

Community Blog
Keep up-to-date on postgraduate related issues with our quick reads written by students, postdocs, professors and industry leaders.
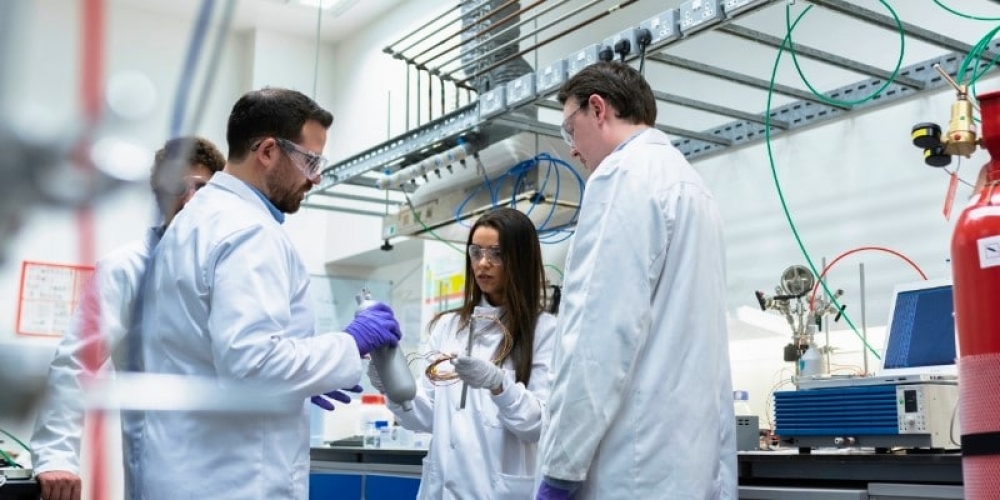
Types of Research – Explained with Examples
- By DiscoverPhDs
- October 2, 2020

Types of Research
Research is about using established methods to investigate a problem or question in detail with the aim of generating new knowledge about it.
It is a vital tool for scientific advancement because it allows researchers to prove or refute hypotheses based on clearly defined parameters, environments and assumptions. Due to this, it enables us to confidently contribute to knowledge as it allows research to be verified and replicated.
Knowing the types of research and what each of them focuses on will allow you to better plan your project, utilises the most appropriate methodologies and techniques and better communicate your findings to other researchers and supervisors.
Classification of Types of Research
There are various types of research that are classified according to their objective, depth of study, analysed data, time required to study the phenomenon and other factors. It’s important to note that a research project will not be limited to one type of research, but will likely use several.
According to its Purpose
Theoretical research.
Theoretical research, also referred to as pure or basic research, focuses on generating knowledge , regardless of its practical application. Here, data collection is used to generate new general concepts for a better understanding of a particular field or to answer a theoretical research question.
Results of this kind are usually oriented towards the formulation of theories and are usually based on documentary analysis, the development of mathematical formulas and the reflection of high-level researchers.
Applied Research
Here, the goal is to find strategies that can be used to address a specific research problem. Applied research draws on theory to generate practical scientific knowledge, and its use is very common in STEM fields such as engineering, computer science and medicine.
This type of research is subdivided into two types:
- Technological applied research : looks towards improving efficiency in a particular productive sector through the improvement of processes or machinery related to said productive processes.
- Scientific applied research : has predictive purposes. Through this type of research design, we can measure certain variables to predict behaviours useful to the goods and services sector, such as consumption patterns and viability of commercial projects.

According to your Depth of Scope
Exploratory research.
Exploratory research is used for the preliminary investigation of a subject that is not yet well understood or sufficiently researched. It serves to establish a frame of reference and a hypothesis from which an in-depth study can be developed that will enable conclusive results to be generated.
Because exploratory research is based on the study of little-studied phenomena, it relies less on theory and more on the collection of data to identify patterns that explain these phenomena.
Descriptive Research
The primary objective of descriptive research is to define the characteristics of a particular phenomenon without necessarily investigating the causes that produce it.
In this type of research, the researcher must take particular care not to intervene in the observed object or phenomenon, as its behaviour may change if an external factor is involved.
Explanatory Research
Explanatory research is the most common type of research method and is responsible for establishing cause-and-effect relationships that allow generalisations to be extended to similar realities. It is closely related to descriptive research, although it provides additional information about the observed object and its interactions with the environment.
Correlational Research
The purpose of this type of scientific research is to identify the relationship between two or more variables. A correlational study aims to determine whether a variable changes, how much the other elements of the observed system change.
According to the Type of Data Used
Qualitative research.
Qualitative methods are often used in the social sciences to collect, compare and interpret information, has a linguistic-semiotic basis and is used in techniques such as discourse analysis, interviews, surveys, records and participant observations.
In order to use statistical methods to validate their results, the observations collected must be evaluated numerically. Qualitative research, however, tends to be subjective, since not all data can be fully controlled. Therefore, this type of research design is better suited to extracting meaning from an event or phenomenon (the ‘why’) than its cause (the ‘how’).
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research study delves into a phenomena through quantitative data collection and using mathematical, statistical and computer-aided tools to measure them . This allows generalised conclusions to be projected over time.

According to the Degree of Manipulation of Variables
Experimental research.
It is about designing or replicating a phenomenon whose variables are manipulated under strictly controlled conditions in order to identify or discover its effect on another independent variable or object. The phenomenon to be studied is measured through study and control groups, and according to the guidelines of the scientific method.
Non-Experimental Research
Also known as an observational study, it focuses on the analysis of a phenomenon in its natural context. As such, the researcher does not intervene directly, but limits their involvement to measuring the variables required for the study. Due to its observational nature, it is often used in descriptive research.
Quasi-Experimental Research
It controls only some variables of the phenomenon under investigation and is therefore not entirely experimental. In this case, the study and the focus group cannot be randomly selected, but are chosen from existing groups or populations . This is to ensure the collected data is relevant and that the knowledge, perspectives and opinions of the population can be incorporated into the study.
According to the Type of Inference
Deductive investigation.
In this type of research, reality is explained by general laws that point to certain conclusions; conclusions are expected to be part of the premise of the research problem and considered correct if the premise is valid and the inductive method is applied correctly.
Inductive Research
In this type of research, knowledge is generated from an observation to achieve a generalisation. It is based on the collection of specific data to develop new theories.
Hypothetical-Deductive Investigation
It is based on observing reality to make a hypothesis, then use deduction to obtain a conclusion and finally verify or reject it through experience.

According to the Time in Which it is Carried Out
Longitudinal study (also referred to as diachronic research).
It is the monitoring of the same event, individual or group over a defined period of time. It aims to track changes in a number of variables and see how they evolve over time. It is often used in medical, psychological and social areas .
Cross-Sectional Study (also referred to as Synchronous Research)
Cross-sectional research design is used to observe phenomena, an individual or a group of research subjects at a given time.
According to The Sources of Information
Primary research.
This fundamental research type is defined by the fact that the data is collected directly from the source, that is, it consists of primary, first-hand information.
Secondary research
Unlike primary research, secondary research is developed with information from secondary sources, which are generally based on scientific literature and other documents compiled by another researcher.
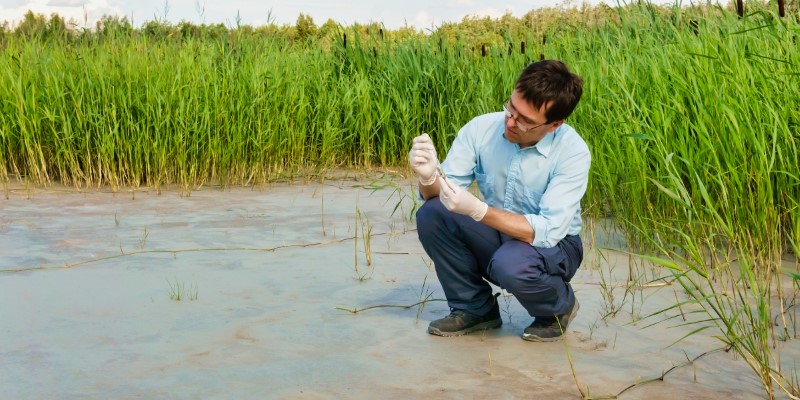

According to How the Data is Obtained
Documentary (cabinet).
Documentary research, or secondary sources, is based on a systematic review of existing sources of information on a particular subject. This type of scientific research is commonly used when undertaking literature reviews or producing a case study.
Field research study involves the direct collection of information at the location where the observed phenomenon occurs.
From Laboratory
Laboratory research is carried out in a controlled environment in order to isolate a dependent variable and establish its relationship with other variables through scientific methods.
Mixed-Method: Documentary, Field and/or Laboratory
Mixed research methodologies combine results from both secondary (documentary) sources and primary sources through field or laboratory research.

Academic conferences are expensive and it can be tough finding the funds to go; this naturally leads to the question of are academic conferences worth it?

The term research instrument refers to any tool that you may use to collect, measure and analyse research data.

Being a new graduate teaching assistant can be a scary but rewarding undertaking – our 7 tips will help make your teaching journey as smooth as possible.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Browse PhDs Now

An abstract and introduction are the first two sections of your paper or thesis. This guide explains the differences between them and how to write them.

Fabian’s in the final year of his PhD research at Maastricht University. His project is about how humans learn numbers and how hands might help that process; this is especially useful for children developing their maths skills.

Dr Dillon gained her PhD in Molecular Cancer Studies at the University of Manchester in 2015. She now works at a biotech company called HairClone, optimising treatments for androgenic alopecia.
Join Thousands of Students
The Research Problem & Statement
What they are & how to write them (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | March 2023
If you’re new to academic research, you’re bound to encounter the concept of a “ research problem ” or “ problem statement ” fairly early in your learning journey. Having a good research problem is essential, as it provides a foundation for developing high-quality research, from relatively small research papers to a full-length PhD dissertations and theses.
In this post, we’ll unpack what a research problem is and how it’s related to a problem statement . We’ll also share some examples and provide a step-by-step process you can follow to identify and evaluate study-worthy research problems for your own project.
Overview: Research Problem 101
What is a research problem.
- What is a problem statement?
Where do research problems come from?
- How to find a suitable research problem
- Key takeaways
A research problem is, at the simplest level, the core issue that a study will try to solve or (at least) examine. In other words, it’s an explicit declaration about the problem that your dissertation, thesis or research paper will address. More technically, it identifies the research gap that the study will attempt to fill (more on that later).
Let’s look at an example to make the research problem a little more tangible.
To justify a hypothetical study, you might argue that there’s currently a lack of research regarding the challenges experienced by first-generation college students when writing their dissertations [ PROBLEM ] . As a result, these students struggle to successfully complete their dissertations, leading to higher-than-average dropout rates [ CONSEQUENCE ]. Therefore, your study will aim to address this lack of research – i.e., this research problem [ SOLUTION ].
A research problem can be theoretical in nature, focusing on an area of academic research that is lacking in some way. Alternatively, a research problem can be more applied in nature, focused on finding a practical solution to an established problem within an industry or an organisation. In other words, theoretical research problems are motivated by the desire to grow the overall body of knowledge , while applied research problems are motivated by the need to find practical solutions to current real-world problems (such as the one in the example above).
As you can probably see, the research problem acts as the driving force behind any study , as it directly shapes the research aims, objectives and research questions , as well as the research approach. Therefore, it’s really important to develop a very clearly articulated research problem before you even start your research proposal . A vague research problem will lead to unfocused, potentially conflicting research aims, objectives and research questions .

What is a research problem statement?
As the name suggests, a problem statement (within a research context, at least) is an explicit statement that clearly and concisely articulates the specific research problem your study will address. While your research problem can span over multiple paragraphs, your problem statement should be brief , ideally no longer than one paragraph . Importantly, it must clearly state what the problem is (whether theoretical or practical in nature) and how the study will address it.
Here’s an example of a statement of the problem in a research context:
Rural communities across Ghana lack access to clean water, leading to high rates of waterborne illnesses and infant mortality. Despite this, there is little research investigating the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects within the Ghanaian context. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the effectiveness of such projects in improving access to clean water and reducing rates of waterborne illnesses in these communities.
As you can see, this problem statement clearly and concisely identifies the issue that needs to be addressed (i.e., a lack of research regarding the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects) and the research question that the study aims to answer (i.e., are community-led water supply projects effective in reducing waterborne illnesses?), all within one short paragraph.
Need a helping hand?
Wherever there is a lack of well-established and agreed-upon academic literature , there is an opportunity for research problems to arise, since there is a paucity of (credible) knowledge. In other words, research problems are derived from research gaps . These gaps can arise from various sources, including the emergence of new frontiers or new contexts, as well as disagreements within the existing research.
Let’s look at each of these scenarios:
New frontiers – new technologies, discoveries or breakthroughs can open up entirely new frontiers where there is very little existing research, thereby creating fresh research gaps. For example, as generative AI technology became accessible to the general public in 2023, the full implications and knock-on effects of this were (or perhaps, still are) largely unknown and therefore present multiple avenues for researchers to explore.
New contexts – very often, existing research tends to be concentrated on specific contexts and geographies. Therefore, even within well-studied fields, there is often a lack of research within niche contexts. For example, just because a study finds certain results within a western context doesn’t mean that it would necessarily find the same within an eastern context. If there’s reason to believe that results may vary across these geographies, a potential research gap emerges.
Disagreements – within many areas of existing research, there are (quite naturally) conflicting views between researchers, where each side presents strong points that pull in opposing directions. In such cases, it’s still somewhat uncertain as to which viewpoint (if any) is more accurate. As a result, there is room for further research in an attempt to “settle” the debate.
Of course, many other potential scenarios can give rise to research gaps, and consequently, research problems, but these common ones are a useful starting point. If you’re interested in research gaps, you can learn more here .
How to find a research problem
Given that research problems flow from research gaps , finding a strong research problem for your research project means that you’ll need to first identify a clear research gap. Below, we’ll present a four-step process to help you find and evaluate potential research problems.
If you’ve read our other articles about finding a research topic , you’ll find the process below very familiar as the research problem is the foundation of any study . In other words, finding a research problem is much the same as finding a research topic.
Step 1 – Identify your area of interest
Naturally, the starting point is to first identify a general area of interest . Chances are you already have something in mind, but if not, have a look at past dissertations and theses within your institution to get some inspiration. These present a goldmine of information as they’ll not only give you ideas for your own research, but they’ll also help you see exactly what the norms and expectations are for these types of projects.
At this stage, you don’t need to get super specific. The objective is simply to identify a couple of potential research areas that interest you. For example, if you’re undertaking research as part of a business degree, you may be interested in social media marketing strategies for small businesses, leadership strategies for multinational companies, etc.
Depending on the type of project you’re undertaking, there may also be restrictions or requirements regarding what topic areas you’re allowed to investigate, what type of methodology you can utilise, etc. So, be sure to first familiarise yourself with your institution’s specific requirements and keep these front of mind as you explore potential research ideas.
Step 2 – Review the literature and develop a shortlist
Once you’ve decided on an area that interests you, it’s time to sink your teeth into the literature . In other words, you’ll need to familiarise yourself with the existing research regarding your interest area. Google Scholar is a good starting point for this, as you can simply enter a few keywords and quickly get a feel for what’s out there. Keep an eye out for recent literature reviews and systematic review-type journal articles, as these will provide a good overview of the current state of research.
At this stage, you don’t need to read every journal article from start to finish . A good strategy is to pay attention to the abstract, intro and conclusion , as together these provide a snapshot of the key takeaways. As you work your way through the literature, keep an eye out for what’s missing – in other words, what questions does the current research not answer adequately (or at all)? Importantly, pay attention to the section titled “ further research is needed ”, typically found towards the very end of each journal article. This section will specifically outline potential research gaps that you can explore, based on the current state of knowledge (provided the article you’re looking at is recent).
Take the time to engage with the literature and develop a big-picture understanding of the current state of knowledge. Reviewing the literature takes time and is an iterative process , but it’s an essential part of the research process, so don’t cut corners at this stage.
As you work through the review process, take note of any potential research gaps that are of interest to you. From there, develop a shortlist of potential research gaps (and resultant research problems) – ideally 3 – 5 options that interest you.

