
- Ask a Librarian

Civics Literacy Study & Resource Guide
- Introduction
- Civic Life, Politics, and Government
- Foundations of American Political System
- Constitution and American Democracy
- Citizenship and Participation
Voting and Elections
Researching issues and candidates, other forms of civic participation.
- Individuals & Events in U.S. History
Other Relevant Guides
- American Studies by J.P. Herubel Last Updated Apr 1, 2024 121 views this year
- Indiana Government by Bert Chapman Last Updated Feb 26, 2024 192 views this year
The Role of Citizens in American Democracy
U.s. constitution.
The U.S. Constitution includes amendments regarding citizenship and participation of citizens in politics. Some examples include:
- Granted citizenship to “all persons born or naturalized in the United States." In addition, it forbids states from denying any person "life, liberty or property, without due process of law" or to "deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.” (From the Library of Congress )
- Granted African American men the right to vote by declaring that the "right of citizens of the United States to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any state on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude." Although ratified on February 3, 1870, the promise of the 15th Amendment would not be fully realized for almost a century. Through the use of poll taxes, literacy tests and other means, Southern states were able to effectively disenfranchise African Americans. It would take the passage of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 before the majority of African Americans in the South were registered to vote. (From the Library of Congress )
- Passed by Congress June 4, 1919, and ratified on August 18, 1920, the 19th amendment guarantees all American women the right to vote. Achieving this milestone required a lengthy and difficult struggle; victory took decades of agitation and protest. Beginning in the mid-19th century, several generations of woman suffrage supporters lectured, wrote, marched, lobbied, and practiced civil disobedience to achieve what many Americans considered a radical change of the Constitution. ( From the National Archives )
- Passed by Congress March 23, 1971, and ratified July 1, 1971, the 26th amendment granted the right to vote to American citizens aged eighteen or older. (From the National Archives )
In the American Democracy, citizens are granted the right to vote for elected representatives in government positions. You can learn more about voting through the following resources:
- Can I Vote (NASS) This nonpartisan website was created by state election officials to help eligible voters figure out how and where to go vote.
- Fair Elections Center Fair Elections Center is a national, nonpartisan voting rights and election reform 501(c)(3) organization with the mission of using litigation and advocacy to remove barriers to registration and voting, particularly those disenfranchising underrepresented and marginalized communities, and to improve election administration.
- Federal Voting Assistance Project Absentee voting assistance and verification for servicemembers & their families and overseas citizens. Plus, links to state/territory-specific election & legislative websites.
- How To Vote How to Vote is your guide to everything you need to know to register and vote in your state. If you have a question about participating in elections, you’ll find the answer here.
- Indiana State Voting Requirements Courtesy of Indiana Secretary of State Elections Division
- State and Local Election Search (USA.gov) Locate your state’s election office website for state-wide voting guidance.
- VoteRiders VoteRiders offers free assistance for any eligible voter who encounters barriers to securing his or her ID to vote, including financial and legal help obtaining underlying documents like birth certificates, change of name documentation, etc.
- Voting & Elections Toolkits Voting and election reference guide for each state provided by GODORT.
- Voting and Elections (USA.gov) Information on where to register, finding state and local elections, and voting and election laws.
Library Resources
- CQ Researcher CQ Researcher explores a single, current issue in the news each week on topics ranging from social issues to environment, health, education, science and technology. Each 12,000-word report features comments from experts, lawmakers and citizens on all sides of the issue. Charts, graphs, a pro-con feature, chronology, bibliographies and a list of contacts complete each report. more... less... Forty-four reports are produced each year, with four expanded reports. Each 12,000-word report features comments from experts, lawmakers and citizens on all sides of the issue. Charts, graphs, a pro-con feature, chronology, bibliographies and a list of contacts complete each report.
- News, Policy & Politics Magazine Archive (feat. Newsweek) This link opens in a new window An archival collection comprising the backfiles of 15 major magazines (including the Newsweek archive), spanning areas including current events, international relations, and public policy. These titles offer multiple perspectives on the contemporary contexts of the major events, trends, and interests in these fields throughout the twentieth century. The collection will provide valuable primary source content for researchers in fields ranging from history and political science, through to law and economics. more... less... Note: Due to the rarity of some of the original print volumes, there are small gaps (issues or pages) in the runs of some publications.
- ProQuest Congressional Publications Provides access to historic and recent U.S. Government publications from 1789-1969 on including U.S. Congressional Serial Set documents, federal agency reports, congressional committee publications including reports on legislation, statistics, maps, and congressional debates. Coverage includes Congressional Record and predecessor publication debates from 1789-1997 and Executive branch agency publications not included in the U.S. Congressional Serial Set from 1789-1932.
- Political Extremism & Radicalism This link opens in a new window Provides primary source material on far-right and fascist movements as well as radical left groups in one resource . Explores the origins and development of present-day issues, including the resurgence of right-wing politics, evolution of various civil rights movements and the nature of extreme or radical political thought.
Voter Guides
- AARP Government & Elections Guide Includes news & analysis, political issues, and other information on government and elections.
- I Side With... Offers quizzes to help match citizens with potential candidates based on their beliefs. Also includes information on popular issues, data, candidates, and more.
- Voting Information Tool This website is an initiative of the Voting Information Project (VIP), a partnership between state election officials and Democracy Works to connect voters with the election information they need to cast a ballot. Launched in 2008, VIP works with state and local election officials to provide official and up-to-date election information.
Research Tools
- Political Issues by Topic (Pew Research Center) Browse reports and articles by political issue. Provided by the Pew Research Center.
- PolitiFact Truth-O-Meter PolitiFact's evaluates political information from transcripts, speeches, news stories, press releases, campaign brochures, TV, social media, and emailed requests. The evaluated content also includes a list of sources with every fact-check.
- FactCheck.org A nonpartisan, nonprofit “consumer advocate” for voters that aims to reduce the level of deception and confusion in U.S. politics.
- Washington Post Fact Checker The purpose of this website, and an accompanying column in the Sunday print edition of The Washington Post, is to “truth squad” the statements of political figures regarding issues of great importance, be they national, international or local (excerpt from website).
- C-SPAN Video Archives The C-SPAN Archives contains over 270,000 hours of C-SPAN programming and are located in the Purdue Research Park next to Purdue University. The Archives represents a record of over thirty years of our nation’s political history. Details on the API can be found under the mycspan tab at the top of c-span.org for individuals who create an account. Use Chrome browser for best results.
- Congressional Research Service (CRS) The Library of Congress' Congressional Research Service (CRS) presents unbiased reports on various public policy issues for members of Congress, their staff, and the American public.
Volunteerism
Form of civic action and commitment that demonstrates a willingness to make positive contributions to society. The following provides resources for how to get involved in Indiana and Tippecanoe County.
- Indiana Volunteer Centers Directory of volunteer centers in Indiana by county.
- Serve Indiana (IN.gov) Serve Indiana is a division of the Department of Workforce Development for the State of Indiana. The mission of Serve Indiana is to advance service and volunteerism by informing, connecting, and promoting opportunities and resources that enrich the lives of Hoosiers.
- State Emergency Registry of Volunteers for Indiana SERV-IN is a statewide electronic registration system of medical and non-medical volunteers who want to assist our public health and healthcare system during an event or disaster.
- Volunteer.gov America’s Natural and Cultural Resources Volunteer Portal was built and is maintained by the Federal Interagency Team on Volunteerism (FITV) that is comprised of volunteer program coordinators from three Cabinet level departments.
- Volunteer Engagement Center (United Way) Browse local volunteer opportunities within the greater Lafayette area.
- VolunteerMatch Database of virtual and on location volunteer opportunities. Searchable by cause areas, skills, keyword, and more.
- Inspired to Serve: Report of the National Commission on Military, National, and Public Service 2020 report by congressionally authorized commission.
Back to Introduction
- << Previous: Constitution and American Democracy
- Next: Individuals & Events in U.S. History >>
- Last Edited: May 23, 2024 11:54 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.purdue.edu/civicsliteracy
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
9. The responsibilities of citizenship
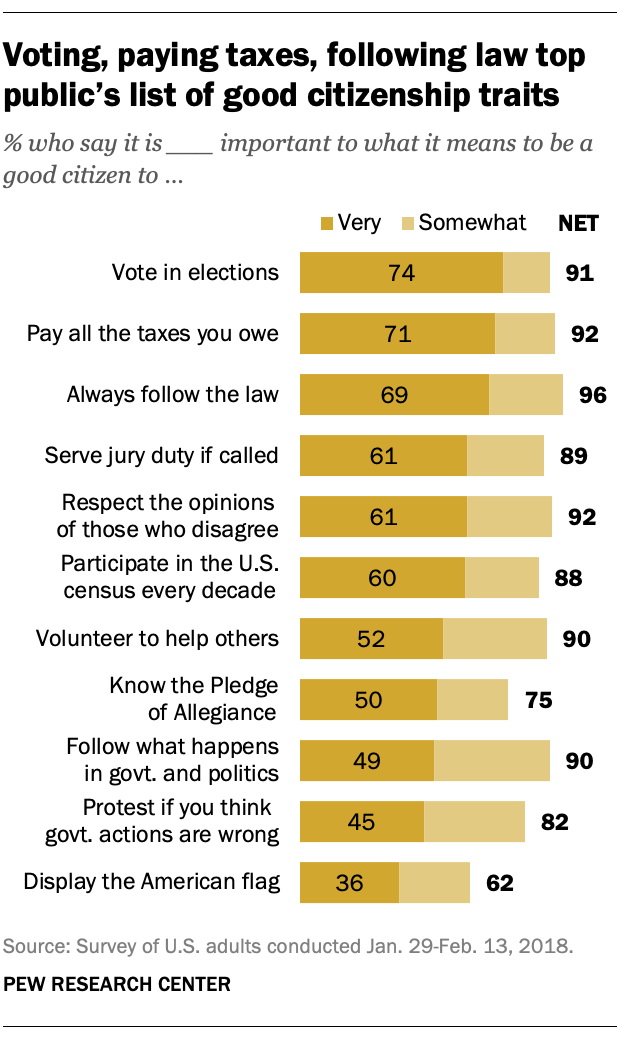
When it comes to what it takes to be a good citizen, the public has a long list of traits and behaviors that it says are important. And there’s a fair amount of agreement across groups about what it takes to be a good citizen.
Still, there are differences when it comes to which aspects are considered very important (as opposed to somewhat important), and points of emphasis differ by party identification as well as by age.
Overall, 91% say it is either very (74%) or somewhat (17%) important to vote in elections in order to be a good citizen; just 8% say this is not too or not at all important.
Large shares also say it is important to pay all the taxes you owe (92%) and to always follow the law (96%), including about seven-in-ten who say each is very important (71% and 69%, respectively).
For several other traits and behaviors, about nine-in-ten say they are at least somewhat important to good citizenship. However, the share saying each is very important varies significantly. For example, 89% say it’s important to serve jury duty if called, including 61% who say this is very important. While a comparable 90% say it’s important to follow what’s happening in government and politics as part of good citizenship, a smaller share (49%) says this very important.
Protesting government actions you think are wrong and knowing the Pledge of Allegiance are considered important parts of what it means to be a good citizen, though they rank somewhat lower on the public’s list. Displaying the American flag ranks last among the 11 items tested in the survey. Still, a majority says this is either a very (36%) or somewhat (26%) important part of what it means to be a good citizen.
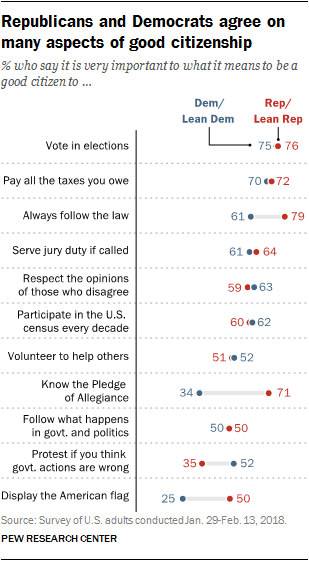
Republicans and Democrats largely agree on the importance of most responsibilities of citizenship.
About three-quarters of Republicans and Republican leaners (76%) and Democrats and Democratic leaners (75%) say it’s very important to vote in elections.
Similarly, comparable majorities of Republicans and Democrats say it’s very important to pay all the taxes you owe, serve jury duty if called, respect the opinions of those you disagree with and participate in the census. There also are no partisan divides over the importance of volunteering to help others and following what’s going on in government and politics.
However, Republicans (79%) are more likely than Democrats (61%) to say it’s very important to always follow the law to be a good citizen.
Knowing the Pledge of Allegiance ranks higher on Republicans’ list (71% say it’s very important) than Democrats’ (just 34% say it’s very important). In addition to placing greater importance on the Pledge of Allegiance, Republicans are twice as likely as Democrats to say it is very important to display the American flag (50% vs. 25%).
By contrast, Democrats are more likely than Republicans to think it is very important to protest if government actions are believed to be wrong: About half of Democrats (52%) this is very important to what it means to be a good citizen, compared with just about a third (35%) of Republicans.
Partisans and ‘leaners’ differ over importance of aspects of citizenship
On many items, the views of independents that lean toward one of the two major parties diverge from those of self-identifying Republicans and Democrats. In general, partisan leaners tend to be less likely than straight Republicans and Democrats to view a range of responsibilities as important to what it means to be a good citizen.
Overall, 83% of Republicans say voting in elections is a very important aspect of being a good citizen, compared with a smaller majority of Republican leaners (67%). There is an even wider 28-point gap between the share of Democrats (86%) and Democratic leaners (58%) who say this is very important.
Similarly, roughly two-thirds of both Republicans (64%) and Democrats (68%) say participating in the U.S. census every 10 years is very important to being a good citizen; slightly fewer Republican leaners (55%) and Democratic leaners (53%) say the same.
This pattern is seen across other items as well: Those who identify with a party are more likely than independents who lean to a party to say it is very important to serve jury duty if called, pay all owed taxes and to follow what is happening in government.
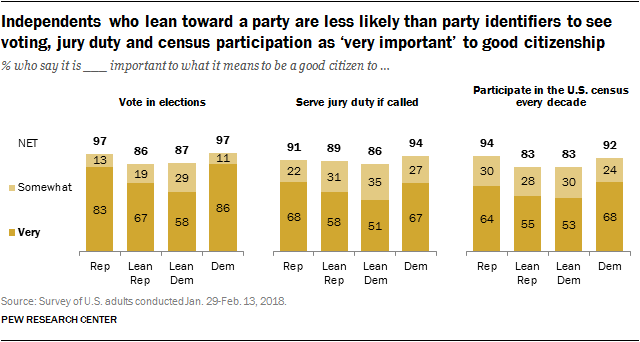
While large shares of Republicans (96%) and Republican leaners (87%) say it is important to know the Pledge of Allegiance, Republican identifiers are somewhat more likely than leaners to say this is very important to good citizenship.
By comparison, smaller majorities of Democrats (67%) and Democratic leaners (60%) say it’s important to know the pledge. Self-identifying Democrats (42%) are significantly more likely to say knowing the pledge is a very important part of good citizenship than Democratic leaners (24%).
There is a 22-point gap between the share of Republicans (90%) and Republican leaners (68%) who say displaying the American flag is at least somewhat important to being a good citizen. And 63% of Republicans call this very important, compared with 35% of Republican leaners. About half of Democrats (52%) think this is a very or somewhat important aspect of good citizenship; 43% of Democratic leaners say the same.
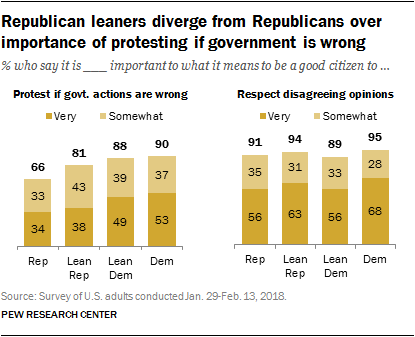
In contrast to the patterns seen on many items, Republican leaners (81%) are more likely than Republicans (66%) to say protesting government actions you think are wrong is an important part of being a good citizen. The views of Republican leaners place them closer to those of Democrats and Democratic leaners in terms of the overall importance they place on this aspect of citizenship.
Age differences in views of the responsibilities of citizenship
Young adults place less importance on many aspects of citizenship than older adults, especially when it comes to the share that describes a trait or behavior as very important for being a good citizen.
Majorities of adults across all ages say it is very important to vote in elections in order to be a good citizen. Still, a smaller majority of those under 30 say this (56%), compared with larger shares of those ages 30 to 49 (72%), 50 to 64 (76%) and 65 and older (92%).
And while fully 81% of those 65 and older say that to be a good citizen it is very important to serve jury duty if called, just about half (47%) of those under 30 say the same.
On other items, the pattern is similar. Young adults are less likely to call paying the taxes you owe, following the law, participating in the census, and following government and politics very important. Still, large majorities of young adults say each of these is at least somewhat important to being a good citizen.
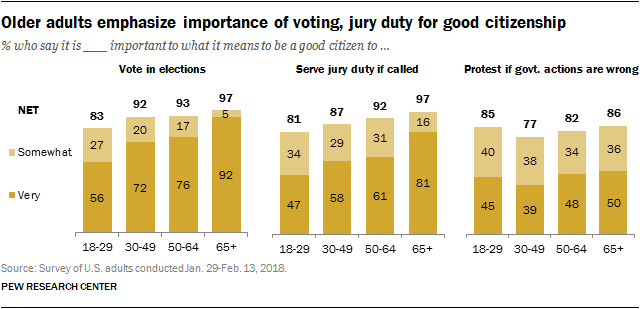
There is no meaningful age gap in views of the importance of protesting government actions you think are wrong. Overall, 85% of those ages 18 to 29 say this is either very (45%) or somewhat (40%) important to being a good citizen. Views among those ages 65 and older are similar (50% very important, 36% somewhat important).
Displaying the American flag and knowing the Pledge of Allegiance do not rank particularly highly for young adults on their list of important characteristics for good citizenship. Among those ages 18 to 29, 63% say it is important to know the Pledge of Allegiance (38% very important) and 53% say it is important to display the American flag (19% very important). These items do not top the list of older adults either, though those 65 and older are more likely than the youngest adults to say both are important parts of being a good citizen.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
Most Popular
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Why Voting Is Important
“Voting is your civic duty.” This is a pretty common sentiment, especially each November as Election Day approaches. But what does it really mean? And what does it mean for Americans in particular?
Social Studies, Civics, U.S. History
Americans Voting
Typically in the United States, national elections draw large numbers of voters compared to local elections.
Hill Street Studios

