What is a scientific hypothesis?
It's the initial building block in the scientific method.


Hypothesis basics
What makes a hypothesis testable.
- Types of hypotheses
- Hypothesis versus theory
Additional resources
Bibliography.
A scientific hypothesis is a tentative, testable explanation for a phenomenon in the natural world. It's the initial building block in the scientific method . Many describe it as an "educated guess" based on prior knowledge and observation. While this is true, a hypothesis is more informed than a guess. While an "educated guess" suggests a random prediction based on a person's expertise, developing a hypothesis requires active observation and background research.
The basic idea of a hypothesis is that there is no predetermined outcome. For a solution to be termed a scientific hypothesis, it has to be an idea that can be supported or refuted through carefully crafted experimentation or observation. This concept, called falsifiability and testability, was advanced in the mid-20th century by Austrian-British philosopher Karl Popper in his famous book "The Logic of Scientific Discovery" (Routledge, 1959).
A key function of a hypothesis is to derive predictions about the results of future experiments and then perform those experiments to see whether they support the predictions.
A hypothesis is usually written in the form of an if-then statement, which gives a possibility (if) and explains what may happen because of the possibility (then). The statement could also include "may," according to California State University, Bakersfield .
Here are some examples of hypothesis statements:
- If garlic repels fleas, then a dog that is given garlic every day will not get fleas.
- If sugar causes cavities, then people who eat a lot of candy may be more prone to cavities.
- If ultraviolet light can damage the eyes, then maybe this light can cause blindness.
A useful hypothesis should be testable and falsifiable. That means that it should be possible to prove it wrong. A theory that can't be proved wrong is nonscientific, according to Karl Popper's 1963 book " Conjectures and Refutations ."
An example of an untestable statement is, "Dogs are better than cats." That's because the definition of "better" is vague and subjective. However, an untestable statement can be reworded to make it testable. For example, the previous statement could be changed to this: "Owning a dog is associated with higher levels of physical fitness than owning a cat." With this statement, the researcher can take measures of physical fitness from dog and cat owners and compare the two.
Types of scientific hypotheses

In an experiment, researchers generally state their hypotheses in two ways. The null hypothesis predicts that there will be no relationship between the variables tested, or no difference between the experimental groups. The alternative hypothesis predicts the opposite: that there will be a difference between the experimental groups. This is usually the hypothesis scientists are most interested in, according to the University of Miami .
For example, a null hypothesis might state, "There will be no difference in the rate of muscle growth between people who take a protein supplement and people who don't." The alternative hypothesis would state, "There will be a difference in the rate of muscle growth between people who take a protein supplement and people who don't."
If the results of the experiment show a relationship between the variables, then the null hypothesis has been rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis, according to the book " Research Methods in Psychology " (BCcampus, 2015).
There are other ways to describe an alternative hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis above does not specify a direction of the effect, only that there will be a difference between the two groups. That type of prediction is called a two-tailed hypothesis. If a hypothesis specifies a certain direction — for example, that people who take a protein supplement will gain more muscle than people who don't — it is called a one-tailed hypothesis, according to William M. K. Trochim , a professor of Policy Analysis and Management at Cornell University.
Sometimes, errors take place during an experiment. These errors can happen in one of two ways. A type I error is when the null hypothesis is rejected when it is true. This is also known as a false positive. A type II error occurs when the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is false. This is also known as a false negative, according to the University of California, Berkeley .
A hypothesis can be rejected or modified, but it can never be proved correct 100% of the time. For example, a scientist can form a hypothesis stating that if a certain type of tomato has a gene for red pigment, that type of tomato will be red. During research, the scientist then finds that each tomato of this type is red. Though the findings confirm the hypothesis, there may be a tomato of that type somewhere in the world that isn't red. Thus, the hypothesis is true, but it may not be true 100% of the time.
Scientific theory vs. scientific hypothesis
The best hypotheses are simple. They deal with a relatively narrow set of phenomena. But theories are broader; they generally combine multiple hypotheses into a general explanation for a wide range of phenomena, according to the University of California, Berkeley . For example, a hypothesis might state, "If animals adapt to suit their environments, then birds that live on islands with lots of seeds to eat will have differently shaped beaks than birds that live on islands with lots of insects to eat." After testing many hypotheses like these, Charles Darwin formulated an overarching theory: the theory of evolution by natural selection.
"Theories are the ways that we make sense of what we observe in the natural world," Tanner said. "Theories are structures of ideas that explain and interpret facts."
- Read more about writing a hypothesis, from the American Medical Writers Association.
- Find out why a hypothesis isn't always necessary in science, from The American Biology Teacher.
- Learn about null and alternative hypotheses, from Prof. Essa on YouTube .
Encyclopedia Britannica. Scientific Hypothesis. Jan. 13, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/science/scientific-hypothesis
Karl Popper, "The Logic of Scientific Discovery," Routledge, 1959.
California State University, Bakersfield, "Formatting a testable hypothesis." https://www.csub.edu/~ddodenhoff/Bio100/Bio100sp04/formattingahypothesis.htm
Karl Popper, "Conjectures and Refutations," Routledge, 1963.
Price, P., Jhangiani, R., & Chiang, I., "Research Methods of Psychology — 2nd Canadian Edition," BCcampus, 2015.
University of Miami, "The Scientific Method" http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/161/evolution/161app1_scimethod.pdf
William M.K. Trochim, "Research Methods Knowledge Base," https://conjointly.com/kb/hypotheses-explained/
University of California, Berkeley, "Multiple Hypothesis Testing and False Discovery Rate" https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~hhuang/STAT141/Lecture-FDR.pdf
University of California, Berkeley, "Science at multiple levels" https://undsci.berkeley.edu/article/0_0_0/howscienceworks_19
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Warm ocean water is rushing beneath Antarctica's 'Doomsday Glacier,' making its collapse more likely
Earth from space: Rare phenomenon transforms African thunderstorm into giant ethereal 'jellyfish'
Scientists grow diamonds from scratch in 15 minutes thanks to groundbreaking new process
Most Popular
- 2 James Webb telescope confirms there is something seriously wrong with our understanding of the universe
- 3 Earth from space: Rare phenomenon transforms African thunderstorm into giant ethereal 'jellyfish'
- 4 Some of the oldest stars in the universe found hiding near the Milky Way's edge — and they may not be alone
- 5 See May's full 'Flower Moon' rise this week close to a red supergiant star
- 2 Scientists finally solve mystery of why Europeans have less Neanderthal DNA than East Asians
- 3 'We are approaching the tipping point': Marker for the collapse of key Atlantic current discovered
- 4 Can a commercial airplane do a barrel roll?
- 5 Why is there sometimes a green flash at sunset and sunrise?
Hypothesis n., plural: hypotheses [/haɪˈpɑːθəsɪs/] Definition: Testable scientific prediction
Table of Contents
What Is Hypothesis?
A scientific hypothesis is a foundational element of the scientific method . It’s a testable statement proposing a potential explanation for natural phenomena. The term hypothesis means “little theory” . A hypothesis is a short statement that can be tested and gives a possible reason for a phenomenon or a possible link between two variables . In the setting of scientific research, a hypothesis is a tentative explanation or statement that can be proven wrong and is used to guide experiments and empirical research.

