- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault

Cold War History
By: History.com Editors
Updated: June 26, 2023 | Original: October 27, 2009

The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension marked by competition and confrontation between communist nations led by the Soviet Union and Western democracies including the United States. During World War II , the United States and the Soviets fought together as allies against Nazi Germany . However, U.S./Soviet relations were never truly friendly: Americans had long been wary of Soviet communism and Russian leader Joseph Stalin ’s tyrannical rule. The Soviets resented Americans’ refusal to give them a leading role in the international community, as well as America’s delayed entry into World War II, in which millions of Russians died.
These grievances ripened into an overwhelming sense of mutual distrust and enmity that never developed into open warfare (thus the term “cold war”). Soviet expansionism into Eastern Europe fueled many Americans’ fears of a Russian plan to control the world. Meanwhile, the USSR came to resent what they perceived as U.S. officials’ bellicose rhetoric, arms buildup and strident approach to international relations. In such a hostile atmosphere, no single party was entirely to blame for the Cold War; in fact, some historians believe it was inevitable.
Containment
By the time World War II ended, most American officials agreed that the best defense against the Soviet threat was a strategy called “containment.” In his famous “Long Telegram,” the diplomat George Kennan (1904-2005) explained the policy: The Soviet Union, he wrote, was “a political force committed fanatically to the belief that with the U.S. there can be no permanent modus vivendi [agreement between parties that disagree].” As a result, America’s only choice was the “long-term, patient but firm and vigilant containment of Russian expansive tendencies.”
“It must be the policy of the United States,” he declared before Congress in 1947, “to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation…by outside pressures.” This way of thinking would shape American foreign policy for the next four decades.
Did you know? The term 'cold war' first appeared in a 1945 essay by the English writer George Orwell called 'You and the Atomic Bomb.'
The Cold War: The Atomic Age
The containment strategy also provided the rationale for an unprecedented arms buildup in the United States. In 1950, a National Security Council Report known as NSC–68 had echoed Truman’s recommendation that the country use military force to contain communist expansionism anywhere it seemed to be occurring. To that end, the report called for a four-fold increase in defense spending.
In particular, American officials encouraged the development of atomic weapons like the ones that had ended World War II. Thus began a deadly “ arms race .” In 1949, the Soviets tested an atom bomb of their own. In response, President Truman announced that the United States would build an even more destructive atomic weapon: the hydrogen bomb, or “superbomb.” Stalin followed suit.
As a result, the stakes of the Cold War were perilously high. The first H-bomb test, in the Eniwetok atoll in the Marshall Islands, showed just how fearsome the nuclear age could be. It created a 25-square-mile fireball that vaporized an island, blew a huge hole in the ocean floor and had the power to destroy half of Manhattan. Subsequent American and Soviet tests spewed radioactive waste into the atmosphere.
The ever-present threat of nuclear annihilation had a great impact on American domestic life as well. People built bomb shelters in their backyards. They practiced attack drills in schools and other public places. The 1950s and 1960s saw an epidemic of popular films that horrified moviegoers with depictions of nuclear devastation and mutant creatures. In these and other ways, the Cold War was a constant presence in Americans’ everyday lives.

HISTORY Vault: Nuclear Terror
Now more than ever, terrorist groups are obtaining nuclear weapons. With increasing cases of theft and re-sale at dozens of Russian sites, it's becoming more and more likely for terrorists to succeed.
The Cold War and the Space Race
Space exploration served as another dramatic arena for Cold War competition. On October 4, 1957, a Soviet R-7 intercontinental ballistic missile launched Sputnik (Russian for “traveling companion”), the world’s first artificial satellite and the first man-made object to be placed into the Earth’s orbit. Sputnik’s launch came as a surprise, and not a pleasant one, to most Americans.
In the United States, space was seen as the next frontier, a logical extension of the grand American tradition of exploration, and it was crucial not to lose too much ground to the Soviets. In addition, this demonstration of the overwhelming power of the R-7 missile–seemingly capable of delivering a nuclear warhead into U.S. air space–made gathering intelligence about Soviet military activities particularly urgent.
In 1958, the U.S. launched its own satellite, Explorer I, designed by the U.S. Army under the direction of rocket scientist Wernher von Braun, and what came to be known as the Space Race was underway. That same year, President Dwight Eisenhower signed a public order creating the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), a federal agency dedicated to space exploration, as well as several programs seeking to exploit the military potential of space. Still, the Soviets were one step ahead, launching the first man into space in April 1961.
That May, after Alan Shepard become the first American man in space, President John F. Kennedy (1917-1963) made the bold public claim that the U.S. would land a man on the moon by the end of the decade. His prediction came true on July 20, 1969, when Neil Armstrong of NASA’s Apollo 11 mission , became the first man to set foot on the moon, effectively winning the Space Race for the Americans.
U.S. astronauts came to be seen as the ultimate American heroes. Soviets, in turn, were pictured as the ultimate villains, with their massive, relentless efforts to surpass America and prove the power of the communist system.
The Cold War and the Red Scare
Meanwhile, beginning in 1947, the House Un-American Activities Committee ( HUAC ) brought the Cold War home in another way. The committee began a series of hearings designed to show that communist subversion in the United States was alive and well.
In Hollywood , HUAC forced hundreds of people who worked in the movie industry to renounce left-wing political beliefs and testify against one another. More than 500 people lost their jobs. Many of these “blacklisted” writers, directors, actors and others were unable to work again for more than a decade. HUAC also accused State Department workers of engaging in subversive activities. Soon, other anticommunist politicians, most notably Senator Joseph McCarthy (1908-1957), expanded this probe to include anyone who worked in the federal government.
Thousands of federal employees were investigated, fired and even prosecuted. As this anticommunist hysteria spread throughout the 1950s, liberal college professors lost their jobs, people were asked to testify against colleagues and “loyalty oaths” became commonplace.
The Cold War Abroad
The fight against subversion at home mirrored a growing concern with the Soviet threat abroad. In June 1950, the first military action of the Cold War began when the Soviet-backed North Korean People’s Army invaded its pro-Western neighbor to the south. Many American officials feared this was the first step in a communist campaign to take over the world and deemed that nonintervention was not an option. Truman sent the American military into Korea, but the Korean War dragged to a stalemate and ended in 1953.
In 1955, the United States and other members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) made West Germany a member of NATO and permitted it to remilitarize. The Soviets responded with the Warsaw Pact , a mutual defense organization between the Soviet Union, Albania, Poland, Romania, Hungary, East Germany, Czechoslovakia and Bulgaria that set up a unified military command under Marshal Ivan S. Konev of the Soviet Union.
Other international disputes followed. In the early 1960s, President Kennedy faced a number of troubling situations in his own hemisphere. The Bay of Pigs invasion in 1961 and the Cuban missile crisis the following year seemed to prove that the real communist threat now lay in the unstable, postcolonial “Third World.”
Nowhere was this more apparent than in Vietnam , where the collapse of the French colonial regime had led to a struggle between the American-backed nationalist Ngo Dinh Diem in the south and the communist nationalist Ho Chi Minh in the north. Since the 1950s, the United States had been committed to the survival of an anticommunist government in the region, and by the early 1960s it seemed clear to American leaders that if they were to successfully “contain” communist expansionism there, they would have to intervene more actively on Diem’s behalf. However, what was intended to be a brief military action spiraled into a 10-year conflict .
The End of the Cold War and Effects
Almost as soon as he took office, President Richard Nixon (1913-1994) began to implement a new approach to international relations. Instead of viewing the world as a hostile, “bi-polar” place, he suggested, why not use diplomacy instead of military action to create more poles? To that end, he encouraged the United Nations to recognize the communist Chinese government and, after a trip there in 1972, began to establish diplomatic relations with Beijing.
At the same time, he adopted a policy of “détente”—”relaxation”—toward the Soviet Union. In 1972, he and Soviet premier Leonid Brezhnev (1906-1982) signed the Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty (SALT I), which prohibited the manufacture of nuclear missiles by both sides and took a step toward reducing the decades-old threat of nuclear war.
Despite Nixon’s efforts, the Cold War heated up again under President Ronald Reagan (1911-2004). Like many leaders of his generation, Reagan believed that the spread of communism anywhere threatened freedom everywhere. As a result, he worked to provide financial and military aid to anticommunist governments and insurgencies around the world. This policy, particularly as it was applied in the developing world in places like Grenada and El Salvador, was known as the Reagan Doctrine .
Even as Reagan fought communism in Central America, however, the Soviet Union was disintegrating. In response to severe economic problems and growing political ferment in the USSR, Premier Mikhail Gorbachev (1931-2022) took office in 1985 and introduced two policies that redefined Russia’s relationship to the rest of the world: “glasnost,” or political openness, and “ perestroika ,” or economic reform.
Soviet influence in Eastern Europe waned. In 1989, every other communist state in the region replaced its government with a noncommunist one. In November of that year, the Berlin Wall –the most visible symbol of the decades-long Cold War–was finally destroyed, just over two years after Reagan had challenged the Soviet premier in a speech at Brandenburg Gate in Berlin: “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall.” By 1991, the Soviet Union itself had fallen apart. The Cold War was over.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us

- HISTORY & CULTURE
What was the Cold War—and are we headed to another one?
The 45-year standoff between the West and the U.S.S.R. ended when the Soviet Union dissolved. Some say another could be starting as tensions with Russia rise.
As World War II dragged to an end in 1945, the leaders of the “Big Three” allied powers—the United States, Soviet Union, and Great Britain—met in Potsdam, Germany, to hash out terms to conclude the bloodiest conflict the world had ever seen. The great powers split Germany into occupation zones, recognized a Soviet-backed government in Poland, and partitioned Vietnam, monumental decisions that shaped the postwar global order. The talks were meant to forge a lasting peace, but within 18 months, a Cold War began that lasted more than four decades.
One of the most important moments at Potsdam was not captured in a memo or proclaimed at a press conference. Late in the conference, U.S. President Harry Truman took aside Soviet premier Joseph Stalin to share some explosive news: The U.S. had just successfully tested a weapon of “unusual destructive force.” It was a nuclear weapon capable of destroying entire cities, the most dangerous and powerful armament the world had ever seen.
( Subscriber exclusive: For Hiroshima's survivors, memories of the bomb are impossible to forget .)
Within weeks, the U.S. used the atomic bomb to force Japan’s surrender. With a devastating and proven weapon in its armory, the U.S. suddenly had the upper hand among the powers who were allies in the war. What followed was a dangerous struggle for supremacy between two superpowers, the U.S. and the U.S.S.R., that lasted until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991.