A History of Voting in the United States Today, most American citizens over the age of 18 are entitled to vote in federal and state elections , but voting was not always a default right for all Americans. The United States Constitution, as originally written, did not define specifically who could or could not vote—but it did establish how the new country would vote. Article 1 of the Constitution determined that members of the Senate and House of Representatives would both be elected directly by popular vote . The president, however, would be elected not by direct vote, but rather by the Electoral College . The Electoral College assigns a number of representative votes per state, typically based on the state’s population. This indirect election method was seen as a balance between the popular vote and using a state’s representatives in Congress to elect a president. Because the Constitution did not specifically say who could vote, this question was largely left to the states into the 1800s. In most cases, landowning white men were eligible to vote, while white women, black people, and other disadvantaged groups of the time were excluded from voting (known as disenfranchisement ).
While no longer explicitly excluded, voter suppression is a problem in many parts of the country. Some politicians try to win re election by making it harder for certain populations and demographics to vote. These politicians may use strategies such as reducing polling locations in predominantly African American or Lantinx neighborhoods, or only having polling stations open during business hours, when many disenfranchised populations are working and unable to take time off. It was not until the 15th Amendment was passed in 1869 that black men were allowed to vote. But even so, many would-be voters faced artificial hurdles like poll taxes , literacy tests, and other measures meant to discourage them from exercising their voting right. This would continue until the 24th Amendment in 1964, which eliminated the poll tax , and the Voting Rights Act of 1965, which ended Jim Crow laws. Women were denied the right to vote until 1920, when the long efforts of the women’s suffrage movement resulted in the 19th Amendment. With these amendments removing the previous barriers to voting (particularly sex and race), theoretically all American citizens over the age of 21 could vote by the mid 1960s. Later, in 1971, the American voting age was lowered to 18, building on the idea that if a person was old enough to serve their country in the military, they should be allowed to vote. With these constitutional amendments and legislation like the Voting Rights Act of 1965, the struggle for widespread voting rights evolved from the Founding Fathers’ era to the late 20th century. Why Your Vote Matters If you ever think that just one vote in a sea of millions cannot make much of a difference, consider some of the closest elections in U.S. history. In 2000, Al Gore narrowly lost the Electoral College vote to George W. Bush. The election came down to a recount in Florida, where Bush had won the popular vote by such a small margin that it triggered an automatic recount and a Supreme Court case ( Bush v. Gore ). In the end, Bush won Florida by 0.009 percent of the votes cast in the state, or 537 votes. Had 600 more pro-Gore voters gone to the polls in Florida that November, there may have been an entirely different president from 2000–2008. More recently, Donald Trump defeated Hillary Clinton in 2016 by securing a close Electoral College win. Although the election did not come down to a handful of votes in one state, Trump’s votes in the Electoral College decided a tight race. Clinton had won the national popular vote by nearly three million votes, but the concentration of Trump voters in key districts in “swing” states like Wisconsin, Pennsylvania, and Michigan helped seal enough electoral votes to win the presidency. Your vote may not directly elect the president, but if your vote joins enough others in your voting district or county, your vote undoubtedly matters when it comes to electoral results. Most states have a “winner take all” system where the popular vote winner gets the state’s electoral votes. There are also local and state elections to consider. While presidential or other national elections usually get a significant voter turnout, local elections are typically decided by a much smaller group of voters. A Portland State University study found that fewer than 15 percent of eligible voters were turning out to vote for mayors, council members, and other local offices. Low turnout means that important local issues are determined by a limited group of voters, making a single vote even more statistically meaningful. How You Can Make Your Voice Heard If you are not yet 18, or are not a U.S. citizen, you can still participate in the election process. You may not be able to walk into a voting booth, but there are things you can do to get involved:
- Be informed! Read up on political issues (both local and national) and figure out where you stand.
- Get out and talk to people. Even if you cannot vote, you can still voice opinions on social media, in your school or local newspaper, or other public forums. You never know who might be listening.
- Volunteer. If you support a particular candidate, you can work on their campaign by participating in phone banks, doing door-to-door outreach, writing postcards, or volunteering at campaign headquarters. Your work can help get candidates elected, even if you are not able to vote yourself.
Participating in elections is one of the key freedoms of American life. Many people in countries around the world do not have the same freedom, nor did many Americans in centuries past. No matter what you believe or whom you support, it is important to exercise your rights.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
October 19, 2023
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
Home — Essay Samples — Government & Politics — Voting — The Importance of Voting for Strengthening Democracy
The Importance of Voting for Strengthening Democracy
- Categories: Voting
About this sample

Words: 630 |
Published: Sep 5, 2023
Words: 630 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Shaping government policies, promoting representation and inclusivity, fostering civic participation, challenges and the importance of overcoming them.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Government & Politics

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1169 words
7 pages / 3200 words
1 pages / 649 words
2 pages / 811 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Voting
Felony disenfranchisement, the practice of restricting voting rights for individuals convicted of felony offenses, has long been a controversial topic in the United States. Supporters argue that felons have forfeited their right [...]
Voter suppression is a contentious issue that strikes at the heart of democratic principles and the right to fair representation. In recent years, concerns about voter suppression tactics have intensified, sparking debates on [...]
In many countries around the world, the voting age is set at 18 years old. This age is seen as a crucial milestone in a person's life, as it marks the transition from adolescence to adulthood. It is also the age at which [...]
In the ever-evolving realm of American politics, the Republican primaries serve as a critical battleground where candidates vie for their party's nomination to run for the presidency. These primaries have seen pivotal moments [...]
The right to vote, often considered the cornerstone of democracy, is a fundamental civic privilege that empowers citizens to participate in shaping their government and society. e began as a nation where rights were restricted [...]
Voting is a fundamental component of any democratic society, as it allows individuals to have a say in the decisions that affect their lives. It is a right that has been fought for and protected by countless individuals [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Essay on Election and Democracy for Students and Children
500 words essay on election and democracy.
A democratic government is said to be the best kind of government. It ensures the active participation of the people where the citizens get the chance to choose their government. The candidate or party whom the people choose is through elections.

Therefore, we see how elections play a pivotal role in a democracy. The party which secures the highest number of votes in the election process forms the government for the next term. That is why we see how elections are greatly crucial for a democracy.
Election Process in a Democracy
The election process in a democracy is usually similar in most ways. It is responsible for shaping the government of a democracy. Elections are conducted at regular intervals. In a democracy like India, they take place every five years. A committee is set to monitor the whole electoral procedure from the voters’ list to the results.
During the election process, various parties enroll themselves to contest in the elections. After thorough campaigning and more, dates are decided on which voting happens. People turn up in great numbers to cast their votes to make their candidate or party win.
Most importantly, in a democracy, the election process follows the method of a secret ballot. It is very beneficial for maintaining the fairness of the contest. Moreover, they also protect the privacy and safety of the voter as they are not liable to answer to anyone regarding their vote. It is one of the fairest ways to decide who wins the election.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Importance of Election in Democracy
The election procedure just shows how important and crucial it is for a democracy. The process is very grand and takes place on a great level. As it requires a lot of work and attention, there are certain people who specifically get the responsibility of handling and managing the entire process.
Elections form the basis of democracy. They are very important as they help the people in getting a chance to contest the elections. It allows people to get a fair chance to work for their country and make a brighter future. Moreover, it also ensures that any person can become a part of the government without any discrimination on the basis of caste, creed, sex, religion or more.
Most importantly, elections entrust a big responsibility on the shoulders of the citizens. It helps in empowering the citizens of a democracy. You see that when a person earns the right to vote, they choose their government responsibly as they realize the power that lies within their hands.
Above all, the election process ensures fair play. They are a great way of preventing dishonest people from rigging the procedure. In short, fair and regular elections are a vital part of a democratic government. Similarly, they empower the common citizens of the nation to elect their government and also change it after a period of time to ensure everyone works for the best in the country.
FAQs on Election and Democracy
Q.1 What is the election process in a democracy?
A.1 The election process takes place at a regular period of time. People cast their vote to whomever they think id serving of being in power. Thus, the party with the majority of votes wins and serves the term.
Q.2 Why are elections important in a democracy?
A.2 Elections form the basis of any democracy. It ensures that the power resides within the people. It also ensures fair play and stops any unfair means from taking place. They are important to strengthen the essence of democracy.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Civics-Online.org
Promoting civics education in America
Four important responsibilities of voters

More Voting Rights :
- Exercising the right to vote is essential to being a good citizen
- Reasons why you should vote
- The right to vote should not be taken for granted
- Voting rights you might not know about
During his presidency, Abraham Lincoln preached the importance of the government being of, for, and by the people. He argued that voters played the most important role in making sure the government reflected their desires and functioned according to the guidelines of the Constitution.
Despite Lincoln’s appeal to the public, it can be argued that many people today fail to appreciate or acknowledge their role in shaping the government. As U.S. citizens, people maintain these four important responsibilities as eligible voters.
Registering to Vote
Most notably, people’s most important responsibility as citizens involves registering to vote. If they are legal U.S. citizens, 18 years of age or older, and have no felony convictions on their record, people are eligible to vote in local, state, and federal elections. Registering to vote can be done online or in person. The process of becoming a registered voter is simple and can be taken care of in a matter of minutes.
Voting in Elections
Once they are registered to vote, people should then make every effort to vote in local, state, and federal elections. Many people dismiss this responsibility by saying that they do not care about the issues on the ballot or that they are unfamiliar with the candidates up for election. However, by failing to use their privilege to vote, people essentially allow other voters to make decisions for them, to let their voices be heard over voters who make no effort go to the polls. This is one of the primary reasons why you need to vote !
The outcomes of elections can impact voters’ personal freedoms, taxes, and other aspects of daily life that they take for granted. Because of the far reaching impact that an election can have, people have the duty to cast their vote if they want a say in how their futures play out.
Casting Absentee Votes
People who have a legitimate reason for not making it to the polls can still cast their vote by requesting an absentee ballot. The ballot can be mailed to them or they can cast an absentee vote in person at their local election office. Despite not being able to vote on Election Day, they can still make sure that their voice is heard and that they make use of their voting privilege.
Updating Personal Information Regularly
State and federal election laws can change at a moment’s notice, so it is important for people to keep their voting information updated as needed. If they move or want to change their party affiliation, for example, they should update this information well before the next election takes place.
They should also stay up-to-date about the location of their polling place. The locations of polling places change regularly. A school, church, or business that was utilized as a polling place during the last election may not be used again for the next. Voters can find out their polling places online or by contacting their local election office.
Voters play a central role in shaping the government and their very futures. They can satisfy their duty as voters by observing these four important responsibilities.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

3.5: The Role of Political Parties
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 127401

- Robert W. Maloy & Torrey Trust
- University of Massachusetts via EdTech Books
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Standard 3.5: The Role of Political Parties
Describe the role of political parties in elections at the state and national levels. (Massachusetts Curriculum Framework for History and Social Studies) [8.T3.5]
FOCUS QUESTION: What are the roles and impacts of political parties in American politics?

Political parties can be defined as " a group of people who share the same ideas about how the government should be run and what it should do " ( League of Women Voters California Education Fund, 2013, para. 2 ).
Mention the term political party and many people think of today's two major parties and their animal symbols—the Democrats' donkey (which first appeared during Andrew Jackson's 1828 Presidential campaign) and the Republicans' elephant (first drawn by political cartoonist Thomas Nast in 1874). You can learn more at " How Did the US Political Parties Get Their Mascots " from Wisconsin Public Radio (November 8, 2016).
For other people, political parties mean sharply different visions for how American society should be organized and they align themselves with the party that matches their viewpoint. The Gallup Poll reports that in 2019, 27% consider themselves Democrats, 26% Republicans, and 46% Independents or not aligned to any party (Gallup, 2019).
Members of a political party work together to win elections and influence the making of public policy. Political parties are much more than promotional symbols or ideological home bases for policy-interested voters. Political parties determine the candidates for President, members of Congress, and many state and local positions. They establish the majority party/minority party organization of Congress. They raise enormous sums of money to support those running in state and local elections. They influence policy through political advocacy and public information campaigns.
What are different ways that political parties function within the nation's political system? The modules for this standard explore that question by examining the evolution of the political party system, the roles of third parties and radical political parties at different times in history, and the question of whether every voter should join a political party.
Modules for this Standard Include:
- INVESTIGATE: The Party System, Political Parties Today, and the 2020 Census
- UNCOVER: Radical Political Parties in United States Politics: Populists, Socialists, and Black Panthers
- MEDIA LITERACY CONNECTIONS: Website Design for New Political Parties
3.5.1 INVESTIGATE: The Party System, Political Parties Today, and the 2020 Census
Political parties have been part of the U.S. political system since the nation's founding, beginning with debates over the federal Constitution of 1787 between the Federalists (led by Alexander Hamilton) and the Anti-Federalists (led by Thomas Jefferson). Party divisions and rivalries have continued ever since, despite George Washington's warning in his Farewell Address on September 19, 1796:
"It [party conflicts] serves always to distract the public councils and enfeeble the public administration. It agitates the community with ill-founded jealousies and false alarms; kindles the animosity [hatred] of one part against another; foments [provokes] occasionally riot and insurrection."
Since just before the Civil War, American politics has been dominated by "two large-tent parties battling for primacy against each other, but often battling themselves" (Tomasky, 2020, p. 60). Evolution of Political Parties in American Politics offers an overview of the party system. This Political Party Timeline Prezi features a historical overview of political parties in American politics.
Political Parties Today
According to Ballotpedia , there were 225 recognized political parties in the United States during the 2020 election.