Step 3 – Evaluate your potential options
Once you’ve developed your shortlist, you’ll need to evaluate your options to identify a winner. There are many potential evaluation criteria that you can use, but we’ll outline three common ones here: value, practicality and personal appeal.
Value – a good research problem needs to create value when successfully addressed. Ask yourself:
- Who will this study benefit (e.g., practitioners, researchers, academia)?
- How will it benefit them specifically?
- How much will it benefit them?
Practicality – a good research problem needs to be manageable in light of your resources. Ask yourself:
- What data will I need access to?
- What knowledge and skills will I need to undertake the analysis?
- What equipment or software will I need to process and/or analyse the data?
- How much time will I need?
- What costs might I incur?
Personal appeal – a research project is a commitment, so the research problem that you choose needs to be genuinely attractive and interesting to you. Ask yourself:
- How appealing is the prospect of solving this research problem (on a scale of 1 – 10)?
- Why, specifically, is it attractive (or unattractive) to me?
- Does the research align with my longer-term goals (e.g., career goals, educational path, etc)?
Depending on how many potential options you have, you may want to consider creating a spreadsheet where you numerically rate each of the options in terms of these criteria. Remember to also include any criteria specified by your institution . From there, tally up the numbers and pick a winner.
Step 4 – Craft your problem statement
Once you’ve selected your research problem, the final step is to craft a problem statement. Remember, your problem statement needs to be a concise outline of what the core issue is and how your study will address it. Aim to fit this within one paragraph – don’t waffle on. Have a look at the problem statement example we mentioned earlier if you need some inspiration.
Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- A research problem is an explanation of the issue that your study will try to solve. This explanation needs to highlight the problem , the consequence and the solution or response.
- A problem statement is a clear and concise summary of the research problem , typically contained within one paragraph.
- Research problems emerge from research gaps , which themselves can emerge from multiple potential sources, including new frontiers, new contexts or disagreements within the existing literature.
- To find a research problem, you need to first identify your area of interest , then review the literature and develop a shortlist, after which you’ll evaluate your options, select a winner and craft a problem statement .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

I APPRECIATE YOUR CONCISE AND MIND-CAPTIVATING INSIGHTS ON THE STATEMENT OF PROBLEMS. PLEASE I STILL NEED SOME SAMPLES RELATED TO SUICIDES.
Very pleased and appreciate clear information.
Your videos and information have been a life saver for me throughout my dissertation journey. I wish I’d discovered them sooner. Thank you!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 1. Choosing a Research Problem
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
In the social and behavioral sciences, the subject of analysis is most often framed as a problem that must be researched in order to obtain a greater understanding, formulate a set of solutions or recommended courses of action, and/or develop a better approach to practice. The research problem, therefore, is the main organizing principle guiding the analysis of your research. The problem under investigation establishes an occasion for writing and a focus that governs what you want to say. It represents the core subject matter of scholarly communication and the means by which scholars arrive at other topics of conversation and the discovery of new knowledge and understanding.
Alvesson, Mats and Jörgen Sandberg. Constructing Research Questions: Doing Interesting Research . London: Sage, 2013; Jacobs, Ronald L. “Developing a Dissertation Research Problem: A Guide for Doctoral Students in Human Resource Development and Adult Education.” New Horizons in Adult Education and Human Resource Development 25 (Summer 2013): 103-117; Chapter 1: Research and the Research Problem. Nicholas Walliman . Your Research Project: Designing and Planning Your Work . 3rd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2011.
Choosing a Research Problem / How to Begin
Do not assume that identifying a research problem to investigate will be a quick and easy task! You should be thinking about it during the beginning of the course. There are generally three ways you are asked to write about a research problem : 1) your professor provides you with a general topic from which you study a particular aspect; 2) your professor provides you with a list of possible topics to study and you choose a topic from that list; or, 3) your professor leaves it up to you to choose a topic and you only have to obtain permission to write about it before beginning your investigation. Here are some strategies for getting started for each scenario.
I. How To Begin: You are given the topic to write about
Step 1 : Identify concepts and terms that make up the topic statement . For example, your professor wants the class to focus on the following research problem: “Is the European Union a credible security actor with the capacity to contribute to confronting global terrorism?" The main concepts in this problem are: European Union, security, global terrorism, credibility [ hint : focus on identifying proper nouns, nouns or noun phrases, and action verbs in the assignment description]. Step 2 : Review related literature to help refine how you will approach examining the topic and finding a way to analyze it . You can begin by doing any or all of the following: reading through background information from materials listed in your course syllabus; searching the USC Libraries Catalog to find a recent book on the topic and, if appropriate, more specialized works about the topic; conducting a preliminary review of the research literature using multidisciplinary databases such as ProQuest or subject-specific databases from the " By Subject Area " drop down menu located above the list of databases.
Choose the advanced search option in the database and enter into each search box the main concept terms you developed in Step 1. Also consider using their synonyms to retrieve additional relevant records. This will help you refine and frame the scope of the research problem. You will likely need to do this several times before you can finalize how to approach writing about the topic. NOTE : Always review the references from your most relevant research results cited by the authors in footnotes, endnotes, or a bibliography to locate related research on your topic. This is a good strategy for identifying important prior research about the topic because titles that are repeatedly cited indicate their significance in laying a foundation for understanding the problem. However, if you’re having trouble at this point locating relevant research literature, ask a librarian for help!
ANOTHER NOTE : If you find an article from a database that's particularly helpful, paste it into Google Scholar , placing the title of the article in quotes. If the article record appears, look for a "cited by" reference followed by a number [e.g., C ited by 37] just below the record. This link indicates how many times other scholars have subsequently cited that article in their own research since it was first published. This is an effective strategy for identifying more current, related research on your topic. Finding additional cited by references from your original list of cited by references helps you navigate through the literature and, by so doing, understand the evolution of thought around a particular research problem. Step 3 : Since social science research papers are generally designed to encourage you to develop your own ideas and arguments, look for sources that can help broaden, modify, or strengthen your initial thoughts and arguments. For example, if you decide to argue that the European Union is inadequately prepared to take on responsibilities for broader global security because of the debt crisis in many EU countries, then focus on identifying sources that support as well as refute this position. From the advanced search option in ProQuest , a sample search would use "European Union" in one search box, "global security" in the second search box, and adding a third search box to include "debt crisis."
There are least four appropriate roles your related literature plays in helping you formulate how to begin your analysis :
- Sources of criticism -- frequently, you'll find yourself reading materials that are relevant to your chosen topic, but you disagree with the author's position. Therefore, one way that you can use a source is to describe the counter-argument, provide evidence from your own review of the literature as to why the prevailing argument is unsatisfactory, and to discuss how your approach is more appropriate based upon your interpretation of the evidence.
- Sources of new ideas -- while a general goal in writing college research papers in the social sciences is to examine a research problem with some basic idea of what position you'd like to take and on what basis you'd like to defend your position, it is certainly acceptable [and often encouraged] to read the literature and extend, modify, and refine your own position in light of the ideas proposed by others. Just make sure that you cite the sources !
- Sources for historical context -- another role your related literature plays in formulating how to begin your analysis is to place issues and events in proper historical context. This can help to demonstrate familiarity with developments in relevant scholarship about your topic, provide a means of comparing historical versus contemporary issues and events, and identifying key people, places, and events that had an important role related to the research problem. Given its archival journal coverage, a good multidisciplnary database to use in this case is JSTOR .
- Sources of interdisciplinary insight -- an advantage of using databases like ProQuest to begin exploring your topic is that it covers publications from a variety of different disciplines. Another way to formulate how to study the topic is to look at it from different disciplinary perspectives. If the topic concerns immigration reform, for example, ask yourself, how do studies from sociological journals found by searching ProQuest vary in their analysis from those in political science journals. A goal in reviewing related literature is to provide a means of approaching a topic from multiple perspectives rather than the perspective offered from just one discipline.
NOTE : Remember to keep careful notes at every stage or utilize a citation management system like EndNotes or RefWorks . You may think you'll remember what you have searched and where you found things, but it’s easy to forget or get confused. Most databases have a search history feature that allows you to go back and see what searches you conducted previously as long as you haven't closed your session. If you start over, that history could be deleted.
Step 4 : Assuming you have done an effective job of synthesizing and thinking about the results of your initial search for related literature, you're ready to prepare a detailed outline for your paper that lays the foundation for a more in-depth and focused review of relevant research literature [after consulting with a librarian, if needed!]. How will you know you haven't done an effective job of synthesizing and thinking about the results of our initial search for related literature? A good indication is that you start composing the outline and gaps appear in how you want to approach the study. This indicates the need to gather further background information and analysis about the research problem.
II. How To Begin: You are provided a list of possible topics to choose from Step 1 : I know what you’re thinking--which topic on this list will be the easiest to find the most information on? An effective instructor would never include a topic that is so obscure or complex that no research is available to examine and from which to design an effective study. Therefore, don't approach a list of possible topics to study from the perspective of trying to identify the path of least resistance; choose a topic that you find interesting in some way, that is controversial and that you have a strong opinion about, that has some personal meaning for you, or relates to your major or a minor. You're going to be working on the topic for quite some time, so choose one that you find interesting and engaging or that motivates you to take a position. Embrace the opportunity to learn something new! Once you’ve settled on a topic of interest from the list provided by your professor, follow Steps 1 - 4 listed above to further develop it into a research paper.
NOTE : It’s ok to review related literature to help refine how you will approach analyzing a topic, and then discover that the topic isn’t all that interesting to you. In that case, choose a different topic from the list. Just don’t wait too long to make a switch and, of course, be sure to inform your professor that you are changing your topic.
III. How To Begin: Your professor leaves it up to you to choose a topic
Step 1 : Under this scenario, the key process is turning an idea or general thought into a topic that can be configured into a research problem. When given an assignment where you choose the topic, don't begin by thinking about what to write about, but rather, ask yourself the question, "What do I want to understand or learn about?" Treat an open-ended research assignment as an opportunity to gain new knowledge about something that's important or exciting to you in the context of the overall subject of the course.
Step 2 : If you lack ideas, or wish to gain focus, try any or all of the following strategies:
- Review your course readings, particularly the suggested readings, for topic ideas. Don't just review what you've already read, but jump ahead in the syllabus to readings that have not been covered yet.
- Search the USC Libraries Catalog for a recently published book and, if appropriate, more specialized works related to the discipline area of the course [e.g., for the course SOCI 335: Society and Population, search for books on "population and society" or "population and social impact"]. Reviewing the contents of a book about your area of interest can give you insight into what conversations scholars are having about the topic and, thus, how you might want to contribute your own ideas to these conversations through the research paper you write for the class.
- Browse through some current scholarly [a.k.a., academic, peer reviewed] journals in your subject discipline. Even if most of the articles are not relevant, you can skim through the contents quickly. You only need one to be the spark that begins the process of wanting to learn more about a topic. Consult with a librarian and/or your professor about what constitutes the core journals within the subject area of the writing assignment.
- Think about essays you have written for other courses you have taken or academic lectures and programs you have attended outside of class. Thinking back, ask yourself why did you want to take this class or attend this event? What interested you the most? What would you like to know more about? Place this question in the context of the current course assignment. Note that this strategy also applies to anything you've watched on TV or has been shared on social media.
- Search online news media sources, such as CNN , the Los Angeles Times , Huffington Post , MSNBC , Fox News , or Newsweek , to see if your idea has been covered by the media. Use this coverage to refine your idea into something that you'd like to investigate further, but in a more deliberate, scholarly way in relation to a particular problem that needs to be researched.
Step 3 : To build upon your initial idea, use the suggestions under this tab to help narrow , broaden , or increase the timeliness of your idea so you can write it out as a research problem.
Once you are comfortable with having turned your idea into a research problem, follow Steps 1 - 4 listed in Part I above to further develop it into an outline for a research paper.
Alderman, Jim. "Choosing a Research Topic." Beginning Library and Information Systems Strategies. Paper 17. Jacksonville, FL: University of North Florida Digital Commons, 2014; Alvesson, Mats and Jörgen Sandberg. Constructing Research Questions: Doing Interesting Research . London: Sage, 2013; Chapter 2: Choosing a Research Topic. Adrian R. Eley. Becoming a Successful Early Career Researcher . New York: Routledge, 2012; Answering the Question. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra; Brainstorming. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University; Brainstorming. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Chapter 1: Research and the Research Problem. Nicholas Walliman . Your Research Project: Designing and Planning Your Work . 3rd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2011; Choosing a Topic. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Mullaney, Thomas S. and Christopher Rea. Where Research Begins: Choosing a Research Project That Matters to You (and the World) . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2022; Coming Up With Your Topic. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College; How To Write a Thesis Statement. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Identify Your Question. Start Your Research. University Library, University of California, Santa Cruz; The Process of Writing a Research Paper. Department of History. Trent University; Trochim, William M.K. Problem Formulation. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006.
Resources for Identifying a Topic
Resources for Identifying a Research Problem
If you are having difficulty identifying a topic to study or need basic background information, the following web resources and databases can be useful:
- CQ Researcher -- a collection of single-themed public policy reports that provide an overview of an issue. Each report includes background information, an assessment of the current policy situation, statistical tables and maps, pro/con statements from representatives of opposing positions, and a bibliography of key sources.
- New York Times Topics -- each topic page collects news articles, reference and archival information, photos, graphics, audio and video files. Content is available without charge on articles going back to 1981.
- Opposing Viewpoints In Context -- an online resource covering a wide range of social issues from a variety of perspectives. The database contains a media-rich collection of materials, including pro/con viewpoint essays, topic overviews, primary source materials, biographies of social activists and reformers, journal articles, statistical tables, charts and graphs, images, videos, and podcasts.
- Policy Commons -- platform for objective, fact-based research from the world’s leading policy experts, nonpartisan think tanks, and intergovernmental and non-governmental organizations. The database provides advanced searching across millions of pages of books, articles, working papers, reports, policy briefs, data sets, tables, charts, media, case studies, and statistical publications, including archived reports from more than 200 defunct think tanks. Coverage is international in scope.
Descriptions of resources are adapted or quoted from vendor websites.
Writing Tip
Not Finding Anything on Your Topic? Ask a Librarian!
Don't assume or jump to the conclusion that your topic is too narrowly defined or obscure just because your initial search has failed to identify relevant research. Librarians are experts in locating and critically assessing information and how it is organized. This knowledge will help you develop strategies for analyzing existing knowledge in new ways. Therefore, always consult with a librarian before you consider giving up on finding information about the topic you want to investigate. If there isn't a lot of information about your topic, a librarian can help you identify a closely related topic that you can study. Use the Ask-A-Librarian link above to identify a librarian in your subject area.
Another Writing Tip
Don't be a Martyr!
In thinking about what to study, don't adopt the mindset of pursuing an esoteric or overly complicated topic just to impress your professor but that, in reality, does not have any real interest to you. Choose a topic that is challenging but that has at least some interest to you or that you care about. Obviously, this is easier for courses within your major, but even for those nasty prerequisite classes that you must take in order to graduate [and that provide an additional tuition revenue for the university], try to apply issues associated with your major to the general topic given to you. For example, if you are an international relations major taking a GE philosophy class where the assignment asks you to apply the question of "what is truth" to some aspect of life, you could choose to study how government leaders attempt to shape truth through the use of nationalistic propaganda.
Still Another Writing Tip
A Research Problem is Not a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement and a research problem are two different parts of the introduction section of your paper. The thesis statement succinctly describes in one or two sentences, usually in the last paragraph of the introduction, what position you have reached about a topic. It includes an assertion that requires evidence and support along with your opinion or argument about what you are researching. There are three general types of thesis statements: analytical statements that break down and evaluate the topic; argumentative statements that make a claim about the topic and defend that claim; and, expository statements that present facts and research about the topic. Each are intended to set forth a claim that you will seek to validate through the research you describe in your paper.
Before the thesis statement, your introduction must include a description of a problem that describes either a key area of concern, a condition to be improved upon, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling issue that exists . The research problem describes something that can be empirically verified and measured; it is often followed by a set of questions that underpin how you plan to approach investigating that problem. In short, the thesis statement states your opinion or argument about the research problem and summarizes how you plan to address it.
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Write a Strong Thesis Statement! The Writing Center, University of Evansville; Thesis Statements. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tutorial #26: Thesis Statements and Topic Sentences. Writing Center, College of San Mateo; Creswell, John W. and J. David Creswell. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . 5th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2017.
- << Previous: Glossary of Research Terms
- Next: Reading Research Effectively >>
- Last Updated: May 15, 2024 9:39 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Research Problem – Explanation & Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

