How to Write an Article Critique Step-by-Step
Table of contents
- 1 What is an Article Critique Writing?
- 2 How to Critique an Article: The Main Steps
- 3 Article Critique Outline
- 4 Article Critique Formatting
- 5 How to Write a Journal Article Critique
- 6 How to Write a Research Article Critique
- 7 Research Methods in Article Critique Writing
- 8 Tips for writing an Article Critique
Do you know how to critique an article? If not, don’t worry – this guide will walk you through the writing process step-by-step. First, we’ll discuss what a research article critique is and its importance. Then, we’ll outline the key points to consider when critiquing a scientific article. Finally, we’ll provide a step-by-step guide on how to write an article critique including introduction, body and summary. Read more to get the main idea of crafting a critique paper.

What is an Article Critique Writing?
An article critique is a formal analysis and evaluation of a piece of writing. It is often written in response to a particular text but can also be a response to a book, a movie, or any other form of writing. There are many different types of review articles . Before writing an article critique, you should have an idea about each of them.
To start writing a good critique, you must first read the article thoroughly and examine and make sure you understand the article’s purpose. Then, you should outline the article’s key points and discuss how well they are presented. Next, you should offer your comments and opinions on the article, discussing whether you agree or disagree with the author’s points and subject. Finally, concluding your critique with a brief summary of your thoughts on the article would be best. Ensure that the general audience understands your perspective on the piece.
How to Critique an Article: The Main Steps
If you are wondering “what is included in an article critique,” the answer is:
An article critique typically includes the following:
- A brief summary of the article .
- A critical evaluation of the article’s strengths and weaknesses.
- A conclusion.
When critiquing an article, it is essential to critically read the piece and consider the author’s purpose and research strategies that the author chose. Next, provide a brief summary of the text, highlighting the author’s main points and ideas. Critique an article using formal language and relevant literature in the body paragraphs. Finally, describe the thesis statement, main idea, and author’s interpretations in your language using specific examples from the article. It is also vital to discuss the statistical methods used and whether they are appropriate for the research question. Make notes of the points you think need to be discussed, and also do a literature review from where the author ground their research. Offer your perspective on the article and whether it is well-written. Finally, provide background information on the topic if necessary.
When you are reading an article, it is vital to take notes and critique the text to understand it fully and to be able to use the information in it. Here are the main steps for critiquing an article:
- Read the piece thoroughly, taking notes as you go. Ensure you understand the main points and the author’s argument.
- Take a look at the author’s perspective. Is it powerful? Does it back up the author’s point of view?
- Carefully examine the article’s tone. Is it biased? Are you being persuaded by the author in any way?
- Look at the structure. Is it well organized? Does it make sense?
- Consider the writing style. Is it clear? Is it well-written?
- Evaluate the sources the author uses. Are they credible?
- Think about your own opinion. With what do you concur or disagree? Why?

Article Critique Outline
When assigned an article critique, your instructor asks you to read and analyze it and provide feedback. A specific format is typically followed when writing an article critique.
An article critique usually has three sections: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion.
- The introduction of your article critique should have a summary and key points.
- The critique’s main body should thoroughly evaluate the piece, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses, and state your ideas and opinions with supporting evidence.
- The conclusion should restate your research and describe your opinion.
You should provide your analysis rather than simply agreeing or disagreeing with the author. When writing an article review , it is essential to be objective and critical. Describe your perspective on the subject and create an article review summary. Be sure to use proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation, write it in the third person, and cite your sources.
Article Critique Formatting
When writing an article critique, you should follow a few formatting guidelines. The importance of using a proper format is to make your review clear and easy to read.
Make sure to use double spacing throughout your critique. It will make it easy to understand and read for your instructor.
Indent each new paragraph. It will help to separate your critique into different sections visually.
Use headings to organize your critique. Your introduction, body, and conclusion should stand out. It will make it easy for your instructor to follow your thoughts.
Use standard fonts, such as Times New Roman or Arial. It will make your critique easy to read.
Use 12-point font size. It will ensure that your critique is easy to read.

How to Write a Journal Article Critique
When critiquing a journal article, there are a few key points to keep in mind:
- Good critiques should be objective, meaning that the author’s ideas and arguments should be evaluated without personal bias.
- Critiques should be critical, meaning that all aspects of the article should be examined, including the author’s introduction, main ideas, and discussion.
- Critiques should be informative, providing the reader with a clear understanding of the article’s strengths and weaknesses.
When critiquing a research article, evaluating the author’s argument and the evidence they present is important. The author should state their thesis or the main point in the introductory paragraph. You should explain the article’s main ideas and evaluate the evidence critically. In the discussion section, the author should explain the implications of their findings and suggest future research.
It is also essential to keep a critical eye when reading scientific articles. In order to be credible, the scientific article must be based on evidence and previous literature. The author’s argument should be well-supported by data and logical reasoning.
How to Write a Research Article Critique
When you are assigned a research article, the first thing you need to do is read the piece carefully. Make sure you understand the subject matter and the author’s chosen approach. Next, you need to assess the importance of the author’s work. What are the key findings, and how do they contribute to the field of research?
Finally, you need to provide a critical point-by-point analysis of the article. This should include discussing the research questions, the main findings, and the overall impression of the scientific piece. In conclusion, you should state whether the text is good or bad. Read more to get an idea about curating a research article critique. But if you are not confident, you can ask “ write my papers ” and hire a professional to craft a critique paper for you. Explore your options online and get high-quality work quickly.
However, test yourself and use the following tips to write a research article critique that is clear, concise, and properly formatted.
- Take notes while you read the text in its entirety. Right down each point you agree and disagree with.
- Write a thesis statement that concisely and clearly outlines the main points.
- Write a paragraph that introduces the article and provides context for the critique.
- Write a paragraph for each of the following points, summarizing the main points and providing your own analysis:
- The purpose of the study
- The research question or questions
- The methods used
- The outcomes
- The conclusions were drawn by the author(s)
- Mention the strengths and weaknesses of the piece in a separate paragraph.
- Write a conclusion that summarizes your thoughts about the article.
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
Research Methods in Article Critique Writing
When writing an article critique, it is important to use research methods to support your arguments. There are a variety of research methods that you can use, and each has its strengths and weaknesses. In this text, we will discuss four of the most common research methods used in article critique writing: quantitative research, qualitative research, systematic reviews, and meta-analysis.
Quantitative research is a research method that uses numbers and statistics to analyze data. This type of research is used to test hypotheses or measure a treatment’s effects. Quantitative research is normally considered more reliable than qualitative research because it considers a large amount of information. But, it might be difficult to find enough data to complete it properly.
Qualitative research is a research method that uses words and interviews to analyze data. This type of research is used to understand people’s thoughts and feelings. Qualitative research is usually more reliable than quantitative research because it is less likely to be biased. Though it is more expensive and tedious.
Systematic reviews are a type of research that uses a set of rules to search for and analyze studies on a particular topic. Some think that systematic reviews are more reliable than other research methods because they use a rigorous process to find and analyze studies. However, they can be pricy and long to carry out.
Meta-analysis is a type of research that combines several studies’ results to understand a treatment’s overall effect better. Meta-analysis is generally considered one of the most reliable type of research because it uses data from several approved studies. Conversely, it involves a long and costly process.
Are you still struggling to understand the critique of an article concept? You can contact an online review writing service to get help from skilled writers. You can get custom, and unique article reviews easily.
Tips for writing an Article Critique
It’s crucial to keep in mind that you’re not just sharing your opinion of the content when you write an article critique. Instead, you are providing a critical analysis, looking at its strengths and weaknesses. In order to write a compelling critique, you should follow these tips: Take note carefully of the essential elements as you read it.
- Make sure that you understand the thesis statement.
- Write down your thoughts, including strengths and weaknesses.
- Use evidence from to support your points.
- Create a clear and concise critique, making sure to avoid giving your opinion.
It is important to be clear and concise when creating an article critique. You should avoid giving your opinion and instead focus on providing a critical analysis. You should also use evidence from the article to support your points.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
- All eBooks & Audiobooks
- Academic eBook Collection
- Home Grown eBook Collection
- Off-Campus Access
- Literature Resource Center
- Opposing Viewpoints
- ProQuest Central
- Course Guides
- Citing Sources
- Library Research
- Websites by Topic
- Book-a-Librarian
- Research Tutorials
- Use the Catalog
- Use Databases
- Use Films on Demand
- Use Home Grown eBooks
- Use NC LIVE
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary vs. Secondary
- Scholarly vs. Popular
- Make an Appointment
- Writing Tools
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing Center
Service Alert

Article Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing an article SUMMARY
- Writing an article REVIEW
Writing an article CRITIQUE
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- About RCC Library
Text: 336-308-8801
Email: [email protected]
Call: 336-633-0204
Schedule: Book-a-Librarian
Like us on Facebook
Links on this guide may go to external web sites not connected with Randolph Community College. Their inclusion is not an endorsement by Randolph Community College and the College is not responsible for the accuracy of their content or the security of their site.
A critique asks you to evaluate an article and the author’s argument. You will need to look critically at what the author is claiming, evaluate the research methods, and look for possible problems with, or applications of, the researcher’s claims.
Introduction
Give an overview of the author’s main points and how the author supports those points. Explain what the author found and describe the process they used to arrive at this conclusion.
Body Paragraphs
Interpret the information from the article:
- Does the author review previous studies? Is current and relevant research used?
- What type of research was used – empirical studies, anecdotal material, or personal observations?
- Was the sample too small to generalize from?
- Was the participant group lacking in diversity (race, gender, age, education, socioeconomic status, etc.)
- For instance, volunteers gathered at a health food store might have different attitudes about nutrition than the population at large.
- How useful does this work seem to you? How does the author suggest the findings could be applied and how do you believe they could be applied?
- How could the study have been improved in your opinion?
- Does the author appear to have any biases (related to gender, race, class, or politics)?
- Is the writing clear and easy to follow? Does the author’s tone add to or detract from the article?
- How useful are the visuals (such as tables, charts, maps, photographs) included, if any? How do they help to illustrate the argument? Are they confusing or hard to read?
- What further research might be conducted on this subject?
Try to synthesize the pieces of your critique to emphasize your own main points about the author’s work, relating the researcher’s work to your own knowledge or to topics being discussed in your course.
From the Center for Academic Excellence (opens in a new window), University of Saint Joseph Connecticut
Additional Resources
All links open in a new window.
Writing an Article Critique (from The University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center)
How to Critique an Article (from Essaypro.com)
How to Write an Article Critique (from EliteEditing.com.au)
- << Previous: Writing an article REVIEW
- Next: Citing Sources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 9:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.randolph.edu/summaries

SPH Writing Support Services
- Appointment System
- ESL Conversation Group
- Mini-Courses
- Thesis/Dissertation Writing Group
- Career Writing
- Citing Sources
- Critiquing Research Articles
- Project Planning for the Beginner This link opens in a new window
- Grant Writing
- Publishing in the Sciences
- Systematic Review Overview
- Systematic Review Resources This link opens in a new window
- Writing Across Borders / Writing Across the Curriculum
- Conducting an article critique for a quantitative research study: Perspectives for doctoral students and other novice readers (Vance et al.)
- Critique Process (Boswell & Cannon)
- The experience of critiquing published research: Learning from the student and researcher perspective (Knowles & Gray)
- A guide to critiquing a research paper. Methodological appraisal of a paper on nurses in abortion care (Lipp & Fothergill)
- Step-by-step guide to critiquing research. Part 1: Quantitative research (Coughlan et al.)
- Step-by-step guide to critiquing research. Part 2: Qualitative research (Coughlan et al.)
Guidelines:
- Critiquing Research Articles (Flinders University)
- Framework for How to Read and Critique a Research Study (American Nurses Association)
- How to Critique a Journal Article (UIS)
- How to Critique a Research Paper (University of Michigan)
- How to Write an Article Critique
- Research Article Critique Form
- Writing a Critique or Review of a Research Article (University of Calgary)
Presentations:
- The Critique Process: Reviewing and Critiquing Research
- Writing a Critique
- << Previous: Citing Sources
- Next: Project Planning for the Beginner >>
- Last Updated: Apr 30, 2024 12:52 PM
- URL: https://libguides.sph.uth.tmc.edu/writing_support_services
You are using an outdated browser
Unfortunately Ausmed.com does not support your browser. Please upgrade your browser to continue.
How to Critique a Research Article
Published: 01 October 2023

Let's briefly examine some basic pointers on how to perform a literature review.
If you've managed to get your hands on peer-reviewed articles, then you may wonder why it is necessary for you to perform your own article critique. Surely the article will be of good quality if it has made it through the peer-review process?
Unfortunately, this is not always the case.
Publication bias can occur when editors only accept manuscripts that have a bearing on the direction of their own research, or reject manuscripts with negative findings. Additionally, not all peer reviewers have expert knowledge on certain subject matters , which can introduce bias and sometimes a conflict of interest.
Performing your own critical analysis of an article allows you to consider its value to you and to your workplace.
Critical evaluation is defined as a systematic way of considering the truthfulness of a piece of research, its results and how relevant and applicable they are.
How to Critique
It can be a little overwhelming trying to critique an article when you're not sure where to start. Considering the article under the following headings may be of some use:
Title of Study/Research
You may be a better judge of this after reading the article, but the title should succinctly reflect the content of the work, stimulating readers' interest.
Three to six keywords that encapsulate the main topics of the research will have been drawn from the body of the article.
Introduction
This should include:
- Evidence of a literature review that is relevant and recent, critically appraising other works rather than merely describing them
- Background information on the study to orientate the reader to the problem
- Hypothesis or aims of the study
- Rationale for the study that justifies its need, i.e. to explore an un-investigated gap in the literature.

Materials and Methods
Similar to a recipe, the description of materials and methods will allow others to replicate the study elsewhere if needed. It should both contain and justify the exact specifications of selection criteria, sample size, response rate and any statistics used. This will demonstrate how the study is capable of achieving its aims. Things to consider in this section are:
- What sort of sampling technique and size was used?
- What proportion of the eligible sample participated? (e.g. '553 responded to a survey sent to 750 medical technologists'
- Were all eligible groups sampled? (e.g. was the survey sent only in English?)
- What were the strengths and weaknesses of the study?
- Were there threats to the reliability and validity of the study, and were these controlled for?
- Were there any obvious biases?
- If a trial was undertaken, was it randomised, case-controlled, blinded or double-blinded?
Results should be statistically analysed and presented in a way that an average reader of the journal will understand. Graphs and tables should be clear and promote clarity of the text. Consider whether:
- There were any major omissions in the results, which could indicate bias
- Percentages have been used to disguise small sample sizes
- The data generated is consistent with the data collected.
Negative results are just as relevant as research that produces positive results (but, as mentioned previously, may be omitted in publication due to editorial bias).
This should show insight into the meaning and significance of the research findings. It should not introduce any new material but should address how the aims of the study have been met. The discussion should use previous research work and theoretical concepts as the context in which the new study can be interpreted. Any limitations of the study, including bias, should be clearly presented. You will need to evaluate whether the author has clearly interpreted the results of the study, or whether the results could be interpreted another way.
Conclusions
These should be clearly stated and will only be valid if the study was reliable, valid and used a representative sample size. There may also be recommendations for further research.
These should be relevant to the study, be up-to-date, and should provide a comprehensive list of citations within the text.
Final Thoughts
Undertaking a critique of a research article may seem challenging at first, but will help you to evaluate whether the article has relevance to your own practice and workplace. Reading a single article can act as a springboard into researching the topic more widely, and aids in ensuring your nursing practice remains current and is supported by existing literature.
- Marshall, G 2005, ‘Critiquing a Research Article’, Radiography , vol. 11, no. 1, viewed 2 October 2023, https://www.radiographyonline.com/article/S1078-8174(04)00119-1/fulltext
Sarah Vogel View profile
Help and feedback, publications.
Ausmed Education is a Trusted Information Partner of Healthdirect Australia. Verify here .
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write an Article Critique
Tips for Writing a Psychology Critique Paper
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Cultura RM / Gu Cultura / Getty Images
- Steps for Writing a Critique
Evaluating the Article
- How to Write It
- Helpful Tips
An article critique involves critically analyzing a written work to assess its strengths and flaws. If you need to write an article critique, you will need to describe the article, analyze its contents, interpret its meaning, and make an overall assessment of the importance of the work.
Critique papers require students to conduct a critical analysis of another piece of writing, often a book, journal article, or essay . No matter your major, you will probably be expected to write a critique paper at some point.
For psychology students, critiquing a professional paper is a great way to learn more about psychology articles, writing, and the research process itself. Students will analyze how researchers conduct experiments, interpret results, and discuss the impact of the results.
At a Glance
An article critique involves making a critical assessment of a single work. This is often an article, but it might also be a book or other written source. It summarizes the contents of the article and then evaluates both the strengths and weaknesses of the piece. Knowing how to write an article critique can help you learn how to evaluate sources with a discerning eye.
Steps for Writing an Effective Article Critique
While these tips are designed to help students write a psychology critique paper, many of the same principles apply to writing article critiques in other subject areas.
Your first step should always be a thorough read-through of the material you will be analyzing and critiquing. It needs to be more than just a casual skim read. It should be in-depth with an eye toward key elements.
To write an article critique, you should:
- Read the article , noting your first impressions, questions, thoughts, and observations
- Describe the contents of the article in your own words, focusing on the main themes or ideas
- Interpret the meaning of the article and its overall importance
- Critically evaluate the contents of the article, including any strong points as well as potential weaknesses
The following guidelines can help you assess the article you are reading and make better sense of the material.
Read the Introduction Section of the Article
Start by reading the introduction . Think about how this part of the article sets up the main body and how it helps you get a background on the topic.
- Is the hypothesis clearly stated?
- Is the necessary background information and previous research described in the introduction?
In addition to answering these basic questions, note other information provided in the introduction and any questions you have.
Read the Methods Section of the Article
Is the study procedure clearly outlined in the methods section ? Can you determine which variables the researchers are measuring?
Remember to jot down questions and thoughts that come to mind as you are reading. Once you have finished reading the paper, you can then refer back to your initial questions and see which ones remain unanswered.
Read the Results Section of the Article
Are all tables and graphs clearly labeled in the results section ? Do researchers provide enough statistical information? Did the researchers collect all of the data needed to measure the variables in question?
Make a note of any questions or information that does not seem to make sense. You can refer back to these questions later as you are writing your final critique.
Read the Discussion Section of the Article
Experts suggest that it is helpful to take notes while reading through sections of the paper you are evaluating. Ask yourself key questions:
- How do the researchers interpret the results of the study?
- Did the results support their hypothesis?
- Do the conclusions drawn by the researchers seem reasonable?
The discussion section offers students an excellent opportunity to take a position. If you agree with the researcher's conclusions, explain why. If you feel the researchers are incorrect or off-base, point out problems with the conclusions and suggest alternative explanations.
Another alternative is to point out questions the researchers failed to answer in the discussion section.
Begin Writing Your Own Critique of the Paper
Once you have read the article, compile your notes and develop an outline that you can follow as you write your psychology critique paper. Here's a guide that will walk you through how to structure your critique paper.
Introduction
Begin your paper by describing the journal article and authors you are critiquing. Provide the main hypothesis (or thesis) of the paper. Explain why you think the information is relevant.
Thesis Statement
The final part of your introduction should include your thesis statement. Your thesis statement is the main idea of your critique. Your thesis should briefly sum up the main points of your critique.
Article Summary
Provide a brief summary of the article. Outline the main points, results, and discussion.
When describing the study or paper, experts suggest that you include a summary of the questions being addressed, study participants, interventions, comparisons, outcomes, and study design.
Don't get bogged down by your summary. This section should highlight the main points of the article you are critiquing. Don't feel obligated to summarize each little detail of the main paper. Focus on giving the reader an overall idea of the article's content.
Your Analysis
In this section, you will provide your critique of the article. Describe any problems you had with the author's premise, methods, or conclusions. You might focus your critique on problems with the author's argument, presentation, information, and alternatives that have been overlooked.
When evaluating a study, summarize the main findings—including the strength of evidence for each main outcome—and consider their relevance to key demographic groups.
Organize your paper carefully. Be careful not to jump around from one argument to the next. Arguing one point at a time ensures that your paper flows well and is easy to read.
Your critique paper should end with an overview of the article's argument, your conclusions, and your reactions.
More Tips When Writing an Article Critique
- As you are editing your paper, utilize a style guide published by the American Psychological Association, such as the official Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association .
- Reading scientific articles can be challenging at first. Remember that this is a skill that takes time to learn but that your skills will become stronger the more that you read.
- Take a rough draft of your paper to your school's writing lab for additional feedback and use your university library's resources.
What This Means For You
Being able to write a solid article critique is a useful academic skill. While it can be challenging, start by breaking down the sections of the paper, noting your initial thoughts and questions. Then structure your own critique so that you present a summary followed by your evaluation. In your critique, include the strengths and the weaknesses of the article.
Archibald D, Martimianakis MA. Writing, reading, and critiquing reviews . Can Med Educ J . 2021;12(3):1-7. doi:10.36834/cmej.72945
Pautasso M. Ten simple rules for writing a literature review . PLoS Comput Biol . 2013;9(7):e1003149. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
Gülpınar Ö, Güçlü AG. How to write a review article? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):44–48. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.054
Erol A. Basics of writing review articles . Noro Psikiyatr Ars . 2022;59(1):1-2. doi:10.29399/npa.28093
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2019.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
How to Critique an Article: Mastering the Article Evaluation Process

Did you know that approximately 4.6 billion pieces of content are produced every day? From news articles and blog posts to scholarly papers and social media updates, the digital landscape is flooded with information at an unprecedented rate. In this age of information overload, honing the skill of articles critique has never been more crucial. Whether you're seeking to bolster your academic prowess, stay well-informed, or improve your writing, mastering the art of article critique is a powerful tool to navigate the vast sea of information and discern the pearls of wisdom.
How to Critique an Article: Short Description
In this article, we will equip you with valuable tips and techniques to become an insightful evaluator of written content. We present a real-life article critique example to guide your learning process and help you develop your unique critique style. Additionally, we explore the key differences between critiquing scientific articles and journals. Whether you're a student, researcher, or avid reader, this guide will empower you to navigate the vast ocean of information with confidence and discernment. Still, have questions? Don't worry! We've got you covered with a helpful FAQ section to address any lingering doubts. Get ready to unleash your analytical prowess and uncover the true potential of every article that comes your way!
What Is an Article Critique: Understanding The Power of Evaluation
An article critique is a valuable skill that involves carefully analyzing and evaluating a written piece, such as a journal article, blog post, or news article. It goes beyond mere summarization and delves into the deeper layers of the content, examining its strengths, weaknesses, and overall effectiveness. Think of it as an engaging conversation with the author, where you provide constructive feedback and insights.
For instance, let's consider a scenario where you're critiquing a research paper on climate change. Instead of simply summarizing the findings, you would scrutinize the methodology, data interpretation, and potential biases, offering thoughtful observations to enrich the discussion. Through the process of writing an article critique, you develop a critical eye, honing your ability to appreciate well-crafted work while also identifying areas for improvement.
In the following sections, our ' write my paper ' experts will uncover valuable tips on and key points on how to write a stellar critique, so let's explore more!
Unveiling the Key Aims of Writing an Article Critique
Writing an article critique serves several essential purposes that go beyond a simple review or summary. When engaging in the art of critique, as when you learn how to write a review article , you embark on a journey of in-depth analysis, sharpening your critical thinking skills and contributing to the academic and intellectual discourse. Primarily, an article critique allows you to:
%20(3).webp)
- Evaluate the Content : By critiquing an article, you delve into its content, structure, and arguments, assessing its credibility and relevance.
- Strengthen Your Critical Thinking : This practice hones your ability to identify strengths and weaknesses in written works, fostering a deeper understanding of complex topics and critical evaluation skills.
- Engage in Scholarly Dialogue : Your critique contributes to the ongoing academic conversation, offering valuable insights and thoughtful observations to the existing body of knowledge.
- Enhance Writing Skills : By analyzing and providing feedback, you develop a keen eye for effective writing techniques, benefiting your own writing endeavors.
- Promote Continuous Learning : Through the writing process, you continually refine your analytical abilities, becoming an avid and astute learner in the pursuit of knowledge.
How to Critique an Article: Steps to Follow
The process of crafting an article critique may seem overwhelming, especially when dealing with intricate academic writing. However, fear not, for it is more straightforward than it appears! To excel in this art, all you require is a clear starting point and the skill to align your critique with the complexities of the content. To help you on your journey, follow these 3 simple steps and unlock the potential to provide insightful evaluations:
%20(4).webp)
Step 1: Read the Article
The first and most crucial step when wondering how to do an article critique is to thoroughly read and absorb its content. As you delve into the written piece, consider these valuable tips from our custom essay writer to make your reading process more effective:
- Take Notes : Keep a notebook or digital document handy while reading. Jot down key points, noteworthy arguments, and any questions or observations that arise.
- Annotate the Text : Underline or highlight significant passages, quotes, or sections that stand out to you. Use different colors to differentiate between positive aspects and areas that may need improvement.
- Consider the Author's Purpose : Reflect on the author's main critical point and the intended audience. Much like an explanatory essay , evaluate how effectively the article conveys its message to the target readership.
Now, let's say you are writing an article critique on climate change. While reading, you come across a compelling quote from a renowned environmental scientist highlighting the urgency of addressing global warming. By taking notes and underlining this impactful quote, you can later incorporate it into your critique as evidence of the article's effectiveness in conveying the severity of the issue.
Step 2: Take Notes/ Make sketches
Once you've thoroughly read the article, it's time to capture your thoughts and observations by taking comprehensive notes or creating sketches. This step plays a crucial role in organizing your critique and ensuring you don't miss any critical points. Here's how to make the most out of this process:
- Highlight Key Arguments : Identify the main arguments presented by the author and highlight them in your notes. This will help you focus on the core ideas that shape the article.
- Record Supporting Evidence : Take note of any evidence, examples, or data the author uses to support their arguments. Assess the credibility and effectiveness of this evidence in bolstering their claims.
- Examine Structure and Flow : Pay attention to the article's structure and how each section flows into the next. Analyze how well the author transitions between ideas and whether the organization enhances or hinders the reader's understanding.
- Create Visual Aids : If you're a visual learner, consider using sketches or diagrams to map out the article's key points and their relationships. Visual representations can aid in better grasping the content's structure and complexities.
Step 3: Format Your Paper
Once you've gathered your notes and insights, it's time to give structure to your article critique. Proper formatting ensures your critique is organized, coherent, and easy to follow. Here are essential tips for formatting an article critique effectively:
- Introduction : Begin with a clear and engaging introduction that provides context for the article you are critiquing. Include the article's title, author's name, publication details, and a brief overview of the main theme or thesis.
- Thesis Statement : Present a strong and concise thesis statement that conveys your overall assessment of the article. Your thesis should reflect whether you found the article compelling, convincing, or in need of improvement.
- Body Paragraphs : Organize your critique into well-structured body paragraphs. Each paragraph should address a specific point or aspect of the article, supported by evidence and examples from your notes.
- Use Evidence : Back up your critique with evidence from the article itself. Quote relevant passages, cite examples, and reference data to strengthen your analysis and demonstrate your understanding of the article's content.
- Conclusion : Conclude your critique by summarizing your main points and reiterating your overall evaluation. Avoid introducing new arguments in the conclusion and instead provide a concise and compelling closing statement.
- Citation Style : If required, adhere to the specific citation style guidelines (e.g., APA, MLA) for in-text citations and the reference list. Properly crediting the original article and any additional sources you use in your critique is essential.
How to Critique a Journal Article: Mastering the Steps
So, you've been assigned the task of critiquing a journal article, and not sure where to start? Worry not, as we've prepared a comprehensive guide with different steps to help you navigate this process with confidence. Journal articles are esteemed sources of scholarly knowledge, and effectively critiquing them requires a systematic approach. Let's dive into the steps to expertly evaluate and analyze a journal article:
Step 1: Understanding the Research Context
Begin by familiarizing yourself with the broader research context in which the journal article is situated. Learn about the field, the topic's significance, and any previous relevant research. This foundational knowledge will provide a valuable backdrop for your journal article critique example.
Step 2: Evaluating the Article's Structure
Assess the article's overall structure and organization. Examine how the introduction sets the stage for the research and how the discussion flows logically from the methodology and results. A well-structured article enhances readability and comprehension.
Step 3: Analyzing the Research Methodology
Dive into the research methodology section, which outlines the approach used to gather and analyze data. Scrutinize the study's design, data collection methods, sample size, and any potential biases or limitations. Understanding the research process will enable you to gauge the article's reliability.
Step 4: Assessing the Data and Results
Examine the presentation of data and results in the article. Are the findings clear and effectively communicated? Look for any discrepancies between the data presented and the interpretations made by the authors.
Step 5: Analyzing the Discussion and Conclusions
Evaluate the discussion section, where the authors interpret their findings and place them in the broader context. Assess the soundness of their conclusions, considering whether they are adequately supported by the data.
Step 6: Considering Ethical Considerations
Reflect on any ethical considerations raised by the research. Assess whether the study respects the rights and privacy of participants and adheres to ethical guidelines.
Step 7: Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses
Identify the article's strengths, such as well-designed experiments, comprehensive, relevant literature reviews, or innovative approaches. Also, pinpoint any weaknesses, like gaps in the research, unclear explanations, or insufficient evidence.
Step 8: Offering Constructive Feedback
Provide constructive feedback to the authors, highlighting both positive aspects and areas for improvement for future research. Suggest ways to enhance the research methods, data analysis, or discussion to bolster its overall quality.
Step 9: Presenting Your Critique
Organize your critique into a well-structured paper, starting with an introduction that outlines the article's context and purpose. Develop a clear and focused thesis statement that conveys your assessment. Support your points with evidence from the article and other credible sources.
By following these steps on how to critique a journal article, you'll be well-equipped to craft a thoughtful and insightful piece, contributing to the scholarly discourse in your field of study!
Got an Article that Needs Some Serious Critiquing?
Don't sweat it! Our critique maestros are armed with wit, wisdom, and a dash of magic to whip that piece into shape.
An Article Critique: Journal Vs. Research
In the realm of academic writing, the terms 'journal article' and 'research paper' are often used interchangeably, which can lead to confusion about their differences. Understanding the distinctions between critiquing a research article and a journal piece is essential. Let's delve into the key characteristics that set apart a journal article from a research paper and explore how the critique process may differ for each:
Publication Scope:
- Journal Article: Presents focused and concise research findings or new insights within a specific subject area.
- Research Paper: Explores a broader range of topics and can cover extensive research on a particular subject.
Format and Structure:
- Journal Article: Follows a standardized format with sections such as abstract, introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- Research Paper: May not adhere to a specific format and allows flexibility in organizing content based on the research scope.
Depth of Analysis:
- Journal Article: Provides a more concise and targeted analysis of the research topic or findings.
- Research Paper: Offers a more comprehensive and in-depth analysis, often including extensive literature reviews and data analyses.
- Journal Article: Typically shorter in length, ranging from a few pages to around 10-15 pages.
- Research Paper: Tends to be longer, spanning from 20 to several hundred pages, depending on the research complexity.
Publication Type:
- Journal Article: Published in academic journals after undergoing rigorous peer review.
- Research Paper: May be published as a standalone work or as part of a thesis, dissertation, or academic report.
- Journal Article: Targeted at academics, researchers, and professionals within the specific field of study.
- Research Paper: Can cater to a broader audience, including students, researchers, policymakers, and the general public.
- Journal Article: Primarily aimed at sharing new research findings, contributing to academic discourse, and advancing knowledge in the field.
- Research Paper: Focuses on comprehensive exploration and analysis of a research topic, aiming to make a substantial contribution to the body of knowledge.
Appreciating these differences becomes paramount when engaging in the critique of these two forms of scholarly publications, as they each demand a unique approach and thoughtful consideration of their distinctive attributes. And if you find yourself desiring a flawlessly crafted research article critique example, entrusting the task to professional writers is always an excellent option – you can easily order essay that meets your needs.
Article Critique Example
Our collection of essay samples offers a comprehensive and practical illustration of the critique process, granting you access to valuable insights.
Tips on How to Critique an Article
Critiquing an article requires a keen eye, critical thinking, and a thoughtful approach to evaluating its content. To enhance your article critique skills and provide insightful analyses, consider incorporating these five original and practical tips into your process:
1. Analyze the Author's Bias : Be mindful of potential biases in the article, whether they are political, cultural, or personal. Consider how these biases may influence the author's perspective and the presentation of information. Evaluating the presence of bias enables you to discern the objectivity and credibility of the article's arguments.
2. Examine the Supporting Evidence : Scrutinize the quality and relevance of the evidence used to support the article's claims. Look for well-researched data, credible sources, and up-to-date statistics. Assess how effectively the author integrates evidence to build a compelling case for their arguments.
3. Consider the Audience's Perspective : Put yourself in the shoes of the intended audience and assess how well the article communicates its ideas. Consider whether the language, tone, and level of complexity are appropriate for the target readership. A well-tailored article is more likely to engage and resonate with its audience.
4. Investigate the Research Methodology : If the article involves research or empirical data, delve into the methodology used to gather and analyze the information. Evaluate the soundness of the study design, sample size, and data collection methods. Understanding the research process adds depth to your critique.
5. Discuss the Implications and Application : Consider the broader implications of the article's findings or arguments. Discuss how the insights presented in the article could impact the field of study or have practical applications in real-world scenarios. Identifying the potential consequences of the article's content strengthens your critique's depth and relevance.
Wrapping Up
In a nutshell, article critique is an essential skill that helps us grow as critical thinkers and active participants in academia. Embrace the opportunity to analyze and offer constructive feedback, contributing to a brighter future of knowledge and understanding. Remember, each critique is a chance to engage with new ideas and expand our horizons. So, keep honing your critique skills and enjoy the journey of discovery in the world of academic exploration!
Tired of Ordinary Critiques?
Brace yourself for an extraordinary experience! Our critique geniuses are on standby, ready to unleash their extraordinary skills on your article!
What Steps Need to Be Taken in Writing an Article Critique?
What is the recommended length for an article critique.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.

Related Articles
%20(3).webp)

- Queen's University Library
- Research Guides
How to Critique an Article (Psychology)
Introduction.
- The introduction is a justification for why the study was conducted.
- By the end of the introduction you should have a very good idea of what the researchers are going to study, and be convinced that the study is absolutely necessary to advance the field.
- The justification should be a combination of improving on previous research and good theoretical reasons and practical reasons for why the study is important.
- If the authors are talking about a controversial issue, are they presenting both sides in a reasonable way? Is their choice of one side over the other based on hard evidence?
- Do you understand what their hypotheses are e.g. what they expect to find?
- It is not good enough just to say that the study has not been done before. There are plenty of topics that have not been scientifically researched before but that doesn't mean that they should be. For example, I doubt that anyone has ever looked at the correlation between favorite color of Skittles and personality, but that doesn't mean that it should be researched unless there is a good theoretical reason for why we would expect a relationship and a good reason to think that knowing the relationship would advance our understanding of personality in some meaningful way.

- Last Updated: Nov 5, 2021 9:46 AM
- Subjects: Psychology
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Can Med Educ J
- v.12(3); 2021 Jun