Though the two nations were technically at peace, the period was characterized by an aggressive and costly arms race; bloody proxy wars fought across Latin America, Africa, and Asia; and competing bids for world dominance between U.S.-led capitalist governments and the Soviet-led communist bloc.
The Cold War lasted nearly half a century. Here’s a look at why it began, how it escalated, its legacy today—and why some analysts think another Cold War is already underway.
Why’s it called the Cold War?
The term “cold war” had existed since the 1930s, when guerre froide was used in France to describe increasingly fraught relationships between European countries. In 1945, shortly after the United States dropped the atomic bomb on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, British writer George Orwell used the term in an essay that explored what the atom bomb meant for international relations.
The atom bombs killed more than 100,000 Japanese citizens, unveiling a destructive power so terrifying that Orwell predicted it would discourage open warfare among great powers, creating instead “a state which was at once unconquerable and in a permanent state of ‘cold war’ with its neighbours.”
Orwell’s prediction of a “peace that is no peace” came true as seeds of distrust between the former allies grew.
Okay, so how did the Cold War begin?
The U.S.S.R. had borne the highest number of military and civilian casualties in the war— an estimated 24 million —while liberating huge swaths of Eastern Europe from Nazi control. Soviet leader Josef Stalin was dissatisfied with the postwar division of Europe, which he felt didn’t fairly reflect his nation’s contribution.
In the U.S., diplomat George Kennan outlined the Soviet Union’s growing distrust in the 1946 “Long Telegram,” as it is now known. Kennan warned that the U.S.S.R. was illogical and insecure and would not cooperate with the West in the long-term. In response, Washington began to pursue a policy of “containment” to prevent the spread of Soviet ideology and influence.

The U.S. soon got an opportunity to flex its new policy. In 1947, Britain announced it would withdraw aid from Greece and Turkey, which were both battling communist uprisings. President Harry Truman seized the occasion to ask Congress for funds to assist both countries, establishing what became known as the Truman Doctrine —the principle that the U.S. should support countries or people threatened by Soviet forces or communist insurrection. Stalin saw the move as the opening shot of a shadow war.
The term “Cold War” became a shorthand to describe the ideological struggle between capitalism in the West and communism in the East. American journalist Walter Lippmann popularized the term in a series of articles in 1947 as nations chose sides in the standoff.
Why was NATO created?
The U.S. wasn’t alone in worrying about Stalin’s push to extend Soviet influence westward and bring other states under communist rule. In 1948, the U.S.S.R. backed a communist coup in Czechoslovakia and launched a blockade of west Berlin, which had been divided into occupation zones controlled by communists in the east and capitalists in the west.
To demonstrate a united front, the U.S. and its allies formed a transatlantic mutual defense alliance known as the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, or NATO. On April 4, 1949, the U.S., Canada, Belgium, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxemburg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, and the U.K. signed a treaty agreeing that “an armed attack against one or more…shall be considered an attack against them all.”

The U.S.S.R. responded by creating a defensive alliance of its own. Signed in 1955, the Warsaw Pact included the Soviet Union and seven satellite states, including Poland and East Germany, reinforcing the ideological and military barrier between Eastern and Western Europe that Winston Churchill had dubbed the “ Iron Curtain ” in a 1946 speech.
How close did the world come to nuclear war?
As the two sides faced off across that Iron Curtain, the U.S. and U.S.S.R. engaged in an arms race, pouring trillions of dollars into accumulating nuclear arsenals .
The U.S. had an advantage at the start of the arms race. But once the U.S.S.R. built its own nuclear arsenal, the two sides were at a standoff over “mutually assured destruction” —the idea that if either side attacked, the other would retaliate, unleashing apocalyptic consequences for both parties.
You May Also Like

A military spouse reflects on life over two decades of war—and what comes next

What the end of the war in Afghanistan means to one mother and her family

‘A ball of blinding light’: Atomic bomb survivors share their stories
( See the abandoned Soviet bunkers hidden beneath Georgia's capital city .)
Both countries had missile defenses pointed at one another, and in 1962, the Cuban Missile Crisis brought the countries closer to the brink than any other event in the Cold War. The U.S. detected Soviet missile bases and arms in communist Cuba, just 90 miles south of Florida. Demanding they be removed, President John F. Kennedy declared that a strike on U.S. territory would trigger an immediate nuclear strike on the U.S.S.R.

The threat of imminent nuclear war hung over nearly two weeks of tense negotiations. Finally, the U.S.S.R. agreed to dismantle its weapons facilities if the U.S. pledged not to invade Cuba. Behind the scenes, the U.S. agreed to remove nuclear weapons from Turkey; that agreement did not become public until 1987.
Nevertheless, both sides’ nuclear arsenals continued to grow exponentially. By the late 1980s, the United States had an estimated 23,000 nuclear weapons to the Soviet Union’s 39,000.
How else was the Cold War fought?
Over more than four decades of Cold War, the U.S. and Soviet Union waged multiple proxy wars across the globe. In the Korean War , the Vietnam War , and other armed conflicts, the superpowers funded opposing sides or fought directly against communist or capitalist militias. Both sides funded revolutions, insurgencies, and political assassinations in Latin America, Africa, Asia, and the Middle East.
The U.S. and Soviet Union also jockeyed to prove technological dominance in a 20-year Space Race . The Soviet Union scored first with the 1957 launch of Sputnik-1, the first artificial satellite, while the U.S. was first to send a man to the moon in 1969. Only in the mid 1970s did the two nations begin to cooperate on joint missions.
( 50 years after Apollo 11, a new moon race is on .)

How did the Cold War end?
By the mid 1980s, life behind the Iron Curtain had changed. Democratic uprisings were percolating in Soviet bloc nations, and the U.S.S.R. itself struggled with economic and political chaos. The U.S. and U.S.S.R. forged a more open relationship, even brokering a nuclear treaty in 1987 that eliminated a class of particularly dangerous ground-launched missiles from the nations’ arsenals.
By 1991, the Soviet Union had lost most of its bloc to democratic revolutions, and the Warsaw Pact was formally dissolved. Mikhail Gorbachev, the last leader of the U.S.S.R., opened his country to the West and instituted economic reforms that undercut institutions that relied on nationalized goods. In December 1991, the U.S.S.R. was dissolved into separate nations.
What does all this mean now?
The U.S.S.R. is gone, and nuclear arsenals have dramatically decreased thanks to nonproliferation treaties between Washington and Moscow in the 1980s and 1990s. In recent decades, the U.S. and Russia have cooperated on a number of global issues, including Afghanistan and the war on terror.
But the Cold War still affects modern geopolitics. Both nations still have divergent geopolitical interests, large defense budgets, and international military bases. NATO still wields political power and has grown to include 30 member states. The alliance now stretches to Russia’s borders and includes former Soviet states and Warsaw Pact members, such as Poland and the Baltic States. Since the 1990s, Russia has seen the eastward expansion of NATO as a threat to its security .
Tensions between Russia and the West reached a new high point following the February 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, which had applied to take the first steps toward NATO membership in 2008, before a new president shelved the plan two years later. Some commentators have likened the current crisis to the beginnings of a new Cold War.
( Follow Ukraine's 30-year struggle for independence with this visual timeline .)
Is a 21st-century Cold War already being waged? It remains to be seen. Though historians say the decisions at Potsdam set the stage for a long post-World War II rivalry, we may not recognize the beginnings of a new Cold War until it’s visible in history’s rear-view mirror.
Related Topics
- VIETNAM WAR
- NUCLEAR WEAPONS

This pill could protect us from radiation after a nuclear meltdown

Oppenheimer: The secrets he protected and the suspicions that followed him

The true history of Einstein's role in developing the atomic bomb

How Chien-Shiung Wu changed the laws of physics


How does ‘Oppenheimer’ re-create history? We asked Christopher Nolan.
- Paid Content
- Environment
- Photography
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Access your Commentary account.
Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive a link to create a new password via email.
The monthly magazine of opinion.
The Long Peace, by John Lewis Gaddis
The Long Peace: Inquiries into the History of the Cold War. by John Lewis Gaddis Oxford University Press. 332 pp. $24.95.
In the spectrum of historians writing about the cold war, John Lewis Gaddis belongs in the category of post-revisionists. The revisionists, mainly in the 1960’s, challenged the widespread Western view attributing the origins and development of the cold war chiefly to the expansive actions and ambitions of the Soviet Union and the attempt of the U.S. and its allies to stop and contain that expansion. The revisionists attacked that consensus from the Left, excusing the Soviet Union’s behavior as coming from a natural and justified sense of insecurity and blaming the U.S. for misunderstanding Soviet fears, for acting not in defense of freedom but in pursuit of its own economic interests, from an inordinate and irrational fear of Communism, and, in some cases, from an aggressive imperialism of its own, inherent in capitalist societies.
Gaddis, one of the first post-revisionists, is also one of the ablest and most influential. His first book, The United States and the Origins of the Cold War (1972), was a sensible and scholarly examination of the issues raised by the revisionists which for the most part refuted and rejected their interpretations. His subsequent works have placed him near the center of a newly emerging consensus that seems to take an impartial position between the two antagonistic “superpowers,” seeking to understand the position of each and willing to criticize both. His latest book is a collection of essays, most of them occasional pieces written for conferences, that provides a good opportunity for examining the strengths and weaknesses of such an approach in the hands of one of its abler practitioners.
Gaddis is a sober and hard-working professional who has read all the scholarly literature and has worked with the primary sources. As the Western nations, especially the U.S., have made new historical evidence available, he has examined it and used the results to answer some interesting and important questions. Thus he finds unsupported by evidence the charges of the revisionists that the U.S. feigned alarm at Soviet action soon after the war as an excuse for intervention, expansion, and hegemony. In fact the threat posed by the Soviets had been seen earlier, and its dangers felt far more urgently, by the free nations of Europe. Their chief concern was to get the Americans to take the lead in stopping it. The U.S. did not press itself upon unwilling allies but was eagerly invited to extend its involvement and influences. If American actions can be called expansion, this was “expansion by invitation.” Far from seeking to establish a sphere of influence in Western Europe, as George Kennan advised it to do soon after the war, the U.S. tried hard to establish an independent set of free, European nations that could and would defend themselves and permit the Americans to reduce their involvement.
Why did the attempt fail? Gaddis’s answer is sensible and convincing:
The reason, almost certainly, is that the Europeans themselves did not want it. Confronted by what they perceived to be a malevolent challenge to the balance of power from the East, they set about inviting in a more benign form of countervailing power from the West rather than undertake the costly, protracted, and problematic process of rebuilding their own. The United States, with some reluctance, went along.
Perhaps the most interesting question illuminated by the availability of new evidence concerns the American attitude toward the Communist world. The traditional view is that American statesmen always looked on the Communist movement in the world as a unit and failed to exploit the real divisions among Communist nations in the interests of the United States. Gaddis, on the contrary, suggests that “despite what they said in public, American policy-makers at no point during the postwar era actually believed in the existence of an international Communist monolith.” He sees the Eisenhower administration as seeking to create a “wedge through pressure,” particularly between the Soviet Union and China. The hard line taken on the islands of Quemoy and Matsu, for example, was not merely a response to domestic political pressure but also was meant “to undermine the relationship between Moscow and Beijing.” Nixon’s later opening to China is seen as a continuation of the earlier policy, where “a public policy of hard-line anti-Communism created greater opportunities for exploiting differences within the Communist world than did less rigid ideological stances.”
_____________
Such interpretations are well-argued and persuasive, but too much of this sort of thing will earn a post-revisionist scholar a reputation as a cold warrior. To avoid such a stigma requires a considerable effort to look at matters from the Soviet side, and such efforts are not lacking in these essays. Even while conceding that Americans’ fear of “Soviet and/or Communist expansionism” has been genuine, Gaddis says that “Fear, after all, can be genuine without being rational. And as Sigmund Freud once pointed out, even paranoids can have real enemies.” But nothing in these essays or anywhere else shows that American fears—and those of many others—have been unfounded. With Soviet intentions unknown and unlikely ever to be documented, why should Americans be thought insane, especially since Gaddis more than once calls their reactions to the perceived danger sensible and restrained?
Much of the revisionist case for the absence of Soviet evil intentions rests on the fact that the Soviets never did invade Western Europe or other places, nor did Communist parties in the West undertake revolutions. In the same spirit, Gaddis cites with approval the view that “The security of nations now rests . . . not so much on the exertions they themselves make, but on the restraint exhibited by their adversaries.” But what has created that restraint (such as it is) is precisely exertions like the Marshall Plan, NATO, nuclear weapons, and the demonstrated capacity and will to make use of such devices. The measures taken to achieve deterrence and containment of Soviet ambition tend to be ignored in analyses like Gaddis’s and their results taken for granted.
The last essay in this collection, “The Long Peace: Elements of Stability in the Postwar International Systems,” presents Gaddis’s current understanding of developments since 1945. Here he argues, contrary to conventional thinking among theorists of international relations, that the “bipolar” system may in fact be more stable than the “multipolar” alternative, because it happens to reflect the realities of power. The distance between the two great powers, their relative lack of mutual communication and interdependence, may, paradoxically, be a force for stability. The presence of nuclear weapons has had a sobering effect on statesmen on each side. Technological innovation, by permitting mutual surveillance, has also had a stabilizing effect. Ideological hostilities have modified and yielded to the practical needs of mutual survival. Thus, the period 1945-87 might better be seen as one of “Long Peace” than of cold war.
Gaddis is attracted by ideas arising from game theory to help explain why the “Long Peace” evolved and continues and what is needed to preserve it. The problem with this approach, as with the “evenhanded” analysis of the cold war, is that it treats all players as fundamentally the same and thereby loses touch with reality. The United States and the Soviet Union not only have very different political and constitutional systems and moral attitudes; more to the point, they have had quite different goals. The Soviets have wanted to change the balance of power in the world in their favor, while the United States has tried to maintain the status quo as much as possible. To preach, therefore, as Gaddis does, that stability requires “a sense of caution, maturity, and responsibility on both sides,” is pointless if one side wants not stability but change. In those circumstances, stability must require that the nation seeking it should be strong and determined enough to deter reckless actions by the dissatisfied power. Up to now the United States has been willing to pay the price. Whether it will continue to do so will determine if the “Long Peace” will persist.