A recognized political party is an organization that has followed a state's rules for being on an election ballot. The Democratic and Republican Parties appeared on the ballot in all 50 states and the District of Columbia, accounting for 102 of the 225 recognized parties. The Libertarian Party appeared in 35 states, the Green Party in 22 states, and the Constitution Party in 15 states.
The resourcesforhistoryteachers wiki page, The Conservative Movement in American Politics , charts the rise of conservative politics since 1980 and includes material on the Tea Party.
Take a Quiz: If America Had Six Parties, Which Would You Belong To?
The Democrats and the Republicans
Contemporary American politics is dominated by the Democratic and Republican political parties. We often refer to states or Congressional election districts as red (Republican) or blue (Democrat) as a way to characterize how people tend to vote in those places.
Researchers use election data to measure how red or blue a state or district is politically, what is known as partisan lean . A partisan lean is "the average margin difference between how a state or district votes and how the country votes overall" ( FiveThirtyEight , May 27, 2021, para. 3). A score of R+5 or D+5, for example, means that state or district is 5 percentage points more Republican (R) or Democratic (D) than the country as a whole. Following the 2020 elections, the District of Columbia followed by Massachusetts and Hawaii have the largest partisan lean toward the Democrats; Wyoming, North Dakota, Oklahoma, and Idaho have the greatest lean toward Republicans. New Hampshire is the only state that does not lean to either party.
You can explore partisan lean further at the FiveThirtyEight Partisan Lean Metric or the 2021 Cook Political Report Partisan Voter Index .
Fundamental Shifts Among the Parties
Political scientists Mathew Grossman and David H. Hopkins (2016) see fundamental shifts happening to both major parties . Historically, Republicans have been organized around broad symbolic principles whereas Democrats were a coalition of social groups with particular policy concerns. The 2020 election and the impeachments of Donald Trump show both parties being reshaped in ways that are breaking apart those frameworks.
Writing in the The New York Review of Books 2020 Election issue , historian David W. Blight (2020) defines the parties thusly:
Democrats represent a coalition held together loosely by an ideology of inclusion, a commitment to active government, faith in humanistic and scientific expertise, and an abhorrence of what they perceive as the monstrous presidency of Donald J. Trump. Republicans, with notable defections, are a party held together by a commitment to tax reduction, corporate power, anti-abortion, white nationalism, and the sheer will for power. (para. 2)
Assessing the changes in U.S. political parties following the 2016 Presidential election, Jacob S. Hacker and Paul Pierson (2020) see the Republican Party as a mix of big-money corporate elites and socially conservative white working-class voters who have partly adopted policies of "plutocratic populism," including corporate tax cuts and government deregulation along with efforts to curb and eliminate health care and social safety net programs directed toward women and people of color. Ironically, in the 2016 Presidential election, the votes of people in rural, predominantly white lower-income counties across the nation, which have fewer doctors, fewer healthcare resources, and higher rates of obesity and diabetes, shifted to a Republican candidate whose policies would not respond to those health needs (Wasfy, Stewart & Bhamahani, 2017).
Historian Heather Cox Richardson, in her ongoing series Letters from an American , has been tracking the profound disagreements between the Republicans and the Democrats over the role of government in American society. Since the 1980s, a wing of the Republican Party has sought to return to the business-dominated policies of the early 20th century before the Great Depression and the subsequent expansion of the federal government during the New Deal. In that Republican vision, business groups control the government, scaling down or eliminating entirely social and environmental regulations, infrastructure spending, social safety nets, and federal efforts to ensure equality for all. Democrats reject those policies, supporting an activist federal government to support efforts against racial injustice, climate change, and poverty while seeking to expand social services and educational opportunities for low-income and diverse Americans.
During the 2016 and 2020 elections, the business wing of Republican Party supported and enabled the Trump wing of the party, but following the 2020 election and the subsequent attack on the Capitol by an organized group of insurrectionists, the Trump wing has risen to dominance. The Republican Choice by Clare Malone (2020) offers a thoughtful review of the recent history of the Republican Party, its Southern Strategy used to attract white voters, and the impacts of the Trump Presidency.
Political Parties and Political Polarization
In their book Polarized America , three political scientists contend that since a mid-twentieth century period of ongoing compromise and collaboration between Republicans and Democrats, the "parties have deserted the center of the dance for the wings" (McCarty, Poole, & Rosenthal, 2016, p. 2). The result is a growing gap between the parties and their members known as political polarization.
In political polarization, members of political parties move away from each other toward ideological extremes, making it harder and harder to reach compromise on public policy issues. This results in legislative gridlock, where Congress and even some state legislatures are unable to reach agreement on how to respond to social and economic problems. To learn more, go to Explainer: Political Polarization in the United States from Facing History and Ourselves (2020).
In the view of some researchers, increased political polarization is directly connected to growing economic inequality. Those with economic resources and political power take whatever steps they can to maintain their position and status; those without oppose these steps. Compromise is harder to achieve; politics becomes increasingly more divisive; and " c onservative and liberal have become almost perfect synonyms for Republican and Democrat " (McCarty, Poole, & Rosenthal, 2016, p. 4).
Interestingly, the messages that political parties offer voters can serve to deepen political polarization. Most Americans tend to agree on society's problems and how to solve them. For example, they want to prohibit workplace discrimination, create racial equity, fight climate change, and wear masks to curb the pandemic. But, as two political scientists found, when politicians frame these issues as a matter of partisan politics, then people's positions polarize into separate camps (Gadarian & Albertson, 2014).
Gerrymandering and Electoral Redistricting
Gerrymandering is the practice of redrawing legislative district lines in order to help one political party win elections and maintain political control. It is a fundamentally undemocratic process, since its intent is to institutionalize political power and make it harder for voters to create change.
The practice goes back to the early days of the republic when Massachusetts governor Elbridge Gerry (who was also the nation's fifth Vice President) had the state legislature create voting districts to favor the candidates of the incumbent Democratic-Republican party over the Federalists in the 1812 election. Political parties have been seeking to dilute the voting power of the other party by redrawing districts to ensure that their party holds a majority ever since.
By law, under the Constitution, state legislatures must divide their state into voting districts every ten years, following the results of the U.S. Census. The goal is for voting districts to reflect population changes while maintaining the principle of " one person, one vote ."
Under one person, one vote, each person's vote should count essentially the same as the next person's. Since those who are elected represent "people, not trees" (that is, actual people who live in a place rather than the geographic size of a region), each state voting district is supposed to have an equal share of the state's population. But election mapmakers can manipulate the shape of those districts to favor one party over another.
Our country's winner-take-all election system, where 51% of the voters get 100% of the representation, encourages gerrymandering (Gerrymandering, Fair Vote). Politicians can readjust the size of voting districts, often along racial and ethnic lines, so that one party is essentially ensured of winning most elections. Racial Gerrymandering in North Carolina offers a case study on how politicians in that state exploited redistricting to influence the outcome of elections.
Redistricting the Nation offers another view of how political districts were redrawn in Pennsylvania, North Carolina, and Arizona, along with ideas for how citizens might go about creating their own districts to more fairly represent their interests.
To draw your own Fair Election Districts, visit GeoCivics from the University of Colorado Colorado Springs.
The 2020 Census and Congressional Redistricting
The release of the 2020 Census data in August 2021 showed dramatic changes in the society of the U.S. Within a total population growing at the slowest rate in nearly a century, people identifying as Hispanic, Asian, or more than one race increased while the total number of white people fell for the first time. Population diversity rose in nearly every county in the nation (The Morning Newsletter: A Changing Country, New York Time s, August 13, 2021).
All of the ten largest cities increased their population from 2010; Phoenix was the fastest-growing city. New York City grew by 8% as well. The fastest-growing metropolitan area was The Villages - the nation's largest retirement community, located just outside Orlando, Florida.
Population changes have huge political implications, since states must redraw their Congressional districts every 10 years to determine apportionment of the 435 seats in the House of Representatives. The latest Census data shows declines, in some cases larger than expected, in rural and white population groups and areas that traditionally vote for Republicans, and increases in cities and suburbs that vote largely for Democrats. At the same time, Republican-controlled legislatures will decide 187 new district maps while Democrats decide 84.
You can go to Topic 3.3 INVESTIGATE to learn more about the House of Representatives.
You can follow what redistricting looks like in every state with an interactive from the FiveThirtyEight blog.
History of Third Parties in American Politics
In addition to the Democratic and Republican parties, short-term third parties have influenced public policy debates as well as the outcomes of national and state elections. Historically, third parties arise around a major issue of interest that attracts support from voters. In the election of 1860, the Republican party candidate Abraham Lincoln, who opposed expansion of slavery into new territories, defeated candidates from the Democrat, Southern Democrat, and Constitutional Union parties. Following Lincoln's election, southern states seceded from the Union and the Civil War began.
The Progressive, or Bull Moose Party , led by former President Theodore Roosevelt, and the Socialist Party, led by Eugene V. Debs, were among the most impactful third parties in American history. In 1912, Roosevelt, running as the Bull Moose candidate, won six states and 27% of the popular vote; Debs received nearly one million votes in that same election. Other important third parties include the American Independent Party , whose candidate, the segregationist George C. Wallace, won 46 electoral votes and over 9 million popular votes in 1968. In 1980, when Republican Ronald Reagan defeated Democrat Jimmy Carter, independent party candidate John B. Anderson received nearly 7% of the popular vote.
Many observers believe that the 2000 Green Party candidate Ralph Nader, who won nearly 3% of the popular vote, took enough votes away from Democrat Al Gore to enable Republican George W. Bush to win the Presidency. In 2016, when Donald Trump lost the popular vote but defeated Hillary Clinton in the electoral college, third-party candidates received 6% of the total national vote.
Suggested Learning Activities
- Political Parties: Two is Company, Three's a Crowd , PBS Newshour
- Third Parties in the U.S. Political Process from PBS Newshour provides an overview of third parties in American history.
- The Third Party Impact on American Politics , UVA Today , University of Virginia (August 3, 2016)
- Compare and contrast American Political Party Platforms, 1840 to 2008 from the American Presidency Project (includes only parties that received electoral votes)
- Research a major metropolitan area in your state at the site Where Democrats and Republicans Live in Your City ( FiveThirtyEight , May 20, 2019).
- What do you think explained the political party patterns revealed in the data?
- Research the 2020 Election and see if voting patterns have changed or remained the same.
Online Resources for Political Parties
- "What Unites Republicans May Be Changing. Same with Democrats" , FiveThiryEight , December 17, 2019
- Politics and Public Policy , iCivics
- Political Parties Learning Plan that includes a rap song.
3.5.2 UNCOVER: Radical Political Parties in United States Politics: Populists, Socialists, and Black Panthers
The populist party.
The period from the late 1890s through the first two decades of the 20th century saw the rise of radical political parties associated with unions and working people, notably the Populist Party and the Socialist Party . Both sought to represent workers in politics.

This period in United States History was known as the Gilded Age , when expansive growth in industry led to vast inequalities of wealth and power. A class of industrial entrepreneurs alternatively called "captains of industry" or "robber barons" dominated American politics. Many different industries were dominated by a few corporations and people; for example:
- Oil --------------> Standard Oil, John D. Rockefeller
- Steel -----------> Carnegie Steel, Andrew Carnegie
- Railroads ------> Central Pacific Railroad, Cornelius Vanderbilt
- Automobiles --> Ford Motor Company, Henry Ford
In 1860, there were 400 millionaires in the United States; by 1892, there were 4,047. John D. Rockefeller became the nation's first billionaire in 1916. In 2018, there were 11.8 million Americans with a net worth of at least $1 million (Spectrum Group, 2019).
Radical political parties offered a sharp critique of the economic and social class structure. These parties supported changes in laws as well as efforts by labor unions to create change in conditions for workers through strikes and political action ( Labor Unions and Radical Political Parties in the Industrial Era ).
The Black Panther Party
The Black Panther Party for Self-Defense, a militant political organization, was founded in 1966 in Oakland, California by Huey P. Newton and Bobby Seale ( Overview of the Black Panther Party ). Political activism by women was also an important party of the Black Panther Party ( People's Historians Online: Women in the Black Panther Party , Zinn Education Project).

The Panthers set forth a 10-Point Platform for political, economic. and social change that "contained basic demands such as self-determination, decent housing, full employment, education that included African-American history, and an end to police brutality" ( Weise, 2016, para. 20 ). Watch Bobby Seale Speech: The BPP Ten Point Program/Platform.
The Black Panthers are frequently labeled extremists, but the historical reality is quite different ( 27 Important Facts Everyone Should Know About the Black Panthers ). Learn more the Black Panthers at the resourcesforhistoryteachers wiki page about the Accomplishments of the Civil Rights Movement .
Public interest in the origin of the name "Black Panther" followed from the 2018 movie Black Panther about King T'Challa of the fictional land of Wakanda. In the movie, Blacks have power, money, technology and high culture and a superhero to lead them. But the name goes back much further. During World War II, the name "Black Panthers" referred to the majority-Black 761st Tank Battalion that engaged in combat for 183 days in a row in France and Germany throughout 1944 and 1945, its members earning 7 Silver Stars, 246 Purple Hearts, and one Congressional Medal of Honor.
Some have speculated that the Black Panther Party was connected to the appearance of the Black Panther comic book character . Both appeared in 1966 and both sought to express the pride and power of Black people. Black Panther party founders Huey Newton and Bobby Seale said they adopted the black panther symbol from Alabama's Lowndes County Freedom Organization. Black Panther comic creators Jack Kirby and Stan Lee have said they were not specifically influenced by the Black Panther Party. While the Black Panther Party dissolved in 1982, the Black Panther comic has continued, explicitly addressing themes of Black empowerment and opposition to White racism, notably when the Christopher Priest , the comic's first African American cartoonist, drew the strip in the 1990s. Ta-Nehisi Coates currently writes the Black Panther strip for Marvel Comics.
- What would be the party's symbol?
- What would be its slogan?
- What would be its platform for change? For background, read the Progressive Party Platform of 1912 .
- What connections and parallels do you see between what Du Bois was writing about then and people are seeking and encountering today?
3.5.3 ENGAGE: Should Voters Join a Political Party?
When registering to vote, each person has a choice whether or not to join a political party.

