Essay on Art
500 words essay on art.
Each morning we see the sunshine outside and relax while some draw it to feel relaxed. Thus, you see that art is everywhere and anywhere if we look closely. In other words, everything in life is artwork. The essay on art will help us go through the importance of art and its meaning for a better understanding.


What is Art?
For as long as humanity has existed, art has been part of our lives. For many years, people have been creating and enjoying art. It expresses emotions or expression of life. It is one such creation that enables interpretation of any kind.
It is a skill that applies to music, painting, poetry, dance and more. Moreover, nature is no less than art. For instance, if nature creates something unique, it is also art. Artists use their artwork for passing along their feelings.
Thus, art and artists bring value to society and have been doing so throughout history. Art gives us an innovative way to view the world or society around us. Most important thing is that it lets us interpret it on our own individual experiences and associations.
Art is similar to live which has many definitions and examples. What is constant is that art is not perfect or does not revolve around perfection. It is something that continues growing and developing to express emotions, thoughts and human capacities.
Importance of Art
Art comes in many different forms which include audios, visuals and more. Audios comprise songs, music, poems and more whereas visuals include painting, photography, movies and more.
You will notice that we consume a lot of audio art in the form of music, songs and more. It is because they help us to relax our mind. Moreover, it also has the ability to change our mood and brighten it up.
After that, it also motivates us and strengthens our emotions. Poetries are audio arts that help the author express their feelings in writings. We also have music that requires musical instruments to create a piece of art.
Other than that, visual arts help artists communicate with the viewer. It also allows the viewer to interpret the art in their own way. Thus, it invokes a variety of emotions among us. Thus, you see how essential art is for humankind.
Without art, the world would be a dull place. Take the recent pandemic, for example, it was not the sports or news which kept us entertained but the artists. Their work of arts in the form of shows, songs, music and more added meaning to our boring lives.
Therefore, art adds happiness and colours to our lives and save us from the boring monotony of daily life.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Conclusion of the Essay on Art
All in all, art is universal and can be found everywhere. It is not only for people who exercise work art but for those who consume it. If there were no art, we wouldn’t have been able to see the beauty in things. In other words, art helps us feel relaxed and forget about our problems.
FAQ of Essay on Art
Question 1: How can art help us?
Answer 1: Art can help us in a lot of ways. It can stimulate the release of dopamine in your bodies. This will in turn lower the feelings of depression and increase the feeling of confidence. Moreover, it makes us feel better about ourselves.
Question 2: What is the importance of art?
Answer 2: Art is essential as it covers all the developmental domains in child development. Moreover, it helps in physical development and enhancing gross and motor skills. For example, playing with dough can fine-tune your muscle control in your fingers.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

10 Famous Artworks of Barbara Hepworth
10 famous artworks of damien hirst, 7 famous artworks of isamu noguchi, subscribe to updates.
Get the latest creative news from FooBar about art, design and business.
By signing up, you agree to the our terms and our Privacy Policy agreement.

What is Art? Why is Art Important?

What is art? – The dictionary definition of art says that it is “the conscious use of skill and creative imagination , especially in the production of aesthetic objects” (Merriam-Webster). Art is essential to society as it stimulates creativity , reflects culture, fosters empathy, provokes thought, and offers a medium for expression. It enhances society’s intellectual and emotional understanding of the world.
But the thing about art is that it’s so diverse that there are as many ways to understand it as there are people.
That’s why there are scholars who give their special definition of the word, such as the one penned by this famous Russian novelist, which goes:
“Art is the activity by which a person, having experienced an emotion, intentionally transmits it to others” – Leo Tolstoy
During his life, Tolstoy was known to write based on his life experiences, such as his most famous work, “War and Peace,” which used much of his experience during the Crimean War.
Whether or not his definition of art is the best, the point is that people look at art based on how they have experienced it.
What is Art?
There are many common definitions of art as per many books by famous artists and authors . Few to quote:
- any creative work of a human being
- a form of expressing oneself
- resides in the quality of doing; the process is not magic
- an act of making something visually entertaining
- an activity that manifests beauty ( What is Beauty in Art? )
- the mastery, an ideal way of doing things
- not a thing — it is a way (Elbert Hubbard)
- the most intense mode of individualism that the world has known
- discovery and development of elementary principles of nature into beautiful forms suitable for human use (Frank Lloyd Wright)
Why is Art Important?
Probably, the most prominent theory which best explains – Why is art important – is from Van Jones, which subtly provides a great response to What is art?
Van Jones presented a graph that accurately represents the interaction between the four aspects of society and its different members.
Consequently, Vones depicts why art is important to our society.
The graph (below) represents our society.
Society is driven by the powerful elites, the dependent masses, the government, cultural producers, and artists

On the left, you have action, and on the right, ideas; elites are at the top, and the masses are below. There’s an inside act and an outside act.
On the inside, there’s big money: elites are spending millions of dollars to influence politicians and policymakers. The inside act has the power to influence policy creators.
On the outside, we at the grassroots set our expectations and needs so that the elected candidates pass laws that give us power. Masses reflect what society wants (heart)
The left side, “action,” often means quantifiable policy changes. The right side, “ideas,” can be harder to see. We are not necessarily talking about concrete things here, but rather, a “headspace.”
Academic institutions and think tanks, which are not always involved in the immediate policy wins, are significant in creating a culture of thought
While the left side, “action,” continues to produce quantifiable policy changes and new laws, the right side, “ïdeas,” can be hard to quantify its outcome. Although “head” talks about theories and academics, it fails to contribute significantly to policymakers.
Artists come into the play here at this moment
Artists are represented here on the side of ideas, in the “heart space.”
Art is uniquely positioned to move people—inspiring us, inciting new questions, and provoking curiosity, excitement, and outrage.
Artists can strengthen the will and push people to act. They do not think like policymakers or academics people.
Artists think from their heart – big, revolutionary, and visionary ideas.
This is why artists are able to move people to action, thus creates a significant cultural and political contributions.
This is what makes art powerful.
Impact of Art on Politics, Culture, and People
Art is essential in society because it is an essential ingredient in empowering people’s hearts.
When activists show images of children suffering from poverty or oppression in their campaigns, this is the art of pulling the heartstrings of society’s elite and powerful to make changes.
Similarly, when photographers publish photos of war-torn areas, it catches the attention of the masses whose hearts reach out to those who need help.
When an artist creates great music and movies, it entertains people worldwide. This is art, making a difference in society.
A very modern example of art in action is street art. When the famous Italian street artist Blu created the mural in Kreuzberg , it sparked a lot of solid and different reactions rooted deeply in the differences between East and West Berlin.
Who would have thought that a wall painting depicting two masked figures trying to unmask each other could elicit such strong reactions?

Now, the issue behind this mural is a different matter to discuss. But whether or not the effect of the mural was good, it cannot be denied how a well-crafted piece of art can have a significant impact on society.
Art is also a remarkable mode of depicting culture from all over the world
When you see a Zen garden in Sydney or San Francisco, you know that it’s a practice that originated from China.
Likewise, when you see paper swans swarming a beautiful wedding ceremony, you know that this is origami, an art from Japan.
When you see films featuring Bollywood music and dancing, you know that it’s a movie from India. Art can take cultural practices from their origins and transport and integrate them into different parts of the world without losing their identity.
There, these art forms can entertain, create awareness, and even inspire foreigners to accept these cultures, no matter how strange or alien they may seem.
And that’s precisely what John Dewey implies in Art as an Experience:
“Barriers are dissolved; limiting prejudices melt away when we enter into the spirit of Negro or Polynesian Art. This insensible melting is far more efficacious than the change effected by reasoning, because it enters directly into attitude.”
This is especially important in our highly globalized world.
Art has played an essential role in helping fight against intolerance of different cultures, racism, and other forms of unjust societal segregation.
With immigration becoming a trend, the world’s countries are expected to be more tolerant and accepting of those who enter their borders.
Art helps make that happen by making sure that identities and their cultures are given due recognition around the world.
Art stimulates creativity and innovation.
Art inspires creativity and innovation beyond boundaries, encouraging imagination, lateral thinking, and risk-taking. The process of creating art involves experimentation and novel ideas, which can influence progress in various industries.
Art also challenges perceptions and assumptions, encouraging critical thinking and open-mindedness, which are essential for innovation. By presenting alternative realities or questioning the status quo, art inspires individuals to think differently and to approach problems from unique angles.
Furthermore, the aesthetic experience of art can lead to epiphanies and insights.
The beauty or emotional impact of a piece of art can trigger ideas and spark the imagination in ways that logical reasoning alone may not. This can lead to breakthroughs in creative and scientific endeavors, as individuals draw inspiration from the emotions evoked by art.
Art plays a subtle yet significant role in our daily lives.
For instance, when a child takes part in a school art project, they are given a variety of materials to create a collage. As they construct a 3D model of an imaginary winged vehicle with multiple wheels, the textures and shapes inspire them. This hands-on exploration of materials and forms sparks the child’s interest in engineering and design, planting the seeds for future innovation.
The above example illustrates how art can engage young minds, encouraging them to think creatively and envision innovative solutions beyond conventional boundaries.
In essence, art fuels the creative fire, providing the sparks that can ignite the next wave of innovation in society.
Great Art elicits powerful sentiments and tells meaningful stories
Art can take the form of film, music, theatre, and pop culture , all of which aim to entertain and make people happy. But when films, songs, or plays are made for a specific audience or purpose, the art begins to diversify.
Films, for example, can be made to spread awareness or cultural appreciation. Songs can also be composed in a way that brings out certain emotions, give inspiration, or boost the morale of people.
During the Victorian period in England, women started to make a name for themselves with classic artworks such as Elizabeth Sirani’s “ Portia Wounding Her Thigh ”, a painting that signifies the message that a woman is now willing to distance herself from gender biasedness.

The painting’s subject depicts an act of a woman possessing the same strength as that of a man. “Portia” represents surrender because she isn’t the same type of woman known in society as weak and prone to gossip.
One of the revolutionary works in history that ultimately opened the doors of art to women in general showed the power of women in art
There are also works of art that illicit intellectual solid discourse – the kind that can question norms and change the behavior of society.
Sometimes, still, art is there to reach out to a person who shares the same thoughts, feelings, and experiences as the artist.
The truth is that art is more than just a practice – it is a way of life. Art is more than just a skill – it is a passion. Art is more than just an image – each one tells a story.
The fact that art is quite connected to human experience makes it unsurprising that we have always made it part of our ways of living.
This is why ancient and present-day indigenous groups from all over the world have a knack for mixing art and their traditional artifacts or rituals without them knowing, which in fact one of the fundamental reasons why art is essential.
Why is Art so Powerful? Why is art important to human society?
Perhaps the most straightforward answer to this question is that art touches us emotionally.
Art is influential because it can potentially influence our culture, politics, and even the economy. When we see a powerful work of art, we feel it touching deep within our core, giving us the power to make real-life changes.
In the words of Leo Tolstoy:
“The activity of art is based on the capacity of people to infect others with their own emotions and to be infected by the emotions of others. Strong emotions, weak emotions, important emotions or irrelevant emotions, good emotions or bad emotions – if they contaminate the reader, the spectator, or the listener – it attains the function of art.”
In sum, art can be considered powerful because of the following reasons, among others:
- It has the power to educate people about almost anything. It can create awareness and present information in a way that could be absorbed by many quickly. In a world where some don’t even have access to good education, art makes education an even greater equalizer of society.
- It promotes cultural appreciation among a generation that’s currently preoccupied with their technology. It can be said that if it weren’t for art, our history, culture, and traditions would be in more danger of being forgotten than they already are.
- It breaks cultural, social, and economic barriers . While art can’t solve poverty or promote social justice alone, it can be a leveled playing field for discourse and expression. The reason why everyone can relate to art is that everyone has emotions and personal experiences. Therefore, anyone can learn to appreciate art regardless of social background, economic standing, or political affiliation.
- It accesses higher orders of thinking . Art doesn’t just make you absorb information. Instead, it makes you think about current ideas and inspire you to make your own. This is why creativity is a form of intelligence – it is a unique ability that unlocks the potential of the human mind. Studies have shown that exposure to art can improve you in other fields of knowledge.
The truth is that people have recognized how influential art can be.
Many times in history, I have heard of people being criticized, threatened, censored, and even killed because of their artwork.
Those responsible for these reactions, whether a belligerent government or a dissident group, take these measures against artists, knowing how much their works can affect the politics in a given area.
In the hands of good people, however, art can be used to give back hope or instill courage in a society that’s undergoing a lot of hardships.
Art is a powerful form of therapy .