It is an important part of the scientific method because it gives a basis for planning tests, gathering data, and judging evidence to see if it is true and could help us understand how natural things work. Several hypotheses can be tested in the real world, and the results of careful and systematic observation and analysis can be used to support, reject, or improve them.
Researchers and scientists often use the word hypothesis to refer to this educated guess . These hypotheses are firmly established based on scientific principles and the rigorous testing of new technology and experiments .
For example, in astrophysics, the Big Bang Theory is a working hypothesis that explains the origins of the universe and considers it as a natural phenomenon. It is among the most prominent scientific hypotheses in the field.
“The scientific method: steps, terms, and examples” by Scishow:
Biology definition: A hypothesis is a supposition or tentative explanation for (a group of) phenomena, (a set of) facts, or a scientific inquiry that may be tested, verified or answered by further investigation or methodological experiment. It is like a scientific guess . It’s an idea or prediction that scientists make before they do experiments. They use it to guess what might happen and then test it to see if they were right. It’s like a smart guess that helps them learn new things. A scientific hypothesis that has been verified through scientific experiment and research may well be considered a scientific theory .
Etymology: The word “hypothesis” comes from the Greek word “hupothesis,” which means “a basis” or “a supposition.” It combines “hupo” (under) and “thesis” (placing). Synonym: proposition; assumption; conjecture; postulate Compare: theory See also: null hypothesis
Characteristics Of Hypothesis
A useful hypothesis must have the following qualities:
- It should never be written as a question.
- You should be able to test it in the real world to see if it’s right or wrong.
- It needs to be clear and exact.
- It should list the factors that will be used to figure out the relationship.
- It should only talk about one thing. You can make a theory in either a descriptive or form of relationship.
- It shouldn’t go against any natural rule that everyone knows is true. Verification will be done well with the tools and methods that are available.
- It should be written in as simple a way as possible so that everyone can understand it.
- It must explain what happened to make an answer necessary.
- It should be testable in a fair amount of time.
- It shouldn’t say different things.
Sources Of Hypothesis
Sources of hypothesis are:
- Patterns of similarity between the phenomenon under investigation and existing hypotheses.
- Insights derived from prior research, concurrent observations, and insights from opposing perspectives.
- The formulations are derived from accepted scientific theories and proposed by researchers.
- In research, it’s essential to consider hypothesis as different subject areas may require various hypotheses (plural form of hypothesis). Researchers also establish a significance level to determine the strength of evidence supporting a hypothesis.
- Individual cognitive processes also contribute to the formation of hypotheses.
One hypothesis is a tentative explanation for an observation or phenomenon. It is based on prior knowledge and understanding of the world, and it can be tested by gathering and analyzing data. Observed facts are the data that are collected to test a hypothesis. They can support or refute the hypothesis.
For example, the hypothesis that “eating more fruits and vegetables will improve your health” can be tested by gathering data on the health of people who eat different amounts of fruits and vegetables. If the people who eat more fruits and vegetables are healthier than those who eat less fruits and vegetables, then the hypothesis is supported.
Hypotheses are essential for scientific inquiry. They help scientists to focus their research, to design experiments, and to interpret their results. They are also essential for the development of scientific theories.
Types Of Hypothesis
In research, you typically encounter two types of hypothesis: the alternative hypothesis (which proposes a relationship between variables) and the null hypothesis (which suggests no relationship).
Simple Hypothesis
It illustrates the association between one dependent variable and one independent variable. For instance, if you consume more vegetables, you will lose weight more quickly. Here, increasing vegetable consumption is the independent variable, while weight loss is the dependent variable.
Complex Hypothesis
It exhibits the relationship between at least two dependent variables and at least two independent variables. Eating more vegetables and fruits results in weight loss, radiant skin, and a decreased risk of numerous diseases, including heart disease.
Directional Hypothesis
It shows that a researcher wants to reach a certain goal. The way the factors are related can also tell us about their nature. For example, four-year-old children who eat well over a time of five years have a higher IQ than children who don’t eat well. This shows what happened and how it happened.
Non-directional Hypothesis
When there is no theory involved, it is used. It is a statement that there is a connection between two variables, but it doesn’t say what that relationship is or which way it goes.
Null Hypothesis
It says something that goes against the theory. It’s a statement that says something is not true, and there is no link between the independent and dependent factors. “H 0 ” represents the null hypothesis.
Associative and Causal Hypothesis
When a change in one variable causes a change in the other variable, this is called the associative hypothesis . The causal hypothesis, on the other hand, says that there is a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more factors.
Examples Of Hypothesis
Examples of simple hypotheses:
- Students who consume breakfast before taking a math test will have a better overall performance than students who do not consume breakfast.
- Students who experience test anxiety before an English examination will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety.
- Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone, is a statement that suggests that drivers who talk on the phone while driving are more likely to make mistakes.
Examples of a complex hypothesis:
- Individuals who consume a lot of sugar and don’t get much exercise are at an increased risk of developing depression.
- Younger people who are routinely exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces, according to a new study.
- Increased levels of air pollution led to higher rates of respiratory illnesses, which in turn resulted in increased costs for healthcare for the affected communities.
Examples of Directional Hypothesis:
- The crop yield will go up a lot if the amount of fertilizer is increased.
- Patients who have surgery and are exposed to more stress will need more time to get better.
- Increasing the frequency of brand advertising on social media will lead to a significant increase in brand awareness among the target audience.
Examples of Non-Directional Hypothesis (or Two-Tailed Hypothesis):
- The test scores of two groups of students are very different from each other.
- There is a link between gender and being happy at work.
- There is a correlation between the amount of caffeine an individual consumes and the speed with which they react.
Examples of a null hypothesis:
- Children who receive a new reading intervention will have scores that are different than students who do not receive the intervention.
- The results of a memory recall test will not reveal any significant gap in performance between children and adults.
- There is not a significant relationship between the number of hours spent playing video games and academic performance.
Examples of Associative Hypothesis:
- There is a link between how many hours you spend studying and how well you do in school.
- Drinking sugary drinks is bad for your health as a whole.
- There is an association between socioeconomic status and access to quality healthcare services in urban neighborhoods.
Functions Of Hypothesis
The research issue can be understood better with the help of a hypothesis, which is why developing one is crucial. The following are some of the specific roles that a hypothesis plays: (Rashid, Apr 20, 2022)
- A hypothesis gives a study a point of concentration. It enlightens us as to the specific characteristics of a study subject we need to look into.
- It instructs us on what data to acquire as well as what data we should not collect, giving the study a focal point .
- The development of a hypothesis improves objectivity since it enables the establishment of a focal point.
- A hypothesis makes it possible for us to contribute to the development of the theory. Because of this, we are in a position to definitively determine what is true and what is untrue .
How will Hypothesis help in the Scientific Method?
- The scientific method begins with observation and inquiry about the natural world when formulating research questions. Researchers can refine their observations and queries into specific, testable research questions with the aid of hypothesis. They provide an investigation with a focused starting point.
- Hypothesis generate specific predictions regarding the expected outcomes of experiments or observations. These forecasts are founded on the researcher’s current knowledge of the subject. They elucidate what researchers anticipate observing if the hypothesis is true.
- Hypothesis direct the design of experiments and data collection techniques. Researchers can use them to determine which variables to measure or manipulate, which data to obtain, and how to conduct systematic and controlled research.
- Following the formulation of a hypothesis and the design of an experiment, researchers collect data through observation, measurement, or experimentation. The collected data is used to verify the hypothesis’s predictions.
- Hypothesis establish the criteria for evaluating experiment results. The observed data are compared to the predictions generated by the hypothesis. This analysis helps determine whether empirical evidence supports or refutes the hypothesis.
- The results of experiments or observations are used to derive conclusions regarding the hypothesis. If the data support the predictions, then the hypothesis is supported. If this is not the case, the hypothesis may be revised or rejected, leading to the formulation of new queries and hypothesis.
- The scientific approach is iterative, resulting in new hypothesis and research issues from previous trials. This cycle of hypothesis generation, testing, and refining drives scientific progress.

Importance Of Hypothesis
- Hypothesis are testable statements that enable scientists to determine if their predictions are accurate. This assessment is essential to the scientific method, which is based on empirical evidence.
- Hypothesis serve as the foundation for designing experiments or data collection techniques. They can be used by researchers to develop protocols and procedures that will produce meaningful results.
- Hypothesis hold scientists accountable for their assertions. They establish expectations for what the research should reveal and enable others to assess the validity of the findings.
- Hypothesis aid in identifying the most important variables of a study. The variables can then be measured, manipulated, or analyzed to determine their relationships.
- Hypothesis assist researchers in allocating their resources efficiently. They ensure that time, money, and effort are spent investigating specific concerns, as opposed to exploring random concepts.
- Testing hypothesis contribute to the scientific body of knowledge. Whether or not a hypothesis is supported, the results contribute to our understanding of a phenomenon.
- Hypothesis can result in the creation of theories. When supported by substantive evidence, hypothesis can serve as the foundation for larger theoretical frameworks that explain complex phenomena.
- Beyond scientific research, hypothesis play a role in the solution of problems in a variety of domains. They enable professionals to make educated assumptions about the causes of problems and to devise solutions.
Research Hypotheses: Did you know that a hypothesis refers to an educated guess or prediction about the outcome of a research study?
It’s like a roadmap guiding researchers towards their destination of knowledge. Just like a compass points north, a well-crafted hypothesis points the way to valuable discoveries in the world of science and inquiry.
Choose the best answer.
Send Your Results (Optional)

Further Reading
- RNA-DNA World Hypothesis
- BYJU’S. (2023). Hypothesis. Retrieved 01 Septermber 2023, from https://byjus.com/physics/hypothesis/#sources-of-hypothesis
- Collegedunia. (2023). Hypothesis. Retrieved 1 September 2023, from https://collegedunia.com/exams/hypothesis-science-articleid-7026#d
- Hussain, D. J. (2022). Hypothesis. Retrieved 01 September 2023, from https://mmhapu.ac.in/doc/eContent/Management/JamesHusain/Research%20Hypothesis%20-Meaning,%20Nature%20&%20Importance-Characteristics%20of%20Good%20%20Hypothesis%20Sem2.pdf
- Media, D. (2023). Hypothesis in the Scientific Method. Retrieved 01 September 2023, from https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-a-hypothesis-2795239#toc-hypotheses-examples
- Rashid, M. H. A. (Apr 20, 2022). Research Methodology. Retrieved 01 September 2023, from https://limbd.org/hypothesis-definitions-functions-characteristics-types-errors-the-process-of-testing-a-hypothesis-hypotheses-in-qualitative-research/#:~:text=Functions%20of%20a%20Hypothesis%3A&text=Specifically%2C%20a%20hypothesis%20serves%20the,providing%20focus%20to%20the%20study.
©BiologyOnline.com. Content provided and moderated by Biology Online Editors.
Last updated on September 8th, 2023
You will also like...

Gene Action – Operon Hypothesis

Water in Plants

Growth and Plant Hormones

Sigmund Freud and Carl Gustav Jung

Population Growth and Survivorship
Related articles....

RNA-DNA World Hypothesis?

On Mate Selection Evolution: Are intelligent males more attractive?

Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use

Dead Man Walking
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
High school biology
Course: high school biology > unit 1.
- Biology overview
- Preparing to study biology
- What is life?
- The scientific method
- Data to justify experimental claims examples
- Scientific method and data analysis
- Introduction to experimental design
- Controlled experiments
Biology and the scientific method review
- Experimental design and bias
The nature of biology
Properties of life.
- Organization: Living things are highly organized (meaning they contain specialized, coordinated parts) and are made up of one or more cells .
- Metabolism: Living things must use energy and consume nutrients to carry out the chemical reactions that sustain life. The sum total of the biochemical reactions occurring in an organism is called its metabolism .
- Homeostasis : Living organisms regulate their internal environment to maintain the relatively narrow range of conditions needed for cell function.
- Growth : Living organisms undergo regulated growth. Individual cells become larger in size, and multicellular organisms accumulate many cells through cell division.
- Reproduction : Living organisms can reproduce themselves to create new organisms.
- Response : Living organisms respond to stimuli or changes in their environment.
- Evolution : Populations of living organisms can undergo evolution , meaning that the genetic makeup of a population may change over time.
Scientific methodology
Scientific method example: failure to toast.
- Observation: the toaster won't toast.
- Question: Why won't my toaster toast?
- Hypothesis: Maybe the outlet is broken.
- Prediction: If I plug the toaster into a different outlet, then it will toast the bread.
- Test of prediction: Plug the toaster into a different outlet and try again.
- Iteration time!
Experimental design
Reducing errors and bias.
- Having a large sample size in the experiment: This helps to account for any small differences among the test subjects that may provide unexpected results.
- Repeating experimental trials multiple times: Errors may result from slight differences in test subjects, or mistakes in methodology or data collection. Repeating trials helps reduce those effects.
- Including all data points: Sometimes it is tempting to throw away data points that are inconsistent with the proposed hypothesis. However, this makes for an inaccurate study! All data points need to be included, whether they support the hypothesis or not.
- Using placebos , when appropriate: Placebos prevent the test subjects from knowing whether they received a real therapeutic substance. This helps researchers determine whether a substance has a true effect.
- Implementing double-blind studies , when appropriate: Double-blind studies prevent researchers from knowing the status of a particular participant. This helps eliminate observer bias.
Communicating findings
Things to remember.
- A hypothesis is not necessarily the right explanation. Instead, it is a possible explanation that can be tested to see if it is likely correct, or if a new hypothesis needs to be made.
- Not all explanations can be considered a hypothesis. A hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable in order to be valid. For example, “The universe is beautiful" is not a good hypothesis, because there is no experiment that could test this statement and show it to be false.
- In most cases, the scientific method is an iterative process. In other words, it's a cycle rather than a straight line. The result of one experiment often becomes feedback that raises questions for more experimentation.
- Scientists use the word "theory" in a very different way than non-scientists. When many people say "I have a theory," they really mean "I have a guess." Scientific theories, on the other hand, are well-tested and highly reliable scientific explanations of natural phenomena. They unify many repeated observations and data collected from lots of experiments.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.3: The Science of Biology - The Scientific Method
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 12645