Hitler’s Unnecessary Rise

A Blessing and a Bunch of Curses

East of Eden
Scroll Down For the Next Article
Type and press enter
- More Networks

The Cold War
After World War II, the United States and its allies, and the Soviet Union and its satellite states began a decades-long struggle for supremacy known as the Cold War. Soldiers of the Soviet Union and the United States did not do battle directly during the Cold War. But the two superpowers continually antagonized each other through political maneuvering, military coalitions, espionage, propaganda, arms buildups, economic aid, and proxy wars between other nations.
From Allies to Adversaries
The Soviet Union and the United States had fought as allies against Nazi Germany during World War II. But the alliance began to crumble as soon as the war in Europe ended in May 1945. Tensions were apparent in July during the Potsdam Conference, where the victorious Allies negotiated the joint occupation of Germany.
The Soviet Union was determined to have a buffer zone between its borders and Western Europe. It set up pro-communist regimes in Poland, Hungary, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, Romania, Albania, and eventually in East Germany.
As the Soviets tightened their grip on Eastern Europe, the United States embarked on a policy of containment to prevent the spread of Soviet and communist influence in Western European nations such as France, Italy, and Greece.
During the 1940s, the United States reversed its traditional reluctance to become involved in European affairs. The Truman Doctrine (1947) pledged aid to governments threatened by communist subversion. The Marshall Plan (1947) provided billions of dollars in economic assistance to eliminate the political instability that could open the way for communist takeovers of democratically elected governments.
France, England, and the United States administered sectors of the city of Berlin, deep inside communist East Germany. When the Soviets cut off all road and rail traffic to the city in 1948, the United States and Great Britain responded with a massive airlift that supplied the besieged city for 231 days until the blockade was lifted. In 1949, the United States joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), the first mutual security and military alliance in American history. The establishment of NATO also spurred the Soviet Union to create an alliance with the communist governments of Eastern Europe that was formalized in 1955 by the Warsaw Pact.
The Worldwide Cold War
In Europe, the dividing line between East and West remained essentially frozen during the next decades. But conflict spread to Asia, Africa, and Latin America. The struggle to overthrow colonial regimes frequently became entangled in Cold War tensions, and the superpowers competed to influence anti-colonial movements.
In 1949, the communists triumphed in the Chinese civil war, and the world's most populous nation joined the Soviet Union as a Cold War adversary. In 1950, North Korea invaded South Korea, and the United Nations and the United States sent troops and military aid. Communist China intervened to support North Korea, and bloody campaigns stretched on for three years until a truce was signed in 1953.
In 1954, the colonial French regime fell in Vietnam.
The United States supported a military government in South Vietnam and worked to prevent free elections that might have unified the country under the control of communist North Vietnam. In response to the threat, the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO) was formed in 1955 to prevent communist expansion, and President Eisenhower sent some 700 military personnel as well as military and economic aid to the government of South Vietnam. The effort was foundering when John F. Kennedy took office.
Closer to home, the Cuban resistance movement led by Fidel Castro deposed the pro-American military dictatorship of Fulgencio Batista in 1959. Castro's Cuba quickly became militarily and economically dependent on the Soviet Union. The United States' main rival in the Cold War had established a foothold just ninety miles off the coast of Florida.
Kennedy and the Cold War
Cold War rhetoric dominated the 1960 presidential campaign. Senator John F. Kennedy and Vice President Richard M. Nixon both pledged to strengthen American military forces and promised a tough stance against the Soviet Union and international communism. Kennedy warned of the Soviet's growing arsenal of intercontinental ballistic missiles and pledged to revitalize American nuclear forces. He also criticized the Eisenhower administration for permitting the establishment of a pro-Soviet government in Cuba.
John F. Kennedy was the first American president born in the 20th century. The Cold War and the nuclear arms race with the Soviet Union were vital international issues throughout his political career. His inaugural address stressed the contest between the free world and the communist world, and he pledged that the American people would "pay any price, bear any burden, meet any hardship, support any friend, oppose any foe to assure the survival and success of liberty."
The Bay of Pigs
Before his inauguration, JFK was briefed on a plan drafted during the Eisenhower administration to train Cuban exiles for an invasion of their homeland. The plan anticipated that support from the Cuban people and perhaps even elements of the Cuban military would lead to the overthrow of Castro and the establishment of a non-communist government friendly to the United States.
Kennedy approved the operation and some 1,400 exiles landed at Cuba's Bay of Pigs on April 17. The entire force was either killed or captured, and Kennedy took full responsibility for the failure of the operation.
The Arms Race
In June 1961, Kennedy met with Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev in Vienna, Austria. (See a memorandum below outlining the main points of conversation between President Kennedy and Khrushchev at their first lunch meeting.) Kennedy was surprised by Khrushchev's combative tone during the summit. At one point, Khrushchev threatened to cut off Allied access to Berlin. The Soviet leader pointed out the Lenin Peace Medals he was wearing, and Kennedy answered, "I hope you keep them." Just two months later, Khrushchev ordered the construction of the Berlin Wall to stop the flood of East Germans into West Germany.
As a result of these threatening developments, Kennedy ordered substantial increases in American intercontinental ballistic missile forces. He also added five new army divisions and increased the nation's air power and military reserves. The Soviets meanwhile resumed nuclear testing and President Kennedy responded by reluctantly reactivating American tests in early 1962.
JFKPOF-126-009-p0024. Memorandum relaying the main points of the conversation between John F. Kennedy and Nikita Khrushchev during their first lunch meeting in Vienna, on June 3, 1961.
During this meeting, President Kennedy and Premier Khrushchev discussed Soviet agriculture, Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin's space flight, the possibility of putting a man on the moon, and their hopes that their two nations would have good relations in the future.
More information
JFKPOF-126-009-p0025. Memorandum relaying the main points of the conversation between John F. Kennedy and Nikita Khrushchev during their first lunch meeting in Vienna, on June 3, 1961.
JFKPOF-126-009-p0026. Memorandum relaying the main points of the conversation between John F. Kennedy and Nikita Khrushchev during their first lunch meeting in Vienna, on June 3, 1961.
JFKPOF-126-009-p0027. Memorandum relaying the main points of the conversation between John F. Kennedy and Nikita Khrushchev during their first lunch meeting in Vienna, on June 3, 1961.
The Cuban Missile Crisis
In the summer of 1962, Khrushchev reached a secret agreement with the Cuban government to supply nuclear missiles capable of protecting the island against another US-sponsored invasion. In mid-October, American spy planes photographed the missile sites under construction. Kennedy responded by placing a naval blockade, which he referred to as a "quarantine," around Cuba. He also demanded the removal of the missiles and the destruction of the sites. Recognizing that the crisis could easily escalate into nuclear war, Khrushchev finally agreed to remove the missiles in return for an American pledge not to reinvade Cuba. But the end of Cuban Missile Crisis did little to ease the tensions of the Cold War. The Soviet leader decided to commit whatever resources were required for upgrading the Soviet nuclear strike force. His decision led to a major escalation of the nuclear arms race.
In June 1963, President Kennedy spoke at the American University commencement in Washington, DC. He urged Americans to critically reexamine Cold War stereotypes and myths and called for a strategy of peace that would make the world safe for diversity. In the final months of the Kennedy presidency Cold War tensions seemed to soften as the Limited Nuclear Test Ban Treaty was negotiated and signed. In addition, Washington and Moscow established a direct line of communication known as the "Hotline" to help reduce the possibility of war by miscalculation.
In May 1961, JFK had authorized sending 500 Special Forces troops and military advisers to assist the government of South Vietnam. They joined 700 Americans already sent by the Eisenhower administration. In February 1962, the president sent an additional 12,000 military advisers to support the South Vietnamese army. By early November 1963, the number of US military advisers had reached 16,000.
Even as the military commitment in Vietnam grew, JFK told an interviewer, "In the final analysis, it is their war. They are the ones who have to win it or lose it. We can help them, we can give them equipment, we can send our men out there as advisers, but they have to win it—the people of Vietnam against the Communists. . . . But I don't agree with those who say we should withdraw. That would be a great mistake. . . . [The United States] made this effort to defend Europe. Now Europe is quite secure. We also have to participate—we may not like it—in the defense of Asia." In the final weeks of his life, JFK wrestled with the need to decide the future of the United States commitment in Vietnam—and very likely had not made a final decision before his death.
- Search Menu
- About OAH Magazine of History
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
- < Previous
“A Peace that is No Peace”: The Cold War as Contemporary History
Jeremi Suri is the E. Gordon Fox Professor of History at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, where he directs the European Union Center of Excellence and the Grand Strategy Program. He is author of four books on contemporary politics and foreign policy, most recently , Henry Kissinger and the American Century (Harvard University Press, 2007). In 2007 Smithsonian Magazine named Professor Suri one of America's “Top Young Innovators” in the Arts and Sciences.) .
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Jeremi Suri, “A Peace that is No Peace”: The Cold War as Contemporary History, OAH Magazine of History , Volume 24, Issue 4, October 2010, Pages 5–6, https://doi.org/10.1093/maghis/24.4.5
- Permissions Icon Permissions
In October 1945, George Orwell warned that “the drift for many decades has been not towards anarchy but towards the reimposition of slavery. We may be heading not for general breakdown but for an epoch as horribly stable as the slave empires of antiquity.” Orwell foresaw how the emergence of two superpowers on the ashes of fascism, the deployment of new destructive technologies, and the manipulation of terror would deprive the postwar world of many promised freedoms. The second half of the twentieth century would be frozen, Orwell predicted, in “a peace that is no peace,” when war preparation, controlled conflict, and targeted repression became “normal.” The British journalist famously labeled his global diagnosis “a permanent state of cold war” ( 1).
Although many contemporary observers did not share Orwell's dark vision, they adopted his terminology. The Cold War was an era of proliferating conflict short of total war. During the decades after 1945, virtually every corner of the globe was enveloped in competition, intervention, and violence due to a clash of two world systems: liberal capitalism and authoritarian communism. The United States and the Soviet Union were the self-conscious embodiments of these respective systems, and they built alliances of similar states and prepared to contain, attract, and, if necessary, destroy their adversaries. Both Washington and Moscow defended their long-term security and prosperity by spreading their “ways of life,” and undermining alternatives. The superpowers managed to avoid World War III, but they employed almost every mode of competition short of Armageddon ( 2).
Email alerts
Citing articles via, affiliations.
- Online ISSN 1938-2340
- Print ISSN 0882-228X
- Copyright © 2024 Organization of American Historians
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
PODCAST: HISTORY UNPLUGGED J. Edgar Hoover’s 50-Year Career of Blackmail, Entrapment, and Taking Down Communist Spies
The Encyclopedia: One Book’s Quest to Hold the Sum of All Knowledge PODCAST: HISTORY UNPLUGGED