Some say art is boring . But the fact remains that art has the power to take cultural practices from where they are from and then transport and integrate them into different parts of the world without losing their identity.
Art helps make that happen by making sure that identities and their cultures are given due recognition around the world. Thus, it is essential to reflect upon – Why art is critical – which, in fact, provides you the answer to – What is art?
This is why we at The Artist believe that art is a form of creative human expression, a way of enriching the human experience.
NFTs: The Future of Art
Now, the world of art is shifting towards a digital and alternative world. And NFT is becoming a game-changing variable in the future of art .
What is NFT artwork?
An NFT , which stands for “non-fungible token” can be defined as a digital file that can be simply and easily transferred across a blockchain network.
Many people around the world are seeking out these digital assets to sell and trade in their everyday market trading, since these items are able to be traced, have value and oftentimes also have considerable rarity for collectors.
While artistic works are certainly a part of the NFT market, a variety of different players are getting involved through gaming systems, avatars, and even entire virtual worlds.
Such tokens have a wide variety of usage and while for many these are out of reach, for serious investors NFTs can prove to be a profitable source of income.
Art plays a significant role in society by acting as an educational equalizer, fostering cultural appreciation, bridging cultural and social divides, and stimulating higher orders of thinking and creativity.
Art and its definition will always be controversial.
There will always be debates about what art is and what is not.
But no matter what the definition may be, it has been around us for as long as humans have existed (i.e. cave paintings, hieroglyphics).
Whether or not we are aware of it, we allow art to affect our lives one way or another, and the reasons why we make art are many!
We use the arts for our entertainment, cultural appreciation, aesthetics, personal improvement, and even social change. We use the arts to thrive in this world.
So, share your thoughts – What does art mean to you? Art plays a subtle yet significant role in our daily lives. For instance, when a child takes part in a school art project, they are given a variety of materials to create a collage. As they construct a 3D model of an imaginary winged vehicle with multiple wheels, the textures and shapes inspire them. This hands-on exploration of materials and forms sparks the child’s interest in engineering and design, planting the seeds for future innovation. This example illustrates how art can engage young minds, encouraging them to think creatively and envision innovative solutions beyond conventional boundaries.
Passionate experimenter with a heart for art, design, and tech. A relentless explorer of the culture, creative and innovative realms.
Related Posts
16 comments.
Pingback: 7 Functions of Art That Make Us Empathetic Human Beings
Pingback: A world full of colors | Ashley's blog
Pingback: The importance of art and fashion. – BlissfulReject
Pingback: Art is Important – {thy smile is quite toothy}
Pingback: Arts influence society, change the world - The Feather Online
Hello there! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I genuinely enjoy reading your posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that cover the same topics? Thanks a lot!
Agreed with the summation, that art is a tricky thing to define. Shall we leave it at that and let the artist get on with it?
Hello! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this page to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
I got this web site from my pal who informed me on the topic of this website and at the moment this time I am browsing this website and reading very informative articles or reviews at this place.
Very good article! We will be linjking to this particularly great content onn our website. Keep up thhe great writing.
Every day we Delhiites shorten our lives due too choking air. This blog was extremely useful!
Great! Thank you so much. Keep up the good work.
Amazing! This has helped me out so much!
I do consider all the concepts you have introduced for your post. They are really convincing and can certainly work. Nonetheless, the posts are too quick for novices. Could you please extend them a little from subsequent time? Thanks for the post.
I love this! It was so interesting to read this!
Appreciating the commitment you put into your website and detailed information you offer. It’s good to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same unwanted rehashed information. Excellent read!
I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
Leave A Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
The Definition of Art
The definition of art is controversial in contemporary philosophy. Whether art can be defined has also been a matter of controversy. The philosophical usefulness of a definition of art has also been debated.
Contemporary definitions can be classified with respect to the dimensions of art they emphasize. One distinctively modern, conventionalist, sort of definition focuses on art’s institutional features, emphasizing the way art changes over time, modern works that appear to break radically with all traditional art, the relational properties of artworks that depend on works’ relations to art history, art genres, etc. – more broadly, on the undeniable heterogeneity of the class of artworks. The more traditional, less conventionalist sort of definition defended in contemporary philosophy makes use of a broader, more traditional concept of aesthetic properties that includes more than art-relational ones, and puts more emphasis on art’s pan-cultural and trans-historical characteristics – in sum, on commonalities across the class of artworks. Hybrid definitions aim to do justice to both the traditional aesthetic dimension as well as to the institutional and art-historical dimensions of art, while privileging neither.
1. Constraints on Definitions of Art
2.1 some examples, 3.1 skepticisms inspired by views of concepts, history, marxism, feminism, 3.2 some descendants of skepticism, 4.1 conventionalist definitions: institutional and historical, 4.2 institutional definitions, 4.3 historical definitions.
- 4.4 Functional (mainly aesthetic) definitions
4.5 Hybrid (Disjunctive) Definitions
5. conclusion, other internet resources, related entries.
Any definition of art has to square with the following uncontroversial facts: (i) entities (artifacts or performances) intentionally endowed by their makers with a significant degree of aesthetic interest, often greatly surpassing that of most everyday objects, first appeared hundreds of thousands of years ago and exist in virtually every known human culture (Davies 2012); (ii) such entities are partially comprehensible to cultural outsiders – they are neither opaque nor completely transparent; (iii) such entities sometimes have non-aesthetic – ceremonial or religious or propagandistic – functions, and sometimes do not; (iv) such entities might conceivably be produced by non-human species, terrestrial or otherwise; and it seems at least in principle possible that they be extraspecifically recognizable as such; (v) traditionally, artworks are intentionally endowed by their makers with properties, often sensory, having a significant degree of aesthetic interest, usually surpassing that of most everyday objects; (vi) art’s normative dimension – the high value placed on making and consuming art – appears to be essential to it, and artworks can have considerable moral and political as well as aesthetic power; (vii) the arts are always changing, just as the rest of culture is: as artists experiment creatively, new genres, art-forms, and styles develop; standards of taste and sensibilities evolve; understandings of aesthetic properties, aesthetic experience, and the nature of art evolve; (viii) there are institutions in some but not all cultures which involve a focus on artifacts and performances that have a high degree of aesthetic interest but lack any practical, ceremonial, or religious use; (ix) entities seemingly lacking aesthetic interest, and entities having a high degree of aesthetic interest, are not infrequently grouped together as artworks by such institutions; (x) lots of things besides artworks – for example, natural entities (sunsets, landscapes, flowers, shadows), human beings, and abstract entities (theories, proofs, mathematical entities) – have interesting aesthetic properties.
Of these facts, those having to do with art’s contingent cultural and historical features are emphasized by some definitions of art. Other definitions of art give priority to explaining those facts that reflect art’s universality and continuity with other aesthetic phenomena. Still other definitions attempt to explain both art’s contingent characteristics and its more abiding ones while giving priority to neither.
Two general constraints on definitions are particularly relevant to definitions of art. First, given that accepting that something is inexplicable is generally a philosophical last resort, and granting the importance of extensional adequacy, list-like or enumerative definitions are if possible to be avoided. Enumerative definitions, lacking principles that explain why what is on the list is on the list, don’t, notoriously, apply to definienda that evolve, and provide no clue to the next or general case (Tarski’s definition of truth, for example, is standardly criticized as unenlightening because it rests on a list-like definition of primitive denotation; see Field 1972; Devitt 2001; Davidson 2005). Corollary: when everything else is equal (and it is controversial whether and when that condition is satisfied in the case of definitions of art), non-disjunctive definitions are preferable to disjunctive ones. Second, given that most classes outside of mathematics are vague, and that the existence of borderline cases is characteristic of vague classes, definitions that take the class of artworks to have borderline cases are preferable to definitions that don’t (Davies 1991 and 2006; Stecker 2005).
Whether any definition of art does account for these facts and satisfy these constraints, or could account for these facts and satisfy these constraints, are key questions for aesthetics and the philosophy of art.
2. Definitions From the History of Philosophy
Classical definitions, at least as they are portrayed in contemporary discussions of the definition of art, take artworks to be characterized by a single type of property. The standard candidates are representational properties, expressive properties, and formal properties. So there are representational or mimetic definitions, expressive definitions, and formalist definitions, which hold that artworks are characterized by their possession of, respectively, representational, expressive, and formal properties. It is not difficult to find fault with these simple definitions. For example, possessing representational, expressive, and formal properties cannot be sufficient conditions, since, obviously, instructional manuals are representations, but not typically artworks, human faces and gestures have expressive properties without being works of art, and both natural objects and artifacts produced solely for homely utilitarian purposes have formal properties but are not artworks.
The ease of these dismissals, though, serves as a reminder of the fact that classical definitions of art are significantly less philosophically self-contained or freestanding than are most contemporary definitions of art. Each classical definition stands in close and complicated relationships to its system’s other complexly interwoven parts – epistemology, ontology, value theory, philosophy of mind, etc. Relatedly, great philosophers characteristically analyze the key theoretical components of their definitions of art in distinctive and subtle ways. For these reasons, understanding such definitions in isolation from the systems or corpuses of which they are parts is difficult, and brief summaries are invariably somewhat misleading. Nevertheless, some representative examples of historically influential definitions of art offered by major figures in the history of philosophy should be mentioned.
Plato holds in the Republic and elsewhere that the arts are representational, or mimetic (sometimes translated “imitative”). Artworks are ontologically dependent on, imitations of, and therefore inferior to, ordinary physical objects. Physical objects in turn are ontologically dependent on, and imitations of, and hence inferior to, what is most real, the non-physical unchanging Forms. Grasped perceptually, artworks present only an appearance of an appearance of the Forms, which are grasped by reason alone. Consequently, artistic experience cannot yield knowledge. Nor do the makers of artworks work from knowledge. Because artworks engage an unstable, lower part of the soul, art should be subservient to moral realities, which, along with truth, are more metaphysically fundamental and, properly understood, more humanly important than, beauty. The arts are not, for Plato, the primary sphere in which beauty operates. The Platonic conception of beauty is extremely wide and metaphysical: there is a Form of Beauty, which can only be known non-perceptually, but it is more closely related to the erotic than to the arts. (See Janaway 1998, the entry on Plato’s aesthetics , and the entry on Plato on Rhetoric and Poetry .)
Kant has a definition of art, and of fine art; the latter, which Kant calls the art of genius, is “a kind of representation that is purposive in itself and, though without an end, nevertheless promotes the cultivation of the mental powers for sociable communication” (Kant, Critique of the Power of Judgment , Guyer translation, section 44, 46).) When fully unpacked, the definition has representational, formalist and expressivist elements, and focuses as much on the creative activity of the artistic genius (who, according to Kant, possesses an “innate mental aptitude through which nature gives the rule to art”) as on the artworks produced by that activity. Kant’s aesthetic theory is, for architectonic reasons, not focused on art. Art for Kant falls under the broader topic of aesthetic judgment, which covers judgments of the beautiful, judgments of the sublime, and teleological judgments of natural organisms and of nature itself. So Kant’s definition of art is a relatively small part of his theory of aesthetic judgment. And Kant’s theory of aesthetic judgment is itself situated in a hugely ambitious theoretical structure that, famously, aims, to account for, and work out the interconnections between, scientific knowledge, morality, and religious faith. (See the entry on Kant’s Aesthetics and Teleology and the general entry on Immanuel Kant .)
Hegel’s account of art incorporates his view of beauty; he defines beauty as the sensuous/perceptual appearance or expression of absolute truth. The best artworks convey, by sensory/perceptual means, the deepest metaphysical truth. The deepest metaphysical truth, according to Hegel, is that the universe is the concrete realization of what is conceptual or rational. That is, what is conceptual or rational is real, and is the imminent force that animates and propels the self-consciously developing universe. The universe is the concrete realization of what is conceptual or rational, and the rational or conceptual is superior to the sensory. So, as the mind and its products alone are capable of truth, artistic beauty is metaphysically superior to natural beauty (Hegel, Lectures , [1886, 4]). A central and defining feature of beautiful works of art is that, through the medium of sensation, each one presents the most fundamental values of its civilization. [ 1 ] Art, therefore, as a cultural expression, operates in the same sphere as religion and philosophy, and expresses the same content as they. But art “reveals to consciousness the deepest interests of humanity” in a different manner than do religion and philosophy, because art alone, of the three, works by sensuous means. So, given the superiority of the conceptual to the non-conceptual, and the fact that art’s medium for expressing/presenting culture’s deepest values is the sensual or perceptual, art’s medium is limited and inferior in comparison with the medium that religion uses to express the same content, viz., mental imagery. Art and religion in turn are, in this respect, inferior to philosophy, which employs a conceptual medium to present its content. Art initially predominates, in each civilization, as the supreme mode of cultural expression, followed, successively, by religion and philosophy. Similarly, because the broadly “logical” relations between art, religion and philosophy determine the actual structure of art, religion, and philosophy, and because cultural ideas about what is intrinsically valuable develop from sensuous to non-sensuous conceptions, history is divided into periods that reflect the teleological development from the sensuous to the conceptual. Art in general, too, develops in accord with the historical growth of non-sensuous or conceptual conceptions from sensuous conceptions, and each individual art-form develops historically in the same way (Hegel, Lectures ; Wicks 1993, see also the entries on Hegel and on Hegel’s Aesthetics ).
For treatments of other influential definitions of art, inseparable from the complex philosophical systems or corpuses in which they occur, see, for example, the entries on 18th Century German Aesthetics , Arthur Schopenhauer , Friedrich Nietzsche , and Dewey’s Aesthetics .
3. Skepticism about Definitions of Art
Skeptical doubts about the possibility and value of a definition of art have figured importantly in the discussion in aesthetics since the 1950s, and though their influence has subsided somewhat, uneasiness about the definitional project persists. (See section 4, below, and also Kivy 1997, Brand 2000, and Walton 2007).
A common family of arguments, inspired by Wittgenstein’s famous remarks about games (Wittgenstein 1953), has it that the phenomena of art are, by their nature, too diverse to admit of the unification that a satisfactory definition strives for, or that a definition of art, were there to be such a thing, would exert a stifling influence on artistic creativity. One expression of this impulse is Weitz’s Open Concept Argument: any concept is open if a case can be imagined which would call for some sort of decision on our part to extend the use of the concept to cover it, or to close the concept and invent a new one to deal with the new case; all open concepts are indefinable; and there are cases calling for a decision about whether to extend or close the concept of art. Hence art is indefinable (Weitz 1956). Against this it is claimed that change does not, in general, rule out the preservation of identity over time, that decisions about concept-expansion may be principled rather than capricious, and that nothing bars a definition of art from incorporating a novelty requirement.
A second sort of argument, less common today than in the heyday of a certain form of extreme Wittgensteinianism, urges that the concepts that make up the stuff of most definitions of art (expressiveness, form) are embedded in general philosophical theories which incorporate traditional metaphysics and epistemology. But since traditional metaphysics and epistemology are prime instances of language gone on conceptually confused holiday, definitions of art share in the conceptual confusions of traditional philosophy (Tilghman 1984).
A third sort of argument, more historically inflected than the first, takes off from an influential study by the historian of philosophy Paul Kristeller, in which he argued that the modern system of the five major arts [painting, sculpture, architecture, poetry, and music] which underlies all modern aesthetics … is of comparatively recent origin and did not assume definite shape before the eighteenth century, although it had many ingredients which go back to classical, mediaeval, and Renaissance thought. (Kristeller, 1951) Since that list of five arts is somewhat arbitrary, and since even those five do not share a single common nature, but rather are united, at best, only by several overlapping features, and since the number of art forms has increased since the eighteenth century, Kristeller’s work may be taken to suggest that our concept of art differs from that of the eighteenth century. As a matter of historical fact, there simply is no stable definiendum for a definition of art to capture.
A fourth sort of argument suggests that a definition of art stating individually necessary and jointly sufficient conditions for a thing to be an artwork, is likely to be discoverable only if cognitive science makes it plausible to think that humans categorize things in terms of necessary and sufficient conditions. But, the argument continues, cognitive science actually supports the view that the structure of concepts mirrors the way humans categorize things – which is with respect to their similarity to prototypes (or exemplars), and not in terms of necessary and sufficient conditions. So the quest for a definition of art that states individually necessary and jointly sufficient conditions is misguided and not likely to succeed (Dean 2003). Against this it has been urged that psychological theories of concepts like the prototype theory and its relatives can provide at best an account of how people in fact classify things, but not an account of correct classifications of extra-psychological phenomena, and that, even if relevant, prototype theory and other psychological theories of concepts are at present too controversial to draw substantive philosophical morals from (Rey 1983; Adajian 2005).
A fifth argument against defining art, with a normative tinge that is psychologistic rather than sociopolitical, takes the fact that there is no philosophical consensus about the definition of art as reason to hold that no unitary concept of art exists. Concepts of art, like all concepts, after all, should be used for the purpose(s) they best serve. But not all concepts of art serve all purposes equally well. So not all art concepts should be used for the same purposes. Art should be defined only if there is a unitary concept of art that serves all of art’s various purposes – historical, conventional, aesthetic, appreciative, communicative, and so on. So, since there is no purpose-independent use of the concept of art, art should not be defined (Mag Uidhir and Magnus 2011; cf. Meskin 2008). In response, it is noted that some account of what makes various concepts of art concepts of art is still required; this leaves open the possibility of some degree of unity beneath the apparent multiplicity. The fact (if it is one) that different concepts of art are used for different purposes does not itself imply that they are not connected in ordered, to-some-degree systematic ways. The relation between (say) the historical concept of art and the appreciative concept of art is not an accidental, unsystematic relation, like that between river banks and savings banks, but is something like the relation between Socrates’ healthiness and the healthiness of Socrates’ diet. That is, it is not evident that there exist a mere arbitrary heap or disjunction of art concepts, constituting an unsystematic patchwork. Perhaps there is a single concept of art with different facets that interlock in an ordered way, or else a multiplicity of concepts that constitute a unity because one is at the core, and the others depend asymmetrically on it. (The last is an instance of core-dependent homonymy; see the entry on Aristotle , section on Essentialism and Homonymy.) Multiplicity alone doesn’t entail pluralism.
A sixth, broadly Marxian sort of objection rejects the project of defining art as an unwitting (and confused) expression of a harmful ideology. On this view, the search for a definition of art presupposes, wrongly, that the concept of the aesthetic is a creditable one. But since the concept of the aesthetic necessarily involves the equally bankrupt concept of disinterestedness, its use advances the illusion that what is most real about things can and should be grasped or contemplated without attending to the social and economic conditions of their production. Definitions of art, consequently, spuriously confer ontological dignity and respectability on social phenomena that probably in fact call more properly for rigorous social criticism and change. Their real function is ideological, not philosophical (Eagleton 1990).
Seventh, the members of a complex of skeptically-flavored arguments, from feminist philosophy of art, begin with premises to the effect that art and art-related concepts and practices have been systematically skewed by sex or gender. Such premises are supported by a variety of considerations. (a) The artworks the Western artistic canon recognizes as great are dominated by male-centered perspectives and stereotypes, and almost all the artists the canon recognizes as great are men – unsurprisingly, given economic, social, and institutional impediments that prevented women from making art at all. Moreover, the concept of genius developed historically in such a way as to exclude women artists (Battersby, 1989, Korsmeyer 2004). (b) The fine arts’ focus on purely aesthetic, non-utilitarian value resulted in the marginalization as mere “crafts” of items of considerable aesthetic interest made and used by women for domestic practical purposes. Moreover, because all aesthetic judgments are situated and particular, there can be no such thing as disinterested taste. If there is no such thing as disinterested taste, then it is hard to see how there could be universal standards of aesthetic excellence. The non-existence of universal standards of aesthetic excellence undermines the idea of an artistic canon (and with it the project of defining art). Art as historically constituted, and art-related practices and concepts, then, reflect views and practices that presuppose and perpetuate the subordination of women. The data that definitions of art are supposed to explain are biased, corrupt and incomplete. As a consequence, present definitions of art, incorporating or presupposing as they do a framework that incorporates a history of systematically biased, hierarchical, fragmentary, and mistaken understandings of art and art-related phenomena and concepts, may be so androcentric as to be untenable. Some theorists have suggested that different genders have systematically unique artistic styles, methods, or modes of appreciating and valuing art. If so, then a separate canon and gynocentric definitions of art are indicated (Battersby 1989, Frueh 1991). In any case, in the face of these facts, the project of defining art in anything like the traditional way is to be regarded with suspicion (Brand, 2000).
An eighth argument sort of skeptical argument concludes that, insofar as almost all contemporary definitions foreground the nature of art works , rather than the individual arts to which (most? all?) artworks belong, they are philosophically unproductive (Lopes, 2014). [ 2 ] The grounds for this conclusion concern disagreements among standard definitions as to the artistic status of entities whose status is for theoretical reasons unclear – e.g., things like ordinary bottleracks (Duchamp’s Bottlerack ) and silence (John Cage’s 4′33″ ). If these hard cases are artworks, what makes them so, given their apparent lack of any of the traditional properties of artworks? Are, they, at best, marginal cases? On the other hand, if they are not artworks, then why have generations of experts – art historians, critics, and collectors – classified them as such? And to whom else should one look to determine the true nature of art? (There are, it is claimed, few or no empirical studies of art full stop, though empirical studies of the individual arts abound.) Such disputes inevitably end in stalemate. Stalemate results because (a) standard artwork-focused definitions of art endorse different criteria of theory choice, and (b) on the basis of their preferred criteria, appeal to incompatible intuitions about the status of such theoretically-vexed cases. In consequence, disagreements between standard definitions of art that foreground artworks are unresolvable. To avoid this stalemate, an alternative definitional strategy that foregrounds the arts rather than individual artworks, is indicated. (See section 4.5.)
Philosophers influenced by the moderate Wittgensteinian strictures discussed above have offered family resemblance accounts of art, which, as they purport to be non-definitions, may be usefully considered at this point. Two species of family resemblance views will be considered: the resemblance-to-a-paradigm version, and the cluster version.
On the resemblance-to-a-paradigm version, something is, or is identifiable as, an artwork if it resembles, in the right way, certain paradigm artworks, which possess most although not necessarily all of art’s typical features. (The “is identifiable” qualification is intended to make the family resemblance view something more epistemological than a definition, although it is unclear that this really avoids a commitment to constitutive claims about art’s nature.) Against this view: since things do not resemble each other simpliciter , but only in at least one respect or other, the account is either far too inclusive, since everything resembles everything else in some respect or other, or, if the variety of resemblance is specified, tantamount to a definition, since resemblance in that respect will be either a necessary or sufficient condition for being an artwork. The family resemblance view raises questions, moreover, about the membership and unity of the class of paradigm artworks. If the account lacks an explanation of why some items and not others go on the list of paradigm works, it seems explanatorily deficient. But if it includes a principle that governs membership on the list, or if expertise is required to constitute the list, then the principle, or whatever properties the experts’ judgments track, seem to be doing the philosophical work.
The cluster version of the family resemblance view has been defended by a number of philosophers (Bond 1975, Dissanayake 1990, Dutton 2006, Gaut 2000). The view typically provides a list of properties, no one of which is a necessary condition for being a work of art, but which are jointly sufficient for being a work of art, and which is such that at least one proper subset thereof is sufficient for being a work of art. Lists offered vary, but overlap considerably. Here is one, due to Gaut: (1) possessing positive aesthetic properties; (2) being expressive of emotion; (3) being intellectually challenging; (4) being formally complex and coherent; (5) having the capacity to convey complex meanings; (6) exhibiting an individual point of view; (7) being original; (8) being an artifact or performance which is the product of a high degree of skill; (9) belonging to an established artistic form; (10) being the product of an intention to make a work of art (Gaut 2000). The cluster account has been criticized on several grounds. First, given its logical structure, it is in fact equivalent to a long, complicated, but finite, disjunction, which makes it difficult to see why it isn’t a definition (Davies 2006). Second, if the list of properties is incomplete, as some cluster theorists hold, then some justification or principle would be needed for extending it. Third, the inclusion of the ninth property on the list, belonging to an established art form , seems to regenerate (or duck), rather than answer, the definitional question. Finally, it is worth noting that, although cluster theorists stress what they take to be the motley heterogeneity of the class of artworks, they tend with surprising regularity to tacitly give the aesthetic a special, perhaps unifying, status among the properties they put forward as merely disjunctive. One cluster theorist, for example, gives a list very similar to the one discussed above (it includes representational properties, expressiveness, creativity, exhibiting a high degree of skill, belonging to an established artform), but omits aesthetic properties on the grounds that it is the combination of the other items on the list which, combined in the experience of the work of art, are precisely the aesthetic qualities of the work (Dutton 2006). Gaut, whose list is cited above, includes aesthetic properties as a separate item on the list, but construes them very narrowly; the difference between these ways of formulating the cluster view appears to be mainly nominal. And an earlier cluster theorist defines artworks as all and only those things that belong to any instantiation of an artform, offers a list of seven properties all of which together are intended to capture the core of what it is to be an artform, though none is either necessary or sufficient, and then claims that having aesthetic value (of the same sort as mountains, sunsets, mathematical theorems) is “what art is for ” (Bond 1975).
4. Contemporary Definitions
Definitions of art attempt to make sense of two different sorts of facts: art has important historically contingent cultural features, as well as trans-historical, pan-cultural characteristics that point in the direction of a relatively stable aesthetic core. (Theorists who regard art as an invention of eighteenth-century Europe will, of course, regard this way of putting the matter as tendentious, on the grounds that entities produced outside that culturally distinctive institution do not fall under the extension of “art” and hence are irrelevant to the art-defining project (Shiner 2001). Whether the concept of art is precise enough to justify this much confidence about what falls under its extension claim is unclear.) Conventionalist definitions take art’s contingent cultural features to be explanatorily fundamental, and aim to capture the phenomena – revolutionary modern art, the traditional close connection of art with the aesthetic, the possibility of autonomous art traditions, etc. – in social/historical terms. Classically-flavored or traditional definitions (also sometimes called “functionalist”) definitions reverse this explanatory order. Such classically-flavored definitions take traditional concepts like the aesthetic (or allied concepts like the formal, or the expressive) as basic, and aim to account for the phenomena by making those concepts harder – for example, by endorsing a concept of the aesthetic rich enough to include non-perceptual properties, or by attempting an integration of those concepts (e.g., Eldridge, section 4.4 below) .
Conventionalist definitions deny that art has essential connection to aesthetic properties, or to formal properties, or to expressive properties, or to any type of property taken by traditional definitions to be essential to art. Conventionalist definitions have been strongly influenced by the emergence, in the twentieth century, of artworks that seem to differ radically from all previous artworks. Avant-garde works like Marcel Duchamp’s “ready-mades” – ordinary unaltered objects like snow-shovels ( In Advance of the Broken Arm ) and bottle-racks – conceptual works like Robert Barry’s All the things I know but of which I am not at the moment thinking – 1:36 PM; June 15, 1969 , and John Cage’s 4′33″ , have seemed to many philosophers to lack or even, somehow, repudiate, the traditional properties of art: intended aesthetic interest, artifactuality, even perceivability. Conventionalist definitions have also been strongly influenced by the work of a number of historically-minded philosophers, who have documented the rise and development of modern ideas of the fine arts, the individual arts, the work of art, and the aesthetic (Kristeller, Shiner, Carroll, Goehr, Kivy).
Conventionalist definitions come in two varieties, institutional and historical. Institutionalist conventionalism, or institutionalism, a synchronic view, typically hold that to be a work of art is to be an artifact of a kind created, by an artist, to be presented to an artworld public (Dickie 1984). Historical conventionalism, a diachronic view, holds that artworks necessarily stand in an art-historical relation to some set of earlier artworks.
The groundwork for institutional definitions was laid by Arthur Danto, better known to non-philosophers as the long-time influential art critic for the Nation . Danto coined the term “artworld”, by which he meant “an atmosphere of art theory.” Danto’s definition has been glossed as follows: something is a work of art if and only if (i) it has a subject (ii) about which it projects some attitude or point of view (has a style) (iii) by means of rhetorical ellipsis (usually metaphorical) which ellipsis engages audience participation in filling in what is missing, and (iv) where the work in question and the interpretations thereof require an art historical context (Danto, Carroll). Clause (iv) is what makes the definition institutionalist. The view has been criticized for entailing that art criticism written in a highly rhetorical style is art, lacking but requiring an independent account of what makes a context art historical , and for not applying to music.
The most prominent and influential institutionalism is that of George Dickie. Dickie’s institutionalism has evolved over time. According to an early version, a work of art is an artifact upon which some person(s) acting on behalf of the artworld has conferred the status of candidate for appreciation (Dickie 1974). Dickie’s more recent version consists of an interlocking set of five definitions: (1) An artist is a person who participates with understanding in the making of a work of art. (2) A work of art is an artifact of a kind created to be presented to an artworld public. (3) A public is a set of persons the members of which are prepared in some degree to understand an object which is presented to them. (4) The artworld is the totality of all artworld systems. (5) An artworld system is a framework for the presentation of a work of art by an artist to an artworld public (Dickie 1984). Both versions have been widely criticized. Philosophers have objected that art created outside any institution seems possible, although the definition rules it out, and that the artworld, like any institution, seems capable of error. It has also been urged that the definition’s obvious circularity is vicious, and that, given the inter-definition of the key concepts (artwork, artworld system, artist, artworld public) it lacks any informative way of distinguishing art institutions systems from other, structurally similar, social institutions (D. Davies 2004, pp. 248–249, notes that both the artworld and the “commerceworld” seem to fall under that definition). Early on, Dickie claimed that anyone who sees herself as a member of the artworld is a member of the artworld: if this is true, then unless there are constraints on the kinds of things the artworld can put forward as artworks or candidate artworks, any entity can be an artwork (though not all are), which appears overly expansive. Finally, Matravers has helpfully distinguished strong and weak institutionalism. Strong institutionalism holds that there is some reason that is always the reason the art institution has for saying that something is a work of art. Weak institutionalism holds that, for every work of art, there is some reason or other that the institution has for saying that it is a work of art (Matravers 2000). Weak institutionalism, in particular, raises questions about art’s unity: if absolutely nothing unifies the reasons that the artworld gives for conferring art-hood on things, then the unity of the class of artworks is vanishingly small. Conventionalist views, with their emphasis on art’s heterogeneity, swallow this implication. From the perspective of traditional definitions, doings so underplays art’s substantial if incomplete unity, while leaving it a puzzle why art would be worth caring about.
Some recent versions of institutionalism depart from Dickie’s by accepting the burden, which Dickie rejected, of providing a substantive, non-circular account of what it is to be an art institution or an artworld. One, due to David Davies, does so by building in Nelson Goodman’s account of aesthetic symbolic functions. Another, due to Abell, combines Searle’s account of social institutions with Gaut’s characterization of art-making properties, and builds an account of artistic value on that coupling.
Davies’ neo-institutionalism holds that making an artwork requires articulating an artistic statement, which requires specifying artistic properties, which in turn requires the manipulation of an artistic vehicle. Goodman’s “symptoms of the aesthetic” are utilized to clarify the conditions under which a practice of making is a practice of artistic making: on Goodman’s view, a symbol functions aesthetically when it is syntactically dense, semantically dense, relatively replete, and characterized by multiple and complex reference (D. Davies 2004; Goodman 1968; see the entry on Goodman’s aesthetics ). Manipulating an artistic vehicle is in turn possible only if the artist consciously operates with reference to shared understandings embodied in the practices of a community of receivers. So art’s nature is institutional in the broad sense (or, perhaps better, socio-cultural). By way of criticism, Davies’ neo-institutionalism may be questioned on the grounds that, since all pictorial symbols are syntactically dense, semantically dense, relatively replete, and often exemplify the properties they represent, it seems to entail that every colored picture, including those in any catalog of industrial products, is an artwork (Abell 2012).
Abell’s institutional definition adapts Searle’s view of social kinds: what it is for some social kind, F , to be F is for it to be collectively believed to be F (Abell 2012; Searle 1995, 2010; and see the entry on social institutions ). On Abell’s view, more specifically, an institution’s type is determined by the valued function(s) that it was collectively believed at its inception to promote. The valued functions collective belief in which make an institution an art institution are those spelled out by Gaut in his cluster account (see section 3.1, above). That is, something is an art institution if and only if it is an institution whose existence is due to its being perceived to perform certain functions, which functions form a significant subset of the following: promoting positive aesthetic qualities; promoting the expression of emotion; facilitating the posing of intellectual challenges, and the rest of Gaut’s list. Plugging in Gaut’s list yields the final definition: something is an artwork if and only if it is the product of an art institution (as just defined) and it directly effects the effectiveness with which that institution performs the perceived functions to which its existence is due. One worry is whether Searle’s account of institutions is up to the task required of it. Some institutional social kinds have this trait: something can fail to be a token of that kind even if there is collective agreement that it counts as a token of that kind. Suppose someone gives a big cocktail party, to which everyone in Paris invited, and things get so out of hand that the casualty rate is greater than the Battle of Austerlitz. Even if everyone thinks the event was a cocktail party, it is possible (contrary to Searle) that they are mistaken: it may have been a war or battle. It’s not clear that art isn’t like this. If so, then the fact that an institution is collectively believed to be an art institution needn’t suffice to make it so (Khalidi 2013; see also the entry on social institutions ). [ 3 ] A second worry: if its failure to specify which subsets of the ten cluster properties suffice to make something an artwork significantly flaws Gaut’s cluster account, then failure to specify which subsets of Gaut’s ten properties suffice to make something an art institution significantly flaws Abellian institutionalism.
Historical definitions hold that what characterizes artworks is standing in some specified art-historical relation to some specified earlier artworks, and disavow any commitment to a trans-historical concept of art, or the “artish.” Historical definitions come in several varieties. All of them are, or resemble, inductive definitions: they claim that certain entities belong unconditionally to the class of artworks, while others do so because they stand in the appropriate relations thereto. According to the best known version, Levinson’s intentional-historical definition, an artwork is a thing that has been seriously intended for regard in any way preexisting or prior artworks are or were correctly regarded (Levinson 1990). A second version, historical narrativism, comes in several varieties. On one, a sufficient but not necessary condition for the identification of a candidate as a work of art is the construction of a true historical narrative according to which the candidate was created by an artist in an artistic context with a recognized and live artistic motivation, and as a result of being so created, it resembles at least one acknowledged artwork (Carroll 1993). On another, more ambitious and overtly nominalistic version of historical narrativism, something is an artwork if and only if (1) there are internal historical relations between it and already established artworks; (2) these relations are correctly identified in a narrative; and (3) that narrative is accepted by the relevant experts. The experts do not detect that certain entities are artworks; rather, the fact that the experts assert that certain properties are significant in particular cases is constitutive of art (Stock 2003).
The similarity of these views to institutionalism is obvious, and the criticisms offered parallel those urged against institutionalism. First, historical definitions appear to require, but lack, any informative characterization of art traditions (art functions, artistic contexts, etc.) and hence any way of informatively distinguishing them (and likewise art functions, or artistic predecessors) from non -art traditions (non-art functions, non-artistic predecessors). Correlatively, non-Western art, or alien, autonomous art of any kind appears to pose a problem for historical views: any autonomous art tradition or artworks – terrestrial, extra-terrestrial, or merely possible – causally isolated from our art tradition, is either ruled out by the definition, which seems to be a reductio , or included, which concedes the existence of a supra-historical concept of art. So, too, there could be entities that for adventitious reasons are not correctly identified in historical narratives, although in actual fact they stand in relations to established artworks that make them correctly describable in narratives of the appropriate sort. Historical definitions entail that such entities aren’t artworks, but it seems at least as plausible to say that they are artworks that are not identified as such. Second, historical definitions also require, but do not provide a satisfactory, informative account of the basis case – the first artworks, or ur-artworks, in the case of the intentional-historical definitions, or the first or central art-forms, in the case of historical functionalism. Third, nominalistic historical definitions seem to face a version of the Euthyphro dilemma. For either such definitions include substantive characterizations of what it is to be an expert, or they don’t. If, on one hand, they include no characterization of what it is to be an expert, and hence no explanation as to why the list of experts contains the people it does, then they imply that what makes things artworks is inexplicable. On the other hand, suppose such definitions provide a substantive account of what it is to be an expert, so that to be an expert is to possess some ability lacked by non-experts (taste, say) in virtue of the possession of which they are able to discern historical connections between established artworks and candidate artworks. Then the definition’s claim to be interestingly historical is questionable, because it makes art status a function of whatever ability it is that permits experts to discern the art-making properties.
Defenders of historical definitions have replies. First, as regards autonomous art traditions, it can be held that anything we would recognize as an art tradition or an artistic practice would display aesthetic concerns, because aesthetic concerns have been central from the start, and persisted centrally for thousands of years, in the Western art tradition. Hence it is an historical, not a conceptual truth that anything we recognize as an art practice will centrally involve the aesthetic; it is just that aesthetic concerns that have always dominated our art tradition (Levinson 2002). The idea here is that if the reason that anything we’d take to be a Φ-tradition would have Ψ-concerns is that our Φ-tradition has focused on Ψ-concerns since its inception, then it is not essential to Φ-traditions that they have Ψ-concerns, and Φ is a purely historical concept . But this principle entails, implausibly, that every concept is purely historical. Suppose that we discovered a new civilization whose inhabitants could predict how the physical world works with great precision, on the basis of a substantial body of empirically acquired knowledge that they had accumulated over centuries. The reason we would credit them with having a scientific tradition might well be that our own scientific tradition has since its inception focused on explaining things. It does not seem to follow that science is a purely historical concept with no essential connection to explanatory aims. (Other theorists hold that it is historically necessary that art begins with the aesthetic, but deny that art’s nature is to be defined in terms of its historical unfolding (Davies 1997).) Second, as to the first artworks, or the central art-forms or functions, some theorists hold that an account of them can only take the form of an enumeration. Stecker takes this approach: he says that the account of what makes something a central art form at a given time is, at its core, institutional, and that the central artforms can only be listed (Stecker 1997 and 2005). Whether relocating the list at a different, albeit deeper, level in the definition renders the definition sufficiently informative is an open question. Third, as to the Euthyphro -style dilemma, it might be held that the categorial distinction between artworks and “mere real things” (Danto 1981) explains the distinction between experts and non-experts. Experts are able, it is said, to create new categories of art. When created, new categories bring with them new universes of discourse. New universes of discourse in turn make reasons available that otherwise would not be available. Hence, on this view, it is both the case that the experts’ say-so alone suffices to make mere real things into artworks, and also true that experts’ conferrals of art-status have reasons (McFee 2011).
4.4 Traditional (mainly aesthetic) definitions
Traditional definitions take some function(s) or intended function(s) to be definitive of artworks. Here only aesthetic definitions, which connect art essentially with the aesthetic – aesthetic judgments, experience, or properties – will be considered. Different aesthetic definitions incorporate different views of aesthetic properties and judgments. See the entry on aesthetic judgment .
As noted above, some philosophers lean heavily on a distinction between aesthetic properties and artistic properties, taking the former to be perceptually striking qualities that can be directly perceived in works, without knowledge of their origin and purpose, and the latter to be relational properties that works possess in virtue of their relations to art history, art genres, etc. It is also, of course, possible to hold a less restrictive view of aesthetic properties, on which aesthetic properties need not be perceptual; on this broader view, it is unnecessary to deny what it seems pointless to deny, that abstracta like mathematical entities and scientific laws possess aesthetic properties.)
Monroe Beardsley’s definition holds that an artwork: “either an arrangement of conditions intended to be capable of affording an experience with marked aesthetic character or (incidentally) an arrangement belonging to a class or type of arrangements that is typically intended to have this capacity” (Beardsley 1982, 299). (For more on Beardsley, see the entry on Beardsley’s aesthetics .) Beardsley’s conception of aesthetic experience is Deweyan: aesthetic experiences are experiences that are complete, unified, intense experiences of the way things appear to us, and are, moreover, experiences which are controlled by the things experienced (see the entry on Dewey’s aesthetics ). Zangwill’s aesthetic definition of art says that something is a work of art if and only if someone had an insight that certain aesthetic properties would be determined by certain nonaesthetic properties, and for this reason the thing was intentionally endowed with the aesthetic properties in virtue of the nonaesthetic properties as envisaged in the insight (Zangwill 1995a,b). Aesthetic properties for Zangwill are those judgments that are the subject of “verdictive aesthetic judgments” (judgements of beauty and ugliness) and “substantive aesthetic judgements” (e.g., of daintiness, elegance, delicacy, etc.). The latter are ways of being beautiful or ugly; aesthetic in virtue of a special close relation to verdictive judgments, which are subjectively universal. Other aesthetic definitions build in different accounts of the aesthetic. Eldridge’s aesthetic definition holds that the satisfying appropriateness to one another of a thing’s form and content is the aesthetic quality possession of which is necessary and sufficient for a thing’s being art (Eldridge 1985). Or one might define aesthetic properties as those having an evaluative component, whose perception involves the perception of certain formal base properties, such as shape and color (De Clercq 2002), and construct an aesthetic definition incorporating that view.
Views which combine features of institutional and aesthetic definitions also exist. Iseminger, for example, builds a definition on an account of appreciation, on which to appreciate a thing’s being F is to find experiencing its being F to be valuable in itself, and an account of aesthetic communication (which it is the function of the artworld to promote) (Iseminger 2004).
Aesthetic definitions have been criticized for being both too narrow and too broad. They are held to be too narrow because they are unable to cover influential modern works like Duchamp’s ready-mades and conceptual works like Robert Barry’s All the things I know but of which I am not at the moment thinking – 1:36 PM; June 15, 1969 , which appear to lack aesthetic properties. (Duchamp famously asserted that his urinal, Fountain , was selected for its lack of aesthetic features.) Aesthetic definitions are held to be too broad because beautifully designed automobiles, neatly manicured lawns, and products of commercial design are often created with the intention of being objects of aesthetic appreciation, but are not artworks. Moreover, aesthetic views have been held to have trouble making sense of bad art (see Dickie 2001; Davies 2006, p. 37). Finally, more radical doubts about aesthetic definitions center on the intelligibility and usefulness of the aesthetic. Beardsley’s view, for example, has been criticized by Dickie, who has also offered influential criticisms of the idea of an aesthetic attitude (Dickie 1965, Cohen 1973, Kivy 1975).
To these criticisms several responses have been offered. First, the less restrictive conception of aesthetic properties mentioned above, on which they may be based on non-perceptual formal properties, can be deployed. On this view, conceptual works would have aesthetic features, much the same way that mathematical entities are often claimed to (Shelley 2003, Carroll 2004). Second, a distinction may be drawn between time-sensitive properties, whose standard observation conditions include an essential reference to the temporal location of the observer, and non-time-sensitive properties, which do not. Higher-order aesthetic properties like drama, humor, and irony, which account for a significant part of the appeal of Duchamp’s and Cage’s works, on this view, would derive from time-sensitive properties (Zemach 1997). Third, it might be held that it is the creative act of presenting something that is in the relevant sense unfamiliar, into a new context, the artworld, which has aesthetic properties. Or, fourth, it might be held that (Zangwill’s “second-order” strategy) works like ready-mades lack aesthetic functions, but are parasitic upon, because meant to be considered in the context of, works that do have aesthetic functions, and therefore constitute marginal borderline cases of art that do not merit the theoretical primacy they are often given. Finally, it can be flatly denied that the ready-mades were works of art (Beardsley 1982).
As to the over-inclusiveness of aesthetic definitions, a distinction might be drawn between primary and secondary functions. Or it may be maintained that some cars, lawns, and products of industrial design are on the art/non-art borderline, and so don’t constitute clear and decisive counter-examples. Or, if the claim that aesthetic theories fail to account for bad art depends on holding that some works have absolutely no aesthetic value whatsoever, as opposed to some non-zero amount, however infinitesimal, it may be wondered what justifies that assumption.
Hybrid definitions characteristically disjoin at least one institutional component with at least one aesthetic component, aiming thereby to accommodate both more traditional art and avant-garde art that appears to lack any significant aesthetic dimension. (Such definitions could also be classified as institutional, on the grounds that they make provenance sufficient for being a work of art.) Hence they inherit a feature of conventionalist definitions: in appealing to art institutions, artworlds, arts, art functions, and so on, they either include substantive accounts of what it is to be an art institution/world/genre/-form/function, or are uninformatively circular.
One such disjunctive definition, Longworth and Scarantino’s, adapts Gaut’s list of ten clustering properties, where that list (see 3.5 above) includes institutional properties (e.g., belonging to an established art form) and traditional ones (e.g., possessing positive aesthetic properties); see also Longworth and Scarantino 2010. The core idea is that art is defined by a disjunction of minimally sufficient and disjunctively necessary conditions; to say that a disjunct is a minimally sufficient constitutive condition for art-hood, is to say that every proper subset of it is insufficient for art-hood. An account of what it is for a concept to have disjunctive defining conditions is also supplied. The definition of art itself is as follows: ∃ Z ∃ Y (Art iff ( Z ∨ Y )), where (a) Z and Y , formed from properties on Gaut’s cluster list, are either non-empty conjunctions or non-empty disjunctions of conjunctions or individual properties; (b) there is some indeterminacy over exactly which disjuncts are sufficient; (c) Z does not entail Y and Y does not entail Z ; (d) Z does not entail Art and Y does not entail Art. Instantiation of either Z or Y suffices for art-hood; something can be art only if at least one of Z , Y is instantiated; and the third condition is included to prevent the definition from collapsing into a classical one. The account of what it is for concept C to have disjunctive defining conditions is as follows: C iff ( Z ∨ Y ), where (i) Z and Y are non-empty conjunctions or non-empty disjunctions of conjunctions or individual properties; (ii) Z does not entail Y and Y does not entail Z ; (iii) Z does not entail C and Y does not entail C. A worry concerns condition (iii): as written, it seems to render the account of disjunctive defining conditions self-contradictory. For if Z and Y are each minimally sufficient for C , it is impossible that Z does not entail C and that Y does not entail C . If so, then nothing can satisfy the conditions said to be necessary and sufficient for a concept to have disjunctive defining conditions.
A second disjunctive hybrid definition, with an historical cast, Robert Stecker’s historical functionalism, holds that an item is an artwork at time t , where t is not earlier than the time at which the item is made, if and only if it is in one of the central art forms at t and is made with the intention of fulfilling a function art has at t or it is an artifact that achieves excellence in achieving such a function (Stecker 2005). A question for Stecker’s view is whether or not it provides an adequate account of what it is for a function to be an art function, and whether, consequently, it can accommodate anti-aesthetic or non-aesthetic art. The grounds given for thinking that it can are that, while art’s original functions were aesthetic, those functions, and the intentions with which art is made, can change in unforeseeable ways. Moreover, aesthetic properties are not always preeminent in art’s predecessor concepts (Stecker 2000). A worry is that if the operative assumption is that if x belongs to a predecessor tradition of T then x belongs to T , the possibility is not ruled out that if, for example, the tradition of magic is a predecessor tradition of the scientific tradition, then entities that belong to the magic tradition but lacking any of the standard hallmarks of science are scientific entities.
A third hybrid definition, also disjunctive, is the cladistic definition defended by Stephen Davies. who holds that something is art (a) if it shows excellence of skill and achievement in realizing significant aesthetic goals, and either doing so is its primary, identifying function or doing so makes a vital contribution to the realization of its primary, identifying function, or (b) if it falls under an art genre or art form established and publicly recognized within an art tradition, or (c) if it is intended by its maker/presenter to be art and its maker/presenter does what is necessary and appropriate to realizing that intention (Davies, 2015). (In biology, a clade is a segment in the tree of life: a group of organisms and the common ancestor they share.) Artworlds are to be characterized in terms of their origins: they begin with prehistoric art ancestors, and grow into artworlds. Hence all artworks occupy a line of descent from their prehistoric art ancestors; that line of descent comprises an art tradition that grows into an artworld. So the definition is bottom-up and resolutely anthropocentric. A worry: the view seems to entail that art traditions can undergo any changes whatsoever and remain art traditions, since, no matter how distant, every occupant of the right line of descent is part of the art tradition. This seems to amount to saying that as long as they remain traditions at all, art traditions cannot die. Whether art is immortal in this sense seems open to question. A second worry is that the requirement that every art tradition and artworld stand in some line of descent from prehistoric humanoids makes it in principle impossible for any nonhuman species to make art, as long as that species fails to occupy the right location in the tree of life. While the epistemological challenges that identifying artworks made by nonhumans might pose could be very considerable, this consequence of the cladistic definition’s emphasis on lineage rather than traits raises a concern about excessively insularity.
A fourth hybrid definition is the “buck-passing” view of Lopes, which attempts an escape from the stalemate between artwork-focused definitions over avant-garde anti-aesthetic cases by adopting a strategy that shifts the focus of the definition of art away from artworks. The strategy is to recenter philosophical efforts on different problems, which require attention anyway: (a) the problem of giving an account of each individual art, and (b) the problem of defining what it is to be an art, the latter by giving an account of the larger class of normative/appreciative kinds to which the arts (and some non-arts) belong. For, given definitions of the individual arts, and a definition of what it is to be an art, if every artwork belongs to at least one art (if it belongs to no existing art, then it pioneers a new art), then a definition of artwork falls out: x is a work of art if and only if x is a work of K, where K is an art (Lopes 2014). When fully spelled out, the definition is disjunctive: x is a work of art if and only if x is a work belonging to art 1 or x is a work belonging to art 2 or x is a work belonging to art 3 …. Most of the explanatory work is done by the theories of the individual arts, since, given the assumption that every artwork belongs to at least one art, possession of theories of the individual arts would be necessary and sufficient for settling the artistic or non-artistic status of any hard case, once it is determined what art a given work belongs to. As to what makes a practice an art, Lopes’ preferred answer seems to be institutionalism of a Dickiean variety: an art is an institution in which artists (persons who participate with understanding in the making of artworks) make artworks to be presented to an artworld public. (Lopes 2014, Dickie 1984) Thus, on this view, it is arbitrary which activities are artworld systems: there is no deeper answer to the question of what makes music an art than that it has the right institutional structure. [ 4 ] So it is arbitrary which activities are arts. Two worries. First, the key claim that every work of art belonging to no extant art pioneers a new art may be defended on the grounds that any reason to say that a work belonging to no extant artform is an artwork is a reason to say that it pioneers a new artform. In response, it is noted that the question of whether or not a thing belongs to an art arises only when, and because, there is a prior reason for thinking that the thing is an artwork. So it seems that what it is to be an artwork is prior, in some sense, to what it is to be an art. Second, on the buck-passing theory’s institutional theory of the arts, which activities are arts is arbitrary. This raises a version of the question that was raised about the cladistic definition’s ability to account for the existence of art outside our (Hominin) tradition. Suppose the connection between a practice’s traits and its status as an art are wholly contingent. Then the fact that a practice in another culture that although not part of our tradition had most of the traits of one of our own arts would be no reason to think that practice was an art, and no reason to think that the objects belonging to it were artworks. It is not clear that we are really so in the dark when it comes to determining whether practices in alien cultures or traditions are arts.
Conventionalist definitions account well for modern art, but have difficulty accounting for art’s universality – especially the fact that there can be art disconnected from “our” (Western) institutions and traditions, and our species. They also struggle to account for the fact that the same aesthetic terms are routinely applied to artworks, natural objects, humans, and abstracta. Aesthetic definitions do better accounting for art’s traditional, universal features, but less well, at least according to their critics, with revolutionary modern art; their further defense requires an account of the aesthetic which can be extended in a principled way to conceptual and other radical art. (An aesthetic definition and a conventionalist one could simply be conjoined. But that would merely raise, without answering, the fundamental question of the unity or disunity of the class of artworks.) Which defect is the more serious one depends on which explananda are the more important. Arguments at this level are hard to come by, because positions are hard to motivate in ways that do not depend on prior conventionalist and functionalist sympathies. If list-like definitions are flawed because uninformative, then so are conventionalist definitions, whether institutional or historical. Of course, if the class of artworks, or of the arts, is a mere chaotic heap, lacking any genuine unity, then enumerative definitions cannot be faulted for being uninformative: they do all the explaining that it is possible to do, because they capture all the unity that there is to capture. In that case the worry articulated by one prominent aesthetician, who wrote earlier of the “bloated, unwieldy” concept of art which institutional definitions aim to capture, needs to be taken seriously, even if it turns out to be ungrounded: “It is not at all clear that these words – ‘What is art?’ – express anything like a single question, to which competing answers are given, or whether philosophers proposing answers are even engaged in the same debate…. The sheer variety of proposed definitions should give us pause. One cannot help wondering whether there is any sense in which they are attempts to … clarify the same cultural practices, or address the same issue” (Walton 2007).
- Abell, Catharine, 2012, “Art: What It Is and Why It Matters,” Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 85: 671–691.
- Adajian, Thomas, 2005, “On the Prototype Theory of Concepts and the Definition of Art,” Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , 63: 231–236.
- –––, 2012, “Defining Art,” in A. Ribeiro (ed.) 2012, pp. 39–56.
- Battersby, Christine, 1989, Gender and Genius: Towards a Feminist Aesthetics , London: The Women’s Press.
- Beardsley, Monroe, 1982, The Aesthetic Point of View , Ithaca, New York: Cornell University Press.
- Bond, E. J., 1975, “The Essential Nature of Art.” American Philosophical Quarterly , 12: 177–183.
- Brand, Peggy Zeglin, 2000, “Glaring Omissions in Traditional Theories of Art,” in N. Carroll (ed.) 2000, pp. 175–198.
- Carroll, Noel, 1993, “Historical Narratives and the Philosophy of Art”, The Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , 51(3): 313–26.
- –––, 2001, Beyond Aesthetics , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- –––, 2004, “Non-Perceptual Aesthetic Properties.” British Journal of Aesthetics , 44: 413–423.
- Carroll, Noel (ed.), 2000, Theories of Art Today , Madison: University of Wisconsin Press.
- Cohen, Ted, 1973, “Aesthetic/Non-aesthetic and the concept of taste: a critique of Sibley’s position”, Theoria , 39(1–3): 113–152.
- Danto, Arthur, 1981, The Transfiguration of the Commonplace , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Davidson, Donald, 2005, Truth and Predication , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Davies, David, 2004, Art as Performance , Oxford: Blackwell Publishing.
- Davies, Stephen, 1991, Definitions of Art , Ithaca: Cornell University Press.
- –––, 1997, “First Art and Art’s Definition,” Southern Journal of Philosophy , 35: 19–34
- –––, 2000, “Non-Western Art and Art’s Definition,” in N. Carroll (ed.) 2000, pp. 199–217 .
- –––, 2006, The Philosophy of Art , Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
- –––, 2012, The Artful Species , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2015, “ Defining Art and Artworlds,” Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism 73(4): 375–384.
- Davies, Stephen, and Sukla, Ananta (eds.), 2003, Art and Essence , Westport, CT: Praeger.
- Dean, Jeffery, 2003, “The Nature of Concepts and the Definition of Art,” Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , 61: 29–35.
- Devitt, Michael, 2001, “The Metaphysics of Truth,” in Michael Lynch (ed.), The Nature of Truth , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, pp. 579–611.
- DeClerq, Rafael, 2002, “The Concept of an Aesthetic Property,” Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , 60: 167–172.
- Dickie, George, 1965, “Beardsley’s Phantom Aesthetic Experience”, Journal of Philosophy , 62(5): 129–136.
- –––, 1974, Art and the Aesthetic: An Institutional Analysis , Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- –––, 1984, The Art Circle , New York: Haven.
- –––, 2001, Art and Value , Oxford: Blackwell Publishing.
- Dissanayake, Ellen, 1990, What is Art For? , Bellingham: University of Washington Press.
- Dutton, Denis, 2006, “A Naturalist Definition of Art,” Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , 64: 367–377.
- –––, 2008, The Art Instinct , New York: Bloomsbury Press.
- Eagleton, Terry, 1990, The Ideology of the Aesthetic , London: Basil Blackwell.
- Eldridge, Richard, 1985, “Form and Content: An Aesthetic Theory of Art,” British Journal of Aesthetics , 25(4): 303–316.
- Field, Hartry, 1972, “Tarski’s Theory of Truth,” The Journal of Philosophy , 69: 347–375.
- Frueh, Joanna, 1991, “Towards a Feminist Theory of Art,” in Feminist Art Criticism: An Anthology , A. Raven, C. Langer and J. Frueh (eds.), Boulder: Westview Press, pp. 153–165.
- Gaut, Berys, 2000, “The Cluster Account of Art,” in N. Carroll (ed.) 2000, pp. 25–45.
- Goehr, Lydia, 1994, The Imaginary Museum of Musical Works , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Goldman, Alan, 1995, Aesthetic Value , Boulder, CO: Westview Press.
- Goodman, Nelson, 1968, Languages of Art: An Approach to a Theory of Symbols , Indianapolis: The Bobbs-Merrill Company.
- Hegel, G.W.F., Lectures , translated by Bernard Bosanquet in The Introduction to Hegel's Philosophy of Fine Art , London: Kegan Paul, Trench, & Co., 1886; reprinted as Introductory Lectures on Aesthetics , edited and with an Introduction by Michael Inwood, London: Penguin, 1993. [Page reference is to the 1886 translation.]
- Iseminger, Gary, 2004, The Aesthetic Function of Art , Ithaca: Cornell University Press.
- Janaway, Christopher, 1998, Images of Excellence: Plato’s Critique of the Arts , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Kant, Immanuel, 2000, Critique of the Power of Judgment , Paul Guyer and Eric Matthews (trans.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Khalidi, Muhammed, 2013, “Three Kinds of Social Kinds,” Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 90(1): 96–112.
- Kivy, Peter, 1975, “What Makes ‘Aesthetic’ Terms Aesthetic?” Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 36(2): 197–211.
- –––, 1997, Philosophies of the Arts , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Kristeller, Paul, 1951, “The Modern System of the Arts,” Journal of the History of Ideas , 12: 496–527.
- Levinson, Jerrold, 1990, Music, Art, and Metaphysics , Ithaca: Cornell University Press.
- –––, 2002, “The Irreducible Historicality of the Concept of Art”, British Journal of Aesthetics , 42(4): 367–379.
- –––, 2005, “What Are Aesthetic Properties?” Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society , 79: 191–210.
- Longworth, F., and A. Scarantino, 2010, “The Disjunctive Theory of Art: The Cluster Account Reformulated,” British Journal of Aesthetics , 50(2): 151–167.
- Lopes, D.M., 2008,“Nobody Needs a Theory of Art” Journal of Philosophy , 105: 109–127.
- –––, 2014, Beyond Art , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- McFee, Graham, 2011, Artistic Judgment: A Framework for Philosophical Aesthetics , London: Springer.
- Mag Uidhir, C. and Magnus, P. D., 2011, “Art Concept Pluralism” Metaphilosophy , 42: 183–97.
- Matravers, Derek, 2000, “The Institutional Theory: A Protean Creature,” British Journal of Aesthetics , 40: 242–250.
- Meskin, Aaron, 2008,“From Defining Art to Defining the Individual Arts: The Role of Theory in the Philosophies of Arts” in Stock and Thomson-Jones (eds.) 2008, pp. 125–150.
- Plato, 1997, Complete Works , John M. Cooper (ed.), Indianapolis: Hackett.
- Rey, Georges, 1983, “Concepts and Stereotypes,” Cognition , 15: 237–262.
- Ribeiro, Anna Christina (ed.), 2012, Continuum Companion to Aesthetics , London: Continuum.
- Shelley, James, 2003, “The Problem of Non-Perceptual Art.” British Journal of Aesthetics , 43: 363–378.
- Sibley, Frank, 1959, “Aesthetic Concepts,” Philosophical Review , 74: 135–159.
- Shiner, Larry, 2001, The Invention of Art , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- –––, 2003, “Western and Non-Western Concepts of Art: Universality and Authenticity” in S. Davies and A. Sukla (eds.) 2003, pp. 143–157.
- Stecker, Robert, 1997, Artworks: Definition, Meaning, Value , University Park, PA: Pennsylvania State University Press.
- Stecker, Robert, 2000, “Is It Reasonable to Attempt to Define Art” in N. Carroll (ed.) 2000, pp. 45–64.
- –––, 2005, Aesthetics and the Philosophy of Art , Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield.
- Stock, Kathleen, and Thomson-Jones, Katherine, 2008, New Waves in Aesthetics , London: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Tilghman, Benjamin, 1984, But Is It Art? , Oxford: Blackwell.
- Walton, Kendall, 1997, “Review of Art and the Aesthetic ,” Philosophical Review , 86: 97–101.
- –––, 2007, “Aesthetics – What?, Why?, and Wherefore?” Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , 65(2): 147–162.
- Wicks, R., 1993, “ Hegel’s Aesthetics,” in F. Beiser (ed.), Cambridge Companion to Hegel , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 348–377.
- Wittgenstein, Ludwig, 1953, Philosophical Investigations , G.E.M. Anscombe and R. Rhees (eds.), G.E.M. Anscombe (trans.), Oxford: Blackwell.
- –––, 1968, Philosophical Investigations , Oxford: Blackwell.
- Weitz, Morris, 1956, “The Role of Theory in Aesthetics,” Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , 15: 27–35.
- Zangwill, Nick, 1995a, “Groundrules in the Philosophy of Art,” Philosophy , 70: 533–544.
- –––, 1995b, “The Creative Theory of Art,” American Philosophical Quarterly , 32: 315–332
- –––, 2001, The Metaphysics of Beauty , Ithaca: Cornell University Press.
- Zemach, Eddy, 1997, Real Beauty , University Park, PA: Pennsylvania State University Press.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
[Please contact the author with suggestions.]
aesthetics: aesthetic judgment | aesthetics: German, in the 18th century | Aristotle, General Topics: aesthetics | Dewey, John: aesthetics | Kant, Immanuel: aesthetics and teleology | Nietzsche, Friedrich | Plato: rhetoric and poetry | Schopenhauer, Arthur
Copyright © 2018 by Thomas Adajian < adajiatr @ jmu . edu >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054