A research problem sets the course of investigation in any research process . It can probe practical issues with the aim of suggesting modifications, or scrutinize theoretical quandaries to augment the current understanding in a discipline.
In this article, we delve into the crucial role of a research problem in the research process, as well as offer guidance on how to properly articulate it to steer your research endeavors.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Research Problem – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Research problem
- 3 Why is the research problem important?
- 4 Step 1: Finding a general research problem area
- 5 Step 2: Narrowing down the research problem
- 6 Example of a research problem
Research Problem – In a Nutshell
- A research problem is an issue that raises concern about a particular topic.
- Researchers formulate research problems by examining other literature on the topic and assessing the significance and relevance of the problem.
- Creating a research problem involves an overview of a broad problem area and then narrowing it down to the specifics by creating a framework for the topic.
- General problem areas used in formulating research problems include workplace and theoretical research.
Definition: Research problem
A research problem is a specific challenge or knowledge gap that sets the foundation for research. It is the primary statement about a topic in a field of study, and the findings from a research undertaking provide solutions to the research problem.
The research problem is the defining statement that informs the sources and methodologies to be applied to find and recommend proposals for the area of contention.
Why is the research problem important?
Research should adopt a precise approach for analysis to be relevant and applicable in a real-world context. Researchers can pick any area of study, and in most cases, the topic in question will have a broad scope; a well-formulated problem forms the basis of a strong research paper which illustrates a clear focus.
Writing a research problem is the first step in planning for a research paper, and a well-structured problem prevents a runaway project that lacks a clear direction.
Step 1: Finding a general research problem area
Your primary goal should be to find gaps and meaningful ways your research project offers a solution to a problem or broadens the knowledge bank in the field.
A good approach is to read and hold discussions about the topic , identify areas with insufficient information, highlight areas of contention and form more in-depth conclusions in under-researched areas.
Workplace research
You can carry out workplace research using a practical approach . This aims to identify a problem by analyzing reports, engaging with people in the organization or field of interest, and examining previous research. Some pointers include:
- Efficiency and performance-related issues within an organization.
- Areas or processes that can be improved in the organization.
- Matters of concern among professionals in the field of study.
- Challenges faced by identifiable groups in society.
- Crime in a particular region has been decreasing compared to the rest of the country.
- Stores in one location of a chain have been reporting lower sales in contrast with others in other parts of the country.
- One subsidiary of a company is experiencing high staff turnover, affecting the group’s bottom line.
In theoretical research , researchers aim to offer new insights which contribute to the larger knowledge body in the field rather than proposing change. You can formulate a problem by studying recent studies, debates, and theories to identify gaps. Identifying a research problem in theoretical research may examine the following:
- A context or phenomenon that has not been extensively studied.
- A contrast between two or more thought patterns.
- A position that is not clearly understood.
- A bothersome scenario or question that remains unsolved.
Theoretical problems don’t focus on solving a practical problem but have practical implications in their field. Many theoretical frameworks offer a guide to other practical and applied research scenarios.
- The relationship between genetics and mental issues in adulthood is not clearly understood.
- The effects of racial differences in long-term relationships are yet to be investigated in the modern dating scene.
- Social scientists disagree on the impact of neocolonialism on the socio-economic conditions of black people.
Step 2: Narrowing down the research problem
After identifying a general problem area, you need to zero in on the specific aspect you want to analyze further in the context of your research.
The problem can be narrowed down using the following criteria to create a relevant problem whose solutions adequately answer the research questions . Some questions you can ask to understand the contextual framework of the research problem include:
Significance
Evaluating the significance of a research problem is a necessary step for identifying issues that contribute to the solution of an issue. There are several ways of determining the significance of a research problem. The following questions can help you to evaluate the significance and relevance of a proposed research problem:
- Which area, group or time do you plan to situate your study?
- What attributes will you examine?
- What is the repercussion of not solving the problem?
- Who stands to benefit if the problem is resolved?
Example of a research problem
A fashion retail chain is attempting to increase the number of visitors to its stores, but the management is unaware of the measures to achieve this.
To improve its sales and compete with other chains, the chain requires research into ways of increasing traffic in its stores.
By narrowing down the research problem, you can create the problem statement , hypothesis , and relevant research questions .
What is an example of a research problem?
There has been an upward trend in the immigration of professionals from other countries to the UK. Research is needed to determine the likely causes and effects.
How do you formulate a research problem?
Begin by examining available sources and previous research on your topic of interest. You can narrow down the scope from the literature or observable phenomenon and focus on under-researched areas.
How can you determine the significance of a research problem?
Investigate the specific aspects you would like to investigate. Furthermore, you can determine the consequences of the problem remaining unresolved and the biggest beneficiaries if a solution is found.
What is the context in a research problem?
Context refers to the nature of the problem. It entails studying existing work on the issue, who is affected by it, and the proposed solutions.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
- How it works

Research Problem – Definition, Steps & Tips
Published by Jamie Walker at August 12th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
Once you have chosen a research topic, the next stage is to explain the research problem: the detailed issue, ambiguity of the research, gap analysis, or gaps in knowledge and findings that you will discuss.
Here, in this article, we explore a research problem in a dissertation or an essay with some research problem examples to help you better understand how and when you should write a research problem.
“A research problem is a specific statement relating to an area of concern and is contingent on the type of research. Some research studies focus on theoretical and practical problems, while some focus on only one.”
The problem statement in the dissertation, essay, research paper, and other academic papers should be clearly stated and intended to expand information, knowledge, and contribution to change.
This article will assist in identifying and elaborating a research problem if you are unsure how to define your research problem. The most notable challenge in the research process is to formulate and identify a research problem. Formulating a problem statement and research questions while finalizing the research proposal or introduction for your dissertation or thesis is necessary.
Why is Research Problem Critical?
An interesting research topic is only the first step. The real challenge of the research process is to develop a well-rounded research problem.
A well-formulated research problem helps understand the research procedure; without it, your research will appear unforeseeable and awkward.
Research is a procedure based on a sequence and a research problem aids in following and completing the research in a sequence. Repetition of existing literature is something that should be avoided in research.
Therefore research problem in a dissertation or an essay needs to be well thought out and presented with a clear purpose. Hence, your research work contributes more value to existing knowledge. You need to be well aware of the problem so you can present logical solutions.
Formulating a research problem is the first step of conducting research, whether you are writing an essay, research paper, dissertation , or research proposal .
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with dissertations across a variety of STEM disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

Step 1: Identifying Problem Area – What is Research Problem
The most significant step in any research is to look for unexplored areas, topics, and controversies . You aim to find gaps that your work will fill. Here are some research problem examples for you to better understand the concept.
Practical Research Problems
To conduct practical research, you will need practical research problems that are typically identified by analysing reports, previous research studies, and interactions with the experienced personals of pertinent disciplines. You might search for:
- Problems with performance or competence in an organization
- Institutional practices that could be enhanced
- Practitioners of relevant fields and their areas of concern
- Problems confronted by specific groups of people within your area of study
If your research work relates to an internship or a job, then it will be critical for you to identify a research problem that addresses certain issues faced by the firm the job or internship pertains to.
Examples of Practical Research Problems
Decreased voter participation in county A, as compared to the rest of the country.
The high employee turnover rate of department X of company Y influenced efficiency and team performance.
A charity institution, Y, suffers a lack of funding resulting in budget cuts for its programmes.
Theoretical Research Problems
Theoretical research relates to predicting, explaining, and understanding various phenomena. It also expands and challenges existing information and knowledge.
Identification of a research problem in theoretical research is achieved by analysing theories and fresh research literature relating to a broad area of research. This practice helps to find gaps in the research done by others and endorse the argument of your topic.
Here are some questions that you should bear in mind.
- A case or framework that has not been deeply analysed
- An ambiguity between more than one viewpoints
- An unstudied condition or relationships
- A problematic issue that needs to be addressed
Theoretical issues often contain practical implications, but immediate issues are often not resolved by these results. If that is the case, you might want to adopt a different research approach to achieve the desired outcomes.
Examples of Theoretical Research Problems
Long-term Vitamin D deficiency affects cardiac patients are not well researched.
The relationship between races, sex, and income imbalances needs to be studied with reference to the economy of a specific country or region.
The disagreement among historians of Scottish nationalism regarding the contributions of Imperial Britain in the creation of the national identity for Scotland.
Hire an Expert Writer
Proposal and dissertation orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in academic style
- Plagiarism free
- 100% Confidential
- Never Resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements
Step 2: Understanding the Research Problem
The researcher further investigates the selected area of research to find knowledge and information relating to the research problem to address the findings in the research.
Background and Rationale
- Population influenced by the problem?
- Is it a persistent problem, or is it recently revealed?
- Research that has already been conducted on this problem?
- Any proposed solution to the problem?
- Recent arguments concerning the problem, what are the gaps in the problem?
How to Write a First Class Dissertation Proposal or Research Proposal
Particularity and Suitability
- What specific place, time, and/or people will be focused on?
- Any aspects of research that you may not be able to deal with?
- What will be the concerns if the problem remains unresolved?
- What are the benefices of the problem resolution (e.g. future researcher or organisation’s management)?
Example of a Specific Research Problem
A non-profit institution X has been examined on their existing support base retention, but the existing research does not incorporate an understanding of how to effectively target new donors. To continue their work, the institution needs more research and find strategies for effective fundraising.
Once the problem is narrowed down, the next stage is to propose a problem statement and hypothesis or research questions.
If you are unsure about what a research problem is and how to define the research problem, then you might want to take advantage of our dissertation proposal writing service. You may also want to take a look at our essay writing service if you need help with identifying a research problem for your essay.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is research problem with example.
A research problem is a specific challenge that requires investigation. Example: “What is the impact of social media on mental health among adolescents?” This problem drives research to analyse the relationship between social media use and mental well-being in young people.
How many types of research problems do we have?
- Descriptive: Describing phenomena as they exist.
- Explanatory: Understanding causes and effects.
- Exploratory: Investigating little-understood phenomena.
- Predictive: Forecasting future outcomes.
- Prescriptive: Recommending actions.
- Normative: Describing what ought to be.
What are the principles of the research problem?
- Relevance: Addresses a significant issue.
- Re searchability: Amenable to empirical investigation.
- Clarity: Clearly defined without ambiguity.
- Specificity: Narrowly framed, avoiding vagueness.
- Feasibility: Realistic to conduct with available resources.
- Novelty: Offers new insights or challenges existing knowledge.
- Ethical considerations: Respect rights, dignity, and safety.
Why is research problem important?
A research problem is crucial because it identifies knowledge gaps, directs the inquiry’s focus, and forms the foundation for generating hypotheses or questions. It drives the methodology and determination of study relevance, ensuring that research contributes meaningfully to academic discourse and potentially addresses real-world challenges.
How do you write a research problem?
To write a research problem, identify a knowledge gap or an unresolved issue in your field. Start with a broad topic, then narrow it down. Clearly articulate the problem in a concise statement, ensuring it’s researchable, significant, and relevant. Ground it in the existing literature to highlight its importance and context.
How can we solve research problem?
To solve a research problem, start by conducting a thorough literature review. Formulate hypotheses or research questions. Choose an appropriate research methodology. Collect and analyse data systematically. Interpret findings in the context of existing knowledge. Ensure validity and reliability, and discuss implications, limitations, and potential future research directions.
You May Also Like
Find how to write research questions with the mentioned steps required for a perfect research question. Choose an interesting topic and begin your research.
Penning your dissertation proposal can be a rather daunting task. Here are comprehensive guidelines on how to write a dissertation proposal.
How to write a hypothesis for dissertation,? A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested with the help of experimental or theoretical research.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
45 Research Problem Examples & Inspiration
A research problem is an issue of concern that is the catalyst for your research. It demonstrates why the research problem needs to take place in the first place.
Generally, you will write your research problem as a clear, concise, and focused statement that identifies an issue or gap in current knowledge that requires investigation.
The problem will likely also guide the direction and purpose of a study. Depending on the problem, you will identify a suitable methodology that will help address the problem and bring solutions to light.
Research Problem Examples
In the following examples, I’ll present some problems worth addressing, and some suggested theoretical frameworks and research methodologies that might fit with the study. Note, however, that these aren’t the only ways to approach the problems. Keep an open mind and consult with your dissertation supervisor!