The Cold War Timeline

This post is a comprehensive timeline of the Cold War, from the origins of the Russian-American conflict following World War Two to the final dissolution of the Soviet Union and the fall of the Berlin Wall at the end of the 20th century.
Scroll down to learn more. Alternatively, watch this nine-minute explainer video for an overview of the Cold War.
This article is part of our larger collection of resources on the Cold War. For a comprehensive outline of the origins, key events, and conclusion of the Cold War, click here.
This article is also part of our larger selection of posts about the Vietnam War. To learn more, click here for our comprehensive guide to the Vietnam War .
This article is part of our larger selection of posts about the Cold War. To learn more, click here for our comprehensive guide to the Cold War .
Additional Resources About Cold War
What was the iron curtain and how did it collapse, the origins of the cold war timeline, cold war detente — us/soviet enmity cools, when did china become communist, cite this article.
- How Much Can One Individual Alter History? More and Less...
- Why Did Hitler Hate Jews? We Have Some Answers
- Reasons Against Dropping the Atomic Bomb
- Is Russia Communist Today? Find Out Here!
- Phonetic Alphabet: How Soldiers Communicated
- How Many Americans Died in WW2? Here Is A Breakdown
Peer Reviewed
US-skepticism and transnational conspiracy in the 2024 Taiwanese presidential election
Article metrics.
CrossRef Citations
Altmetric Score
PDF Downloads
Taiwan has one of the highest freedom of speech indexes while it also encounters the largest amount of foreign interference due to its contentious history with China. Because of the large influx of misinformation, Taiwan has taken a public crowdsourcing approach to combatting misinformation, using both fact-checking ChatBots and public dataset called CoFacts. Combining CoFacts with large-language models (LLM), we investigated misinformation across three platforms (Line, PTT, and Facebook) during the 2024 Taiwanese presidential election. We found that most misinformation appears within China-friendly political groups and attacks US-Taiwan relations through visual media like images and videos. A considerable proportion of misinformation does not question U.S. foreign policy directly. Rather, it exaggerates domestic issues in the United States to create a sense of declining U.S. state capacity. Curiously, we found misinformation rhetoric that references conspiracy groups in the West.
Program in Quantitative Social Science, Dartmouth College, USA
Department of Political Science, University of Nevada Las Vegas, USA
Department of Computer Science, Barnard College, USA

