates its resources. You can also consider different scenarios more easily when you understand the breakdown of labor costs.
For example, you can simulate the impact of adding or reducing staff in specific departments or assess the effects of different compensation structures on different teams.
An accurate forecast of labor costs ensures you can sustainably meet your staffing needs and can help you make informed hiring decisions. Down the road, it can also help you determine if you can afford to give your staff raises, bonuses, or additional benefits.
6. Cash flow budget template
Best for: Businesses with fluctuating income and expenses; Seasonal businesses; Retail
As important as it is to be mindful of how much money you're spending, you should also track how much money you're making . A cash flow budget helps estimate how money is flowing in and out of your business. It includes:
Starting balance (set at the beginning of the month, quarter, or year)
Projected cash inflow from all revenue streams
Estimated cash expenditures
Ending balance (calculated at the end of the month, quarter, or year)
This type of budget lets you proactively manage your resources, anticipate potential cash shortages, and strategize for growth. For instance, if you know you're only going to break even this year, you may wait on expanding or making a large investment.
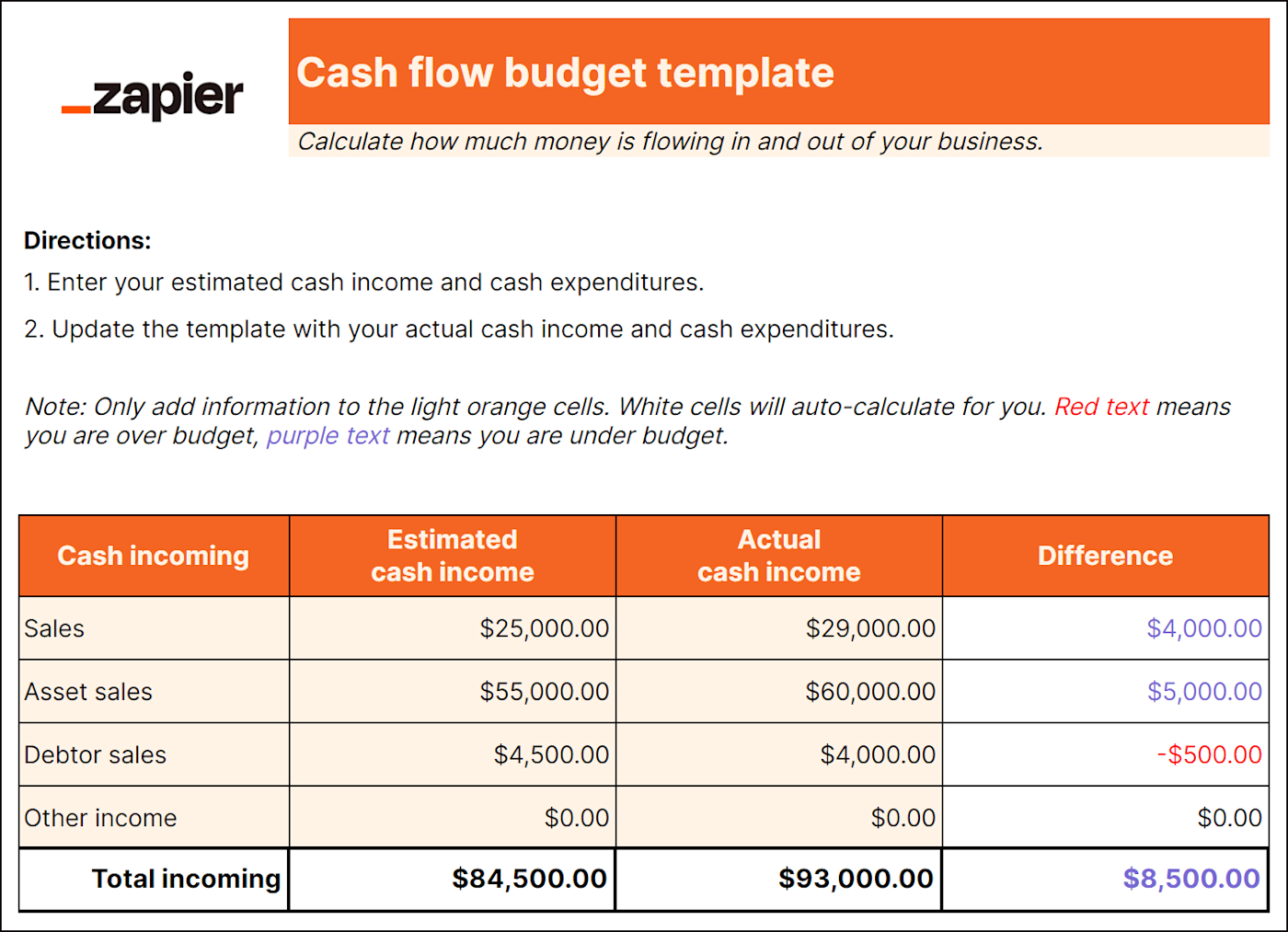
7. Administrative budget template
Best for: Businesses focused on streamlining operations
An administrative budget includes all those general expenses that the company as a whole needs to function. This type of budget accounts for:
Depreciation expenses
Training and development
Communication expenses
Accounting fees
While you could technically include administrative expenses in an overhead budget and call it a day, a separate administrative budget gives more of an eagle-eye view of how well your business is operating.
Without an eye on administrative costs, you may be spending unnecessarily or lose focus on areas where it'd be wiser to invest your money. In other words, you could be spending way too much on fancy pens when you should be saving up to upgrade your cash register.

Periodic budget reviews
A budget isn't a "set it and forget it" deal. Regular budget reviews can help you stay on track with your financial goals and respond proactively to changing market conditions.
You should compare your estimated budget to actual spending. Then you can see where you went over and where you can splurge more. Try to review your budget monthly, quarterly, and yearly.
Monthly: Compare actual performance against your budgeted figures for the month. Identify any deviations and look for insights into cash flow, sales trends, and expense management.
Quarterly: Dive deeper into performance over the last three months. Use trends to project revenue and expenses for the upcoming quarter and identify areas for improvement.
Yearly: Reflect on your long-term financial objectives for the fiscal year. Assess the effectiveness of your budgeting strategies, and set new budget targets for the upcoming year.
How to design your small business budget plan
It's cliched but true: you gotta spend money to make money. But that's no excuse to start throwing cash at your business willy-nilly.
Budgeting forces you to prioritize your objectives, so you spend money on the things that matter most. Here's how to create a small business budget in four steps:
Identify your working capital for the budgeting period. Add up your current assets like cash, accounts receivable, and inventory. Then subtract current liabilities like accounts payable and short-term debt. The remaining amount is what you have left to cover your operational expenses during the budgeting period.
Separate business and personal expenses. If you haven't already, open a dedicated business bank account. This makes it easier to track, categorize, and analyze your finances.
Determine your fixed and variable costs. Make a list of costs that stay the same every month (fixed costs) and what changes (variable costs). These will change based on the purpose of the budget. For instance, a labor budget will only consider employee-related costs.
Calculate your total expenses. Add up all the costs for your business, including fixed costs, variable costs, labor, and any other applicable expenses. This total is how much your business needs to run. Any leftover money from your working capital can be allocated toward other business investments.
Budgeting methods
If you've budgeted before and hated it, you may just have been using an ineffective budgeting method for your preferences. Here are a few budgeting methods to try instead:
Traditional: This budget is set for a determined amount of time and uses last year's numbers as a benchmark. Once you set your budget, you don't change it unless you get approval for an adjustment.
Rolling: This dynamic approach spans a continuous time frame instead of a fixed time period. As each month or quarter passes, you add a new budget period and drop the oldest period. This lets businesses adjust projections based on real-time performance and market conditions.
Flexible: This budget changes along with your sales forecast. As real-time sales activity deviates from budgeted amounts, you recalculate the budget to reflect the new data.
Small business budget FAQ
Still don't know where to start with your small business budget? Check out the answers to these common questions before you open a new Google Sheet.
What should a business budget include?
A business budget should include all income sources and expenses. Income sources could include projected revenue from sales, loans, or potential investor funding. Expenses may include items like office space rent, employee salaries, insurance, and marketing. Add anything that helps paint a full picture of your finances.
How much does the average small business startup cost?
What is the best free business budgeting software.
The best free budgeting business software will depend on what your business needs, but you can try apps like Mint or Wave. Or you can use a spreadsheet—scroll up for some free small business budget templates.
Automate your small business
Related reading:
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Cecilia Gillen
Cecilia is a content marketer with a degree in Media and Journalism from the University of South Dakota. After graduating, Cecilia moved to Omaha, Nebraska where she enjoys reading (almost as much as book buying), decor hunting at garage sales, and spending time with her two cats.
- Small business
- Finance & accounting
Related articles

How to start a successful side hustle

11 management styles, plus tips for applying each type
11 management styles, plus tips for applying...
Keep your company adaptable with automation
How to enrich lead data for personalized outreach
How to enrich lead data for personalized...
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

Please note that the contents of this site are not being updated since October 1, 2023.
As of October 2, 2023, Acclr Business Information Services (Info entrepreneurs) will be delivered directly by CED’s Business Information Services . To find out more about CCMM’s other Acclr services, please visit this page: Acclr – Business Services | CCMM.

- Advice and guidance
- Starting a business
- Personalized Guidance
- Seminars on Business Opportunities
- Certification of Export Documents
- Market Studies
- Export Financing
- International Trade Training
- Connection with the World Bank
- Trade Missions
- SME Passport
- Export Resources
- Import Resources
- Networking Activities
- Networking Training
- CCMM Member Directory
- Market Studies and Research Services
- Business plan
- Registration and legal structures
- Guidance for Drafting a Business Plan
- Help in Seeking Funding
- News, Grants, and Competitions
- Funding Meet-and-Greet
- Resources for Drafting a Business Plan
- Regulations / Permits / Licences
- Personalized Market Information Research
- Personalized Meetings with Guest Experts
- Government Subsidies and Programs
- Training for your employees
- Employee Management
- Interconnection Program
- Wage Subsidies
- French courses
- Merchant-Student Pairing
- Intellectual property
- Marketing and sales
- Operations management
- Hiring and managing human resources
- Growth and innovation
- Importing and exporting
- Calls for tenders
- Support organizations
- Sale / Closure / Bankruptcy
- Business intelligence
- Business lists and profiles
- Market data
- Market trends
- Business advice
- Business plan management consultant
- Legal structures consultant
- Accounting consultant
- Legal consultant
- Export certification
- Resource centre
Budgeting and business planning
Once your business is operational, it's essential to plan and tightly manage its financial performance. Creating a budgeting process is the most effective way to keep your business - and its finances - on track.
This guide outlines the advantages of business planning and budgeting and explains how to go about it. It suggests action points to help you manage your business' financial position more effectively and ensure your plans are practical.
Planning for business success
The benefits, what to include in your annual plan, a typical business planning cycle, budgets and business planning, benefits of a business budget, creating a budget, key steps in drawing up a budget, what your budget should cover, what your budget will need to include, use your budget to measure performance, review your budget regularly.
When you're running a business, it's easy to get bogged down in day-to-day problems and forget the bigger picture. However, successful businesses invest time to create and manage budgets, prepare and review business plans and regularly monitor finance and performance.
Structured planning can make all the difference to the growth of your business. It will enable you to concentrate resources on improving profits, reducing costs and increasing returns on investment.
In fact, even without a formal process, many businesses carry out the majority of the activities associated with business planning, such as thinking about growth areas, competitors, cashflow and profit.
Converting this into a cohesive process to manage your business' development doesn't have to be difficult or time-consuming. The most important thing is that plans are made, they are dynamic and are communicated to everyone involved. See the page in this guide on what to include in your annual plan.
The key benefit of business planning is that it allows you to create a focus for the direction of your business and provides targets that will help your business grow. It will also give you the opportunity to stand back and review your performance and the factors affecting your business. Business planning can give you:
- a greater ability to make continuous improvements and anticipate problems
- sound financial information on which to base decisions
- improved clarity and focus
- a greater confidence in your decision-making
The main aim of your annual business plan is to set out the strategy and action plan for your business. This should include a clear financial picture of where you stand - and expect to stand - over the coming year. Your annual business plan should include:
- an outline of changes that you want to make to your business
- potential changes to your market, customers and competition
- your objectives and goals for the year
- your key performance indicators
- any issues or problems
- any operational changes
- information about your management and people
- your financial performance and forecasts
- details of investment in the business
Business planning is most effective when it's an ongoing process. This allows you to act quickly where necessary, rather than simply reacting to events after they've happened.
- Review your current performance against last year/current year targets.
- Work out your opportunities and threats.
- Analyse your successes and failures during the previous year.
- Look at your key objectives for the coming year and change or re-establish your longer-term planning.
- Identify and refine the resource implications of your review and build a budget.
- Define the new financial year's profit-and-loss and balance-sheet targets.
- Conclude the plan.
- Review it regularly - for example, on a monthly basis - by monitoring performance, reviewing progress and achieving objectives.
- Go back to 1.
New small business owners may run their businesses in a relaxed way and may not see the need to budget. However, if you are planning for your business' future, you will need to fund your plans. Budgeting is the most effective way to control your cashflow, allowing you to invest in new opportunities at the appropriate time.
If your business is growing, you may not always be able to be hands-on with every part of it. You may have to split your budget up between different areas such as sales, production, marketing etc. You'll find that money starts to move in many different directions through your organisation - budgets are a vital tool in ensuring that you stay in control of expenditure.
A budget is a plan to:
- control your finances
- ensure you can continue to fund your current commitments
- enable you to make confident financial decisions and meet your objectives
- ensure you have enough money for your future projects
It outlines what you will spend your money on and how that spending will be financed. However, it is not a forecast. A forecast is a prediction of the future whereas a budget is a planned outcome of the future - defined by your plan that your business wants to achieve.
There are a number of benefits of drawing up a business budget, including being better able to:
- manage your money effectively
- allocate appropriate resources to projects
- monitor performance
- meet your objectives
- improve decision-making
- identify problems before they occur - such as the need to raise finance or cash flow difficulties
- plan for the future
- increase staff motivation
Creating, monitoring and managing a budget is key to business success. It should help you allocate resources where they are needed, so that your business remains profitable and successful. It need not be complicated. You simply need to work out what you are likely to earn and spend in the budget period.
Begin by asking these questions:
- What are the projected sales for the budget period? Be realistic - if you overestimate, it will cause you problems in the future.
- What are the direct costs of sales – i.e. costs of materials, components or subcontractors to make the product or supply the service?
- What are the fixed costs or overheads?
You should break down the fixed costs and overheads by type, e.g.:
- cost of premises, including rent, municipal taxes and service charges
- staff costs –e.g. wages, benefits, Québec Parental Insurance Plan (QPIP) premiums, contributions to the Québec Pension Plan (QPP) and to the financing of the Commission des normes du travail (CNT)
- utilities – e.g. heating, lighting, telephone
- printing, postage and stationery
- vehicle expenses
- equipment costs
- advertising and promotion
- travel and subsistence expenses
- legal and professional costs, including insurance
Your business may have different types of expenses, and you may need to divide up the budget by department. Don't forget to add in how much you need to pay yourself, and include an allowance for tax.
Your business plan should help in establishing projected sales, cost of sales, fixed costs and overheads, so it would be worthwhile preparing this first. See the page in this guide on planning for business success.
Once you've got figures for income and expenditure, you can work out how much money you're making. You can look at costs and work out ways to reduce them. You can see if you are likely to have cash flow problems, giving yourself time to do something about them.
When you've made a budget, you should stick to it as far as possible, but review and revise it as needed. Successful businesses often have a rolling budget, so that they are continually budgeting, e.g. for a year in advance.
There are a number of key steps you should follow to make sure your budgets and plans are as realistic and useful as possible.
Make time for budgeting
If you invest some time in creating a comprehensive and realistic budget, it will be easier to manage and ultimately more effective.
Use last year's figures - but only as a guide
Collect historical information on sales and costs if they are available - these could give you a good indication of likely sales and costs. But it's also essential to consider what your sales plans are, how your sales resources will be used and any changes in the competitive environment.
Create realistic budgets
Use historical information, your business plan and any changes in operations or priorities to budget for overheads and other fixed costs.
It's useful to work out the relationship between variable costs and sales and then use your sales forecast to project variable costs. For example, if your unit costs reduce by 10 per cent for each additional 20 per cent of sales, how much will your unit costs decrease if you have a 33 per cent rise in sales?
Make sure your budgets contain enough information for you to easily monitor the key drivers of your business such as sales, costs and working capital. Accounting software can help you manage your accounts.
Involve the right people
It's best to ask staff with financial responsibilities to provide you with estimates of figures for your budget - for example, sales targets, production costs or specific project control. If you balance their estimates against your own, you will achieve a more realistic budget. This involvement will also give them greater commitment to meeting the budget.
Decide how many budgets you really need. Many small businesses have one overall operating budget which sets out how much money is needed to run the business over the coming period - usually a year. As your business grows, your total operating budget is likely to be made up of several individual budgets such as your marketing or sales budgets.
Projected cash flow -your cash budget projects your future cash position on a month-by-month basis. Budgeting in this way is vital for small businesses as it can pinpoint any difficulties you might be having. It should be reviewed at least monthly.
Costs - typically, your business will have three kinds of costs:
- fixed costs - items such as rent, salaries and financing costs
- variable costs - including raw materials and overtime
- one-off capital costs - purchases of computer equipment or premises, for example
To forecast your costs, it can help to look at last year's records and contact your suppliers for quotes.
Revenues - sales or revenue forecasts are typically based on a combination of your sales history and how effective you expect your future efforts to be.
Using your sales and expenditure forecasts, you can prepare projected profits for the next 12 months. This will enable you to analyse your margins and other key ratios such as your return on investment.
If you base your budget on your business plan, you will be creating a financial action plan. This can serve several useful functions, particularly if you review your budgets regularly as part of your annual planning cycle.
Your budget can serve as:
- an indicator of the costs and revenues linked to each of your activities
- a way of providing information and supporting management decisions throughout the year
- a means of monitoring and controlling your business, particularly if you analyse the differences between your actual and budgeted income
Benchmarking performance
Comparing your budget year on year can be an excellent way of benchmarking your business' performance - you can compare your projected figures, for example, with previous years to measure your performance.
You can also compare your figures for projected margins and growth with those of other companies in the same sector, or across different parts of your business.
Key performance indicators
To boost your business' performance you need to understand and monitor the key "drivers" of your business - a driver is something that has a major impact on your business. There are many factors affecting every business' performance, so it is vital to focus on a handful of these and monitor them carefully.
The three key drivers for most businesses are:
- working capital
Any trends towards cash flow problems or falling profitability will show up in these figures when measured against your budgets and forecasts. They can help you spot problems early on if they are calculated on a consistent basis.
To use your budgets effectively, you will need to review and revise them frequently. This is particularly true if your business is growing and you are planning to move into new areas.
Using up to date budgets enables you to be flexible and also lets you manage your cash flow and identify what needs to be achieved in the next budgeting period.
Two main areas to consider
Your actual income - each month compare your actual income with your sales budget, by:
- analysing the reasons for any shortfall - for example lower sales volumes, flat markets, underperforming products
- considering the reasons for a particularly high turnover - for example whether your targets were too low
- comparing the timing of your income with your projections and checking that they fit
Analysing these variations will help you to set future budgets more accurately and also allow you to take action where needed.
Your actual expenditure - regularly review your actual expenditure against your budget. This will help you to predict future costs with better reliability. You should:
- look at how your fixed costs differed from your budget
- check that your variable costs were in line with your budget - normally variable costs adjust in line with your sales volume
- analyse any reasons for changes in the relationship between costs and turnover
- analyse any differences in the timing of your expenditure, for example by checking suppliers' payment terms
Original document, Budgeting and business planning , © Crown copyright 2009 Source: Business Link UK (now GOV.UK/Business ) Adapted for Québec by Info entrepreneurs
Our information is provided free of charge and is intended to be helpful to a large range of UK-based (gov.uk/business) and Québec-based (infoentrepreneurs.org) businesses. Because of its general nature the information cannot be taken as comprehensive and should never be used as a substitute for legal or professional advice. We cannot guarantee that the information applies to the individual circumstances of your business. Despite our best efforts it is possible that some information may be out of date.
- The websites operators cannot take any responsibility for the consequences of errors or omissions.
- You should always follow the links to more detailed information from the relevant government department or agency.
- Any reliance you place on our information or linked to on other websites will be at your own risk. You should consider seeking the advice of independent advisors, and should always check your decisions against your normal business methods and best practice in your field of business.
- The websites operators, their agents and employees, are not liable for any losses or damages arising from your use of our websites, other than in respect of death or personal injury caused by their negligence or in respect of fraud.
Need help? Our qualified agents can help you. Contact us!
- Create my account

