

Chapter 13. Participant Observation
Introduction.
Although there are many possible forms of data collection in the qualitative researcher’s toolkit, the two predominant forms are interviewing and observing. This chapter and the following chapter explore observational data collection. While most observers also include interviewing, many interviewers do not also include observation. It takes some special skills and a certain confidence to be a successful observer. There is also a rich tradition of what I am going to call “deep ethnography” that will be covered in chapter 14. In this chapter, we tackle the basics of observational data collection.

What is Participant Observation?
While interviewing helps us understand how people make sense of their worlds, observing them helps us understand how they act and behave. Sometimes, these actions and behaviors belie what people think or say about their beliefs and values and practices. For example, a person can tell you they would never racially discriminate, but observing how they actually interact with racialized others might undercut those statements. This is not always about dishonesty. Most of us tend to act differently than we think we do or think we should. That is part of being human. If you are interested in what people say and believe , interviewing is a useful technique for data collection. If you are interested in how people act and behave , observing them is essential. And if you want to know both, particularly how thinking/believing and acting/behaving complement or contradict each other, then a combination of interviewing and observing is ideal.
There are a variety of terms we use for observational data collection, from ethnography to fieldwork to participant observation . Many researchers use these terms fairly interchangeably, but here I will separately define them. The subject of this chapter is observation in general, or participant observation, to highlight the fact that observers can also be participants. The subject of chapter 14 will be deep ethnography , a particularly immersive form of study that is attractive for a certain subset of qualitative researchers. Both participant observation and deep ethnography are forms of fieldwork in which the researcher leaves their office and goes into a natural setting to record observations that take place in that setting. [1]
Participant observation (PO) is a field approach to gathering data in which the researcher enters a specific site for purposes of engagement or observation. Participation and observation can be conceptualized as a continuum, and any given study can fall somewhere on that line between full participation (researcher is a member of the community or organization being studied) and observation (researcher pretends to be a fly on the wall surreptitiously but mostly by permission, recording what happens). Participant observation forms the heart of ethnographic research, an approach, if you remember, that seeks to understand and write about a particular culture or subculture. We’ll discuss what I am calling deep ethnography in the next chapter, where researchers often embed themselves for months if not years or even decades with a particular group to be able to fully capture “what it’s like.” But there are lighter versions of PO that can form the basis of a research study or that can supplement or work with other forms of data collection, such as interviews or archival research. This chapter will focus on these lighter versions, although note that much of what is said here can also apply to deep ethnography (chapter 14).
PO methods of gathering data present some special considerations—How involved is the researcher? How close is she to the subjects or site being studied? And how might her own social location—identity, position—affect the study? These are actually great questions for any kind of qualitative data collection but particularly apt when the researcher “enters the field,” so to speak. It is helpful to visualize where one falls on a continuum or series of continua (figure 13.1).
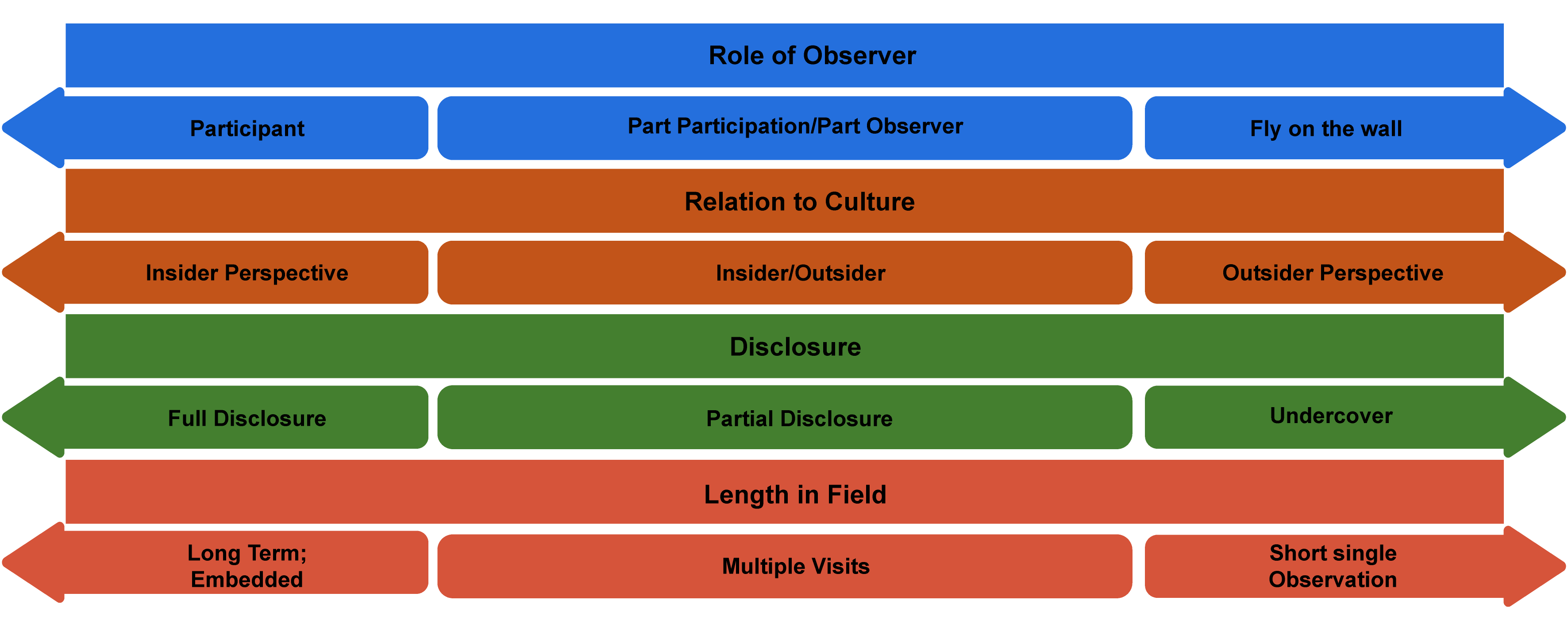
Let’s take a few examples and see how these continua work. Think about each of the following scenarios, and map them onto the possibilities of figure 13.1:
- a nursing student during COVID doing research on patient/doctor interactions in the ICU
- a graduate student accompanying a police officer during her rounds one day in a part of the city the graduate student has never visited
- a professor raised Amish who goes back to her hometown to conduct research on Amish marriage practices for one month
- (What if the sociologist was also a member of the OCF board and camping crew?)
Depending on how the researcher answers those questions and where they stand on the P.O. continuum, various techniques will be more or less effective. For example, in cases where the researcher is a participant, writing reflective fieldnotes at the end of the day may be the primary form of data collected. After all, if the researcher is fully participating, they probably don’t have the time or ability to pull out a notepad and ask people questions. On the other side, when a researcher is more of an observer, this is exactly what they might do, so long as the people they are interrogating are able to answer while they are going about their business. The more an observer, the more likely the researcher will engage in relatively structured interviews (using techniques discussed in chapters 11 and 12); the more a participant, the more likely casual conversations or “unstructured interviews” will form the core of the data collected. [2]
Observation and Qualitative Traditions
Observational techniques are used whenever the researcher wants to document actual behaviors and practices as they happen (not as they are explained or recorded historically). Many traditions of inquiry employ observational data collection, but not all traditions employ them in the same way. Chapter 14 will cover one very specific tradition: ethnography. Because the word ethnography is sometimes used for all fieldwork, I am calling the subject of chapter 14 deep ethnography, those studies that take as their focus the documentation through the description of a culture or subculture. Deeply immersive, this tradition of ethnography typically entails several months or even years in the field. But there are plenty of other uses of observation that are less burdensome to the researcher.
Grounded Theory, in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction, is amenable to both interviewing and observing forms of data collection, and some of the best Grounded Theory works employ a deft combination of both. Often closely aligned with Grounded Theory in sociology is the tradition of symbolic interactionism (SI). Interviews and observations in combination are necessary to properly address the SI question, What common understandings give meaning to people’s interactions ? Gary Alan Fine’s body of work fruitfully combines interviews and observations to build theory in response to this SI question. His Authors of the Storm: Meteorologists and the Culture of Prediction is based on field observation and interviews at the Storm Prediction Center in Oklahoma; the National Weather Service in Washington, DC; and a few regional weather forecasting outlets in the Midwest. Using what he heard and what he observed, he builds a theory of weather forecasting based on social and cultural factors that take place inside local offices. In Morel Tales: The Culture of Mushrooming , Fine investigates the world of mushroom hunters through participant observation and interviews, eventually building a theory of “naturework” to describe how the meanings people hold about the world are constructed and are socially organized—our understanding of “nature” is based on human nature, if you will.
Phenomenology typically foregrounds interviewing, as the purpose of this tradition is to gather people’s understandings and meanings about a phenomenon. However, it is quite common for phenomenological interviewing to be supplemented with some observational data, especially as a check on the “reality” of the situations being described by those interviewed. In my own work, for example, I supplemented primary interviews with working-class college students with some participant observational work on the campus in which they were studying. This helped me gather information on the general silence about class on campus, which made the salience of class in the interviews even more striking ( Hurst 2010a ).
Critical theories such as standpoint approaches, feminist theory, and Critical Race Theory are often multimethod in design. Interviews, observations (possibly participation), and archival/historical data are all employed to gather an understanding of how a group of persons experiences a particular setting or institution or phenomenon and how things can be made more just . In Making Elite Lawyers , Robert Granfield ( 1992 ) drew on both classroom observations and in-depth interviews with students to document the conservatizing effects of the Harvard legal education on working-class students, female students, and students of color. In this case, stories recounted by students were amplified by searing examples of discrimination and bias observed by Granfield and reported in full detail through his fieldnotes.
Entry Access and Issues
Managing your entry into a field site is one of the most important and nerve-wracking aspects of doing ethnographic research. Unlike interviews, which can be conducted in neutral settings, the field is an actual place with its own rules and customs that you are seeking to explore. How you “gain access” will depend on what kind of field you are entering. If your field site is a physical location with walls and a front desk (such as an office building or an elementary school), you will need permission from someone in the organization to enter and to conduct your study. Negotiating this might take weeks or even months. If your field site is a public site (such as a public dog park or city sidewalks), there is no “official” gatekeeper, but you will still probably need to find a person present at the site who can vouch for you (e.g., other dog owners or people hanging out on their stoops). [3] And if your field site is semipublic, as in a shopping mall, you might have to weigh the pros and cons of gaining “official” permission, as this might impede your progress or be difficult to ascertain whose permission to request. If you recall, many of the ethical dilemmas discussed in chapter 7 were about just such issues.
Even with official (or unofficial) permission to enter the site, however, your quest to gain access is not done. You will still need to gain the trust and permission of the people you encounter at that site. If you are a mere observer in a public setting, you probably do not need each person you observe to sign a consent form, but if you are a participant in an event or enterprise who is also taking notes and asking people questions, you probably do. Each study is unique here, so I recommend talking through the ethics of permission and consent seeking with a faculty mentor.
A separate but related issue from permission is how you will introduce yourself and your presence. How you introduce yourself to people in the field will depend very much on what level of participation you have chosen as well as whether you are an insider or outsider. Sometimes your presence will go unremarked, whereas other times you may stick out like a very sore thumb. Lareau ( 2021 ) advises that you be “vague but accurate” when explaining your presence. You don’t want to use academic jargon (unless your field is the academy!) that would be off-putting to the people you meet. Nor do you want to deceive anyone. “Hi, I’m Allison, and I am here to observe how students use career services” is accurate and simple and more effective than “I am here to study how race, class, and gender affect college students’ interactions with career services personnel.”
Researcher Note
Something that surprised me and that I still think about a lot is how to explain to respondents what I’m doing and why and how to help them feel comfortable with field work. When I was planning fieldwork for my dissertation, I was thinking of it from a researcher’s perspective and not from a respondent’s perspective. It wasn’t until I got into the field that I started to realize what a strange thing I was planning to spend my time on and asking others to allow me to do. Like, can I follow you around and write notes? This varied a bit by site—it was easier to ask to sit in on meetings, for example—but asking people to let me spend a lot of time with them was awkward for me and for them. I ended up asking if I could shadow them, a verb that seemed to make clear what I hoped to be able to do. But even this didn’t get around issues like respondents’ self-consciousness or my own. For example, respondents sometimes told me that their lives were “boring” and that they felt embarrassed to have someone else shadow them when they weren’t “doing anything.” Similarly, I would feel uncomfortable in social settings where I knew only one person. Taking field notes is not something to do at a party, and when introduced as a researcher, people would sometimes ask, “So are you researching me right now?” The answer to that is always yes. I figured out ways of taking notes that worked (I often sent myself text messages with jotted notes) and how to get more comfortable explaining what I wanted to be able to do (wanting to see the campus from the respondent’s perspective, for example), but it is still something I work to improve.
—Elizabeth M. Lee, Associate Professor of Sociology at Saint Joseph’s University, author of Class and Campus Life and coauthor of Geographies of Campus Inequality
Reflexivity in Fieldwork
As always, being aware of who you are, how you are likely to be read by others in the field, and how your own experiences and understandings of the world are likely to affect your reading of others in the field are all very important to conducting successful research. When Annette Lareau ( 2021 ) was managing a team of graduate student researchers in her study of parents and children, she noticed that her middle-class graduate students took in stride the fact that children called adults by their first names, while her working-class-origin graduate students “were shocked by what they considered the rudeness and disrespect middle-class children showed toward their parents and other adults” ( 151 ). This “finding” emerged from particular fieldnotes taken by particular research assistants. Having graduate students with different class backgrounds turned out to be useful. Being reflexive in this case meant interrogating one’s own expectations about how children should act toward adults. Creating thick descriptions in the fieldnotes (e.g., describing how children name adults) is important, but thinking about one’s response to those descriptions is equally so. Without reflection, it is possible that important aspects never even make it into the fieldnotes because they seem “unremarkable.”
The Data of Observational Work: Fieldnotes
In interview data collection, recordings of interviews are transcribed into the data of the study. This is not possible for much PO work because (1) aural recordings of observations aren’t possible and (2) conversations that take place on-site are not easily recorded. Instead, the participant observer takes notes, either during the fieldwork or at the day’s end. These notes, called “fieldnotes,” are then the primary form of data for PO work.
Writing fieldnotes takes a lot of time. Because fieldnotes are your primary form of data, you cannot be stingy with the time it takes. Most practitioners suggest it takes at least the same amount of time to write up notes as it takes to be in the field, and many suggest it takes double the time. If you spend three hours at a meeting of the organization you are observing, it is a good idea to set aside five to six hours to write out your fieldnotes. Different researchers use different strategies about how and when to do this. Somewhat obviously, the earlier you can write down your notes, the more likely they are to be accurate. Writing them down at the end of the day is thus the default practice. However, if you are plainly exhausted, spending several hours trying to recall important details may be counterproductive. Writing fieldnotes the next morning, when you are refreshed and alert, may work better.
Reseaarcher Note
How do you take fieldnotes ? Any advice for those wanting to conduct an ethnographic study?
Fieldnotes are so important, especially for qualitative researchers. A little advice when considering how you approach fieldnotes: Record as much as possible! Sometimes I write down fieldnotes, and I often audio-record them as well to transcribe later. Sometimes the space to speak what I observed is helpful and allows me to be able to go a little more in-depth or to talk out something that I might not quite have the words for just yet. Within my fieldnote, I include feelings and think about the following questions: How do I feel before data collection? How did I feel when I was engaging/watching? How do I feel after data collection? What was going on for me before this particular data collection? What did I notice about how folks were engaging? How were participants feeling, and how do I know this? Is there anything that seems different than other data collections? What might be going on in the world that might be impacting the participants? As a qualitative researcher, it’s also important to remember our own influences on the research—our feelings or current world news may impact how we observe or what we might capture in fieldnotes.
—Kim McAloney, PhD, College Student Services Administration Ecampus coordinator and instructor
What should be included in those fieldnotes? The obvious answer is “everything you observed and heard relevant to your research question.” The difficulty is that you often don’t know what is relevant to your research question when you begin, as your research question itself can develop and transform during the course of your observations. For example, let us say you begin a study of second-grade classrooms with the idea that you will observe gender dynamics between both teacher and students and students and students. But after five weeks of observation, you realize you are taking a lot of notes about how teachers validate certain attention-seeking behaviors among some students while ignoring those of others. For example, when Daisy (White female) interrupts a discussion on frogs to tell everyone she has a frog named Ribbit, the teacher smiles and asks her to tell the students what Ribbit is like. In contrast, when Solomon (Black male) interrupts a discussion on the planets to tell everyone his big brother is called Jupiter by their stepfather, the teacher frowns and shushes him. These notes spark interest in how teachers favor and develop some students over others and the role of gender, race, and class in these teacher practices. You then begin to be much more careful in recording these observations, and you are a little less attentive to the gender dynamics among students. But note that had you not been fairly thorough in the first place, these crucial insights about teacher favoritism might never have been made.
Here are some suggestions for things to include in your fieldnotes as you begin: (1) descriptions of the physical setting; (2) people in the site: who they are and how they interact with one another (what roles they are taking on); and (3) things overheard: conversations, exchanges, questions. While you should develop your own personal system for organizing these fieldnotes (computer vs. printed journal, for example), at a minimum, each set of fieldnotes should include the date, time in the field, persons observed, and location specifics. You might also add keywords to each set so that you can search by names of participants, dates, and locations. Lareau ( 2021:167 ) recommends covering the following key issues, which mnemonically spell out WRITE— W : who, what, when, where, how; R: reaction (responses to the action in question and the response to the response); I: inaction (silence or nonverbal response to an action); T: timing (how slowly or quickly someone is speaking); and E: emotions (nonverbal signs of emotion and/or stoicism).
In addition to the observational fieldnotes, if you have time, it is a good practice to write reflective memos in which you ask yourself what you have learned (either about the study or about your abilities in the field). If you don’t have time to do this for every set of fieldnotes, at least get in the practice of memoing at certain key junctures, perhaps after reading through a certain number of fieldnotes (e.g., every third day of fieldnotes, you set aside two hours to read through the notes and memo). These memos can then be appended to relevant fieldnotes. You will be grateful for them when it comes time to analyze your data, as they are a preliminary by-the-seat-of-your-pants analysis. They also help steer you toward the study you want to pursue rather than allow you to wallow in unfocused data.
Ethics of Fieldwork
Because most fieldwork requires multiple and intense interactions (even if merely observational) with real living people as they go about their business, there are potentially more ethical choices to be made. In addition to the ethics of gaining entry and permission discussed above, there are issues of accurate representation, of respecting privacy, of adequate financial compensation, and sometimes of financial and other forms of assistance (when observing/interacting with low-income persons or other marginalized populations). In other words, the ethical decision of fieldwork is never concluded by obtaining a signature on a consent form. Read this brief selection from Pascale’s ( 2021 ) methods description (observation plus interviews) to see how many ethical decisions she made:
Throughout I kept detailed ethnographic field and interview records, which included written notes, recorded notes, and photographs. I asked everyone who was willing to sit for a formal interview to speak only for themselves and offered each of them a prepaid Visa Card worth $25–40. I also offered everyone the opportunity to keep the card and erase the tape completely at any time they were dissatisfied with the interview in any way. No one asked for the tape to be erased; rather, people remarked on the interview being a really good experience because they felt heard. Each interview was professionally transcribed and for the most part the excerpts in this book are literal transcriptions. In a few places, the excerpta have been edited to reduce colloquial features of speech (e.g., you know, like, um) and some recursive elements common to spoken language. A few excerpts were placed into standard English for clarity. I made this choice for the benefit of readers who might otherwise find the insights and ideas harder to parse in the original. However, I have to acknowledge this as an act of class-based violence. I tried to keep the original phrasing whenever possible. ( 235 )
Summary Checklist for Successful Participant Observation
The following are ten suggestions for being successful in the field, slightly paraphrased from Patton ( 2002:331 ). Here, I take those ten suggestions and turn them into an extended “checklist” to use when designing and conducting fieldwork.
- Consider all possible approaches to your field and your position relative to that field (see figure 13.2). Choose wisely and purposely. If you have access to a particular site or are part of a particular culture, consider the advantages (and disadvantages) of pursuing research in that area. Clarify the amount of disclosure you are willing to share with those you are observing, and justify that decision.
- Take thorough and descriptive field notes. Consider how you will record them. Where your research is located will affect what kinds of field notes you can take and when, but do not fail to write them! Commit to a regular recording time. Your field notes will probably be the primary data source you collect, so your study’s success will depend on thick descriptions and analytical memos you write to yourself about what you are observing.
- Permit yourself to be flexible. Consider alternative lines of inquiry as you proceed. You might enter the field expecting to find something only to have your attention grabbed by something else entirely. This is perfectly fine (and, in some traditions, absolutely crucial for excellent results). When you do see your attention shift to an emerging new focus, take a step back, look at your original research design, and make careful decisions about what might need revising to adapt to these new circumstances.
- Include triangulated data as a means of checking your observations. If you are that ICU nurse watching patient/doctor interactions, you might want to add a few interviews with patients to verify your interpretation of the interaction. Or perhaps pull some public data on the number of arrests for jaywalking if you are the student accompanying police on their rounds to find out if the large number of arrests you witnessed was typical.
- Respect the people you are witnessing and recording, and allow them to speak for themselves whenever possible. Using direct quotes (recorded in your field notes or as supplementary recorded interviews) is another way to check the validity of the analyses of your observations. When designing your research, think about how you can ensure the voices of those you are interested in get included.
- Choose your informants wisely. Who are they relative to the field you are exploring? What are the limitations (ethical and strategic) in using those particular informants, guides, and gatekeepers? Limit your reliance on them to the extent possible.
- Consider all the stages of fieldwork, and have appropriate plans for each. Recognize that different talents are required at different stages of the data-collection process. In the beginning, you will probably spend a great deal of time building trust and rapport and will have less time to focus on what is actually occurring. That’s normal. Later, however, you will want to be more focused on and disciplined in collecting data while also still attending to maintaining relationships necessary for your study’s success. Sometimes, especially when you have been invited to the site, those granting access to you will ask for feedback. Be strategic about when giving that feedback is appropriate. Consider how to extricate yourself from the site and the participants when your study is coming to an end. Have an ethical exit plan.
- Allow yourself to be immersed in the scene you are observing. This is true even if you are observing a site as an outsider just one time. Make an effort to see things through the eyes of the participants while at the same time maintaining an analytical stance. This is a tricky balance to do, of course, and is more of an art than a science. Practice it. Read about how others have achieved it.
- Create a practice of separating your descriptive notes from your analytical observations. This may be as clear as dividing a sheet of paper into two columns, one for description only and the other for questions or interpretation (as we saw in chapter 11 on interviewing), or it may mean separating out the time you dedicate to descriptions from the time you reread and think deeply about those detailed descriptions. However you decide to do it, recognize that these are two separate activities, both of which are essential to your study’s success.
- As always with qualitative research, be reflective and reflexive. Do not forget how your own experience and social location may affect both your interpretation of what you observe and the very things you observe themselves (e.g., where a patient says more forgiving things about an observably rude doctor because they read you, a nursing student, as likely to report any negative comments back to the doctor). Keep a research journal!
Further Readings
Emerson, Robert M., Rachel I. Fretz, and Linda L. Shaw. 2011. Writing Ethnographic Fieldnotes . 2nd ed. University of Chicago Press. Excellent guide that uses actual unfinished fieldnote to illustrate various options for composing, reviewing, and incorporating fieldnote into publications.
Lareau, Annette. 2021. Listening to People: A Practical Guide to Interviewing, Participant Observation, Data Analysis, and Writing It All Up . Chicago: University of Chicago Press. Includes actual fieldnote from various studies with a really helpful accompanying discussion about how to improve them!
Wolfinger, Nicholas H. 2002. “On Writing Fieldnotes: Collection Strategies and Background Expectancies.” Qualitative Research 2(1):85–95. Uses fieldnote from various sources to show how the researcher’s expectations and preexisting knowledge affect what gets written about; offers strategies for taking useful fieldnote.
- Note that leaving one’s office to interview someone in a coffee shop would not be considered fieldwork because the coffee shop is not an element of the study. If one sat down in a coffee shop and recorded observations, then this would be fieldwork. ↵
- This is one reason why I have chosen to discuss deep ethnography in a separate chapter (chapter 14). ↵
- This person is sometimes referred to as the [pb_glossary id="389"]informant [/pb_glossary](and more on these characters in chapter 14). ↵
Methodological tradition of inquiry that holds the view that all social interaction is dependent on shared views of the world and each other, characterized through people’s use of language and non-verbal communication. Through interactions, society comes to be. The goal of the researcher in this tradition is to trace that construction, as in the case of documenting how gender is “done” or performed, demonstrating the fluidity of the concept (and how it is constantly being made and remade through daily interactions).
Used primarily in ethnography , as in the goal of fieldnotes is to produce a thick description of what is both observed directly (actions, actors, setting, etc.) and the meanings and interpretations being made by those actors at the time. In this way, the observed cultural and social relationships are contextualized for future interpretation. The opposite of a thick description is a thin description, in which observations are recorded without any social context or cues to help explain them. The term was coined by anthropologist Clifford Geertz (see chapter 14 ).
Reflective summaries of findings that emerge during analysis of qualitative data; they can include reminders to oneself for future analyses or considerations, reinterpretations or generations of codes, or brainstorms and concept mapping.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Observation? | Definition & Examples
What Is Qualitative Observation? | Definition & Examples
Published on 18 March 2023 by Tegan George .
Qualitative observation is a research method where the characteristics or qualities of a phenomenon are described without using any quantitative measurements or data. Rather, the observation is based on the observer’s subjective interpretation of what they see, hear, smell, taste, or feel.
Qualitative observations can be done using various methods, including direct observation, interviews , focus groups , or case studies . They can provide rich and detailed information about the behaviour, attitudes, perceptions, and experiences of individuals or groups.
Table of contents
When to use qualitative observation, examples of qualitative observation, types of qualitative observations, advantages and disadvantages of qualitative observations, frequently asked questions.
Qualitative observation is a type of observational study , often used in conjunction with other types of research through triangulation . It is often used in fields like social sciences, education, healthcare, marketing, and design. This type of study is especially well suited for gaining rich and detailed insights into complex and/or subjective phenomena.
A qualitative observation could be a good fit for your research if:
- You are conducting exploratory research . If the goal of your research is to gain a better understanding of a phenomenon, object, or situation, qualitative observation is a good place to start.
- When your research topic is complex, subjective, or cannot be examined numerically. Qualitative observation is often able to capture the complexity and subjectivity of human behaviour, particularly for topics like emotions, attitudes, perceptions, or cultural practices. These may not be quantifiable or measurable through other methods.
- You are relying on triangulation within your research approach. Qualitative observation is a solid addition to triangulation approaches, where multiple sources of data are used to validate and verify research findings.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Qualitative observation is commonly used in marketing to study consumer behaviour, preferences, and attitudes towards products or services.
During the focus group, you focus particularly on qualitative observations, taking note of the participants’ facial expressions, body language, word choice, and tone of voice.
Qualitative observation is often also used in design fields, to better understand user needs, preferences, and behaviours. This can aid in the development of products and services that better meet user needs.
You are particularly focused on any usability issues that could impact customer satisfaction. You run a series of testing sessions, focusing on reactions like facial expressions, body language, and verbal feedback.
There are several types of qualitative observation. Here are some of the most common types to help you choose the best one for your work.
Qualitative observations are a great choice of research method for some projects, but they definitely have their share of disadvantages to consider.
Advantages of qualitative observations
- Qualitative observations allow you to generate rich and nuanced qualitative data – aiding you in understanding a phenomenon or object and providing insights into the more complex and subjective aspects of human experience.