Those who do not select a party designation are considered to be "independent" or “unenrolled," joining the 39% of all Americans who are not members of a political party. Importantly, registered voters can vote in any general election whether or not they belong to a political party. In general elections at the national, state, and local level, everyone receives the same ballot and can choose from among the same number of candidates.
Four parties hold primaries in Massachusetts: Democrat, Republican, Green-Rainbow, and Libertarian ( Political Parties in Massachusetts ). The state also has five other political parties: America First, Communist, Constitution, Labor and Veterans.
A voter's political party choices are different in other states. In California, for example, there are seven qualified political parties: Americans Elect, American Independent, Democratic, Green, Libertarian, Peace and Freedom, and Republican. Visit the link to National Political Parties from Votesmart.org for a state-by-state listing of political parties.
Does it make sense for every voter to join a political party? Party membership enables one to vote in that party's primary election, where its candidates for general elections are chosen. In states that hold what are called "closed" or "semi-closed" primaries, however, individuals cannot participate unless registered as a member of a political party ( Congressional and Presidential Primaries: Open, Closed, Semi-Closed, and Others ). Still, to be able to vote in a primary is not the only reason to belong or not belong to a political party. Many people value being associated with other individuals who share similar views on political, social, and economic matters.
Young People and Political Party Membership
What about young people and political party membership? The Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning and Engagement at Tufts University found the although young people tend to be excited about political change, that enthusiasm does not carry over to joining a political party. Rather seeking out membership, many young people express disinterest and distrust toward political parties and the larger electoral process ( Young People's Ambivalent Relationship with Political Parties , CIRCLE , October 24, 2018).
Media Literacy Connections: Website Design for New Political Parties
In theory, multiple political parties give voters multiple choices during elections. In 2020, there were 21 Presidential candidates on the ballot in Vermont and Colorado and in all other states voters could choose between 3 and 13 different candidates.
In reality, though, candidates from parties other than the Democratic or Republican parties have only a small chance of winning a state-wide election (Independent Senators Bernie Sanders of Vermont and Angus King of Maine are exceptions to that statement). In Minnesota, for example, the Legal Marijuana Now Party candidate for U.S. Senate won 185,064 votes (5.77% of all votes cast) while the winner, Democrat Tina Smith, received 1,566,522 votes (48.81% of total votes).
Still, this does not mean that supporting a third party candidate means "wasting" one's vote on someone who cannot win an election. Multiple political parties raise public awareness of issues facing society which can lead to social, economic, and political change.
In politics today, a new political party needs to utilize social media to communicate with voters. A party website can serve as a hub or home base for information, showcasing the party's logo, highlighting its policies, introducing its candidates, and raising funds to support itself and its efforts. In this activity, you get to design a website for a new political party.
- Activity: Design a Website for a New Political Party
- Do you plan to join a political party when registering to vote? Why or why not?
- Take a 2020 Political Quiz from Isidewith.com to establish which political party aligns to your views on important issues.
- How to Choose a Political Party, League of Women Voters California Education Fund (May 1, 2019)
- Six Reasons Progressive Activists Should Join a Political Party, Open Democracy (November 19, 2013)
Online Resources for Political Party Membership
- Sick of Political Parties, Unaffiliated Voters are Changing Politics, NPR (February 28, 2016)
- Massachusetts Directory of Political Parties and Designations from the Secretary of the Commonwealth's office provides a listing of parties in present-day Massachusetts, as well as links to the websites of the Democratic Party, Republican Party, Green Party, and others.
Standard 3.5 Conclusion
Political parties are central to the nation's system of elections at all levels of government. Parties nominate candidates and organize voters. Two major parties, the Democrat and Republican, dominate national politics today. INVESTIGATE explored how the system of political parties evolved in U.S. history, including how third parties influence elections and policies. UNCOVER examined the emergence of radical political parties in different time periods - the Populists, the Socialists, and the Black Panthers. ENGAGE asked whether every voter should join a political party.
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Advanced Admit Card
- JEE Advanced Admit Card 2024
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Answer Key
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Result 2024
- NEET Asnwer Key 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET DU Cut off 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET Result 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET 2024 Exam Live
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Essay on Election
An election is a formal decision-making process in which people choose their political representatives. Since the 17th century, elections have been the primary method used to carry out representative democracy in modern times. Elections may be held to fill legislative, occasionally executive, occasionally judicial, and occasionally regional and municipal positions. Numerous other private and commercial organisations, including clubs, nonprofit organisations, and corporations, also use this procedure to elect their leaders.

100 Words Essay on Election
India is one of the most populous democratic countries in the world, and democracy plays a vital role in our country. Elections in our country are held once in every five years. The results of the elections are often subject to numerous rumors, analyses, and opinions in the news. During times of election, the entire nation is engulfed in a frenzy. But we know that the Election Commission of India (ECI), established in 1950 and responsible for monitoring and election procedures, also has a strong sense of style. The ECI is a massive organisation with several duties to carry out with regard to organising and processing elections in the country. The current Chief Election Commissioner of India is Rajiv Kumar.
200 Words Essay on Election
Elections are a way for a group of people (citizens of a country, employees of an organisation, students of a class, etc.) to come to a consensus about who will be their leading representatives. Ever since India became independent in 1947 and took up a democratic form of government, elections have been the medium through which people have chosen their leaders. Elections take place every five years in India. It is believed to be the mark of a responsible citizen to go and caste their vote in elections.
Conducting Body
The primary organisation in charge of overseeing elections in India is the Election Commission of India (ECI). The Indian constitution established the Election Commission, a body with the power to supervise the conduct of elections and referendums across the nation. Under Lok Sabha's confirmation, the president appoints the chairman of the commission for a 5-year tenure (House of the People). The president appoints the other members of the commission for a 7-year term at the suggestion of the prime minister, subject to the Lok Sabha’s approval.
Why Are Elections Necessary?
India is a democratic country, which essentially means that it is “ruled by its people”. Hence, elections become a mechanism through which citizens of the country voice their opinions as to who they want should lead them, giving everyone a fair say, and also appropriate feedback to those already in leading positions about how well their rule was received.
500 Words Essay on Elections
In a democratic country, people have the freedom to choose their leaders. Without democracy, people have no voice and are reduced to subservient slaves who obey their rulers. They had no choice but to obey their rules and their laws. Under British rule, India was monarchy. However, after independence, it became a democratic country.
Types of Elections In India
Presidential, Lok Sabha (General Election), Rajya Sabha, State Legislature, and local body elections are the main types of elections held in India. The General Elections (MP) and State Legislature Assembly (MLA) for the selection of the Prime Minister and Chief Minister of State, respectively, are the elections in which the public is directly involved.
Presidential Elections | The Electoral College is made up of a total of 538 electors. After the general election, each elector casts one vote. 270 votes or more are required to win. Following that, on January 20, the newly-elected President and Vice President come to power.
Lok Sabha (General Election) | The Lok Sabha elections are held once in five years to elect 543 members of the Lok Sabha. The first general elections or elections to the Lok Sabha after India became independent were held between October 25, 1951, and February 21, 1952.
Local Body Elections | Local Body Elections (India) are elections held in the states and union territories of the nation to choose representatives for local bodies, following the 73rd amendment to the Indian Constitution.
Election Campaigns
The parties contesting in the elections run their respective campaigns few days prior to the election date, wherein they pitch to the citizens as to why the latter should vote for them and bring them to power. Here is why election campaigns are important:-
Structuring Public Opinion | Political parties use methods like public meetings, rallies, road shows, interviews, etc. during election campaigns to try and shape the public's opinion. It provides them with a platform via which they may communicate with the public and ask them to support them in the elections.
Platform For Debate | Political campaigns offer a stage for constructive discussion between political opponents. It allows them an equal opportunity to promote their successes and expose the flaws of their opponents, assisting the general public in forming opinions about the election.
Reaching Out To The Public | The election campaign facilitates public outreach through neighborhood public meetings, open forums, one-on-one conversations, direct engagement with the public, and other means to let people understand the realities of a region.
Election Process in India
In India, the election process begins with the announcement of the election dates, which is followed by the candidates submitting their nominations, which are then reviewed and approved by the electoral commission. Voting is done through electronic voting machines (EVMs) throughout the election day in the relevant constituencies. Any Indian citizen who has reached the age of 18 and possesses a valid form of identification is eligible to vote in the election. Votes are counted on the day results are announced, and the candidate with the highest number of votes is proclaimed the winner.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in
Describe the role of citizens in a democracy
The following are the roles of citizens in democracy: the citizens of a country vote in the elections and choose the representatives of the government. citizens have a very important role in a democracy as they exercise their rights and freedoms and benefit from the democratic setup of the country they cooperate with the law and order and rules and regulations. they have to be aware about the policies of the government. citizens have right to speak so they can criticize the bad will of government and protest against it..


- _Grade VIII
- _ _Social Studies
- _ _(Grade XI- New Course)
- _ _ _Language Development
- _ _ _Literary Studies
- _ _ _ _Short Stories
- _ _ _ _Poems
- _ _(Grade XII- New Course)
- _Basic Level
- Moral Stories
- General Knowledge
- Information
Tuesday, September 1, 2020
Social Studies Note for Grade X | Unit- 5 | Lesson- 8 Role of Citizens in the Election

Role of Citizens in the Election
A periodical election provides an opportunity to people for electing representatives as per their choice in different times. People can choose their preferred candidate or party in the election to form their government. A fair, independent and impartial election can help in the resolution of national problems. The citizens have to play important role to make the election successful, respectable and disciplined. They should play various roles before, during and after election. The role of citizens in the election is presented as follows:
Role of citizens
Before election.
- Verify the electoral roll and make sure that the name of family members who have attained 18 years of age is included in the electoral roll.
- Help the Election Commission to update and revise the electoral roll if found any error in personal details.
- Encourage and help the neighbors and relatives to verify and update the electoral roll.
- Encourage the voters in the family and neighborhood to participate in the election for casting their votes.
- Study the manifestos of different political parties and discuss with the voters to elect the best candidate.
- Learn and teach other people about the technique of casting vote so that it would not be invalid, and
- Counsel the voters that they should not fall in greed and threat.
During Election
- Carry the voter identity card and remind others to do so.
- Stand in queue to cast the vote in disciplined manner.
- Cast the vote regardless of nepotism and favoritism.
- Help the aged, differently able and needy ones to cast the vote.
- Raise the voice if there is any irregularity or violation of election code of conduct, and
- Support the electoral officials to conduct election in peaceful environment.
After Election
- Wait for the result patiently.
- Congratulate and suggest the winner candidate to carry out the works in favor of people and the country, and
- Carry out the clean up campaign in and around the polling station, or booths.

Role of students in the election
- Providing correct information and helping the election commission to update the electoral roll
- Encouraging people to cast vote for electing the best candidate or party
- Teaching people about proper stamping on ballot paper
- Helping to maintain peaceful environment in the polling station, and
- Supporting aged and physically challenged people to cast their votes in the polling station
Short Questions:
- Prepare a dialogue between two friends on the role of a responsible citizen in the election.
- A good citizen must participate in an election. Prepare a dialogue on it.
- How do you convince your family members who don’t wish to vote in the election?
- What suggestions would you give to your guardians and neighborhood to cast the vote?
No comments:
Post a comment, email subscription.
Enter your email address:
Delivered by FeedBurner
Subscribe Our Youtube Channel
Total pageviews.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and conditions
Popular Posts