The address of this page is: https://www.infoentrepreneurs.org/en/guides/budgeting-and-business-planning/
INFO ENTREPRENEURS
380 St-Antoine West Suite W204 (mezzanine level) Montréal, Québec, Canada H2Y 3X7
www.infoentrepreneurs.org
514-496-4636 | 888-576-4444 [email protected]

Consent to Cookies
This website uses necessary cookies to ensure its proper functioning and security. Other cookies and optional technologies make it possible to facilitate, improve or personalize your navigation on our website. If you click "Refuse", some portions of our website may not function properly. Learn more about our privacy policy.
Click on one of the two buttons to access the content you wish to view.
The Ultimate Guide to Budgeting for Small Businesses
By Andy Marker | March 4, 2022
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Creating a budget for your small business can be daunting, but doing so is essential for any successful company. We’ve rounded up expert tips and created a step-by-step guide for designing a strong small business budget.
Included on this page, you’ll learn why a budget is necessary for small businesses and how to create a budget using Excel . Plus, you’ll find a free, downloadable small business budget starter kit .
What Is a Small Business Budget?
A small business budget is a detailed outline of your financial status and projection, based on your historical financial data. It includes your projected income and expenses and is used to determine where your money is best spent.

Ahmet Yüzbaşıoğlu, the Co-Founder of Peak Plans , explains the importance of budgeting for small businesses: “The success of your business is determined by the quality of your decisions. If you want to make informed decisions, you must have a budget. A budget can help you create a plan for the future, whether it's for your company as a whole or for smaller departments. More importantly, [a budget] gives you guidelines with which to make decisions. If budgeting is not yet a part of your business strategy, it may be worth considering it as an option to provide you with insights that can help you to better plan for all aspects of your company.”
Do Small Businesses Need a Budget?
All businesses should have a budget, especially small ones with less room for errors. A small business can better weather periods of low income by knowing exactly where its money is going, forecasting sales, and identifying what can be cut when needed.

Stephen Light, the Co-Owner of Nolah Mattress , gives his take on why all small businesses should have a budget in place: “For small businesses, creating an effective budget is one of the most important tools to carve a successful path to profitability. Budgets are crucial for allocating funds efficiently and curbing any unnecessary or wasteful spending, [which is] an easy trap to fall into if you don’t have a framework or goalposts to stay within. Budgets are especially important to small business owners who might be using their personal funds.”
How Much Should a Small Business Budget Be?
Your budget should be based on historical financial data and not exceed what you expect to make in the budgeted period. Be realistic with your numbers and projections so that you do not find yourself in a position you cannot recover from.
Your budget should take into account all of your sources of revenue and all of your expenses, as well as an additional percentage for any emergencies or surprises.
“Small businesses should absolutely be sure to pad their budget with contingency funds for unseen expenses,” suggests Light.
Larger businesses tend to make budgets annually , but for a small business, especially at first, it is a good idea to break down your budget monthly. To get started and identify a realistic monthly budget for your business check out our small business monthly budget templates for Google Sheets.
Importance of Budgeting in a Small Business
A budget helps a small business anticipate challenges, achieve and track financial targets, and secure investment opportunities. A well-considered budget should help a small business to encounter fewer unforeseen expenses and more opportunities.
Below are some benefits of having a strong budget:
- Make Informed Decisions: A company can make more informed decisions more efficiently when they have a budget. A good budget is built on historical data and allows you to learn from your experience. “Budgeting is a great strategy for maintaining informed control of your business. You can use data insights to plan with greater clarity and organize all of your finances in one place. This allows your leadership team to have the necessary information to drive their decision-making processes more efficiently, which is a great way for your business to act on its data,” explains Yüzbaşıoğlu.
- Identify Growth Opportunities: With a budget in place, you can identify the most profitable projects for your company. Use your budget data over time to see where current resource allocation provides the most payoff. As Yüzbaşıoğlu says, “You can use budgeting to create assumptions about your business projections by measuring the effects of different investments on your business. For example, you can make conclusions about how much revenue an investment in sales will bring in with the information gathered from your marketing efforts. By evaluating different scenarios, you can consider your options for best achieving your goals. Observing different scenarios will soon help you find which strategies work best for your business.”
- Weather Leaner Business Times: All businesses should expect to encounter lean times. Having a budget in place can help you stay afloat by tracking which times are historically slow and by establishing an emergency fund. Knowing when to spend your money can be just as important as what you spend it on.

- Manage Risk: A well-crafted budget can help you to identify potential risks by gaining visibility into your spending. If you don’t track your money, it is easy to spend much more than you had planned (on an unsound investment). “Looking ahead is important for risk management ,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “Budgeting is a good way of looking ahead and contains similar methodologies as risk management. A budget allows you to look ahead and see how your activities in different areas will affect the company’s cash flow, earnings, and profitability.”
- Measure Performance: Having access to current and historical financial data from your business allows you to measure financial performance year over year. Without tracking this information, you cannot know which goals you are meeting. “Budgets are the most important tools that managers use to measure how well an organization is doing. Although budgets are commonly perceived to exist for financial purposes only, they can also be key tools to provide insight into how an organization and its departments are performing. Identifying variances — such as differences in expenses and costs and increase or decrease in sales and profits — will give a good overview to management about the performance of the company and its departments,” explains Yüzbaşıoğlu.
- Set Company Goals: A budget is a great place to start goal setting. Whether you aim to spend less over time or drive more sales, a budget gives you concrete numbers on which to base your financial goals. “When all parties are on the same page about the strategic goals of the company and the means of attaining them, it is much simpler to monitor success and work together to keep the organization on track to achieve its goals,” suggests Mains.

What Should a Small Business Budget Include?
A small business budget should include all income and expenses the business accrues over a given period. These numbers may change month to month, so it is important to either use an average, or to overestimate expenses and underestimate income.

Linn Atiyeh, the CEO and Founder of Bemana , highlights some major small business budget expenses that may not be immediately obvious. “[The expenses] need to include everything, from the employees themselves to the office spaces that they work in. They need to include technology, software, onboarding, training, client acquisition, insurance payments, marketing, product development, employee compensation, and any other anticipated costs,” she says.
The following bullets outline what to include in your budget:
- All Income and Expenses: Your budget should consider the entirety of your income and expenses. Note fixed and variable costs. It may also be beneficial to keep track of which expenses you can easily cut during lean times.
- Small Business Financial Plan: When creating your budget, consult your financial plan. If you do not have one, create an income statement and a cash flow statement . “You must incorporate your cash flow in your projections. Cash flow refers to the total amount of money that flows into and out of a firm. If you have positive cash flow in your firm over a certain period of time, this means that more money is flowing into your business than is leaving it,” says Mains. To learn more, read our how-to guide on creating a small business financial plan.
- Historical Sales Numbers: If you have them, use your historical sales numbers to project your income during the same time period in the future. If you don’t have historical data, start tracking it. As you continue to track this information, you will get a better idea of how much money your company is making and spending at different times of the year.
- Sales Forecasts: Create a sales forecast and use it to estimate your projected income. This information will help give you a target number for your budget.
- Emergency Fund: Any strong budget will include some wiggle room for emergencies and surprise expenses. Most sources recommend keeping three to six months’ worth of business expenses in an emergency fund — but remember that some money saved is better than none at all.
- Seasonal and Industry Trend Information: Most industries have slow seasons and busy seasons, and it is important to know when those times are. If you don’t have this information from your own business, a quick Google search can often tell you the answer.
- Growth Projections: Factor any expectations for major growth into your budget, such as opening a new storefront, buying new equipment, or hiring and training a new department.
How to Create a Budget for a Small Business
To create a budget for your small business, determine how much money your company spends and makes, and estimate how it will do so in the future. We’ve outlined how to create a budget in the steps below:
1. Gather Your Financial Information
This includes all income and expense information from previous years and any previous budget information you may have.

“To begin with, collect financial data, predictions, and market analysis to aid in the development of your small company's budget planning,” suggests Lattice Hudson, Business Coach and Owner of Lattice and Co . “To design your budget, consider the company's overall business and overall strategy in addition to the crucial financial data and analytics.”
2. Add Up Your Income
Use a small business budget template or spreadsheet to itemize and add up your income. Consider using a tool that tracks itemized income monthly so that you can more easily note changes over time.
3. Subtract Fixed Costs
Your fixed costs won’t change month to month, so they are the easiest to subtract from your income. Fixed costs might include rent, salaried employees, and non-variable utilities.
4. Determine and Subtract Variable Expenses
Not all costs are fixed, so you may need to do a little digging to determine some of your expenses. Calculate how much the company spent on hourly employees, variable utilities, and break room snacks and business lunches.
“Variable costs are those that change from month to month depending on your company's success, [such as] consumption-based utilities, delivery charges, transport costs, and sales commissions. When your earnings are greater, you may spend more on variable costs, but when your earnings are lower, you should aim to cut back where you can,” says Hudson.
5. Profit and Loss Statement
Prepare a profit and loss statement from the data you’ve collected. Outline how much your company made and spent in a given time period. This will be the first indicator of what your budget numbers should look like.
6. Outline a Forward-Looking Budget
Create your budget using the numbers from historical profit and loss statements. Your income and expenses may grow or shrink over time, so it is important to calculate an average or to add a buffer to your expenses. Your budget should always have money left over for incidentals, as well as allocation to an emergency fund.
Hays Bailey, the CEO and Founder of Sheqsy , recommends that you also include allocations for expansions or growth if you can see either on the horizon.
7. Review on a Schedule
Review your budget periodically. Track your income and expenses monthly, and update your budget as things change. “Over time, you will gain a better understanding of your company's operations and will be able to make more informed decisions regarding your budgeting plan,” says Hudson.
How to Create a Small Business Budget Spreadsheet in Excel
Microsoft Excel makes it easy to organize and chart your small business budget over time. The following tutorial lays out step by step how to use a template in Excel to add up your income and expenses and determine your business’s cash flow.
Gather and Organize All Relevant Financial Information for Your Business
To start your budget, you will need to gather and organize all of your financial information for the previous period. This includes income statements, expense reports, cash flow documentation, and any other relevant documents. If this is your first budget and you do not have these items, organize your bank statements, invoices, payroll information, and receipts.
By organizing your data into these documents, each month becomes easier to track than the last. The more you stay organized, the simpler it will be to maintain your budget.
Download a Small Business Budget Template
- Download the small business budget template for Microsoft Excel.
Record Your Monthly Income
Record Your Monthly Expenses
Record Your Cash Flow
Save and Update Your Budget Regularly
Store your budget template on an accessible drive and update it regularly. Small businesses should update their budget and cash flow as often as possible to stay up to date.
Small Business Budget Example
Download Small Business Budget Example Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
In this example of a small business budget, we’ve listed sample income, expense, and cash flow information using categories that are relevant to a small retail business. This template is fully customizable and can be used for a small business in any industry. You can also download a blank version of this template in the small business budget starter kit below.
Tips for Creating a Small Business Budget
Creating a budget for your small business can be daunting. To help you get started, we’ve gathered expert tips, from finding a mentor to setting realistic goals.
- Be Realistic: Keep all financial estimates in the realm of reality. Use historical financial data from your own past whenever possible. “My best tip is to avoid any wishful thinking or dreaming about best-case scenarios because it’s always better to use the real data from years past and to be realistic — you’ll avoid disappointment and tricky financial situations that way,” suggests Light.
- Note Changing Costs: Products and services don’t always cost the same amount every year. Be sure that the expenses listed in your budget are accurate at all times. “Be very mindful of the rapid rate at which prices can change and to get as many quotes as possible to inform your budget,” says Atiyeh. “On the first of these points, you may incorrectly assume that the amount you paid for a service in the past is still a good indicator of how much it would cost today. However, services are priced based on a multitude of factors, such as demand and market circumstances. Keep this in mind when creating a budget.”
- Find a Mentor: Doing so can cut down on the time it might take you to learn about business budgeting on your own. “Find someone who has experience in making budgets. Making a budget is technical and it requires experience if you want it to be done right. Of course, you are also allowed to do it on your own, but expect that it is going to take time and that you are in for lots of revisions,” warns Bailey.
- Overestimate Your Costs: Overestimating your costs helps ensure that your finances aren’t threatened when surprises come up or projects go over budget. You will be much better equipped to weather financial hardship if you’ve made room in your budget to respond to unexpected changes. “If your company works on a project-by-project basis, you are well aware that every customer is unique and no two projects will be precisely the same in their outcome. It is often impossible to forecast when a project may run over budget,” says Mains. “So much of running a company is about anticipating and responding to the unexpected. For small company owners, failure to predict an expenditure or its scale may be devastating and may cause the organization to become crippled before it has had a chance to mature and develop. Company owners must overestimate their costs to protect themselves from financial risk. This is a survival strategy that will assist business owners to protect themselves against danger and failure.”