- Qualitative observation is a flexible research method that can be adjusted based on research goals and timeline. It also has the potential to be quite non-intrusive, allowing observation of participants in their natural settings without disrupting or influencing their behaviour.
- Qualitative observation is often used in combination with other research methods, such as interviews or surveys , to provide a more complete picture of the phenomenon being studied. This triangulation can help improve the reliability and validity of the research findings.
Disadvantages of qualitative observations
- Like many observational studies, qualitative observations are at high risk for many research biases , particularly on the side of the researcher in the case of observer bias . These biases can also bleed over to the participant size, in the case of the Hawthorne effect or social desirability bias .
- Qualitative observations are typically based on a small sample size , which makes them very unlikely to be representative of the larger population. This greatly limits the generalisability of the findings if used as a standalone method, and the data collection process can be long and onerous.
- Like other human subject research, qualitative observation has its share of ethical considerations to keep in mind and protect, particularly informed consent, privacy, and confidentiality.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
Data analysis in qualitative observation often involves searching for any recurring patterns, themes, and categories in your data. This process may involve coding the data, developing conceptual frameworks or models, and conducting thematic analysis . This can help you generate strong hypotheses or theories based on your data.
An observational study is a great choice for you if your research question is based purely on observations. If there are ethical, logistical, or practical concerns that prevent you from conducting a traditional experiment , an observational study may be a good choice. In an observational study, there is no interference or manipulation of the research subjects, as well as no control or treatment groups .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2023, March 18). What Is Qualitative Observation? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/qualitative-observations/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is participant observation | definition & examples, naturalistic observation | definition, guide & examples, what is a cohort study | definition & examples.
Qualitative study design: Observation
- Qualitative study design
- Phenomenology
- Grounded theory
- Ethnography
- Narrative inquiry
- Action research
- Case Studies
- Field research
- Focus groups
Observation
- Surveys & questionnaires
- Study Designs Home
A way to gather data by watching people, events, or noting physical characteristics in their natural setting. Seeks to answer the question: “What is going on here?”. While rooted in ethnographic research it can be applied to other methodologies. Observations may often be supplemented with interviews.
There are three main categories:
Participant observation
- Researcher becomes a participant in the culture or context being observed.
- Requires researcher to be accepted as part of culture being observed in order for success
Direct Observation
- Researcher strives to be as unobtrusive as possible so as not to bias the observations; must remain detached.
- Technology can be useful (i.e. video, audio recording).
Indirect Observation
- Results of an interaction, process or behaviour are observed (for example, measuring the amount of plate waste left by students in a school cafeteria to determine whether a new food is acceptable to them).
Observations may be unstructured, semi-structured or structured. The latter two involve the use of an observation template that includes prompting questions such as: “What are people doing?”; “What are they trying to accomplish?”; How are they doing this?” etc.
What form does observation take?
Field notes; audio and video recordings.
- Allows for insight into contexts, relationships, and behaviours;
- Can provide information previously unknown to researchers that is crucial for project design, data collection, and interpretation of other data.
Limitations
- Not suited to all research inquiries since not all phenomena can be observed.
- Time-consuming.
- Documentation relies on memory, personal discipline, and diligence of researcher.
- Requires conscious effort at objectivity because method is inherently subjective.
- Critics maintain that different observers will make different observations of the same phenomena so that no single account can be held up as the source of truth.
Example questions
- How do members of operating theatres communicate with each other?
- How do nurses interact with their patients when administering medication?
- How do parents deal with their adolescent children who suffer chronic pain?
Example studies
- Bolster, D., & Manias, E. (2010). Person-centred interactions between nurses and patients during medication activities in an acute hospital setting: Qualitative observation and interview study. International Journal of Nursing Studies , 47(2), 154-165. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2009.05.021
- Bombeke, K., De Winter, B., Debaene, L., Van Royen, P., Van Roosbroeck, S., Van Hal, G., & Schol, S. (2011). Medical students trained in communication skills show a decline in patient-centred attitudes: An observational study comparing two cohorts during clinical clerkships . Patient Education and Counseling , 84(3), 310-318. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2011.03.007
- Given, L. M. (2008). The SAGE encyclopedia of qualitative research methods (Vols 1-0). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc. doi: 10.4135/9781412963909
- Holloway, I. & Galvin, K. (2017). Qualitative research in nursing and healthcare (Fourth ed.) John Wiley & Sons Inc.
- << Previous: Focus groups
- Next: Documents >>
- Last Updated: Apr 8, 2024 11:12 AM
- URL: https://deakin.libguides.com/qualitative-study-designs
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- Qualitative Research:...
Qualitative Research: Observational methods in health care settings
- Related content
- Peer review
- Nicholas Mays a , director of health services research ,
- Catherine Pope , director of health services research
- a King's Fund Institute, London W2 4HT
- b Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, University of Leicester, Leicester LE1 6TP
- a Correspondence to: Mr Mays
Clinicians used to observing individual patients, and epidemiologists trained to observe the course of disease, may be forgiven for misunderstanding the term observational method as used in qualitative research. In contrast to the clinician or epidemiologist, the qualitative researcher systematically watches people and events to find out about behaviours and interactions in natural settings. Observation, in this sense, epitomises the idea of the researcher as the research instrument. It involves “going into the field”—describing and analysing what has been seen. In health care settings this method has been insightful and illuminating, but it is not without pitfalls for the unprepared researcher.
The term “observational methods” seems to be a source of some confusion in medical research circles. Qualitative observational studies are very different from the category of observational studies (non-experimental research designs) used in epidemiology, nor are they like the clinical observation of a patient. Observational methods used in social science involve the systematic, detailed observation of behaviour and talk: watching and recording what people do and say. Goffman neatly captured this distinct research method with his recommendation that, in order to learn about a social group, one should “submit oneself in the company of the members to the daily round of petty contingencies to which they are subject.” 1 Thus, observational methods can involve asking questions and analysing documents, but the primary focus on observation makes it distinct from a qualitative research interview (see the next paper in this series) or history taking during patient consultation. Another crucial point about qualitative observation is that it takes place in natural settings not experimental ones; hence, this type of work is often described as “naturalistic research.”
- View inline
Research roles
In an attempt to minimise the impact on the environment being studied the researcher sometimes adopts a “participant observer” role, becoming involved in the activities taking place while also observing them. The degree of participation varies according to the nature of the setting and the research questions, but broadly corresponds to the first two research roles described in Gold's typology (box 1). 2 There are obviously important ethical considerations about the decision to conduct covert research, and for this reason examples of this type of observational study are rare. However, its use may be justified in some settings, and it has been used to research sensitive topics such as homosexuality 3 and difficult to access areas such as fascist organisations 4 and football hooliganism. 5 Overt research—Gold's “participant as observer”—may pose fewer ethical dilemmas, but this may be offset by the group or individuals reacting to being observed. At its most basic, having a researcher observing actions may stimulate modifications in behaviour or action—the so-called “Hawthorne effect,” 6 or encourage introspection or self questioning among those being researched. In his classic study of street gangs in the United States, Whyte recounted how a key group member said, “You've slowed me up plenty since you've been down here. Now when I do something I have to think what Bill Whyte would want to know about it and how I can explain it. Before I used to do things by instinct.” 7
In addition to these potential problems for the subjects of observational research, there are important considerations for researchers “entering the field.” In essence these involve “getting in and getting out.” In the initial phases there may be problems gaining access to a setting, and then in striking up sufficient rapport and empathy with the group to enable research to be conducted. In medical settings, such as a hospital ward, this may involve negotiating with several different staff groups ranging from consultants and junior doctors, to nurse managers, staff nurses, social workers, and auxiliary professions. Once “inside” there is the problem of avoiding “going native”; that is, becoming so immersed in the group culture that the research agenda is lost, or that it becomes extremely difficult or emotionally draining to exit the field and conclude the data collection.
Observation of transactions with patients presenting to casualty departments found that staff classified patients into “normal rubbish” (the inappropriate attenders) and “good” patients, who were viewed as more deserving.
**FIGURE OMITTED**
What can observation tell us that other methods cannot?
Given these difficulties, observational methods may seem a peculiar choice for studying health and health services. However, an important advantage of observation is that it can help to overcome the discrepancy between what people say and what they actually do. It circumvents the biases inherent in the accounts people give of their actions caused by factors such as the wish to present themselves in a good light, differences in recall, selectivity, and the influences of the roles they occupy. For these reasons, observational methods are particularly well suited to the study of the working of organisations and how the people within them perform their functions. It may also uncover behaviours or routines of which the participants themselves may be unaware. For example, Jeffery's observation of casualty wards in Edinburgh indicated that, because of the conflicting demands and pressures on staff, some patients, who were seen as inappropriate attenders, were labelled as “normal rubbish” and treated differently from “good” patients, who were viewed as more deserving. 8 A similar picture emerges from Hughes's work on the decisions made by reception clerks when patients present themselves at casualty department. 9 It is unlikely that interviews alone would have elicited these different patterns of care. Indeed the labelling of certain cases as “normal rubbish” may have been so embedded in the culture of the casualty setting that only an outsider or newcomer to the scene would have considered it noteworthy.
Another observational study provides an example of how qualitative work can build on existing quantitative research. 10 Against the background of large variations in rates of common surgical procedures such as hysterectomy, cholecystectomy, and tonsillectomy, Bloor observed ear, nose, and throat outpatient clinics to see how decisions to admit children for surgery were made. He systematically analysed how surgeons made their decisions to operate and discovered that individual doctors had different “rules of thumb” for coming to a decision. While one surgeon might take clinical signs as the chief indication for surgery, another might be prepared to operate in the absence of such indications at the time of consultation if there was evidence that repeated episodes of tonsillitis were severely affecting a child's education. Understanding the behaviour of these surgeons, knowing why they made their decisions, provided considerable insight into how the variation in surgical rates occurred.
Similar variation and patterning occurs in the statistics on inpatient waiting lists: some surgeons have long lists, others do not; some specialties have long waits, others do not. An observational study showed that rules and routines akin to those discovered by Bloor could be discerned in the day to day management of waiting lists. 11 Surgical and administrative preferences were important in deciding who came off the list. Different reasons for admitting a patient might range from case mix demands for teaching juniors, through ensuring a balanced list, to the ease with which a patient could be contacted and offered admission. Thus, observing how waiting lists work can indicate which policy and administrative changes are likely to have an impact in reducing lists and which are not: a policy which assumed that waiting lists operated as first come, first served queues would be unlikely to affect the day to day routines described above.
Some rules about observation
Before any recording and analysis can take place, the setting to be observed has to be chosen. As in other qualitative research, this sampling is seldom statistically based. Instead, it is likely to be purposive, whereby the researcher deliberately samples a particular group or setting (see Mays and Pope 12 in this series for more on this). The idea of this type of sampling is not to generalise to the whole population but to indicate common links or categories shared between the setting observed and others like it. At its most powerful, the single case can demonstrate features or provide categories relevant to a wide number of settings. Goffman's observation of mental hospitals in the 1960s generated the valuable concept of the “total institution,” of which the asylum was one example alongside others such as prisons and monasteries. 1
Qualitative observation involves watching and recording what people say and do. As it is impossible to record everything, this process is inevitably selective and relies heavily on the researcher to act as the research instrument and document the world he or she observes. Therefore it is vital that the observations are systematically recorded and analysed, either through the traditional medium of field notes written during or immediately after the events occur or by using audio or video recording facilities. From his unique position as a patient in a tuberculosis sanatorium, Roth was able to record events as they happened, 13 but such situations are rare and most researchers, whether in covert or more participative roles, find that recording necessitates the development of memory skills and frequent trips to the lavatory to “write up.”
The systematic recording of data in qualitative observation distinguishes it from other types of observation such as a tourist recording with a camcorder or a nosey neighbour peering over the fence. Even with video and sound recording it is impossible to “get everything,” but as far as possible the researcher aims to record exactly what happened, including his or her own feelings and responses to the situations witnessed. The subjective nature of this type of research contrasts with the objective stance aspired to in the experimental method, but in fact it is a crucial component of the process of analysing qualitative observational data. The researcher usually keeps a field diary or record of the research process to detail events, personal reactions to events, and changes in his or her views over time. Frequently this is the basis of tentative hypotheses or the evolution of systems of classification. In developing classifications or hypotheses it is particularly important to detail any contradictory or negative cases—the unusual, out of the ordinary things which often reveal most about the setting or situation. Tentative classifications and the search for negative cases during the data collection are important facets of the analytic technique used in observational research.
The fieldnotes gathered during observational research are likely to be detailed, highly descriptive accounts and are therefore cumbersome. As descriptions alone they cannot provide explanations. The researcher's task is to sift and decode the data to make sense of the situation, events, and interactions observed. Often this analytical process starts during the data collection phase, a quite different model of the research process to that found in quantitative research, where data collection is completed before any analysis begins (box 2).
Just as the data are systematically recorded, so they are also systematically analysed. Various ways of dealing with observational data have been described, including “analytic induction” and “constant comparison.” 14 Stripped of their theoretical trappings, these methods are all variants of content analysis and involve an iterative process of developing categories from the transcripts or fieldnotes, testing them against hypotheses, and refining them. This analytical process is described in detail by Bloor, based on the observational study of ear, nose, and throat clinics described earlier (box 3). 15
Box 3 AnalysisStages in the analysis of field notes in a qualitative study of ear, nose, and throat surgeons' disposal decisions for children referred for possible tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy (T&A) 11
Provisional classification—For each surgeon all cases categorised according to the disposal category used (for example, T&A or tonsillectomy alone)
Identification of provisional case features—Common features of cases in each disposal category identified (for example, most T&A cases found to have three main clinical signs present)
Scrutiny of deviant cases—Include in (2) or modify
to accommodate deviant cases (for example, T&A performed when only two of three signs present)
Identification of shared case features—Features common to other disposal categories (history of several episodes of tonsillitis, for example)
Derivation of surgeons' decision rules—From the common case features (for example, case history more important than physical examination)
Derivation of surgeons' search procedures (for each decision rule)—The particular clinical signs looked for by each surgeon
Repeat (2) to (6) for each disposal category
As with quantitative work, it is important that evidence from the data is presented to support the conclusions reached. This can take the form of examples of specific cases, descriptions of events, or quotations. The validity of observational accounts relies on the truthful and systematic representation of the research; in many ways it is honesty which separates the observational account from a novel. Hughes says that observational studies should communicate the culture and rules of the setting well enough to allow another researcher to learn them and “pass” as a member of the group. 16 This is not an easy task, and observational research is therefore particularly demanding of the individual researcher.
This brief review has indicated how observational methods can be used to “reach the parts that other methods cannot.” Done well, there is no reason why observation should not be as systematic, rigorous, or valid as other research styles and deserve its place in the health researcher's methodological tool box.
Further reading
Fielding N. Researching social life. London: Sage, 1993.
- Humphreys L
- Roethlisberger FJ ,

Qualitative Research: Observation
- Getting Started
- Focus Groups
- Observation
- Case Studies
- Data Collection
- Cleaning Text
- Analysis Tools
- Institutional Review
Participant Observation

Photo: https://slideplayer.com/slide/4599875/
Field Guide
- Participant Observation Field Guide
What is an observation?
A way to gather data by watching people, events, or noting physical characteristics in their natural setting. Observations can be overt (subjects know they are being observed) or covert (do not know they are being watched).
- Researcher becomes a participant in the culture or context being observed.
- Requires researcher to be accepted as part of culture being observed in order for success
Direct Observation
- Researcher strives to be as unobtrusive as possible so as not to bias the observations; more detached.
- Technology can be useful (i.e video, audiorecording).
Indirect Observation
- Results of an interaction, process or behavior are observed (for example, measuring the amount of plate waste left by students in a school cafeteria to determine whether a new food is acceptable to them).
Suggested Readings and Film
- Born into Brothels . (2004) Oscar winning documentary, an example of participatory observation, portrays the life of children born to prostitutes in Calcutta. New York-based photographer Zana Briski gave cameras to the children of prostitutes and taught them photography
- Davies, J. P., & Spencer, D. (2010). Emotions in the field: The psychology and anthropology of fieldwork experience . Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- DeWalt, K. M., & DeWalt, B. R. (2011). Participant observation : A guide for fieldworkers . Lanham, Md: Rowman & Littlefield.
- Reinharz, S. (2011). Observing the observer: Understanding our selves in field research . NY: Oxford University Press.
- Schensul, J. J., & LeCompte, M. D. (2013). Essential ethnographic methods: A mixed methods approach . Lanham, MD: AltaMira Press.
- Skinner, J. (2012). The interview: An ethnographic approach . NY: Berg.
- << Previous: Focus Groups
- Next: Case Studies >>
- Last Updated: Mar 1, 2024 10:13 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/qualitative-research

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries

- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Original Language Spotlight
- Alternative and Non-formal Education
- Cognition, Emotion, and Learning
- Curriculum and Pedagogy
- Education and Society
- Education, Change, and Development
- Education, Cultures, and Ethnicities
- Education, Gender, and Sexualities
- Education, Health, and Social Services
- Educational Administration and Leadership
- Educational History
- Educational Politics and Policy
- Educational Purposes and Ideals
- Educational Systems
- Educational Theories and Philosophies
- Globalization, Economics, and Education
- Languages and Literacies
- Professional Learning and Development
- Research and Assessment Methods
- Technology and Education
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Observing schools and classrooms.
- Alison LaGarry Alison LaGarry University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190264093.013.983
- Published online: 29 July 2019
Qualitative observation is an attempt to view and interpret social worlds by immersing oneself in a particular setting. Observation draws on theoretical assumptions associated with the interpretivist paradigm. Thus, researchers who engage in qualitative observations believe that the world cannot be fully known, but must be interpreted. Observation is one way for researchers to seek to understand and interpret situations based on the social and cultural meanings of those involved. In the field of education, observation can be a meaningful tool for understanding the experiences of teachers, students, caregivers, and administrators.
Rigorous qualitative research is long-term, and demands in-depth engagement in the field. In general, the research process is cyclical, with the researcher(s) moving through three domains: prior-to-field, in-field, and post- or inter-field. Prior to entering the field, the researcher(s) examine their assumptions about research as well as their own biases, and obtain approval from an Institutional Review Board. This is also the time when researcher(s) make decisions about how data will be collected. Upon entering the field of study, the researcher(s) work to establish rapport with participants, take detailed “jottings,” and record their own feelings or preliminary impressions alongside these quick notes. After leaving an observation, the researcher(s) should expand jottings into extended field notes that include significant detail. This should be completed no later than 48 hours after the observation, to preserve recall. At this point, the researcher may return to the field to collect additional data. Focus should move from observation to analysis when the researcher(s) feel that they have reached theoretical data saturation.
- education research
- qualitative
- observation
- ethnography
Introduction
Observation, as a concept, can refer to many things. Yet, in terms of social research and ethnography, observation is the act of “record[ing] the ongoing experiences of those observed, through their symbolic world” (Denzin, 2017 , p. 185). It is an attempt to view and interpret social worlds by immersing oneself in a particular setting—a way to “see from the inside” (Emerson, Fretz, & Shaw, 2011 , p. 3). Observation draws on theoretical assumptions of the interpretivist paradigm, and is associated with methodologies such as ethnography, narrative inquiry, discourse analysis, grounded theory, phenomenology, and symbolic interactionism. It is one of many ways for researchers to understand situations based on the meanings of those involved. The particular approach to observation presented here considers the process and implications of observations in educational settings such as schools and classrooms.
The Interpretivist Paradigm
All research methods and methodologies are based on assumptions about reality and knowledge. In order to understand how one might study a particular research question or explore a phenomenon, it is important for researchers to examine their beliefs about whether the world around them can be objectively known. Researchers who approach their work from the interpretivist paradigm believe that the world cannot be objectively understood, and does not exist independently of thoughts or ideas. Since there is no objective truth, the world must be interpreted (Glesne, 2016 ). Further, the goal of such research is not just to interpret the social world, but to do so through the lens of actors in that particular setting or context. Through observation, then, qualitative researchers “access . . . others’ interpretations of some social phenomenon” and also use their own lens to interpret the actions and motivations of others (Glesne, 2016 , p. 9).
Because interpretivist qualitative research, as described in this article, is centered on interpretation, it is not considered “objective” research. Throughout the observation process, the researcher’s identity and subjectivity are always implicated. Interpretivist research engages participants’ multiple ways of knowing and making meaning, at the same time engaging socially constructed meanings agreed upon by society. Thus, while interpretations may be unique to individuals, to some degree, it is also possible to access the “perspectives of several members of the same social group about some phenomena,” which can “suggest some cultural patterns of thought and action for that group as a whole” (Glesne, 2016 , p. 9). In order to collect substantial evidence of such cultural patterns, interpretivist researchers prioritize significant, long-term engagement in the field. While one might observe and use the techniques described in this article on a short-term or ad hoc basis, sustained presence in the field and interaction with participants are vital for interpreting cultural understandings unique to the context.
Nearly every researcher has experienced schooling in some manner, making informal “insider” status somewhat universal for researchers who choose to study education. This amplifies researcher subjectivity such that most researchers entering the field have an a priori vision of what the student experience is like, and how educators are, or should be, in an educational setting. For those who have experienced traditional schooling, their experience is not insignificant, spanning more than a decade of their lives. Additionally, some education researchers are former educators, adding a further layer of knowledge and experience that influences how they engage in observation-based qualitative research. All this is to say that the cultural meanings that each of us bring to bear on educational research are heavily laden with our own schooling experiences and the social powers that shape them. This can be both a benefit and a reason for increased attentiveness or caution.
Another concern regarding observation in the field of education is that there are significant contextual implications for observations in classrooms. Thus, the term is doubly fraught with meaning. Generally, when teachers (or students) think about being observed, they assume judgement. While a fear or wariness about researcher judgement is not uncommon in observational research, the apprenticeship model for teachers invokes observation as a form of evaluation with real professional consequences. This is the case for pre service teachers and in-service teachers alike. In conjunction with student achievement, observation ratings may also be tied to teacher performance evaluations and merit pay. This discursive and symbolic conundrum can be problematic for qualitative researchers both in terms of gaining entry into the field, and also in terms of managing their own biases toward judgement. In conducting observation in classrooms, the aura of evaluation is ever-present. This is not to say that observation, as associated with educational evaluation, is bad. There are vast benefits to apprenticeship, directed feedback, legitimate peripheral participation (Lave & Wenger, 1991 ), and experiential learning (Dewey, 1938 ). When it comes to qualitative research, however, there is a necessary translation that must occur to orient both the reflexive approach of the researcher, and the understanding of the teacher or students being observed.
While interpretivist participant observation engages the subjectivity of the researcher, novice researchers are encouraged to take field notes as objectively as possible, reserving analysis and interpretation for a later phase. That said, our experiences as researchers in the field always engage some level of analysis as we integrate what we see and experience into our own extant frames of reference. Denzin ( 2017 ) reminded researchers that participant observation “entails a continuous movement between emerging conceptualizations of reality and empirical observations. Theory and method combine to allow the simultaneous generation and verification of theory” (p. 186). This article presents a methodological perspective on how one might conduct participant observation in educational settings, while paying particular attention to the movement between empirical or “objective” observation, subjective interpretation, and further evaluation. While the article focuses primarily on observation rather than analysis, it is necessary to consider how a researcher navigates the continuous push in the field to detach (concrete observation) and connect (understanding emerging concepts). The article thus includes some discussion of preliminary analysis and how it may be recorded.
It is always tricky to lay out methodological procedure when, in reality, the process is layered, cyclical, or non-linear (Spradley, 1980 ). For the researcher interested in observation, it is important to keep in mind the idea of “movement between” as stated by Denzin ( 2017 ). A vital skill for expert qualitative observation is to actually exist and think “between.” This allows for subjectivity and emic or insider understandings to inform, but not supersede, concrete thick descriptions (Geertz, 1973 ) of interaction in the field. This skill takes significant practice and mentorship. The included examples describe the process of a novice researcher, to show how one might begin to build capacity for observation and subsequent interpretation. Following the discussion of methodological procedure, there is a brief discussion of implications and encouragements for the use of ethnographic observation in educational settings.
Methodological Cycles of Observation
This section breaks the methodological process of observation in school settings into three domains: Prior-to-field , in-field , and post- or inter-field . These domains can be viewed as somewhat cyclical in nature and, realistically speaking, are not always discrete. As the researcher becomes more embedded in the research setting, more familiar with the context, and more adept at the “move between” description and analysis, the lines between the domains become blurry. So while one may separate these domains for the sake of explanation, they should be taken not as singular, but rather as guiding moments in the process of qualitative observation.
In the prior-to-field domain, the researcher examines or states their own epistemological stance toward the work, as well as their own biases toward the setting or subject matter. This reflexive work not only sets the tone for the in-field domain, but also allows the researcher to consider appropriate research questions. In the post- or inter-field domain, the researcher revisits their in-field observations to again navigate between the concrete field notes taken and their own subjective interpretations. This domain also provides opportunity to further focus observation and refine the research questions. Additionally, researchers may consider this an apt moment to check with participants for their own interpretations of interactions observed.
Prior-to-Field
Observation is more than simple data collection and, despite differing epistemological orientations, nearly all sources agree that observation-based research should be rigorously conducted. In other words, data gathered through observation or ethnography is “more than casually observed opinion” (Angrosino & Rosenberg, 2011 , p. 468). In more recent iterations of ethnographic methodology, observation is highlighted as a site of interaction. In this postmodern context, researcher subjectivity is acknowledged—rendering the researcher a participant, co-constructor, and co-negotiator of meaning at the study site. Angrosino and Rosenberg ( 2011 ) stated, “our social scientific powers of observation must, however, be turned on ourselves and the ways in which our experiences interface with those of others in the same context if we are to come to an understanding of sociocultural processes” (p. 470). This discussion of the nature of observation-based research is a vital starting point since it orients the researcher to the cultural meanings of the study site and encourages them to acknowledge their own subjectivity. As in post-critical ethnography (Noblit, Flores, & Murillo, 2004 ), this orientation serves to situate the project as theory and methodology that are inextricably intertwined. This means that the researcher needs to be aware of the experiences, meanings, and biases they bring to the field.
From a sociological standpoint, each of us moves in the world based on a number of more or less abstract identity markers that influence how others interact with us. A particular caution for educational researchers exists in the vast differences we know that students have in their schooling experiences. These differences are often based on social markers such as race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, gender, sexuality, and religion. Schooling, as an institution, mirrors and even amplifies the social hierarchies of society such that some are distinctly privileged in educational settings, while others experience oppression and disadvantage. So, to build on the assertion that nearly all education researchers have “insider” experience with schooling, it is important to note that these experiences can differ greatly. Sometimes parallel or similar experiences may limit the view of the researcher in that they may see only their own experiences, and may not look beyond that feeling to truly engage what others might experience. Additionally, differing experiences or social positioning may result in misinterpretation of cultural meaning. Thus, educational researchers must prioritize the move between social meanings of their own and those of participants observed. This is one reason, in particular, why it is so important to record concrete sensory detail in the field.
When a researcher records concrete details, they are recording what is seen . If a researcher were to record only what they think about the events taking place in the field, this judgement (for that is what it is) may supplant other potential meanings that may be discovered. Recording concrete sensory details allows the researcher the space to later move between their own subjectivity and those of the participants—particularly during the process of writing expanded field notes. This process takes time and practice. Indeed, it takes a vigilant researcher to parse out the expectations overlaid on educational research settings by their own experiences from the experiences of others. In consideration of the ways that a researcher might begin to identify and examine their own biases, a good starting point is Sensoy and DiAngelo ( 2017 ). In their book Is Everyone Really Equal: An Introduction to Key Concepts in Social Justice Education , the authors guide the reader through an approachable exploration of concepts such as power, oppression, prejudice, discrimination, privilege, and social construction. Each of these concepts is vital for understanding researcher biases and how they influence interpretations in the field. In general, this examination process is referred to in the field as reflexivity, or “critical reflection on how researcher, research participants, setting, and research procedures interact with and influence each other” (Glesne, 2016 , p. 145). Pillow ( 2003 ) pointed out that this reflective process does not absolve the researcher of their own biases, yet has important ramifications for the analysis and findings.