Copyright (c) 2021 Surya Xetri

Essay on Importance of Voting in Democracy
Students are often asked to write an essay on Importance of Voting in Democracy in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Importance of Voting in Democracy
The essence of democracy.
Voting is the cornerstone of a democracy. It’s the tool that allows citizens to choose their leaders and voice their opinions on important issues.
Why Voting Matters
By voting, you get to influence the society you live in. It’s a way to ensure that your interests are represented in government.
The Power of Each Vote
Every vote counts. In many cases, elections have been decided by just a few votes. Therefore, your vote can make a real difference.
In summary, voting is a crucial component of democracy. So, always exercise your right to vote!
250 Words Essay on Importance of Voting in Democracy
Democracy is often defined as ‘government of the people, by the people, for the people.’ It is a system that bestows power in the hands of the citizens to choose their representatives. The cornerstone of this power lies in the act of voting.
The Role of Voting
Voting is not just a right, but a duty and a moral responsibility. It is the most direct and effective way of participating in the democratic process. The vote of every citizen contributes to the formation of a government and the trajectory of the nation.
Empowering the Masses
Voting gives citizens the power to express their opinion and choose leaders who align with their views. It is a tool to effect change and ensure the government reflects the will of the people. Voting also empowers marginalized groups, providing an equal platform for their voices to be heard.
Accountability and Transparency
Voting ensures accountability and transparency in the democratic system. It acts as a check on the government, reminding them of their responsibility towards the electorate. If the government fails to deliver, voters have the power to change the administration in the next election.
The importance of voting in democracy cannot be overstated. It is the fundamental right and duty of every citizen to participate in this process. It is through voting that we shape our society, influence policies, and ensure the government serves the common good. By voting, we uphold the democratic values of freedom, equality, and justice.
500 Words Essay on Importance of Voting in Democracy
Introduction.
Democracy is a system of governance where citizens participate directly or indirectly in the decision-making process. At the heart of this system lies the act of voting, an essential tool through which citizens express their will, choose their leaders, and influence public policy. The importance of voting in a democratic society cannot be overstated as it forms the basis for the exercise of political and civil rights.
The Pillar of Democratic Governance
Voting is a fundamental pillar of democratic governance. It is the mechanism through which citizens exercise their sovereignty and control over the government. By voting, citizens choose their representatives who will make laws, shape public policy, and steer the direction of the nation. This process ensures that the government is accountable to the people, and not the other way round. The act of voting is, therefore, a powerful expression of political freedom and self-determination.
Instrument for Social Change
Voting is not only a political act but also a tool for social change. It gives citizens the power to influence public policy and the direction of societal evolution. Through the ballot box, citizens can express their views on critical issues such as education, health, economy, and social justice. Voting, therefore, serves as a peaceful means of effecting change and shaping the society we want to live in.
Equality and Inclusivity
In a democracy, voting underscores the principle of equality. Regardless of social, economic, or cultural backgrounds, every citizen has an equal vote. This inclusivity strengthens social cohesion and fosters a sense of belonging among citizens. Moreover, it ensures that marginalized and underrepresented groups have a voice in the political process, thereby promoting social equity.
Responsibility of Citizenship
Voting is not just a right; it is a responsibility. By participating in elections, citizens contribute to the democratic process and the overall health of the political system. Abstaining from voting leads to a skewed representation, which may not reflect the true will of the people. Therefore, every vote counts, and each citizen ought to take this responsibility seriously.
In conclusion, the act of voting is a cornerstone of democracy, serving as a tool for change, a symbol of equality, and a responsibility of citizenship. It gives power to the people, ensuring that the government remains accountable and responsive to their needs. Hence, for a democracy to be truly representative and effective, it is essential that citizens understand the importance of voting and actively participate in the electoral process. The future of our democratic society depends on the collective action of informed and engaged citizens.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Electoral Literacy for Stronger Democracy
- Essay on Democracy in Sri Lanka
- Essay on New Delhi
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Unit:-5, Lesson:-8 Role of Citizens in the Election
Unit-5 Lesson-8
Role of Citizens in the Election
A. Short answer questions
1. Prepare a model of dialogue between two friends who were discussing the role of a responsible citizen in the election.
Ans:- (Pooja and Sonam are discussing about the role of a responsible citizen in the election)
Pooja : Hi Sonam, what you are reading now?
Sonam : Hi puja, I am reading an election manifesto prepared for the election.
Pooja : Is it necessary to study the manifesto?
Sonam : Yes Pooja, it is our duty to select the best party in the election to develop our country.
Pooja : What the people should do in the time of election?
Sonam : Good question. Listen! Election is the base of democracy. To cast the vote is the right and duty of citizen. We should use our voting right to select capable, energetic candidate for the development of nation. Not only this, we should teach our neighbor about the technique of casting vote, encourage the votes to participate in the election, we should counsel the voters to not to fall in greed and threat. We can support to conduct election in peaceful environment. We also can help the Election commission as volunteer.
Pooja : thank you so much for your information.
(Both of them exit from the room for refreshment)
2. “A good citizen must participate in an election”. Prepare a dialogue on this topic.
Ans:- (A conversation between Sunil and Gauri Shankar on election)
Sunil : “Gauri Shankar, can you tell me what is an election?”
Gauri Shankar : “Election is a democratic process to choose the candidates for various posts through the voting.”
Sunil : “Gauri Shankar, can you tell me why a good citizen must participate in election?”
Gauri Shankar : “Of course Sunil, you have asked a good question. Listen, election is an important event of a country because we can choose our government by ourselves through the election. If we participate in the election and vote to the right person, a good governance is possible. After all it is a duty of every citizen to take part in election.”
Sunil : “What will happen if we do not participate in any election, Gauri Shankar?”
Gauri Shankar : “If good citizens do not participate in election, wrong persons may go to the power and country may not develop properly. Corruption main take place and they may be political instability in the country which is not good for the country as well as the people.”
Sunil : “What types of election there in the country and who are to be elected?”
Gauri Shankar : “There are various types of election that take place in our country such as election for parliament, election of local bodies like VDC, municipality, DDC, etc. The most Richard the right candidates in all these bodies so that country can be ruled smoothly and develop faster”.
Sunil : “Thank you Gauri Shankar for your information. I will also take part in all the election and choose the right candidate.”
3. What suggestions would you give to your guardians and neighbor to cast the vote?
Ans:- I would suggest in the following ways to my guardians and neighbor to cast their vote:
i) To select good, active, patriotic and capable candidate.
ii) To stamp on only one symbol and to fold the ballot paper properly.
iii) To go to the polling booth turn-by-turn.
iv) To stand in queue to cast vote.
v) To carry the voter identity card and remind others to do the same.
vi) Not to fall for greed and threat.
4. How do you convince your family members who don’t wish to vote in the election?
Ans:- I will convince my family members who don’t wish to vote in the election in the following ways:
i) To get voting right is great chance to elect right candidate.
ii) To vote is to utilize the civic right.
iii) We can select right candidate who can run the government, make act, laws and rules.
iv) A single vote also has great importance in the election to elect right candidate.
Please Share This Share this content
- Opens in a new window
You Might Also Like
Unit:-5, lesson:-2 executive, unit:-6 lesson:-12 africa : geographical and natural environment, unit:-8 lesson:-1 current plan, this post has one comment.
Long answer questions isn’t here ? Please provide us long answer questions 🙏
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Doha Declaration
Education for justice.
- Agenda Day 1
- Agenda Day 2
- Agenda Day 3
- Agenda Day 4
- Registration
- Breakout Sessions for Primary and Secondary Level
- Breakout Sessions for Tertiary Level
- E4J Youth Competition
- India - Lockdown Learners
- Chuka, Break the Silence
- The Online Zoo
- I would like a community where ...
- Staying safe online
- Let's be respectful online
- We can all be heroes
- Respect for all
- We all have rights
- A mosaic of differences
- The right thing to do
- Solving ethical dilemmas
- UNODC-UNESCO Guide for Policymakers
- UNODC-UNESCO Handbooks for Teachers
- Justice Accelerators
- Introduction
- Organized Crime
- Trafficking in Persons & Smuggling of Migrants
- Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice Reform
- Crime Prevention, Criminal Justice & SDGs
- UN Congress on Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice
- Commission on Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice
- Conference of the Parties to UNTOC
- Conference of the States Parties to UNCAC
- Rules for Simulating Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice Bodies
- Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice
- Engage with Us
- Contact Us about MUN
- Conferences Supporting E4J
- Cyberstrike
- Play for Integrity
- Running out of Time
- Zorbs Reloaded
- Developing a Rationale for Using the Video
- Previewing the Anti-Corruption Video
- Viewing the Video with a Purpose
- Post-viewing Activities
- Previewing the Firearms Video
- Rationale for Using the Video
- Previewing the Human Trafficking Video
- Previewing the Organized Crime Video
- Previewing the Video
- Criminal Justice & Crime Prevention
- Corruption & Integrity
- Human Trafficking & Migrant Smuggling
- Firearms Trafficking
- Terrorism & Violent Extremism
- Introduction & Learning Outcomes
- Corruption - Baseline Definition
- Effects of Corruption
- Deeper Meanings of Corruption
- Measuring Corruption
- Possible Class Structure
- Core Reading
- Advanced Reading
- Student Assessment
- Additional Teaching Tools
- Guidelines for Stand-Alone Course
- Appendix: How Corruption Affects the SDGs
- What is Governance?
- What is Good Governance?
- Corruption and Bad Governance
- Governance Reforms and Anti-Corruption
- Guidelines for Stand-alone Course
- Corruption and Democracy
- Corruption and Authoritarian Systems
- Hybrid Systems and Syndromes of Corruption
- The Deep Democratization Approach
- Political Parties and Political Finance
- Political Institution-building as a Means to Counter Corruption
- Manifestations and Consequences of Public Sector Corruption
- Causes of Public Sector Corruption
- Theories that Explain Corruption
- Corruption in Public Procurement
- Corruption in State-Owned Enterprises
- Responses to Public Sector Corruption
- Preventing Public Sector Corruption
- Forms & Manifestations of Private Sector Corruption
- Consequences of Private Sector Corruption
- Causes of Private Sector Corruption
- Responses to Private Sector Corruption
- Preventing Private Sector Corruption
- Collective Action & Public-Private Partnerships against Corruption
- Transparency as a Precondition
- Detection Mechanisms - Auditing and Reporting
- Whistle-blowing Systems and Protections
- Investigation of Corruption
- Introduction and Learning Outcomes
- Brief background on the human rights system
- Overview of the corruption-human rights nexus
- Impact of corruption on specific human rights
- Approaches to assessing the corruption-human rights nexus
- Human-rights based approach
- Defining sex, gender and gender mainstreaming
- Gender differences in corruption
- Theories explaining the gender–corruption nexus
- Gendered impacts of corruption
- Anti-corruption and gender mainstreaming
- Manifestations of corruption in education
- Costs of corruption in education
- Causes of corruption in education
- Fighting corruption in education
- Core terms and concepts
The role of citizens in fighting corruption
- The role, risks and challenges of CSOs fighting corruption
- The role of the media in fighting corruption
- Access to information: a condition for citizen participation
- ICT as a tool for citizen participation in anti-corruption efforts
- Government obligations to ensure citizen participation in anti-corruption efforts
- Teaching Guide
- Brief History of Terrorism
- 19th Century Terrorism
- League of Nations & Terrorism
- United Nations & Terrorism
- Terrorist Victimization
- Exercises & Case Studies
- Radicalization & Violent Extremism
- Preventing & Countering Violent Extremism
- Drivers of Violent Extremism
- International Approaches to PVE &CVE
- Regional & Multilateral Approaches
- Defining Rule of Law
- UN Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy
- International Cooperation & UN CT Strategy
- Legal Sources & UN CT Strategy
- Regional & National Approaches
- International Legal Frameworks
- International Human Rights Law
- International Humanitarian Law
- International Refugee Law
- Current Challenges to International Legal Framework
- Defining Terrorism
- Criminal Justice Responses
- Treaty-based Crimes of Terrorism
- Core International Crimes
- International Courts and Tribunals
- African Region
- Inter-American Region
- Asian Region
- European Region
- Middle East & Gulf Regions
- Core Principles of IHL
- Categorization of Armed Conflict
- Classification of Persons
- IHL, Terrorism & Counter-Terrorism
- Relationship between IHL & intern. human rights law
- Limitations Permitted by Human Rights Law
- Derogation during Public Emergency
- Examples of States of Emergency & Derogations
- International Human Rights Instruments
- Regional Human Rights Instruments
- Extra-territorial Application of Right to Life
- Arbitrary Deprivation of Life
- Death Penalty
- Enforced Disappearances
- Armed Conflict Context
- International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights
- Convention against Torture et al.
- International Legal Framework
- Key Contemporary Issues
- Investigative Phase
- Trial & Sentencing Phase
- Armed Conflict
- Case Studies
- Special Investigative Techniques
- Surveillance & Interception of Communications
- Privacy & Intelligence Gathering in Armed Conflict
- Accountability & Oversight of Intelligence Gathering
- Principle of Non-Discrimination
- Freedom of Religion
- Freedom of Expression
- Freedom of Assembly
- Freedom of Association
- Fundamental Freedoms
- Definition of 'Victim'
- Effects of Terrorism
- Access to Justice
- Recognition of the Victim
- Human Rights Instruments
- Criminal Justice Mechanisms
- Instruments for Victims of Terrorism
- National Approaches
- Key Challenges in Securing Reparation
- Topic 1. Contemporary issues relating to conditions conducive both to the spread of terrorism and the rule of law
- Topic 2. Contemporary issues relating to the right to life
- Topic 3. Contemporary issues relating to foreign terrorist fighters
- Topic 4. Contemporary issues relating to non-discrimination and fundamental freedoms
- Module 16: Linkages between Organized Crime and Terrorism
- Thematic Areas
- Content Breakdown
- Module Adaptation & Design Guidelines
- Teaching Methods
- Acknowledgements
- 1. Introducing United Nations Standards & Norms on CPCJ vis-à-vis International Law
- 2. Scope of United Nations Standards & Norms on CPCJ
- 3. United Nations Standards & Norms on CPCJ in Operation
- 1. Definition of Crime Prevention
- 2. Key Crime Prevention Typologies
- 2. (cont.) Tonry & Farrington’s Typology
- 3. Crime Problem-Solving Approaches
- 4. What Works
- United Nations Entities
- Regional Crime Prevention Councils/Institutions
- Key Clearinghouses
- Systematic Reviews
- 1. Introduction to International Standards & Norms
- 2. Identifying the Need for Legal Aid
- 3. Key Components of the Right of Access to Legal Aid
- 4. Access to Legal Aid for Those with Specific Needs
- 5. Models for Governing, Administering and Funding Legal Aid
- 6. Models for Delivering Legal Aid Services
- 7. Roles and Responsibilities of Legal Aid Providers
- 8. Quality Assurance and Legal Aid Services
- 1. Context for Use of Force by Law Enforcement Officials
- 2. Legal Framework
- 3. General Principles of Use of Force in Law Enforcement
- 4. Use of Firearms
- 5. Use of “Less-Lethal” Weapons
- 6. Protection of Especially Vulnerable Groups
- 7. Use of Force during Assemblies
- 1. Policing in democracies & need for accountability, integrity, oversight
- 2. Key mechanisms & actors in police accountability, oversight
- 3. Crosscutting & contemporary issues in police accountability
- 1. Introducing Aims of Punishment, Imprisonment & Prison Reform
- 2. Current Trends, Challenges & Human Rights
- 3. Towards Humane Prisons & Alternative Sanctions
- 1. Aims and Significance of Alternatives to Imprisonment
- 2. Justifying Punishment in the Community
- 3. Pretrial Alternatives
- 4. Post Trial Alternatives
- 5. Evaluating Alternatives
- 1. Concept, Values and Origin of Restorative Justice
- 2. Overview of Restorative Justice Processes
- 3. How Cost Effective is Restorative Justice?
- 4. Issues in Implementing Restorative Justice
- 1. Gender-Based Discrimination & Women in Conflict with the Law
- 2. Vulnerabilities of Girls in Conflict with the Law
- 3. Discrimination and Violence against LGBTI Individuals
- 4. Gender Diversity in Criminal Justice Workforce
- 1. Ending Violence against Women
- 2. Human Rights Approaches to Violence against Women
- 3. Who Has Rights in this Situation?
- 4. What about the Men?
- 5. Local, Regional & Global Solutions to Violence against Women & Girls
- 1. Understanding the Concept of Victims of Crime
- 2. Impact of Crime, including Trauma
- 3. Right of Victims to Adequate Response to their Needs
- 4. Collecting Victim Data
- 5. Victims and their Participation in Criminal Justice Process
- 6. Victim Services: Institutional and Non-Governmental Organizations
- 7. Outlook on Current Developments Regarding Victims
- 8. Victims of Crime and International Law
- 1. The Many Forms of Violence against Children
- 2. The Impact of Violence on Children
- 3. States' Obligations to Prevent VAC and Protect Child Victims
- 4. Improving the Prevention of Violence against Children
- 5. Improving the Criminal Justice Response to VAC
- 6. Addressing Violence against Children within the Justice System
- 1. The Role of the Justice System
- 2. Convention on the Rights of the Child & International Legal Framework on Children's Rights
- 3. Justice for Children
- 4. Justice for Children in Conflict with the Law
- 5. Realizing Justice for Children
- 1a. Judicial Independence as Fundamental Value of Rule of Law & of Constitutionalism
- 1b. Main Factors Aimed at Securing Judicial Independence
- 2a. Public Prosecutors as ‘Gate Keepers’ of Criminal Justice
- 2b. Institutional and Functional Role of Prosecutors
- 2c. Other Factors Affecting the Role of Prosecutors
- Basics of Computing
- Global Connectivity and Technology Usage Trends
- Cybercrime in Brief
- Cybercrime Trends
- Cybercrime Prevention
- Offences against computer data and systems
- Computer-related offences
- Content-related offences
- The Role of Cybercrime Law
- Harmonization of Laws
- International and Regional Instruments
- International Human Rights and Cybercrime Law
- Digital Evidence
- Digital Forensics
- Standards and Best Practices for Digital Forensics
- Reporting Cybercrime
- Who Conducts Cybercrime Investigations?
- Obstacles to Cybercrime Investigations
- Knowledge Management
- Legal and Ethical Obligations
- Handling of Digital Evidence
- Digital Evidence Admissibility
- Sovereignty and Jurisdiction
- Formal International Cooperation Mechanisms
- Informal International Cooperation Mechanisms
- Data Retention, Preservation and Access
- Challenges Relating to Extraterritorial Evidence
- National Capacity and International Cooperation
- Internet Governance
- Cybersecurity Strategies: Basic Features
- National Cybersecurity Strategies
- International Cooperation on Cybersecurity Matters
- Cybersecurity Posture
- Assets, Vulnerabilities and Threats
- Vulnerability Disclosure
- Cybersecurity Measures and Usability
- Situational Crime Prevention
- Incident Detection, Response, Recovery & Preparedness
- Privacy: What it is and Why it is Important
- Privacy and Security
- Cybercrime that Compromises Privacy
- Data Protection Legislation
- Data Breach Notification Laws
- Enforcement of Privacy and Data Protection Laws
- Intellectual Property: What it is
- Types of Intellectual Property
- Causes for Cyber-Enabled Copyright & Trademark Offences
- Protection & Prevention Efforts
- Online Child Sexual Exploitation and Abuse
- Cyberstalking and Cyberharassment
- Cyberbullying
- Gender-Based Interpersonal Cybercrime
- Interpersonal Cybercrime Prevention
- Cyber Organized Crime: What is it?
- Conceptualizing Organized Crime & Defining Actors Involved
- Criminal Groups Engaging in Cyber Organized Crime
- Cyber Organized Crime Activities
- Preventing & Countering Cyber Organized Crime
- Cyberespionage
- Cyberterrorism
- Cyberwarfare
- Information Warfare, Disinformation & Electoral Fraud
- Responses to Cyberinterventions
- Framing the Issue of Firearms
- Direct Impact of Firearms
- Indirect Impacts of Firearms on States or Communities
- International and National Responses
- Typology and Classification of Firearms
- Common Firearms Types
- 'Other' Types of Firearms
- Parts and Components
- History of the Legitimate Arms Market
- Need for a Legitimate Market
- Key Actors in the Legitimate Market
- Authorized & Unauthorized Arms Transfers
- Illegal Firearms in Social, Cultural & Political Context
- Supply, Demand & Criminal Motivations
- Larger Scale Firearms Trafficking Activities
- Smaller Scale Trafficking Activities
- Sources of Illicit Firearms
- Consequences of Illicit Markets
- International Public Law & Transnational Law
- International Instruments with Global Outreach
- Commonalities, Differences & Complementarity between Global Instruments
- Tools to Support Implementation of Global Instruments
- Other United Nations Processes
- The Sustainable Development Goals
- Multilateral & Regional Instruments
- Scope of National Firearms Regulations
- National Firearms Strategies & Action Plans
- Harmonization of National Legislation with International Firearms Instruments
- Assistance for Development of National Firearms Legislation
- Firearms Trafficking as a Cross-Cutting Element
- Organized Crime and Organized Criminal Groups
- Criminal Gangs
- Terrorist Groups
- Interconnections between Organized Criminal Groups & Terrorist Groups
- Gangs - Organized Crime & Terrorism: An Evolving Continuum
- International Response
- International and National Legal Framework
- Firearms Related Offences
- Role of Law Enforcement
- Firearms as Evidence
- Use of Special Investigative Techniques
- International Cooperation and Information Exchange
- Prosecution and Adjudication of Firearms Trafficking
- Teaching Methods & Principles
- Ethical Learning Environments
- Overview of Modules
- Module Adaption & Design Guidelines
- Table of Exercises
- Basic Terms
- Forms of Gender Discrimination
- Ethics of Care
- Case Studies for Professional Ethics
- Case Studies for Role Morality
- Additional Exercises
- Defining Organized Crime
- Definition in Convention
- Similarities & Differences
- Activities, Organization, Composition
- Thinking Critically Through Fiction
- Excerpts of Legislation
- Research & Independent Study Questions
- Legal Definitions of Organized Crimes
- Criminal Association
- Definitions in the Organized Crime Convention
- Criminal Organizations and Enterprise Laws
- Enabling Offence: Obstruction of Justice
- Drug Trafficking
- Wildlife & Forest Crime
- Counterfeit Products Trafficking
- Falsified Medical Products
- Trafficking in Cultural Property
- Trafficking in Persons
- Case Studies & Exercises
- Extortion Racketeering
- Loansharking
- Links to Corruption
- Bribery versus Extortion
- Money-Laundering
- Liability of Legal Persons
- How much Organized Crime is there?
- Alternative Ways for Measuring
- Measuring Product Markets
- Risk Assessment
- Key Concepts of Risk Assessment
- Risk Assessment of Organized Crime Groups
- Risk Assessment of Product Markets
- Risk Assessment in Practice
- Positivism: Environmental Influences
- Classical: Pain-Pleasure Decisions
- Structural Factors
- Ethical Perspective
- Crime Causes & Facilitating Factors
- Models and Structure
- Hierarchical Model
- Local, Cultural Model
- Enterprise or Business Model
- Groups vs Activities
- Networked Structure
- Jurisdiction
- Investigators of Organized Crime
- Controlled Deliveries
- Physical & Electronic Surveillance
- Undercover Operations
- Financial Analysis
- Use of Informants
- Rights of Victims & Witnesses
- Role of Prosecutors
- Adversarial vs Inquisitorial Legal Systems
- Mitigating Punishment
- Granting Immunity from Prosecution
- Witness Protection
- Aggravating & Mitigating Factors
- Sentencing Options
- Alternatives to Imprisonment
- Death Penalty & Organized Crime
- Backgrounds of Convicted Offenders
- Confiscation
- Confiscation in Practice
- Mutual Legal Assistance (MLA)
- Extradition
- Transfer of Criminal Proceedings
- Transfer of Sentenced Persons
- Module 12: Prevention of Organized Crime
- Adoption of Organized Crime Convention
- Historical Context
- Features of the Convention
- Related international instruments
- Conference of the Parties
- Roles of Participants
- Structure and Flow
- Recommended Topics
- Background Materials
- What is Sex / Gender / Intersectionality?
- Knowledge about Gender in Organized Crime
- Gender and Organized Crime
- Gender and Different Types of Organized Crime
- Definitions and Terminology
- Organized crime and Terrorism - International Legal Framework
- International Terrorism-related Conventions
- UNSC Resolutions on Terrorism
- Organized Crime Convention and its Protocols
- Theoretical Frameworks on Linkages between Organized Crime and Terrorism
- Typologies of Criminal Behaviour Associated with Terrorism
- Terrorism and Drug Trafficking
- Terrorism and Trafficking in Weapons
- Terrorism, Crime and Trafficking in Cultural Property
- Trafficking in Persons and Terrorism
- Intellectual Property Crime and Terrorism
- Kidnapping for Ransom and Terrorism
- Exploitation of Natural Resources and Terrorism
- Review and Assessment Questions
- Research and Independent Study Questions
- Criminalization of Smuggling of Migrants
- UNTOC & the Protocol against Smuggling of Migrants
- Offences under the Protocol
- Financial & Other Material Benefits
- Aggravating Circumstances
- Criminal Liability
- Non-Criminalization of Smuggled Migrants
- Scope of the Protocol
- Humanitarian Exemption
- Migrant Smuggling v. Irregular Migration
- Migrant Smuggling vis-a-vis Other Crime Types
- Other Resources
- Assistance and Protection in the Protocol
- International Human Rights and Refugee Law
- Vulnerable groups
- Positive and Negative Obligations of the State
- Identification of Smuggled Migrants
- Participation in Legal Proceedings
- Role of Non-Governmental Organizations
- Smuggled Migrants & Other Categories of Migrants
- Short-, Mid- and Long-Term Measures
- Criminal Justice Reponse: Scope
- Investigative & Prosecutorial Approaches
- Different Relevant Actors & Their Roles
- Testimonial Evidence
- Financial Investigations
- Non-Governmental Organizations
- ‘Outside the Box’ Methodologies
- Intra- and Inter-Agency Coordination
- Admissibility of Evidence
- International Cooperation
- Exchange of Information
- Non-Criminal Law Relevant to Smuggling of Migrants
- Administrative Approach
- Complementary Activities & Role of Non-criminal Justice Actors
- Macro-Perspective in Addressing Smuggling of Migrants
- Human Security
- International Aid and Cooperation
- Migration & Migrant Smuggling
- Mixed Migration Flows
- Social Politics of Migrant Smuggling
- Vulnerability
- Profile of Smugglers
- Role of Organized Criminal Groups
- Humanitarianism, Security and Migrant Smuggling
- Crime of Trafficking in Persons
- The Issue of Consent
- The Purpose of Exploitation
- The abuse of a position of vulnerability
- Indicators of Trafficking in Persons
- Distinction between Trafficking in Persons and Other Crimes
- Misconceptions Regarding Trafficking in Persons
- Root Causes
- Supply Side Prevention Strategies
- Demand Side Prevention Strategies
- Role of the Media
- Safe Migration Channels
- Crime Prevention Strategies
- Monitoring, Evaluating & Reporting on Effectiveness of Prevention
- Trafficked Persons as Victims
- Protection under the Protocol against Trafficking in Persons
- Broader International Framework
- State Responsibility for Trafficking in Persons
- Identification of Victims
- Principle of Non-Criminalization of Victims
- Criminal Justice Duties Imposed on States
- Role of the Criminal Justice System
- Current Low Levels of Prosecutions and Convictions
- Challenges to an Effective Criminal Justice Response
- Rights of Victims to Justice and Protection
- Potential Strategies to “Turn the Tide”
- State Cooperation with Civil Society
- Civil Society Actors
- The Private Sector
- Comparing SOM and TIP
- Differences and Commonalities
- Vulnerability and Continuum between SOM & TIP
- Labour Exploitation
- Forced Marriage
- Other Examples
- Children on the Move
- Protecting Smuggled and Trafficked Children
- Protection in Practice
- Children Alleged as Having Committed Smuggling or Trafficking Offences
- Basic Terms - Gender and Gender Stereotypes
- International Legal Frameworks and Definitions of TIP and SOM
- Global Overview on TIP and SOM
- Gender and Migration
- Key Debates in the Scholarship on TIP and SOM
- Gender and TIP and SOM Offenders
- Responses to TIP and SOM
- Use of Technology to Facilitate TIP and SOM
- Technology Facilitating Trafficking in Persons
- Technology in Smuggling of Migrants
- Using Technology to Prevent and Combat TIP and SOM
- Privacy and Data Concerns
- Emerging Trends
- Demand and Consumption
- Supply and Demand
- Implications of Wildlife Trafficking
- Legal and Illegal Markets
- Perpetrators and their Networks
- Locations and Activities relating to Wildlife Trafficking
- Environmental Protection & Conservation
- CITES & the International Trade in Endangered Species
- Organized Crime & Corruption
- Animal Welfare
- Criminal Justice Actors and Agencies
- Criminalization of Wildlife Trafficking
- Challenges for Law Enforcement
- Investigation Measures and Detection Methods
- Prosecution and Judiciary
- Wild Flora as the Target of Illegal Trafficking
- Purposes for which Wild Flora is Illegally Targeted
- How is it Done and Who is Involved?
- Consequences of Harms to Wild Flora
- Terminology
- Background: Communities and conservation: A history of disenfranchisement
- Incentives for communities to get involved in illegal wildlife trafficking: the cost of conservation
- Incentives to participate in illegal wildlife, logging and fishing economies
- International and regional responses that fight wildlife trafficking while supporting IPLCs
- Mechanisms for incentivizing community conservation and reducing wildlife trafficking
- Critiques of community engagement
- Other challenges posed by wildlife trafficking that affect local populations
- Global Podcast Series
- Apr. 2021: Call for Expressions of Interest: Online training for academics from francophone Africa
- Feb. 2021: Series of Seminars for Universities of Central Asia
- Dec. 2020: UNODC and TISS Conference on Access to Justice to End Violence
- Nov. 2020: Expert Workshop for University Lecturers and Trainers from the Commonwealth of Independent States
- Oct. 2020: E4J Webinar Series: Youth Empowerment through Education for Justice
- Interview: How to use E4J's tool in teaching on TIP and SOM
- E4J-Open University Online Training-of-Trainers Course
- Teaching Integrity and Ethics Modules: Survey Results
- Grants Programmes
- E4J MUN Resource Guide
- Library of Resources
- Anti-Corruption
- Module 10: Citizen Participation in Anti-Corruption Efforts
- {{item.name}} ({{item.items.length}}) items
- Add new list
University Module Series: Anti-Corruption
Module 10: citizen participation in anti-corruption efforts.