Writing, reading, and critiquing reviews
Écrire, lire et revue critique, douglas archibald.
1 University of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada;
Maria Athina Martimianakis
2 University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Why reviews matter
What do all authors of the CMEJ have in common? For that matter what do all health professions education scholars have in common? We all engage with literature. When you have an idea or question the first thing you do is find out what has been published on the topic of interest. Literature reviews are foundational to any study. They describe what is known about given topic and lead us to identify a knowledge gap to study. All reviews require authors to be able accurately summarize, synthesize, interpret and even critique the research literature. 1 , 2 In fact, for this editorial we have had to review the literature on reviews . Knowledge and evidence are expanding in our field of health professions education at an ever increasing rate and so to help keep pace, well written reviews are essential. Though reviews may be difficult to write, they will always be read. In this editorial we survey the various forms review articles can take. As well we want to provide authors and reviewers at CMEJ with some guidance and resources to be able write and/or review a review article.
What are the types of reviews conducted in Health Professions Education?
Health professions education attracts scholars from across disciplines and professions. For this reason, there are numerous ways to conduct reviews and it is important to familiarize oneself with these different forms to be able to effectively situate your work and write a compelling rationale for choosing your review methodology. 1 , 2 To do this, authors must contend with an ever-increasing lexicon of review type articles. In 2009 Grant and colleagues conducted a typology of reviews to aid readers makes sense of the different review types, listing fourteen different ways of conducting reviews, not all of which are mutually exclusive. 3 Interestingly, in their typology they did not include narrative reviews which are often used by authors in health professions education. In Table 1 , we offer a short description of three common types of review articles submitted to CMEJ.
Three common types of review articles submitted to CMEJ
More recently, authors such as Greenhalgh 4 have drawn attention to the perceived hierarchy of systematic reviews over scoping and narrative reviews. Like Greenhalgh, 4 we argue that systematic reviews are not to be seen as the gold standard of all reviews. Instead, it is important to align the method of review to what the authors hope to achieve, and pursue the review rigorously, according to the tenets of the chosen review type. Sometimes it is helpful to read part of the literature on your topic before deciding on a methodology for organizing and assessing its usefulness. Importantly, whether you are conducting a review or reading reviews, appreciating the differences between different types of reviews can also help you weigh the author’s interpretation of their findings.
In the next section we summarize some general tips for conducting successful reviews.
How to write and review a review article
In 2016 David Cook wrote an editorial for Medical Education on tips for a great review article. 13 These tips are excellent suggestions for all types of articles you are considering to submit to the CMEJ. First, start with a clear question: focused or more general depending on the type of review you are conducting. Systematic reviews tend to address very focused questions often summarizing the evidence of your topic. Other types of reviews tend to have broader questions and are more exploratory in nature.
Following your question, choose an approach and plan your methods to match your question…just like you would for a research study. Fortunately, there are guidelines for many types of reviews. As Cook points out the most important consideration is to be sure that the methods you follow lead to a defensible answer to your review question. To help you prepare for a defensible answer there are many guides available. For systematic reviews consult PRISMA guidelines ; 13 for scoping reviews PRISMA-ScR ; 14 and SANRA 15 for narrative reviews. It is also important to explain to readers why you have chosen to conduct a review. You may be introducing a new way for addressing an old problem, drawing links across literatures, filling in gaps in our knowledge about a phenomenon or educational practice. Cook refers to this as setting the stage. Linking back to the literature is important. In systematic reviews for example, you must be clear in explaining how your review builds on existing literature and previous reviews. This is your opportunity to be critical. What are the gaps and limitations of previous reviews? So, how will your systematic review resolve the shortcomings of previous work? In other types of reviews, such as narrative reviews, its less about filling a specific knowledge gap, and more about generating new research topic areas, exposing blind spots in our thinking, or making creative new links across issues. Whatever, type of review paper you are working on, the next steps are ones that can be applied to any scholarly writing. Be clear and offer insight. What is your main message? A review is more than just listing studies or referencing literature on your topic. Lead your readers to a convincing message. Provide commentary and interpretation for the studies in your review that will help you to inform your conclusions. For systematic reviews, Cook’s final tip is most likely the most important– report completely. You need to explain all your methods and report enough detail that readers can verify the main findings of each study you review. The most common reasons CMEJ reviewers recommend to decline a review article is because authors do not follow these last tips. In these instances authors do not provide the readers with enough detail to substantiate their interpretations or the message is not clear. Our recommendation for writing a great review is to ensure you have followed the previous tips and to have colleagues read over your paper to ensure you have provided a clear, detailed description and interpretation.
Finally, we leave you with some resources to guide your review writing. 3 , 7 , 8 , 10 , 11 , 16 , 17 We look forward to seeing your future work. One thing is certain, a better appreciation of what different reviews provide to the field will contribute to more purposeful exploration of the literature and better manuscript writing in general.
In this issue we present many interesting and worthwhile papers, two of which are, in fact, reviews.
Major Contributions
A chance for reform: the environmental impact of travel for general surgery residency interviews by Fung et al. 18 estimated the CO 2 emissions associated with traveling for residency position interviews. Due to the high emissions levels (mean 1.82 tonnes per applicant), they called for the consideration of alternative options such as videoconference interviews.
Understanding community family medicine preceptors’ involvement in educational scholarship: perceptions, influencing factors and promising areas for action by Ward and team 19 identified barriers, enablers, and opportunities to grow educational scholarship at community-based teaching sites. They discovered a growing interest in educational scholarship among community-based family medicine preceptors and hope the identification of successful processes will be beneficial for other community-based Family Medicine preceptors.
Exploring the global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on medical education: an international cross-sectional study of medical learners by Allison Brown and team 20 studied the impact of COVID-19 on medical learners around the world. There were different concerns depending on the levels of training, such as residents’ concerns with career timeline compared to trainees’ concerns with the quality of learning. Overall, the learners negatively perceived the disruption at all levels and geographic regions.
The impact of local health professions education grants: is it worth the investment? by Susan Humphrey-Murto and co-authors 21 considered factors that lead to the publication of studies supported by local medical education grants. They identified several factors associated with publication success, including previous oral or poster presentations. They hope their results will be valuable for Canadian centres with local grant programs.
Exploring the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on medical learner wellness: a needs assessment for the development of learner wellness interventions by Stephana Cherak and team 22 studied learner-wellness in various training environments disrupted by the pandemic. They reported a negative impact on learner wellness at all stages of training. Their results can benefit the development of future wellness interventions.
Program directors’ reflections on national policy change in medical education: insights on decision-making, accreditation, and the CanMEDS framework by Dore, Bogie, et al. 23 invited program directors to reflect on the introduction of the CanMEDS framework into Canadian postgraduate medical education programs. Their survey revealed that while program directors (PDs) recognized the necessity of the accreditation process, they did not feel they had a voice when the change occurred. The authors concluded that collaborations with PDs would lead to more successful outcomes.
Experiential learning, collaboration and reflection: key ingredients in longitudinal faculty development by Laura Farrell and team 24 stressed several elements for effective longitudinal faculty development (LFD) initiatives. They found that participants benefited from a supportive and collaborative environment while trying to learn a new skill or concept.
Brief Reports
The effect of COVID-19 on medical students’ education and wellbeing: a cross-sectional survey by Stephanie Thibaudeau and team 25 assessed the impact of COVID-19 on medical students. They reported an overall perceived negative impact, including increased depressive symptoms, increased anxiety, and reduced quality of education.
In Do PGY-1 residents in Emergency Medicine have enough experiences in resuscitations and other clinical procedures to meet the requirements of a Competence by Design curriculum? Meshkat and co-authors 26 recorded the number of adult medical resuscitations and clinical procedures completed by PGY1 Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians in Emergency Medicine residents to compare them to the Competence by Design requirements. Their study underscored the importance of monitoring collection against pre-set targets. They concluded that residency program curricula should be regularly reviewed to allow for adequate clinical experiences.
Rehearsal simulation for antenatal consults by Anita Cheng and team 27 studied whether rehearsal simulation for antenatal consults helped residents prepare for difficult conversations with parents expecting complications with their baby before birth. They found that while rehearsal simulation improved residents’ confidence and communication techniques, it did not prepare them for unexpected parent responses.
Review Papers and Meta-Analyses
Peer support programs in the fields of medicine and nursing: a systematic search and narrative review by Haykal and co-authors 28 described and evaluated peer support programs in the medical field published in the literature. They found numerous diverse programs and concluded that including a variety of delivery methods to meet the needs of all participants is a key aspect for future peer-support initiatives.
Towards competency-based medical education in addictions psychiatry: a systematic review by Bahji et al. 6 identified addiction interventions to build competency for psychiatry residents and fellows. They found that current psychiatry entrustable professional activities need to be better identified and evaluated to ensure sustained competence in addictions.
Six ways to get a grip on leveraging the expertise of Instructional Design and Technology professionals by Chen and Kleinheksel 29 provided ways to improve technology implementation by clarifying the role that Instructional Design and Technology professionals can play in technology initiatives and technology-enhanced learning. They concluded that a strong collaboration is to the benefit of both the learners and their future patients.
In his article, Seven ways to get a grip on running a successful promotions process, 30 Simon Field provided guidelines for maximizing opportunities for successful promotion experiences. His seven tips included creating a rubric for both self-assessment of likeliness of success and adjudication by the committee.
Six ways to get a grip on your first health education leadership role by Stasiuk and Scott 31 provided tips for considering a health education leadership position. They advised readers to be intentional and methodical in accepting or rejecting positions.
Re-examining the value proposition for Competency-Based Medical Education by Dagnone and team 32 described the excitement and controversy surrounding the implementation of competency-based medical education (CBME) by Canadian postgraduate training programs. They proposed observing which elements of CBME had a positive impact on various outcomes.
You Should Try This
In their work, Interprofessional culinary education workshops at the University of Saskatchewan, Lieffers et al. 33 described the implementation of interprofessional culinary education workshops that were designed to provide health professions students with an experiential and cooperative learning experience while learning about important topics in nutrition. They reported an enthusiastic response and cooperation among students from different health professional programs.
In their article, Physiotherapist-led musculoskeletal education: an innovative approach to teach medical students musculoskeletal assessment techniques, Boulila and team 34 described the implementation of physiotherapist-led workshops, whether the workshops increased medical students’ musculoskeletal knowledge, and if they increased confidence in assessment techniques.
Instagram as a virtual art display for medical students by Karly Pippitt and team 35 used social media as a platform for showcasing artwork done by first-year medical students. They described this shift to online learning due to COVID-19. Using Instagram was cost-saving and widely accessible. They intend to continue with both online and in-person displays in the future.
Adapting clinical skills volunteer patient recruitment and retention during COVID-19 by Nazerali-Maitland et al. 36 proposed a SLIM-COVID framework as a solution to the problem of dwindling volunteer patients due to COVID-19. Their framework is intended to provide actionable solutions to recruit and engage volunteers in a challenging environment.
In Quick Response codes for virtual learner evaluation of teaching and attendance monitoring, Roxana Mo and co-authors 37 used Quick Response (QR) codes to monitor attendance and obtain evaluations for virtual teaching sessions. They found QR codes valuable for quick and simple feedback that could be used for many educational applications.
In Creation and implementation of the Ottawa Handbook of Emergency Medicine Kaitlin Endres and team 38 described the creation of a handbook they made as an academic resource for medical students as they shift to clerkship. It includes relevant content encountered in Emergency Medicine. While they intended it for medical students, they also see its value for nurses, paramedics, and other medical professionals.
Commentary and Opinions
The alarming situation of medical student mental health by D’Eon and team 39 appealed to medical education leaders to respond to the high numbers of mental health concerns among medical students. They urged leaders to address the underlying problems, such as the excessive demands of the curriculum.
In the shadows: medical student clinical observerships and career exploration in the face of COVID-19 by Law and co-authors 40 offered potential solutions to replace in-person shadowing that has been disrupted due to the COVID-19 pandemic. They hope the alternatives such as virtual shadowing will close the gap in learning caused by the pandemic.
Letters to the Editor
Canadian Federation of Medical Students' response to “ The alarming situation of medical student mental health” King et al. 41 on behalf of the Canadian Federation of Medical Students (CFMS) responded to the commentary by D’Eon and team 39 on medical students' mental health. King called upon the medical education community to join the CFMS in its commitment to improving medical student wellbeing.
Re: “Development of a medical education podcast in obstetrics and gynecology” 42 was written by Kirubarajan in response to the article by Development of a medical education podcast in obstetrics and gynecology by Black and team. 43 Kirubarajan applauded the development of the podcast to meet a need in medical education, and suggested potential future topics such as interventions to prevent learner burnout.
Response to “First year medical student experiences with a clinical skills seminar emphasizing sexual and gender minority population complexity” by Kumar and Hassan 44 acknowledged the previously published article by Biro et al. 45 that explored limitations in medical training for the LGBTQ2S community. However, Kumar and Hassen advocated for further progress and reform for medical training to address the health requirements for sexual and gender minorities.
In her letter, Journey to the unknown: road closed!, 46 Rosemary Pawliuk responded to the article, Journey into the unknown: considering the international medical graduate perspective on the road to Canadian residency during the COVID-19 pandemic, by Gutman et al. 47 Pawliuk agreed that international medical students (IMGs) do not have adequate formal representation when it comes to residency training decisions. Therefore, Pawliuk challenged health organizations to make changes to give a voice in decision-making to the organizations representing IMGs.
In Connections, 48 Sara Guzman created a digital painting to portray her approach to learning. Her image of a hand touching a neuron showed her desire to physically see and touch an active neuron in order to further understand the brain and its connections.
Making sense of research: A guide for critiquing a paper
Affiliation.
- 1 School of Nursing, Griffith University, Meadowbrook, Queensland.
- PMID: 16114192
- DOI: 10.5172/conu.14.1.38
Learning how to critique research articles is one of the fundamental skills of scholarship in any discipline. The range, quantity and quality of publications available today via print, electronic and Internet databases means it has become essential to equip students and practitioners with the prerequisites to judge the integrity and usefulness of published research. Finding, understanding and critiquing quality articles can be a difficult process. This article sets out some helpful indicators to assist the novice to make sense of research.
Publication types
- Data Interpretation, Statistical
- Research Design
- Review Literature as Topic

Cultural Relativity and Acceptance of Embryonic Stem Cell Research
Article sidebar.