Those who have trained and served as educators may have particular insight to offer in the field of educational research. They may understand the field in more depth, having recently experienced the nuance and pressures of policy. To those who say that prior experience in the field may bias the investigation—it does. However, all researchers are biased in that they experience the world in a particular manner and ascribe specific cultural and social meanings to settings and events. It is also necessary to acknowledge here that effective use of this depth of understanding for qualitative observation does not come without caution.
Prior to entering the field, researchers may make preliminary decisions about their level of involvement, participation, and immersion. While older iterations of ethnographic methodology encouraged the observer to participate as little as possible, this can hinder the researcher’s ability to truly understand indigenous meanings of the social situation being observed. Certainly, the lesser-involved researcher will have greater opportunity to record copious notes. However, simply being present in the setting does have an effect on participants and may alter the way that they act or interact. Furthermore, researchers need not see the roles of participant and researcher as two poles. Rather, it is useful to think of these as two ends of a continuum, where the researcher(s’) role is never static.
While research ethics are not the primary focus of this article, it would not be appropriate to advocate for observation without mentioning that participants’ rights and confidentiality should be considered at every step of the process. Prior to entering the observation setting, the researcher must obtain approval from an Institutional Review Board (IRB). This is particularly important for research in schools, where participants may be minors and parental consent for participation may be required. Once approval is granted, the researcher should obtain consent from participants and provide a disclosure of nature of the study and time requirements for engaging in the study. Additionally, participants should be reminded that they can opt out of the study at any time. The IRB will also provide explicit guidelines on how all sensitive or identifiable data should be stored to protect participants’ identity.
Another key decision to make prior to entering the field is how field notes will be recorded. While notes can certainly be recorded on paper, or using a word-processing program on a laptop, pervasive use of personal digital technology (smartphones, tablets, etc.) has transformed the available options for documenting the field. As long as one has received approval for photo or video documentation from IRB, digital photography is instantaneous and can help document the research setting in greater detail. Digital videos can record activities and interactions such that the researcher can return to these when expanding field notes for further verification or perspective. Aside from simple dialogue, voice recorders can also record soundscapes , a growing area of qualitative research analysis (Gershon, 2013 ). There are also a number of app-based note-taking and qualitative-analysis programs helpful for observational research, including: Atlas.ti Mobile, Evernote, EverClip, MAXApp (corollary to MAXQDA), and Indeemo. Additionally, Google Could now offers a free speech-to-text function that can capture dialogue in more detail than one might be able to do on paper or by typing.
The choice of note-taking platform should take into account participants’ wishes, as well as the needs inherent to the setting. This decision is not just a simple question of what will work best for the researcher and their research product. Returning to the prior discussion of educator evaluation, teachers may associate note-taking—on paper or electronically—with recording judgement. When I have mentored student teachers, they have expressed that the tapping sound produced by typing on a laptop can increase their anxiety exponentially. While these considerations may sound superficial, the comfort level of participants is of utmost importance for the researcher in establishing themselves as collegial, and not intrusive. In fact, I have found it to be useful to ask a classroom teacher how they would prefer for me to record my observations. Regardless of their choice, I always assure them that I am “documenting” the events taking place, and not recording judgement.
Before moving on, it is worth noting that any prior-to-field decision-making may shift and evolve throughout the process of the research engagement. Qualitative research, by nature, seeks to understand meaning from the perspective of the actors in a particular context. Thus, the researcher must be willing to follow threads of understanding or thought, even if they are unexpected. For example, one may plan for low participation (Spradley, 1980 ) in the setting, but one day during the field visit the teacher may invite the researcher to lead a group of students through a math activity. In the interest of building rapport and trust with the participants, it may be necessary to move to a higher level of participation in response to this invitation. This will be discussed in further detail relating to the in-field domain. Emerson et al. ( 2011 ) stated that a good participant observer must be both “sensitive and perceptive about how they are seen by others” (p. 4). If the participants see the researcher as detached, unhelpful, or otherwise standoffish, this can affect their level of comfort and shift the insights they choose to share. Changes in the researcher’s level of participation should be recorded in field notes, and do not negate the reliability of eventual findings. In fact, participants may share additional insights with researchers who show interest in their perspectives, actions, and thoughts.
This section details two major considerations for researcher(s) embarking upon in-field observations: What to look for, and how to record what is seen. This is obviously oversimplified, but these two considerations will help to organize the process of collecting qualitative data via observation. These decisions can be made by an individual researcher or by research teams working together to investigate a particular setting or phenomenon.
What Should the Researcher Look For?
The first thing a novice researcher often asks about observation in the field is “What should I be looking for?” This question is loaded, and takes some time to unpack. While there may be something that the researcher hopes will happen, it is important to focus explicitly on what does happen, and how it happens. One of the first skills that a participant observer must begin to hone is explicit awareness of a situation (Spradley, 1980 ). This awareness can be compared to that of a wide-angle camera lens that takes in as much as possible. The goal, Spradley stated, is to overcome the “selective inattention” most people employ to conduct daily tasks and interactions (p. 55). This explicit awareness is not solely directed outward. Spradley also noted that the researcher must increase their introspectiveness so that they are better able to see and reflect upon the cultural frames and meanings associated with that which is observed.
Using the metaphor of a wide-angle lens, one common way to begin observation is through descriptive observation . In this case, the researcher approaches the observation with very general questions in mind. For example: “What is happening here?” or “What is going on?” These broad, open questions allow for the researcher to see and feel the setting as it is, without overlaying a priori meanings or assumptions.
Table 1. Spradley’s Descriptive Question Matrix
Source: . Spradley ( 1980 , pp. 82–83).
Spradley ( 1980 ) outlined a “Grand Tour” as a procedure for descriptive observation. In this overview, the researcher would take note of various facets of the setting and participants including:
The first three facets are presented in bold (author’s emphasis) because these three form a meaningful starting point for any observation, and the remaining six provide additional nuance. A diagram can be useful for illustrating the set-up of the space, mapping objects as well as actors. After examining each of these facets of the setting, Spradley recommended creating a descriptive question matrix wherein the researcher integrates observations from two or more of the facets to examine how they might interact. For example, consider how a student who is disabled might interact with a space that is not accessible for mobility. More detail is provided in Table 1 .
Emerson et al. ( 2011 ) also advocated for a wide-angle lens and prioritized the senses in helping to establish initial impressions. They expanded on the facets listed by Spradley, encouraging the researcher to consider physical space and environment in terms of characteristics such as size, space, noise, and layout. It terms of actors in a setting, they also suggested observing such characteristics as perceived race and gender, dress, comportment, and proximity to other actors. Moving beyond these facets, Emerson et al. also advocate that the researcher ask the question “What is significant or unexpected?” in the field. In other words, what seems out of place or out of the expected flow? Such unexpected moments are often of the most interest, and also represent some of the most significant cultural learning for the researcher. For instance, do the actors in the field react as though the same event is unexpected? If not, the researcher will need to examine the event, activities preceding the event, and those following the event to work to understand the significance. It is also important to register one’s own feelings, as the researcher, when observing in the field. Then, in working to understand one’s own reactions, feelings, and biases in comparison to those in the field, one may reveal cultural meanings unique to the context. It is important to note that the researcher should not take their own feelings as findings. Rather, they should move beyond their own reactions toward an analysis of what those in the setting may find significant (Emerson et al., 2011 ).
Focused observation takes place after the researcher has been in the field for some time, and serves to limit the inquiry in a meaningful manner. Whereas in descriptive observation, the research questions were general, in focused observation the researcher engages more structural questions (Spradley, 1980 ). For example: What are all the ways that a teacher asks a student to focus on their work? Focused observations may be conducted as surface or in-depth investigations. According to Spradley, surface investigations examine a number of cultural domains in some depth. In-depth observations are just that, observations where the researcher selects one domain and examines it thoroughly. These cultural domains may be selected based on personal interest, suggestion by informant, theoretical interest, or other strategic reasoning (Spradley, 1980 ). Additionally, this can lead the researcher to a potential taxonomy of events or codes occurring at the site ( selective observation ).
While Spradley’s approach can be useful and meaningful, there is also room to hone the initial general research question of “What is happening here?” to a more structured prompt that does not demand taxonomic reduction. An example of such a prompt engages the significant or unexpected events described by Emerson et al. ( 2011 ). In this case, the researcher might choose to further examine a particular event or occurrence, asking the questions: When this event happens, how does it happen? What else is happening? What changes? This way, the researcher is not limited to types of interaction, but can also consider the means by which these interactions take place and the dynamics that are set into motion.
Recording Field Notes
Field notes are the first phase of documenting happenings as data via observation—a method of inscription or textualization which later serves as a basis for iterative analysis. Further, according to Emerson et al., “Field notes are distinctively a method for capturing and preserving insights and understandings” ( 2011 , p. 14). There is no best way to record field notes, and none approaches a truly objective accounting of the events that occurred. One observer may choose to record significant events or key phrases that another observer does not choose to record. Thus, when conducting research in teams, it is useful to cross-check notes with others who observed the same events. This can be done in formal calibration meetings or informal conversations post-observation. Cross-checking can also be performed as a type of member check with participants, where the researcher might ask if anything was missed. Subjectivity is always implicated, since each observer filters events through their own cultural meanings and understanding of the social world. Yet, researchers observing in social settings are still encouraged to record what they see as concretely as possible. Taking a step back, researchers must decide the appropriate method for recording notes in the field. In the moment, researchers will need some method to record jottings, which are “a brief written record of events and impressions captured in key words and phrases” (Emerson et al., 2011 , p. 29). These quickly written or typed fragments are used to help the researcher as they later create detailed expanded field notes.
A researcher may choose to take notes on paper or another electronic device. When permission is appropriately obtained, the researcher may also create video or audio recordings of the setting. Even when a recording is made, the researcher should still take jottings when possible as a source for both back up and further detail. The choice of paper or electronic device should be made based on the setting and the researcher’s level of participation in the field. In any case, the method used should be as unobtrusive as possible and should not disturb the events taking place. The researcher may choose to take jottings down openly—so that participants can see them writing or typing—or in a hidden manner (Emerson et al., 2011 ). The decision of how to record jottings in the field is also dependent on a number of other factors, including the nature of the research questions, the skill of the researcher, the mobility required by the setting, availability of power or Internet, and the language of the researcher as compared to the participants.
As events in a research setting unfold, the researcher should take down short notes in order to later remember the events when assembling expanded field notes. These jottings may be fragments of interactions, keywords, phrases, or verbatim quotes (when possible). For example:
Music Education Class Participants: 1 Instructor, 8 Students (college-aged), 1 researcher 2:15 p.m . Instructor (Dr. Hart) tells class they are making a chart about assumptions Hope: Learning takes place in a building Hart: So, learning should look a certain way Hope: No! Not what I meant Hart says translating to fit in chart Hope: No, no! (shakes head and looks at me) Me: I think she is saying that learning could happen outdoors, or at home . Hope: Yes!! Hart writes “Learning should look a certain way” on chart, ignoring our protestations Hope frowns scrunches eyebrows together. Looks down at phone . 1
Jottings may also consist of drawings and diagrams that document the space. Jottings should always show time and date, and it is useful to check the clock and record the time every 5–10 minutes or so throughout the observation. This will help later, when considering and analyzing the pace of events. The question of when a researcher should take down jottings is also worth consideration. If the researcher is involved in a conversation, or is an otherwise active participant in the situation or events, they should prioritize this interaction over note-taking. Tact and rapport are vitally important to qualitative observation, and sometimes note-taking may come across as if the researcher is rude or not listening. Wait for breaks or lulls in the conversation to record jottings. If your participation requires that you move around a room or other space, it may be best to use a small notebook or electronic tablet that is easily carried.
Our inclination as educational researchers is often to provide evaluative feedback on the performance of the educator being observed. When recording field notes, it is important to resist this urge. Jottings should include as much detail as possible, using descriptive and concrete language. Emerson et al. ( 2011 ) suggest the following recommendations on how one might document what is observed. First, one should describe all key components of the setting, using concrete sensory details that would help a third-party reader gain a reasonable vision of the actors and events. Rather than stating that a participant looked defeated, for instance, it would be more appropriate to record the details of their bearing that lead you to believe this is the case. In this example, the researcher might record: The participant’s eyes were cast down toward the ground and their shoulders were hunched forward . Additionally, researchers should avoid characterizing events through generalization or summary in field notes, since these represent a form of analysis or judgement. The purpose in avoiding generalization at this phase is to leave the possibility open for alternative interpretation once the full data set is established. It is possible that later events may clarify or alter the meaning of a particular social act.
Feelings and emotions will always be present in a research setting, and should be acknowledged and recorded. Emerson et al. ( 2011 ) noted that it can be informative to describe actors’ emotional expressions and responses to the events occurring throughout the observation. They also recommend that the researcher record their own impressions and feelings about the events. Having recorded these feelings and responses, the researcher can compare their own reactions to those of the participants in order better to understand the cultural and social meanings unique to that setting and those actors. However, the impressions and feelings of the researcher do represent a form of analysis, and should be specifically recorded as such.
In field notes, the researcher should differentiate between the types of information they record so that it will be recognizable when they return to the jottings to expand them into completed field notes. Concrete descriptions of sensory details and verbatim interactions should be recorded in one manner or place, and impressions or personal feelings should be recorded differently. For example, some researchers choose to separate these types of jottings into two columns in their notebook before entering the field. Others use the comment function in word-processing software to separate analytic commentary from notes. These parallel notes can also be recorded using the advanced functionality of apps such as Evernote and MAXApp.
Both types of recording are important, and serve to help the researcher remember what they were seeing and feeling while in the field. These reminders will serve as recall prompts when the researcher goes to expand their field notes into full notes, and later when they use those notes to create analytic memos.
Post-Field or Inter-Field
This domain is dually named to highlight the fact that qualitative participant observers should complete multiple observations over a significant length of time. A single observation is not sufficient for allowing the researcher to understand contextual cultural meanings, and most qualitative methodologists encourage in-depth, long-term engagement in the field. Thus, the inter-field domain name refers to the idea that researchers will likely need to enter and exit the field a number of times. Expanded field notes, notes-on-notes, and memos should be created in between visits to help focus the study. At some point, examination of field notes and other qualitative data (i.e., interviews, documents) will start to seem redundant. In other words, the researcher(s) will begin to see the same phenomena occurring, with nothing new arising in successive observations. In other words, they have reached the point of data saturation (Glesne, 2016 ). There is not a set number of observations, or a pre determined length of field observation, necessary for rigorous qualitative observation. Rather, the researcher(s) must determine this point of theoretical saturation for themselves.
Expanded Field Notes
The process of observation does not stop once the researcher leaves the field. One cannot possibly record every detail of the observation in the moment, so jottings should be re-read and expanded after the fact. In order to preserve detail with the freshest memory, a number of sources recommend that the researcher read over jottings and expand them into fully realized field notes within 24 to 48 hours. This expansion process involves recreating a record of the events and interactions observed in full, rich detail (Geertz, 1973 ). In the field, the researcher may not have had time to record these happenings fully, but the jottings serve to jog the memory so that the researcher can later recall the field more fully. Expanded field notes may take the form of prose (paragraphs), a script of dialogue, figures, or diagrams. Time notations from jottings should be preserved in expanded field notes, and researcher asides or commentaries should also be kept separate from concrete sensory observations. Here is an example of field notes expanded from the jottings provided in the section “ Recording Field Notes ”:
Music Education Class Participants: 1 Instructor, 8 Students (college-aged), 1 researcher 2:15 p.m . The instructor, Dr. Hart asks the students what assumptions we make about learning. Hope, a white woman, raises her hand and says, “We assume that learning takes place in a building.” I feel that I understand what she’s saying and nod in agreement. Though I’ve nodded my head somewhat unconsciously, I notice that Hope has seen me agreeing with her. Dr. Hart says: “Yes, we assume that a school should look a certain way.” She says “No, that’s not what I mean!” and looks at me. Dr. Hart says that he’s going to translate her meaning a bit so that it will fit the chart they’ve been creating, and that, basically, it’s the same meaning anyway [paraphrased]. Hope looks disconcerted, with her eyebrows scrunched together. She is also shaking her head to left and right (as if to disagree) and frowning. She tries to reiterate her point, [paraphrase] “I am saying that learning experiences don’t need to happen in a building.” She again looks at me and I feel compelled to speak up. I say, “I think I know what you’re saying, you mean that you don’t have to be inside a school to learn, that you can learn outdoors, and at home with your family.” She says, “Yes! That’s what I mean!” Dr. Hart says “Oh, Ok!” but then asks John to write-up his original statement of “Schools look a certain way.” Hope slouches in her chair and rounds her shoulders, picks up her phone and begins to type .
In a first visit to a setting, it may be useful to assign pseudonyms or codes to participants to help with de-identifying participant data throughout the field notes. In addition to assigning such codes, the researcher should keep a code book or identifying document, preferably stored separately.
Expanded field notes should include as much detail as possible. Emerson et al. ( 2011 ) elaborated on this descriptive writing strategy that “calls for concrete details rather than abstract generalizations, for sensory imagery rather than evaluative labels, and for immediacy through details presented at close range” (p. 58). By necessity, this means that field notes will be long and labor intensive, with the added pressure that the researcher should record them as soon as possible to avoid losing detail. It is important not to skip this step of the process. It is easy to forget the particularities of the social field over time, and expanded field notes preserve complexity and richness of the data. Additionally, expanded field notes are vital when collaborating with other researchers, as they allow the others to experience a full description of events even if they were not present.
Notes-on-Notes
While writing expanded field notes, the researcher will inevitably begin to develop preliminary commentary and impressions. These impressions should not be considered findings when they arise from a single observation. Rather, they should be noted clearly so that the researcher may confirm or disconfirm their impressions in subsequent observations, interviews, or document analysis. To do this, researchers should create a short memo containing notes-on-notes for each field observation. Such a memo should move beyond impressions and begin to comment or theorize on what is observed. That said, notes-on-notes should not be considered findings until they have been compared to observations and triangulated with other types of data. Notes-on-notes can help to focus and narrow the research questions, and aid in moving the research project from descriptive to focused observation. Additionally, they may help in generating interview guides for focus groups or individual interviews where preliminary findings can be confirmed or ruled out. This is also a place for the researcher to record their own feelings in more detail. For example, if the researcher is experiencing frustration because they are not able to observe interactions between particular participants, they may note this frustration in the notes-on-notes memo. Notes-on-notes need not be lengthy; sometimes a paragraph or two is enough to express whatever should be noted for follow-up or later confirmation.
The process of qualitative observation is cyclical. Expanded field notes, along with the corresponding notes-on-notes, will most often direct the researcher back to the field to gather further information. The requisite information may represent a broadening of perspective, or a narrowing, depending on the setting and participants. Experienced researchers often begin the analytic process immediately upon entering a field of study, parsing out codes and themes in the data that they can further clarify (and sometimes quantify) as the study progresses. Analysis and coding are not included in this article, though the authors cited herein offer great insight on that topic.
Encouragements
One of the most encouraging aspects of observational research in educational settings is the opportunity to build partnerships and rapport with those who are currently working in the field. Very often there is a perceived divide between academics and P–12 teachers who work in classrooms. Again, the importance of developing rapport, basic trust, as well as collegiality cannot be overstated. Meaningful partnerships across these perceived divides are one of the most productive potential sites for educational change and reform to occur. These are the sites where, together, we might exert the most influence over policy, equity, and curriculum.
Rapport building should be genuine. It is not advisable to fake an interest in a site of study or associated stakeholders simply to benefits one’s own research agenda. Such an approach echoes the exploitative measures of early ethnographers, and is considered highly unethical. Thus, a skill that we have not yet explored regarding qualitative observation in educational settings is the ability of the researcher to seek and build meaningful, ethical relationships with those they study. The conundrum here then becomes that when we establish real relationships with participants, our subjectivity is engaged on yet another level. However, the benefits largely outweigh any potential pitfalls.
Moving beyond the stereotypical idea of one observer recording the events of a classroom, another opportunity is that of participatory action research. By engaging stakeholders in the design and execution of the research, the research may address issues that are pressing or of great importance to participants. This serves to generate educational change regarding issues that are of urgent concern to those engaged in the field on a day-to-day basis. A particular arena of possibility here involves engaging students in research.
Final Thoughts
To summarize, observation in educational settings is a detailed and rigorous process. This process involves self-reflection, attention to concrete and sensory details, and, most important, the ability to build rapport with participants. This article has detailed one methodological perspective and approach toward qualitative observation in educational settings. This approach can be used in both traditional and nontraditional educational settings, provided that the researcher maintains flexibility and an introspective approach to observation and, later, analysis. Cornerstone observational studies such as Ladson-Billings’s ( 2009 ) The Dreamkeepers , Lareau’s ( 2011 ) Unequal Childhoods , and Willis’s ( 2017 ) Learning to Labour provide useful examples of the insights that can be gleaned from observation.
The reflective “move between” one’s own subjectivity and that of participants is truly the generative site of observational research (Denzin, 2017 ). When done well, this moving in between can reveal similarities and differences, and can help people to take the time to understand diverse experiences, rather than approaching them from a stance of judgement and evaluation. Truly, observational research is a place where we have the opportunity to focus deeply on the experience of others. This is not just to walk in their shoes, but to understand the forces and meanings that influence their daily lives. These are some of the most exciting moments of potential change that qualitative research has to offer.
Methodological Texts
- Emerson, R. M. , Fretz, R. I. , & Shaw, L. L. (2011). Writing ethnographic fieldnotes (2nd ed.). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Spradley, J. P. (1980). Participant observation . New York, NY: Holt, Rhinehart, and Winston.
Representative Studies
- Ladson-Billings, G. (2009). The dreamkeepers: Successful teachers of African American children . San Francisco, CA: John Wiley & Sons.
- Lareau, A. (2011). Unequal childhoods: Class, race, and family life . Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Willis, P. (2017). Learning to labour: How working class kids get working class jobs . New York, NY: Routledge.
- Angrosino, M. , & Rosenberg, J. (2011). Observations on observation: Continuities and challenges. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of qualitative research (4th ed., pp. 467–478). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Denzin, N. K. (2017). The research act: A theoretical introduction to sociological methods . New York, NY: Routledge.
- Dewey, J. (1938). Experience and education . Indianapolis, IN: Kappa Delta Pi.
- Geertz, C. (1973). Thick description: Toward an interpretive theory of culture. The interpretation of cultures (pp. 3–30). New York, NY: Basic Books.
- Gershon, W. S. (2013). Vibrational affect: Sound theory and practice in qualitative research. Cultural Studies?↔Critical Methodologies, 13 (4), 257–262.
- Glesne, C. (2016). Becoming qualitative researchers: An introduction (5th ed.) New York, NY: Pearson.
- Lave, J. , & Wenger, E. (1991). Situated learning: Legitimate peripheral participation . Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- Noblit, G. W. , Flores, S. Y. , & Murillo, E. G. (2004). Postcritical ethnography: Reinscribing critique . Cresskill, NJ: Hampton Press.
- Pillow, W. (2003). Confession, catharsis, or cure? Rethinking the uses of reflexivity as methodological power in qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education , 16 (2), 175–196.
- Sensoy, O. , & DiAngelo, R. (2017). Is everyone really equal? An introduction to key concepts in social justice education . New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
1. Expanded field notes from these jottings are included in the section “ Expanded Field Notes .”
Related Articles
- Ethnography and Education
- Qualitative Design Research Methods
- Interviews and Interviewing in the Ethnography of Education
- Writing and Managing Multimodal Field Notes
- Ethnography Across Borders
- Mixed Methods Approaches and Qualitative Methodology for Higher Education Policy Research
- Qualitative Data Analysis and the Use of Theory
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Education. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 19 May 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|81.177.182.136]
- 81.177.182.136
Character limit 500 /500

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Non-Experimental Research
32 Observational Research
Learning objectives.
- List the various types of observational research methods and distinguish between each.
- Describe the strengths and weakness of each observational research method.
What Is Observational Research?
The term observational research is used to refer to several different types of non-experimental studies in which behavior is systematically observed and recorded. The goal of observational research is to describe a variable or set of variables. More generally, the goal is to obtain a snapshot of specific characteristics of an individual, group, or setting. As described previously, observational research is non-experimental because nothing is manipulated or controlled, and as such we cannot arrive at causal conclusions using this approach. The data that are collected in observational research studies are often qualitative in nature but they may also be quantitative or both (mixed-methods). There are several different types of observational methods that will be described below.
Naturalistic Observation
Naturalistic observation is an observational method that involves observing people’s behavior in the environment in which it typically occurs. Thus naturalistic observation is a type of field research (as opposed to a type of laboratory research). Jane Goodall’s famous research on chimpanzees is a classic example of naturalistic observation. Dr. Goodall spent three decades observing chimpanzees in their natural environment in East Africa. She examined such things as chimpanzee’s social structure, mating patterns, gender roles, family structure, and care of offspring by observing them in the wild. However, naturalistic observation could more simply involve observing shoppers in a grocery store, children on a school playground, or psychiatric inpatients in their wards. Researchers engaged in naturalistic observation usually make their observations as unobtrusively as possible so that participants are not aware that they are being studied. Such an approach is called disguised naturalistic observation . Ethically, this method is considered to be acceptable if the participants remain anonymous and the behavior occurs in a public setting where people would not normally have an expectation of privacy. Grocery shoppers putting items into their shopping carts, for example, are engaged in public behavior that is easily observable by store employees and other shoppers. For this reason, most researchers would consider it ethically acceptable to observe them for a study. On the other hand, one of the arguments against the ethicality of the naturalistic observation of “bathroom behavior” discussed earlier in the book is that people have a reasonable expectation of privacy even in a public restroom and that this expectation was violated.
In cases where it is not ethical or practical to conduct disguised naturalistic observation, researchers can conduct undisguised naturalistic observation where the participants are made aware of the researcher presence and monitoring of their behavior. However, one concern with undisguised naturalistic observation is reactivity. Reactivity refers to when a measure changes participants’ behavior. In the case of undisguised naturalistic observation, the concern with reactivity is that when people know they are being observed and studied, they may act differently than they normally would. This type of reactivity is known as the Hawthorne effect . For instance, you may act much differently in a bar if you know that someone is observing you and recording your behaviors and this would invalidate the study. So disguised observation is less reactive and therefore can have higher validity because people are not aware that their behaviors are being observed and recorded. However, we now know that people often become used to being observed and with time they begin to behave naturally in the researcher’s presence. In other words, over time people habituate to being observed. Think about reality shows like Big Brother or Survivor where people are constantly being observed and recorded. While they may be on their best behavior at first, in a fairly short amount of time they are flirting, having sex, wearing next to nothing, screaming at each other, and occasionally behaving in ways that are embarrassing.
Participant Observation
Another approach to data collection in observational research is participant observation. In participant observation , researchers become active participants in the group or situation they are studying. Participant observation is very similar to naturalistic observation in that it involves observing people’s behavior in the environment in which it typically occurs. As with naturalistic observation, the data that are collected can include interviews (usually unstructured), notes based on their observations and interactions, documents, photographs, and other artifacts. The only difference between naturalistic observation and participant observation is that researchers engaged in participant observation become active members of the group or situations they are studying. The basic rationale for participant observation is that there may be important information that is only accessible to, or can be interpreted only by, someone who is an active participant in the group or situation. Like naturalistic observation, participant observation can be either disguised or undisguised. In disguised participant observation , the researchers pretend to be members of the social group they are observing and conceal their true identity as researchers.