Psychology Problems
1. Social Media and Self-Esteem: “How does prolonged exposure to social media platforms influence the self-esteem of adolescents?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Comparison Theory
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking adolescents’ social media usage and self-esteem measures over time, combined with qualitative interviews.
2. Sleep and Cognitive Performance: “How does sleep quality and duration impact cognitive performance in adults?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Psychology
- Methodology : Experimental design with controlled sleep conditions, followed by cognitive tests. Participant sleep patterns can also be monitored using actigraphy.
3. Childhood Trauma and Adult Relationships: “How does unresolved childhood trauma influence attachment styles and relationship dynamics in adulthood?
- Theoretical Framework : Attachment Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of attachment styles with qualitative in-depth interviews exploring past trauma and current relationship dynamics.
4. Mindfulness and Stress Reduction: “How effective is mindfulness meditation in reducing perceived stress and physiological markers of stress in working professionals?”
- Theoretical Framework : Humanist Psychology
- Methodology : Randomized controlled trial comparing a group practicing mindfulness meditation to a control group, measuring both self-reported stress and physiological markers (e.g., cortisol levels).
5. Implicit Bias and Decision Making: “To what extent do implicit biases influence decision-making processes in hiring practices?
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Dissonance Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design using Implicit Association Tests (IAT) to measure implicit biases, followed by simulated hiring tasks to observe decision-making behaviors.
6. Emotional Regulation and Academic Performance: “How does the ability to regulate emotions impact academic performance in college students?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Theory of Emotion
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys measuring emotional regulation strategies, combined with academic performance metrics (e.g., GPA).
7. Nature Exposure and Mental Well-being: “Does regular exposure to natural environments improve mental well-being and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression?”
- Theoretical Framework : Biophilia Hypothesis
- Methodology : Longitudinal study comparing mental health measures of individuals with regular nature exposure to those without, possibly using ecological momentary assessment for real-time data collection.
8. Video Games and Cognitive Skills: “How do action video games influence cognitive skills such as attention, spatial reasoning, and problem-solving?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Load Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design with pre- and post-tests, comparing cognitive skills of participants before and after a period of action video game play.
9. Parenting Styles and Child Resilience: “How do different parenting styles influence the development of resilience in children facing adversities?”
- Theoretical Framework : Baumrind’s Parenting Styles Inventory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of resilience and parenting styles with qualitative interviews exploring children’s experiences and perceptions.
10. Memory and Aging: “How does the aging process impact episodic memory , and what strategies can mitigate age-related memory decline?
- Theoretical Framework : Information Processing Theory
- Methodology : Cross-sectional study comparing episodic memory performance across different age groups, combined with interventions like memory training or mnemonic strategies to assess potential improvements.
Education Problems
11. Equity and Access : “How do socioeconomic factors influence students’ access to quality education, and what interventions can bridge the gap?
- Theoretical Framework : Critical Pedagogy
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative data on student outcomes with qualitative interviews and focus groups with students, parents, and educators.
12. Digital Divide : How does the lack of access to technology and the internet affect remote learning outcomes, and how can this divide be addressed?
- Theoretical Framework : Social Construction of Technology Theory
- Methodology : Survey research to gather data on access to technology, followed by case studies in selected areas.
13. Teacher Efficacy : “What factors contribute to teacher self-efficacy, and how does it impact student achievement?”
- Theoretical Framework : Bandura’s Self-Efficacy Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys to measure teacher self-efficacy, combined with qualitative interviews to explore factors affecting it.
14. Curriculum Relevance : “How can curricula be made more relevant to diverse student populations, incorporating cultural and local contexts?”
- Theoretical Framework : Sociocultural Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of curricula, combined with focus groups with students and teachers.
15. Special Education : “What are the most effective instructional strategies for students with specific learning disabilities?
- Theoretical Framework : Social Learning Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing different instructional strategies, with pre- and post-tests to measure student achievement.
16. Dropout Rates : “What factors contribute to high school dropout rates, and what interventions can help retain students?”
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking students over time, combined with interviews with dropouts.
17. Bilingual Education : “How does bilingual education impact cognitive development and academic achievement?
- Methodology : Comparative study of students in bilingual vs. monolingual programs, using standardized tests and qualitative interviews.
18. Classroom Management: “What reward strategies are most effective in managing diverse classrooms and promoting a positive learning environment?
- Theoretical Framework : Behaviorism (e.g., Skinner’s Operant Conditioning)
- Methodology : Observational research in classrooms , combined with teacher interviews.
19. Standardized Testing : “How do standardized tests affect student motivation, learning, and curriculum design?”
- Theoretical Framework : Critical Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative analysis of test scores and student outcomes, combined with qualitative interviews with educators and students.
20. STEM Education : “What methods can be employed to increase interest and proficiency in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields among underrepresented student groups?”
- Theoretical Framework : Constructivist Learning Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing different instructional methods, with pre- and post-tests.
21. Social-Emotional Learning : “How can social-emotional learning be effectively integrated into the curriculum, and what are its impacts on student well-being and academic outcomes?”
- Theoretical Framework : Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of student well-being with qualitative interviews.
22. Parental Involvement : “How does parental involvement influence student achievement, and what strategies can schools use to increase it?”
- Theoretical Framework : Reggio Emilia’s Model (Community Engagement Focus)
- Methodology : Survey research with parents and teachers, combined with case studies in selected schools.
23. Early Childhood Education : “What are the long-term impacts of quality early childhood education on academic and life outcomes?”
- Theoretical Framework : Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development
- Methodology : Longitudinal study comparing students with and without early childhood education, combined with observational research.
24. Teacher Training and Professional Development : “How can teacher training programs be improved to address the evolving needs of the 21st-century classroom?”
- Theoretical Framework : Adult Learning Theory (Andragogy)
- Methodology : Pre- and post-assessments of teacher competencies, combined with focus groups.
25. Educational Technology : “How can technology be effectively integrated into the classroom to enhance learning, and what are the potential drawbacks or challenges?”
- Theoretical Framework : Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK)
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing classrooms with and without specific technologies, combined with teacher and student interviews.
Sociology Problems
26. Urbanization and Social Ties: “How does rapid urbanization impact the strength and nature of social ties in communities?”
- Theoretical Framework : Structural Functionalism
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative surveys on social ties with qualitative interviews in urbanizing areas.
27. Gender Roles in Modern Families: “How have traditional gender roles evolved in families with dual-income households?”
- Theoretical Framework : Gender Schema Theory
- Methodology : Qualitative interviews with dual-income families, combined with historical data analysis.
28. Social Media and Collective Behavior: “How does social media influence collective behaviors and the formation of social movements?”
- Theoretical Framework : Emergent Norm Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of social media platforms, combined with quantitative surveys on participation in social movements.
29. Education and Social Mobility: “To what extent does access to quality education influence social mobility in socioeconomically diverse settings?”
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking educational access and subsequent socioeconomic status, combined with qualitative interviews.
30. Religion and Social Cohesion: “How do religious beliefs and practices contribute to social cohesion in multicultural societies?”
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys on religious beliefs and perceptions of social cohesion, combined with ethnographic studies.
31. Consumer Culture and Identity Formation: “How does consumer culture influence individual identity formation and personal values?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Identity Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining content analysis of advertising with qualitative interviews on identity and values.
32. Migration and Cultural Assimilation: “How do migrants negotiate cultural assimilation and preservation of their original cultural identities in their host countries?”
- Theoretical Framework : Post-Structuralism
- Methodology : Qualitative interviews with migrants, combined with observational studies in multicultural communities.
33. Social Networks and Mental Health: “How do social networks, both online and offline, impact mental health and well-being?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Network Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys assessing social network characteristics and mental health metrics, combined with qualitative interviews.
34. Crime, Deviance, and Social Control: “How do societal norms and values shape definitions of crime and deviance, and how are these definitions enforced?”
- Theoretical Framework : Labeling Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of legal documents and media, combined with ethnographic studies in diverse communities.
35. Technology and Social Interaction: “How has the proliferation of digital technology influenced face-to-face social interactions and community building?”
- Theoretical Framework : Technological Determinism
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative surveys on technology use with qualitative observations of social interactions in various settings.
Nursing Problems
36. Patient Communication and Recovery: “How does effective nurse-patient communication influence patient recovery rates and overall satisfaction with care?”
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys assessing patient satisfaction and recovery metrics, combined with observational studies on nurse-patient interactions.
37. Stress Management in Nursing: “What are the primary sources of occupational stress for nurses, and how can they be effectively managed to prevent burnout?”
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of stress and burnout with qualitative interviews exploring personal experiences and coping mechanisms.
38. Hand Hygiene Compliance: “How effective are different interventions in improving hand hygiene compliance among nursing staff, and what are the barriers to consistent hand hygiene?”
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing hand hygiene rates before and after specific interventions, combined with focus groups to understand barriers.
39. Nurse-Patient Ratios and Patient Outcomes: “How do nurse-patient ratios impact patient outcomes, including recovery rates, complications, and hospital readmissions?”
- Methodology : Quantitative study analyzing patient outcomes in relation to staffing levels, possibly using retrospective chart reviews.
40. Continuing Education and Clinical Competence: “How does regular continuing education influence clinical competence and confidence among nurses?”
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking nurses’ clinical skills and confidence over time as they engage in continuing education, combined with patient outcome measures to assess potential impacts on care quality.
Communication Studies Problems
41. Media Representation and Public Perception: “How does media representation of minority groups influence public perceptions and biases?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cultivation Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of media representations combined with quantitative surveys assessing public perceptions and attitudes.
42. Digital Communication and Relationship Building: “How has the rise of digital communication platforms impacted the way individuals build and maintain personal relationships?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Penetration Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative surveys on digital communication habits with qualitative interviews exploring personal relationship dynamics.
43. Crisis Communication Effectiveness: “What strategies are most effective in managing public relations during organizational crises, and how do they influence public trust?”
- Theoretical Framework : Situational Crisis Communication Theory (SCCT)
- Methodology : Case study analysis of past organizational crises, assessing communication strategies used and subsequent public trust metrics.
44. Nonverbal Cues in Virtual Communication: “How do nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions and gestures, influence message interpretation in virtual communication platforms?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Semiotics
- Methodology : Experimental design using video conferencing tools, analyzing participants’ interpretations of messages with varying nonverbal cues.
45. Influence of Social Media on Political Engagement: “How does exposure to political content on social media platforms influence individuals’ political engagement and activism?”
- Theoretical Framework : Uses and Gratifications Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys assessing social media habits and political engagement levels, combined with content analysis of political posts on popular platforms.
Before you Go: Tips and Tricks for Writing a Research Problem
This is an incredibly stressful time for research students. The research problem is going to lock you into a specific line of inquiry for the rest of your studies.
So, here’s what I tend to suggest to my students:
- Start with something you find intellectually stimulating – Too many students choose projects because they think it hasn’t been studies or they’ve found a research gap. Don’t over-estimate the importance of finding a research gap. There are gaps in every line of inquiry. For now, just find a topic you think you can really sink your teeth into and will enjoy learning about.
- Take 5 ideas to your supervisor – Approach your research supervisor, professor, lecturer, TA, our course leader with 5 research problem ideas and run each by them. The supervisor will have valuable insights that you didn’t consider that will help you narrow-down and refine your problem even more.
- Trust your supervisor – The supervisor-student relationship is often very strained and stressful. While of course this is your project, your supervisor knows the internal politics and conventions of academic research. The depth of knowledge about how to navigate academia and get you out the other end with your degree is invaluable. Don’t underestimate their advice.
I’ve got a full article on all my tips and tricks for doing research projects right here – I recommend reading it:
- 9 Tips on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
What is Research: Definition, Methods, Types & Examples

The search for knowledge is closely linked to the object of study; that is, to the reconstruction of the facts that will provide an explanation to an observed event and that at first sight can be considered as a problem. It is very human to seek answers and satisfy our curiosity. Let’s talk about research.
Content Index
What is Research?
What are the characteristics of research.
- Comparative analysis chart
Qualitative methods
Quantitative methods, 8 tips for conducting accurate research.
Research is the careful consideration of study regarding a particular concern or research problem using scientific methods. According to the American sociologist Earl Robert Babbie, “research is a systematic inquiry to describe, explain, predict, and control the observed phenomenon. It involves inductive and deductive methods.”
Inductive methods analyze an observed event, while deductive methods verify the observed event. Inductive approaches are associated with qualitative research , and deductive methods are more commonly associated with quantitative analysis .
Research is conducted with a purpose to:
- Identify potential and new customers
- Understand existing customers
- Set pragmatic goals
- Develop productive market strategies
- Address business challenges
- Put together a business expansion plan
- Identify new business opportunities
- Good research follows a systematic approach to capture accurate data. Researchers need to practice ethics and a code of conduct while making observations or drawing conclusions.
- The analysis is based on logical reasoning and involves both inductive and deductive methods.
- Real-time data and knowledge is derived from actual observations in natural settings.
- There is an in-depth analysis of all data collected so that there are no anomalies associated with it.
- It creates a path for generating new questions. Existing data helps create more research opportunities.
- It is analytical and uses all the available data so that there is no ambiguity in inference.
- Accuracy is one of the most critical aspects of research. The information must be accurate and correct. For example, laboratories provide a controlled environment to collect data. Accuracy is measured in the instruments used, the calibrations of instruments or tools, and the experiment’s final result.
What is the purpose of research?
There are three main purposes:
- Exploratory: As the name suggests, researchers conduct exploratory studies to explore a group of questions. The answers and analytics may not offer a conclusion to the perceived problem. It is undertaken to handle new problem areas that haven’t been explored before. This exploratory data analysis process lays the foundation for more conclusive data collection and analysis.
LEARN ABOUT: Descriptive Analysis
- Descriptive: It focuses on expanding knowledge on current issues through a process of data collection. Descriptive research describe the behavior of a sample population. Only one variable is required to conduct the study. The three primary purposes of descriptive studies are describing, explaining, and validating the findings. For example, a study conducted to know if top-level management leaders in the 21st century possess the moral right to receive a considerable sum of money from the company profit.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
- Explanatory: Causal research or explanatory research is conducted to understand the impact of specific changes in existing standard procedures. Running experiments is the most popular form. For example, a study that is conducted to understand the effect of rebranding on customer loyalty.
Here is a comparative analysis chart for a better understanding:
It begins by asking the right questions and choosing an appropriate method to investigate the problem. After collecting answers to your questions, you can analyze the findings or observations to draw reasonable conclusions.
When it comes to customers and market studies, the more thorough your questions, the better the analysis. You get essential insights into brand perception and product needs by thoroughly collecting customer data through surveys and questionnaires . You can use this data to make smart decisions about your marketing strategies to position your business effectively.
To make sense of your study and get insights faster, it helps to use a research repository as a single source of truth in your organization and manage your research data in one centralized data repository .
Types of research methods and Examples

Research methods are broadly classified as Qualitative and Quantitative .
Both methods have distinctive properties and data collection methods .
Qualitative research is a method that collects data using conversational methods, usually open-ended questions . The responses collected are essentially non-numerical. This method helps a researcher understand what participants think and why they think in a particular way.
Types of qualitative methods include:
- One-to-one Interview
- Focus Groups
- Ethnographic studies
- Text Analysis
Quantitative methods deal with numbers and measurable forms . It uses a systematic way of investigating events or data. It answers questions to justify relationships with measurable variables to either explain, predict, or control a phenomenon.
Types of quantitative methods include:
- Survey research
- Descriptive research
- Correlational research
LEARN MORE: Descriptive Research vs Correlational Research
Remember, it is only valuable and useful when it is valid, accurate, and reliable. Incorrect results can lead to customer churn and a decrease in sales.
It is essential to ensure that your data is:
- Valid – founded, logical, rigorous, and impartial.
- Accurate – free of errors and including required details.
- Reliable – other people who investigate in the same way can produce similar results.
- Timely – current and collected within an appropriate time frame.
- Complete – includes all the data you need to support your business decisions.
Gather insights

- Identify the main trends and issues, opportunities, and problems you observe. Write a sentence describing each one.
- Keep track of the frequency with which each of the main findings appears.
- Make a list of your findings from the most common to the least common.
- Evaluate a list of the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats identified in a SWOT analysis .
- Prepare conclusions and recommendations about your study.
- Act on your strategies
- Look for gaps in the information, and consider doing additional inquiry if necessary
- Plan to review the results and consider efficient methods to analyze and interpret results.
Review your goals before making any conclusions about your study. Remember how the process you have completed and the data you have gathered help answer your questions. Ask yourself if what your analysis revealed facilitates the identification of your conclusions and recommendations.
LEARN MORE ABOUT OUR SOFTWARE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS
Data Information vs Insight: Essential differences
May 14, 2024