Main Article Content
There is a debate about the ethical implications of using human embryos in stem cell research, which can be influenced by cultural, moral, and social values. This paper argues for an adaptable framework to accommodate diverse cultural and religious perspectives. By using an adaptive ethics model, research protections can reflect various populations and foster growth in stem cell research possibilities.
INTRODUCTION
Stem cell research combines biology, medicine, and technology, promising to alter health care and the understanding of human development. Yet, ethical contention exists because of individuals’ perceptions of using human embryos based on their various cultural, moral, and social values. While these disagreements concerning policy, use, and general acceptance have prompted the development of an international ethics policy, such a uniform approach can overlook the nuanced ethical landscapes between cultures. With diverse viewpoints in public health, a single global policy, especially one reflecting Western ethics or the ethics prevalent in high-income countries, is impractical. This paper argues for a culturally sensitive, adaptable framework for the use of embryonic stem cells. Stem cell policy should accommodate varying ethical viewpoints and promote an effective global dialogue. With an extension of an ethics model that can adapt to various cultures, we recommend localized guidelines that reflect the moral views of the people those guidelines serve.
Stem cells, characterized by their unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, enable the repair or replacement of damaged tissues. Two primary types of stem cells are somatic stem cells (adult stem cells) and embryonic stem cells. Adult stem cells exist in developed tissues and maintain the body’s repair processes. [1] Embryonic stem cells (ESC) are remarkably pluripotent or versatile, making them valuable in research. [2] However, the use of ESCs has sparked ethics debates. Considering the potential of embryonic stem cells, research guidelines are essential. The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) provides international stem cell research guidelines. They call for “public conversations touching on the scientific significance as well as the societal and ethical issues raised by ESC research.” [3] The ISSCR also publishes updates about culturing human embryos 14 days post fertilization, suggesting local policies and regulations should continue to evolve as ESC research develops. [4] Like the ISSCR, which calls for local law and policy to adapt to developing stem cell research given cultural acceptance, this paper highlights the importance of local social factors such as religion and culture.
I. Global Cultural Perspective of Embryonic Stem Cells
Views on ESCs vary throughout the world. Some countries readily embrace stem cell research and therapies, while others have stricter regulations due to ethical concerns surrounding embryonic stem cells and when an embryo becomes entitled to moral consideration. The philosophical issue of when the “someone” begins to be a human after fertilization, in the morally relevant sense, [5] impacts when an embryo becomes not just worthy of protection but morally entitled to it. The process of creating embryonic stem cell lines involves the destruction of the embryos for research. [6] Consequently, global engagement in ESC research depends on social-cultural acceptability.
a. US and Rights-Based Cultures
In the United States, attitudes toward stem cell therapies are diverse. The ethics and social approaches, which value individualism, [7] trigger debates regarding the destruction of human embryos, creating a complex regulatory environment. For example, the 1996 Dickey-Wicker Amendment prohibited federal funding for the creation of embryos for research and the destruction of embryos for “more than allowed for research on fetuses in utero.” [8] Following suit, in 2001, the Bush Administration heavily restricted stem cell lines for research. However, the Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005 was proposed to help develop ESC research but was ultimately vetoed. [9] Under the Obama administration, in 2009, an executive order lifted restrictions allowing for more development in this field. [10] The flux of research capacity and funding parallels the different cultural perceptions of human dignity of the embryo and how it is socially presented within the country’s research culture. [11]
b. Ubuntu and Collective Cultures
African bioethics differs from Western individualism because of the different traditions and values. African traditions, as described by individuals from South Africa and supported by some studies in other African countries, including Ghana and Kenya, follow the African moral philosophies of Ubuntu or Botho and Ukama , which “advocates for a form of wholeness that comes through one’s relationship and connectedness with other people in the society,” [12] making autonomy a socially collective concept. In this context, for the community to act autonomously, individuals would come together to decide what is best for the collective. Thus, stem cell research would require examining the value of the research to society as a whole and the use of the embryos as a collective societal resource. If society views the source as part of the collective whole, and opposes using stem cells, compromising the cultural values to pursue research may cause social detachment and stunt research growth. [13] Based on local culture and moral philosophy, the permissibility of stem cell research depends on how embryo, stem cell, and cell line therapies relate to the community as a whole. Ubuntu is the expression of humanness, with the person’s identity drawn from the “’I am because we are’” value. [14] The decision in a collectivistic culture becomes one born of cultural context, and individual decisions give deference to others in the society.
Consent differs in cultures where thought and moral philosophy are based on a collective paradigm. So, applying Western bioethical concepts is unrealistic. For one, Africa is a diverse continent with many countries with different belief systems, access to health care, and reliance on traditional or Western medicines. Where traditional medicine is the primary treatment, the “’restrictive focus on biomedically-related bioethics’” [is] problematic in African contexts because it neglects bioethical issues raised by traditional systems.” [15] No single approach applies in all areas or contexts. Rather than evaluating the permissibility of ESC research according to Western concepts such as the four principles approach, different ethics approaches should prevail.
Another consideration is the socio-economic standing of countries. In parts of South Africa, researchers have not focused heavily on contributing to the stem cell discourse, either because it is not considered health care or a health science priority or because resources are unavailable. [16] Each country’s priorities differ given different social, political, and economic factors. In South Africa, for instance, areas such as maternal mortality, non-communicable diseases, telemedicine, and the strength of health systems need improvement and require more focus. [17] Stem cell research could benefit the population, but it also could divert resources from basic medical care. Researchers in South Africa adhere to the National Health Act and Medicines Control Act in South Africa and international guidelines; however, the Act is not strictly enforced, and there is no clear legislation for research conduct or ethical guidelines. [18]
Some parts of Africa condemn stem cell research. For example, 98.2 percent of the Tunisian population is Muslim. [19] Tunisia does not permit stem cell research because of moral conflict with a Fatwa. Religion heavily saturates the regulation and direction of research. [20] Stem cell use became permissible for reproductive purposes only recently, with tight restrictions preventing cells from being used in any research other than procedures concerning ART/IVF. Their use is conditioned on consent, and available only to married couples. [21] The community's receptiveness to stem cell research depends on including communitarian African ethics.
c. Asia
Some Asian countries also have a collective model of ethics and decision making. [22] In China, the ethics model promotes a sincere respect for life or human dignity, [23] based on protective medicine. This model, influenced by Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), [24] recognizes Qi as the vital energy delivered via the meridians of the body; it connects illness to body systems, the body’s entire constitution, and the universe for a holistic bond of nature, health, and quality of life. [25] Following a protective ethics model, and traditional customs of wholeness, investment in stem cell research is heavily desired for its applications in regenerative therapies, disease modeling, and protective medicines. In a survey of medical students and healthcare practitioners, 30.8 percent considered stem cell research morally unacceptable while 63.5 percent accepted medical research using human embryonic stem cells. Of these individuals, 89.9 percent supported increased funding for stem cell research. [26] The scientific community might not reflect the overall population. From 1997 to 2019, China spent a total of $576 million (USD) on stem cell research at 8,050 stem cell programs, increased published presence from 0.6 percent to 14.01 percent of total global stem cell publications as of 2014, and made significant strides in cell-based therapies for various medical conditions. [27] However, while China has made substantial investments in stem cell research and achieved notable progress in clinical applications, concerns linger regarding ethical oversight and transparency. [28] For example, the China Biosecurity Law, promoted by the National Health Commission and China Hospital Association, attempted to mitigate risks by introducing an institutional review board (IRB) in the regulatory bodies. 5800 IRBs registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry since 2021. [29] However, issues still need to be addressed in implementing effective IRB review and approval procedures.
The substantial government funding and focus on scientific advancement have sometimes overshadowed considerations of regional cultures, ethnic minorities, and individual perspectives, particularly evident during the one-child policy era. As government policy adapts to promote public stability, such as the change from the one-child to the two-child policy, [30] research ethics should also adapt to ensure respect for the values of its represented peoples.
Japan is also relatively supportive of stem cell research and therapies. Japan has a more transparent regulatory framework, allowing for faster approval of regenerative medicine products, which has led to several advanced clinical trials and therapies. [31] South Korea is also actively engaged in stem cell research and has a history of breakthroughs in cloning and embryonic stem cells. [32] However, the field is controversial, and there are issues of scientific integrity. For example, the Korean FDA fast-tracked products for approval, [33] and in another instance, the oocyte source was unclear and possibly violated ethical standards. [34] Trust is important in research, as it builds collaborative foundations between colleagues, trial participant comfort, open-mindedness for complicated and sensitive discussions, and supports regulatory procedures for stakeholders. There is a need to respect the culture’s interest, engagement, and for research and clinical trials to be transparent and have ethical oversight to promote global research discourse and trust.
d. Middle East
Countries in the Middle East have varying degrees of acceptance of or restrictions to policies related to using embryonic stem cells due to cultural and religious influences. Saudi Arabia has made significant contributions to stem cell research, and conducts research based on international guidelines for ethical conduct and under strict adherence to guidelines in accordance with Islamic principles. Specifically, the Saudi government and people require ESC research to adhere to Sharia law. In addition to umbilical and placental stem cells, [35] Saudi Arabia permits the use of embryonic stem cells as long as they come from miscarriages, therapeutic abortions permissible by Sharia law, or are left over from in vitro fertilization and donated to research. [36] Laws and ethical guidelines for stem cell research allow the development of research institutions such as the King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, which has a cord blood bank and a stem cell registry with nearly 10,000 donors. [37] Such volume and acceptance are due to the ethical ‘permissibility’ of the donor sources, which do not conflict with religious pillars. However, some researchers err on the side of caution, choosing not to use embryos or fetal tissue as they feel it is unethical to do so. [38]
Jordan has a positive research ethics culture. [39] However, there is a significant issue of lack of trust in researchers, with 45.23 percent (38.66 percent agreeing and 6.57 percent strongly agreeing) of Jordanians holding a low level of trust in researchers, compared to 81.34 percent of Jordanians agreeing that they feel safe to participate in a research trial. [40] Safety testifies to the feeling of confidence that adequate measures are in place to protect participants from harm, whereas trust in researchers could represent the confidence in researchers to act in the participants’ best interests, adhere to ethical guidelines, provide accurate information, and respect participants’ rights and dignity. One method to improve trust would be to address communication issues relevant to ESC. Legislation surrounding stem cell research has adopted specific language, especially concerning clarification “between ‘stem cells’ and ‘embryonic stem cells’” in translation. [41] Furthermore, legislation “mandates the creation of a national committee… laying out specific regulations for stem-cell banking in accordance with international standards.” [42] This broad regulation opens the door for future global engagement and maintains transparency. However, these regulations may also constrain the influence of research direction, pace, and accessibility of research outcomes.
e. Europe
In the European Union (EU), ethics is also principle-based, but the principles of autonomy, dignity, integrity, and vulnerability are interconnected. [43] As such, the opportunity for cohesion and concessions between individuals’ thoughts and ideals allows for a more adaptable ethics model due to the flexible principles that relate to the human experience The EU has put forth a framework in its Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being allowing member states to take different approaches. Each European state applies these principles to its specific conventions, leading to or reflecting different acceptance levels of stem cell research. [44]
For example, in Germany, Lebenzusammenhang , or the coherence of life, references integrity in the unity of human culture. Namely, the personal sphere “should not be subject to external intervention.” [45] Stem cell interventions could affect this concept of bodily completeness, leading to heavy restrictions. Under the Grundgesetz, human dignity and the right to life with physical integrity are paramount. [46] The Embryo Protection Act of 1991 made producing cell lines illegal. Cell lines can be imported if approved by the Central Ethics Commission for Stem Cell Research only if they were derived before May 2007. [47] Stem cell research respects the integrity of life for the embryo with heavy specifications and intense oversight. This is vastly different in Finland, where the regulatory bodies find research more permissible in IVF excess, but only up to 14 days after fertilization. [48] Spain’s approach differs still, with a comprehensive regulatory framework. [49] Thus, research regulation can be culture-specific due to variations in applied principles. Diverse cultures call for various approaches to ethical permissibility. [50] Only an adaptive-deliberative model can address the cultural constructions of self and achieve positive, culturally sensitive stem cell research practices. [51]
II. Religious Perspectives on ESC
Embryonic stem cell sources are the main consideration within religious contexts. While individuals may not regard their own religious texts as authoritative or factual, religion can shape their foundations or perspectives.
The Qur'an states:
“And indeed We created man from a quintessence of clay. Then We placed within him a small quantity of nutfa (sperm to fertilize) in a safe place. Then We have fashioned the nutfa into an ‘alaqa (clinging clot or cell cluster), then We developed the ‘alaqa into mudgha (a lump of flesh), and We made mudgha into bones, and clothed the bones with flesh, then We brought it into being as a new creation. So Blessed is Allah, the Best of Creators.” [52]
Many scholars of Islam estimate the time of soul installment, marked by the angel breathing in the soul to bring the individual into creation, as 120 days from conception. [53] Personhood begins at this point, and the value of life would prohibit research or experimentation that could harm the individual. If the fetus is more than 120 days old, the time ensoulment is interpreted to occur according to Islamic law, abortion is no longer permissible. [54] There are a few opposing opinions about early embryos in Islamic traditions. According to some Islamic theologians, there is no ensoulment of the early embryo, which is the source of stem cells for ESC research. [55]
In Buddhism, the stance on stem cell research is not settled. The main tenets, the prohibition against harming or destroying others (ahimsa) and the pursuit of knowledge (prajña) and compassion (karuna), leave Buddhist scholars and communities divided. [56] Some scholars argue stem cell research is in accordance with the Buddhist tenet of seeking knowledge and ending human suffering. Others feel it violates the principle of not harming others. Finding the balance between these two points relies on the karmic burden of Buddhist morality. In trying to prevent ahimsa towards the embryo, Buddhist scholars suggest that to comply with Buddhist tenets, research cannot be done as the embryo has personhood at the moment of conception and would reincarnate immediately, harming the individual's ability to build their karmic burden. [57] On the other hand, the Bodhisattvas, those considered to be on the path to enlightenment or Nirvana, have given organs and flesh to others to help alleviate grieving and to benefit all. [58] Acceptance varies on applied beliefs and interpretations.
Catholicism does not support embryonic stem cell research, as it entails creation or destruction of human embryos. This destruction conflicts with the belief in the sanctity of life. For example, in the Old Testament, Genesis describes humanity as being created in God’s image and multiplying on the Earth, referencing the sacred rights to human conception and the purpose of development and life. In the Ten Commandments, the tenet that one should not kill has numerous interpretations where killing could mean murder or shedding of the sanctity of life, demonstrating the high value of human personhood. In other books, the theological conception of when life begins is interpreted as in utero, [59] highlighting the inviolability of life and its formation in vivo to make a religious point for accepting such research as relatively limited, if at all. [60] The Vatican has released ethical directives to help apply a theological basis to modern-day conflicts. The Magisterium of the Church states that “unless there is a moral certainty of not causing harm,” experimentation on fetuses, fertilized cells, stem cells, or embryos constitutes a crime. [61] Such procedures would not respect the human person who exists at these stages, according to Catholicism. Damages to the embryo are considered gravely immoral and illicit. [62] Although the Catholic Church officially opposes abortion, surveys demonstrate that many Catholic people hold pro-choice views, whether due to the context of conception, stage of pregnancy, threat to the mother’s life, or for other reasons, demonstrating that practicing members can also accept some but not all tenets. [63]
Some major Jewish denominations, such as the Reform, Conservative, and Reconstructionist movements, are open to supporting ESC use or research as long as it is for saving a life. [64] Within Judaism, the Talmud, or study, gives personhood to the child at birth and emphasizes that life does not begin at conception: [65]
“If she is found pregnant, until the fortieth day it is mere fluid,” [66]
Whereas most religions prioritize the status of human embryos, the Halakah (Jewish religious law) states that to save one life, most other religious laws can be ignored because it is in pursuit of preservation. [67] Stem cell research is accepted due to application of these religious laws.
We recognize that all religions contain subsets and sects. The variety of environmental and cultural differences within religious groups requires further analysis to respect the flexibility of religious thoughts and practices. We make no presumptions that all cultures require notions of autonomy or morality as under the common morality theory , which asserts a set of universal moral norms that all individuals share provides moral reasoning and guides ethical decisions. [68] We only wish to show that the interaction with morality varies between cultures and countries.
III. A Flexible Ethical Approach
The plurality of different moral approaches described above demonstrates that there can be no universally acceptable uniform law for ESC on a global scale. Instead of developing one standard, flexible ethical applications must be continued. We recommend local guidelines that incorporate important cultural and ethical priorities.
While the Declaration of Helsinki is more relevant to people in clinical trials receiving ESC products, in keeping with the tradition of protections for research subjects, consent of the donor is an ethical requirement for ESC donation in many jurisdictions including the US, Canada, and Europe. [69] The Declaration of Helsinki provides a reference point for regulatory standards and could potentially be used as a universal baseline for obtaining consent prior to gamete or embryo donation.
For instance, in Columbia University’s egg donor program for stem cell research, donors followed standard screening protocols and “underwent counseling sessions that included information as to the purpose of oocyte donation for research, what the oocytes would be used for, the risks and benefits of donation, and process of oocyte stimulation” to ensure transparency for consent. [70] The program helped advance stem cell research and provided clear and safe research methods with paid participants. Though paid participation or covering costs of incidental expenses may not be socially acceptable in every culture or context, [71] and creating embryos for ESC research is illegal in many jurisdictions, Columbia’s program was effective because of the clear and honest communications with donors, IRBs, and related stakeholders. This example demonstrates that cultural acceptance of scientific research and of the idea that an egg or embryo does not have personhood is likely behind societal acceptance of donating eggs for ESC research. As noted, many countries do not permit the creation of embryos for research.
Proper communication and education regarding the process and purpose of stem cell research may bolster comprehension and garner more acceptance. “Given the sensitive subject material, a complete consent process can support voluntary participation through trust, understanding, and ethical norms from the cultures and morals participants value. This can be hard for researchers entering countries of different socioeconomic stability, with different languages and different societal values. [72]
An adequate moral foundation in medical ethics is derived from the cultural and religious basis that informs knowledge and actions. [73] Understanding local cultural and religious values and their impact on research could help researchers develop humility and promote inclusion.
IV. Concerns
Some may argue that if researchers all adhere to one ethics standard, protection will be satisfied across all borders, and the global public will trust researchers. However, defining what needs to be protected and how to define such research standards is very specific to the people to which standards are applied. We suggest that applying one uniform guide cannot accurately protect each individual because we all possess our own perceptions and interpretations of social values. [74] Therefore, the issue of not adjusting to the moral pluralism between peoples in applying one standard of ethics can be resolved by building out ethics models that can be adapted to different cultures and religions.
Other concerns include medical tourism, which may promote health inequities. [75] Some countries may develop and approve products derived from ESC research before others, compromising research ethics or drug approval processes. There are also concerns about the sale of unauthorized stem cell treatments, for example, those without FDA approval in the United States. Countries with robust research infrastructures may be tempted to attract medical tourists, and some customers will have false hopes based on aggressive publicity of unproven treatments. [76]
For example, in China, stem cell clinics can market to foreign clients who are not protected under the regulatory regimes. Companies employ a marketing strategy of “ethically friendly” therapies. Specifically, in the case of Beike, China’s leading stem cell tourism company and sprouting network, ethical oversight of administrators or health bureaus at one site has “the unintended consequence of shifting questionable activities to another node in Beike's diffuse network.” [77] In contrast, Jordan is aware of stem cell research’s potential abuse and its own status as a “health-care hub.” Jordan’s expanded regulations include preserving the interests of individuals in clinical trials and banning private companies from ESC research to preserve transparency and the integrity of research practices. [78]
The social priorities of the community are also a concern. The ISSCR explicitly states that guidelines “should be periodically revised to accommodate scientific advances, new challenges, and evolving social priorities.” [79] The adaptable ethics model extends this consideration further by addressing whether research is warranted given the varying degrees of socioeconomic conditions, political stability, and healthcare accessibilities and limitations. An ethical approach would require discussion about resource allocation and appropriate distribution of funds. [80]
While some religions emphasize the sanctity of life from conception, which may lead to public opposition to ESC research, others encourage ESC research due to its potential for healing and alleviating human pain. Many countries have special regulations that balance local views on embryonic personhood, the benefits of research as individual or societal goods, and the protection of human research subjects. To foster understanding and constructive dialogue, global policy frameworks should prioritize the protection of universal human rights, transparency, and informed consent. In addition to these foundational global policies, we recommend tailoring local guidelines to reflect the diverse cultural and religious perspectives of the populations they govern. Ethics models should be adapted to local populations to effectively establish research protections, growth, and possibilities of stem cell research.
For example, in countries with strong beliefs in the moral sanctity of embryos or heavy religious restrictions, an adaptive model can allow for discussion instead of immediate rejection. In countries with limited individual rights and voice in science policy, an adaptive model ensures cultural, moral, and religious views are taken into consideration, thereby building social inclusion. While this ethical consideration by the government may not give a complete voice to every individual, it will help balance policies and maintain the diverse perspectives of those it affects. Embracing an adaptive ethics model of ESC research promotes open-minded dialogue and respect for the importance of human belief and tradition. By actively engaging with cultural and religious values, researchers can better handle disagreements and promote ethical research practices that benefit each society.
This brief exploration of the religious and cultural differences that impact ESC research reveals the nuances of relative ethics and highlights a need for local policymakers to apply a more intense adaptive model.
[1] Poliwoda, S., Noor, N., Downs, E., Schaaf, A., Cantwell, A., Ganti, L., Kaye, A. D., Mosel, L. I., Carroll, C. B., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2022). Stem cells: a comprehensive review of origins and emerging clinical roles in medical practice. Orthopedic reviews , 14 (3), 37498. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.37498
[2] Poliwoda, S., Noor, N., Downs, E., Schaaf, A., Cantwell, A., Ganti, L., Kaye, A. D., Mosel, L. I., Carroll, C. B., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2022). Stem cells: a comprehensive review of origins and emerging clinical roles in medical practice. Orthopedic reviews , 14 (3), 37498. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.37498
[3] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2023). Laboratory-based human embryonic stem cell research, embryo research, and related research activities . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/blog-post-title-one-ed2td-6fcdk ; Kimmelman, J., Hyun, I., Benvenisty, N. et al. Policy: Global standards for stem-cell research. Nature 533 , 311–313 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/533311a
[4] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2023). Laboratory-based human embryonic stem cell research, embryo research, and related research activities . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/blog-post-title-one-ed2td-6fcdk
[5] Concerning the moral philosophies of stem cell research, our paper does not posit a personal moral stance nor delve into the “when” of human life begins. To read further about the philosophical debate, consider the following sources:
Sandel M. J. (2004). Embryo ethics--the moral logic of stem-cell research. The New England journal of medicine , 351 (3), 207–209. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp048145 ; George, R. P., & Lee, P. (2020, September 26). Acorns and Embryos . The New Atlantis. https://www.thenewatlantis.com/publications/acorns-and-embryos ; Sagan, A., & Singer, P. (2007). The moral status of stem cells. Metaphilosophy , 38 (2/3), 264–284. http://www.jstor.org/stable/24439776 ; McHugh P. R. (2004). Zygote and "clonote"--the ethical use of embryonic stem cells. The New England journal of medicine , 351 (3), 209–211. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp048147 ; Kurjak, A., & Tripalo, A. (2004). The facts and doubts about beginning of the human life and personality. Bosnian journal of basic medical sciences , 4 (1), 5–14. https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2004.3453
[6] Vazin, T., & Freed, W. J. (2010). Human embryonic stem cells: derivation, culture, and differentiation: a review. Restorative neurology and neuroscience , 28 (4), 589–603. https://doi.org/10.3233/RNN-2010-0543
[7] Socially, at its core, the Western approach to ethics is widely principle-based, autonomy being one of the key factors to ensure a fundamental respect for persons within research. For information regarding autonomy in research, see: Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, & National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research (1978). The Belmont Report. Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research.; For a more in-depth review of autonomy within the US, see: Beauchamp, T. L., & Childress, J. F. (1994). Principles of Biomedical Ethics . Oxford University Press.
[8] Sherley v. Sebelius , 644 F.3d 388 (D.C. Cir. 2011), citing 45 C.F.R. 46.204(b) and [42 U.S.C. § 289g(b)]. https://www.cadc.uscourts.gov/internet/opinions.nsf/6c690438a9b43dd685257a64004ebf99/$file/11-5241-1391178.pdf
[9] Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005, H. R. 810, 109 th Cong. (2001). https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/109/hr810/text ; Bush, G. W. (2006, July 19). Message to the House of Representatives . National Archives and Records Administration. https://georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov/news/releases/2006/07/20060719-5.html
[10] National Archives and Records Administration. (2009, March 9). Executive order 13505 -- removing barriers to responsible scientific research involving human stem cells . National Archives and Records Administration. https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/removing-barriers-responsible-scientific-research-involving-human-stem-cells
[11] Hurlbut, W. B. (2006). Science, Religion, and the Politics of Stem Cells. Social Research , 73 (3), 819–834. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40971854
[12] Akpa-Inyang, Francis & Chima, Sylvester. (2021). South African traditional values and beliefs regarding informed consent and limitations of the principle of respect for autonomy in African communities: a cross-cultural qualitative study. BMC Medical Ethics . 22. 10.1186/s12910-021-00678-4.
[13] Source for further reading: Tangwa G. B. (2007). Moral status of embryonic stem cells: perspective of an African villager. Bioethics , 21(8), 449–457. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8519.2007.00582.x , see also Mnisi, F. M. (2020). An African analysis based on ethics of Ubuntu - are human embryonic stem cell patents morally justifiable? African Insight , 49 (4).
[14] Jecker, N. S., & Atuire, C. (2021). Bioethics in Africa: A contextually enlightened analysis of three cases. Developing World Bioethics , 22 (2), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12324
[15] Jecker, N. S., & Atuire, C. (2021). Bioethics in Africa: A contextually enlightened analysis of three cases. Developing World Bioethics, 22(2), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12324
[16] Jackson, C.S., Pepper, M.S. Opportunities and barriers to establishing a cell therapy programme in South Africa. Stem Cell Res Ther 4 , 54 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt204 ; Pew Research Center. (2014, May 1). Public health a major priority in African nations . Pew Research Center’s Global Attitudes Project. https://www.pewresearch.org/global/2014/05/01/public-health-a-major-priority-in-african-nations/
[17] Department of Health Republic of South Africa. (2021). Health Research Priorities (revised) for South Africa 2021-2024 . National Health Research Strategy. https://www.health.gov.za/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/National-Health-Research-Priorities-2021-2024.pdf
[18] Oosthuizen, H. (2013). Legal and Ethical Issues in Stem Cell Research in South Africa. In: Beran, R. (eds) Legal and Forensic Medicine. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32338-6_80 , see also: Gaobotse G (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[19] United States Bureau of Citizenship and Immigration Services. (1998). Tunisia: Information on the status of Christian conversions in Tunisia . UNHCR Web Archive. https://webarchive.archive.unhcr.org/20230522142618/https://www.refworld.org/docid/3df0be9a2.html
[20] Gaobotse, G. (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[21] Kooli, C. Review of assisted reproduction techniques, laws, and regulations in Muslim countries. Middle East Fertil Soc J 24 , 8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43043-019-0011-0 ; Gaobotse, G. (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[22] Pang M. C. (1999). Protective truthfulness: the Chinese way of safeguarding patients in informed treatment decisions. Journal of medical ethics , 25(3), 247–253. https://doi.org/10.1136/jme.25.3.247
[23] Wang, L., Wang, F., & Zhang, W. (2021). Bioethics in China’s biosecurity law: Forms, effects, and unsettled issues. Journal of law and the biosciences , 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsab019 https://academic.oup.com/jlb/article/8/1/lsab019/6299199
[24] Wang, Y., Xue, Y., & Guo, H. D. (2022). Intervention effects of traditional Chinese medicine on stem cell therapy of myocardial infarction. Frontiers in pharmacology , 13 , 1013740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1013740
[25] Li, X.-T., & Zhao, J. (2012). Chapter 4: An Approach to the Nature of Qi in TCM- Qi and Bioenergy. In Recent Advances in Theories and Practice of Chinese Medicine (p. 79). InTech.
[26] Luo, D., Xu, Z., Wang, Z., & Ran, W. (2021). China's Stem Cell Research and Knowledge Levels of Medical Practitioners and Students. Stem cells international , 2021 , 6667743. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6667743
[27] Luo, D., Xu, Z., Wang, Z., & Ran, W. (2021). China's Stem Cell Research and Knowledge Levels of Medical Practitioners and Students. Stem cells international , 2021 , 6667743. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6667743
[28] Zhang, J. Y. (2017). Lost in translation? accountability and governance of Clinical Stem Cell Research in China. Regenerative Medicine , 12 (6), 647–656. https://doi.org/10.2217/rme-2017-0035
[29] Wang, L., Wang, F., & Zhang, W. (2021). Bioethics in China’s biosecurity law: Forms, effects, and unsettled issues. Journal of law and the biosciences , 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsab019 https://academic.oup.com/jlb/article/8/1/lsab019/6299199
[30] Chen, H., Wei, T., Wang, H. et al. Association of China’s two-child policy with changes in number of births and birth defects rate, 2008–2017. BMC Public Health 22 , 434 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-12839-0
[31] Azuma, K. Regulatory Landscape of Regenerative Medicine in Japan. Curr Stem Cell Rep 1 , 118–128 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40778-015-0012-6
[32] Harris, R. (2005, May 19). Researchers Report Advance in Stem Cell Production . NPR. https://www.npr.org/2005/05/19/4658967/researchers-report-advance-in-stem-cell-production
[33] Park, S. (2012). South Korea steps up stem-cell work. Nature . https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2012.10565
[34] Resnik, D. B., Shamoo, A. E., & Krimsky, S. (2006). Fraudulent human embryonic stem cell research in South Korea: lessons learned. Accountability in research , 13 (1), 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/08989620600634193 .
[35] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics, 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
[36] Association for the Advancement of Blood and Biotherapies. https://www.aabb.org/regulatory-and-advocacy/regulatory-affairs/regulatory-for-cellular-therapies/international-competent-authorities/saudi-arabia
[37] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: Interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics , 21 (1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
[38] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: Interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics , 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
Culturally, autonomy practices follow a relational autonomy approach based on a paternalistic deontological health care model. The adherence to strict international research policies and religious pillars within the regulatory environment is a great foundation for research ethics. However, there is a need to develop locally targeted ethics approaches for research (as called for in Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics, 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6), this decision-making approach may help advise a research decision model. For more on the clinical cultural autonomy approaches, see: Alabdullah, Y. Y., Alzaid, E., Alsaad, S., Alamri, T., Alolayan, S. W., Bah, S., & Aljoudi, A. S. (2022). Autonomy and paternalism in Shared decision‐making in a Saudi Arabian tertiary hospital: A cross‐sectional study. Developing World Bioethics , 23 (3), 260–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12355 ; Bukhari, A. A. (2017). Universal Principles of Bioethics and Patient Rights in Saudi Arabia (Doctoral dissertation, Duquesne University). https://dsc.duq.edu/etd/124; Ladha, S., Nakshawani, S. A., Alzaidy, A., & Tarab, B. (2023, October 26). Islam and Bioethics: What We All Need to Know . Columbia University School of Professional Studies. https://sps.columbia.edu/events/islam-and-bioethics-what-we-all-need-know
[39] Ababneh, M. A., Al-Azzam, S. I., Alzoubi, K., Rababa’h, A., & Al Demour, S. (2021). Understanding and attitudes of the Jordanian public about clinical research ethics. Research Ethics , 17 (2), 228-241. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016120966779
[40] Ababneh, M. A., Al-Azzam, S. I., Alzoubi, K., Rababa’h, A., & Al Demour, S. (2021). Understanding and attitudes of the Jordanian public about clinical research ethics. Research Ethics , 17 (2), 228-241. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016120966779
[41] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[42] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[43] The EU’s definition of autonomy relates to the capacity for creating ideas, moral insight, decisions, and actions without constraint, personal responsibility, and informed consent. However, the EU views autonomy as not completely able to protect individuals and depends on other principles, such as dignity, which “expresses the intrinsic worth and fundamental equality of all human beings.” Rendtorff, J.D., Kemp, P. (2019). Four Ethical Principles in European Bioethics and Biolaw: Autonomy, Dignity, Integrity and Vulnerability. In: Valdés, E., Lecaros, J. (eds) Biolaw and Policy in the Twenty-First Century. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 78. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05903-3_3
[44] Council of Europe. Convention for the protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being with regard to the Application of Biology and Medicine: Convention on Human Rights and Biomedicine (ETS No. 164) https://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/full-list?module=treaty-detail&treatynum=164 (forbidding the creation of embryos for research purposes only, and suggests embryos in vitro have protections.); Also see Drabiak-Syed B. K. (2013). New President, New Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research Policy: Comparative International Perspectives and Embryonic Stem Cell Research Laws in France. Biotechnology Law Report , 32 (6), 349–356. https://doi.org/10.1089/blr.2013.9865
[45] Rendtorff, J.D., Kemp, P. (2019). Four Ethical Principles in European Bioethics and Biolaw: Autonomy, Dignity, Integrity and Vulnerability. In: Valdés, E., Lecaros, J. (eds) Biolaw and Policy in the Twenty-First Century. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 78. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05903-3_3
[46] Tomuschat, C., Currie, D. P., Kommers, D. P., & Kerr, R. (Trans.). (1949, May 23). Basic law for the Federal Republic of Germany. https://www.btg-bestellservice.de/pdf/80201000.pdf
[47] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Germany . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-germany
[48] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Finland . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-finland
[49] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Spain . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-spain
[50] Some sources to consider regarding ethics models or regulatory oversights of other cultures not covered:
Kara MA. Applicability of the principle of respect for autonomy: the perspective of Turkey. J Med Ethics. 2007 Nov;33(11):627-30. doi: 10.1136/jme.2006.017400. PMID: 17971462; PMCID: PMC2598110.
Ugarte, O. N., & Acioly, M. A. (2014). The principle of autonomy in Brazil: one needs to discuss it ... Revista do Colegio Brasileiro de Cirurgioes , 41 (5), 374–377. https://doi.org/10.1590/0100-69912014005013
Bharadwaj, A., & Glasner, P. E. (2012). Local cells, global science: The rise of embryonic stem cell research in India . Routledge.
For further research on specific European countries regarding ethical and regulatory framework, we recommend this database: Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Europe . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-europe
[51] Klitzman, R. (2006). Complications of culture in obtaining informed consent. The American Journal of Bioethics, 6(1), 20–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15265160500394671 see also: Ekmekci, P. E., & Arda, B. (2017). Interculturalism and Informed Consent: Respecting Cultural Differences without Breaching Human Rights. Cultura (Iasi, Romania) , 14 (2), 159–172.; For why trust is important in research, see also: Gray, B., Hilder, J., Macdonald, L., Tester, R., Dowell, A., & Stubbe, M. (2017). Are research ethics guidelines culturally competent? Research Ethics , 13 (1), 23-41. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016116650235
[52] The Qur'an (M. Khattab, Trans.). (1965). Al-Mu’minun, 23: 12-14. https://quran.com/23
[53] Lenfest, Y. (2017, December 8). Islam and the beginning of human life . Bill of Health. https://blog.petrieflom.law.harvard.edu/2017/12/08/islam-and-the-beginning-of-human-life/
[54] Aksoy, S. (2005). Making regulations and drawing up legislation in Islamic countries under conditions of uncertainty, with special reference to embryonic stem cell research. Journal of Medical Ethics , 31: 399-403.; see also: Mahmoud, Azza. "Islamic Bioethics: National Regulations and Guidelines of Human Stem Cell Research in the Muslim World." Master's thesis, Chapman University, 2022. https://doi.org/10.36837/ chapman.000386
[55] Rashid, R. (2022). When does Ensoulment occur in the Human Foetus. Journal of the British Islamic Medical Association , 12 (4). ISSN 2634 8071. https://www.jbima.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/2-Ethics-3_-Ensoulment_Rafaqat.pdf.
[56] Sivaraman, M. & Noor, S. (2017). Ethics of embryonic stem cell research according to Buddhist, Hindu, Catholic, and Islamic religions: perspective from Malaysia. Asian Biomedicine,8(1) 43-52. https://doi.org/10.5372/1905-7415.0801.260
[57] Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[58] Lecso, P. A. (1991). The Bodhisattva Ideal and Organ Transplantation. Journal of Religion and Health , 30 (1), 35–41. http://www.jstor.org/stable/27510629 ; Bodhisattva, S. (n.d.). The Key of Becoming a Bodhisattva . A Guide to the Bodhisattva Way of Life. http://www.buddhism.org/Sutras/2/BodhisattvaWay.htm
[59] There is no explicit religious reference to when life begins or how to conduct research that interacts with the concept of life. However, these are relevant verses pertaining to how the fetus is viewed. (( King James Bible . (1999). Oxford University Press. (original work published 1769))
Jerimiah 1: 5 “Before I formed thee in the belly I knew thee; and before thou camest forth out of the womb I sanctified thee…”
In prophet Jerimiah’s insight, God set him apart as a person known before childbirth, a theme carried within the Psalm of David.
Psalm 139: 13-14 “…Thou hast covered me in my mother's womb. I will praise thee; for I am fearfully and wonderfully made…”
These verses demonstrate David’s respect for God as an entity that would know of all man’s thoughts and doings even before birth.
[60] It should be noted that abortion is not supported as well.
[61] The Vatican. (1987, February 22). Instruction on Respect for Human Life in Its Origin and on the Dignity of Procreation Replies to Certain Questions of the Day . Congregation For the Doctrine of the Faith. https://www.vatican.va/roman_curia/congregations/cfaith/documents/rc_con_cfaith_doc_19870222_respect-for-human-life_en.html
[62] The Vatican. (2000, August 25). Declaration On the Production and the Scientific and Therapeutic Use of Human Embryonic Stem Cells . Pontifical Academy for Life. https://www.vatican.va/roman_curia/pontifical_academies/acdlife/documents/rc_pa_acdlife_doc_20000824_cellule-staminali_en.html ; Ohara, N. (2003). Ethical Consideration of Experimentation Using Living Human Embryos: The Catholic Church’s Position on Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research and Human Cloning. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology . Retrieved from https://article.imrpress.com/journal/CEOG/30/2-3/pii/2003018/77-81.pdf.
[63] Smith, G. A. (2022, May 23). Like Americans overall, Catholics vary in their abortion views, with regular mass attenders most opposed . Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2022/05/23/like-americans-overall-catholics-vary-in-their-abortion-views-with-regular-mass-attenders-most-opposed/
[64] Rosner, F., & Reichman, E. (2002). Embryonic stem cell research in Jewish law. Journal of halacha and contemporary society , (43), 49–68.; Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[65] Schenker J. G. (2008). The beginning of human life: status of embryo. Perspectives in Halakha (Jewish Religious Law). Journal of assisted reproduction and genetics , 25 (6), 271–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-008-9221-6
[66] Ruttenberg, D. (2020, May 5). The Torah of Abortion Justice (annotated source sheet) . Sefaria. https://www.sefaria.org/sheets/234926.7?lang=bi&with=all&lang2=en
[67] Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[68] Gert, B. (2007). Common morality: Deciding what to do . Oxford Univ. Press.
[69] World Medical Association (2013). World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA , 310(20), 2191–2194. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.281053 Declaration of Helsinki – WMA – The World Medical Association .; see also: National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research. (1979). The Belmont report: Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research . U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.hhs.gov/ohrp/regulations-and-policy/belmont-report/read-the-belmont-report/index.html
[70] Zakarin Safier, L., Gumer, A., Kline, M., Egli, D., & Sauer, M. V. (2018). Compensating human subjects providing oocytes for stem cell research: 9-year experience and outcomes. Journal of assisted reproduction and genetics , 35 (7), 1219–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-018-1171-z https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6063839/ see also: Riordan, N. H., & Paz Rodríguez, J. (2021). Addressing concerns regarding associated costs, transparency, and integrity of research in recent stem cell trial. Stem Cells Translational Medicine , 10 (12), 1715–1716. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.21-0234
[71] Klitzman, R., & Sauer, M. V. (2009). Payment of egg donors in stem cell research in the USA. Reproductive biomedicine online , 18 (5), 603–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1472-6483(10)60002-8
[72] Krosin, M. T., Klitzman, R., Levin, B., Cheng, J., & Ranney, M. L. (2006). Problems in comprehension of informed consent in rural and peri-urban Mali, West Africa. Clinical trials (London, England) , 3 (3), 306–313. https://doi.org/10.1191/1740774506cn150oa
[73] Veatch, Robert M. Hippocratic, Religious, and Secular Medical Ethics: The Points of Conflict . Georgetown University Press, 2012.
[74] Msoroka, M. S., & Amundsen, D. (2018). One size fits not quite all: Universal research ethics with diversity. Research Ethics , 14 (3), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016117739939
[75] Pirzada, N. (2022). The Expansion of Turkey’s Medical Tourism Industry. Voices in Bioethics , 8 . https://doi.org/10.52214/vib.v8i.9894
[76] Stem Cell Tourism: False Hope for Real Money . Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI). (2023). https://hsci.harvard.edu/stem-cell-tourism , See also: Bissassar, M. (2017). Transnational Stem Cell Tourism: An ethical analysis. Voices in Bioethics , 3 . https://doi.org/10.7916/vib.v3i.6027
[77] Song, P. (2011) The proliferation of stem cell therapies in post-Mao China: problematizing ethical regulation, New Genetics and Society , 30:2, 141-153, DOI: 10.1080/14636778.2011.574375
[78] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[79] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2024). Standards in stem cell research . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/5-standards-in-stem-cell-research
[80] Benjamin, R. (2013). People’s science bodies and rights on the Stem Cell Frontier . Stanford University Press.
Mifrah Hayath
SM Candidate Harvard Medical School, MS Biotechnology Johns Hopkins University
Olivia Bowers
MS Bioethics Columbia University (Disclosure: affiliated with Voices in Bioethics)
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
- Open access
- Published: 15 May 2024
The association between ultra-processed food and common pregnancy adverse outcomes: a dose-response systematic review and meta-analysis
- Sepide Talebi 1 , 2 ,
- Sanaz Mehrabani 3 ,
- Seyed Mojtaba Ghoreishy 4 , 5 ,
- Alexei Wong 6 ,
- Aliasghar Moghaddam 7 ,
- Peyman Rahimi Feyli 7 ,
- Parsa Amirian 8 ,
- Mahsa Zarpoosh 8 ,
- Mohammad Ali Hojjati Kermani 9 &
- Sajjad Moradi 10
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth volume 24 , Article number: 369 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Given the increasing incidence of negative outcomes during pregnancy, our research team conducted a dose-response systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the relationship between ultra-processed foods (UPFs) consumption and common adverse pregnancy outcomes including gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), preeclampsia (PE), preterm birth (PTB), low birth weight (LBW), and small for gestational age (SGA) infants. UPFs are described as formulations of food substances often modified by chemical processes and then assembled into ready-to-consume hyper-palatable food and drink products using flavors, colors, emulsifiers, and other cosmetic additives. Examples include savory snacks, reconstituted meat products, frozen meals that have already been made, and soft drinks.
A comprehensive search was performed using the Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science databases up to December 2023. We pooled relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) using a random-effects model.
Our analysis (encompassing 54 studies with 552,686 individuals) revealed a significant association between UPFs intake and increased risks of GDM (RR = 1.19; 95% CI: 1.10, 1.27; I 2 = 77.5%; p < 0.001; studies = 44; number of participants = 180,824), PE (RR = 1.28; 95% CI: 1.03, 1.59; I 2 = 80.0%; p = 0.025; studies = 12; number of participants = 54,955), while no significant relationships were found for PTB, LBW and SGA infants. Importantly, a 100 g increment in UPFs intake was related to a 27% increase in GDM risk (RR = 1.27; 95% CI: 1.07, 1.51; I 2 = 81.0%; p = 0.007; studies = 9; number of participants = 39,812). The non-linear dose-response analysis further indicated a positive, non-linear relationship between UPFs intake and GDM risk P nonlinearity = 0.034, P dose-response = 0.034), although no such relationship was observed for PE (P nonlinearity = 0.696, P dose-response = 0.812).
In summary, both prior to and during pregnancy, chronic and excessive intake of UPFs is associated with an increased risk of GDM and PE. However, further observational studies, particularly among diverse ethnic groups with precise UPFs consumption measurement tools, are imperative for a more comprehensive understanding.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC’s) 2022 National Center for Health Statistics report alarmingly indicates a persistent rise in pregnancy-related mortality in the US across three decades, highlighting significant disparities in “race” and maternal age [ 1 ]. This trend underscores the pivotal role of addressing common pregnancy adverse outcomes as a critical component of maternal morbidity and mortality prevention strategies [ 2 ].
Promoting healthy dietary habits during pregnancy is imperative to meet the increased physiological needs of expectant mothers. The phenomenon of “nutritional transition”, characterized by a shift towards high-calorie, low-micronutrient foods, culminates in malnutrition and obesity [ 3 ]. The significance of maternal nutrition in prenatal care is heavily emphasized by researchers as a preventive measure against adverse pregnancy outcomes [ 4 ]. The consumption of diets rich in refined carbohydrates, fats, and sweets is linked to an increased risk of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and preterm birth (PTB) [ 5 ]. Moreover, such dietary patterns adversely affect women’s health by exacerbating hypertensive disorders and contributing to conditions like preeclampsia (PE), low birth weight (LBW), and small-for-gestational-age (SGA) infants [ 6 ]. Recognizing the detrimental impact of these unhealthy dietary patterns, it becomes crucial to consider the role of food processing in the maternal diet.
The NOVA classification, a framework for grouping edible substances, categorizes foods into four groups based on the extent and purpose of food processing applied, ranging from unprocessed or minimally processed foods to ultra-processed foods (UPFs) [ 7 , 8 ]. UPFs are characterized by their high content of additives such as preservatives, artificial flavors, colors, and sweeteners, and are typically devoid of whole or minimally processed ingredients [ 9 ]. The consumption of UPFs has been associated with higher risks of obesity, hypertension, cancer, and other chronic diseases [ 8 , 10 , 11 , 12 ]. These foods are implicated in disrupting insulin signaling, promoting excessive energy intake, weight gain, and increased urinary concentrations of phthalate metabolites, which act as endocrine disruptors [ 13 , 14 ]. In the context of adverse pregnancy outcomes, recent meta-analytic work highlighted a heightened risk of GDM (odds ratio (OR): 1.48; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.17, 1.87) and PE (OR: 1.28; 95% CI: 1.15, 1.42) among high UPFs consumers, with no significant associations observed in LBW, PTB, and Large for Gestational Age (LGA) [ 15 ]. However, the previous meta-analysis did not encompass a comprehensive set of extant studies for each adverse outcome (as evidenced by the inclusion of only 10 studies for GDM in contrast to the 44 studies incorporated in our current investigation), thereby underscoring the challenge posed by the unutilized data in previous analyses. Additionally, recent studies of relevance have emerged [ 16 , 17 , 18 ] and the preceding meta-analytic work did not include a dose-response analysis [ 15 ]. The integration of dose-response analysis offers benefits such as facilitating the formulation of public health directives, augmenting precision, and quantifying the dose-response relationship. Consequently, we decided to conduct an updated dose-response systematic review and meta-analysis to rigorously evaluate the association between UPFs consumption and common adverse pregnancy outcomes, including GDM, SGA, LBW, PTB, and PE.
This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted according to the guidelines specified in the 2020 Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [ 19 ]. The study protocol was registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews Database (PROSPERO) under the registration number CRD42023486135.
Literature search and selection
A systematic literature search was done employing PubMed/MEDLINE, ISI Web of Science and Scopus, with no date restrictions, up to December 6, 2023. The search keywords and strategy are reported in Supplementary Table 1 . Data from grey literature sources such as notes, conference abstracts, reviews, case reports, letters, short surveys, and reports were obtained from a manual search of references mentioned in original research articles published in one of these databases. To augment the breadth of research identified, references within reviews and pertinent studies that met eligibility criteria were further subjected to manual examination.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria were defined as follows: a) observational studies (cohort, case-control, or cross-sectional,) in adult subjects (≥18 years) reporting data on the association between UPFs intake and the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes (including GDM PE, PTB, LBW, and SGA infants), and reporting effect estimates in the form of hazard ratio (HR), relative risk (RR), or odds ratios (OR), each with at least 95% confidence interval (95% CI). Exclusion criteria included: a) studies done in children and adolescents (< 18 years), b) studies without sufficient data (for instance, those failing to report effect sizes or 95% CIs, instead reporting beta coefficients), and c) those with no relevant exposure. Study titles and abstracts, as well as full-text reviews from database searches meeting the inclusion criteria, were assessed by two reviewers (ST and SM). Any disagreements regarding study inclusion/exclusion criteria were resolved by consensus following discussion. The PICOS tool for each article was reported in Supplementary Table 2 .
Data extraction
Two investigators (FJ and SM) extracted the following data, based on a standardized extraction form, from the studies that met the inclusion criteria: a) first author’s name, year of publication, and country of origin; b) study characteristics (design, follow-up period, and source of data on health status); c) participant characteristics (number of participants/cases, age and sex); d) methods of evaluating UPFs intake; e) the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes; f) main study results (outcomes), and g) covariates utilized for adjustments in multivariate analyses. Any disagreement regarding data extraction characteristics was decided by consensus following the discussion.
Quality assessment