In a famous example of disguised participant observation, Leon Festinger and his colleagues infiltrated a doomsday cult known as the Seekers, whose members believed that the apocalypse would occur on December 21, 1954. Interested in studying how members of the group would cope psychologically when the prophecy inevitably failed, they carefully recorded the events and reactions of the cult members in the days before and after the supposed end of the world. Unsurprisingly, the cult members did not give up their belief but instead convinced themselves that it was their faith and efforts that saved the world from destruction. Festinger and his colleagues later published a book about this experience, which they used to illustrate the theory of cognitive dissonance (Festinger, Riecken, & Schachter, 1956) [1] .
In contrast with undisguised participant observation , the researchers become a part of the group they are studying and they disclose their true identity as researchers to the group under investigation. Once again there are important ethical issues to consider with disguised participant observation. First no informed consent can be obtained and second deception is being used. The researcher is deceiving the participants by intentionally withholding information about their motivations for being a part of the social group they are studying. But sometimes disguised participation is the only way to access a protective group (like a cult). Further, disguised participant observation is less prone to reactivity than undisguised participant observation.
Rosenhan’s study (1973) [2] of the experience of people in a psychiatric ward would be considered disguised participant observation because Rosenhan and his pseudopatients were admitted into psychiatric hospitals on the pretense of being patients so that they could observe the way that psychiatric patients are treated by staff. The staff and other patients were unaware of their true identities as researchers.
Another example of participant observation comes from a study by sociologist Amy Wilkins on a university-based religious organization that emphasized how happy its members were (Wilkins, 2008) [3] . Wilkins spent 12 months attending and participating in the group’s meetings and social events, and she interviewed several group members. In her study, Wilkins identified several ways in which the group “enforced” happiness—for example, by continually talking about happiness, discouraging the expression of negative emotions, and using happiness as a way to distinguish themselves from other groups.
One of the primary benefits of participant observation is that the researchers are in a much better position to understand the viewpoint and experiences of the people they are studying when they are a part of the social group. The primary limitation with this approach is that the mere presence of the observer could affect the behavior of the people being observed. While this is also a concern with naturalistic observation, additional concerns arise when researchers become active members of the social group they are studying because that they may change the social dynamics and/or influence the behavior of the people they are studying. Similarly, if the researcher acts as a participant observer there can be concerns with biases resulting from developing relationships with the participants. Concretely, the researcher may become less objective resulting in more experimenter bias.
Structured Observation
Another observational method is structured observation . Here the investigator makes careful observations of one or more specific behaviors in a particular setting that is more structured than the settings used in naturalistic or participant observation. Often the setting in which the observations are made is not the natural setting. Instead, the researcher may observe people in the laboratory environment. Alternatively, the researcher may observe people in a natural setting (like a classroom setting) that they have structured some way, for instance by introducing some specific task participants are to engage in or by introducing a specific social situation or manipulation.
Structured observation is very similar to naturalistic observation and participant observation in that in all three cases researchers are observing naturally occurring behavior; however, the emphasis in structured observation is on gathering quantitative rather than qualitative data. Researchers using this approach are interested in a limited set of behaviors. This allows them to quantify the behaviors they are observing. In other words, structured observation is less global than naturalistic or participant observation because the researcher engaged in structured observations is interested in a small number of specific behaviors. Therefore, rather than recording everything that happens, the researcher only focuses on very specific behaviors of interest.
Researchers Robert Levine and Ara Norenzayan used structured observation to study differences in the “pace of life” across countries (Levine & Norenzayan, 1999) [4] . One of their measures involved observing pedestrians in a large city to see how long it took them to walk 60 feet. They found that people in some countries walked reliably faster than people in other countries. For example, people in Canada and Sweden covered 60 feet in just under 13 seconds on average, while people in Brazil and Romania took close to 17 seconds. When structured observation takes place in the complex and even chaotic “real world,” the questions of when, where, and under what conditions the observations will be made, and who exactly will be observed are important to consider. Levine and Norenzayan described their sampling process as follows:
“Male and female walking speed over a distance of 60 feet was measured in at least two locations in main downtown areas in each city. Measurements were taken during main business hours on clear summer days. All locations were flat, unobstructed, had broad sidewalks, and were sufficiently uncrowded to allow pedestrians to move at potentially maximum speeds. To control for the effects of socializing, only pedestrians walking alone were used. Children, individuals with obvious physical handicaps, and window-shoppers were not timed. Thirty-five men and 35 women were timed in most cities.” (p. 186).
Precise specification of the sampling process in this way makes data collection manageable for the observers, and it also provides some control over important extraneous variables. For example, by making their observations on clear summer days in all countries, Levine and Norenzayan controlled for effects of the weather on people’s walking speeds. In Levine and Norenzayan’s study, measurement was relatively straightforward. They simply measured out a 60-foot distance along a city sidewalk and then used a stopwatch to time participants as they walked over that distance.
As another example, researchers Robert Kraut and Robert Johnston wanted to study bowlers’ reactions to their shots, both when they were facing the pins and then when they turned toward their companions (Kraut & Johnston, 1979) [5] . But what “reactions” should they observe? Based on previous research and their own pilot testing, Kraut and Johnston created a list of reactions that included “closed smile,” “open smile,” “laugh,” “neutral face,” “look down,” “look away,” and “face cover” (covering one’s face with one’s hands). The observers committed this list to memory and then practiced by coding the reactions of bowlers who had been videotaped. During the actual study, the observers spoke into an audio recorder, describing the reactions they observed. Among the most interesting results of this study was that bowlers rarely smiled while they still faced the pins. They were much more likely to smile after they turned toward their companions, suggesting that smiling is not purely an expression of happiness but also a form of social communication.
In yet another example (this one in a laboratory environment), Dov Cohen and his colleagues had observers rate the emotional reactions of participants who had just been deliberately bumped and insulted by a confederate after they dropped off a completed questionnaire at the end of a hallway. The confederate was posing as someone who worked in the same building and who was frustrated by having to close a file drawer twice in order to permit the participants to walk past them (first to drop off the questionnaire at the end of the hallway and once again on their way back to the room where they believed the study they signed up for was taking place). The two observers were positioned at different ends of the hallway so that they could read the participants’ body language and hear anything they might say. Interestingly, the researchers hypothesized that participants from the southern United States, which is one of several places in the world that has a “culture of honor,” would react with more aggression than participants from the northern United States, a prediction that was in fact supported by the observational data (Cohen, Nisbett, Bowdle, & Schwarz, 1996) [6] .
When the observations require a judgment on the part of the observers—as in the studies by Kraut and Johnston and Cohen and his colleagues—a process referred to as coding is typically required . Coding generally requires clearly defining a set of target behaviors. The observers then categorize participants individually in terms of which behavior they have engaged in and the number of times they engaged in each behavior. The observers might even record the duration of each behavior. The target behaviors must be defined in such a way that guides different observers to code them in the same way. This difficulty with coding illustrates the issue of interrater reliability, as mentioned in Chapter 4. Researchers are expected to demonstrate the interrater reliability of their coding procedure by having multiple raters code the same behaviors independently and then showing that the different observers are in close agreement. Kraut and Johnston, for example, video recorded a subset of their participants’ reactions and had two observers independently code them. The two observers showed that they agreed on the reactions that were exhibited 97% of the time, indicating good interrater reliability.
One of the primary benefits of structured observation is that it is far more efficient than naturalistic and participant observation. Since the researchers are focused on specific behaviors this reduces time and expense. Also, often times the environment is structured to encourage the behaviors of interest which again means that researchers do not have to invest as much time in waiting for the behaviors of interest to naturally occur. Finally, researchers using this approach can clearly exert greater control over the environment. However, when researchers exert more control over the environment it may make the environment less natural which decreases external validity. It is less clear for instance whether structured observations made in a laboratory environment will generalize to a real world environment. Furthermore, since researchers engaged in structured observation are often not disguised there may be more concerns with reactivity.
Case Studies
A case study is an in-depth examination of an individual. Sometimes case studies are also completed on social units (e.g., a cult) and events (e.g., a natural disaster). Most commonly in psychology, however, case studies provide a detailed description and analysis of an individual. Often the individual has a rare or unusual condition or disorder or has damage to a specific region of the brain.
Like many observational research methods, case studies tend to be more qualitative in nature. Case study methods involve an in-depth, and often a longitudinal examination of an individual. Depending on the focus of the case study, individuals may or may not be observed in their natural setting. If the natural setting is not what is of interest, then the individual may be brought into a therapist’s office or a researcher’s lab for study. Also, the bulk of the case study report will focus on in-depth descriptions of the person rather than on statistical analyses. With that said some quantitative data may also be included in the write-up of a case study. For instance, an individual’s depression score may be compared to normative scores or their score before and after treatment may be compared. As with other qualitative methods, a variety of different methods and tools can be used to collect information on the case. For instance, interviews, naturalistic observation, structured observation, psychological testing (e.g., IQ test), and/or physiological measurements (e.g., brain scans) may be used to collect information on the individual.
HM is one of the most notorious case studies in psychology. HM suffered from intractable and very severe epilepsy. A surgeon localized HM’s epilepsy to his medial temporal lobe and in 1953 he removed large sections of his hippocampus in an attempt to stop the seizures. The treatment was a success, in that it resolved his epilepsy and his IQ and personality were unaffected. However, the doctors soon realized that HM exhibited a strange form of amnesia, called anterograde amnesia. HM was able to carry out a conversation and he could remember short strings of letters, digits, and words. Basically, his short term memory was preserved. However, HM could not commit new events to memory. He lost the ability to transfer information from his short-term memory to his long term memory, something memory researchers call consolidation. So while he could carry on a conversation with someone, he would completely forget the conversation after it ended. This was an extremely important case study for memory researchers because it suggested that there’s a dissociation between short-term memory and long-term memory, it suggested that these were two different abilities sub-served by different areas of the brain. It also suggested that the temporal lobes are particularly important for consolidating new information (i.e., for transferring information from short-term memory to long-term memory).

The history of psychology is filled with influential cases studies, such as Sigmund Freud’s description of “Anna O.” (see Note 6.1 “The Case of “Anna O.””) and John Watson and Rosalie Rayner’s description of Little Albert (Watson & Rayner, 1920) [7] , who allegedly learned to fear a white rat—along with other furry objects—when the researchers repeatedly made a loud noise every time the rat approached him.
The Case of “Anna O.”
Sigmund Freud used the case of a young woman he called “Anna O.” to illustrate many principles of his theory of psychoanalysis (Freud, 1961) [8] . (Her real name was Bertha Pappenheim, and she was an early feminist who went on to make important contributions to the field of social work.) Anna had come to Freud’s colleague Josef Breuer around 1880 with a variety of odd physical and psychological symptoms. One of them was that for several weeks she was unable to drink any fluids. According to Freud,
She would take up the glass of water that she longed for, but as soon as it touched her lips she would push it away like someone suffering from hydrophobia.…She lived only on fruit, such as melons, etc., so as to lessen her tormenting thirst. (p. 9)
But according to Freud, a breakthrough came one day while Anna was under hypnosis.
[S]he grumbled about her English “lady-companion,” whom she did not care for, and went on to describe, with every sign of disgust, how she had once gone into this lady’s room and how her little dog—horrid creature!—had drunk out of a glass there. The patient had said nothing, as she had wanted to be polite. After giving further energetic expression to the anger she had held back, she asked for something to drink, drank a large quantity of water without any difficulty, and awoke from her hypnosis with the glass at her lips; and thereupon the disturbance vanished, never to return. (p.9)
Freud’s interpretation was that Anna had repressed the memory of this incident along with the emotion that it triggered and that this was what had caused her inability to drink. Furthermore, he believed that her recollection of the incident, along with her expression of the emotion she had repressed, caused the symptom to go away.
As an illustration of Freud’s theory, the case study of Anna O. is quite effective. As evidence for the theory, however, it is essentially worthless. The description provides no way of knowing whether Anna had really repressed the memory of the dog drinking from the glass, whether this repression had caused her inability to drink, or whether recalling this “trauma” relieved the symptom. It is also unclear from this case study how typical or atypical Anna’s experience was.

Case studies are useful because they provide a level of detailed analysis not found in many other research methods and greater insights may be gained from this more detailed analysis. As a result of the case study, the researcher may gain a sharpened understanding of what might become important to look at more extensively in future more controlled research. Case studies are also often the only way to study rare conditions because it may be impossible to find a large enough sample of individuals with the condition to use quantitative methods. Although at first glance a case study of a rare individual might seem to tell us little about ourselves, they often do provide insights into normal behavior. The case of HM provided important insights into the role of the hippocampus in memory consolidation.
However, it is important to note that while case studies can provide insights into certain areas and variables to study, and can be useful in helping develop theories, they should never be used as evidence for theories. In other words, case studies can be used as inspiration to formulate theories and hypotheses, but those hypotheses and theories then need to be formally tested using more rigorous quantitative methods. The reason case studies shouldn’t be used to provide support for theories is that they suffer from problems with both internal and external validity. Case studies lack the proper controls that true experiments contain. As such, they suffer from problems with internal validity, so they cannot be used to determine causation. For instance, during HM’s surgery, the surgeon may have accidentally lesioned another area of HM’s brain (a possibility suggested by the dissection of HM’s brain following his death) and that lesion may have contributed to his inability to consolidate new information. The fact is, with case studies we cannot rule out these sorts of alternative explanations. So, as with all observational methods, case studies do not permit determination of causation. In addition, because case studies are often of a single individual, and typically an abnormal individual, researchers cannot generalize their conclusions to other individuals. Recall that with most research designs there is a trade-off between internal and external validity. With case studies, however, there are problems with both internal validity and external validity. So there are limits both to the ability to determine causation and to generalize the results. A final limitation of case studies is that ample opportunity exists for the theoretical biases of the researcher to color or bias the case description. Indeed, there have been accusations that the woman who studied HM destroyed a lot of her data that were not published and she has been called into question for destroying contradictory data that didn’t support her theory about how memories are consolidated. There is a fascinating New York Times article that describes some of the controversies that ensued after HM’s death and analysis of his brain that can be found at: https://www.nytimes.com/2016/08/07/magazine/the-brain-that-couldnt-remember.html?_r=0
Archival Research
Another approach that is often considered observational research involves analyzing archival data that have already been collected for some other purpose. An example is a study by Brett Pelham and his colleagues on “implicit egotism”—the tendency for people to prefer people, places, and things that are similar to themselves (Pelham, Carvallo, & Jones, 2005) [9] . In one study, they examined Social Security records to show that women with the names Virginia, Georgia, Louise, and Florence were especially likely to have moved to the states of Virginia, Georgia, Louisiana, and Florida, respectively.
As with naturalistic observation, measurement can be more or less straightforward when working with archival data. For example, counting the number of people named Virginia who live in various states based on Social Security records is relatively straightforward. But consider a study by Christopher Peterson and his colleagues on the relationship between optimism and health using data that had been collected many years before for a study on adult development (Peterson, Seligman, & Vaillant, 1988) [10] . In the 1940s, healthy male college students had completed an open-ended questionnaire about difficult wartime experiences. In the late 1980s, Peterson and his colleagues reviewed the men’s questionnaire responses to obtain a measure of explanatory style—their habitual ways of explaining bad events that happen to them. More pessimistic people tend to blame themselves and expect long-term negative consequences that affect many aspects of their lives, while more optimistic people tend to blame outside forces and expect limited negative consequences. To obtain a measure of explanatory style for each participant, the researchers used a procedure in which all negative events mentioned in the questionnaire responses, and any causal explanations for them were identified and written on index cards. These were given to a separate group of raters who rated each explanation in terms of three separate dimensions of optimism-pessimism. These ratings were then averaged to produce an explanatory style score for each participant. The researchers then assessed the statistical relationship between the men’s explanatory style as undergraduate students and archival measures of their health at approximately 60 years of age. The primary result was that the more optimistic the men were as undergraduate students, the healthier they were as older men. Pearson’s r was +.25.
This method is an example of content analysis —a family of systematic approaches to measurement using complex archival data. Just as structured observation requires specifying the behaviors of interest and then noting them as they occur, content analysis requires specifying keywords, phrases, or ideas and then finding all occurrences of them in the data. These occurrences can then be counted, timed (e.g., the amount of time devoted to entertainment topics on the nightly news show), or analyzed in a variety of other ways.
Media Attributions
- What happens when you remove the hippocampus? – Sam Kean by TED-Ed licensed under a standard YouTube License
- Pappenheim 1882 by unknown is in the Public Domain .
- Festinger, L., Riecken, H., & Schachter, S. (1956). When prophecy fails: A social and psychological study of a modern group that predicted the destruction of the world. University of Minnesota Press. ↵
- Rosenhan, D. L. (1973). On being sane in insane places. Science, 179 , 250–258. ↵
- Wilkins, A. (2008). “Happier than Non-Christians”: Collective emotions and symbolic boundaries among evangelical Christians. Social Psychology Quarterly, 71 , 281–301. ↵
- Levine, R. V., & Norenzayan, A. (1999). The pace of life in 31 countries. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 30 , 178–205. ↵
- Kraut, R. E., & Johnston, R. E. (1979). Social and emotional messages of smiling: An ethological approach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 37 , 1539–1553. ↵
- Cohen, D., Nisbett, R. E., Bowdle, B. F., & Schwarz, N. (1996). Insult, aggression, and the southern culture of honor: An "experimental ethnography." Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 70 (5), 945-960. ↵
- Watson, J. B., & Rayner, R. (1920). Conditioned emotional reactions. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 3 , 1–14. ↵
- Freud, S. (1961). Five lectures on psycho-analysis . New York, NY: Norton. ↵
- Pelham, B. W., Carvallo, M., & Jones, J. T. (2005). Implicit egotism. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 14 , 106–110. ↵
- Peterson, C., Seligman, M. E. P., & Vaillant, G. E. (1988). Pessimistic explanatory style is a risk factor for physical illness: A thirty-five year longitudinal study. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 55 , 23–27. ↵
Research that is non-experimental because it focuses on recording systemic observations of behavior in a natural or laboratory setting without manipulating anything.
An observational method that involves observing people’s behavior in the environment in which it typically occurs.
When researchers engage in naturalistic observation by making their observations as unobtrusively as possible so that participants are not aware that they are being studied.
Where the participants are made aware of the researcher presence and monitoring of their behavior.
Refers to when a measure changes participants’ behavior.
In the case of undisguised naturalistic observation, it is a type of reactivity when people know they are being observed and studied, they may act differently than they normally would.
Researchers become active participants in the group or situation they are studying.
Researchers pretend to be members of the social group they are observing and conceal their true identity as researchers.
Researchers become a part of the group they are studying and they disclose their true identity as researchers to the group under investigation.
When a researcher makes careful observations of one or more specific behaviors in a particular setting that is more structured than the settings used in naturalistic or participant observation.
A part of structured observation whereby the observers use a clearly defined set of guidelines to "code" behaviors—assigning specific behaviors they are observing to a category—and count the number of times or the duration that the behavior occurs.
An in-depth examination of an individual.
A family of systematic approaches to measurement using qualitative methods to analyze complex archival data.
Research Methods in Psychology Copyright © 2019 by Rajiv S. Jhangiani, I-Chant A. Chiang, Carrie Cuttler, & Dana C. Leighton is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
CRO Platform
Test your insights. Run experiments. Win. Or learn. And then win.
eCommerce Customer Analytics Platform
Acquisition matters. But retention matters more. Understand, monitor & nurture the best customers.
- Case Studies
- Ebooks, Tools, Templates
- Digital Marketing Glossary
- eCommerce Growth Stories
- eCommerce Growth Show
- Help & Technical Documentation
CRO Guide > Chapter 3.1
Qualitative Research: Definition, Methodology, Limitation, Examples
Qualitative research is a method focused on understanding human behavior and experiences through non-numerical data. Examples of qualitative research include:
- One-on-one interviews,
- Focus groups, Ethnographic research,
- Case studies,
- Record keeping,
- Qualitative observations
In this article, we’ll provide tips and tricks on how to use qualitative research to better understand your audience through real world examples and improve your ROI. We’ll also learn the difference between qualitative and quantitative data.
Table of Contents
Marketers often seek to understand their customers deeply. Qualitative research methods such as face-to-face interviews, focus groups, and qualitative observations can provide valuable insights into your products, your market, and your customers’ opinions and motivations. Understanding these nuances can significantly enhance marketing strategies and overall customer satisfaction.
What is Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a market research method that focuses on obtaining data through open-ended and conversational communication. This method focuses on the “why” rather than the “what” people think about you. Thus, qualitative research seeks to uncover the underlying motivations, attitudes, and beliefs that drive people’s actions.
Let’s say you have an online shop catering to a general audience. You do a demographic analysis and you find out that most of your customers are male. Naturally, you will want to find out why women are not buying from you. And that’s what qualitative research will help you find out.
In the case of your online shop, qualitative research would involve reaching out to female non-customers through methods such as in-depth interviews or focus groups. These interactions provide a platform for women to express their thoughts, feelings, and concerns regarding your products or brand. Through qualitative analysis, you can uncover valuable insights into factors such as product preferences, user experience, brand perception, and barriers to purchase.
Types of Qualitative Research Methods
1. one-on-one interviews.
- A company might conduct interviews to understand why a product failed to meet sales expectations.
- A researcher might use interviews to gather personal stories about experiences with healthcare.
2. Focus groups
- A focus group could be used to test reactions to a new product concept.
- Marketers might use focus groups to see how different demographic groups react to an advertising campaign.
3. Ethnographic research
- A study of workplace culture within a tech startup.
- Observational research in a remote village to understand local traditions.
4. Case study research
- Analyzing a single school’s innovative teaching method.
- A detailed study of a patient’s medical treatment over several years.
H3: 5. Record keeping
- Historical research using old newspapers and letters.
- A study on policy changes over the years by examining government records.
6. Qualitative observation
- Sight : Observing the way customers visually interact with product displays in a store to understand their browsing behaviors and preferences.
- Smell : Noting reactions of consumers to different scents in a fragrance shop to study the impact of olfactory elements on product preference.
- Touch : Watching how individuals interact with different materials in a clothing store to assess the importance of texture in fabric selection.
- Taste : Evaluating reactions of participants in a taste test to identify flavor profiles that appeal to different demographic groups.
- Hearing : Documenting responses to changes in background music within a retail environment to determine its effect on shopping behavior and mood.
Qualitative Research Real World Examples
1. online grocery shop with a predominantly male audience, 2. software company launching a new product, 3. alan pushkin’s “god’s choice: the total world of a fundamentalist christian school”, 4. understanding buyers’ trends, 5. determining products/services missing from the market, real-time customer lifetime value (clv) benchmark report.
See where your business stands compared to 1,000+ e-stores in different industries.
Qualitative Research Approaches
- Narrative : This method focuses on individual life stories to understand personal experiences and journeys. It examines how people structure their stories and the themes within them to explore human existence. For example, a narrative study might look at cancer survivors to understand their resilience and coping strategies.
- Phenomenology : attempts to understand or explain life experiences or phenomena; It aims to reveal the depth of human consciousness and perception, such as by studying the daily lives of those with chronic illnesses.
- Grounded theory : investigates the process, action, or interaction with the goal of developing a theory “grounded” in observations and empirical data.
- Ethnography : describes and interprets an ethnic, cultural, or social group;
- Case study : examines episodic events in a definable framework, develops in-depth analyses of single or multiple cases, and generally explains “how”. An example might be studying a community health program to evaluate its success and impact.
How to Analyze Qualitative Data
1. data collection, 2. data preparation, 3. familiarization.
- Descriptive Coding : Summarize the primary topic of the data.
- In Vivo Coding : Use language and terms used by the participants themselves.
- Process Coding : Use gerunds (“-ing” words) to label the processes at play.
- Emotion Coding : Identify and record the emotions conveyed or experienced.
5. Thematic Development
6. interpreting the data, 7. validation, 8. reporting, limitations of qualitative research, 1. it’s a time-consuming process, 2. you can’t verify the results of qualitative research, 3. it’s a labor-intensive approach, 4. it’s difficult to investigate causality, 5. qualitative research is not statistically representative, quantitative vs. qualitative research.
Image source
Nature of Data:
- Quantitative research : Involves numerical data that can be measured and analyzed statistically.
- Qualitative research : Focuses on non-numerical data, such as words, images, and observations, to capture subjective experiences and meanings.
Research Questions:
- Quantitative research : Typically addresses questions related to “how many,” “how much,” or “to what extent,” aiming to quantify relationships and patterns.
- Qualitative research: Explores questions related to “why” and “how,” aiming to understand the underlying motivations, beliefs, and perceptions of individuals.
Data Collection Methods:
- Quantitative research : Relies on structured surveys, experiments, or observations with predefined variables and measures.
- Qualitative research : Utilizes open-ended interviews, focus groups, participant observations, and textual analysis to gather rich, contextually nuanced data.
Analysis Techniques:
- Quantitative research: Involves statistical analysis to identify correlations, associations, or differences between variables.
- Qualitative research: Employs thematic analysis, coding, and interpretation to uncover patterns, themes, and insights within qualitative data.

Do Conversion Rate Optimization the Right way.
Explore helps you make the most out of your CRO efforts through advanced A/B testing, surveys, advanced segmentation and optimised customer journeys.
Like what you’re reading?
Join the informed ecommerce crowd.
We will never bug you with irrelevant info.
By clicking the Button, you confirm that you agree with our Terms and Conditions .
Continue your Conversion Rate Optimization Journey
- Last modified: January 3, 2023
- Conversion Rate Optimization , User Research
Valentin Radu
We’re a team of people that want to empower marketers around the world to create marketing campaigns that matter to consumers in a smart way. Meet us at the intersection of creativity, integrity, and development, and let us show you how to optimize your marketing.
Our Software
- > Book a Demo
- > Partner Program
- > Affiliate Program
- Blog Sitemap
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy & Security
- Cookies Policy
- REVEAL Terms and Conditions

- Liberty University
- Jerry Falwell Library
- Special Collections
- < Previous
Home > ETD > Doctoral > 5543
Doctoral Dissertations and Projects
Virtual coaching, self-directed learning, and the implementation of evidence-based practices: a single qualitative case study.
Elisabeth Myers , Liberty University Follow
School of Education
Doctor of Philosophy in Education (PhD)
Christine Saba
virtual coaching, self-directed learning, evidence-based practices, self-determination theory, sustained implementation
Disciplines
Education | Educational Leadership
Recommended Citation
Myers, Elisabeth, "Virtual Coaching, Self-Directed Learning, and the Implementation of Evidence-Based Practices: A Single Qualitative Case Study" (2024). Doctoral Dissertations and Projects . 5543. https://digitalcommons.liberty.edu/doctoral/5543
The purpose of this single instrumental case study was to understand how a virtual coaching program provides opportunities for self-directed learning during the implementation of evidence-based practices for adults at Navigator Coaching. The theory guiding this study was Deci and Ryan’s self-determination theory as conceptualizations of self-directed learning described in the literature mirror descriptions of self-determination. The central research question was: How does a virtual coaching program provide opportunities for self-directed learning during the implementation of evidence-based practices? As a single instrumental case, the setting for this study was one virtual life-coaching program in North America. The sample of participants included 12 adults who were currently enrolled in the program for a minimum of 6 months and participated in weekly program activities. Multiple data collection methods were employed to describe and understand the case: observations, audiovisual materials, and individual interviews. Interpretational analysis and a multistep data analysis process including direct interpretation, categorical aggregation, correspondence tables, and interpretive commentaries were utilized to develop the themes and overall synthesis of the case. Opportunities for self-directed learning were provided in weekly live sessions, modules in the program library, and in the Facebook group. Program members utilized instructional opportunities to satisfy their need for autonomy, thus becoming students of self. Participation in a purposeful community that was focused on solutions provided opportunities for program members to satisfy competence and relatedness needs. Program members implemented evidence-based practices and developed skills to create weekly learning plans, which assisted them in becoming agents of their highest selves.