\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Discuss hypotheses and the components of a scientific experiment as part of the scientific method
The Scientific Method
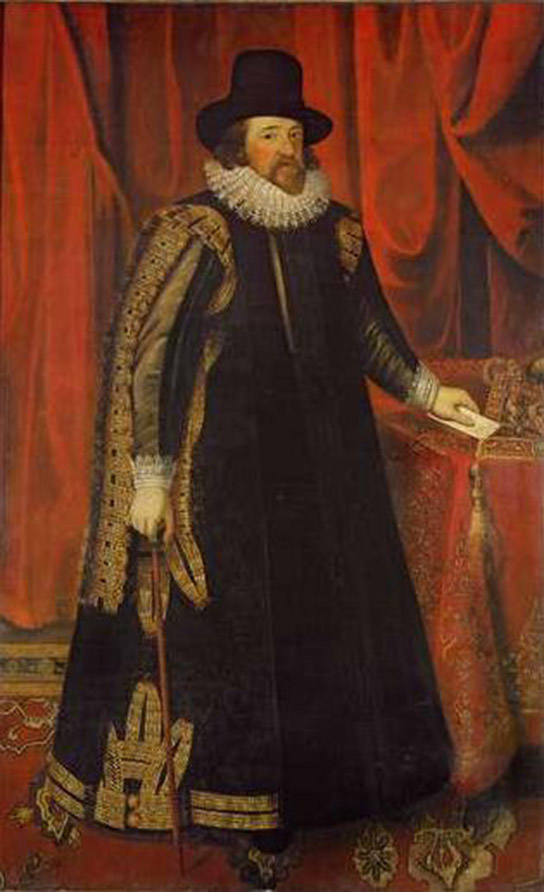
Biologists study the living world by posing questions about it and seeking science -based responses. This approach is common to other sciences as well and is often referred to as the scientific method. The scientific method was used even in ancient times, but it was first documented by England’s Sir Francis Bacon (1561–1626) who set up inductive methods for scientific inquiry. The scientific method can be applied to almost all fields of study as a logical, rational, problem-solving method.

The scientific process typically starts with an observation (often a problem to be solved) that leads to a question. Let’s think about a simple problem that starts with an observation and apply the scientific method to solve the problem. A teenager notices that his friend is really tall and wonders why. So his question might be, “Why is my friend so tall? ”
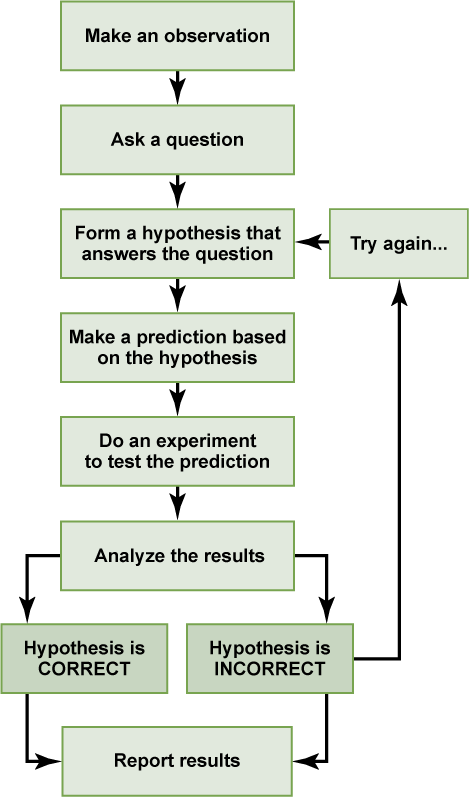
Proposing a Hypothesis
Recall that a hypothesis is an educated guess that can be tested. Hypotheses often also include an explanation for the educated guess. To solve one problem, several hypotheses may be proposed. For example, the student might believe that his friend is tall because he drinks a lot of milk. So his hypothesis might be “If a person drinks a lot of milk, then they will grow to be very tall because milk is good for your bones.” Generally, hypotheses have the format “If…then…” Keep in mind that there could be other responses to the question; therefore, other hypotheses may be proposed. A second hypothesis might be, “If a person has tall parents, then they will also be tall, because they have the genes to be tall. ”
Once a hypothesis has been selected, the student can make a prediction. A prediction is similar to a hypothesis but it is truly a guess. For instance, they might predict that their friend is tall because he drinks a lot of milk.
Testing a Hypothesis
A valid hypothesis must be testable. It should also be falsifiable, meaning that it can be disproven by experimental results. Importantly, science does not claim to “prove” anything because scientific understandings are always subject to modification with further information. This step—openness to disproving ideas—is what distinguishes sciences from non-sciences. The presence of the supernatural, for instance, is neither testable nor falsifiable. To test a hypothesis, a researcher will conduct one or more experiments designed to eliminate one or more of the hypotheses. Each experiment will have one or more variables and one or more controls. A variable is any part of the experiment that can vary or change during the experiment. The control group contains every feature of the experimental group except it is not given the manipulation that is hypothesized. For example, a control group could be a group of varied teenagers that did not drink milk and they could be compared to the experimental group, a group of varied teenagers that did drink milk. Thus, if the results of the experimental group differ from the control group, the difference must be due to the hypothesized manipulation rather than some outside factor. To test the first hypothesis, the student would find out if drinking milk affects height. If drinking milk has no affect on height, then there must be another reason for the height of the friend. To test the second hypothesis, the student could check whether or not his friend has tall parents. Each hypothesis should be tested by carrying out appropriate experiments. Be aware that rejecting one hypothesis does not determine whether or not the other hypotheses can be accepted. It simply eliminates one hypothesis that is not valid. Using the scientific method, the hypotheses that are inconsistent with experimental data are rejected.
While this “tallness” example is based on observational results, other hypotheses and experiments might have clearer controls. For instance, a student might attend class on Monday and realize she had difficulty concentrating on the lecture. One hypothesis to explain this occurrence might be, “If I eat breakfast before class, then I am better able to pay attention.” The student could then design an experiment with a control to test this hypothesis.
The scientific method may seem too rigid and structured. It is important to keep in mind that although scientists often follow this sequence, there is flexibility. Many times, science does not operate in a linear fashion. Instead, scientists continually draw inferences and make generalizations, finding patterns as their research proceeds. Scientific reasoning is more complex than the scientific method alone suggests.
- In the scientific method, observations lead to questions that require answers.
- In the scientific method, the hypothesis is a testable statement proposed to answer a question.
- In the scientific method, experiments (often with controls and variables) are devised to test hypotheses.
- In the scientific method, analysis of the results of an experiment will lead to the hypothesis being accepted or rejected.
- scientific method : a way of discovering knowledge based on making falsifiable predictions (hypotheses), testing them, and developing theories based on collected data
- hypothesis : an educated guess that usually is found in an “if…then…” format
- control group : a group that contains every feature of the experimental group except it is not given the manipulation that is hypothesized
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
Hypothesis Examples

A hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a test. It forms the basis for designing an experiment in the scientific method . A good hypothesis is testable, meaning it makes a prediction you can check with observation or experimentation. Here are different hypothesis examples.
Null Hypothesis Examples
The null hypothesis (H 0 ) is also known as the zero-difference or no-difference hypothesis. It predicts that changing one variable ( independent variable ) will have no effect on the variable being measured ( dependent variable ). Here are null hypothesis examples:
- Plant growth is unaffected by temperature.
- If you increase temperature, then solubility of salt will increase.
- Incidence of skin cancer is unrelated to ultraviolet light exposure.
- All brands of light bulb last equally long.
- Cats have no preference for the color of cat food.
- All daisies have the same number of petals.
Sometimes the null hypothesis shows there is a suspected correlation between two variables. For example, if you think plant growth is affected by temperature, you state the null hypothesis: “Plant growth is not affected by temperature.” Why do you do this, rather than say “If you change temperature, plant growth will be affected”? The answer is because it’s easier applying a statistical test that shows, with a high level of confidence, a null hypothesis is correct or incorrect.
Research Hypothesis Examples
A research hypothesis (H 1 ) is a type of hypothesis used to design an experiment. This type of hypothesis is often written as an if-then statement because it’s easy identifying the independent and dependent variables and seeing how one affects the other. If-then statements explore cause and effect. In other cases, the hypothesis shows a correlation between two variables. Here are some research hypothesis examples:
- If you leave the lights on, then it takes longer for people to fall asleep.
- If you refrigerate apples, they last longer before going bad.
- If you keep the curtains closed, then you need less electricity to heat or cool the house (the electric bill is lower).
- If you leave a bucket of water uncovered, then it evaporates more quickly.
- Goldfish lose their color if they are not exposed to light.
- Workers who take vacations are more productive than those who never take time off.
Is It Okay to Disprove a Hypothesis?
Yes! You may even choose to write your hypothesis in such a way that it can be disproved because it’s easier to prove a statement is wrong than to prove it is right. In other cases, if your prediction is incorrect, that doesn’t mean the science is bad. Revising a hypothesis is common. It demonstrates you learned something you did not know before you conducted the experiment.
Test yourself with a Scientific Method Quiz .
- Mellenbergh, G.J. (2008). Chapter 8: Research designs: Testing of research hypotheses. In H.J. Adèr & G.J. Mellenbergh (eds.), Advising on Research Methods: A Consultant’s Companion . Huizen, The Netherlands: Johannes van Kessel Publishing.
- Popper, Karl R. (1959). The Logic of Scientific Discovery . Hutchinson & Co. ISBN 3-1614-8410-X.
- Schick, Theodore; Vaughn, Lewis (2002). How to think about weird things: critical thinking for a New Age . Boston: McGraw-Hill Higher Education. ISBN 0-7674-2048-9.
- Tobi, Hilde; Kampen, Jarl K. (2018). “Research design: the methodology for interdisciplinary research framework”. Quality & Quantity . 52 (3): 1209–1225. doi: 10.1007/s11135-017-0513-8
Related Posts
- First Online: 01 January 2024
Cite this chapter