Introduction to Art: Design, Context, and Meaning
(58 reviews)
Pamela Sachant, University of North Georgia
Peggy Blood, Savannah State University
Jeffery A LeMieux, Brunswick, GA
Copyright Year: 2016
Publisher: University of North Georgia Press
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Eddy Mora, Faculty, Johnson County Community College on 5/8/22
Very comprehensive touching on subjects required not only to understand art but design as well. Topics were related to visual communication, visual literacy, and meaning. I love that the author does not stop at aesthetics but follows with cultural... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
Very comprehensive touching on subjects required not only to understand art but design as well. Topics were related to visual communication, visual literacy, and meaning. I love that the author does not stop at aesthetics but follows with cultural and societal values.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
Having studied art for the last 30 years I can recognize the subject in reference and it appears to be accurate.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
Very relevant. I loved the introduction to the text because it makes it relevant to current and future generations of students, linking image use to cultural context and meaning.
Clarity rating: 5
Very clear and easy to follow and understand.
Consistency rating: 5
I like the sequential consistency of the text.
Modularity rating: 5
Very easy to pick up were left off.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The book is very relevant in the progression of topics. I love how is organized. The organization logic could help teachers focused on specific topics.
Interface rating: 5
Beautiful interface put together and easy to follow. Very well documented with images and captions.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical errors that I found.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
The text is very inclusive culturally. I liked how it helps the reader travel through continents with different styles, modes, histories, and artists.
I would recommend this book not only for its relevance to art history or fine art students but also to use with graphic design students. The many topics touched such as art structure, materials relevancy, communication, art analysis, and design formalities are more needed in design now more than ever, especially in face of the open cultural globalization our youth is experiencing.
Reviewed by Monika Meler, Assistant Professor of Art and Foundations Coordinator, University of Saint Francis on 12/30/21
This book is a good and comprehensive text outlining themes and ideas. I see the audience for this text being complete beginners. It focuses less on formal principles and elements and tackles larger, more comprehensive themes like defining art,... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
This book is a good and comprehensive text outlining themes and ideas. I see the audience for this text being complete beginners. It focuses less on formal principles and elements and tackles larger, more comprehensive themes like defining art, audience, and really large and complex ideas like identity, and power. Because it is a large survey textbook, these topics are not discussed in depth but do offer a brief introduction. The text does have a lot of questions at the end of chapters that would spark great conversation about these topics from beginning students. I don't mean to suggest that the book doesn't discuss elements and principles, but not nearly in as much depth as the textbook we use for foundations courses currently. I would use portions of this book for a 2D, 3D, or beginning drawing class, but it would not be an accurate replacement text for an intro/foundations course. For instance, the chapter on "describing art" would be very applicable to introduce students to critique. There are great examples of formal analysis that would be excellent to start the process of critique with.
The content of the book is very accurate.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 3
This is tricky to evaluate because this book is extremely relevant to beginning students. I could see this book being used in an art appreciation class or a class for non-majors not looking to go very deep. In our program, we teach a series of 1 credit beginning seminars for art majors that introduce them to different areas of study in studio art, audience, content, materials, and meaning. If I have the opportunity to teach one of these classes, I will definitely be pulling parts of this book. As you know, I am a fan of the "Describing Art" chapter and foresee using the "Connecting Art to Our Lives" chapter in the class as well as "Meaning on Art" in the courses.
My vote of "3" here is because of the lack of cultural diversity in the art that is represented and the fact that there are very few examples of more contemporary art. The examples are very European and this is why I would not use this as the sole text for any class. I would need to supplement with more contemporary/culturally diverse perspectives. Contemporary artists are mentioned, but few visual examples are used.
I think the book is very clear and consistent and believe that it communicates well to a beginning audience.
The book is very consistent. I like that each chapter begins with a section on "learning outcomes" and concludes with a review of key concepts. If your course includes tests or quizzes, this consistent structure would make it easier to construct the texts/quizzes and would serve as a nice study guide for students.
I addressed some of this in the "consistency" review above but this is one of the books biggest strengths. It is very easy to pull just one part of the book and teach from sections. The sections do no depend on the student having knowledge of previous chapters/sections.
As I have mentioned in previous points, this is a strength of the book.
There are no interface/navigation problems. I am impressed with the quality of images used.
I do not see any grammar issues.
Cultural Relevance rating: 1
This is one of the major issues I see with the book and I mentioned that in the points above. Other reviewers have also mentioned the lack of focus on cultural inclusion/diversity. If this book is to be used as a sole text for any course, it would have to be much more inclusive.
Reviewed by Christine Shearer, Adjunct Professor, Cleveland State University on 7/11/21
The book is a good resource for a basic art appreciation course that plans to focus more on topics and themes and less on formal qualities. Most of the examples are of a Western focus and provide a very Eurocentric viewpoint. There is a lack of... read more
The book is a good resource for a basic art appreciation course that plans to focus more on topics and themes and less on formal qualities. Most of the examples are of a Western focus and provide a very Eurocentric viewpoint. There is a lack of female representation, both as maker and patron, providing a male-centric focus—a common occurrence in art historical textbooks.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
The images are great examples; however, they do not include any information that most professors would include in their lectures and PowerPoints—artist, title, date, medium, location.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
For a survey it has relevance, but it is not relevant for an upper division art history course. The book does not include much material post-1960, lacks representation beyond Europe and Western civilization, and is light on female contributions.
The template of the book is clear, nicely designed, and consistent. The writers have expressed their ideas in easy-to-understand language and have provided images and/or links to images to expand the learning experience visually. At the beginning of each chapter there is a list of learning objectives, and at the end of each chapter there is a review of key concepts, a test yourself section, and key terms.
The book is arranged thematically throughout, and the format is the same for each chapter.
Each chapter is broken down into subsections that are easy to pull out and assign in a different order than they are presented or as part of another course.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The organization of the book is by theme. It is structured to cover what is art and how to make art in the beginning chapters and then progresses through different forms before landing on specific themes. It can be used as presented or re-arranged to fit another format.
There are hyperlinks that are a little long. These could perhaps by converted to bitly links to make it less distracting when you come across them in the text.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
There are a few grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
As stated above, the book is heavily Eurocentric and focused on Western art. Very little material on women and post-1960 is included within that focus as well. It does not include non-Western art and culture which is often lacking from many art historical texts. Sections could be used for supplementing material in other courses, but overall, it is a good source for an introductory art appreciation course.
Reviewed by David Chatfield, Adjunct Instructor, Community College of Aurora on 5/24/21
This text is not especially comprehensive. The first, and the most egregious example is the lack of historical and cultural contexts, normally found in the form of sections on art history. The authors attempt to embed art history into... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 2 see less
This text is not especially comprehensive.
The first, and the most egregious example is the lack of historical and cultural contexts, normally found in the form of sections on art history. The authors attempt to embed art history into sections on material, Formal Elements, and Themes in Art, but it lacks a lot of context. This is especially the case when it comes to representation in non-western cultures. While I understand it is difficult to represent all cultures in dedicated chapters in this kind of text, and while I like the idea of embedding art history into other sections, they do not provide enough historical context and non-western cultures. One can choose a select group of representative cultures that demonstrate the relevant ideas that can give the students the structure and critical thinking skills needed to analyze the omitted cultures. Exposure to other cultures and other contexts is essential to developing empathy, essential in developing critical thinking skills when considering new and unfamiliar contexts.
Finally, while it is fairly comprehensive in describing other ideas, like materials, Formal vocabulary, and themes it's not very comprehensive on the application of those ideas.
Content Accuracy rating: 3
While the content seems accurate, it is not unbiased. As stated above this text is pretty typical in so far as the overrepresentation of Western cultures (and cultures generally accepted by the Western Canon like Egypt or China) in textbooks. This shows a bias toward an outdated Eurocentric viewpoint.
The content is not up-to-date. As an example, in the chapter on Protest and Shock, the most recent example is from 2001. There is a plethora of protest art from recent years, for example, BLM to the continued LGBTQ+ rights movements.
Though the text does include some contemporary artists, like Mel Chin, the examples are outdated.
The text also has at least 2 outdated links to image examples. Relying on links to other sources does not ensure longevity as the web is ever-changing. One could PDF the source and include that, or just include the images directly.
Clarity rating: 2
This text is pretty academic/inaccessible in its prose and doesn't provide much context for the terminology. For example, in the description of the often confusing Complimentary Colors, the authors state: "There is a slight delay between the depletion and restoration of this chemical supply within the neuron. In the interim, an afterimage occurs. Look at the green, orange, and black flag for 10 seconds, then look at a blank wall or empty white space. (Figure 2.52) For a few moments, you will see the complement, or opposite, of green (red), the complement of orange (blue), and the complement of black (white)..."
This idea is deceptively hard to teach, and even experienced art students are confused by Complimentary Colors. Describing chemical reactions and neurons might require one to explain what neurons are as well as what color wavelengths are on top of the cultural specificity of color and so-on and so-on only to additionally complicate a complicated idea, when what the student's need to know is how Complimentary Colors behave visually in contrast to Harmonious Colors, and why that is important to an artist. Compliments clash, while Harmonies don't.
Consistency rating: 4
The text is fairly consistent in its terminology and seems to be organized by an overall framework, starting with the vocabulary, then materials, then finally themes of Art. I would like to see more ties between the different sections using the vocabulary. For example, in the earlier section on the Formal Elements and the later section on visual analysis, the vocabulary used in the early section isn't brought forward in a clear and consistent way.
Modularity rating: 4
The text is modular, with sections delineated out into broader ideas that are then explored specifically, that can be viewed independently if needed.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 3
As stated above the text is well organized. Looking at the table of contents one can easily find specific ideas and jump to them using the page number feature. That being said, it would be far more intuitive and accessible if the sections in the table of contents linked directly to their corresponding sections.
Interface rating: 2
Though this text has some accessibility problems.
As to the interface, I have been able to copy and paste text easily, making me think the text accessible to an eReader. I'd like to see how this text works with an eReader for visually impaired or neuro-divergent students. As of now, I do not see an option for the text to be read within this interface requiring a third-party eReader.
The images are small and cannot be enlarged or opened in another tab. Being able to zoom in helps students interact with the work in a more intimate way. This is also a huge problem for visually impaired students.
There are several broken links, and I've found that the PDF takes a lot of time to load, even on a stable internet connection. This could be problematic if a user's computer or internet connection is slow. Could the sections be broken into smaller, linkable sectons?
Beyond a few links, the user experience is limited.
As best as I can tell there are or no grammatical or spelling errors. Though I'm no editor.
I did a keyword search and found a striking lack of non-Western Art. Renaissance is mentioned 30 times, while Africa/African: 8, Mesoamerica: 0, Aztec: 3, Mayan: 1. Aboriginal: 2, Pacific Island: 1, and so on. A cursory glance at the imagery is equally unrepresentative. I mostly see artwork from movements typically seen in Eurocentric Textbooks that dominate Academia (or cultures like Egypt or China, generally accepted into the Western Canon). The purpose of seeking out an OER is to move away from these types of texts. This lack of representation is highly problematic.
As to Higher Order Learning skills, specifically analysis/evaluation, I don't see enough in the text on how to analyze a work of art. They simply include a brief section with only two images and all too brief corresponding paragraphs of academic visual analysis. I don't see many connections to previous sections on the vocabulary used in visual analysis. The authors academically explain an idea, or a theme, but give the students much opportunity to apply those ideas.
A good book should lay the groundwork first on the necessary ideas, concepts, and vocabulary. When a student gets to the analysis in this book I don't think they would be prepared to understand the analysis the authors provide.
Then they need to have an immediate opportunity to apply those ideas. I realize this is part of my job, however, a good text does add exercises the authors find relevant to their text. My assignments may not be enough. At any rate, it's nice for the students to have additional options for the application of ideas.
This text also does not contain enough modalities in presenting the information. There are no supplemental videos, hands-on projects, or audio components. Just providing text and pictures is not enough. This particular text would require me to heavily supplement information, in which case I might as well toss the text and curate content that comes from multiple modalities myself.
Finally, quizzes at the end of each section may provide decent quantitative assessments, there is little here to help me provide qualitative assessments. Again, I understand that is my job to provide those opportunities, but I've found good text does as well.
Reviewed by Ines Corujo-Martin, Adjunct Assistant Professor, New York City College of Technology on 5/4/21
This textbook seeks to offer a deep and comprehensive insight into the world of art, including a broad variety of perspectives, such as art and meaning; art and power; art and ethics, among many other subjects. It contains over 400 high-quality... read more
This textbook seeks to offer a deep and comprehensive insight into the world of art, including a broad variety of perspectives, such as art and meaning; art and power; art and ethics, among many other subjects. It contains over 400 high-quality images that illustrate the various forms of art, its technical applications, and its many uses. The table of contents seems detailed at first, but a closer look reveals the lack of logical and coherent progression. While Chapters 1 and 2 analyze the meaning of visual art, what is an artist, and the structure of art, Chapter 3 jumps into the study of materials, introducing jargon and technical terms that belong to an art history or more specialized course. Chapters 4 and 5, which respectively explore “Describing Art” and “Meaning in Art,” should have been placed right after Chapter 1, as they cover basic topics and terms. On the other hand, Chapter 7 delves into art in architecture, while other forms of art like painting, sculpture, or photography are neglected and find no space of deep analysis in the textbook. Overall, the content is imbalanced and needs more work, as well as the inclusion of updated materials and examples. Relevant chapters that could introduce thought-provoking and add new perspectives into the classroom (e.g., Chapter 8: Art and Identity; Chapter 9: Art and Power) are brief in comparison to other sections and offer a superficial and simplistic overview on very complex topics. For example, the authors do not illustrate the relationship between art and the construction of intersectional identities of race, gender, nationality, and ethnicity, mainly centering on religious and spiritual values (Chapter 6 and Chapter 10). Although each chapter ends with a section of "Key Terms," there is no glossary or list of illustrations at the end of the textbook. It includes footnotes citing the references employed, but there is no final bibliography, which is detrimental for an introductory college textbook that should provide a condensed view of documentation in the field. This textbook is inaccurately described online as “digital in nature,” when it takes on a conventional approach to teaching and learning. The only digital component is the inclusion of links embedded throughout the text, most of which are not contextualized. Some of these links do not work, and others send students to artworks with poor image quality. The textbook as a whole fails to provide digital activities and/or projects to expand students’ educational experiences beyond the textbook, helping them master concepts (i.e., quizlets, flashcards, videos, interactive images, etc.). It does not contain learning features like annotate and bookmark, which increase engagement with course content. Besides, there is no way to monitor students’ progress. It would have been useful to incorporate review, summary, and expansion activities at the end of the chapters, in addition to self-quizzes, to enhance student performance and facilitate the grasp of content.
The images do not include information on the artist, title, size, medium, date, and museum/collection of the works of art, and the emphasis is solely placed on the open source. Names of artists are sometimes misspelled and show no consistency like Vassily Kandinsky instead of Wassily Kandinsky (p.106).
As previously noted, this textbook takes on a traditional approach both in content and format, failing to add innovative insights to the art field. It mostly focuses on the pre-1960s period, and there is a notable absence of contemporary art, non-Western cultures, and art produced by female artists and people of color. There is barely no discussion of subculture art, urban art, or popular art, and the importance given to museums for the dissemination of art is minimal. There are stances in which the authors delve into topics that seem irrelevant to an introductory art course. For instance, the emphasis on the cultural value of materials (Chapter 3) seems very off-topic and, as already mentioned, should belong to an art history or material culture course. In contrast, relevant ongoing topics like digital art and the relationship between art and technology, often students’ favorite section, should be organized as a separate chapter instead of inserting disconnected and vague references throughout the text. The textbook does not provide enough opportunities for students to develop their critical thinking. This aspect could have been polished by designing exercises to analyze the works of art presented or by adding case studies on current and relevant artistic activities to interpret practical scenarios. To give an example, the eleventh chapter--"Art and Ethics"--could be greatly improved by introducing recent articles and real-world examples to explore ethical dilemmas related to the concepts of intellectual property, collecting, and censorship.
Clarity rating: 4
Overall, the language is clear and accessible, except for instances in which the authors use jargon and obscure terminology not appropriate for an introductory art course. Some of these technical words are not even included in the "Key Terms" sections at the end of each chapter, forcing the readers to figure it out by themselves and confusing students who might have little or no background in art.
The template used is consistent through the chapters. There is consistency regarding structure, framework, and terminology.
Each of the eleven chapters that comprise the textbook are organized into topics followed by subsections that are meant to connect back to the main theme. All chapters start off with a section of "Learning Outcomes," summarizing the learning objectives that should be attained at the end. After this, an introductory part provides background and presents the main themes and ideas that will be covered. The constant inclusion of rhetorical questions throughout the text allows students to reflect on their own learning process and to recognize the impact of art in their daily lives. Moreover, each chapter ends with two conclusive sections: "Before You Move On" and "Key Terms." The first one gives a list of discussion prompts to test the knowledge gained so far and to connect the content to students’ personal experiences. These self-reflection questions are particularly useful to engage students in their knowledge-building process and can be easily assigned to discuss in small groups during class or adapted for online forums to extend the exchange of views beyond the classroom.
There is no introduction/preface in which the authors explain the structure they follow, their educational goals or the relevance and application of the content in this textbook. Having a preface at the beginning of the textbook is useful to specify and give more information on the intended audience, as well as the educational level for which it is recommended (although we assume it is addressed to introductory college/university courses on visual art, art history, and art appreciation). There are no suggestions for planning the course and using the textbook in the classroom. This lack of pedagogical guidance could be greatly improved in the future.
Interface rating: 4
This is an aspect that needs improvement, as many of the links do not work or the linked images and pages are missing. In other cases, when referring to previously discussed images, the labeling tends to be incorrect. It is frustrating that the links within the body of the text are so long and that they are not enclosed with a period, which distracts the reader. Other than that, navigation through the text is straightforward and the text is clearly displayed.
The text does not include grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 2
The approach of this textbook is clearly Eurocentric and Westernized, leaving out examples of art from Africa, Latin America, indigenous tribes, or any other non-Western culture. The only part in which the authors make some explicit references to other cultures (in this case Asian) takes place is Chapter 10 on "Art and Ritual Life"; however, this discussion occurs within the framework of Western themes. The vast majority of artworks in the textbook display white men and, as mentioned elsewhere in this review, there is no representation of female artists or people of color. This omission of diversity is problematic and one of its main downfalls. Art is one of the most powerful mediums to educate others on issues of inclusivity, social justice, and cultural sensitivity, which is key to forming well-rounded, global citizens. This textbook perpetuates a white-male-dominant perspective, following the typical works of art found within the canon of Western Art History. It is highly recommended that the authors revise the selection of pictures, citations, and examples to represent diverse cultures, races, ethnicities, genders, and backgrounds. In this respect, it is noteworthy to mention that the eighth chapter on the subject "Art and Identity" is one of the shortest and most superficial ones (in comparison, for example, to the previous chapter devoted to architecture that occupies more than 30 pages). The chapter "Art and Identity" provides over simplified conceptions of what cultural identity means (and constantly from a Westernized perspective) and misses out the fertile intersection of art with gendered and racialized identities over the course of history.
This textbook is not recommended as the main reference material or as a tool for organizing the course structure due to all the weaknesses in regard to content, structure, and cultural relevance detailed in this review. However, some of its sections can be incorporated into already prepared lessons, in particular Chapter 1, 4, 5, and 11, which from my perspective are the strongest. The textbook is not overly self-referential and some parts can be easily used as a supplemental material in combination with other educational resources.
Reviewed by Meidor Hu, Professor, Hawaii Community College on 4/23/21
This text is a comprehensive survey of ideas and subjects— theoretically and historically, similar to other text for an introduction to visual arts course. A wide variety of artistic media styles, time periods, and regions are covered, mostly with... read more
This text is a comprehensive survey of ideas and subjects— theoretically and historically, similar to other text for an introduction to visual arts course. A wide variety of artistic media styles, time periods, and regions are covered, mostly with examples from Western art. Love the "Test Yourself" and "Key Terms" section at the end. It is lacking an index and glossary at the end of the text. I can see how this text can be easily incorporated with my previously prepared lessons.
The text reads unbiased and highly accurate. Although the image examples left out info on size, media, date and location of the art work.
The text is current but could give more focus on art since the 1960s and inclusion of more women artists.
The writing is clear and easy to read. The "Test Yourself" section at the end of each chapter is a great addition to check for understanding.
There is consistency in the logical structure and presentation.
The chapters and subheadings are logical. Each chapter opens with Learning Outcomes and ends Key Concepts, Test Yourself, and Key Terms sections to check for understanding. The subheadings are in easily digestible sections.
The text's organization is clear in format and structure.
The basic design is clear and non-distracting. The image quality were also good.
No issues with grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
Although the text incorporated examples from different cultural and geological region, the majority of the discussions are Eurocentric in perspective. More attention to Asian, African, Pacific and the Americas would give the content more diversity.
Reviewed by Daniel Vedamuthu, Instructor of Art and Design, Rochester Community & Technical College on 4/1/21, updated 6/1/21
Books for Introduction to Art / Art Appreciation courses usually cover some standard topics: the definition of art, materials used to make, the elements of art and the principles of design, reasons for creating art, and methods of formal analysis... read more
Books for Introduction to Art / Art Appreciation courses usually cover some standard topics: the definition of art, materials used to make, the elements of art and the principles of design, reasons for creating art, and methods of formal analysis of art. Introduction to Art: Design, Context, and Meaning covers these topics in the appropriate amount of depth. Texts usually then present a thematic, chronological, or cultural history of art. Introduction to Art: Design, Context, and Meaning focuses on a thematic approach. Figures often appear without dates. Courses that focus on a chronological approach will find this text lacking. The text lacks a “whole book” glossary of key terms. The Key Terms are found at the end of each chapter. The text includes a Table of Contents but does not have a formal index. This would have a negative impact on a printed version of the text. In the PDF version, searching the text is only a click away.
The text is accurate. One of the most important aspects of accuracy in a text in this subject is ensuring that the Artist, Artwork Name, and Date of Creation are correct. Doing a few random spot checks, when this information is present, the information is correct. Figures are labelled with the source author, source location, and the license. One area the text could improve is the lack of pronunciation guides in the text and in the Key Terms areas.
Being a text covering the thematic history of visual art, the content itself will not go out of date. The lack of contemporary imagery is the biggest drawback to the text, due to licensing of the figures. To include contemporary artwork in the text, links to outside images are provided in the text. Outdated links or redirects could cause the text to become obsolete. I believe it would be helpful to have a section after the copyright page or at the end of the text describing when links have last been updated or revised. However, the text is organizing in such a way that adding new images requires revising the thematic examples throughout the text instead of having to add and reorganize chapters. This is a benefit for adding new contemporary or cultural examples through the text.
The text is very clear. Art terms are clearly explained. Written examples are used to explain difficult terms. Even more importantly, Figures are used to demonstrate the meaning of art terms. When there are contrasting ideas, the text provides multiple Figures to demonstrate those competing ideas and provide instant opportunities for students to discussion about compare-and-contrast between the two figures.
The text is consistent on how it approaches topics. Art terms are using consistently throughout the text.
The text is built to be modular. Each chapter could be assigned in any order, though it’s obvious that the editor has an intended order for reading at the beginning of the text in order to logically introduce readers to the topics. Toward the end of the text, the topics become more thematic, and these chapters could be easily reorganized and adapted. Each Chapter’s main Chapter Content has clear headings and well-defined sub-headings. Each level of heading seem to be good breaking points to create smaller readings or to remix and rearrange the text.
Chapters in the text follow a logical and consistent structure. Each chapter establishes Learning Outcomes (which are meaningfully written), and Introduction, Chapter Content with well-defined subheadings, a conclusion named “Before You Move On” that includes Key Concepts and Chapter Questions, and finally, a list of Key Terms from the Chapter. Chapters build in a logical progression a the beginning of the text.
The real point of concern with any art appreciation text is the quality of the images. The resolution of most images appears to be sufficient for screen and print. Images are no distorted. Navigating the text is easy through PDF Bookmarks.
I observed no grammatical errors in the text.
This book features many examples that vary from the traditional art appreciation “textbook examples.” Images still tend to represent a “western art” perspective. There are examples from a range of different cultures but compared to some of the best commercial textbooks for cultural relevance, this text does compare to those standards. Are there any other comments you would like to make about this book? I am not fond of the typographic and typesetting choices made for the text. Multiple columns of text would reduce some of the very long line lengths found in the text. With a long line length and narrow leading, the lines seem to blend together. Figures do not seem to follow a strict layout grid that enhances the layout of the information. The drop-shadows on Figures are unnecessary. Fake small cap on Chapter names in the Table of Contents isn’t high quality.
Reviewed by Andrea Lepage, Professor of Art History, Washington & Lee University on 12/13/20
The text integrates all of the key areas traditionally covered in an art appreciation course with an emphasis on cultivating an art specific vocabulary and understanding the materials of art. The authors incorporate a wide variety of artistic... read more
The text integrates all of the key areas traditionally covered in an art appreciation course with an emphasis on cultivating an art specific vocabulary and understanding the materials of art. The authors incorporate a wide variety of artistic media, traditions, styles, time periods, and regions into their discussions. The majority of the examples provided are drawn from Western art historical traditions, but the authors also include examples from regions beyond the West—especially China, Japan, and India. The text features some examples from Nigeria, Ghana, and North American indigenous traditions, but greater attention to African, Latin American, Central and South Asian, Oceanic, and indigenous traditions would be welcome. The work of male artists, mostly drawn from the Western art historical canon, dominate the discussions; greater coverage of women artists would also be welcome. The Table of Contents is hyperlinked and clearly organized, and each chapter concludes with an excellent glossary of terms. Including an index would assist students in navigating the book.
The content is mainly accurate throughout the text, with some typographical, spelling, and technical errors (broken links), especially in the second half of the book. As noted below, the text includes some inaccuracies or inconsistencies pertaining to indigenous cultures and artists. On occasion, the authors present controversial viewpoints in a straightforward manner. The 2003 toppling of the Saddam Hussein monument in Baghdad (p. 249) is one example. In a section dedicated to propaganda, the authors make no reference to the controversial nature of this incident, which may have been initiated or manipulated by U.S. military forces for propagandistic purposes.
The text is arranged in such a way that extended discussions and additional examples would be relatively easy to introduce. Updates might include extended discussions about artwork produced by women, indigenous, black, and other artists of color. In some cases, updates might simply expand the discussion around examples already introduced into the text (for example Gee’s Bend quilt maker Lucy Mingo, page 7; Judith Baca’s Great Wall of Los Angeles, pages 23-24; Jaune Quick-to-See Smith’s multi-media work, page 168). Such updates would help to further decenter traditional canonical Western art historical narratives. In addition, references to LGBTQ artists would be a welcome addition, as would including supplementary sections dedicated to contemporary artistic production. The authors have been careful to include discussions of more contemporary art forms like new media and graphic novels, and additional examples would be relatively easy to insert into the text. Discussions of early modern and modern art are already strong.
The text is written in clear and accessible prose. The learning outcomes at the beginning of each chapter give readers the necessary information to navigate each chapter. The concluding section in each chapter (“Before You Move On: Key Concepts”) does an excellent job of synthesizing the key points included in each chapter.
The text is arranged thematically rather than chronologically and is internally consistent throughout. Each chapter is well organized and easy to follow with a consistent arrangement that will be especially helpful for students as they study key points presented in the text.
The authors organize the text thematically, rather than chronologically as is the case with many introductory art history textbooks. Each chapter is organized consistently with learning outcomes, an introduction, a series of content sections that could be assigned at different points in the course, followed by a recap section entitled ‘Before You Move On,” and a list of key terms. The key term/glossary sections are extremely useful. In particular, the key terms included in chapter three, “Significance of Materials Used in Art”, provide an excellent and comprehensive glossary of artistic materials. It is easy to imagine students consulting this resource routinely throughout the course. Many of the ‘Test Yourself’ questions included at the end of each chapter could also double as in-class discussion prompts.
The book contains eleven chapters, organized thematically. The chapters cover conceptual questions, including: What is art, who is considered an artist, and why is art powerful (chapters one and nine)? How does art connect to our lives (chapter six), our identity (chapter eight), ritual life (chapter ten), and ethical world views (chapter eleven)? These conceptual discussions bookend chapters focused of the materials of art, and later chapters effectively circle back to themes briefly presented in the introductory chapter.
The remaining chapters provide students with art specific vocabulary and the descriptive and analytical tools to view, discuss, and interpret art and architecture. Chapters two (“The Structure of Art”) and three (“The Significance of Materials Used in Art”) provide students with an excellent and thorough description of the materials of art, which will be especially useful to students without a background in studio art. The authors are careful to include discussions of a wide variety of media including architecture (chapter seven), painting, printmaking, sculpture, video, performance, and new media. Chapters four (“Describing Art”) and five (“Meaning in Art”) provide students with an overview of strategies for formal and contextual analysis.
The Table of Contents provides links to each subsection, which is an effective navigational feature. The artworks and charts embedded in the text are high quality, well placed, and increase reader understanding of the concepts presented. The consistent design layout makes it easy for the reader to shift between image and text. Due to copyright restrictions, however, the authors are unable to include reproductions of all of the artworks discussed in the text. In those instances, the text includes links to the images. Some of the links to artworks are broken or point to sites that will require students to sift through extensive texts or image sets to find the artwork mentioned in the textbook. Along with the artist and title, it would be helpful to include the date, medium, size, and location in the label accompanying each artwork. This is a highly accessible textbook—the authors offer a variety of ways to download the PDF as both low- and high-resolution files, chapter sets (1-3; 4-7; 8-11), and in Japanese translation. The work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 License.
The text does not contain obvious grammatical errors. However, it does contain typographical and spelling errors; accents are omitted at times.
Overall, the text makes use of examples that are inclusive of a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds. At times, the text misses opportunities to bring the discussion into communication with cultures that flourish beyond the Western world. Greater attention to indigenous cultural specificity is warranted. For example, the authors reference the Aztec Plumed Serpent deity Quetzalcóatl (p. 256) in the context of Chichén Itzá, which is a Maya site located in the Mexican state of Yucatán. However, Kukulcán is the name of the Yucatec Maya deity to which the main temple at Chichén Itzá is dedicated. The authors should reconsider using the word ‘Eskimo’ (p. 270) or explain that ‘Eskimo’ is a designation imposed upon Inuit and Yupik people that has been rejected by Inuit communities for decades. This is one of several instances in which the authors could engage more significantly and critically with histories of settler colonialism. Other opportunities to confront biased Western narratives could occur in the sections focused on mahogany harvesting in the Caribbean (p. 88), Manifest Destiny (p. 161-162), and discussions of transatlantic trade in general. The discussion of Jaune Quick–to–See Smith's (an enrolled Salish member of the Confederated Salish and Kootenai Nation) "Montana’s Trade (Gifts for Trading Land with White People)" presents one such opportunity (p. 168), but both links to her work are broken. Because the artist’s name is misspelled twice in this section, students may encounter difficulties finding a reproduction of the work independently. Similarly, the authors could confront histories of enslavement more frequently, modeling their discussions on the section dedicated to Fred Wilson’s "Mining the Museum" exhibition (p. 289-290).
This text represents an important contribution in the effort to make art and the study of art accessible to students. Undergraduates studying art appreciation will benefit from the accessible prose, clear design layout, and high-quality in-text illustrations.
Reviewed by Julia May, Assistant Professor, University of Virginia on 11/30/20
I would use this text in my art appreciation/visual culture course. I very much appreciate the arrangement of the book, the first section dedicated to the fundamentals of art and the second, to central themes. These aspects provide a solid... read more
I would use this text in my art appreciation/visual culture course. I very much appreciate the arrangement of the book, the first section dedicated to the fundamentals of art and the second, to central themes. These aspects provide a solid foundation for students who will want to know more. It is a sufficient balance of form and meaning, which you don't often see in introductory texts. It is accessible and easy to follow. The embedded hyperlinks to supplemental information is also a unique feature that students will find helpful.
The information is accurate and consistent.
Any updates will be easy to make. I don't see anything going out of date too soon.
The language is clear and accessible. Including glossaries at the end of each chapter is a great way for students to have ready access to key definitions.
The text is consistent.
I feel that the modularity of the text is adequate. The reader should not be overwhelmed by the above elements. Being able to zoom in on the images - is a great feature - they remain very crisp and clear, at least for me.
The authors organized the text effectively, considering the amount of material covered (see above). I appreciate how the authors include a set of learning outcomes at the start of each chapter and have "tests" throughout as well as "key concepts" and glossaries. My only concern is that there is no index, nor is there a bibliography (unless I missed them).
I think the interface is sufficient. I was able to access the material embedded in the hyperlinks. Using hyperlinks to supplemental content is a terrific way for students to obtain details on particular objects. I also like that authors used them judiciously.
I did not see any grammatical errors.
The chapter on art and ritual life serves as an excellent example of presenting the traditions of a variety of cultures in a balanced and respectful manner.
This book is a perfect companion to any college-level art appreciation course - and for today's student. The balance of form and meaning, the inclusion of learning objectives for each chapter, the "tests," and hyperlinks to supplemental material makes it unique and a text I would consider using in my course.
Reviewed by Danielle Bell, Adjunct Professor of Art and Art History, Community College of Aurora on 8/14/20
In reviewing this text, there were many things that I had issues with: 1. The text condenses the discussion on artistic mediums to half a chapter. This does not give students enough time to fully engage with the mediums since there is no context... read more
In reviewing this text, there were many things that I had issues with: 1. The text condenses the discussion on artistic mediums to half a chapter. This does not give students enough time to fully engage with the mediums since there is no context given. 2. There is a whole chapter dedicated to architecture, but only smaller sections within a chapter dedicated to other art mediums, such as painting, printmaking, and drawing. The chapter on architecture could have been condensed so much more and included in the mediums section. 3. In the sections on mediums, the text does not always show examples. For instance, in the printmaking section, they do not show an art example for each process, so the students reading would have no idea what a screen print even looks like. 4. My other issue with chapter 2 is directed at the sections on the elements of art and principles of design. These sections are very rushed. Its information overload. The authors do not spend an adequate amount of time/space on each element. Again, no context is given for each element and its many facets. There needs to be more time given to the elements and principles and more art examples given so that students are better equipped to identify such things when doing a formal analysis. 5. My next issue is that there is no definition of formal analysis given before the authors, in Chapter 4, begin performing a formal analysis on two different works of art. 6. Chapter 4 also has a rather quick, but comprehensive art historical section, but it doesn't really belong in this chapter as its supposed to be about "describing art." 7. The chapter on identity in art is incredibly Eurocentric, and is also is very focused on art before 1900. There is a significant lack of contemporary art discussed in this text.
The content that is presented and discussed is done so accurately and seemingly unbiased.
For the most part, the text is very relevant, especially its chapters on themes in art. However, there are times the authors delve into topics that seem irrelevant to an intro to art text. For instance, Chapter 3 on cultural value of materials is very out of place in this text.
Clarity rating: 3
The book is at times accessible and yet also full of scholarly jargon that is confusing to those not familiar with that type of writing. Throughout the text, the authors "name drop" scholars, art schools, historical figures and events, etc. without providing context. Even the metadata for artworks is always clear as there are times where the text will omit information rather than indicating that the information is unknown.
I encountered some inconsistency in the spelling of artist names. In the text, there are conventional transliterations of artist’s names. For instance, for artist Do Ho Suh, the name is spelled Do Ho Su on page 92, and Wassily Kandinsky is spelled Vasily Kandinsky on page 106.
The text is not overly self-referential and would be easy for any professor to cherry-pick sections to assign to students. I think the strongest chapters in this book that any intro to art class could benefit from are chapters 1, 5, and 11.
The organization of topics is strange and, at times, confusing. One area that really stood out to me as disorganized is found in Chapters 2, 3, and 4. Chapter 2 is titled "Structure of Art", which is already a confusing name for this chapter as the topics range from mediums of art to the elements and principles of art and design. Chapter 3 then gets into the intrinsic value of materials, which already seems of out place in this textbook as it seems like something more relevant to an art history class than an introduction to art class. Finally, in Chapter 4, there is a discussion on formal analysis, which really should have been included in, or put after, chapter 2 since it discussed the elements and principles.
There are a number of links given in the text that do not work and others send students to works of art with low image quality.
I found no grammatical errors in this text.
This text is pretty Eurocentric. While it does have sections where the authors discuss non-Western topics, such as Chapter 10 on ritual life and art, its only in the context of Western themes. African, Mesoamerican, and Native American art are some notable cultures that are either left out or barely discussed.
This is a decent textbook for cherry-picking specific topics from, but all together it is not a great text to use as a tool for creating course structure.
Reviewed by Don Oberheu, Lecturer, Leeward Community College on 7/14/20
The text does an excellent job of covering the areas and ideas that one expects from an introduction to art textbook. The table of contents is clear and provides easy navigation within the text. While there is no glossary at the end of the text,... read more
The text does an excellent job of covering the areas and ideas that one expects from an introduction to art textbook. The table of contents is clear and provides easy navigation within the text. While there is no glossary at the end of the text, there is a chapter-specific glossary at the end of each chapter providing a convenient review of the concepts and terms covered in each chapter.
The content is accurate, error-free, and, with its many comparative references to different cultures and times, very unbiased.
The content is up-to-date and covers all of the mediums, including photography, that one would expect from an introduction to art text. It is written and arranged in such a way that any necessary updates will be relatively easy and straightforward to implement.
The text is written in organized and well-flowing prose that introduces and explains the ideas, the technical terminology, and the historical flow of the material it covers.
The text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
The text is easily and readily divisible into smaller reading sections that can be assigned at different points within a course. The text is not overly self-referential. One can cherry-pick whole chapters or sub-sections within a chapter to align with various subunits of a course without presenting much disruption to the reader.
The topics in the text are presented in a logical, clear fashion.
The interface is the only area of this text that needs some improvement. While the text is not overly self-referential, when it does refer to previously introduced and discussed images, the reference tends to be incorrect. The image referred to does exist however, the given labeling is often incorrect. Likewise, while it is great that the text is peppered with hyperlinks to images on the web, many of the links are not valid. The hyperlinks work, however, the linked images or pages are often missing.
The text contains no grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way. In fact, it makes great use of examples that are inclusive of a variety of races, ethnicities, backgrounds, and time periods.
In addition to serving as a textbook for introduction to art courses, this text can also be used in more medium-specific introductory art courses, e.g., Introduction to Digital Photography, to help learners in the courses better understand both composition and the potential role of their own art as it relates to the medium they are learning.
Reviewed by Sandra Clyne, Adjunct Instructor, Bunker Hill Community College on 6/30/20
Although the text provides a detailed analysis of ancient, traditional, and modern visual art, it is notably deficient in its treatment of contemporary (post 1960s) art. This omission would lessen the appeal to college students of this otherwise... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
Although the text provides a detailed analysis of ancient, traditional, and modern visual art, it is notably deficient in its treatment of contemporary (post 1960s) art. This omission would lessen the appeal to college students of this otherwise encyclopedic and well reasoned introduction to the critical awareness of visual art.
The text's treatment of anthropological and art historical detail is meticulous.
Art students require a text that provides insight into the revelatory role of visual art within human consciousness. This text is far too pedantic and does not invite exploration and imagination by the students in interpreting the works of art presented.
The text would be quite accessible for undergraduate college or university students. The concepts discussed are adequately introduced and the terms are well defined. The style of writing is quite clear and straightforward.
The text is quite internally consistent, without notable contradictions in its key propositions and theses.
The text is quite clearly divided into chapters and subheadings, and there is a "Key Terms" section at the end of every chapter. However, the text lacks an omnibus glossary and subject index.
The text "flows" from basic to more complex concepts. The text approaches the critical analysis of visual art from distinct perspectives that are clearly signaled by chapter headings.
The display features employed in this text are its beautiful illustrations, which bring to life the adjacent verbal analysis.
The grammar and sentence structure utilized in this text are impeccable.
The text examines visual art from a wide variety of cultures over a range of geographical sites, but is somewhat Eurocentric. More emphasis on African, Asian, South Asian, Native American and Oceanic art would have diversified its approaches and content.
Because of its logical structure and clear writing style, this text would provide an accessible introduction to the highly complex field of visual art for undergraduate community college, college, or university students.
Reviewed by Meridyth Espindola, Adjunct Professor, Bunker Hill Community College on 6/26/20
This book does a great job covering a broad spectrum of the context and meaning of art and design, and consistently provides visual examples. read more
This book does a great job covering a broad spectrum of the context and meaning of art and design, and consistently provides visual examples.
This book presents information in an accurate way, although it includes a very limited perspective on art by BIPOC. While this is characteristic of traditional art and design history texts, it is important to be aware of and address in the classroom.
The text focuses mainly on historical art history, and will not quickly become obsolete.
The text is well-written, easy to read, and follows a natural hierarchy of information. Visually, the page formatting is digestible, easy to follow, and well organized. This text is more inviting than other digital resources because of the visual design system in place.
Consistent tone of text and organization of information.
The division of content into small, clearly labeled and organized sections makes it easy to approach, navigate, and understand.
Well organized, clear structure and easy to follow. Both the written text and the visual design facilitate a clear hierarchy of information and digestible content.
Easy to use interface.
(Did not find any grammatical errors.)
The text is not directly insensitive or offensive, but examples of artwork by BIPOC are limited and presented from colonial perspectives. This is not a problem stemming from this book alone, rather the traditional Western perspective of recorded art history, theory, and criticism. However, this text also misses the opportunity to address cultural appropriation. In a section titled and devoted to "Appropriation" (Chapter 11), the only perspective offered is that appropriation is a "legitimate way" for artists to "re-contextualize" images. The singular artist example is photographer Sherrie Levine. To devote a section to appropriation, and yet leave out cultural conflicts entirely, misses an incredibly problematic aspect of appropriation in both the historical and contemporary landscapes of art and design. This is a critical discussion that belongs in the classroom, and a disappointing absence in this text.
The typography, image formatting, and layout system do a nice job of keeping information easy to read and navigate.
Reviewed by Talicia Honkola, Art Instructor, Mesabi Range College on 6/25/20
The textbook is comprehensive, offering topics on elements and principles covered in my course. In my opinion the first half would work better to introduce students to visual art. The book is arranged well and is easy to comprehend. read more
The textbook is comprehensive, offering topics on elements and principles covered in my course. In my opinion the first half would work better to introduce students to visual art. The book is arranged well and is easy to comprehend.
Reviewed by Marla Sweeney, Adjunct Instrcutor, Middlesex Community College on 6/17/20
The text is a good introduction to art and art history . It is not a chronological art history text but covers several periods, art forms and ideas related to understanding art. read more
The text is a good introduction to art and art history . It is not a chronological art history text but covers several periods, art forms and ideas related to understanding art.
The text is well researched and unbiased.
Although examples of art from many periods are addressed the final chapter on Ethics includes the most contemporary art examples. The text is arranged in a format that would allow updates to be easily implemented.
The text is written in clear understandable prose. Each chapter ends with an overview of key concepts, vocabulary and good test questions on the material.
The text is consistent in framework and terminology.
The text is organized in consistent module format. The format introduces each chapter with learning outcomes and a brief introduction. Each chapter ends with key concepts, vocabulary and good test questions as a review of the material.
The text is organized logically and the chapters are based on clear topics.
There are no navigation issues with the text or the display of image examples.
The text gives examples of varied types of art from diverse cultures. There are good visual examples from historical to contemporary.
This is a good introductory text to art. I feel it would be a good accompaniment to a chronological art history text. It addresses topics that may not be covered in other art texts as fully including a definition of art, the distinction between fine art and craft, art and identity and ethics in art .
Reviewed by Julia May, Assistant Professor, University of Virginia on 5/7/20
The authors organized the text effectively, considering the amount of material covered (see above). I appreciate how the authors include a set of learning outcomes at the start of each chapter and have "tests" throughout as well as "key concepts" and glossaries.
My only concern is that there is no index, nor is there a bibliography (unless I missed them).
Reviewed by WangLing Chou, Associate Professor of Art, Louisiana College on 4/30/20
The text is comprehensive, offering a wide range of material on the subject. Several of the chapters--mostly the latter ones--are more conceptual and/or philosophical and while they would be excellent for Art majors or upper level students, they... read more
The text is comprehensive, offering a wide range of material on the subject. Several of the chapters--mostly the latter ones--are more conceptual and/or philosophical and while they would be excellent for Art majors or upper level students, they would not be as useful for a general education Art Appreciation course. Still, many of the other chapters are more than sufficient in terms of comprehensiveness. In terms of an index or glossary, neither are present at the end of the book; however, at the conclusion of each chapter, all vocabulary from that chapter are listed and defined. An index and the end of the text would be helpful.
No inaccuracies were detected in the text. The book is unbiased except that is obviously favors a greater understanding of art, such as at the end of section 1.3.2. Chapter 11 briefly deviates from the text's usual objective tone, calling on the need for both society and artists to have a particular understanding of one another.
Even with the later chapters that touch on more recent phenomena in the art world such as identity and ethics, the material in the text is written in a way that it will be relevant for an indefinite period of time. Updating content should present no problems in terms of ease of implementation.
The text is easy to read and would be accessible to college students. All specialized terminology are conveniently in boldface type and are defined both in-chapter as well as in a section at the end of the chapter. The prose is not clinical and dry but is often inviting, making use of an inclusive third person perspective and sometimes directly addressing the readers with "you."
The text is largely consistent. One area to improve might be in the learning outcomes at the beginning of each chapter. While many of verbs are measurable such as identify, name, analyze, distinguish, explain, etc., the verb "understand" is used frequently in the outcomes and is not measurable based on Bloom's Taxonomy of educational objectives.
All chapters are divided into smaller, easily identifiable sections, ranging from anywhere to 5 up to 12. Most sections within chapters are only a couple of pages. Understandably, some sections are significantly longer, but multiple images can be a contributing factor to the increased length. The text does reference itself (i.e. "this text," etc.) on occasion, but such references are minimal.
The text is well organized, both in terms of the arrangement of chapters, as well as the divisions within the chapters. The text begins generally, moves to historical, practical, and knowledge-based content, and finishes with conceptual/philosophical content.
Interface rating: 3
One issue of concern is that in Chapter 11, every other page is incorrectly labeled at the top as "CHAPTER 10: ART AND RITUAL LIFE." Such a mislabelling could confuse readers. Also, the justified text is generally not a problem, but the inconsistency in spacing between characters is sometimes problematic. For example, the first line of the last paragraph on page 19 includes no spacing between any of the characters, making the sentence almost unreadable. Finally, while the images graphics are relevant and helpful, the text as a whole feels cramped and could use some negative space--more white space around images and graphics.
Few grammatical errors were detected. It should be noted that the writers employ all three points of view--often writing in first person. Such an approach likely makes the text more accessible to college readers. However, a small issue that arises is when the writer first mentions "the viewer," singular, but subsequently uses the pronoun "we" (plural). This agreement error was only noted a couple of times on page 14 and may or may not occur in other places. A simple fix is to change "the viewer" to "viewers."
The text does an excellent job on covering a broad spectrum of cultures, ethnicities, and backgrounds. At no point could any content be misconstrued as culturally inoffensive, as the writers did a good job in remaining objective in presenting the facts. For example, the section on The Dome of the Rock in Chapter Six is a sensitive topic, but the writers treated it with historical accuracy and cultural and religious sensitivity.
Even though several chapters are above and beyond what I need for my gen. ed. Art Appreciation course, I would still find this text useful.
Reviewed by Alexis Rusch, Adjunct Instructor, Oakland City University on 3/30/20
This book is easy to comprehend. I do think the first half is better than the second. There is no index which I do find useful. In the area of visual elements and principles of design, I do wish they went more into depth. read more
This book is easy to comprehend. I do think the first half is better than the second. There is no index which I do find useful. In the area of visual elements and principles of design, I do wish they went more into depth.
I find the information presented to be accurate.
The contemporary art could easily be updated to keep this as a current and relevant text especially since links are used.
I do think the first half of the book is a bit more clear than the second half. When teaching, I find it useful to have just 1-2 examples of art for each idea/concept I am discussing. The second half almost gives too many examples of some ideas and becomes confusing for students.
The book has an overall good and consistent structure. The terms being given at the end of each chapter are good and easy for students to find and study.
The organization of the chapters and subheadings is logical and makes sense. This book is easy to break up into small sections of readings for students.
I would consider the organization the best thing about this book!
All the links worked! The quality of images and text for those links varied from website to website.
No grammatical errors observed.
Examples of artwork are given from all over the world. Although the examples and content is heavy on Western Art, there is some reference to Non-Western Art. I did not find anything culturally offensive.
Closest thing you will find that is free to use for an art appreciation course. I would not use this as my only book for the course but would use it and have some online resources to supplement areas such as visual elements and principles of design. I do feel like this book relies heavily on European art as examples.
Reviewed by Kimberly Jones, Associate Professor, Sweet Briar College on 1/29/20
While the text is relatively comprehensive, I wish that it would have cast the net wider in terms of art forms to include a more extensive coverage of film, video games, textiles, typography, etc. Nonwestern art is included, but I would have like... read more
While the text is relatively comprehensive, I wish that it would have cast the net wider in terms of art forms to include a more extensive coverage of film, video games, textiles, typography, etc. Nonwestern art is included, but I would have like to have seen more.
I do wish the authors would have expanded their discussions a bit more. In their attempt to be succinct, a choice, I imagine, made to keep the reader engaged, I'm afraid some important content is lost.
Additional information in the captions is also needed. Important facts, such as year, medium, size, etc., are not included.
I did not identify any errors. It appears to be unbiased.
I appreciate that the text stresses, right from the beginning, the importance of images in contemporary society. Asking the question -- how does Bouguereau's work relate to today -- is a good way to connect past art to the present. I do wish it would have given more examples though of new media art. I thought this was a lost opportunity to add relevancy.
I believe the text is organized in a way so as to easily implement updated material.
The style of writing is much more readable than other textbooks I've used. I believe today's students will find this style more accessible and will therefore be more likely to actually read the text. While the authors acknowledge art history's (and presumably their own) use of jargon, which they argue is "unavoidable" in any discipline, they avoid the use of unnecessary jargon. Key vocabulary words (jargon if you like) relating to art and art history are clearly and concisely defined.
I found the tone and style to be consistent throughout.
I very much like the way the text is organized. I appreciate that blocks of text are short. I think it would be easy to organize this text anyway you like when teaching, although the flow, the way one chapter leads into another, is nice, so I personally would not change it. The text is easily customizable, in my opinion.
Overall the interface is fine, but it is pretty basic. Extra features, like allowing users to zoom in on pieces, or adding arrows to specific parts of images under discussion might make this more accessible and interactive.
I did not identify any grammatical errors.
I did not find the text to be culturally insensitive.
I was surprised that the text did not take advantage of its online format to include links to videos, especially when discussing various techniques. The different printmaking methods, for instance, are much more easily understood when demonstrated. It could also have included actual videos in its discussion of video art and performance art, rather than a link to a photograph.
While I do see room for improvement, I appreciate what this text has to offer. I may even consider adopting it for my introductory course.
Reviewed by Mary Shira, Instructor, James Madison University on 1/8/20
This is not a book I feel I could adapt in its present form in my course, Art in the General Culture, a general education course designed to introduce students with little or no background in art. While it contains a wealth of information that I... read more
This is not a book I feel I could adapt in its present form in my course, Art in the General Culture, a general education course designed to introduce students with little or no background in art. While it contains a wealth of information that I can adapt within my course, it is not laid out in such a way as to communicate new concepts, such as the elements and principles of design and the history of art following a timeline that is easily followed by novice students hoping to grasp the major concepts and apply them to their lives in a meaningful way. My biggest concern is with the layout of the content as it is. In broad terms it does introduce a wide range of cultures and artforms which is wonderful but would be overwhelming to my population. Early chapters contain media spanning history and techniques (architecture, photography, craft and fine art) that need defining before the more complex concepts such as aesthetics and criticism can be attempted
I found only two minor errors while reading the text: Page 123, in the hypertext notes mid page Beckmann has an “r”, Breckmann before the link. And in the discussion of the Palette of Narmer on page 239 it states the image on the back of the palette shows Narmer with the crown of Lower Egypt, when in fact he displays both Upper and Lower Egypt’s symbols as he is “The Great Unifier”.
The inclusion of contemporary art is well placed throughout. I do feel the inclusion of so many art forms and cultures throughout most chapters is confusing however. For example, Chapter 2 attempts too many media such as painting, printmaking, sculpture plus the elements and principles of design making it hard to absorb in a meaningful way.
Most of the technical information is well presented with good visuals to back it up. I particularly appreciated the inclusion of definitions for artist made prints versus reproductions to be helpful for students to understand the difference. As an artist and college instructor myself, I can easily follow all the information but my students would be challenged to absorb much of the technical aspects of the art presented as it jumps around in application from selfies and digital art to Renaissance to ancient works. The chapter on architecture, often student’s favorite section, is too broad and yet has little nineteenth and twentieth century urban examples such as the significance of The Crystal Palace and the contribution of Le Corbusier.
Yes, the text is consistent throughout in terminology and framework. It is as I have stated however the framework that doesn’t work for me in my class setting. I believe the user would be better served by grouping less broad concepts within chapters, for example, photography. By discussing its history from the Camera Obscura to the iphone, students could see how it affected the history of artmaking while understanding also the development of criteria for judging it as an artform in the twentieth century. It is something students today will need to develop for computer generated art in their lifetime.
Modularity rating: 3
I don’t agree that the text can be easily absorbed or supplanted into an existing course as it is initially challenging in the early chapters to define art without giving students the tools to make these decisions and injects historical imagery again without a way for placing it in a useful framework. Chapter One in particular, is heavy on theory and would lose many of my students at the outset. Discussions of labyrinths and terms such as circumambulate would be off putting and unnecessarily confusing. Chapter Two is too ambitious and would serve students better if it followed a thread beginning with Gestalt and following up with two-dimensional media and only later addressing three-dimensional media such as sculpture and pottery.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 2
Here is the rub, I am confused by the organization here. I would like to adapt portions of the text but the way topics are presented makes it challenging. The text contains a wealth of information but the format and general layout of the chapters makes it a daunting task to absorb it into my course. I do really feel that a timeline of some sort coming later in the text is essential for students to place work in its social, political and historical context. All art can only be appreciated fully beyond its formal aspects when the viewer has access to the context in which it was created. The format of this text confuses that by jumping around culturally and historically too much.
I do feel the inclusion of maps to place the art in the world would greatly advance comprehension. I don’t think students will likely access links referenced within the text though I appreciate the concept so that can create a navigational problem if the art is essential to understanding the concept. I also found the diagram used to explain the Lost Wax method of casting to be poor.
Only the one I mentioned previously. All in all the writing is engaging and easy to follow
If anything, I think the effort to be inclusive of cultures is overdone. Women could be better represented, though again within the framework of the text it is more challenging since their contribution has historically been ignored until the modern era.
I really enjoyed the text. I made copious notes and underlined passages on many of the pages that I will absorb into my own course as the information expands topics I touch on throughout the semester. I do feel it would be a monumental task to adapt this book to my course, given the population I deal with in an introductory course on art history and culture. In addition, my course concentrates on Western culture, and so references world art only in so much as it has influenced that aspect of our culture. I am not quite sure what sort of student your text would address in so much as it is technical and expansive while not really addressing the needs of the novice in art history. I think it would be better suited for an aesthetics course than my introductory one. The class I teach is designed to help students develop a cultural understanding and appreciation of the visual arts, such as architecture, painting, sculpture and design. Lectures, videos, projects and discussions focus on issues related to the practice and techniques of creating and valuing visual imagery. Special emphasis is given to developing an understanding of the language of visual art and design, learning the basics of art criticism method, and gaining an overview of the history of the visual arts with a priority given to contemporary works of art. .
Reviewed by Billi London-Gray, Adjunct Assistant Professor, University of Texas at Arlington on 12/30/19
The text is comprehensive, providing an introduction to design concepts and terminology as well as an historical survey of (mostly Western-centric) ideas around the production and interpretation of art. Topics like ethical considerations in art,... read more
The text is comprehensive, providing an introduction to design concepts and terminology as well as an historical survey of (mostly Western-centric) ideas around the production and interpretation of art. Topics like ethical considerations in art, originality, meaning and materiality, and community purposes for art are given thoughtful treatment, encouraging multiple viewpoints for class discussions. The book lacks back matter — no comprehensive glossary, index, image list, or bibliography. As an e-book, this can be solved with a CTRL + F search. If printed, it’s a limitation for users.
I did not find any factual errors in the text, but I did find some errors in image captions (ex: Figures 7.5 and 7.36) and spellings. I encountered some variation from conventional transliterations of artist’s names (ex: Do Ho Suh is spelled Do Ho Su, page 92, and Wassily Kandinsky is spelled Vasily Kandinsky, page 106). I also encountered numerous broken or misdirected hyperlinks. These broken links were especially disappointing when they failed to show works by underrepresented artists, such as Jaune Quick-to-See Smith (page 168).
This text offers a lot of relevant material, especially given that it’s free for students to access. The content could be more up to date, with examples by new media, performance, and social-practice artists. I would also find examples by contemporary mid-career and emerging artists instructive and relevant.
The bolded key terms and glossary in each chapter are very useful. The prose is clear but drifts between accessible and academically clunky. I wish the images of artworks were captioned with the date completed and, where applicable, an indication that the artist is unknown rather than omitting artist information. For most images, the date was provided in the running text, but this requires re-reading and could confuse context for students who don’t know what to look for.
The text is internally consistent with respect to terminology used and the framework of each chapter. There is some inconsistency with including locations of architectural sites in image captions.
The text is divided into chapters that can be digested in one reading assignment or broken into shorter assignments. The divisions are clear and logical. This makes the text scalable for classes that meet multiple times per week, once per week, or on accelerated schedules. Individual chapters (for example, Chapter 2 on form and composition, or Chapter 4 on formal and critical analysis) could also be assigned as stand-alone readings, in lieu of adopting the entire textbook for a course, especially given the inclusion of a glossary within each chapter.
The organization of this text builds progressively on concepts chapter by chapter, but is not self-referential in a way that requires reading the book from cover to cover. The structure of each chapter, with learning objectives followed by content followed by a recap, comprehension questions, and key terms, provides a clear framework for students to prioritize information and test themselves. It is also conducive to reflective and indirect instructional activities in class or online.
The interface is clean but has some leading issues in the text, where letters are slightly stretched, slightly squished, or cut off below the baseline. The multi-decimal section numbering system is visually noisy and, in my opinion, no more useful than section titles and page numbers in helping students find reading assignments or refer to passages. In general, page layouts are tight, with minimal margins between images and text. This seems like a decision driven by printing concerns (minimizing page count), but additional white space would improve readability. The text worked well with the text-to-speech reader in Google Chrome.
I encountered numerous typos and grammatical errors, mostly in the form of missing punctuation, missing words, missing letters, and awkward sentence constructions. None of these obscured the author’s meaning, but it could use another round of proofreading.
This text presents more than the usual suspects found in introductory art appreciation and visual literacy books. Images by pre-modern American and European women artists are refreshing and demonstrate efforts to go outside the traditional canon. That being said, it could still be much more representative and inclusive. For example, the first chapter addresses the definition of art but approaches the debate through the ideas of notable white men without acknowledging the hegemony around this question. No examples in this chapter are truly contemporary, with Maya Lin’s Vietnam Memorial, completed a generation before today’s students were born, being the most recent image example. This trend continues throughout the book, where the vast majority of text and images are devoted to long-dead Western artists (mostly white European and American men) and static forms of art (mostly painting and traditional sculpture), with good representation for Ancient Near East art traditions, less for Eastern traditions, and little consideration for new media or performance art, artists of color, and global south art and artists. Good opportunities are missed: while there’s more than a page of text devoted to Kehinde Wiley, the image of his work is accessed via hyperlink rather than embedded (pages 221-222) for effective appreciation of his art-historical reference. In the section “11.5 Ethical Considerations in the Collecting and Display of Art,” Nazi looting is criticized but there’s no mention of the colonial plunder that still resides in American and European institutions. It would be great to see a more inclusive second edition of this book.
While I have listed specific areas that need improvement, I am thrilled that this book exists as an accessible, free, and user-friendly resource for students and instructors. Its shortcomings are far less than other texts I’ve used, and its virtues are numerous, especially given the flexibility to make immediate improvements using the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license. Many thanks to the authors, editor, and publisher who have generously shared this work.
Reviewed by Rick Lostutter, Associate Professor of Art and Design, Hanover College on 12/20/19
This textbook is a fairly comprehensive primer on art from the approach of purpose, materials, structure and meaning. It provides readers with the foundational tools of understanding how to more formally assess art and the creation of many... read more
This textbook is a fairly comprehensive primer on art from the approach of purpose, materials, structure and meaning. It provides readers with the foundational tools of understanding how to more formally assess art and the creation of many different kinds of visual representation. Having the "test yourself" and key terms sections at the end of each chapter allows the reader to develop a language and vocabulary that applies across the breadth of the nature and definition of visual art and helps solidify the elements presented within each area of art exploration. There are plenty of cultural references to the context of historical examples as well as the impact that art and design has had on society and the importance of art as a timeless reflection of the world. The structure of the book is an easy introduction into many different aspects of the study of art. I really enjoyed the inclusion and focused chapter on architecture within the greater context on art.
Having read through this text several times, I find it to be very accurate from an art perspective, technical reference and grammatical work. Statements made throughout the book are presented in a way that is supported with referenced examples and well agreed-upon art and design principles. The evaluation of art is traditionally an objective process, yet this text allows for expert opinion and fact to reside together in a way that allows for appropriate and open evaluation by the reader. So many art texts try to push specific agendas pertaining to narrow views of what art is or is supposed to be and this book avoids that in a very skillful manner.
The references and visual material presented in this book are of generally-accepted and representative examples of historic art. I would have liked to have seen some more contemporary art and artists represented as a comparison to art that has traditionally been used to illustrate the principles of art and conceptual design work. Given that this is a digital text that can easily be updated, it seems to provide a platform for having up-to-date and even current artists and their work represented. Students need to see that current work is being created that adheres to the traditional standards of the historical works referenced through the ages of art instruction. Having said that, the works used do not represent an obsolete view on art evaluation and instruction.
The reading acuity and age-appropriateness of the terminology, vocabulary and description are adequate and what I would expect for a college-level resource material. Again, the terms at the end of each chapter provide an easy reference tool for any language that a reader might not be familiar. It not only helps in the reading and retention of the material, but creates a great study guide for review after the reading of each section.
Having read many co-authored texts on specific subjects, the voice of the work is consistent and reads as though one author was the source for the entirety of the book. This is important, especially for a subject such as art, so the reader can begin to develop their own assessment of the topic without struggling through many different styles of evaluation.
The sections and chapters of this book are appropriately divided in a way that makes the subject digestible. The pacing of each chapter is segmented so that the ideas and concepts are easily incorporated into the overall topic of that chapter. This makes it a much better tool for grouping concepts from several different chapters into a lesson that requires many different elements to work together as a conceptual theme. Some chapters or sections may not be as relevant at particular times within a structured curriculum segment and the format allows for easy coordination of those individual concepts that will seamlessly integrate a cohesive lesson plan.
The organization of the topics in this book are clearly stated and work as a logical progression from one theme and area of art to another. Having said that, the topics can stand alone as needed for any given presentation within a class lesson.
The interface of this book is very clear and easy to use. Locating relevant topics from the table of contents and then quickly finding those topics within the text was thoughtfully accommodated with the section titles at the top of each page.
I have not found any grammatical errors in my assessment of each segment of this book.
Art is a discipline that has traditionally focused on the western culture and therefore has not been a very inclusive, historical representation af all cultures and races. This text does an adequate job in presenting examples that bleed outside of the traditional western historical examples of other texts. I would have liked to see more diversity which could have come from more contemporary examples of art. Given that, I did not find anything that I felt was culturally insensitive or inappropriate.
I would highly recommend this book as a great introductory supplement to any foundational art course that is meant to provide students with a base-level understanding of the complexities of art and design as a visual exploration. This should be incorporated as an essential text for students who are beginning their journey of the study of the creation of art and design. I could see this as a supplement to an introductory art history course as well.
Reviewed by Mike Morelli, Director Entertainment Management, University of Montana - Missoula on 12/19/19
This book provides a nice broad survey of styles, periods, artists' and types of art. read more
This book provides a nice broad survey of styles, periods, artists' and types of art.
The content is accurate for the vast majority of the book with few technical and grammatical errors. That being said, the errors (which appear in the second half of the book) have drawn notice from some of my students.
As an introduction, this book provides an excellent basis for discussion with students. The chapters and content are relevant, presented in a clear concise manner, and are supported by facts.
I appreciate the clarity of the material and the structure of chapters as well as the tone of the book. Color images with good labels and attribution make it easy to discuss and research further for students.
The text consistently presents concepts with supporting images and documentation in a logical and straightforward manner.
Good modularity for the most part. Given the way in which artists'/styles/concepts are presented in chapters, by necessity some ideas can only be examined contextually, and require a broader framework for understanding. The authors to a great degree provide that background and break down segments through titling with numbers to show flow while creating "bite sized pieces".
Excellent organization. Well laid out.
A logical combination of text, images, and titles delivered in a visually pleasing way.
As noted previously, few grammatical errors although enough to draw comment from students.
This text explores art as expressed by a wide variety of artist's with differing races, ethnicities, and backgrounds in inclusive and thoughtful ways. While I have had students react strongly to images or concepts in the book, (i.e. Hindu Swastika) it is not an objection to the manner in which the material is presented but often a strong initial personal reaction to a specific image, which is then discussed contextually in a manner that is both sensitive and dispassionate.
This book has worked well in several first semester Introduction to Art courses. It's clear, concise, and well written with logical and consistent organization.
Reviewed by David Riep, Associate Professor, Colorado State University on 12/10/19
I found this textbook to be very comprehensive. As one can quickly grasp from the table of contents, this book covers all of the major introductory topics for approaching and discussing art and visual culture (as well as some focused topics that... read more
I found this textbook to be very comprehensive. As one can quickly grasp from the table of contents, this book covers all of the major introductory topics for approaching and discussing art and visual culture (as well as some focused topics that are not typically found in "Intro to Art" texts). The authors organize the information in a manner that effectively builds upon previous sections, while also maintaining the ability to assign specific chapters and sections independently. Although this is not meant to be an art history text, I was impressed at how the content engages with numerous art historical methodologies (formalism, semiotics, social art history, feminist art history, iconography, connoisseurship, and even some key points coming from Hegel’s theories) without becoming cumbersome. The images of techniques and processes are also helpful (i.e. relief wood carving), as are the detailed explanations of media (i.e. what is egg tempera?). The key terms found throughout the text are also very helpful and are perhaps more useful at the end of each chapter, rather than a comprehensive glossary at the end of the book.
While it can be difficult to address global art production with an unbiased voice, I found the overall content to be thoughtful and generally balanced. I appreciated the broad questions posed to the reader, and found them to be very interesting and engaging (i.e. Why do we make art?, What defines an artist? What is the difference between Art V Craft?) as they provided the reader with the opportunity to further explore such topics. I also appreciated the authors’ openness regarding the strengths and limits of various perspectives and explanations throughout the text. While the discussion of some specific works are at times perhaps too narrow, and draw upon singular, declarative statements in order to support a point, the authors generally promote critical thinking and exploration of broad concepts. It is perhaps noteworthy to mention that some chapters were more effective in presenting a global perspective than others, although this is addressed in more detail below. Overall, I found the content to be accurate and well-researched.
One of the strengths of this text centers on the timely content, which references modern technology and concepts, as well as popular culture. I also really like the ability to pull up supplementary images throughout the text by clicking on imbedded links, although I found several of them in need of updates. I appreciated the inclusion kinetic art and new media within the comprehensive list of formal elements for 2D, 3D, 4D art, and found the overview of Aesthetics to be intentionally geared toward contemporary readers. There were many sections of the text that seemed to be specifically aimed at addressing current trends in art production and interpretation. For example, I enjoyed the dialog regarding architecture’s response to changing social development and advances, as well as the discussion in Chapter 8 which ties visual content to contemporary culture (popular media and activities such as genealogical websites, etc.). Chapter 9 equally engaged with the role of visual culture in contemporary societies by addressing Art and Power (propaganda, both symbolic and documentary), and offered an interesting dialog on building visual literacy. This chapter addresses the role and limits of media in recording or presenting images of power, and also addresses how imagery can appear “objective,” but can often contain specific messages. I found this to be extremely relevant, especially given the role of visual imagery in popular culture and social media. The chapter on Ethics is also quite relevant, and highlights the perception of visual culture and how it changes over time. Finally, the discussion on appropriation is very timely, as is the component that addresses museums. The questions posed regarding collecting and display practices are often left out of introductory texts, but are extremely relevant in contemporary times.
Overall, the text is approachable and clear in tone, and effectively guides the reader on how to best use this resource (i.e. explaining how the book will present content, and where the reader can expect to find various components). I found it to be a very useful text that presents complex concepts in a manner that non-specialists will easily understand. I also found the various case studies that are used to guide the reader in applying theories and methods to be very effective. The text presents content in a clear and concise manner, and I found the “Test Yourself” questions to be well constructed, approachable, and effectively open ended (when appropriate).
Another strength of this text is its consistency in presenting and disseminating content. The authors developed a number of components that are found in each chapter which draw the reader's attention to recognizing and applying key concepts. I found each chapter to be clearly and effectively structured, with appropriate subheadings and use of bold text to highlight important ideas and terms. This made the text very easy to navigate. I also found that the overall content maintained a consistency in tone, in spite of the fact that multiple contributors were working on any given chapter. The text is very clear and approachable, yet engages with complex theories and concepts.
It would be very easy to assign portions of this textbook throughout a teaching term, as most chapters can function as independent units, while also effectively engaging with other sections. I like the overarching themes of each chapter, which could easily be realigned as needed, and the fact that the subunits are of a manageable length. This book offers instructors a great amount of flexibility.
The book’s overall organization is clear and concise, with each chapter presenting measurable learning outcomes and ending with practical applications of concepts. I also found the subheadings to be very thoughtful in expounding upon the overall topic in each respective chapter. It is very easy to navigate through the various subunits, and the overall content is very appropriate in building an effective discussion of the various topics at hand.
While I really like the use of imbedded links to view images and expound upon concepts, some of the links did not work and need to be updated. Regardless, I like the fact that the use of links allows for the text to remain current, and to highlight contemporary content, developments, and artists.
I did not find any grammatical errors.
The text offers a sound explanation of artistic concepts, and makes an effort to present a global perspective. I appreciated the attempt to use both recognizable images from the Western canon as well as lesser known works, although some chapters were more effective in presenting a global perspective than others. For example, I was intrigued by the in-depth discussion / case study in Chapter 3 covering media in the eras of Constantine through the Ottonian Empire, although it could have been balanced by non-Western case studies (for example, the use and significance of metals in African cultures). Chapter 4 addresses formal analysis, although the overall discussion is largely focused on degrees of representation in the arts. This seemed to present a very "Western" perspective of artistic development, and could perhaps benefit by highlighting western and non-western objects, as well as naturalistic and abstract pieces. I especially liked the focus on “Interpretation” and highlighting how meaning is formed from multiple perspectives (the individual, society, and the impact of time), although I found the section on “Evaluation” to be rather narrow and perhaps unnecessary (what, for example, is the “verdict of history” that determines great art? Who / what determines this "verdict"? Why are museums placed at the center of this discussion, along with the suggestion that a work’s presence in a museum determines its artistic value? What do the authors mean by the phrase “best art”?). I appreciated the discussion of conventions in Chapter 4, and how the text traces them across cultures. However, when addressing cultural style, it might be helpful in some cases to note the role of "time" (the Western examples were presented according to how various artistic conventions developed over time, while many of the the non-Western examples, such as the Ancient Near East, are not given this same treatment). In a similar manner, the topic of individual artistic style could also benefit from exploring non-Western “anonymous” artists through a brief discussion of the history of collecting, and how one can trace the hands of unknown artists in the same way that Western artists have an identifiable style. I appreciate the inclusion of female artists such as Lilly Martin Spencer and Frances Palmer in Chapter 5, as well as the addition of a few non-Western pieces, but the chapter is still quite heavily Western, as is Chapter 6, which maintains a Judeo-Christian focus. This chapter could perhaps be broadened by engaging with diverse belief systems. This seemed to be rectified in numerous other chapters. For example, Chapter 7, which focused on architecture, was more intentional toward representing global perspectives and works of art, which I found to be very helpful in understanding global art production. Along the same lines, I found Chapter 8 to be very effective and inclusive in presenting concise notions of "the self" within expanding social spheres, and in discussing individual identity/gender, and external influences such as economics and class. I also appreciated how Chapter 10 highlighted global engagement with sacred structures, sites, rituals, and performances, as well as their significance.
The open source text "Introduction to Art: Design, Context, and Meaning" is an impressive resource that addresses the foundations of approaching, discussing, and understanding art through both historical and contemporary lenses. The authors took on an impressive amount of work to create a textbook that engages with contemporary topics, while laying the foundations for effective visual literacy.
Reviewed by Elizabeth Morton, Associate Professor, Wabash College on 11/6/19
This text covers almost all of the bases one would expect for an introductory class. Its biggest problem is the lack of inclusion of non-western examples in its presentation. The European art tradition dominates the discussion, with some... read more
This text covers almost all of the bases one would expect for an introductory class. Its biggest problem is the lack of inclusion of non-western examples in its presentation. The European art tradition dominates the discussion, with some allowance for Chinese and Japanese. You look in vain for references to African, Latin American, Oceanic, or indigenous art, even when they would be an obvious choice given the ongoing discussion.
This text has been written and edited carefully by veteran teachers. I did not see any errors or the use of suspect research
I believe the thematic approach to the material is far more relevant to today’s student than the classic approach based on historical progression. The chapters are judiciously chosen and are placed in a logical order. Again, the only thing old-fashioned here are the relentless insistence on using the western canon as the basis of discussion.
This text has been carefully written and has been painstakingly edited. I particularly thought Ch 2 was a standout in the way it presented the basic categories of art. At many points I berated myself for failing to present material so clearly in my own classes!
Once again, it is worth stating that the editing is of admirable quality. A lot of thought has gone into maintaining similar terminology and reference points as the chapters progress, even though they have different sets of authors. The use of keywords is also a strong feature, since many of them recur as the book progresses.
A definite strength of the text. Very easy to divide up the text by week, class, group, etc.
The editor is to be commended as the text flows smoothly from on section to another.
I liked the yellow bars on the right side which assist in moving between chapters. The “find” feature works well, and overall it was easy to use the extext. This is very user-friendly.
Once again, the editing here has been thorough and painstaking
Chapters 8-10 in particular are disappointing in that they offered a chance to move away from a traditional, Eurocentric approach. While the authors do include some non-western examples as they proceed, they still rely too much on European art. Chapter 11 is also disappointing—with non-western art having been plundered systematically for a long time and its placement in First World museums being increasingly problematic, it is not even mentioned.
Well done on a very user-friendly text. However, some extra work in terms of broadening the geographical base of examples is definitely in order
Reviewed by Jade Hoyer, Assistant Professor of Art, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 10/25/19
As other reviewers have noted, the text covers elements of design, rationale, context, and impact for and of making art. It’s a lot for a work to cover, and is generally successful, if sweeping, in doing this. I didn't note an index. The... read more
As other reviewers have noted, the text covers elements of design, rationale, context, and impact for and of making art. It’s a lot for a work to cover, and is generally successful, if sweeping, in doing this. I didn't note an index.
The exception to this for me is Chapter 2, which is essentially a studio class in a chapter (a rapid-fire discussion of all artistic media, design elements, design principles, and color theory for good measure. This chapter contains no less than 150 "Key Terms!"
I found the content to be generally accurate.
It was frustrating that most of the work’s contemporary examples were hyperlinked instead of embedded as images and potentially impermanent. Though likely a result of copyright issues, to present most contemporary accounts as a block of black text visually diminishes their importance. (It’s also likely that students won’t bother clicking the links.) Would like to see links changed to more persistent format.
With regard to writing, the work is generally clearly written, and approachable to beginning students. The tone of the writing is quite generous- the first chapter explains how art is ultimately about the viewer’s interpretation and adds “but we do have help if we want it. People who have made a disciplined study of art can offer ideas about what art is important and why.”
With regard to imagery, I thought that no dates, media, or sizes were listed for the works to be a big miss.
The work also had a tendency to bounce around. I felt many sections leapt centuries and continents (and often both centuries and continents) within a single page with transitions akin to “meanwhile in Russia…,” or “a few hundred years later.” I appreciate that many of these about faces were connected to efforts to be inclusive, but it presented a dizzying narrative, that was made more confusing for lack of timelines or context (like dates!) provided in the imagery.
Writing seemed consistent throughout. However, I found instances of sloppy formatting: definitions were often in bold a few letters or even a word beyond the word being defined. Beyond this, I could imagine this formatting being confusing for students as words that were in bold indicated definitions and sometimes, but not always, were designated as Key Words at the end of each chapter. For example, on p 63, four terms are defined in one paragraph (unity, variety, conceptual, interval, scale, proportion), but only two words (interval, scale) are designated as Key Words. I find using a different formatting technique in this case, such as color, would be helpful in assisting students in identifying Key Words earlier at the beginning of the chapter.
I enjoyed this aspect of the work! I would especially use the final chapters for my classes (such as Art and Power, Art and Ethics). I found these chapters to be thoughtful and relevant to students, and especially appreciated their being structured around case-studies.
I appreciated the general flow of the work beginning from simple definitions “what is art?,” “who is an artist?” to contemplating identity, power, ethics, and controversies in artmaking, though some sections seemed redundant. Good summaries and questions to accompany the readings, especially later in the text.
Worked great for me! I also appreciated how the Hyperlinks took me to new works, and that I could return to my spot on the page when I clicked the back button. Please note Relevance section regarding links.
I found limited grammatical errors.
I appreciated the interweaving of Western and Non-Western narratives, though found that, especially if one were focusing on the imagery, that the works presented felt skewed Western.
Great resource- will definitely utilize sections in my teaching.
Reviewed by Maria Guzman, Instructor - Art & Art History , Peralta Community College District on 9/26/19
I found this book to be a good "skeleton" text for a variety of courses. I liked that it had chapters dedicated to both formal analysis (Chapters Two, Four, and Five) but also managed to include global perspectives (Chapter Eleven: Art and Ethics... read more
I found this book to be a good "skeleton" text for a variety of courses. I liked that it had chapters dedicated to both formal analysis (Chapters Two, Four, and Five) but also managed to include global perspectives (Chapter Eleven: Art and Ethics was especially thought-provoking). The themed chapters (Chapter Eight: Art and Identity and Chapter Nine: Art and Power) are relevant for any Art History course, and I use them for all courses, including World Art, Art 1, 2, and 3 (these cover the prehistoric to contemporary periods, collectively). The addition of Key Terms at the end of chapters was also helpful.
When I decided to use this text, my main concern was regarding whether the content would be easy to connect to my prior courses' designs. I used Henry M. Sayre's "A World of Art" and the Marilyn Stokstad "Art History" textbooks. Thanks to the chapter that discussed the general theories about what art "is" (Chapter One), and the clear language that mirrored Sayre's creative drives (found in Chapter 6, mainly), I easily transitioned to using this book for my course. Most recently, I have adopted it for Art 101: Western Art History and ART 103: History of Modern Art.
Inclusivity is consistent in the discussion of works from different cultures and geographic areas. I was impressed by the mention of postcolonial topics, and even the addition of 4-D in relation to formal descriptions. This is a text that has incorporated recent scholarly perspectives and new genres in art. I had fun adding OER readings about identity, especially, in order to complement the chapter in this text.
I have had feedback from students regarding the easy-to-follow format and text used in this book. I also find it easy to get through in a short amount of time.
Overall, the terminology was clear and consistent.
Yes. I usually remix the chapter order, based on what type/periods I am addressing in a course. Chapters One, and Two are great for the first few weeks. I save Chapter Four for the middle of most classes, in which we are beginning to do more art descriptions as a group. I use Chapter Six towards the end of the courses, where the class begins to conduct research and observe more creative drives and themes. I apply Chapters Eight and Nine based on the time periods, and how relevant they are the subject matter or styles covered in the course. I have thought about inserting Chapters Eight and Nine right after Chapter One in order to address the modern period and the growing individualism in modern art.
Chapter Ten is especially good for any ART 1, 2, or World Art course, especially (ART 101 or 102 as well).
I will be teaching a short-term course about Architecture this semester, and am excited to use Chapter Seven: Form in Architecture.
Excellent -- these are short, include many genres, mediums, and cultural styles in a sensible way. Usually, the chapters include a variety, and this enhances the global perspectives that the authors encourage. It also makes it easier to select works of art to focus on, if you are covering particularly modern or World Art, for example.
No issues with interface. The format is easy to navigate, and my only suggestion is to create hyperlinked headings for chapters in the Table of Contents, so that you could jump to the chapters a little sooner. Small suggestion, though. It's very well formatted and designed.
As stated in the Relevance section, this book offered good topics that were easy to connect to contemporary or recent studies in non-Western art (Global Art perspectives). See pages 5, 8, and 9 for a few points made about this text's open format and my review of The Met Museum's OER text, "Art in Africa". It was a compatible text and I would recommend "Introduction to Art" for its culturally-sensitive and unbiased perspectives, especially if building a course about global approaches to art. Read my summary here: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1cSG4MWFta-nE9yTgSC__QP22D2dHpYjsg9evVysBQFg/edit?usp=sharing
No additional comments.
Reviewed by Mara Pierce, Assistant Professor of Art Education, TRAILS on 9/16/19
This text covers several, if not all, the bases needed to fully appreciate art making processes, historical perspectives, variations, time periods, methods, criticism, purposes, associations, and artists. Each chapter opens with objectives and... read more
This text covers several, if not all, the bases needed to fully appreciate art making processes, historical perspectives, variations, time periods, methods, criticism, purposes, associations, and artists. Each chapter opens with objectives and concludes with an evaluative activity. The authors present varied perspectives that are appropriate to understanding the diversities that are encompassed in the art world. The images included are also significant and comprehensively representative. However, many of the images also depict the same imagery found in other books. Students reading this material need to also see work from a more balanced sampling of artist genders. The topic is discussed in Chapter 8, but not visual samples of women’s or other-gendered artists included there. I applaud the discussion of the Nazi art theft.
The text contains mostly accurate information, but could use further clarity. For example, if using Indigenous names, use tribal identifiers, such as Piikani for those who identify as Blackfeet. A piece of dance regalia is referred to as a “costume,” which elucidates the author’s limited understanding of the role of garb in ritual. While appropriation, as covered in Chapter 11, is an integral part of the contemporary artworld, it is also presented as acceptable and normalized. It should also be included that appropriation is not universally accepted and is fought by several artists today. For example, there was recently a court case by Ai Weiwei brought against Volkswagen for copyright infringement based on appropriation of his work used in an ad.
For a General Education class, there is no doubt that this text would work toward appreciation of art making, art history, criticism, and aesthetics. There is a great deal of insightful information that would be relevant to undergraduate students’ first exposure to the art world. Additionally, some points would be relevant to students who have been practicing in the art field already, as well as those who plan on teaching art at the K-12 level.
The authors have written using clear language and vocabulary that are appropriate and relevant to the early college student. However, it would be more effective to have the vocabulary listed at the onset of the chapter, as opposed to the end. In doing so, the students can reinforce learned words and make connections throughout the reading. It also acts as an introductory feature.
The flow and voice are consistent. Level of difficulty is upheld and relevant throughout, as well.
Each chapter in this text can work independently of each other. However, in being able to comprehend and apply information in some of the latter chapters, one would have needed to cover material, specifically, in Chapter 1 and 3-5.
The text is excellently organized. The authors began with the foundation of defining art through discussions of contemporary diverse purviews held. The organization is logical and would be in a manner that I would present in my course.
The text file is easy to access and navigate. The URL links are clear, as well. However, it would be helpful in supporting the learning to provide links on the images to their sources, as well.
There are no perceivable grammatical mistakes.
I found the cultural aspects of the text to be limiting. The authors touch on the fact that art is not viewed identically throughout the world, which I applaud given that this is a tremendous part of the art perspective today. However, there is also a need for greater underrepresented Indigenous discussion/examples. Between Chapter 1 & 2, for example, there is only one image of Aboriginal origin. Ch. 7 includes three architectural pieces. Consider Anasazi examples, such as Pueblo Pintado or Mesa Verde as part of early architecture. Chapter 10 discusses masks, but only examples one. There are thousands of cultural groups across the globe that use masks for purposes from theater to holidays.
The text is a good resource for basic understandings. It may be best served for an online course given that much of the relevant information is laid out in the text.
Reviewed by Stephanie Newton, Professor, Aims Community College on 7/26/19
The book could spend more time with processes of creating--the different types of paint, printmaking, etc. It seems to be very brief in introducing the elements and principles of art as well. Although each chapter has a glossary, it does not have... read more
The book could spend more time with processes of creating--the different types of paint, printmaking, etc. It seems to be very brief in introducing the elements and principles of art as well. Although each chapter has a glossary, it does not have an index, which I usually find to be helpful in textbooks. The images also lack some key information that is standard in other art textbooks--no dates, no dimensions, no media. I truly disliked that about the text.
While I appreciate the gender-neutral language of the text (craftsperson), I do not feel that it is totally error free and accurate. For example, the authors use the dated notion of "sympathetic magic" when discussing cave paintings, which is a theory, but is not widely accepted any longer. They also refer to cherubs or putti as cupids. Cupid is a specific deity. One really glaring problem is the use of "Eskimo" on page 270. They need to reframe the use of that term to indicate it is not an acceptable way of describing the Inuit or Yupik cultures.
The text has a nice mixture of old and new art, and examples of contemporary art could easily be updated. My one issue with the relevancy is that many of the contemporary works of art (and other examples they employ) are not pictured, but given as hyperlinks. Those links could easily be broken in the future. I understand that obtaining copyrights to those works could be prohibitive, but it's a distraction from reading the text to send students to a website to look for the example provided.
On page 208, paragraph three, the authors are referring to a conceptual artist, but they omit the word artist, and don't define what a conceptual artist is. They also often refer to historical styles of art without defining what that means. How are my students supposed to know what Beaux Arts or Art Nouveau are without some sort of explanation (p. 193)? On page 203, they mention the Franks, but don't explain who the Franks are. On page 205, they mention a tympanum, but don't define what a tympanum is, nor is it in bold (to indicate that it is in the glossary), although it is defined in the glossary. There are also some areas that are not very clearly written, such as paragraph 2 on page 202. On page 256, while discussing Chichen Itza, they discuss Quetzalcoatl but don't tie it to the pyramid in anyway at all.
Consistency rating: 3
I found the beginning of the text to be much more clearly written and compelling than the second half of the book. It provides almost too many examples of art to discuss an idea.
You could fairly easily rearrange the order of chapters or omit a chapter without needing the others to support the content. This for my class would be necessary in chapter 2, where bizarrely, they discuss processes before elements and principles.
It seems to be organized fairly well, although chapter 2 does have me a bit confused. It would also be good of them to introduce abstract vs. naturalistic earlier, perhaps in chapter 2.
Again, I worry about using so many hyperlinks in a text such as this. They could easily become dated or broken, leaving the reader frustrated. Some of the images are low quality, and some of the diagrams are very hard to see, so I am concerned about students with vision issues.
Grammatical Errors rating: 1
Oh boy! Again, I didn't start seeing major problems here until around page 200. Page 178, Fig 7.5, Skara Brae is misspelled as Sjara Brae Page 218, the word artist is missing after conceptual Page 235, Persepolis is spelled Persepholis Page 246: Iconoclasm is spelled as iconoclas Page 250: Bamiyan is spelled as Bamyan
I felt that it was very culturally inclusive, using artistic examples from around the globe, but perhaps focused too much energy on Christianity. Again, framing the use of the word Eskimo would be worthwhile.
There were some things I thought were really unique and wonderful about this textbook. The first four chapters had me very excited about the possibility of a OER book for my students. I especially thought chapter 3 had some valuable and unique ideas that would be super fun to share with my students. Chapter 5 is where it started to lose me. They discuss how important iconography is, but don't really give any analysis of specific symbols in a deep and meaningful way. They could have used the Merode Altarpiece as a platform to really dive deep into Christian symbolism, but only mention a few of the icons that are present. I know these are things that can be done in the classroom, but I was a little disappointed by the vagueness of their analyses and the overabundance of examples.
Reviewed by Michael Takemoto, Associate Professor, University of Hawaii Maui College on 5/24/19
This is a review of the hard copy, purchased from Amazon. Overall, for an art appreciation / introduction to visual art text, it is fairly comprehensive. However, compared to other books of a similar nature, it lacks in some aspects: it doesn’t... read more
This is a review of the hard copy, purchased from Amazon. Overall, for an art appreciation / introduction to visual art text, it is fairly comprehensive. However, compared to other books of a similar nature, it lacks in some aspects: it doesn’t include a glossary, many significant 20th and 21st century artists and their works are not included. A more in-depth exploration of the elements of design (or visual elements), the principles of design, as well as the deeper exploration of various art mediums and techniques would be helpful.
Each chapter begins with learning outcomes and ends with review questions and key term definitions, this is definitely helpful for students to understand the basic concepts of the text.
The book has accurate historical and cultural facts, and includes the correct titles of works and artists. However, most of the printed images have no dates, mediums, and dimensions.
The text is relevant for our times, as it introduces a wide range of Western and non-Western, multicultural artforms and traditions. It also includes sections on the role of politics, economics, and ethics in the visual arts.
The writing is clear and concise, it is easy to follow and understand. The Key Terms at the end of each chapter serve as a good review of the introduced vocabulary.
There is good internal consistency in the text, as each section follows a similar format.
Each chapter is broken up into smaller sections, so readers can proceed at their own pace and know what to expect is each subsequent chapter.
The text is organized in a logical, but not historical manner. The concepts presented flow smoothly from one postulation into the next.
Iʻm somewhat neutral on this, since Iʻm reviewing the hard copy. However, when exploring the PDF version, the links throughout the text are a great asset. Some links took a while to download, I’m sure this part will need constant updating.
The text is clearly written and grammatically correct. Readers are able to comprehend and understand the concepts and ideas presented.
While the content is dominated with Western Art concepts and examples, it still includes a number of diverse cultural works and traditions from different historical eras and locations.
Iʻve used this text for one semester so far, and plan to continue its usage. As a basic introductory book, it is more than adequate. Instructors can definitely pick and choose the parts they find useful and add their own additional content when needed. Students will understand the content and like its cost, even if they decide to order a hard copy.
Reviewed by Leila Armstrong, Visiting Faculty, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 5/9/19
The text covers a broad array of art movements both geographically, and temporally, though I think the non-Western selections are a bit slim. There are a number of mentions of modern/contemporary art, but the authors often provide links to images... read more
The text covers a broad array of art movements both geographically, and temporally, though I think the non-Western selections are a bit slim. There are a number of mentions of modern/contemporary art, but the authors often provide links to images rather than embedding them. I imagine it has to do with copywright issues, but I think our student body would skip clicking on the links. The learning outcomes, key concepts, test yourself, and key terms sections provide a nice loop for students to reinforce material learned, and to give quick but accurate definitions of key terms that appear throughout the text.
The setup is different from most textbooks I've used, and some of the terminology is different (e.g. elements of design instead of visual elements). There are also some terms I've never seen used before (e.g. psychic line). I found some visual elements and some principles of design commonly found in other texts either missing or placed in categories that aren't where I'd put them (light//value, pattern, motion, isometric perspective), but overall the information is presented in an unbiased manner and the content is accurate.
The content is up to date and there's not much that will change in the historical sections of the textbook (particularly at this level), and making additions of new artworks, or updating the images used would be relatviely simple.
Again, the key terms, definitions etc will help students with new terminology, and I found the writing straight-forward, concise, and conrete. The explanation of terms are clear, and the authors have a number of good charts, diagrams and the like to help students understand the terms better and how they can be applied to different media.
The authors are consistent in their use of terminology throughout and each chapter is set up the same.
Each chapter and the text within each chapter follows a similar format, and the authors have made a number of subdivisions of the text with numbes which makes breaking the chapters up into modules very easy. The information is parsed in readable sections, but each subunit aligns with the ones before and after it.
The organization is logical, beginning with the the basic questions, moving into formal analysis and then into thematic units. Overall the text flows easily from one topic to the next.
The images, diagrams, etc. are all clear. I tested a number of the links (but not all) and they worked, but I've found links are one of the most problematic additions to course content, because the links often break. Furthermore, depending on whether the student is reading the text in Adobe or online, the link will take them out of one program and into another, which isn't a seamless reader experience, or in the case of online, if the link isn't right-clicked, you go straight to the web page and lose you spot in the text.
The text didn't contain any grammatical errors that I could see.
Although I found the non-Western selections slim, the book was inclusive of a variety of works from different cultures and time periods. I didn't come across any information that I would consider insenstitive or offensive, but since art often deals with subjects that can be considered controversial, there are there certainly sections that may offend (nude bodies, or looking at past representations of race that are unacceptable today). The book does have a nice section that covers some of the controversies of art.
Reviewed by Anthony Marchetti, Full-Time Faculty, Minnesota State on 5/4/19
This textbook is an impressive guide to the introduction of art and visual literacy. It is not an art history textbook. There is room for further examples of artwork or at least links to more visual resources. Also, more contemporary image... read more
This textbook is an impressive guide to the introduction of art and visual literacy. It is not an art history textbook. There is room for further examples of artwork or at least links to more visual resources. Also, more contemporary image examples would only strengthen this title. The Learning Outcomes provide a solid reference for the main themes presented in each chapter. The Key Terms, however, are less developed and seem more like an after thought. The text is organized thematically, but there is room for chronology to play a larger role, perhaps in individual topics/chapters or with an appendix that can trace back to image examples throughout the textbook.
The text is accurate, error-free and also unbiased. The shortcoming is one of omission - there should be more information presented with the images. Title, artist, scale/size, medium, current location, and any other pertinent information about process should be included.
Aside from the need for more contemporary examples (or links to contemporary work outside of the text), the information presented is relevant. Much of the text is historical so will remain so for as long as the text is available. The arrangement of content is easily modifiable for future editions. More contemporary work could be added, making the content even more up-to-date.
he text is written in a style that is easy to understand. Simple repeated visual devices (differences in color or size of text, bold text for important terms, etc.) organize the text. Topics and subtopics are broken up into manageable blocks of text that should retain student interest. As mentioned previously, more information is needed about the individual sample images.
The organizational template used and the writing style are consistent throughout the text.
The division of topics and subtopics is supportive of student comprehension. The organization of the text would allow for multiple class formats - one class session per week, multiple classes per week, or an online Art Appreciation/Intro to Art.
The thematic nature of this textbook would work well for an Art Appreciation or Introduction to Art seminar/survey course but would not be applicable to an Art History course that demands more chronological order. The text is successfully organized so a student would easily understand what to expect from chapters and subtopics. Text formatting unobtrusively guides the viewer to important concepts and key terms.
The PDF interface was a strength of this work - links to outside content supplement the text. Still, there is room for more of this type of content in this text. Images in the text are high quality reproductions. I found no navigational problems.
I did not detect any grammatical errors in the text.
In general, the text draws from different cultures to connect main concepts and themes throughout - this is an important distinction from some art appreciation texts that place the majority of non-Western cultural/artistic traditions into a single chapter. More contemporary examples are needed in this text.
Reviewed by Jeff Brown, Associate Professor of Art, Nicholls State University on 4/29/19
In its 11 chapters, the book covers the essentials for the overall subject. I appreciate how it is divided up, especially in the beginning where it starts with basic ideas and concepts of what is art. It can seem elementary to discuss this, but... read more
In its 11 chapters, the book covers the essentials for the overall subject. I appreciate how it is divided up, especially in the beginning where it starts with basic ideas and concepts of what is art. It can seem elementary to discuss this, but is so important to establish this with students who may not have had any or much interaction with fine art. The book includes learning outcomes for each chapter, which works well for instructors who use learning outcomes within their syllabus and for assessment purposes. I feel the selection of images are a good choice and diverse, using the traditional images found in just about all the other hardcover textbooks. A nice addition is the use of images of process and where artists are working. The inclusion of key words and meanings at the end of the end chapter is a useful tool for students utilize. One item that could use more attention would be to include dates and materials used for the chosen artworks.
Accuracy of content was error free and unbiased.
The content is current information about a historical event or current event as we know to this day. Updates can easily be made without much restructuring of the textbook.
The book was written in an easy read way with lots of imagery to match concepts. Key terms placed in bold text makes it possible for readers to easily locate if going back and forth from text to key term definitions, located at the end of each chapter.
The book is full of terms and its consistency to the concept or subject. Terms that may not seem clear to the reader are defined at the end of each chapter. This would allow the reader a more user-friendly way of referencing a term then the typical glossary at the end of the book.
The framework of the book that remained consistent from chapter one to the final chapter. An overall good structure to the textbook.
This is probably the toughest part to putting a book together in my view. Choosing what to include or how much to include of one topic or concept can truly make or break it for a textbook. This book is setup in a conventional way, such as chapters with subheadings. This way does work for the textbook, but is nice is that within each chapter the subheadings do not linger on and on when it could have been much shorter.
Organization of the chapters and subheadings work well. Easy to work through
I give the interface a low rating due to its setup of links and workings as a PDF. I like the fact that the textbook utilizes web links. This can be exciting for the reader to potentially experience other useful visuals or resources to help relate to a topic. Some web links within the text of the subheadings are sometimes often just images with no actual source listed and lack further information. This part could be revisited for better interfacing. One thing I noticed and hope it can be remedied, are the workings of the table of contents. Many dead jump links existed in the table of contents page. Some worked great, allowing you to jump to a chapter or subheading with the press of button. Frustrating when it did not.
It would be nice to be able to easily return to the table of contents from anywhere, rather than having to scroll back up to the table of contents page.
The text of book seemed to have no grammatical errors.
No cultural insensitivity stood out.
A useful online textbook. Images are of a choice and quality. However, more information is needed for each image used, such as dates, materials, and dimensions.
Reviewed by Michelle Dean, Assistant Professor, Thomas Nelson Community College on 3/27/19
Introduction to Art: Design, Context and Meaning is an appropriate title for this text. The 11 chapters explore structure, materials, meaning and context of artistic production in a somewhat comprehensive manner. It certainly provides a solid... read more
Introduction to Art: Design, Context and Meaning is an appropriate title for this text. The 11 chapters explore structure, materials, meaning and context of artistic production in a somewhat comprehensive manner. It certainly provides a solid foundation for visual literacy and aligns with content in standard art history courses. This text is also well organized. Learning outcomes and an introduction are found at the beginning of each chapter. Key concepts, key terms and a self-test are found at the end of each chapter. This text, however lacks a comprehensive index or glossary.
The content of this text is accurate and essentially unbiased and error-free. Key terms are often defined in a universal manner and therefore aligns with terminology in standard art history texts. The text does not display any particular bias and appears error- free. The main criticism I have in this area is the information provided for images does not align with the standards. Title, artist, medium, size, and location for each image should be provided for the reader not just a reference to where the image was obtained.
The bulk of the content in this text will remain relevant for an extended period of time. Topics such as structure, materials, meaning and context of artistic production leading up to the modern age do not change significantly over time. The one criticism I have in this area is that there is not much contemporary art and that fact may lead to the text feeling out dated over time. Additional chapters would be perhaps the easiest way to update the content however this text in not arranged in chronological sequence and integrating contemporary example in previous chapter will be challenging.
This text is written for students who are new to art. It is an introduction to art. It presents information in an accessible manner and clearly defines most terms. Although the learning outcomes are stated in perhaps on overly cumbersome manner. The main criticism I have in this area is that the history of art and perhaps more importantly the evolution of art is difficult to ascertain when works of are referenced without regard to chronological sequencing. To talk about classical and modern examples in a section can be challenging for a new student in art to compare and comprehend.
The framework of this text is very consistent. The content of each chapter is organized in the same manner. As previously stated, learning outcomes and an introduction are found at the beginning of each chapter. Key concepts, key terms and a self-test are found at the end of each chapter. Key terms are in bold type in the chapter and also included in the list of key terms at the end of the chapters. Terms are used consistently throughout the text.
The chapters of this text are divided into sub-sections. For example Chapter 3 on materials is divided into 11 sub-sections which include sections on learning outcomes and introduction at the beginning and self-tests and key terms at the end. And although there are numerous sub-divisions in this chapter it is still reads as large blocks of text. Text boxes might be a more effective manner to present the content in a more accessible manner for our current student populations.
The overall organization of the content is presented in a clear a logical fashion. The first chapter asks the appropriate question ... What Is Art? Chapters 2-4 discuss the structures of art, the materials used in art and describing art. Chapters 5 and 6 discuss meaning in art and connecting with art. Chapter 7 is specifically focuses on architecture. And chapters 8-11 address art as related to special topics such as identity, power, ritual and ethics. A concern here is that architecture is not fully integrated into broader discussions.
The images and diagrams in this text were clear and of good quality. The inclusion of various links in the body of the text were well placed and on topic. But I could not open all the links.
I did not notice any significant grammatical errors.
This text is somewhat unbiased. I did not notice any culturally insensitive or offensive content. However, the content is primarily a discussion of the western tradition. Although, Eurocentric approaches are common in art education it is perhaps more appropriate to intentionally be inclusive of non-western traditions.
Reviewed by Mandy Keathley, part time professor, Linn-Benton Community College on 1/28/19
Considering how entry level and accessible the text is, it is also fairly comprehensive. I wish there were more contemporary art examples, but I was able to fill in as needed. I found it sufficient as an outline, and did a lot to fill in the gaps. read more
Considering how entry level and accessible the text is, it is also fairly comprehensive. I wish there were more contemporary art examples, but I was able to fill in as needed. I found it sufficient as an outline, and did a lot to fill in the gaps.
No errors noticed.
The book feels a bit out of date as it is, though not in danger of becoming more so over time.
The text is great on clarity and accessibility, written in a way that most entry-level students could understand. If anything, it errs on the side of over-simplification.
Very consistent
The modularity was one of the strongest aspects of this book which made it easy to teach in a course. Each unit feels contained and leads into the next. However, I think that some modules could be expanded.
The book is organized well. It is not in chronological order like might be expected, but this can be used effectively. I found it helpful to teach chapter 5 & 6 first, to get students to think about the meaning in art as a way to get them interested.
The interface was adequate. The design could be improved, including the sub-headings and organization of images.
no errors noticed
The book does a decent job of touching on a few global art examples, but could do better.
Reviewed by Bob Casper, Adjunct Faculty, Boise State University on 1/9/19
I used it a supplement for a Webdesign course, reinforcing artistic concepts, and it was well received by the students. read more
I used it a supplement for a Webdesign course, reinforcing artistic concepts, and it was well received by the students.
When it really comes down to it, some issues of toughness may have come up here and there, but, all in it was acceptable for my student's level.
Seemed to work well and present ideas and concepts that were relevant to for my students.
My students were a novice level and some details were not too in-depth.
Elements of the book followed a framework that as easily followed.
The book was presented in chapters that worked well in the course and for what I needed.
Each area was well put to together and bridged nicely.
Simple read, clear text.
Did not notice any errors.
Presented historical and cultural ideas and issues without calling out marginalised students.
Seemed to meet ADA standards.
Reviewed by Lori Parks, Visiting Assistant Professor, Art History, Miami University on 8/2/18
The focus and organization of this text is similar to a number of other Art Appreciation textbooks currently available. For example, there are a number of texts that present Art Appreciation through a thematic structure. The material is... read more
The focus and organization of this text is similar to a number of other Art Appreciation textbooks currently available. For example, there are a number of texts that present Art Appreciation through a thematic structure. The material is introductory which is positive in that it is very accessible to readers and thus would not be too intimidating to students new to this subject. The text also does a good job with listing and creating Learning Outcomes for each chapter along with a wide variety of mostly good quality open sourced images. While there are lists of Key Terms included in each chapter, they are minimal at best and there does not seem to be enough cross connection with the terms and their use within the body of the text. There is also some problems with being too simplistic with terms and concepts, one example being the use of icon which is very much dependent on both the historic and cultural context. Although the text is organized somewhat thematically, it would help to have chronology play a part within each chapter/topic as well as some form of an appendix or place where an overview of the history of art might be placed. This is often the problem with Art Appreciation texts and the reason why so many of them have a very condensed overview/history of the various periods. It is difficult to provide any depth without the context.
There are a number of issues with accuracy, which could also overlap with other subsections of this review. For example, the terminology is often overly simplified and inaccurate. While readability is important, it is equally important for a student to expand their vocabulary and become familiar with the language of the discipline. Simplification also comes in the form of analysis and description of the works of art without connecting it to formal elements and historical and cultural context. There are also assumptions being made in the analysis (e.g. students knowing what Prairie Style is and how that might influence another artist/movement). Another problem area are the huge leaps in time and generalizations made in content, for example, in connecting the ancient Greeks to Jackson Pollock on page 4. Another area of concern is the labeling and citations. The labels for the images give weight to the open sourced “author” rather than the information that is important to the work of art (artist, title, date, medium, dimensions, and museum/collection), this could be better by creating a reference page at the end of the text for the open sourced images. More examples of non-western art would also be important.
Overall good, I would have liked to see more contemporary art and topics/themes including areas like performance. The images chosen generally follow the typical works of art found within the canon of Western Art History.
Generally clear and readable, although as mentioned elsewhere in this review, at times overly simplistic and rambling and repetitive. And, as mentioned earlier, the labels for the works of art are in need of correction with emphasis placed on the artwork rather than open source.
The template used is consistent through the chapters. There are issues with consistency in use of terms, and citations/websites etc. This should be strengthened more. I also wonder about the sources and context with regards to the discussion of historical development of art.
Each chapter is organized into topic/theme and subsections that are meant to connect back to the theme of the chapter. While this is a good way to allow for quick access there is room for further development both by the authors and also within the classroom setting and by the teacher.
While the thematic approach is important, the chapters read as disjointed and the text is at places overly general and at times repetitious. There should be more focus on an overarching question of “what is art” which would allow the various themes explored in each chapter to read as more cohesive. The chapter on Art and Ethics could be strengthened more.
While there is a really good attempt at organizing the text, there are a number of issues that make it difficult. For example, the placement of the imagery and discussion becomes somewhat confusing when there are also a number of images that are discussed but not shown the body of the text. The reader is instead supposed to go to the link and toggle back and forth. Such long links in the body of the text are distracting and confusing. A better way to organize this might be creating case studies which would allow for more in depth focus on the particular artist/artwork. The lack of continuity would be confusing for a student who is new to the topic of art and art history. Overall the clarity of the images are okay with only a few that could be improved upon in quality.
While there are some typos, the formatting and use of citation is more distracting. As mentioned, the inclusion of large links in the midst of the text is frustrating as well as the lack of period to enclose this before beginning a new sentence. There are also things like the indentation in the footnotes that can be easily fixed.
Overall there is an attempt to draw from different cultures to connect to the themes and concepts without being overly biased. As mentioned earlier, more examples of non-western art might be helpful. Also, more contemporary examples and connecting them to issues that are currently relevant like identity and protest etc.
Overall an impressive project and a good foundation to build upon. This text is best for Art Appreciation or potentially studio classes (supplement).
Reviewed by Peter Spooner, Instructor, Lake Superior College on 5/21/18
With eleven chapters in just under 300 pages, the text provides a comprehensive framework with which to explore the topic of art appreciation. It does not (nor does it claim to) offer a complete art historical survey, but rather uses examples of... read more
With eleven chapters in just under 300 pages, the text provides a comprehensive framework with which to explore the topic of art appreciation. It does not (nor does it claim to) offer a complete art historical survey, but rather uses examples of visual imagery from a variety of cultures, time periods and genres to make larger points about how we actually use art. Its chapter and sub headings suggest a view where art is fully relational to its users, whether they are individuals, communities or nations. Rather than a comprehensive glossary, the authors place key terms at the end of each chapter. The text is searchable, making an index unnecessary. The text successfully presents art as both an individual and collective enterprise, appropriately offering a variety of ways to explore its multiple functions, from self-identity and spirituality to commerce and communication. It makes an attempt to compare artworks from different time periods and cultures in terms of their function in life, and looks specifically at the viewer’s role in the process. To its credit, the text concludes with a chapter devoted to ethics and art.
The text seems to be free of any overt bias, and authors attempt to bring a variety of viewpoints to bear on the art and ideas they present. The text is well balanced between the authors’ assertions and well-documented quotes and information from a variety of sources.
The text is organized thematically and in terms of large ideas, thus guaranteeing a degree of longevity and future relevance. With so many web links in the text, it will be important to check regularly to make sure they are active. While this text is not based only on contemporary art, it uses many examples of current art throughout. For this reason, longevity is always a concern in art appreciation and introductory art texts. Since by definition contemporary art is a moving target, and at times local or regional in its relevance, instructors may want to supplement the text with their own references to contemporary art.
The text is clear and accessible, written to encourage understanding, not to prove points or advance opinions. It is appropriately written for students who are introducing themselves to art, and contains a minimum of jargon and hyperbole. Relevant key words and technical terms are defined at the end of each chapter, as befits any introduction to a subject.
The organization of the text and its components is consistent throughout, as is tone and flow of the text. Care is given throughout to maintain a consistent tone, level of detail, and depth in the text. Each chapter contains the same useful sequence: Learning Outcomes, Introduction, “Before You Move On” and Key Terms. Generally, students find such consistent organization reassuring and helpful.
Each chapter of 25-30 pages is sub-divided into seven or eight subtopics, and these sub-topics are themselves broken down into easily readable paragraphs, were key ideas are evident. These subtopics are well related to chapter themes, but by themselves could be used as lessons or topics for assignments. Beyond the first two chapters, the tone of which is more introductory, it seems as though instructors could and should feel free to present chapter and subtopics in whatever order serves their needs. The text is flexible and relational to the degree that some, but not all, chapters and/or subtopics would need to be used in a course. Given the modular organization of sub-topics within chapters, the text could be efficiently updated, and it is easy to see how instructors could insert their own material into chapters. The sub-topics contain plenty of specific examples, yet it is always possible to trace their connection to the chapter’s larger ideas.
Major topics are presented in a clear fashion that has a logical sense of development. The subtopics within each chapter are also clearly organized. Blocks of text are broken up by copious illustrations, photographs and live links. Each chapter begins with a list of learning outcomes, and ends with a section titled “Before You Move On,” which reviews key concepts, and provides a list of study questions. In addition, key terms are defined at the end of each chapter, as opposed to a single glossary, which makes it likely that students will review terms after reading chapters.
The PDF form with live links to websites and on-line resources was easy to use. Links were placed within text immediately following the artist or artwork under discussion, making them easy to find. The links themselves were relevant and added to the topic(s) at hand. All of the links I checked were operational, but as one might expect, the quality and size of images and text varied from website to website.
I did not detect any grammatical errors in the text. However, in Chapter Eleven: Art and Ethics, a number of the pages contain the heading Chapter Ten: Art and Ritual Life.
The text makes reference to art from a wide variety of cultures and to the experience of people from diverse backgrounds. It is true that many of the artworks and artists are familiar and part of a standard canon of Western art and its cultural touchstones. However, each chapter also contains references to non-Western art, and a cross-cultural approach is evident throughout the book, not only in isolated chapters.
The inclusion of an entire chapter devoted to “Art and Ethics” is refreshing, and somewhat overdue. The authors discuss and provide examples of art that has provoked controversy in terms of censorship, first amendment rights, copyright, appropriation, and the role of artists and institutions in examining sensitive societal and political issues.
Reviewed by Arianne Fernandez, Full - Time Lecturer, LaGuardia Community College on 5/21/18
The range of topics this book covers provides a great resource for teaching students the basics of visual art and introducing them to various media and techniques as well as the process of art making, from multiple. Since the text covers a wide... read more
The range of topics this book covers provides a great resource for teaching students the basics of visual art and introducing them to various media and techniques as well as the process of art making, from multiple. Since the text covers a wide range of time periods, styles, and works from Western and non-Western cultures - enhanced by good images-it is appropriate for both Introduction to Art and Art in Society courses. Despite the minimal attention in regards to Contemporary Art, the text is well written , with great descriptions of the pieces presented, with accurate explanations of art vocabulary. Overall, a great source for students.
The text appears accurate.
The textbook is arranged in a logical manner that introduces students to important concepts which enable them to understand how to describe a work within its cultural framework and uses a logical sequencing of information. The textbook has many high-quality images of the works discussed within the chapters. A fallacy, however, is that the bulk of art emphasized is predominately pre-1960 art. Thus, the instructor will need to go beyond this book to discuss Contemporary works within a global spectrum.
The language used is appropriate for college-level readers, with sentences easily understood. The ned of chapter glossaries provided, re-enforce the art vocabulary presented in each topic. The images support the content effectively and illustrate beautiful the in depth discussions presented within the chapters of the text.
The writing throughout the text is consistent. Each is well organized: outcomes are highlighted. The vocabulary is written in bold type and the end chapter glossary provided enforces the vocabulary. The summary and review questions provided at the end, are a great way for students to check both comprehension and progress.
The manner in which the text is organized supports teaching visual literacy in a logical sequence with each chapter’s subcategories allowing for the topics discussed to be highlighted. Thus, the reader can approach these topics from various viewpoints. Having more contemporary images / historical information can allow for students to make more meaningful connections with the art of today.
Overall, the chapters are consistently and straight forward which allows students to understand the topics presented clearly, as the book seamlessly weaves introductory concepts – i.e. what art is, its function and various use of media- and makes connections in the way that art shapes society as a whole.
The images provided in the text, are clear and high quality. The chapter sections and subsections are clear. The font is appropriate and easy to read and the inclusion of vocabulary words in bold, allows students to pay closer attention to the material covered.
The textbook contains a few typographical errors but nothing major.
This text provides a solid foundation in the visual arts. By analyzing historical artworks in depth and including works from non-Western cultures – African, Asian cultures- and women -which despite significant contributions are always glossed over In introductory texts- providing a global platform for students. An instructor would need to bring in additional examples to strengthen student understanding. Specially in regard to contemporary art. The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive. The thematic approach instead of a chronological approach makes it reader friendly and not tedious to read.
Overall, this is a great introductory text that discusses important styles, concepts and historical context. Some chapters need expanding, or the instructor can mix and match chapters in this text with other supplementary material in areas that are lacking.
Reviewed by Jonathan Johnson, Associate Professor, Otterbein University on 5/21/18
This textbook is ambitious and covers a lot of ground—both theoretically and historically. The thematic (as opposed to purely chronological or geographical) approach and interface allows the soaring comprehensiveness of this text to take a... read more
This textbook is ambitious and covers a lot of ground—both theoretically and historically. The thematic (as opposed to purely chronological or geographical) approach and interface allows the soaring comprehensiveness of this text to take a digestible and highly modular form. The position of the writing seems to be educator and student centric, with pedagogical concerns. Art historical (or disciplinary) outcomes aren’t the main focus here—and that should please those looking for an introductory or non-major textbook. I imagine this would facilitate the outline and planning of a course—where course outcomes could be developed with this text in mind as opposed to developing the course and then searching for an appropriate textbook and supplements.
The themes address in the text are sufficiently supported and explored with ideas and artwork reproductions that flesh out the major social issues contained within the artwork. The process and historical/social conditions of the work’s creation are also covered in each section. In this way, these art works are placed within the time they were made and viewed through a contemporary lens.
Table of contents, key terms and “Test Yourself” sections are comprehensive and helpful from a teaching perspective.
The textbook is accurate and without bias according to my reading.
The overarching “big questions” are up to date, however it could beneficial to have more contemporary examples representing these themes/questions embedded within the pdf version of the book. Are there more recent examples of art that tackle issues of race, history and identity as in the given example of figure8.25, for instance?
As mentioned below in “Clarity”, the writing is clear—but undergraduate students might be more immediately engaged with the material if it was more often connected to a contemporary iteration of the social issue at hand. We are introduced to Maria Luisa of Parma immediately within the Class section (8.3.4)—which I find quite interesting. However, I wonder if an undergraduate or non-major might desire a class reference that they can relate more to? At least at first, and then delve into something more “historical”? I’m thinking a bit of the Oxford University Press’ A Very Short Introduction series here.
With this being said, I did enjoy looking at more historical works and works from the 19th century through the lens of these very contemporary themes. I was also newly introduced to a few engaging works such as Sargent’s Gassed (Fig. 9.10) and Daumier’s The Third Class Carriage (Fig. 8.20). When connected to these larger questions and contextual frameworks, these two pieces (and many others included in the book) seem fresh and imbued with a renewed relevance.
The writing style is very straight-forward and clear of unnecessary jargon. Well suited for non-majors and for building student interest in Art History. Writing style seems to match the audience and outcomes.
Visual and organizational layout is consistent and becomes helpfully predictable as you move through the text.
Thoughtful and relevant groupings and subheadings. The order is logical and terraced to build upon previously presented ideas and themes. Would function well as a “pick and choose” text for a introductory art course or a course designed for non-majors.
Structure, flow, sequencing and logic are amongst the greatest strengths of this text.
Overall, the interface is easy to follow and basic in design. The off-white framing of the images and figures is reminiscent of a Polaroid border, and is a little distracting. Having the date(s) of the artwork underneath each image would be convenient for reference. Having to go between the text body and the image for the date is a little inefficient. Image reproduction is mostly sufficient, but the Nocturne in Black and Gold: The Falling Rocket I (Fig. 1.14) would have benefited from a larger reproduction, especially since the text references technical nuances of the work in its analysis.
I found no grammatical errors in the textbook.
The larger questions and themes are well chosen, sequenced and organized. How do they manifest more directly today? Showcasing the cultural relevance of more established canonical artists is a strength of this text. Pairing up Auguste Clésinger (Fig. 8.17) and Kehinde Wiley (pp. 221-2) in the early portion of the 8.3.3 Sex/Gender Identity section is a great example of answering this question I’ve posed, but I think more of it would add a depth and extend the relevance.
It goes without saying that pursuing a textbook writing project such as this truly serves the greater good and the authors should be commended.
Reviewed by Dina Pizzarello, Adjunct Assistant Professor, LaGuardia Community College on 5/21/18
This textbook would be a wonderful source for any beginner art or art appreciation class. It does not delve too deeply, but that is a plus for the beginner and/or typical non-artist using this resource. An index and glossary would be great... read more
This textbook would be a wonderful source for any beginner art or art appreciation class. It does not delve too deeply, but that is a plus for the beginner and/or typical non-artist using this resource. An index and glossary would be great additions to help students search for information and make connections more easily.
I found this textbook to be accurate and unbiased, although more examples of Non-Western art could have been added. Some of the CH 11 pages and titled CH 10 at the end of the text.
This text is current enough for the average art appreciation class. All of the links I checked worked perfectly. Since it is mostly based on works of the past, it will need little updating.
Clarity rating: 1
This text is written simply, clearly and with brevity. This can be especially helpful to international students and students with cognitive disabilities. Beginners can easily understand definitions and concepts.
The organization and writting are consistent throughout.
The chapter organization and subdivisions wold work really well for classes taught on single or multiple days. This is a big plus for those of us that teach at community colleges.
One strength is that the text is arranged thematically, not chronologically. This format has been proven to work better in art appreciation classes. Each chapter has a comprehensible and logical flow to the breadth of information covered.
I found no interface issues.
I found no grammatical errors.
I found this text to be un-biased and culturally sensitive.
I liked how the text included non-traditional images to explain some concepts. This gave the book a fresher feel that millennials could more easily connect with. Most of the images are of small or medium scale. It would be a nice to incorporate larger image examples of select artworks. This would be more visually impactful.
Reviewed by Eleanor Johnston, Academic Skills Librarian, Staffordshire University on 2/1/18
This texts provides a comprehensive introduction to the world of Art and contains 11 chapters, thematically arranged, to give an overview for beginners to the subject. The text contains enough content and examples to ensure that there in... read more
This texts provides a comprehensive introduction to the world of Art and contains 11 chapters, thematically arranged, to give an overview for beginners to the subject. The text contains enough content and examples to ensure that there in appropriate contextualisation and that the idea of Art as a concept is covered with sufficient depth and clarity. At the end of each chapter, there is a Key Terms list, which acts as a glossary for the readings just completed. There is no index at the end of the book, but this is not a problem as online PDFs can all be searched using the 'find text' function. There are areas where the text is not greatly detailed - any book of under 300 pages could not possibly cover all areas of art without omissions, so there is a greater emphasis on older works when used as examples. There is little on contemporary art, although it is covered in most detail in the final chapter. As there is no index of Artists, it can be tricky to locate movements using the 'find text' function. The outcome to 'build a broader, more comprehensive view of the nature and definition of visual art' (p.1) is impressively achieved.
The content of the book is accurate and I did not detect any particular biases or error. Of course, any Introduction to Art may inherently contain the biases of Western Culture in relation to the choice of themes and narrative, but there has genuinely been an acknowledgement of the importance of all cultures, and there has not simply been one token chapter to shoehorn in all other civilisations. There is one error in the layout - on pages 280, 282, 284, 286, 288, 290 and 292 in Chapter 11, these are titled 'Chapter 10: Art and Ritual Life" on the top right of these pages.
This text is arranged thematically, so this structure does ensure that there will not be any aspect of the contents that would quickly become obsolete or outdated. Any weblinks used within the text would have to be checked and maintained. These are contained throughout the book - I would surmise they were used if no Creative Commons image was available to illustrate a concept or technique. I did click through to a large number of the weblinks and am pleased to report that they not only were, without fail linking through, they also provided further details and areas for discussion that built upon the content of the text.
This area is a real strength of the book. The book explains complex concepts in a very clear and concise way, ensuring that any new or unfamiliar terms are included in the 'Key Terms' pages at the end of each chapter. I was particularly impressed with this in Chapter Seven: Form in Architecture. I think the authors had an intention to provide clear, accessible prose and to ensure that a reader with no knowledge of the areas of design, meaning and context would be able to understand and appreciate them.
Again, with the chapters arranged thematically with the same structure scaffolding each one (learning outcomes, introduction, before you move on and key terms) the text was consistent and the framework extremely clear. I did not find any examples where key terms were overlapping, confusing or contradictory.
As an Introduction to Art with easily digestible sections, these text deserves commendation. Each chapter is approximately 30 pages long, and sections within the chapters are subdivided into smaller sections (e.g. Chapter 8: Art and Identity contains 21 pages and has 5 subsections. The visual aspects of the text -multiple examples, images, photographs, artworks etc, ensure that there are no giant blocks of text, and the book taken as a whole is aesthetically pleasing and a pleasure to consult.
I would suggest that this area could be improved by expanding on descriptions in the contents page - there were sometimes cases of repetition when a concept was discussed across multiple chapters (e.g. the Sacred). This is a hazard of the thematic approach, but I understand that without reverting to a chronological timeline of art, it is very difficult to cover these in one or two paragraphs in one section of a text. The subjects of design, structure and materials provided better scaffolding for chapters.
The text was extremely clear and the images were reproduced at a high definition. Any links taking students through also provided clear images, although these were sometimes rather small. There was no confusion with the image labelling or creative commons attributions, and I found the single column view easy to read.
There were no grammatical errors that I was able to detect.
The text provided references to a variety of cultures throughout the pages. Once again it should be highlighted that non-Western cultural artistic traditions were not simply shoehorned into a chapter, but there was a great deal of inclusivity in the whole book. Indeed, the cultural relevance and variety mentioned is of great artistic importance and is refereed to as crucial to the ethics and raison d'etre of many prominent artists (see especially Chapter Eight: Art and Identity).
This Open Textbook is a valuable addition to the canon of texts currently recommended as an introduction to art. The thematic chapters provide a perfect platform to commence a discussion on a topic (for example, meaning in art). Students would be advised to read the chapter in advance of lectures / tutorials and to use this as a starting point for their research.
Reviewed by Victoria Hutson, Art Faculty, Lake Superior College on 2/1/18
This book covers a broad range of areas that are typically included in a college level art appreciation book. Because it covers so many different areas—it doesn’t go into a lot of depth in any one area. However, an instructor could easily provide... read more
This book covers a broad range of areas that are typically included in a college level art appreciation book. Because it covers so many different areas—it doesn’t go into a lot of depth in any one area. However, an instructor could easily provide more depth by providing supplementary material for specific areas. The book is arranged by topics or themes which is typical for most art appreciation books. It is not arranged chronological--which is usually the format for art history books.
The book appears to be accurate, error-free and unbiased--although I did catch one inaccurate statement regarding the Vietnam War Memorial. The memorial is below ground level but the book claims that this reflects “the belief that the Vietnam War was initially conducted ‘beneath the surface,’ that is, unknown to most Americans.” However, in the 1995 documentary, “A Strong Clear Vision” the designer (Maya Lin) explains a totally different reason why it is underground. This conflict between what the artist says and what the book says is worth noting. It did make me a bit concerned that other material may also be inaccurate—but I did not catch any other inaccurate statements.
This book should have relevance for a long time because the material it covers is primarily about past art—which for the most part doesn’t change. While it is possible that new information may become available that changes our understanding of the work—for the most part our educated guesses about the message, meaning, or function of the works will remain the same. In addition, the vast majority of images and information included in this book are also found in most of the standard art appreciation textbooks.
The textbook is written in a style that is clear and easy to understand and follow. Specific terms are written in bold text with their definitions listed at the end of each chapter.
There is a consistency in the way the material is presented in each chapter.
Each of the chapters are divided into smaller sections that make it easy to assign or highlight a specific portion of the text. In addition, each chapter starts with Learning Outcomes and ends with Key Concepts, Test Yourself, and Key Terms sections.
The topics in the text are presented in a fairly logical and clear fashion. It is very similar to other art appreciation textbooks I have used in the past. The book starts with fundamental concepts (what is art, art materials and techniques, describing art, finding the meaning, etc.) and then it proceeds into more advanced topics (connecting art to our lives, identity, power, ritual Life, and ethics). There is a separate chapter on architecture which seems a bit odd since no other area was given a specific chapter of its own.
The pdf interface is very functional to use and easy to navigate and download. While I understand the reasons for including links to copyright protected images I did find having to click on the link cumbersome and somewhat disruptive. In addition, often I felt a bit confused when I started reading about a work of art that did not have a printed picture to accompany it. I found myself glancing around the page trying to find the image that I was reading about only to see that later in the paragraph there was a link. Perhaps having the link at the beginning of the paragraph would have worked better. Plus, it would serve as a notice that the following text is about an image that needs to be viewed via a link. A few of the links brought me to pages that were no longer active.
I did not notice any grammatical errors.
The material in this book does includes examples from a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds—although most of the material is from what is traditional considered the origins and evolution of western civilizations.
This would be a good book for an art appreciation course. Because of its modularity it would be easy for an instructor to assign specific areas to establish a basic foundation and then provide supplementary material for in-depth explorations of chosen topics.
Reviewed by Elizabeth Maynard, Adjunct Professor, Rhode Island College on 2/1/18
This books is not an historical survey, but it offers a wide range of artworks from throughout history and the world to elucidate major themes and concepts. Even while it is non-linear or chronological, the text nonetheless covers terms and ideas... read more
This books is not an historical survey, but it offers a wide range of artworks from throughout history and the world to elucidate major themes and concepts. Even while it is non-linear or chronological, the text nonetheless covers terms and ideas specific to historical moments, taking them as case studies to illustrate larger themes. The end of each chapter includes questions to consider and a list of major terms with definitions.
excellent, to my knowledge.
While the book references very contemporary technology, including 3D printing, etc., it contextualizes them in more traditional methods; the themes and of the text remain timeless.
Both the imagery and the phrasing read easily. The images are very detailed and include helpful close ups.
The progression of chapter creates a very readable narrative.
The book is well divided up, and I appreciate the integration of both historical and formal terms throughout, to offer new historical information throughout without becoming dense.
The book lays out a great foundation for material and terms of analysis to get into deeper themes and modes of interpretation.
One thing I would add/change, is for the images to include the dates in the caption, not just in the text. While the text is non-linear, I think it's important for the dates to be readily available to understand the historical breadth of the works.
none that I encountered.
I especially enjoyed the integration of works from throughout the world. Often in more conventional texts, art of the non-western world gets relegated to their own, atemporal chapters. This format allows for thematic comparisons that helps to breakdown the hierarchies of the canon.
Reviewed by Renee Couture, Assistant Professor of Art, Umpqua Community College on 2/1/18
This book covers just about everything needed for teaching students the basics of visual literacy and introducing them to art. This text has a range of images and includes various time periods, styles, and works from Western and non-Western... read more
This book covers just about everything needed for teaching students the basics of visual literacy and introducing them to art. This text has a range of images and includes various time periods, styles, and works from Western and non-Western cultures. The textbook, however, lacks significant references to contemporary art. A vast majority of the work presented is pre-1960 and most of the media covered is traditional fine art media (painting, sculpture, drawing). That being said, the authors provide glossaries at the end of each chapter of target vocabulary, a comprehensive index, and write thoughtfully and thoroughly to provide a solid context to the works/images shown within the text.
The text appears to be accurate.
The textbook profiles works from ancient through modern times. The text is arranged in a way that introduces students to important concepts for viewing and considering artwork, and uses a logical sequencing of information. The textbook introduces students to some of the major “movers and shakers” in art history, and has many high-quality images of the works discussed within the chapters. The text, however, largely emphasizes pre-1960 art. In fact, it seems only a handful of post-1960 artists are mentioned and very few supporting images are provided of post-1960 artwork. To be fair, there are links provided, which will require upkeep. An instructor will need to find examples from other sources to expose students to contemporary art (artists, media, themes, and modes of working).
The text’s language is appropriate for college-level readers. Sentences are easily understood and the use of art-specific vocabulary (along with providing a glossary at the end of each chapters) shows students appropriate use of target vocabulary. Chapter topics are presented in clearly, accessibly, and with depth. Images are used effectively in supporting content.
The chapters are uniform in their organization; the writing is consistent. Each chapter starts with outcomes and an introduction. Headings for chapter subsections are clear and specific. Target vocabulary is written in bold type and each chapter has a glossary. Each chapter ends with a summary and review questions to check for student comprehension.
The text is divided in a way that supports teaching a foundation in visual literacy. Each chapter is clearly titled with subsections supporting the chapter’s topic. In some cases, subsections from different chapters could be mixed and matched. One of the strengths is the use of imagery from various time periods within each chapters as opposed to the standard chronological approach to an art history course. This could be further exploited by the addition more contemporary art by the instructor along side more historical examples the text provides.
The chapters are consistently structured. The choice of chapter topics and their flow is appropriate and student-centered. The book starts with basic information (what art is, its structure, media used) and works toward greater complexity (various ways art connects to and shapes our lives).
The supporting images are clear and high quality, allowing the reader to increase the size of the images without losing clarity. Some of the pages feel crowded and a few of the links were nonfunctional. The chapter sections and subsections are clear. The book's font is easy to read with line hierarchy is unmistakable and consistent, and the use of bold lettering indicates target vocabulary for students.
I found no grammatical errors within the text.
The text will provide students with a solid foundation in visual literacy using historical artworks as examples. It includes work and architecture of non-Western cultures and women. However, it (generally) ignores contemporary art (artists, media, modes of working, and thematics) which students will see in today’s world. There are missed opportunities to discuss more recent attitudes & intentions within the arts (for example, in Ch 4: Describing Art, it would seem appropriate to have subsections on Modernism and Post Modernism). It would be helpful if were either more examples of contemporary art along side the more historical examples or if there was final chapter on art post-1960. An instructor will need to find examples of contemporary art (through resources such as Art 21, museum catalogs, artist websites, articles/interviews for arts-related sources) to expose students to contemporary artists and art. Inclusion of more art post-1960 would: 1) present students with more challenging imagery, 2) expose students to themes that are more relevant to them, and 3) further introduce students to the works of more women and minorities. Nonetheless, this book would be an effective tool for an Intro to Art or Art Appreciation course. A strength of the book is its thematic approach instead of the standard chronological approach. I did not find it culturally offensive or insensitive.
This book has enough general information that certain chapters (or parts of chapters) can be used in a Basic Design or Drawing course as well as a general Art Appreciation/Intro to Visual Literacy course..
Reviewed by Nancy Pettigrew, Associate Instructor, Tidewater Community College on 8/15/17
For an art appreciation textbook, there is no set of required information that must be included and, therefore, a textbook's comprehensiveness is somewhat subjective. This textbook does cover some core areas for this discipline: the definition of... read more
For an art appreciation textbook, there is no set of required information that must be included and, therefore, a textbook's comprehensiveness is somewhat subjective. This textbook does cover some core areas for this discipline: the definition of art; the function of art; elements of art and principles of design; and different media used to make art. I thought that the treatment of the elements and principles and of the media was cursory. Beyond that the textbook is thematic, with the choices of themes being somewhat idiosyncratic.
The treatment of the subject was constrained by the authors' focus primarily on the traditional media associated with fine arts, such as painting, sculpture, and architecture. Other current art appreciation textbooks also include more modern media, such as film and design. The scope was also hampered, in part, by the distinction the authors' drew between art and craft.
The focus of the textbook is mostly on art made before 1960, with most of it produced long before that. There is a dearth of examples of contemporary art being made by artists in the last 20 years. An exception to this is the chapter on Art and Ethics, which addresses recent controversies in the field.
The textbook does not include an index or a comprehensive glossary. Terms are defined at the end of each chapter. The table of contents is not sufficient to function as an index.
The content of the textbook is generally error free. There are some opinions expressed that I do not agree with, but these are debates that are not settled within the art history community. The authors do not seem completely up to date on recent scholarship in some areas. For example, the "Snake Goddess" from Crete is included when modern scholarship has called into question the validity of its heavily reconstructed form.
Since much of the art covered in the textbook was made before 1960, the content is up-to date and will not become obsolete quickly. The exceptions to this are the links to external web pages that will need to be maintained on a regular basis. Without this regular maintenance, these links could become obsolete quickly. This could pose a problem since the links are embedded in the content of the text.
The textbook is written in prose that should be accessible for the average college freshman. Specialized discipline-specific terminology is defined in the text and in a list of terms at the end of each chapter. The text does lack an comprehensive glossary of these terms..
The textbook is internally consistent in organizational framework of each chapter and in the use of terminology.
The textbook is divided into small reading sections with clear headings and subheadings. These could easily be reorganized and realigned.
I found it difficult to follow the organization and structure of the text. There seemed to be no clear logic to much of the distribution of the chapters and the chapter sections. Related content can be found in different chapters of the text. For example, both the chapter on Form in Architecture and on Art and Ritual Life contain extensive sections covering sacred architecture.
Within the chapter sections, there is some organization based on chronology, although this is not consistent. This creates a problem in which chronology is repeated without a larger, cohesive historical narrative. .
The interface of the textbook was effective overall with no significant issues that would distract or confuse the reader. Of necessity, the textbook provides links to works of art that are not reproducible in the textbook due to copyright issues. These links can be clunky and I would be concerned that students will not take the time to click on them all while reading the textbook. Links need to be reviewed. At least one of the links within the text to external images was broken. For the most part the images included in the textbook are high quality, although I find their sourcing odd from random users on Wikimedia.
Overall, the textbook contains no major grammatical errors beyond a few typographical errors.
The textbook draws its examples primarily from Western (European and American) and Asian cultures. There is some inclusion of other cultures, races, and ethnicities, such as Native American or African, although this aspect of the textbook could be strengthened. An instructor would need to bring in additional examples to make a course using this textbook truly inclusive. The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive.
This textbook could be appropriate for usage in an Art Appreciation class, if the instructor of the course was comfortable with the somewhat idiosyncratic thematic choices of the authors. For example, the inclusion of the chapter on the Significance of Materials is not typically included in an art appreciation textbook. The textbook would not work for an Art History course that is taught in a chronological framework. Specific dates are not provided for most of the objects discussed, although birth and death dates of artists are. The historical context and timeline of the works covered by the text are subsumed within the thematic organization.
Reviewed by Samantha Moore, Adjunct Instructor, Art History, Northern Virginia Community College on 6/20/17
The text covers information listed in the table of contents adequately. Content is arranged thematically as is common in art appreciation courses. Each chapter includes a glossary of terms covered at the end of the chapter. It does not include an... read more
The text covers information listed in the table of contents adequately. Content is arranged thematically as is common in art appreciation courses. Each chapter includes a glossary of terms covered at the end of the chapter. It does not include an index at the end of the text. Readers must review the table of contents and guess where information may be found.
The historical information listed in the text was accurate. The text included accurate information regarding styles and movements and theory associated with art. However, the text presents basic and surface level information and lacks in depth views on any one topic.
The content of the text is up-to-date particularly in the discussion of media types. Should updates be necessary it would be easy to implement them.
The text clearly defines bolded terminology. Each chapter is divided into sections and information in each section is related to the theme of that content area. The language is clear and easy to read and follow.
The language used, content presented, and organizational themes are consistent throughout the text.
The text follows a pattern of listing objectives, sectioning off each chapter, and following up with review concepts and terminology. Sections of the text can be assigned at different points within the course.
The text includes eleven chapters divided into sections. While each chapter and subsequent section is rich with information, heading and subheadings do not give a clear sense of what content will be present in a given area. Without an index it is not clear to readers when or where readers will find certain information.
When reading the text online I encountered an issue clicking on links to images. The link would bring me to the image in the same window as the text. I would then have to go back to the text and find my place.
The text was inclusive of a variety of races, ethnicities and backgrounds.
This would be a decent text to use in an art appreciation course but not in a survey art history course. The content is not arranged chronologically or by region. Rather it is divided thematically into broad sections. I was pleasantly surprised with the information listed in several portions of the text. While it does not cover any area in depth it does a fair job of presenting a basic foundation for most of the major topics covered in an art appreciation course. Instructors will find they need to expand on most concepts and should plan on supplementing the text with readings and lectures. Without an index it is difficult to gauge when and where readers will find specific content. Chapter titles and section sub heads are very broad and do not help with pinpointing the location of information.
Reviewed by Isabelle Havet, Faculty, Linn-Benton Community College on 6/20/17
The textbook thoroughly covers the topics of each chapter, and each chapter has enough range that it could easily be supplemented and ideas expanded upon. The "Key Concepts" and "Key Terms" sections after each chapter are very useful and would... read more
The textbook thoroughly covers the topics of each chapter, and each chapter has enough range that it could easily be supplemented and ideas expanded upon. The "Key Concepts" and "Key Terms" sections after each chapter are very useful and would prove an effective study tool for students, as would the "Test Yourself" study questions. However, the textbook should have a master glossary of terms at the end for ease of reference. This is a large omission, especially for students studying for midterms and finals, or working on papers or larger group projects.
There are a small number of typos and usages of uncommon words when more simple words would suffice that are confusing and obscure meaning. (E.g., the tile for section 5.4.3: "Prohibition and Destruction of Imagery: Iconoclasm" misspells the word "iconoclasm," which is particularly problematic as "iconoclasm" could easily be reenforced as a key vocabulary word.)
The text is relevant, and one of its strengths is the breadth and depth of the visual examples anchoring the chapters.
The text is fluid, and the language accessible in a way that would be suitable for different levels of students.
While the text is generally well-organized, the organization of the chapters is somewhat confusing. The choice of chapter topics is also somewhat confusing. Certain major topics are omitted (for example, a chapter dedicated to a more in-depth survey of major artistic media), for what are some interesting but less necessary topics (e.g., Significance of materials in art). This will pose a challenge for instructors who might have to carefully weigh which chapters to teach. This might be especially problematic for instructors teaching in a 10-week term system, or who would supplement the text with additional lessons focused on the history of art (which is omitted from this volume).
The text would easily be divided, which is a strength as the organization of the chapters as it stands might not work for every instructor.
The topics are generally presented in a logical, clear fashion. The structure of chapters is easy to read and flows well.
The text cleverly utilizes open access images. The images are generally very compelling and of high-resolution, which is a big bonus in a visual arts textbook. There are only a few images that are grainy or fuzzy and would beed to be replaced (e.g., the statue of Menkaure and Queen). The interface is legible and pleasing to navigate.
The text contains no grammar errors.
An array of images from different time periods, geographical locations, and cultures. This is a huge bonus, as visual arts fields are moving to make curricula more inclusive. It would have been useful to include more contemporary art, as this is an important topic to emphasize when teaching about visual culture, and is relevant to students' lives. It is also important for instructors who might be teaching visual arts and studio students.
A unique text with a compelling choice of images and topics, and worthy entry in the expanding but still very limited field of art appreciation/visual culture textbooks. I would have liked to see a glossary of terms at the end of the text. It would also be useful to have a discussion of art history, and if not a chapter or more dedicated to art history, at least a timeline at the end of the text. The students are presented with an overwhelming number of artworks, so a general historical reference at the end of the text would be useful. Finally, there are some omissions of topics in favor of narrowing or less important topics that would necessitate some supplemental teaching materials or lessons.
Reviewed by Hilary Galián, Instructor, Portland Community College on 6/20/17
The text covers a broad survey of art including many art forms. Photography, digital media and relational aesthetics examples are lacking throughout the text. Chapters include examples of Western and non-Western art and architecture. More context... read more
The text covers a broad survey of art including many art forms. Photography, digital media and relational aesthetics examples are lacking throughout the text. Chapters include examples of Western and non-Western art and architecture. More context could be fleshed out for how works of art were relevant in their own time. The text effectively references images and graphics that are either included in the text or linked on the web. There is no index, and a list of images would benefit the reader by seeing examples listed in chronological order or by medium. Image captions in the text should include mediums, date and location information, which would help with quick reference and to classify a work illustrating an era.
The wrong title is listed in a few image captions. Otherwise, the book appears error-free.
The content of the book spans the ancient world through contemporary art and reflects current art-world values and attitudes in broad terms -- defining art and artists through a contemporary lens and recognizing the omission of women and marginalized groups throughout the canon of art. Though the recognition is valid, more modern and contemporary art examples could be used to reflect the contributions of a broader group of artists. There are many links to outside sources for imagery, and it is unknown how often those may be checked for changes and errors. A safeguard against readers following links to sources that may have changed their content would be to insert those images directly into the text, which would also help the reading flow, particularly when two works are offered for comparison, such as Wiley’s and Clésinger’s "Femme Piquée par un Serpent," in which only Clésinger’s is included in the text.
Text is written clearly using accessible language for students. Adequate context is given for technical terms with minor exception. The questions at the end of each chapter to check for understanding reflect the text, though more attention could be aimed at mirroring the language and terms used in the chapter.
The chapters are subdivided consistently. There are a few instances in which the title of a work in the text narrative does not match the title given in the caption for the image. There are also some terms listed in the glossary that do not appear in the corresponding chapter. Similarly, there are some inconsistencies in the “Test Yourself” questions, in which the corresponding information is missing.
The chapters are clearly defined as are the concise, themed subsections. It could be easily reorganized to fit subunits of a course, though the text is jumbled chronologically due to classification by theme.
The text flows logically by the outlined themes. The book’s organization would benefit from some reference to a chronology. Without this context, a novice student may struggle to follow a somewhat disjointed selection of art and artifacts.
Internal references to images are made sufficiently clear. Over time, the numerous links to other web material may need updating. There is one reference in the text that is missing a link. A few links reveal images and are too small and low-resolution. The handful of formatting mistakes and typos are somewhat distracting, as is the single column layout.
The text appears free of grammatical errors.
The text is inclusive of a variety of races, ethnicities and backgrounds. The balance of art examples still favors a white, male perspective. References to “our” perspective should be made explicit as such. Some general examples given to explain concepts lack universality, such as yoga as an example of art and science.
This book would serve well as primer for beginning art students for its far-reaching historical scope and theme-based approach, though a student would need supplemental material to address contemporary art forms and the contributions of a broader group of artists.
Reviewed by Sasa Miljevich, Adjunct Instructor (Fine Art), Portland Community College on 6/20/17
The text is organized thematically and covers some of the areas of Art. Some of the content is overly simplified , and some important artistic movements are omitted. There is no index, which make it difficult for students to comprehend some key... read more
The text is organized thematically and covers some of the areas of Art. Some of the content is overly simplified , and some important artistic movements are omitted. There is no index, which make it difficult for students to comprehend some key concepts.
Content is accurate and error free. Images shown and links to artists are mostly of Western Art/ Artist, very few examples , in comparison, of Non-Western Art/Artist.
The text is current and few sections would need updating.Necessary updates will be relatively easy and straightforward to implement.
The text is written in clear and concise manner.
The text is consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
The text is easily dividable into smaller sections to fit with various topics of discussion throughout a term.
The topics in the text are presented in a logical, clear fashion, but smoother transitions between the different chapters would help.
The text is free of significant interface issues, easy to navigate , with clear images. very easy to download and print.
The text does not have many examples of non-western artist and is not overly inclusive of a variety of races, ethnicities, backgrounds, gender.
Reviewed by James Jewitt, Manager and Instructor, Arts Minor, Virginia Tech on 6/20/17
This text successfully manages the difficult task of synthesizing a plethora of approaches when studying art and its history. It considers numerous ethical, philosophical, and thematic issues typically left out of traditional survey books. While... read more
This text successfully manages the difficult task of synthesizing a plethora of approaches when studying art and its history. It considers numerous ethical, philosophical, and thematic issues typically left out of traditional survey books. While these comprise a robust and welcome conversation about the reception, agency, epistemology, and meaning of art, it comes at the cost of a slightly anemic treatment of major historical developments along conventional lines. No index is present or list of illustrations.
Some problems with Italian language terminology are evident, such as "giornate."
The content incorporates relevant and informed perspectives on crucial art world debates, including issues of ethical circulation of cultural property and material culture. Its content offers a broad appeal across the humanities and even social sciences, with relevance to students of philosophy and history as well archaeology and communication.
The prose tends to be clear and readable, though veers towards a somewhat overly conversational and colloquial tone. In places it seems imprecise and too rambling, needing much more concise and to the point verbiage. Also, captions for images are not given information relating to date, medium, or dimensions--a crucial oversight!
The text displays consistency throughout and does a good job of integrating key terms and concepts throughout its chapters. The bolded key terms that appear as a glossary at the close of each chapter is especially helpful, as well as the "test yourself" sections and introductory concepts that start each chapter. Such stand-alone devices are a great boon to students and surely aid with comprehension.
One keen advantage of this text is the authors' clever division of the material into cogent modules that mesh well with poignant themes currently driving the discipline of art history and also the best courses at colleges and universities. In this way, the text serves as an indispensable resources in introductory design and art history courses, as well as upper-level seminars focused on interpretation, methodology, and philosophy of art.
Overall the book is logically organized, particularly chapters 1-5 and 8-11. However, chapters 6-7 are oddly placed and the section on architecture is not well integrated into the rest of the text. It is treated like a separate and outlying practice instead of being carefully woven into the rest of the chapters on form, production, materials, etc. Likewise, chapter 7, though integral and vital, seems out of place. It would perhaps best be placed before the chapter on meaning, since it offers background on socio-cultural behavior as foundation through which to better understand art.
In general, the illustrations and figures are crisp and high resolution. However, they are not expandable or zoomable as is common in other electronic or digital textbook platforms currently available. Likewise, the internet hyperlinks could be replaced with embedded content to better increase the longevity of the text. Some odd spacing around the figures and illustrations is distracting as well.
See comment 4 above. In general, the discussions could be edited to offer a more precise and concise analysis that is less conversational and more direct. Right now it reads as if the authors are pandering a bit to a student audience by invoking memes, selfies, and other ostensibly trendy cultural phenomena.
Another great advantage of this text is its admixture of canonical and popular objects, drawing upon mainstays of art history as well as more of-the-moment visual culture. It is particularly adept at addressing themes that weave together global works in many media from makers of many backgrounds, thereby questioning the entrenched and monolithic canon.
Reviewed by Joe Macca, Adjunct Faculty, Portland Community College on 6/20/17
While the text covers such a vast amount of visual art history, genres, meaning, symbolism, materials, etc., because it's so much, it can only very briefly mention these topics. That said, the glossary of terms is thorough and appropriate. The... read more
While the text covers such a vast amount of visual art history, genres, meaning, symbolism, materials, etc., because it's so much, it can only very briefly mention these topics. That said, the glossary of terms is thorough and appropriate. The 'learning outcomes' and 'test yourself' sections are also very well organized. It can help students understand the kinds of questions and testing done in art survey classes.
In terms of studio art though the book can be a supplement only. Textbooks can be excellent but still not substitutes for the instruction of the hands on manipulation of materials.
The book is unbiased (if there is any bias, it's very slightly European. But which comprehensive survey book is?!) and presents its varied historical genres accurately.
The book suffers slightly from not discussing more contemporary artists and genres, especially performance, installation and public- art based works. Mid 20th century and before, the book is quite thorough. Because of this it is perhaps mildly more prone to obsolescence.
The book is excellent in its prose. Very clear, easy to understand, many good images and illustrations.
The book feels consistent overall. As described elsewhere, it may suffer a little from its lack of discussion of contemporary genres, artists, techniques, etc.
The modularity is the book's necessary natural feature since it cover so much. The chapters are quick and concise.
The 'Personal and Communal Need to Create' sections are so important. I appreciate that this was covered at length. Some sections are not elaborated on as much. I believe the isolated discussion of different art materials (a section on oil paint, a section on print, etc.) is clear and organized- I also believe it should be discussed that these techniques and materials are also very interchangeable.
The book is very well organized. Illustrations and pictures are appropriately shown. More images of 'artists at work' could improve the text.
No grammar issues detected.
The book does a good job of being varied and unbiased, especially when describing art made in varying regions by peoples with different ethnic backgrounds.
I believe the book can function very well as an Open Art History/ Survey Textbook.
Reviewed by A.D. Rocha, Fine Arts Advisor and Instructor, Washington State University on 6/20/17
The text presents its themes in an order that is easy to follow. The examples provided are relevant and serve well to illustrate the concept. The prompts at the end of each chapter also present good starting points for class discussion. read more
The text presents its themes in an order that is easy to follow. The examples provided are relevant and serve well to illustrate the concept. The prompts at the end of each chapter also present good starting points for class discussion.
The content is accurate. The definitions provided are concise.
The content is current. The inclusion of "fourth dimensional" art is particularly helpful in discussing contemporary art.
The terminology used is easy to understand. The "key terms" section is also helpful in its definition of terms that are introduced in that chapter.
The terminology used is consistent and works to expand on the content for proceeding chapters.
The arrangement of sections allow for each to be taken separately as necessary. The chapters can be presented in different order or omitted altogether.
The order of each chapter and its individual sections are easy to follow. Presenting basic concepts on the definition of art and the formal qualities that comprise an artwork in the first four chapters provides a good starting point for the context and meaning discussed further into the text. The only issue with the "flow" would be the inclusion of the chapter on architecture.
The images were presented within the appropriate text and were displayed clearly. The size of the PDF makes searching for a specific term or section a bit difficult, but otherwise there are no problems with the interface.
There were no grammatical errors in this version of the text.
A broader cultural range of examples would be more helpful, however, this is something an instructor can easily amend within classroom lecture or discussion.
This is an excellent introductory text to basic art elements and concepts. On its own, it provides a clear overview for students with no art history background. It can also be used to support other texts where more specific art movements are discussed.
Reviewed by Aderonke Adesanya, Associate Professor, James Madison University on 6/20/17
The text is a bold work in terms of content coverage. It focuses on the nuts and bolts of learning about and discussing art and its context, and combines these with some considerable information on art history, It therefore aptly fits the needs of... read more
The text is a bold work in terms of content coverage. It focuses on the nuts and bolts of learning about and discussing art and its context, and combines these with some considerable information on art history, It therefore aptly fits the needs of a foundation class. Although it has semblances of existing studies, this is not your traditional introductory art textbook. Apart from the in-depth discussion of concepts, techniques, and terminologies, the authors have included learning outcomes at the beginning of each chapter, exercises (review questions) at the end plus key terms to help users review and affirm the content of every chapter. I also find very instructive the discussion of ways of looking at and understanding works of art in chapter 4; the distinction between formal and critical analysis, and the distinction in analysis, description, interpretation and evaluation. These comprehensive discussion make the text a great resource. The material is also reader friendly.
I find that there is minimal references to non-western art especially African and African Diaspora Art. This is palpably obvious even under the discussion 4.5.1 Cultural Style in Chapter 4. The illustrations in the text are also geared towards the examination of western art than other categories including Asian and African. In the discussion of two and three dimensional art (with highlights on materials and techniques), almost all illustrations and examples are western art, with some minimal references to Chinese and Japanese preferred materials for art, and their processes.
There are minor typos found in different pages of the text. For instance: i). Introduction: 2.4. Art Forms (cat egories should read categories)
ii). Chapter 8: p. 247 "iconoclas" should read "iconoclasm"'
Additionally, there is issue of consistency when "iconoclasm" is used as a sub-heading but not mentioned again in the body of the text.It also does not appear in the list of terms of reference. Consistency in reference to location: Benin is in Nigeria, West Africa and not just Africa as presented in the text on page 232. It is correctly referenced in previous pages.
Content is up-to-date. However, it may require updating in the next three years to expands coverage particularly the diversity of the subject matter covered, illustrations, and invariably to bring new content into the chapters.
The text is ready friendly, written in straightforward accessible prose. The definitions of terminologies accurate and simplified for readers to grasp the concepts quickly.
A consistent template runs through the chapters.
However, there is an issue with consistency when "iconoclasm" is used as a sub-heading but not mentioned again in the body of the text.It also does not appear in the list of terms of reference. Consistency issue with the way a culture's location is referenced: Benin is in Nigeria, West Africa and not just Africa as presented in the text on page 232. It is somewhat appropriately referenced in previous pages.
Consistency issue with the spelling of terracotta (pages 273-4, and 277)
Excellent compartmentalization, though I find the many sub-headings a bit problematic.
The structure of the book is very well organized. The topics are presented in logical sequence.
The interface appears many and a bit distracting. The links interspersed in the text forces the reader to go in and out of the text to check images being compared with those embedded in the text. It would have been more effective if these were readily accessible in the text for immediate comparison. No evidence of overtly distorted images (Perhaps Figure 10.37?). However, some of them could be improved for clarity (Figure 10.48 and 10.49).
No grammatical errors but there are typos.
The text could do with some examples of ideas and images about diverse cultures that the learner in the introductory class can later build upon.
Nothing beyond the outlined responses to other questions in this review.
Reviewed by Stephanie Wirt, ACA Art History Adjunct Professor, Reynolds Community College on 2/8/17
This text does cover the material its title implies at an introductory level. More depth could be used in some areas. In the chapter on describing art some major stylistic movements were omitted. The approach to describing art changes relevant to... read more
This text does cover the material its title implies at an introductory level. More depth could be used in some areas. In the chapter on describing art some major stylistic movements were omitted. The approach to describing art changes relevant to the time period and that is not addressed here by omitting some of the major Art movements like Impressionism, Cubism, Realism, photography and digital imagine.
All external Links work Information is accurate but seems to lack in depth in some areas. The artwork shown is primarily from the western world and the art of dead white men. In choosing which art to include as examples more diversity in artists’ ethnicity and gender should be included for a more balanced and realistic scope of art
The technical content of the text is up – to – date. The information as far as approaches to understanding art in general don’t change. Many of the artworks used to illustrate concepts are well known and appear in many standard art history textbooks. However, the lack of contemporary art examples makes some of the content less relevant to the life of the contemporary student. Art, how and why its made) is changing and this text does not necessarily address how to understand new practices in art
The text is clearly written in an easy to understand format.
The format, vocabulary and tone of writing is consistent throughout the text.
a. Each chapter is broken down into subsection that focus on a specific aspect of the overall chapter theme. b. Sections could be combined for instructional purposes c. Sections are brief enough to allow for quick coverage but also leave room for individual teacher adjustments to focus more time and discussion on specific concepts
a. The topics and objectives of each chapter are clear and flow in a logical format. While there could be an argument for some readjustment of chapter ordering, it progresses in a thoughtful format.
o This is a pdf text that can be downloaded to computer or tablet form the web. This allows students access to the main content without having to have internet for most of the content. o The outside links to artworks are necessary to view significant artwork that is not in the creative commons directly at this point. However over time that will change as the original artist dies and time has passed from the date of its creation.
The book's grammar is written using correct English.
The text does not show any outright bias against any specific cultural, racial or ethnic groups. However they are not many examples of non-western art or artists or women artists within the examples provided within the book. This is not unusual for many art survey books but there is a new movement in art education to expand the examples of art to include more people of color and women as well as more diversity in cultural arts within educational texts.
o This book is a good introductory text for a basic art survey class. It doesn’t go into depth in art history or studio practices but it does present a basic knowledgebase for understanding art in general and how to interpret and appreciate a variety of elements of art. o A teacher using this text would want to supplement the reading with practical studio experiences to give students a better understanding of some of the media and techniques presented in the book as well as an opportunity to practice the methods of analyzing artworks with more contemporary artworks.
Reviewed by RADFORD THOMAS, Ph.D., PROFESSOR OF ART, VIRGINIA WESTERN COMMUNITY COLLEGE on 2/8/17
Content adequately covers the subjects it purports to include. However, there is no comprehensive index. A brief list of Key Terms is included within each chapter. These lists are barely adequate and probably confusing to neophyte students with no... read more
Content adequately covers the subjects it purports to include. However, there is no comprehensive index. A brief list of Key Terms is included within each chapter. These lists are barely adequate and probably confusing to neophyte students with no art background. For instance, in 1.9 KEY TERMS, p.30, Icon is described primarily as often religious. “Icon”, in art, may have multiple meanings according to the culture that produced the artifact and its use by those members of that group. As an example, the image of “Isis” is an icon found throughout Egyptian culture with various “religious” as well as “power” and other cultural meanings. This criticism can be directed to all KEY TERMS lists in the text to some extent.
Illustrations appear to be consistent with the knowledge base of the written text. In other words, illustrations fit the need and are usually of good quality and reference the dialog effectively. Titles are included for each image along with the artist/author and sources where appropriate. Missing are important notes about media, method, size, and date alongside the illustration. Non-art students are wont to go to the trouble of looking up this important information.
Some KEY TERMS terminology is lacking in completeness or accuracy. Perhaps it is because the editors wished to make definitions simple, too simple. Bias is toward pleasing everyone while skimming over important iconographic details of the art forms examined. Dialog needs to be aimed at describing the iconographic content of art rather than ancillary historic events.
Content appears to be current in a way that will not make the text out-of-date within a normal time period. Updates, except for items that need immediate attention, should be easy to implement.
This text is actually written in a student-oriented manner that makes a connection between current student populations and information required to cover the subject matter. Applause to the editors.
This text is consistent with overall use of terms and organizational framework. Iconographic statements should be revised so they are accurate and clearly defined to explain the focus, use, and understanding of the art.
This text is divided into eleven rather arbitrary chapters. Editors chose these topics to somehow relate not only to history of art but to serious ways of making art. So this text is not aimed at teaching students about the why of art but about the construction of art. This makes it an art appreciation text, not an art history text. The format does not flow historically but topically.
It is difficult for the novice student to follow these disjointed chapters to a conclusion about what art really is. Each module or chapter is an end in itself and does not develop a cohesive theme about art itself. The Art and Ethics chapter is particularly misguided. This chapter’s content should be placed alongside relevant art objects and discussed in relation to that art.
Text is rife with various and confusing imagery placed next to each other making it difficult for the beginning art historian to make sense of it. There is a lack of cohesive structure throughout the text with a few exceptions. One example is the discussion of “porphyry” in chapter three. This dialog goes from the Sarcophagus of Constantina to the Palace Chapel of Aachen with no real discussion of how valuable materials are used for iconographic purposes. It then goes on to explain a "mausolea" for some reason.
In addition, I find reading the book difficult because it does not use two columns as a standard interface. It uses only a single column throughout the text.
I find no essential grammatical errors or problems.
Text is very inclusive and comprehensive in this matter.
In chapter five I found the Key Concepts very well written and useful to students
It is strange that there is a chapter on Architecture alone as an art form. Photography? or Painting? or Sculpture? or Ceramics? or Weaving...
Reviewed by Renee Garris, Adjunct Professor, J Sargent Reynolds Community College on 2/8/17
The text covers Art in a thematic approach. It explains concepts in an easy to understand manner. read more
The text covers Art in a thematic approach. It explains concepts in an easy to understand manner.
The content is accurate and error-free.
The text is current and few sections would need updating.
The text is written is a manner that those who are new to art and art history can easily understand. There are definitions for words that are new for the readers.
The text is consistent in its use of terms and the framework in which it is written.
The text is written with smaller rather than larger sections and is follow throughout the chapters of the book.
There is a logical progression to the text.
It is free of distortion of images and the illustrations are clear.
It is free of grammar errors.
It is culturally sensitive without bias. It could use more examples of art from the non-Western world for some sections to provide better balance.
Enjoyable read and could be used alone or with supplemental material.
Reviewed by Deborah Cibelli, Professor , Nicholls State University on 12/5/16
The text is organized thematically and does not offer a chronological survey of the history of art. Chapters discuss forms and materials, the processes of describing and interpreting art, aesthetics, architectural form, art and identity, art and... read more
The text is organized thematically and does not offer a chronological survey of the history of art. Chapters discuss forms and materials, the processes of describing and interpreting art, aesthetics, architectural form, art and identity, art and power, art and ritual, and art and ethics. These topics are all covered effectively. Chapters include examples of Western and non-Western art and architecture and offer many comparisons of art from different cultures. While there is no index, the reader may refer to the chapter titles and the glossaries found at the end of each chapter.
The factual information provided is accurate, does not contain errors and is sensitive to world views.
The themes that have been selected are well chosen and will remain relevant so that the text will not require constant revision. However, the URLs (Uniform Resource Locators) or web addresses for different web sites may change over time and the authors may want to update the text by adding examples of contemporary art.
The text discusses complex ideas in a clear and concise manner. Terms used in each chapter are clearly defined in the text and in the chapter glossaries.
Each chapter covers material outlined in the table of contents and the introductory chapter. Each chapter also has a summary of key concepts and reinforces the themes developed throughout the text.
The chapters and sections within the chapters are clearly delineated. There are on average, eight sections in every chapter, making it easy to divide the text into discrete units and easy to refer to specific topics.
The themes and ideas covered in the text are clearly delineated. There are clear transitions from section to section and from one idea to the next.
The illustrations are clearly numbered and referenced in the text. The images are from public domain sources on the web and are identified as such. It would be helpful to have dates for the images and references to the museums where the art objects are located either in the text or as additional information added to the labels for the images.
There are few grammatical errors. There are a few typographical errors such as misspellings of memento mori on page 98, of Edgar Allan Poe on page 214, and of iconoclasm on page 246.
The text compares works of art from different cultures and seems inclusive, objective, and balanced in terms of the items included and the content.
The text departs from standard introductory surveys by referring to objects from different cultures and historical periods that have been selected to illustrate the myriad functions of art, that is, art as map, religious work, “secular icon”, etc. Material is organized thematically rather than chronologically using a comparative model. The chapters on forms, materials, description, symbolic interpretation, aesthetics, architectural form, identity, power, ritual, and ethics, also encourage the reader to make connections to contemporary art and culture. Key concepts are reviewed in the chapter summaries and each chapter has a list of questions that can be used by the student to review the material as well as a glossary of key terms. The chapters on forms and materials support the study of art based on media. In the discussion of interpretive methods, the reader also gains insight into the role of the viewer as well as the artist in determining meaning and is asked to consider the continued relevance of artistic expression. The book could be adapted for teaching a more conventional survey of art if sections are assigned based on content. Chapter 10 on art and ritual, for example, largely follows a historical trajectory that begins with Stonehenge and examines architectural forms in Hawaii and Japan before discussing the sacred spaces and art of the medieval period that have been produced in different media. The strength of this work is that students are asked to make comparisons. They are also asked to think contextually about global art.
Table of Contents
- Chapter One: What is Art?
- Chapter Two: The Structure of Art
- Chapter Three: Significance of Materials Used in Art
- Chapter Four: Describing Art
- Chapter Five: Meaning in Art
- Chapter Six: Connecting Art to Our Lives
- Chapter Seven: Form in Architecture
- Chapter Eight: Art and Identity
- Chapter Nine: Art and Power
- Chapter Ten: Art and Ritual Life
- Chapter Eleven: Art and Ethics
Ancillary Material
- Ancillary materials are available by contacting the author or publisher .
About the Book
Introduction to Art: Design, Context, and Meaning offers a comprehensive introduction to the world of Art. Authored by four USG faculty members with advance degrees in the arts, this textbooks offers up-to-date original scholarship. It includes over 400 high-quality images illustrating the history of art, its technical applications, and its many uses. Combining the best elements of both a traditional textbook and a reader, it introduces such issues in art as its meaning and purpose; its meaning and purpose; its structure, material, and form; and its diverse effects on our lives. Its digital nature allows students to follow links to applicable sources and videos, expanding the students' educational experiences beyond the textbook. Introduction to Art: Design, Context, and Meaning provides a new and free alternative to traditional textbooks, making it an invaluable resource in our modern age of technology and advancement.
About the Contributors
Pamela Sachant is an art history professor at North Georgia College & State University located in Dahlonega, Georgia.
Peggy Blood is Director of Confucius Institute and Full Professor in the Department of Fine Arts Humanities & Wellness. Prior to SSU she Directed satellite campuses (Fairfield &Travis AFD) for Chapman Universities in California. Her area of specialization is Fine Arts, Higher Education & Administration. She is a Fulbright Specialist & Fulbright Specialist Program Peer Reviewer, and reviewer for other academic fellowships and scholarships. Blood is a visiting scholar at Jiujiang University in Jiujiang, China.
Jeffery A. LeMieux is Professor Emeritus of Art at the College of Coastal Georgia. He is a practicing artist with works in private and public collections including the University System of Georgia Board of Regents and the College of Coastal Georgia. He holds an M.F.A in 2D Studio Art from the University of Wisconsin-Madison, and a B.S. in Philosophy from the University of Wisconsin-Oshkosh. His area of specialization is college level art foundations and art appreciation which he has been teaching for over 20 years.
Contribute to this Page
- Corrections
“Without Art Mankind Could Not Exist”: Leo Tolstoy’s Essay What is Art
In his essay “What is Art?” Leo Tolstoy, the author of War and Peace, defines art as a way to communicate emotion with the ultimate goal of uniting humanity.
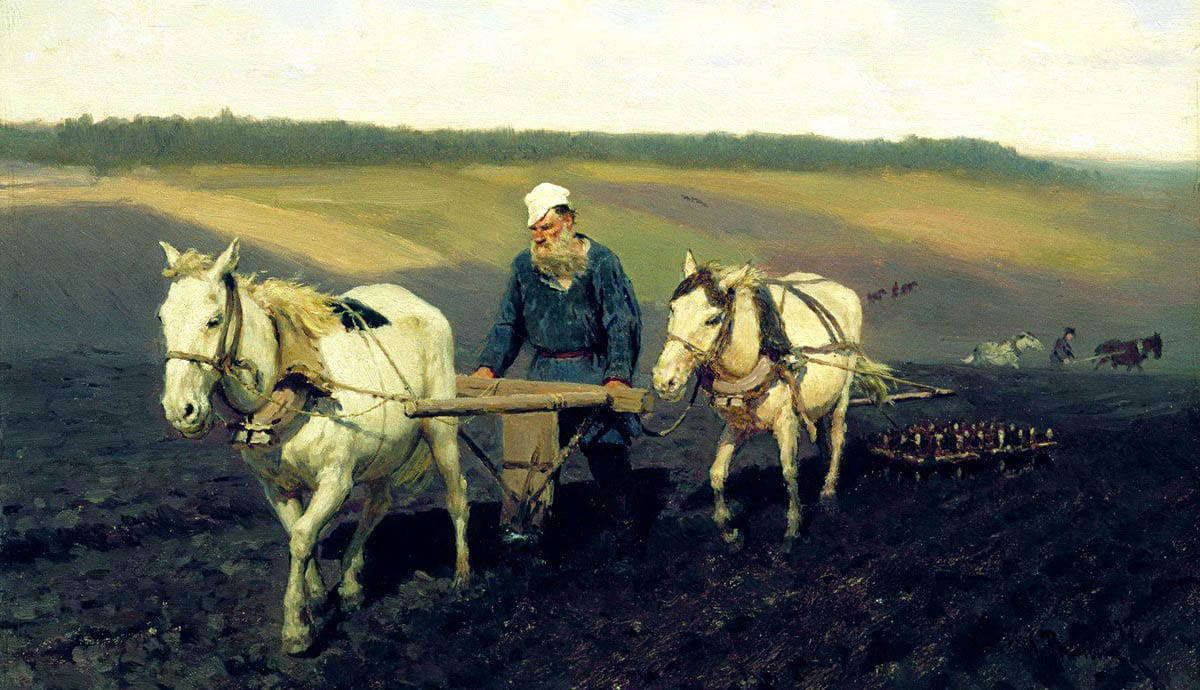