Pricing Analytics Software: Optimize Your Pricing Strategy
May 13, 2024

Relationship Marketing: What It Is, Examples & Top 7 Benefits
May 8, 2024

The Best Email Survey Tool to Boost Your Feedback Game
May 7, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Design
Definition:
Research design refers to the overall strategy or plan for conducting a research study. It outlines the methods and procedures that will be used to collect and analyze data, as well as the goals and objectives of the study. Research design is important because it guides the entire research process and ensures that the study is conducted in a systematic and rigorous manner.
Types of Research Design
Types of Research Design are as follows:
Descriptive Research Design
This type of research design is used to describe a phenomenon or situation. It involves collecting data through surveys, questionnaires, interviews, and observations. The aim of descriptive research is to provide an accurate and detailed portrayal of a particular group, event, or situation. It can be useful in identifying patterns, trends, and relationships in the data.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is used to determine if there is a relationship between two or more variables. This type of research design involves collecting data from participants and analyzing the relationship between the variables using statistical methods. The aim of correlational research is to identify the strength and direction of the relationship between the variables.
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This type of research design involves manipulating one variable and measuring the effect on another variable. It usually involves randomly assigning participants to groups and manipulating an independent variable to determine its effect on a dependent variable. The aim of experimental research is to establish causality.
Quasi-experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks one or more of the features of a true experiment. For example, there may not be random assignment to groups or a control group. This type of research design is used when it is not feasible or ethical to conduct a true experiment.
Case Study Research Design
Case study research design is used to investigate a single case or a small number of cases in depth. It involves collecting data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis. The aim of case study research is to provide an in-depth understanding of a particular case or situation.
Longitudinal Research Design
Longitudinal research design is used to study changes in a particular phenomenon over time. It involves collecting data at multiple time points and analyzing the changes that occur. The aim of longitudinal research is to provide insights into the development, growth, or decline of a particular phenomenon over time.
Structure of Research Design
The format of a research design typically includes the following sections:
- Introduction : This section provides an overview of the research problem, the research questions, and the importance of the study. It also includes a brief literature review that summarizes previous research on the topic and identifies gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Research Questions or Hypotheses: This section identifies the specific research questions or hypotheses that the study will address. These questions should be clear, specific, and testable.
- Research Methods : This section describes the methods that will be used to collect and analyze data. It includes details about the study design, the sampling strategy, the data collection instruments, and the data analysis techniques.
- Data Collection: This section describes how the data will be collected, including the sample size, data collection procedures, and any ethical considerations.
- Data Analysis: This section describes how the data will be analyzed, including the statistical techniques that will be used to test the research questions or hypotheses.
- Results : This section presents the findings of the study, including descriptive statistics and statistical tests.
- Discussion and Conclusion : This section summarizes the key findings of the study, interprets the results, and discusses the implications of the findings. It also includes recommendations for future research.
- References : This section lists the sources cited in the research design.
Example of Research Design
An Example of Research Design could be:
Research question: Does the use of social media affect the academic performance of high school students?
Research design:
- Research approach : The research approach will be quantitative as it involves collecting numerical data to test the hypothesis.
- Research design : The research design will be a quasi-experimental design, with a pretest-posttest control group design.
- Sample : The sample will be 200 high school students from two schools, with 100 students in the experimental group and 100 students in the control group.
- Data collection : The data will be collected through surveys administered to the students at the beginning and end of the academic year. The surveys will include questions about their social media usage and academic performance.
- Data analysis : The data collected will be analyzed using statistical software. The mean scores of the experimental and control groups will be compared to determine whether there is a significant difference in academic performance between the two groups.
- Limitations : The limitations of the study will be acknowledged, including the fact that social media usage can vary greatly among individuals, and the study only focuses on two schools, which may not be representative of the entire population.
- Ethical considerations: Ethical considerations will be taken into account, such as obtaining informed consent from the participants and ensuring their anonymity and confidentiality.
How to Write Research Design
Writing a research design involves planning and outlining the methodology and approach that will be used to answer a research question or hypothesis. Here are some steps to help you write a research design:
- Define the research question or hypothesis : Before beginning your research design, you should clearly define your research question or hypothesis. This will guide your research design and help you select appropriate methods.
- Select a research design: There are many different research designs to choose from, including experimental, survey, case study, and qualitative designs. Choose a design that best fits your research question and objectives.
- Develop a sampling plan : If your research involves collecting data from a sample, you will need to develop a sampling plan. This should outline how you will select participants and how many participants you will include.
- Define variables: Clearly define the variables you will be measuring or manipulating in your study. This will help ensure that your results are meaningful and relevant to your research question.
- Choose data collection methods : Decide on the data collection methods you will use to gather information. This may include surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, or secondary data sources.
- Create a data analysis plan: Develop a plan for analyzing your data, including the statistical or qualitative techniques you will use.
- Consider ethical concerns : Finally, be sure to consider any ethical concerns related to your research, such as participant confidentiality or potential harm.
When to Write Research Design
Research design should be written before conducting any research study. It is an important planning phase that outlines the research methodology, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques that will be used to investigate a research question or problem. The research design helps to ensure that the research is conducted in a systematic and logical manner, and that the data collected is relevant and reliable.
Ideally, the research design should be developed as early as possible in the research process, before any data is collected. This allows the researcher to carefully consider the research question, identify the most appropriate research methodology, and plan the data collection and analysis procedures in advance. By doing so, the research can be conducted in a more efficient and effective manner, and the results are more likely to be valid and reliable.
Purpose of Research Design
The purpose of research design is to plan and structure a research study in a way that enables the researcher to achieve the desired research goals with accuracy, validity, and reliability. Research design is the blueprint or the framework for conducting a study that outlines the methods, procedures, techniques, and tools for data collection and analysis.
Some of the key purposes of research design include:
- Providing a clear and concise plan of action for the research study.
- Ensuring that the research is conducted ethically and with rigor.
- Maximizing the accuracy and reliability of the research findings.
- Minimizing the possibility of errors, biases, or confounding variables.
- Ensuring that the research is feasible, practical, and cost-effective.
- Determining the appropriate research methodology to answer the research question(s).
- Identifying the sample size, sampling method, and data collection techniques.
- Determining the data analysis method and statistical tests to be used.
- Facilitating the replication of the study by other researchers.
- Enhancing the validity and generalizability of the research findings.
Applications of Research Design
There are numerous applications of research design in various fields, some of which are:
- Social sciences: In fields such as psychology, sociology, and anthropology, research design is used to investigate human behavior and social phenomena. Researchers use various research designs, such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and correlational designs, to study different aspects of social behavior.
- Education : Research design is essential in the field of education to investigate the effectiveness of different teaching methods and learning strategies. Researchers use various designs such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and case study designs to understand how students learn and how to improve teaching practices.
- Health sciences : In the health sciences, research design is used to investigate the causes, prevention, and treatment of diseases. Researchers use various designs, such as randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, and case-control studies, to study different aspects of health and healthcare.
- Business : Research design is used in the field of business to investigate consumer behavior, marketing strategies, and the impact of different business practices. Researchers use various designs, such as survey research, experimental research, and case studies, to study different aspects of the business world.
- Engineering : In the field of engineering, research design is used to investigate the development and implementation of new technologies. Researchers use various designs, such as experimental research and case studies, to study the effectiveness of new technologies and to identify areas for improvement.
Advantages of Research Design
Here are some advantages of research design:
- Systematic and organized approach : A well-designed research plan ensures that the research is conducted in a systematic and organized manner, which makes it easier to manage and analyze the data.
- Clear objectives: The research design helps to clarify the objectives of the study, which makes it easier to identify the variables that need to be measured, and the methods that need to be used to collect and analyze data.
- Minimizes bias: A well-designed research plan minimizes the chances of bias, by ensuring that the data is collected and analyzed objectively, and that the results are not influenced by the researcher’s personal biases or preferences.
- Efficient use of resources: A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the resources (time, money, and personnel) are used efficiently and effectively, by focusing on the most important variables and methods.
- Replicability: A well-designed research plan makes it easier for other researchers to replicate the study, which enhances the credibility and reliability of the findings.
- Validity: A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the findings are valid, by ensuring that the methods used to collect and analyze data are appropriate for the research question.
- Generalizability : A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the findings can be generalized to other populations, settings, or situations, which increases the external validity of the study.
Research Design Vs Research Methodology
About the author.
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...
Leave a comment x.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Cookie consent
We use our own and third-party cookies to show you more relevant content based on your browsing and navigation history. Please accept or manage your cookie settings below. Here's our cookie policy

- Form Builder Signups and orders
- Survey maker Research and feedback
- Quiz Maker Trivia and product match
- Find Customers Generate more leads
- Get Feedback Discover ways to improve
- Do research Uncover trends and ideas
- Marketers Forms for marketing teams
- Product Forms for product teams
- HR Forms for HR teams
- Customer success Forms for customer success teams
- Business Forms for general business
- Form templates
- Survey templates
- Quiz templates
- Poll templates
- Order forms
- Feedback forms
- Satisfaction surveys
- Application forms
- Feedback surveys
- Evaluation forms
- Request forms
- Signup forms
- Business surveys
- Marketing surveys
- Report forms
- Customer feedback form
- Registration form
- Branding questionnaire
- 360 feedback
- Lead generation
- Contact form
- Signup sheet
- Help center Find quick answers
- Contact us Speak to someone
- Our blog Get inspired
- Our community Share and learn
- Our guides Tips and how-to
- Updates News and announcements
- Brand Our guidelines
- Partners Browse or join
- Careers Join our team
- → The 8 types of market research and ho...
The 8 types of market research and how to use them
There are eight types of marketing research you can try to stay ahead of the competition. Learn more about marketing research methods and how to use them.

Latest posts on Tips
Typeform | 05.2024
Typeform | 04.2024
“If you keep doing what you’ve always done, you’ll keep getting what you’ve always got.”
Doesn’t sound too threatening if you’ve always been successful, right?
Continuing to do what you’ve always done means you’ll fall behind—and probably fade to darkness—to where all the forgotten brands go.
Take Kodak. They were a major player in photography for decades—remember? When digital photography boomed, Kodak kept doing what they always did. Their business floundered and people forgot about them. Well, everyone apart from Pitbull.
Now, look at Fujifilm, one of Kodak’s biggest competitors. They did the opposite and looked for ways to apply their expertise in film to the technology of the new millennium instead. Their company is still going strong.
The same goes for research. If you’re doing the same old types of market research, speaking to the same old people, and doing the same old tired surveys—you’re already behind.
How do you decide what kind of market research you need to do? It all comes down to what you need to know and what your business goals are.
In this article, we’ll explain the various types of market research you can use to solve issues and challenges in your business. We’ll throw you a freebie, too, and provide some market research tips about when to use each strategy.
Let’s get you ahead of the curve.
1. Brand research

Brand research helps with creating and managing a company’s brand, or identity. A company’s brand is the images, narratives, and characteristics people associate with it.
When to use it
Brand research can be used at every stage in a business’s lifecycle, from creation to new product launches and re-branding. There are at least seven types of brand research:
Brand advocacy: How many of your customers are willing to recommend your brand?
Brand awareness : Does your target market know who you are and consider you a serious option?
Brand loyalty: Are you retaining customers?
Brand penetration: What is the proportion of your target market using your brand?
Brand perception : What do people think of as your company’s identity or differentiating qualities?
Brand positioning: What is the best way to differentiate your brand from others in the consumer’s mind and articulate it in a way that resonates?
Brand value: How much are people willing to pay for an experience with your brand over another?
How to do it
A researcher will use several types of market research methods to assess your and your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. Generally, they will conduct competitor research, both qualitative and quantitative, to get a picture of the overall marketplace. Focus groups and interviews can be used to learn about their emotions and associations with certain brands.
Market research surveys are useful to determine features and benefits that differentiate you from competitors . These are then translated into emotionally compelling consumer language.
2. Campaign effectiveness
This type of market research is designed to evaluate whether your advertising messages are reaching the right people and delivering the desired results. Successful campaign effectiveness research can help you sell more and reduce customer acquisition costs.
It’s estimated people see up to 5,000 advertising messages each day. That means attention is a scarce resource, so campaign effectiveness research should be used when you need to spend your advertising dollars effectively.
Campaign effectiveness research depends on which stage of the campaign you use it in (ideally, it’s all of them!). Quantitative research can be conducted to provide a picture of how your target market views advertising and address weaknesses in the advertising campaign.
3. Competitive analysis

Competitive analysis allows you to assess your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses in the marketplace, providing you with fuel to drive a competitive advantage.
No business exists in a vacuum—competitive analysis is an integral part of any business and market plan. Whether you’re just getting started, moving into a new market, or doing a health check of your business, a competitive analysis will be invaluable.
A researcher will typically choose a few of your main competitors and analyze things like their marketing strategy, customer perceptions, revenue or sales volume, and so on.
Secondary sources such as articles, references, and advertising are excellent sources of competitive information; however, primary research, such as mystery shopping and focus groups, can offer valuable information on customer service and current consumer opinions.
4. Consumer insights
Consumer insights research does more than tell you about who your customers are and what they do. It reveals why customers behave in certain ways and helps you leverage that to meet your business goals.
Knowing your customers deeply is integral to creating a strategic marketing plan. This type of market research can help you anticipate consumer needs, spark innovation, personalize your marketing, solve business challenges, and more.
Consumer insights research should be specific to your business—it’s about getting to know your target audience and customers. Various market research methods can be used, such as interviews, ethnography, survey research, social monitoring, and customer journey research.
Here are some of the characteristics you should understand through consumer insights research:
Purchase habits
Interests, hobbies, passions
Personal and professional information
How they consume media and advertising
5. Customer satisfaction research
Customer satisfaction research is a type of market research that measures customers’ experiences with products or services, specifically looking at how those meet, exceed, or fail to live up to their expectations.
Customer satisfaction is a strong indicator of customer retention and overall business performance. Successful customer satisfaction research should help you understand what your customers like, dislike, and feel needs improvement. You can use this type of market research to look at the quality and design of products, speed and timeliness of delivery, staff and service reliability, knowledge, and friendliness, market price, and value for money.
There are several ways to measure customer satisfaction, most commonly using surveys. An NPS or Voice of the Customer Survey can help you measure customer loyalty. Customer Effort Scoring measures how satisfied people are with customer service or problem resolution. CSAT is any survey that measures customer satisfaction , typically measured using Likert scale surveys . They can be conducted at different points in the customer experience, allowing deeper insight into that moment.
6. Customer segmentation research

Customer segmentation studies aim to divide markets or customers into smaller groups or personas with similar characteristics to enable targeted marketing. By understanding how people in each category behave, you can understand how each influences revenue.
Customer segmentation research is best used if you’re ready to give customers individualized experiences. Not every customer in your target market is the same. The more you understand each specific persona, the easier it is to focus on delivering personalized marketing, build loyal relations, price products effectively, and forecast how new products and services will perform in each segment.
Market researchers use four characteristics to segment customers.
Demographics: demographic information such as age, gender, family status, education, household income, occupation and so on
Geography: where people live, from cities and countries to whether they are city dwellers or suburbanites
Psychographics: socioeconomic status, class, lifestyle, personality traits, generation, interests, hobbies, etc.
Behavior: brand affinity, consumption and shopping habits, spending, etc.
A researcher will identify your current customers and collect data about them through various market research methods, such as surveys, database research, website analytics, interviews, and focus groups. The aim is to gather as much information as possible.
7. Product development
Market research for product development involves using customer knowledge to inform the entire process of creating or improving a product, service, or app and bringing it to market.
Innovation is hard work. A quick Google will tell you that 80–95% of new products fail every year. Conducting market research for product and app development helps minimize the risk of a new product or change going bust as it enters the market. There are three stages where you can use market research:
Conception: The moment you’re thinking about adding something new, market research can find market opportunities and provide insights into customer challenges or their jobs-to-be-done, so you can find a way to fill the gap.
Formation: Once you have an idea, market researchers can help you turn it into a concept that can be tested. You can learn more about strategizing pricing, testing advertising and packaging, value proposition, and so on.
Introduction: Market research can help you gauge attitudes toward the product once it’s in the market and adapt your messaging as it rolls out.
Keep making the product better or find opportunities to introduce it to new markets.
Product development research will utilize different market research methods, depending on the goal of the research. A researcher could present focus groups with product concepts and listen to their opinions, conduct interviews to learn more about their pain points, or perform user testing to see how they interact with an app or website.
8. Usability testing
Usability testing is concerned with understanding how customers use your products in real time. It can involve physical products, like a new blender, or digital products like a website or app.
Usability testing is helpful when you need to detect problems or bugs in early prototypes or beta versions before launching them. It typically costs far less to test a product or service beforehand than to pull a flawed product off the shelves or lose sales because of poor functionality.
There are several types of usability tests, which vary based on whether you’re testing a physical or digital product.
Journey testing involves observing the customer experience on an app or website and monitoring how they perform. This type of study can be done online
Eye tracking studies monitor where people’s eyes are drawn. Generally, they are conducted on websites and apps, but can also be done in stores to analyze where people look while shopping
Learn ability studies quantify the learning curve over time to see which problems people encounter after repeating the same task
Click tracking follows users’ activity on websites to evaluate the linking structure of a website
Checklist testing involves giving users tasks to perform and recording or asking them to review their experience
Combining types of market research with Typeform
When it comes to market research, you need to ask yourself what business challenge or question you’re trying to address. Then, select the appropriate methods and tools, such as market research automation , to simplify your process.From there, the world of useful data and actionable insights will open to you.

About the author
We're Typeform - a team on a mission to transform data collection by bringing you refreshingly different forms.
Liked that? Check these out:

Zero-party data: a beginner’s guide
What is zero-party data? And how does it affect your business? Explore the evolution of data collection in a cookieless era and stay ahead in the changing landscape of digital marketing.
Typeform | 01.2024

5 landing page tests to run on your website from day one
You’ve got visitors, and now you need to turn them into customers. It start with knowing their needs. Here’s five tests you should be running on your landing pages.
Jessica Thiefels | 03.2019

Market research automation: A marketer’s guide for 2024
Market research automation uses AI to simplify and enhance traditional research. AI helps interpret data, create data visualizations, pull insights, and more.
Kevin Branscum | 11.2023
Frontiers | Science News
- Science News
Research Topics
Five research topics exploring the science of mental health.

Mental wellbeing is increasingly recognized as an essential aspect of our overall health. It supports our ability to handle challenges, build strong relationships, and live more fulfilling lives. The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the importance of mental health by acknowledging it as a fundamental human right.
This Mental Health Awareness Week, we highlight the remarkable work of scientists driving open research that helps everyone achieve better mental health.
Here are five Research Topics that study themes including how we adapt to a changing world, the impact of loneliness on our wellbeing, and the connection between our diet and mental health.
All articles are openly available to view and download.
1 | Community Series in Mental Health Promotion and Protection, volume II
40.300 views | 16 articles
There is no health without mental health. Thus, this Research Topic collects ideas and research related to strategies that promote mental health across all disciplines. The goal is to raise awareness about mental health promotion and protection to ensure its incorporation in national mental health policies.
This topic is of relevance given the mental health crisis being experienced across the world right now. A reality that has prompted the WHO to declare that health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social wellbeing.
View Research Topic
2 | Dietary and Metabolic Approaches for Mental Health Conditions
176.800 views | 11 articles
There is increased recognition that mental health disorders are, at least in part, a form of diet-related disease. For this reason, we focus attention on a Research Topic that examines the mechanistic interplay between dietary patterns and mental health conditions.
There is a clear consensus that the quality, quantity, and even timing of our human feeding patterns directly impact how brains function. But despite the epidemiological and mechanistic links between mental health and diet-related diseases, these two are often perceived as separate medical issues.
Even more urgent, public health messaging and clinical treatments for mental health conditions place relatively little emphasis on formulating nutrition to ease the underlying drivers of mental health conditions.
3 | Comparing Mental Health Cross-Culturally
94.000 views | 15 articles
Although mental health has been widely discussed in later years, how mental health is perceived across different cultures remains to be examined. This Research Topic addresses this gap and deepens our knowledge of mental health by comparing positive and negative psychological constructs cross-culturally.
The definition and understanding of mental health remain to be refined, partially because of a lack of cross-cultural perspectives on mental health. Also, due to the rapid internationalization taking place in the world today, a culturally aware understanding of, and interventions for mental health problems are essential.
4 | Adaption to Change and Coping Strategies: New Resources for Mental Health
85.000 views | 29 articles
In this Research Topic, scientists study a wider range of variables involved in change and adaptation. They examine changes of any type or magnitude whenever the lack of adaptive response diminishes our development and well-being.
Today’s society is characterized by change, and sometimes, the constant changes are difficult to assimilate. This may be why feelings of frustration and defenselessness appear in the face of the impossibility of responding adequately to the requirements of a changing society.
Therefore, society must develop an updated notion of the processes inherent to changing developmental environments, personal skills, resources, and strategies. This know-how is crucial for achieving and maintaining balanced mental health.
5 | Mental Health Equity
29.900 views | 10 articles
The goal of this Research Topic is to move beyond a synthesis of what is already known about mental health in the context of health equity. Rather, the focus here is on transformative solutions, recommendations, and applied research that have real world implications on policy, practice, and future scholarship.
Attention in the field to upstream factors and the role of social and structural determinants of health in influencing health outcomes, combined with an influx of innovation –particularly the digitalization of healthcare—presents a unique opportunity to solve pressing issues in mental health through a health equity lens.
The topic is opportune because factors such as structural racism and climate change have disproportionately negatively impacted marginalized communities across the world, including Black, Indigenous, People of Color (BIPOC), LGBTQ+, people with disabilities, and transition-age youth and young adults. As a result, existing disparities in mental health have exacerbated.
Post related info
May 13, 2024
Frontiers Science Communications
Post categories, featured news, related subjects, research topics, related content.