This module is a resource for lecturers
Citizen participation is not a new concept, although it has gained traction in the past few decades. As stressed by the National Democratic Institute (a United States-based CSO), citizens have "the right to participate in decisions that affect public welfare" and such "participation is an instrumental driver of democratic and socio-economic change, and a fundamental way to empower citizens". Citizen participation has also been described as "a process which provides private individuals an opportunity to influence public decisions and has long been a component of the democratic decision-making process" (Cogan and Sharpe, 1986, p. 283). Citizen participation is classified as direct or indirect, with direct citizen participation being regarded as "the process by which members of a society share power with public officials in making substantive decisions related to the community" (Roberts, 2008, p. 5). There are even international treaties that highlight the importance of citizen participation, such as the Aarhus Convention on Access to Information, Public Participation in Decision-Making and Access to Justice in Environmental Matters.
The discourse on citizen participation has traditionally focused on participation in democratic decision-making, and there are different ways in which citizen participation is operationalized in democratic processes. This can be through bottom-up measures, such as voting, grass-roots organization and participation, or through top-down mechanisms spurred by organizations such as the Open Government Partnership (discussed in Module 4 of the E4J University Module Series on Anti-Corruption). Innes and Booher (2004) have identified five grounds for upholding citizen participation in public decision-making: 1) to include public preferences in decision-making; 2) to improve decisions by incorporating citizens' local knowledge; 3) to promote fairness and justice, and hear marginalized voices; 4) to legitimize public decisions; and 5) to fulfil the requirements of the law.
Citizen participation in relation to anti-corruption efforts encompasses dynamics and approaches that may differ from citizen participation in other public processes, given that the State may not always provide citizens the same access to space and information in relation to fighting corruption. Corruption bypasses democratic mechanisms to the extent that Mark Warren (2004) has defined corruption as a violation of democratic inclusion. Corruption bypasses the laws and rules that were democratically established and excludes those who do not participate in corrupt exchanges (e.g. services that are meant to be public are allocated to those who bribe or on the basis of clientelism). For this reason, the role of citizens is better understood in terms of social accountability, where the citizens oppose corruption by keeping it in check, critically assessing the conduct and decisions of office holders, reporting corruption misdoings and crimes, and asking for appropriate countermeasures.
Concrete ways in which individual citizens may contribute to the fight against corruption include reporting on corruption to the authority or through the media, and supporting training programmes and sensitization campaigns that aim to create a culture of integrity and zero tolerance for corruption. Sometimes even refusing to participate in corrupt practices is an important act of resistance. It is worthwhile dedicating a few lines to the issue of reporting on corruption, as this is one important avenue through which individual citizens can participate in anti-corruption efforts. As technology has advanced, new methods of citizen reporting have become available. Most anti-corruption agencies now allow reports to be made online. In many countries, smartphone applications are enabling citizens to easily report incidents of corruption. In 2012, the World Bank released its own Integrity App . This app allows users to make confidential reports of fraud and corruption in World Bank projects. It also provides links to the outcomes of investigations. Another approach to reporting corruption outside official channels is through the use of crowdsourcing and social media. In India, for example, Swati and Ramesh Ramanathan created the online platform called " I Paid a Bribe " to expose everyday corruption by allowing people to post their stories anonymously (Strom, 2012). The website has not only served to document corruption, but also to increase awareness among the public. Another example is Digiwhist , a web portal and mobile app technology launched in Europe for the "systematic collection, structuring, analysis, and broad dissemination of information on public procurement and on mechanisms that increase accountability of public officials in all EU and some neighbouring countries". Using the transparency and public accountability of open access, Digiwhist focuses on assessing fiscal transparency, risk assessment and impact of good governance policies.
In many countries around the world, there is a concrete risk of the normalization of corruption and the decline of public criticism of manifestations of corruption. In an ironic twist, corruption ends up being considered a necessary evil or even a shortcut to access some important goods. In such contexts, the critical attitude of citizens toward corruption is weakened or altogether lost. In other cases, high levels of corruption, citizen frustration with public sector corruption and poor governance (which often corresponds to high levels of corruption) may lead to citizen apathy, a lack of civic engagement and a lack of trust in the political and democratic process. Apathy and indifference are dangerous because where citizens fail to hold public officials accountable, corruption spreads even further, together with impunity for corrupt conduct (Olsson, 2014).
Citizen apathy or a lack of civic engagement may be addressed by empowering citizens and by introducing innovative approaches to citizen participation (McCormack and Doran, 2014). For example, the NGO Transparency International launched an anti-corruption tool called the Advocacy and Legal Advice Centre (ALAC) aimed at enhancing awareness of corruption and its negative consequences, and at facilitating the reporting of corruption. It started with three initial ALACs in Romania, North Macedonia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and later established more than 60 centres on all continents. These centres provide victims and witnesses of corruption with practical assistance to pursue complaints and address their grievances. Through providing this support, the centres make it possible for citizens to denounce corruption and participate in anti-corruption efforts.
It is crucial that in all countries, citizens are able to recognize corruption and are empowered to participate, so as to avoid the consequences of unabated corruption, such as deep inequalities (Uslaner, 2008), increased levels of private dishonesty (Gachter and Schulz, 2016), the demoralization of the public (Ariely and Uslaner, 2017), instability and even violent extremism (Chayes, 2015). For a further discussion of the adverse effects of corruption, see Module 1 of the E4J University Module Series on Anti-Corruption.
Where citizens and public officials pursue, use and exchange wealth and power in the absence of appropriate accountability mechanisms, it is common to witness the establishment of what Michael Johnston (2005) called the syndromes of corruption: influence markets, elite cartels, oligarchs and clans, and official moguls. For a further discussion of these syndromes, see Module 2 of the E4J University Module Series on Anti-Corruption.
One should be aware, however, of the possible instrumentalization of citizens' anti-corruption attitudes. Transparency International observers remarked, for example, that corruption is an important element of populist rhetoric. Populist leaders tend to use public outrage for corrupt behaviour to punish political adversaries. Populist movements present themselves as an anti-corruption force drawing on the idea that corrupt elites work against the interest of the people. In many cases, however, such movements are not accompanied by an actual anti-corruption strategy and even facilitate new forms of corruption (Transparency International, 2019). For a further discussion on this topic, see Module 1 of the E4J University Module Series on Anti-Corruption.
Next: The role, risks and challenges of CSOs fighting corruption
Back to top, supported by the state of qatar, 60 years crime congress.
The Federalist Papers
Appearing in New York newspapers as the New York Ratification Convention met in Poughkeepsie, John Jay, Alexander Hamilton and James Madison wrote as Publius and addressed the citizens of New York through the Federalist Papers. These essays subsequently circulated and were reprinted throughout the states as the Ratification process unfolded in other states. Initially appearing as individual items in several New York newspapers, all eighty-five essays were eventually combined and published as The Federalist . Click here to view a chronology of the Printing and Reprintings of The Federalist .
Considerable debate has surrounded these essays since their publication. Many suggest they represent the best exposition of the Constitution to date. Their conceptual design would affirm this view. Others contend that they were mere propaganda to allay fears of the opposition to the Constitution. Regardless, they are often included in the canon of the world’s great political writings. A complete introduction exploring the purpose, authorship, circulation, and reactions to The Federalist can be found here.
General Introduction
- No. 1 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 27 October 1787
Concerning Dangers from Foreign Force and Influence
- No. 2 (Jay) New York Independent Journal , 31 October 1787
- No. 3 (Jay) New York Independent Journal , 3 November 1787
- No. 4 (Jay) New York Independent Journal , 7 November 1787
- No. 5 (Jay) New York Independent Journal , 10 November 1787
Concerning Dangers from Dissensions Between the States
- No. 6 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 14 November 1787
- No. 7 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 17 November 1787
- No. 8 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 20 November 1787
- No. 9 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 21 November 1787
The Union as a Safeguard Against Domestic Faction and Insurrection
- No. 10 (Madison) New York Daily Advertiser , 22 November 1787
The Utility of the Union in Respect to Commercial Relations and a Navy
- No. 11 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 24 November 1787
The Utility of the Union in Respect to Revenue
- No. 12 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 27 November 1787
Advantage of the Union in Respect to Economy in Government
- No. 13 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 28 November 1787
Objections to the Proposed Constitution from Extent of Territory Answered
- No. 14 (Madison) New York Packet , 30 November 1787
The Insufficiency of the Present Confederation to Preserve the Union
- No. 15 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 1 December 1787
- No. 16 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 4 December 1787
- No. 17 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 5 December 1787
- No. 18 (Madison with Hamilton) New York Packet , 7 December 1787
- No. 19 (Madison with Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 8 December 1787
- No. 20 (Madison with Hamilton) New York Packet , 11 December 1787
- No. 21 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 12 December 1787
- No. 22 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 14 December 1787
The Necessity of Energetic Government to Preserve of the Union
- No. 23 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 18 December 1787
Powers Necessary to the Common Defense Further Considered
- No. 24 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 19 December 1787
- No. 25 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 21 December 1787
Restraining the Legislative Authority in Regard to the Common Defense
- No. 26 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 22 December 1787
- No. 27 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 25 December 1787
- No. 28 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 26 December 1787
Concerning the Militia
- No. 29 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 9 January 1788
Concerning the General Power of Taxation
- No. 30 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 28 December 1787
- No. 31 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 1 January 1788
- Nos. 32–33 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 2 January 1788
- No. 34 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 4 January 1788
- No. 35 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 5 January 1788
- No. 36 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 8 January 1788
The Difficulties of the Convention in Devising a Proper Form of Government
- No. 37 (Madison) New York Daily Advertiser , 11 January 1788
- No. 38 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 12 January 1788
The Conformity of the Plan to Republican Principles
- No. 39 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 16 January 1788
The Powers of the Convention to Form a Mixed Government Examined
- No. 40 (Madison) New York Packet , 18 January 1788
General View of the Powers Conferred by the Constitution
- No. 41 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 19 January 1788
- No. 42 (Madison) New York Packet , 22 January 1788
- No. 43 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 23 January 1788
Restrictions on the Authority of the Several States
- No. 44 (Madison) New York Packet , 25 January 1788
Alleged Danger from the Powers of the Union to the State Governments
- No. 45 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 26 January 1788
Influence of the State and Federal Governments Compared
- No. 46 (Madison) New York Packet , 29 January 1788
Structure of the New Government and the Distribution of Powers
- No. 47 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 30 January 1788
Departments Should Not Be So Far Separated
- No. 48 (Madison) New York Packet , 1 February 1788
Guarding Against the Encroachments of Any One Department of Government
- No. 49 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 2 February 1788
Periodic Appeals to the People Considered
- No. 50 (Madison) New York Packet , 5 February 1788
Structure of Government Must Furnish Proper Checks and Balances
- No. 51 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 6 February 1788
The House of Representatives
- No. 52 (Madison?) New York Packet , 8 February 1788
- No. 53 (Madison or Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 9 February 1788
The Apportionment of Members Among the States
- No. 54 (Madison) New York Packet , 12 February 1788
The Total Number of the House of Representatives
- No. 55 (Madison?) New York Independent Journal , 13 February 1788
- No. 56 (Madison?) New York Independent Journal , 16 February 1788
The Alleged Tendency of the Plan to Elevate the Few at the Expense of the Many
- No. 57 (Madison?) New York Packet , 19 February 1788
Objection That the Numbers Will Not Be Augmented as Population Increases
- No. 58 (Madison?) New York Independent Journal , 20 February 1788
Concerning the Power of Congress to Regulate the Election of Members
- No. 59 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 22 February 1788
- No. 60 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 23 February 1788
- No. 61 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 26 February 1788
- No. 62 (Madison?) New York Independent Journal , 27 February 1788
- No. 63 (Madison?) New York Independent Journal , 1 March 1788
- No. 64 (Jay) New York Independent Journal , 5 March 1788
- No. 65 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 7 March 1788
Objections to the Power of the Senate to Set as a Court for Impeachments
- No. 66 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 8 March 1788
The Executive Department
- No. 67 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 11 March 1788
The Mode of Electing the President
- No. 68 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 12 March 1788
The Real Character of the Executive
- No. 69 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 14 March 1788
The Executive Department Further Considered
- No. 70 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 15 March 1788
The Duration in Office of the Executive
- No. 71 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 18 March 1788
Re-Eligibility of the Executive Considered
- No. 72 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 19 March 1788
Provision for The Support of the Executive, and the Veto Power
- No. 73 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 21 March 1788
The Command of the Military and Naval Forces, and the Pardoning Power
- No. 74 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 25 March 1788
The Treaty Making Power of the Executive
- No. 75 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 26 March 1788
The Appointing Power of the Executive
- No. 76 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 1 April 1788
Appointing Power and Other Powers of the Executive Considered
- No. 77 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 2 April 1788
The Judiciary Department
- No. 78 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
- No. 79 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
The Powers of the Judiciary
- No. 80 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
The Judiciary Continued, and the Distribution of the Judicial Authority
- No. 81 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
The Judiciary Continued
- No. 82 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
The Judiciary Continued in Relation to Trial by Jury
- No. 83 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
Miscellaneous Objections to the Constitution Considered
- No. 84 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
Concluding Remarks
- No. 85 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
Noncitizen voting, already illegal in federal elections, becomes a centerpiece of 2024 GOP messaging
In recent months, the specter of people who aren't American citizens and are voting in the United States has become a rallying cry for Republicans
NEW YORK -- One political party is holding urgent news conferences and congressional hearings over the topic. The other says it’s a dangerous distraction meant to seed doubts before this year's presidential election .
In recent months, the specter of immigrants voting illegally in the U.S. has erupted into a leading election-year talking point for Republicans. They argue that legislation is necessary to protect the sanctity of the vote as the country faces unprecedented levels of illegal immigration at the U.S.-Mexico border.
Voting by people who are not U.S. citizens already is illegal in federal elections and there is no indication it’s happening anywhere in significant numbers. Yet Republican lawmakers at the federal and state levels are throwing their energy behind the issue, introducing legislation and fall ballot measures. The activity ensures the issue will remain at the forefront of voters’ minds in the months ahead.
Republicans in Congress are pushing a bill called the SAVE (Safeguard American Voter Eligibility) Act that would require proof of citizenship to register to vote. Meanwhile, Republican legislatures in at least six states have placed noncitizen voting measures on the Nov. 5 ballot, while at least two more are debating whether to do so.
“American elections are for American citizens, and we intend to keep it that way,” House Administration Committee Chairman Rep. Bryan Steil of Wisconsin said during a hearing he hosted on the topic this past week.
Democrats on the committee lambasted their Republican colleagues for focusing on what they called a “nonissue,” arguing it was part of a strategy with former President Donald Trump to lay the groundwork for election challenges this fall.
“It appears the lesson Republicans learned from the fiasco that the former president caused in 2020 was not ‘Don’t steal an election’ — it was just ‘Start earlier,’” said New York Rep. Joe Morelle, the committee's top Democrat. “The coup starts here. This is where it begins.”
The concern that immigrants who are not eligible to vote are illegally casting ballots has prevailed on the right for years. But it gained renewed attention earlier this year when Trump began suggesting without evidence that Democrats were encouraging illegal migration to the U.S. so they could register the newcomers to vote.
Republicans who have been vocal about voting by those who are not citizens have demurred when asked for evidence that it's a problem. Last week, during a news conference on his federal legislation to require proof of citizenship during voter registration, House Speaker Mike Johnson couldn’t provide examples of the crime happening.
“The answer is that it’s unanswerable,” the Louisiana Republican said in response to a question about whether such people were illegally voting. “We all know, intuitively, that a lot of illegals are voting in federal elections, but it’s not been something that is easily provable.”
Election administration experts say it’s not only provable, but it's been demonstrated that the number of noncitizens voting in federal elections is infinitesimal.
To be clear, there have been cases over the years of noncitizens illegally registering and even casting ballots. But states have mechanisms to catch that. Ohio Secretary of State Frank LaRose recently found 137 suspected noncitizens on the state’s rolls — out of roughly 8 million voters — and is taking action to confirm and remove them, he announced this past week.
In 2022, Georgia’s Republican secretary of state, Brad Raffensperger, conducted an audit of his state’s voter rolls specifically looking for noncitizens. His office found that 1,634 had attempted to register to vote over a period of 25 years, but election officials had caught all the applications and none had been able to register.
In North Carolina in 2016, an audit of elections found that 41 legal immigrants who had not yet become citizens cast ballots, out of 4.8 million total ballots cast. The votes didn't make a difference in any of the state's elections.
Voters must confirm under penalty of perjury that they are citizens when they register to vote. If they lie, they can face fines, imprisonment or deportation, said David Becker, founder and executive director of the nonprofit Center for Election Innovation and Research.
On top of that, anyone registering provides their Social Security number, driver’s license or state ID, Becker said. That means they already have shown the government proof of citizenship to receive those documents, or if they are a noncitizen with a state ID or Social Security number, they have been clearly classified that way in the state’s records.
“What they’re asking for is additional proof,” Becker said of Republicans pushing Johnson’s bill. “Why should people have to go to multiple government agencies and have them ask, ’Show us your papers,' when they’ve already shown them?”
Democrats fear adding more ID requirements could disenfranchise eligible voters who don't have their birth certificates or Social Security cards on hand. Republicans counter that the extra step could provide another layer of security and boost voter confidence in an imperfect system in which noncitizen voters have slipped through in the past.
The national focus on noncitizen voting also has brought attention to a related, but different phenomenon: how a small number of local jurisdictions, among them San Francisco and the District of Columbia, have begun allowing immigrants who aren’t citizens to vote in some local contests, such as for school board and city council.
The number of noncitizen voters casting ballots in the towns and cities where they are allowed to do so has been minimal so far. In Winooski, Vermont, where 1,345 people cast ballots in a recent local election, just 11 were not citizens, the clerk told The Associated Press. Still, the gradually growing phenomenon has prompted some state lawmakers to introduce ballot measures that seek to stop cities from trying this in the future.
In South Carolina, voters in November will decide on a constitutional amendment that supporters say will shut the door on any noncitizens voting. The state's constitution currently says every citizen aged 18 and over who qualifies to vote can. The amendment changes the phrasing to say “only citizens.”
Republican state Sen. Chip Campsen called it a safeguard to prevent future problems. California has similar wording to South Carolina’s current provision, and Campsen cited a California Supreme Court decision that ruled “every” didn’t prevent noncitizens from voting.
Democratic state Sen. Darrell Jackson asked Campsen during the debate last month, “Do we have that problem here in South Carolina?”
“You don’t have the problem until the problem arises,” Campsen replied.
On Friday, legislative Republicans in Missouri passed a ballot measure for November that would ban both noncitizen voting and ranked-choice voting.
“I know that scary hypotheticals have been thrown out there: ‘Well, what about St. Louis? What about Kansas City?’” said Democratic state Sen. Lauren Arthur of Kansas City. “It is not a real threat because this is already outlawed. It’s already illegal in Missouri.”
Asked by a Democrat on Thursday about instances of noncitizens voting in Missouri, Republican Rep. Alex Riley said he didn't have “specific data or a scenario that it has happened," but wanted to “address the concern that it could happen in the future.”
In Wisconsin, an important presidential swing state where the Republican-controlled Legislature also put a noncitizen voting measure on the ballot this fall, Democratic state Rep. Lee Snodgrass said during a hearing earlier this week that she couldn't understand why someone who is not a legal citizen would vote.
"I’m trying to wrap my brain around what people think the motivation would be for a noncitizen to go through an enormous amount of hassle to actively commit a felony to vote in an election that’s going to end up putting them in prison or be deported,” she said.
Associated Press writers Summer Ballentine in Jefferson City, Missouri, Jeffrey Collins in Columbia, South Carolina, and Scott Bauer in Madison, Wisconsin, contributed to this report.
The Associated Press receives support from several private foundations to enhance its explanatory coverage of elections and democracy. See more about AP’s democracy initiative here. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Trending Reader Picks