How can we define art? What is authentic art and what is good art? Leo Tolstoy answered these questions in “What is Art?” (1897), his most comprehensive essay on the theory of art. Tolstoy’s theory has a lot of charming aspects. He believes that art is a means of communicating emotion, with the aim of promoting mutual understanding. By gaining awareness of each other’s feelings we can successfully practice empathy and ultimately unite to further mankind’s collective well-being.
Furthermore, Tolstoy firmly denies that pleasure is art’s sole purpose. Instead, he supports a moral-based art able to appeal to everyone and not just the privileged few. Although he takes a clear stance in favor of Christianity as a valid foundation for morality, his definition of religious perception is flexible. As a result, it is possible to easily replace it with all sorts of different ideological schemes.
Personally, I do not approach Tolstoy’s theory as a set of laws for understanding art. More than anything, “What is art?” is a piece of art itself. A work about the meaning of art and a fertile foundation on which truly beautiful ideas can flourish.
Most of the paintings used for this article were drawn by realist painter Ilya Repin. The Russian painter created a series of portraits of Tolstoy, which were exhibited together at the 2019 exhibition “Repin: The Myth of Tolstoy” at the State Museum L.N. Tolstoy. More information regarding the relationship between Tolstoy and Repin can be found in this article .
Who was Tolstoy?