Opening health for all: 7 Research Topics shaping a healthier world

Frontiers' Research Topic publishing program: pioneering the future of scientific publishing

Frontiers institutional partnerships update – winter 2024
Latest posts.


Villars Institute Summit 2024: Catalyzing systematic change through interdisciplinary cooperation

World’s deepest sinkhole discovered in Mexico: Here are five Frontiers articles you won’t want to miss

Bumblebee nests are overheating due to climate change, threatening future populations

Why do male chicks play more than females? Study finds answers in distant ancestor
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples
How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples
Published on 8 November 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George.
A research problem is a specific issue or gap in existing knowledge that you aim to address in your research. You may choose to look for practical problems aimed at contributing to change, or theoretical problems aimed at expanding knowledge.
Some research will do both of these things, but usually the research problem focuses on one or the other. The type of research problem you choose depends on your broad topic of interest and the type of research you think will fit best.
This article helps you identify and refine a research problem. When writing your research proposal or introduction , formulate it as a problem statement and/or research questions .
Table of contents
Why is the research problem important, step 1: identify a broad problem area, step 2: learn more about the problem, frequently asked questions about research problems.
Having an interesting topic isn’t a strong enough basis for academic research. Without a well-defined research problem, you are likely to end up with an unfocused and unmanageable project.
You might end up repeating what other people have already said, trying to say too much, or doing research without a clear purpose and justification. You need a clear problem in order to do research that contributes new and relevant insights.
Whether you’re planning your thesis , starting a research paper , or writing a research proposal , the research problem is the first step towards knowing exactly what you’ll do and why.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
As you read about your topic, look for under-explored aspects or areas of concern, conflict, or controversy. Your goal is to find a gap that your research project can fill.
Practical research problems
If you are doing practical research, you can identify a problem by reading reports, following up on previous research, or talking to people who work in the relevant field or organisation. You might look for:
- Issues with performance or efficiency
- Processes that could be improved
- Areas of concern among practitioners
- Difficulties faced by specific groups of people
Examples of practical research problems
Voter turnout in New England has been decreasing, in contrast to the rest of the country.
The HR department of a local chain of restaurants has a high staff turnover rate.
A non-profit organisation faces a funding gap that means some of its programs will have to be cut.
Theoretical research problems
If you are doing theoretical research, you can identify a research problem by reading existing research, theory, and debates on your topic to find a gap in what is currently known about it. You might look for:
- A phenomenon or context that has not been closely studied
- A contradiction between two or more perspectives
- A situation or relationship that is not well understood
- A troubling question that has yet to be resolved
Examples of theoretical research problems
The effects of long-term Vitamin D deficiency on cardiovascular health are not well understood.
The relationship between gender, race, and income inequality has yet to be closely studied in the context of the millennial gig economy.
Historians of Scottish nationalism disagree about the role of the British Empire in the development of Scotland’s national identity.
Next, you have to find out what is already known about the problem, and pinpoint the exact aspect that your research will address.
Context and background
- Who does the problem affect?
- Is it a newly-discovered problem, or a well-established one?
- What research has already been done?
- What, if any, solutions have been proposed?
- What are the current debates about the problem? What is missing from these debates?
Specificity and relevance
- What particular place, time, and/or group of people will you focus on?
- What aspects will you not be able to tackle?
- What will the consequences be if the problem is not resolved?
Example of a specific research problem
A local non-profit organisation focused on alleviating food insecurity has always fundraised from its existing support base. It lacks understanding of how best to target potential new donors. To be able to continue its work, the organisation requires research into more effective fundraising strategies.
Once you have narrowed down your research problem, the next step is to formulate a problem statement , as well as your research questions or hypotheses .
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarise the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2022, November 08). How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/define-research-problem/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, example theoretical framework of a dissertation or thesis, how to write a strong hypothesis | guide & examples.
share this!
May 13, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
written by researcher(s)
AI-assisted writing is quietly booming in academic journals—here's why that's OK
by Julian Koplin, The Conversation

If you search Google Scholar for the phrase " as an AI language model ," you'll find plenty of AI research literature and also some rather suspicious results. For example, one paper on agricultural technology says,
"As an AI language model, I don't have direct access to current research articles or studies. However, I can provide you with an overview of some recent trends and advancements …"
Obvious gaffes like this aren't the only signs that researchers are increasingly turning to generative AI tools when writing up their research. A recent study examined the frequency of certain words in academic writing (such as "commendable," "meticulously" and "intricate"), and found they became far more common after the launch of ChatGPT—so much so that 1% of all journal articles published in 2023 may have contained AI-generated text.
(Why do AI models overuse these words? There is speculation it's because they are more common in English as spoken in Nigeria, where key elements of model training often occur.)
The aforementioned study also looks at preliminary data from 2024, which indicates that AI writing assistance is only becoming more common. Is this a crisis for modern scholarship, or a boon for academic productivity?
Who should take credit for AI writing?
Many people are worried by the use of AI in academic papers. Indeed, the practice has been described as " contaminating " scholarly literature.
Some argue that using AI output amounts to plagiarism. If your ideas are copy-pasted from ChatGPT, it is questionable whether you really deserve credit for them.
But there are important differences between "plagiarizing" text authored by humans and text authored by AI. Those who plagiarize humans' work receive credit for ideas that ought to have gone to the original author.
By contrast, it is debatable whether AI systems like ChatGPT can have ideas, let alone deserve credit for them. An AI tool is more like your phone's autocomplete function than a human researcher.
The question of bias
Another worry is that AI outputs might be biased in ways that could seep into the scholarly record. Infamously, older language models tended to portray people who are female, black and/or gay in distinctly unflattering ways, compared with people who are male, white and/or straight.
This kind of bias is less pronounced in the current version of ChatGPT.
However, other studies have found a different kind of bias in ChatGPT and other large language models : a tendency to reflect a left-liberal political ideology.
Any such bias could subtly distort scholarly writing produced using these tools.
The hallucination problem
The most serious worry relates to a well-known limitation of generative AI systems: that they often make serious mistakes.
For example, when I asked ChatGPT-4 to generate an ASCII image of a mushroom, it provided me with the following output.

It then confidently told me I could use this image of a "mushroom" for my own purposes.
These kinds of overconfident mistakes have been referred to as "AI hallucinations" and " AI bullshit ." While it is easy to spot that the above ASCII image looks nothing like a mushroom (and quite a bit like a snail), it may be much harder to identify any mistakes ChatGPT makes when surveying scientific literature or describing the state of a philosophical debate.
Unlike (most) humans, AI systems are fundamentally unconcerned with the truth of what they say. If used carelessly, their hallucinations could corrupt the scholarly record.
Should AI-produced text be banned?
One response to the rise of text generators has been to ban them outright. For example, Science—one of the world's most influential academic journals—disallows any use of AI-generated text .
I see two problems with this approach.
The first problem is a practical one: current tools for detecting AI-generated text are highly unreliable. This includes the detector created by ChatGPT's own developers, which was taken offline after it was found to have only a 26% accuracy rate (and a 9% false positive rate ). Humans also make mistakes when assessing whether something was written by AI.
It is also possible to circumvent AI text detectors. Online communities are actively exploring how to prompt ChatGPT in ways that allow the user to evade detection. Human users can also superficially rewrite AI outputs, effectively scrubbing away the traces of AI (like its overuse of the words "commendable," "meticulously" and "intricate").
The second problem is that banning generative AI outright prevents us from realizing these technologies' benefits. Used well, generative AI can boost academic productivity by streamlining the writing process. In this way, it could help further human knowledge. Ideally, we should try to reap these benefits while avoiding the problems.
The problem is poor quality control, not AI
The most serious problem with AI is the risk of introducing unnoticed errors, leading to sloppy scholarship. Instead of banning AI, we should try to ensure that mistaken, implausible or biased claims cannot make it onto the academic record.
After all, humans can also produce writing with serious errors, and mechanisms such as peer review often fail to prevent its publication.
We need to get better at ensuring academic papers are free from serious mistakes, regardless of whether these mistakes are caused by careless use of AI or sloppy human scholarship. Not only is this more achievable than policing AI usage, it will improve the standards of academic research as a whole.
This would be (as ChatGPT might say) a commendable and meticulously intricate solution.
Provided by The Conversation
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Researchers use AI to boost image quality of metalens camera
27 minutes ago

Research examines how embryonic development decisions are controlled by multiple pathways simultaneously
36 minutes ago

Polyglycerol coating offers safer nanoparticle environmental remediation

Iron-sulfur minerals may bear witness to first microbes on Earth that lived billions of years ago
How high-pressure techniques can induce changes in crystalline materials

Scientists control daily biological clock of algae, advancing biomedicine
How neighboring whales learn each other's language
Physicists demonstrate first metro-area quantum computer network in Boston

Unwrapping the origin story of the baobab
Scientists discover some mice are monogamous due to previously unknown hormone-generating cells
Relevant physicsforums posts, is "college algebra" really just high school "algebra ii".
22 hours ago
Physics education is 60 years out of date
Plagiarism & chatgpt: is cheating with ai the new normal, physics instructor minimum education to teach community college.
May 11, 2024
Studying "Useful" vs. "Useless" Stuff in School
Apr 30, 2024
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Apr 29, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

AI-generated academic science writing can be identified with over 99% accuracy
Jun 7, 2023

ChatGPT maker fields tool for spotting AI-written text
Feb 1, 2023
Is the genie out of the bottle? Can you trust ChatGPT in scientific writing?
Oct 19, 2023

What is ChatGPT: Here's what you need to know
Feb 16, 2023

Tool detects AI-generated text in science journals
Nov 7, 2023
Could artificial intelligence help or hurt medical research articles?
Feb 6, 2024
Recommended for you

Investigation reveals varied impact of preschool programs on long-term school success
May 2, 2024

Training of brain processes makes reading more efficient
Apr 18, 2024

Researchers find lower grades given to students with surnames that come later in alphabetical order
Apr 17, 2024

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024

More than money, family and community bonds prep teens for college success: Study
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

19 Different Types of Malware Attacks: Examples & Defenses
Kaye Timonera
eSecurity Planet content and product recommendations are editorially independent. We may make money when you click on links to our partners. Learn More .
Malware, short for malicious software, is any unwanted software that is designed to disrupt, damage, or gain illegal access to computer systems and networks. Malware may take many different forms, such as viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, adware, and many other types.
Malware typically enters computer systems through malicious emails, attachments, downloads, links, and ads, often taking advantage of unpatched vulnerabilities and inadequate security defenses. We’ll discuss 19 different types of malware in-depth, including examples of cyber attacks that used them and the steps you need to take to protect against each, followed by some general malware protections for businesses and individuals. Below is a chart summarizing each malware type, with a link to a deeper discussion below.
If you’ve been hit by malware and are looking for help, see How to Remove Malware: Removal Steps for Windows & Mac .
Featured Partners