Included in
Educational Leadership Commons
- Collections
- Faculty Expert Gallery
- Theses and Dissertations
- Conferences and Events
- Open Educational Resources (OER)
- Explore Disciplines
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS .
Faculty Authors
- Submit Research
- Expert Gallery Login
Student Authors
- Undergraduate Submissions
- Graduate Submissions
- Honors Submissions
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
- Open access
- Published: 10 May 2024
Barriers to equitable healthcare services for under-five children in Ethiopia: a qualitative exploratory study
- Hailu Fekadu 1 ,
- Wubegzier Mekonnen 2 ,
- Aynalem Adugna 3 ,
- Helmut Kloos 4 &
- Damen Hailemariam 2
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 613 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
192 Accesses
Metrics details
Disparities in child healthcare service utilization are unacceptably high in Ethiopia. Nevertheless, little is known about underlying barriers to accessing child health services, especially among low socioeconomic subgroups and in remote areas. This study aims to identify barriers to equity in the use of child healthcare services in Ethiopia.
Data were obtained from 20 key- informant interviews (KII) and 6 focus group discussions (FGD) with mothers and care givers. This study was conducted in Oromia Region, Arsi Zone, Zuway Dugda District from June 1–30, 2023. The study participants for this research were selected purposively. The information was collected based on the principle of saturation after sixteen consecutives interview were conducted. Both KII and FGD were audio-recorded and complementary notes were taken to record observations about the participants’ comments and their interactions. Each interview and FGD data were transcribed word-for-word in the local Afaan Oromo and Amaharic languages and then translated to English language. Finally, the data were analyzed thematically using NVivo 14 software and narrated in the linked pattern of child health service utilization.
This study identified six major themes which emerged as barriers to healthcare utilization equity for caregivers and their -under-five children. Barriers related to equity in low level of awareness regarding need, low socioeconomic status, geographical inaccessibility, barriers related to deficient healthcare system, community perception and cultural restrictions, and barriers of equity related to political instability and conflict . The most commonly recognized barriers of equity at the community level were political instability, conflict, and a tremendous distance to a health facility. Transportation challenges, poor functional services, closure of the health facility in working hours, and lack of proper planning to address the marginalized populations were identified barriers of equity at organizational or policy level.
This study showed that inequity in child healthcare utilization is an important challenge confronting Ethiopia. To achieve equity, policy makers and planners need to change health policy and structure to be pro-poor. It is also necessary to improve the healthcare system to increase service utilization and access for impoverished women, individuals with lower levels of education, and residents of isolated rural areas. Furthermore, context specific information pertaining to cultural barriers and political ecology are required.
Peer Review reports
Over the last few decades, the issue of equitable distribution and utilization of healthcare services has captured the attention of scholars, governments, and policy makers. While some countries have made much improvement in this regard, others have lagged behind. Child healthcare service use is no exception, and it has recently become a global concern [ 1 ].
Equity in health and health service utilization is a focus in the global health discourse as one of the cornerstones of primary health care (PHC) [ 2 ]. The United Nations has set a goal to reduce global neonatal deaths from 25 per 1,000 live births to 12 per 1,000 by the year 2030 [ 3 ]. Achieving this target will require strong commitment from both service providers as well as financiers of the health sector, including government and community leaders [ 3 ]. Among the World Health Organization’s main focus areas for under-five health, is the reduction of inequities in accordance with the universal health coverage principles. This includes addressing the health needs of children in poor and remote communities. Many countries have implemented various programs aimed at minimizing unnecessary disparities in health service utilization [ 4 ]. Community based health services in particular have been found to be effective in minimizing inequities in health status and health service utilization [ 4 ]. For instance, the Ethiopian government is committed to improve equity through the health extension program and other initiatives [ 5 ]. Moreover, Ethiopia included the equity objective in its health sector transformation plan [ 6 ]. Nevertheless, inequities in service coverage and difference in maternal and child health outcomes remain a challenge [ 7 , 8 ]. The coverage of child health services and basic child immunizations has favored wealthier, more educated, and urban populations. [ 9 ]. For instance, despite significant decline is observed in under five mortality from 123 per 1,000 live births in 2005 to 59 in 2019, still there exists a disparity between different population groups [ 9 ].
Ethiopia met the MDGS for child mortality rate (CMR) in 2013 [ 10 ]. However, the gains made between 1990 and 2013 were not uniformly distributed among Ethiopians; inequity indicators of mortality by wealth had not significantly decreased. During this 23-year period, the mortality among the poorest was unchanged. Even though child health services are supposed to be provided free of charge at public facilities, the disparity in access to or utilization of the services is high in Ethiopia. Like mortality disparity, there is a considerable disparity in coverage of life-saving interventions by wealth status and place of residence [ 11 ].
Addressing equity is a significant challenge in healthcare delivery in Ethiopia. The barriers that were reported to be significantly associated with service utilization included geographical access as a function of distance; financial barriers; and socio-cultural factors such as language, cultural norms, health beliefs and perceptions, maternal education and decision making power and lack of knowledge and awareness, which in the aggregate can lead to low demand for and use of services, particularly by the poor [ 12 , 13 ]. Long distances and extended travel times remain key barriers to access health facilities in many rural communities in Ethiopia [ 11 , 14 ]. For instance, in Indonesia proximity to healthcare facilities significantly decreases child mortality [ 15 ]. Furthermore, according to a study from Uganda, Nigeria and Ethiopia long distances to health care facilities cause delays seeking care [ 16 , 17 , 18 ]. Even where health care services are available, the cost of seeking care may delay or prevent poor households from accessing them. This problem is particularly discriminating in rural areas where the density of modern health care facilities is low and in settings where transportation systems and road infrastructures are poor [ 18 ]. Furthermore, over the last five years, Ethiopia has faced internal conflict and political instability which exacerbated inequity in the utilization of child health services among the poor and in rural communities. Both insecurity and scarce resources are critical issues in child healthcare accessibility for women living in conflict zones and socioeconomically unstable settings [ 19 ].
Political instability disrupts electricity, water, and food supplies, destabilizes social and welfare systems, including the health and transportation systems, and increases unemployment, homelessness, and poverty—all of which have a negative impact on the use of maternal and child health services [ 20 ]. Hence, these issues did not addressed in any of the studies done so far.
Thus, while many studies have been conducted on the utilization of healthcare services, there is insufficient comprehensive evidence on the barriers of equity in accessing and in utilization of healthcare services for under-five children from policy makers and community level perspective. Therefore, the objective of this study is to examine the context of specific barriers to achieving equity in child health-care services utilization in Ethiopia.
Inequity in child health care service is a major public health problem in developing countries, including Ethiopia. Accordingly, the study explored barriers to equitable healthcare services for under-five children, their health seeking behavior, geographical variation, their awareness, perceptions, attitude and political impact and policy contents of the country. The findings will benefit program leaders, policy makers on health inequality reduction and serve as an input to policy documents related to the new health sector strategic plan. Moreover, mothers and under-five children’s are directly benefited from the finding. Conceptual framework shows how different barriers affect equity in utilization of child health services (Fig. 1 ).
Modified Andersen and WHO conceptual framework, on social determinants of health inequity
The study setting and approach
This study was conducted in Oromia Region, Arsi Zone, Zuway Dugda District from June 1–30, 2023. The Ethiopian healthcare system is three-tiered, comprising primary, secondary, and tertiary care [Fig. 2 ]. The primary level healthcare system is responsible for providing child health services, such as immunizations, and the treatment of sick children. The primary care unit includes primary hospitals, health centers, and health posts which are responsible for providing services to rural communities ([ 17 ]; Arsi Zone Health Department report, Unpublished data, 2022). Women's development armies (WDAs) provide support to health extension workers (HEWs) by organizing and connecting women and their children with healthcare facilities. Based on 2022, the Arsi Zone report, Zuway Dugda district was low in utilization of child healthcare services and the population is low in socioeconomic status and mostly depends on the Safety Net program for nutritional and financial needs (Arsi Zone Health Department report, Unpublished data, 2022). The goal of the Safety Net program is to preserve family assets while generating new ones for the community. To achieve this, the program offers food or cash incentives in exchange for public works projects that improve the environment or create local infrastructure, like roads (e.g. terracing).
Ethiopian health care system [ 17 ]
Participant selection
The study includes 20 in-depth interviews of key informants (KII) and six focus group discussions (FGD). By taking into account various factors that contribute to variations in the use of child healthcare services, study participants were selected from a variety of demographic subgroups. The study participants were drawn from different segments of the population by considering different dimensions that explain disparities in utilization of child healthcare services. The selection of participants was based on their experience of child healthcare services as well as the information they possessed. For the purposes of this research, to ensure representativeness, and to understand the multifaceted levels of the study framework within society and how individuals and the environment interact within a social system, we used maximum variations sampling technique and we classified the participants into four groups. They were “mothers or caregivers who have under- five children”, “males who have under-five children”, “healthcare leaders at different levels” and “healthcare providers at different health facility”. The first group,, “women” refers to mothers who were gave birth prior to the study period and currently having under-five children. The second group were “males or husbands of the women who have under-five children”. The third groups, “healthcare leaders” like; heads of the health centers, district health office, expertise working on child health programs in district, Zonal, regional or national level. The fourth group, “health-care providers”, refers to health professionals, including doctors, health officers, nurses, midwives, and health extension workers working at different health facilities in Arsi Zone and having direct relation with child healthcare services.
Participants in the focus group discussions (FGDs) could be women and their partners who had under-five children at the time of the study. The participant mothers or caregivers were recruited by the HEWs and kebe le (neighborhood associations) leaders. They were identified on a purposive basis with the help of health extension workers and were contacted a few days before the planned FGD to explain the objectives of the study and request their participation. For the key informant interviews, the study participants were contacted by the principal investigator two weeks before the interviews. The information was collected based on the principle of saturation; for our case at least 16 interviewees were needed to reach information saturation principles. Then, data collection was terminated when no new information was generated.
An interview guide was prepared for both the key informant interviews (KII) and FGDs. First, the guides were prepared in English language and then translated into the local language [ 21 ]. Then, the guides were pre-tested and problems relating to the sequence of questions, conceptually similar questions, and sensitive wording were corrected. The data collectors for the KII and FGD were professionals with the background in health and health related fields with master and who are experienced in collecting qualitative data. Moreover, they are fluent in the local language and familiar with the culture of the local community. Key informant interviews were conducted at the office or at the health facility where the interviewee worked and FGDs were conducted in community halls or public rooms. Both key informant-interviews and focus group discussions were audio-recorded. Additionally, complementary observations and notes regarding the remarks made by the participants and their interactions were made.
Data analysis
The principal investigator and the moderator transcribed each interview and FGD word-for-word in the local Afaan Oromo and Amaharic languages and then translated the transcripts back into English. The translations were verified by listening to the recordings while re-reading the transcripts. The data were analyzed thematically using NVivo 12 software and narrated in the pattern linked to child health service utilization. Major themes representing the FGD participants and in-depth interviews are presented in the findings section, with illustrative quotes included to support the main findings.
Trustworthiness
In qualitative research, trustworthiness is determined by credibility, dependability, conformability and transferability. Establishing credibility involved the primary researcher spending a considerable amount of time at the study site to get a feel for the environment, receiving ongoing feedback from peers during peer debriefing, and applying negative case analysis. Dependability was demonstrated by providing an in-depth explanation of the techniques employed, keeping careful interview records, and recording the analytical procedure. All events that took place in the field, the researchers' personal reflections on the study, any phenomena that emerged during the investigation, and pertinent details of their personal histories were documented in order to verify that the interpretations of the findings were derived from the data and were not the product of their imagination. The investigators attempted to build rapport and trust with the informants by developing a long-term attachment because they were skeptical or doubtful if the information felt off. Triangulation of data sources was also employed. A thorough description that includes explaining each step of the research process was employed to aid in the transferability of research findings. At the end of each qualitative data collection session, the data collectors rephrased the collected information by summarizing major points and obtained approval from the participants for the corrected summary.
Characteristics of the study participants
A total of six focus group discussions (FGD)- three with mothers and three with fathers of under five children were conducted. And 20 key informant interview (KII) were held. The number of FGD participants ranged from 8 -12 in each groups. The majorities of women’s participating in FGDs were housewives and had at least one child under the age of 5 years in their care at the time of the FGD. The key informant interviews were conducted with leaders and policy makers at different levels of the health care system and a healthcare worker, including FMoH child health directors, Regional Health bureaus experts, Zonal Health office child health experts, woreda health office heads, Health center heads and health extension workers at health posts were involved. In all, 28 men and 30 women took part in the FGDs. In contrast, six HEW, three heads of health centers, one head of the district health office and with ten experts participated in the key informant interview. Each FGD took on average 42 min (38–52 min), while the key informant interviews took about 36 min (19 to 55 min) (Tables 1 and 2 ).
Barriers to equitable healthcare services for under-five children
Six major themes emerged from the findings.
These include; barriers related to low awareness, low socioeconomic status, geographical inaccessibility, barriers related to deficient healthcare system, cultural and behavioral constraints, and political instability and conflict, all of which lead to unmet healthcare needs such as delay in receiving appropriate care and inability to obtain healthcare services (Table 3 ).
Lack of awareness about benefits of the services
Lack of awareness and misconceptions were one of the top reasons raised by KII and FGD participants for not using healthcare services for under-five children especially in rural communities. Recognition of illness and the potential benefits of treatment are pre-requisites for health care demand. Communities who lived in remote areas and are undereducated tend to have little knowledge concerning health issues. Rural people have insufficient exposure to the media, attending low level of schooling to grasp and understand health related information. The key-informant interviewees and FGD discussants reported that because of low health literacy, rural community and the poor households have less access to health facilities to get treatment for childhood diseases, and for immunization services. One of the key informants mentioned that there are variation or differences among urban and rural rich and poor, literate and uneducated people in child health care service utilization.
“… . Children who visited our health center with malnutrition were from remote and far to reach areas and were brought to our health facility only after these cases were seriously complicated. So there is great variation among urban and rural, rich and poor, literate and illiterate communities in child health care service utilization in our district .” Male , KII, age 34years
One FGD discussant from women group added her experience and her awareness of immunization and availability of free service in health post in such ways;
“Yes, if I had been aware of the benefit of immunization and informed that they were given free of charge, I would have used these services for my sick child from health posts, not from traditional healers” Female FGD discussant, age 35 years, Seeking care from traditional healer
The health extension workers at health posts also approved the lack of awareness among mothers and caregivers on the availability of health service which jeopardizes health- seeking and utilization of health service for their under-five children. One worker said that.
“Most of the women’s and care givers did not know about the availability of treatment at the health post, especially for diarrhea and pneumonia. Those women’s who live near a health facility, are educated and young have more awareness about childhood illnesses and seek care from health posts than uneducated mothers; this may result in inequitable utilization of health services by illiterate care givers ” KII, Female 35 years
In some areas there is a mix of knowledge about utilization of healthcare services for under-five children. Health professionals used abbaa gadaa, or hadha sinqee (male and female cultural leaders) and members of the female development army (FDA) to raise the level of awareness in the community. One key informant interviewee shared the experience of his districts in utilizing women’s development army and these cultural leaders to increase the knowledge of the community as follows;
“We improve the awareness of our community on child healthcare utilization through women’s development army and cultural leaders, we trained these women about early recognition of maternal and child health danger sign. we provide them local COC for them. By now in our district, women’s development armies have equivalent knowledge with HEW and, we used them to teach the community”. Male, Key informant, age 42 year.
Socioeconomic barriers
Lack of sufficient income at household level and low level of maternal and paternal education were identified as major barriers for equity in utilization of healthcare services for under-five children. As part of its HSDP II strategic objectives, the Ethiopian Government intends to address equity in maternal and child health, particularly for the impoverished and rural communities, by providing free health services to these subgroups and allocating a sufficient budget. However, the actual and perceived cost of seeking care keeps some people from traveling to medical facilities. Out-of- pocket costs of health care, cost of transportation and living cost may prevent poor people from using services, leading to untreated childhood illness.
For instance after they reached to health facility, they obligated to pay for medical treatment or drugs they used to treat their children. In this case some advanced diagnosis and treatment is not available in governmental health facilities.. For example, CT scan and MRI to diagnose severe childhood diseases and some essential drugs to treat pneumonia, sepsis and diarrhea were not available in health centers and in health posts. They were advised to get this treatment from private clinics and to buy the drugs from private pharmacies. However, or mothers could not afford to purchase them from private clinic.
A woman from FGD discussant explained her experience of an availability of certain services in Government health facility and high cost of services in private clinic as follows:
“Yes, nowadays, the cost of drugs and treatment for childhood illness is increasing, when I used to get treatment for my sick child from a health center or health post the health professional referred me to a private clinic to be seen or diagnosed by a highly expensive machine; I am unable to afford for this machine. Moreover there were no drugs at the health post and the health center. They told us to purchase them from private clinics. So, how can the poor people get treatment from Governmental health facility?” Female FGD discussant age, 34 years, with low income.
Another FGD discussant described this problem as follows:
“Yes, getting treatment in this health facility is good but sometimes you go here and there to get examined and prescribed for drugs and you need money for those drugs. If you don’t have money, then you remain with the illness” Female FGD discussant, age 29 years.
The study participants suggested that, socioeconomic healthcare inequity must be addressed by healthcare system revisions such as the provision of health insurance, fee retention; waiving and exemptions from fees for poor people, and subsiding the cost of the transportation were considered as solution to reduce inequity in health care services.
Geographical barriers
Distance of health facilities from home and unavailability of motorized transportation were another major barrier to health services utilization. Pit the fact that availability of some community based services should increase health service utilization to caregivers, distance from homes to health facilities, poor roads and unavailability of motorized transport were major barriers for many people. Distance from health centers and health posts and lack of transportation and cost of transportation were cited as barberries of equity for child health service utilization by rural and the poor communities. Long distances, shoddy road construction, and a shortage of ambulances make it difficult for residents of remote communities and low-income families to get to medical facilities and thus have fewer opportunities to vaccinate their children. One key informant said that.
“…the primary issue facing this district is the lack of transportation and the distance between the residential area and the medical facilities . The caregivers were unable to get transportation service easily. In some areas the distance between health facilities and residential areas of the community is too far, besides there is no road to get access to health facility. We need more vehicles at health center level; moreover, the transportation issue cannot be solved unless quality roads will be constructed for the community.”Male, key-informant interview, age 40 years.
Another FGD discussant said that.
“ Yaa, we move more than 30 km on foot to access health facilities, especially health centers, there is no road for cars., we carry our sick child on our backs to get treatment from this health facility” FGD, Male, age 44 years.
One FGD described the transportation problem a follows:
“…even though roads were constructed, there is no reliable transportation system in our area. Ambulance service is not available in our area, no mobile network to call to ambulance service. Moreover, if we were hardly access the ambulance, we are requested to pay 1000 Birr for fuel. Therefore, the Government and concerned body has to understand and solve our situation related to distance and transportation problem.” Male, FGD discussant, Age 49 year.
The study participant also suggested that geographical and financial accessibility barriers have to be addressed by bringing services closer to homes or residential areas.
Healthcare system barriers
Certain aspects of healthcare system were identified as barriers to equitable healthcare services for under-five children. In Ethiopia, important deterrents include unavailability, unaffordability of the service, and closure of health posts during working hours and issues related to behaviors of the health professionals were the emerged theme from this study.
One of the important barriers of equity in utilization of child healthcare services especially by poor were unavailability of child care services at health posts. Even though the health posts are supposed to give services for the rural and poor populations, it was closed on many working days and at weekends. In addition, absence of health extension workers from the duty during working hours, services inconsistently and unavailability of drugs in the health posts were barberries of equity raised by KII and FGD discussants. One of key informant interviewees explained his observations as follows;
“Even though, the health posts are expected to give maternal and child health services for the rural community free of charge, how the poor and the rural community get these services, the health posts were closed during working hours, most of the time the HEW workers are in another duty, they were assigned to collect taxes and insurance from the community, so the richest household will get these services from private health institution but the poor and the rural community is in problem in accessing these services” Key-informant interview, Male, 45 years.
Besides giving health services, in some rural areas the health extension workers are assigned to other administrative and political activities. A health extension worker in health post acknowledged the absence of health services during working hour in such ways;
“ How can we give health services for the poor community, we are assigned to collect insurance, taxes and to register member for the political parties, if we say no we will be fired, most of the time the health posts were closed, all services were intercepted, mothers from rural area repeatedly came for immunization, but they did not get us in the health post, those mothers who were educated and have the money for transportation may went to health centers and Hospitals to get immunization service, but the poor mother were waiting us till the health post is opened” Female, Age 39 year.
One woman from FGD participant also explains her experience as follows;
“One day my 3 years old child was sick and I came to consult the HEW, but, the door is closed and she was not around” Female, FGD discussant, Age 38year, rural community
Another important finding from this qualitative study was issue of marginalized populations. The health services do not cover marginalized and poor people, like, beggars, around churches, mosques and along roads on child health services especially immunization . Key informant participants from the one woreda health office described this issue as follows;
“Here is the gap, now the health facilities have no plan and willing to give immunization services to marginalized poor people like; beggars around the mosque, church, and on roads. These poor people are totally forgotten, the motivation of health workers to serve this community is almost zero or near to nil. All vaccination mandates are given to HEW, but now health centers and health posts are not connected to these people and their children’s are not vaccinated at all. There is no supervision or support from higher officials, no accountability among HEW “KII M ale, 45yer.
Lack of adequate supply of medicines and other medical supplies emerged as a recurring theme in FGDs and KII at both the policy and service delivery levels. The health posts do not have all basic medicines available and end up giving inadequate drugs, no separate budget is allocated for child health by Ministry of Health or the regional health bureaus. Donors, NGO,s and partners have reduced their budgets and support of child health programs.
One KII participant shared his perceived cause of inadequate supplies and budgeting for health facility as follows:
“…Currently only limited budgets are allocated to the health sector, especially for maternal and child health. There are no donors and partners who support the healthcare system; this is probably linked to the current Ethiopian political upheavals. This creates problems for free services for maternal and child care. In my opinion this is the cause of an availability of materials and some drugs at health facility” key-informant-interview, age 44 year.
Disrespectful care and treatment was the issue raised as barriers to equity by caregivers for their under-five children. Ethiopian communities pay attention to respectful and quality of care, therefore giving preference to urban health centers, which generally meet patient expectation. But urban health facilities also discriminate against poor people. A female FGD discussant raised the issue of non-compassionate and disrespectful care given to her at an urban health facility, as follows:
“Yes, we looked unclean and came from rural areas, the health professionals treated us as not as humans and gave us poor care. They did not touch us by their hands or used apparatus to examine our problem. They simply asked us about our illness and gave us prescription to buy drugs” Female, FGD, 42 years.
Respondents suggest that, the government need to ensure the availability of adequate essential vaccines, drugs and supplies in health facilities. The FGD discussants further emphasized that, both central and local healthcare systems need to allocate adequate financial resources and procure adequate logistic and material supplies towards effective implementation of quality healthcare services.
Cultural and behavioral barriers
Low demand and utilization of modern health interventions often derives from deep-rooted attitudes that reflect culture, social norms and traditions of the community. Few FGD participants mentioned that cultural barriers such as using traditional medicines at home and taking the children to traditional healers were barriers to using child health services, especially in rural areas. In some areas peoples believed that the cause of the illness is caused by supernatural agents, exposure to cold, wind or the devil eye. Therefore they do not bring their children to health facilities. Many poor mothers and care givers in rural areas use traditional medicine or religious interventions such as payer as the first treatment for childhood illness because of their ready accessibility and low cost, as stated by one father:
“I have encountered people in some districts who delayed treatment because of traditional beliefs. One of them said … If my child gets sick, I will not bring it to a health facility immediately, I will wait until the disease matures and shows full blown sign can l be observed or till it will resolved by itself” key-informant interview, Male 42 years.
There are also other traditions, customs and beliefs among some rural communities which are barriers to equity of child health services. For instance haamachisaa is a kind of blessing used as the first treatment by traditional healers for neonates aged less than 3 months before seeking care services from health facilities. They believe that haamachisaa prevent malicious birds or the evil eye to inflict illness on neonates, as described by one mother:
“ in our area some of the rural communities will not send their “ children below three months of age” to get immunization services from health facilities before they practice haamchisaa or blessing services from a traditional healer because a bird or the evil eye may see the neonate “ Female, key- informant, 39 years.
In some rural districts, obstacles to child health care service utilization include the use of traditional uvulectomy, getting treatment for measles from traditional healers and using holy water (tsebel) at churches when children fall ill.
“In our area, when their child develops measles some of them refuse to take their children to health facility because they believe that the treatment there will cause girsha, the dissemination of the rash to different organ systems” Male, key-informant, 30 years head of HC.
Another FGD discussant described her preference of traditional healers for her sick child because of cost of the drug as follows;
“I visited a traditional healer for my child when he had tonsil, because drugs and repeated treatment from a health facility are expensive; After the tonsils are removed by a traditional healer there is no recurrence, so it is less costly for me” Female, FG, Age 40 year.
In another way less attention was given for morbidity and mortality of the child by rural community, especially to the neonate (if a neonate died) the funeral ceremony will not be practice in the church or mosque. The burial or funeral ceremony is accomplished at near house of the parents; the dead body is not brought to church or mosque. The community did not consider a neonatal death as a death of human being or adult death but, is concealed, as described by a male key-informant:
“ Here in the community less attention is given to child health, especially for the newborns; if the newborn dies the dead body will not brought to a church or mosque but it will be buried around the home. Nobody will go to that home to morn with the parents” Male key-informant, 42 years.
In many Ethiopian communities, women’s have low autonomy to decide for her own and their children’s health in Ethiopia. They need the permission of their husbands to seek care for their children, because of economic, psychological and material dependence. The norms and values of the community also reinforce this behavior.
One of the important finding of this study was inequity related to ethnicity. Almost all KII and FGD participants stated that there is no disparity in healthcare service utilization because of ethnicity.
“…..Even though Ethiopia is having a diversified ethnic group still there is no marginalization or inequity in utilization of child health services from health facility because of ethnicity; rather they encounter barriers related to language in understanding and to get consultation from service providers” Key-informant, Male, Age 39 year.
The study participants further suggested that barriers related to health illiteracy or mistrust of the healthcare system have to be addressed by involving different stakeholders such as community leaders, traditional healers and religious leaders .
Politics, conflict and security issues
Over the last few years, Ethiopia is suffering from different types of military conflicts between the Ethiopian government and insurgent forces in most regions and administrative areas. This protracted conflict hinders maternal and child health service delivery affected communities, especially in isolated rural areas. As a result, health services could not operate safely in the war zone, Increasing the incidence of vaccine-preventable diseases and malnutrition. A male FGD discussant explained the effects of conflict on maternal and children service utilization as follows:
“ In our district there is continuous military conflict between the government and rebel forces; most of the time the health facilities were closed, there is diversion of supplies for maternal and child health services to the armed forces, no immunization services was given to the community during this conflict period, roads were closed, the health professionals fled health facilities because they felt insecure, even ambulances assigned to MCH services were used for military purposes;, the rich may get the service from private clinic, the poor did not get anything, simply waiting an interventions from God,, or simply wait to die or migrate to other places” Male, FGD, age 45 years.
One key-informant interview participant reported his observation of security problem on child health services in his district as follows:
“Regarding the issue of security problem, currently in our area there is a military conflict between government and rebellions. Due to this there is no maternal and child healthcare services, 24 h ambulance was served for political purposes, as a result mothers and children are dying from severe anemia and severe pneumonia at their home, therefore, politically instability and conflict among Government and armed rebellion force exacerbate the existed disparity in utilization of healthcare services for mothers and children in our district”. Key –informant, male, age 41 years.