Get the latest articles delivered to your inbox
Please check your inbox to activate your subscription.
Leo Tolstoy ( Count Lev Nikolayevich Tolstoy) was born in 1828 in his family estate of Yasnaya Polyana, some 200km from Moscow. His family belonged in the Russian aristocracy and thus Leo inherited the title of count. In 1851 he joined the tsarist army to pay off his accumulated debt but quickly regretted this decision. Eventually, he left the army right after the end of the Crimean War in 1856.
After traveling Europe and witnessing the suffering and cruelty of the world, Tolstoy was transformed. From a privileged aristocrat, he became a Christian anarchist arguing against the State and propagating non-violence. This was the doctrine that inspired Gandhi and was expressed as non-resistance to evil. This means that evil cannot be fought with evil means and one should neither accept nor resist it.
Tolstoy’s writing made him famous around the world and he is justly considered among the four giants of Russian Literature next to Dostoevsky, Chekhov, and Turgenev. His most famous novels are War and Peace (1869) and Anna Karenina (1877). However, he also wrote multiple philosophical and theological texts as well as theatrical plays and short stories. Upon completing his masterpiece Anna Karenina , Tolstoy fell into a state of insufferable existential despair.
Charmed by the faith of the common people, he turned to Christianity. Eventually, he dismissed the Russian Church and every other Church as corrupted and looked for his own answers. His theological explorations led to the formulation of his own version of Christianity, which deeply influenced his social vision. He died in 1910 at the age of 82 after suffering from pneumonia.
Art Based On Beauty And Taste