What Specific Types of Businesses Should Consider when Budgeting for a Small Business
Budgeting for any business involves adding up income, subtracting expenses, and identifying where to spend and save money. Because different industries require different strategies, we’ve created a list of things to consider for specific small business types.

“One thing that is unique to small businesses as a whole is that there are so many different types of businesses. This means that there is no one-size-fits-all budget plan for small businesses. Each business should tailor its budget plan to its own specific needs and circumstances,” explains Lindsey Hyland, Founder of Urban Organic Yield .
- Seasonal Businesses: Some small businesses, such as those based around holidays or gardening, operate at a much higher business volume at certain times of the year. These businesses need to consider that their busy season will bring in much more income than their slow season(s). One way to tackle this is to take an average of your monthly income for the year and use that as your monthly operating budget. Don’t project based on the biggest numbers — use the smaller numbers or an average. For these businesses, it is especially important to establish an emergency fund so that a surprise expense during the slow season doesn’t become a catastrophe.
- Recruitment and Staffing: Businesses that deal with recruitment and staffing need to have a finger on the pulse of the businesses they work with. Do outside research into the growth or downscaling of other businesses to determine budget numbers for a given period. “Since my company is in the industrial and equipment recruiting industry, one unique challenge that we face is having to incorporate the needs of other businesses into our budget. For instance, it's important that we stay mindful of how much these businesses are upscaling or downscaling their operations at any given time, as that directly impacts the provision of our services,” says Atiyeh.
- E-commerce: Online businesses may have fewer fixed costs, such as rent, but may have more variable ones. Shipping costs, shipping zones, import taxes, and shipping supplies will change based on sales volume, so find an average or inflated number that works for these budget items. Companies that operate exclusively online should also invest in a well-made, working website and have a system in place for potential returns. These two things will help improve remote customer service, which can lead to more sales — and a larger budget — in the future.
- Nonprofits: Not-for-profit businesses are funded in a variety of ways, including through grants, donations, and dues. For these businesses, it is even more important to keep the budget as realistic as possible at all times, as there is commonly less money to move around. For more information and to help keep your budget balanced, peruse our list of free nonprofit budget templates .
- Inventory Business: Remember that it can be very expensive to keep large amounts of inventory on hand. Buying more of a product to sell can sometimes be cheaper because of the economy of scale, but ensure you have the space and capacity to hold on to things that don’t sell right away. Consider that you may need to spend more on rent and temperature control for a place to store these items.
- Custom Orders: The price of a custom order is not only the cost of the finished product, but a combination of factors. Determine a cost for your time and labor for conception, execution, materials, and delivery, and factor those into your expenses.
- Startups: Budgeting for a company with no existing financial history can be tough. Company owners will need to do research on the industry and use those numbers to create a rough estimate for their budget. When you are estimating a budget from scratch, be sure to overestimate your costs to mitigate risks. It is always a good idea to ask professionals and people with experience. Visit this list of free customizable startup budget templates to get started.
- Construction: Construction companies need to factor in the cost of all associated permits and insurance on top of all of the general costs of doing business. Permits and insurances may change based on the specific job you are doing, so it is critical to factor those costs into the relevant monthly budget. To help keep you organized, check out this list of free construction budget templates .
- Service: Businesses based on service need to put a larger portion of their budget toward staff training and retention. Better employees mean better service, and much of an employee's ability comes from their training. Additionally, you do not want to lose the valuable employees you spend time and money training, so these businesses need to factor in rising pay scales for more qualified staff.
- All Small Businesses: Do not forget to factor in taxes and fees involved in running your business. If you don’t know what they are, ask a professional for help. “There are a shocking number of people that do not make any self-employment tax payments to the IRS for lack of fear or know-how,” says Stevenson.
How to Manage a Small Business Budget
Manage your small business budget by spending within your means and saving money where you can. Make sure your budget is as realistic as possible, and update and revise it on a regular basis.
- Spend Within Your Means: Whenever possible, do not spend more money than you make. Use loans and credit wisely so as not to dig yourself into a hole. “Make do with what you have, start small with the free versions of software before you upgrade. Save for equipment. Make room in the budget later if you can’t afford it now,” advises Stevenson.
- Get Multiple Quotes: When you work with other businesses, it is in your best interest to get multiple quotes. You can use these quotes to negotiate the prices of goods or services that you need to run your own business, and save money in your budget. “By getting as many quotes as possible, you can build a more accurate understanding of the true prices of what you'll need throughout the period of time that you're budgeting for. By getting quotes from several sources rather than just one or two, you can make sure that your estimates are fair and accurate,” suggests Atiyeh.
- Revisit Your Budget Regularly: Circumstances can easily change from month to month or year to year. “The best way to stay on budget is to revisit the budget regularly. Budgets shouldn’t be set and then put away, they should be consistently reassessed and adjusted. If you’re committed to tweaking and allowing your budget to evolve with a watchful eye, you’re far more likely to stay within its bounds,” says Light.
- Be Realistic from the Outset: It is easy to get carried away with lofty goals and underestimated expenses. The closer your budget reflects reality, the easier it will be to stick to the plan. “Don’t underestimate expenses just to make your budget look conservative, because a budget that’s unrealistic is so much worse than not having a budget at all. It is misleading and it can cause lots of problems in the long run,” warns Bailey.
How to Do a Small Business Budget Efficiently
There are three key ways to help ensure that you manage your small business’s budget efficiently: Use the tools that are available to you, review your financial data on a schedule, and seek help when you need it.
- Use Software Tools: There are many software tools that can help you to create a budget. Many offer free trials so that you can find the one that works best for you. You may also find that a template suits your needs.
- Hire Help: Consider using the professional services of a financial advisor, or hire an accountant to manage your budget. For many businesses, hiring someone to manage the money is an inevitability that should be considered sooner than later.
- Create a Review Schedule: Small businesses should record budgets monthly. Track and store your monthly budget data so that you can reference it for future months and make changes as needed.
Small Business Budget Starter Kit
Download Small Business Budget Starter Kit
We’ve created this small business budget starter kit to help you get started creating and maintaining a budget. We’ve included a blank budget template from the example above, plus powerful cash flow and income statement templates to help keep you organized and on track. We’ve also included a customizable budget checklist so that you can ensure you’re tracking all of the information you need, every time.
Small Business Budget Template
Download Small Business Budget Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets | Smartsheet
Use this blank small business template to calculate your income, expenses, and a simplified cash flow. This powerful template adds up your itemized income and expenses each month, giving you a running total while in progress and a yearly total once completed.
Small Business Budget Checklist
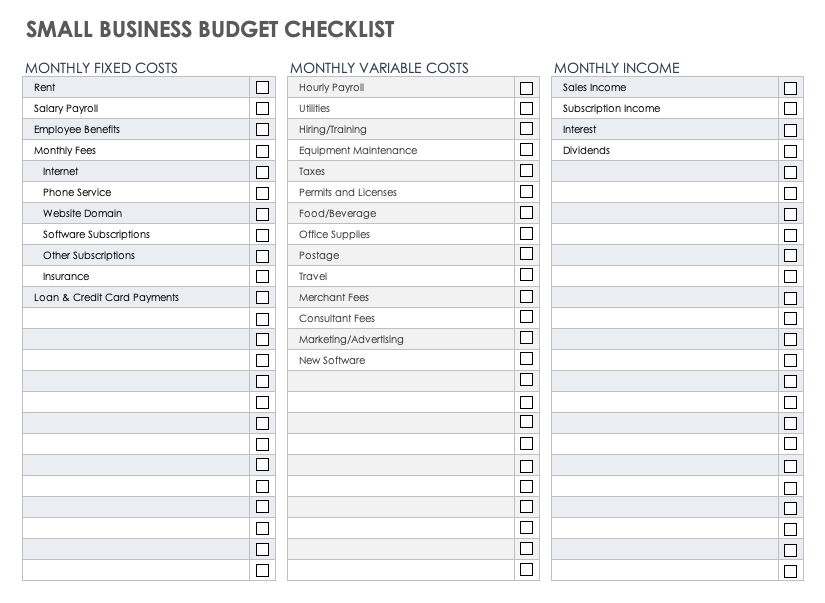
Download Small Business Budget Checklist Microsoft Excel | Adobe PDF | Google Sheets
This customizable small business budget checklist will help ensure that you’ve included all income and expenses in your monthly budget. The checklist includes a list of some of the most common business expenses, but you can edit it as needed.
Small Business Income Statement Template
Download Small Business Income Statement Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this small business income statement template to track your company’s total income and expenses over time. Customize it to track by month, quarter, or year, and use it to complete the income and expense information on your budget template.
Small Business Cash Flow Statement Template
Download Small Business Cash Flow Statement Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this small business cash flow statement template to follow your cash income and expenses. Input your cash flow in the appropriate cell, and compare the current to the previous time period. The template will generate your total cash payments and ending cash position, which will help you fill in your budget template.
Streamline Small Business Budgeting Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Discover a better way to connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform that empowers your team to get more done, faster.
With Smartsheet, you can align your team on strategic initiatives, improve collaboration efforts, and automate repetitive processes, giving you the ability to make better business decisions and boost effectiveness as you scale.
When you wear a lot of hats, you need a tool that empowers you to get more done in less time. Smartsheet helps you achieve that. Try free for 30 days, today .
Connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform.
Business Plan Budget Example: Everything You Need to Know
A business plan budget example is smart to have when managing a company. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
A business plan budget example is smart to have when managing a company. It sets the outline for how much money you'll spend in your business and what you'll spend it on. This isn't a forecast, however, which is where you predict the future of your budget. A budget is the assumed plan for the future's outcome.
Is Budget and Business Planning Required for Small Businesses?
New owners of small businesses can run their company in a way that's more relaxed and not find it necessary to set a budget. However, it is a smart idea to have a plan for the future of your business and fund those plans. The best way to control your money is by budgeting, which lets you invest in any potential new business opportunities when it's appropriate. If you find your company grows, you won't always be able to interact with it as much and be hands-on with the daily operations.
You might need to split the budget up into different sections such as production, sales, and marketing. It's common for money to begin in a variety of directions through the organization. Budgets are an essential tool to help you control how much you're spending.
Benefits of Business Budget Planning
There are many benefits to creating a business budget . These include being better at the following:
- Planning for the future.
- Improving decision-making.
- Monitoring performance.
- Effectively managing money.
- Giving out the right resources to projects.
- Meeting your objectives.
- Solving problems before they become bigger.
- Increasing staff motivation.
How to Draft a Business Budget Plan
The key to having success in a business is to form, monitor, and manage your budget. This will help you designate resources where you need them so your company stays successful and profitable. The process doesn't necessarily need to be complicated, as you'll just need to figure out how much you think you'll earn and make in your budget period. You can start by asking yourself what the project sales might be for your budget period. It's better to be realistic and not overestimate, as this will cause issues in the future.
You'll also need to think about any direct costs of sales. This includes the costs of materials, subcontractors, and components to make your product or supply your service. The overhead costs or fixed costs also need to be included in the business budget. You can break these down by the cost of the premises, which include municipal taxes, monthly rent, and service charges. The staff costs also need to be taken into consideration, which includes benefits, wages, insurance, and pension plans.
Utilities are another expense to budget for , which include lighting, heating, and telephone costs. If you'll be printing or shipping anything, you'll have to factor in costs for postage, stationery, and printing. There may be costs for promotion, advertising, vehicles, equipment, and subsistence and travel expenses. The exact expenses your company will have will vary, and it's best to budget for each department. Make sure to include how much you'll pay yourself and a tax allowance. There are many costs to consider that you probably haven't thought about, which is why creating a business plan for your budget is important.
Once you have an estimate of how much you'll make and how much you'll spend, you'll be able to figure out exactly how much profit you're making. This lets you look at the budget you just made and see where costs can be cut. If you think you'll have problems with cash flow, you may need to rethink the budget and cut out entire departments.
Once you've created this budget, it's important to stick it as closely as possible. You should review it on a continuous basis and revise it if you need to, however. Many businesses have a rolling budget so they're constantly budgeting for the next year.
It's crucial to be realistic when it comes to your budget projects. If you're unsure if they're accurate, it 's better to be conservative and underestimate the revenue while overestimating the expenses. This can be hard if you're just starting a company, as you may not know exactly how much you'll need to spend on items and services.
If you need help with a business plan budget example, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Fees for Starting a Business
- Business Plan Startup Costs Template
- Bottom Up Budgeting Definition
- Software Development Contracts
- Variable Costs in a Business
- Cash Requirements From Startup
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide for Entrepreneurs
- Do It Yourself Business Plan
- IT Company Business Plan
- Actual Cost
How to create a business budget
Advertiser disclosure.
We are an independent, advertising-supported comparison service. Our goal is to help you make smarter financial decisions by providing you with interactive tools and financial calculators, publishing original and objective content, by enabling you to conduct research and compare information for free - so that you can make financial decisions with confidence.
Bankrate has partnerships with issuers including, but not limited to, American Express, Bank of America, Capital One, Chase, Citi and Discover.
How We Make Money
The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site, including, for example, the order in which they may appear within the listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site. We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you.
- Share this article on Facebook Facebook
- Share this article on Twitter Twitter
- Share this article on LinkedIn Linkedin
- Share this article via email Email