- Hiroshi Ishikawa 3
Part of the book series: Studies in Big Data ((SBD,volume 139))
239 Accesses
This chapter will explain the definition and properties of a hypothesis, the related concepts, and basic methods of hypothesis generation as follows.
Describe the definition, properties, and life cycle of a hypothesis.
Describe relationships between a hypothesis and a theory, a model, and data.
Categorize and explain research questions that provide hints for hypothesis generation.
Explain how to visualize data and analysis results.
Explain the philosophy of science and scientific methods in relation to hypothesis generation in science.
Explain deduction, induction, plausible reasoning, and analogy concretely as reasoning methods useful for hypothesis generation.
Explain problem solving as hypothesis generation methods by using familiar examples.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Aufmann RN, Lockwood JS et al (2018) Mathematical excursions. CENGAGE
Google Scholar
Bortolotti L (2008) An introduction to the philosophy of science. Polity
Cairo A (2016) The truthful art: data, charts, and maps for communication. New Riders
Cellucci C (2017) Rethinking knowledge: the heuristic view. Springer
Chang M (2014) Principles of scientific methods. CRC Press
Crease RP (2010) The great equations: breakthroughs in science from Pythagoras to Heisenberg. W. W. Norton & Company
Danks D, Ippoliti E (eds) Building theories: Heuristics and hypotheses in sciences. Springer
Diggle PJ, Chetwynd AG (2011) Statistics and scientific method: an introduction for students and researchers. Oxford University Press
DOAJ (2022) Directory of open access journal. https://doaj.org/ Accessed 2022
Gilchrist P, Wheaton B (2011) Lifestyle sport, public policy and youth engagement: examining the emergence of Parkour. Int J Sport Policy Polit 3(1):109–131. https://doi.org/10.1080/19406940.2010.547866
Article Google Scholar
Google Maps. https://www.google.com/maps Accessed 2022.
Ishikawa H (2015) Social big data mining. CRC Press
Järvinen P (2008) Mapping research questions to research methods. In: Avison D, Kasper GM, Pernici B, Ramos I, Roode D (eds) Advances in information systems research, education and practice. Proceedings of IFIP 20th world computer congress, TC 8, information systems, vol 274. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-09682-7-9_3
JAXA (2022) Martian moons eXploration. http://www.mmx.jaxa.jp/en/ . Accessed 2022
Lewton T (2020) How the bits of quantum gravity can buzz. Quanta Magazine. 2020. https://www.quantamagazine.org/gravitons-revealed-in-the-noise-of-gravitational-waves-20200723/ . Accessed 2022
Mahajan S (2014) The art of insight in science and engineering: Mastering complexity. The MIT Press
Méndez A, Rivera–Valentín EG (2017) The equilibrium temperature of planets in elliptical orbits. Astrophys J Lett 837(1)
NASA (2022) Mars sample return. https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/missions/mars-sample-return-msr Accessed 2022
OpenStreetMap (2022). https://www.openstreetmap.org . Accessed 2022
Pólya G (2009) Mathematics and plausible reasoning: vol I: induction and analogy in mathematics. Ishi Press
Pólya G, Conway JH (2014) How to solve it. Princeton University Press
Rehm J (2019) The four fundamental forces of nature. Live science https://www.livescience.com/the-fundamental-forces-of-nature.html
Sadler-Smith E (2015) Wallas’ four-stage model of the creative process: more than meets the eye? Creat Res J 27(4):342–352. https://doi.org/10.1080/10400419.2015.1087277
Siegel E, This is why physicists think string theory might be our ‘theory of everything.’ Forbes, 2018. https://www.forbes.com/sites/startswithabang/2018/05/31/this-is-why-physicists-think-string-theory-might-be-our-theory-of-everything/?sh=b01d79758c25
Zeitz P (2006) The art and craft of problem solving. Wiley
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Systems Design, Tokyo Metropolitan University, Hino, Tokyo, Japan
Hiroshi Ishikawa
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hiroshi Ishikawa .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Ishikawa, H. (2024). Hypothesis. In: Hypothesis Generation and Interpretation. Studies in Big Data, vol 139. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43540-9_2

Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43540-9_2
Published : 01 January 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-43539-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-43540-9
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
We think you are located in South Africa . Is this correct?
- Yes, I reside in South Africa
- Change country/curriculum
We use this information to present the correct curriculum and to personalise content to better meet the needs of our users.
Open Textbooks
Download our open textbooks in different formats to use them in the way that suits you. Click on each book cover to see the available files to download, in English and Afrikaans. Better than just free, these books are also openly-licensed (except Information Technology and Computer Applications Technology)! Refer to the different open licences for each download and the explanations of the licenses at the bottom of the page.

- Read online
- 7A PDF (CC-BY-ND)
- 7B PDF (CC-BY-ND)

- 8A PDF (CC-BY-ND)
- 8B PDF (CC-BY-ND)

- 9A PDF (CC-BY-ND)
- 9B PDF (CC-BY-ND)

- PDF (CC-BY-ND)
- ePUB (CC-BY-ND)
- ePUB (CC-BY)

Information Technology

- ePUB (Closed copyright)
- Data files (Closed copyright)