Applying the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) [ 20 ], two investigators assessed the quality of each shortlisted study. The NOS was specifically chosen due to its comprehensive framework designed to evaluate the quality of non-randomized studies. This scale excels in its design, content, and user-friendliness, making it particularly suitable for integrating quality assessments into the interpretation of meta-analytic results. The NOS scale for systematic reviews or meta-analyses, allocating up to 9 points across three domains: study group selection (four points), study group comparability (two points), and exposure and outcomes ascertainment for case-control or cohort studies (three points). Studies scoring 7–9 are deemed high quality/low risk of bias, whereas a score of 0–3 indicates a high risk of bias. Table 1 shows the consensus from this assessment.
Statistical analyses and data synthesis
Statistical analyses were performed applying STATA version 14.0 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA) and SPSS version 25.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). The RR and 95% CI were established as overall effect sizes in this work, similar to effect estimates reported in observational articles meeting the inclusion criteria for this meta-analysis [ 21 ]. The synthesized effect estimates were reported as pooled RR with 95% CI. Due to anticipated heterogeneity between studies, effect estimates were calculated using the DerSimonian-Laird weighted random-effects model [ 22 ]. A pairwise meta-analysis combined the effect size results for the highest and lowest categories of UPFs intake. Heterogeneity among the articles was examined by the Cochran Q and I-squared (I 2 ) statistics, with the I 2 value estimated from [(Q-df)/Q × 100%]; where Q is the χ 2 value and df the corresponding degrees of freedom. Between-study heterogeneity was considered significant when the Cochran Q statistic was significant ( p < 0.05) or if I 2 > 50%; specifically, low, moderate, high, and extreme heterogeneity was defined based on the I 2 statistics cut-offs of < 25%, 25–50%, 50–75%, and >75%, respectively.
Furthermore, subgroup analyses were conducted to evaluate any potential effects due to the study design (cross-sectional, case-control, or cohort), UPFs classification method (NOVA food classification, Western-type diet pattern, fast-food, or sweets consumption), the study region of origin (North America, South America, Asia, Europe, and Australia), pre-pregnancy body mass index (< 25 kg/m 2 and ≥ 25 kg/m 2 ) [ 23 , 24 ], age (< 30 years and ≥ 30 years) [ 24 ], number of cases (< 100 or ≥ 100), number of participants (< 1000 or ≥ 1000), dietary assessment method (food frequency questionnaires [FFQ], 24 h recall, or food records), dietary assessment period (pre-pregnancy, early pregnancy, mid-pregnancy), and other covariate adjustments. Sensitivity analysis was conducted by omitting each study and evaluating the remaining pooled effect estimates. Publication bias was evaluated by visual inspection of funnel plots, and formal testing using Egger’s regression asymmetry and Begg’s rank correlation tests [ 25 , 26 ], with outcomes considered as significant at p < 0.05.
A dose-response meta-analysis was completed to estimate the RRs per 100 g increment in UPFs intake, based on the method introduced by Greenland and colleagues [ 27 , 28 ]. For this process, studies needed to report the number of cases (i.e., participants with incidence) and non-cases (i.e., participants without incidence) or person-years (i.e., the number of people in the study and the duration of their participation) as well as the median point of UPFs intake across more than three categories of intake. Ultimately, a one-stage linear mixed-effects meta-analysis was undertaken to model the dose-response associations, estimating and combining study-specific slope lines to obtain an average slope in a single stage. This linear mixed-effects meta-analysis includes studies with two categories of exposures (at least two effect sizes) in the dose-response analysis.
Quality of evidence
The quality of evidence across articles was ranked employing the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) working group guidelines. The GRADE criteria categorize evidence quality into high, moderate, low, or very low levels [ 29 ].
Study characteristics
Our systematic search and examination of reference lists yielded a total of 3433 records. After omitting duplicates, 2787 articles remained for assessment (Fig. 1 ). A title and abstract review led to the removal of 2707 articles. Subsequent full-text assessment of the 80 remaining studies resulted in the exclusion of a further 26 articles for the following reasons: five articles reported outcomes not relevant to our research scope, six lacked sufficient data, and 15 did not focus on relevant exposure (Supplemental Table 3 ). Consequently, 54 studies met our inclusion criteria and were selected in the present meta-analysis [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 ].
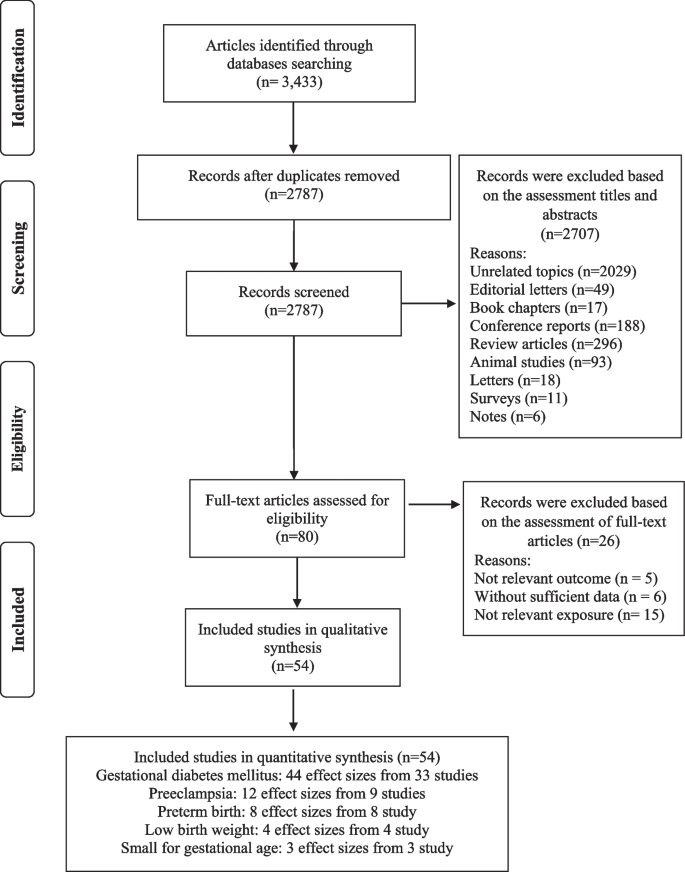
Flow chart of the process of the study selection
The selected studies (detailed in Supplemental Table 4 ) encompass 38 cohort studies [ 16 , 31 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 39 , 40 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 51 , 52 , 54 , 55 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 78 ], 11 case-control studies [ 17 , 18 , 30 , 32 , 34 , 50 , 63 , 66 , 68 , 72 , 77 ], and five cross-sectional studies [ 38 , 46 , 64 , 76 , 79 ]. These articles, conducted between 1988 and 2023, originated from different countries including the USA [ 33 , 36 , 53 , 58 , 60 , 62 , 69 , 74 , 78 ], the UK [ 16 ], China [ 43 , 49 , 51 , 71 , 73 ], Brazil [ 31 , 59 , 63 , 64 , 68 , 79 ], Spain [ 39 , 40 , 42 , 55 , 57 ], Iran [ 17 , 18 , 30 , 32 , 48 , 54 , 66 , 76 , 77 ], Malaysia [ 75 ], Palestine [ 72 ], Australia [ 45 , 46 , 65 ], Singapore [ 37 , 38 ], Norway [ 35 , 44 , 47 ], Japan [ 41 , 67 ], Czech Republic [ 34 ], Iceland [ 70 ] and Denmark [ 61 ]. The study-specific, maximally adjusted RR was reported for 552,686 individuals across the included articles and was pooled for meta-analysis to assess the association between UPFs and the risk GDM [ 16 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 36 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 43 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 59 , 60 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 77 , 78 , 79 ], PE [ 17 , 18 , 30 , 35 , 48 , 52 , 62 , 69 , 74 , 76 ], PTB [ 31 , 37 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 48 , 52 , 58 , 61 , 67 ], LBW [ 45 , 63 , 67 ] and SGA infants [ 46 , 67 , 68 ]. The Newcastle-Ottawa grade (used for quality assessment) categorized 27 studies as high quality [ 17 , 33 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 47 , 51 , 53 , 55 , 57 , 58 , 60 , 62 , 65 , 67 , 69 , 74 , 75 , 78 ] and 27 as medium quality [ 16 , 18 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 34 , 38 , 46 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 52 , 54 , 56 , 59 , 61 , 63 , 64 , 66 , 68 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 76 , 77 , 79 ]. Moreover, the outcomes revealed that the level of agreement between investigators for data collection as well as for quality assessment was appropriate (Kappa = 0.897).
Ultra-processed food and common adverse pregnancy outcomes
Our results suggested a significant relationship between higher UPF intake and an increased risk of GDM (RR = 1.19; 95% CI: 1.10, 1.27; I 2 = 77.5%; p < 0.001; n = 44), PE (RR = 1.28; 95% CI: 1.03, 1.59; I 2 = 80.0%; p = 0.025; n = 12), but not PTB (RR = 1.06; 95% CI: 0.97, 1.17; I 2 = 34.2%; p = 0.231; n = 8), LBW (RR = 1.01; 95% CI: 0.91, 1.12; I 2 = 52.2%; p = 0.905; n = 4) and SGA infants (RR = 1.11; 95% CI: 0.81, 1.52; I 2 = 66.3%; p = 0.532; n = 3), (Refer to Table 1 , Supplementary Fig. 1 ).
In the context of GDM, subgroup analysis showed that a greater UPFs intake was significantly associated with an enhanced risk in cohort studies (vs. cross-sectional) (RR = 1.18; 95% CI: 1.09, 1.27; I 2 = 79.3%; p < 0.001; n = 31) and case-control studies (RR = 2.06; 95% CI: 1.31, 3.35; I 2 = 77.7%; p = 0.002; n = 10), particularly in studies assessed western dietary pattern (RR = 1.34; 95% CI: 1.01, 1.76; I 2 = 43.0%; p = 0.040; n = 7) or fast-foods (RR = 1.32; 95% CI: 1.15, 1.51; I 2 = 79.3%; p < 0.001; n = 22), (vs. NOVA classification or sweets consumption), in North America (vs. Europe, South America, Asia and Australia) (RR = 1.43; 95% CI: 1.27, 1.53; I 2 = 45.4%; p < 0.001; n = 10), and across studies with > 100 number of case (RR = 1.38; 95% CI: 1.21, 1.58; I 2 = 74.8%; p < 0.001; n = 12)(vs. < 100 number of case), in studies with > 1000 number of participants (RR = 1.33; 95% CI: 1.15, 1.54; I 2 = 76.9%; p < 0.001; n = 21)(vs. < 1000 number of participants), in studies used FFQ for dietary assessment (RR = 1.27; 95% CI: 1.14, 1.43; I 2 = 78.6%; p < 0.001; n = 34) (vs. 24 h recall or food record), particularly in studies where the period of dietary assessment was at early pregnancy (RR = 1.26; 95% CI: 1.09, 1.46; I 2 = 80.5%; p = 0.002; n = 19) (vs. pre-pregnancy or mid-pregnancy). Moreover, subgroup analysis for covariates adjustment showed that BMI and physical activity may influence the association between UPF intake and the risk of GDM (Table 2 ).
For PE, the subgroup analysis also highlighted that greater UPFs intake was significantly associated with an enhanced risk in studies assessed western dietary pattern (RR = 2.51; 95% CI: 1.13, 5.57; I 2 = 91.1%; p = 0.023; n = 3) or NOVA classification (RR = 1.22; 95% CI: 1.04, 1.42; I 2 = 0.0%; p = 0.013; n = 3), (vs. sweets consumption), in Asia (vs. Europe or US areas) (RR = 1.65; 95% CI: 1.07, 2.55; I 2 = 86.1%; p < 0.001; n = 6), and across studies with > 100 number of case (RR = 1.57; 95% CI: 1.03, 2.40; I 2 = 93.2%; p < 0.001; n = 4)(vs. < 100 number of case), in studies with number of < 1000 participants (RR = 1.65; 95% CI: 1.07, 2.55; I 2 = 86.1%; p = 0.023; n = 6)(vs. > 1000 number of participants), in participants aged ≥30 years (RR = 1.28; 95% CI: 1.07, 1.54; I 2 = 50.4%; p = 0.089; n = 5)(vs. participants aged < 30 years), in participants with pre-pregnancy-BMI > 25 (RR = 1.52; 95% CI: 1.07, 2.15; I 2 = 84.7%; p = 0.021; n = 1)(vs. participants with pre-pregnancy-BMI ≤ 25), in studies used FFQ for dietary assessment (RR = 1.38; 95% CI: 1.10, 1.72; I 2 = 82.6%; p = 0.005; n = 10) (vs. questions), and particularly in studies where the period of dietary assessment was at mid-pregnancy (RR = 1.23; 95% CI: 1.05, 1.43; I 2 = 38.8%; p = 0.009; n = 3) (vs. early pregnancy). Furthermore, subgroup analysis for covariates adjustment showed that BMI and physical activity may influence the association between UPF intake and the risk of PE (Table 3 ).
Linear and non-linear dose-response analysis
The linear dose-response analysis (refer to Table 1 and Fig. 2 ) indicates a 27% increase in GDM risk per 100 g increment in UPF intake RR = 1.27; 95% CI: 1.07, 1.51; I 2 = 81.0%; p = 0.007; n = 9). However, the linear dose-response analysis for other outcomes was not undertaken due to the limited number of studies available.
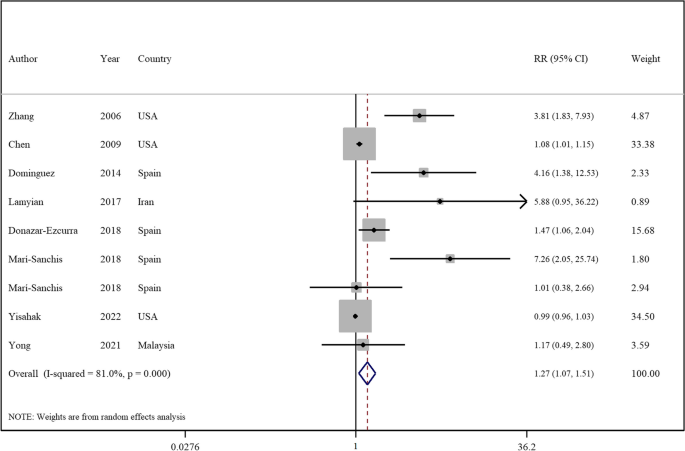
Forest plots showing the linear dose-response meta-analysis of mortality risk for 100 g change in ultra-processed food consumption in daily intake and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus
The non-linear dose-response analysis revealed a positive non-linear relationship between UPFs intake and GDM risk (P nonlinearity = 0.034, P dose-response = 0.034, Fig. 3 ), but not for PE (P nonlinearity = 0.696, P dose-response = 0.812, Fig. 4 ). The non-linear dose-response analysis was not conducted for other outcomes due to insufficient studies.
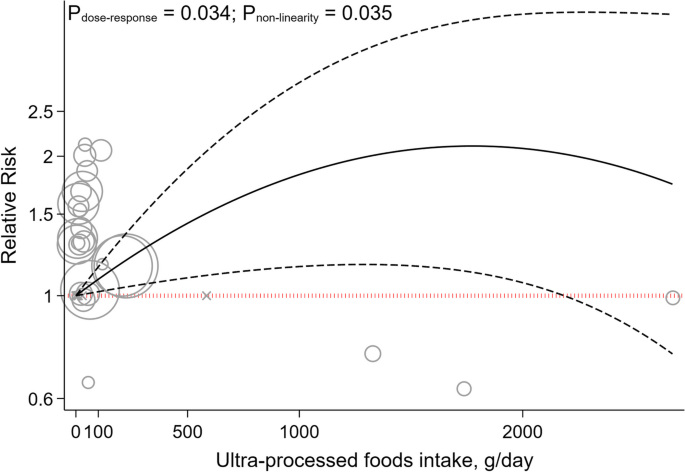
Non-linear dose-response indicated associations between UPF intake and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus
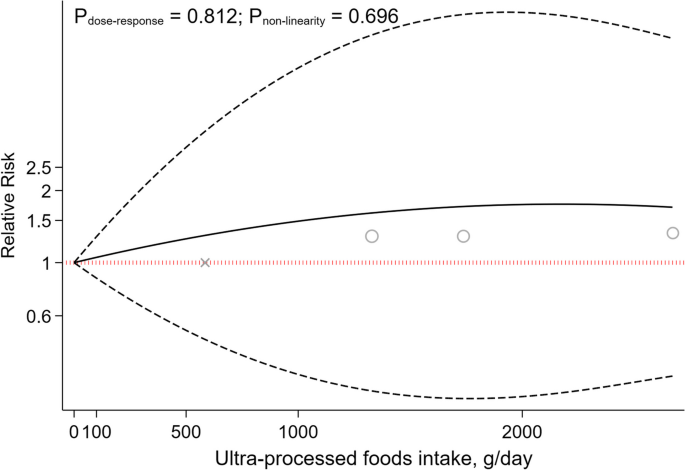
Non-linear dose-response indicated associations between UPF intake and the risk of preeclampsia
Sensitivity analyses and publication bias
Sensitivity analysis across the highest to the lowest meta-analysis for GDM, PE, PTB, LBW and SGA infants showed no significant influence of any single study (Supplemental Fig. 2 ).
No evidence of publication bias was found in articles related to the association with an increased risk of PE ( p = 0.529, Egger’s test; p = 0.891, Begg’s), PTB ( p = 0.458, Egger’s test; p = 0.473, Begg’s), LBW ( p = 0.905, Egger’s test; p = 1.00, Begg’s test), and SGA infants ( p = 0.348, Egger’s test; p = 1.00, Begg’s test). Although, for GDM, Egger’s test indicated potential publication bias ( p < 0.001), not corroborated by Begg’s test ( p = 0.241). As illustrated in Supplemental Fig. 3 , the funnel plot was symmetrical for the association between the UPFs intake and all outcomes, except for studies that reported the risk of GDM disease.
Utilizing the GRADE scale for quality evaluation, we detected the evidence for associations between UPFs intake and risk of GDM, PE, PTB, LBW and SGA infants was classified as moderate (Refer to Table 1 ).
In the realm of maternal and fetal health, the quality of dietary intake during pregnancy is of paramount significance. Accumulating evidence suggests a correlation between the consumption of UPFs and the deterioration of diet quality, potentially elevating the risk of various health complications [ 80 , 81 , 82 ]. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to elucidate the relationship between UPFs intake and adverse pregnancy outcomes including GDM, SGA, LBW, PTB, and PE, through an integrative analysis of existing studies. Our outcomes indicate a significant association between UPFs consumption and increased risks of PE, and GDM either prior to or during pregnancy. However, no significant association was found between UPFs intake and the risks of LBW, SGA, and PTB. Importantly, a 27% increment in the incidence of GDM was linked to a 100 g increase in UPF intake. Furthermore, a positive, non-linear relationship between UPF intake and GDM risk was identified through non-linear dose-response analysis, albeit no analogous association was found for PE.
The results of the current work showed a positive association between UPFs consumption and the risk of PE. In addition, subgroup analysis revealed this relationship to be more pronounced in studies using the NOVA-food classification and a Western dietary pattern for UPFs intake assessment, compared to those focusing on sweet intake. The NOVA classification categorizes foods based on the extent of processing, encompassing various UPFs. Moreover, the association between UPFs consumption and the risk of PE was significant in studies conducted in Asia (vs other regions). Prevalence of PE varies globally, ranging from 0.2–6.7% in Asia, 2.8–9.2% in Oceania, 2.8–5.2% in Europe, 2.6–4.0% in North America, and 1.8–7.7% in South America and the Caribbean [ 83 ]. However, the high heterogeneity in Asian studies should be noted when interpreting this result. Furthermore, a significant association was observed in studies involving women aged 30 years or older, aligning with the increased PE risk associated with advanced maternal age [ 84 ]. Additionally, a significant association was identified between PE risk and UPFs intake in women with pre-pregnancy BMI higher than 25 kg/m 2 (vs BMI ≤25). This aligns with previous findings linking excessive weight gain in expectant mothers to an elevated PE risk, with overweight and obese mothers facing substantially higher risks [ 85 ].
The association between UPFs intake and PE can be elucidated through several mechanisms. The risk factors for PE, including GDM, maternal obesity, and advanced maternal age, are extensively documented in the literature [ 84 , 85 , 86 ]. It has been established that adopting healthy lifestyle habits (including dietary patterns) can mitigate these risk factors [ 87 ]. A higher intake of UPFs is associated with a diminished dietary quality, marked by an increased consumption of sugars and fats, alongside a decrease in fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals [ 88 , 89 ]. UPFs are known to contain elevated levels of pro-inflammatory agents such as refined sugars, salt, and trans fats. The ingestion of these inflammatory components can precipitate oxidative stress and systemic inflammation [ 90 , 91 , 92 ], which are implicated in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia [ 93 , 94 ]. Additionally, the presence of trans fatty acids, added phosphates, and a high salt content in UPFs may impair endothelial function [ 95 , 96 , 97 ], a critical factor in the pathophysiology of hypertension observed in preeclampsia [ 98 ]. Furthermore, the intake of UPFs can alter the composition and diversity of the gut microbiota [ 99 ]. Studies have shown that food additives commonly found in UPFs, such as emulsifiers, sweeteners, and colorants, adversely affect the gut flora [ 100 ]. The interplay between the gut microbiota and the placenta, referred to as the “gut–placenta” axis, is crucial for understanding the etiology of PE. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota and bacterial products like lipopolysaccharide (LPS) have been identified as promotive of PE [ 101 , 102 ]. According to Kell et al., microbial infection, particularly through bacterial products such as LPS (also known as endotoxin), which is highly inflammatory, can initiate an innate immune response that exacerbates inflammation [ 103 ]. Hence, it is hypothesized that dysbiosis induced by UPFs consumption may play a significant role in the promotion of preeclampsia. Moreover, UPFs intake is positively associated with a risk of obesity [ 104 ], a condition marked by insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia, crucial factors in PE development [ 105 ]. Pregnant women with obesity and PE exhibit higher leptin levels, correlating with increased Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alfa (TNF-α), Interleukin 6 (IL-6), and C-reactive protein concentrations [ 106 , 107 ]. Additionally, excessive adipose tissue near the reproductive tract is the source of increased complement components and fragments in preeclamptic pregnancies. These complement proteins may promote an imbalance in angiogenic factors (characterized by increased production of antiangiogenic factors and a decrease in proangiogenic factors). This imbalance leads to placental injury, resulting in decreased blood flow to the tissue, and is accompanied by changes in cytokines levels (decreased IL-10 and increased TNF-α) before the onset of PE [ 108 ].
Our pooled analysis also revealed that higher UPFs intake was related to an increased risk of GDM. This association was significant in studies employing cohort and case-control designs (as opposed to those with cross-sectional methodologies). The inherent recall bias in cross-sectional studies that rely on self-reporting, is a notable limitation affecting the reliability of outcomes [ 109 ]. Moreover, this association was more pronounced in studies that used Western dietary patterns and fast-food consumption for the assessment of UPFs intake (vs those employing NOVA food classification and sweet consumption metrics). The concept of a dietary pattern, which represents the aggregate of eating and drinking habits, is critical as it exerts a greater impact on health and chronic diseases than any individual food item [ 110 ]. Additionally, the application of the NOVA food classification in existing studies is less frequent, suggesting the need for further research utilizing this methodology to derive more meaningful results. Geographical variations were also evident, with significant associations observed in studies conducted in America, compared to those in Asia and Europe. This is in context with the differing regional prevalences of GDM: 7.1% in North America and the Caribbean, 7.8% in Europe and 20.8% in South-East Asia [ 111 ]. Despite the higher prevalence of GDM in Asian populations, the greater intake of UPFs in American and European cohorts may have influenced the study outcomes [ 112 , 113 , 114 , 115 ]. Additionally, a positive association between UPFs intake and GDM risk was observed in studies focusing on women with a pre-pregnancy BMI > 25. Previous research indicates that being overweight or obese before and during pregnancy is a significant risk factor for GDM [ 116 , 117 , 118 ]. However, the scarcity of studies in women with pre-pregnancy BMI > 25 kg/m 2 kg/m suggests the need for more research in this demographic for robust conclusions.
Our outcomes also indicated that a 100 g increase in UPF intake was associated with a 27% increase in the risk of GDM. Moreover, the non-linear dose-response analysis similarly showed a positive, non-linear association between the consumption of UPFs and the risk of GDM. These findings underscore the significant impact that UPF consumption can have on GDM risk. The evidence points towards a robust and worrying correlation where even moderate increases in UPF intake can precipitate a marked rise in GDM risk, highlighting the critical need for dietary awareness and intervention among pregnant women. This aligns with broader nutritional science, emphasizing the importance of minimizing UPF consumption to mitigate not only GDM risk but potentially other metabolic disorders as well, given the multitude of adverse mechanisms through which UPFs affect glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
Pathophysiologically, UPFs intake may increase GDM risk through several mechanisms. In pregnant women with GDM, pre-pregnancy reduced insulin sensitivity and β-cell dysfunction lead to hyperglycemia [ 119 , 120 ]. The hypothesis that excessive sugar intake may augment body mass, thereby indirectly precipitating insulin resistance and subsequent diabetes, is widely recognized. Moreover, the liver’s capacity to assimilate and metabolize refined sugars prevalent in UPFs (such as fructose and sucrose) may be compromised, leading to augmented fat deposition and deteriorated insulin sensitivity [ 121 ]. Furthermore, insulin resistance may be induced by cosmetic ingredients present in UPFs. For example, dietary additives like carrageenan, employed as a thickening and stabilizing agent, may interfere with insulin signaling and thus foster insulin resistance [ 122 ]. Additionally, UPFs intake correlates with increased production of reactive oxygen species and inflammatory biomarkers [ 123 ], inducing insulin resistance through molecular pathways such as β-cell and mitochondrial dysfunction, decreased GLUT4 expression, impaired insulin signaling and heightened inflammatory responses [ 124 ]. Furthermore, UPFs often contain packaging materials like phthalates and bisphenol A, known to have endocrine disruption properties that may contribute to insulin resistance and diabetes development [ 125 , 126 ]. The ingestion of substantial quantities of UPFs also elevates inflammation, a pivotal factor in the genesis of insulin resistance, culminating in hyperglycemia and the development of GDM [ 127 ]. A diet replete with saturated fats, trans fats, sugars, and salt, characteristic of high UPFs consumption, may contribute to chronic inflammation [ 128 ]. Furthermore, excessive UPFs consumption may supplant essential components of a balanced and nutritious diet. For instance, fruits and vegetables are associated with an anti-inflammatory effect [ 129 ]. In addition, the leaching of chemicals from food packaging into UPFs could introduce non-nutritional elements such as phthalates or bisphenol A, potentially eliciting an inflammatory response [ 130 ].
The present study did not establish a significant association between UPFs consumption and the risk of LBW. This result may be attributable to several factors. Firstly, a limited number of studies have evaluated the association between UPFs intake and LBW risk. Additionally, the intake of high-sugar foods (such as sugar-sweetened beverages) has been correlated with an increased risk of LBW in non-GDM subjects [ 34 , 40 ]. This could be attributed to impaired fetal nutrition due to reduced vascular function, potentially induced by oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction associated with high sugar consumption [ 131 ]. However, in GDM subjects this association may not be found due to the higher glucose loads in the fetus [ 47 ]. Therefore, additional research is warranted in both GDM and non-GDM populations to elucidate these relationships comprehensively.
Moreover, SGA was not associated with the intake of UPFs according to the pooled analysis of conducted studies. Although additional studies are necessary to explore this relationship further, existing evidence suggests that a fast-food dietary pattern may lead to increased fat intake and a reduced intake of essential micronutrients crucial for fetal development [ 132 ]. Maternal UPFs intake is linked to lower protein intake, reduced overall nutrition quality, and higher intake of trans fats, carbohydrates and saturated fats, which may increase the risk of neonatal adiposity [ 133 , 134 , 135 ]. Furthermore, higher fast-food intake during pregnancy has been linked with an elevated risk of maternal obesity, which in turn, may increase the likelihood of LGA babies [ 132 , 136 ].
Regarding PTB, the current study found no association with UPFs consumption. Previous research has indicated that dietary patterns rich in fruits and vegetables are associated with a lower risk of PTB [ 37 , 45 ]. Inadequate nutrition before and during pregnancy can lead to health issues for both the mother and fetus, increasing the risk of preterm delivery and intrauterine growth retardation [ 137 ]. The absence of an association between UPFs consumption and preterm delivery in this study could be due to various factors, including the need for a higher UPFs consumption threshold during pregnancy to manifest negative impacts on preterm birth. Additionally, the varied diet of pregnant women, typically including beneficial foods such as fruits, vegetables and nuts, may mitigate the adverse effects of UPFs.
The current investigation has several crucial strengths that make its findings highly significant. Firstly, by pooling all available observational data on the topic, the study provides a comprehensive and robust analysis of the relationship between UPFs intake and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Secondly, the study’s use of a dose-response analysis adds further weight to its conclusions and bolsters our understanding of the link between these two factors. However, there are limitations to consider. These include potential information and recall biases due to the self-reported nature of dietary intake assessments (such as the FFQ) and the absence of specific dietary tools for assessing UPFs consumption. Additionally, this meta-analysis included studies that did not use NOVA’s specialized dietary assessments. Moreover, dietary changes following pregnancy discovery could affect results, and the observational nature of the included studies precludes causal inference. Despite the inclusion of numerous confounding variables, several factors must be cautiously considered in the interpretation of the research findings. For instance, the socio-economic status of participants influences their dietary habits, while race and ethnicity may affect pregnancy outcomes. Furthermore, disparities in access to healthcare services can impact dietary choices and pregnancy outcomes. Other health statuses, such as mental health conditions among pregnant subjects, also influence dietary selections and pregnancy results [ 138 , 139 ]. Finally, the availability of data on broader categories such as diabetes in pregnancy and hypertensive disorders was limited, hindering our ability to conduct a comprehensive analysis on these broader categories.
Our outcomes indicate that prior to or during pregnancy, UPFs intake is associated with a higher risk of GDM and PE. However, no significant link tying UPFs intake to SGA, LWB and PTB was established. Importantly, a 100 g increment in UPFs intake was related to a 27% increase in GDM risk. This study aligns with global trends, where a rise in adverse pregnancy outcomes seems to align with the escalation of industrialization and the corresponding surge in UPFs production and consumption. Investigating the potential linkage between UPFs intake and the rise of adverse pregnancy outcomes may help in the development of nutrition-centric policies for expecting mothers and promote more health-conscious decision-making. To further substantiate these findings, extensive empirical research is required. Future studies should encompass observational research across diverse ethnic groups. Moreover, the adoption of more precise tools for measuring UPFs consumption is imperative. In observational research, it may be challenging to ascertain whether the consumption of UPFs directly contributes to adverse pregnancy outcomes or if it serves as an indicator of other underlying factors. Components of UPFs may escalate the risk of negative pregnancy outcomes. Moreover, UPF consumption could be part of a complex interplay affecting other variables that directly result in adverse outcomes. For instance, UPF intake could influence gestational weight gain, potentially leading to insulin resistance, which is known to correlate with unfavorable pregnancy outcomes, including GDM. Additionally, the consumption of UPFs may not only diminish dietary quality but also be linked with various lifestyle and dietary factors, such as poor diet quality, thereby increasing the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes [ 140 ]. The bidirectional correlation between UPF consumption and unfavorable pregnancy outcomes also merits consideration. For example, individuals experiencing depression or other health conditions might alter their dietary patterns to include a higher intake of UPFs [ 138 ]. Evaluating changes in UPF consumption over time, utilizing precise questionnaires that assess food items classified as UPFs according to the NOVA food classification system, and their association with other health outcomes affecting pregnancy, such as obesity, could offer insights into this relationship. Considering these approaches is essential to enhance the depth and accuracy of investigations into the potential association between UPFs intake and the incidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Hoyert DL, Miniño AM. Maternal Mortality in the United States: Changes in Coding, Publication, and Data Release, 2018. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2020;69(2):1–18.
PubMed Google Scholar
Parikh NI, Gonzalez JM, Anderson CA, Judd SE, Rexrode KM, Hlatky MA, et al. Adverse pregnancy outcomes and cardiovascular disease risk: unique opportunities for cardiovascular disease prevention in women: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143(18):e902–e16.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Hashmi AH, Solomon N, Lee SJ, Min AM, Gilder ME, Wiladphaingern J, et al. Nutrition in transition: historical cohort analysis summarising trends in under-and over-nutrition among pregnant women in a marginalised population along the Thailand–Myanmar border from 1986 to 2016. Br J Nutr. 2019;121(12):1413–23.
Lind JM, Hennessy A, McLean M. Cardiovascular disease in women: the significance of hypertension and gestational diabetes during pregnancy. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2014;29(5):447–53.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Englund-Ögge L, Birgisdottir BE, Sengpiel V, Brantsæter AL, Haugen M, Myhre R, et al. Meal frequency patterns and glycemic properties of maternal diet in relation to preterm delivery: results from a large prospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0172896.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mekie M, Mekonnen W, Assegid M. Cohabitation duration, obstetric, behavioral and nutritional factors predict preeclampsia among nulliparous women in West Amhara zones of Ethiopia: age matched case control study. PLoS One. 2020;15(1):e0228127.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Monteiro CA, Cannon G, Levy R, Moubarac J-C, Jaime P, Martins AP, et al. NOVA The star shines bright. World Nutrition. 2016;7(1–3):28–38.
Google Scholar
da Costa Louzada ML, Baraldi LG, Steele EM, Martins APB, Canella DS, Moubarac J-C, et al. Consumption of ultra-processed foods and obesity in Brazilian adolescents and adults. Prev Med. 2015;81:9–15.
Article Google Scholar
Monteiro CA, Levy RB, Claro RM, Castro IRR, Cannon G. A new classification of foods based on the extent and purpose of their processing. Cadernos de saude publica. 2010;26:2039–49.
Mendonça RD, Pimenta AM, Gea A, de la Fuente-Arrillaga C, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Lopes ACS, et al. Ultraprocessed food consumption and risk of overweight and obesity: the University of Navarra Follow-up (SUN) cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;104(5):1433–40.
Mendonça RD, Lopes ACS, Pimenta AM, Gea A, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Bes-Rastrollo M. Ultra-processed food consumption and the incidence of hypertension in a Mediterranean cohort: the Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra project. Am J Hypertens. 2017;30(4):358–66.
Fiolet T, Srour B, Sellem L, Kesse-Guyot E, Allès B, Méjean C, Deschasaux M, Fassier P, Latino-Martel P, Beslay M, Hercberg S, Lavalette C, Monteiro CA, Julia C, Touvier M. Consumption of ultra-processed foods and cancer risk: results from NutriNet-Santé prospective cohort. BMJ. 2018;360:k322. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k322 .
Bhattacharyya S, Feferman L, Tobacman JK. Carrageenan inhibits insulin signaling through GRB10-mediated decrease in Tyr (P)-IRS1 and through inflammation-induced increase in Ser (P) 307-IRS1. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(17):10764–74.
Buckley JP, Kim H, Wong E, Rebholz CM. Ultra-processed food consumption and exposure to phthalates and bisphenols in the US National Health and nutrition examination survey, 2013–2014. Environ Int. 2019;131:105057.
Paula WO, Patriota ES, Gonçalves VS, Pizato N. Maternal consumption of ultra-processed foods-rich diet and perinatal outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2022;14(15):3242.
Mahendra A, Kehoe SH, Kumaran K, Krishnaveni GV, Arun N, Pidaparthy P, et al. Periconceptional diet and the risk of gestational diabetes in south Indian women: findings from the BAngalore nutrition gestational diabetes LiFEstyle study (BANGLES). Lancet Glob Health. 2023;11:S4.
Kooshki A, Sovizi B, Mahmoudi R, Ghezi S, Foroumandi E. The association between food groups and preeclampsia: a case-control study. Hyperten Pregnancy. 2022;41(1):64–9.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Moradi M, Niazi A, Selajgeh F, Mazloumi E. Comparing dietary patterns during pregnancy in women with preeclampsia and healthy women: a case-control study. J Midwife Reproduct Health. 2022;10(1)
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Oxford: Ottawa Hospital Research Institute; 2000.
Symons M, Moore D. Hazard rate ratio and prospective epidemiological studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2002;55(9):893–9.
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7(3):177–88.
Jayedi A, Soltani S, Zargar MS, Khan TA, Shab-Bidar SJB. Central fatness and risk of all cause mortality: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of 72 prospective cohort studies. 2020;370.
Song C, Lyu Y, Li C, Liu P, Li J, Ma R, et al. Long-term risk of diabetes in women at varying durations after gestational diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis with more than 2 million women 2018;19(3):421–9.
Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994;50(4):1088–101.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ (Clin res ed). 1997;315(7109):629–34.
Berlin JA, Longnecker MP, Greenland S. Meta-analysis of epidemiologic dose-response data. Epidemiology. 1993;4(3):218–28. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001648-199305000-00005 .
Orsini N, Bellocco R, Greenland SJTsj. Generalized least squares for trend estimation of summarized dose–response data 2006;6(1):40–57.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. Bmj. 2008;336(7650):924–6.
Abbasi R, Bakhshimoghaddam F, Alizadeh M. Major dietary patterns in relation to preeclampsia among Iranian pregnant women: a case–control study. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021;34(21):3529–36.
Alves-Santos NH, Cocate PG, Benaim C, Farias DR, Emmett PM, Kac G. Prepregnancy dietary patterns and their association with perinatal outcomes: a prospective cohort study. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2019;119(9):1439–51.
Asadi M, Shahzeidi M, Nadjarzadeh A, Hashemi Yusefabad H, Mansoori A. The relationship between pre-pregnancy dietary patterns adherence and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in Iran: a case–control study. Nutr Diet. 2019;76(5):597–603.
Bao W, Tobias DK, Olsen SF, Zhang C. Pre-pregnancy fried food consumption and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort study. Diabetol. 2014;57(12):2485–91.
Bartáková V, Kuricová K, Zlámal F, Bělobrádková J, Kaňková K. Differences in food intake and genetic variability in taste receptors between Czech pregnant women with and without gestational diabetes mellitus. Eur J Nutr. 2018;57(2):513–21.
Brantsæter AL, Haugen M, Samuelsen SO, Torjusen H, Trogstad L, Alexander J, et al. A dietary pattern characterized by high intake of vegetables, fruits, and vegetable oils is associated with reduced risk of preeclampsia in nulliparous pregnant Norwegian women. J Nutr. 2009;139(6):1162–8.
Chen LW, Hu FB, Yeung E, Willett W, Zhang CL. Prospective study of pre-gravid sugar-sweetened beverage consumption and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(12):2236–41.
Chia AR, de Seymour JV, Colega M, Chen LW, Chan YH, Aris IM, et al. A vegetable, fruit, and white rice dietary pattern during pregnancy is associated with a lower risk of preterm birth and larger birth size in a multiethnic Asian cohort: the growing up in Singapore towards healthy outcomes (GUSTO) cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;104(5):1416–23.
de Seymour J, Chia AR, Colega M, Jones B, McKenzie E, Cai SR, et al. Maternal dietary patterns and gestational diabetes mellitus in a multi-ethnic Asian cohort: the GUSTO study. Nutrients. 2016;8(9)
Dominguez LJ, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Basterra-Gortari FJ, Gea A, Barbagallo M, Bes-Rastrollo M. Fast food consumption and gestational diabetes incidence in the SUN project. PLoS One. 2014;9(9):e106627.
Donazar-Ezcurra M, Lopez-del Burgo C, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Basterra-Gortari FJ, de Irala J, Bes-Rastrollo M. Soft drink consumption and gestational diabetes risk in the SUN project. Clin Nutr. 2018;37(2):638–45.
Dong JY, Kimura T, Ikehara S, Cui M, Kawanishi Y, Yamagishi K, et al. Chocolate consumption and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: the Japan environment and Children's study. Br J Nutr. 2019;122(8):936–41.
Drozd-Dąbrowska M, Trusewicz R, Ganczak M. Selected risk factors of developmental delay in polish infants: a case-control study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15(12)
Du HY, Jiang H, Karmin O, Bo C, Xu LJ, Liu SP, et al. Association of dietary pattern during pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort study in northern China. Biomed Environ Sci. 2017;30(12):887–97.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Englund-Ögge L, Brantsæter AL, Sengpiel V, Haugen M, Birgisdottir BE, Myhre R, et al. Maternal dietary patterns and preterm delivery: Results from large prospective cohort study. BMJ (Online). 2014;348
Gete DG, Waller M, Mishra GD. Prepregnancy dietary patterns and risk of preterm birth and low birth weight: findings from the Australian longitudinal study on Women's health. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020;111(5):1048–58.
Grieger JA, Grzeskowiak LE, Clifton VL. Preconception dietary patterns in human pregnancies are associated with preterm delivery. J Nutr. 2014;144(7):1075–80.
Grundt JH, Eide GE, Brantsæter AL, Haugen M, Markestad T. Is consumption of sugar-sweetened soft drinks during pregnancy associated with birth weight? Mater Child Nutrit. 2017;13(4):e12405.
Hajianfar H, Esmaillzadeh A, Feizi A, Shahshahan Z, Azadbakht L. The association between major dietary patterns and pregnancy-related complications. Archiv Iran Med. 2018;21(10):443–51.
Hehua Z, Yang X, Qing C, Shanyan G, Yuhong Z. Dietary patterns and associations between air pollution and gestational diabetes mellitus. Environ Int. 2021;147
Hezaveh ZS, Feizy Z, Dehghani F, Sarbakhsh P, Moini A, Vafa M. The association between maternal dietary protein intake and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. International journal of. Prev Med. 2019;10(1)
Hu JJ, Oken E, Aris IM, Lin PID, Ma YA, Ding N, et al. Dietary patterns during pregnancy are associated with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: evidence from a Chinese prospective birth cohort study. Nutrients. 2019;11(2)
Ikem E, Halldorsson TI, Birgisdóttir BE, Rasmussen MA, Olsen SF, Maslova E. Dietary patterns and the risk of pregnancy-associated hypertension in the Danish National Birth Cohort: a prospective longitudinal study. BJOG: An Int J Obstetr Gynaecol. 2019;126(5):663–73.
Kahr MK, Suter MA, Ballas J, Ramin SM, Monga M, Lee W, et al. Geospatial analysis of food environment demonstrates associations with gestational diabetes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;214(1):110.e1-.e9.
Lamyian M, Hosseinpour-Niazi S, Mirmiran P, Banaem LM, Goshtasebi A, Azizi F. Pre-pregnancy fast food consumption is associated with gestational diabetes mellitus among tehranian women. Nutrients. 2017;9(3)
Leone A, Martínez-González M, Craig W, Fresán U, Gómez-Donoso C, Bes-Rastrollo M. Pre-gestational consumption of ultra-processed foods and risk of gestational diabetes in a Mediterranean cohort. The SUN project. Nutrients. 2021;13(7)
Lotfi MH, Fallahzadeh H, Rahmanian M, Hosseinzadeh M, Lashkardoost H, Doaei S, et al. Association of food groups intake and physical activity with gestational diabetes mellitus in Iranian women. J Mater -Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020;33(21):3559–64.
Marí-Sanchis A, Díaz-Jurado G, Basterra-Gortari FJ, de la Fuente-Arrillaga C, Martínez-González MA, Bes-Rastrollo M. Association between pre-pregnancy consumption of meat, iron intake, and the risk of gestational diabetes: the SUN project. Eur J Nutr. 2018;57(3):939–49.
Martin CL, Sotres-Alvarez D, Siega-Riz AM. Maternal dietary patterns during the second trimester are associated with preterm birth. J Nutr. 2015;145(8):1857–64.
Nascimento GR, Alves LV, Fonseca CL, Figueiroa JN, Alves JG. Dietary patterns and gestational diabetes mellitus in a low income pregnant women population in Brazil - a cohort study. Archivos Latinoamericanos de Nutricion. 2016;66(4):301–8.
Osorio-Yáñez C, Gelaye B, Qiu C, Bao W, Cardenas A, Enquobahrie DA, et al. Maternal intake of fried foods and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Ann Epidemiol. 2017;27(6):384–90.e1.
Rasmussen MA, Maslova E, Halldorsson TI, Olsen SF. Characterization of dietary patterns in the Danish National Birth Cohort in relation to preterm birth. PLoS One. 2014;9(4)
Saftlas AF, Triche EW, Beydoun H, Bracken MB. Does chocolate intake during pregnancy reduce the risks of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension? Ann Epidemiol. 2010;20(8):584–91.
Santos IS, Victora CG, Huttly S, Carvalhal JB. Caffeine intake and low birth weight: a population-based case-control study. Am J Epidemiol. 1998;147(7):620–7.
Sartorelli DS, Crivellenti LC, Zuccolotto DCC, Franco LJ. Relationship between minimally and ultra-processed food intake during pregnancy with obesity and gestational diabetes mellitus. Cadernos de Saude Publica. 2019;35(4)
Schoenaker DA, Soedamah-Muthu SS, Callaway LK, Mishra GD. Pre-pregnancy dietary patterns and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: results from an Australian population-based prospective cohort study. Diabetol. 2015;58(12):2726–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-015-3742-1 . Epub 2015 Sep 10.
Sedaghat F, Akhoondan M, Ehteshami M, Aghamohammadi V, Ghanei N, Mirmiran P, Rashidkhani B. Maternal Dietary Patterns and Gestational Diabetes Risk: A Case-Control Study. J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:5173926. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5173926 . Epub 2017 Dec 6.
Tamada H, Ebara T, Matsuki T, Kato S, Sato H, Ito Y, et al. Ready-meal consumption during pregnancy is a risk factor for stillbirth: the Japan environment and Children’s study (JECS). Japan environment and Children’s study, Ready-Meal Consumption During Pregnancy is a Risk Factor for Stillbirth: The Japan Environment and Children’s Study (JECS).
Teixeira JA, Hoffman DJ, Castro TG, Saldiva S, Francisco RPV, Vieira SE, et al. Pre-pregnancy dietary pattern is associated with newborn size: results from ProcriAr study. Br J Nutr. 2021;126(6):903–12.
Triche EW, Grosso LM, Belanger K, Darefsky AS, Benowitz NL, Bracken MB. Chocolate consumption in pregnancy and reduced likelihood of preeclampsia. Epidemiol. 2008;19(3):459–64.
Tryggvadottir EA, Medek H, Birgisdottir BE, Geirsson RT, Gunnarsdottir I. Association between healthy maternal dietary pattern and risk for gestational diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2016;70(2):237–42.
Tsoi KY, Chan RSM, Tam CH, Li LS, Tam WH, Ma RCW. Dietary patterns of Chinese pregnant women in Hong Kong. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2022;31(3):378–93.
Wahedy K, El Bilbeisi AHH, Bakry MJ. DIETARY PATTERNS and THEIR ASSOCIATION with GLYCEMIC CONTROL and RISK of GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS in GAZA STRIP, PALESTINE: a CASE-CONTROL STUDY. Bullet Pharmaceut Sci Assiut. 2021;44(2):537–49.
Wen L, Ge H, Qiao J, Zhang L, Chen X, Kilby MD, et al. Maternal dietary patterns and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in twin pregnancies: a longitudinal twin pregnancies birth cohort study. Nutr J. 2020;19(1)
Yisahak SF, Hinkle SN, Mumford SL, Gleason JL, Grantz KL, Zhang C, et al. Periconceptional and first trimester Ultraprocessed food intake and maternal Cardiometabolic outcomes. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(9):2028–36.
Yong HY, Mohd Shariff Z, Mohd Yusof BN, Rejali Z, Tee YYS, Bindels J, van der Beek EM. Beverage Intake and the Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: The SECOST. Nutrients. 2021;13(7):2208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072208 .
Zareei S, Homayounfar R, Naghizadeh MM, Ehrampoush E, Amiri Z, Rahimi M, et al. Dietary pattern in patients with preeclampsia in Fasa. Iran Shiraz E Med J. 2019;20(11)
Zareei S, Homayounfar R, Naghizadeh MM, Ehrampoush E, Rahimi M. Dietary pattern in pregnancy and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). Diabet Metabol Syndrome: Clin Res Rev. 2018;12(3):399–404.
Zhang C, Schulze MB, Solomon CG, Hu FB. A prospective study of dietary patterns, meat intake and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2006;49(11):2604-13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-006-0422-1 . Epub 2006 Sep 7.
Zuccolotto DCC, Crivellenti LC, Franco LJ, Sarotelli DS. Dietary patterns of pregnant women, maternal excessive body weight and gestational diabetes. Revista de Saude Publica. 2019;53.
Moradi S, Hojjati Kermani MA, Bagheri R, Mohammadi H, Jayedi A, Lane MM, et al. Ultra-processed food consumption and adult diabetes risk: a systematic review and dose-response Meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2021;13(12)
Suksatan W, Moradi S, Naeini F, Bagheri R, Mohammadi H, Talebi S, Mehrabani S, Hojjati Kermani MA, Suzuki K. Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Adult Mortality Risk: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of 207,291 Participants. Nutrients. 2021;14(1):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010174 .
Babaei A, Pourmotabbed A, Talebi S, Mehrabani S, Bagheri R, Ghoreishy SM, et al. The association of ultra-processed food consumption with adult inflammatory bowel disease risk: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of 4 035 694 participants. Nutr Rev. 2023;
Umesawa M, Kobashi G. Epidemiology of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy: prevalence, risk factors, predictors and prognosis. Hyperten res: official j Japan Soc Hypert. 2017;40(3):213–20.
Sutan R, Aminuddin NA, Mahdy ZA. Prevalence, maternal characteristics, and birth outcomes of preeclampsia: a cross-sectional study in a single tertiary healthcare center in greater Kuala Lumpur Malaysia. Front Public Health. 2022;10:973271.
Bodnar LM, Ness RB, Markovic N, Roberts JM. The risk of preeclampsia rises with increasing prepregnancy body mass index. Ann Epidemiol. 2005;15(7):475–82.
Catalano PM, McIntyre HD, Cruickshank JK, McCance DR, Dyer AR, Metzger BE, et al. The hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcome study: associations of GDM and obesity with pregnancy outcomes. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(4):780–6.
Perry A, Stephanou A, Rayman MP. Dietary factors that affect the risk of pre-eclampsia. BMJ nutrit prevent health. 2022;5(1):118–33.
Martini D, Godos J, Bonaccio M, Vitaglione P, Grosso G. Ultra-processed foods and nutritional dietary profile: a Meta-analysis of nationally representative samples. Nutrients. 2021;13(10)
Maldonado-Pereira L, Barnaba C, de Los CG, Medina-Meza IG. Evaluation of the nutritional quality of ultra-processed foods (ready to eat + fast food): fatty acids, sugar, and sodium. J Food Sci. 2022;87(8):3659–76.
Monguchi T, Hara T, Hasokawa M, Nakajima H, Mori K, Toh R, et al. Excessive intake of trans fatty acid accelerates atherosclerosis through promoting inflammation and oxidative stress in a mouse model of hyperlipidemia. J Cardiol. 2017;70(2):121–7.
Ma X, Nan F, Liang H, Shu P, Fan X, Song X, et al. Excessive intake of sugar: an accomplice of inflammation. Front Immunol. 2022;13:988481.
Wojcik M, Krawczyk M, Zieleniak A, Mac Marcjanek K, Wozniak LA. Chapter 14 - associations of high blood sugar with oxidative stress and inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes. In: Preuss HG, Bagchi D, editors. Dietary Sugar Salt and Fat in Human Health. Academic Press; 2020. p. 305–23.
Chapter Google Scholar
Chiarello DI, Abad C, Rojas D, Toledo F, Vázquez CM, Mate A, et al. Oxidative stress: Normal pregnancy versus preeclampsia. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(2):165354.
Harmon AC, Cornelius DC, Amaral LM, Faulkner JL, Cunningham MW, Jr., Wallace K, et al. The role of inflammation in the pathology of preeclampsia. Clinical science (London, England : 1979). 2016;130(6):409–19.
Patik JC, Lennon SL, Farquhar WB, Edwards DG. Mechanisms of dietary sodium-induced impairments in Endothelial function and potential countermeasures. Nutrients. 2021;13(1)
Shuto E, Taketani Y, Tanaka R, Harada N, Isshiki M, Sato M, et al. Dietary phosphorus acutely impairs endothelial function. J Am Soc Nephrol: JASN. 2009;20(7):1504–12.
Lopez-Garcia E, Schulze MB, Meigs JB, Manson JE, Rifai N, Stampfer MJ, et al. Consumption of trans fatty acids is related to plasma biomarkers of inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction1. J Nutr. 2005;135(3):562–6.
Lamarca B. Endothelial dysfunction. An important mediator in the pathophysiology of hypertension during pre-eclampsia. Minerva Ginecol 2012;64(4):309–20.
Fernandes AE, Rosa PWL, Melo ME, Martins RCR, Santin FGO, Moura AMSH, et al. Differences in the gut microbiota of women according to ultra-processed food consumption. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2023;33(1):84–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2022.09.025 . Epub 2022 Oct 11.
Whelan K, Bancil AS, Lindsay JO, Chassaing B. Ultra-processed foods and food additives in gut health and disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;22:1–22.
Fan M, Li X, Gao X, Dong L, Xin G, Chen L, et al. LPS induces preeclampsia-like phenotype in rats and HTR8/SVneo cells dysfunction through TLR4/p38 MAPK pathway. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1030.
Jin J, Gao L, Zou X, Zhang Y, Zheng Z, Zhang X, et al. Gut Dysbiosis promotes preeclampsia by regulating macrophages and trophoblasts. Circ Res. 2022;131(6):492–506.
Kell DB, Kenny LC. A dormant microbial component in the development of preeclampsia. Front Med. 2016;3:60.
Rauber F, Chang K, Vamos EP, da Costa Louzada ML, Monteiro CA, Millett C, et al. Ultra-processed food consumption and risk of obesity: a prospective cohort study of UK biobank. Eur J Nutr. 2021;60(4):2169–80.
Wondmkun YT. Obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes: associations and therapeutic implications. Diabet metab syndrome obes: targets therapy. 2020;13:3611–6.
Teran E, Escudero C, Moya W, Flores M, Vallance P, Lopez-Jaramillo P. Elevated C-reactive protein and pro-inflammatory cytokines in Andean women with pre-eclampsia. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2001;75(3):243–9.
Palei AC, Spradley FT, Granger JP. Chronic hyperleptinemia results in the development of hypertension in pregnant rats. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys. 2015;308(10):R855–R61.
CAS Google Scholar
Olson KN, Redman LM, Sones JL. Obesity "complements" preeclampsia. Physiol Genom. 2019;51(3):73–6.
Wang X, Cheng Z. Cross-sectional studies: strengths, weaknesses, and recommendations. Chest. 2020;158(1 Supplement):S65–71.
Mozaffarian D, Ludwig DS. Dietary guidelines in the 21st century—a time for food. Jama. 2010;304(6):681–2.
Wang H, Li N, Chivese T, Werfalli M, Sun H, Yuen L, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: estimation of global and regional gestational diabetes mellitus prevalence for 2021 by International Association of Diabetes in pregnancy study Group's criteria. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109050.
Kityo A, Lee SA. The intake of ultra-processed foods and prevalence of chronic kidney disease: the health examinees study. Nutrients. 2022;14(17)
Nardocci M, Leclerc B-S, Louzada M-L, Monteiro CA, Batal M, Moubarac J-C. Consumption of ultra-processed foods and obesity in Canada. Can J Public Health. 2019;110:4–14.
Rauber F, Louzada MLC, Steele EM, Millett C, Monteiro CA, Levy RB. Ultra-processed food consumption and chronic non-communicable diseases-related dietary nutrient profile in the UK (2008–2014). Nutrients. 2018;10(5):587.
Lavigne-Robichaud M, Moubarac J-C, Lantagne-Lopez S, Johnson-Down L, Batal M, Sidi EAL, et al. Diet quality indices in relation to metabolic syndrome in an indigenous Cree (Eeyouch) population in northern Québec. Canada Pub health nutrit. 2018;21(1):172–80.
Sun Y, Shen Z, Zhan Y, Wang Y, Ma S, Zhang S, et al. Effects of pre-pregnancy body mass index and gestational weight gain on maternal and infant complications. BMC pregnan childbirth. 2020;20(1):1–13.
Linder T, Eder A, Monod C, Rosicky I, Eppel D, Redling K, et al. Impact of prepregnancy overweight and obesity on treatment modality and pregnancy outcome in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:799625.
Najafi F, Hasani J, Izadi N, Hashemi-Nazari S-S, Namvar Z, Shamsi H, et al. Risk of gestational diabetes mellitus by pre-pregnancy body mass index: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabet Metab Syndrome: Clin Res Rev. 2021;15(4):102181.
McIntyre HD, Catalano P, Zhang C, Desoye G, Mathiesen ER, Damm P. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5(1):47.
Plows JF, Stanley JL, Baker PN, Reynolds CM, Vickers MH. The pathophysiology of gestational diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3342.
Stanhope KL. Sugar consumption, metabolic disease and obesity: the state of the controversy. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2016;53(1):52–67.
Bhattacharyya S, I OS, Katyal S, Unterman T, Tobacman JK. Exposure to the common food additive carrageenan leads to glucose intolerance, insulin resistance and inhibition of insulin signalling in HepG2 cells and C57BL/6J mice. Diabetologia. 2012;55(1):194–203.
Quetglas-Llabrés MM, Monserrat-Mesquida M, Bouzas C, Mateos D, Ugarriza L, Gómez C, et al. Oxidative stress and inflammatory biomarkers are related to high intake of ultra-processed food in old adults with metabolic syndrome. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland). 2023;12(8).
Yaribeygi H, Sathyapalan T, Atkin SL, Sahebkar A. Molecular mechanisms linking oxidative stress and diabetes mellitus. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:8609213.
Bertoli S, Leone A, Battezzati A. Human bisphenol a exposure and the “diabesity phenotype”. Dose-Response. 2015;13(3):1559325815599173.
Rolfo A, Nuzzo AM, De Amicis R, Moretti L, Bertoli S, Leone A. Fetal–maternal exposure to endocrine disruptors: correlation with diet intake and pregnancy outcomes. Nutrients. 2020;12(6):1744.
Lorenzo PI, Martín-Montalvo A, Cobo Vuilleumier N, Gauthier BR. Molecular modelling of islet β-cell adaptation to inflammation in pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24)
Christ A, Lauterbach M, Latz E. Western diet and the immune system: an inflammatory connection. Immunity. 2019;51(5):794–811.
Neale E, Batterham M, Tapsell LC. Consumption of a healthy dietary pattern results in significant reductions in C-reactive protein levels in adults: a meta-analysis. Nutr Res. 2016;36(5):391–401.
Liu Z, Lu Y, Zhong K, Wang C, Xu X. The associations between endocrine disrupting chemicals and markers of inflammation and immune responses: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022;234:113382.
Node K, Inoue T. Postprandial hyperglycemia as an etiological factor in vascular failure. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2009;8:23.
Hu Z, Tylavsky FA, Kocak M, Fowke JH, Han JC, Davis RL, et al. Effects of maternal dietary patterns during pregnancy on early childhood growth trajectories and obesity risk: the CANDLE study. Nutrients. 2020;12(2)
Wang Y, Wang K, Du M, Khandpur N, Rossato SL, Lo C-H, et al. Maternal consumption of ultra-processed foods and subsequent risk of offspring overweight or obesity: results from three prospective cohort studies. Bmj. 2022:379.
Paula WO, Gonçalves VSS, Patriota ESO, Franceschini SCC, Pizato N. Impact of ultra-processed food consumption on quality of diet among Brazilian pregnant women assisted in primary health care. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(2)
Crume TL, Brinton JT, Shapiro A, Kaar J, Glueck DH, Siega-Riz AM, et al. Maternal dietary intake during pregnancy and offspring body composition: the healthy start study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215(5):609–e1-e8.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wan Y, Chen Y, Wu X, Yin A, Tian F, Zhang H, et al. Mediation effect of maternal triglyceride and fasting glucose level on the relationship between maternal overweight/ obesity and fetal growth: a prospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. 2023;23(1):449.
Akbari Z, Mansourian M, Kelishadi R. Relationship of the intake of different food groups by pregnant mothers with the birth weight and gestational age: need for public and individual educational programs. J educ health promot. 2015;4:23.
Fischer S, Morales-Suárez-Varela M. The bidirectional relationship between gestational diabetes and depression in pregnant women: a systematic search and review. Healthcare (Basel, Switzerland). 2023;11(3).
Khan R, Waqas A, Bilal A, Mustehsan ZH, Omar J, Rahman A. Association of Maternal depression with diet: a systematic review. Asian J Psychiatr. 2020;52:102098.
Ancira-Moreno M, O'Neill MS, Rivera-Dommarco J, Batis C, Rodríguez Ramírez S, Sánchez BN, et al. Dietary patterns and diet quality during pregnancy and low birthweight: the PRINCESA cohort. Matern Child Nutr. 2020;16(3):e12972.
Download references
Acknowledgments
Author information, authors and affiliations.
Students’ Scientific Research Center (SSRC), Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Sepide Talebi
Department of Clinical Nutrition, School of Nutritional Sciences and Dietetics, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Food Security Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
Sanaz Mehrabani
Department of Nutrition, School of Public Health, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Seyed Mojtaba Ghoreishy
Student research committee, School of Public Health, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Department of Health and Human Performance, Marymount University, Arlington, VA, USA
Alexei Wong
Department of Clinical Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Razi University, Kermanshah, Iran
Aliasghar Moghaddam & Peyman Rahimi Feyli
General Practitioner, Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences (KUMS), Kermanshah, Iran
Parsa Amirian & Mahsa Zarpoosh
Clinical Tuberculosis and Epidemiology Research Center, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases (NRITLD), Masih Daneshvari Hospital, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Mohammad Ali Hojjati Kermani
Department of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Research Center for Evidence-Based Health Management, Maragheh University of Medical Sciences, Maragheh, Iran
Sajjad Moradi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
SM and ST designed this study. SM, MZ and PA contributed to the conduct of the search. SM and ST performed the statistical analysis and interpreted the results. SM, SM-GH, Sanaz Merabani, and MA-HK wrote the initial manuscript. AW, AM and PR_F critically revised the manuscript and contributed to the subsequent drafts of the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sajjad Moradi .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., supplementary material 3., supplementary material 4., supplementary material 5., supplementary material 6., supplementary material 7., supplementary material 8., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Talebi, S., Mehrabani, S., Ghoreishy, S.M. et al. The association between ultra-processed food and common pregnancy adverse outcomes: a dose-response systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 24 , 369 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-024-06489-w
Download citation
Received : 18 January 2024
Accepted : 07 April 2024
Published : 15 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-024-06489-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Ultra-processed foods
- Gestational diabetes mellitus
- Preeclampsia
- Preterm birth
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth
ISSN: 1471-2393
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.

Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

‘The scientist is not in the business of following instructions.’

Glimpse of next-generation internet

Science is making anti-aging progress. But do we want to live forever?
Epic science inside a cubic millimeter of brain.

Six layers of excitatory neurons color-coded by depth.
Credit: Google Research and Lichtman Lab
Anne J. Manning
Harvard Staff Writer
Researchers publish largest-ever dataset of neural connections
A cubic millimeter of brain tissue may not sound like much. But considering that that tiny square contains 57,000 cells, 230 millimeters of blood vessels, and 150 million synapses, all amounting to 1,400 terabytes of data, Harvard and Google researchers have just accomplished something stupendous.
Led by Jeff Lichtman, the Jeremy R. Knowles Professor of Molecular and Cellular Biology and newly appointed dean of science , the Harvard team helped create the largest 3D brain reconstruction to date, showing in vivid detail each cell and its web of connections in a piece of temporal cortex about half the size of a rice grain.
Published in Science, the study is the latest development in a nearly 10-year collaboration with scientists at Google Research, combining Lichtman’s electron microscopy imaging with AI algorithms to color-code and reconstruct the extremely complex wiring of mammal brains. The paper’s three first co-authors are former Harvard postdoc Alexander Shapson-Coe, Michał Januszewski of Google Research, and Harvard postdoc Daniel Berger.
The ultimate goal, supported by the National Institutes of Health BRAIN Initiative , is to create a comprehensive, high-resolution map of a mouse’s neural wiring, which would entail about 1,000 times the amount of data the group just produced from the 1-cubic-millimeter fragment of human cortex.
“The word ‘fragment’ is ironic,” Lichtman said. “A terabyte is, for most people, gigantic, yet a fragment of a human brain — just a minuscule, teeny-weeny little bit of human brain — is still thousands of terabytes.”