Adware is a type of malware that downloads or displays advertisements to the user interface. Rather than stealing data, adware is more of an irritant, forcing users to see unwanted ads. Many users are familiar with adware in the form of unclosable browser pop-ups. Users sometimes unknowingly infect themselves with adware installed by default when they download and install other applications.
Risks of Adware Attacks
Adware not only shows unwanted advertisements but may also track user activity in great detail and create backdoors and other windows for future attacks. It can gather information about surfing behavior, search history, and even personal information. This data is frequently sold to advertisers, resulting in a loss of privacy and the possibility of targeted fraud.
How To Defend Against Adware
Install an antivirus solution that includes anti-adware capabilities. Enable ad blockers and disable pop-ups on your browsers, and pay close attention to the installation process when installing new software, making sure to un-select any boxes that will install additional software by default. And a somewhat different category: Be careful with online ads too, as malvertising campaigns have appeared in even the best known ad networks like Google . Adware is perhaps more of a mobile malware issue these days, but malvertising has been on the rise across the board. Regardless of trends, always be sure to only download from or visit known entities.
Real Examples of Adware Attacks
While there are hundreds of different types of adware, some of the most prevalent adware attacks include Fireball, Appearch, DollarRevenue, Gator, and DeskAd. These adware outbreaks frequently appear as a video, banner, full-screen, or other pop-up annoyance.
A backdoor is a trojan that offers an attacker remote access into the victim’s device. Most device or software manufacturers place backdoors in their products intentionally, so company personnel or law enforcement can use the backdoor to access the system if needed. However, in a bad actor’s hands, a backdoor can do anything the user does. Backdoors can also be installed by other types of malware, such as viruses or rootkits.
Risks of Backdoor Attacks
Backdoors can provide illegal access to networks and systems, allowing attackers to enter networks and systems invisibly. Cybercriminals can exploit them to maintain control, steal sensitive data, or launch long-term assaults undetected.
How To Defend Against Backdoors
Backdoors are among the most challenging types of threats to protect against. For businesses, experts say the best defense is a multi-pronged network security strategy that includes a firewall , anti-malware or EDR software, network monitoring , SIEM systems , intrusion detection and prevention (IDPS), and data protection. For individual users, the best defenses will be good antivirus software and timely updates, plus a properly configured home router .
Also read: How to Prevent Malware: 15 Best Practices for Malware Prevention
Real Examples of Backdoor Attacks
Microsoft SQL Server experienced a major backdoor malware attack in late 2022. DoublePulsar, an NSA-developed malware implant, was leaked by Shadow Brokers in 2017 and infects Windows systems. ShadowPad, a sophisticated backdoor malware, was discovered in 2017 embedded in software products like CCleaner, providing remote access for attackers to steal sensitive data. It is associated with the threat group APT17 and has been involved in high-profile cyberattacks targeting intellectual property and financial information. Backdoors, intentional or not, have also been discovered by security researchers; a recent one was found in PowerShell .
Bots and Botnets
Bots are software performing automated tasks, making attacks known as “botnets” overwhelming for victims. In cybersecurity, a bot typically refers to an infected device containing malicious software. Without the user’s knowledge or permission, a bot can corrupt the device. Botnet attacks are targeted efforts by an army of bots, directed by their bot herder.
Risks of Botnet Attacks
Bots, particularly when organized into botnets, have the ability to execute orders on a vast scale. They are capable of launching distributed denial-of-service ( DDoS ) attacks, which overwhelm servers and render websites or services unreachable. Bots can also commit identity theft, credit card fraud, and other sorts of online crime.
How To Defend Against Botnets
Organizations can help prevent their computers from becoming part of a botnet by installing anti-malware or EDR software, using firewalls , keeping software up-to-date via patch management , and forcing users to use strong passwords. Network monitoring software can also help determine when a system has become part of a botnet, and botnet protection and DDoS solutions are essential for critically important systems. Always change the default passwords for any IoT devices you install before use.
Real Examples of Botnet Attacks
While botnets may be best known for their role in DDoS attacks, their growing sophistication in fraud and credential theft are possibly even more alarming. Meanwhile, botnets remain quite active in DDoS attacks, with Mirai perhaps the most frequently mentioned. Cybercriminals continue to evolve here too, witness the recent record DDoS attacks based on a widespread HTTP/2 protocol flaw.
See our articles on stopping and preventing DDoS attacks
Browser Hijacker
A browser hijacker also called “hijackware,” noticeably changes the behavior of your web browser. This change could be sending you to a new search page, slow-loading, changing your homepage, installing unwanted toolbars, directing you to sites you did not intend to visit, and displaying unwanted ads. Attackers can make money off advertising fees, steal information from users, spy, or direct users to websites or apps that download more malware.
Risks of Browser Hijacker Attacks
Browser hijackers can not only reroute users but also change search results and introduce malicious advertisements. They can direct visitors to phishing sites, where personal information such as login passwords and financial information can be stolen, resulting in serious security breaches.
How To Defend Against Browser Hijacker
Be careful when installing new software and browser extensions on your system. Many browser hijackers piggyback on wanted software, much like adware does. Ensure you install and run anti-malware software on your system and maintain high-security settings for browser activity.
Because hijackware is related to your browser, therein lies the solution to exterminating a browser hijacker. If your antivirus software fails to notice a new strain, you can reinstall the browser. If that fails to work, clearing the contents of the device might be required. Follow browser security rankings from time to time; as of this writing, Firefox is well regarded.
Real Examples of Browser Hijacker Attacks
Ask Toolbar, Conduit, CoolWebSearch, Coupon Saver, GoSave, and RockTab are a few noteworthy browser hijackers. These browser hijackers often take the shape of an additional toolbar, and because they are frequently included in software downloads, consumers are often unaware of their potential danger.
Bugs are a generic term for flaws in segments of code. All software has bugs, and most go unnoticed or are mildly impactful to the user. Sometimes, however, a bug represents a severe security vulnerability, and using software with this type of bug can open your system up to attacks.
Risks of Bug Attacks
Attackers can use bugs to obtain unauthorized access to systems. Depending on the nature of the problem, it might cause system crashes, data theft and corruption, or alteration of vital files, posing serious threats to a system’s stability and security.
How To Defend Against Bugs
The best way to minimize potentially nasty bugs is consistent updates for your software. With vulnerabilities at the top of software vendors’ minds, they are usually quick to release patches to prevent user system damage. For organizations writing or configuring their code, it’s imperative to follow best practices for secure code and potentially seek third-party review. On the dev side, code security tools can also help.
Real Examples of Bug Attacks
The Y2K issue, also known as the Millennium Bug or Year 2000 Problem, was a significant computer bug-related concern due to its global scope, widespread fear, technological dependence, complex interconnected systems, massive preparations, and unprecedented media coverage. Fortunately that turned out to be a relatively benign issue, but there are more than 20,000 new vulnerabilities discovered every year. To stay on top of them, follow our frequent vulnerability reports , the best known of which is Microsoft’s Patch Tuesday updates on the second Tuesday of every month.
Some vendors use “crimeware” to refer to malware that is criminally executed and often financially benefits the attacker. Much like malware, it is an inclusive category that encompasses a wide variety of malicious software. Unlike ransomware , it might be a criminal operation that does not involve the collection of a ransom. As a term, crimeware encompasses much of the malware types listed in this article.
Risks of Crimeware Attacks
Crimeware is particularly developed for monetary gain. It contains a variety of infections, including banking trojans and credit card stealers. These threats are often aimed at financial institutions and users, resulting in financial losses, hacked accounts, and a loss of faith in online transactions.
How To Defend Against Crimeware
For businesses, best network security practices are essential, including using anti-malware, firewalls, intrusion prevention and detection (IPDS), network and log monitoring, data protection, security information and event management (SIEM), and threat intelligence .
For individuals, the usual best practices apply: good antivirus software, timely updates, good router security, and most of all, if you don’t know what it is, don’t click on it.
Real Examples of Crimeware Attacks
Because crimeware is an umbrella term for most malware types, the examples are endless. Some malware like keyloggers and backdoors come with the product design for later maintenance of the device. All crimeware programs are inherently malicious, and their successful activation is prosecutable.
Fileless Malware
Fileless malware, also known as non-malware or memory-resident malware, operates without relying on executable files on a victim’s system. It resides in the system’s memory or uses legitimate system tools, making it harder to detect and remove. It often exploits scripting languages, macros, or other programs, often delivered through malicious email attachments, compromised websites, or phishing attacks. Once executed, fileless malware can exploit vulnerabilities to execute malicious actions, such as stealing sensitive information or initiating unauthorized transactions.
Risks of Fileless Malware Attacks
Fileless malware operates in computer memory, avoiding detection by regular antivirus software. It leaves no traces on the file system, making analysis and removal difficult, allowing attackers to maintain persistent access and carry out covert operations.
How To Defend Against Fileless Malware
To reduce the risk of fileless malware infections, both users and organizations should follow the security best practices we’ve already discussed. Detection of fileless malware can be difficult. Enterprises should look for behavioral anomalies and other indicators of compromise such as abnormal code execution and lateral movement. These are good things to look for in threat hunting exercises too. The good news is that EDR and even consumer antivirus software are getting better at behavioral detection. The bad news is that fileless malware is difficult to remove; for Windows users, Autoruns and Process Explorer may help.
Real Examples of Fileless Attacks
Fileless malware assaults have been present for a while, but they became more common in 2017. Frodo, Number of the Beast, and The Dark Avenger were early examples of fileless malware. The Democratic National Committee hack and the Equifax breach are two recent high-profile fileless attacks. This is one area where hackers continue to evolve, witness reports last year that Windows Event Logs had become a source of fileless malware. The use of legitimate tools like PowerShell and Windows Event Logs for cyber attacks is also part of the growing tactics of Living off the Land (LOTL) attacks.
A keylogger is a software program that records all of the keys a user touches. This exposed data includes everything from emails and documents typed to passwords entered for authentication purposes. By obtaining sensitive authentication credentials, attackers can break into a victim’s network or user accounts.
Risks of Keylogger Attacks
Keyloggers discreetly record keystrokes, acquiring sensitive data such as passwords and credit card information, and can lead to identity theft or illegal access to critical systems.
How To Defend Against Keyloggers
Good password hygiene is one of the best ways to prevent access to keyloggers. Using strong passwords that you update regularly can go a long way towards keeping you safe. Firewalls and anti-malware solutions can help, but keyloggers are also a good argument in favor of using biometric authentication , or at least MFA that uses a second device for authentication.
Real Examples of Keylogger Attacks
Keylogging is often used by vendors and organizations working with sensitive information. Employers can enable a keylogger through hardware or software to detect any criminal or unethical behavior on company systems. For malicious keyloggers outside your organization, initial access to a device or user’s account would be necessary, typically through a malicious download.
A strain of keylogger malware dubbed LokiBot notably increased in 2020. CISA reported that LokiBot “employs Trojan malware to steal sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, cryptocurrency wallets, and other credentials.” Just this year, security researchers demonstrated how AI could be used to steal keystrokes.
Malicious Mobile Apps
In the sea of apps available today, not all of them are desirable, and the problem is even more acute with third-party app stores. While app store vendors try to prevent malicious apps from becoming available, some inevitably slip through, occasionally even through Apple’s App Store and the Google Play Store. Malicious mobile apps can steal user information, attempt to extort money from users, gain access to corporate networks, force users to view unwanted ads or engage in other undesirable activity types.
Risks of Malicious Mobile App Attacks
Malicious mobile apps can steal data or damage device operation. They frequently seek overly broad permissions, allowing them to access personal information, communications, or location data, jeopardizing user privacy.
How To Defend Against A Malicious Mobile App
User education is one of the most powerful tools for preventing malicious mobile apps. By avoiding third-party app stores and investigating app data before downloading, users can significantly mitigate this risk. Deploying mobile anti-malware and company-wide mobile security management is essential for large organizations. This is one place where paying for mobile antivirus software is absolutely worth the cost, and pay attention to reports of malicious apps to make sure you don’t have any installed on your devices.
Real Examples of Malicious Mobile Apps Attacks
Google Play Store was hit by a banking trojan earlier this year. Google has taken steps to make Play Store more secure , but all mobile users should still exercise caution, keep devices updated, and use a paid anti-malware solution; free versions typically offer little.
Learn more about mobile malware
Phishing and Social Engineering
Phishing and social engineering are a type of email attack that attempts to trick users into divulging passwords, downloading an attachment, or visiting a website that installs malware on their systems. More targeted efforts at specific users are known as spear phishing . Because the goal is to trick the user, attackers will research the victim to maximize trick potential, often using spoofing to make the email seem legitimate.
Risks of Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Phishing and social engineering are deceptive techniques that can trick victims into disclosing sensitive information or other undesirable outcomes. Attackers utilize psychological manipulation to trick users into revealing private data, leading to identity theft, unlawful access and other cybersecurity issues.
How To Defend Against Phishing and Social Engineering
Because phishing relies on social engineering — tricking users into doing something — employee training is one of the best defenses against these attacks. Users should deploy anti-spam and anti-malware solutions, and staff should know not to divulge personal and financial information or passwords in email messages. Training users to avoid downloading attachments or clicking website links in messages, even if they appear to come from a known source, is imperative given phishing attackers often pretend to be a company or person known to the victim. Email is also a common attack vector for ransomware.
Real Examples of Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Ram scraper.
RAM scraper malware, also known as Point-of-Sale (POS) malware , harvests data temporarily stored in a system’s memory, also known as random access memory (RAM). This type of malware targets POS systems like cash registers or vendor portals where an attacker can access unencrypted credit card numbers. While this sensitive payment data is only available for milliseconds before passing the encrypted numbers to back-end systems, attackers can still access millions of records.
Risks of RAM Scraper Attacks
RAM Scraper uses computer memory to retrieve sensitive information such as credit card numbers during transactions. Attackers obtain access to payment information by intercepting data in real-time, resulting in financial theft and hurting client trust.
How To Defend Against Ram Scraper Attacks
Organizations can help prevent RAM scraper attacks by using hardened POS systems and separating payment-related systems from non-payment systems. Usual precautions such as anti-malware software, firewalls, data encryption, and complying with any relevant standards or regulations for protecting customer data are a must.
Real Examples of RAM Scraper Attacks
Home Depot and Target were hit by RAM scraping techniques in two of the largest-ever data breaches in 2014. The Home Depot attack, discovered in September 2014, compromised over 50 million customer records, and the Target attack, discovered in December 2014, resulting in over 40 million. The attacks underscored the need for ongoing vigilance by both businesses and consumers.
Ransomware has quickly become one of the scariest and most prevalent types of malware. The most common malware variants encrypt a system or specific files, stopping any work from being done until the victim pays a ransom to the attacker — even though the decryption keys provided by attackers often don’t work. Other forms of ransomware threaten to publicize sensitive information within the encrypted or stolen data.
Risks of Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware encrypts files and demands money for decryption, frequently resulting in data loss and financial harm. “ Double extortion ” attacks carry the added risk of sensitive data exposure and reputational damage.
How To Defend Against Ransomware Attacks
Often organizations and users can mitigate ransomware attacks by having up-to-date, immutable, air-gapped data backups so they can simply wipe the system and reboot from an offline backup. Organizations should train users about the threat, patch their software as necessary, and follow all recommended security best practices.
Real Examples of Ransomware Attacks
The Colonial Pipeline attack that nearly shut down the Eastern U.S. was one of the most dramatic in recent years, but healthcare attacks have perhaps been even more concerning. The Clop ransomware group is one of the newest threats in a long line that includes CryptoLocker , Locky, WannaCry , Hermes, GandCrab, and Ryuk.
Read more about ransomware:
- Ransomware Protection: How to Prevent Ransomware Attacks
- How to Recover From a Ransomware Attack
- Best Ransomware Removal Tools
- Best Ransomware Removal and Recovery Services
- How to Decrypt Ransomware Files – And What to Do When That Fails
Rogue Security Software
Rogue security software is a form of ransomware or scareware. An attacker enabling this method tricks users into thinking their system or device is at risk. The malware program will present itself as a fake security tool to remove the problem at a cost. In actuality, the user pays and the artificial security software installs even more malware onto their systems.
Risks of Rogue Security Software Attacks
Rogue security software dupes users into paying for unneeded services and even giving away their payment info while receiving only further damage. While attempting to delete the fraudulent software, users may unintentionally install further malware, exacerbating the security concern.
How To Defend Against Rogue Security Software Attacks
As with many other malware forms, you can prevent most rogue security software from being installed on your system by using a firewall and anti-malware solution and by being careful when clicking on links or attachments in email messages. Also, organizations should educate users about the threat, as rogue security software attackers have become particularly good at social engineering.
Real Examples of Rogue Security Software Attacks
Some of the most common rogue security software attacks have come in spam campaigns and adware. However, a different infection vector for this malware is the technique known as Black Hat SEO. By following the most popular keywords on the internet through public records like Google Trends, attackers use malicious scripts to generate websites that appear legitimate.
Rootkits are one of the most insidious malware types because they allow attackers to have administrator-level access to systems without users’ knowledge. Once an attacker has root access, they can do almost anything with the system, including recording activity, changing system settings, accessing data, and mounting attacks on other systems.
Risks of Rootkit Attacks
Rootkits are frequently used in persistent, covert attacks. With admin-level control, rootkits have high-level system privileges while circumventing security safeguards, allowing attackers to maintain control over infected computers for lengthy periods of time and enabling a wide range of destructive behaviors, including data and credential theft.
How To Defend Against Rootkit Attacks
You can prevent most rootkit infections by installing appropriate security software (anti-malware, firewall, log monitoring) and keeping your operating system and other software up-to-date with patches. There are rootkit scanning and removal tools , but many of their capabilities can now be found in good EDR and antivirus tools. You should also be careful when installing any software on your system and when clicking on email attachments and links. If a rootkit infects your system, it can be nearly impossible to detect and remove; in many cases, you may have to wipe your hard drive and start over from scratch to get rid of it.
Real Examples of Rootkit Attacks
In IT security, spam is unwanted email. Usually, it includes unsolicited advertisements, but it can also contain attempted fraud, links or attachments that could install malware on your system. Many spam emails contain:
- Poor spelling and grammar
- An unusual sender address
- Unrealistic claims
- Links that look risky
However, AI tools and chatbots have made crafting email attacks easier, requiring even more caution on the part of end users.
Risks of Spam
These unwanted, bulk emails clutter inboxes by containing harmful links or schemes. Clicking on spam links can take you to phishing sites, malware downloads, or scams, all of which can compromise your personal and financial information.
How To Defend Against Spam
Most email solutions or services include anti-spam features, and major email services like Gmail have continually improved at spam detection. Using these capabilities is the best way to prevent spam from showing up on your systems. If your inbox contains thousands of unread emails and a dozen subscriptions no longer pertinent, do yourself a favor and unsubscribe. Businesses should also consider email security tools and other ways to make email more secure .
Real Examples of Spam
Spam might be one of the most universally understood forms of malware. As billions of people use email in their everyday lives, it makes sense that malicious actors try to sneak into your inbox. Some of the most common types of spam emails include fake responses, PayPal, returned mail, and social media, all of which are disguised as legitimate but contain malware.
Spyware is any type of software that gathers information about someone without their knowledge or consent. For example, website tracking cookies that monitor a user’s browsing history is considered a form of spyware. Other types of spyware might attempt to steal personal or corporate information. Government agencies and law enforcement often use spyware to investigate domestic suspects or international threat actors. It is challenging for the user to detect spyware symptoms, ranging from performance issues to unusual modem or router activity.
Risks of Spyware Attacks
Spyware secretly monitors user actions, gathering personal information, passwords, surfing patterns, location and more. As attackers get access to critical information without the user’s awareness, it can lead to identity theft, privacy breaches, and financial losses. In cases of political surveillance, spyware can endanger opponents of authoritarian regimes, as happened with the NSO Group’s Pegasus spyware in Apple iPhones .
How To Defend Spyware Attacks
Install anti-spyware software on your computer. Luckily, anti-spyware capabilities are included in most antivirus or anti-malware packages, but in the case of a sophisticated foe, spyware can still be difficult to detect. Using a firewall and caution when downloading software is a must. And finally, scanning for potential threats often can be a lifesaver. Amnesty International published a detailed article on detecting Pegasus spyware and released a forensics tool for mobile devices .
Real Examples of Spyware Attacks
Adware, trojans, keyloggers, and rootkits are common forms of spyware. CoolWebSearch, Gator, Internet Optimizer, TIBS Dialer, and Zlob are some of the most well-known spyware strains. CoolWebSearch, for example, utilizes browser flaws to redirect traffic to advertising, infect host files, and rewrite search engine results. In the case of the iPhone spyware exploit, Apple patched its devices , but the incident showed that nothing is safe from determined, sophisticated hackers.
In computer security, a trojan is any malware that pretends to be something else but serves a malicious purpose. For example, a trojan might appear to be a free game, but once installed, it might destroy your hard drive, steal data, install a backdoor, or take other harmful actions.
Risks of Trojan Attacks
A Trojan is often disguised as legitimate software, but once installed it enables unwanted access and control. Trojans can download additional malware, steal sensitive data, or provide attackers backdoor access to an infected machine, creating severe security threats.
How To Defend Against Trojan Attacks
Because trojans use social engineering for targeted attacks, educating users is imperative. Caution when installing new software or clicking email links and attachments is the name of the game. Organizations can defend against most trojans with security software such as anti-malware software and sufficient firewalls.
Real Examples of Trojan Attacks
While some refer to malware and viruses interchangeably, a virus is a specific type of malware that requires human activation — a click on an attachment, image, link, or even a file you access every day. Often hidden, a click by someone could unknowingly boot up a virus. Viruses infect a device and then attempt to spread to other devices and systems.
Risks of Virus Attacks
As far as damage to the user goes, a virus can perform several undesirable commands. These include:
- Incorporating systems into a botnet
- Sending spam to contacts
- Stealing sensitive information
- Locking the system
- Deleting or damaging files and programs
How To Defend Virus Attacks
Any internet-enabled system in your network should have antivirus software installed and up-to-date. Deploying a firewall is essential, but also use care when clicking on email attachments or URL links. Inspecting website security by its SSL is imperative to avoid visiting unknown or untrusted websites.
Real Examples of Virus Attacks
Also Read: Antivirus vs. EPP vs. EDR: How to Secure Your Endpoints
A worm is similar to a virus because it spreads itself, but a worm does not need an attacker’s permission for activation. Instead, it is a standalone piece of malware that extends within a system or network. Like viruses, it can cause just as much damage to the device.
Risks of Worm Attacks
Worms are self-replicating malware that spread over networks, wasting bandwidth, interfering with services, and swiftly infecting a large number of devices, potentially resulting in a loss of vital services.
How To Defend Worm Attacks
As with viruses, the best way to prevent worm infections is with antivirus or anti-malware software. And as always, users should only click on email links or attachments when confident of the contents.
Real Examples of Worm Attacks
Defending against all types of malware.
Defending against various types of malware necessitates a comprehensive strategy that includes proactive and reactive measures. Here are key approaches for safeguarding your systems and devices from malware.
Utilize Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Install trustworthy antivirus and anti-malware programs on each of your devices. Also, ensure these tools are regularly updated to identify and remove the latest threats.
Keep Software Updated
Keep your operating system, software, and applications up-to-date, as outdated software often contains vulnerabilities that malware exploits.
Educate Users
Train users to recognize common malware delivery methods, like phishing emails and dubious websites. Encourage caution when interacting with emails, files or links from unknown sources.
Implement Firewalls
Use firewalls to block malicious inbound and outbound traffic. Regularly configure firewalls to limit unnecessary ports and services. For individual users, make sure your router is secure and properly configured, and activate firewalls on your router and/or laptop.
Enhance Email Security
Employ robust email security measures to filter out spam, phishing emails, and malicious attachments. Advise users to exercise caution with email attachments or links, especially from unfamiliar senders.
Secure Web Browsing
Utilize web security tools such as gateways to prevent access to malicious websites. In addition, educate users about the risks associated with visiting suspicious sites.
Strengthen Network Security
Segment your network to minimize lateral movement within your organization. Deploy intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor network traffic for signs of malicious activity.
Application Whitelisting
Consider using application whitelisting to permit only authorized software to run. This reduces the chance of unauthorized or malicious applications executing.
Adopt Least Privilege
Limit user and system privileges to the minimum required for their tasks, also known as zero trust . This minimizes the potential impact if a system or account is compromised.
Regular Data Backups
Create regular automated, immutable backups of crucial data. In the case of malware, clean backups enable restoration of systems and data.
Utilize Behavior Analysis
Employ security software utilizing behavior analysis to identify and block malware based on actions and characteristics, not just signatures.
Develop an Incident Response Plan
Establish and routinely test an incident response plan to react swiftly and efficiently to malware incidents. Isolate infected systems and take necessary actions to eliminate the malware.
Manage Patches
Establish a patch management process to promptly apply security updates, as many malware attacks exploit unpatched vulnerabilities.
Ensure Mobile Device Security
Apply good security practices to mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to guard against mobile malware. Employ mobile security solutions and remote device management tools.
Monitor and Use Threat Intelligence
Continuously monitor your network for signs of malicious activity. Stay updated on the latest malware threats and trends through reliable threat intelligence sources.
Bottom Line: Prepare For All Malware Types
To protect against malware, it’s crucial to have up-to-date antivirus and anti-malware solutions, and regularly update operating systems, software, and applications. Educate your team about common cybercriminal tactics and promote a security-conscious culture. Firewalls, web and email security tools, and advanced technologies like behavior analysis can help block unauthorized traffic and access. A robust data backup system is essential.
Establish a well-defined incident response plan, outlining steps for isolating systems, removing malware, and restoring data from backups. Regular testing ensures swift and effective response. Stay informed about emerging malware trends and adapt your cybersecurity strategy as threats evolve.
By fostering a security-conscious culture, implementing robust technical defenses, and having a well-rehearsed incident response plan, you can significantly enhance your organization’s resilience against malware threats.
Read next: How You Get Malware: 8 Ways Malware Creeps Onto Your Device
This updates a February 2021 article by Sam Ingalls
Get the Free Cybersecurity Newsletter
Strengthen your organization’s IT security defenses by keeping up to date on the latest cybersecurity news, solutions, and best practices. Delivered every Monday, Tuesday and Thursday
Previous article
Next article