The research participant added that communication between opposing groups is necessary to resolve political unrest and conflict which has direct impact on child healthcare utilization.
This study aimed at exploring barriers of equity that mothers and their children face in accessing and utilization of healthcare services for under-five children. The findings point out multiple dynamics of barriers of equity to care-seeking and utilization of healthcare services in Ethiopia.
In this study the barriers and challenges linked with access and utilization of equitable healthcare services for under-five children were found to fall under six themes ; lack of awareness about availability of the service, socioeconomic barriers, geographic barriers, health system related barriers, cultural and behavioral barriers and political instability and military conflict related barriers. These barriers are inter-related and complex in nature. As key-informants and FGD discussants reported that lack of awareness was one of the top barriers for not using healthcare services for under-five children, especially in rural communities. Populations who have settled in far to reach areas and uneducated have no equal awareness about health related issues compared to urban and well educated populations. Their reasons are people leave in rural area has insufficient exposure to media, attending low level of schooling to grasp and understand health related information. Most studies reported that because of low health related literacy, rural community and the poor household had delayed to access health facility to get treatment for most of childhood illnesses, and vaccination services [ 22 ]. In this study having participants confirm that there is a gap in knowledge regarding the causes of childhood illness and regarding the availability of treatments at health posts, it is clear that a campaign to educate and mobilize community members will be necessary. The need for transmission of information about the availability of services was also highlighted by several other studies [ 23 ]. Studies in Ethiopia reported that, HEW home visits were reportedly valuable for increasing awareness and use of services and mothers of under-fives who received health information [ 24 ]. Different studies suggest that community education and mobilization campaigns may increase level of awareness of communities. One study also reported that HEWs and HDA were credible sources of health-related information [ 25 , 26 ]. For example, the HEW increased the awareness of communities during pregnant woman conferences, vaccination campaigns, and other community meetings.
This study further highlights that, socioeconomic barriers to health care utilization are strong deterrents that increase under-five mortality in Ethiopia. Limited financial resources for medical treatment and low educational level of parents are barriers to the use of healthcare services for children among disadvantaged populations. In this regard, the Ethiopian government plans to provide free health services for women and under-five children, through the HSTP. II but our finding revealed that low household income, low level of maternal education, and out-of- pocket payments for health care prevent poorer people from using services for under-five children. Furthermore it should be noted that the government of Ethiopia has adopted a waiver fee policy for the vulnerable groups. However, cost of services still play a major role in access to service since the exemption from paying for the services is unevenly applied.
Several studies corroborate our findings of the socioeconomic impact on health service utilization [ 27 , 28 ]. A study conducted by Daniel et al. confirmed that the levels of household income and health literacy affect access to healthcare services [ 27 ]. Moreover, indirect costs such as loss of work time, loss of income and transportation cost have a significant economic impact on poorer families [ 28 ]. Implementing health insurance scheme and waiving user fees may shield the poor from these charges and weaken household health budget constraints.
Our findings of the negative impact of low education of parents is corroborated by several studies. [ 29 , 30 ]. Pregnant mothers with higher education are more aware of the significance of good nutrition and child care as well as the prerequisites for being healthy [ 31 ]. Education plays a vital role in shaping attitudes, opinions, customs, and norms and also promotes the adoption of new ideas and values.
The result of our study revealed that, distance from health facility, lack of transportation and uncomfortable road topography especially in summer were mentioned as an important barriers of equity in healthcare service utilization for under –five children. Previous studies in Ethiopia confirmed that far to reach regions, districts and areas often face special issues and problems compared to non-far to reach areas [ 32 , 33 ]. Several studies in other countries also showed that travelling to a health center was challenging for caregivers of children residing in far to reach areas and cost of transportation, unreliability and its unavailability of services were the main impairments of equity in accessing healthcare services [ 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 ]. For example, a study of measles vaccination coverage in various African countries found that distance was a key factor in determining the level of immunization coverage [ 39 , 40 , 41 ]. In addition to the inverse relationship between distance and health services utilization, geographical location of health facilities in isolated rural areas also jeopardizes the staffing of health facilities. Doctors, midwifes and nurses are less eager to serve in such areas than in urban communities and vaccines and flooding may prevent the delivery of vaccines and drugs to distant mountain communities during the rainy season.
Respondents highlighted the need to ensure reliable availability of HEWs at the health post during opening hours and extending the hours of the health post so that services would be available working hours and on weekends. Such closures have been shown to be a major challenge in previous studies [ 42 ]. HEWs travel for activities such as collecting taxes registering political membership from the residential and payment for health insurance from the community should be stunned by the community and so that there is at least one HEW in each health post to give services for the community . Another important finding from this study was issue of marginalized populations. Some key-informant and FGD discussant cited that, the health facility is not have especial plan to address the services to marginalized poor people, like, baggers around the church, mosques and around roads on child health services especially for immunization services. Hence this may create critical inequity in child healthcare service utilization among the poor.
Barriers to equity in access and utilization of services extend beyond accessibility and availability issues, disrespectful care and negative attitude acts as a barrier to accessing health care services. Negative attitude of health workers in the form of verbal expression, represented a theme of recurrence as a barrier of equity in utilization of the services. Female FGD discussant raised the issue of non-compassionate and disrespectful care given to them by health professionals at health facility and they were receiving poor quality of care, and there is no companionate care for the poor. Improving quality and outcomes at health centers offers an incentive for the utilization of a service. In many African countries, low quality of health services has been identified as a hindrance to equitable access of services [ 43 ]. In the current study, few participants mentioned that cultural factors like home remedies taking the children to traditional healers were obstacles to utilization equity. Other studies from Sub-Saharan Africa show similar results [ 44 ]. This shows that, traditional beliefs and norms of the community impede from seeking-care modern healthcare and utilization of the services from health facility.
One of the promising finding in this study was, even though Ethiopia have a diversified ethnic group there is no report related disparity or inequity in utilization of child health services because of his/her ethnicity, rather they encounter barrier related to language in understanding and to get consultation from service provider.
Our finding revealed that, war and political instability disrupt health services accessibility and utilization. There was also reported from several other countries, including Afghanistan, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Pakistan, and Somalia [ 45 ]. Key impacts include disrupted infrastructure and supply chain; violence against health workers; difficulties retaining health workers; delivery service interruptions; and displacement and migration [ 46 ]. For populations affected by military conflict, adopting flexibility surrounding age and eligibility criteria can increase immunization coverage.
Strength and limitation of this study
Strengths of this study include the collection of data by experienced interviewers, efforts made to increase trustworthiness of the study, checking transcripts against audio-records and field notes by two independent experts, and use of the participants’ own language for data collection. In addition, inclusion of participants from all levels of the healthcare system and caregivers (both mothers and father) of the children broadened the range of experiences and opinions on inequity in child health services accessibility and utilization. The major limitation of this qualitative study is that its findings are may not be generalized to other settings. Furthermore, since the study was only conducted in one district, it might not be representative of the entire nation.
Conclusions and recommendations
We conclude that inequity in child healthcare utilization continues to be an important challenge confronting Ethiopia. Constraints such as poor community awareness of the availability of curative healthcare services, geographic inaccessibility, inadequate healthcare resources, socioeconomic barriers, and constraints related to the functioning of the healthcare system and political instability and military conflict were the most cited barriers to equity.
To achieve equity, Ethiopian policymakers and partners need to invest in health infrastructure, including bringing services closer to people by constructing new health posts, health centers and roads in rural areas, and increasing the quality of services. In addition, context-specific cultural barriers such as the use of traditional medicines and illness beliefs need to be addressed through health promotion and military conflict needs to be solved through dialog between opposing bodies.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the finding of this study are available and attached as related files.
Abbreviations
Certificate of competency
Compassionate respectful care
Focus group discussion
Federal Ministry of Health
Health care workers
Health extension workers
Key-informant interview
Maternal and child health
Millennium developmental goals
Oromia Regional Health Bureau
Primary health care
United Nations
Berndt DJ, Fisher JW, Rajendrababu RV, Studnicki J. Measuring healthcare inequities using the Gini index. In: System Sciences, Proceedings of the 36th Annual Hawaii International Conference on IEEE. 2003. p. 10.
Google Scholar
Hosseinpoor AR, Bergen N, Schlotheuber A, Williams JS. Monitoring health determinants with an equity focus, promoting health equity: WHO health inequality monitoring at global and national levels. Glob Health Action. 2015;8:1–8. https://doi.org/10.3402/gha.v8.29034 .
Article Google Scholar
United Nations. Transforming our world: the 2030 agenda for sustainable development. In: A new era in global health. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1891/9780826190123.ap02 .
Chapter Google Scholar
Houweling TAJ, Looman CWN, Azad K, et al. Neonatal and child mortality: the equity impact of community women’s groups to reduce neonatal mortality: a meta- analysis of four cluster randomized trials. Int J Epidemiol. 2019;48(1):168–82. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyx160 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Assefa Y, Gelaw YA, Hill PS, Taye BW, Damme W. Van community health extension program of Ethiopia, 2003–2018:successes and challenges toward universal coverage for primary healthcare services. Glob Health. 2019;15:24.
Federal Ministry of Health of Ethiopia. Health sector transformation plan (2015/16–2019/20). Addis Ababa: Ministry of Health of Ethiopia; 2015. p. 1–118.
Dhaliwal LK. Health equity and sustainable development goals: role and the complexity. In: Filho WL, editor. Good health and well-being. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland AG; 2019. p. 316–24.
Boerma T, Requejo J, Victora CG, Amouzou A, George A, Agyepong I, Barroso C, Barros AJD, Bhutta ZA, Black RE, et al. Countdown to 2030 collaboration review countdown to 2030: tracking progress towards universal coverage for reproductive, maternal, newborn, and child health. Lancet. 2018;391:1538–48.
Ethiopian Public Health Institute (EPHI) [Ethiopia]; ICF. Ethiopia mini demographic and health survey 2019: key indicators. Rockville: EPHI;ICF; 2019.
Bergen N, Zhu G, Yedenekal SA, Mamo A, Abebe Gebretsadik L, Morankar S, Labonté R. Promoting equity in maternal, newborn and child health–how does gender factor in? Perceptions of public servants in the Ethiopian health sector. Glob Health Action. 2020;13: 1704530.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Okwaraji YB, Cousens S, Berhane Y, Mulholland K, Edmond K. Effect of geographical access to health facilities on child mortality in Rural Ethiopia: a community based cross sectional study. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33564. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033564 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wuneh AD, Medhanyie AA, Bezabih AM, Persson LÅ, Schellenberg J, Okwaraji YB. Wealth-based equity in maternal, neonatal, and child health services utilization: a cross-sectional study from Ethiopia. Int J Equity Health. 2019;18(1):1–9.
Tiruneh FN, Chuang K, Chuang Y. Women ’ s autonomy and maternal healthcare service utilization in Ethiopia. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(718):1–12.
UNICEF. 2014, Level and trends in child mortality. New York: UNICEF; 2014.
Frankenberg E. The effects of access to health care on infant mortality in Indonesia. Health Transit Rev. 1995;5:14363.
Amooti-Kaguna B, Nuwaha F. Factors influencing choice of delivery sites in Rakai district of Uganda. Soc Sci Med. 2000;50:20313.
Federal Ministry of Health of Ethiopia. Essential health services package of Ethiopia. Addis Ababa: Ministry of Health of Ethiopia; 2019.
Stock R. Distance and the utilization of health facilities in rural Nigeria. Soc Sci Med. 1983;17:56370.
Bulage P, Urdal H, Sundby J. A qualitative study exploring the determinants of maternal health service uptake in post-conflict Burundi and Northern Uganda. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2015;15:18.
Murray CJL, King G, Lopez AD, Tomijima N, Krug EG. Armed conflict as a public health problem. BMJ. 2002;324(7333):346–9. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.324.7333.346 . PMID: 11834565.
Key-informant and focus group guiding tools.
Tesfaye G, Chojenta C, Smith R, Loxton D. Delaying factors for maternal health service utilization in eastern Ethiopia: a qualitative exploratory study. Women Birth. 2020;33(3):e216–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wombi.2019.04.006 .
Shaw B, Amouzou A, Miller NP, et al. Determinants of utilization of health extension workers in the context of scale-up of integrated community case management of childhood illnesses in Ethiopia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;93:636–47.
Yitayal M, Berhane Y, Worku A, Kebede Y. Health extension program factors, frequency of household visits and being model households, improved utilization of basic health services in Ethiopia. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14:156.
Save the children report, Rapid Assessment of Determinants, Factors and Opportunities to Early Pregnancy Identification, Focused Antenatal Care, Skilled Birth Attendance and Postnatal Care Service Utilization in Gurage and Sidama Zones of SNNPR. Addis Ababa; 2015.
Central Statistical Agency [Ethiopia] and ICF International. Ethiopia demographic and health survey. 2016.
Daniel H, Bornstein SS, Kane GC, Health and Public Policy Committee of the American College of Physicians*. Addressing social determinants to improve patient care and promote health equity: an American College of Physicians position paper. Ann Intern Med. 2018;168(8):577–8.
Eide AH, Mannan H, Khogali M, et al. Perceived barriers for accessing health services among individuals with disability in four African countries. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0125915.
Mirowsky J, Ross CE. Education, social status, and health. Routledge; 2017.
Book Google Scholar
Berkman ND, Sheridan SL, Donahue KE, Halpern DJ, Crotty K. Low health literacy and health outcomes: an updated systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(2):97–107.
Sayakhot P, Carolan-Olah M. Internet use by pregnant women seeking pregnancy-related information: a systematic review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016;16:65.
Defar A, Okwaraji YB, Tigabu Z, et al. Geographic differences in maternal and child health care utilization in four Ethiopian regions; a cross-sectional study. Int J Equity Health. 2019;18:173. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-019-1079-y .
Geremew TT, Gezie LD, Abejie AN. Geographical variation and associated factors of childhood measles vaccination in Ethiopia: a spatial and multilevel analysis. BMC Public Health. 2019;19:1194. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-7529-z .
Sritart H, Tuntiwong K, Miyazaki H, Taertulakarn S. Disparities in healthcare services and spatial assessments of mobile health clinics in the border regions of Thailand. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(20):10782.
Gazzeh K, Abubakar IR. Regional disparity in access to basic public services in Saudi Arabia: a sustainability challenge. Utilities Policy. 2018;52:70–80.
Yourkavitch J, Burgert-Brucker C, Assaf S, Delgado S. Using geographical analysis to identify child health inequality in sub-saharan Africa. PLoS One. 2018;13(8):e0201870.
Bright T, Felix L, Kuper H, et al. A systematic review of strategies to increase access to health services among children in low and middle income countries. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17:252. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-017-2180-9 .
Tefera W, Tesfaye H, Bekele A, Kayessa E, Waltensperger KZ, Marsh DR. Factors influencing the low utilization of curative child health services in Shebedino District, Sidama Zone, Ethiopia. Ethiop Med J. 2014;52 Suppl 3:109–17.
PubMed Google Scholar
Metcalf CJE, Tatem A, Bjornstad ON, Lessler J, O’Reilly K, Takahashi S, et al. Transport networks and inequities in vaccination: remoteness shapes measles vaccine coverage and prospects for elimination across Africa. Epidemiol Infect. 2015;143(7):1457–66.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Levine O, Lemango ET, Bernson J, Gurley N, Rowley E, McIlvaine B. ERG Discussion paper No. 8. Tackling inequities in immunization outcomes in remote rural contexts. Equity Reference Group for Immunization; 2018. https://sites.google.com/view/erg4immunisation/discussion-papers . Accessed 6 Sept 2019.
Colvin CJ, Smith HJ, Swartz A, Ahs JW, De Heer J, Opiyo N, Kim JC, Marraccini T, George A. Understanding careseeking for child illness in sub-saharan Africa: a systematic review and conceptual framework based on qualitative research of household recognition and response to child diarrhoea, pneumonia and malaria. Soc Sci Med. 2013;86:66–78.
Shaw B, Amouzou A, Miller NP, Tafesse M, Bryce J, Surkan PJ. Access to integrated community case management of childhood illnesses services in rural Ethiopia: a qualitative study of the perspectives and experiences of caregivers. Health Policy and Planning. 2016;31(5):656–66. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapol/czv115 .
Kuwana MR. Barriers to accessing health care services for children with disabilities in Southern Africa: The case of Namibia. 2014. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:68841196 .
Konje ET, Hatfield J, Kuhn S, Sauve RS, Magoma M, Dewey D. Is it home delivery or health facility? Community perceptions on place of childbirth in rural Northwest Tanzania using a qualitative approach. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020;20:270.
Nnadi C, Etsano A, Uba B, Ohuabunwo C, Melton M, Wa Nganda G, et al. Approaches to vaccination among populations in areas of conflict. J Infect Dis. 2017;216:S368–72.
Okwo-Bele JM, Conner R, McIlvaine B, Rowley E, Bernson J. ERG Discussion paper No. 6. Tackling inequities in immunization outcomes in conflict contexts. Equity Reference Group for Immunization; 2018. https://sites.google.com/view/erg4immunisation/discussion-papers . Accessed 6 Sept 2019.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the study participants, the Federal Ministry of Health, regional health bureaus, and zonal and district level health leaders. We also acknowledge Addis Ababa University and Professor Helmut Kloos for funding this study.
Addis Ababa University School of Public Health, and support from Professor Helmut Kloos.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Public Health, Arsi University College of Health Science, Assela, Ethiopia
Hailu Fekadu
School of Public Health, Addis Ababa University College of Health Science, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Wubegzier Mekonnen & Damen Hailemariam
Department of Geography, Planning and Environmental Sonoma State University, Sonoma, San Francisco, USA
Aynalem Adugna
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, University of California, San Francisco, USA
Helmut Kloos
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
H.F and D.H contributed to the design and conception of the study and analyzed and interpreted the data. W.M, H.K, and A.A participated in data analysis, interpretation and revision of the manuscript. All authors read and revised the draft of this manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hailu Fekadu .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
A written ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the College of Health Sciences at Addis Ababa University (Ref. No. 046/22/SPH). In addition a verbal informed consent was obtained from all interviewees and focus group discussion participants. All of the respondents were informed that their participation in the study was voluntary, and that the data would be stored safely, without identifiers, and would only be accessed by the involved researchers. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant institutional guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Fekadu, H., Mekonnen, W., Adugna, A. et al. Barriers to equitable healthcare services for under-five children in Ethiopia: a qualitative exploratory study. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 613 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11074-0
Download citation
Received : 11 November 2023
Accepted : 03 May 2024
Published : 10 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11074-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Accessibility barriers
- Healthcare utilization
- Under-five children
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 17 May 2024
Risk factors and incidence of central venous access device-related thrombosis in hospitalized children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Maoling Fu 1 , 2 ,
- Quan Yuan 2 ,
- Qiaoyue Yang 1 , 2 ,
- Yaqi Yu 1 , 2 ,
- Wenshuai Song 1 , 2 ,
- Xiuli Qin 1 ,
- Ying Luo 1 ,
- Xiaoju Xiong 1 &
- Genzhen Yu 1
Pediatric Research ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
The risk factors for central venous access device-related thrombosis (CRT) in children are not fully understood. We used evidence-based medicine to find the risk factors for CRT by pooling current studies reporting risk factors of CRT, aiming to guide clinical diagnosis and treatment.
A systematic search of PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Cochrane Library, Scopus, CNKI, Sinomed, and Wanfang databases was conducted. RevMan 5.4 was employed for data analysis.
The review included 47 studies evaluating 262,587 children with CVAD placement. Qualitative synthesis and quantitative meta-analysis identified D-dimer, location of insertion, type of catheter, number of lumens, catheter indwelling time, and central line-associated bloodstream infection as the most critical risk factors for CRT. Primarily due to observational design, the quality of evidence was regarded as low certainty for these risk factors according to the GRADE approach.
Because fewer high-quality studies are available, larger sample sizes and well-designed prospective studies are still needed to clarify the risk factors affecting CRT. In the future, developing pediatric-specific CRT risk assessment tools is important. Appropriate stratified preventive strategies for CRT according to risk assessment level will help improve clinical efficiency, avoid the occurrence of CRT, and alleviate unnecessary suffering of children.
This is the latest systematic review of risk factors and incidence of CRT in children.
A total of 47 studies involving 262,587 patients were included in our meta-analysis, according to which the pooled prevalence of CRT was 9.1%.
This study identified several of the most critical risk factors affecting CRT in children, including D-dimer, insertion location, type of catheter, number of lumens, catheter indwelling time, and central line-associated bloodstream infection (CLABSI).
Similar content being viewed by others
Pediatric central venous access devices: practice, performance, and costs
Predictors of venous thromboembolism among infants in children’s hospitals in the United States: a retrospective Pediatric Health Information Study
A clinical study of peripherally inserted central catheter-related venous thromboembolism in patients with hematological malignancies
Introduction.
Central venous access device (CVAD) is an infusion device inserted through different parts to make the tip of the catheter to the vena cava. In the clinic, CVAD is mainly divided into the following four categories: tunneled central venous catheter (CVC), nontunneled CVC, peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC), and totally implantable venous access port (TIVAP). 1 Pediatric patients often require stable, multifunctional, and comfortable long-term vascular access due to factors such as poor puncture cooperation, small vessel diameter, poor peripheral venous visibility and tolerance, high water content in the body leading to easy dehydration, and easy changes in condition after diseases. 2 The application of CVAD can significantly reduce the frequency of venipuncture, relieve the stimulation of drugs on the venous blood vessels, alleviate the pain and fear of the children, improve their medication compliance, ensure the effectiveness of intravenous infusion, and improve the quality of disease treatment. 3 , 4 , 5 Therefore, CVAD is widely used in pediatric clinics and has become an indispensable aspect of complex medical care for children with severe and chronic diseases.
Although CVAD has become an important tool in the pediatric treatment and nursing process, there are also risks of complications related to it, including CVAD-related thrombosis (CRT), phlebitis, fluid and blood leakage at the puncture point, catheter displacement, catheter obstruction, central line-associated bloodstream infection (CLABSI) and so on. 6 , 7 Among these, CRT is one of the most common and serious complications. The prevalence of CRT in children varies significantly by country, age, disease, and medical institution, ranging from 2 to 81%, 4 , 8 , 9 , 10 while in Chinese children without prophylactic treatment ranges from 20 to 66%. 11 , 12 CRT has no obvious clinical symptoms in the early stage, but it may still cause serious side effects, not only increasing the patient pain and medical costs but also delaying treatment timing, affecting prognosis and quality of life, and in severe cases, may even lead to thromboembolism, endangering life. 13 , 14 , 15
Identifying risk factors and incidence of CRT facilitates clinical practitioners in the early identification of high-risk patients, designing specific preventive strategies, treatment regimens, and management plans, thereby effectively reducing the incidence of CRT in hospitalized children and alleviating unnecessary patient suffering. However, most current research on CRT involves only small-scale groups in isolated nursing units or specific disease types. To date, no up-to-date systematic review provides pooled estimates of the risk factors and prevalence of CRT in children. Therefore, this study had a dual purpose: 1. to explore potential risk factors for CRT in children and to determine a pooled level of CRT prevalence; and 2. to provide evidence-based recommendations to improve the recognition, control, and treatment of CRT in children, as well as better nursing management for CRT.
This review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. 16 The detailed research protocol can be accessed on the PROSPERO website (registration number: CRD42023421353).
Search strategy
Eight electronic databases were utilized to conduct a thorough literature search: PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Cochrane Library, Scopus, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Sinomed, and Wanfang. The search in these databases was conducted from the earliest records available up to January 31st, 2024. The search strategy used a combination of Mesh terms and free words. The following Mesh terms and free words were mainly used: “child,” “children,” “adolescent,” “infant,” “pediatrics,” “central venous access device-related thrombosis,” “CRT,” “catheter-related thrombosis,” “catheter-related venous thrombosis,” “CVC-related thrombosis,” “risk factors,” “protective factors,” “predictors,” “causality,” “influencing factors”. The full search strategy for each database is available in the Supplementary Materials. In addition, we screened the reference lists of all included studies for relevant studies that met the criteria. Grey literature was searched as well. Some authors were contacted through email to gather more information or clarify any uncertainties.
Inclusion criteria
The study population was hospitalized children aged ≤18 years.
The primary research objective was to explore the risk factors for CRT.
The study results have at least one statistically significant predictor.
Case-control studies or cohort studies.
Published in English or Chinese.
Exclusion criteria
Catheter-related infection, catheter dysfunction, or other catheter complications as the primary outcome indicators.
Repeated published research.
Case reports, study designs, or clinical trials.
Reviews, editorials, letters, and conference abstracts.
In vitro or animal research.
Data were incomplete and could not be extracted.
Unable to find the original article.
Data extraction
Data from each eligible study were independently extracted by two reviewers using a pre-designed data collection form. Any disagreements were resolved by discussions among all authors. Data on the following characteristics were obtained from all included studies (see Supplementary Table S 1 for details):
Basic information: first author, country, year of publication, study duration, and study design.
Demographic characteristics: study population, sample size, number of CRT, and CRT rate.
Catheter-related features: catheter type, CRT type, and diagnostic method.
Potential risk factors for CRT: odds ratios (OR) or relative risks (RR) values and 95% confidence interval (CI) were extracted for each risk factor. If the study did not provide specific values, it was calculated by constructing a 2 × 2 contingency table.
Quality assessment
Two reviewers evaluated the quality of each study independently using the Risk of Bias Assessment for Nonrandomized Studies tool, 17 with any differences settled via group discussion. The tool assessed six domains of risk of bias: participant selection, confounding variables, exposure measurement, blinding of outcome assessment, incomplete outcome data, and selective outcome reporting. If all six domains were rated as low risk, the overall risk of bias for the study was low. The overall risk of bias was moderate if at least one domain was rated as unclear risk, and no domain was rated as high risk, and high if one or more domains were rated as high risk.
To ensure the accuracy of the assessment results, a third reviewer randomly selected five studies to check the data extraction and quality assessment.
Qualitative synthesis and quantitative meta-analysis
Qualitatively classify each risk factor as definite, likely, unclear, or not a risk factor based on the total number of studies with low and moderate bias risks and the proportion of studies demonstrating positive association (Box 1 in the supplementary material). If a risk factor was reported by more than two studies with low or moderate risk of bias, and the definition and reference range were sufficiently consistent, a quantitative meta-analysis was performed to estimate the combined OR.
Data were analyzed using Revman 5.4 software. In the meta-analysis of risk factors and CRT rate, the generic inverse variance method was applied, which only required effect estimate and standard error (SE). 18 The SE was obtained by inverse transforming the 95% CI applying the standard normal distribution. Heterogeneity tests were performed on the studies included in the Meta-analysis to examine for the combinability of the results of each independent study. P ≥ 0.05 and I-squared ( I 2 ) < 50% considered less heterogeneity between studies and therefore a fixed-effects model was chosen for the analysis, conversely, P < 0.05 or I 2 ≥ 50% considered greater heterogeneity, and a random-effects model was chosen.
Certainty of the evidence
The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) method was used to assess the certainty of the evidence. In this method, observational studies were initially classified as low-quality evidence and then downgraded and upgraded according to five downgrading and three upgrading principles. The 5 downgrading factors included risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision, and publication bias, and the 3 upgrading factors included the magnitude of an effect, dose-response gradient, and effect of plausible residual confounding. Based on these considerations, the overall certainty of each piece of evidence was rated as one of four levels: high, moderate, low, or very low.