Research Questions
- What are the misinformation narratives surrounding the election in Taiwan and how do they target international relations with the United States?
- What geographical or temporal patterns emerge from misinformation data?
- Who are the targets of these misinformation narratives and through what modalities?
Essay Summary
- We leveraged a dataset of 41,291 labeled articles from Line, 911,510 posts from Facebook, and 2,005,972 posts and comments from PTT to understand misinformation dynamics through topic modeling and network analysis.
- The primary form of misinformation is narratives that attack international relations with the United States (henceforth referred to as US-skepticism), specifically referencing the economy, health policy, the threat of war through Ukraine, and other U.S. domestic issues.
- Temporal and spatial evidence suggests VPN-based coordination, focused on U.S. issues and addresses.
- Misinformation is most common among pan-Blue and ROC identity groups on social media and is spread through visual media. These groups share many themes with conspiracy groups in Western countries.
- Our study shows the prevalence of misinformation strategies using visual media and fake news websites. It also highlights how crowdsourcing and advances in large-language models can be used to identify misinformation in cross-platform workflows.
Implications
According to Freedom House, Taiwan has one of the highest indices for free speech in Asia (Freedom House, 2022). Additionally, due to its contentious history with China, it receives significant foreign interference and misinformation, especially during its presidential elections. Due to the large influx of dis- and misinformation, Taiwan has developed many strategies to counter misleading narratives, including fact-checking ChatBots on its most popular chatroom app (Chang et al., 2020). Under this information environment, the 2024 Taiwanese presidential election emerged as one of the most divisive elections in Taiwan’s history, featuring at one point a doubling of presidential candidates in a typically two-party race, from two to four. As such, Taiwan is regarded as a “canary for disinformation” against elections in 2024, as a first indicator to how foreign interference may take place in other democracies (Welch, 2024).
In this paper, we study the misinformation ecosystem in Taiwan starting a year prior to the election. First, our findings highlight the interaction between misinformation and international relations. As was reported in The Economist and The New York Times , a considerable portion of the misinformation spread in Taiwan before the 2024 election is about US-skepticism, which aims at undermining the reputation of the United States among Taiwanese people (“China is flooding Taiwan with disinformation,” 2023; Hsu, Chien, and Myers, 2023). This phenomenon is significant because it does not target specific candidates or parties in the election but may indirectly influence the vote choice between pro- and anti-U.S. parties. Given the US-China global competition and the Russia-Ukraine ongoing conflict, the reputation of the United States is crucial for the strength and reliability of democratic allies (Cohen, 2003). Hence, it is not surprising that misinformation about the United States may propagate globally and influence elections across democracies. However, our findings surprisingly show that US-skepticism also includes a considerable number of attacks on U.S. domestic politics. Such content does not question the U.S. foreign policy but undermines the perceived reliability and state capacity of the United States. Here, s tate capacity is defined as whether a state is capable of mobilizing its resources to realize its goal, which is conceptually different from motivation and trust.
US-skepticism is commonly characterized as mistrusting the motivations of the United States, as illustrated in the Latin American context due to long histories of political influence (see dependency theory; Galeano, 1997), but our findings suggest that perceived U.S. state capacity is also an important narrative. As most foreign disinformation arises from China, this indicates a greater trend where authoritarian countries turn to sharp power tactics to distort information and defame global competitors rather than winning hearts and minds through soft power. Sharp power refers to the ways in which authoritarian regimes project their influence abroad to pierce, penetrate, or perforate the informational environments in targeted countries (Walker, 2018). In Taiwan’s case, China may not be able to tell China’s story well, but can still influence Taiwanese voters by making them believe that the United States is declining. Our findings suggest that future work analyzing the topics and keywords of misinformation in elections outside the United States should also consider the US-skepticism as one latent category, not just the politicians and countries as is common with electoral misinformation (Tenove et al., 2018). These findings are corroborated by narratives identified by a recent report including drug issues, race relations, and urban decay (Microsoft Threat Intelligence, 2024).
Additionally, our research investigates both misinformation and conspiracy theories, which are closely related. Whereas misinformation is broadly described as “false or inaccurate information” (Jerit & Zhao, 2020), a conspiracy theory is the belief that harmful events are caused by a powerful, often secretive, group. In particular, conspiracy communities often coalesce around activities of “truth-seeking,” embodying a contrarian view toward commonly held beliefs (Enders et al., 2022; Harambam, 2020; Konkes & Lester, 2017). Our findings also provide evidence of transnational similarities between conspiracy groups in Taiwan and the United States. Whereas the domestic context has been explored (Chen et al., 2023; Jerit & Zhao, 2020), the intersection of partisanship and conspiracy groups as conduits for cross-national misinformation flow deserves further investigation.
Second, our findings reemphasize that an IP address is not a reliable criterion for attributing foreign intervention. Previous studies on Chinese cyber armies show that they use a VPN for their activities on Twitter (now X) (Wang et al., 2020) and Facebook (Frenkel, 2023). Commonly known as the Reddit of Taiwan, PTT is a public forum in Taiwan that by default contains the IP address of the poster. Our analysis of PTT located a group of accounts with US IP addresses that have the same activity pattern as other Taiwan-based accounts. Therefore, it is likely that these accounts use VPN to hide their geolocation. Our results provide additional evidence that this VPN strategy also appears on secondary and localized social media platforms. Our results suggest that the analysis of the originating location of misinformation should not be based entirely on IP addresses.
Third, our findings show that text is far from the only format used in the spread of misinformation. A considerable amount of misinformation identified on Facebook is spread through links (47%), videos (21%), and photos (15%). These items may echo each other’s content or even feature cross-platform flow. Proper tools are needed to extract and juxtapose content from different types of media so that researchers can have a holistic analysis of the spread and development of misinformation (Tucker et al., 2018). Such tools are urgent since mainstream social media has adopted and highly encouraged short videos—a crucial area for researchers to assess how misinformation spreads across platforms in the upcoming year of elections. This understanding is also important for fact-check agencies because they must prepare for collecting and reviewing information on various topics found in multiple media types across platforms. Crowdsourcing, data science, expert inputs, and international collaboration are all needed to deal with multi-format misinformation environments.
With prior studies showing that the aggregated fact checks (known as wisdom of the crowds) perform on par with expert ratings (see Arechar et al., 2023; Martel et al., 2023), our case study also evidences how crowdsourcing and LLM approaches can not only quickly fact-check but also summarize larger narrative trends. In Taiwan, this takes form of the CoFacts open dataset, which we use to identify misinformation narratives. CoFacts is a project initiated by g0v (pronounced “gov zero”), a civic hacktivism community in Taiwan that started in 2012. CoFacts started as a fact-checking ChatBot that circumvents the closed nature of chatroom apps, where users can forward suspicious messages or integrate the ChatBot into private rooms. These narratives are then sent to a database. Individual narratives are subsequently reviewed by more than 2,000 volunteers, including teachers, doctors, students, engineers, and retirees (Haime, 2022). As a citizen-initiated project, it is not affiliated with any government entity or party.
Crucially, these reviews provide valuable labels that are used to train AI models and fine-tune LLMs. The dataset is available open source on the popular deep-learning platform HuggingFace. Just as AI and automation can be used to spread misinformation (Chang, 2023; Chang & Ferrara, 2022; Ferrara et al., 2020; Monaco & Woolley, 2022), it can also help combat “fake news” through human-AI collaboration.
Finding 1: The primary form of misinformation is narratives that attack international relations with the United States (henceforth referred to as US-skepticism), specifically referencing the economy, health policy, the threat of war through Ukraine, and other U.S. domestic issues.
The status quo between China and Taiwan is marked by Taiwan’s self-identification as a sovereign state, which is in contrast to China’s view of Taiwan as part of its territory under the “One China” policy. As brief context, China has claimed Taiwan as its territory since 1949, but the United States has helped maintain the status quo and peace after the outbreak of the Korean War in 1950. After democratization in 1987, Taiwan’s politics have been dominated by a clear blue-green division. The blue camp is led by Kuomintang (Nationalist Party, KMT hereafter), the founding party of the Republic of China (ROC, the formal name of Taiwan’s government based on its constitution) who was defeated by the People’s Republic of China (PRC) and retreated to Taiwan in 1949. The green camp is led by the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), which pursues revising the ROC Constitution and changing the country’s name to Taiwan. The political cleavage between the blue and green camps is dictated by Taiwan’s relationship with the PRC and the United States. The blue camp’s position is that the PRC and ROC are under civil war but belong to the same Chinese nation, and thus the blue camp appreciates military support from the United States while enhancing economic and cultural cooperation with the PRC. The green camp believes that the necessary conditions for Taiwan to be free and independent are to stand firmly with the United States and maintain distance from the PRC. After 2020, the two major camps’ insufficient attention to domestic and social issues caused the rise of nonpartisans and a third party, the Taiwan People’s Party (TPP or the white camp), which strategically avoids discussing foreign policies. In the 2024 election, the ruling DPP party (green) was reelected with 40% of votes for the third consecutive presidency (from 2016 to 2028), while KMT (blue) and TPP (white) received 33% and 26% of votes, respectively.
The U.S. “One China” policy since 1979 indicates that the United States opposes any change to the status quo unless it is solved peacefully. This has motivated the PRC to persuade Taiwanese citizens to support unification using misinformation targeted at China-friendly political groups, as the cost of unification would be greatly reduced if sufficient Taiwanese citizens opposed U.S. military intervention. This history between the United States and Taiwan serves as the foundation of US-skepticism. In the literature, US-skepticism in Taiwan is composed of two key psychological elements: trust and motivation (Wu & Lin, 2019; Wu, 2023). First, many Taiwanese no longer trust the United States after the United States switched diplomatic ties from Taiwan (ROC) to the PRC in 1979. Many blue-camp supporters doubt the commitment of the United States to send troops should China invade, per the Taiwan Relations Act (Wu & Lin, 2019). Second, Taiwanese citizens question Taiwan’s role as a proxy in a potential war with China instead of sincerely protecting democracy and human rights in Taiwan (Wu, 2023).