- • Small business loans
- • Bad credit loans

- • Funding inequality
- Connect with Emily Maracle on LinkedIn Linkedin
The Bankrate promise
At Bankrate we strive to help you make smarter financial decisions. While we adhere to strict editorial integrity , this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for how we make money .
Founded in 1976, Bankrate has a long track record of helping people make smart financial choices. We’ve maintained this reputation for over four decades by demystifying the financial decision-making process and giving people confidence in which actions to take next.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. All of our content is authored by highly qualified professionals and edited by subject matter experts , who ensure everything we publish is objective, accurate and trustworthy.
Our banking reporters and editors focus on the points consumers care about most — the best banks, latest rates, different types of accounts, money-saving tips and more — so you can feel confident as you’re managing your money.
Editorial integrity
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions.
Key Principles
We value your trust. Our mission is to provide readers with accurate and unbiased information, and we have editorial standards in place to ensure that happens. Our editors and reporters thoroughly fact-check editorial content to ensure the information you’re reading is accurate. We maintain a firewall between our advertisers and our editorial team. Our editorial team does not receive direct compensation from our advertisers.
Editorial Independence
Bankrate’s editorial team writes on behalf of YOU – the reader. Our goal is to give you the best advice to help you make smart personal finance decisions. We follow strict guidelines to ensure that our editorial content is not influenced by advertisers. Our editorial team receives no direct compensation from advertisers, and our content is thoroughly fact-checked to ensure accuracy. So, whether you’re reading an article or a review, you can trust that you’re getting credible and dependable information.
How we make money
You have money questions. Bankrate has answers. Our experts have been helping you master your money for over four decades. We continually strive to provide consumers with the expert advice and tools needed to succeed throughout life’s financial journey.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that our content is honest and accurate. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions. The content created by our editorial staff is objective, factual, and not influenced by our advertisers.
We’re transparent about how we are able to bring quality content, competitive rates, and useful tools to you by explaining how we make money.
Bankrate.com is an independent, advertising-supported publisher and comparison service. We are compensated in exchange for placement of sponsored products and services, or by you clicking on certain links posted on our site. Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. Other factors, such as our own proprietary website rules and whether a product is offered in your area or at your self-selected credit score range, can also impact how and where products appear on this site. While we strive to provide a wide range of offers, Bankrate does not include information about every financial or credit product or service.
Our writers and editors used an in-house natural language generation platform to assist with portions of this article, allowing them to focus on adding information that is uniquely helpful. The article was reviewed, fact-checked and edited by our editorial staff prior to publication.
Key takeaways
- A business budget is a financial plan that helps estimate a company's revenue and expenses, making it an essential tool for small businesses
- The steps to creating a business budget include choosing budget and accounting software, listing expenses and forecasting revenue
- If a business finds itself in a budget deficit, strategies such as cutting costs, negotiating with suppliers and diversifying revenue streams can help
As a small business owner, keeping your finances organized through a business budget is crucial to running a successful company.
Business budgeting involves creating a financial plan that estimates future revenue and expenses to make informed financial decisions, which can ultimately move the needle on your business’s financial goals and help it grow in profitability.
What is a business budget?
A business budget is a financial plan that outlines the company’s current revenue and expenses. The budget also forecasts expected revenue that can be used for future business activities, such as purchasing equipment. It sets targets for your business’s revenue, expenses and profit and helps you determine if you’ll have more money coming in than you pay out.
A business budget is an essential tool that helps you make wise business decisions. Without it, it’s difficult to gauge your business’s financial health.
What is the difference between a cash flow statement and a business budget?
A cash flow statement (CFS) is a financial document that summarizes the movement of cash coming in and going out of a company. The CFS gauges how effectively a company manages its finances, including how it manages debt responsibilities and funds day-to-day operations.
It’s similar to a business budget in that you can see expenses and revenue. But while a budget gives a moment-in-time snapshot of your business’s financial performance compared to forecasts, the cash flow statement focuses on the actual inflows and outflows of money through your business.
Follow these steps to ensure a well-developed budget, from understanding your expenses to generating revenue and adjusting expenses to balance the budget.
1. Choose a budget and accounting software
First, you’ll want to store your expense and revenue information with accounting software to help you track your numbers and generate reports. Some software may also help you assign categories to the transactions, identify tax deductions and file taxes. Quickbooks is an example of accounting software.
Some business bank accounts also have accounting software built in, helping you stay organized by keeping your accounting and banking in one place.
2. List your business expenses
The next step in creating a small business budget is to list all your business expenses. Here are the types of expenses you want to include in your budget:
- Fixed expenses: Fixed expenses cost a fixed amount monthly or within the assessed period. Those costs include rent, insurance, salaries and loan payments.
- Variable expenses: Variable expenses can change monthly or over time, making them trickier to budget. This might include materials, direct labor, utility bills or marketing expenses.
- Annual or one-time costs: Some costs only occur a few times per year, while others you’ll only pay for as needed, such as buying new equipment. You still want to budget for these expenses by allocating a portion of your weekly or monthly budget toward one-time expenses.
- Contingency funds: Unexpected business costs can throw a wrench in your budget if not planned for. Such costs could include emergency repairs, necessary equipment purchases, sudden tax increases or unforeseen legal fees. To plan for these costs, you can create a contingency or emergency fund that’s separate from your operational budget.
- Maintenance costs: To allocate funds for maintenance costs, begin by including regular inspections and maintenance in your budget. Then, make sure to leave room for changes and unexpected maintenance costs.
3. Forecast your revenue
To estimate your future revenue, start by deciding on a timeline for your forecast. A good place to start is the previous 12 months. Your accounting software may also include revenue forecasting as one of its features, which can automate this step for you.
The timeline and your recent past growth can help you understand how much revenue you’ll generate in the future. Consider external factors that could drive revenue growth, such as planned business activities like expansion, marketing campaigns or new product launches.
You’ll also want to think about anything that might slow your growth. Many businesses experience seasonal fluctuations, which can impact your budget if you don’t plan for it. To account for these changes, list the minimum expenses required to keep your business running. Use your financial statements to understand these costs, and consider averaging out irregular expenses over the year to avoid surprises.
Ideally, your business should build a cash reserve during profitable periods to cover expenses during slower seasons. If necessary, consider various financing options, such as a business credit card or line of credit, that you can draw from to manage cash flow during peak or off times.
4. Calculate your profits
The next step in creating a business budget is to calculate your business profits. You can look at your total profits by calculating revenue minus expenses. That way, you see how much money you have to work with, called your working capital .
You should also understand your profit margins for each of your products and services, which can help you set prices or decide whether to offer a new product or service.
How to calculate your profit margins
To find out your gross profit margin, you’ll first need to calculate the gross profit. To calculate your business’s gross profit, subtract the cost of goods sold (COGS) from your total revenue. COGS includes all the expenses related to producing your products and services.
Once you have the gross profit, use the gross profit margin formula: (Revenue – COGS) / Revenue x 100. This will give you a percentage that shows how much profit you gain from that particular product after accounting for the product’s costs.
5. Make a strategy for your working capital
Knowing what to do with extra revenue, which is your working capital, is crucial for managing your business finances and growth. Here’s how to get started with a financial strategy that propels your business goals forward:
- Set spending limits for different categories in your budget. When listing your expenses, you should have set a dollar amount for each category. You can estimate this by a monthly average or a general forecasted amount.
- Set realistic short- and long-term goals. These goals will motivate you to stick to your budget and guide your spending decisions.
- Compare your actual spending with your net income and priorities. Look at the areas you’re spending and consider whether you need to reallocate money to different categories. Consider separating expenses into business needs and extras.
- Adjust your budget and actual spending. Adjust your spending to ensure you do not overspend and can allocate money towards your goals. If you need to cut spending, consider the categories that are extras, such as types of marketing that you don’t know will generate a return on investment.
6. Review your budget and forecasts regularly
Finally, review your budget regularly. By frequently checking in on your budget, you can identify any discrepancies between your planned and actual expenses and adjust accordingly. This allows you to proactively handle any financial issues that may arise rather than reacting to them after they’ve become a problem.
Regular reviews also allow you to refine your budgeting process and improve its accuracy over time. Keep in mind that your budget is not set in stone but rather a tool to guide your financial decisions and help you achieve your business goals.
What to do if you have a deficit in your business budget
Finding a deficit in your small business budget can be alarming, but there are several strategies you can employ to handle this situation.
- Do a cash flow analysis. Begin by doing a cash flow analysis to review what your business is earning and spending money on. Identify potential problems and adjust the budget as needed to prevent overspending.
- Cut nonessential business costs. Cutting spending may involve eliminating nonessential costs and transferring funds from other categories to overspent categories. Your goal is a balanced or profitable budget.
- Negotiate with suppliers. Be transparent in your communications with suppliers and explain your quality standards and why you’re seeking cost reduction. Explore options for cost reduction that do not compromise quality, such as process improvements or ordering in larger quantities.
- Create a lean business model. By removing anything that doesn’t benefit your customer, your business can potentially save time and resources. Lean business models focus on continually improving processes and customer experience without adding additional resources, time or funds.
- Add revenue and diversify revenue streams. Raising revenue requires a realistic plan with measurable goals to increase sales and overall business income. You can also consider other products and services you could offer that would make your business profitable.
- Use financing to cover temporary gaps. Applying for a small business loan can help pay bills during an unplanned shortfall. Since this will add an expense to your budget, make sure you can handle the loan repayments and your regular expenses.
- Plan for a deficit. In some cases, a planned budget deficit might be a strategic decision, such as investing in new opportunities that promise long-term benefits.
Bottom line
Having a well-developed business budget is crucial for making informed decisions. You can effectively manage your small business’s finances by tracking and analyzing your business’s inflows and outflows, forecasting your expected revenue and adjusting your budget to stay balanced.
Even in the face of a budget deficit, there are various strategies you can use to keep your business profitable, including negotiating costs with your suppliers, assessing your business operations and offering new products and services.
With a solid business budget in place, you can confidently navigate financial challenges and drive long-term success for your small business.
Frequently asked questions
What are the benefits of a business budget, what are the components of a business budget, how do you calculate fixed and variable costs in a business budget.

Related Articles

How to get a small business loan without collateral

How to get a small business loan when self employed

How to finance a small business for the holidays

How to start a small business
How to Create a Business Budget for Your Small Business