The initial search of the databases extracted a total of 4193 articles, of which 1656 were duplicates and removed. The titles and abstracts of the remaining 2537 articles were screened according to the inclusion criteria and 142 were selected for full-text search. After a rigorous eligibility review, 45 articles met the inclusion criteria. In addition, two articles were found to meet the eligibility criteria in a search of the reference lists of the selected articles and grey literature. In the end, a total of 47 articles were included in this review, of which 43 contributed to the qualitative synthesis and quantitative meta-analysis (Fig. 1 ).
Demonstrate the screening and inclusion process for systematic literature search.
Of the 47 studies, 19 were prospective 4 , 13 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 and the rest were retrospective, 9 , 12 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 of which 10 were multicenter 4 , 9 , 13 , 21 , 23 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 49 , 59 and 37 were single-center. 12 , 19 , 20 , 22 , 24 , 25 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 60 , 61 The sample sizes ranged from 47 to 158,299, with the two largest being 71,782 13 and 158,299, 59 respectively. In addition, three studies constructed clinical prediction models. 22 , 28 , 47 Table 1 lists the summary characteristics of the included studies.
Study populations and CRT rates in included studies
These studies investigated a series of hospitalized children of different ages and departments, of which 12 studies with all hospitalized children as the study population, 12 studies with PICU hospitalized children as the study population, six studies with NICU hospitalized children as the study population, one study with all ICU hospitalized children as the study population, four studies with leukemia children as the study population, two studies with infants under 1-year-old as the study population, and the other ten studies with children with a specific disease as the study population.
The combined CRT rate was 9.1% (95% CI : 5.7–14.5%) with a high degree of heterogeneity ( I 2 = 100%). The combined CRT rate was 11.5% (95% CI : 5.7–23.1%; I 2 = 99%) in both male and female children. The frequency of CRT in PICU and NICU was available from 13 articles with 234,464 children and 7 articles with 6093 infants, which combined CRT rates were 10.7% (95% CI : 3.8–23.7%; I 2 = 100%), 2.9% (95% CI : 1.0–6.5%; I 2 = 96%), respectively. The combined CRT rate of children with leukemia was 13.0% (95% CI : 2.9–38.3%; I 2 = 98%) (Supplementary Material Figs. S 1 – 6 )
Quality of the CRT studies
The methodological quality of the included studies varied (Fig. 2 and Supplementary Material Fig. S 7 ). Nine studies had a low overall risk of bias, as all six domains were categorized as low risk. Four studies had a high overall risk of bias, three of which were associated with confounding variables and one to participant selection. The remaining 34 studies had a moderate overall risk of bias, with at least one of the six domains having an unclear risk.
A summary presentation of the assessment results of risk of bias for the 47 studies.
Risk factors of CRT in included studies
The 47 included studies reported 61 statistically significant risk factors for CRT (Table 1 ). These factors were classified into three categories: patient-related risk factors (37.7%, 23/61); CVAD-related risk factors (34.4%, 21/61), and treatment-related risk factors (27.9%, 17/61).
Based on the qualitative synthesis, six variables were considered to be definite risk factors for CRT, including D-dimer, location of insertion, type of catheter, number of lumens, catheter indwelling time, and CLABSI. Eleven variables were considered likely associated with CRT, including gastrointestinal diseases, history of catheterization, thrombophilia, geographic location of line placement, catheter dysfunction, number of catheters, insertion length (cm), catheter to vein ratio, dialysis, hypertonic liquid, and cardiac catheterization. For 42 variables, the relationship with CRT was deemed unclear due to conflicting results from studies assessed as having low and moderate risk of bias, or because they were positively associated in only one study. Additionally, birth weight and gestational age were considered non-risk factors (Table 2 ).
Meta-analyses were implemented for risk factors that were reported by at least two low or moderate risk of bias studies with a consistent definition and reference range (Table 3 and Figs. 3 – 6 ).
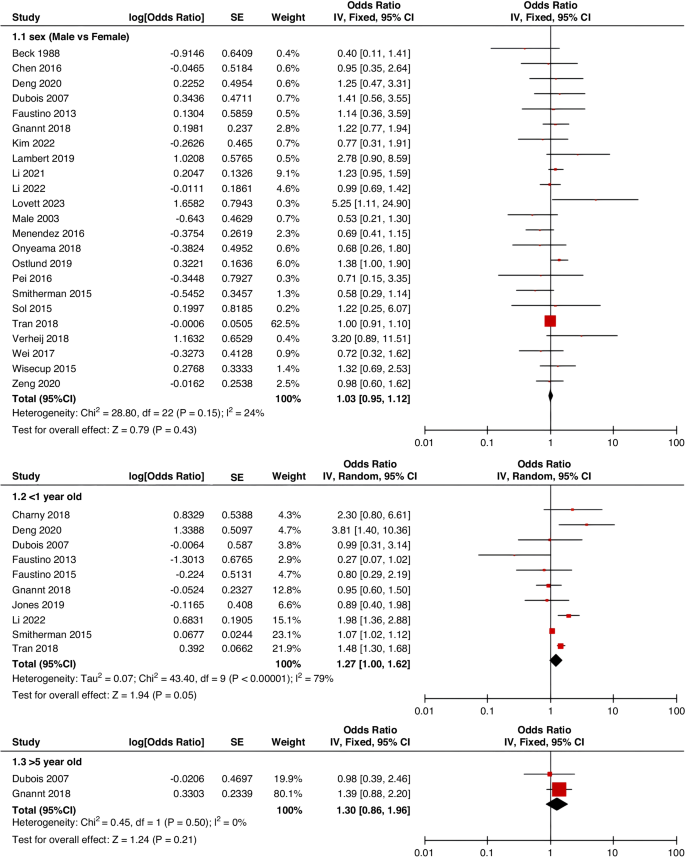
Forest plots of odds ratios (OR) that were included in the quantitative meta-analysis and the associated overall OR. For each OR, the size of the red square region is proportional to the corresponding study weight. Diamond shape intervals represent the overall OR. I 2 represents the fraction of variability among the individual OR that cannot be explained by sampling variability.
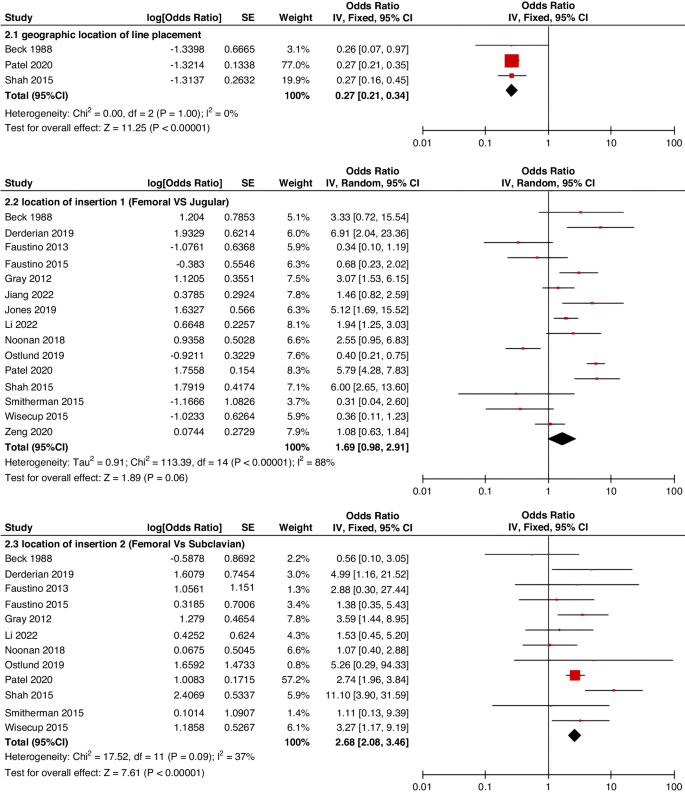
Forest plots of odds ratios (OR) that were included in the quantitative meta-analysis and the associated overall OR. For each OR, the size of the red square region is proportional to the corresponding study weight. Diamond shape intervals represent the overall OR. I 2 represents the fraction of variability among the individual OR that cannot be explained by sampling variability.
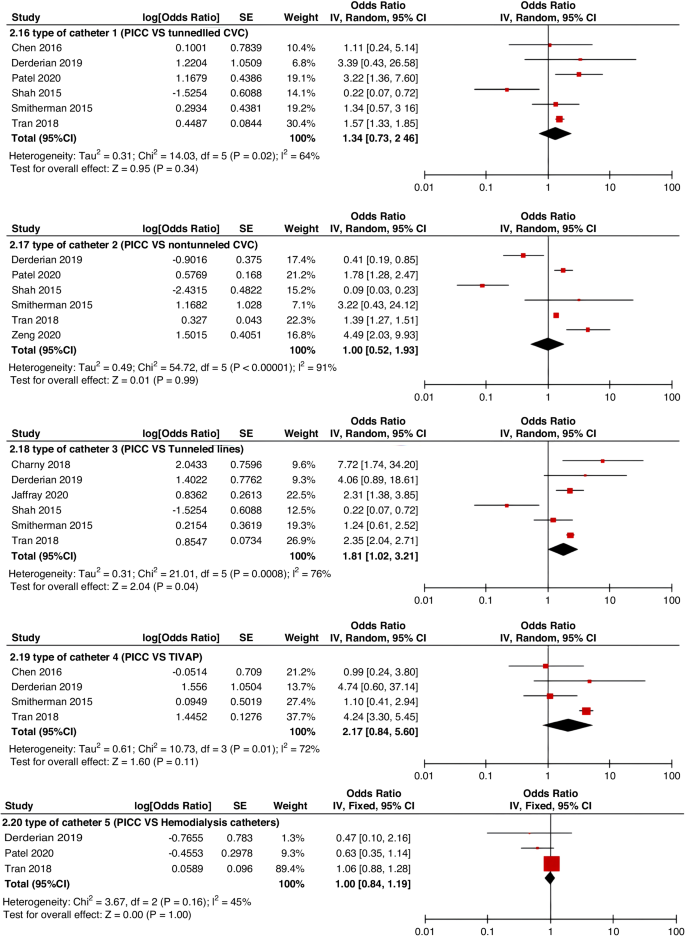
GRADE assessment of evidence
Supplementary Table S 2 shows GRADE assessments for the certainty of evidence. Due to the design of the observational studies, all evidence was initially rated as low certainty. Based on five downgrading and three upgrading principles, 17 pieces of evidence were still rated as low certainty, and the remaining 44 pieces of evidence were downgraded to very low certainty for serious inconsistency and imprecision.
Our study is the latest systematic review of risk factors and the incidence of CRT in hospitalized children. Based on 47 studies included in the current meta-analysis, which involved a total of 262,587 patients, the pooled prevalence of CRT is 9.1%. We conducted a qualitative synthesis analysis of 61 predictive factors and a quantitative meta-analysis of 38 factors, identifying six definite factors, 11 likely factors, and 42 unclear factors associated with CRT. Definite predictors included being of D-dimer, location of insertion, type of catheter, number of lumens, catheter indwelling time and CLABSI. The findings of our systematic review provide the latest comprehensive evidence summary that can inform the early identification of children at risk for CRT and the development of intervention measures to prevent and reduce CRT.
Implantable and temporary medical devices such as CVAD are exposed to blood for weeks to years depending on the type of CVAD in place. Since CVAD is an artificial surface and lacks an endothelial layer that inhibits platelet coagulation and adhesion, it is thought to potentially activate the contact pathways, ultimately leading to thrombosis. Assembly of artificial surface contact systems might be part of the host defense mechanism against foreign substances, but it can lead to kinin and thrombin generation, and complement activation. 62 This eventually promotes thrombosis and inflammation. The presence of CVAD is the most common risk factor for venous thromboembolism (VTE). CRT accounts for 10% of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in adults and 50–80% in children. 10 , 55 , 63 The incidence of CRT in hospitalized children has increased significantly by 30–70% over the past 20 years, 64 , 65 which may cause serious medical complications besides increasing healthcare expenditures and length of stay.
We discover that a higher level of D-dimer is an independent risk factor for CRT in hospitalized children, consistent with the results of adult studies. 66 D-dimer is a soluble fibrin degradation product deriving from the plasmin-mediated degradation of cross-linked fibrin that is increased or positive in secondary hyperfibrinolysis, such as hypercoagulable states, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and thrombolytic therapy. 67 , 68 Increased D-dimer suggests an association with thrombotic disorders in the body of various origins and an increase in fibrinolytic activity. D-dimer has been extensively investigated for excluding the diagnosis of VTE and is used routinely for this indication. 67 , 69 Therefore, for early recognition and to reduce the incidence of CRT, D-dimer levels should be closely monitored before and after catheterization. However, the elevated D-dimer test results cannot fully explain the cause and location of CRT formation and must be analyzed in conjunction with clinical and other test results. Inherited thrombophilia, caused by genetic defects leading to a deficiency or abnormality in associated proteins, including protein C, protein S, antithrombin, the coagulation factor V Leiden mutation, and factor II mutation G20210A, 70 is considered a potential risk factor for CRT. The prevalence of thrombophilia varies widely among different populations, with a reported prevalence of 10% to 59% in pediatric VTE patients. 71 Children with gastrointestinal diseases like short bowel syndrome (SBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have an increased risk of developing CRT during hospitalization. The precise mechanism behind this association is still uncertain according to current research. It may be attributed to the heightened inflammation levels during catheterization, particularly in patients with active IBD episodes or admissions during surgery, which leads to a period of increased inactivity. 55 This suggests that delaying placement during the most active period of inflammation may reduce the rate of thrombosis.
A narrative review pointed out that age is one of the most significant risk factors for VTE. In children, CRT shows a bimodal distribution, with the highest incidence rate in infancy and adolescence. 10 The higher incidence in infancy may be due in part to the smaller diameter of the vein, making insertion difficult and requiring multiple attempts. However, whether age is a risk factor for CRT is still highly controversial. The study by Chojnacka et al. did not find a statistically significant difference, 39 although a trend toward a similar bimodal distribution was found in the study population. Cancer, cardiovascular disease, sepsis, asphyxia, and neurological diseases are also considered unclear factors for CRT. Pediatric patients diagnosed with leukemia have multiple risk factors for VTE formation, such as the presence of hypercoagulable blast cells, the pro-thrombotic nature of the cancer itself, and treatment with steroids and L-asparaginase. Chen et al. 38 and Jaffray et al. 4 concluded that children with leukemia are more likely to develop CRT. Sepsis causes the coagulation mechanism to become fragile, which in turn activates the coagulation system and creates thrombosis. 72 However, a study by Onyeama et al. 52 showed that sepsis was significantly associated with a reduced incidence of CRT, and the exact mechanism is currently unknown.
The location of insertion and type of catheter are critical risk factors for CRT. The incidence of CRT is higher in femoral vein catheterizations compared to subclavian and jugular vein catheterizations in children, which is contrary to findings in adult patients. 73 The femoral location is a larger vessel and allows placement of a larger size catheter. Femoral CVAD is prioritized in urgent and emergency situations. In such cases, the patients tend to be more critically ill and often immobilized, further exacerbating the low-flow state. In addition, there may be vein compression and kinking beneath the inguinal ligament with leg movement, which may increase the risk of CRT. 27 PICC catheters provide a reliable medium to long-term route to intravenous therapy for children, but compared with other types of catheters, the risk of CRT is higher. We speculate that the long tunnel length and relatively large lumen size of the PICC, compared to the diameter of the vessel at the insertion site, may lead to increased blood flow obstruction. 52 Additionally, patients with PICC may be more likely to be diagnosed with symptomatic VTE than tunneled lines (TLs) because PICC is often placed in smaller vessels and journeys through the arm or leg causing limb pain and swelling, whereas TLs are located in the chest.
The risk of CRT increases with the number of lumens. A possible explanation for this finding is that multilumen catheters tend to have larger catheter sizes and thus occupy more area within the vessel lumen, leading to obstruction of normal blood flow within the veins. The relationship between CRT and CLABSI is bidirectional. Following catheter insertion, a fibrin sheath forms around the catheter. Microorganisms, especially staphylococcus aureus, easily adhere to the fibrin sheaths, and may lead to CLABSI. 74 Conversely, CLABSI can trigger inflammatory reactions, leading to further progression of thrombosis. CVAD duration is positively associated with the risk of CRT. Catheter placement may cause mechanical injury to the vein. As the indwelling duration increases, many damaged smooth muscle and endothelial cells become embedded within the fibrin, resulting in thrombus formation. In addition, prolonged indwelling increases the chance of platelet contact with the vessel lining, activating coagulation factors and thrombin, increasing the risk of thrombosis. 22 Therefore, nurses should perform routine maintenance of the catheter in children who require long-term CVAD indwelling. The duration of CVAD should be monitored, the necessity of its indwelling should be assessed daily, and the catheter should be removed as early as possible while ensuring treatment.
As obstruction of venous blood flow from the CVAD is considered an essential causative mechanism for the development of VTE, a high ratio between catheter size and vein diameter could be a risk factor for CRT. The 2012 international guidelines on pediatric CVC insertion recommend that the ratio between the catheter’s external diameter and the cannulated vein’s diameter should not exceed 0.33. 75 However, this suggestion is only based on expert opinions and currently lacks relevant clinical data support. Therefore, further research is still needed to verify it. Catheter dysfunction is mainly caused by small clots or fibrous sheaths wrapping around the tip of the catheter. Prolonged accumulation may lead to incomplete or complete blockage of blood vessels, becoming a gathering point for thrombosis. 74 Journeycake et al. observed that the risk of VTE was highest in pediatric cancer patients with multiple episodes of catheter dysfunction. 76 A study of pediatric brain tumor patients reported that VTE was more common in patients with catheter dysfunction. 77 Thus, these studies and the current data support the need to consider catheter dysfunction as a possible risk factor for CRT and to design further screening and intervention studies for early identification and prevention of catheter dysfunction.
The rationale for studying the relationship between the insertion side of CVAD and the risk of CRT is based on the anatomy of the upper body venous system. The left brachiocephalic vein is longer and courses more horizontally than the right side, thus entering the superior vena cava at a sharper angle. The right jugular vein is the most direct and shortest route for the CVAD to enter the heart. By contrast, the CVAD located in the left jugular vein has a greater distance to the heart and passes through 2 angles in the venous system, which may cause endothelial damage and increase the likelihood of blood flow obstruction and venous wall adhesion. 26 However, our meta-analysis did not find a statistically significant increase in the risk of CRT with left-sided placement compared to right-sided placement. The ideal location for the catheter tip is the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. This location is preferred because of the higher blood flow rate, which may be protective against thrombosis. 43 Currently, the pediatric literature on the effect of optimal tip position on CRT is scarce and inconclusive. In addition, catheter tips do not always remain in that position after initial placement. Therefore, tip movement should be a significant concern in pediatric patients, especially active, growing, and requiring long-term catheter use.
Providing renal replacement therapy is a lifelong task for pediatric end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients. Although successful transplantation can be achieved even in young patients, the lifespan of the graft is limited. Consequently, many transplant recipients may be put back on dialysis as part of their ESRD treatment. 78 CVC remains the main vascular access for hemodialysis in children. Long-term reliance on CVC is related to a high incidence of catheter dysfunction and failure. The frequent need for recurrent CVC placement in such patients leads to an elevated risk of central vein stenosis and CRT. Cardiac catheterization is also a possible risk factor for CRT. Appropriate anticoagulation is required during catheterization, without which the risk of thrombosis is up to 40%. However, the use of unfractionated heparin in pediatric patients is challenging because the coagulation system and heparin response are different from that of adults. 79 There’s a need for further research to determine if children are receiving adequate doses of heparin during cardiac catheterization to prevent thrombosis without increasing the risk of bleeding complications. The incidence of VTE in adult patients who are chronically bedridden and braked is 3.59 times higher than in patients with normal activity levels. 80 In critically ill or surgical children, mechanical ventilation is often performed in the early stages, requiring continuous use of multiple sedative or inotropic drugs to reduce cardiac load and protect pulmonary function. During sedation, the child is in a braked state, limb activity is reduced or even inactive, blood flow slows down, and blood stagnates in the veins, increasing the chance of platelet adhesion to the endothelium, which may increase the risk of CRT. Therefore, passive movements such as limb abduction, internal rotation, elbow flexion and elbow extension should be performed appropriately when the child’s condition permits.
Nutritional support is an important part of critical illness treatment, including enteral and parenteral nutrition (PN). CVAD is the supply channel for total parenteral nutrition (TPN), and some children may even need this method to provide calories for a long time. High glucose and calcium concentrations in PN are both possible triggers of CRT, and PN has been shown to upregulate the extrinsic coagulation cascade, especially with long-term use. 60 Diamanti et al. reported that the incidence rate of TPN complicated with CRT was 20%. 81 Mannitol or glycerol fructose are widely used as hypertonic drugs in clinical practice, which can increase plasma osmolality to dehydrate tissues after entering the body. At the same time, it may cause a cellular stress response, induce apoptosis, and can activate inflammatory cytokines and coagulation pathways to induce thrombosis. Jiang et al. 22 found vasoactive drugs to be a risk factor for CRT. The possible reason is that vasoactive drugs can cause strong vasoconstriction, endothelial function damage or impairment, and promote fibrinogen synthesis. However, this is contrary to the findings of Marquez et al. 28 and Faustino et al. 21 Therefore, larger prospective studies are still needed to assess this risk factor more precisely.
The strengths of this study include the systematic identification of all relevant studies of risk factors for CRT in hospitalized children and the classification of risk factors into three categories, patient-related risk factors, CVAD-related risk factors, and treatment-related risk factors, to offer a logical progression of the possible causes of CRT in children. However, several limitations of this systematic review should be stated. Firstly, as most of the studies originate from Western countries, extrapolating these results to Eastern populations is questionable. Second, significant heterogeneity was encountered in our analysis, potentially stemming from variations in regimen, duration, population enrolled, and center setting, among other factors. This diversity necessitates a cautious interpretation of the results. In addition, only a few high-quality studies with a low risk of bias, and many of the studies suffer from significant sources of bias. Furthermore, the effect in many occasions was assessed by very few studies. Therefore, the evidence to support it is low, which needs to be validated in future studies. Finally, risk factors for CRT could not be made causal assertions since the majority of studies were retrospective.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we have identified several critical factors that affect CRT, including D-dimer, location of insertion, type of catheter, number of lumens, catheter indwelling time, and CLABSI. Nevertheless, none of the included studies considered the impact of socio-demographic factors on CRT, such as parental education level, occupation, and family economic status. Therefore, larger sample sizes and well-designed prospective studies are still needed to clarify the predictors affecting CRT in the future. In addition, there is a lack of pediatric-specific CRT risk assessment tools, which need to be further developed and validated. Machine learning (ML), as a method for designing risk assessment models that help to efficiently explore and mine useful information, has been widely used in recent years to solve a variety of challenging medical problems. Likewise, the application of ML in CRT risk diagnosis may contribute to a more precise assessment. In clinical practice, it is necessary to take appropriate stratified preventive measures according to the level of CRT risk assessment of children, to improve the efficiency of clinical work, reduce the burden of clinical work, and minimize the occurrence of CRT under the premise of ensuring the safety of children.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Yeow, M. et al. A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on choice of central venous access device for delivery of chemotherapy. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 10 , 1184–91.e8 (2022).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Cellini, M. et al. Guidelines of the Italian Association of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology for the management of the central venous access devices in pediatric patients with onco-hematological disease. J. Vasc. Access 23 , 3–17 (2022).
Ares, G. & Hunter, C. J. Central venous access in children: indications, devices, and risks. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 29 , 340–346 (2017).
Jaffray, J. et al. Peripherally inserted central catheters lead to a high risk of venous thromboembolism in children. Blood 135 , 220–226 (2020).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Zhang, J. J. et al. Factors affecting mechanical complications of central venous access devices in children. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 38 , 1067–1073 (2022).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Akhtar, N. & Lee, L. Utilization and Complications of Central Venous Access Devices in Oncology Patients. Curr. Oncol. 28 , 367–377 (2021).
Ullman, A. J., Marsh, N., Mihala, G., Cooke, M. & Rickard, C. M. Complications of Central Venous Access Devices: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics 136 , e1331–e1344 (2015).
Östlund, Å. et al. Erratum to ‘Incidence of and risk factors for venous thrombosis in children with percutaneous non-tunnelled central venous catheters’ (Br J Anaesth 2019; 123: 316-24). Br. J. Anaesth. 123 , 918 (2019).
McLaughlin, C. M. et al. Symptomatic catheter-associated thrombosis in pediatric trauma patients: Choose your access wisely. Surgery 166 , 1117–1121 (2019).
Citla Sridhar, D., Abou-Ismail, M. Y. & Ahuja, S. P. Central venous catheter-related thrombosis in children and adults. Thromb. Res. 187 , 103–112 (2020).
Zhou, X. et al. A retrospective analysis of risk factors associated with catheter-related thrombosis: a single-center study. Perfusion 35 , 806–813 (2020).
Li, S. et al. Risk factors for central venous catheter-related thrombosis in hospitalized children: a single-center a retrospective cohort study. Transl. Pediatr. 11 , 1840–1851 (2022).
Patel, N., Petersen, T. L., Simpson, P. M., Feng, M. & Hanson, S. J. Rates of Venous Thromboembolism and Central Line-Associated Bloodstream Infections Among Types of Central Venous Access Devices in Critically Ill Children. Crit. Care Med. 48 , 1340–1348 (2020).
Timsit, J. F. et al. A state of the art review on optimal practices to prevent, recognize, and manage complications associated with intravascular devices in the critically ill. Intensive Care Med. 44 , 742–759 (2018).
Ullman, A. J. et al. Pediatric central venous access devices: practice, performance, and costs. Pediatr. Res. 92 , 1381–1390 (2022).
Hutton, B. et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern Med. 162 , 777–784 (2015).
Kim, S. Y. et al. Testing a tool for assessing the risk of bias for nonrandomized studies showed moderate reliability and promising validity. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 66 , 408–414 (2013).
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. & Rothstein, H. R. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 1 , 97–111 (2010).
Beck, C., Dubois, J., Grignon, A., Lacroix, J. & David, M. Incidence and risk factors of catheter-related deep vein thrombosis in a pediatric intensive care unit: a prospective study. J. Pediatr. 133 , 237–241 (1998).
Dubois, J. et al. Incidence of deep vein thrombosis related to peripherally inserted central catheters in children and adolescents. Cmaj 177 , 1185–1190 (2007).
Faustino, E. V. et al. Incidence and acute complications of asymptomatic central venous catheter-related deep venous thrombosis in critically ill children. J. Pediatr. 162 , 387–391 (2013).
Jiang, W. et al. Construction and validation of a risk prediction model for central venous catheter-associated deep venous thromboses in children with congenital heart disease after surgery. Chin. J. Nurs. 57 , 2217–2224 (2022).
Google Scholar
Faustino, E. V. et al. Factor VIII May Predict Catheter-Related Thrombosis in Critically Ill Children: A Preliminary Study. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 16 , 497–504 (2015).
Jones, S., Butt, W., Monagle, P., Cain, T. & Newall, F. The natural history of asymptomatic central venous catheter-related thrombosis in critically ill children. Blood 133 , 857–866 (2019).
Kim, E. H. et al. Central venous catheter-related thrombosis in pediatric surgical patients: A prospective observational study. Paediatr. Anaesth. 32 , 563–571 (2022).
Male, C. et al. Central venous line-related thrombosis in children: association with central venous line location and insertion technique. Blood 101 , 4273–4278 (2003).
Male, C., Julian, J. A., Massicotte, P., Gent, M. & Mitchell, L. Significant association with location of central venous line placement and risk of venous thrombosis in children. Thromb. Haemost. 94 , 516–521 (2005).
Marquez, A., Shabanova, V. & Faustino, E. V. Prediction of Catheter-Associated Thrombosis in Critically Ill Children. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 17 , e521–e528 (2016).