Computer Applications Technology

Our book licensing
Better than just free, these books (except Information Technology and Computer Applications Technology) are also openly-licensed! The same content, but different versions (branded or not) have different licenses, as explained:
CC-BY-ND (branded versions)
You are allowed and encouraged to freely copy these versions. You can photocopy, print and distribute them as often as you like. You can download them onto your mobile phone, iPad, PC or flash drive. You can burn them to CD, email them around or upload them to your website. The only restriction is that you cannot adapt or change these versions of the textbooks, their content or covers in any way as they contain the relevant Siyavula brands, the sponsorship logos and are endorsed by the Department of Basic Education. For more information, visit Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported .
Find out more here about the sponsorships and partnerships with others that made the production of each of the open textbooks possible.
CC-BY (unbranded versions)
These unbranded versions of the same content are available for you to share, adapt, transform, modify or build upon in any way, with the only requirement being to give appropriate credit to Siyavula. For more information, visit Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported .
Information Technology and Computer Applications Technology
These books have been provided by MTN and are under a closed copyright license.
1.2 The Process of Science
Learning objectives.
- Identify the shared characteristics of the natural sciences
- Understand the process of scientific inquiry
- Compare inductive reasoning with deductive reasoning
- Describe the goals of basic science and applied science
Like geology, physics, and chemistry, biology is a science that gathers knowledge about the natural world. Specifically, biology is the study of life. The discoveries of biology are made by a community of researchers who work individually and together using agreed-on methods. In this sense, biology, like all sciences is a social enterprise like politics or the arts. The methods of science include careful observation, record keeping, logical and mathematical reasoning, experimentation, and submitting conclusions to the scrutiny of others. Science also requires considerable imagination and creativity; a well-designed experiment is commonly described as elegant, or beautiful. Like politics, science has considerable practical implications and some science is dedicated to practical applications, such as the prevention of disease (see Figure 1.15 ). Other science proceeds largely motivated by curiosity. Whatever its goal, there is no doubt that science, including biology, has transformed human existence and will continue to do so.
The Nature of Science
Biology is a science, but what exactly is science? What does the study of biology share with other scientific disciplines? Science (from the Latin scientia, meaning "knowledge") can be defined as knowledge about the natural world.
Science is a very specific way of learning, or knowing, about the world. The history of the past 500 years demonstrates that science is a very powerful way of knowing about the world; it is largely responsible for the technological revolutions that have taken place during this time. There are however, areas of knowledge and human experience that the methods of science cannot be applied to. These include such things as answering purely moral questions, aesthetic questions, or what can be generally categorized as spiritual questions. Science cannot investigate these areas because they are outside the realm of material phenomena, the phenomena of matter and energy, and cannot be observed and measured.
The scientific method is a method of research with defined steps that include experiments and careful observation. The steps of the scientific method will be examined in detail later, but one of the most important aspects of this method is the testing of hypotheses. A hypothesis is a suggested explanation for an event, which can be tested. Hypotheses, or tentative explanations, are generally produced within the context of a scientific theory . A generally accepted scientific theory is thoroughly tested and confirmed explanation for a set of observations or phenomena. Scientific theory is the foundation of scientific knowledge. In addition, in many scientific disciplines (less so in biology) there are scientific laws , often expressed in mathematical formulas, which describe how elements of nature will behave under certain specific conditions. There is not an evolution of hypotheses through theories to laws as if they represented some increase in certainty about the world. Hypotheses are the day-to-day material that scientists work with and they are developed within the context of theories. Laws are concise descriptions of parts of the world that are amenable to formulaic or mathematical description.
Natural Sciences
What would you expect to see in a museum of natural sciences? Frogs? Plants? Dinosaur skeletons? Exhibits about how the brain functions? A planetarium? Gems and minerals? Or maybe all of the above? Science includes such diverse fields as astronomy, biology, computer sciences, geology, logic, physics, chemistry, and mathematics ( Figure 1.16 ). However, those fields of science related to the physical world and its phenomena and processes are considered natural sciences . Thus, a museum of natural sciences might contain any of the items listed above.
There is no complete agreement when it comes to defining what the natural sciences include. For some experts, the natural sciences are astronomy, biology, chemistry, earth science, and physics. Other scholars choose to divide natural sciences into life sciences , which study living things and include biology, and physical sciences , which study nonliving matter and include astronomy, physics, and chemistry. Some disciplines such as biophysics and biochemistry build on two sciences and are interdisciplinary.
Scientific Inquiry
One thing is common to all forms of science: an ultimate goal “to know.” Curiosity and inquiry are the driving forces for the development of science. Scientists seek to understand the world and the way it operates. Two methods of logical thinking are used: inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning is a form of logical thinking that uses related observations to arrive at a general conclusion. This type of reasoning is common in descriptive science. A life scientist such as a biologist makes observations and records them. These data can be qualitative (descriptive) or quantitative (consisting of numbers), and the raw data can be supplemented with drawings, pictures, photos, or videos. From many observations, the scientist can infer conclusions (inductions) based on evidence. Inductive reasoning involves formulating generalizations inferred from careful observation and the analysis of a large amount of data. Brain studies often work this way. Many brains are observed while people are doing a task. The part of the brain that lights up, indicating activity, is then demonstrated to be the part controlling the response to that task.
Deductive reasoning or deduction is the type of logic used in hypothesis-based science. In deductive reasoning, the pattern of thinking moves in the opposite direction as compared to inductive reasoning. Deductive reasoning is a form of logical thinking that uses a general principle or law to predict specific results. From those general principles, a scientist can deduce and predict the specific results that would be valid as long as the general principles are valid. For example, a prediction would be that if the climate is becoming warmer in a region, the distribution of plants and animals should change. Comparisons have been made between distributions in the past and the present, and the many changes that have been found are consistent with a warming climate. Finding the change in distribution is evidence that the climate change conclusion is a valid one.
Both types of logical thinking are related to the two main pathways of scientific study: descriptive science and hypothesis-based science. Descriptive (or discovery) science aims to observe, explore, and discover, while hypothesis-based science begins with a specific question or problem and a potential answer or solution that can be tested. The boundary between these two forms of study is often blurred, because most scientific endeavors combine both approaches. Observations lead to questions, questions lead to forming a hypothesis as a possible answer to those questions, and then the hypothesis is tested. Thus, descriptive science and hypothesis-based science are in continuous dialogue.
Hypothesis Testing
Biologists study the living world by posing questions about it and seeking science-based responses. This approach is common to other sciences as well and is often referred to as the scientific method. The scientific method was used even in ancient times, but it was first documented by England’s Sir Francis Bacon (1561–1626) ( Figure 1.17 ), who set up inductive methods for scientific inquiry. The scientific method is not exclusively used by biologists but can be applied to almost anything as a logical problem-solving method.
The scientific process typically starts with an observation (often a problem to be solved) that leads to a question. Let’s think about a simple problem that starts with an observation and apply the scientific method to solve the problem. One Monday morning, a student arrives at class and quickly discovers that the classroom is too warm. That is an observation that also describes a problem: the classroom is too warm. The student then asks a question: “Why is the classroom so warm?”
Recall that a hypothesis is a suggested explanation that can be tested. To solve a problem, several hypotheses may be proposed. For example, one hypothesis might be, “The classroom is warm because no one turned on the air conditioning.” But there could be other responses to the question, and therefore other hypotheses may be proposed. A second hypothesis might be, “The classroom is warm because there is a power failure, and so the air conditioning doesn’t work.”
Once a hypothesis has been selected, a prediction may be made. A prediction is similar to a hypothesis but it typically has the format “If . . . then . . . .” For example, the prediction for the first hypothesis might be, “ If the student turns on the air conditioning, then the classroom will no longer be too warm.”
A hypothesis must be testable to ensure that it is valid. For example, a hypothesis that depends on what a bear thinks is not testable, because it can never be known what a bear thinks. It should also be falsifiable , meaning that it can be disproven by experimental results. An example of an unfalsifiable hypothesis is “Botticelli’s Birth of Venus is beautiful.” There is no experiment that might show this statement to be false. To test a hypothesis, a researcher will conduct one or more experiments designed to eliminate one or more of the hypotheses. This is important. A hypothesis can be disproven, or eliminated, but it can never be proven. Science does not deal in proofs like mathematics. If an experiment fails to disprove a hypothesis, then we find support for that explanation, but this is not to say that down the road a better explanation will not be found, or a more carefully designed experiment will be found to falsify the hypothesis.
Each experiment will have one or more variables and one or more controls. A variable is any part of the experiment that can vary or change during the experiment. A control is a part of the experiment that does not change. Look for the variables and controls in the example that follows. As a simple example, an experiment might be conducted to test the hypothesis that phosphate limits the growth of algae in freshwater ponds. A series of artificial ponds are filled with water and half of them are treated by adding phosphate each week, while the other half are treated by adding a salt that is known not to be used by algae. The variable here is the phosphate (or lack of phosphate), the experimental or treatment cases are the ponds with added phosphate and the control ponds are those with something inert added, such as the salt. Just adding something is also a control against the possibility that adding extra matter to the pond has an effect. If the treated ponds show lesser growth of algae, then we have found support for our hypothesis. If they do not, then we reject our hypothesis. Be aware that rejecting one hypothesis does not determine whether or not the other hypotheses can be accepted; it simply eliminates one hypothesis that is not valid ( Figure 1.18 ). Using the scientific method, the hypotheses that are inconsistent with experimental data are rejected.
In recent years a new approach of testing hypotheses has developed as a result of an exponential growth of data deposited in various databases. Using computer algorithms and statistical analyses of data in databases, a new field of so-called "data research" (also referred to as "in silico" research) provides new methods of data analyses and their interpretation. This will increase the demand for specialists in both biology and computer science, a promising career opportunity.
Visual Connection
In the example below, the scientific method is used to solve an everyday problem. Which part in the example below is the hypothesis? Which is the prediction? Based on the results of the experiment, is the hypothesis supported? If it is not supported, propose some alternative hypotheses.
- My toaster doesn’t toast my bread.
- Why doesn’t my toaster work?
- There is something wrong with the electrical outlet.
- If something is wrong with the outlet, my coffeemaker also won’t work when plugged into it.
- I plug my coffeemaker into the outlet.
- My coffeemaker works.
In practice, the scientific method is not as rigid and structured as it might at first appear. Sometimes an experiment leads to conclusions that favor a change in approach; often, an experiment brings entirely new scientific questions to the puzzle. Many times, science does not operate in a linear fashion; instead, scientists continually draw inferences and make generalizations, finding patterns as their research proceeds. Scientific reasoning is more complex than the scientific method alone suggests.
Basic and Applied Science
The scientific community has been debating for the last few decades about the value of different types of science. Is it valuable to pursue science for the sake of simply gaining knowledge, or does scientific knowledge only have worth if we can apply it to solving a specific problem or bettering our lives? This question focuses on the differences between two types of science: basic science and applied science.
Basic science or “pure” science seeks to expand knowledge regardless of the short-term application of that knowledge. It is not focused on developing a product or a service of immediate public or commercial value. The immediate goal of basic science is knowledge for knowledge’s sake, though this does not mean that in the end it may not result in an application.
In contrast, applied science or “technology,” aims to use science to solve real-world problems, making it possible, for example, to improve a crop yield, find a cure for a particular disease, or save animals threatened by a natural disaster. In applied science, the problem is usually defined for the researcher.
Some individuals may perceive applied science as “useful” and basic science as “useless.” A question these people might pose to a scientist advocating knowledge acquisition would be, “What for?” A careful look at the history of science, however, reveals that basic knowledge has resulted in many remarkable applications of great value. Many scientists think that a basic understanding of science is necessary before an application is developed; therefore, applied science relies on the results generated through basic science. Other scientists think that it is time to move on from basic science and instead to find solutions to actual problems. Both approaches are valid. It is true that there are problems that demand immediate attention; however, few solutions would be found without the help of the knowledge generated through basic science.
One example of how basic and applied science can work together to solve practical problems occurred after the discovery of DNA structure led to an understanding of the molecular mechanisms governing DNA replication. Strands of DNA, unique in every human, are found in our cells, where they provide the instructions necessary for life. During DNA replication, new copies of DNA are made, shortly before a cell divides to form new cells. Understanding the mechanisms of DNA replication enabled scientists to develop laboratory techniques that are now used to identify genetic diseases, pinpoint individuals who were at a crime scene, and determine paternity. Without basic science, it is unlikely that applied science could exist.
Another example of the link between basic and applied research is the Human Genome Project, a study in which each human chromosome was analyzed and mapped to determine the precise sequence of DNA subunits and the exact location of each gene. (The gene is the basic unit of heredity represented by a specific DNA segment that codes for a functional molecule.) Other organisms have also been studied as part of this project to gain a better understanding of human chromosomes. The Human Genome Project ( Figure 1.19 ) relied on basic research carried out with non-human organisms and, later, with the human genome. An important end goal eventually became using the data for applied research seeking cures for genetically related diseases.
While research efforts in both basic science and applied science are usually carefully planned, it is important to note that some discoveries are made by serendipity, that is, by means of a fortunate accident or a lucky surprise. Penicillin was discovered when biologist Alexander Fleming accidentally left a petri dish of Staphylococcus bacteria open. An unwanted mold grew, killing the bacteria. The mold turned out to be Penicillium , and a new critically important antibiotic was discovered. In a similar manner, Percy Lavon Julian was an established medicinal chemist working on a way to mass produce compounds with which to manufacture important drugs. He was focused on using soybean oil in the production of progesterone (a hormone important in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy), but it wasn't until water accidentally leaked into a large soybean oil storage tank that he found his method. Immediately recognizing the resulting substance as stigmasterol, a primary ingredient in progesterone and similar drugs, he began the process of replicating and industrializing the process in a manner that has helped millions of people. Even in the highly organized world of science, luck—when combined with an observant, curious mind focused on the types of reasoning discussed above—can lead to unexpected breakthroughs.
Reporting Scientific Work
Whether scientific research is basic science or applied science, scientists must share their findings for other researchers to expand and build upon their discoveries. Communication and collaboration within and between sub disciplines of science are key to the advancement of knowledge in science. For this reason, an important aspect of a scientist’s work is disseminating results and communicating with peers. Scientists can share results by presenting them at a scientific meeting or conference, but this approach can reach only the limited few who are present. Instead, most scientists present their results in peer-reviewed articles that are published in scientific journals. Peer-reviewed articles are scientific papers that are reviewed, usually anonymously by a scientist’s colleagues, or peers. These colleagues are qualified individuals, often experts in the same research area, who judge whether or not the scientist’s work is suitable for publication. The process of peer review helps to ensure that the research described in a scientific paper or grant proposal is original, significant, logical, and thorough. Grant proposals, which are requests for research funding, are also subject to peer review. Scientists publish their work so other scientists can reproduce their experiments under similar or different conditions to expand on the findings.
There are many journals and the popular press that do not use a peer-review system. A large number of online open-access journals, journals with articles available without cost, are now available many of which use rigorous peer-review systems, but some of which do not. Results of any studies published in these forums without peer review are not reliable and should not form the basis for other scientific work. In one exception, journals may allow a researcher to cite a personal communication from another researcher about unpublished results with the cited author’s permission.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/concepts-biology/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Concepts of Biology
- Publication date: Apr 25, 2013
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/concepts-biology/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/concepts-biology/pages/1-2-the-process-of-science
© Apr 26, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Subscriber Services
- For Authors
- Publications
- Archaeology
- Art & Architecture
- Bilingual dictionaries
- Classical studies
- Encyclopedias
- English Dictionaries and Thesauri
- Language reference
- Linguistics
- Media studies
- Medicine and health
- Names studies
- Performing arts
- Science and technology
- Social sciences
- Society and culture
- Overview Pages
- Subject Reference
- English Dictionaries
- Bilingual Dictionaries
Recently viewed (0)
- Save Search
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Related Content
Related overviews.
hypothetico-deductive method
See all related overviews in Oxford Reference »
More Like This
Show all results sharing these subjects:
- Life Sciences
Quick Reference
A statement of the expected relationship between things being studied, which is intended to explain certain facts or observations. An idea to be tested.
From: hypothesis in A Dictionary of Environment and Conservation »
Subjects: Science and technology — Life Sciences
Related content in Oxford Reference
Reference entries.
View all reference entries »
View all related items in Oxford Reference »
Search for: 'hypothesis' in Oxford Reference »
- Oxford University Press
PRINTED FROM OXFORD REFERENCE (www.oxfordreference.com). (c) Copyright Oxford University Press, 2023. All Rights Reserved. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a PDF of a single entry from a reference work in OR for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice ).
date: 24 May 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|185.66.14.133]
- 185.66.14.133
Character limit 500 /500
What Are Examples of a Hypothesis?
- Scientific Method
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A hypothesis is an explanation for a set of observations. Here are examples of a scientific hypothesis.
Although you could state a scientific hypothesis in various ways, most hypotheses are either "If, then" statements or forms of the null hypothesis . The null hypothesis is sometimes called the "no difference" hypothesis. The null hypothesis is good for experimentation because it's simple to disprove. If you disprove a null hypothesis, that is evidence for a relationship between the variables you are examining.
Examples of Null Hypotheses
- Hyperactivity is unrelated to eating sugar.
- All daisies have the same number of petals.
- The number of pets in a household is unrelated to the number of people living in it.
- A person's preference for a shirt is unrelated to its color.
Examples of If, Then Hypotheses
- If you get at least 6 hours of sleep, you will do better on tests than if you get less sleep.
- If you drop a ball, it will fall toward the ground.
- If you drink coffee before going to bed, then it will take longer to fall asleep.
- If you cover a wound with a bandage, then it will heal with less scarring.
Improving a Hypothesis to Make It Testable
You may wish to revise your first hypothesis in order to make it easier to design an experiment to test. For example, let's say you have a bad breakout the morning after eating a lot of greasy food. You may wonder if there is a correlation between eating greasy food and getting pimples. You propose the hypothesis:
Eating greasy food causes pimples.
Next, you need to design an experiment to test this hypothesis. Let's say you decide to eat greasy food every day for a week and record the effect on your face. Then, as a control, you'll avoid greasy food for the next week and see what happens. Now, this is not a good experiment because it does not take into account other factors such as hormone levels, stress, sun exposure, exercise, or any number of other variables that might conceivably affect your skin.
The problem is that you cannot assign cause to your effect . If you eat french fries for a week and suffer a breakout, can you definitely say it was the grease in the food that caused it? Maybe it was the salt. Maybe it was the potato. Maybe it was unrelated to diet. You can't prove your hypothesis. It's much easier to disprove a hypothesis.
So, let's restate the hypothesis to make it easier to evaluate the data:
Getting pimples is unaffected by eating greasy food.
So, if you eat fatty food every day for a week and suffer breakouts and then don't break out the week that you avoid greasy food, you can be pretty sure something is up. Can you disprove the hypothesis? Probably not, since it is so hard to assign cause and effect. However, you can make a strong case that there is some relationship between diet and acne.
If your skin stays clear for the entire test, you may decide to accept your hypothesis . Again, you didn't prove or disprove anything, which is fine
- Null Hypothesis Examples
- Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- Difference Between Independent and Dependent Variables
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- What Is a Testable Hypothesis?
- What 'Fail to Reject' Means in a Hypothesis Test
- Scientific Hypothesis Examples
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- How To Design a Science Fair Experiment
- An Example of a Hypothesis Test
- Definition of a Hypothesis
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
- School Guide
- Mathematics
- Number System and Arithmetic
- Trigonometry
- Probability
- Mensuration
- Maths Formulas
- Class 8 Maths Notes
- Class 9 Maths Notes
- Class 10 Maths Notes
- Class 11 Maths Notes
- Class 12 Maths Notes
- Null Hypothesis
- Hypothesis Testing Formula
- Difference Between Hypothesis And Theory
- Real-life Applications of Hypothesis Testing
- Permutation Hypothesis Test in R Programming
- Bayes' Theorem
- Hypothesis in Machine Learning
- Current Best Hypothesis Search
- Understanding Hypothesis Testing
- Hypothesis Testing in R Programming
- Jobathon | Stats | Question 10
- Jobathon | Stats | Question 17
- Testing | Question 1
- Difference between Null and Alternate Hypothesis
- ML | Find S Algorithm
- Python - Pearson's Chi-Square Test
Hypothesis is a testable statement that explains what is happening or observed. It proposes the relation between the various participating variables. Hypothesis is also called Theory, Thesis, Guess, Assumption, or Suggestion. Hypothesis creates a structure that guides the search for knowledge.
In this article, we will learn what is hypothesis, its characteristics, types, and examples. We will also learn how hypothesis helps in scientific research.