According to a study done by CBinsights, a few of the top reasons why small businesses fail include include pricing and cost issues, losing focus and running out of cash. These issues can be prevented by having a realistic budget in place.
Before you can focus on the budget, however, you need to identify what aspects of your business you’d like to improve. This will allow you to decide what can be done with your funds. Based on that list, you can set up short-term and long-term goals.
These goals will be directly affected by your incoming and outgoing cash. A short-term goal can be paying off a debt or purchasing new equipment. Long-term goals, like keeping aside marketing expenses, are crucial because they are connected to the overall growth of your business.
You should be practical about the goals you set. They should be purely based on your business’ capacity to spend and save. Once you have your goals in place, you can create an effective, foolproof budget by following these steps.
1. Analyze costs
Before you start drafting a budget, you must research the operating costs involved in your business. Knowing your costs inside and out gives you the baseline knowledge needed to craft an effective spending plan.
If you create a rough budget and later discover that you need more money for your business activities, this will jeopardize your goals. Your budget should be such that you can increase your revenue and profit enough as your business expands to handle your growing expenses. Your budget should factor in fixed, variable, one-time, and unexpected costs. Some examples of a fixed expense are rent, mortgages, salaries, internet, accounting services, and insurance. Examples of variable costs include cost of goods sold and commissions for labor.
There is not much harm in overestimating the costs involved since you will need enough cash to handle your future expenditures. If your business is new, then you must include start-up costs as well. Planning the budget this way will help you make informed decisions and tackle any unwanted financial surprises.
2. Negotiate costs with suppliers
This step will be useful for those businesses which have been functional for more than a year and are dependent on suppliers to sell products. Before you get started on your yearly budget, have a chat with your suppliers and try getting discounted rates for the materials, products, or services you need before you make your payments.
Negotiations allow you to create trustworthy relationships with your suppliers. This will be helpful when incoming cash is thin. For example, you might have a seasonal business. When you have enough cash saved, you can pay advance amounts to your suppliers as compensation for the times when you are unable to make payments. The main goal here is to find efficient ways to reduce cost of doing business.
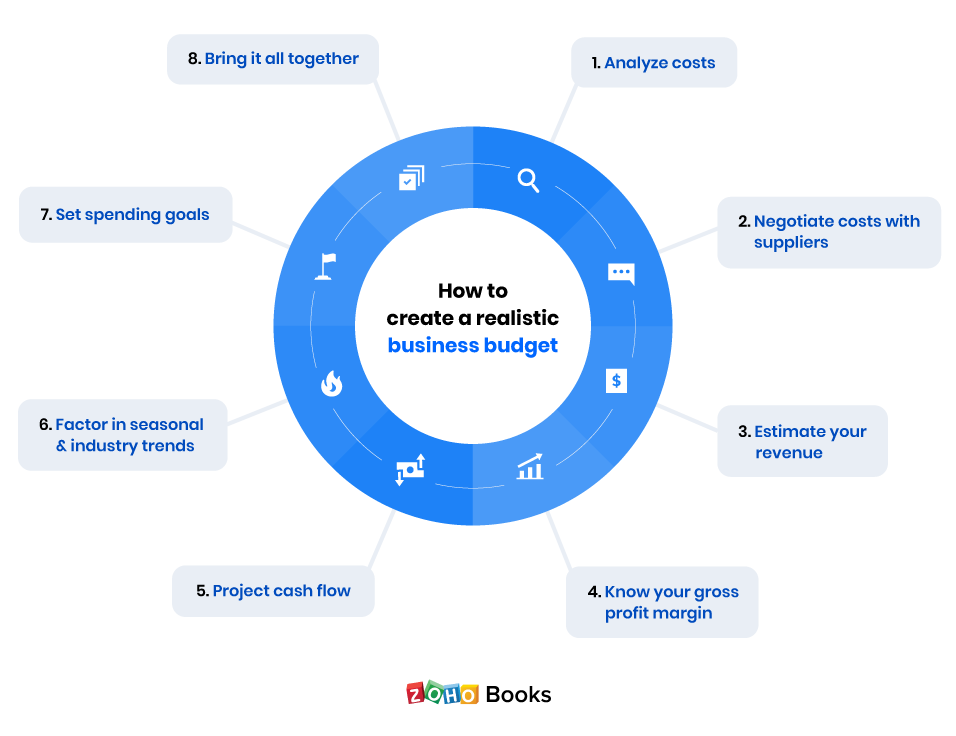
3. Estimate your revenue
Many businesses have failed in the past by overestimating revenue and borrowing more cash to meet operational needs. This defeats the very purpose of creating a budget. To keep things realistic, it’s a good idea to analyze previously recorded revenue. Businesses must track revenue periodically on a monthly, quarterly and annual basis.
Your previous year’s revenue figures can act as a reference point for the upcoming year. It’s important to rely solely on this empirical data. This will help you set realistic goals for your team, leading to the eventual growth of your business.
4. Know your gross profit margin
The gross profit margin is the cash you are left with after your business has dealt with all the expenses at the end of the year. It gives insight into the financial health of your business. Here’s an example of why you need to understand this parameter while creating a budget.
Suppose your business made a revenue $5,000,000 and yet there are debts to be paid. At the end of the year, your expenses are more than your revenue, which is not a good sign for a growing business. This tells you that you must identify the expenses that are not benefiting the business in any way and eliminate them. The best way to do this would be to list out the cost of goods sold for all materials and deduct them from the overall sales revenue. This information is needed to get a real picture on how your business is faring, allowing you to increase profit and reduce costs.
5. Project cash flow
There are two components to cash flow : customer payments and vendor payments. You need to balance these two components to keep the cash flowing in your organization.
To do your best to ensure timely customer payments, it’s important to have flexible payment terms and the ability to receive payments through common payment channels. Unfortunately you will need to deal with customers who might not comply to the stated terms. This might affect your cash flow forecast due to missing payments.
You can encourage payment by giving customers a grace period and creating strict business policies for paying late. Beyond this, you must have some money allocated in your budget for ‘bad debt,’ in case the customer never pays.
When you know your incoming cash flow, you can fix an amount for your employee salaries and travel expenses. You can also allocate some money to pay off your fixed vendor expenses. If you are still left with cash, you can then spend on business initiatives such as professional development or new equipment.
6. Factor in seasonal and industry trends
It’s unrealistic to expect that you will achieve every business goal and reach your estimates every month. In an annual cycle, there will be months where your business will be booming, and there may be a few months where sales are slow. Due to seasonal inconsistency and industry trends, you will have to spend cash effectively so that the business isn’t at risk of shutting down during slower periods.
To overcome this challenge while creating a budget, gather insights as to when your business performs better. The aim should be to generate enough revenue during peak months to sustain the business during off seasons.
For example, let’s assume that you are a business owner of a winter clothing company. Your products are on demand only during that season, so most of your revenue comes during that period. For the rest of the year, you can use the earnings to keep the business going and market to specific target groups, like hikers or travelers. This will help you gauge how successful your products are during off seasons, what revenue to expect, and how much to save during your peak periods.
7. Set spending goals
Making a budget is more than just adding your costs and subtracting them from your earnings. How wisely you spend your money determines how well your business will fare. Goals provide a system to check if your money is being spent on the right areas to avoid unwanted expenses.
For example, if you are spending money on stationary that is going unused for operational or marketing efforts, it may be time to cut those costs. This money can be better applied to your marketing campaigns, bringing in more leads and revenue. Gauge and invest in those expenses that would benefit your business in the long run.
8. Bring it all together
Once you have gathered all the information from the previous steps, it’s time to create your budget. After you have subtracted your fixed and variable expenses from your income, you will get an idea of the amount that you can work with. Be prepared to tackle the unexpected one-time expenses that come your way. You can then find ways to use the money effectively to achieve your short-term and long-term goals.
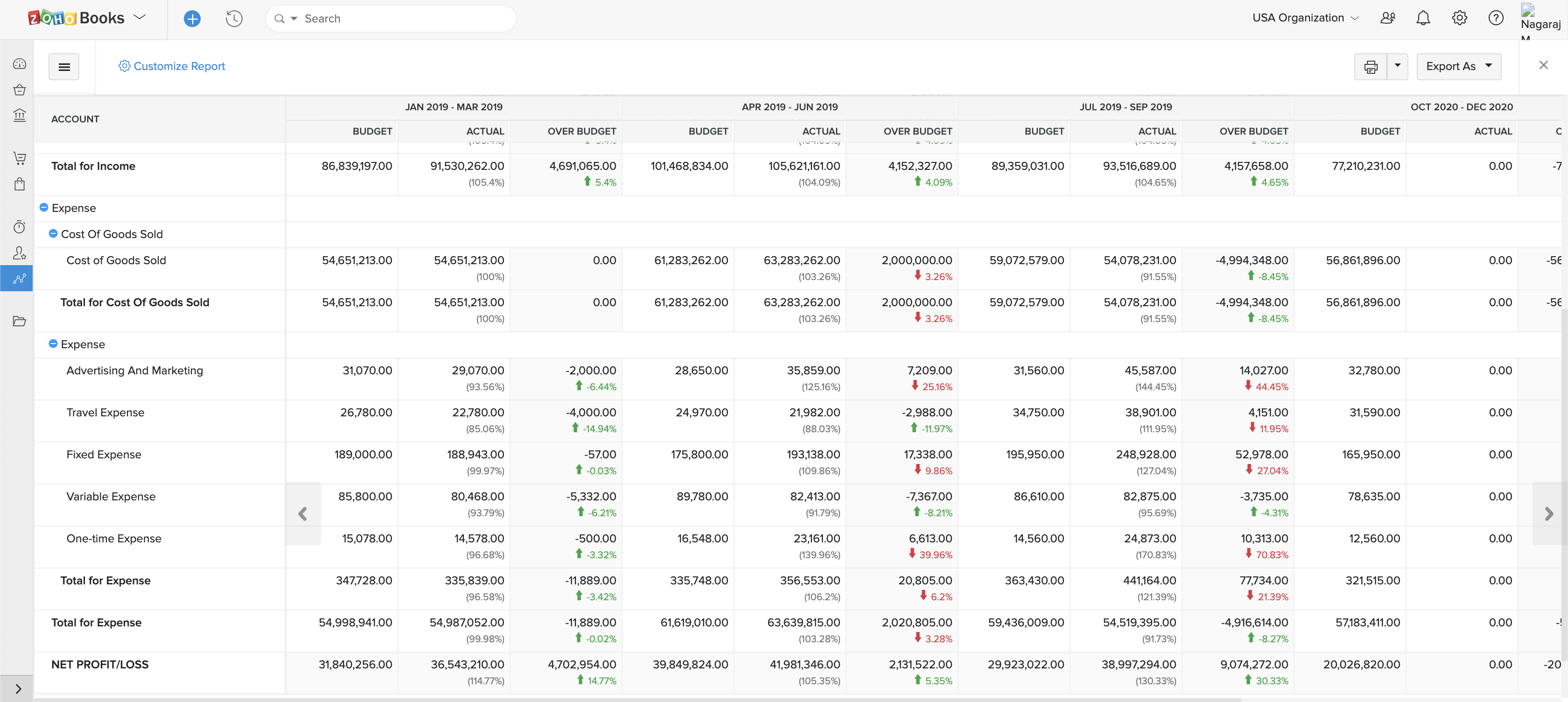
Role of accounting software in budgeting
Budgeting for a business is a large task, which is why you might need assistance. Creating a budget will involve analyzing costs, estimating revenue, and projecting cash flow. Having an accounting system in place will give you real-time information about your finances, helping you to create a feasible budget.
The key to creating a good budget is to evaluate the previous years’ data and draw realistic projections. An accounting system can give you access to all this information in one place, no matter when you need it.
The effectiveness of a budget also depends on how well any projected goals have been achieved by your business. To check this, an accounting system generates financial reports that record your actuals, and those can then be compared with the budget. Comparing your budget with your actuals is an important step to gauge the effectiveness of a budget.
Budgeting is an essential process, especially for small businesses, as it allows business owners to estimate and allocate money for different business activities. Preparing a budget also gives you a clear idea of the money that can be used to achieve business goals and ensure that there is enough in hand to handle a crisis. For small businesses, it might get a bit difficult to make estimations for the whole year as the initial stages of growing an organization are often volatile. In such cases, you can create smaller budget estimates for a duration of two or three months and keep reviewing it for better results. When an accounting system is introduced, the process becomes even more manageable. You can easily handle tasks like projecting cash flow or estimating costs, and you can set realistic goals for your business.
Related Posts
- Business Budget: What is it & Why is it important?
- How Is Cash Flow Calculated?
Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Great article, Easy to read, straight to the point, very informative.
Wonderful article! Just what I needed
a valuable information for person like me who doesn’t has finance background.
wonderful said,
I really like this article, it is very easy to read, gives an idea and try to make the budget process a much easier task
Simple and precise article
You might also like
Switch to smart accounting. try zoho books today.
Get expert advice delivered straight to your inbox.
How to Create a Basic Business Budget
8 Min Read | May 16, 2024
You’d never intentionally set your business up to fail, right? But if you don’t know your numbers and how to make a business budget, that’s exactly what you’re doing. Money problems and bad accounting are two reasons why many small businesses don’t make it past their first five years. 1
Talking about budgets can feel overwhelming. We get it. For a lot of business leaders, it’s a lot more comfortable dreaming up big ideas and getting stuff done than digging into numbers. But you can’t set yourself up for steady growth until you have a handle on the money flowing in and out of your company. You also can’t enjoy financial peace in your business.
Not a numbers person? That’s okay. Follow the simple steps below to learn how to create a budget for a business and manage your finances with confidence. We’ll even give you a link to an easy-to-use small-business budget template in the EntreLeader’s Guide to Business Finances .
But before we get to that, let’s unpack what a budget is and why you need one.
Don't Let Your Numbers Intimidate You
With the EntreLeader’s Guide to Business Finances, you can grow your profits without debt—even if numbers aren’t your thing. Plus, get a free business budget template as part of the guide!
What Is a Business Budget?
A business budget is a plan for how you’ll use the money your business generates every month, quarter and year. It’s like looking through a windshield to see the expenses, revenue and profit coming down the road. Your business budget helps you decide what to do with business profit, when and where to cut spending and grow revenue, and how to invest for growth when the time comes. Leadership expert John Maxwell sums it up: “A budget is telling your money where to go instead of wondering where it went.”
But here’s what a business budget is not: a profit and loss (P&L) report you read at the end of the month. Your P&L is like a rearview mirror—it lets you look backward at what’s already happened. Your P&L statement and budget are meant to work together so you can see your financial problems and opportunities and use those findings to forecast your future, set educated goals, and stay on track.
Why Do I Need to Budget for My Business?
Creating a budget should be your very first accounting task because your business won’t survive without it. Sound dramatic? Check this out: There are 33.2 million small businesses in the United States. Out of the small businesses that opened from 1994 to 2020, 67.7% survived at least two years. But less than half survived past five years. 2 The top reasons these businesses went under? They hit a wall with cash-flow problems, faced pricing and cost issues, and failed to plan strategically . 3
As a business owner, one of the worst feelings in the world is wondering whether you’ll be able to make payroll and keep your doors open. That’s why we can’t say it enough: Make a business budget to stay more in control and have more financial peace in running your business.
A budget won’t help you earn more money, but it will help you:
- Maximize the money you’ve got
- Manage your cash flow
- Spend less than your business earns
- Stay on top of tax payments and other bills
- Know if you’re hitting your numbers so you can move at the true speed of cash
How to Create a Budget for a Business
Your ultimate goal is to create a 12–18-month business budget—and you will get there! But start by building out your first month. Don’t even worry about using a fancy accounting program yet. Good ol’ pen and paper or a simple computer document is fine. Just start! Plus, setting up a monthly budget could become a keystone habit that helps kick-start other smart business habits.
Here’s how to create your first budget for business:
1. Write down your revenue streams.
Your revenue is the money you earn in exchange for your products or services. You’ll start your small- business budget by listing all the ways you make money. Look at last month’s P&L—or even just your checking account statement—to help you account for all your revenue streams. You’re not filling in numbers yet. Just list what brings in revenue.
For example, if you run an HVAC business, your revenue streams could be:
- Maintenance service calls
- Repair services and sales
- New unit installation
- Insulation installation
- Air duct cleaning
2. Write down the cost of goods sold (if you have them).
Cost of goods is also called inventory. These expenses are directly related to producing your product or service. In the HVAC example, your cost of goods would be the price you pay for each furnace and air conditioning unit you sell and install. It could also include the cost of thermostats, insulation and new ductwork.
3. List your expense categories.
It’s crazy how much money can slip through the cracks when we’re not careful about putting it in the budget. Think through all your business expenses—down to the last shoe cover your technicians wear to protect your customers’ flooring during house calls. Here’s a list of common business budget categories for expenses to get you started:
- Office supplies and equipment
- Technology services
- Training and education
Related articles : Product Launch: 10 Questions to Ask Before You Launch a New Product New Product Launch: Your 10-Step Checklist
4. Fill in your own numbers.
Now that you have a solid list of revenue and expense categories, plug in your real (or projected) numbers associated with them. It’s okay if you’re not sure how much you’ll sell just yet or exactly how much you’ll spend. Make an educated guess if you’re just starting out. If your business has been earning money for a while, use past P&L statements to guide what you expect to bring in. Your first budget is about combining thoughtful guesswork with history and then getting a more realistic picture month over month.
5. Calculate your expected profit (or loss).
Now, number nerds and number haters alike—buckle in. We’re about to do some basic accounting so you know whether you have a profit or loss. This is your chance to figure out exactly how much you’re spending and making in your business.
Take your gross revenue (the total amount of money you expect to make this month) and subtract your expenses and cost of goods sold to find your profit or loss. Here’s what that calculation looks like:
Revenue - Expenses - Cost of Goods Sold = Profit or Loss
Don’t freak out if your first budget shows a loss. That actually happens a lot with your first few monthly budgets. You’re learning and getting context on what’s coming in and going out so you can make adjustments. Keep doing your budget, and before you know it, you’ll be a rock star at telling your money where to go, planning for emergencies , investments and opportunities , and building momentum.
6. Review your budget often.
Whew! Once you get that first business budget under your belt, take a deep breath and celebrate. You’ve just done something huge for your business! (You’ll also be happy to know, budgeting gets easier from here since you can copy and paste your first one and tweak your income and expenses each month.)
But here’s the thing: Your budget can’t just sit in a drawer or on your computer. You’ve got to look at it consistently to make sure you’re actually following it.
Weekly Review
At least once a week, someone in your business (whether it’s you, a qualified team member or a bookkeeper) needs to track your transactions so you know what’s happening with your money all month. Then you can make adjustments before you have more month than money.
Every time you review your budget, ask yourself these three questions:
- Are we on target to hit our revenue goal this month?
- If not, what we can change to get there?
- Are there any expenses we can cut or minimize?
Monthly Review
You also need to review your business budget when you close your books every month to compare it to your actuals—your P&L. Otherwise, how can you know how you’re doing?
7. Work toward a 12–18-month budget.
Now that you’ve created your first month’s budget, move on to the next one. You’ve got this! The more budget-building reps you get in, the better you’ll be at looking forward and planning for growth. In no time, you’ll reach that ultimate goal of a 12–18-month budget. Just keep adjusting as you go based on all you’re learning about getting an accurate road map for your finances.
As you start owning your numbers, remember: It’s okay if you’re a little intimidated by the process of accounting and making a budget for business. But it’s not okay to avoid the financial details that will make or break you. So just keep applying the basics we covered and keep moving forward.
Follow the steps above to create your budget, and review it often to stay on track.
Want a tool to make budget building simpler? Check out the EntreLeader’s Guide to Business Finances. It includes an easy-to-use small-business budget template in the extra resources section.
What are the benefits of budgeting?
A business budget will help you:
- Make informed, strategic decisions
- Invest in under-resourced areas
- Trim over-resourced areas
- Plan for the future
- Set goals and track your progress
Does using a small-business budget template save time?
Yes! Using a small-business budget template helps you plug in the numbers you need to operate with more confidence and fewer wrong turns. Check out the small-business-budget template inside our EntreLeader’s Guide to Business Finances .
How do I budget if I own a seasonal business?
Just like farmers put extra hay in the barn to cover leaner months, if you’re a seasonal business owner, you need to set aside resources in times of plenty to cover months your business turns down. Use your P&L statements to go back in time and look at financial performance year over year. Then, create your business budget based on what you learn and on any changes you see coming. You can also go to trade conferences to get an idea of your industry’s seasonal benchmarks.
Did you find this article helpful? Share it!
About the author
EntreLeadership
EntreLeadership is the part of Ramsey Solutions that exists to help small-business owners thrive by mastering themselves, rallying their teams, and imposing their will on the marketplace. Thousands of leaders use our proven EntreLeadership System and resources to develop as leaders and grow their businesses. These resources include The EntreLeadership Podcast , EntreLeadership Elite digital membership , books, live events, coaching sessions and business workshops. Learn More.
7 Tips for How to Run a Business Debt-Free
True or false: Running a business requires debt. The answer? False. The truth is, you can’t run a business if you’re broke—and debt increases your risk of going broke when a storm hits. Here’s how to run a business debt-free.
How to Create a Profit-Sharing Plan
It's easy to feel discouraged when trying to compete for top talent and keep your team happy. Learn how a profit-sharing plan can help you build and keep an awesome team even when the market shifts.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Finance and Business
- Managing Your Money
How to Create a Business Budget
Last Updated: November 18, 2021 Approved
This article was co-authored by Samantha Gorelick, CFP® . Samantha Gorelick is a Lead Financial Planner at Brunch & Budget, a financial planning and coaching organization. Samantha has over 6 years of experience in the financial services industry, and has held the Certified Financial Planner™ designation since 2017. Samantha specializes in personal finance, working with clients to understand their money personality while teaching them how to build their credit, manage cash flow, and accomplish their goals. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, several readers have written to tell us that this article was helpful to them, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 181,448 times.
Building a realistic budget is an effective way to help keep your business profitable. To create your budget, you'll need to make a revenue forecast, estimate your costs, and leave enough room for a reasonable profit margin. Don't worry though—it's easier than it sounds. Our how-to guide will walk you through the simple steps of creating your own financial plan, even if you're a total beginner to budgeting!
Understand the Basics of Budgeting

- For example, assume your business is planning for next year. A budget will outline your estimated revenues, and then include a plan for expenses that is less than those revenues, so that you can earn a profit.
- A balanced budget means your revenues are equal to your expenses. A surplus means your revenues exceed expenses, and a deficit means expenses exceed revenues. As a business, your budget should always strive to be in a surplus state.

- A budget should guide every single business expenditure. For example, if you realize midway through a year that your business desperately needs updated computers, you can consult your budget to see how much estimated surplus revenue you will generate for the remainder of the year. You can then explore costs for computer upgrades and see if that fits within the surplus figure while allowing you to earn a profit, or alternatively, if you have the additional revenue to support taking out a loan for the computers.

- Sales: Sales refer to how much total money your business brings in from all sources. A budget will involve an estimate or forecast of your future sales.
- Total costs: Total costs are what it costs your business to generate your sales. These include fixed costs (like rent), variable costs (like materials used to make your products), and semi-variable costs (like salaries).
- Profits: Profits are equal to revenues minus total costs. Since profit is the goal of business, your budget should include expenses that are low enough to earn you a decent return on your investment.
Forecasting Revenue

- Remember that revenue forecasts are rarely accurate. The point is to provide the best possible estimate using the knowledge you have. [6] X Research source
- Always be conservative. This means assume you will receive sales volumes and pricing on the low end of the possible range.

- For example, assume you are opening a therapy practice. Therapists in your region may charge $100 to $200 per hour. Compare your qualifications, experience, and service offerings to your competition, and estimate your price. You may decide $100 is wise.
- If you offer multiple products and services, make sure to research prices for those too.

- Do you have any customers or contracts lined up? If so, include these. You can then assume referrals from customers and advertising will add to these volumes over the year.
- Compare to existing businesses. If you have colleagues who have established businesses, ask them what their volumes were like early on. For a therapy practice, your colleagues may tell you during their first year they averaged about 10 client hours a week.
- Look at what drives sales volumes. If you are opening a therapy practice, for example, your reputation, referrals, and advertising will bring in people. You could decide that based on these resources, one new client every two weeks is reasonable. You could then go further and make an estimate that each client will pay for one hour a week, and last for an average of six months.
- Once again, remember that revenue forecasts are purely estimates.

- Look at pricing. Do you have reason to believe your prices will increase or decrease?
- Look at volume. Are more people going to be purchasing your product or service? If your business has been growing by 2% annually, you can assume the same for the following year if no significant changes have occurred. If you plan on aggressively advertising, you could bump that up to 3%.
- Look at the market. Is your market growing? For example, imagine that you run a coffee shop in a downtown neighborhood. You may be aware that the neighborhood is rapidly growing due to new people moving in. This could be reason to add to your growth forecast.
Creating the Budget

- Contact an accountant if you are having difficulties. Chartered Professional Accountants in the UK and Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) in the US are trained to advise businesses in the area of budgeting, and for a fee they can assist you in any aspect of the budget creation process.
- A simple online search of "business budget template" can yield thousands of results. You can even find custom templates for your particular type of business.