The CoFacts dataset contains 140,314 articles submitted by Line users, which are then fact-checked by volunteers as rumor (47%), not a rumor (21%), not an article (19%), and opinion (13%). Here, rumor is synonymous with misinformation. Using the CoFacts dataset, we trained a BERTopic model to identify 34 forms of misinformation and then ranked them by their overlap with the word “elections” in Mandarin Chinese (George & Sumathy, 2023; Nguyen et al., 2020). Table 1 shows the top nine narratives.
Many of these narratives are directly related to political parties or the democratic process. For instance, the highest-ranked topic is attacking the incumbent party (the DPP) at 18.1%, which contains 2,371 total posts. The subsequent misinformation topics focus on policy issues and specific narratives—international relations, issues of marriage and birth rate, vaccines, nuclear energy, biometrics, egg imports, and the war in Ukraine. These are known cleavage issues and overlap with the eight central concerns during the election cycle—economic prosperity, cross-strait affairs, wealth distribution, political corruption, national security, social reform/stability, and environmental protection (Achen & Wang, 2017; Achen & Wang, 2019; Chang & Fang, 2023).
We focus on the third type of misinformation, which is the relationship between Taiwan, the United States, and China. US-skepticism is not only the largest at 10,826 individual posts, but one flagged by journalists, policymakers, and politicians as one of the most crucial themes. This is a relatively new phenomenon in terms of proportion, which aims to sow distrust toward the United States (“China is flooding Taiwan with disinformation,” 2023). In contrast, questioning the fairness of process (i.e. ballot numbers) and policy positions (i.e. gay marriage) are common during elections. However, US-skeptical misinformation diverges in that there is no explicit political candidate or party targeted. By sampling the topic articles within this category and validating using an LLM-summarizer through the ChatGPT API, we identified three specific narratives:
(a) The United States and the threat of war: Ukraine intersects frequently in this topic, with videos of direct military actions. Example: “Did you hear former USA military strategist Jack Keane say the Ukrainian war is an investment. The USA spends just $66,000,000,000 and can make Ukraine and Russia fight… Keane then mentions Taiwan is the same, where Taiwanese citizens are an ‘investment’ for Americans to fight a cheap war. The USA is cold and calculating, without any actual intent to help Taiwan!”
(b) Economic atrophy due to fiscal actions by the United States: These narratives focus on domestic policy issues in Taiwan such as minimum wage and housing costs. Example: “The USA printed 4 trillion dollars and bought stocks everywhere in the world, including Taiwan, and caused inflation and depressed wages. Be prepared!”
(c) Vaccine supply and the United States: While some narratives focus on the efficacy of vaccines, several describe the United States intentionally limiting supply during the pandemic. Example: “Taiwanese Dr. Lin is a leading scientist at Moderna, yet sells domestically at $39 per two doses, $50 to Israel. Taiwan must bid at least $60! The United States clearly does not value Taiwan.”
These narratives reveal a new element to US-skepticism: state capacity. As previously mentioned, state capacity is defined as whether a state is capable of mobilizing its resources to realize its goal. The Ukraine war and vaccine supply narratives both question the United States’ motivations in foreign policies and perceived trustworthiness. Meanwhile, the economic atrophy narrative is based on the United States’ domestic budgetary deficit and downstream impact on Taiwanese economy. These narratives frame U.S. state capacity as declining and imply that the United States could no longer realize any other commitment due to its lack of resources and capacity. The goal of such a narrative is to lower the Taiwanese audience’s belief that the United States will help. But such a narrative does not include keywords of its target group (e.g., Taiwan) nor the PCR’s goal (e.g., unification) and only works through framing and priming as an example of sharp power.
The specific focus of misinformation narratives related to the United States is composed of Ukraine (28.8%), the economy and fiscal policies (33.1%), technology (25.2%), and vaccine supply (9.9%). Misinformation related to state capacity takes up approximately 52.4%, more than half of all narratives (see Figure A1, part a in the Appendix). In all narratives, political parties are only referenced 27.8% of the time with the DPP the primary target (26.2%), which is almost half of the proportion for state capacity. China is only mentioned in tandem with the United States in 38.4% of the posts (see Figure A1, part b in the Appendix).
Finding 2: Temporal and spatial evidence suggests VPN-based coordination, focused on U.S. issues and addresses.
Once we identified the top misinformation narratives using Line, we investigated information operations or coordination. Line is one of Taiwan’s most popular communication apps featuring chatrooms (similar to WhatsApp), with 83% usage. One limitation of Line is that although we can analyze message content, Line chatrooms can be seen as conversations behind “closed doors”—platforms cannot impose content moderation and researchers have no access to the users themselves nor to the private chatroom in which users engage with misinformation (Chang et al., 2020). PTT, on the other hand, provides a public forum-like environment in which users can interact. Figure 1 shows the co-occurrence network of users who post comments under the same forum. Each circle (node) represents a user who posts on PTT. If two users make mutual comments on more than 200 posts, then they are connected (form a tie). Intuitively, this means if two users are connected or “close” to each other by mutual connections, then they are likely coordinating or have extremely similar behaviors. The placement of the users reflects this and is determined by their connections.
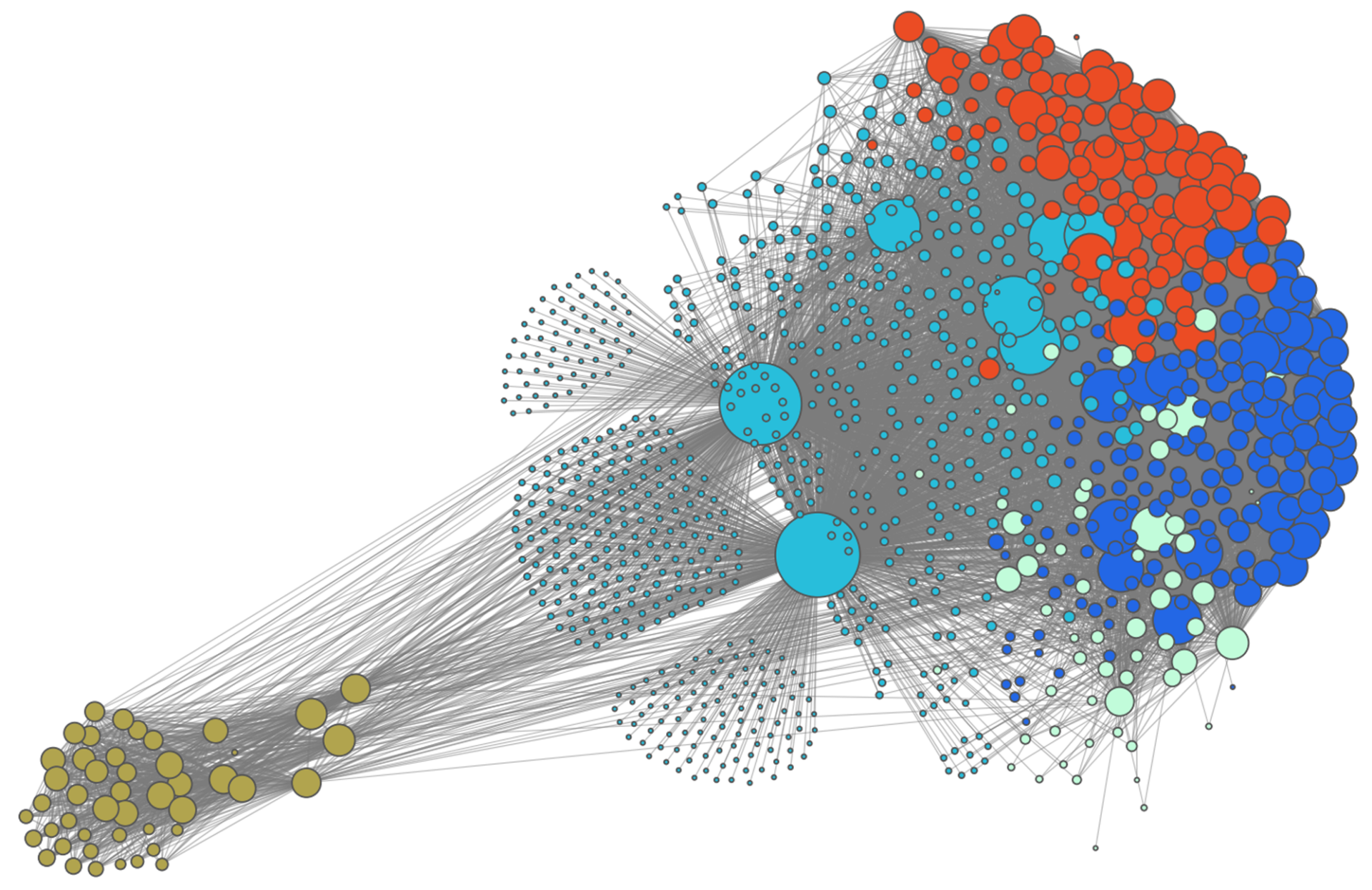
Using the Louvain algorithm (Traag, 2015), a common method to identify communities on social networks, five communities emerged from our dataset. Each community is colored separately, with clear clusters, except for teal which is more integrated. In particular, the yellow cluster is significantly separate from the others. This means they share significant activity amongst their own community, but less so with other communities. This suggests premeditated coordination rather than organic discussion, as the users would have to target the same post with high frequency. Prior studies have shown analyzing temporal patterns can provide insight into information operations. Specifically, overseas content farms often follow a regular cadence, posting content before peak hours in Taiwan on Twitter (Wang et al., 2020) and YouTube (Hsu & Lin, 2023).
To better understand the temporal dynamics on PTT, we plotted the distribution of posts and comments over a 24-hour period. Specifically, we focused on the top two countries by volume—Taiwan and the United States. Figure 2, part a shows the time of posting. Taiwan’s activity increases from 6 in the morning until it peaks at noon (when people are on lunch break), then steadily declines into the night. In contrast, posts from the United States peak at midnight and 8 a.m. Taipei time, which corresponds to around noon and 8 p.m. in New York, respectively. This provides an organic baseline as to when we might expect people to post.
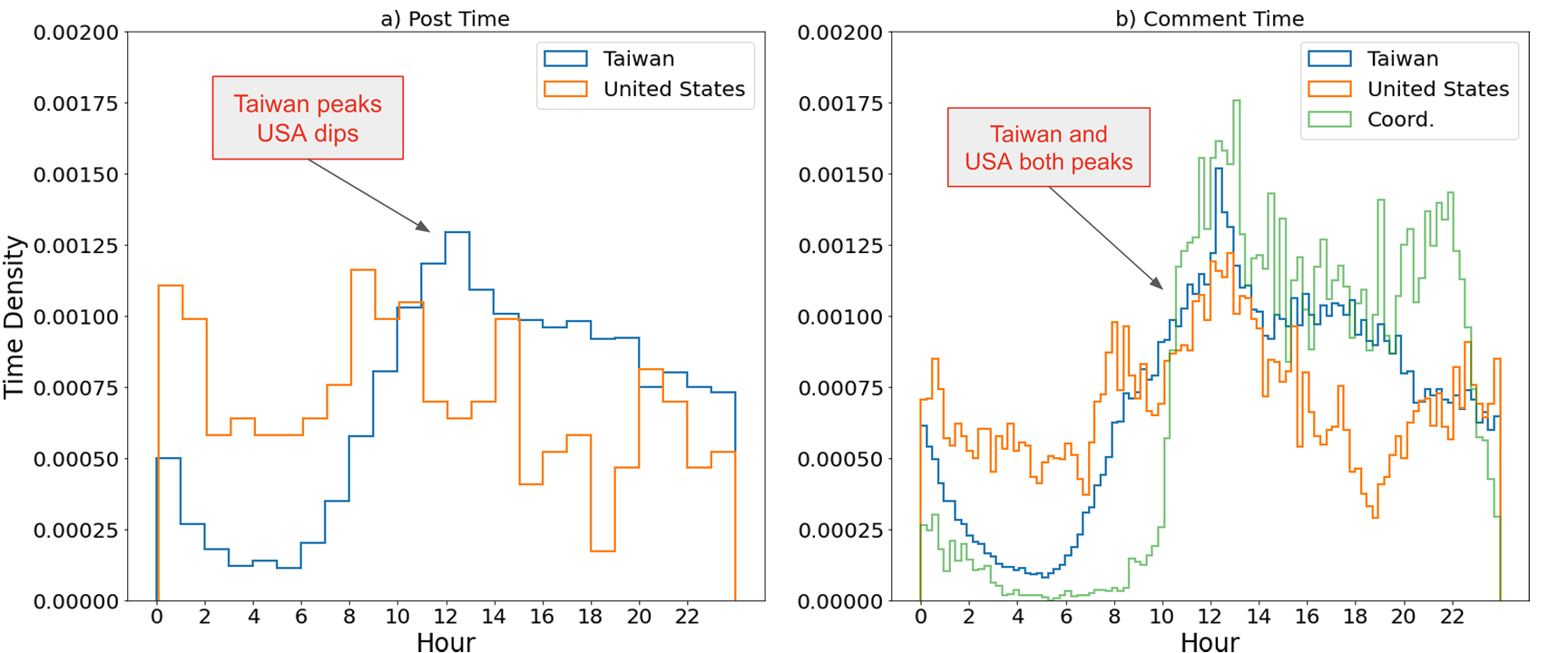
However, in Figure 2, part b, while the distribution for Taiwan (blue) remains unchanged, the peak for the United States (orange) occurs at the same time as Taiwan. One explanation is that users are responding to posts in Taiwan. The second is that users in Asia—potentially China—are using a VPN to appear as if they are in the United States. This coincides with a report by Meta Platforms that found large numbers of CCP-operated Facebook accounts and subsequently removed them (Frenkel, 2023).
The more curious issue is when considering the activity of the yellow group from Figure 1, the temporal pattern (green) shows a sharp increase in activity at 10 a.m., which then coincides with both the peaks for Taiwan (12) and the United States (22). The sudden burst of activity is consistent with prior findings on content farms from China, where posting behavior occurs when content farm workers clock in regularly for work (Wang et al., 2020). While it is difficult to prove the authenticity of these accounts, the structural and temporal aspects suggest coordination. Figure A2 in the appendix shows further evidence of coordination through the frequency distribution of counts for co-occurring posts. For the US-based group, a distribution akin to a power law appears, commonly found within social systems (Adamic & Huberman, 2000; Chang et al., 2023; Clauset et al., 2009). In contrast, the coordinated group features a significantly heavier tail, with a secondary, “unnatural,” peak at around 15 co-occurrences.
To better understand the content of these groups, Table A1 shows the summary of comments of each group and the originating post, using a large-language model for abstractive summarization (see Methods). We report the top points for comments and posts in Table A1. The coordinated community focuses on businessman Terry Gou, who considered running as a blue-leaning independent. The comments attack the incumbent DPP and their stance toward foreign policy. One popular post features President Tsai’s controversial meeting with Kevin McCarthy, then the Speaker of the U.S. House of Representatives. When a journalist asked McCarthy if he would “invite President Tsai to Congress… or… Washington,” McCarthy replied, “I don’t have any invitation out there right now. Today we were able to meet her as she transits through America, I thought that was very productive.” While this was positively framed, the title of the post itself was translated as “McCarthy will not invite Tsai to the United States” (Doomdied, 2023). This takes on a common tactic in misinformation where statements are intentionally distorted to produce negative framings of a particular candidate.
Comments from U.S. IP addresses between 11 a.m. and 2 p.m. focus on the potential alliance between the KMT and TPP. These posts are KMT-leaning with criticism toward both Lai and Ko, who are two oppositional candidates to the KMT. Some users argue that while the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) is a negative force, the United States is not automatically a positive force, as the United States does not explicitly support Taiwan’s international recognition or economic integration. In general, both posts and comments express that Taiwan should not rely too heavily on either China or the United States. This echoes the element of trust in the US-skepticism from the historical experience between ROC and the United States.
Both the U.S.-based and coordinated groups appear as blue-leaning audiences. What differentiates the first and second case is clear evidence of misinformation in the former through inaccurate framing. While US-skepticism may be a valid political stance, if the ambient information environment contains inaccurate information, then the democratic deliberative process is at risk. The case of US-skepticism is also one where stance and truth-value are often conflated, which may influence the process of voter deliberation.
Finding 3: Misinformation is most common among pan-Blue and ROC identity groups on social media and is spread through visual media. These groups share themes with conspiracy groups in Western countries.