What is Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is a suggested idea or plan that has little proof, meant to lead to more study. It’s mainly a smart guess or suggested answer to a problem that can be checked through study and trial. In science work, we make guesses called hypotheses to try and figure out what will happen in tests or watching. These are not sure things but rather ideas that can be proved or disproved based on real-life proofs. A good theory is clear and can be tested and found wrong if the proof doesn’t support it.
Hypothesis Meaning
A hypothesis is a proposed statement that is testable and is given for something that happens or observed.
- It is made using what we already know and have seen, and it’s the basis for scientific research.
- A clear guess tells us what we think will happen in an experiment or study.
- It’s a testable clue that can be proven true or wrong with real-life facts and checking it out carefully.
- It usually looks like a “if-then” rule, showing the expected cause and effect relationship between what’s being studied.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some key characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable: An idea (hypothesis) should be made so it can be tested and proven true through doing experiments or watching. It should show a clear connection between things.
- Specific: It needs to be easy and on target, talking about a certain part or connection between things in a study.
- Falsifiable: A good guess should be able to show it’s wrong. This means there must be a chance for proof or seeing something that goes against the guess.
- Logical and Rational: It should be based on things we know now or have seen, giving a reasonable reason that fits with what we already know.
- Predictive: A guess often tells what to expect from an experiment or observation. It gives a guide for what someone might see if the guess is right.
- Concise: It should be short and clear, showing the suggested link or explanation simply without extra confusion.
- Grounded in Research: A guess is usually made from before studies, ideas or watching things. It comes from a deep understanding of what is already known in that area.
- Flexible: A guess helps in the research but it needs to change or fix when new information comes up.
- Relevant: It should be related to the question or problem being studied, helping to direct what the research is about.
- Empirical: Hypotheses come from observations and can be tested using methods based on real-world experiences.
Sources of Hypothesis
Hypotheses can come from different places based on what you’re studying and the kind of research. Here are some common sources from which hypotheses may originate:
- Existing Theories: Often, guesses come from well-known science ideas. These ideas may show connections between things or occurrences that scientists can look into more.
- Observation and Experience: Watching something happen or having personal experiences can lead to guesses. We notice odd things or repeat events in everyday life and experiments. This can make us think of guesses called hypotheses.
- Previous Research: Using old studies or discoveries can help come up with new ideas. Scientists might try to expand or question current findings, making guesses that further study old results.
- Literature Review: Looking at books and research in a subject can help make guesses. Noticing missing parts or mismatches in previous studies might make researchers think up guesses to deal with these spots.
- Problem Statement or Research Question: Often, ideas come from questions or problems in the study. Making clear what needs to be looked into can help create ideas that tackle certain parts of the issue.
- Analogies or Comparisons: Making comparisons between similar things or finding connections from related areas can lead to theories. Understanding from other fields could create new guesses in a different situation.
- Hunches and Speculation: Sometimes, scientists might get a gut feeling or make guesses that help create ideas to test. Though these may not have proof at first, they can be a beginning for looking deeper.
- Technology and Innovations: New technology or tools might make guesses by letting us look at things that were hard to study before.
- Personal Interest and Curiosity: People’s curiosity and personal interests in a topic can help create guesses. Scientists could make guesses based on their own likes or love for a subject.
Types of Hypothesis
Here are some common types of hypotheses:
Simple Hypothesis
Complex hypothesis, directional hypothesis.
- Non-directional Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis (H0)
Alternative hypothesis (h1 or ha), statistical hypothesis, research hypothesis, associative hypothesis, causal hypothesis.
Simple Hypothesis guesses a connection between two things. It says that there is a connection or difference between variables, but it doesn’t tell us which way the relationship goes.
Complex Hypothesis tells us what will happen when more than two things are connected. It looks at how different things interact and may be linked together.
Directional Hypothesis says how one thing is related to another. For example, it guesses that one thing will help or hurt another thing.
Non-Directional Hypothesis
Non-Directional Hypothesis are the one that don’t say how the relationship between things will be. They just say that there is a connection, without telling which way it goes.
Null hypothesis is a statement that says there’s no connection or difference between different things. It implies that any seen impacts are because of luck or random changes in the information.
Alternative Hypothesis is different from the null hypothesis and shows that there’s a big connection or gap between variables. Scientists want to say no to the null hypothesis and choose the alternative one.
Statistical Hypotheis are used in math testing and include making ideas about what groups or bits of them look like. You aim to get information or test certain things using these top-level, common words only.
Research Hypothesis comes from the research question and tells what link is expected between things or factors. It leads the study and chooses where to look more closely.
Associative Hypotheis guesses that there is a link or connection between things without really saying it caused them. It means that when one thing changes, it is connected to another thing changing.
Causal Hypothesis are different from other ideas because they say that one thing causes another. This means there’s a cause and effect relationship between variables involved in the situation. They say that when one thing changes, it directly makes another thing change.
Hypothesis Examples
Following are the examples of hypotheses based on their types:
Simple Hypothesis Example
- Studying more can help you do better on tests.
- Getting more sun makes people have higher amounts of vitamin D.
Complex Hypothesis Example
- How rich you are, how easy it is to get education and healthcare greatly affects the number of years people live.
- A new medicine’s success relies on the amount used, how old a person is who takes it and their genes.
Directional Hypothesis Example
- Drinking more sweet drinks is linked to a higher body weight score.
- Too much stress makes people less productive at work.
Non-directional Hypothesis Example
- Drinking caffeine can affect how well you sleep.
- People often like different kinds of music based on their gender.
- The average test scores of Group A and Group B are not much different.
- There is no connection between using a certain fertilizer and how much it helps crops grow.
Alternative Hypothesis (Ha)
- Patients on Diet A have much different cholesterol levels than those following Diet B.
- Exposure to a certain type of light can change how plants grow compared to normal sunlight.
- The average smarts score of kids in a certain school area is 100.
- The usual time it takes to finish a job using Method A is the same as with Method B.
- Having more kids go to early learning classes helps them do better in school when they get older.
- Using specific ways of talking affects how much customers get involved in marketing activities.
- Regular exercise helps to lower the chances of heart disease.
- Going to school more can help people make more money.
- Playing violent video games makes teens more likely to act aggressively.
- Less clean air directly impacts breathing health in city populations.
Functions of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have many important jobs in the process of scientific research. Here are the key functions of hypotheses:
- Guiding Research: Hypotheses give a clear and exact way for research. They act like guides, showing the predicted connections or results that scientists want to study.
- Formulating Research Questions: Research questions often create guesses. They assist in changing big questions into particular, checkable things. They guide what the study should be focused on.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Hypotheses set the goals of a study by saying what connections between variables should be found. They set the targets that scientists try to reach with their studies.
- Testing Predictions: Theories guess what will happen in experiments or observations. By doing tests in a planned way, scientists can check if what they see matches the guesses made by their ideas.
- Providing Structure: Theories give structure to the study process by arranging thoughts and ideas. They aid scientists in thinking about connections between things and plan experiments to match.
- Focusing Investigations: Hypotheses help scientists focus on certain parts of their study question by clearly saying what they expect links or results to be. This focus makes the study work better.
- Facilitating Communication: Theories help scientists talk to each other effectively. Clearly made guesses help scientists to tell others what they plan, how they will do it and the results expected. This explains things well with colleagues in a wide range of audiences.
- Generating Testable Statements: A good guess can be checked, which means it can be looked at carefully or tested by doing experiments. This feature makes sure that guesses add to the real information used in science knowledge.
- Promoting Objectivity: Guesses give a clear reason for study that helps guide the process while reducing personal bias. They motivate scientists to use facts and data as proofs or disprovals for their proposed answers.
- Driving Scientific Progress: Making, trying out and adjusting ideas is a cycle. Even if a guess is proven right or wrong, the information learned helps to grow knowledge in one specific area.
How Hypothesis help in Scientific Research?
Researchers use hypotheses to put down their thoughts directing how the experiment would take place. Following are the steps that are involved in the scientific method:
- Initiating Investigations: Hypotheses are the beginning of science research. They come from watching, knowing what’s already known or asking questions. This makes scientists make certain explanations that need to be checked with tests.
- Formulating Research Questions: Ideas usually come from bigger questions in study. They help scientists make these questions more exact and testable, guiding the study’s main point.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Hypotheses set the goals of a study by stating what we think will happen between different things. They set the goals that scientists want to reach by doing their studies.
- Designing Experiments and Studies: Assumptions help plan experiments and watchful studies. They assist scientists in knowing what factors to measure, the techniques they will use and gather data for a proposed reason.
- Testing Predictions: Ideas guess what will happen in experiments or observations. By checking these guesses carefully, scientists can see if the seen results match up with what was predicted in each hypothesis.
- Analysis and Interpretation of Data: Hypotheses give us a way to study and make sense of information. Researchers look at what they found and see if it matches the guesses made in their theories. They decide if the proof backs up or disagrees with these suggested reasons why things are happening as expected.
- Encouraging Objectivity: Hypotheses help make things fair by making sure scientists use facts and information to either agree or disagree with their suggested reasons. They lessen personal preferences by needing proof from experience.
- Iterative Process: People either agree or disagree with guesses, but they still help the ongoing process of science. Findings from testing ideas make us ask new questions, improve those ideas and do more tests. It keeps going on in the work of science to keep learning things.
People Also View:
Mathematics Maths Formulas Branches of Mathematics
Summary – Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a testable statement serving as an initial explanation for phenomena, based on observations, theories, or existing knowledge. It acts as a guiding light for scientific research, proposing potential relationships between variables that can be empirically tested through experiments and observations. The hypothesis must be specific, testable, falsifiable, and grounded in prior research or observation, laying out a predictive, if-then scenario that details a cause-and-effect relationship. It originates from various sources including existing theories, observations, previous research, and even personal curiosity, leading to different types, such as simple, complex, directional, non-directional, null, and alternative hypotheses, each serving distinct roles in research methodology. The hypothesis not only guides the research process by shaping objectives and designing experiments but also facilitates objective analysis and interpretation of data, ultimately driving scientific progress through a cycle of testing, validation, and refinement.
FAQs on Hypothesis
What is a hypothesis.
A guess is a possible explanation or forecast that can be checked by doing research and experiments.
What are Components of a Hypothesis?
The components of a Hypothesis are Independent Variable, Dependent Variable, Relationship between Variables, Directionality etc.
What makes a Good Hypothesis?
Testability, Falsifiability, Clarity and Precision, Relevance are some parameters that makes a Good Hypothesis
Can a Hypothesis be Proven True?
You cannot prove conclusively that most hypotheses are true because it’s generally impossible to examine all possible cases for exceptions that would disprove them.
How are Hypotheses Tested?
Hypothesis testing is used to assess the plausibility of a hypothesis by using sample data
Can Hypotheses change during Research?
Yes, you can change or improve your ideas based on new information discovered during the research process.
What is the Role of a Hypothesis in Scientific Research?
Hypotheses are used to support scientific research and bring about advancements in knowledge.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.