Tolstoy wrote “What is art?” in 1897. There, he laid down his opinions on several art-related issues. Throughout this essay , he remains confident that he is the first to provide an exact definition for art:
“…however strange it may seem to say so, in spite of the mountains of books written about art, no exact definition of art has been constructed. And the reason of this is that the conception of art has been based on the conception of beauty.”
So, what is art for Tolstoy? Before answering the question, the Russian novelist seeks a proper basis for his definition. Examining works of other philosophers and artists, he notices that they usually assume that beauty is art’s foundation. For them beauty is either that which provides a certain kind of pleasure or that which is perfect according to objective, universal laws.
Tolstoy thinks that both cases lead to subjective definitions of beauty and in turn to subjective definitions of art. Those who realize the impossibility of objectively defining beauty, turn to a study of taste asking why a thing pleases. Again, Tolstoy sees no point in this, as taste is also subjective. There is no way of explaining why one thing pleases someone but displeases someone else, he concludes.
Theories that Justify the Canon

Theories of art based on beauty or taste inescapably include only that type of art that appeals to certain people:
“First acknowledging a certain set of productions to be art (because they please us) and then framing such a theory of art that all those productions which please a certain circle of people should fit into it.”
These theories are made to justify the existing art canon which covers anything from Greek art to Shakespeare and Beethoven. In reality, the canon is nothing more than the artworks appreciated by the upper classes. To justify new productions that please the elites, new theories that expand and reaffirm the canon are constantly created:
“No matter what insanities appear in art, when once they find acceptance among the upper classes of our society, a theory is quickly invented to explain and sanction them; just as if there had never been periods in history when certain special circles of people recognized and approved false, deformed, and insensate art which subsequently left no trace and has been utterly forgotten.”
The true definition of art, according to Tolstoy, should be based on moral principles. Before anything, we need to question if a work of art is moral. If it is moral, then it is good art. If it is not moral, it is bad. This rationale leads Tolstoy to a very bizarre idea. At one point in his essay, he states that Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliette, Goethe’s Wilhelm Meister, and his own War and Peace are immoral and therefore bad art. But what does Tolstoy exactly mean when he says that something is good or bad art? And what is the nature of the morality he uses for his artistic judgments?
What is Art?

Art is a means of communicating feelings the same way words transmit thoughts. In art, someone transmits a feeling and “infects” others with what he/she feels. Tolstoy encapsulates his definition of art in the following passages:
“To evoke in oneself a feeling one has once experienced, and having evoked it in oneself, then, by means of movements, lines, colors, sounds, or forms expressed in words, so to transmit that feeling that others may experience the same feeling – this is the activity of art. Art is a human activity consisting in this, that one man consciously, by means of certain external signs, hand on to others feelings he has lived through, and that other people are infected by these feelings and also experience them.”
In its essence, art is a means of union among men brought together by commonly experienced feelings. It facilitates access to the psychology of others fostering empathy and understanding by tearing down the walls of the Subject. This function of art is not only useful but also necessary for the progress and wellbeing of humanity.
The innumerable feelings experienced by humans both in past and present are available to us only through art. The loss of such a unique ability would be a catastrophe. “Men would be like beasts”, says Tolstoy, and even goes as far as to claim that without art, mankind could not exist. This is a bold declaration, which recalls the Nietzschean aphorism that human existence is justified only as an aesthetic phenomenon.
Art in the Extended and Limited Sense of the Word

Tolstoy’s definition expands to almost every aspect of human activity way beyond the fine arts. Even a boy telling the story of how he met a wolf can be art. That is, however, only if the boy succeeds in making the listeners feel the fear and anguish of the encounter. Works of art are everywhere, according to this view. Cradlesong, jest, mimicry, house ornamentation, dress and utensils, even triumphal processions are all works of art.
This is, in my view, the strongest point of Tolstoy’s theory. Namely, that it considers almost the totality of human activity as art. However, there is a distinction between this expanded art, and art in the limited sense of the word. The latter corresponds to the fine arts and is the area that Tolstoy investigates further in his essay. A weak point of the theory is that it never examines the act of creation and art that is not shared with others.
Real and Counterfeit Art

The distinction between real and counterfeit, good and bad art is Tolstoy’s contribution to the field of art criticism. Despite its many weaknesses, this system offers an interesting alternative to judging and appreciating art.
Tolstoy names real art (i.e. authentic, true to itself) the one resulting from an honest, internal need for expression. The product of this internal urge becomes a real work of art, if it successfully evokes feelings to other people. In this process, the receiver of the artistic impression becomes so united with the artist’s experience, that he/she feels like the artwork is his/her own. Therefore, real art removes the barrier between Subject and Object, and between receiver and sender of an artistic impression. In addition, it removes the barrier between the receivers who experience unity through a common feeling.
“In this freeing of our personality from its separation and isolation, in this uniting of it with others, lies the chief characteristic and the great attractive force of art.” Furthermore, a work that does not evoke feelings and spiritual union with others is counterfeit art. No matter how poetical, realistic, effectful, or interesting it is, it must meet these conditions to succeed. Otherwise it is just a counterfeit posing as real art.
Emotional Infectiousness

Emotional infectiousness is a necessary quality of a work of art. The degree of infectiousness is not always the same but varies according to three conditions:
- The individuality of the feeling transmitted: the more specific to a person the feeling, the more successful the artwork.
- The clearness of the feeling transmitted: the clearness of expression assists the transition of feelings and increases the pleasure derived from art.
- The sincerity of the artist: the force with which the artist feels the emotion he/she transmits through his/her art.
Out of all three, sincerity is the most important. Without it, the other two conditions cannot exist. Worth noting is that Tolstoy finds sincerity almost always present in “peasant art” but almost always absent in “upper-class art”. If a work lacks even one of the three qualities, it is counterfeit art. In contrast, it is real if it possesses all three. In that case, it only remains to judge whether this real artwork is good or bad, more or less successful. The success of an artwork is based firstly on the degree of its infectiousness. The more infectious the artwork, the better.

The Religious Perception of Art

Tolstoy believes that art is a means of progress towards perfection. With time, art evolves rendering accessible the experience of humanity for humanity’s sake. This is a process of moral realization and results in society becoming kinder and more compassionate. A genuinely good artwork ought to make accessible these good feelings that move humanity closer to its moral completion. Within this framework, a good work of art must also be moral.
But how can we judge what feelings are morally good? Tolstoy’s answer lies in what he calls “the religious perception of the age”. This is defined as the understanding of the meaning of life as conceived by a group of people. This understanding is the moral compass of a society and always points towards certain values. For Tolstoy, the religious perception of his time is found in Christianity. As a result, all good art must carry the foundational message of this religion understood as brotherhood among all people. This union of man aiming at his collective well-being, argues Tolstoy, must be revered as the highest value of all.
Although it relates to religion, religious perception is not the same with religious cult. In fact, the definition of religious perception is so wide, that it describes ideology in general. To this interpretation leads Tolstoy’s view that, even if a society recognizes no religion, it always has a religious morality. This can be compared with the direction of a flowing river:
If the river flows at all, it must have a direction. If a society lives, there must be a religious perception indicating the direction in which, more or less consciously, all its members tend.

It is safe to say that more than a century after Tolstoy’s death, “What is Art?” retains its appeal. We should not easily dismiss the idea that (good) art communicates feelings and promotes unity through universal understanding. This is especially the case in our time where many question art’s importance and see it as a source of confusion and division.
- Tolstoy, L.N. 1902. What is Art? In the Novels and Other Works of Lyof N. Tolstoy . translated by Aline Delano. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons. pp. 328-527. Available at: http://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/43409
- Jahn, G.R. 1975. ‘The Aesthetic Theory of Leo Tolstoy’s What Is Art?’. The Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , Vol. 34, No. 1. pp. 59-65. Available at: https://www.jstor.org/stable/428645
- Morson, G.S. 2019. ‘Leo Tolstoy’. Encyclopædia Britannica. Available at: https://www.britannica.com/biography/Leo-Tolstoy

Theodor Adorno on the Essay: An Antidote to Modernity

By Antonis Chaliakopoulos MSc Museum Studies, BA History & Archaeology Antonis is an archaeologist with a passion for museums and heritage and a keen interest in aesthetics and the reception of classical art. He holds an MSc in Museum Studies from the University of Glasgow and a BA in History and Archaeology from the University of Athens (NKUA) where he is currently working on his PhD.