Lastly, we considered the groups in which misinformation is common and the way misinformation is delivered. To do so, we queried CrowdTangle using the titles and links from the CoFacts dataset specific to US-Taiwan relations. This yielded 4,632 posts from public groups. Table 2 shows the groups ranked by the total number of misinformation articles identified.
There are two themes to these groups. First, they are often pan-Blue media outlets ( CTI News ), politician support groups ( Wang Yo-Zeng Support Group ), and ROC national identity groups ( I’m an ROC Fan ). The second type is somewhat unexpected but extremely interesting; it consists of groups that espouse freedom of speech ( Support CTI News and Free Speech ) and truth-seeking ( Truth Engineering Taiwan Graduate School ), topics often regarded as conspiracies. These topics are reminiscent of those in the West, such as the rhetoric around “fake news” and “truthers,” and paint a transnational picture of how misinformation coalesces. The second largest group is Trump for the World , which supports a politician known to court conspiracy theory groups such as QAnon. These groups also serve as the “capacity” element of US-skepticism, implying that the United States is in trouble for its domestic issues and is not a reliable partner to Taiwan. Furthermore, these groups have sizable followings—ranging from 8,279 to 43,481. We show the mean, as the total number of members fluctuated over our one-year period.
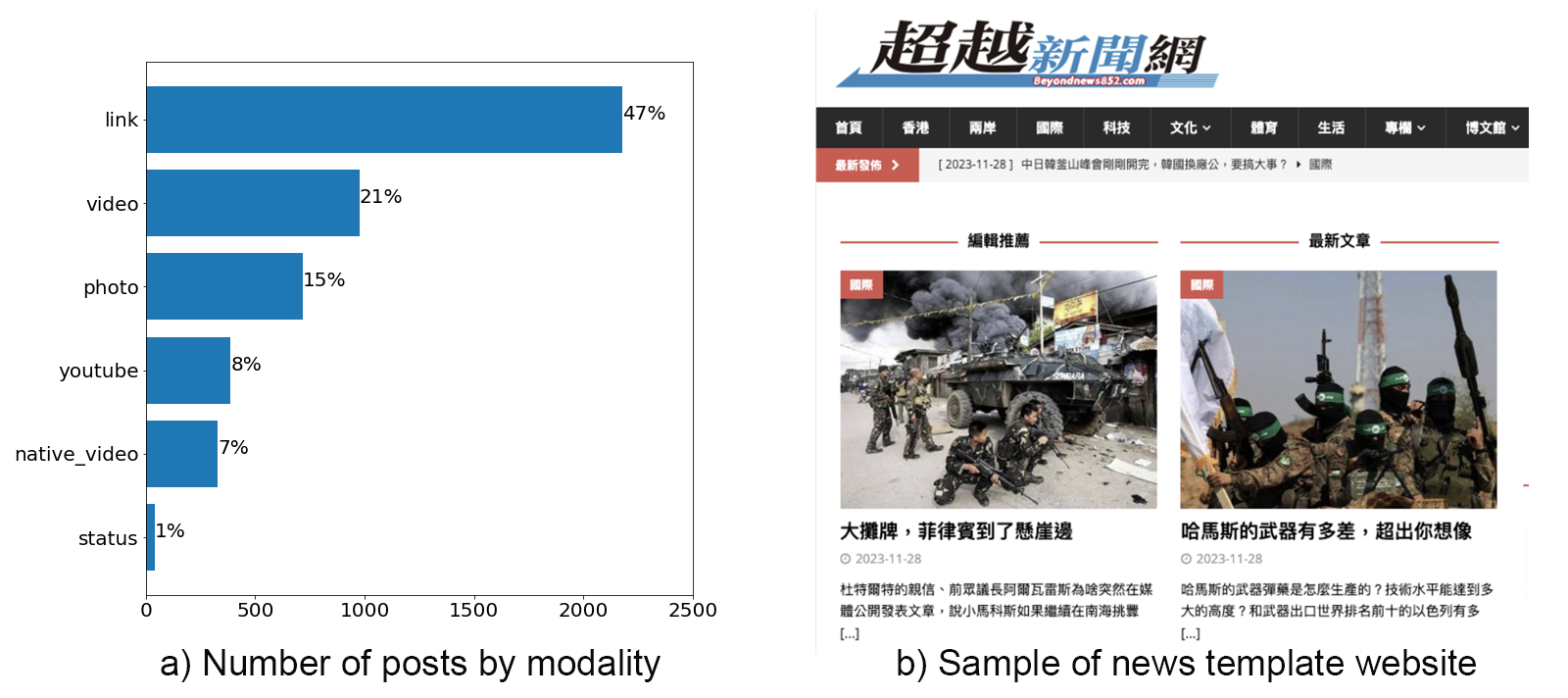
Lastly, we found that the majority of misinformation contains some form of multimedia, such as video (36%) or photos (15%), as shown in Figure 3, part a. Only 1% is a direct status. This may be due to CrowdTangle not surfacing results from normal users, but the ratio of multimedia to text is quite high. This aligns with extant studies showing the growth of multimodal misinformation (Micallef et al., 2022) and also user behavior in algorithm optimization (Chang et al., 2022; Dhanesh et al., 2022; Pulley, 2020)—posts with multimedia tend to do better than posts with only text.
Moreover, 47% contain a URL. Figure 3, part b shows one of the top domains containing misinformation (beyondnews852.com) after filtering out common domains such as YouTube. The site is named “Beyond News Net” and is visually formatted like a legitimate news site to increase the perceived credibility of information (Flanagin & Metzger, 2007; Wölker & Powell, 2021). The ability to rapidly generate legitimate-looking news sites as a tactic for misinformation may become a challenge for both media literacy and technical approaches to fight misinformation.
We utilized three unique misinformation datasets—Line, Facebook, and PTT—with dates between 01/12/2023 and 11/10/2023. The CoFacts dataset includes 140,193 received messages, 96,432 that have been labeled as misinformation, facts, opinion, or not relevant. Of this, 41,564 entries are misinformation. The CoFacts dataset is not only methodologically useful but exemplifies a crowd-sourced approach to fact-checking misinformation as an actual platform intervention. Moreover, it is public and transparent, allowing for replicability. Using a subset of articles and posts containing misinformation, we trained a topic model using BERTopic (Grootendorst, 2022). On a high level, using BERTopic involves five steps: 1) extract embeddings using a sentence transformer, 2) reduce dimensionality, 3) cluster reduced embeddings, 4) tokenize topics, and 5) create topic representation.
We conducted several trials, experimenting with parameters such as different sentence transformer models and minimum cluster sizes for the HDBSCAN clustering algorithm. The model used to extract topics for this paper utilized paraphrase-multilingual-MiniLM-L12-v2 for our sentence embedding model (Reimers & Gurevych, 2019), had a minimum cluster size of 80 for the clustering algorithm, and used tokenize_zh for our tokenizer. Our model yielded 34 topics. We also trained a model based on latent-Dirichlet allocation (LDA) (Blei et al., 2003), but found the BERTopic results to be more interpretable. We then labeled all messages to indicate whether they included reference to the election or not, and ranked the topics by their election-related percentage to measure electoral salience. For our subsequent analysis, we focused on topic 3 (see Table 1), which captures general discourse about the relations between the United States, China, and Taiwan.
The Facebook dataset was extracted using CrowdTangle. We queried posts containing links and headlines from topic 3. We also cross-sectioned these links and headlines with a general election-based dataset with 911,510 posts. This yielded a total of 4,632 of posts shared on public Facebook groups and 227,125 engagements. Due to privacy concerns, it is not possible to obtain private posts from users on their own Facebook timelines, private groups, or messages. However, public groups are a good proxy for general discourse, in addition to providing ethnic or partisan affiliations via their group name (Chang & Fang, 2023). In other words, while CoFacts provides the misinformation narratives, Facebook public groups give insight into the targets of misinformation.
Lastly, we scraped PTT using Selenium. Commonly known as the Reddit of Taiwan, PTT is unique in that it contains the IP address of the poster, though this could be shrouded by proxy farms or VPNs. First, we scraped all posts that contained reference to the United States and the election, which yielded 22,576 posts and 1,983,396 comments, all with IP addresses, addresses provided by PTT, and the time of posting. We expanded the scope of this analysis as we were interested in the general discourse directly related to the United States, and the geospatial and temporal patterns that arose.
Due to the large amount of data, there are three general approaches we could have taken—local extractive summarization with LLMs, local abstractive summarization with LLMs, and server-based abstractive summarization (such as ChatGPT). Local extractive summarization is a method that embeds each of the input sentences and then outputs five of the most representative sentences. However, this approach is often too coarse, as it returns sentences with the highest centrality but does not summarize general themes across all the different comments or posts. On the other hand, abstractive summarization works by considering the entire context by ingesting many documents and then summarizing across them. This provides a more generalized characterization of key themes. However, the input size is the primary bottleneck as large-language models can only ingest so many tokens (or words), which also need to be held in memory—the case for our project, as we are summarizing more than 10,000 posts.
To circumvent these issues, we sampled the maximum number of posts or comments that could fit within 16,000 tokens and then made a query call using the ChatGPT API. This provided a summary based on a probabilistic sample of the posts and comments.
- / Elections
Cite this Essay
Chang, H. C. H., Wang, A. H. E., & Fang Y. S. (2024). US-skepticism and transnational conspiracy in the 2024 Taiwanese presidential election. Harvard Kennedy School (HKS) Misinformation Review . https://doi.org/10.37016/mr-2020-144
Bibliography
Achen, C. H., & Wang, T. Y. (2017). The Taiwan voter . University of Michigan Press. https://doi.org/10.3998/mpub.9375036
Achen, C. H., & Wang, T. Y. (2019). Declining voter turnout in Taiwan: A generational effect? Electoral Studies , 58 , 113–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electstud.2018.12.011
Adamic, L. A., & Huberman, B. A. (2000). Power-law distribution of the World Wide Web. Science, 287 (5461), 2115–2115. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.287.5461.2115a
Arechar, A. A., Allen, J., Berinsky, A. J., Cole, R., Epstein, Z., Garimella, K., Gully, A., Lu, J. G., Ross, R. M., Stagnaro, M. N., Zhang, Y., Pennycook, G., & Rand, D. G. (2023). Understanding and combatting misinformation across 16 countries on six continents. Nature Human Behaviour , 7 (9), 1502–1513. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-023-01641-6
Blei, D. M., Ng, A. Y., & Jordan, M. I. (2003). Latent Dirichlet allocation. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 3, 993–1022. https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/944919.944937
Chang, H.-C. H. (2023). Nick Monaco and Samuel Woolley, Bots. [Review of the book Bots , by N. Monaco, & S. Woolley]. International Journal of Communication , 17 , 3.
Chang, H.-C. H., & Fang, Y. S. (2024). The 2024 Taiwanese Presidential Election on social media: Identity, policy, and affective virality. PNAS Nexus, 3 (4). https://doi.org/10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae130
Chang, H.-C. H., & Ferrara, E. (2022). Comparative analysis of social bots and humans during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Computational Social Science , 5, 1409–1425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42001-022-00173-9
Chang, H.-C. H., Haider, S., & Ferrara, E. (2021). Digital civic participation and misinformation during the 2020 Taiwanese presidential election. Media and Communication, 9 (1), 144–157. https://doi.org/10.17645/mac.v9i1.3405
Chang, H.-C. H., Harrington, B., Fu, F., & Rockmore, D. N. (2023). Complex systems of secrecy: The offshore networks of oligarchs. PNAS Nexus, 2 (4), pgad051. https://doi.org/10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad112
Chang, H.-C. H., Richardson, A., & Ferrara, E. (2022). #JusticeforGeorgeFloyd: How Instagram facilitated the 2020 Black Lives Matter protests. PLOS ONE , 17 (12), e0277864. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0277864
China is flooding Taiwan with disinformation. (2023, September 26). The Economist . https://www.economist.com/asia/2023/09/26/china-is-flooding-taiwan-with-disinformation
Clauset, A., Shalizi, C. R., & Newman, M. E. (2009). Power-law distributions in empirical data. SIAM Review, 51 (4), 661–703. https://doi.org/10.1137/070710111
Dhanesh, G., Duthler, G., & Li, K. (2022). Social media engagement with organization-generated content: Role of visuals in enhancing public engagement with organizations on Facebook and Instagram. Public Relations Review , 48 (2), 102174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2022.102174
Doomdied. (2023, April 6). [Hot Gossip] McCarthy: Will not invite President Tsai to congress or DC . PTT. https://disp.cc/b/Gossiping/fXNG
Enders, A., Farhart, C., Miller, J., Uscinski, J., Saunders, K., & Drochon, H. (2022). Are Republicans and conservatives more likely to believe conspiracy theories? Political Behavior , 45 , 2001–2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11109-022-09812-3
Ferrara, E., Chang, H., Chen, E., Muric, G., & Patel, J. (2020). Characterizing social media manipulation in the 2020 US presidential election. First Monday, 25 (11). https://doi.org/10.5210/fm.v25i11.11431
Flanagin, A. J., & Metzger, M. J. (2007). The role of site features, user attributes, and information verification behaviors on the perceived credibility of web-based information. New Media & Society , 9 (2), 319–342. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444807075015
Freedom House (2022). Freedom index by country. https://freedomhouse.org/countries/freedom-world/scores
Frenkel, S. (2023, August 29). Meta’s “biggest single takedown” removes Chinese influence campaign. The New York Times . https://www.nytimes.com/2023/08/29/technology/meta-china-influence-campaign.html
Galeano, E. H., & Galeano, E. (1997). Open veins of Latin America: Five centuries of the pillage of a continent. NYU Press.
George, L., & Sumathy, P. (2023). An integrated clustering and BERT framework for improved topic modeling. International Journal of Information Technology , 15 (4), 2187–2195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-023-01268-w
Grootendorst, M. (2022). BERTopic: Neural topic modeling with a class-based TF-IDF procedure . arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.05794
Haime, J. (2022, September 19). Taiwan’s amateur fact-checkers wage war on fake news from China. Al Jazeera . https://www.aljazeera.com/economy/2022/9/19/taiwan
Harambam, J. (2020). Contemporary conspiracy culture: Truth and knowledge in an era of epistemic instability . Routledge.