Subscribe to Cybersecurity Insider
Strengthen your organization’s IT security defenses by keeping abreast of the latest cybersecurity news, solutions, and best practices.
IT Security Resources
Vulnerability recap 5/13/24 – f5, citrix & chrome.

Network Protection: How to Secure a Network in 13 Steps

How to Block a Program in a Firewall (Windows & Mac)

Vulnerability Recap 5/6/24 – Aruba, Dropbox, GitLab Bugs

Top Cybersecurity Companies
Top 10 cybersecurity companies.
- 1 Uniqkey – Business Password Manager
See full list
Get the Free Newsletter!
Subscribe to Cybersecurity Insider for top news, trends & analysis
Related Articles

2024 State of Cybersecurity: Reports of More Threats & Prioritization Issues
New machine learning algorithm promises advances in computing
Digital twin models may enhance future autonomous systems.
Systems controlled by next-generation computing algorithms could give rise to better and more efficient machine learning products, a new study suggests.
Using machine learning tools to create a digital twin, or a virtual copy, of an electronic circuit that exhibits chaotic behavior, researchers found that they were successful at predicting how it would behave and using that information to control it.
Many everyday devices, like thermostats and cruise control, utilize linear controllers -- which use simple rules to direct a system to a desired value. Thermostats, for example, employ such rules to determine how much to heat or cool a space based on the difference between the current and desired temperatures.
Yet because of how straightforward these algorithms are, they struggle to control systems that display complex behavior, like chaos.
As a result, advanced devices like self-driving cars and aircraft often rely on machine learning-based controllers, which use intricate networks to learn the optimal control algorithm needed to best operate. However, these algorithms have significant drawbacks, the most demanding of which is that they can be extremely challenging and computationally expensive to implement.
Now, having access to an efficient digital twin is likely to have a sweeping impact on how scientists develop future autonomous technologies, said Robert Kent, lead author of the study and a graduate student in physics at The Ohio State University.
"The problem with most machine learning-based controllers is that they use a lot of energy or power and they take a long time to evaluate," said Kent. "Developing traditional controllers for them has also been difficult because chaotic systems are extremely sensitive to small changes."
These issues, he said, are critical in situations where milliseconds can make a difference between life and death, such as when self-driving vehicles must decide to brake to prevent an accident.
The study was published recently in Nature Communications.
Compact enough to fit on an inexpensive computer chip capable of balancing on your fingertip and able to run without an internet connection, the team's digital twin was built to optimize a controller's efficiency and performance, which researchers found resulted in a reduction of power consumption. It achieves this quite easily, mainly because it was trained using a type of machine learning approach called reservoir computing.
"The great thing about the machine learning architecture we used is that it's very good at learning the behavior of systems that evolve in time," Kent said. "It's inspired by how connections spark in the human brain."
Although similarly sized computer chips have been used in devices like smart fridges, according to the study, this novel computing ability makes the new model especially well-equipped to handle dynamic systems such as self-driving vehicles as well as heart monitors, which must be able to quickly adapt to a patient's heartbeat.
"Big machine learning models have to consume lots of power to crunch data and come out with the right parameters, whereas our model and training is so extremely simple that you could have systems learning on the fly," he said.
To test this theory, researchers directed their model to complete complex control tasks and compared its results to those from previous control techniques. The study revealed that their approach achieved a higher accuracy at the tasks than its linear counterpart and is significantly less computationally complex than a previous machine learning-based controller.
"The increase in accuracy was pretty significant in some cases," said Kent. Though the outcome showed that their algorithm does require more energy than a linear controller to operate, this tradeoff means that when it is powered up, the team's model lasts longer and is considerably more efficient than current machine learning-based controllers on the market.
"People will find good use out of it just based on how efficient it is," Kent said. "You can implement it on pretty much any platform and it's very simple to understand." The algorithm was recently made available to scientists.
Outside of inspiring potential advances in engineering, there's also an equally important economic and environmental incentive for creating more power-friendly algorithms, said Kent.
As society becomes more dependent on computers and AI for nearly all aspects of daily life, demand for data centers is soaring, leading many experts to worry over digital systems' enormous power appetite and what future industries will need to do to keep up with it.
And because building these data centers as well as large-scale computing experiments can generate a large carbon footprint, scientists are looking for ways to curb carbon emissions from this technology.
To advance their results, future work will likely be steered toward training the model to explore other applications like quantum information processing, Kent said. In the meantime, he expects that these new elements will reach far into the scientific community.
"Not enough people know about these types of algorithms in the industry and engineering, and one of the big goals of this project is to get more people to learn about them," said Kent. "This work is a great first step toward reaching that potential."
This study was supported by the U.S. Air Force's Office of Scientific Research. Other Ohio State co-authors include Wendson A.S. Barbosa and Daniel J. Gauthier.
- Electronics
- Telecommunications
- Energy Technology
- Computers and Internet
- Neural Interfaces
- Information Technology
- Computer Science
- Artificial intelligence
- Alan Turing
- Computing power everywhere
- Grid computing
- Data mining
Story Source:
Materials provided by Ohio State University . Original written by Tatyana Woodall. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Robert M. Kent, Wendson A. S. Barbosa, Daniel J. Gauthier. Controlling chaos using edge computing hardware . Nature Communications , 2024; 15 (1) DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-48133-3
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Nature's 3D Printer: Bristle Worms
- Giant ' Cotton Candy' Planet
- A Young Whale's Journey
- No Inner Voice Linked to Poorer Verbal Memory
- Bird Flu A(H5N1) Transmitted from Cow to Human
- Universe's Oldest Stars in Our Galactic Backyard
- Polygenic Embryo Screening for IVF: Opinions
- VR With Cinematoghraphics More Engaging
- 2023 Was the Hottest Summer in 2000 Years
- Fastest Rate of CO2 Rise Over Last 50,000 Years
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.

COMMENTS
Research problem is a specific and well-defined issue or question that a researcher seeks to investigate through research. It is the starting point of any research project, as it sets the direction, scope, and purpose of the study. Types of Research Problems. Types of Research Problems are as follows: Descriptive problems
Casual research problem. Relational research problem. Aim/purpose. The aim is to depict what already exists in a group of the population. To identify the extent and nature of cause and effect relationships. The aim is to investigate the qualities or characteristics that are connected in some way or the other.
Here, the goal is to find strategies that can be used to address a specific research problem. Applied research draws on theory to generate practical scientific knowledge, and its use is very common in STEM fields such as engineering, computer science and medicine. This type of research is subdivided into two types:
Characteristics, Types, and Examples. August 22, 2023 Sunaina Singh. Knowing the basics of defining a research problem is instrumental in formulating a research inquiry. A research problem is a gap in existing knowledge, a contradiction in an established theory, or a real-world challenge that a researcher aims to address in their research.
A research problem is a specific issue or gap in existing knowledge that you aim to address in your research. You may choose to look for practical problems aimed at contributing to change, or theoretical problems aimed at expanding knowledge. Some research will do both of these things, but usually the research problem focuses on one or the other.
A research problem can be theoretical in nature, focusing on an area of academic research that is lacking in some way. Alternatively, a research problem can be more applied in nature, focused on finding a practical solution to an established problem within an industry or an organisation. In other words, theoretical research problems are motivated by the desire to grow the overall body of ...
A research problem is a definite or clear expression [statement] about an area of concern, a condition to be improved upon, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or within existing practice that points to a need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation.
Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples. Published on June 20, 2019 by Shona McCombes.Revised on June 22, 2023. When you start planning a research project, developing research questions and creating a research design, you will have to make various decisions about the type of research you want to do.. There are many ways to categorize different types of research.
A Research Problem is Not a Thesis Statement. A thesis statement and a research problem are two different parts of the introduction section of your paper. The thesis statement succinctly describes in one or two sentences, usually in the last paragraph of the introduction, what position you have reached about a topic. It includes an assertion ...
Research Problem - In a Nutshell. A research problem is an issue that raises concern about a particular topic. Researchers formulate research problems by examining other literature on the topic and assessing the significance and relevance of the problem.; Creating a research problem involves an overview of a broad problem area and then narrowing it down to the specifics by creating a ...
Here, in this article, we explore a research problem in a dissertation or an essay with some research problem examples to help you better understand how and when you should write a research problem. "A research problem is a specific statement relating to an area of concern and is contingent on the type of research.
45 Research Problem Examples & Inspiration. A research problem is an issue of concern that is the catalyst for your research. It demonstrates why the research problem needs to take place in the first place. Generally, you will write your research problem as a clear, concise, and focused statement that identifies an issue or gap in current ...
Related: 19 Types of Research (With Definitions and Examples) 3 types of research problems Here are three types of research problems that can help you decide on the best format to use: 1. Theoretical research problems Theoretical research problems allow you to contribute to the overall information and knowledge in an area of study. These kinds ...
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
This research focuses on a defined problem and is solution-based. Show Transcript. Video: Types of Research: Definitions and Examples Data-informed decisions are critical to a successful business. Research is the first step in collecting data. This video breaks down two main types of research: applied and fundamental research. ...
Research is the careful consideration of study regarding a particular concern or research problem using scientific methods. According to the American sociologist Earl Robert Babbie, "research is a systematic inquiry to describe, explain, predict, and control the observed phenomenon. It involves inductive and deductive methods.".
It is an important planning phase that outlines the research methodology, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques that will be used to investigate a research question or problem. The research design helps to ensure that the research is conducted in a systematic and logical manner, and that the data collected is relevant and reliable.
Various market research methods can be used, such as interviews, ethnography, survey research, social monitoring, and customer journey research. Here are some of the characteristics you should understand through consumer insights research: Purchase habits. Interests, hobbies, passions.
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
This Mental Health Awareness Week, we highlight the remarkable work of scientists driving open research that helps everyone achieve better mental health. Here are five Research Topics that study themes including how we adapt to a changing world, the impact of loneliness on our wellbeing, and the connection between our diet and mental health.
A research problem is a specific issue or gap in existing knowledge that you aim to address in your research. You may choose to look for practical problems aimed at contributing to change, or theoretical problems aimed at expanding knowledge. Some research will do both of these things, but usually the research problem focuses on one or the other.
Many people are worried by the use of AI in academic papers. Indeed, the practice has been described as "contaminating" scholarly literature. Some argue that using AI output amounts to plagiarism ...
Summary of H.R.8377 - 118th Congress (2023-2024): To amend the Advancing Research to Prevent Suicide Act to expand the areas of focus regarding childhood suicide, and for other purposes.
Email attack that attempts to trick users into divulging passwords, downloading an attachment, or visiting a website that installs malware. Deceptive Phishing, Spear Phishing, Whaling, Vishing ...
Step 1: Consider your aims and approach. Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method. Step 4: Choose your data collection methods. Step 5: Plan your data collection procedures. Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies. Other interesting articles.
Systems controlled by next-generation computing algorithms could give rise to better and more efficient machine learning products, a new study suggests. Using machine learning tools to create a ...
This paper presents a proximal bundle (PB) framework based on a generic bundle update scheme for solving the hybrid convex composite optimization (HCCO) problem and establishes a common iteration-complexity bound for any variant belonging to it. As a ...