- Research online or ask a financial adviser what the typical margins for your kind of business should be.
- If 10% is typical for your business, you know that if you are forecasting $100,000 of revenues, your expenses should equal no more than $90,000.

- Add up all these costs to get an idea of your fixed costs for the next year.
- If you have past financial data, use these fixed costs and adjust them for any rent increases, bill increases, or new costs.

- This will vary depending on how much you sell, which is why it is known as a variable cost. You can use your revenue forecast to determine this. For example, if you estimate you will sell 12 cars in your first year, your inventory costs will be the cost to purchase 12 cars.

- Add up all your estimated semi-variable costs.

- Are your total costs less than your revenues?
- Do your total costs provide a profit margin greater than or equal to your target?
- If the answer to either of these questions are no, you will need to look into making cuts. To do this, look at all your costs, and examine what you can do without. Labor costs are one of the most flexible areas to find savings (though you risk upsetting your employees when you cut hours). You can also look into finding a location with lower rents, or reducing utilities costs.
Expert Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ Samantha Gorelick, CFP®. Financial Planner. Expert Interview. 6 May 2020.
- ↑ http://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/budget.asp
- ↑ http://www.inc.com/encyclopedia/businessbudget.html
- ↑ http://www.entrepreneur.com/article/76418
- ↑ http://articles.bplans.com/how-to-forecast-sales/
- ↑ http://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/semivariablecost.asp
About This Article

To create a business budget, start by forecasting your yearly expenditures. To do this, add together fixed costs like rent, insurance, and property taxes. Then, add variable costs like inventory purchases and semi-variable costs like internet packages or employee salaries. Compare this number to your forecasted yearly revenue, which you can determine by comparing to last year’s revenue, or if you’re a new business, by doing market research to figure out what similar businesses make in a year. If your revenue is lower than your expenditures, figure out places you can cut from your budget. To learn how market forecasting can help give you an accurate estimate, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Kathleen Coyle
Mar 9, 2017
Did this article help you?

Daniel Aremu
May 17, 2018
Aug 17, 2016
Kirti Singh
Feb 14, 2017
Mohammad Zia
Nov 3, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
How to Prepare a Budget for an Organization: 4 Steps

- 16 Nov 2021
An organization’s budget dictates how it leverages capital to work toward goals. For this reason, the ability to prepare a budget is one of the most crucial skills for any business leader —whether a current or aspiring entrepreneur, executive, functional lead, or manager.
Before preparing your first organizational budget, it’s important to understand what goes into a budget and the key steps involved in creating one.
What Is a Budget?
A budget is a document businesses use to track income and expenses in a detailed enough way to make operational decisions.
Budgets are typically forward-looking in nature. Income is based on projections and estimates for the periods they cover, as are expenses. For this reason, organizations often create both short- (monthly or quarterly) and long-term (annual) budgets, where the short-term budget is regularly adjusted to ensure the long-term budget stays on track.
Access your free e-book today.
Most organizations also prepare what’s known as an “actual budget” or “actual report” to compare estimates against reality following the period covered by the budget. This allows an organization to understand where it went wrong in the budgeting process and adjust estimates moving forward.
Budget vs. Cash Flow Statement
If the definition above sounds similar to a cash flow statement , you’re right: Your organization’s budget and cash flow statement are similar in that they both monitor the flow of money into and out of your business. Yet, they differ in key ways.
First, a budget typically offers more granular details about how money is spent than a cash flow statement does. This provides greater context for making tactical business decisions, such as considering where to trim business expenses.
Related: The Beginner’s Guide to Reading & Understanding Financial Statements
Second, a budget is, quite literally, a tool used to direct work done within an organization. The cash flow statement plays a different role by offering a higher-level overview of how money moves into, throughout, and out of an organization.
Instead of thinking of the two documents as competing, view them as complementary, with each playing a role in driving your business’s performance.
Steps to Prepare a Budget for Your Organization
The steps below can be followed whether creating a budget for a project, initiative, department, or entire organization.
1. Understand Your Organization’s Goals
Before you compile your budget, it’s important to have a firm understanding of the goals your organization is working toward in the period covered by it. By understanding those goals, you can prepare a budget that aligns with and facilitates them.
Related: The Advantages of Data-Driven Decision-Making
For example, consider a business that regularly experiences year-over-year revenue growth that’s offset by rising expenses. That organization might benefit from focusing efforts on better controlling expenses during the budgeting process.
Alternatively, consider a company launching a new product or service. The company may invest more heavily in the fledgling business line to grow it. With this goal, the company may need to trim expenses or growth initiatives elsewhere in its budget.
2. Estimate Your Income for the Period Covered by the Budget
To allocate funds for business expenses, you first need to determine your income and cash flow for the period to the best of your ability.
Depending on the nature of your organization, this can be a simple or complicated process. For example, a business that sells products or services to known clients locked in with contracts will likely have an easier time estimating income than a business that depends on active sales activity. In the second case, it would be important to reference historical sales and marketing data to understand whether the market is changing in a way that might cause you to miss or exceed historical trends.
Related: How to Read & Understand an Income Statement
Beyond income from sales activity, you should include other income sources, such as returns on investments, asset sales, and bond or share offerings.

3. Identify Your Expenses
Once you understand your projected income for the period, you need to estimate your expenses. This process involves three main categories: fixed costs, variable expenses, and one-time expenses.
Fixed costs are any expenses that remain constant over time and don’t dramatically vary from week to week or month to month. In many cases, those expenses are locked in by some form of contract, making it easy to anticipate and account for them. This category usually includes expenses related to overhead, such as rent payments and utilities. Phone, data, and software subscriptions can also fall into this category, along with debt payments. Any expense that’s regular and expected should be included.
Related: 6 Budgeting Tips for Managers
Variable expenses are those your business incurs, which vary over time depending on several factors, including sales activities. Your shipping and distribution costs, for example, are likely to be higher during a period when you sell more product than one when you sell less product. Likewise, utilities such as water, gas, and electricity will be higher during periods of increased use. This is especially true for businesses that manufacture their own products. Sales commissions, materials costs, and labor costs are other examples of variable expenses.
Both fixed expenses and variable expenses are recurring in nature, making it easy to account for them (even if variable expenses must be projected). One-time expenses , also called “one-time spends,” don’t recur and happen more rarely. Purchasing equipment or facilities, developing a new product or service, hiring a consultant, and handling a security breach are all examples of one-time expenses. Understanding major initiatives—and what it will take to accomplish them—and what you’ve spent in previous years on similar expenses can help account for them in your budget, even if you’re unsure of their exact values.
4. Determine Your Budget Surplus or Deficit
After you’ve accounted for all your income and expenses, you can apply them to your budget. This is where you determine whether you have enough projected income to cover all your expenses.
If you have more than enough income to cover your expenses, you have a budget surplus. Knowing this, you should determine how to use additional funds best. You may, for example, move the money into a rainy day fund you can access should your actual income fall short of projections. Alternatively, you may deploy the funds to grow your business.
On the other hand, if your expenses exceed your income, you have a budget deficit. At this point, you must identify the best path forward to close the gap. Can you bring in additional funds by selling more aggressively? Can you lower your fixed or variable expenses? Would you consider selling bonds or shares of company stock to infuse the business with additional capital?

An Important Financial Statement
The person responsible for generating a budget varies depending on an organization’s nature and its budgetary goals. An entrepreneur or small business owner, for example, is likely to prepare an organizational budget on their own. Meanwhile, a larger organization may rely on a member of the accounting department to generate a budget for the entire business. Individual department heads or functional leads might also be called on to submit budget proposals for their teams.
With this in mind, anyone who aspires to start their own business or move into an organizational leadership position can benefit from learning how to prepare a budget.
Do you want to take your career to the next level? Consider enrolling in our eight-week Financial Accounting course or three-course Credential of Readiness (CORe) program to learn financial concepts that can enable you to unlock critical insights into business performance and potential. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author
IT Services
How to build a scalable IT budget
How much business could your business do without IT?
These days, “none” is far and away the most common answer.
Yet many organizations struggle with how to approach spending and budgeting related to IT. Information technology may be the backbone of a business, but it usually isn’t front and center in strategic discussions and high-level decision-making. And whatever spending is happening, the budgeting process underneath it often doesn’t scale well.
We know that IT budgets are growing: 57% of CIOs expected their IT budgets to increase last year. An effective IT budget is about more than just spending more money. It’s about spending that money wisely — and determining how much money should be spent on IT in the first place.
How often should an IT budget be evaluated?
)
Many organizations with established IT budgeting procedures evaluate that budget yearly.
Why yearly? Because the process can be lengthy, involving numerous stakeholders and significant amounts of documentation. And the larger your organization, the more complex this business process gets. It’s not uncommon for the evaluation process to take months, so it’s impractical to shorten the budget lifecycle.
For IT services firms supporting clients in the IT budget evaluation and creation process, a yearly cycle can prevent overburdening your team and allow you to stagger clients throughout the calendar year.
)
Easy client management for IT Services teams
Learn how Teamwork.com helps IT Services teams to optimize workstreams, automate manunal tasks, and securely centralize their client operations.
Discover Teamwork.com
Who should be involved in the process?
Keeping the right stakeholders involved in the IT budgeting process helps ensure that the budget is holistic (covering everything necessary), realistic (within the company’s overall financial means), and well-managed (administered and allocated responsibly).
The personnel involved should include any of the following, where they exist:
Chief information officer (CIO)
Chief financial officer (CFO)
IT managers, IT directors, IT department heads
IT project managers and project leads
Representatives from major divisions/departments
If the organization has a project management office (PMO), that group should also play a role.
It’s worth noting that entities outside the CIO and IT domains play an increasing role in IT budgeting as the process gets democratized across lines of business. Teodora Siman, an IDC research manager , elaborates:
“We’re seeing more influence come from outside of IT, where the CIO orchestrates technology across the business, and [technology decisions] are a collaborative conversation with business leaders who are focused on outcomes and customer-centricity.”
)
Spin up web projects faster
Our free website project planning template helps you keep track of timelines and smash your goals.
Use template
- Key items to include in an IT budget
Organizations differ in where certain expenses fall in the budget, but most IT budgets should include at least these five areas:
Physical employee equipment: IT money is used to purchase laptops, desktops, printers, phones, networking equipment, servers, and other hardware.
Staff salaries: Employees within the IT department or division are typically paid out of the IT budget
Cybersecurity, backup, and disaster recovery (DR): Preventive expenditures here help to hedge against disasters, natural or otherwise.
Infrastructure and maintenance: Money is allocated to repair and upgrade devices and infrastructure and to pay for ongoing IT infrastructure operational costs (internet access, cloud services, software licenses, etc.).
IT project management: IT project management costs that are not accounted for in your overall project management budget should appear here.
How to plan a budget that serves the future of the organization
)
Planning an IT budget can be relatively simple for a startup or small professional services firm, a massive months-long process at an enterprise level, or anywhere in between.
Whatever the size and scope of your IT budget planning, we’ve boiled the process down to six key elements. Below, we’ll provide clear, concise planning tips to help you create an IT budget to propel your organization forward.
Assess the current landscape (internal and external)
One key strategy for planning is considering the context around your IT budget. Is business booming? Is your industry more broadly in flux? Are you growing (and if so, how quickly)? Or is this a year where it’s clear the purse strings need to tighten?
And what about the technology landscape? We aren’t necessarily seeing quantum leaps in computing power at the individual user or device level. But consider the capabilities of AI and machine learning to churn through data or for generative AI to enhance workflows and extend human capacity.
Any successful IT budget needs to be grounded in these realities. They inform how much is likely to be available and what sorts of changes that budget needs to accommodate.
Integrate business objectives and cross-department goals
Next, remember that your IT budget isn’t an island or a destination. It’s a way to achieve goals and objectives. So make sure your budget doesn’t live in a silo. Instead, it should be built atop existing business objectives and priorities.
Including business objectives and cross-departmental goals in budget planning ensures that your IT division is growing with, not against, the broader organization. By building your IT budget around the business’s core objectives, you can avoid unnecessary spending on IT projects that don’t further the mission.
This improves the organization’s financial health, affects employee morale and effectiveness, and can even advance market competitiveness.
)
Buyer's Guide for Professional Services Automation
Compare the top PSA platforms, see a detailed breakdown of key features, and get advice from industry experts on how to trial, shortlist, and onboard PSA successfully.
Read the guide
Set clear guidelines for expense categories
One principle is consistent for any kind of budgeting: the more clarity, the better.
It’d be preposterous to lump your entire IT budget into a single line item: you need to know where the money’s going more specifically than that. But true clarity requires more than a few vague expense categories. You’ll need to get as specific as possible and set clear guidelines with team members on what expenses go where.
With clearer and more numerous expense categories, it will be easier to understand IT spend after the fact, helping you create progressively more accurate IT budgets year after year.
Consider flexible purchase options
IT costs can be inconsistent and spiky: it’s easy enough to plan for an upgrade cycle on PCs for your workforce, but the cost of replacing a server is a different beast. Big technology investments are sometimes needed, and the larger your organization scales, the more unwieldy these IT expenditures can become.
So, as you plan your IT budget, consider flexible purchasing options for your IT investments, including fair market value leases, consumption-based billing, and installment payment agreements.
This is one reason so many organizations are turning to the cloud: procuring your computing and software needs from a cloud provider tends to flatten out these spikes. Managed IT service providers can provide a similar cost-leveling function, and in the right situations, this business model can deliver notable cost savings alongside better IT support and the broad expertise needed to meet diverse IT needs.
Use KPIs to monitor effectiveness
Next, make sure to track the effectiveness of your IT budget processes by tracking the right metrics. Key performance indicators (KPIs) can help here, but the trick is finding the KPIs that deliver the right information in the right way.
For example, IT project team efficiency , on-time project completion percentage, average hardware age, software utilization rate, and a few dozen other measures could all be helpful — but not all are helpful all the time.
Which KPIs are right for monitoring budget effectiveness depends on what your business is trying to achieve. Cost savings, increased efficiency, greater accuracy, and better customer responsiveness are all fantastic priorities, but they may compete against one another in some ways.
So first, you must establish which priorities take precedence. Only then can you select the KPIs to help you measure progress on those priorities.
Educate stakeholders about IT spending
Last, make sure you continually educate stakeholders in the IT budget about how spending works in IT. You’ll be working with people across a spectrum of specialties and skill sets, and not everyone will be a financial or IT expert.
It’s up to you to invest in these stakeholders. By teaching them about the mechanisms for IT spending (such as those flexible purchase options), your budgetary goals, and the tools you’ll use to measure success, you’ll garner better support and get more useful feedback.
Manage your IT projects and budgets effectively with Teamwork.com
For a successful overall IT strategy, businesses and IT leaders must prioritize the IT initiatives that best fit a company’s business goals and strategic needs — while staying within appropriate levels of IT spending.
Because while digital transformation is key to continued growth, it’s neither easy nor inexpensive.
For most professional services firms, managing IT projects and budgets well requires understanding and adhering to the business’s strategic plan and creating a technology roadmap that supports the overall business strategy. It also demands the ability to plan, visualize, strategize, organize, and ultimately execute projects well.
Teamwork.com is project management software that’s perfect for IT project management — including IT budgeting projects.
)
The only all-in-one platform for client work
Trusted by 20,000 businesses and 6,000 agencies, Teamwork.com lets you easily manage, track, and customize multiple complex projects. Get started with a free 30-day trial.
Try Teamwork.com for free
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- How often should an IT budget be evaluated?
- Who should be involved in the process?
- How to plan a budget that serves the future of the organization
)
Ben is a Senior Content Marketing Specialist at Teamwork.com. Having held content roles at agencies and SaaS companies for the past 8 years, Ben loves writing about the latest tech trends and work hacks in the agency space.
)
8 types of IT projects and their business impact
)
8 new IT challenges businesses face in 2024
)
The definitive guide to website project management
)
The ultimate guide to creating a web design workflow
)
How IT project managers succeed with project management software
)
12 Web Dev Projects for Beginners & Intermediate
- Grand Rapids/Muskegon
- Saginaw/Bay City
- All Michigan
Grand Rapids passes $690M budget with dollars for more firefighters, 911 dispatchers
- Updated: May. 23, 2024, 12:53 p.m. |
- Published: May. 23, 2024, 12:50 p.m.