Hsu, L.-Y., & Lin, S.-H. (2023). Party identification and YouTube usage patterns: An exploratory analysis. Taiwan Politics. https://taiwanpolitics.org/article/88117-party-identification-and-youtube-usage-patterns-an-exploratory-analysis
Hsu, T., Chien, A. C., & Myers, S. L. (2023, November 26). Can Taiwan continue to fight off Chinese disinformation? The New York Times . https://www.nytimes.com/2023/11/26/business/media/taiwan-china-disinformation.html
Jerit, J., & Zhao, Y. (2020). Political misinformation. Annual Review of Political Science , 23 (1), 77–94. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-polisci-050718-032814
Konkes, C., & Lester, L. (2017). Incomplete knowledge, rumour and truth seeking. Journalism Studies , 18 (7), 826–844. https://doi.org/10.1080/1461670X.2015.1089182
Martel, C., Allen, J., Pennycook, G., & Rand, D. G. (2023). Crowds can effectively identify misinformation at scale. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 19 (2), 316–319. https://doi.org/10.1177/17456916231190388
Micallef, N., Sandoval-Castañeda, M., Cohen, A., Ahamad, M., Kumar, S., & Memon, N. (2022). Cross-platform multimodal misinformation: Taxonomy, characteristics and detection for textual posts and videos. Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media , 16 , 651–662. https://doi.org/10.1609/icwsm.v16i1.19323
Microsoft Threat Intelligence (2024). Same targets, new playbooks: East Asia threat actors employ unique methods. Microsoft Threat Analysis Center. https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/security-insider/intelligence-reports/east-asia-threat-actors-employ-unique-methods
Monaco, N., & Woolley, S. (2022). Bots . John Wiley & Sons.
Nguyen, D. Q., Vu, T., & Nguyen, A. T. (2020). BERTweet: A pre-trained language model for English Tweets . arXiv. http://arxiv.org/abs/2005.10200
Pulley, P. G. (2020). Increase engagement and learning: Blend in the visuals, memes, and GIFs for online content. In Emerging Techniques and Applications for Blended Learning in K-20 Classrooms (pp. 137–147). IGI Global.
Reimers, N., & Gurevych, I. (2019). Sentence-BERT: Sentence embeddings using Siamese BERT-networks . arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1908.10084
Traag, V. A. (2015). Faster unfolding of communities: Speeding up the Louvain algorithm. Physical Review. E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics , 92 (3), 032801. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.92.032801
Walker, C. (2018). What Is “Sharp Power”? Journal of Democracy, 29 (3) , 9–23. https://doi.org/10.1353/jod.2018.0041
Wang, A. H.-E., Lee, M.-C., Wu, M.-H., & Shen, P. (2020). Influencing overseas Chinese by tweets: text-images as the key tactic of Chinese propaganda. Journal of Computational Social Science, 3 (2), 469–486. https://doi.org/10.1007%2Fs42001-020-00091-8
Welch, D. (2024, January 19). Taiwan’s election: 2024’s canary in the coal mine for disinformation against democracy. Alliance For Securing Democracy. https://securingdemocracy.gmfus.org/taiwans-election-2024s-canary-in-the-coal-mine-for-disinformation-against-democracy/
Wölker, A., & Powell, T. E. (2021). Algorithms in the newsroom? News readers’ perceived credibility and selection of automated journalism. Journalism , 22 (1), 86–103. https://doi.org/10.1177/1464884918757072
Wu, A. (2023). To reassure Taiwan and deter China, the United States should learn from history. Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, 79 (2), 72–79. https://doi.org/10.1080/00963402.2023.2178174
Wu, C. L., & Lin, A. M. W. (2019). The certainty of uncertainty: Taiwanese public opinion on US–Taiwan relations in the early Trump presidency. World Affairs, 182 (4), 350–369.
No funding has been received to conduct this research.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
No human subjects were included in this study.
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original author and source are properly credited.
Data Availability
All materials needed to replicate this study are available via the Harvard Dataverse: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/5SPGDY . The Cofacts database is available on HuggingFace and Facebook via CrowdTangle per regulation of Meta Platforms.
Acknowledgements
H. C. would like to thank Brendan Nyhan, Sharanya Majumder, John Carey, and Adrian Rauschfleish for their comments. H. C. would like to thank the Dartmouth Burke Research Initiation Award.
All authors contributed equally.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Cold War was an ongoing political rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies that developed after World War II.This hostility between the two superpowers was first given its name by George Orwell in an article published in 1945. Orwell understood it as a nuclear stalemate between "super-states": each possessed weapons of mass destruction and was ...
This essay was originally prepared for presentation at the 90th Anniversary Nobel Jubilee Symposium "Beyond the Cold War: Future Dimensions in International Relations," held in Oslo, Norway, 6-8 December 1991. ... the simple fact is that the Cold War did evolve into a Long Peace. 1 Whether the Long Peace can survive the end of the Cold ...
Realism and the long peace Security specialists consider it remarkable that the superpowers did not go to war as did rival hegemons of the past. Many realist theories attribute the absence of war to the bipolar nature of the postwar international system, which they consider less war-prone than the multipolar world it replaced. All of them
The term 'cold war' first appeared in a 1945 essay by the English writer George Orwell called 'You and the Atomic Bomb.' ... the Berlin Wall-the most visible symbol of the decades-long Cold War ...
At the end of World War II, English writer George Orwell used cold war, as a general term, in his essay "You and the Atomic Bomb", published 19 October 1945 in the British newspaper Tribune.Contemplating a world living in the shadow of the threat of nuclear warfare, Orwell looked at James Burnham's predictions of a polarized world, writing: . Looking at the world as a whole, the drift for many ...
A distinguished historian of post-1945 international relations presents eight substantial, thoroughly researched essays on the overall theme of the war the United States and the Soviet Union have managed to avoid with each other. Topics include why the United States did not use nuclear weapons against the Soviet Union in the years of its superiority, how the U.S. tried to exploit divisions ...
The talks were meant to forge a lasting peace, but within 18 months, a Cold War began that lasted more than four decades. One of the most important moments at Potsdam was not captured in a memo or ...
Cold War or Cold Peace RANDALL B. WOODS John Lewis Gaddis. The United States and the End of the Cold War. ... affairs for the past half century has spawned a host of essays and books on its causes and consequences, reopening old historiographical controversies, ... Gaddis is, of course, a proponent of the concept of the 'long peace'. That is ...
The Long Peace: Inquiries into the History of the Cold War. By John Lewis Gaddis. New York: Oxford University Press, 1987, 245 pp., ... its eight essays on the early history of the Cold War as follows: one, the makers of U.S. foreign policy were shrewder than we might have thought; and, two, nuclear weapons might not be as evil as we think they ...
The Cold War (the term was first used by Bernard Baruch during a congressional debate in 1947) was waged mainly on political, economic, and propaganda fronts and had only limited recourse to weapons. It was at its peak in 1948-53 with the Berlin blockade and airlift, the formation of NATO, the victory of the communists in the Chinese civil ...
The phrase 'cold war' was itself coined by British author George Orwell, first appearing in an October 1945 essay on the atomic bomb. Orwell predicted that the rise of atomic weapons would "put an end to large-scale wars, at the cost of prolonging indefinitely a 'peace that is no peace'."
READ: Cold War — An Overview. Google Classroom. The aftermath of World War Two shifted the global balance of power and created a bi-polar world led by two competing superpowers: The United States (US) and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR). We call this global competition the Cold War. The article below uses "Three Close Reads".
The Long Peace: Inquiries into the History of the Cold War. by John Lewis Gaddis. Oxford University Press. 332 pp. $24.95. In the spectrum of historians writing about the cold war, John Lewis Gaddis belongs in the category of post-revisionists. The revisionists, mainly in the 1960's, challenged the widespread Western view attributing the ...
Stephen M. Walt; The Long Peace: Inquiries into the History of the Cold War, by John Lewis Gaddis, Political Science Quarterly, Volume 103, Issue 2, 1 June
The Cold War. After World War II, the United States and its allies, and the Soviet Union and its satellite states began a decades-long struggle for supremacy known as the Cold War. Soldiers of the Soviet Union and the United States did not do battle directly during the Cold War. But the two superpowers continually antagonized each other through ...
The object of this essay is to review some of the most important new scholarship, ... Grasping the Democratic Peace: Principles for a Post-Cold War World (Princeton, 1993). ... authoritarian government, and on Communist ideology. As long as Stalin was running the Soviet Union, "a cold war was unavoidable." He waged cold wars
2. Numerous historians have written useful surveys of the Cold War. For a start, see John Lewis Gaddis, The Cold War: A New History (New York: Penguin, 2005); Melvyn P. Leffler, For the Soul of Mankind: The United States, the Soviet Union, and the Cold War (New York: Hill and Wang, 2007); Campbell Craig and Fredrik Logevall, America's Cold War: The Politics of Insecurity (Cambridge, Mass ...
The Cold War, the Long Peace, and the Future * JOHN LEWIS GADDIS, JOHN LEWIS GADDIS. ... This essay was originally prepared for presentation at the 90th Anniversary Nobel Jubilee Symposium "Beyond the Cold War: Future Dimensions in International Relations," held in Oslo, Norway, 6-8 December 1991.
Cold War: An Overview. By Burleigh Hendrickson. The aftermath of World War Two shifted the global balance of power and created a bi-polar world led by two competing superpowers: The United States (US) and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR). We call this global competition the Cold War.
This post is a comprehensive timeline of the Cold War, from the origins of the Russian-American conflict following World War Two to the final dissolution of the Soviet Union and the fall of the Berlin Wall at the end of the 20th century. Scroll down to learn more. Alternatively, watch this nine-minute explainer video for an overview of the Cold ...
These Americanised views of the Cold War as exampled by John Gaddis contribute significantly to widespread misunderstandings and ignorance in the U. and the world concerning the nature of the Cold War, the way it ended, and its troubling legacies which contrast the widely accepted narrative of a completely 'long peace'.
A cold war is a state of conflict between nations that does not involve direct military action but is pursued primarily through economic and political actions, propaganda, acts of espionage or proxy wars waged by surrogates. This term is most commonly used to refer to the American-Soviet Cold War of 1947-1989. The surrogates are typically states that are satellites of the conflicting nations ...
Essay Summary. We leveraged a dataset of 41,291 labeled articles from Line, 911,510 posts from Facebook, and 2,005,972 posts and comments from PTT to understand misinformation dynamics through topic modeling and network analysis. ... but the United States has helped maintain the status quo and peace after the outbreak of the Korean War in 1950 ...
The Long Peace John Lewis Gaddis. Elements of Stability in the Postwar International System. I should like to begin. this essay with a fable. Once upon a time, there was a great war that involved the slaughter of millions upon millions of people. When, after years of fighting, one side finally prevailed over the other and the war ended, every-.