Jeff Lichtman.
Kris Snibbe/Harvard Staff Photographer
The latest map contains never-before-seen details of brain structure, including a rare but powerful set of axons connected by up to 50 synapses. The team also noted oddities in the tissue, such as a small number of axons that formed extensive whorls. Because the sample was taken from a patient with epilepsy, the researchers don’t know whether such formations are pathological or simply rare.
Lichtman’s field is connectomics, which seeks to create comprehensive catalogs of brain structure, down to individual cells. Such completed maps would unlock insights into brain function and disease, about which scientists still know very little.
Google’s state-of-the-art AI algorithms allow for reconstruction and mapping of brain tissue in three dimensions. The team has also developed a suite of publicly available tools researchers can use to examine and annotate the connectome.
“Given the enormous investment put into this project, it was important to present the results in a way that anybody else can now go and benefit from them,” said Google collaborator Viren Jain.
Next the team will tackle the mouse hippocampal formation, which is important to neuroscience for its role in memory and neurological disease.
Share this article
You might like.
George Whitesides became a giant of chemistry by keeping it simple

Physicists demo first metro-area quantum computer network in Boston

Nobel laureate details new book, which surveys research, touches on larger philosophical questions
Pop star on one continent, college student on another
Model and musician Kazuma Mitchell managed to (mostly) avoid the spotlight while at Harvard
Finding right mix on campus speech policies
Legal, political scholars discuss balancing personal safety, constitutional rights, academic freedom amid roiling protests, cultural shifts
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 12 May 2024
Association between problematic social networking use and anxiety symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Mingxuan Du 1 ,
- Chengjia Zhao 2 ,
- Haiyan Hu 1 ,
- Ningning Ding 1 ,
- Jiankang He 1 ,
- Wenwen Tian 1 ,
- Wenqian Zhao 1 ,
- Xiujian Lin 1 ,
- Gaoyang Liu 1 ,
- Wendan Chen 1 ,
- ShuangLiu Wang 1 ,
- Pengcheng Wang 3 ,
- Dongwu Xu 1 ,
- Xinhua Shen 4 &
- Guohua Zhang 1
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 263 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
186 Accesses
Metrics details
A growing number of studies have reported that problematic social networking use (PSNU) is strongly associated with anxiety symptoms. However, due to the presence of multiple anxiety subtypes, existing research findings on the extent of this association vary widely, leading to a lack of consensus. The current meta-analysis aimed to summarize studies exploring the relationship between PSNU levels and anxiety symptoms, including generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out. 209 studies with a total of 172 articles were included in the meta-analysis, involving 252,337 participants from 28 countries. The results showed a moderately positive association between PSNU and generalized anxiety (GA), social anxiety (SA), attachment anxiety (AA), and fear of missing out (FoMO) respectively (GA: r = 0.388, 95% CI [0.362, 0.413]; SA: r = 0.437, 95% CI [0.395, 0.478]; AA: r = 0.345, 95% CI [0.286, 0.402]; FoMO: r = 0.496, 95% CI [0.461, 0.529]), and there were different regulatory factors between PSNU and different anxiety subtypes. This study provides the first comprehensive estimate of the association of PSNU with multiple anxiety subtypes, which vary by time of measurement, region, gender, and measurement tool.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Social network refers to online platforms that allow users to create, share, and exchange information, encompassing text, images, audio, and video [ 1 ]. The use of social network, a term encompassing various activities on these platforms, has been measured from angles such as frequency, duration, intensity, and addictive behavior, all indicative of the extent of social networking usage [ 2 ]. As of April 2023, there are 4.8 billion social network users globally, representing 59.9% of the world’s population [ 3 ]. The usage of social network is considered a normal behavior and a part of everyday life [ 4 , 5 ]. Although social network offers convenience in daily life, excessive use can lead to PSNU [ 6 , 7 ], posing potential threats to mental health, particularly anxiety symptoms (Rasmussen et al., 2020). Empirical research has shown that anxiety symptoms, including generalized anxiety (GA), social anxiety (SA), attachment anxiety (AA), and fear of missing out (FoMO), are closely related to PSNU [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ]. While some empirical studies have explored the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms, their conclusions are not consistent. Some studies have found a significant positive correlation [ 13 , 14 , 15 ], while others have found no significant correlation [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Furthermore, the degree of correlation varies widely in existing research, with reported r-values ranging from 0.12 to 0.80 [ 20 , 21 ]. Therefore, a systematic meta-analysis is necessary to clarify the impact of PSNU on individual anxiety symptoms.
Previous research lacks a unified concept of PSNU, primarily due to differing theoretical interpretations by various authors, and the use of varied standards and diagnostic tools. Currently, this phenomenon is referred to by several terms, including compulsive social networking use, problematic social networking use, excessive social networking use, social networking dependency, and social networking addiction [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]. These conceptual differences hinder the development of a cohesive and systematic research framework, as it remains unclear whether these definitions and tools capture the same underlying construct [ 27 ]. To address this lack of uniformity, this paper will use the term “problematic use” to encompass all the aforementioned nomenclatures (i.e., compulsive, excessive, dependent, and addictive use).
Regarding the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms, two main perspectives exist: the first suggests a positive correlation, while the second proposes a U-shaped relationship. The former perspective, advocating a positive correlation, aligns with the social cognitive theory of mass communication. It posits that PSNU can reinforce certain cognitions, emotions, attitudes, and behaviors [ 28 , 29 ], potentially elevating individuals’ anxiety levels [ 30 ]. Additionally, the cognitive-behavioral model of pathological use, a primary framework for explaining factors related to internet-based addictions, indicates that psychiatric symptoms like depression or anxiety may precede internet addiction, implying that individuals experiencing anxiety may turn to social networking platforms as a coping mechanism [ 31 ]. Empirical research also suggests that highly anxious individuals prefer computer-mediated communication due to the control and social liberation it offers and are more likely to have maladaptive emotional regulation, potentially leading to problematic social network service use [ 32 ]. Turning to the alternate perspective, it proposes a U-shaped relationship as per the digital Goldilocks hypothesis. In this view, moderate social networking usage is considered beneficial for psychosocial adaptation, providing individuals with opportunities for social connection and support. Conversely, both excessive use and abstinence can negatively impact psychosocial adaptation [ 33 ]. In summary, both perspectives offer plausible explanations.
Incorporating findings from previous meta-analyses, we identified seven systematic reviews and two meta-analyses that investigated the association between PSNU and anxiety. The results of these meta-analyses indicated a significant positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety (ranging from 0.33 to 0.38). However, it is evident that these previous meta-analyses had certain limitations. Firstly, they focused only on specific subtypes of anxiety; secondly, they were limited to adolescents and emerging adults in terms of age. In summary, this systematic review aims to ascertain which theoretical perspective more effectively explains the relationship between PSNU and anxiety, addressing the gaps in previous meta-analyses. Additionally, the association between PSNU and anxiety could be moderated by various factors. Drawing from a broad research perspective, any individual study is influenced by researcher-specific designs and associated sample estimates. These may lead to bias compared to the broader population. Considering the selection criteria for moderating variables in empirical studies and meta-analyses [ 34 , 35 ], the heterogeneity of findings on problematic social network usage and anxiety symptoms could be driven by divergence in sample characteristics (e.g., gender, age, region) and research characteristics (measurement instrument of study variables). Since the 2019 coronavirus pandemic, heightened public anxiety may be attributed to the fear of the virus or heightened real life stress. The increased use of electronic devices, particularly smartphones during the pandemic, also instigates the prevalence of problematic social networking. Thus, our analysis focuses on three moderators: sample characteristics (participants’ gender, age, region), measurement tools (for PSNU and anxiety symptoms) and the time of measurement (before COVID-19 vs. during COVID-19).
The present study was conducted in accordance with the 2020 statement on Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [ 36 ]. To facilitate transparency and to avoid unnecessary duplication of research, this study was registered on PROSPERO, and the number is CRD42022350902.
Literature search
Studies on the relationship between the PSNU and anxiety symptoms from 2000 to 2023 were retrieved from seven databases. These databases included China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Data, Chongqing VIP Information Co. Ltd. (VIP), Web of Science, ScienceDirect, PubMed, and PsycARTICLES. The search strings consisted of (a) anxiety symptoms, (b) social network, and (c) Problematic use. As shown in Table 1 , the keywords for anxiety are as follows: anxiety, generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, fear of missing out, and FoMO. The keywords for social network are as follows: social network, social media, social networking site, Instagram, and Facebook. The keywords for addiction are as follows: addiction, dependence, problem/problematic use, excessive use. The search deadline was March 19, 2023. A total of 2078 studies were initially retrieved and all were identified ultimately.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Retrieved studies were eligible for the present meta-analysis if they met the following inclusion criteria: (a) the study provided Pearson correlation coefficients used to measure the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms; (b) the study reported the sample size and the measurement instruments for the variables; (c) the study was written in English and Chinese; (d) the study provided sufficient statistics to calculate the effect sizes; (e) effect sizes were extracted from independent samples. If multiple independent samples were investigated in the same study, they were coded separately; if the study was a longitudinal study, they were coded by the first measurement. In addition, studies were excluded if they: (a) examined non-problematic social network use; (b) had an abnormal sample population; (c) the results of the same sample were included in another study and (d) were case reports or review articles. Two evaluators with master’s degrees independently assessed the eligibility of the articles. A third evaluator with a PhD examined the results and resolved dissenting views.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two evaluators independently coded the selected articles according to the following characteristics: literature information, time of measurement (before the COVID-19 vs. during the COVID-19), sample source (developed country vs. developing country), sample size, proportion of males, mean age, type of anxiety, and measurement instruments for PSNU and anxiety symptoms. The following principles needed to be adhered to in the coding process: (a) effect sizes were extracted from independent samples. If multiple independent samples were investigated in the same study, they were coded separately; if the study was a longitudinal study, it was coded by the first measurement; (b) if multiple studies used the same data, the one with the most complete information was selected; (c) If studies reported t or F values rather than r , the following formula \( r=\sqrt{\frac{{t}^{2}}{{t}^{2}+df}}\) ; \( r=\sqrt{\frac{F}{F+d{f}_{e}}}\) was used to convert them into r values [ 37 , 38 ]. Additionally, if some studies only reported the correlation matrix between each dimension of PSNU and anxiety symptoms, the following formula \( {r}_{xy}=\frac{\sum {r}_{xi}{r}_{yj}}{\sqrt{n+n(n-1){r}_{xixj}}\sqrt{m+m(m-1){r}_{yiyj}}}\) was used to synthesize the r values [ 39 ], where n or m is the number of dimensions of variable x or variable y, respectively, and \( {r}_{xixj} \) or \( {r}_{yiyj}\) represents the mean of the correlation coefficients between the dimensions of variable x or variable y, respectively.
Literature quality was determined according to the meta-analysis quality evaluation scale developed [ 40 ]. The quality of the post-screening studies was assessed by five dimensions: sampling method, efficiency of sample collection, level of publication, and reliability of PSNU and anxiety symptom measurement instruments. The total score of the scale ranged from 0 to 10; higher scores indicated better quality of the literature.
Data analysis
All data were performed using Comprehensive Meta Analysis 3.3 (CMA 3.3). Pearson’s product-moment coefficient r was selected as the effect size index in this meta-analysis. Firstly, \( {\text{F}\text{i}\text{s}\text{h}\text{e}\text{r}}^{{\prime }}\text{s} Z=\frac{1}{2}\times \text{ln}\left(\frac{1+r}{1-r}\right)\) was used to convert the correlation coefficient to Fisher Z . Then the formula \( SE=\sqrt{\frac{1}{n-3}}\) was used to calculate the standard error ( SE ). Finally, the summary of r was obtained from the formula \( r=\frac{{e}^{2z}-1}{{e}^{2z}+1}\) for a comprehensive measure of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms [ 37 , 41 ].
Although the effect sizes estimated by the included studies may be similar, considering the actual differences between studies (e.g., region and gender), the random effects model was a better choice for data analysis for the current meta-analysis. The heterogeneity of the included study effect sizes was measured for significance by Cochran’s Q test and estimated quantitatively by the I 2 statistic [ 42 ]. If the results indicate there is a significant heterogeneity (the Q test: p -value < 0.05, I 2 > 75) and the results of different studies are significantly different from the overall effect size. Conversely, it indicates there are no differences between the studies and the overall effect size. And significant heterogeneity tends to indicate the possible presence of potential moderating variables. Subgroup analysis and meta-regression analysis were used to examine the moderating effect of categorical and continuous variables, respectively.
Funnel plots, fail-safe number (Nfs) and Egger linear regression were utilized to evaluate the publication bias [ 43 , 44 , 45 ]. The likelihood of publication bias was considered low if the intercept obtained from Egger linear regression was not significant. A larger Nfs indicated a lower risk of publication bias, and if Nfs < 5k + 10 (k representing the original number of studies), publication bias should be a concern [ 46 ]. When Egger’s linear regression was significant, the Duval and Tweedie’s trim-and-fill was performed to correct the effect size. If there was no significant change in the effect size, it was assumed that there was no serious publication bias [ 47 ].
A significance level of P < 0.05 was deemed applicable in this study.
Sample characteristics
The PRISMA search process is depicted in Fig. 1 . The database search yielded 2078 records. After removing duplicate records and screening the title and abstract, the full text was subject to further evaluation. Ultimately, 172 records fit the inclusion criteria, including 209 independent effect sizes. The present meta-analysis included 68 studies on generalized anxiety, 44 on social anxiety, 22 on attachment anxiety, and 75 on fear of missing out. The characteristics of the selected studies are summarized in Table 2 . The majority of the sample group were adults. Quality scores for selected studies ranged from 0 to 10, with only 34 effect sizes below the theoretical mean, indicating high quality for the included studies. The literature included utilized BSMAS as the primary tool to measure PSNU, DASS-21-A to measure GA, IAS to measure SA, ECR to measure AA, and FoMOS to measure FoMO.
Flow chart of the search and selection strategy
Overall analysis, homogeneity tests and publication bias
As shown in Table 3 , there was significant heterogeneity between PSNU and all four anxiety symptoms (GA: Q = 1623.090, I 2 = 95.872%; SA: Q = 1396.828, I 2 = 96.922%; AA: Q = 264.899, I 2 = 92.072%; FoMO: Q = 1847.110, I 2 = 95.994%), so a random effects model was chosen. The results of the random effects model indicate a moderate positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety symptoms (GA: r = 0.350, 95% CI [0.323, 0.378]; SA: r = 0.390, 95% CI [0.347, 0.431]; AA: r = 0.345, 95% CI [0.286, 0.402]; FoMO: r = 0.496, 95% CI [0.461, 0.529]).
Figure 2 shows the funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms. No significant symmetry was seen in the funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and GA and between PSNU and SA. And the Egger’s regression results also indicated that there might be publication bias ( t = 3.775, p < 0.001; t = 2.309, p < 0.05). Therefore, it was necessary to use fail-safe number (Nfs) and the trim and fill method for further examination and correction. The Nfs for PSNU and GA as well as PSNU and SA are 4591 and 7568, respectively. Both Nfs were much larger than the standard 5 k + 10. After performing the trim and fill method, 14 effect sizes were added to the right side of the funnel plat (Fig. 2 .a), the correlation coefficient between PSNU and GA changed to ( r = 0.388, 95% CI [0.362, 0.413]); 10 effect sizes were added to the right side of the funnel plat (Fig. 2 .b), the correlation coefficient between PSNU and SA changed to ( r = 0.437, 95% CI [0.395, 0.478]). The correlation coefficients did not change significantly, indicating that there was no significant publication bias associated with the relationship between PSNU and these two anxiety symptoms (GA and SA).
Funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms. Note: Black dots indicated additional studies after using trim and fill method; ( a ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and GA; ( b ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and SA; ( c ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and AA; ( d ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and FoMO
Sensitivity analyses
Initially, the findings obtained through the one-study-removed approach indicated that the heterogeneities in the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms were not attributed to any individual study. Nevertheless, it is important to note that sensitivity analysis should be performed based on literature quality [ 223 ] since low-quality literature could potentially impact result stability. In the relationship between PSNU and GA, the 10 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.402, 95% CI [0.375, 0.428]); In the relationship between PSNU and SA, the 8 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.431, 95% CI [0.387, 0.472]); In the relationship between PSNU and AA, the 5 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.367, 95% CI [0.298, 0.433]); In the relationship between PSNU and FoMO, the 11 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.508, 95% CI [0.470, 0.544]). The revised estimates indicate that meta-analysis results were stable.
Moderator analysis
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between psnu and ga.
The results of subgroup analysis and meta-regression are shown in Table 4 , the time of measurement significantly moderated the correlation between PSNU and GA ( Q between = 19.268, df = 2, p < 0.001). The relation between the two variables was significantly higher during the COVID-19 ( r = 0.392, 95% CI [0.357, 0.425]) than before the COVID-19 ( r = 0.270, 95% CI [0.227, 0.313]) or measurement time uncertain ( r = 0.352, 95% CI [0.285, 0.415]).
The moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 6.852, df = 1, p = 0.009). The relation was significantly higher when PSNU was measured with the BSMAS ( r = 0.373, 95% CI [0.341, 0.404]) compared to others ( r = 0.301, 95% CI [0.256, 0.344]).
The moderating effect of the GA measurement was significant ( Q between = 60.061, df = 5, p < 0.001). Specifically, when GA measured by the GAD ( r = 0.398, 95% CI [0.356, 0.438]) and the DASS-21-A ( r = 0.433, 95% CI [0.389, 0.475]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the STAI ( r = 0.232, 95% CI [0.187, 0.276]).
For the relation between PSNU and GA, the moderating effect of region, gender and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and SA
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and SA were shown in Table 5 . The results revealed a gender-moderated variances between the two variables (b = 0.601, 95% CI [ 0.041, 1.161], Q model (1, k = 41) = 4.705, p = 0.036).
For the relation between PSNU and SA, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, measurement of PSNU and SA, and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and AA
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and AA were shown in Table 6 , region significantly moderated the correlation between PSNU and AA ( Q between = 6.410, df = 2, p = 0.041). The correlation between the two variables was significantly higher in developing country ( r = 0.378, 95% CI [0.304, 0.448]) than in developed country ( r = 0.242, 95% CI [0.162, 0.319]).
The moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 6.852, df = 1, p = 0.009). Specifically, when AA was measured by the GPIUS-2 ( r = 0.484, 95% CI [0.200, 0.692]) and the PMSMUAQ ( r = 0.443, 95% CI [0.381, 0.501]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the BSMAS ( r = 0.248, 95% CI [0.161, 0.331]) and others ( r = 0.313, 95% CI [0.250, 0.372]).
The moderating effect of the AA measurement was significant ( Q between = 17.283, df = 2, p < 0.001). The correlation was significantly higher when measured using the ECR ( r = 0.386, 95% CI [0.338, 0.432]) compared to the RQ ( r = 0.200, 95% CI [0.123, 0.275]).
For the relation between PSNU and AA, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, gender, and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and FoMO
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and FoMO were shown in Table 7 , the moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 8.170, df = 2, p = 0.017). Among the sub-dimensions, the others was excluded because there was only one sample. Specifically, when measured using the FoMOS-MSME ( r = 0.630, 95% CI [0.513, 0.725]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the FoMOS ( r = 0.472, 95% CI [0.432, 0.509]) and the T-S FoMOS ( r = 0.557, 95% CI [0.463, 0.639]).
For the relationship between PSNU and FoMO, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, measurement of PSNU, gender and age were not significant.
Through systematic review and meta-analysis, this study established a positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety symptoms (i.e., generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out), confirming a linear relationship and partially supporting the Social Cognitive Theory of Mass Communication [ 28 ] and the Cognitive Behavioral Model of Pathological Use [ 31 ]. Specifically, a significant positive correlation between PSNU and GA was observed, implying that GA sufferers might resort to social network for validation or as an escape from reality, potentially alleviating their anxiety. Similarly, the meta-analysis demonstrated a strong positive correlation between PSNU and SA, suggesting a preference for computer-mediated communication among those with high social anxiety due to perceived control and liberation offered by social network. This preference is often accompanied by maladaptive emotional regulation, predisposing them to problematic use. In AA, a robust positive correlation was found with PSNU, indicating a higher propensity for such use among individuals with attachment anxiety. Notably, the study identified the strongest correlation in the context of FoMO. FoMO’s significant association with PSNU is multifaceted, stemming from the real-time nature of social networks that engenders a continuous concern about missing crucial updates or events. This drives frequent engagement with social network, thereby establishing a direct link to problematic usage patterns. Additionally, social network’s feedback loops amplify this effect, intensifying FoMO. The culture of social comparison on these platforms further exacerbates FoMO, as users frequently compare their lives with others’ selectively curated portrayals, enhancing both their social networking usage frequency and the pursuit for social validation. Furthermore, the integral role of social network in modern life broadens FoMO’s scope, encompassing anxieties about staying informed and connected.
The notable correlation between FoMO and PSNU can be comprehensively understood through various perspectives. FoMO is inherently linked to the real-time nature of social networks, which cultivates an ongoing concern about missing significant updates or events in one’s social circle [ 221 ]. This anxiety prompts frequent engagement with social network, leading to patterns of problematic use. Moreover, the feedback loops in social network algorithms, designed to enhance user engagement, further intensify this fear [ 224 ]. Additionally, social comparison, a common phenomenon on these platforms, exacerbates FoMO as users continuously compare their lives with the idealized representations of others, amplifying feelings of missing out on key social experiences [ 225 ]. This behavior not only increases social networking usage but also is closely linked to the quest for social validation and identity construction on these platforms. The extensive role of social network in modern life further amplifies FoMO, as these platforms are crucial for information exchange and maintaining social ties. FoMO thus encompasses more than social concerns, extending to anxieties about staying informed with trends and dynamics within social networks [ 226 ]. The multifaceted nature of FoMO in relation to social network underscores its pronounced correlation with problematic social networking usage. In essence, the combination of social network’s intrinsic characteristics, psychological drivers of user behavior, the culture of social comparison, and the pervasiveness of social network in everyday life collectively make FoMO the most pronouncedly correlated anxiety type with PSNU.
Additionally, we conducted subgroup analyses on the timing of measurement (before COVID-19 vs. during COVID-19), measurement tools (for PSNU and anxiety symptoms), sample characteristics (participants’ region), and performed a meta-regression analysis on gender and age in the context of PSNU and anxiety symptoms. It was found that the timing of measurement, tools used for assessing PSNU and anxiety, region, and gender had a moderating effect, whereas age did not show a significant moderating impact.
Firstly, the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms was significantly higher during the COVID-19 period than before, especially between PSNU and GA. However, the moderating effect of measurement timing was not significant in the relationship between PSNU and other types of anxiety. This could be attributed to the increased uncertainty and stress during the pandemic, leading to heightened levels of general anxiety [ 227 ]. The overuse of social network for information seeking and anxiety alleviation might have paradoxically exacerbated anxiety symptoms, particularly among individuals with broad future-related worries [ 228 ]. While the COVID-19 pandemic altered the relationship between PSNU and GA, its impact on other types of anxiety (such as SA and AA) may not have been significant, likely due to these anxiety types being more influenced by other factors like social skills and attachment styles, which were minimally impacted by the epidemic.
Secondly, the observed variance in the relationship between PSNU and AA across different economic contexts, notably between developing and developed countries, underscores the multifaceted influence of socio-economic, cultural, and technological factors on this dynamic. The amplified connection in developing countries may be attributed to greater socio-economic challenges, distinct cultural norms regarding social support and interaction, rising social network penetration, especially among younger demographics, and technological disparities influencing accessibility and user experience [ 229 , 230 ]. Moreover, the role of social network as a coping mechanism for emotional distress, potentially fostering insecure attachment patterns, is more pronounced in these settings [ 231 ]. These findings highlight the necessity of considering contextual variations in assessing the psychological impacts of social network, advocating for a nuanced understanding of how socio-economic and cultural backgrounds mediate the relationship between PSNU and mental health outcomes [ 232 ]. Additionally, the relationship between PSNU and other types of anxiety (such as GA and SA) presents uniform characteristics across different economic contexts.
Thirdly, the significant moderating effects of measurement tools in the context of PSNU and its correlation with various forms of anxiety, including GA, and AA, are crucial in interpreting the research findings. Specifically, the study reveals that the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale (BSMAS) demonstrates a stronger correlation between PSNU and GA, compared to other tools. Similarly, for AA, the Griffiths’ Problematic Internet Use Scale 2 (GPIUS2) and the Problematic Media Social Media Use Assessment Questionnaire (PMSMUAQ) show a more pronounced correlation with AA than the BSMAS or other instruments, but for SA and FoMO, the PSNU instrument doesn’t significantly moderate the correlation. The PSNU measurement tool typically contains an emotional change dimension. SA and FoMO, due to their specific conditional stimuli triggers and correlation with social networks [ 233 , 234 ], are likely to yield more consistent scores in this dimension, while GA and AA may be less reliable due to their lesser sensitivity to specific conditional stimuli. Consequently, the adjustment effects of PSNU measurements vary across anxiety symptoms. Regarding the measurement tools for anxiety, different scales exhibit varying degrees of sensitivity in detecting the relationship with PSNU. The Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD) and the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales 21 (DASS-21) are more effective in illustrating a strong relationship between GA and PSNU than the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI). In the case of AA, the Experiences in Close Relationships-21 (ECR-21) provides a more substantial correlation than the Relationship Questionnaire (RQ). Furthermore, for FoMO, the Fear of Missing Out Scale - Multi-Social Media Environment (FoMOS-MSME) is more indicative of a strong relationship with PSNU compared to the standard FoMOS or the T-S FoMOS. These findings underscore the importance of the selection of appropriate measurement tools in research. Different tools, due to their unique design, focus, and sensitivity, can reveal varying degrees of correlation between PSNU and anxiety disorders. This highlights the need for careful consideration of tool characteristics and their potential impact on research outcomes. It also cautions against drawing direct comparisons between studies without acknowledging the possible variances introduced by the use of different measurement instruments.
Fourthly, the significant moderating role of gender in the relationship between PSNU and SA, particularly pronounced in samples with a higher proportion of females. Women tend to engage more actively and emotionally with social network, potentially leading to an increased dependency on these platforms when confronting social anxiety [ 235 ]. This intensified use might amplify the association between PSNU and SA. Societal and cultural pressures, especially those related to appearance and social status, are known to disproportionately affect women, possibly exacerbating their experience of social anxiety and prompting a greater reliance on social network for validation and support [ 236 ]. Furthermore, women’s propensity to seek emotional support and express themselves on social network platforms [ 237 ] could strengthen this link, particularly in the context of managing social anxiety. Consequently, the observed gender differences in the relationship between PSNU and SA underscore the importance of considering gender-specific dynamics and cultural influences in psychological research related to social network use. In addition, gender consistency was observed in the association between PSNU and other types of anxiety, indicating no significant gender disparities.
Fifthly, the absence of a significant moderating effect of age on the relationship between PSNU and various forms of anxiety suggests a pervasive influence of social network across different age groups. This finding indicates that the impact of PSNU on anxiety is relatively consistent, irrespective of age, highlighting the universal nature of social network’s psychological implications [ 238 ]. Furthermore, this uniformity suggests that other factors, such as individual psychological traits or socio-cultural influences, might play a more crucial role in the development of anxiety related to social networking usage than age [ 239 ]. The non-significant role of age also points towards a potential generational overlap in social networking usage patterns and their psychological effects, challenging the notion that younger individuals are uniquely susceptible to the adverse effects of social network on mental health [ 240 ]. Therefore, this insight necessitates a broader perspective in understanding the dynamics of social network and mental health, one that transcends age-based assumptions.
Limitations
There are some limitations in this research. First, most of the studies were cross-sectional surveys, resulting in difficulties in inferring causality of variables, longitudinal study data will be needed to evaluate causal interactions in the future. Second, considerable heterogeneity was found in the estimated results, although heterogeneity can be partially explained by differences in study design (e.g., Time of measurement, region, gender, and measurement tools), but this can introduce some uncertainty in the aggregation and generalization of the estimated results. Third, most studies were based on Asian samples, which limits the generality of the results. Fourth, to minimize potential sources of heterogeneity, some less frequently used measurement tools were not included in the classification of measurement tools, which may have some impact on the results of heterogeneity interpretation. Finally, since most of the included studies used self-reported scales, it is possible to get results that deviate from the actual situation to some extent.
This meta-analysis aims to quantifies the correlations between PSNU and four specific types of anxiety symptoms (i.e., generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out). The results revealed a significant moderate positive association between PSNU and each of these anxiety symptoms. Furthermore, Subgroup analysis and meta-regression analysis indicated that gender, region, time of measurement, and instrument of measurement significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and specific anxiety symptoms. Specifically, the measurement time and GA measurement tools significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and GA. Gender significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and SA. Region, PSNU measurement tools, and AA measurement tools all significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and AA. The FoMO measurement tool significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and FoMO. Regarding these findings, prevention interventions for PSNU and anxiety symptoms are important.
Data availability
The datasets are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Problematic social networking use
- Generalized anxiety
- Social anxiety
- Attachment anxiety
Fear of miss out
Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale
Facebook Addiction Scale
Facebook Intrusion Questionnaire
Generalized Problematic Internet Use Scale 2
Problematic Mobile Social Media Usage Assessment Questionnaire
Social Network Addiction Tendency Scale
Brief Symptom Inventory
The anxiety subscale of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
The anxiety subscale of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale
State-Trait Anxiety Inventory
Interaction Anxiousness Scale
Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale
Social Anxiety Scale for Social Media Users
Social Anxiety for Adolescents
Social Anxiety Subscale of the Self-Consciousness Scale
Social Interaction Anxiety Scale
Experiences in Close Relationship Scale
Relationship questionnaire
Fear of Missing Out Scale
FoMO Measurement Scale in the Mobile Social Media Environment
Trait-State Fear of missing Out Scale
Rozgonjuk D, Sindermann C, Elhai JD, Montag C. Fear of missing out (FoMO) and social media’s impact on daily-life and productivity at work: do WhatsApp, Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat Use disorders mediate that association? Addict Behav. 2020;110:106487.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Mieczkowski H, Lee AY, Hancock JT. Priming effects of social media use scales on well-being outcomes: the influence of intensity and addiction scales on self-reported depression. Social Media + Soc. 2020;6(4):2056305120961784.
Article Google Scholar
Global digital population as of April. 2023 [ https://www.statista.com/statistics/617136/digital-population-worldwide/ ].
Marengo D, Settanni M, Fabris MA, Longobardi C. Alone, together: fear of missing out mediates the link between peer exclusion in WhatsApp classmate groups and psychological adjustment in early-adolescent teens. J Social Personal Relationships. 2021;38(4):1371–9.
Marengo D, Fabris MA, Longobardi C, Settanni M. Smartphone and social media use contributed to individual tendencies towards social media addiction in Italian adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic. Addict Behav. 2022;126:107204.
Müller SM, Wegmann E, Stolze D, Brand M. Maximizing social outcomes? Social zapping and fear of missing out mediate the effects of maximization and procrastination on problematic social networks use. Comput Hum Behav. 2020;107:106296.
Sun Y, Zhang Y. A review of theories and models applied in studies of social media addiction and implications for future research. Addict Behav. 2021;114:106699.
Boustead R, Flack M. Moderated-mediation analysis of problematic social networking use: the role of anxious attachment orientation, fear of missing out and satisfaction with life. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Hussain Z, Griffiths MD. The associations between problematic social networking Site Use and Sleep Quality, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, Depression, anxiety and stress. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2021;19(3):686–700.
Gori A, Topino E, Griffiths MD. The associations between attachment, self-esteem, fear of missing out, daily time expenditure, and problematic social media use: a path analysis model. Addict Behav. 2023;141:107633.
Marino C, Manari T, Vieno A, Imperato C, Spada MM, Franceschini C, Musetti A. Problematic social networking sites use and online social anxiety: the role of attachment, emotion dysregulation and motives. Addict Behav. 2023;138:107572.
Tobin SJ, Graham S. Feedback sensitivity as a mediator of the relationship between attachment anxiety and problematic Facebook Use. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2020;23(8):562–6.
Brailovskaia J, Rohmann E, Bierhoff H-W, Margraf J. The anxious addictive narcissist: the relationship between grandiose and vulnerable narcissism, anxiety symptoms and Facebook Addiction. PLoS ONE 2020, 15(11).
Kim S-S, Bae S-M. Social Anxiety and Social Networking Service Addiction Proneness in University students: the Mediating effects of Experiential Avoidance and interpersonal problems. Psychiatry Invest. 2022;19(8):702–702.
Zhao J, Ye B, Yu L, Xia F. Effects of Stressors of COVID-19 on Chinese College Students’ Problematic Social Media Use: A Mediated Moderation Model. Front Psychiatry 2022, 13.
Astolfi Cury GS, Takannune DM, Prates Herrerias GS, Rivera-Sequeiros A, de Barros JR, Baima JP, Saad-Hossne R, Sassaki LY. Clinical and Psychological Factors Associated with Addiction and Compensatory Use of Facebook among patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a cross-sectional study. Int J Gen Med. 2022;15:1447–57.
Balta S, Emirtekin E, Kircaburun K, Griffiths MD. Neuroticism, trait fear of missing out, and Phubbing: the mediating role of state fear of missing out and problematic Instagram Use. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2020;18(3):628–39.
Boursier V, Gioia F, Griffiths MD. Do selfie-expectancies and social appearance anxiety predict adolescents’ problematic social media use? Comput Hum Behav. 2020;110:106395.
Worsley JD, McIntyre JC, Bentall RP, Corcoran R. Childhood maltreatment and problematic social media use: the role of attachment and depression. Psychiatry Res. 2018;267:88–93.
de Bérail P, Guillon M, Bungener C. The relations between YouTube addiction, social anxiety and parasocial relationships with YouTubers: a moderated-mediation model based on a cognitive-behavioral framework. Comput Hum Behav. 2019;99:190–204.
Naidu S, Chand A, Pandaram A, Patel A. Problematic internet and social network site use in young adults: the role of emotional intelligence and fear of negative evaluation. Pers Indiv Differ. 2023;200:111915.
Apaolaza V, Hartmann P, D’Souza C, Gilsanz A. Mindfulness, compulsive Mobile Social Media Use, and derived stress: the mediating roles of self-esteem and social anxiety. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2019;22(6):388–96.
Demircioglu ZI, Goncu-Kose A. Antecedents of problematic social media use and cyberbullying among adolescents: attachment, the dark triad and rejection sensitivity. Curr Psychol (New Brunsw NJ) 2022:1–19.
Gao Q, Li Y, Zhu Z, Fu E, Bu X, Peng S, Xiang Y. What links to psychological needs satisfaction and excessive WeChat use? The mediating role of anxiety, depression and WeChat use intensity. BMC Psychol. 2021;9(1):105–105.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Malak MZ, Shuhaiber AH, Al-amer RM, Abuadas MH, Aburoomi RJ. Correlation between psychological factors, academic performance and social media addiction: model-based testing. Behav Inform Technol. 2022;41(8):1583–95.
Song C. The effect of the need to belong on mobile phone social media dependence of middle school students: Chain mediating roles of fear of missing out and maladaptive cognition. Sichuan Normal University; 2022.
Tokunaga RS, Rains SA. A review and meta-analysis examining conceptual and operational definitions of problematic internet use. Hum Commun Res. 2016;42(2):165–99.
Bandura A. Social cognitive theory of mass communication. Media effects. edn.: Routledge; 2009. pp. 110–40.
Valkenburg PM, Peter J, Walther JB. Media effects: theory and research. Ann Rev Psychol. 2016;67:315–38.
Slater MD. Reinforcing spirals: the mutual influence of media selectivity and media effects and their impact on individual behavior and social identity. Communication Theory. 2007;17(3):281–303.
Ahmed E, Vaghefi I. Social media addiction: A systematic review through cognitive-behavior model of pathological use. 2021.
She R, han Mo PK, Li J, Liu X, Jiang H, Chen Y, Ma L, fai Lau JT. The double-edged sword effect of social networking use intensity on problematic social networking use among college students: the role of social skills and social anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;140:107555.
Przybylski AK, Weinstein N. A large-scale test of the goldilocks hypothesis: quantifying the relations between digital-screen use and the mental well-being of adolescents. Psychol Sci. 2017;28(2):204–15.
Ran G, Li J, Zhang Q, Niu X. The association between social anxiety and mobile phone addiction: a three-level meta-analysis. Comput Hum Behav. 2022;130:107198.
Fioravanti G, Casale S, Benucci SB, Prostamo A, Falone A, Ricca V, Rotella F. Fear of missing out and social networking sites use and abuse: a meta-analysis. Comput Hum Behav. 2021;122:106839.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group* P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264–9.
Card NA. Applied meta-analysis for social science research. Guilford; 2015.
Peterson RA, Brown SP. On the use of beta coefficients in meta-analysis. J Appl Psychol. 2005;90(1):175.
Hunter JE, Schmidt FL. Methods of meta-analysis: correcting error and bias in research findings. Sage; 2004.
Zhang Y, Li S, Yu G. The relationship between self-esteem and social anxiety: a meta-analysis with Chinese students. Adv Psychol Sci. 2019;27(6):1005–18.
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JP, Rothstein HR. Introduction to meta-analysis. Wiley; 2021.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–58.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109):629–34.
Light RJ, Pillemer DB. Summing up: the science of reviewing research. Harvard University Press; 1984.
Rosenthal R. Meta-Analytic Procedures for Social Science Research Sage Publications: Beverly Hills, 1984, 148 pp. Educational Researcher 1986;15(8):18–20.
Rothstein HR, Sutton AJ, Borenstein M. Publication bias in meta-analysis. Publication bias meta‐analysis: Prev Assess Adjustments 2005:1–7.
Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot–based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta‐analysis. Biometrics. 2000;56(2):455–63.
Al-Mamun F, Hosen I, Griffiths MD, Mamun MA. Facebook use and its predictive factors among students: evidence from a lower- and middle-income country, Bangladesh. Front Psychiatry 2022, 13.
Schou Andreassen C, Billieux J, Griffiths MD, Kuss DJ, Demetrovics Z, Mazzoni E, Pallesen S. The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: a large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychol Addict Behaviors: J Soc Psychologists Addict Behav. 2016;30(2):252–62.
Arikan G, Acar IH, Ustundag-Budak AM. A two-generation study: The transmission of attachment and young adults’ depression, anxiety, and social media addiction. Addict Behav 2022, 124.
Arpaci I, Karatas K, Kiran F, Kusci I, Topcu A. Mediating role of positivity in the relationship between state anxiety and problematic social media use during the COVID-19 pandemic. Death Stud. 2022;46(10):2287–97.
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. Facebook Addiction Disorder (FAD) among German students-A longitudinal approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12(12).
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. The relationship between burden caused by coronavirus (Covid-19), addictive social media use, sense of control and anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2021;119:106720–106720.
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. Addictive social media use during Covid-19 outbreak: validation of the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale (BSMAS) and investigation of protective factors in nine countries. Curr Psychol (New Brunsw NJ) 2022:1–19.
Brailovskaia J, Krasavtseva Y, Kochetkov Y, Tour P, Margraf J. Social media use, mental health, and suicide-related outcomes in Russian women: a cross-sectional comparison between two age groups. Women’s Health (London England). 2022;18:17455057221141292–17455057221141292.
PubMed Google Scholar
Chang C-W, Huang R-Y, Strong C, Lin Y-C, Tsai M-C, Chen IH, Lin C-Y, Pakpour AHH, Griffiths MDD. Reciprocal relationships between Problematic Social Media Use, problematic gaming, and psychological distress among University students: a 9-Month Longitudinal Study. Front Public Health 2022, 10.
Charzynska E, Sussman S, Atroszko PA. Profiles of potential behavioral addictions’ severity and their associations with gender, personality, and well-being: A person-centered approach. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Chen C-Y, Chen IH, Pakpour AH, Lin C-Y, Griffiths MD. Internet-related behaviors and psychological distress among Schoolchildren during the COVID-19 School Hiatus. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2021;24(10):654–63.
Da Veiga GF, Sotero L, Pontes HM, Cunha D, Portugal A, Relvas AP. Emerging adults and Facebook Use: the validation of the Bergen Facebook Addiction Scale (BFAS). Int J Mental Health Addict. 2019;17(2):279–94.
Dadiotis A, Bacopoulou F, Kokka I, Vlachakis D, Chrousos GP, Darviri C, Roussos P. Validation of the Greek version of the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale in Undergraduate Students. EMBnetjournal 2021, 26.
Fekih-Romdhane F, Jahrami H, Away R, Trabelsi K, Pandi-Perumal SR, Seeman MV, Hallit S, Cheour M. The relationship between technology addictions and schizotypal traits: mediating roles of depression, anxiety, and stress. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23(1).
Flynn S, Noone C, Sarma KM. An exploration of the link between adult attachment and problematic Facebook use. BMC Psychol. 2018;6(1):34–34.
Fung XCC, Siu AMH, Potenza MN, O’Brien KS, Latner JD, Chen C-Y, Chen IH, Lin C-Y. Problematic use of internet-related activities and Perceived Weight Stigma in Schoolchildren: a longitudinal study across different epidemic periods of COVID-19 in China. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Gonzalez-Nuevo C, Cuesta M, Muniz J, Postigo A, Menendez-Aller A, Kuss DJ. Problematic Use of Social Networks during the First Lockdown: User Profiles and the Protective Effect of Resilience and Optimism. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022, 11(24).
Hou X-L, Wang H-Z, Hu T-Q, Gentile DA, Gaskin J, Wang J-L. The relationship between perceived stress and problematic social networking site use among Chinese college students. J Behav Addictions. 2019;8(2):306–17.
Hussain Z, Wegmann E. Problematic social networking site use and associations with anxiety, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and resilience. Computers Hum Behav Rep. 2021;4:100125.
Imani V, Ahorsu DK, Taghizadeh N, Parsapour Z, Nejati B, Chen H-P, Pakpour AH. The mediating roles of anxiety, Depression, Sleepiness, Insomnia, and Sleep Quality in the Association between Problematic Social Media Use and Quality of Life among patients with Cancer. Healthcare 2022, 10(9).
Islam MS, Sujan MSH, Tasnim R, Mohona RA, Ferdous MZ, Kamruzzaman S, Toma TY, Sakib MN, Pinky KN, Islam MR et al. Problematic smartphone and Social Media Use among Bangladeshi College and University students amid COVID-19: the role of Psychological Well-Being and Pandemic related factors. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Islam MS, Jahan I, Dewan MAA, Pontes HM, Koly KN, Sikder MT, Rahman M. Psychometric properties of three online-related addictive behavior instruments among Bangladeshi school-going adolescents. PLoS ONE 2022, 17(12).
Jahan I, Hosen I, Al Mamun F, Kaggwa MM, Griffiths MD, Mamun MA. How has the COVID-19 pandemic impacted Internet Use behaviors and facilitated problematic internet use? A Bangladeshi study. Psychol Res Behav Manage. 2021;14:1127–38.
Jiang Y. Problematic social media usage and anxiety among University Students during the COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating role of Psychological Capital and the moderating role of academic burnout. Front Psychol. 2021;12:612007–612007.
Kim M-R, Oh J-W, Huh B-Y. Analysis of factors related to Social Network Service Addiction among Korean High School Students. J Addictions Nurs. 2020;31(3):203–12.
Koc M, Gulyagci S. Facebook addiction among Turkish college students: the role of psychological health, demographic, and usage characteristics. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2013;16(4):279–84.
Lin C-Y, Namdar P, Griffiths MD, Pakpour AH. Mediated roles of generalized trust and perceived social support in the effects of problematic social media use on mental health: a cross-sectional study. Health Expect. 2021;24(1):165–73.
Lin C-Y, Imani V, Griffiths MD, Brostrom A, Nygardh A, Demetrovics Z, Pakpour AH. Temporal associations between morningness/eveningness, problematic social media use, psychological distress and daytime sleepiness: mediated roles of sleep quality and insomnia among young adults. J Sleep Res 2021, 30(1).
Lozano Blasco R, Latorre Cosculluela C, Quilez Robres A. Social Network Addiction and its impact on anxiety level among University students. Sustainability 2020, 12(13).
Marino C, Musetti A, Vieno A, Manari T, Franceschini C. Is psychological distress the key factor in the association between problematic social networking sites and poor sleep quality? Addict Behav 2022, 133.
Meshi D, Ellithorpe ME. Problematic social media use and social support received in real-life versus on social media: associations with depression, anxiety and social isolation. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Mitropoulou EM, Karagianni M, Thomadakis C. Social Media Addiction, Self-Compassion, and Psychological Well-Being: a structural equation Model. Alpha Psychiatry. 2022;23(6):298–304.
Ozimek P, Brailovskaia J, Bierhoff H-W. Active and passive behavior in social media: validating the Social Media Activity Questionnaire (SMAQ). Telematics Inf Rep. 2023;10:100048.
Phillips WJ, Wisniewski AT. Self-compassion moderates the predictive effects of social media use profiles on depression and anxiety. Computers Hum Behav Rep. 2021;4:100128.
Reer F, Festl R, Quandt T. Investigating problematic social media and game use in a nationally representative sample of adolescents and younger adults. Behav Inform Technol. 2021;40(8):776–89.
Satici B, Kayis AR, Griffiths MD. Exploring the Association between Social Media Addiction and relationship satisfaction: psychological distress as a Mediator. Int J Mental Health Addict 2021.
Sediri S, Zgueb Y, Ouanes S, Ouali U, Bourgou S, Jomli R, Nacef F. Women’s mental health: acute impact of COVID-19 pandemic on domestic violence. Archives Womens Mental Health. 2020;23(6):749–56.
Shabahang R, Shim H, Aruguete MS, Zsila A. Oversharing on Social Media: anxiety, Attention-Seeking, and Social Media Addiction Predict the breadth and depth of sharing. Psychol Rep 2022:332941221122861–332941221122861.
Sotero L, Ferreira Da Veiga G, Carreira D, Portugal A, Relvas AP. Facebook Addiction and emerging adults: the influence of sociodemographic variables, family communication, and differentiation of self. Escritos De Psicología - Psychol Writings. 2019;12(2):81–92.
Stockdale LA, Coyne SM. Bored and online: reasons for using social media, problematic social networking site use, and behavioral outcomes across the transition from adolescence to emerging adulthood. J Adolesc. 2020;79:173–83.
Wang Z, Yang H, Elhai JD. Are there gender differences in comorbidity symptoms networks of problematic social media use, anxiety and depression symptoms? Evidence from network analysis. Pers Indiv Differ. 2022;195:111705.
White-Gosselin C-E, Poulin F. Associations Between Young Adults’ Social Media Addiction, Relationship Quality With Parents, and Internalizing Problems: A Path Analysis Model. 2022.
Wong HY, Mo HY, Potenza MN, Chan MNM, Lau WM, Chui TK, Pakpour AH, Lin C-Y. Relationships between Severity of Internet Gaming Disorder, Severity of Problematic Social Media Use, Sleep Quality and Psychological Distress. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17(6).
Yam C-W, Pakpour AH, Griffiths MD, Yau W-Y, Lo C-LM, Ng JMT, Lin C-Y, Leung H. Psychometric testing of three Chinese online-related addictive Behavior instruments among Hong Kong University students. Psychiatr Q. 2019;90(1):117–28.
Yuan Y, Zhong Y. A survey on the use of social networks and mental health of college students during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Campus Life Mental Health\. 2021;19(3):209–12.
Google Scholar
Yurdagul C, Kircaburun K, Emirtekin E, Wang P, Griffiths MD. Psychopathological consequences related to problematic Instagram Use among adolescents: the mediating role of body image dissatisfaction and moderating role of gender. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2021;19(5):1385–97.
Zhang W, Pu J, He R, Yu M, Xu L, He X, Chen Z, Gan Z, Liu K, Tan Y, et al. Demographic characteristics, family environment and psychosocial factors affecting internet addiction in Chinese adolescents. J Affect Disord. 2022;315:130–8.
Zhang L, Wu Y, Jin T, Jia Y. Revision and validation of the Chinese short version of social media disorder. Mod Prev Med. 2021;48(8):1350–3.
Zhang X, Fan L. The influence of anxiety on colleges’ life satisfaction. Chin J Health Educ. 2021;37(5):469–72.
Zhao M, Wang H, Dong Y, Niu Y, Fang Y. The relationship between self-esteem and wechat addiction among undergraduate students: the multiple mediating roles of state anxiety and online interpersonal trust. J Psychol Sci. 2021;44(1):104–10.
Zhao J, Zhou Z, Sun B, Zhang X, Zhang L, Fu S. Attentional Bias is Associated with negative emotions in problematic users of Social Media as measured by a dot-probe Task. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(24).
Atroszko PA, Balcerowska JM, Bereznowski P, Biernatowska A, Pallesen S, Schou Andreassen C. Facebook addiction among Polish undergraduate students: validity of measurement and relationship with personality and well-being. Comput Hum Behav. 2018;85:329–38.
Chen Y, Li R, Zhang P, Liu X. The moderating role of state attachment anxiety and avoidance between social anxiety and social networking sites Addiction. Psychol Rep. 2020;123(3):633–47.
Chen B, Zheng X, Sun X. The relationship between problematic social media use and online social anxiety: the roles of social media cognitive overload and dispositional mindfulness. Psychol Dev Educ. 2023;39(5):743–51.
Chentsova VO, Bravo AJ, Mezquita L, Pilatti A, Hogarth L, Cross-Cultural AS. Internalizing symptoms, rumination, and problematic social networking site use: a cross national examination among young adults in seven countries. Addict Behav 2023, 136.
Chu X, Ji S, Wang X, Yu J, Chen Y, Lei L. Peer phubbing and social networking site addiction: the mediating role of social anxiety and the moderating role of Family Financial Difficulty. Front Psychol. 2021;12:670065–670065.
Dempsey AE, O’Brien KD, Tiamiyu MF, Elhai JD. Fear of missing out (FoMO) and rumination mediate relations between social anxiety and problematic Facebook use. Addict Behav Rep. 2019;9:100150–100150.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yildiz Durak H, Seferoglu SS. Modeling of variables related to problematic social media usage: Social desirability tendency example. Scand J Psychol. 2019;60(3):277–88.
Ekinci N, Akat M. The relationship between anxious-ambivalent attachment and social appearance anxiety in adolescents: the serial mediation of positive Youth Development and Instagram Addiction. Psychol Rep 2023:332941231159600–332941231159600.
Foroughi B, Griffiths MD, Iranmanesh M, Salamzadeh Y. Associations between Instagram Addiction, academic performance, social anxiety, Depression, and life satisfaction among University students. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2022;20(4):2221–42.
He L. Influence mechanism and intervention suggestions on addiction of social network addiction. Gannan Normal University; 2021.
Hu Y. The influencing mechanism of type D personality on problematic social networking sites use among adolescents and intervention research. Central China Normal University; 2020.
Jia L. A study of the relationship between neuroticism, perceived social support, social anxiety and problematic social network use in high school students. Harbin Normal University; 2022.
Lee-Won RJ, Herzog L, Park SG. Hooked on Facebook: the role of social anxiety and need for Social Assurance in Problematic Use of Facebook. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2015;18(10):567–74.
Li H. Social anxiety and internet interpersonal addiction in adolescents and countermeasures. Central China Normal University; 2022.
Lin W-S, Chen H-R, Lee TS-H, Feng JY. Role of social anxiety on high engagement and addictive behavior in the context of social networking sites. Data Technol Appl. 2019;53(2):156–70.
Liu Y. The influence of family function on social media addiction in adolescents: the chain mediation effect of social anxiety and resilience. Hunan Normal University; 2021.
Lyvers M, Salviani A, Costan S, Thorberg FA. Alexithymia, narcissism and social anxiety in relation to social media and internet addiction symptoms. Int J Psychology: J Int De Psychologie. 2022;57(5):606–12.
Majid A, Yasir M, Javed A, Ali P. From envy to social anxiety and rumination: how social media site addiction triggers task distraction amongst nurses. J Nurs Adm Manag. 2020;28(3):504–13.
Mou Q, Zhuang J, Gao Y, Zhong Y, Lu Q, Gao F, Zhao M. The relationship between social anxiety and academic engagement among Chinese college students: a serial mediation model. J Affect Disord. 2022;311:247–53.
Ruggieri S, Santoro G, Pace U, Passanisi A, Schimmenti A. Problematic Facebook use and anxiety concerning use of social media in mothers and their offspring: an actor-partner interdependence model. Addict Behav Rep. 2020;11:100256–100256.
Ruiz MJ, Saez G, Villanueva-Moya L, Exposito F. Adolescent sexting: the role of body shame, Social Physique anxiety, and social networking site addiction. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2021;24(12):799–805.
She R, Kit Han Mo P, Li J, Liu X, Jiang H, Chen Y, Ma L, Tak Fai Lau J. The double-edged sword effect of social networking use intensity on problematic social networking use among college students: the role of social skills and social anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;140:107555.
Stănculescu E. The Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale Validity in a Romanian sample using item response theory and network analysis. Int J Mental Health Addict 2022.
Teng X, Lei H, Li J, Wen Z. The influence of social anxiety on social network site addiction of college students: the moderator of intentional self-regulation. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(3):514–7.
Tong W. Influence of boredom on the problematic mobile social networks usage in adolescents: multiple chain mediator. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(5):932–6.
Tu W, Jiang H, Liu Q. Peer victimization and adolescent Mobile Social Addiction: mediation of social anxiety and gender differences. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(17).
Wang S. The influence of college students self-esteem, social anxiety and fear of missing out on the problematic mobile social networks usage. Huaibei Normal University; 2021.
Wang X. The impact of peer relationship and social anxiety on secondary vocational school students’ problematic social network use and intervention study. Huaibei Normal University; 2022.
Wegmann E, Stodt B, Brand M. Addictive use of social networking sites can be explained by the interaction of internet use expectancies, internet literacy, and psychopathological symptoms. J Behav Addictions. 2015;4(3):155–62.
Yang W. The relationship between the type of internet addiction and the personality traits in college students. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2004.
Yang Z. The relationship between social variables and social networking usage among shanghai working population. East China Normal University; 2013.
Zhang C. The relationship between perceived social support and problematic social network use among junior high school students: a chain mediation model and an intervention study. Hebei University; 2022.
Zhang J, Chang F, Huang D, Wen X. The relationship between neuroticism and the problematic mobile social networks use in adolescents: the mediating role of anxiety and positive self-presentation. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(3):598–602.
Zhang Z. College students’ loneliness and problematic social networking use: Chain mediation of social self-efficacy and social anxiety. Shanghai Normal University; 2019.
Zhu B. Discussion on mechanism of social networking addiction——Social anxiety, craving and excitability. Liaoning Normal University; 2017.
Blackwell D, Leaman C, Tramposch R, Osborne C, Liss M. Extraversion, neuroticism, attachment style and fear of missing out as predictors of social media use and addiction. Pers Indiv Differ. 2017;116:69–72.
Chen A. From attachment to addiction: the mediating role of need satisfaction on social networking sites. Comput Hum Behav. 2019;98:80–92.
Chen Y, Zhong S, Dai L, Deng Y, Liu X. Attachment anxiety and social networking sites addiction in college students: a moderated mediating model. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(3):497–500.
Li J. The relations among problematic social networks usage behavior, Childhood Trauma and adult attachment in University students. Hunan Agricultural University; 2020.
Liu C, Ma J-L. Adult attachment orientations and social networking site addiction: the Mediating effects of Online Social Support and the fear of missing out. Front Psychol. 2019;10:2629–2629.
Mo S, Huang W, Xu Y, Tang Z, Nie G. The impact of medical students’ attachment anxiety on the use of problematic social networking sites during the epidemic. Psychol Monthly. 2022;17(9):1–4.
Teng X. The effect of attachment anxiety on problematic mobile social network use: the role of loneliness and self-control. Harbin Normal University; 2021.
Worsley JD, Mansfield R, Corcoran R. Attachment anxiety and problematic social media use: the Mediating Role of Well-Being. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2018;21(9):563–8.
Wu Z. The effect of adult attachment on problematic social network use: the chain mediating effect of loneliness and fear of missing out. Jilin University; 2022.
Xia N. The impact of attachment anxiety on adolescent problem social networking site use: a moderated mediation model. Shihezi University; 2022.
Young L, Kolubinski DC, Frings D. Attachment style moderates the relationship between social media use and user mental health and wellbeing. Heliyon 2020, 6(6).
Bakioglu F, Deniz M, Griffiths MD, Pakpour AH. Adaptation and validation of the online-fear of missing out inventory into Turkish and the association with social media addiction, smartphone addiction, and life satisfaction. BMC Psychol. 2022;10(1):154–154.
Bendayan R, Blanca MJ. Spanish version of the Facebook Intrusion Questionnaire (FIQ-S). Psicothema. 2019;31(2):204–9.
Blachnio A, Przepiorka A. Facebook intrusion, fear of missing out, narcissism, and life satisfaction: a cross-sectional study. Psychiatry Res. 2018;259:514–9.
Casale S, Rugai L, Fioravanti G. Exploring the role of positive metacognitions in explaining the association between the fear of missing out and social media addiction. Addict Behav. 2018;85:83–7.
Chen Y, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Wang K. Effect of fear of’ missing out on college students negative social adaptation: Chain¬ - mediating effect of rumination and problematic social media use. China J Health Psychol. 2022;30(4):581–6.