Average US vehicle age hits record 12.6 years
- May 21, 5:38 PM

Experts detail possible outcomes of Trump trial
- May 20, 5:24 AM

Smith suspected added obstruction effort by Trump
- May 21, 4:50 PM

Nikki Haley says she 'will be voting for Trump'
- May 22, 6:23 PM

Election deniers moving closer to GOP mainstream, report shows, as Trump allies fill Congress
- May 21, 12:01 AM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events
- Skip to Nav
- Skip to Main
- Skip to Footer
Mexican Citizens In California Could Play Key Role In Country's Upcoming Election
Please try again

Here are the morning’s top stories on Wednesday, May 22, 2024:
- Next month, voters will go to the polls in Mexico to select the country’s next president. The election is already historic because the two leading candidates, Claudia Sheinbaum and Xóchitl Gálvez are women. The election will also be notable because of the likely record number of Mexican citizens living in California and the rest of the U.S. who will cast ballots.
- Republican Assemblyman Vince Fong won a special election Tuesday to complete the remainder of the term of ousted House Speaker Kevin McCarthy. A McCarthy protege who was also endorsed by former President Donald Trump, Fong defeated fellow Republican and Tulare County Sheriff Mike Boudreaux in the race for the 20th Congressional District. The two will square off again in November, with the winner serving a full two-year term in the district.
- On Tuesday, the California Supreme Court heard arguments in a case that could have a profound impact on app-based companies like Uber and Lyft as well as on their drivers. Proposition 22, which was passed by voters four years ago, allowed gig companies to reclassify workers as self-employed contractors, rather than employees. Now the state Supreme Court will decide whether to uphold the law, strike it down or strip out part and leave the rest intact.
With Mexico’s Election Coming Up, Californians Could Play A Role In Deciding The Winner
Mexico’s presidential election takes place on June 2 . The election is historic, as both of Mexico’s front-running presidential candidates are women, Claudia Sheinbaum and Xóchitl Gálvez. And more than 20,000 different positions are at stake, from the presidency to the entire federal congress, along with several local races.
In California and across the United States, Mexican citizens are taking part in the election process . There are about 12 million people who were born in Mexico who now live in the U.S. and are eligible to vote in the election.
The number of people voting abroad has grown steadily, and this year there could be a record turnout.
Republican Assemblyman Wins Special Election In Central Valley District
Vince Fong, a California State Assembly member backed by former President Donald Trump, won a special election Tuesday to complete the remainder of the term of former U.S. House Speaker Kevin McCarthy , which runs through January.
Fong defeated fellow Republican and Tulare County Sheriff Mike Boudreaux in the 20th Congressional District, in the state’s Central Valley farm belt.
The two will face off once again in November, but this time, the winner will serve a full two-year term.
Fate of Gig Workers’ Benefits Now Up to the State Supreme Court
Based on their line of questioning, California Supreme Court justices seemed to be reaching for a compromise as they heard oral arguments Tuesday in the long-running legal saga over whether gig workers should be considered independent contractors or employees.
Proposition 22 , the gig industry-backed initiative that 58% of state voters passed in 2020, has been mired in a legal back-and-forth since it became law — including being ruled unconstitutional by a Superior Court judge before being upheld by a state appeals court. Uber, Lyft, DoorDash, Instacart and other companies have used the law to treat their drivers and delivery workers in California as independent contractors, not as employees.
The specific question before the state’s highest court is whether Prop. 22 conflicts with the state Legislature’s constitutional power to enforce a complete workers’ compensation system.
To learn more about how we use your information, please read our privacy policy.