Frequently Read Together

Timeline of Ancient Greek Art & Sculpture
Definition of Art Definition Essay
The practice of creating artistic works is something that is as old as the human species. Historically, different societies had their own ways of defining art, because of the significance that societies placed on artistic works. Although such traditional definitions are still appreciated in some contemporary societies, the birth of modernism has revolutionized most historical definitions, to include institutional and relational properties of art.
One common thing with traditional and conventional definitions of arts is that, these definitions share some common concepts of human agency, which are in form of manual handiness, intellectual manipulation, and expression of ideas, aimed at communicating certain concepts of the human culture. As a result of the failure to blend all this aspects of art, most individuals have a tendency of confusing visual culture, craft, and art.
Although anything constructed skillfully with a symbolic significance and which can have some effect on people’s emotions and mental power can be termed as art, such a definition of art will be lacking, as it will not have appreciated the relevance of the artistic skill itself. Therefore, art is a symbolic expression of an individual’s ideas using certain elements of art to create objects or images that are meant to arouse people’s emotions and express ideas, for purposes of communicating certain messages.
For a piece of work to be called an art, it has to be an outcome of a conscious intention or self-rewarding activity, which unites things that are not similar to convey certain messages or evoke specific feelings in people. Art goes beyond reasoning, because it is a magnificent expression of certain ideas in a form that goes beyond the realm of such ideas. In addition, to a large extent art tends to appreciate the formal elements of an individual’s emotions.
Therefore, for individuals to be able to create some pieces of art, they have to have such ideas in their mind in form of mental images; hence, visible works of art are just a depiction of the mental images and ideas held by individuals. Secondly, for a piece of work to be called an art, it has to have form and content.
Form primarily includes all elements of art and principles of design. Primary elements of art include texture, line, shape, form, space, color, and value. In any artistic work, these elements have to be blended properly by using certain set principles of design. Such blending of these elements is important in artistic works, because it provides a way of interpreting and understanding different works of art.
It is important for individuals to note that, art is susceptible to diverse interpretations, because of the fact that art tends to encourage visceral rather than rational understanding. This like a scenario arises due to the fact that, one does not require some special interpreting powers to be able to understand any piece of art, but rather the ability to interpret art depends on the emotional connection that an individual from with a piece of art.
Any artistic work must also create a certain emotional and philosophical link between its creator and audience. For any piece of work to achieve this it must embrace two main concepts genuineness and clearness, as these are two of the primary properties that qualify any piece of work as an art.
Clearness and genuineness also make art to have the power of connecting people, as it helps to communicate certain emotions or ideas. Further, to be able to act as a communication tool, art has to be able to use creative skill to formulate works which have symbolic meaning. The interpretation of this meaning will depend on the products of such creative works, them being the primary determinant of the nature of emotions a work of art will excite in its viewers.
One of the artistic works that fits in this definition of art is Francisco De Goya’s “The shooting of May Third, 1808. Goya has blended different elements of art, which include color, value, line, and space to excite different feelings in the viewers of the picture. In addition, Goya has also used different principles of design, which include balance, contrast, and proportion, features which are important in helping the viewers of the picture to visualize how the shooting scenario was.
In addition to this, because the shooting was a real historical event, through looking at the picture, viewers are able to form a connection with what happened, because of the painful, resentment, and grief feelings that the picture excites in its viewers.
On the other hand, this picture is also a representation of the creativity of Goya, because through visualizing how the shootings took place, he was able to paint a pictorial representation of this historical occurrence; hence, proving the fact that, art is a product of visual images and representations in an artist’s mind.
In conclusion, art is primarily the outcome of the human drive to express mental images and representations meant to create an expressive exchange between artists and audiences. To achieve this, artists must use different elements and designs to represent mental images and expressions. As a result of the symbolism represented in artistic works, art is a mental stimulator, as it excites different emotions that are the basis of any form of interpretation given to any artistic work.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, February 20). Definition of Art. https://ivypanda.com/essays/definition-of-art/
"Definition of Art." IvyPanda , 20 Feb. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/definition-of-art/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Definition of Art'. 20 February.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Definition of Art." February 20, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/definition-of-art/.
1. IvyPanda . "Definition of Art." February 20, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/definition-of-art/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Definition of Art." February 20, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/definition-of-art/.
- Renaissance and Romanticism: Concepts of Beauty
- Repackaging a Bald Product
- Cultural Artifacts and Their Theme
- A 21st Century Manifestation of the Enlightenment: Jean-Pierre Gauthier, Battements et Papillons
- Modernism in Art and Painting
- Caribbean Art History
- Concepts of the Baroque Era
- "Notes on Camp" by Susan Sontag

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing Essays in Art History

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Art History Analysis – Formal Analysis and Stylistic Analysis
Typically in an art history class the main essay students will need to write for a final paper or for an exam is a formal or stylistic analysis.
A formal analysis is just what it sounds like – you need to analyze the form of the artwork. This includes the individual design elements – composition, color, line, texture, scale, contrast, etc. Questions to consider in a formal analysis is how do all these elements come together to create this work of art? Think of formal analysis in relation to literature – authors give descriptions of characters or places through the written word. How does an artist convey this same information?
Organize your information and focus on each feature before moving onto the text – it is not ideal to discuss color and jump from line to then in the conclusion discuss color again. First summarize the overall appearance of the work of art – is this a painting? Does the artist use only dark colors? Why heavy brushstrokes? etc and then discuss details of the object – this specific animal is gray, the sky is missing a moon, etc. Again, it is best to be organized and focused in your writing – if you discuss the animals and then the individuals and go back to the animals you run the risk of making your writing unorganized and hard to read. It is also ideal to discuss the focal of the piece – what is in the center? What stands out the most in the piece or takes up most of the composition?
A stylistic approach can be described as an indicator of unique characteristics that analyzes and uses the formal elements (2-D: Line, color, value, shape and 3-D all of those and mass).The point of style is to see all the commonalities in a person’s works, such as the use of paint and brush strokes in Van Gogh’s work. Style can distinguish an artist’s work from others and within their own timeline, geographical regions, etc.
Methods & Theories To Consider:
Expressionism
Instructuralism
Postmodernism
Social Art History
Biographical Approach
Poststructuralism
Museum Studies
Visual Cultural Studies
Stylistic Analysis Example:
The following is a brief stylistic analysis of two Greek statues, an example of how style has changed because of the “essence of the age.” Over the years, sculptures of women started off as being plain and fully clothed with no distinct features, to the beautiful Venus/Aphrodite figures most people recognize today. In the mid-seventh century to the early fifth, life-sized standing marble statues of young women, often elaborately dress in gaily painted garments were created known as korai. The earliest korai is a Naxian women to Artemis. The statue wears a tight-fitted, belted peplos, giving the body a very plain look. The earliest korai wore the simpler Dorian peplos, which was a heavy woolen garment. From about 530, most wear a thinner, more elaborate, and brightly painted Ionic linen and himation. A largely contrasting Greek statue to the korai is the Venus de Milo. The Venus from head to toe is six feet seven inches tall. Her hips suggest that she has had several children. Though her body shows to be heavy, she still seems to almost be weightless. Viewing the Venus de Milo, she changes from side to side. From her right side she seems almost like a pillar and her leg bears most of the weight. She seems be firmly planted into the earth, and since she is looking at the left, her big features such as her waist define her. The Venus de Milo had a band around her right bicep. She had earrings that were brutally stolen, ripping her ears away. Venus was noted for loving necklaces, so it is very possibly she would have had one. It is also possible she had a tiara and bracelets. Venus was normally defined as “golden,” so her hair would have been painted. Two statues in the same region, have throughout history, changed in their style.
Compare and Contrast Essay
Most introductory art history classes will ask students to write a compare and contrast essay about two pieces – examples include comparing and contrasting a medieval to a renaissance painting. It is always best to start with smaller comparisons between the two works of art such as the medium of the piece. Then the comparison can include attention to detail so use of color, subject matter, or iconography. Do the same for contrasting the two pieces – start small. After the foundation is set move on to the analysis and what these comparisons or contrasting material mean – ‘what is the bigger picture here?’ Consider why one artist would wish to show the same subject matter in a different way, how, when, etc are all questions to ask in the compare and contrast essay. If during an exam it would be best to quickly outline the points to make before tackling writing the essay.
Compare and Contrast Example:
Stele of Hammurabi from Susa (modern Shush, Iran), ca. 1792 – 1750 BCE, Basalt, height of stele approx. 7’ height of relief 28’
Stele, relief sculpture, Art as propaganda – Hammurabi shows that his law code is approved by the gods, depiction of land in background, Hammurabi on the same place of importance as the god, etc.
Top of this stele shows the relief image of Hammurabi receiving the law code from Shamash, god of justice, Code of Babylonian social law, only two figures shown, different area and time period, etc.
Stele of Naram-sin , Sippar Found at Susa c. 2220 - 2184 bce. Limestone, height 6'6"
Stele, relief sculpture, Example of propaganda because the ruler (like the Stele of Hammurabi) shows his power through divine authority, Naramsin is the main character due to his large size, depiction of land in background, etc.
Akkadian art, made of limestone, the stele commemorates a victory of Naramsin, multiple figures are shown specifically soldiers, different area and time period, etc.
Iconography
Regardless of what essay approach you take in class it is absolutely necessary to understand how to analyze the iconography of a work of art and to incorporate into your paper. Iconography is defined as subject matter, what the image means. For example, why do things such as a small dog in a painting in early Northern Renaissance paintings represent sexuality? Additionally, how can an individual perhaps identify these motifs that keep coming up?
The following is a list of symbols and their meaning in Marriage a la Mode by William Hogarth (1743) that is a series of six paintings that show the story of marriage in Hogarth’s eyes.
- Man has pockets turned out symbolizing he has lost money and was recently in a fight by the state of his clothes.
- Lap dog shows loyalty but sniffs at woman’s hat in the husband’s pocket showing sexual exploits.
- Black dot on husband’s neck believed to be symbol of syphilis.
- Mantel full of ugly Chinese porcelain statues symbolizing that the couple has no class.
- Butler had to go pay bills, you can tell this by the distasteful look on his face and that his pockets are stuffed with bills and papers.
- Card game just finished up, women has directions to game under foot, shows her easily cheating nature.
- Paintings of saints line a wall of the background room, isolated from the living, shows the couple’s complete disregard to faith and religion.
- The dangers of sexual excess are underscored in the Hograth by placing Cupid among ruins, foreshadowing the inevitable ruin of the marriage.
- Eventually the series (other five paintings) shows that the woman has an affair, the men duel and die, the woman hangs herself and the father takes her ring off her finger symbolizing the one thing he could salvage from the marriage.
The Elements of Art Eight tools, infinite expression
All artwork speaks the same language through a vocabulary of eight terms expressed in infinite ways. We all understand the vocabulary of art subconsciously, but recognizing how it’s applied enriches our experience of art and allows for nuanced discussion of artworks and appreciation of the artist's passion and skill. The vocabulary of art is made up of the Formal Elements of Design: line, shape, form, space, color, texture, motion, and time.

The most basic element of design is the line: a mark with greater length than width, the path traced by a moving point. In mathematics, a line has no width, but in art, lines can be thin, thick, rough or smooth. Lines can convey tremendous emotion, from aggressive zig-zags or tranquil waves to nauseating spirals. Artists can convey confidence in bold lines, or precision with straight lines.

A shape is formed when lines enclose a space. The edges of the shape are its contour, which can be geometric or organic, open or closed. Like lines, shapes can be expressive, sharp or soft, architecturally rigid or flowing. Simple shapes form a common vocabulary that stretches back millenia, often associated with specific attributes. Roman Architects believed the circle to be divinely perfect, and used it when designing their temples. Triangles were imagined to point to the heavens.

Form is the real or perceived dimensionality of a shape, expressing length, width, and depth. Spheres, cubes, pyramids are three-dimensional forms, and some of the fundamental building blocks for expression in art. Form can also describe the structure of a work of art. The composition of a painting or the chapters of a book. Form can be used to talk about the arrangement of formal elements that present the whole.

Space is the area between and around objects. In art and design, the space is as important as the forms it surrounds. Space can be two or three dimensional, and is often referred to as negative space. Space holds the objects it contains, providing context. Space is as emotive as lines and shapes, and can create feelings of isolation, claustrofobia, or wide open possibility.

Color is possibly the most complex tool at the artist's disposal. Color is scientifically defined as the light that reflects off illuminated objects, whose pigmentation absorbs some wavelengths, and the wavelengths that remain enter the eye. The colors we see are part of the visible spectrum: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and indigo, but these colors combine into millions of perceivable colors. To talk about the variations of colors, we use the terms hue, value, and intensity. Hue defines the range the color sits within, like a greenish yellow or a yellowy green. Value is the relative lightness or darkness of the color, and intensity is the relative brightness or dullness of the color.

Texture comes from the latin word texo , meaning 'to weave' and refers to the qualities of a material surface. Texture may be seen and felt in dimensional objects, such as canvas or a marble sculpture, and two-dimensional objects can create the illusion of texture, like a photograph of a rough wooden surface. Texture can be evocative. Smooth objects can feel refined, and rough surfaces may create a gritty, aggressive appearance.

Motion is the movement or change of an object over time. In art motion can be applied to sculpture, called kinetic sculpture , and is a natural element of video and performance art.

The effect of time on artwork is an oft overlooked element of design. All objects change over time, though in different ways. A stone artifact from 30,000 BCE may be nearly unchanged from the time of its creation, but paintings fade. Time is also part of how we consume art. A book may take weeks to read, and that time creates a different context for the experience than an article read in minutes. Video uses time the same way a painter uses negative space, employing pacing, momentum, and balance over the length of the film.
Reed Enger, "The Elements of Art, Eight tools, infinite expression," in Obelisk Art History , Published June 24, 2017; last modified November 08, 2022, http://www.arthistoryproject.com/essays/the-elements-of-art/.

Is there such a thing as Bad Art?
Yes, but it's complicated
The Value of Art
Why should we care about art?
The Principles of Design
By continuing to browse Obelisk you agree to our Cookie Policy
Visual Analysis: How to Analyze a Painting and Write an Essay

A visual analysis essay is an entry-level essay sometimes taught in high school and early university courses. Both communications and art history students use visual analysis to understand art and other visual messages. In our article, we will define the term and give an in-depth guide on how to look at a piece of art and write a visual analysis essay. Stay tuned until the end for a handy visual analysis essay example from our graduate paper writing service .
What Is Visual Analysis?
Visual analysis is the process of looking at a piece of visual art (painting, photography, film, etc.) and dissecting it for the artist’s intended meaning and means of execution. In some cases, works are also analyzed for historical significance and their impact on culture, art, politics, and the social consciousness of the time. This article will teach you how to perform a formal analysis of art.
Need Help With Your Visual Analysis?
You only need to send your paper requirements to get help from professional writers.
A visual analysis essay is a type of essay written mostly by students majoring in Art History and Communications. The process of visual analysis can be applied to painting, visual art, journalism, photo-journalism, photography, film, and writing. Works in these mediums are often meant to be consumed for entertainment or informative purposes. Visual analysis goes beyond that, focusing on form, themes, execution, and the compositional elements that make up the work.
Classical paintings are a common topic for a visual analysis essay because of their depth and historical significance. Take the famous Raphael painting Transfiguration. At first glance, it is an attractive image showing a famous scene from the Bible. But a more in-depth look reveals practical painting techniques, relationships between figures, heavy symbolism, and a remarkable choice of colors by the talented Raphael. This deeper look at a painting, a photograph, visual or written art is the process of visual analysis.
Get term paper writer from our professionals. Leave us a message ' write my paper for me ' and we'll deliver the task asap.
Formal Analysis of Art: Who Does It?
Most people who face visual analysis essays are Communication, English, and Art History students. Communications students explore mediums such as theater, print media, news, films, photos — basically anything. Comm is basically a giant, all-encompassing major where visual analysis is synonymous with Tuesday.
Art History students study the world of art to understand how it developed. They do visual analysis with every painting they look it at and discuss it in class.
English Literature students perform visual analysis too. Every writer paints an image in the head of their reader. This image, like a painting, can be clear, or purposefully unclear. It can be factual, to the point, or emotional and abstract like Ulysses, challenging you to search your emotions rather than facts and realities.
How to Conduct Visual Analysis: What to Look For
Whether you study journalism or art, writing a visual analysis essay will be a frequent challenge on your academic journey. The primary principles can be learned and applied to any medium, regardless of whether it’s photography or painting.
For the sake of clarity, we’ve chosen to talk about painting, the most common medium for the formal analysis of art.

In analyzing a painting, there are a few essential points that the writer must know.
- Who is the painter, and what era of art did they belong to? Classical painters depict scenes from the Bible, literature, or historical events (like the burning of Rome or the death of Socrates). Modernists, on the other hand, tend to subvert classical themes and offer a different approach to art. Modernism was born as a reaction to classical painting, therefore analyzing modernist art by the standards of classical art would not work.
- What was the painter’s purpose? Classical painters like Michelangelo were usually hired by the Vatican or by noble families. Michelangelo didn’t paint the Sistine Chapel just for fun; he was paid to do it.
- Who is the audience? Artists like Andy Warhol tried to appeal to the masses. Others like Marcel Duchamp made art for art people, aiming to evolve the art form.
- What is the historical context? Research your artist/painting thoroughly before you write. The points of analysis that can be applied to a Renaissance painter cannot be applied to a Surrealist painter. Surrealism is an artistic movement, and understanding its essence is the key to analyzing any surrealist painting.
Familiarizing yourself with these essential points will give you all the information and context, you need to write a good visual analysis essay.
But visual analysis can go deeper than that — especially when dealing with historic pieces of visual art. Students explore different angles of interpretation, the interplay of colors and themes, how the piece was made and various reactions, and critiques of it. Let’s dig deeper.
A Detailed Process of Analyzing Visual Art
Performing a formal analysis of art is a fundamental skill taught at entry-level art history classes. Students who study art or communications further develop this skill through the years. Not all types of analysis apply to every work of art; every art piece is unique. When performing visual analysis, it’s essential to keep in mind why this particular work of art is important in its own way.

Step 1: General Info
To begin, identify the following necessary information on the work of art and the artist.
- Subject — who or what does this work represent?
- Artist — who is the author of this piece? Refer to them by their last name.
- Date and Provenance — when and where this work of art was made. Is it typical to its historical period or geographical location?
- Past and Current Locations — where was this work was displayed initially, and where is it now?
- Medium and Creation Techniques — what medium was this piece made for and why is it important to that medium? Note which materials were used in its execution and its size.
Step 2: Describe the Painting
Next, describe what the painting depicts or represents. This section will be like an abstract, summarizing all the visible aspects of the piece, painting the image in the reader’s mind. Here are the dominant features to look for in a painting:
- Characters or Figures: who they are and what they represent.
- If this is a classical painting, identify the story or theme depicted.
- If this is an abstract painting, pay attention to shapes and colors.
- Lighting and overall mood of the painting.
- Identify the setting.
Step 3: Detailed Analysis
The largest chunk of your paper will focus on a detailed visual analysis of the work. This is where you go past the basics and look at the art elements and the principles of design of the work.
Art elements deal mostly with the artist’s intricate painting techniques and basics of composition.
- Lines — painters use a variety of lines ranging from straight and horizontal to thick, curved, even implied lines.
- Shapes — shapes can be distinct or hidden in plain sight; note all the geometrical patterns of the painting.
- Use of Light — identify the source of light, or whether the lighting is flat; see whether the painter chooses contrasting or even colors and explain the significance of their choice in relation to the painting.
- Colors — identify how the painter uses color; which colors are primary, which are secondary; what is the tone of the painting (warm or cool?)
- Patterns — are there repeating patterns in the painting? These could be figures as well as hidden textural patterns.
- Use of Space — what kind of perspective is used in the painting; how does the artist show depth (if they do).
- Passage of Time and Motion
Design principles look at the painting from a broader perspective; how the art elements are used to create a rounded experience from an artistic and a thematic perspective.
- Variety and Unity - explore how rich and varied the artists’ techniques are and whether they create a sense of unity or chaos.
- Symmetry or Asymmetry - identify points of balance in the painting, whether it’s patterns, shapes, or use of colors.
- Emphasis - identify the points of focus, both from a thematic and artistic perspective. Does the painter emphasize a particular color or element of architecture?
- Proportions - explain how objects and figures work together to provide a sense of scale, mass, and volume to the overall painting.
- Use of Rhythm - identify how the artist implies a particular rhythm through their techniques and figures.
Seeing as each work of art is unique, be thoughtful in which art elements and design principles you wish to discuss in your essay. Visual analysis does not limit itself to painting and can also be applied to mediums like photography.
Got Stuck While writing your paper?
Count on the support of the professional writers of our essay writing service .
The Structure: How to Write a Visual Analysis Paper
It’s safe to use the five-paragraph essay structure for your visual analysis essay. If you are looking at a painting, take the most important aspects of it that stand out to you and discuss them in relation to your thesis. Structure it with the simple essay structure:
Introduction: An introduction to a visual analysis essay serves to give basic information on the work of art and briefly summarize the points of discussion.
- Give a brief description of the painting: name of artist, year, artistic movement (if necessary), and the artist’s purpose in creating this work.
- Briefly describe what is in the painting.
- Add interesting facts about the artist, painting, or historical period to give your reader some context.
- As in all introductions, don’t forget to include an attention-grabber to get your audience interested in reading your work.
Thesis: In your thesis, state the points of analysis on this work of art which you will discuss in your essay.
Body: Explore the work of art and all of its aspects in detail. Refer to the section above titled “A Detailed Process of Analyzing Visual Art,” which will comprise most of your essay’s body.
Conclusion: After you’ve thoroughly analyzed the painting and the artist’s techniques, give your thoughts and opinions on the work. Your observations should be based on the points of analysis in your essay. Discuss how the art elements and design principles of the artist give the painting meaning and support your observations with facts from your essay.
Citation: Standard citation rules apply to these essays. Use in-text citations when quoting a book, website, journal, or a movie, and include a sources cited page listing your sources. And there’s no need to worry about how to cite a piece of art throughout the text. Explain thoroughly what work of art you’re analyzing in your introduction, and refer to it by name in the body of your essay like this — Transfiguration by Raphael.
If you want a more in-depth look at the classic essay structure, feel free to visit our 5 PARAGRAPH ESSAY blog
Learn From a Visual Analysis Example
Many YouTube videos are analyzing famous paintings like the Death of Socrates, which can be a great art analysis example to go by. But the best way to understand the format and presentation is by looking at a painting analysis essay example done by a scholarly writer. One of our writers has penned an outstanding piece on Leonardo Da Vinci’s La Belle Ferronnière, which you may find below. Use it as a reference point for your visual analysis essay, and you can’t go wrong!
Leonardo da Vinci was an Italian artist born in April 1452 and died in May 1519who lived in the Renaissance era. His fame and popularity were based on his painting sand contribution to the Italian artwork. Leonardo was also an active inventor, a vibrant musician, writer, and scientist as well as a talented sculptor amongst other fields. His various career fields proved that he wanted to know everything about nature. In the book “Leonardo Da Vinci: The Mind of the Renaissance” by Alessandro Vezzosi, it is argued that Leonardo was one of the most successful and versatile artists and anatomists of the Italian renaissance based on his unique artwork and paintings (Vezzosi, p1454). Some of his groundbreaking research in medicine, metal-casting, natural science, architecture, and weaponry amongst other fields have been explored in the book. He was doing all these in the renaissance period in Italy from the 1470s till his death.
Visual analysis essays will appear early in your communications and art history degrees. Learning how to formally analyze art is an essential skill, whether you intend to pursue a career in art or communications.
Before diving into analysis, get a solid historical background on the painter and their life. Analyzing a painting isn’t mere entertainment; one must pay attention to intricate details which the painter might have hidden from plain sight.
We live in an environment saturated by digital media. By gaining the skill of visual analysis, you will not only heighten your appreciation of the arts but be able to thoroughly analyze the media messages you face in your daily life.
Also, don't forget to read summary of Lord of the Flies , and the article about Beowulf characters .
Need Someone to Write Your Paper?
If you read the whole article and still have no idea how to start your visual analysis essay, let a professional writer do this job for you. Contact us, and we’ll write your work for a higher grade you deserve. All ' college essay service ' requests are processed fast.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.

Related Articles
%20(3).webp)