Cheng S, Zhang X, Han Y. Relationship between fear of missing out and phubbing on college students: the chain intermediary effect of intolerance of uncertainty and problematic social media use. China J Health Psychol. 2022;30(9):1296–300.
Cui Q, Wang J, Zhang J, Li W, Li Q. The relationship between loneliness and negative emotion in college students: the chain-mediating role of fear of missing out and social network sites addiction. J Jining Med Univ. 2022;45(4):248–51.
Ding Q, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Zhou Z. The more gossip, the more addicted: the relationship between interpersonal curiosity and social networking sites addiction tendencies in college students. Psychol Dev Educ. 2022;38(1):118–25.
Fabris MA, Marengo D, Longobardi C, Settanni M. Investigating the links between fear of missing out, social media addiction, and emotional symptoms in adolescence: the role of stress associated with neglect and negative reactions on social media. Addict Behav. 2020;106:106364.
Fang J, Wang X, Wen Z, Zhou J. Fear of missing out and problematic social media use as mediators between emotional support from social media and phubbing behavior. Addict Behav. 2020;107:106430.
Gao Z. The study on the relationship and intervention among fear of missing out self-differentiation and problematic social media use of college students. Yunnan Normal University; 2021.
Gioia F, Fioravanti G, Casale S, Boursier V. The Effects of the Fear of Missing Out on People’s Social Networking Sites Use During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Mediating Role of Online Relational Closeness and Individuals’ Online Communication Attitude. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Gu X. Study on the Inhibitory Effect of Mindfulness Training on Social Media Addiction of College Students. Wuhan University; 2020.
Gugushvili N, Taht K, Schruff-Lim EM, Ruiter RA, Verduyn P. The Association between Neuroticism and problematic social networking sites Use: the role of fear of missing out and Self-Control. Psychol Rep 2022:332941221142003–332941221142003.
Hou J. The study on FoMO and content social media addiction among young people. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Hu R, Zhang B, Yang Y, Mao H, Peng Y, Xiong S. Relationship between college students’ fear of missing and wechat addiction: a cross-lagged analysis. J Bio-education. 2022;10(5):369–73.
Hu G. The relationship between basic psychological needs satisfaction and the use of problematic social networks by college students: a moderated mediation model and online intervention studies. Jiangxi Normal University; 2020.
Jiang Y, Jin T. The relationship between adolescents’ narcissistic personality and their use of problematic mobile social networks: the effects of fear of missing out and positive self-presentation. Chin J Special Educ 2018(11):64–70.
Li J. The effect of positive self-presentation on social networking sites on problematic use of social networking sites: a moderated mediation model. Henan University; 2020.
Li J, Zhang Y, Zhang X. The impact of Freshmen Social Exclusion on problematic Social Network Use: a Moderated Mediation Model. J Heilongjiang Vocat Inst Ecol Eng. 2023;36(1):118–22.
Li M. The relationship between fear of missing out and social media addiction among middle school students——The moderating role of self-control. Kashi University; 2022.
Li R, Dong X, Wang M, Wang R. A study on the relationship between fear of missing out and social network addiction. New Educ Era 2021(52):122–3.
Li Y. Fear of missing out or social avoidance? The influence of peer exclusion on problematic social media use among adolescents in Guangdong Province and Macao. Guangzhou University; 2020.
Ma J, Liu C. The effect of fear of missing out on social networking sites addiction among college students: the mediating roles of social networking site integration use and social support. Psychol Dev Educ. 2019;35(5):605–14.
Mao H. A follow-up study on the mechanism of the influence of university students’ Qi deficiency quality on WeChat addiction. Hunan University of Chinese Medicine; 2021.
Mao Y. The effect of dual filial piety to the college students ’internet social dependence: the mediation of maladaptive cognition and fear of missing out. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Moore K, Craciun G. Fear of missing out and personality as predictors of Social networking sites usage: the Instagram Case. Psychol Rep. 2021;124(4):1761–87.
Niu J. The relationship of college students’ basic psychological needs and social media dependence: the mediating role of fear of missing out. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Pi L, Li X. Research on the relationship between loneliness and problematic mobile social media usage: evidence from variable-oriented and person-oriented analyses. China J Health Psychol. 2023;31(6):936–42.
Pontes HM, Taylor M, Stavropoulos V. Beyond Facebook Addiction: the role of cognitive-related factors and Psychiatric Distress in Social networking site addiction. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2018;21(4):240–7.
Quaglieri A, Biondi S, Roma P, Varchetta M, Fraschetti A, Burrai J, Lausi G, Marti-Vilar M, Gonzalez-Sala F, Di Domenico A et al. From Emotional (Dys) Regulation to Internet Addiction: A Mediation Model of Problematic Social Media Use among Italian Young Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022, 11(1).
Servidio R, Koronczai B, Griffiths MD, Demetrovics Z. Problematic smartphone Use and Problematic Social Media Use: the predictive role of Self-Construal and the Mediating Effect of Fear Missing Out. Front Public Health 2022, 10.
Sheldon P, Antony MG, Sykes B. Predictors of problematic social media use: personality and life-position indicators. Psychol Rep. 2021;124(3):1110–33.
Sun C, Li Y, Kwok SYCL, Mu W. The relationship between intolerance of uncertainty and problematic Social Media Use during the COVID-19 pandemic: a serial mediation model. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(22).
Tang Z. The relationship between loneliness and problematic social networks use among college students: the mediation of fear of missing out and the moderation of social support. Jilin University; 2022.
Tomczyk Ł, Selmanagic-Lizde E. Fear of missing out (FOMO) among youth in Bosnia and Herzegovina — Scale and selected mechanisms. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2018;88:541–9.
Unal-Aydin P, Ozkan Y, Ozturk M, Aydin O, Spada MM. The role of metacognitions in cyberbullying and cybervictimization among adolescents diagnosed with major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders: a case-control study. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy; 2023.
Uram P, Skalski S. Still logged in? The Link between Facebook Addiction, FoMO, Self-Esteem, Life satisfaction and loneliness in social media users. Psychol Rep. 2022;125(1):218–31.
Varchetta M, Fraschetti A, Mari E, Giannini AM. Social Media Addiction, fear of missing out (FoMO) and online vulnerability in university students. Revista Digit De Investigación en Docencia Universitaria. 2020;14(1):e1187.
Wang H. Study on the relationship and intervention between fear of missing and social network addiction in college students. Yunnan Normal University; 2021.
Wang M, Yin Z, Xu Q, Niu G. The relationship between shyness and adolescents’ social network sites addiction: Moderated mediation model. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2020;28(5):906–9.
Wegmann E, Oberst U, Stodt B, Brand M. Online-specific fear of missing out and internet-use expectancies contribute to symptoms of internet-communication disorder. Addict Behav Rep. 2017;5:33–42.
Wegmann E, Brandtner A, Brand M. Perceived strain due to COVID-19-Related restrictions mediates the Effect of Social needs and fear of missing out on the risk of a problematic use of Social Networks. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Wei Q. Negative emotions and problematic social network sites usage: the mediating role of fear of missing out and the moderating role of gender. Central China Normal University; 2018.
Xiong L. Effect of social network site use on college students’ social network site addiction: A moderated mediation model and attention bias training intervention study. Jiangxi Normal University; 2022.
Yan H. The influence of college students’ basic psychological needs on social network addiction: The intermediary role of fear of missing out. Wuhan University; 2020.
Yan H. The status and factors associated with social media addiction among young people——Evidence from WeChat. Chongqing University; 2021.
Yang L. Research on the relationship of fear of missing out, excessive use of Wechat and life satisfaction. Beijing Forestry University; 2020.
Yin Y, Cai X, Ouyang M, Li S, Li X, Wang P. FoMO and the brain: loneliness and problematic social networking site use mediate the association between the topology of the resting-state EEG brain network and fear of missing out. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;141:107624.
Zhang C. The parental rejection and problematic social network sites with adolescents: the chain mediating effect of basic psychological needs and fear of missing out. Central China Normal University; 2022.
Zhang J. The influence of basic psychological needs on problematic mobile social networks usage of adolescent: a moderated mediation model. Liaocheng University; 2020.
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Jin J, Yu G. The relationship between fear of missing out and social media addiction: a cross-lagged analysis. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(5):1082–5.
Zhang Y, Jiang W, Ding Q, Hong M. Social comparison orientation and social network sites addiction in college students: the mediating role of fear of missing out. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(5):928–31.
Zhou J, Fang J. Social network sites support and addiction among college students: a moderated mediation model. Psychology: Techniques Appl. 2021;9(5):293–9.
Andreassen CS, Torsheim T, Brunborg GS, Pallesen S. Development of a Facebook addiction scale. Psychol Rep. 2012;110(2):501–17.
Andreassen CS, Billieux J, Griffiths MD, Kuss DJ, Demetrovics Z, Mazzoni E, Pallesen S. The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: a large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychol Addict Behav. 2016;30(2):252.
Elphinston RA, Noller P. Time to face it! Facebook intrusion and the implications for romantic jealousy and relationship satisfaction. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2011;14(11):631–5.
Caplan SE. Theory and measurement of generalized problematic internet use: a two-step approach. Comput Hum Behav. 2010;26(5):1089–97.
Jiang Y. Development of problematic mobile social media usage assessment questionnaire for adolescents. Psychology: Techniques Appl. 2018;6(10):613–21.
Wang X. College students’ social network addiction tendency: Questionnaire construction and correlation research. Master’s thesis Southwest University; 2016.
Derogatis LR. Brief symptom inventory 18. Johns Hopkins University Baltimore; 2001.
Lovibond PF, Lovibond SH. The structure of negative emotional states: comparison of the Depression anxiety stress scales (DASS) with the Beck Depression and anxiety inventories. Behav Res Ther. 1995;33(3):335–43.
Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, Löwe B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(10):1092–7.
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 1983;67(6):361–70.
Spielberger CD, Gonzalez-Reigosa F, Martinez-Urrutia A, Natalicio LF, Natalicio DS. The state-trait anxiety inventory. Revista Interamericana de Psicologia/Interamerican Journal of Psychology 1971, 5(3&4).
Marteau TM, Bekker H. The development of a six-item short‐form of the state scale of the Spielberger State—trait anxiety inventory (STAI). Br J Clin Psychol. 1992;31(3):301–6.
Leary MR. Social anxiousness: the construct and its measurement. J Pers Assess. 1983;47(1):66–75.
Liebowitz MR. Social phobia. Modern problems of pharmacopsychiatry 1987.
Alkis Y, Kadirhan Z, Sat M. Development and validation of social anxiety scale for social media users. Comput Hum Behav. 2017;72:296–303.
La Greca AM, Stone WL. Social anxiety scale for children-revised: factor structure and concurrent validity. J Clin Child Psychol. 1993;22(1):17–27.
Fenigstein A, Scheier MF, Buss AH. Public and private self-consciousness: Assessment and theory. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1975;43(4):522.
Mattick RP, Clarke JC. Development and validation of measures of social phobia scrutiny fear and social interaction anxiety. Behav Res Ther. 1998;36(4):455–70.
Peters L, Sunderland M, Andrews G, Rapee RM, Mattick RP. Development of a short form Social Interaction anxiety (SIAS) and Social Phobia Scale (SPS) using nonparametric item response theory: the SIAS-6 and the SPS-6. Psychol Assess. 2012;24(1):66.
Brennan KA, Clark CL, Shaver PR. Self-report measurement of adult attachment: an integrative overview. Attachment Theory Close Relationships. 1998;46:76.
Wei M, Russell DW, Mallinckrodt B, Vogel DL. The experiences in Close Relationship Scale (ECR)-short form: reliability, validity, and factor structure. J Pers Assess. 2007;88(2):187–204.
Bartholomew K, Horowitz LM. Attachment styles among young adults: a test of a four-category model. J Personal Soc Psychol. 1991;61(2):226.
Przybylski AK, Murayama K, DeHaan CR, Gladwell V. Motivational, emotional, and behavioral correlates of fear of missing out. Comput Hum Behav. 2013;29(4):1841–8.
Xiaokang S, Yuxiang Z, Xuanhui Z. Developing a fear of missing out (FoMO) measurement scale in the mobile social media environment. Libr Inform Service. 2017;61(11):96.
Bown M, Sutton A. Quality control in systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2010;40(5):669–77.
Turel O, Qahri-Saremi H. Problematic use of social networking sites: antecedents and consequence from a dual-system theory perspective. J Manage Inform Syst. 2016;33(4):1087–116.
Chou H-TG, Edge N. They are happier and having better lives than I am: the impact of using Facebook on perceptions of others’ lives. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2012;15(2):117–21.
Beyens I, Frison E, Eggermont S. I don’t want to miss a thing: adolescents’ fear of missing out and its relationship to adolescents’ social needs, Facebook use, and Facebook related stress. Comput Hum Behav. 2016;64:1–8.
Di Blasi M, Gullo S, Mancinelli E, Freda MF, Esposito G, Gelo OCG, Lagetto G, Giordano C, Mazzeschi C, Pazzagli C. Psychological distress associated with the COVID-19 lockdown: a two-wave network analysis. J Affect Disord. 2021;284:18–26.
Yang X, Hu H, Zhao C, Xu H, Tu X, Zhang G. A longitudinal study of changes in smart phone addiction and depressive symptoms and potential risk factors among Chinese college students. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):252.
Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD. Social networking sites and addiction: ten lessons learned. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017;14(3):311.
Ryan T, Chester A, Reece J, Xenos S. The uses and abuses of Facebook: a review of Facebook addiction. J Behav Addictions. 2014;3(3):133–48.
Elhai JD, Levine JC, Dvorak RD, Hall BJ. Non-social features of smartphone use are most related to depression, anxiety and problematic smartphone use. Comput Hum Behav. 2017;69:75–82.
Jackson LA, Wang J-L. Cultural differences in social networking site use: a comparative study of China and the United States. Comput Hum Behav. 2013;29(3):910–21.
Ahrens LM, Mühlberger A, Pauli P, Wieser MJ. Impaired visuocortical discrimination learning of socially conditioned stimuli in social anxiety. Soc Cognit Affect Neurosci. 2014;10(7):929–37.
Elhai JD, Yang H, Montag C. Fear of missing out (FOMO): overview, theoretical underpinnings, and literature review on relations with severity of negative affectivity and problematic technology use. Brazilian J Psychiatry. 2020;43:203–9.
Barker V. Older adolescents’ motivations for social network site use: the influence of gender, group identity, and collective self-esteem. Cyberpsychology Behav. 2009;12(2):209–13.
Krasnova H, Veltri NF, Eling N, Buxmann P. Why men and women continue to use social networking sites: the role of gender differences. J Strateg Inf Syst. 2017;26(4):261–84.
Palmer J. The role of gender on social network websites. Stylus Knights Write Showc 2012:35–46.
Vannucci A, Flannery KM, Ohannessian CM. Social media use and anxiety in emerging adults. J Affect Disord. 2017;207:163–6.
Primack BA, Shensa A, Sidani JE, Whaite EO, yi Lin L, Rosen D, Colditz JB, Radovic A, Miller E. Social media use and perceived social isolation among young adults in the US. Am J Prev Med. 2017;53(1):1–8.
Twenge JM, Campbell WK. Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: evidence from a population-based study. Prev Med Rep. 2018;12:271–83.
Download references
This research was supported by the Social Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 23BSH135).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Mental Health, Wenzhou Medical University, 325035, Wenzhou, China
Mingxuan Du, Haiyan Hu, Ningning Ding, Jiankang He, Wenwen Tian, Wenqian Zhao, Xiujian Lin, Gaoyang Liu, Wendan Chen, ShuangLiu Wang, Dongwu Xu & Guohua Zhang
School of Education, Renmin University of China, 100872, Beijing, China
Chengjia Zhao
School of Media and Communication, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Dongchuan Road 800, 200240, Shanghai, China
Pengcheng Wang
Department of Neurosis and Psychosomatic Diseases, Huzhou Third Municipal Hospital, 313002, Huzhou, China
Xinhua Shen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
GZ, XS, XL and MD prepared the study design, writing - review and editing. MD and CZ wrote the main manuscript text. MD and HH analyzed data and edited the draft. ND, JH, WT, WZ, GL, WC, SW, PW and DX conducted resources and data curation. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Xinhua Shen or Guohua Zhang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Du, M., Zhao, C., Hu, H. et al. Association between problematic social networking use and anxiety symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychol 12 , 263 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01705-w
Download citation
Received : 25 January 2024
Accepted : 03 April 2024
Published : 12 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01705-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Fear of missing out
- Meta-analysis
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 08 May 2024
Does health voucher intervention increase antenatal consultations and skilled birth attendances in Cameroon? Results from an interrupted time series analysis
- Isidore Sieleunou ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7264-4540 1 , 2 &
- Roland Pascal Enok Bonong ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9552-5365 2
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 602 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
294 Accesses
Metrics details
Limited access to health services during the antenatal period and during childbirth, due to financial barriers, is an obstacle to reducing maternal and child mortality. To improve the use of health services in the three regions of Cameroon, which have the worst reproductive, maternal, neonatal, child and adolescent health indicators, a health voucher project aiming to reduce financial barriers has been progressively implemented since 2015 in these three regions. Our research aimed to assess the impact of the voucher scheme on first antenatal consultation (ANC) and skilled birth attendance (SBA).
Routine aggregated data by month over the period January 2013 to May 2018 for each of the 33 and 37 health facilities included in the study sample were used to measure the effect of the voucher project on the first ANC and SBA, respectively. We estimated changes attributable to the intervention in terms of the levels of outcome indicators immediately after the start of the project and over time using an interrupted time series regression. A meta-analysis was used to obtain the overall estimates.
Overall, the voucher project contributed to an immediate and statistically significant increase, one month after the start of the project, in the monthly number of ANCs (by 26%) and the monthly number of SBAs (by 57%). Compared to the period before the start of the project, a statistically significant monthly increase was observed during the project implementation for SBAs but not for the first ANCs. The results at the level of health facilities (HFs) were mixed. Some HFs experienced an improvement, while others were faced with the status quo or a decrease.
Conclusions
Unlike SBAs, the voucher project in Cameroon had mixed results in improving first ANCs. These limited effects were likely the consequence of poor design and implementation challenges.
Peer Review reports
Reducing maternal, newborn, and child mortality is one of the world's top public health priorities. The third of the seventeen Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) reflects the international commitment to improving maternal and child health. By 2030, the goals include reducing the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births, neonatal mortality to 12 per 1,000 live births at most, and under-five mortality to less than 25 per 1,000 live births [ 1 ].
However, despite considerable improvements in recent decades, maternal mortality has remained a major public health concern globally, with more than 295,000 maternal deaths in 2017 and sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) alone accounting for approximately 66% of this global picture [ 2 ]. On the other hand, despite dramatic reductions in child mortality over the last 30 years, the global burden of child deaths has remained immense, with a total of 5.2 million under-five deaths in 2019, representing an average of 14,000 deaths every day [ 3 ].
While from 2000 to 2017, the global maternal mortality ratio (MMR) decreased by 38% [ 2 ], Cameroon's MMR skyrocketed from 511 in 1998 to 782 in 2011 before declining to 467 in 2018 [ 4 ].
A priority toward ending preventable maternal and child deaths is to improve access to and use of quality health services and qualified nurses at birth [ 5 , 6 ]. One of the basic elements is the presence of pregnant women at antenatal consultations. Previous studies have shown that performing prenatal consultations reduces the risk of neonatal mortality [ 7 , 8 ].
However, women in developing countries encounter significant barriers to accessing conventional health services, including poor education, physical and financial barriers, and limited voice and decision-making power [ 9 , 10 ]. The poor quality of available health services offers a further disincentive [ 6 ]. This translates to only half of parturient women receiving skilled assistance at delivery and many fewer receiving postpartum cares [ 6 ].
In Cameroon, the country’s comparatively slow reduction in maternal and child mortalities is likely due to insufficient coverage of reproductive, maternal, neonatal, child and adolescent health (RMNCAH) services; for instance, in 2018, an estimated 65% of women in Cameroon attended at least four antenatal consultations (ANC) visits, 69% gave birth with the assistance of qualified personnel, and 59% received postnatal care (PNC) [ 11 ]. In addition, these general estimates hide enormous disparities. Overall, 65% of the pregnant women who attended the four ANCs included more than 79% of those in urban areas but only 52% of those in rural areas. Moreover, while this rate was 91% in the richest quintile, only one-third (37%) of the poorest pregnant women attended the four ANCs [ 11 ].
The complexity of barriers to accessing care in developing countries indicates that any solution to improving maternal health service utilization must be comprehensive and address both supply- and demand-side health system constraints. This is particularly important in a context such as Cameroon where household out-of-pocket (OOP) spending was the single largest source of financing for the health sector, at 71 percent of total health spending in 2017, well above the WHO benchmark of 15-20 percent, and exceeding the average for SSA (33 percent) and countries of similar income such as Kenya (24 percent) and Ghana (40 percent) [ 12 ].
As ability to pay remains an important determinant of women’s access to healthcare, many countries have sought to improve coverage of maternal services by reducing financial barriers to seeking services [ 13 , 14 ]. Strategies implemented at the country level include national health insurance and user fee removals/exemptions, and at the subnational level, community-based health insurance, health vouchers and conditional cash transfers [ 15 ].
Given that limited access to emergency obstetric and neonatal care (EmONC) is a major contributor to high maternal mortality [ 16 ], increasing pregnant women's use of health facilities for assisted delivery could help reduce maternal and new born morbidity and mortality, as previous studies have indicated [ 17 , 18 ].
In recent years, there has been growing interest in the use of vouchers and other innovative financing mechanisms to increase access to EmONCs for low-income women [ 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 ]. By providing a financial or in-kind reward conditioned on the achievement of agreed-upon performance goals, vouchers are described as a promising holistic approach to foster the use of cost-effective services by the poor and other disadvantaged populations [ 22 ].
Vouchers can act on the demand side, the supply side, or both sides. Demand-side incentives encourage service use not only by reducing the financial burden but also by offering women a choice of providers and informing them of the benefits of using maternal health services. Supply-side incentives aim to improve the quality and responsiveness of service delivery.
To date, findings from the few assessments of reproductive health voucher programs suggest that, if implemented well, they have the potential to improve both assisted and facility-based deliveries [ 19 , 20 , 22 , 24 , 26 ]. Yet, there is a paucity of evidence based on rigorous evaluation studies, making it challenging to draw consistent conclusions about the impact of voucher initiatives and to make subsequent policy recommendations.
The current study evaluated a pilot voucher program in Cameroon, a country where approximately 39% of all deliveries took place at home at the time of the program’s inception [ 27 ]. The research aimed to assess the impact of the voucher scheme on first antenatal consultation and skilled birth attendance (SBA). In the following, we present a brief description of the Cameroon voucher program. We then present our data and methods, followed by the results. We end with a discussion of the study’s results, as well as the implications of these findings.
Voucher program in Cameroon
Results from the 2014 Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey (MICS) indicate an enormous disparity in health outcomes among Cameroon's ten regions, with the three northern regions (Adamawa, North, Far North) bearing the brunt of the disease burden [ 27 ]. For example, while the Far North and North regions represented 27.5% of the total population of children under five years in 2014, both regions accounted for 63% of the total excess mortality during the same period [ 27 ]. In addition, while 65% of women nationwide gave birth with the help of qualified personnel, only 29%, 36% and 53% in the Far North, North and Adamawa regions, respectively, gave birth in the same conditions. Moreover, these three regions featuring the lowest frequencies of ANCs and assisted deliveries, were home to more than 60% of the country’s poorest population [ 28 ].
Initiated in 2015, the voucher programme is a government programme, supported with funding from German and French partners, that aims to reduce financial barriers to maternal and neonatal care in the three northern regions of Cameroon.
Under the project, (poor) women can purchase subsidized vouchers for 6000 FCFA (≈$11), a co-payment of 10% of the actual cost of the service package estimated at 60,000 FCFA (approximately USD109), that covered the cost of a benefit package including services for pregnant women and their new-borns up to 42 days after delivery. In addition, beneficiaries are provided with transportation from their house to the nearest health facility and transportation from health centers to referral hospitals. Health facilities offering services for the voucher scheme are compensated for extra costs incurred. All pregnant women living within the 3 northern regions of Cameroon were eligible for the programme. To be included in the programme, health facilities are required to meet minimum quality standards based on national guidelines for the provision of maternal care. Women can redeem vouchers at any participating facility, and the contracted facilities submit claims to be reimbursed at standard rates for each service provided.
At its inception, the programme implementation was outsourced to the ‘Centre International de Développement et de Recherche’ (CIDR), an international organization. Since November 2018, the management of the scheme has been transferred to a national entity: the Regional Funds for Health Promotion (RFHP). A transfer protocol signed between the ministry of public health (MPH) and CIDR made provisions for the training of the RFHP personnel to take over the implementation.
Study design, data source and study sample
To achieve the study objectives, we used a quasi-experimental study design. Specifically, for each health facility (HF) that was enrolled in the health voucher project, the potential effect of the project was measured using an analysis of interrupted time series [ 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 ]. This method compares changes in the indicators of interest before and after the start of the intervention. It is based on the fundamental assumption that, in the absence of intervention, the trend of the interest indicator remains unchanged over time [ 31 ]. It is desirable to have at least 12 observation points for the indicator or variable of interest before and after the start of the intervention, respectively [ 29 ].
We used secondary data from the monitoring and evaluation system database populated by the three regional implementing agencies of the health voucher project, let by the CIDR-CARE prior to the transfer of the project to the RFHP that began in 2018. These databases were updated quarterly by trained research assistants after monthly data collection from the registries of all health facilities enrolled in the project. Data quality control was carried out jointly by the team from the MPH in charge of monitoring project implementation and by the project team. The data used in this study are monthly aggregates of the variables of interest over the period from January 2013 to May 2018 (i.e., 65 months of observation).
The database contains information on 42 health facilities (HFs) enrolled in the health voucher project, spread across three regions: 12 HFs in the Adamawa region, 15 in the North region and 14 in the Far North region. These HFs were sequentially enrolled in the health voucher project and not at the same time. In the Adamawa region, activities started in 9 HFs in May 2015 and in 3 HFs in March 2016. In the North region, the implementation of activities started in May 2015 in one HF, in June 2015 in 5 HFs and in July 2016 in 9 HFs. For the Far North region, the intervention started in 4 HFs in June 2015, in 3 HFs in March 2016 and in 7 HFs in July 2016. For the analysis of each outcome, HFs included in the sample were those with at least 90% data completeness over the selected period. Thus, the sample sizes for analysis of the outcomes associated with the first antenatal consultation and assisted deliveries were 33 and 37, respectively.
Study variables
Two dependent variables were considered for this evaluation: (i) the monthly number of first ANC visits in each HF and (ii) the monthly number of SBA in each HF.
Covariables
X it : a time-dependent dichotomous variable that takes the value 0 for the months before the start of the health voucher project in HF i and 1 after the start of the project.
T t : time variable measured in months, with values ranging from 0 (January 2013) to 64 (May 2018).
X it *(T t -θ i ): interaction variable between the variables X it and T t centered on the value corresponding to the month of project start in HF i (θ i ).
Statistical analysis
Descriptive analysis.
To explore the outcomes, we used descriptive statistics (mean, median, standard deviation, interquartile range, absolute frequency, relative frequency) and trend curves.
Statistical modeling
For each HF and for each outcome, the estimation of the effects of the health voucher project was carried out using a negative binomial regression.
Since both outcomes are count variables, the choice of negative binomial regression instead of Poisson regression, which is the classic model for this type of variable, was considered to overcome the violation of the fundamental assumption underlying Poisson regression, which states that the mean is equal to the variance. Let Y it be the value of the considered outcome observed in HF i at time t. Y it follows a Poisson distribution with parameter μ it (Y it ~Poisson (μ it )). The general equation of the model used is shown below:
The other parameters of the model are described below.
β 0 = intercept (value of the dependent variable at month 1 of follow-up);
β 1 = slope of the outcome trajectory before the start of the health voucher project;
β 2 = change in the level of outcome at the end of the first month of implementation of the health voucher project;
β 3 = difference between the slope of the outcome trajectory after and before the start of the health voucher project;
variable γ it is the term that differentiates Poisson regression from negative binomial regression. In other words, e γit follows a gamma distribution with mean 1 and variance α (e γit ~ gamma (1/α, α)), with α being the overdispersion parameter.
The coefficient β 2 assesses the immediate effect of the project and β 3 assesses the effect of the project over time.
The graphs used to explore the evolution of outcomes over time highlighted the presence of seasonality. Thus, 11 dichotomous variables were considered in the different models. Equation ( 1 ) becomes log (μ it ) = β 0 + β 1 T t + β 2 X it + β 3 X it *(T t -θ i ) + ɸ 1 February + ɸ 2 March + ɸ 3 April + ɸ 4 May + ɸ 5 June + ɸ 6 July + ɸ 7 August + ɸ 8 September + ɸ 9 October + ɸ 10 November + ɸ 11 December + γ it .
The variables February, March … December take the value 1 if the observation relates to this month and 0 otherwise. The month of January was considered a reference.
Because the project did not start at the same time in all HFs, to obtain estimates representing the overall situation, a meta-analysis was used [ 33 ]. Thus, the pooled estimates and their confidence intervals were obtained by combining the regression coefficients of each HF using the inverse variance method. Random effects models were used to consider the strong heterogeneity highlighted by the statistics I 2 =100*(Q-df)/Q (with Q the statistics of Cochran's Q-test of heterogeneity and df the number of degrees of freedom corresponding here to the number of HFs minus one). The values 0%, 25%, 50% and 75% of the I 2 statistics represent the following levels of heterogeneity: absent, weak, moderate, and strong, respectively [ 33 , 34 ]. The incidence-rate ratio (IRR) for each HF per month as well as the aggregate estimates were graphically represented using a "forest plot". The analysis was stratified by region.
The statistical significance threshold used for interpreting the results was 5%. All the statistical analyses were performed with Stata/SE software version 14.2.
Descriptive statistics
The results in Table 1 show that the overall level of data completeness is 98.9% for the monthly number of first ANC visits and 99.3% for the monthly number of SBAs. In all regions, better data completeness was observed in the post-start period of the intervention. For the descriptive statistics of the two variables of interest, overall, the average (respectively the median) of the monthly number of first ANC visits was 58.6 (respectively 50.0). For the monthly number of SBAs, the mean and median were 52.3 and 31.0, respectively. The observed differences between the means and medians illustrate the asymmetry of the distributions of these variables. We also found that the means and medians of these two variables appeared to be greater during the implementation period of the project than during the period prior to the intervention.
Furthermore, Fig. 1 shows that there was an increasing trend over time for the monthly average of the first ANC and the monthly average of the SBA. It also emerged that the positive slope was more abrupt for SBA.
Evolution of the monthly averages of the number of first ANC visits and SBAs in the selected Health facilities between January 2013 and May 2018
Effects of the health voucher project
First antenatal consultation (anc).
Table 2 and Figure S 3 displays contrasting results. Overall, at the end of the first month of implementation of the project, controlling for other variables, a statistically significant increase of nearly 26% in the monthly number of first ANCs was observed in the 33 HFs considered in the study sample (IRR = 1.258 [95% CI: 1.075, 1.472]). A similar increase was recorded in the North region but was not statistically significant (IRR = 1.246 [95% CI: 0.976, 1.591]). In the Adamawa region, the increase was nearly 73% (IRR = 1.726 [95% CI: 1.117, 2.668]). Conversely, in the Far North region, a nonsignificant reduction of 0.2% was noted (IRR = 0.998 [95% CI: 0.882, 1.129]). These overall results hid disparities across facilities. In the Adamawa region, out of 10 HFs, there was a statistically significant increase in the monthly number of first ANCs at the end of the first month of project implementation in five HFs and a statistically significant decrease in one HF. In the Far North region, of the 10 HFs, a statistically significant increase was recorded in two HFs, and a statistically significant reduction was recorded in one HF. In the North region, of the 13 HFs, six exhibited a statistically significant increase in the aforementioned indicator and one exhibited a statistically significant decrease.
Moreover, regarding the difference between the slope of the trajectory of the first ANC after and before the start of the project, Table 2 and Figure S 4 does not show statistically significant results, either overall or by region. However, in one HF in the Adamawa region, a statistically significant increase in the slope of the trajectory of the first ANC was observed during the project implementation period compared to the situation prior to the intervention. Conversely, a statistically significant decrease was recorded in one HF. In the Far North region, no HF exhibited a statistically significant increase, but a statistically significant decrease was observed in two HFs. In the North region, two HFs exhibited a statistically significant increase, and five HFs exhibited a statistically significant decrease.
Skilled birth attendance (SBA)
Table 2 and Figure S 7 shows that by the end of the first month of implementation of the project, a statistically significant increase of nearly 57% in the monthly number of SBAs was recorded in the 37 HFs selected in the study sample, controlling for other variables (IRR = 1.566 [95% CI: 1.358, 1.806]).
A statistically significant increase in this indicator was also observed in each of the three regions. However, there were disparities between HFs. In the Adamawa region, out of 13 health facilities, there was a statistically significant increase in the monthly number of assisted deliveries at the end of the first month of project implementation in nine HFs and a statistically significant decrease in one HF. In the Far North region, of the 11 HFs, a statistically significant increase was recorded in eight HFs and a statistically significant decrease was recorded in two HFs. In the North region, of the 13 HFs, seven recorded a statistically significant increase and one a statistically significant decrease in the indicator of interest.
In addition, Table 2 and Figure S 8 indicates that, overall, the intervention had a positive effect on SBAs (IRR = 1.009 [95% CI: 1.002, 1.016]). A similar finding is observed in the three regions, with the Far North region being the only region that was statistically significant. When considering the analysis of HFs, the results are mixed. In the Adamawa region, a positive and statistically significant result was recorded for four HFs while a negative and statistically significant result was observed for three HFs. In the Far North region, statistically significant results were recorded for five HFs and all these results were positive. In the North region, two HFs recorded a positive result and three recorded a negative result.
The high values of the I 2 statistics reveal that a very large proportion of the total observed variance is due to a real difference in effect measures between HFs (Figure S 1 to S 8 ).
Our study explored the effect of the Health voucher Project on the use of health services. Overall, a statistically significant increase was observed in the number of first ANCs at the end of the first month of project implementation (success). However, this improvement was not sustained over time, with less than 10% of all HFs (3/33) experiencing an increase in ANCs.
For the SBAs, there was a statistically significant increase at the end of the first month of project implementation, with a sustained pattern over time. When looking at the individual HFs, 2/3 (65%) recorded success at the end of the first month of implementation, while 30% experienced overall improvement during the project implementation compared to the period before the start of the project.
These findings suggest that between the pre-intervention/roll-out and full implementation phases, the Cameroon voucher programme modestly increased the use of facility for ANC and SBA, consistent with previously reported results from evaluations of maternal health voucher programmes from other LMICs [ 21 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 ].
Our results therefore indicate that in a country such as Cameroon, where progress toward universal health coverage is still to be achieved [ 39 ], reducing financial risk by providing subsidies to offset the costs of receiving RMNCAH services may be a good cost-effective intervention to improve service utilization.
Pregnant women were more likely to use the voucher system for SBAs than for the first ANC visits. One explanation could be the late attendance of pregnant women at health facilities, as more than 70% of pregnant women in these three regions are reported to have their first contact with a health facility after the first trimester of pregnancy [ 27 ], or the late acquisition of vouchers. In-depth discussions with health care providers and direct beneficiaries are needed to better understand the realities underlying these trends.
The decrease in first ANC and SBA over time in some HFs could be explained by the increasing expansion of service coverage, with the opening of new health facilities that were not yet included in the project and that were used by some pregnant women. On the other hand, the context of growing insecurity linked to Boko Haram and other rebel groups in neighboring countries could also constitute a barrier to the use of health facilities in these regions.
It is also important to note that the voucher program is conceptually designed to target the poorest populations. In Cameroon, however, the project covers all women of reproductive age in the intervention areas, regardless of socioeconomic status. We suspect that the contribution of the 6,000 FCFA ($11 US) remains a major barrier to the use of health services for the poorest women, especially since the project covers mostly urban areas, raising the question of program equity as reported elsewhere [ 13 , 14 , 16 ]. This challenge was also highlighted in an unpublished qualitative study.
Focusing on strategies that prioritize the poorest women and strengthen community engagement can ensure equity and achieve sustainable results over time. For example, in Bangladesh and Cambodia, the voucher programme focused on those most in need and reimbursed care givers in facilities to motivate them [ 40 , 41 ]. Moreover, both countries have successfully partnered with recipient communities to improve the targeting of the poor [ 40 , 41 , 42 ].
In addition to stimulating demand, voucher schemes are often proposed as a way to improve the quality of care, as is the case in Cameroon, where health facility accreditation mechanisms are used, alongside the performance-based financing scheme implemented nationwide. However, experiences show that providers may find reimbursement rates to be unattractive and engage in practices such as providing inconsistent quality of care or ‘skimming’ programme users who require minimal intervention. Moreover, as reported in other voucher programs, the most significant problem faced by the voucher scheme in Cameroon was the delay in paying for health facilities, which led to staff demotivation and mistrust between the managers of the scheme and the beneficiaries [ 41 ] and suggested a need for greater attention to issues related to implementation in such a program [ 26 ].
This study helps to extend the body of knowledge generated by previous research on health voucher programmes in LMICs. However, in interpreting our findings, the strengths and limitations of the study design should be considered.
First, most studies on voucher programmes to date have examined the immediate or shorter-term impact of the intervention on service utilization [ 21 ]. Our study examined the immediate to longer-term effects of the intervention and used a quasi-experimental design, known as a reliable approach, to provide robust estimates of the effect of an intervention when a randomized controlled trial cannot be conducted or when a control group is lacking [ 29 , 31 ]. Unlike in cross-sectional observational studies, interrupted time series analysis allows us to estimate the dynamics of change driven by the intervention, controlling for secular changes that might have occurred in the absence of the intervention [ 29 , 43 ]. This approach thus makes it possible to observe whether the intervention has an immediate or delayed, sudden or gradual effect and whether this effect persists or is temporary. Furthermore, there is no real consensus on the number of observation points needed to use the interrupted time series method. However, the statistical power increases with the number of time points [ 30 ]. Some authors recommend 12 observation points before and after the start of the intervention [ 29 ]. In our study, only one HF had 10 observation points before the start of the project, and the others had observation points ranging from 14 and 42. During the project implementation period, the number of observations varied between 23 and 37.
At the time of the study, 81 facilities had already enrolled in the voucher project. We limited ourselves to 33 HFs for the first ANC and to 37 HFs for the SBA analysis because the data prior to the project were either unavailable or insufficient. Therefore, the results presented in this study may be a fragmented view of the project’s effect. In addition, analysis that could provide insight into the RMNCAH continuum of care was not possible due to the limited quality of data (high frequency of missing data) for some key indicators, such as the fourth ANC and postnatal consultation, as reported with other voucher programs [ 22 , 44 , 45 , 46 ].
In identifying the impact of an intervention, it is important that there are no exogenous factors influencing the results. During the implementation of the voucher program in Cameroon, there were no closures of health facilities that could have an impact on the two selected indicators. Population growth naturally leads to an increase in the number of pregnant women in absolute terms, and consequently to an increase in the number of SBAs. Because demographic data were only available for each health district and not for each health facility, estimates of expected populations or pregnant women were not included into the various negative binomial regression models as a control variable. As a result, the estimates obtained may be biased.
It is also important to point out that due to its fragility, the northern part of the country is a convergence zone of several programs and projects, including those of health. Therefore, other interventions may have also contributed to the achievement of these outcome levels. One of the most important programmes is the National Multi-sector Program to Combat Maternal, Newborn and Child Mortality, which was created in 2013.
Finally, we would like to underline that the fidelity of the program's implementation was hampered by deviations, leading for instance to extending the intervention to all women of childbearing age. At present, the program is more akin to an obstetric risk insurance system, as described for example in Mauritania [ 47 ].
This study provided important insight into the Cameroon voucher scheme. The intervention had a significant early effect on the first ANC and SBA but failed to effectively sustain these results over time for the first indicator. These mixed effects were likely the consequence of poor design and implementation challenges, including the fact that the programme did not include specific equity measures to facilitate uptake by the poorest people. This suggests that for a complex intervention such as a voucher, it is critical to properly implement practice strategies that can sustain the long-term impact of the programme.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the Ministry of Public Health (MPH) of Cameroon, but restrictions apply due to the terms of our contract with the MPH, and so, data are not publicly available. The corresponding author should be contacted for the process to request data access.
Abbreviations
- Antenatal consultation
Centre International de Développement et de Recherche
Emergency obstetric and neonatal care
Communauté financière africaine
Health facility
Low- and middle-income country
Maternal mortality ratio
Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey
Ministry of public health
Out-of-pocket
Post-natal care
Regional Funds for Health Promotion
Reproductive, maternal, neonatal, child and adolescent health
- Skilled birth attendance
Sustainable Development Goals
Sub Saharan Africa
United States dollar
World health organization
Nations Unies. Développement durable. 2021. Objectif de Développement Durable - Santé et Bien-Être pour tous. 2021. Available at: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/fr/health/ . Accessed 3 June 2023.
WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, World Bank Group, United Nations Population Division. Trends in maternal mortality: 2000 to 2017. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2019. p. 119. Available at: http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/maternal-mortality-2000-2017/en/ . Accessed 10 May 2023.
UN Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation. Levels & Trends in Child Mortality. New York, NY 10017 États-Unis: United Nations Children’s Fund; 2020 p. 56. Available at: https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/sites/www.un.org.development.desa.pd/files/unpd_2020_levels-and-trends-in-child-mortality-igme-.pdf . Accessed 2 Jul 2023.
Institut National de la Statistique (INS). Enquête Démographique et de Santé et à Indicateurs Multiples EDS-MICS 2011. 2011. Available at: https://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/fr260/fr260.pdf . Accessed 2 Feb 2023.
Donnay F. Maternal survival in developing countries: what has been done, what can be achieved in the next decade. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2000;70(1):89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7292(00)00236-8 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Singh S, Darroch JE, Ashford LS, Vlassoff M. Adding It Up: The costs and Benefits of Investing in family Planning and maternal and new born health. GUTTMACHER INSTITUTE; 2009. Available at: https://www.guttmacher.org/sites/default/files/pdfs/pubs/AddingItUp2009.pdf . Accessed 20 April 2023.
Tekelab T, Chojenta C, Smith R, Loxton D. The impact of antenatal care on neonatal mortality in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLOS One. 2019;14(9):e0222566. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0222566 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wondemagegn AT, Alebel A, Tesema C, Abie W. The effect of antenatal care follow-up on neonatal health outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Public Health Rev. 2018;39(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40985-018-0110-y .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Matsuoka S, Aiga H, Rasmey LC, Rathavy T, Okitsu A. Perceived barriers to utilization of maternal health services in rural Cambodia. Health Policy. 2010;95(2):255–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2009.12.011 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Sharma S, Smith S, Sonneveldt E, Pine M, Dayaratna V, Sanders R. Formal and Informal Fees for Maternal Health Care Services in Five Countries. USAID; 2005. Available at: http://www.policyproject.com/pubs/workingpapers/WPS16.pdf . Accessed 30 Jan 2023.
Institut National de la Statistique (INS) and IFC. Enquête Démographique et de Santé EDS 2018. INS et IFC 2020. Available at: https://dhsprogram.com/what-we-do/survey/survey-display-511.cfm . Accessed 4 Jan 2023.
WHO. World Health Organization. 2020. Global Health Expenditure Database. Available at: https://apps.who.int/nha/database/Home/Index/en . Accessed 13 Feb 2023.
Gabrysch S, Campbell OM. Still too far to walk: Literature review of the determinants of delivery service use. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2009;11(9):34. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2393-9-34 .
Article Google Scholar
Dzakpasu S, Powell-Jackson T, Campbell OMR. Impact of user fees on maternal health service utilization and related health outcomes: a systematic review. Health Policy Plan. 2014;29(2):137–50. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapol/czs142 .
Ensor T, Ronoh J. Effective financing of maternal health services: a review of the literature. Health Policy. 2005;75(1):49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2005.02.002 .
Richard F, Witter S, de Brouwere V. Innovative approaches to reducing financial barriers to obstetric care in low-income countries. Am J Public Health. 2010;100(10):1845–52. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2009.179689 .
World Health Organization. Making pregnancy safer: the critical role of the skilled attendant: a joint statement by WHO, ICM and FIGO. Geneva: WHO; 2004. 24 p. Available at: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/42955/9241591692.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y . Accessed 15 April 2023.
Baral YR, Lyons K, Skinner J, van Teijlingen ER. Determinants of skilled birth attendants for delivery in Nepal. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2010;8(3):325–32. https://doi.org/10.3126/kumj.v8i3.6223 .
Bellows NM, Bellows BW, Warren C. Systematic review: the use of vouchers for reproductive health services in developing countries: systematic review. Trop Med Int Health TM IH. 2011;16(1):84–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3156.2010.02667.x .
Brody CM, Bellows N, Campbell M, Potts M. The impact of vouchers on the use and quality of health care in developing countries: a systematic review. Glob Public Health. 2013;8(4):363–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/17441692.2012.759254 .
Hunter BM, Harrison S, Portela A, Bick D. The effects of cash transfers and vouchers on the use and quality of maternity care services: a systematic review. PLOS One. 2017;12(3):e0173068. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173068 .
Nguyen HTH, Hatt L, Islam M, Sloan NL, Chowdhury J, Schmidt JO, et al. Encouraging maternal health service utilization: an evaluation of the Bangladesh voucher program. Soc Sci Med. 2012;74(7):989–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2011.11.030 .
Azmat SK, Ali M, Rahman MdM. Assessing the sustainability of two independent voucher-based family planning programs in Pakistan: a 24-months post-intervention evaluation. Contracept Reprod Med. 2023;8(1):43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40834-023-00244-w .
Nandi A, Charters TJ, Quamruzzaman A, Strumpf EC, Kaufman JS, Heymann J, et al. Health care services use, stillbirth, and neonatal and infant survival following implementation of the Maternal Health Voucher Scheme in Bangladesh: A difference-in-differences analysis of Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey data, 2000 to 2016. PLOS Med. 2022;19(8):e1004022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1004022 .
Sultana N, Hossain A, Das H, Pallikadavath S, Koeryaman M, Rahman M, et al. Is the maternal health voucher scheme associated with increasing routine immunization coverage? Experience from Bangladesh. Front Public Health. 2023;2(11):963162. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.963162 .
Hunter BM, Murray SF. Demand-side financing for maternal and newborn health: what do we know about factors that affect implementation of cash transfers and voucher programmes? BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17(1):262. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-017-1445-y .
Institut National de la Statistique. Cameroon - Enquête par Grappes à Indicateurs Multiples 2014. Yaoundé, Cameroun: Institut National de la Statistique; 2015; p. 504. Available at: https://mics-surveys-prod.s3.amazonaws.com/MICS5/West%20and%20Central%20Africa/Cameroon/2014/Final/Cameroon%202014%20MICS_French.pdf . Accessed 22 Jan 2023
Institut National de la Statistique. Annuaire statistique 2017. 2018. Available at: http://www.statistics-cameroon.org/news.php?id=513 . Accessed May 10, 2023.
Wagner AK, Soumerai SB, Zhang F, Ross-Degnan D. Segmented regression analysis of interrupted time series studies in medication use research. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2002;27(4):299–309. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2710.2002.00430.x .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Bernal JL, Cummins S, Gasparrini A. Interrupted time series regression for the evaluation of public health interventions: a tutorial. Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46(1):348–55. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyw098 .
Linden A. ITSA: Stata module to perform interrupted time series analysis for single and multiple groups. Statistical Software Components. Boston College Department of Economics; 2021. Available at: https://ideas.repec.org/c/boc/bocode/s457793.html . Accessed 21Oct 2023.
Ramsay CR, Matowe L, Grilli R, Grimshaw JM, Thomas RE. Interrupted time series designs in health technology assessment: Lessons from two systematic reviews of behavior change strategies. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2003;19(4):613–23. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0266462303000576 .
Gebski V, Ellingson K, Edwards J, Jernigan J, Kleinbaum D. Modelling interrupted time series to evaluate prevention and control of infection in healthcare. Epidemiol Infect. 2012;140(12):2131–41. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268812000179 .
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins J, Rothstein HR. Introduction to Meta-Analysis. 2nd ed. Hoboken: Wiley; 2021. p. 500.
Book Google Scholar
Obare F., Warren C., Abuya T., Askew I., Bellows B. Assessing the population-level impact of vouchers on access to health facility delivery for women in Kenya. Soc Sci Med. 2014;183–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2013.12.007 .
Obare F, Warren C, Kanya L, Abuya T, Bellows B. Community-level effect of the reproductive health vouchers program on out-of-pocket spending on family planning and safe motherhood services in Kenya. BMC Health Serv Res. 2015;15(1):343. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-015-1000-3 .
Bellows B, Kyobutungi C, Mutua MK, Warren C, Ezeh A. Increase in facility-based deliveries associated with a maternal health voucher programme in informal settlements in Nairobi Kenya. Health Policy Plan. 2013;28(2):134–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapol/czs030 .
Amendah DD, Mutua MK, Kyobutungi C, Buliva E, Bellows B. Reproductive health voucher program and facility based delivery in informal settlements in nairobi: a longitudinal analysis. PLOS One. 2013;8(11):e80582. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080582 .
Sieleunou I, Tamga DM, Maabo Tankwa J, Aseh Munteh P, Longang Tchatchouang EV. Strategic health purchasing progress mapping in cameroon: a scoping review. Health Syst Reform. 2021;10(7):1. https://doi.org/10.1080/23288604.2021.1909311 .
Ir P, Horemans D, Souk N, Van Damme W. Using targeted vouchers and health equity funds to improve access to skilled birth attendants for poor women: a case study in three rural health districts in Cambodia. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2010;10(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2393-10-1 .
Ahmed S, Khan MM. A maternal health voucher scheme: what have we learned from the demand-side financing scheme in Bangladesh? Health Policy Plan. 2011;26(1):25–32. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapol/czq015 .
Ridde V, Yaogo M, Kafando Y, Sanfo O, Coulibaly N, Nitiema PA, et al. A community-based targeting approach to exempt the worst-off from user fees in Burkina Faso. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2010;64(01):10–5. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.2008.086793 .
Eccles M, Grimshaw J, Campbell M, Ramsay C. Research designs for studies evaluating the effectiveness of change and improvement strategies. BMJ Qual Saf. 2003;12(1):47–52. https://doi.org/10.1136/qhc.12.1.47 .
Ahmed S, Khan MM. Is demand-side financing equity enhancing? Lessons from a maternal health voucher scheme in Bangladesh. Soc Sci Med. 2011;72(10):1704–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2011.03.031 .
Agha S. Impact of a maternal health voucher scheme on institutional delivery among low income women in Pakistan. Reprod Health. 2011;8(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4755-8-10 .
Van de Poel E, Flores G, Ir P, O’Donnell O, Van Doorslaer E. Can vouchers deliver? An evaluation of subsidies for maternal health care in Cambodia. Bull World Health Organ. 2014;92(5):331–9. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.13.129122 .
Philibert A, Ravit M, Ridde V, Dossa I, Bonnet E, Bedecarrats F, Dumont A. Maternal and neonatal health impact of obstetrical risk insurance scheme in Mauritania: a quasi experimental before-and-after study. Health Policy Plan. 2017;32(3):405–17. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapol/czw142 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr Bassirou Bouba and Dr Okala from the voucher project, Dr Yumo Habakkuk and Bashirou Ndindumouh from Research for Development International, Dr Denise Tamga from the Worlb Bank Office, and Dr Aubin Baleba from UNFPA. We are much indebted to the SPARC team for continuously reviewed our work and provided valuable comments. Finally, the authors would also like to acknowledge the work of the anonymous reviewers who provided us with extremely helpful comments and feedback.
This work was supported by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation [Grant number: OPP1179622].
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Global Financing Facility (GFF), Dakar, Senegal
Isidore Sieleunou
Research for Development International, 30883, Yaoundé, Cameroon
Isidore Sieleunou & Roland Pascal Enok Bonong
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
IS and RPEB conceived and designed the study. RPEB managed the data, including quality control, provided statistical advice on study design and analyzed the data. IS drafted the manuscript, and all authors contributed substantially to its revision. All authors agreed to the final approval of the version to be published. All authors agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Isidore Sieleunou .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Cameroon National Ethics Committee for Human Health Research (CNECHHR) (N0 2020/07/1274/CE/CNERSH/SP). Administrative authorization was granted by the Cameroonian Ministry of Health (D30-607/N/MINSANTE/SG/DROS/CRSPE/BBM, N0 631-32-20). All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. The CNECHHR waived the need for participants’ informed consent in this retrospective study because the data used were fully anonymised and aggregated.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Sieleunou, I., Enok Bonong, R.P. Does health voucher intervention increase antenatal consultations and skilled birth attendances in Cameroon? Results from an interrupted time series analysis. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 602 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10962-9
Download citation
Received : 27 December 2023
Accepted : 08 April 2024
Published : 08 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10962-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Results-based financing
- Health financing
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 14 May 2024
Exploring predictors and prevalence of postpartum depression among mothers: Multinational study
- Samar A. Amer ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9475-6372 1 ,
- Nahla A. Zaitoun ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5274-6061 2 ,
- Heba A. Abdelsalam 3 ,
- Abdallah Abbas ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5101-5972 4 ,
- Mohamed Sh Ramadan 5 ,
- Hassan M. Ayal 6 ,
- Samaher Edhah Ahmed Ba-Gais 7 ,
- Nawal Mahboob Basha 8 ,
- Abdulrahman Allahham 9 ,
- Emmanuael Boateng Agyenim 10 &
- Walid Amin Al-Shroby 11
BMC Public Health volume 24 , Article number: 1308 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
119 Accesses
Metrics details
Postpartum depression (PPD) affects around 10% of women, or 1 in 7 women, after giving birth. Undiagnosed PPD was observed among 50% of mothers. PPD has an unfavorable relationship with women’s functioning, marital and personal relationships, the quality of the mother-infant connection, and the social, behavioral, and cognitive development of children. We aim to determine the frequency of PPD and explore associated determinants or predictors (demographic, obstetric, infant-related, and psychosocial factors) and coping strategies from June to August 2023 in six countries.
An analytical cross-sectional study included a total of 674 mothers who visited primary health care centers (PHCs) in Egypt, Yemen, Iraq, India, Ghana, and Syria. They were asked to complete self-administered assessments using the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS). The data underwent logistic regression analysis using SPSS-IBM 27 to list potential factors that could predict PPD.
The overall frequency of PPD in the total sample was 92(13.6%). It ranged from 2.3% in Syria to 26% in Ghana. Only 42 (6.2%) were diagnosed. Multiple logistic regression analysis revealed there were significant predictors of PPD. These factors included having unhealthy baby adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 11.685, 95% CI: 1.405–97.139, p = 0.023), having a precious baby (aOR 7.717, 95% CI: 1.822–32.689, p = 0.006), who don’t receive support (aOR 9.784, 95% CI: 5.373–17.816, p = 0.001), and those who are suffering from PPD. However, being married and comfortable discussing mental health with family relatives are significant protective factors (aOR = 0.141 (95% CI: 0.04–0.494; p = 0.002) and (aOR = 0.369, 95% CI: 0.146–0.933, p = 0.035), respectively.