- Geeks Premier League 2023
- Maths-Class-12
- Geeks Premier League
- School Learning
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

What if aliens exist—but they're just hiding from us? The Dark Forest theory, explained
The chilling theory depicted in the Netflix series ‘3 Body Problem’ is just one explanation for our lack of encounters with extraterrestrial intelligence.
The famed Fermi paradox has bewitched astronomers for more than half a century. To put it concisely: If the cosmos is nearly 14 billion years old, then where are all the interstellar societies? Why haven’t they popped over to say hello? Myriad solutions to this conundrum have been proposed, but perhaps none more chilling than the Dark Forest theory.
As the supposition holds, the reason we can’t see these alien civilizations is because they’re all in hiding. Unlike humanity—whose radio transmissions have long echoed throughout our local galactic neighborhood—these societies have all concluded that it’s simply too dangerous to broadcast their location to potentially hostile neighbors.
It's a sobering thought—and one that’s gaining attention now that it’s being depicted in 3 Body Problem , a Netflix adaptation of author Cixin Liu’s literary trilogy. But is it a plausible solution to the Fermi paradox? Of all the posited answers, experts say the Dark Forest hypothesis seems less likely to be correct.
It’s possible that several extraterrestrial intelligences, or ETIs, would conceal themselves. But it’s improbable that all of them will come to the same fear-based conclusion and hide away.
( In the hunt for alien life, this planet just became a top suspect .)
“We don’t even see that same behavior on cultures here on Earth,” says Moiya McTier , an astrophysicist, author, and folklorist. Some ETIs might have members that all act in perfect unison. But others will have divergent, independently behaving groups—some who trend more toward aggression or pacifism, curiosity, or reclusiveness. If one of them waves hello, then that Dark Forest will get a brightly lit campfire for us to see.
For Hungry Minds
But technically anything is possible considering we don’t have any evidence for ETIs to begin with. Perhaps everyone really is hiding. Maybe there truly is a threat lurking out there, somewhere in the dark. And maybe humanity just hasn’t realized it yet.
The case for the Dark Forest theory
The Fermi Paradox was casually raised by physicist Enrico Fermi during a lunchtime chat way back in 1950. It has many nuances, but at its heart is this central premise: Our solar system is just 4.6 billion years old, whereas the universe is 13.8 billion years old. That is plenty of time for life on other planets to develop into technologically advanced societies, those that could set forth across the sea of stars and create outposts or new societies on countless worlds.
But we have yet to find any sign of these societies. So where is everybody?
“There are so many possible overlapping solutions to the Fermi paradox,” says McTier. Is space simply too vast for alien societies to have reached Earth yet? Do all of them destroy themselves before becoming interstellar? Are we the only technologically advanced society in our corner of the cosmos? Is the evolution of life vanishingly rare?
( This man launched the quest to find alien intelligence. It changed astronomy .)
“All the Fermi paradox tells you is that civilizations are rare. It doesn’t tell you why they’re rare,” says Ian Crawford , a planetary scientist and astrobiologist at Birkbeck, University of London. “One of the solutions is: yeah, they’re all out there, but they’re all hiding. If they give themselves away, someone will come and destroy them.”
The idea that these spacefaring aliens are simply reluctant to reveal themselves has featured in sci-fi storytelling for many decades . Liu, in his 2008 book, gave the hypothesis a catchy name. He describes the universe as a dark forest , wherein each alien society is like a fearful, armed hunter gingerly moving forth. If that hunter finds “other life—another hunter, an angel or a demon, a delicate infant or a tottering old man, a fairy or a demigod—there’s only one thing he can do: open fire and eliminate them. In this forest, hell is other people.”
Being fearful has its evolutionary benefits: We may flinch at a strange noise in the night, and although most of the time it’s harmless, our caution may save our lives the one time it’s coming from a genuine threat.
“It can’t be denied that there is some survival value in being aggressive,” Seth Shostak , a senior astronomer at the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Institute in California. Preemptively take out the competition, and you may sleep more securely while getting extra resources. The history of humanity—and its present—is littered with grim examples of this.