Here is everything you need to know about the Elections 2024
He iec is ready and excited for the country's seventh democratic elections. here is everything you need to know..

South Africans will again get an opportunity to exercise their crucial right to vote in the 2024 National and Provincial elections, which marks the country’s seventh democratic elections.
According to the Electoral Commission (IEC) of South Africa, the Bill of Rights in South Africa ‘s pioneering Constitution grants all citizens aged 18 and older the right to vote. Still, the question often asked is whether voting will make a difference.
https://x.com/IECSouthAfrica/status/1787808805398401175
ALSO READ: Police investigate, hijacking and ATM bombing in Knopjeslaagte
Your vote matters! It’s your chance to be part of decision-making that directly impacts your life and the future of our country. If you don’t vote, you’re letting others decide for you.
Here is everything you need to know:
- On election day, go to the voting station where you’re registered (check your voter registration status to find out where you’re registered). During national and provincial elections, you can vote at any station countrywide. If you vote at a station outside the province you are registered in; you will only be able to vote in the national Election.
- Show the voting officer your green, bar-coded South African ID book or a temporary identification certificate.
- The voting officer checks that your name appears on the voters’ roll. If you are not on the voters’ roll but have proof that you have registered ( e.g. registration sticker), the Presiding Officer must validate your proof of registration. If satisfied with the proof , you must complete a VEC4 form (national elections) or MEC7 form (municipal elections) and will then proceed as an ordinary voter.
- Once the voting officer confirms that you possess the correct ID, are a registered voter, and have not already voted, they mark your name off the roll, stamp your ID on the second page, and ink your thumbnail.
- The voting officer stamps the back of the correct number of official ballot papers (one per Election) and gives them to you.
- Take your ballot paper to an empty ballot booth, mark it, fold it so that your choice isn’t visible, and place it in the ballot box.
- In these elections, voters will receive three ballot papers: the national compensatory ballot for political parties, provincial and regional ballots for parties and independent candidates. We wish to remind voters to make only one mark against the party or candidate of their choice. In other words, “One ballot, One Mark “.
Do you have more information about the story?
Please send us an email to [email protected] or phone us on 083 625 4114.
For free breaking and community news, visit Rekord’s websites: Rekord East
For more news and interesting articles, like Rekord on Facebook , follow us on Twitter or Instagram

This former Trump intern has no chance of being the Fulton County DA. But she has to try.
Courtney kramer has a history of working for trump and with lawyers who went on to be indicted for lying about voter fraud..
Courtney Kramer has been an attorney for just under 3 1/2 years .
In that relatively short career, three of her former bosses – including former President Donald Trump – have been indicted on attempting to overturn the 2020 election results in Georgia.
Kramer, who has no criminal trial experience, became the Republican nominee for district attorney in Fulton County on Tuesday. She's trying to oust Democratic incumbent Fani Willis, who is prosecuting Trump and 14 other defendants. Four others charged in the case already pleaded guilty .
This is not a hard call – Kramer will not defeat Willis in the general election.
That's not the point of her candidacy. The former Trump White House intern who would go on to work on his desperate and doomed attempt to undo the 2020 election is on the ballot as yet another way to attack his criminal case and the prosecutor leading it.
A Republican has no chance of winning Fulton
Just having a Republican on the ballot for district attorney in Fulton County is unusual. I searched county and state records as far back as they go online – 1972 – and could not find a Republican who sought the office in that time. That's more than half a century of GOP ballot no-shows.
Pete Skandalakis, executive director of the Prosecuting Attorneys’ Council of Georgia , told me that he's 68 years old and can't recall a Republican running for district attorney in Fulton County.
The office was led by Democrat Lewis Slaton from 1965 to 1996 and then Democrat Paul Howard Jr. from 1997 to 2020, when Willis defeated his bid for a seventh term . That's at least six decades of Democratic district attorneys.
Trump attacks mail-in ballots: Trump and the RNC want slow counting of mail ballots to target Biden supporters
Kramer on Tuesday told a local television station that she thinks conservatives deserve a voice in Fulton County. Then she quickly pivoted to attack Willis, who had suggested she was not qualified for the job.
"You have to have a good head on your shoulders," Kramer said of district attorneys. "You have to know the rules of professional conduct. You have to know when you have a conflict of interest. And I have that. Fani Willis has proven that she does not have that."
Expect Courtney Kramer to attempt to attack the Trump case
The judge overseeing Trump's election interference case in March ruled that Willis could keep control of it but that the lead prosecutor she hired to run it, Nathan Wade, had to step down after it was revealed that they had started and then ended a romantic relationship.
Judge Scott McAfee, in an order now being appealed by Trump and some of his co-defendants, said Willis showed a "tremendous lapse in judgment" at the intersection of her personal and professional lives. I agree ( and said so a month before the ruling ).
That's fair game for any political challenger to poke at. Willis left herself wide open with her behavior. Trump and his campaign were always going to capitalize on that.
And this appears to be Kramer's entire reason for running in a race she can't win. She can signal boost any Trump attacks on Willis, as she did in a social media post earlier this month, knocking Willis and other prosecutors with cases pending against Trump as "self-interested politicians who use their office for political law fare."
Kramer is so close to the Trump camp's 2020 election efforts that she said in an interview Tuesday if she's elected in November: "I have to recuse myself because I was involved with President Trump."
So while attacking Willis for acting with an apparent conflict of interest, Kramer acknowledges a conflict of her own large enough to keep her away from the biggest criminal case in the history of the office she claims she's trying to win.
Kramer's connection to Trump includes indicted bosses
Which brings us back to Kramer's former bosses . She interned in Trump's White House for four months in 2018 and then served as a "litigation consultant" for his campaign legal team from November 2020 to June 2021.
She was also a special counsel for the Georgia Republican Party during that time before moving on the the law firm of Smith & Liss.
Trump's political tricks: Trump calls for 'election integrity' again. It's same ploy he used in 2020 and 2016.
David Shafer, who was chair of the Georgia Republican Party while Kramer worked there, is accused in the August indictment of organizing a slate of fake electors in an effort to overturn the election.
Ray Smith III, a partner in the firm Kramer joined after the election, is charged on making now-debunked claims in state legislative hearings about widespread voter fraud in the 2020 election.
Both, like Trump, have pleaded not guilty.
That's some LinkedIn page and campaign pitch for Kramer: Here's my work experience and my bosses now under indictment. And that's why I want your vote for district attorney!
Kramer has a role to play in helping Trump
How long are the odds for Kramer? In 2020, Biden won Georgia by a margin of 2% but beat Trump in Fulton County that year by nearly 3 to 1.
Even so, Willis told supporters after she defeated a Democratic primary challenger Tuesday with 87% of the vote that super PACs will sweep into the race to help boost Kramer's attacks on her and the Trump prosecution.
"While she is inexperienced and unqualified and does not represent the values of my county, don’t get confused," Willis warned. "She is a real threat because of who backs her and how they back her.”
Willis didn't mention Trump by name but threw plenty of shade his way, noting that homicide and other crime rates are declining in Fulton County as her office went after "violent criminals and the powerful, no matter how powerful they think they are ."
Kramer could have a long and distinguished career in law that someday leads her to office as an elected prosecutor. That's not going to happen this year. Instead, she's playing the part of provocateur for a presidential contender who is also an accused racketeer .
Given the wreckage other Trump lawyers have seen from their service to him, I wonder if she'll look back on all this and consider it worth it.
Follow USA TODAY elections columnist Chris Brennan on X, formerly known as Twitter: @ByChrisBrennan

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Role of Citizens in American Democracy U.S. Constitution. ... Fair Elections Center is a national, nonpartisan voting rights and election reform 501(c)(3) organization with the mission of using litigation and advocacy to remove barriers to registration and voting, particularly those disenfranchising underrepresented and marginalized ...
The role of money in elections, and where it can be sourced. This page titled 4: Rights and Responsibilities of Citizens is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Robert W. Maloy & Torrey Trust ( EdTech Books ) via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform ...
Republicans and Democrats largely agree on the importance of most responsibilities of citizenship. About three-quarters of Republicans and Republican leaners (76%) and Democrats and Democratic leaners (75%) say it's very important to vote in elections. Similarly, comparable majorities of Republicans and Democrats say it's very important to ...
A History of Voting in the United States Today, most American citizens over the age of 18 are entitled to vote in federal and state elections, but voting was not always a default right for all Americans.The United States Constitution, as originally written, did not define specifically who could or could not vote—but it did establish how the new country would vote.
Standard 4.5: Voting and Citizen Participation in the Political Process. Describe how a democracy provides opportunities for citizens to participate in the political process through elections, political parties and interest groups. ( Massachusetts Curriculum Framework for History and Social Studies) [8.T4.5]
This essay explores the importance of voting, examining its role in shaping government policies, promoting representation, and fostering a sense of community participation. By understanding the significance of voting, we can appreciate its impact on governance and the collective voice of citizens.
Functions of elections. Elections make a fundamental contribution to democratic governance. Because direct democracy—a form of government in which political decisions are made directly by the entire body of qualified citizens—is impractical in most modern societies, democratic government must be conducted through representatives. Elections enable voters to select leaders and to hold them ...
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas. Importance of Election. First of all, the Election is a peaceful and efficient way of choosing political leaders. Furthermore, citizens of a Nation choose a leader by casting their votes. In this way, the citizens are able to choose an individual whose views appeal to them most.
500 Words Essay on Election and Democracy. A democratic government is said to be the best kind of government. It ensures the active participation of the people where the citizens get the chance to choose their government. The candidate or party whom the people choose is through elections.
The outcomes of elections can impact voters' personal freedoms, taxes, and other aspects of daily life that they take for granted. Because of the far reaching impact that an election can have, people have the duty to cast their vote if they want a say in how their futures play out. Casting Absentee Votes. People who have a legitimate reason ...
The period from the late 1890s through the first two decades of the 20th century saw the rise of radical political parties associated with unions and working people, notably the Populist Party and the Socialist Party. Both sought to represent workers in politics. Figure 3.5.4 3.5. 4: "Debs campaign" | Public domain.
Many democratic theorists resist the idea that democracy should aim at the full participation of citizens, arguing that participatory democracy misunderstands the role of democratic institutions, fails to protect minorities from the whims of majorities, and places too much power in the hands of people who cannot be reasonably expected to wield ...
supervision. Elections thus form the cornerstone of a modern civil society. Over time, elections have become the prevailing method for forming governments and legislative bodies, serving multiple functions, including nationwide opinion gathering. Despite their significant role in modern Democracy, elections face limitations in representing the
100 Words Essay on Election. India is one of the most populous democratic countries in the world, and democracy plays a vital role in our country. Elections in our country are held once in every five years. The results of the elections are often subject to numerous rumors, analyses, and opinions in the news.
The following are the roles of citizens in democracy: The citizens of a country vote in the elections and choose the representatives of the government. Citizens have a very important role in a democracy as they exercise their rights and freedoms and benefit from the democratic setup of the country
500 Words Essay on Importance of Election Introduction. Elections are the cornerstone of a vibrant democracy, providing the mechanism through which citizens exercise their right to choose their representatives. They are the conduit for the expression of public will, ensuring that governance is in the hands of those who have the mandate of the ...
Role of Citizens in the Election. A periodical election provides an opportunity to people for electing representatives as per their choice in different times. People can choose their preferred candidate or party in the election to form their government. A fair, independent and impartial election can help in the resolution of national problems.
The article actualizes the need to develop effective mechanisms for conducting elections on the basis of democracy with the minimization of risks of violations and further improvement of the electoral system of Ukraine. The democratic principles of the election process were analyzed, in particular, the compliance of the elections with the principles of democracy. It is emphasized that the ...
250 Words Essay on Importance of Voting in Democracy The Essence of Democracy. Democracy is often defined as 'government of the people, by the people, for the people.' It is a system that bestows power in the hands of the citizens to choose their representatives. The cornerstone of this power lies in the act of voting. The Role of Voting
Unit-5 Lesson-8. Role of Citizens in the Election. A. Short answer questions. 1. Prepare a model of dialogue between two friends who were discussing the role of a responsible citizen in the election. Ans:- (Pooja and Sonam are discussing about the role of a responsible citizen in the election)
Long Essay on Importance of Voting 500 Words in English. Long Essay on Importance of Voting is usually given to classes 7, 8, 9, and 10. The process by which people can express their political opinion is known as voting. Citizens of the country express their political opinion by choosing the desired political leader.
The study, published in the American Political Science Review, uncovers a more pragmatic motivation behind these stances. According to University of Florida political scientist Hannah Alarian, co-author of the study, "U.S. voters are more likely to support granting noncitizens the right to vote locally if it benefits their own party.
Citizens were disappointed with the electoral process, including those who supported the candidates who were declared winners. Among other issues, many polling stations opened late, and poll workers reported material shortages. ... Elections are an important benchmark in democratic development, but the real work of building democratic ...
Through providing this support, the centres make it possible for citizens to denounce corruption and participate in anti-corruption efforts. It is crucial that in all countries, citizens are able to recognize corruption and are empowered to participate, so as to avoid the consequences of unabated corruption, such as deep inequalities (Uslaner ...
South Africa's 29 May election has been tipped as the most important since the first democratic poll in 1994 and an important inflection point. Most polls have indicated that the ruling ANC will lose its majority but retain a leading role in national government and most of the provinces. The ...
The Federalist Papers. Appearing in New York newspapers as the New York Ratification Convention met in Poughkeepsie, John Jay, Alexander Hamilton and James Madison wrote as Publius and addressed the citizens of New York through the Federalist Papers. These essays subsequently circulated and were reprinted throughout the states as the ...
In North Carolina in 2016, an audit of elections found that 41 legal immigrants who had not yet become citizens cast ballots, out of 4.8 million total ballots cast. The votes didn't make a ...
Here are the morning's top stories on Wednesday, May 22, 2024: Next month, voters will go to the polls in Mexico to select the country's next president. The election is already historic because the two leading candidates, Claudia Sheinbaum and Xóchitl Gálvez are women. The election will also be notable because of the likely record number of Mexican citizens living in California and the ...
According to the Electoral Commission (IEC) of South Africa, the Bill of Rights in South Africa's pioneering Constitution grants all citizens aged 18 and older the right to vote.
In that relatively short career, three of her former bosses - including former President Donald Trump - have been indicted on attempting to overturn the 2020 election results in Georgia ...