Your complimentary articles
You’ve read one of your four complimentary articles for this month.
You can read four articles free per month. To have complete access to the thousands of philosophy articles on this site, please
Question of the Month
What is art and/or what is beauty, the following answers to this artful question each win a random book..
Art is something we do, a verb. Art is an expression of our thoughts, emotions, intuitions, and desires, but it is even more personal than that: it’s about sharing the way we experience the world, which for many is an extension of personality. It is the communication of intimate concepts that cannot be faithfully portrayed by words alone. And because words alone are not enough, we must find some other vehicle to carry our intent. But the content that we instill on or in our chosen media is not in itself the art. Art is to be found in how the media is used, the way in which the content is expressed.
What then is beauty? Beauty is much more than cosmetic: it is not about prettiness. There are plenty of pretty pictures available at the neighborhood home furnishing store; but these we might not refer to as beautiful; and it is not difficult to find works of artistic expression that we might agree are beautiful that are not necessarily pretty. Beauty is rather a measure of affect, a measure of emotion. In the context of art, beauty is the gauge of successful communication between participants – the conveyance of a concept between the artist and the perceiver. Beautiful art is successful in portraying the artist’s most profound intended emotions, the desired concepts, whether they be pretty and bright, or dark and sinister. But neither the artist nor the observer can be certain of successful communication in the end. So beauty in art is eternally subjective.
Wm. Joseph Nieters, Lake Ozark, Missouri
Works of art may elicit a sense of wonder or cynicism, hope or despair, adoration or spite; the work of art may be direct or complex, subtle or explicit, intelligible or obscure; and the subjects and approaches to the creation of art are bounded only by the imagination of the artist. Consequently, I believe that defining art based upon its content is a doomed enterprise.
Now a theme in aesthetics, the study of art, is the claim that there is a detachment or distance between works of art and the flow of everyday life. Thus, works of art rise like islands from a current of more pragmatic concerns. When you step out of a river and onto an island, you’ve reached your destination. Similarly, the aesthetic attitude requires you to treat artistic experience as an end-in-itself : art asks us to arrive empty of preconceptions and attend to the way in which we experience the work of art. And although a person can have an ‘aesthetic experience’ of a natural scene, flavor or texture, art is different in that it is produced . Therefore, art is the intentional communication of an experience as an end-in-itself . The content of that experience in its cultural context may determine whether the artwork is popular or ridiculed, significant or trivial, but it is art either way.
One of the initial reactions to this approach may be that it seems overly broad. An older brother who sneaks up behind his younger sibling and shouts “Booo!” can be said to be creating art. But isn’t the difference between this and a Freddy Krueger movie just one of degree? On the other hand, my definition would exclude graphics used in advertising or political propaganda, as they are created as a means to an end and not for their own sakes. Furthermore, ‘communication’ is not the best word for what I have in mind because it implies an unwarranted intention about the content represented. Aesthetic responses are often underdetermined by the artist’s intentions.
Mike Mallory, Everett, WA
The fundamental difference between art and beauty is that art is about who has produced it, whereas beauty depends on who’s looking.
Of course there are standards of beauty – that which is seen as ‘traditionally’ beautiful. The game changers – the square pegs, so to speak – are those who saw traditional standards of beauty and decided specifically to go against them, perhaps just to prove a point. Take Picasso, Munch, Schoenberg, to name just three. They have made a stand against these norms in their art. Otherwise their art is like all other art: its only function is to be experienced, appraised, and understood (or not).
Art is a means to state an opinion or a feeling, or else to create a different view of the world, whether it be inspired by the work of other people or something invented that’s entirely new. Beauty is whatever aspect of that or anything else that makes an individual feel positive or grateful. Beauty alone is not art, but art can be made of, about or for beautiful things. Beauty can be found in a snowy mountain scene: art is the photograph of it shown to family, the oil interpretation of it hung in a gallery, or the music score recreating the scene in crotchets and quavers.
However, art is not necessarily positive: it can be deliberately hurtful or displeasing: it can make you think about or consider things that you would rather not. But if it evokes an emotion in you, then it is art.
Chiara Leonardi, Reading, Berks
Art is a way of grasping the world. Not merely the physical world, which is what science attempts to do; but the whole world, and specifically, the human world, the world of society and spiritual experience.
Art emerged around 50,000 years ago, long before cities and civilisation, yet in forms to which we can still directly relate. The wall paintings in the Lascaux caves, which so startled Picasso, have been carbon-dated at around 17,000 years old. Now, following the invention of photography and the devastating attack made by Duchamp on the self-appointed Art Establishment [see Brief Lives this issue], art cannot be simply defined on the basis of concrete tests like ‘fidelity of representation’ or vague abstract concepts like ‘beauty’. So how can we define art in terms applying to both cave-dwellers and modern city sophisticates? To do this we need to ask: What does art do ? And the answer is surely that it provokes an emotional, rather than a simply cognitive response. One way of approaching the problem of defining art, then, could be to say: Art consists of shareable ideas that have a shareable emotional impact. Art need not produce beautiful objects or events, since a great piece of art could validly arouse emotions other than those aroused by beauty, such as terror, anxiety, or laughter. Yet to derive an acceptable philosophical theory of art from this understanding means tackling the concept of ‘emotion’ head on, and philosophers have been notoriously reluctant to do this. But not all of them: Robert Solomon’s book The Passions (1993) has made an excellent start, and this seems to me to be the way to go.
It won’t be easy. Poor old Richard Rorty was jumped on from a very great height when all he said was that literature, poetry, patriotism, love and stuff like that were philosophically important. Art is vitally important to maintaining broad standards in civilisation. Its pedigree long predates philosophy, which is only 3,000 years old, and science, which is a mere 500 years old. Art deserves much more attention from philosophers.
Alistair MacFarlane, Gwynedd
Some years ago I went looking for art. To begin my journey I went to an art gallery. At that stage art to me was whatever I found in an art gallery. I found paintings, mostly, and because they were in the gallery I recognised them as art. A particular Rothko painting was one colour and large. I observed a further piece that did not have an obvious label. It was also of one colour – white – and gigantically large, occupying one complete wall of the very high and spacious room and standing on small roller wheels. On closer inspection I saw that it was a moveable wall, not a piece of art. Why could one piece of work be considered ‘art’ and the other not?
The answer to the question could, perhaps, be found in the criteria of Berys Gaut to decide if some artefact is, indeed, art – that art pieces function only as pieces of art, just as their creators intended.
But were they beautiful? Did they evoke an emotional response in me? Beauty is frequently associated with art. There is sometimes an expectation of encountering a ‘beautiful’ object when going to see a work of art, be it painting, sculpture, book or performance. Of course, that expectation quickly changes as one widens the range of installations encountered. The classic example is Duchamp’s Fountain (1917), a rather un-beautiful urinal.
Can we define beauty? Let me try by suggesting that beauty is the capacity of an artefact to evoke a pleasurable emotional response. This might be categorised as the ‘like’ response.
I definitely did not like Fountain at the initial level of appreciation. There was skill, of course, in its construction. But what was the skill in its presentation as art?
So I began to reach a definition of art. A work of art is that which asks a question which a non-art object such as a wall does not: What am I? What am I communicating? The responses, both of the creator artist and of the recipient audience, vary, but they invariably involve a judgement, a response to the invitation to answer. The answer, too, goes towards deciphering that deeper question – the ‘Who am I?’ which goes towards defining humanity.
Neil Hallinan, Maynooth, Co. Kildare
‘Art’ is where we make meaning beyond language. Art consists in the making of meaning through intelligent agency, eliciting an aesthetic response. It’s a means of communication where language is not sufficient to explain or describe its content. Art can render visible and known what was previously unspoken. Because what art expresses and evokes is in part ineffable, we find it difficult to define and delineate it. It is known through the experience of the audience as well as the intention and expression of the artist. The meaning is made by all the participants, and so can never be fully known. It is multifarious and on-going. Even a disagreement is a tension which is itself an expression of something.
Art drives the development of a civilisation, both supporting the establishment and also preventing subversive messages from being silenced – art leads, mirrors and reveals change in politics and morality. Art plays a central part in the creation of culture, and is an outpouring of thought and ideas from it, and so it cannot be fully understood in isolation from its context. Paradoxically, however, art can communicate beyond language and time, appealing to our common humanity and linking disparate communities. Perhaps if wider audiences engaged with a greater variety of the world’s artistic traditions it could engender increased tolerance and mutual respect.
Another inescapable facet of art is that it is a commodity. This fact feeds the creative process, whether motivating the artist to form an item of monetary value, or to avoid creating one, or to artistically commodify the aesthetic experience. The commodification of art also affects who is considered qualified to create art, comment on it, and even define it, as those who benefit most strive to keep the value of ‘art objects’ high. These influences must feed into a culture’s understanding of what art is at any time, making thoughts about art culturally dependent. However, this commodification and the consequent closely-guarded role of the art critic also gives rise to a counter culture within art culture, often expressed through the creation of art that cannot be sold. The stratification of art by value and the resultant tension also adds to its meaning, and the meaning of art to society.
Catherine Bosley, Monk Soham, Suffolk
First of all we must recognize the obvious. ‘Art’ is a word, and words and concepts are organic and change their meaning through time. So in the olden days, art meant craft. It was something you could excel at through practise and hard work. You learnt how to paint or sculpt, and you learnt the special symbolism of your era. Through Romanticism and the birth of individualism, art came to mean originality. To do something new and never-heard-of defined the artist. His or her personality became essentially as important as the artwork itself. During the era of Modernism, the search for originality led artists to reevaluate art. What could art do? What could it represent? Could you paint movement (Cubism, Futurism)? Could you paint the non-material (Abstract Expressionism)? Fundamentally: could anything be regarded as art? A way of trying to solve this problem was to look beyond the work itself, and focus on the art world: art was that which the institution of art – artists, critics, art historians, etc – was prepared to regard as art, and which was made public through the institution, e.g. galleries. That’s Institutionalism – made famous through Marcel Duchamp’s ready-mades.
Institutionalism has been the prevailing notion through the later part of the twentieth century, at least in academia, and I would say it still holds a firm grip on our conceptions. One example is the Swedish artist Anna Odell. Her film sequence Unknown woman 2009-349701 , for which she faked psychosis to be admitted to a psychiatric hospital, was widely debated, and by many was not regarded as art. But because it was debated by the art world, it succeeded in breaking into the art world, and is today regarded as art, and Odell is regarded an artist.
Of course there are those who try and break out of this hegemony, for example by refusing to play by the art world’s unwritten rules. Andy Warhol with his Factory was one, even though he is today totally embraced by the art world. Another example is Damien Hirst, who, much like Warhol, pays people to create the physical manifestations of his ideas. He doesn’t use galleries and other art world-approved arenas to advertise, and instead sells his objects directly to private individuals. This liberal approach to capitalism is one way of attacking the hegemony of the art world.
What does all this teach us about art? Probably that art is a fleeting and chimeric concept. We will always have art, but for the most part we will only really learn in retrospect what the art of our era was.
Tommy Törnsten, Linköping, Sweden
Art periods such as Classical, Byzantine, neo-Classical, Romantic, Modern and post-Modern reflect the changing nature of art in social and cultural contexts; and shifting values are evident in varying content, forms and styles. These changes are encompassed, more or less in sequence, by Imitationalist, Emotionalist, Expressivist, Formalist and Institutionalist theories of art. In The Transfiguration of the Commonplace (1981), Arthur Danto claims a distinctiveness for art that inextricably links its instances with acts of observation, without which all that could exist are ‘material counterparts’ or ‘mere real things’ rather than artworks. Notwithstanding the competing theories, works of art can be seen to possess ‘family resemblances’ or ‘strands of resemblance’ linking very different instances as art. Identifying instances of art is relatively straightforward, but a definition of art that includes all possible cases is elusive. Consequently, art has been claimed to be an ‘open’ concept.
According to Raymond Williams’ Keywords (1976), capitalised ‘Art’ appears in general use in the nineteenth century, with ‘Fine Art’; whereas ‘art’ has a history of previous applications, such as in music, poetry, comedy, tragedy and dance; and we should also mention literature, media arts, even gardening, which for David Cooper in A Philosophy of Gardens (2006) can provide “epiphanies of co-dependence”. Art, then, is perhaps “anything presented for our aesthetic contemplation” – a phrase coined by John Davies, former tutor at the School of Art Education, Birmingham, in 1971 – although ‘anything’ may seem too inclusive. Gaining our aesthetic interest is at least a necessary requirement of art. Sufficiency for something to be art requires significance to art appreciators which endures as long as tokens or types of the artwork persist. Paradoxically, such significance is sometimes attributed to objects neither intended as art, nor especially intended to be perceived aesthetically – for instance, votive, devotional, commemorative or utilitarian artefacts. Furthermore, aesthetic interests can be eclipsed by dubious investment practices and social kudos. When combined with celebrity and harmful forms of narcissism, they can egregiously affect artistic authenticity. These interests can be overriding, and spawn products masquerading as art. Then it’s up to discerning observers to spot any Fads, Fakes and Fantasies (Sjoerd Hannema, 1970).
Colin Brookes, Loughborough, Leicestershire
For me art is nothing more and nothing less than the creative ability of individuals to express their understanding of some aspect of private or public life, like love, conflict, fear, or pain. As I read a war poem by Edward Thomas, enjoy a Mozart piano concerto, or contemplate a M.C. Escher drawing, I am often emotionally inspired by the moment and intellectually stimulated by the thought-process that follows. At this moment of discovery I humbly realize my views may be those shared by thousands, even millions across the globe. This is due in large part to the mass media’s ability to control and exploit our emotions. The commercial success of a performance or production becomes the metric by which art is now almost exclusively gauged: quality in art has been sadly reduced to equating great art with sale of books, number of views, or the downloading of recordings. Too bad if personal sensibilities about a particular piece of art are lost in the greater rush for immediate acceptance.
So where does that leave the subjective notion that beauty can still be found in art? If beauty is the outcome of a process by which art gives pleasure to our senses, then it should remain a matter of personal discernment, even if outside forces clamour to take control of it. In other words, nobody, including the art critic, should be able to tell the individual what is beautiful and what is not. The world of art is one of a constant tension between preserving individual tastes and promoting popular acceptance.
Ian Malcomson, Victoria, British Columbia
What we perceive as beautiful does not offend us on any level. It is a personal judgement, a subjective opinion. A memory from once we gazed upon something beautiful, a sight ever so pleasing to the senses or to the eye, oft time stays with us forever. I shall never forget walking into Balzac’s house in France: the scent of lilies was so overwhelming that I had a numinous moment. The intensity of the emotion evoked may not be possible to explain. I don’t feel it’s important to debate why I think a flower, painting, sunset or how the light streaming through a stained-glass window is beautiful. The power of the sights create an emotional reaction in me. I don’t expect or concern myself that others will agree with me or not. Can all agree that an act of kindness is beautiful?
A thing of beauty is a whole; elements coming together making it so. A single brush stroke of a painting does not alone create the impact of beauty, but all together, it becomes beautiful. A perfect flower is beautiful, when all of the petals together form its perfection; a pleasant, intoxicating scent is also part of the beauty.
In thinking about the question, ‘What is beauty?’, I’ve simply come away with the idea that I am the beholder whose eye it is in. Suffice it to say, my private assessment of what strikes me as beautiful is all I need to know.
Cheryl Anderson, Kenilworth, Illinois
Stendhal said, “Beauty is the promise of happiness”, but this didn’t get to the heart of the matter. Whose beauty are we talking about? Whose happiness?
Consider if a snake made art. What would it believe to be beautiful? What would it deign to make? Snakes have poor eyesight and detect the world largely through a chemosensory organ, the Jacobson’s organ, or through heat-sensing pits. Would a movie in its human form even make sense to a snake? So their art, their beauty, would be entirely alien to ours: it would not be visual, and even if they had songs they would be foreign; after all, snakes do not have ears, they sense vibrations. So fine art would be sensed, and songs would be felt, if it is even possible to conceive that idea.
From this perspective – a view low to the ground – we can see that beauty is truly in the eye of the beholder. It may cross our lips to speak of the nature of beauty in billowy language, but we do so entirely with a forked tongue if we do so seriously. The aesthetics of representing beauty ought not to fool us into thinking beauty, as some abstract concept, truly exists. It requires a viewer and a context, and the value we place on certain combinations of colors or sounds over others speaks of nothing more than preference. Our desire for pictures, moving or otherwise, is because our organs developed in such a way. A snake would have no use for the visual world.
I am thankful to have human art over snake art, but I would no doubt be amazed at serpentine art. It would require an intellectual sloughing of many conceptions we take for granted. For that, considering the possibility of this extreme thought is worthwhile: if snakes could write poetry, what would it be?
Derek Halm, Portland, Oregon
[A: Sssibilance and sussssuration – Ed.]
The questions, ‘What is art?’ and ‘What is beauty?’ are different types and shouldn’t be conflated.
With boring predictability, almost all contemporary discussers of art lapse into a ‘relative-off’, whereby they go to annoying lengths to demonstrate how open-minded they are and how ineluctably loose the concept of art is. If art is just whatever you want it to be, can we not just end the conversation there? It’s a done deal. I’ll throw playdough on to a canvas, and we can pretend to display our modern credentials of acceptance and insight. This just doesn’t work, and we all know it. If art is to mean anything , there has to be some working definition of what it is. If art can be anything to anybody at anytime, then there ends the discussion. What makes art special – and worth discussing – is that it stands above or outside everyday things, such as everyday food, paintwork, or sounds. Art comprises special or exceptional dishes, paintings, and music.
So what, then, is my definition of art? Briefly, I believe there must be at least two considerations to label something as ‘art’. The first is that there must be something recognizable in the way of ‘author-to-audience reception’. I mean to say, there must be the recognition that something was made for an audience of some kind to receive, discuss or enjoy. Implicit in this point is the evident recognizability of what the art actually is – in other words, the author doesn’t have to tell you it’s art when you otherwise wouldn’t have any idea. The second point is simply the recognition of skill: some obvious skill has to be involved in making art. This, in my view, would be the minimum requirements – or definition – of art. Even if you disagree with the particulars, some definition is required to make anything at all art. Otherwise, what are we even discussing? I’m breaking the mold and ask for brass tacks.
Brannon McConkey, Tennessee Author of Student of Life: Why Becoming Engaged in Life, Art, and Philosophy Can Lead to a Happier Existence
Human beings appear to have a compulsion to categorize, to organize and define. We seek to impose order on a welter of sense-impressions and memories, seeing regularities and patterns in repetitions and associations, always on the lookout for correlations, eager to determine cause and effect, so that we might give sense to what might otherwise seem random and inconsequential. However, particularly in the last century, we have also learned to take pleasure in the reflection of unstructured perceptions; our artistic ways of seeing and listening have expanded to encompass disharmony and irregularity. This has meant that culturally, an ever-widening gap has grown between the attitudes and opinions of the majority, who continue to define art in traditional ways, having to do with order, harmony, representation; and the minority, who look for originality, who try to see the world anew, and strive for difference, and whose critical practice is rooted in abstraction. In between there are many who abjure both extremes, and who both find and give pleasure both in defining a personal vision and in practising craftsmanship.
There will always be a challenge to traditional concepts of art from the shock of the new, and tensions around the appropriateness of our understanding. That is how things should be, as innovators push at the boundaries. At the same time, we will continue to take pleasure in the beauty of a mathematical equation, a finely-tuned machine, a successful scientific experiment, the technology of landing a probe on a comet, an accomplished poem, a striking portrait, the sound-world of a symphony. We apportion significance and meaning to what we find of value and wish to share with our fellows. Our art and our definitions of beauty reflect our human nature and the multiplicity of our creative efforts.
In the end, because of our individuality and our varied histories and traditions, our debates will always be inconclusive. If we are wise, we will look and listen with an open spirit, and sometimes with a wry smile, always celebrating the diversity of human imaginings and achievements.
David Howard, Church Stretton, Shropshire
Next Question of the Month
The next question is: What’s The More Important: Freedom, Justice, Happiness, Truth? Please give and justify your rankings in less than 400 words. The prize is a semi-random book from our book mountain. Subject lines should be marked ‘Question of the Month’, and must be received by 11th August. If you want a chance of getting a book, please include your physical address. Submission is permission to reproduce your answer physically and electronically.
This site uses cookies to recognize users and allow us to analyse site usage. By continuing to browse the site with cookies enabled in your browser, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our privacy policy . X
Fostering Imaginative Artists Since 1961
- African Imaginative Art
- All Artists
- Artist of the Month
- Featured Artists
- Gallery A – F
- Gallery A to F
- Gallery G – L
- Gallery G to L
- Gallery M – R
- Gallery M to R
- Gallery S – Z
- Gallery S to Z
- History of the Art of Imagination
- Member Gallery
- Members A to Z
- Opportunities
- Portals, Society for Art of Imagination reception
- Who’s Who
The meaning of art as viewed by various philosophers:
Tolstoy Hegel Wittgenstein Maritain
Leo Tolstoy on What is Art?
Aetheticians have attempted to work backwards by first listing acknowledged works of art, and then trying to find a theory to fit them all. So now, no matter what insanities appear in art, once they find acceptance among the upper classes of society, a theory is quickly invented to explain and sanction them, just as if there had never appeared in history people who produced false and deformed art, which was afterwards discarded and forgotten. And one may see now in the art of our circle, to what lengths the insanity and deformity of art may go.
So that theory of art is nothing but the setting up as good whatever pleases us, that is, pleases a certain class of people. In order define any human activity, it is necessary to understand its sense and importance; to do that one must examine the activity itself, and its causes and effects, not merely in relation to the pleasure we get out of it. If we say that the aim of any activity is merely pleasure, and is defined by that pleasure, our definition will be false. If we compare it to the food question, nobody would affirm that the importance of food consists in the pleasure we get from eating it. We know that the satisfaction of the taste buds is no infallible guide to the best food from a health point of view, in the same way the pleasure we get from a painting is no indication of its worth. People who consider the meaning of art to be pleasure cannot realise its true meaning, in fact, people will come to understand the meaning of art only when they cease to consider that the aim of art is pleasure.
So then – what is art?
The latest definitions are:
The first definition is inexact, because instead of speaking of the human activity itself, it only speaks of the derivation of it The second definition is inexact because a man may express his emotions by means of lines colours etc, and yet may not act on others by his expression so the result is not art. The third definition is inexact, because in the production of objects or actions affording pleasure, conjuring tricks or gymnastic exercises may be included, which are not art. Furthermore, the production of a play which does not afford pleasure to the producer or audience, may yet be a work of art. The inaccuracy of all these definitions arises from the fact that, in them all, the object considered is the pleasure art may give, and not the purpose it may serve in the life of man and of humanity.
In order to define art correctly, it is necessary to cease to consider it as a means to pleasure, and to consider it as one of the conditions of life. Viewed in this way, we see that art is one of the means of communication between man and man.
Every work of art causes the receiver to enter into a certain kind of relationship, both with the artist and all who receive the same impression. Just as words transmit thoughts, so art transmits feelings. The activity of art is based on the fact that when we witness a man experiencing an emotion, we to some extent share it. To evoke in oneself a feeling that one has once experienced, and to transmit that feeling to others through forms and colours, sounds or movements.
That is art. Art is not pleasure, but a means of union among men, joining them together in the same feelings, and indispensable for life and progress towards well-being of individuals and of humanity. Thanks to his capacity to express thoughts by words, every man may know the debt he owes to the past, and be able to hand on what he has acheived to future generations. If humans lacked this capacity, we would be like wild beasts, and if people lacked this capacity for being infected by art, people might be more savage still, and more separated from one another.
All human life is filled with art, from cradle songs to fashion in clothes, but by the word ‘art’, we mean that part of artistic activity which we select as having special importance. This special importance has always been given to that part of art which transmits feelings flowing from religious perception. This was how Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle looked on art, and how all the great religious teachers understood it. Plato was so convinced of the power of art, that he suggested that artists should be banned from his ideal republic. Yet that is a less harmful attitude than the attitude in our European society today, where art is regarded as a good thing only if it affords pleasure.
How has our society come down to this? It is because the estimation of the value of art (that is, the feeling it transmits) depends on man’s perception of the meaning of life. Humanity unceasingly moves forward from a lower, more partial view of life to a higher and broader view. Religions are the exponents of the highest comprehension of life accessible to the best and foremost people at a given time. Later the rest of society follows their lead. Therefore religions have always served as bases for the valuation of human semtiments. If feelings bring men nearer the ideal their religion indicates, they are good, if they oppose it, they are bad.
Thus in the case of the Greeks, if the religion places the meaning of life in earthly happiness, in beauty and strength, then art transmitting the joy and energy of life would be considered good, but art transmitting despondency would be bad. If the meaning of life is seen in the well-being of one’s nation, or in honouring one’s ancestors, as in the case of the Romans and Chinese, then art transmitting joy in self sacrifice for one’s country or exalting one’s ancestors would be good, and the contrary, bad. If the meaning of life is seen in freeing oneself from the yoke of animalism, as in Buddhism, then art which elevates the soul and humbles the flesh is good, whereas art exalting bodily passions would be bad. But art in our society has been so perverted that not only has bad art come to be considered good, but even the very perception of what art really is, has been lost.
In order to find out why, we must distinguish art from counterfeit art. Real art must be infectious – the receiver of a true artistic impression is so united to the artist that he feels as though the work were his own – as if what it expresses was what he had been longing to express. A real work of art destroys the separation between himself and the artist, and even between himself and all those others who also appreciate this art. In this freeing of our personality from its isolation, and uniting it with others, lies the great attractive force of art. Not only is infection a sure sign of art, but the degree of infectiousness is the sole measure of excellence in art.
This depends on three things: 1. The individuality of the feeling transmitted. 2. Its clarity. 3. The sincerity of the artist – ie, the the degree of force with which the artist feels the emotion he transmits.
If the viewer feels that the artist works for himself, he is affected, but if he feels that the artist is not infected, but is trying to influence him, the viewer feels a resistance, and is repelled instead. All can be summed up in a word – sincerity. The artist should be impelled by an inner need to express his feeling. Now, just as the evolution of knowledge proceeds by truer and more necessary knowledge displacing previous knowledge, so the evolution of feeling proceeds through art – feelings more kind and needful to humanity replace the older feelings. That is the purpose of art. In every age there exists an understanding of the meaning of life which represents the highest level which has been attained.
If it appears that in our Society there is no religious perception, this is not because there is none, but because we do not want to see it. And often this is because it exposes the fact that our life is inconsistent with that religious perception. In our times religion is regarded as a superstition which humanity has outgrown, and yet if humanity is to progress there must be a guide to the direction of that movement. Religions have always furnished that guide throughout history. So there must be some form of religious perception today – and in its widest and most practical application, it is the consciousness that or well-being – materially and spiritually – lies in the growth of brotherhood among men – in their loving harmony with one another.
The chief mistake made by the people of the upper classes at the time of the Renaissance was that they set up in place of religious art, an art which aimed only at giving pleasure. It is said that the great evil is not that we do not know God, but that we make a god of something lower. Instead of art which feeds the spirit, an empty and often vicious art is set up, which hides from us our need for true art. And true art for our time would demand the union of all people without exception – above all virtues it sets brotherly love to all men.
G.W.F.Hegel (1770 -1831) on the Philosophy of Fine Art
Art can serve many puposes, and even be a pastime, but we want to examine the kind of art that is free in its aim and means. This is the only true art. Its highest function is only served when it has established itself in a sphere which it shares with religion and philosophy, becoming thereby a mode and form through which the Divine, the profoundest interests of mankind, and spiritual truths of the widest range, are brought home to consciousness and expressed. It is in works of art that nations have deposited the richest ideas they possess, and often art serves as a key of interpretation to the wisdom and understanding of peoples. Philosophy and religion also do this, but art appeals to the senses and is nearer to Nature and to our sensitive and emotional life.
Art is the primary bond of mediation between the external world of the senses and the medium of pure thought and understanding. It could be objected that art was unworthy, being of the world of appearances and its deceptions.
But in the world of Nature appearance is essential to reality.There could be no such thing as truth if it did not actually appear for some person. And appearance in Nature itself is deceptive. It is only beyond the appearance of everyday life that we shall discover reality in any true sense. At least art does not pretend to be reality, whereas Nature, pretending to be the only reality,is more deceptive.
There are three factors determining a work of art:
1. A work of art is not produced by Nature; it is brought into being by the agency of man. 2. It is created essentially for man, and it is addressed to his senses 3. It contains an end bound up with it With regard to the first factor; a work of art cannot be imitated by mere dexterity, art is an activity of the soul, constrained to work out of its own wealth, and to bring before the mind’s eye a wholly other and far richer content; a unique creation.
The essential point to maintain is that although talent and genius imply natural power, yet it is indispensable that
(a) this power be thoughtfully cultivated (b) reflection should be brought to bear on the particular way it is exercised (c) it should be kept alive with use and practice in actual work.
A work of art possesses a purely technical side – that of craft. This is most obvious in architecture and sculpture, less so in painting and music, least in poetry.
Added to this the more exalted the rank of the artist the more profoundly he ought to portray depths of soul and mind. Study is the means by which the artist brings to consciousness such a content.
Is art inferior to Nature? Art originates in the human spirit, it has received the baptism of the human mind and soul of man. The spiritual values are seized in the work of art and emphasized with greater purity and clarity than is possible in ordinary reality, therefore the work of art is greater.
What is the human need that stimulates art production?
Man is a thinking consciousness; he makes explicit to himself all that exists. He has a need to bring himself in his own inner life to consciousness. He needs to assert himself in that which is presented him in immediacy, external to himself, and by doing so at the same time to recognize himself therein. This purpose he achieves by the alteration he effects in external objects, upon which he imprints the seal of his inner life. He does this in order that he may divest the world of its alienation from himself.
A boy throws stones into a stream, and then looks with wonder at the circles which follow in the water, seeing there something of hs own doing. This need runs through everything up to the level of art. Man satisfies his spirit by making explicit to his inner life all that exists, as well as further giving a realized external embodiment to the self thus made explicit. And by this reduplication of what is his own he places before the vision and within the cognition of himself and others what is within him.
The second factor; art is addressed to man’s senses. Writers have asked what feelings art ought to excite. But feelings are subjective and passing, although powerful at the time, which is why people are so proud of having emotions. The trouble is that they do not attempt to study their emotions, which would help by creating thereby a distance from them. Art can give this distance, because by depicting emotions, it helps the onlooker towards the study of his own emotions.
Is art there to excite a feeling for beauty? To appreciate beauty people have cultivated taste, but taste is superficial, and cannot grasp the real profoundity of art. Art scholarship is too often concerned only with externals. Art therefore is not just for the senses. The mind is intended to be affected as well and to receive some kind of satisfaction in it. The creative imagination of a true artist is the imagination of a great mind and a big heart, it grasps the profoundest and most embracing human interests in the wholly definite presentation of imagery borrowed from objective experience.
The third factor: What is the end or aim of art?
Art is not meant to be a mere imitation of Nature – if it attempts a mere copy it will always lag a long way behind. Nevertheless the artist must learn the laws of Nature; of colour and chiaroscuro; of line and form. So what is the true content of art, and what is its aim? One opinion is that it is the the task of art to bring before us everything that the spirit of man can concieve. Is it the task of art to enflame man’s passions and set them staggering about in a Bacchantic riot?
Sensual desire is more brutal and domineering the more it appropriates the entire man, so that he does not retain the power to separate himself, and loses touch with his universal capacity. Sometimes art showing such passions can awaken man to the horror of his condition, he can see them outside himself, they come before him as objects rather than part of himself – he begins to be free from them as aliens.
In the same way, wailing women were hired at funerals, to create an external expression of grief, so that the sufferer can see his sorrow in an objective form and in reflecting on it, his sorrow is made lighter. So art, while still remaining in the sphere of the senses, faces man from the might of his sensitive experience by means of its representations.
It has been said that art’s aim is the purification of passions, that it is its duty to instruct. Is this true? We have seen how art instructs by revealing to man the contents of his nature, but if art tries to bluntly teach, it becomes merely a maxim, with the art added on as bait. Thereby the very nature of art is abused. For a work of art ought not to bring before the creative imagination a content in its universality as such, but rather this universality under the mode of individual concreteness and distinctive sensuous particularity.
An external morality would limit the subject matter of art, but art, unlike history and the sciences, which have their subject matter determined, has a free choice in the selection of its subjects. So when we ask what is the end of art, we must be careful that we are not saying in effect, what is the use of art, as if art had to have a reason for existing other than for itself. On the other hand we must maintain that it is art’s function to reveal
Truth under the mode of art’s sensuous or material configuration, to display reconciled differences and therefore prove that it possesses its final aim in itself. For other ends such as instruction, purification, improvement, riches, fame and honour have nothing to do with a work of art as such, still less with the concept of art.
Ludwig Wittgenstein (1889 – 1951)
Wittgenstein has said that in his opinion the subject of aesthetics is very big and entirely misunderstood. The use of the word “beautiful” is even more apt to be misunderstood. He would like a book on philosophy to contain chapters on words, and confusions that come up with them. He compares language to a tool chest; words are used together in a family of ways – yet the tools could be very different.
As to the word “beautiful”, a child hears the word mainly as an interjection. It is remarkable that in real life adjectives such as “beautiful”, “lovely” etc. play hardly any role at all. The words used are more like “right” or “correct”.
For example, take the question, “How should poetry be read?” For example you might discuss in reading blank verse, how to stress the rhythm correctly. A man says: “It ought to be read this way!” and reads it out, and you say, “Oh yes! Now it makes sense!”
What does a man ordering a suit at the tailor’s say? “That’s the right length. That’s too short!”.
In the case of the word “correct” you have a variety of related cases. In one case you learn the rules. A tailor learns how to measure and cut the coat. A customer comes in and says “This coat is too short!” but the tailor disagrees because he says “I made it according to the rules!”
So judgement is needed as well as rules.
Nevertheless we need the rules. In art, if someone hasn’t learned the rules he wouldn’t be able to make an aesthetic judgement. In learning the rules, you get a more and more refined judgement; in fact learning the rules actually changes your judgement.
The rules of harmony in music came about because they expressed the way most people wanted the chords to follow – their wishes crytallized in these rules. All the greatest composers wrote in accordance with these rules, and yet you can say that every composer changed the rules, but the variation was very slight, not all the rules were changed.
In the Arts, a person who has judgment also changes and develops. We can distinguish between a person who knows what he is talking about and one who does not.
A word we can discuss is the word “appreciate”. What is appreciation? If a man at the tailor’s looks at a great many patterns and says, “This is too dark” or “This is a little too loud’, he is what we call an appreciator of material. Similarly in music he might say, “Does this harmonize? No, the bass is not quite loud enough.”
Although we can see when someone appreciates something, it is impossible to describe. To do this we would have to describe the whole environment. On the subject of correctness, a good tailor won’t use any words except words like “Too long” or “All right”. But when we talk of a symphony by Beethoven we don’t talk of correctness. Entirely different things enter. One wouldn’t even talk of appreciating the really tremendous things in art. In a style of architecture a door may be correct, and you appreciate it, but in the case of a Gothic Cathedral, we do not just find it correct – it has a different role to play in our lives. It is as different as if we were talking about a man and said on the one hand “He behaves well.” and on the other “He made a great impression on me.”
To describe what you mean by a cultured taste, you have to describe a culture. What we describe as a cultured taste perhaps didn’t exist in the Middle Ages. An entirely different game is played in different ages. In order to become clear about aesthetic words you have to describe ways of living. A landlady might love a sentimental painting, you might want to throw it in the fire …. alright! That’s that..
Jacques Maritain b. 1882
Art and poetry come from a deeper part of the intellect – not the reasoning part alone.
There is an interpenetration of art and nature – so that a place comes alive because of its history.
Oriental artists try to forget themselves, and meditate on the subject of nature, rendering it as truly as they can, becoming one with things but leaving their egos out.
In the West, artists evolved from studying things, to the portrayal of the Divine after the Christian Church was established. Man passed from a sense of the human self as object, to the sacred art which depicted Christ’s self as man, to a sense of human self as subject, and then became absorbed in his own inward development. Later artists such as Cezanne became intent on revealing the buried significance of the visible world. Man’s longing for order and harmony emerges from the brute universe of the eye in the act of seeing and brings forth a quality of emotion which finds an echo in other human beings. Three rules on art.
First: the very idea of rules in the fine arts changes and becomes transfigured through the impact of beauty on the activity of art. So the rules must be continually reborn, and the artist is forever exploring the unknown.
Second: the work to be made is unique, and an end in itself. Each time, and for every single work, there is for the artist a new and unique way to strive after the making of his art.
Third: because the work is an end in itself, and a unique participation in beauty, reason alone is not enough for the artist. Because in art as in contemplation, intellectuality at its peak goes beyond concepts and reason, and is achieved through union with the subject, which love alone can bring about.
Artwork Copyright Notice
The copyrights for all artwork used on this website belong to the artists who created the works.
Members Information
Read the back issues of The Society for Art of Imagination Newsletters here
Find us on Facebook
Donate to The Society
© 2024 Society for Art of Imagination Organized Themes

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: What Is Art Appreciation?
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 31973

- Deborah Gustlin & Zoe Gustlin
- Evergreen Valley College via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)

What Is Art Appreciation?
Appreciation of the visual arts goes beyond staring at a painting hanging on the wall of a museum—art is in everything and everywhere you look. Opening your eyes to the world of art is essential in understanding the world around you. Art is more than pretentious museums; only a few enter and comprehend. Instead, art appreciation is:
- Gaining the knowledge to understand the art.
- Acquire the art methods and materials to discuss art verbally or by the written word.
- Ability to identify the movements from ancient cultures to today's contemporary art.
Learning how to appreciate art is a necessary cultural foundation enabling people to critically analyze art, art forms, and how cultures used art. All it takes to understand the art is just to look!
Art appreciation centers on the ability to view art throughout history, focusing on the cultures and the people, and how art developed in the specific periods. It is difficult to understand art without understanding the culture, their use of materials, and a sense of beauty. Art is conveyed by the simple act of creating art for art's sake. Every person is born with the innate desire to create art, and similar to other professions, training is essential in honing skills to produce art. Art education broadens a person's comprehension, development, and visions of art. Art brings an understanding of diversity, how people lived in the past, and connects the issues concerning contemporary life and art today.
The history of the world is similarly the history of art, continually intertwined. For millions of years, as humans roamed the earth, evolution, and environment shaped many different cultures depending on location, weather, natural resources, and food. These cultures formed the foundation of all art today. Art appreciation analyzes art using the methods and materials, allowing people to make connections to the context of art and the interactions of societies.
It is difficult to understand the art without understanding the culture.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
The Mind-Expanding Value of Arts Education
As funding for arts education declines worldwide, experts ponder what students — and the world at large — are losing in the process.

By Ginanne Brownell
This article is part of our special report on the Art for Tomorrow conference that was held in Florence, Italy.
Awuor Onguru says that if it were not for her continued exposure to arts education as a child, she never would have gotten into Yale University.
Growing up in a lower-middle-class family in Nairobi, Kenya, Ms. Onguru, now a 20-year-old junior majoring in English and French, started taking music lessons at the age of four. By 12, she was playing violin in the string quartet at her primary school, where every student was required to play an instrument. As a high school student on scholarship at the International School of Kenya, she was not only being taught Bach concertos, she also became part of Nairobi’s music scene, playing first violin in a number of local orchestras.
During her high school summer breaks, Ms. Onguru — who also has a strong interest in creative writing and poetry — went to the United States, attending the Interlochen Center for the Arts ’ creative writing camp, in Michigan, and the Iowa Young Writers’ Studio . Ms. Onguru, who recently returned to campus after helping organize Yale Glee Club’s spring tour in Kenya, hopes to become a journalist after graduation. She has already made progress toward that goal, serving as the opinion editor for the Yale Daily News, and getting her work published in Teen Vogue and the literary journal Menacing Hedge.
“Whether you’re in sports, whether you end up in STEM, whether you end up in government, seeing my peers — who had different interests in arts — not everyone wanted to be an artist,” she said in a video interview. “But they found places to express themselves, found places to be creative, found places to say things that they didn’t know how else to say them.”
Ms. Onguru’s path shows what a pivotal role arts education can play in a young person’s development. Yet, while the arts and culture space accounts for a significant amount of gross domestic product across the globe — in the United Kingdom in 2021, the arts contributed £109 billion to the economy , while in the U.S., it brought in over $1 trillion that year — arts education budgets in schools continue to get slashed. (In 2021, for instance, the spending on arts education in the U.K. came to an average of just £9.40 per pupil for the year .)
While experts have long espoused the idea that exposure to the arts plays a critical role in primary and secondary schooling, education systems globally have continually failed to hold it in high regard. As Eric Booth, a U.S.-based arts educator and a co-author of “Playing for Their Lives: The Global El Sistema Movement for Social Change Through Music,” said: “There are a whole lot of countries in the world that don’t have the arts in the school, it just isn’t a thing, and it never has been.”
That has led to the arts education trajectory heading in a “dark downward spiral,” said Jelena Trkulja, senior adviser for academic and cultural affairs at Qatar Museums , who moderated a panel entitled “When Arts Education is a Luxury: New Ecosystems” at the Art for Tomorrow conference in Florence, Italy, organized by the Democracy & Culture Foundation, with panels moderated by New York Times journalists.
Part of why that is happening, she said, is that societies still don’t have a sufficient and nuanced understanding of the benefits arts education can bring, in terms of young people’s development. “Arts education is still perceived as an add-on, rather than an essential field creating essential 21st-century skills that are defined as the four C’s of collaboration, creativity, communication and critical thinking,” Dr. Trkulja said in a video interview, “and those skills are being developed in arts education.”
Dennie Palmer Wolf, principal researcher at the U.S.-based arts research consultancy WolfBrown , agreed. “We have to learn to make a much broader argument about arts education,” she said. “It isn’t only playing the cello.”
It is largely through the arts that we as humans understand our own history, from a cave painting in Indonesia thought to be 45,000 years old to “The Tale of Genji,” a book that’s often called the world’s first novel , written by an 11th-century Japanese woman, Murasaki Shikibu; from the art of Michelangelo and Picasso to the music of Mozart and Miriam Makeba and Taylor Swift.
“The arts are one of the fundamental ways that we try to make sense of the world,” said Brian Kisida, an assistant professor at the University of Missouri’s Truman School of Public Affairs and a co-director of the National Endowment for the Arts-sponsored Arts, Humanities & Civic Engagement Lab . “People use the arts to offer a critical perspective of their exploration of the human condition, and that’s what the root of education is in some ways.”
And yet, the arts don’t lend themselves well to hard data, something educators and policymakers need to justify classes in those disciplines in their budgets. “Arts is this visceral thing, this thing inside you, the collective moment of a crescendo,” said Heddy Lahmann , an assistant professor of international education at New York University, who is conducting a global study examining arts education in public schools for the Community Arts Network. “But it’s really hard to qualify what that is.”
Dr. Lahmann’s early research into the decrease in spending by public schools in arts education points to everything from the lack of trained teachers in the arts — partly because those educators are worried about their own job security — to the challenges of teaching arts remotely in the early days of the Covid pandemic. And, of course, standardized tests like the Program for International Student Assessment, which covers reading, math and science, where countries compete on outcomes. “There’s a race to get those indicators,” Dr. Lahmann said, “and arts don’t readily fit into that.” In part, that is because standardized tests don’t cover arts education .
“It’s that unattractive truth that what gets measured gets attended to,” said Mr. Booth, the arts educator who co-authored “Playing for Their Lives.”
While studies over the years have underscored the ways that arts education can lead to better student achievement — in the way that musical skills support literacy, say, and arts activities lead to improved vocabulary, what have traditionally been lacking are large-scale randomized control studies. But a recent research project done in 42 elementary and middle schools in Houston, which was co-directed by Dr. Kisida and Daniel H. Bowen, a professor who teaches education policy at Texas A&M, is the first of its kind to do just that. Their research found that students who had increased arts education experiences saw improvements in writing achievement, emotional and cognitive empathy, school engagement and higher education aspirations, while they had a lower incidence of disciplinary infractions.
As young people are now, more than ever, inundated with images on social media and businesses are increasingly using A.I., it has become even more relevant for students these days to learn how to think more critically and creatively. “Because what is required of us in this coming century is an imaginative capacity that goes far beyond what we have deliberately cultivated in the schooling environment over the last 25 years,” said Mariko Silver, the chief executive of the Henry Luce Foundation, “and that requires truly deep arts education for everyone.”

- Entertainment
- Rex Reed Reviews
- Awards Shows
- Climate Change
- Restaurants
- Gift Guides
- Business of Art
- Nightlife & Dining
- About Observer
- Advertise With Us
Why Defining Exactly Who Is and Isn’t an Artist Matters
Official definitions of 'artist' (of which there are a confusing many) come into play when artists are counted in a census, have to pay income taxes or want to apply for grants and live-work spaces..

The question of how to define art has plagued creatives and philosophers for centuries. Aristotle defined art as a true idea given physical form. Leo Tolstoy called it “a means of union among men, joining them together in the same feelings, and indispensable for the life and progress toward well-being of individuals and of humanity,” and Oscar Wilde identified art as “the most intense mode of individualism the world has known.” It seems we can, individually, define art, but we can’t reach a consensus.
Sign Up For Our Daily Newsletter
Thank you for signing up!
By clicking submit, you agree to our <a rel="noreferrer" href="http://observermedia.com/terms">terms of service</a> and acknowledge we may use your information to send you emails, product samples, and promotions on this website and other properties. You can opt out anytime.
The same issue arises when the goal is to define ‘artist.’ Lots of people want to be viewed as artists, and label themselves such, from tattooists (body artists) to chefs (culinary artists) to, more recently, GPT prompters (A.I. artists). If nailing down the definition of artist is a semantics issue, it’s also one with real-world consequences. In 2023, a Colorado web designer successfully claimed before the U.S. Supreme Court that she was an artist—versus a mere service provider—which meant she was exempt from the state’s public accommodations law and could refuse to create wedding websites for same-sex couples.
SEE ALSO: The Costume Institute’s ‘Sleeping Beauties: Reawakening Fashion’ Is Full of Couture Corpses
In fact, there are numerous spheres in which defining what an artist is and isn’t is important. There are, for instance, grants and studio or residential spaces set aside exclusively for artists, and the organizations or government agencies overseeing their assignment need to be clear on who is and isn’t an artist. Then there are surveys conducted by economic, social and cultural researchers into artists’ employment, artists’ healthcare coverage and needs, the economic benefits of creative communities and other related inquiries for whom broader definitions of artist create a methodological problem. Without the licenses, permits, state testing or reported income requirements of other professionals, determining who is or isn’t an artist starts to feel like a value judgment.
That said, sometimes proving that someone is an artist is not just about cultural cachet or bragging rights—”official” definitions of artist (of which there are a confusing many) come into play when artists are counted in a census or have to pay their income taxes. In these cases, a self-proclaimed artist might have to meet several criteria dictated by the U.S. government to show that they’re also an artist by trade.
An artist’s job is art . The Bureau of the Census (whose data is used by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the National Endowment for the Arts and other agencies) makes a broad national survey every ten years, inquiring about sources of paid employment during the census week. People with more than one source of income are counted occupationally in the job at which they worked the greatest number of hours during the census reference week. Because the focus is on paid employment, rather than the amount of time spent in the studio or the desire to sell art, many artists are likely to be overlooked—that is, not counted as artists. On an individual basis, this doesn’t matter as census information is anonymized, and no art dealers will throw artists out of their galleries because the Census Bureau didn’t classify them as artists. There is, however, a national policy downside: municipal, state and federal legislators are less likely to give money to the arts or to create laws that benefit artists if this group is significantly undercounted.
Artists devote time to their art . Although the National Endowment for the Arts makes use of Census Bureau data, the agency has conducted its own surveys of artists in the visual and performance spaces over the years. One of those surveys, “Visual Artists in Four Cities” (Houston, Minneapolis, San Francisco and Washington, D.C.), identified artists by their level of activity, i.e., how many hours per week they spend on art, counting those who had exhibited in some gallery or other art space in those cities over several years.
An artist turns a profit on their art . If the Census Bureau takes a broad, sweeping view of the definition of artist, the Internal Revenue Service takes a narrow one, examining individual taxpayers’ returns, and the federal agency has its own definition of artists as professionals. There are nine criteria that the IRS applies to separate professionals from hobbyists (an important distinction, as professionals may deduct their expenses, hobbyists may not).
- Is the activity carried on in a businesslike manner?
- Does the artist intend to make the artistic activity profitable?
- Does the individual depend in full or in part from income generated by the artistic work?
- Are business losses to be expected, or are they due to circumstances beyond the artist’s control?
- Are business plans changed to improve profitability?
- Does the artist have the knowledge to make the activity profitable?
- Has the artist been successful in previous professional activities?
- Does the activity generate a profit in some years and, if so, how much?
- Will the artist make a profit in the future?
The artist need not answer “yes” to every question to legitimately deduct business-related expenses – including art supplies and equipment, studio rental, travel (mileage, airfare, parking, tolls, meals and lodging), educational expenses (conferences, master classes, museum membership) and the cost of advertising and promotion (business cards, brochures, photography, postage and shipping), but the IRS demands proof that an artist has made a genuine effort to earn a profit in at least three years out of five.
Artistic credentials, which don’t usually matter to collectors, critics, dealers and curators, may also help an artist make a case that he or she is a professional for tax purposes. These include earning a bachelor’s or master’s degree in the fine arts, membership in an artists’ society, experience teaching art, inclusion in Who’s Who in American Art or a similar directory and an exhibition history.
An artist is someone who requires an artist’s studio . Several private and public agencies certify artists’ eligibility to rent or buy live-work loft space apartments that have both residential and studio components. Artist Certification committees are set up to evaluate applicants’ need for space and their qualifications as serious, but not necessarily professional, artists. According to the artist certification guidelines of the Boston Redevelopment Authority in Massachusetts, “Any artist who can demonstrate to a committee of peers that they have a recent body of work as an artist, and who requires loft-style space to support that work, is eligible.” The definition that these committees use is quite flexible, focusing on subjective factors (“…the nature of the commitment of the artist to his or her art form as his or her primary vocation rather than the amount of financial remuneration earned from his or her creative endeavor,” in the words of the Artist Certification Committee of New York City’s Department of Cultural Affairs) rather than a set of hard numbers like exhibitions dates, sales, awards, memberships or commissions, which would disqualify most applicants. There is no written definition of artist at Artspace, the Minnesota-based developer of live-work spaces for artists around the country, and ad hoc certification committees at various sites look at applicants’ work (“they’re not making qualitative judgments, though,” Artspace spokeswoman Sarah Parker told Observer) to gauge the individual’s reputation within the artistic community.
An artist is an “independent contractor.” Artists are generally self-employed, working in their own studios, setting their own hours and creating objects that are of their own design and making, but sometimes they do work for others. For instance, they may serve as a studio assistant, helping another artist with practical matters, or they may be commissioned to produce an artwork, such as a monument, portrait or mural. In these circumstances, the definition of artist matters a lot, principally because of the issue of copyright. Someone who is an employee is paid a salary (and, perhaps, receives benefits, such as health insurance, sick and vacation pay), works certain set hours per week and is given explicit instructions on what tasks to fulfill and how to fulfill them at the employer’s work site, and the output that the individual produces on the job, which could be anything from paintings to sculpture, belongs to the employer. It is not uncommon, however, for artists who hire assistants to get around the need to pay taxes for these employees by calling them independent contractors, potentially giving those assistants a legal basis to be considered joint authors of the artists’ work if they were involved directly with the finished pieces. That joint authorship would be dependent upon the degree to which the assistant could prove that his or her original ideas and decision-making are part of the final work, according to Joshua Kaufman, a Washington, D.C. lawyer who often represents artists.
There have been some lawsuits brought by former assistants against the artists for whom they worked for joint copyright ownership of works, but they have all been settled out of court. However, in 1989, Kaufman successfully argued before the United States Supreme Court the right of sculptor James Earl Reid to claim copyright ownership of a work that a nonprofit group had commissioned him to create.
An artist is someone whom funding agencies call an artist . Public agencies and private organizations also provide money for individual artists, but nary one has published a formal definition of what an artist is. “We put this into the hands of our panel members,” Julie Gordon Dalgleish , former program director for artist fellowships at the Bush Foundation, told Observer. “We exclude certain things,” such as straight journalism, from the literature category and instructional videos from the category of film and video, but “we accepted an application from someone who braids hair. We would look at a tattoo artist if we felt there was a strong vision, creative energy and perseverance.” By we, of course, she meant the panels that review artists’ applications for fellowships to decide who receives money. Panel members regularly debate the question of whether or not a craft artist is an artist—a topic with a decades-long history. More recent concerns involve new media and digital art in two dimensions and three dimensions.
Ultimately, for most purposes, artists are people who call themselves artists. According to Marcel Duchamp , the artist defines art, and it seems increasingly true that nowadays artists also define who and what they are. Definitions by nature are confining and restrictive, while art and its makers seek to be expansive and inclusive. It may be simpler to state what makes an artist a professional than what defines an artist. ‘Artist’ has become a universal label denoting creativity and using it is often a way to shine a light on someone who does something particularly well. Socially, artists are often defined by the positive (freedom-loving, convention-defying) or negative (egotistical, bohemian) characteristics that other people attribute to them. Part of an artist’s job is to understand how artists are seen and what is expected of them, whether that’s by a certification committee that wants to see their body of work, a funding source that wants to understand the artist’s proposal, a dealer who wants to see what they’re capable of or the government, which more often than not, just wants to see the receipts.

- SEE ALSO : The World’s First Desktop Computer Heads to Auction
We noticed you're using an ad blocker.
We get it: you like to have control of your own internet experience. But advertising revenue helps support our journalism. To read our full stories, please turn off your ad blocker. We'd really appreciate it.
How Do I Whitelist Observer?
Below are steps you can take in order to whitelist Observer.com on your browser:
For Adblock:
Click the AdBlock button on your browser and select Don't run on pages on this domain .
For Adblock Plus on Google Chrome:
Click the AdBlock Plus button on your browser and select Enabled on this site.
For Adblock Plus on Firefox:
Click the AdBlock Plus button on your browser and select Disable on Observer.com.

COMMENTS
Answer 2: Art is essential as it covers all the developmental domains in child development. Moreover, it helps in physical development and enhancing gross and motor skills. For example, playing with dough can fine-tune your muscle control in your fingers. Share with friends. Previous.
What is art? - The dictionary definition of art says that it is "the conscious use of skill and creative imagination, especially in the production of aesthetic objects" (Merriam-Webster). Art is essential to society as it stimulates creativity, reflects culture, fosters empathy, provokes thought, and offers a medium for expression.It enhances society's intellectual and emotional ...
The definition of art is controversial in contemporary philosophy. Whether art can be defined has also been a matter of controversy. The philosophical usefulness of a definition of art has also been debated. Contemporary definitions can be classified with respect to the dimensions of art they emphasize. One distinctively modern, conventionalist ...
Introduction to Art: Design, Context, and Meaning offers a comprehensive introduction to the world of Art. Authored by four USG faculty members with advance degrees in the arts, this textbooks offers up-to-date original scholarship. It includes over 400 high-quality images illustrating the history of art, its technical applications, and its many uses.
Overview. In the perspective of the history of art, artistic works have existed for almost as long as humankind: from early prehistoric art to contemporary art; however, some theorists think that the typical concept of "artistic works" does not fit well outside modern Western societies. One early sense of the definition of art is closely related to the older Latin meaning, which roughly ...
We'll begin with the pragmatic. In 1957, the architect Frank Lloyd Wright wrote: "Art is a discovery and development of elementary principles of nature into beautiful forms suitable for human use.". Another practical definition comes to us from Charles Eames: "Art resides in the quality of doing; process is not magic.".
Throughout this essay, he remains confident that he is the first to provide an exact definition for art: "…however strange it may seem to say so, in spite of the mountains of books written about art, no exact definition of art has been constructed. And the reason of this is that the conception of art has been based on the conception of ...
art, a visual object or experience consciously created through an expression of skill or imagination. The term art encompasses diverse media such as painting, sculpture, printmaking, drawing, decorative arts, photography, and installation. (Read Sister Wendy's Britannica essay on art appreciation.) memorial board. Memorial board, wood.
Definition of Art Definition Essay. The practice of creating artistic works is something that is as old as the human species. Historically, different societies had their own ways of defining art, because of the significance that societies placed on artistic works. Although such traditional definitions are still appreciated in some contemporary ...
An art essay is a literary composition that analyzes different aspects of artwork, including paintings, sculpture, poems, architecture, and music. These essays look at the visual elements of different artworks. An art essay, for example, might look at the optical elements and creative approaches utilized in particular works of art.
The value of creating. At its most basic level, the act of creating is rewarding in itself. Children draw for the joy of it before they can speak, and creating pictures, sculptures and writing is both a valuable means of communicating ideas and simply fun. Creating is instinctive in humans, for the pleasure of exercising creativity.
Structure of the Art Essay and Its Features. The structure of the essay consists of three required elements: introduction, body, and conclusion. The absence of one of the article's composition elements is considered a mistake and taken into account in the assessment. It is challenging to write the introduction and conclusion.
Art History Analysis - Formal Analysis and Stylistic Analysis. Typically in an art history class the main essay students will need to write for a final paper or for an exam is a formal or stylistic analysis. A formal analysis is just what it sounds like - you need to analyze the form of the artwork. This includes the individual design ...
philosophy of art, the study of the nature of art, including concepts such as interpretation, representation and expression, and form.It is closely related to aesthetics, the philosophical study of beauty and taste.. Distinguishing characteristics. The philosophy of art is distinguished from art criticism, which is concerned with the analysis and evaluation of particular works of art.
The vocabulary of art is made up of the Formal Elements of Design: line, shape, form, space, color, texture, motion, and time. Line. The most basic element of design is the line: a mark with greater length than width, the path traced by a moving point. In mathematics, a line has no width, but in art, lines can be thin, thick, rough or smooth.
A visual analysis essay is a type of essay written mostly by students majoring in Art History and Communications. The process of visual analysis can be applied to painting, visual art, journalism, photo-journalism, photography, film, and writing. Works in these mediums are often meant to be consumed for entertainment or informative purposes.
Beauty is rather a measure of affect, a measure of emotion. In the context of art, beauty is the gauge of successful communication between participants - the conveyance of a concept between the artist and the perceiver. Beautiful art is successful in portraying the artist's most profound intended emotions, the desired concepts, whether they ...
Three rules on art. First: the very idea of rules in the fine arts changes and becomes transfigured through the impact of beauty on the activity of art. So the rules must be continually reborn, and the artist is forever exploring the unknown. Second: the work to be made is unique, and an end in itself.
Evaluating the content of art. While Tolstoy's basic conception of art is broad and amoral, his idea of "good" art is strict and moralistic, based on what he sees as the function of art in the development of humanity: . just as in the evolution of knowledge - that is, the forcing out and supplanting of mistaken and unnecessary knowledge by truer and more necessary knowledge - so the ...
Instead, art appreciation is: Gaining the knowledge to understand the art. Acquire the art methods and materials to discuss art verbally or by the written word. Ability to identify the movements from ancient cultures to today's contemporary art. Learning how to appreciate art is a necessary cultural foundation enabling people to critically ...
Renaissance art, painting, sculpture, architecture, music, and literature produced during the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries in Europe under the combined influences of an increased awareness of nature, a revival of classical learning, and a more individualistic view of man.
Life imitating art. Anti-mimesis is a philosophical position that holds the direct opposite of Aristotelian mimesis. Its most notable proponent is Oscar Wilde, who opined in his 1889 essay that, "Life imitates Art far more than Art imitates Life". In the essay, written as a Platonic dialogue, Wilde holds that anti- mimesis "results not merely ...
Ms. Onguru's path shows what a pivotal role arts education can play in a young person's development. Yet, while the arts and culture space accounts for a significant amount of gross domestic ...
abstract art, painting, sculpture, or graphic art in which the portrayal of things from the visible world plays little or no part. All art consists largely of elements that can be called abstract—elements of form, colour, line, tone, and texture. Prior to the 20th century these abstract elements were employed by artists to describe, illustrate, or reproduce the world of nature and of human ...
The definition that these committees use is quite flexible, focusing on subjective factors ("…the nature of the commitment of the artist to his or her art form as his or her primary vocation ...