The case against the Dark Forest theory
Thankfully, the Dark Forest has a plethora of issues that are difficult to resolve—the most obvious being that it’s extremely difficult to conceal a technologically advanced world.
You May Also Like

The 11 most astonishing scientific discoveries of 2023

This supermassive black hole was formed when the universe was a toddler

How fast is the universe really expanding? The mystery deepens.
Long before actively searching for ETIs became a global scientific practice , radio signals from Earth’s quotidian intraspecies communications have been emanating into the void—something that a nearby alien society hoping to find a new ally, or fresh target, could handily spot.
( How many alien civilizations are out there? A galactic survey holds a clue .)
Even as we’ve begun to grasp the hypothetical threat, it's not like we’re about to go completely silent, either. “We’ve never given the slightest thought to turning off all the radars because it might be dangerous,” says Shostak. “It’s just not gonna happen.”
Even if an ETI tried to conceal itself, it may not be sophisticated enough to work. Some alien societies may have found a way to stamp out all their noise, but others may be accidentally still giving the game away without realizing. “The way cavemen might hide is quite different from the way Klingons might hide,” says Shostak.
The forest analogy also falls apart when you consider the true nature of the universe—or simply our own ginormous galaxy. The woods can seem huge and endless in the dark, but that’s peanuts compared to space.
“There may be hostile aliens out there,” says Shostak. But the distances between them are likely to be unfathomably vast, so much so that the idea they would feel the need to preemptively attack one another seems odd. Even if they feared each other, the expanse between them means that they wouldn’t likely need to compete for resources; each would have near-limitless worlds, asteroids, and even stars to exploit.
The fact that Earth is, by universal standards, a young, noisy, and vulnerable technological society, also by default implies that—if there are ETIs out there—then they cannot all be instinctively aggressive.
“If there are so many civilizations, and some of them could destroy us, then we have to explain how that has not happened,” says Karim Jebari , a researcher at the Institute for Futures Studies in Stockholm, Sweden. “Maybe there’s a Galactic Empire that keeps the hostilities down, or maybe it's really difficult… to attack each other over interstellar distances.”
( What we know from decades of UFO government investigations .)
Or, as Jebari has suggested in a recent paper , ETIs have reached the same logical conclusion: that they still exist because other advanced alien societies have chosen not to smite them, perhaps hoping instead to have a mutually beneficial conversation. “We have no reason to attack them in a preemptive strike,” says Jebari. “If they’re smart… maybe they’re thinking the same thing about us.”
That all ETIs would share the very human instinct of assuming the worst about an unknown entity is also a massive presumption.
“For me, [the Dark Forest] is one of the less compelling explanations for the Fermi paradox, because it relies on a few anthropocentric assumptions that I don’t think are fair,” says McTier. Fear is a powerful thing. But so is curiosity.
The nightmare scenario
That doesn’t necessarily mean that the Dark Forest hypothesis is a nonstarter. The problem is that addressing the holes in the theory requires amping up the terror factor.
“The nightmare scenario is that suppose those that are hiding are right,” says Crawford. “Suppose that, sometime in the history of the galaxy, a technological civilization… decided that whenever planets with life or technology were found, they were going to destroy it.”
In other words, if extermination for extermination’s sake was the goal, then the Dark Forest seems more plausible. “If something like that has been going on in the history of the galaxy, then yes it would explain the Fermi paradox,” Crawford says.
So sure, maybe our corner of the cosmos is quiet because life getting started in the first place is an extreme rarity. Perhaps it’s lonely out here because alien societies have a bad habit of annihilating themselves once they discover something like atomic weapons.
Or, just maybe, “we don’t see them because they’re not there,” says Crawford—because a slaughtering entity is going from star to star extinguishing any sign of life. “That’s the really scary thing.”
Related Topics
- EXTRATERRESTRIAL LIFE
- ASTROPHYSICS

The world’s most powerful telescope is rewriting the story of space and time
This is what the first stars looked like as they were being born

Here's how astronomers found one of the rarest phenomenons in space

Saturn’s ‘Death Star’ moon was hiding a secret: an underground ocean

What is the multiverse—and is there any evidence it really exists?
- Paid Content
- Environment
- Photography
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History Magazine
- History & Culture
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Royal Society - On the scope of scientific hypotheses (Apr. 24, 2024) scientific hypothesis, an idea that proposes a tentative explanation about a phenomenon or a narrow set of phenomena observed in the natural world. The two primary features of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability and testability, which are reflected in an "If ...
A scientific hypothesis is a tentative, testable explanation for a phenomenon in the natural world. It's the initial building block in the scientific method. Many describe it as an "educated guess ...
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for an observation. The definition depends on the subject. In science, a hypothesis is part of the scientific method. It is a prediction or explanation that is tested by an experiment. Observations and experiments may disprove a scientific hypothesis, but can never entirely prove one.
The scientific method. At the core of biology and other sciences lies a problem-solving approach called the scientific method. The scientific method has five basic steps, plus one feedback step: Make an observation. Ask a question. Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation. Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
A hypothesis is a supposition or tentative explanation for (a group of) phenomena, (a set of) facts, or a scientific inquiry that may be tested, verified or answered by further investigation or methodological experiment. It is like a scientific guess. It's an idea or prediction that scientists make before they do experiments.
Meaning. Biology. The study of living things. Observation. Noticing and describing events in an orderly way. Hypothesis. A scientific explanation that can be tested through experimentation or observation. Controlled experiment. An experiment in which only one variable is changed.
The scientific method can be applied to almost all fields of study as a logical, rational, problem-solving method. Figure 1.3.1 1.3. 1: Sir Francis Bacon: Sir Francis Bacon (1561-1626) is credited with being the first to define the scientific method. The scientific process typically starts with an observation (often a problem to be solved ...
Words have precise meanings in science. For example, "theory," "law," and "hypothesis" don't all mean the same thing. Outside of science, you might say something is "just a theory," meaning it's a supposition that may or may not be true. In science, however, a theory is an explanation that generally is accepted to be true.
2. The scientific hypothesis. In this section, we will describe a functional and descriptive role regarding how scientists use hypotheses. Jeong & Kwon [] investigated and summarized the different uses the concept of 'hypothesis' had in philosophical and scientific texts.They identified five meanings: assumption, tentative explanation, tentative cause, tentative law, and prediction.
The hypothesis of Andreas Cellarius, showing the planetary motions in eccentric and epicyclical orbits.. A hypothesis (pl.: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon.For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained ...
Hypothesis Versus Theory . Although in common usage the terms hypothesis and theory are used interchangeably, the two words mean something different from each other in science. Like a hypothesis, a theory is testable and may be used to make predictions. However, a theory has been tested using the scientific method many times.
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process. Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test ...
A hypothesis proposes a relationship between the independent and dependent variable. A hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a test. It forms the basis for designing an experiment in the scientific method.A good hypothesis is testable, meaning it makes a prediction you can check with observation or experimentation.
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
This section of Life publishes papers that present new ideas about fundamental aspects of biology. Manuscripts must propose a solution to a particularly important problem or suggest an idea that is broadly relevant to the life sciences. Examples include evolution of cellular or metabolic functions, extreme conditions and the limits of life, and ...
First, we give a general definition and properties of a hypothesis. In a nutshell, a hypothesis is an explanation of an event or a phenomenon. Hypotheses are mainly expressed in words, but they may also be expressed in mathematical formulas, figures, algorithms, or programs, which can be processed formally.
The scientific method is the basic skill process in the world of science. Since the beginning of time humans have been curious as to why and how things happen in the world around us. The scientific method provides scientists with a well structured scientific platform to help find the answers to their questions.
Like geology, physics, and chemistry, biology is a science that gathers knowledge about the natural world. Specifically, biology is the study of life. The discoveries of biology are made by a community of researchers who work individually and together using agreed-on methods. In this sense, biology, like all sciences is a social enterprise like ...
A hypothesis is a tentative, testable answer to a scientific question. Once a scientist has a scientific question she is interested in, the scientist reads up to find out what is already known on the topic. Then she uses that information to form a tentative answer to her scientific question. Sometimes people refer to the tentative answer as "an ...
Quick Reference. A statement of the expected relationship between things being studied, which is intended to explain certain facts or observations. An idea to be tested. From: hypothesis in A Dictionary of Environment and Conservation ». Subjects: Science and technology — Life Sciences.
Here are examples of a scientific hypothesis. Although you could state a scientific hypothesis in various ways, most hypotheses are either "If, then" statements or forms of the null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is sometimes called the "no difference" hypothesis. The null hypothesis is good for experimentation because it's simple to disprove.
In science work, we make guesses called hypotheses to try and figure out what will happen in tests or watching. These are not sure things but rather ideas that can be proved or disproved based on real-life proofs. A good theory is clear and can be tested and found wrong if the proof doesn't support it. Hypothesis Meaning
Our objective here is to test the null hypothesis that the population means are equal against the alternative hypothesis that means are not equal, as described in the …. \ (Y_i = X_ {1i}-X_ {2i}\) and \ (\mu_Y = \mu_1-\mu_2\) Testing the null hypothesis for the equality of the …. 13.3. Test for Relationship Between Canonical Variate Pairs.
(In the hunt for alien life, ... That doesn't necessarily mean that the Dark Forest hypothesis is a nonstarter. The problem is that addressing the holes in the theory requires amping up the ...
Calculation Example: There are six steps you would follow in hypothesis testing: Formulate the null and alternative hypotheses in three different ways: H0: θ = θ0 versus H1: θ ≠ θ0. H0: θ ≤ θ0 versus H1: θ > θ0. H0: θ ≥ θ0 versus H1: θ < θ0.