The Ottawa Ave. NW steps onto Calder Plaza, with Grand Rapids City Hall in the background. (MLive File Photo)
- Michael Kransz | [email protected]
GRAND RAPIDS, MI – Grand Rapids leaders are moving forward with a $690 million spending plan for the upcoming fiscal year with a focus on customer service.
The 2025 fiscal year budget, which takes effect July 1, was unanimously approved Tuesday, May 21, by the Grand Rapids City Commission.
Read more Grand Rapids news on MLive
- Federal prosecutors, local police to crack down on gun violence in West Michigan
- 12 parades and ceremonies around Grand Rapids to observe Memorial Day 2024
- Drivers rejoice! U.S. 131 set to reopen ahead of Memorial Day weekend
- Teen stops man after he allegedly shot woman in their home
- Newly rebuilt Ottawa Beach General Store set to reopen Memorial Day weekend
If you purchase a product or register for an account through a link on our site, we may receive compensation. By using this site, you consent to our User Agreement and agree that your clicks, interactions, and personal information may be collected, recorded, and/or stored by us and social media and other third-party partners in accordance with our Privacy Policy.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
Graduating With Student Loans? Prepare for Your Financial Future

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
College graduation season is underway, and nearly 3.2 million students are slated to pick up their associate or bachelor’s degree diplomas this spring, according to the National Center for Education Statistics. When the cap tosses and festivities wrap up, it’ll be time for job applications, apartment leases — and student loan payments.
It can be challenging to navigate major bills and student debt repayment. This year, new payment plans may complicate matters further.
Investing time now to research repayment options can pay off, says Emma Crawford, a certified financial planner and student loans expert at Perk Planning, a registered financial advisory firm in Madison, Wisconsin: “It's not easy, but it's worth it because it can save them a lot of money in the long run.”
If you’re leaving campus this year and starting your first full-time job, here’s how to prepare for impending student loan bills and a new financial reality.
Complete student loan exit counseling
If you have federal loans, you must complete mandatory student loan exit counseling when you leave school. The process takes about 30 minutes and can be done online at StudentAid.gov . Exit counseling will ask you to update your contact information, walk you through how much you owe and explain the basics of student loan repayment.
Many universities require students to complete loan exit counseling before they will post their official diplomas, Crawford says.
Private student loans won’t appear on StudentAid.gov. To check your loan amount and terms, including any exit counseling requirements, refer to the documents you signed when you took out the loan and reach out to your lender.
Get to know your servicer or lender
Federal student loan servicers act as intermediaries between borrowers and the Education Department. You were assigned a servicer when you first took out your loans. Your servicer’s customer service department can help you with individual questions about your loans and repayment options.
Your federal student loan servicer is listed on the right side of your StudentAid.gov dashboard. You’ll have to set up a separate account on your servicer’s website to manage your bills.
“Understanding who your servicer is is really important, because a lot of people don't know that they're not going to be paying on StudentAid.gov. They have to pay their servicer,” Crawford says.
Spend a few minutes logging into your servicer account and updating your contact information. Here, you can also enroll in autopay, so you don’t have to manually pay your student loan bill each month. Autopay also gives you a 0.25 percentage point interest rate deduction on your bills.
Choose a repayment plan
If you don’t pick a specific student loan repayment plan , your servicer will automatically place you on the standard repayment plan. This splits your total debt into 10 years' worth of monthly payments, plus interest.
The Education Department’s loan simulator will give you estimates for how much you could pay on various repayment plans, including how much forgiveness you could get. Take some time to go through the pros and cons of each repayment plan, and learn about how monthly payments are calculated, Crawford says.
The new income-driven SAVE repayment plan is a good fit for many recent graduates, who tend to earn lower salaries as they start their careers. Beginning in July, SAVE will cap undergraduate student loan payments at 5% of discretionary income.
If you’re unemployed or earn less than $32,800 (roughly $15 an hour) as a single household, you’ll qualify for $0 monthly payments and interest won’t build under SAVE — while also making progress toward loan forgiveness. However, this plan could extend your repayment period from 10 years to up to 25 years, depending on how much you owe.
Reach out to your servicer to switch repayment plans. You can also sign up for an income-driven plan like SAVE on StudentAid.gov/IDR .
Repayment options for private student loans vary by lender.
Prepare for your first bill
You have a six-month student loan “grace period” after graduation or dropping below half-time enrollment, during which you don’t have to make federal student loan payments. After the grace period ends, your first bill is due.
If you start a job before the grace period ends and your federal loans are unsubsidized, consider starting repayment anyway. Interest will accrue during the grace period, which could increase the total amount you’ll repay over time. But if you have need-based subsidized loans, there’s no downside to taking advantage of the grace period — interest won’t start building until after the six months end.
“Take advantage of that grace period to try and get your career up and running,” says Scott Stark, a financial coach and certified financial planner at Financial Finesse, a workplace financial wellness company. “Until you have a job and some income, it's just all about trying to keep your expenses as low as you can, trying to avoid getting into debt or getting into situations that you're going to be digging out of a hole.”
Some private student loan lenders offer grace periods after leaving school. Check with your lender for the specifics.
Plan your financial future
Student loan bills might be a major part of your financial life for the next decade or longer. But as a recent graduate, you should also check in with other parts of your financial life to set yourself up for present and future success.
During your grace period, try to save at least $1,000 for emergencies — and once you start your first full-time job, aim to put 10% to 15% of your income into a workplace retirement account, like a 401(k), Stark says.
“Your future self will be so thankful, because of the benefit of how much time you've got for that to compound,” Stark says. “That is an amazing opportunity to get things started on the right foot.”
If your workplace offers a financial wellness counseling benefit, take advantage of it, Stark says. Some jobs even offer student loan repayment benefits , which can help you pay down the debt faster.
On a similar note...
More From Forbes
Global expansion strategies: how to take your business to new markets successfully.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Jason Miller helps influential brands and celebrities create generational wealth with their businesses | CEO, Strategic Advisor Board .
If you’re an entrepreneur who’s ready to take your business ventures from domestic to global, read on to learn about how to research, create financial and strategic plans, and use marketing to get to global success. These are some of the steps I used when breaking into markets with my company, Strategic Advisor Board.
The obvious reason to go global is with access to more people, you will most likely experience revenue growth. But one of the biggest reasons I recommend doing this is due to risk diversification by not relying solely on one market for your business revenue; this is important because of ongoing changes to the economy. According to research, "shareholders do, in fact, reward companies who grow faster outside of the U.S ."
Expanding to new markets can lead to economies of scale and lower production costs due to bulk purchasing and more streamlined production. Your business could also have access to new talent and resources which could lead to more innovation and creativity as well as tapping into local raw materials. Here is how to do it:
Research & Adaptation
I would argue that this is the most important part of the process and maybe the most in-depth of expanding globally because so much of what you find out determines if it’s a smart company decision to make the move. Research your new market to determine whether your product/service will perform well there but also find out tax and regulatory info. You may be exempt from certain taxes if you open your business to new borders.
Why Is Chief Boden Leaving Chicago Fire Eamonn Walker s Exit Explained
Biden vs. trump 2024 election polls: biden leads trump by only single digits in new york, latest survey shows, here are the major allegations against sean diddy combs as cassie ventura breaks silence on attack video.
Find out if you have a target market in the new area you’re looking at, and if they’d be receptive to your products/services. Make sure you take into account the different cultural aspects that could affect the marketability of your product. Do research on any competitors in the area and figure out what your unique selling proposition is. All this information you’ve gathered will help with making your decision.
Financial Planning
Before you can decide to expand, you need to see if you can afford it. Before creating any sort of budget, find out all the costs associated with expanding. Start with looking at the operational expenses such as infrastructure for office or warehouse spaces and supply chain costs. Supply chain costs can include storage of inventory, or transportation costs of your products to and from manufacturing centers to stores or directly to clients.
Find out if any tariffs or customs fees would affect the profitability of your product. You may want to insure your goods, so look into the costs of doing that as well as how much you should put aside for contingency funds to have on hand for any unforeseen expansion costs.
Strategic Planning
In this part of the process, you will create a roadmap starting with defining clear objectives for your expansion. Then developing a strategy that consists of how to enter the market, including looking into joint ventures, mergers, franchising or partnerships.
Your strategic plan also needs to include adaptive planning. This means you’re flexible in your plan so you can accommodate any unforeseen changes, difficulties or challenges that may occur in the marketplace. Since markets are dynamic and continuously shift, it’s important your strategies adjust as well to include any changing political, economic or cultural conditions. Include these factors in the risk management portion of the plan. Also, include a timeline with realistic expectations of short-term and long-term goals.
Marketing & Talent Management
The marketing strategy you’ve been using domestically may not work globally. It’s a skill to be able to build a consistent brand image while making sure you’re connecting with and being respectful of local market preferences.
One of the best things about having a business operating on a global scale is access to top talent. Hiring the correct talent that goes with your brand’s values and mission is important across all your business locations. That being said, HR policies may be different from domestic HR laws in the workplace. Look into getting work visa support if you need employees to work on international projects.
Global expansion isn’t easy and there’s a lot to consider, but if you’re willing to accept the challenge, there are certain strategies to help you achieve success. Extensive research is the most important to start with. Understand what the new market potential will be like, and find out what the taxes and culture look like. Evaluate how receptive your product will be to locals and what makes it unique. Financial planning is crucial in the early stages and you should assess everything from operational and supply chain costs to insuring your goods. Strategic planning is the roadmap to follow and should include clear objectives, a comprehensive entry strategy, timelines, and adaptive planning. The last steps include using marketing that sits well with locals and hiring top talent to help with the transition. Expanding your company isn’t easy, but if you do your research and plan accordingly, you’ll be on the right track to global success.
Forbes Business Council is the foremost growth and networking organization for business owners and leaders. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

Cost of living help and a future made in Australia
Investing in a future made in australia.
Investing in a Future Made in Australia and the skills to make it a reality
Print or save page
On this page
Attracting investment in key industries
Making Australians the beneficiaries of change
A Future Made in Australia is about creating new jobs and opportunities for every part of our country by maximising the economic and industrial benefits of the move to net zero and securing Australia’s place in a changing global economic and strategic landscape.
The Government’s $22.7 billion Future Made in Australia package will help facilitate the private sector investment required for Australia to be an indispensable part of the global economy.
For more information refer to the Future Made in Australia fact sheet [PDF 438KB]
Better deploying capital in priority areas
The Future Made in Australia package will realise Australia’s potential to become a renewable energy superpower, value‑add to our resources and strengthen economic security by better attracting and enabling investment in priority areas. The Government will create a Future Made in Australia Act and establish a National Interest Framework that identifies priority industries and ensures investments associated with them are responsible and targeted.
The Framework will have a focus on industries that contribute to the net zero transformation where Australia has a comparative advantage, and where Australia has national interest imperatives related to economic resilience and security.
Strengthening and streamlining approvals
This Budget provides a faster pathway to better decisions on environmental, energy, planning, cultural heritage and foreign investment approvals.
This includes:
- $134.2 million to better prioritise approvals for renewable energy projects of national significance, and support faster decisions on environment, cultural heritage and planning approvals.
- Working with the states and territories through the Energy and Climate Change Ministerial Council to accelerate electricity grid connections.
- $20.7 million to improve engagement with communities impacted by the energy transition and accelerate the delivery of key energy projects.
- $15.7 million to strengthen scrutiny of high‑risk foreign investment proposals, enhance monitoring and enforcement activities and support faster decisions.
The Government will also encourage foreign investment by providing refunds of 75 per cent of application fees for unsuccessful competitive bids.
Promoting sustainable finance
The Government is committing $17.3 million to mobilise private sector investment in sustainable activities. This includes extending Australia’s sustainable finance taxonomy to the agriculture sector and developing a labelling regime for financial products marketed as sustainable.
The Government will also examine opportunities to improve data quality and provide $1.3 million to develop and issue guidance for best practice transition plans.
Making Australia a renewable energy superpower
Powering australia with cheaper, cleaner, more reliable energy.
Australia’s potential to produce abundant renewable energy is a powerful source of comparative advantage. To realise this, the Government is unlocking more than $65 billion of investment in renewable capacity through the Capacity Investment Scheme by 2030.
This Budget helps Australians benefit from cheaper, cleaner energy sooner by investing $27.7 million to integrate consumer energy resources like batteries and solar into the grid.
The New Vehicle Efficiency Standard will save Australians around $95 billion at the bowser by 2050 and reduce transport emissions.
Unlocking investment in net zero industries and jobs
This Budget accelerates growth of new industries by establishing the $1.7 billion Future Made in Australia Innovation Fund and delivering a 10‑year extension of funding to the Australian Renewable Energy Agency. It also delivers the $44.4 million Energy Industry Jobs Plan and $134.2 million for skills and employment support in key regions.
The Future Made in Australia package establishes time‑limited incentives to invest in new industries. The Hydrogen Production Tax Incentive will make Australia’s pipeline of hydrogen projects commercial sooner, at an estimated cost of $6.7 billion over the decade. This Budget also expands the Hydrogen Headstart program by $1.3 billion.
Boosting demand for Australia’s green exports
The Government is making it easier for businesses and trading partners to source low‑emissions products by building better markets and product standards for green products.
This Budget provides $32.2 million to fast‑track the initial phase of the Guarantee of Origin scheme, focused on renewable hydrogen, and bring forward the expansion of the scheme to accredit the emissions content of green metals and low‑carbon liquid fuels. The Government is also working closely with trading partners to identify opportunities to drive greater supply chain transparency and better market recognition of high environmental, social and governance standards in the critical minerals sector.
Realising the opportunities of the net zero transformation
Australia is committed to reaching net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 and is developing six sector plans covering:
- electricity and energy
- agriculture and land
- the built environment.
This Budget continues investment in effective emissions abatement, including through $63.8 million to support emissions reduction efforts in the agriculture and land sector.
The Government is also investing $399 million to establish the Net Zero Economy Authority and support the economy‑wide net zero transformation. This Budget also invests an additional $48 million in reforms to the Australian Carbon Credit Unit scheme and $20.7 million to improve community engagement.
Strengthening resources and economic security
Backing a strong resources sector.
The Government is investing $8.8 billion over the decade to add more value to our resources and strengthen critical minerals supply chains. This Budget establishes a production tax incentive for processing and refining critical minerals at an estimated cost of $7 billion over the decade. It commits up to $1.2 billion in strategic critical minerals projects through the Critical Minerals Facility and the Northern Australia Infrastructure Facility, and pre‑feasibility studies for common user precincts.
This is in addition to $566.1 million to support Geoscience Australia to map all of Australia’s critical minerals, strategic materials, groundwater and other resources essential for the transition to net zero.
Manufacturing clean energy technologies
The Government is committing $1.5 billion to manufacturing clean energy technologies, including the $1 billion Solar Sunshot and $523.2 million Battery Breakthrough Initiative. These investments will be delivered by ARENA.
Strengthening supply chains
To support the delivery of the 82 per cent renewable energy target, the Government has formed the National Renewable Energy Supply Chain Action Plan with states and territories. The Government will invest an additional $14.3 million working with trade partners to support global rules on unfair trade practices and to negotiate benchmarks for trade in high quality critical minerals.
Digital, science and innovation
Investing in new technologies and capabilities.
The Government is investing $466.4 million to partner with PsiQuantum and the Queensland Government to build the world’s first commercial‑scale quantum computer in Brisbane.
The Government will undertake a strategic examination of Australia’s research and development (R&D) system with $38.2 million invested in a range of science, technology, engineering, and maths programs.
The Government is providing $448.7 million to partner with the United States in the Landsat Next satellite program to provide access to critical data to monitor the earth’s climate, agricultural production, and natural disasters.
Modernising and digitising industries
This Budget commits $288.1 million to support Australia’s Digital ID System. A National Robotics Strategy will also be released to promote the responsible production and adoption of robotics and automation technologies for advanced manufacturing in Australia.
Reforming tertiary education
The Government is committing $1.6 billion over 5 years, and an additional $2.7 billion from 2028–29 to 2034–35 to reform the tertiary education system and deliver Australia's future workforce.
This includes $1.1 billion for reforms to university funding and tertiary system governance.
Over $500 million will be provided for skills and training in priority industries and to support women’s participation in these sectors.
The Government will set a tertiary attainment target of 80 per cent of the working‑age population by 2050.
Supporting students on placements
The Government will establish Commonwealth Prac Payments (CPP) for students undertaking mandatory placements. From 1 July 2025, the payment will provide more than 73,000 eligible students, including teachers, nurses, midwives and social workers with $319.50 per week during their placements.
Felicity is a full‑time student receiving Youth Allowance, living by herself. She is studying a Bachelor of Nursing and must stop paid work during her mandatory prac placement. During her prac, Felicity receives $712.05 per week from the Government including: $319.50 of CPP, $285.55 of Youth Allowance (YA), $103.50 of Commonwealth Rent Assistance (CRA) and $3.50 of Energy Supplement.
Felicity receives $351.55 a week more than she would have in 2023 before indexation and the changes to YA, CRA and CPP in the current and 2023–24 Budget