The frequency of PPD among the mothers varied significantly across different countries. PPD has many protective and potential factors. We recommend further research and screenings of PPD for all mothers to promote the well-being of the mothers and create a favorable environment for the newborn and all family members.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Postpartum depression (PPD) is among the most prevalent mental health issues [ 1 ]. The onset of depressive episodes after childbirth occurs at a pivotal point in a woman’s life and can last for an extended period of 3 to 6 months; however, this varies based on several factors [ 2 ]. PPD can develop at any time within the first year after childbirth and last for years [ 2 ]. It refers to depressive symptoms that a mother experiences during the postpartum period, which are vastly different from “baby blues,” which many mothers experience within three to five days after the birth of their child [ 3 ].
Depressive episodes are twice as likely to occur during pregnancy compared to other times in a woman’s life, and they frequently go undetected and untreated [ 4 ]. According to estimates, almost 50% of mothers with PPD go undiagnosed [ 4 ]. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) criteria for PPD include mood instability, loss of interest, feelings of guilt, sleep disturbances, sleep disorders, and changes in appetite [ 5 ], as well as decreased libido, crying spells, anxiety, irritability, feelings of isolation, mental liability, thoughts of hurting oneself and/or the infant, and even suicidal ideation [ 6 ].
Approximately 1 in 10 women will experience PPD after giving birth, with some studies reporting 1 in 7 women [ 7 ]. Globally, the prevalence of PPD is estimated to be 17.22% (95% CI: 16.00–18.05) [ 4 ], with a prevalence of up to 15% in the previous year in eighty different countries or regions [ 1 ]. This estimate is lower than the 19% prevalence rate of PPD found in studies from low- and middle-income countries and higher than the 13% prevalence rate (95% CI: 12.3–13.4%) stated in a different meta-analysis of data from high-income countries [ 8 ].
The occurrence of postpartum depression is influenced by various factors, including social aspects like marital status, education level, lack of social support, violence, and financial difficulties, as well as other factors such as maternal age (particularly among younger women), obstetric stressors, parity, and unplanned pregnancy [ 4 ]. When a mother experiences depression, she may face challenges in forming a satisfying bond with her child, which can negatively affect both her partner and the emotional and cognitive development of infants and adolescents [ 4 ]. As a result, adverse effects may be observed in children during their toddlerhood, preschool years, and beyond [ 9 ].
Around one in seven women can develop PPD [ 7 ]. While women experiencing baby blues tend to recover quickly, PPD tends to last longer and severely affects women’s ability to return to normal function. PPD affects the mother and her relationship with the infant [ 7 ]. The prevalence of postpartum depression varies depending on the assessment method, timing of assessment, and cultural disparities among countries [ 7 ]. To address these aspects, we conducted a cross-sectional study focusing on mothers who gave birth within the previous 18 months. Objectives: to determine the frequency of PPD and explore associated determinants or predictors, including demographic, obstetric, infant-related, and psychosocial factors, and coping strategies from June to August 2023 in six countries.
Study design and participants
This is an analytical cross-sectional design and involved 674 mothers during the childbearing period (CBP) from six countries, based on the authors working settings, namely Egypt, Syria, Yemen, Ghana, India, and Iraq. It was conducted from June to August 2023. It involved all mothers who gave birth within the previous 18 months, citizens of one of the targeted countries, and those older than 18 years and less than 40 years. Women who visited for a routine postpartum follow-up visit and immunization of their newborns were surveyed.
Multiple pregnancies, illiteracy, or anyone deemed unfit to participate in accordance with healthcare authorities, mothers who couldn’t access or use the Internet, mothers who couldn’t read or speak Arabic or English and couldn’t deal with the online platform or smart devices, mothers whose babies were diagnosed with serious health problems, were stillborn, or experienced intrauterine fetal death, and participants with complicated medical, mental, or psychological disorders that interfered with completing the questionnaire were all exclusion criteria. There were no incentives offered to encourage participation.
Sample size and techniques
The sample size was estimated according to the following equation: n = Z 2 P (1-P)/d 2 . This calculation was based on the results of a systematic review and meta-analysis in 2020 of 17% as the worldwide prevalence of PPD and 12% as the worldwide incidence of PPD, as well as a 5% precision percentage, 80% power of the study, a 95% confidence level, and an 80% response rate [ 11 ]. The total calculated sample size is 675. The sample was diverse in terms of nationality, with the majority being Egyptian (16.3%), followed by Yemeni (24.3%) and Indian (19.1%), based on many factors discussed in the limitation section.
The sampling process for recruiting mothers utilized a multistage approach. Two governorates were randomly selected from each country. Moreover, we selected one rural and one urban area from each governorate. Through random selection, participants were chosen for the study. Popular and officially recognized online platforms, including websites and social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, WhatsApp groups, and registered emails across various health centers, were utilized for reaching out to participants. Furthermore, a community-based sample was obtained from different public locations, including well-baby clinics, PHCs, and family planning units.
Mothers completed the questionnaire using either tablets or cellphones provided by the data collectors or by scanning the QR code. All questions were mandatory to prevent incomplete forms. Once they provided their informed consent, they received the questionnaire, which they completed and submitted. To enhance the response rate, reminder messages and follow-up communications were employed until the desired sample size was achieved or until the end of August. To avoid seasonal affective disorders, the meteorological autumn season began on the 1st day of September, which may be associated with Autum depressive symptoms that may confound or affect our results.
Data collection tool
Questionnaire development and structure.
The questionnaire was developed and adapted based on data obtained from previous studies [ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ]. Initially, it was created in English and subsequently translated into Arabic. To ensure accuracy, a bilingual panel consisting of two healthcare experts and an externally qualified medical translator translated the English version into Arabic. Additionally, two English-speaking translators performed a back translation, and the original panel was consulted if any concerns arose.
Questionnaire validation
To collect the data, an online, self-administered questionnaire was utilized, designed in Arabic with a well-structured format. We conducted an assessment of the questionnaire’s reliability and validity to ensure a consistent interpretation of the questions. The questionnaire underwent validation by psychiatrists, obstetricians, and gynecologists. Furthermore, in a pilot study involving 20 women of CBA, the questionnaire’s clarity and comprehensibility were evaluated. It is important to note that the findings from the pilot study were not included in our main study.
The participants were asked to rate the questionnaire’s organization, clarity, and length, as well as provide a general opinion. Following that, certain questions were revised in light of their input. To check for reliability and reproducibility, the questionnaire was tested again on the same people one week later. The final data analysis will not include the data collected during the pilot test. We calculated a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.76 for the questionnaire.
The structure of the questionnaire
After giving their permission to take part in the study. The questionnaire consisted of the following sections:
Study information and electronic solicitation of informed consent.
Demographic and health-related factors: age, gender, place of residence, educational level, occupation, marital status, weight, height, and the fees of access to healthcare services.
Obstetric history: number of pregnancies, gravida, history of abortions, number of live children, history of dead children, inter-pregnancy space (y), current pregnancy status, type of the last delivery, weight gain during pregnancy (kg), baby age (months), premature labor, healthy baby, baby admitted to the NICU, Feeding difficulties, pregnancy problems, postnatal problems, and natal problems The nature of baby feeding.
Assessment of postpartum depression (PPD) levels using the Edinburgh 10-question scale: This scale is a simple and effective screening tool for identifying individuals at risk of perinatal depression. The EPDS (Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale) is a valuable instrument that helps identify the likelihood of a mother experiencing depressive symptoms of varying severity. A score exceeding 13 indicates an increased probability of a depressive illness. However, clinical discretion should not be disregarded when interpreting the EPDS score. This scale captures the mother’s feelings over the past week, and in cases of uncertainty, it may be beneficial to repeat the assessment after two weeks. It is important to note that this scale is not capable of identifying mothers with anxiety disorders, phobias, or personality disorders.
For Questions 1, 2, and 4 (without asterisks): Scores range from 0 to 3, with the top box assigned a score of 0 and the bottom box assigned a score of 3. For Questions 3 and 5–10 (with asterisks): Scores are reversed, with the top box assigned a score of 3 and the bottom box assigned a score of 0. The maximum score achievable is 30, and a probability of depression is considered when the score is 10 or higher. It is important to always consider item 10, which pertains to suicidal ideation [ 12 ].
Psychological and social characteristics: received support or treatment for PPD, awareness of symptoms and risk factors, experienced cultural stigma or judgment about PPD in the community, suffer from any disease or mental or psychiatric disorder, have you ever been diagnosed with PPD, problems with the husband, and financial problems.
Coping strategies and causes for not receiving the treatment and reactions to PPD, in descending order: social norms, cultural or traditional beliefs, personal barriers, 48.5% geographical or regional disparities in mental health resources, language or communication barriers, and financial constraints.
Statistical analysis
The collected data was computerized and statistically analyzed using the SPSS program (Statistical Package for Social Science), version 27. The data was tested for normal distribution using the Shapiro-Walk test. Qualitative data was represented as frequencies and relative percentages. Quantitative data was expressed as mean ± SD (standard deviation) if it was normally distributed; otherwise, median and interquartile range (IQR) were used. The Mann-Whitney test (MW) was used to calculate the difference between quantitative variables in two groups for non-parametric variables. Correlation analysis (using Spearman’s method) was used to assess the relationship between two nonparametric quantitative variables. All results were considered statistically significant when the significant probability was < 0.05. The chi-square test (χ 2 ) and Fisher exact were used to calculate the difference between qualitative variables.
The frequency of PPD among mothers (Fig. 1 )
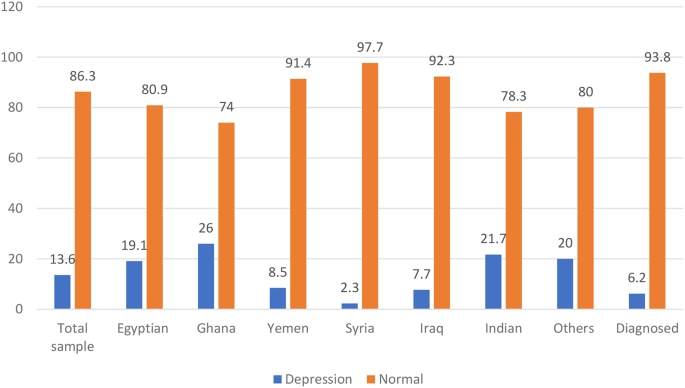
The frequency of PPD among the studied mothers
The frequency of PPD in the total sample using the Edinburgh 10-question scale was 13.5% (Table S1) and 92 (13.6%). Which significantly ( p = 0.001) varied across different countries, being highest among Ghana mothers 13 (26.0%) out of 50 and Indians 28 (21.7%) out of 129. Egyptian 21 (19.1) out of 110, Yemen 14 (8.5%) out of 164, Iraq 13 (7.7%) out of 168, and Syria 1 (2.3%) out of 43 in descending order. Nationality is also significantly associated with PPD ( p = 0.001).
Demographic, and health-related characteristics and their association with PPD (Table 1 )
The study included 674 participants. The median age was 27 years, with 407 (60.3%) of participants falling in the >25 to 40-year-old age group. The majority of participants were married, 650 (96.4%), had sufficient monthly income, 449 (66.6%), 498 (73.9%), had at least a preparatory or high school level of education, and were urban. Regarding health-related factors, 270 (40.01%) smoked, 645 (95.7%) smoked, 365 (54.2%) got the COVID-19 vaccine, and 297 (44.1%) got COVID-19. Moreover, 557 (82.6%) had no comorbidities, 623 (92.4%) had no psychiatric illness or family history, and they charged for health care services for themselves 494 (73.3%).
PPD is significant ( p < 0.05). Higher among single or widowed women 9 (56.3%) and mothers who had both medical, mental, or psychological problems 2 (66.7%), with ex-cigarette smoking 5 (35.7%) ( p = 0.033), alcohol consumption ( p = 0.022) and mothers were charged for the health care services for themselves 59 (11.9%).
Obstetric, current pregnancy, and infant-related characteristics and their association with PPD (Table 2 )
The majority of the studied mothers were on no hormonal treatment or contraceptive pills 411 (60.9%), the current pregnancy was unplanned and wanted 311 (46.1%), they gained 10 ≥ kg 463 (68.6%), 412 (61.1%) delivered vaginal, a healthy baby 613 (90.9%), and, on breastfeeding, only 325 (48.2%).
There was a significant ( P < 0.05) association observed between PPD, which was significantly higher among mothers on contraceptive methods, and those who had 1–2 live births (76.1%) and mothers who had interpregnancy space for less than 2 years. 86 (93.5%), and those who had a history of dead children. Moreover, among those who had postnatal problems (27.2%).
The psychosocial characteristics and their association with PPD (Table 3 )
Regarding the psychological and social characteristics of the mothers, the majority of mothers were unaware of the symptoms of PPD (75%), and only 236 (35.3%) experienced cultural stigma or judgment about PPD in the community. About 41 (6.1%) were diagnosed with PPD during the previous pregnancy, and only 42 (6.2%) were diagnosed and on medications.
A p -value of less than 0.001 demonstrates a highly statistically significant association with the presence of PPD. Mothers with PPD were significantly more likely to have a history of or be currently diagnosed with PPD, as well as financial and marital problems. Experienced cultural stigma or judgment about PPD and received more support.
Coping strategies and causes for not receiving the treatment and reaction to PPD (Table 3 ; Fig. 2 )
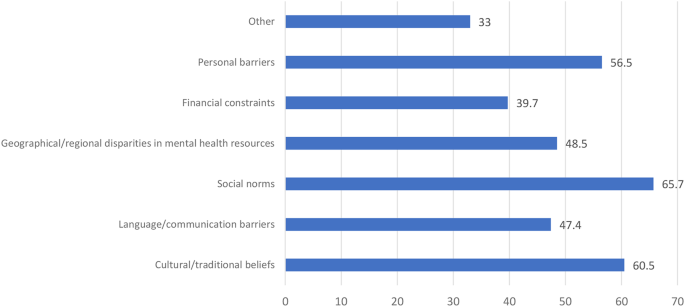
Causes for not receiving the treatment and reaction to PPD
Around half of the mothers didn’t feel comfortable discussing mental health: 292 (43.3%) with a physician, 307 (45.5%) with a husband, 326 (48.4%) with family, and 472 (70.0%) with the community. Moreover, mothers with PPD felt significantly more comfortable discussing mental health in descending order: 46 (50.0%) with a physician, 41 (44.6%) with a husband, and 39 (42.3%) with a family (Table 3 ).
There were different causes for not receiving the treatment and reactions to PPD, in descending order: 65.7% social norms, 60.5% cultural or traditional beliefs, 56.5% personal barriers, 48.5% geographical or regional disparities in mental health resources, 47.4% language or communication barriers, and 39.7% financial constraints.
Prediction of PPD (significant demographics, obstetric, current pregnancy, and infant-related, and psychosocial), and coping strategies derived from multiple logistic regression analysis (Table 4 ).
Significant demographic predictors of ppd.
Marital Status (Married or Single): The adjusted odds ratio (aOR) among PPD mothers who were married in comparison to their single counterparts was 0.141 (95% CI: 0.04–0.494; p -value = 0.002).
Nationality: For PPD Mothers of Yemeni nationality compared to those with Egyptian nationality, the aOR was 0.318 (95% CI: 0.123–0.821, p = 0.018). Similarly, for Syrian nationality in comparison to Egyptian nationality, the aOR was 0.111 (95% CI: 0.0139–0.887, p = 0.038), and for Iraqi nationality compared to Egyptian nationality, the aOR was 0.241 (95% CI: 0.0920–0.633, p = 0.004).
Significant obstetric, current pregnancy, and infant-related characteristics predictors of PPD
Current Pregnancy Status (Precious Baby—Planned): The aOR for the occurrence of PPD among women with a “precious baby” relative to those with a “planned” pregnancy was 7.717 (95% CI: 1.822–32.689, p = 0.006).
Healthy Baby (No-Yes): The aOR for the occurrence of PPD among women with unhealthy babies in comparison to those with healthy ones is 11.685 (95% CI: 1.405–97.139, p = 0.023).
Postnatal Problems (No–Yes): The aOR among PPD mothers reporting postnatal problems relative to those not reporting such problems was 0.234 (95% CI: 0.0785–0.696, p = 0.009).
Significant psychological and social predictors of PPD
Receiving support or treatment for PPD (No-Yes): The aOR among PPD mothers who were not receiving support or treatment relative to those receiving support or treatment was 9.784 (95% CI: 5.373–17.816, p = 0.001).
Awareness of symptoms and risk factors (No-Yes): The aOR among PPD mothers who lack awareness of symptoms and risk factors relative to those with awareness was 2.902 (95% CI: 1.633–5.154, p = 0.001).
Experienced cultural stigma or judgement about PPD in the community (No-Yes): The aOR among PPD mothers who had experienced cultural stigma or judgment in the community relative to those who have not was 4.406 (95% CI: 2.394–8.110, p < 0.001).
Suffering from any disease or mental or psychiatric disorder: For “Now I am suffering—not at all,” the aOR among PPD mothers was 12.871 (95% CI: 3.063–54.073, p = 0.001). Similarly, for “Had a past history but was treated—not at all,” the adjusted odds ratio was 16.6 (95% CI: 2.528–108.965, p = 0.003), and for “Had a family history—not at all,” the adjusted odds ratio was 3.551 (95% CI: 1.012–12.453, p = 0.048).
Significant coping predictors of PPD comfort: discussing mental health with family (maybe yes)
The aOR among PPD mothers who were maybe more comfortable discussing mental health with family relatives was 0.369 (95% CI: 0.146–0.933, p = 0.035).
PDD is a debilitating mental disorder that has many potential and protective risk factors that should be considered to promote the mental and psychological well-being of the mothers and to create a favorable environment for the newborn and all family members. This multinational cross-sectional survey was conducted in six different countries to determine the frequency of PDD using EPDS and to explore its predictors. It was found that PPD was a prevalent problem that varied across different nations.
The frequency of PPD across the studied countries
Using the widely used EPDS to determine the current PPD, we found that the overall frequency of PPD in the total sample was 92 (13.6%). Which significantly ( p = 0.001) varied across different countries, being highest among Ghana mothers 13 (26.0%) out of 50 and Indians 28 (21.7%) out of 129. Egyptian 21 (19.1) out of 110, Yemen 14 (8.5%) out of 164, Iraq 13 (7.7%) out of 169, and Syria 1 (2.3%) out of 43 in descending order. This prevalence was similar to that reported by Hairol et al. (2021) in Malaysia (14.3%) [ 13 ], Yusuff et al. (2010) in Malaysia (14.3%) [ 14 ], and Nakku et al. (2006) in New Delhi (12.75%) [ 15 ].
While the frequency of PPD varied greatly based on the timing, setting, and existence of many psychosocial and post-partum periods, for example, it was higher than that reported in Italy (2012), which was 4.7% [ 16 ], in Turkey (2017) was 9.1%/110 [ 17 ], 9.2% in Sudan [ 18 ], Eritrea (2020) was 7.4% [ 19 ], in the capital Kuala Lumpur (2001) was (3.9%) [ 20 ], in Malaysia (2002) was (9.8%) [ 21 ], and in European countries. (2021) was 13–19% [ 22 ].
Lower frequencies were than those reported; PPD is a predominant problem in Asia, e.g., in Pakistan, the three-month period after childbirth, ranging from 28.8% in 2003 to 36% in 2006 to 94% in 2007, while after 12 months after childbirth, it was 62% in 2021 [ 23 – 24 ]. While in 2022 Afghanistan 45% after their first labour [ 25 ] in Canada (2015) was 40% [ 26 ], in India, the systematic review in 2022 was 22% of Primipara [ 27 ], in Malaysia (2006) was 22.8% [ 28 ], in India (2019) was 21.5% [ 29 ], in the Tigray zone in Ethiopia (2017) was 19% [ 30 ], varied in Iran between 20.3% and 35% [ 31 – 32 ], and in China was 499 (27.37%) out of 1823 [ 33 ]. A possible explanation might be the differences in the study setting and the type of design utilized. Other differences should be considered, like different populations with different socioeconomic characteristics and the variation in the timing of post-partum follow-up. It is vital to consider the role of culture, the impact of patients’ beliefs, and the cultural support for receiving help for PPD.
Demographic and health-related associations, or predictors of PPD (Tables 1 and 4 )
Regarding age, our study found no significant difference between PPD and non-PPD mothers with regard to age. In agreement with our study [ 12 , 34 , 35 ], other studies [ 36 , 37 , 38 ] found an inverse association between women’s age and PPD, with an increased risk of PPD (increases EPDS scores) at a younger age significantly, as teenage mothers, being primiparous, encounter difficulty during the postpartum period due to their inability to cope with financial and emotional difficulties, as well as the challenge of motherhood. Cultural factors and social perspectives of young mothers in different countries could be a reason for this difference. [ 38 – 39 ] and Abdollahi et al. [ 36 ] reported that older mothers were a protective factor for PPD (OR = 0.88, 95% CI: 0.84–0.92].
Regarding marital status, after controlling for other variables, married mothers exhibited a significantly diminished likelihood of experiencing PPD in comparison to single women (0.141; 95% CI: 0.04–0.494; p = 0.002). Also, Gebregziabher et al. [ 19 ] reported that there were statistically significant differences in proportions between mothers’ PPD and marital status.
Regarding the mother’s education, in agreement with our study, Ahmed et al. [ 34 ] showed that there was no statistically significant difference between PPD and a mother’s education. While Agarwala et al. [ 29 ] showed that a higher level of mother’s education. increases the risk of PPD, Gebregziabher et al. [ 19 ] showed that the housewives were 0.24 times less likely to develop PPD as compared to the employed mothers (aOR = 0.24, 95% CI: 0.06–0.97; p = 0.046); those mothers who perceived their socioeconomic status (SES) as low were 13 times more likely to develop PPD as compared to the mothers who had good SES (aOR = 13.33, 95% CI: 2.66–66.78; p = 0.002).
Regarding the SES or monthly income, while other studies [ 18 , 40 ] found that there was a statistically significant association between PPD mothers and different domains of SES, 34% of depressed women were found to live under low SES conditions in comparison to only 15.4% who were found to live in high SES and experienced PPD. In disagreement with our study, Hairol et al. [ 12 ] demonstrated that the incidence of PPD was significantly p = 0.01 higher for participants from the low-income group (27.27%) who were 2.58 times more likely to have PDD symptoms (OR: 2.58, 95% CI: 1.23–5.19; p = 0.01 compared to those from the middle- and high-income groups (8.33%), and low household income (OR = 3.57 [95% CI: 1.49–8.5] increased the odds of PPD [ 41 ].
Adeyemo et al. (2020),and Al Nasr et al. (2020) revealed that there was no significant difference between the occurrence of PPD and socio-demographic characteristics. This difference may be due to a different sample size and ethnicity [ 42 , 43 ]. In agreement with our findings, Abdollahi et al. [ 36 ] demonstrated that after multiple logistic regression analyses, there were increased odds of PPD with a lower state of general health (OR = 1.08 [95% CI: 1.06–1.11]), gestational diabetes (OR = 2.93 [95% CI = 1.46–5.88]), and low household income (OR = 3.57 [95% CI: 1.49–8.5]). The odds of PPD decreased.
Regarding access to health care, in agreement with studies conducted at Gondar University Hospital, Ethiopia [ 18 ], North Carolina, Colorado [ 21 ], Khartoum, Sudan [ 44 ], Asaye et al. [ 45 ], the current study found that participants who did not have free access to the healthcare system were riskier for the development of PPD. the study results may be affected by the care given during the antenatal care (ANC) visits. This can be explained by the fact that PPD was four times higher than that of mothers who did not have ANC, where counseling and anticipatory guidance care are given that build maternal self-esteem and resiliency, along with knowledge about normal and problematic complications to discuss at care visits and their right to mental and physical wellness, including access to care. The increased access to care (including postpartum visits) will increase the diagnosis of PPD and provide guidance, reassurance, and appropriate referrals. Healthcare professionals have the ability to both educate and empower mothers as they care for their babies, their families, and themselves [ 46 ].
Regarding nationality, for PPD mothers of Yemeni nationality compared to those of Egyptian nationality, the aOR is 0.318 (95% CI: 0.123–0.821, p = 0.018). Similarly, for Syrian nationality in comparison to Egyptian nationality, the aOR is 0.111 (95% CI: 0.0139–0.887, p = 0.038), and for Iraqi nationality compared to Egyptian nationality, the aOR is 0.241 (95% CI: 0.0920–0.633, p = 0.004). These findings indicated that, while accounting for other covariates, individuals from the aforementioned nationalities were less predisposed to experiencing PPD than their Egyptian counterparts. These findings can be explained by the fact that, in Egypt, the younger age of marriage, especially in rural areas, poor mental health services, being illiterate, dropping out of school early, unemployment, and the stigma of psychiatric illnesses are cultural factors that hinder the diagnosis and treatment of PPD [ 40 ].
Obstetric, current pregnancy, and infant-related characteristics and their association or predictors of PPD (Tables 2 and 4 )
In the present study, the number of dead children was significantly associated with PPD. This report was supported by studies conducted with Gujarati postpartum women [ 41 ] and rural southern Ethiopia [ 43 ]. This might be because mothers who have dead children pose different psychosocial problems and might regret it for fear of complications developing during their pregnancy. Agarwala et al. [ 29 ] found that a history of previous abortions and having more than two children increased the risk of developing PPD due to a greater psychological burden. The inconsistencies in the findings of these studies indicate that the occurrence of postpartum depression is not solely determined by the number of childbirths.
In obstetric and current pregnancy , there was no significant difference regarding the baby’s age, number of miscarriages, type of last delivery, premature labour, healthy baby, baby admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), or feeding difficulties. In agreement with Al Nasr et al. [ 42 ], inconsistent with Asaye et al. [ 45 ], they showed that concerning multivariable logistic regression analysis, abortion history, birth weight, and gestational age were significant associated factors of postpartum depression at a value of p < 0.05.
However, a close association was noted between the mode of delivery and the presence of PPD in mothers, with p = 0.107. There is a high tendency towards depression seen in mothers who have delivered more than three times (44%). In disagreement with what was reported by Adeyemo et al. [ 41 ], having more than five children ( p = 0.027), cesarean section delivery ( p = 0.002), and mothers’ poor state of health since delivery ( p < 0.001) are associated with an increase in the risk of PPD [ 47 ]. An increased risk of cesarean section as a mode of delivery was observed (OR = 1.958, p = 0.049) in a study by Al Nasr et al. [ 42 ].
We reported breastfeeding mothers had a lower, non-significant frequency of PPD compared to non-breast-feeding mothers (36.6% vs. 45%). In agreement with Ahmed et al. [ 34 ], they showed that with respect to breastfeeding and possible PPD, about 67.3% of women who depend on breastfeeding reported no PPD, while 32.7% only had PP. Inconsistency with Adeyemo et al. [ 41 ], who reported that unexclusive breastfeeding ( p = 0.003) was associated with PPD, while Shao et al. [ 40 ] reported that mothers who were exclusively formula feeding had a higher prevalence of PPD.
Regarding postnatal problems, our results revealed that postnatal problems display a significant association with PPD. In line with our results, Agarwala et al. [ 29 ] and Gebregziabher et al. [ 19 ] showed that mothers who experienced complications during childbirth, those who became ill after delivery, and those whose babies were unhealthy had a statistically significant higher proportion of PPD.
Hormone-related contraception methods were found to have a statistically significant association with PPD, consistent with the literature [ 46 ]; this can be explained by the hormones and neurotransmitters as biological factors that play significant roles in the onset of PPD. Estrogen hormones act as regulators of transcription from brain neurotransmitters and modulate the action of serotonin receptors. This hormone stimulates neurogenesis, the process of generating new neurons in the brain, and promotes the synthesis of neurotransmitters. In the hypothalamus, estrogen modulates neurotransmitters and governs sleep and temperature regulation. Variations in the levels of this hormone or its absence are linked to depression [ 19 ].
Participants whose last pregnancy was unplanned were 3.39 times more likely to have postpartum depression (aOR = 3.39, 95% CI: 1.24–9.28; p = 0.017). Mothers who experienced illness after delivery were more likely to develop PPD as compared to their counterparts (aOR = 7.42, 95% CI: 1.44–34.2; p = 0.016) [ 40 ]. In agreement with Asaye et al. [ 45 ] and Abdollahi et al. [ 36 ], unplanned pregnancy has been associated with the development of PPD (aOR = 2.02, 95% CI: 1.24, 3.31) and OR = 2.5 [95% CI: 1.69–3.7] than those of those who had planned, respectively.
The psychosocial characteristics and their association with PPD
Mothers with a family history of mental illness were significantly associated with PPD. This finding was in accordance with studies conducted in Istanbul, Turkey [ 47 ], and Bahrain [ 48 ]. Other studies also showed that women with PPD were most likely to have psychological symptoms during pregnancy [ 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 ]. A meta-analysis of 24,000 mothers concluded that having depression and anxiety during pregnancy and a previous history of psychiatric illness or a history of depression are strong risk factors for developing PPD [ 50 , 51 , 52 ]. Asaye et al. [ 45 ], mothers whose relatives had mental illness history were (aOR = 1.20, 95% CI: 1.09, 3.05 0) be depressed than those whose relatives did not have mental illness history.
This can be attributed to the links between genetic predisposition and mood disorders, considering both nature and nurture are important to address PDD. PPD may be seen as a “normal” condition for those who are acquainted with relatives with mood disorders, especially during the CBP. A family history of mental illness can be easily elicited in the ANC first visit history and requires special attention during the postnatal period. There are various risk factors for PPD, including stressful life events, low social support, the infant’s gender preference, and low income [ 53 ].
Concerning familial support and possible PPD, a statistically significant association was found between them. We reported that mothers who did not have social support (a partner or the father of the baby) had higher odds (aOR = 5.8, 95% CI: 1.33–25.29; p = 0.019) of experiencing PPD. Furthermore, Al Nasr et al. [ 42 ] revealed a significant association between the PPD and an unsupportive spouse ( P value = 0.023). while it was noted that 66.5% of women who received good familial support after giving birth had no depression, compared to 33.5% who only suffered from possible PPD [ 40 ]]. Also, Adeyemo et al. [ 41 ] showed that some psychosocial factors were significantly associated with having PPD: having an unsupportive partner ( p < 0.001), experiencing intimate partner violence ( p < 0.001), and not getting help in taking care of their baby ( p < 0.001). Al Nasr et al. (2020) revealed that the predictor of PPD was an unsupportive spouse (OR = 4.53, P = 0.049) [ 48 ].
Regarding the perceived stigma, in agreement with our study, Bina (2020) found that shame, stigma, the fear of being labeled mentally ill, and language and communication barriers were significant factors in women’s decisions to seek treatment or accept help [ 53 ]. Other mothers were hesitant about mental health services [ 54 ]. It is noteworthy that some PPD mothers refused to seek treatment due to perceived insufficient time and the inconvenience of attending appointments [ 55 ].
PPD was significantly higher among mothers with financial problems or problems with their husbands. This came in agreement with Ahmed et al. [ 34 ], who showed that, regarding stressful conditions and PPD, there was a statistically significant association with a higher percentage of PPD among mothers who had a history of stressful conditions (59.3%), compared to those with no history of stressful conditions (40.7%). Furthermore, Al Nasr et al. (2020) revealed that stressful life events contributed significantly ( P value = 0.003) to the development of PPD in the sample population. Al Nasr et al. stressful life events (OR = 2.677, p = 0.005) [ 42 ].
Coping strategies: causes of fearing and not seeking
Feeling at ease discussing mental health topics with one’s husband, family, community, and physician and experiencing cultural stigma or judgment regarding PPD within the community was significantly associated with the presence of PPD. In the current study, there were different reasons for not receiving the treatment, including cultural or traditional beliefs, language or communication barriers, social norms, and geographical or regional disparities in mental health resources. Haque and Malebranche [ 56 ] portrayed culture and the various conceptualizations of the maternal role as barriers to women seeking help and treatment.
In the present study, marital status, nationality, current pregnancy status, healthy baby, postnatal problems, receiving support or treatment for PPD, having awareness of symptoms and risk factors of PPD, suffering from any disease or mental or psychiatric disorder, comfort discussing mental health with family, and experiencing cultural stigma or judgment about PPD in the community were the significant predictors of PPD. In agreement with Ahmed et al. [ 34 ], the final logistic regression model contained seven predictors for PPD symptoms: SES, history of depression, history of PPD, history of stressful conditions, familial support, unwanted pregnancy, and male preference.
PPD has been recognized as a public health problem and may cause negative consequences for infants. It is estimated that 20 to 40% of women living in low-income countries experience depression during pregnancy or the postpartum period. The prevalence of PPD shows a wide variation, affecting 8–50% of postnatal mothers across countries [ 19 ].
Strengths and limitations
Strengths of our study include its multinational scope, which involved participants from six different countries, enhancing the generalizability of the findings. The study also boasted a large sample size of 674 participants, increasing the statistical power and reliability of the results. Standardized measures, such as the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS), were used for assessing postpartum depression, ensuring consistency and comparability across diverse settings. Additionally, the study explored a comprehensive range of predictors and associated factors of postpartum depression, including demographic, obstetric, health-related, and psychosocial characteristics. Rigorous analysis techniques, including multiple logistic regression analyses, were employed to identify significant predictors of postpartum depression, controlling for potential confounders and providing robust statistical evidence.
However, the study has several limitations that should be considered. Firstly, its cross-sectional design limits causal inference, as it does not allow for the determination of temporal relationships between variables. Secondly, the reliance on self-reported data, including information on postpartum depression symptoms and associated factors, may be subject to recall bias and social desirability bias. Thirdly, the use of convenience sampling methods may introduce selection bias and limit the generalizability of the findings to a broader population. Lastly, cultural differences in the perception and reporting of postpartum depression symptoms among participants from different countries could influence the results.
Moreover, the variation in sample size and response rates among countries can be attributed to two main variables. (1) The methodology showed that the sample size was determined by considering several parameters, such as allocating proportionately to the mothers who gave birth and fulfilling the selection criteria during the data collection period served by each health center. (2) The political turmoil in Syria affects how often and how well people can use the Internet, especially because the data was gathered using an online survey link, leading to a relatively low number of responses from those areas. (3) Language barrier in Ghana: as we used the Arabic and English-validated versions of the EPDS, Ghana is a multilingual country with approximately eighty languages spoken. Although English is considered an official language, the primarily spoken languages in the southern region are Akan, specifically the Akuapem Twi, Asante Twi, and Fante dialects. In the northern region, primarily spoken are the Mole-Dagbani ethnic languages, Dagaare and Dagbanli. Moreover, there are around seventy ethnic groups, each with its own unique language [ 57 ]. (4) At the end of the data collection period, to avoid seasonal affective disorders, the meteorological autumn season began on the 1st day of September, which may be associated with autumm depressive symptoms that may confound or affect our results. Furthermore, the sampling methods were not universal across all Arabic countries, potentially constraining the generalizability of our findings.
Recommendations
The antenatal programme should incorporate health education programmes about the symptoms of PPD. Health education programs about the symptoms of PPD should be included in the antenatal program.
Mass media awareness campaigns have a vital role in raising public awareness about PPD-related issues. Mass media.
The ANC first visit history should elicit a family history of mental illness, enabling early detection of risky mothers. Family history of mental illness can be easily elicited in the ANC first visit history.
For effective management of PPD, effective support (from husband, friends, and family) is an essential component. For effective management of PPD effectiveness of support.
The maternal (antenatal, natal, and postnatal) services should be provided for free and of high quality The maternal (antenatal, natal, postnatal) services should be provided free and of high quality.
It should be stressed that although numerous studies have been carried out on PPD, further investigation needs to be conducted on the global prevalence and incidence of depressive symptoms in pregnant women and related risk factors, especially in other populations.
Around 14% of the studied mothers had PPD, and the frequency varies across different countries and half of them do not know. Our study identified significant associations and predictors of postpartum depression (PPD) among mothers. Marital status was significantly associated with PPD, with married mothers having lower odds of experiencing PPD compared to single mothers. Nationality also emerged as a significant predictor, with Yemeni, Syrian, and Iraqi mothers showing lower odds of PPD compared to Egyptian mothers. Significant obstetric, current pregnancy, and infant-related predictors included the pregnancy status, the health status of the baby, and the presence of postnatal problems. Among psychological and social predictors, receiving support or treatment for PPD, awareness of symptoms and risk factors, experiencing cultural stigma or judgment about PPD, and suffering from any disease or mental disorder were significantly associated with PPD. Additionally, mothers who were maybe more comfortable discussing mental health with family relatives had lower odds of experiencing PPD.
These findings underscore the importance of considering various demographic, obstetric, psychosocial, and coping factors in the identification and management of PPD among mothers. Targeted interventions addressing these predictors could potentially mitigate the risk of PPD and improve maternal mental health outcomes.
Data availability
Yes, I have research data to declare.The data is available when requested from the corresponding author [email protected].
Abbreviations
Adjusted Odds Ratio
- Postpartum depression
Primary Health Care centers
Socioeconomic Status
program (Statistical Package for Social Science
The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale
The Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Sultan P, Ando K, Elkhateb R, George RB, Lim G, Carvalho B et al. (2022). Assessment of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures for Maternal Postpartum Depression Using the Consensus-Based Standards for the Selection of Health Measurement Instruments Guideline: A Systematic Review. JAMA Network Open; 1;5(6).
Crotty F, Sheehan J. Prevalence and detection of postnatal depression in an Irish community sample. Ir J Psychol Med. 2004;21:117–21.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Goodman SH, Brand SR. Parental psychopathology and its relation to child psychopathology. In: Hersen M, Gross AM, editors. Handbook of clinical psychology vol 2: children and adolescents. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley; 2008. pp. 937–65.
Google Scholar
Wang Z, Liu J, Shuai H, Cai Z, Fu X, Liu Y, Xiao et al. (2021). Mapping global prevalence of depression among postpartum women. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11(1):543. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-021-01663-6 . Erratum in: Transl Psychiatry; 20;11(1):640. PMID: 34671011IF: 6.8 Q1 B1; PMCID: PMC8528847IF: 6.8 Q1 B1.Lase accessed Jan 2024.
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th edition. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association; Lase accessed October 2023.
Robertson E, Grace S, Wallington T, Stewart DE. Antenatal risk factors for postpartum depression: a synthesis of recent literature. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2004;26:289–95.
Gaynes BN, Gavin N, Meltzer-Brody S, Lohr KN, Swinson T, Gartlehner G, Brody S, Miller WC. Perinatal depression: prevalence, screening accuracy, and screening outcomes: Summary. AHRQ evidence report summaries; 2005. pp. 71–9.
O’hara MW, Swain AM. (1996). Rates and risk of postpartum depression: a meta-analysis. Int Rev Psychiatry. 1996; 8:37–54.
Goodman SH, Brand SR. (2008). Parental psychopathology and its relation to child psychopathology. In: Hersen M, Gross AM, editors. Handbook of clinical psychology Vol 2: Children and adolescents. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons; 2008. pp. 937–65.
Cox JL, Holden JM, Sagovsky R. Detection of postnatal depression: development of the 10-item Edinburgh postnatal depression scale. Br J Psychiatry. 1987;150:782–6.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Martín-Gómez C, Moreno-Peral P, Bellón J, SC Cerón S, Campos-Paino H, Gómez-Gómez I, Rigabert A, Benítez I, Motrico E. Effectiveness of psychological, psychoeducational and psychosocial interventions to prevent postpartum depression in adolescent and adult mothers: study protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ open. 2020;10(5):e034424. [accessed Mar 16 2024].
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sehairi Z. (2020). Validation Of The Arabic Version Of The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale And Prevalence Of Postnatal Depression On An Algerian Sample. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:216391386 . Accessed August 2023.
Hairol MI, Ahmad SA, Sharanjeet-Kaur S et al. (2021). Incidence and predictors of postpartum depression among postpartum mothers in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: a cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE, 16(11), e0259782.
Yusuff AS, Tang L, Binns CW, Lee AH. Prevalence and risk factors for postnatal depression in Sabah, Malaysia: a cohort study. Women Birth. 2015;1(1):25–9. pmid:25466643
Article Google Scholar
Nakku JE, Nakasi G, Mirembe F. Postpartum major depression at six weeks in primary health care: prevalence and associated factors. Afr Health Sci. 2006;6(4):207–14. https://doi.org/10.5555/afhs.2006.6.4.207 . PMID: 17604509IF: 1.0 Q4 B4; PMCID: PMC1832062
Clavenna A, Seletti E, Cartabia M, Didoni A, Fortinguerra F, Sciascia T, et al. Postnatal depression screening in a paediatric primary care setting in Italy. BMC Psychiatry. 2017;17(1):42. pmid:28122520
Serhan N, Ege E, Ayrancı U, Kosgeroglu N. (2013). Prevalence of postpartum depression in mothers and fathers and its correlates. Journal of clinical nursing; 1;22(1–2):279–84. pmid:23216556
Deribachew H, Berhe D, Zaid T, et al. Assessment of prevalence and associated factors of postpartum depression among postpartum mothers in eastern zone of Tigray. Eur J Pharm Med Res. 2016;3(10):54–60.
Gebregziabher NK, Netsereab TB, Fessaha YG, et al. Prevalence and associated factors of postpartum depression among postpartum mothers in central region, Eritrea: a health facility based survey. BMC Public Health. 2020;20:1–10.
Grace J, Lee K, Ballard C, et al. The relationship between post-natal depression, somatization and behaviour in Malaysian women. Transcult Psychiatry. 2001;38(1):27–34.
Mahmud WMRW, Shariff S, Yaacob MJ. Postpartum depression: a survey of the incidence and associated risk factors among malay women in Beris Kubor Besar, Bachok, Kelantan. The Malaysian journal of medical sciences. Volume 9. MJMS; 2002. p. 41. 1.
Anna S. Postpartum depression and birthexperience in Russia. Psychol Russia: State Theart. 2021;14(1):28–38.
Yadav T, Shams R, Khan AF, Azam H, Anwar M et al. (2020).,. Postpartum Depression: Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors Among Women in Sindh, Pakistan. Cureus.22;12(12):e12216. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.12216 . PMID: 33489623IF: 1.2 NA NA; PMCID: PMC7815271IF: 1.2 NA NA.
Abdullah M, Ijaz S, Asad S. (2024). Postpartum depression-an exploratory mixed method study for developing an indigenous tool. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 24, 49 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-023-06192-2 .
Upadhyay RP, Chowdhury R, Salehi A, Sarkar K, Singh SK, Sinha B et al. (2022). Postpartum depression in India: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bull World Health Organ [Internet]. 2017 October 10 [cited 2022 October 6];95(10):706. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.17.192237/ .
Khalifa DS, Glavin K, Bjertness E et al. (2016). Determinants of postnatal depression in Sudanese women at 3 months postpartum: a cross-sectional study. BMJ open, 6(3), e00944327).
Khadija Sharifzade BK, Padhi S, Manna etal. (2022). Prevalence and associated factors of postpartum depression among Afghan women: a phase-wise cross-sectional study in Rezaie maternal hospital in Herat province.; Razi International Medical Journa2| 2|59| https://doi.org/10.56101/rimj.v2i2.59 .
Azidah A, Shaiful B, Rusli N, et al. Postnatal depression and socio-cultural practices among postnatal mothers in Kota Bahru, Kelantan, Malaysia. Med J Malay. 2006;61(1):76–83.
CAS Google Scholar
Agarwala A, Rao PA, Narayanan P. Prevalence and predictors of postpartum depression among mothers in the rural areas of Udupi Taluk, Karnataka, India: a cross-sectional study. Clin Epidemiol Global Health. 2019;7(3):342–5.
Arikan I, Korkut Y, Demir BK et al. (2017). The prevalence of postpartum depression and associated factors: a hospital-based descriptive study.
Azimi-Lolaty HMD, Hosaini SH, Khalilian A, et al. Prevalence and predictors of postpartum depression among pregnant women referred to mother-child health care clinics (MCH). Res J Biol Sci. 2007;2:285–90.
Najafi KFA, Nazifi F, Sabrkonandeh S. Prevalence of postpartum depression in Alzahra Hospital in Rasht in 2004. Guilan Univ Med Sci J. 2006;15:97–105. (In Persian.).
Deng AW, Xiong RB, Jiang TT, Luo YP, Chen WZ. (2014). Prevalence and risk factors of postpartum depression in a population-based sample of women in Tangxia Community, Guangzhou. Asian Pacific journal of tropical medicine; 1;7(3):244–9. pmid:24507649
Ahmed GK, Elbeh K, Shams RM, et al. Prevalence and predictors of postpartum depression in Upper Egypt: a multicenter primary health care study. J Affect Disord. 2021;290:211–8.
Cantilino A, Zambaldi CF, Albuquerque T, et al. Postpartum depression in Recife–Brazil: prevalence and association with bio-socio-demographic factors. J Bras Psiquiatr. 2010;59:1–9.
Abdollahi F, Zarghami M, Azhar MZ, et al. Predictors and incidence of post-partum depression: a longitudinal cohort study. J Obstet Gynecol Res. 2014;40(12):2191–200.
McCoy SJB, Beal JM, et al. Risk factors for postpartum depression: a retrospective investigation at 4-weeks postnatal and a review of the literature. JAOA. 2006;106:193–8.
PubMed Google Scholar
Sierra J. (2008). Risk Factors Related to Postpartum Depression in Low-Income Latina Mothers. Ann Arbor: ProQuest Information and Learning Company, 2008.
Çankaya S. The effect of psychosocial risk factors on postpartum depression in antenatal period: a prospective study. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2020;34(3):176–83.
Shao HH, Lee SC, Huang JP, et al. Prevalence of postpartum depression and associated predictors among Taiwanese women in a mother-child friendly hospital. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2021;33(4):411–7.
Adeyemo EO, Oluwole EO, Kanma-Okafor OJ, et al. Prevalence and predictors of postpartum depression among postnatal women in Lagos. Nigeria Afr Health Sci. 2020;20(4):1943–54.
Al Nasr RS, Altharwi K, Derbah MS et al. (2020). Prevalence and predictors of postpartum depression in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: a cross sectional study. PLoS ONE, 15(2), e0228666.
Desai ND, Mehta RY, Ganjiwale J. Study of prevalence and risk factors of postpartum depression. Natl J Med Res. 2012;2(02):194–8.
Azale T, Fekadu A, Medhin G, et al. Coping strategies of women with postpartum depression symptoms in rural Ethiopia: a cross-sectional community study. BMC Psychiatry. 2018;18(1):1–13.
Asaye MM, Muche HA, Zelalem ED. (2020). Prevalence and predictors of postpartum depression: Northwest Ethiopia. Psychiatry journal, 2020.
Ayele TA, Azale T, Alemu K et al. (2016). Prevalence and associated factors of antenatal depression among women attending antenatal care service at Gondar University Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. PLoS ONE, 11(5), e0155125.
Saraswat N, Wal P, Pal RS et al. (2021). A detailed Biological Approach on Hormonal Imbalance Causing Depression in critical periods (Postpartum, Postmenopausal and Perimenopausal Depression) in adult women. Open Biology J, 9.
Guida J, Sundaram S, Leiferman J. Antenatal physical activity: investigating the effects on postpartum depression. Health. 2012;4:1276–86.
Robertson E, Grace S, Wallington T, et al. Antenatal risk factors for postpartum depression: a synthesis of recent literature. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2004;26:289–95.
Watanabe M, Wada K, Sakata Y, et al. Maternity blues as predictor of postpartum depression: a prospective cohort study among Japanese women. J Psychosom Obstet Gynecol. 2008;29:211–7.
Kirpinar I˙, Gözüm S, Pasinliog˘ lu T. Prospective study of post-partum depression in eastern Turkey prevalence, socio- demographic and obstetric correlates, prenatal anxiety and early awareness. J Clin Nurs. 2009;19:422–31.
Zhao XH, Zhang ZH. Risk factors for postpartum depression: an evidence-based systematic review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Asian J Psychiatry. 2020;53:102353.
Bina R. Predictors of postpartum depression service use: a theory-informed, integrative systematic review. Women Birth. 2020;33(1):e24–32.
Jannati N, Farokhzadian J, Ahmadian L. The experience of healthcare professionals providing mental health services to mothers with postpartum depression: a qualitative study. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2021;21(4):554.
Dennis CL, Chung-Lee L. Postpartum depression help‐seeking barriers and maternal treatment preferences: a qualitative systematic review. Birth. 2006;33(4):323–31.
Haque S, Malebranche M. (2020). Impact of culture on refugee women’s conceptualization and experience of postpartum depression in high-income countries of resettlement: a scoping review. PLoS ONE, 15(9), e0238109.
https:// www.statista.com/statistics/1285335/population-in-ghana-by-languages-spoken/ .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our deep thanks to Rovan Hossam Abdulnabi Ali for her role in completing this study and her unlimited support. Special thanks to Dr. Mohamed Liaquat Raza for his role in reviewing the questionnaire. Moreover, we would like to thank all the mothers who participated in this study.
No funding for this project.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Public Health and Community Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt
Samar A. Amer
Department of Family Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt
Nahla A. Zaitoun
Department of Psychiatry, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt
Heba A. Abdelsalam
Faculty of Medicine, Al-Azhar University, Damietta, Egypt
Abdallah Abbas
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt
Mohamed Sh Ramadan
Hammurabi Medical College, University of Babylon, Al-Diwaniyah, Iraq
Hassan M. Ayal
Hardamout University College of Medicine, Almukalla, Yemen
Samaher Edhah Ahmed Ba-Gais
Department of General Medicine, Shadan Institute of Medical Science, Hyderabad, India
Nawal Mahboob Basha
College of Medicine, Sulaiman Alrajhi University, Albukayriah, Al-Qassim, Saudi Arabia
Abdulrahman Allahham
Department of Virology, Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research, University of Ghana Legon, Accra, Ghana
Emmanuael Boateng Agyenim
Department of Public Health and Community Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, Egypt
Walid Amin Al-Shroby
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization: Samar A. Amer (SA); Methodology: SA, Nahal A. Zaitoun (NZ); Validation: Mohamed Ramadan Ali Shaaban (MR), Hassan Majid Abdulameer Aya (HM), Samaher Edhah Ahmed Ba-Gais (SG), Nawal Mahboob Basha (NB), Abdulrahman Allahham (AbAl), Emmanuael Boateng Agyenim (EB); Formal analysis: Abdallah Abbas (AA); Data curation: MR, HM, SG, NB, AbAl, NZ, and EB; Writing original draft preparation: SA, Heba Ahmed Abdelsalam (HAA), and NZ; Writing review and editing: MR, AA, Walid Amin Elshrowby (WE); Visualization: SA, AA; Supervision: SA; Project administration: AA. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Samar A. Amer .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate.
All participants were provided with electronic informed consent after receiving clear explanations regarding the study’s objectives, data confidentiality, voluntary participation, and the right to withdraw. The questionnaire did not contain any sensitive questions, and data collection was performed anonymously. We affirm that all relevant ethical guidelines have been adhered to, and any necessary approvals from the ethics committee have been obtained. Approval was received from the ethical committee of the family medicine department, the faculty of medicine at Zagazig University, and from the patients included in the study. IRP#ZU-IRP#11079-8/10-2023.
Practicing ethical decision-making is crucial for providing clinical treatment. Such decisions are frequently made challenging due to a lack of knowledge and the mother’s ability to handle the associated complexities and uncertainties that affect the patient’s current level of functioning and ability to take care of her child. At the end of the survey, we raised concerns regarding the red flags, such as suicidal thoughts, and called for a revisit for the psychiatrist’s evaluation of the discussion of the risks, benefits, and alternatives to using medication.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Previous publication
We declare that this research paper has not been published elsewhere in any other academic journal or platform.
Generative AI in scientific writing
We declare that we have not used AI in writing any part of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Amer, S.A., Zaitoun, N.A., Abdelsalam, H.A. et al. Exploring predictors and prevalence of postpartum depression among mothers: Multinational study. BMC Public Health 24 , 1308 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18502-0
Download citation
Received : 06 February 2024
Accepted : 02 April 2024
Published : 14 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18502-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- The Edinburgh postnatal depression scale (EPDS)
- Determinants
- Psychosocial
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An article critique requires you to critically read a piece of research and identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the article. ... A summary of a research article requires you to share the key points of the article so your reader can get a ... relevancy, and accuracy of the article, using specific examples from the article to ...
Provide a brief description of why it is important in your specific context. Next, remember to mention all the interesting aspects that help to reveal the value of the article. Finally, talk about the author's intention and vision regarding the subject. The final part of the article critique must offer a summary of the main purpose. Learning ...
When you are reading an article, it is vital to take notes and critique the text to understand it fully and to be able to use the information in it. Here are the main steps for critiquing an article: Read the piece thoroughly, taking notes as you go. Ensure you understand the main points and the author's argument.
1. for Writing a Research Critique. of or by identifying the publication (see Table 1). If the of the publication in which it appeared published it title, author(s), date of publication, and the name in In credentials (and a peer-reviewed applicable, introduction, you should also its consider theoretical of framework credibility researchers.
A critique asks you to evaluate an article and the author's argument. You will need to look critically at what the author is claiming, evaluate the research methods, and look for possible problems with, or applications of, the researcher's claims.
of the article and the supporting points that the article uses. o 3 Read the article again. To write a thorough article critique you must have thorough knowledge of the article. Reading it more than once helps to ensure that you haven't missed any important details. o 4 Consider the credentials of the author. Does the author of the article
Conducting an article critique for a quantitative research study: Perspectives for doctoral students and other novice readers (Vance et al.) Critique Process (Boswell & Cannon) The experience of critiquing published research: Learning from the student and researcher perspective (Knowles & Gray)
Discussion. This should show insight into the meaning and significance of the research findings. It should not introduce any new material but should address how the aims of the study have been met. The discussion should use previous research work and theoretical concepts as the context in which the new study can be interpreted.
To write an article critique, you should: Read the article, noting your first impressions, questions, thoughts, and observations. Describe the contents of the article in your own words, focusing on the main themes or ideas. Interpret the meaning of the article and its overall importance. Critically evaluate the contents of the article ...
Because there are few published examples of critique examples, this article provides the practical points of conducting a formally written quantitative research article critique while providing a ...
1. Use these guidelines to critique your selected research article to be included in your research proposal. You do not need to address all the questions indicated in this guideline, and only include the questions that apply. 2. Prepare your report as a paper with appropriate headings and use APA format 5th edition.
CRITIQUING RESEARCH ARTICLES . When critiquing research articles, it is useful to ask yourself questions about the purpose of each component of the article, and whether it achieves that purpose. THE TITLE . The title should be descriptive enough to give you a clear idea about what the research deals with. Ask yourself:
Step 9: Presenting Your Critique. Organize your critique into a well-structured paper, starting with an introduction that outlines the article's context and purpose. Develop a clear and focused thesis statement that conveys your assessment. Support your points with evidence from the article and other credible sources.
Ev en better you might. consider doing an argument map (see Chapter 9, Critical thinking). Step 5: Put the article aside and think about what you have read. Good critical review. writing requires ...
For example, I doubt that anyone has ever looked at the correlation between favorite color of Skittles and personality, but that doesn't mean that it should be researched unless there is a good theoretical reason for why we would expect a relationship and a good reason to think that knowing the relationship would advance our understanding of ...
All reviews require authors to be able accurately summarize, synthesize, interpret and even critique the research literature. 1, 2 In fact, ... Type of Review Description Examples of published HPE articles using review methodology; Systematic Review: Often associated with Cochrane Reviews, this type of review aims to answer a narrowly focused ...
to identify what is best practice. This article is a step-by step-approach to critiquing quantitative research to help nurses demystify the process and decode the terminology. Key words: Quantitative research methodologies Review process • Research]or many qualified nurses and nursing students research is research, and it is often quite difficult
Learning how to critique research articles is one of the fundamental skills of scholarship in any discipline. The range, quantity and quality of publications available today via print, electronic and Internet databases means it has become essential to equip students and practitioners with the prerequisites to judge the integrity and usefulness of published research.
Agreeing with, defending or confirming a particular point of view. Proposing a new point of view. Conceding to an existing point of view, but qualifying certain points. Reformulating an existing idea for a better explanation. Dismissing a point of view through an evaluation of its criteria. Reconciling two seemingly different points of view.
Pesch cites people like Locke, Montesquieu, and Machiavelli. These are good, well-‐known examples. and authors and I think it adds a great deal credibility to the piece as a whole. Overall this article isn't very straightforward in the beginning and it's not until the.
Example of a critique To help you apply the concepts and steps described above, the following is a condensed example of a critique of an academic article: In the article "Anxiety Among Students: Higher Anxiety Levels Found in New Students," Hunter Allen examined the impact of anxiety across all levels of college students. He argued that students just entering college or who are in their first ...
The first step is to critique and appraise the research evidence. Through critiquing and appraising the research evidence, dialog with colleagues, and changing practice based on evidence, NPs can improve patient outcomes ( Dale, 2005) and successfully translate research into evidence-based practice in today's ever-changing health care ...
The results wer e discussed appropriat ely- No misinterpretation. 11. Streng ths motioned are the true strengths. 12. Limitations are r eported do not aff ec t the applicability of the study-. 13 ...
Voices in Bioethics is currently seeking submissions on philosophical and practical topics, both current and timeless. Papers addressing access to healthcare, the bioethical implications of recent Supreme Court rulings, environmental ethics, data privacy, cybersecurity, law and bioethics, economics and bioethics, reproductive ethics, research ethics, and pediatric bioethics are sought.
Objectives. Given the increasing incidence of negative outcomes during pregnancy, our research team conducted a dose-response systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the relationship between ultra-processed foods (UPFs) consumption and common adverse pregnancy outcomes including gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), preeclampsia (PE), preterm birth (PTB), low birth weight (LBW), and ...
The ultimate goal, supported by the National Institutes of Health BRAIN Initiative, is to create a comprehensive, high-resolution map of a mouse's neural wiring, which would entail about 1,000 times the amount of data the group just produced from the 1-cubic-millimeter fragment of human cortex. "The word 'fragment' is ironic ...
A growing number of studies have reported that problematic social networking use (PSNU) is strongly associated with anxiety symptoms. However, due to the presence of multiple anxiety subtypes, existing research findings on the extent of this association vary widely, leading to a lack of consensus. The current meta-analysis aimed to summarize studies exploring the relationship between PSNU ...
Study design, data source and study sample. To achieve the study objectives, we used a quasi-experimental study design. Specifically, for each health facility (HF) that was enrolled in the health voucher project, the potential effect of the project was measured using an analysis of interrupted time series [29,30,31,32].This method compares changes in the indicators of interest before and after ...
Background and aim: Research on international students conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic has persistently highlighted the vulnerabilities and challenges that they experienced when staying in the host country to continue with their studies. The findings from such research can inevitably create a negative image of international students and their ability to respond to challenges during ...
Background Postpartum depression (PPD) affects around 10% of women, or 1 in 7 women, after giving birth. Undiagnosed PPD was observed among 50% of mothers. PPD has an unfavorable relationship with women's functioning, marital and personal relationships, the quality of the mother-infant connection, and the social, behavioral, and cognitive development of children. We aim to determine the ...