Broadening access to university
From January 2026, needs‑based funding will provide per student funding contributions for under‑represented students. The Government will also provide $350.3 million to fully fund university enabling courses and increase pathways for prospective students to university.
Skills pipeline for priority industries
Skills and training for Future Made in Australia industries
The Government will expand eligibility to the New Energy Apprenticeships Program to include work in the clean energy sector, including in construction and advanced manufacturing. This will provide access to $10,000 incentive payments and support our target of 10,000 new energy apprentices.
The Government will commit $30 million to turbocharge the VET teaching workforce for clean energy courses and $50 million to upgrade and expand clean energy training facilities.
The Government will invest $55.6 million to establish the Building Women’s Careers program to support women’s participation in key industries including clean energy and advanced manufacturing.
Supporting apprentices and building the construction workforce
The $5,000 support payments to apprentices in priority occupations will be maintained for another 12 months to 1 July 2025, up from $3,000 in the absence of any changes. Employers of these apprentices will receive a $5,000 hiring incentive, up from $4,000 in the absence of changes. This will provide certainty to apprentices while the Strategic Review of the Apprenticeship Incentive System is underway.
The Government will also invest $88.8 million to deliver 20,000 new fee‑free TAFE places including pre‑apprenticeships in courses relevant to the construction sector. The Government will provide $1.8 million to deliver streamlined skills assessments for around 1,900 migrants from comparable countries to work in Australia’s housing construction industry.
Strengthening our defence industry capability
An integrated and focused approach to defending Australia
The Government is investing an additional $50.3 billion over ten years to implement the 2024 National Defence Strategy to meet Australia’s strategic needs.
Overall funding for Defence will reach $765 billion over the decade. Defence’s Integrated Investment Program has been rebuilt to create a focused Australian Defence Force, accelerate delivery of priority capabilities, and provide certainty to grow Australia’s defence industry. This includes funding for the Royal Australian Navy’s surface combatant fleet and establishing a guided weapons and explosive ordnance manufacturing capability earlier.
The Government is reforming Defence’s budget to support the National Defence Strategy and delivery of priority capabilities.
Developing defence industry and skills
Industry development grants funding of $165.7 million will also help businesses to scale up and deliver the Sovereign Defence Industrial Priorities, which include continuous naval shipbuilding and sustainment, and development and integration of autonomous systems.
The Government is providing $101.8 million to attract and retain the skilled industrial workforce to support Australian shipbuilding and delivery of conventionally armed, nuclear powered submarines. This includes a pilot apprenticeship program in shipbuilding trades and technologies.
Investing in civil maritime capabilities
The Government is providing $123.8 million to maintain and enhance civil maritime security capabilities. This includes $71.2 million to increase the Australian Border Force’s on‑water response and aerial surveillance capabilities.
Securing Australia’s place in the world
Strengthening relationships and simplifying trade
A stable, prosperous and resilient Pacific region
The Government is delivering over $2 billion in development assistance to the Pacific in 2024–25. This includes the Australia‑Tuvalu Falepili Union.
Investing in our relationship with Southeast Asia
Following the launch of Australia’s Southeast Asia Economic Strategy to 2040, the Government is committing $505.9 million to deepen ties with the region.
Australia recently celebrated 50 years of partnership with the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). At the ASEAN‑Australia Special Summit, the Government announced a range of new and expanded initiatives, including a $2 billion Southeast Asia Investment Financing Facility to boost Australian trade and investment.
Simplifying trade
The Government will abolish 457 nuisance tariffs from 1 July 2024, streamlining $8.5 billion in annual trade and eliminating tariffs on goods such as toothbrushes, fridges, dishwashers, clothing and sanitary products.
The Government will provide $29.9 million to coordinate trade simplification and deliver the Digital Trade Accelerator program, and $10.9 million to enhance the Go Global Toolkit to support exporters.
The Government is expanding the Australia‑India Business Exchange, diversifying trade and helping more Australian businesses build commercial ties with India and across South Asia. There will be $2 million to support Australian agricultural exporters entering the Chinese markets.
Support for small businesses
Helping small businesses
This Budget’s Small Business Statement reaffirms the Government’s commitment to deliver a better deal for small businesses, with $641.4 million in targeted support.
For more information refer to the small business fact sheet [PDF 0.98MB]
Improving cash flow
The Government is providing $290 million to extend the $20,000 instant asset write‑off for 12 months. There will be $25.3 million to improve payment times to small businesses and $23.3 million to increase eInvoicing adoption.
Easing cost pressures and reducing the administrative burden
This Budget provides $3.5 billion of energy bill relief, including rebates of $325 to around one million small businesses.
The Government is reducing the administrative burden for small business by abolishing 457 nuisance tariffs and delivering $10 million to provide additional support for small business employers administering the Paid Parental Leave scheme.
Supporting confidence and resilience in the small business sector
This Budget invests a further $10.8 million in tailored, free and confidential financial and mental wellbeing supports for small business owners.
The Government is providing $20.5 million to the Fair Work Ombudsman to help small businesses understand and comply with recent workplace relations changes.
There will be $3 million to implement the Government’s response to the Review of the Franchising Code of Conduct, including remaking and enhancing the Code, and an additional $2.6 million to support more small businesses through alternative dispute resolution.
A more resilient Australia
Preparing for the future
The Government is preparing Australia for future droughts and heightened risk of natural disasters.
Disaster resilience and preparedness
The Government will provide $138.7 million to improve Australia’s response and resilience to natural hazards and disasters. Support includes: funding for the National Emergency Management Agency to supply communities with vital goods, equipment, and temporary accommodation during an emergency, aerial firefighting capability, and mental health support. This is in addition to the $11.4 billion previously committed for Disaster Recovery Funding Arrangements for the states and territories.
The Government is establishing a pilot program for Australia’s Strategic Fleet. These vessels will improve Australia’s capacity to respond and support communities and supply chains during crises.
Preparing for drought and climate change
This Budget provides $174.6 million from the National Water Grid Fund to deliver new water infrastructure projects that will enhance water security, boost agricultural production and help drought proof regional communities.
The Government will provide $519.1 million from its Future Drought Fund to help farmers and rural communities manage the impacts of climate change and prepare for future droughts.

This investment will build the drought resilience of more farmers like Victorian cropper Ed Rickard.
The Fund supported Ed in developing a better farm business plan, which identified his need for weather stations and soil moisture probes. It also helped him implement a succession plan that ensured his farm’s long-term viability.
Back to top
Breaking News
How should the county spend your money? Weigh in on proposed $8.5 billion budget at community sessions

Today and next week, attendees will be able to learn more about how the budget process works, ask questions about the budget and give feedback
- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
San Diego County is holding two community sessions to give the public an opportunity to weigh in on its $8. 5 billion recommended budget .
The first session, which will be set up as an open house, will take place from 5:30 to 7:30 p.m. Thursday at the County Operations Center, 5520 Overland Ave. in Kearny Mesa.
The second, which will be held virtually on Zoom , is scheduled from 6 to 7:30 p.m. Wednesday, May 29. A recording will be available in English and Spanish after the meeting.
At both sessions, attendees will be able to learn more about how the budget process works, ask questions about the budget and give feedback.
Both will provide the same information, with county staff available to discuss this year’s funding priorities, such as behavioral health, homelessness, housing and public safety.
At the open house, attendees can visit topic stations to review information on each funding priority area. Attendees of the virtual session will hear a presentation, followed by a moderated Q&A and comments session.
This year’s recommended budget is a 3.9 percent increase from last year, retaining funding for core services, like fire protection, libraries and parks, while adding $300 million and 72 county jobs, totaling more than 20,400 full-time staff.

Flush with tax revenue and other income, San Diego County releases $8.5B spending plan
The county’s proposed fiscal plan for 2024-25 adds $317 million in spending and dozens of staff positions
May 2, 2024
The county’s budget avoided some of the proposed cuts that both the biggest city government and school district within its jurisdiction recently have recently faced.
Just last week, Mayor Todd Gloria announced he’d be canceling some of the cuts he had proposed to the city’s budget, while San Diego Unified School District rescinded nearly all of its hundreds of teacher layoffs.
Following the community meetings, budget hearings will take place before the county Board of Supervisors at 9 a.m. on Tuesday, June 4, and at 5:30 p.m. on Thursday, June 6.
If approved by the board later that month, the budget will go into effect July 1 and determine most public spending through June 2025.
The budget is available for review and comment now until 5 p.m. on June 13. Comments can be submitted online or by emailing [email protected] .
To register for either community session and learn more, visit engage.sandiegocounty.gov/countybudget24-26 .
Get Essential San Diego, weekday mornings
Get top headlines from the Union-Tribune in your inbox weekday mornings, including top news, local, sports, business, entertainment and opinion.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the San Diego Union-Tribune.

More from this Author

After a contentious search, county supervisors have chosen a new top executive. But who is it?
May 22, 2024

‘We do not feel safe’: Families are scrambling to fix their flood-damaged homes. But what if they flood again?
May 18, 2024

‘Like you’re in a different world’: What a new Ocean Beach Pier would mean for locals, surfers and San Diego
May 13, 2024

Three cheers, and barks, for new 4S Ranch park’s off-leash dog area
May 11, 2024

Hundreds of people sue San Diego over January floods, saying it ‘absolutely failed’ to manage stormwater
May 8, 2024

Who will be the county’s next top executive? As supervisors near a decision, one candidate’s backers make a very public push
May 3, 2024
More in this section
Beacon’s Beach trail in Encinitas reopens in time for holiday weekend
Cliffside dirt path down to seaside was closed for months due to landslide issues

San Diego Stores: Nordstrom Rack opening soon, changes at Orfila Winery, Brick & Bell expands
Also: Amore Caffe comes to Hillcrest, Circle K kicks off summer pricing and Abbey’s launches Texas Donut
May 23, 2024

South County
County formally asks state to petition CDC to investigate cross-border sewage crisis and its impact on public health
The request marks an important step in getting federal health officials to conduct a formal epidemiological study

Homelessness
San Diego leaders respond to ‘promising’ and ‘troubling’ report showing a continued rise in homelessness
County officials have also expanded the number of older adults who can receive rental assistance under a pilot program.

San Diego council members agree to move forward with affordable housing plans on former luxury hotel site
City wants to begin exclusive talks with developer Chelsea Investment Corp. to redevelop an East Village block with 100 percent low-income housing.

Carlsbad agrees to take Solutions for Change property and forgive $3.1 million loan
City Council members raise concerns about plan to find another buyer who can upgrade apartments and keep units 100 percent affordable

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Profit is what remains after expenses are deducted. 2. Subtract fixed costs. The second step for creating a business budget involves adding up all of your historic fixed costs and using them to ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Common items to include are credit histories, resumes, product pictures, letters of reference, licenses, permits, patents, legal documents, and other contracts. Example traditional business plans. Before you write your business plan, read the following example business plans written by fictional business owners.
4. Your one-off costs. One-off costs fall outside the usual work your business does. These are startup costs like moving offices, equipment, furniture, and software, as well as other costs related to launch and research. 5. Your cash flow. Cash flow is all money traveling into and out of a business.
Step 1: Create a Budget Process. The budget process shows how the different departments of the business create a budget. Without a process, budgeting would be chaotic, and it would result in inefficiencies. In the budget process, you need to consider the following: Budget period: When are budgets created, reviewed, implemented, and evaluated ...
No matter the size of your business, a business budget is vital to planning and guiding your business's growth. By understanding the fixed expenses of a company and accounting for the ebb and flow of work, a proper business budget can help your business maintain itself through the year and create protection around unplanned expenses through well allocated funds.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Having a specific template for each department can help teams keep track of spending and plan for growth. This free template from Template.net works in either document or spreadsheet formats. This budget template can help different departments keep track of their income and spending. 6. Project Budget Template.
To effectively create a business budget plan, it's crucial to establish both short-term and long-term financial objectives. Short-term goals could include reducing overhead costs by a certain percentage within six months, while long-term goals might involve doubling your annual revenue within three years. These objectives provide direction for ...
A business budget is a spending plan for your business based on your income and expenses. It identifies your available capital, estimates your spending, and helps you predict revenue. A budget can help you plan your business activities and can act as a yardstick for setting up financial goals. It can help you tackle both short-term obstacles ...
Business Budget Step 4: Predict One-Time Spends. Many of your business expenses will be regular expenses that you pay for each month, whether they're fixed or variable costs. But there are also costs that will happen far less frequently. Just don't forget to factor those expenses when you create a budget as well.
How to design your small business budget plan. Small business budget FAQ. 1. Static budget template. Best for: Multiple departments or revenue streams; Industries with complex operations. A static budget combines all the function-specific budgets a business uses into one. Typically, a static budget includes the following items (plus any other ...
Budgeting and business planning. Once your business is operational, it's essential to plan and tightly manage its financial performance. Creating a budgeting process is the most effective way to keep your business - and its finances - on track. This guide outlines the advantages of business planning and budgeting and explains how to go about it.
Ahmet Yüzbaşıoğlu, the Co-Founder of Peak Plans, explains the importance of budgeting for small businesses: "The success of your business is determined by the quality of your decisions.If you want to make informed decisions, you must have a budget. A budget can help you create a plan for the future, whether it's for your company as a whole or for smaller departments.
Step 1: Review your revenue. The first step toward creating a budget is to examine your revenue: not just the total for any given time, but specifics, such as months when revenue rose or dipped ...
Benefits of Business Budget Planning. There are many benefits to creating a business budget. These include being better at the following: Planning for the future. Improving decision-making. Monitoring performance. Effectively managing money. Giving out the right resources to projects. Meeting your objectives.
2. List your business expenses. The next step in creating a small business budget is to list all your business expenses. Here are the types of expenses you want to include in your budget: Fixed ...
Knowing your costs inside and out gives you the baseline knowledge needed to craft an effective spending plan. If you create a rough budget and later discover that you need more money for your business activities, this will jeopardize your goals. ... Here's an example of why you need to understand this parameter while creating a budget ...
Plan your expenditure. A budget is a way to assign a job to your business spending so that you have a legitimate reason behind every penny you spend. Hold yourself accountable. Having a budget lets you evaluate your spending plan vs. spending reality so you can see if you're actually meeting your desired goals and achieving forecasted ...
1. Write down your revenue streams. Your revenue is the money you earn in exchange for your products or services. You'll start your small- business budget by listing all the ways you make money. Look at last month's P&L—or even just your checking account statement—to help you account for all your revenue streams.
2. Decide on your target profit margin. Your profit margin will be equal to your revenues minus your total expenses. For example, if your business is estimated to have $100,000 in sales, and total expenses of $90,000, you will have a $10,000 profit. This would equal to a 10% profit margin.
The steps below can be followed whether creating a budget for a project, initiative, department, or entire organization. 1. Understand Your Organization's Goals. Before you compile your budget, it's important to have a firm understanding of the goals your organization is working toward in the period covered by it.
Integrate business objectives and cross-department goals. Next, remember that your IT budget isn't an island or a destination. It's a way to achieve goals and objectives. So make sure your budget doesn't live in a silo. Instead, it should be built atop existing business objectives and priorities.
The proposed $690 million spending plan for the 2025 fiscal year, which begins July 1 and ends June 30, 2025, is a 7.1% increase over the $644 million plan that was approved for the current fiscal ...
The best budget apps. Budget calculator ... Running your business Payment processing E-commerce Marketing Business insurance ... this plan could extend your repayment period from 10 years to up to ...
Step 4: Define the Project Deliverables. Defining your project deliverables is a crucial step during the project proposal process. Stakeholders want to know just what it is you're going to be delivering to them at the end of the project. This could be a product, a program, an upgrade in technology or something similar.
Financial Planning. Before you can decide to expand, you need to see if you can afford it. Before creating any sort of budget, find out all the costs associated with expanding.
This Budget accelerates growth of new industries by establishing the $1.7 billion Future Made in Australia Innovation Fund and delivering a 10‑year extension of funding to the Australian Renewable Energy Agency. It also delivers the $44.4 million Energy Industry Jobs Plan and $134.2 million for skills and employment support in key regions.
May 22, 2024 5:41 PM PT. San Diego County is holding two community sessions to give the public an opportunity to weigh in on its $8. 5 billion recommended budget. The first session, which will be ...