Menéndez, J. J. et al. Incidence and risk factors of superficial and deep vein thrombosis associated with peripherally inserted central catheters in children. J. Thromb. Haemost. 14 , 2158–2168 (2016).
Rubio Longo, M. C. et al. Catheter-related deep vein thrombosis in newborn infants. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 119 , 32–38 (2021).
PubMed Google Scholar
Östlund, Å. et al. Incidence of and risk factors for venous thrombosis in children with percutaneous non-tunnelled central venous catheters. Br. J. Anaesth. 123 , 316–324 (2019).
Sol, J. J. et al. Chronic Complications After Femoral Central Venous Catheter-related Thrombosis in Critically Ill Children. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 37 , 462–467 (2015).
van Rooden, C. J. et al. Infectious complications of central venous catheters increase the risk of catheter-related thrombosis in hematology patients: a prospective study. J. Clin. Oncol. 23 , 2655–2660 (2005).
Zeng, X., Zhang, C. & Shi, Y. Analysis of risk factors for complicated catheter-related thrombosis in children. Chin. J. Emerg. Med. 29 , 719–723 (2020).
Wei, Y. et al. The incidence and risk factors of catheter-related-thrombosis during induction chemotherapy in acute lymphocytic leukemia children. Chin. J. Hematol. 38 , 313–317 (2017).
CAS Google Scholar
Deng, G. & Liao, Q. Analysis of risk factors for venous thrombosis after PICC placement in critically ill children. Int. I Nurs. 39 , 775–777 (2020).
Badheka, A. V. et al. Catheter related thrombosis in hospitalized infants: A neural network approach to predict risk factors. Thromb. Res. 200 , 34–40 (2021).
Chen, K. et al. Risk factors for central venous catheter-related thrombosis in children: a retrospective analysis. Blood Coagul. Fibrinol. 27 , 384–388 (2016).
Article Google Scholar
Chojnacka, K., Krasiński, Z., Wróblewska-Seniuk, K. & Mazela, J. Catheter-related venous thrombosis in NICU: A case-control retrospective study. J. Vasc. Access 23 , 88–93 (2022).
Derderian, S. C., Good, R., Vuille-Dit-Bille, R. N., Carpenter, T. & Bensard, D. D. Central venous lines in critically ill children: Thrombosis but not infection is site dependent. J. Pediatr. Surg. 54 , 1740–1743 (2019).
Diamond, C. E. et al. Catheter-Related Venous Thrombosis in Hospitalized Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Incidence, Characteristics, and Role of Anticoagulant Thromboprophylaxis with Enoxaparin. J. Pediatr. 198 , 53–59 (2018).
Noailly Charny, P. A. et al. Increased Risk of Thrombosis Associated with Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters Compared with Conventional Central Venous Catheters in Children with Leukemia. J. Pediatr. 198 , 46–52 (2018).
Gnannt, R. et al. Increased risk of symptomatic upper-extremity venous thrombosis with multiple peripherally inserted central catheter insertions in pediatric patients. Pediatr. Radio. 48 , 1013–1020 (2018).
Gray, B. W. et al. Characterization of central venous catheter-associated deep venous thrombosis in infants. J. Pediatr. Surg. 47 , 1159–1166 (2012).
Haddad, H. et al. Routine surveillance ultrasound for the management of central venous catheters in neonates. J. Pediatr. 164 , 118–122 (2014).
Lambert, I., Tarima, S., Uhing, M. & Cohen, S. S. Risk Factors Linked to Central Catheter-Associated Thrombosis in Critically Ill Infants in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Am. J. Perinatol. 36 , 291–295 (2019).
Li, H. et al. Prediction of central venous catheter-associated deep venous thrombosis in pediatric critical care settings. BMC Med. Inf. Decis. Mak. 21 , 332 (2021).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Lovett, M. E. et al. Catheter-associated deep vein thrombosis in children with severe traumatic brain injury: A single-center experience. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 70 , e30044 (2023).
MacLean, J. et al. Need for tissue plasminogen activator for central venous catheter dysfunction is significantly associated with thrombosis in pediatric cancer patients. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 65 , e27015 (2018).
Noonan, P. J., Hanson, S. J., Simpson, P. M., Dasgupta, M. & Petersen, T. L. Comparison of Complication Rates of Central Venous Catheters Versus Peripherally Inserted Central Venous Catheters in Pediatric Patients. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 19 , 1097–1105 (2018).
Pei, L. et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of symptomatic central venous catheter-related deep vein thrombosis in children. Chin. Pediatr. Emerg. Med. 23 , 450–454 (2016).
Onyeama, S. N. et al. Central Venous Catheter-associated Venous Thromboembolism in Children With Hematologic Malignancy. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 40 , e519–e524 (2018).
Shah, S. H. et al. Clinical risk factors for central line-associated venous thrombosis in children. Front. Pediatr. 3 , 35 (2015).
Shin, H. S., Towbin, A. J., Zhang, B., Johnson, N. D. & Goldstein, S. L. Venous thrombosis and stenosis after peripherally inserted central catheter placement in children. Pediatr. Radio. 47 , 1670–1675 (2017).
Smitherman, A. B. et al. The incidence of catheter-associated venous thrombosis in noncritically ill children. Hosp. Pediatr. 5 , 59–66 (2015).
Steen, E. H. et al. Central Venous Catheter-Related Deep Vein Thrombosis in the Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit. J. Surg. Res 241 , 149–159 (2019).
Wang, J. & Ren, G. Peripherally inserted central catheter related venous thromboembolism in children with acute leukemia: a factorial analysis. Chin. J. Biomed. Eng. 27 , 288–293 (2021).
Dubbink-Verheij, G. H. et al. Femoral Vein Catheter is an Important Risk Factor for Catheter-related Thrombosis in (Near-)term Neonates. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 40 , e64–e68 (2018).
Tran, M., Shein, S. L., Ji, X. & Ahuja, S. P. Identification of a “VTE-rich” population in pediatrics - Critically ill children with central venous catheters. Thromb. Res 161 , 73–77 (2018).
Wisecup, S., Eades, S. & Turiy, Y. Characterizing the Risk Factors Associated With Venous Thromboembolism in Pediatric Patients After Central Venous Line Placement. J. Pediatr. Pharm. Ther. 20 , 358–366 (2015).
Zhu, W., Zhang, H., Xing, Y. Clinical Characteristics of Venous Thrombosis Associated with Peripherally Inserted Central Venous Catheter in Premature Infants. Children 9 , https://doi.org/10.3390/children9081126 (2022).
Ekdahl, K. N. et al. Innate immunity activation on biomaterial surfaces: a mechanistic model and coping strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 63 , 1042–1050 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Takemoto, C. M. et al. Hospital-associated venous thromboembolism in children: incidence and clinical characteristics. J. Pediatr. 164 , 332–338 (2014).
Boulet, S. L. et al. Trends in venous thromboembolism-related hospitalizations, 1994-2009. Pediatrics 130 , e812–e820 (2012).
Raffini, L., Huang, Y. S., Witmer, C. & Feudtner, C. Dramatic increase in venous thromboembolism in children’s hospitals in the United States from 2001 to 2007. Pediatrics 124 , 1001–1008 (2009).
Lin, S., Zhu, N., YihanZhang, Du, L. & Zhang, S. Development and validation of a prediction model of catheter-related thrombosis in patients with cancer undergoing chemotherapy based on ultrasonography results and clinical information. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 54 , 480–491 (2022).
Johnson, E. D., Schell, J. C. & Rodgers, G. M. The D-dimer assay. Am. J. Hematol. 94 , 833–839 (2019).
Favresse, J. et al. D-dimer: Preanalytical, analytical, postanalytical variables, and clinical applications. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab Sci. 55 , 548–577 (2018).
Weitz, J. I., Fredenburgh, J. C. & Eikelboom, J. W. A Test in Context: D-Dimer. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 70 , 2411–2420 (2017).
Darlow, J. & Mould, H. Thrombophilia testing in the era of direct oral anticoagulants. Clin. Med. 21 , e487–e491 (2021).
Monagle, P. et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: treatment of pediatric venous thromboembolism. Blood Adv. 2 , 3292–3316 (2018).
Meziani, F., Gando, S. & Vincent, J. L. Should all patients with sepsis receive anticoagulation? Yes. Intensive Care Med 43 , 452–454 (2017).
Saber, W. et al. Risk factors for catheter-related thrombosis (CRT) in cancer patients: a patient-level data (IPD) meta-analysis of clinical trials and prospective studies. J. Thromb. Haemost. 9 , 312–319 (2011).
Journeycake, J. M. & Buchanan, G. R. Thrombotic complications of central venous catheters in children. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 10 , 369–374 (2003).
Lamperti, M. et al. International evidence-based recommendations on ultrasound-guided vascular access. Intensive Care Med 38 , 1105–1117 (2012).
Journeycake, J. M. & Buchanan, G. R. Catheter-related deep venous thrombosis and other catheter complications in children with cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 24 , 4575–4580 (2006).
Deitcher, S. R., Gajjar, A., Kun, L. & Heideman, R. L. Clinically evident venous thromboembolic events in children with brain tumors. J. Pediatr. 145 , 848–850 (2004).
Mandel-Shorer, N., Tzvi-Behr, S., Harvey, E. & Revel-Vilk, S. Central venous catheter-related venous thrombosis in children with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis. Thromb. Res 172 , 150–157 (2018).
Chen, D., Långström, S., Petäjä, J., Heikinheimo, M. & Pihkala, J. Thrombin formation and effect of unfractionated heparin during pediatric cardiac catheterization. Catheter Cardiovasc Inter. 81 , 1174–1179 (2013).
Reynolds, P. M. et al. Evaluation of Prophylactic Heparin Dosage Strategies and Risk Factors for Venous Thromboembolism in the Critically Ill Patient. Pharmacotherapy 39 , 232–241 (2019).
Diamanti, A. et al. Prevalence of life-threatening complications in pediatric patients affected by intestinal failure. Transpl. Proc. 39 , 1632–1633 (2007).
Download references
This study was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities [grant numbers YCJJ20230244] and Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology Research Fund [grant numbers 2022C09].
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Nursing, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Maoling Fu, Qiaoyue Yang, Yaqi Yu, Wenshuai Song, Xiuli Qin, Ying Luo, Xiaoju Xiong & Genzhen Yu
School of Nursing, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Maoling Fu, Quan Yuan, Qiaoyue Yang, Yaqi Yu & Wenshuai Song
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
GY and YL framed the review questions on the basis of input from MF and QY. YY and XQ conducted the literature search. MF, WS, and QY screened and evaluated the identified papers. GY and YY performed data extraction and analysis. MF, WS, XQ and QY prepared the initial manuscript with revisions and comments from GY, YL, and XX. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Genzhen Yu .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary checklist, supplemental digital tables1, supplemental digital tables2, supplemental digital, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Fu, M., Yuan, Q., Yang, Q. et al. Risk factors and incidence of central venous access device-related thrombosis in hospitalized children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-024-03225-0
Download citation
Received : 06 October 2023
Revised : 18 March 2024
Accepted : 25 March 2024
Published : 17 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-024-03225-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.58; Jan-Dec 2021
Qualitative Observational Research in the Intensive Care Setting: A Personal Reflection on Navigating Ethical and Methodological Issues
Fredrika sundberg.
1 Research and Development Centre, Skaraborg Hospital Skövde, Skovde, Sweden
2 The School of Health Sciences, University of Skövde, Skovde, Sweden
3 Division of Nursing, Midwifery & Social Work, School of Health Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester,UK
Berit Lindahl
4 Department of Health Sciences, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
The aim of this theoretical paper is to critically reflect on the ethical and methodological issues that arose during a study that observed nurses’ care-giving in an intensive care unit setting. The authors critically discuss the methodological and ethical issues as well as the practical realities that were encountered when evaluating a complex intervention using unstructured qualitative observations. We describe the process with negotiating access and entering into the clinical field. Moreover, we reflect on experiences related to methodological issues such as the observer role, how to construct field notes, and how to encounter ethical dilemmas and other problems when being an observer in a closed and protected setting like an intensive care unit. We argue that qualitative observations give an insider perspective when studying the conditions for health and well-being. Our experiences can be transferred to other contexts and guide researchers interested in doing qualitative observational studies.
- • What Is Known About This Topic?
○ Caring is difficult to express verbally.
○ Observational research is not fully explored.
- • What Does This Contribute to the Field?
○ It reveals the practical realities that were encountered when evaluating a complex intervention.
○ It highlights how unstructured qualitative observations are useful in capturing phenomena that are difficult to express verbally
- • Implications for Theory and Practice
- ○ Qualitative observation provides a valuable perspective when studying caring in different settings. However, careful planning is needed to navigate the ethical and methodological issues this presents.
Introduction
This paper discusses some of the methodological and ethical issues of conducting qualitative observational research, 1 as well as the practical realities that were encountered in evaluating a complex intervention. 2 The intervention aimed to change an intensive care unit (ICU) environment in a Swedish hospital according to evidence-based design principles; altering the environment in relation to sound, lightning, furniture, textiles, and nature. The study aimed to examine if and how such a refurbished ICU patient room influenced nursing care, that is, if the nurses’ caring actions became more sensitive and directed to patients’ well-being and recovery. 1 We concur with Mulhall 3 and Author 4 that unstructured non-participation observation from an interpretative approach is fruitful when examining the physical environment and interaction. To gain access to an ICU is complex per se, and today’s outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic increases this complexity. The pandemic has led to suffering for patients and their families and caused tremendous demands on ICU staff and their work environment. This means that the problems and dilemmas connected to data collection through observations in ICU are particularly relevant to discuss and to further develop.
The concept of environment has received limited attention in nursing research, often being taken for granted as a passive frame of reference within which professional caring occurs, 5 , 6 although interest in the environmental impact of delivered care has had a revival lately. 7 – 9 This neglect is especially the case in relation to the intensive care setting. This is a significant omission given the particular environment of the ICU with its domination by high tech equipment and round-the-clock medical regimens. The change to light sedation regimens have also made patients more aware of their environment, 10 , 11 this coupled with disrupted circadian rhythms leads to up to 80% of patients experiencing delirium. 12 – 15 These disturbances often remain after discharge. Concerns about the traditional ICU environment and its influence on patient well-being led to the development of an innovative program of research which aimed to assess the impact of an evidence-based design approach to the ICU environment on patient health and well-being. 2 , 12 , 16 , 17
Refurbishing a Patient Room According to Evidence-Based Design
The concept of evidence-based design (EBD) means to base decision making about the environment on the best available research findings. 18 , 19 One room in a Swedish hospital ICU was transformed using this approach combined with an additional design goal of sustainability and a desire to create a home-like milieu. 20 At the same time, it was important that the design did not compromise safety, function, and followed national guidelines for an ICU patient room. 21 Interior colorings, textiles, and furniture were chosen according to the “green list” and to be in soft pastel colors. Sound absorbent materials were used on the walls, ceiling, and floor. A cyclic light system was installed that was digitally altered to strengthen the usual 24 hours circadian rhythm. Outside a patio was decorated with small garden furniture and greenery. This green area formed part of the patients’ view through the window but could also be accessed by the patient’s visitors. 2 , 18 The evaluation of the new ICU environment was informed by principles of complex intervention research and health geography 22 , 23 and underpinned by a caring science perspective. 24 – 26 This perspective is fundamental to nursing practice in Scandinavian countries and is characterized by a view of professional care as a commitment to prevent suffering and maintain the health, integrity, and life of others. 27 , 28 The research program used both qualitative and quantitative approaches. This included the use of non-participant unstructured observation which is the focus of this paper.
Designing the Qualitative Observation Study
In an earlier study in the research program, nurses described how they felt that they provided nursing care with a more caring attitude in the refurbished ICU room. 16 Thus, a subsequent study was designed to examine this reported change in caring attitude in more depth including observation. 1 The focus for the observations was to capture the meanings of caring and nursing activities performed in the refurbished room and in a traditionally designed room situated next door. All the observations were conducted by one researcher, who was an experienced critical care nurse but who had not worked in the research setting. The research study involved conducting 4 observations in the intervention room and 6 in the control (non-refurbished) room. 1 Observations were completed in the control room before moving onto the intervention room to gain a sense of usual activities and interactions as a baseline. The data gained from the observations were discussed and analyzed by the research group and the results later published. 1
A working shift, usually consisting of a critical care nurse (CCN) and an assistant nurse (AN), was the focus of each observation. The participants consisted of 7 CCNs, 1 CCN-student, and 7 Ans (15 participants in total). The sample varied in terms of gender, age (22–55 years), and ICU work experience (3 weeks–12 years) Across both rooms a total 47.5 hours of observations were documented by careful field-notes ( Box 1 ). The field-notes were written by hand during the observations and transcribed shortly after each observation. Both daytime and evening shifts were observed for between 4 and 6 hours a day. During the observations, the researcher sat quietly in a corner of the room that provided a full view of the actions of the nurses. However, there were times when she moved her position to obtain a better view of nursing activities or if additional space was needed by the staff. The field-notes recorded both descriptive and reflective notes 29 about the setting, the atmosphere in the room, the activities occurring, and the interactions among the various actors.
Examples of Field Notes From the Observations
The non-participant, unstructured observations were carried out within a naturalistic and interpretive paradigm, 3 , 30 meaning that data were gathered as a process where the everyday experience of people was captured in their natural settings. Following the completion of the observations, participants (nurses) were invited to take part in a qualitative research interview. 31 The observational and interview data were analyzed together using a hermeneutic-phenomenological method built on the writings of Paul Ricoeur and developed for nursing research. 32 , 33
The aim of this actual paper is to highlight and critically reflect on the ethical and methodological issues that arose during a study that observed nurses’ care-giving in an ICU setting. Details on the research methods are provided in another publication.
Negotiating Access to the ICU
The refurbishment of the ICU room itself had involved gaining the approval of the hospital managers, chief physician, and head nurse. Subsequently, it had been important to engage the ICU staff in the planned transformation of the room and in the research program itself. Since the start of the research program, researchers and doctoral students had visited the setting, and data collection for several studies had taken place at the ICU. This collaboration between the researchers and the unit had laid the foundation for future alliances. This involved the research team giving seminars about the research (including the use of observational methods) and experts in environmental design (eg, architecture, textile design, Feng Shui) giving presentations about the planned redesign of the room. These seminars were well attended and proved to be important in ensuring that the ICU nurses fully understood the reason for the researcher’s presence, particularly given they were sharing the same space for lengthy periods of time. In addition, the researcher was dependent on their assistance with the study as well as their commitment to working within a transformed ICU environment.
Despite this previous collaboration, each study and period of data collection required access to be negotiated—to the unit, to the staff, and to the data of interest. Once approval from the hospital had been received, the researcher met with the ICU ward manager to negotiate how the observations would be carried out in practice in both the redesigned room and the control room. This involved obtaining information about staff shift patterns and daily routines. A decision was made by the Ward managers, for the researcher to wear the same “scrubs” that were worn by the staff. This was seen as both enabling the researcher to blend in with the environment and comply with the hygiene regulations of the unit. The observer also gained access to the break room for the staff which enabled social contact between the observations and interviews. However, to ensure that it was clear that the researcher was not a staff member, she wore a university name badge. The researcher was given access to the ICU in the form of an entrance card and codes to the staff’s changing room, so that she could come and go as the rest of the nursing staff.
Procedures and Considerations in Relation to Ethics
In addition to approval from the organization, research ethics committee approval was required before the observations could commence. In Sweden, research ethics approval is governed by the guidelines of the Swedish Research Society (The Swedish Codex), the Helsinki Declaration adopted by the World Medical Association (WMA) in 2013, 34 and the All European Academies (ALLEA), that is, the European code of conduct for research integrity. Written and oral information was provided to staff about the study at its outset and then repeated during the unit’s regular staff meetings. This included information about the voluntary nature of participation, confidentiality, and their right to decline participation. However, the very specific focus of observations was not disclosed to participants prior to the observations, to attempt to prevent this knowledge influencing their actions and interactions. The presence of the researcher was also highlighted by the senior nurse during staff changeovers, and any nurses who did not wish to participate in the study were not allocated to the rooms where observations were being carried out. The study followed what Polit and Beck 35 conceptualize as process consent, meaning that informed content from the participating nurses was viewed as a process that was subject to ongoing negotiation.
For example, if any nurses found the observation to be too intrusive, they would be able to choose to work in a patient room that was not allocated to the study. Informed consent from the research participants was collected before conducting the interviews. At that time, the staff received information about the aim of the observations and the study and had the chance once again to decline or give their consent of participation. Research ethics committee approval (Reg.XXX) was received without any requirements for amendments to be made to the research plan. Later in the paper we will discuss the real-life ethical dilemmas that had to be negotiated during the study itself. According to Swedish legislation, patients are autonomous and therefore capable to make their own decisions regards consenting to participate in research. Although critically ill patients are considered vulnerable research participants and therefore require thorough ethical consideration. 35 The researchers were conscious of the vulnerabilities of ICU patients and the need for their rights and dignity to be protected. 36 , 37 Consequently, this fact was problematized in the ethical approval application form. A particular issue related to whether patients and their next of kin also should give informed consent, despite not being the research participants. Under Swedish research ethics regulations as the focus of the observations was on the ICU nurses’ activities, the consent of families or patients was not required. This interpretation may not be consistent with the research ethics regulations of other countries but complied with the regulation governing the study setting, in this case, Sweden. The Scandinavian countries have different ethical legislations and praxis compared to the US and UK concerning this. We strongly argue that it is crucial to be aware of and following the legislation in the country where observations are taking place. However, if observations were conducted when the patient was awake or if visitors were present, the researcher explained the reason for her presence to them and obtained consent. Furthermore, the researcher did not attend any handover reports where personal information about patients was shared. The research ethics application had highlighted that the observations would be carried out by a researcher who was an experienced ICU nurse who was sensitive both to patient vulnerability and family distress and thus aware of the need to withdraw from observation when appropriate. It was emphasized that the observations would not affect the care of patients or family members or the running of the ICU and that they would focus only on nursing activities. The staff had the mandate to stop the observer from entering the patient rooms if the situation was inappropriate for observation.
Navigating Methodological Issues
Do observations reveal a different perspective or “reality”.
An earlier study in the research program revealed that nurses described how working in the redesigned room made them feel more alert and promoted the quality of their caring. 16 We were interested in exploring these findings further using a naturalistic and interpretive approach to understand how the environment influences caring. 30 Unstructured observations are rarely used in nursing research, yet they provide a valuable means of gaining a holistic insight into interactions and illuminating the contextual influence of the physical environment. 4 However, at the same time, it is important to recognize that the reality perceived by the observer is conditional; it is multi-voiced and open to manipulation (whether deliberate or not) by the observed. 38 The analysis of the observational data from our previous study suggested that the nurses’ caring attitudes, that is, sensitivity to individual patient needs were not influenced by the ICU room in which they were working but were connected to the individual nurse themselves, that is, some displayed a more caring approach than others. 1 This conflicted with the interview data from another study 16 in which nurses related their caring to the environment. Mulhall 3 states that a primary reason to use observations for data collection is to investigate if participants’ accounts are consistent with their actions. She argues that an interviewee has more possibilities to govern the content in the conversation, whereas in observation sessions, the researcher is freer to choose what to observe. Data are always open for interpretation, and a possible interpretation of our findings could be related to the role of the observer and the observer’s preunderstanding and theoretical knowledge in the literature concerning the concepts and application of caring science into clinical practice. It could be that the observer might not interpret an action as being caring, but on the other hand the nurses might see it as a caring act. However, if returning to the analyses of data that were worked through using phenomenological-hermeneutics, 33 , 39 it can be argued that a text or scene is always open for several interpretations. The interpreter, however, must be able to move from a subjective to a distanced position and to present arguments for the most probable interpretation, that is, to consider if it is reasonable and likely. 4 To maintain rigor in unstructured non-participating observations, as in all qualitative analyses, means to comprise a careful collection and critical analysis of data and a transparent reporting of findings.
Being an Insider or an Outsider
In this study, the researcher observing the nursing activities was an insider, that is, someone who shared the characteristics and experiences of those being observed, 29 but had not worked in the actual unit. While there are disadvantages to this role in terms of overfamiliarity with the setting blinding a researcher to the actions and interactions occurring within it, in this study being an insider appeared to facilitate access to the ICU setting and provided a degree of theoretical sensitivity that was important during the observations and data analysis. 4 However, to guard against making assumptions or taking for granted what was being observed, the researcher made detailed descriptive field notes and kept a reflective diary ( Box 1 ). In addition, prior experience as an ICU nurse provided the researcher with the knowledge and confidence to change her role from a non-participant to participant observer if the situation and the safety of the patient required her to act.
The ICU nurses observed were aware that the researcher shared their professional identity. Indeed to “fit-in” and reduce her intrusion in the setting, it was decided by the Ward managers, that the researcher would wear the same uniform as the staff. Nevertheless, there are risks to presenting the same outward appearance as the observed. Despite the different name badge, patients, visitors, and other staff members may have mistaken the researcher for an ICU nurse which highlighted the importance of the researcher introducing herself to people entering the ICU room. Since the staff was aware of the researcher’s professional identity, it is possible that it may have impacted on their professional behavior while the observer was present. While it is unknown if the staff changed their behavior due to the presence of the researcher and their knowledge about the study focus, the follow-up interviews with the participating nurses 1 examined their perceptions of her influence on their actions and interactions. These interviews revealed that they forgot about the presence of the observer after a few minutes.
Moving From a Non-participant to a Participant Role
The researcher adopted a non-participant observer role. However, as noted earlier due to her insider role, there were incidents that led her to moving to a participant observer role. Incidents observed were responded to differently depending on the researcher’s assessment of the level of risk to the patient. In one situation, a life-threatening incident was observed by the researcher but not by the ICU nurse, in which a patient attempted to extubate themselves. Here, the researcher stepped in immediately to prevent this action. In another situation, the researcher observed that the ICU nurses had missed taking a vital blood pressure measurement for a patient. After giving the nurses reasonable time to recognize their omission, she raised the error with them directly. Being an insider meant that the researcher had a professional and moral duty to intervene. Although Angrosino 30 notes that all qualitative researchers using observational methods have obligations to prevent harm to their research participants, but in an ICU environment it may require specialized prior knowledge to identify and appropriately manage observed patient safety incidents.
Encountered ethical and methodological issues when conducting qualitative observational research has been discussed and reflected upon ( Table 1 .). Gaining access to a setting involves dedicating a period to building up confidence with managers and staff. The actual ICU had researchers and 3 doctoral students visiting the unit to collect data in the years preceding the observation study. This meant that confidence in the research team and an interest in the research program had been established. At the same time, this extensive intervention research program could have led to considerable research fatigue among the staff. However, the positive relationships developed between staff and researchers coupled with their interest in the programs of research avoided this situation.
Encountered ethical and methodological issues when conducting qualitative observational research.
The fact that the study had received approval from the ethics committee also facilitated access to the setting. However, of most importance was that the managers and staff were motivated to facilitate data collection as there was a strong desire to improve their work environment. Our experiences suggest that it is a prerequisite for observers to have insight and knowledge both about the type of care and the environment being studied when it comes to entering a clinical field like an ICU. Research has described this area as frightening and shocking for a person who is not familiar with intensive care. 1 , 40 We therefore consider that it was important that the observer was an experienced ICU nurse who could build positive relationships with staff and gain their trust, but with an outsider perspective. Since the aim of the study was to illuminate the meanings of caring and nursing activities performed in different designed ICU patient rooms, 1 it was crucial that the researcher had experience of intensive care and caring practices. We argue that researchers should study phenomenon within their own field of expertise. Moreover, it is the aim of the study that determines whether an insider or outsider perspective is suitable for an observational study. Although there is value in having neutral observers who see the “taken for granted”.
The fact that the observer was an experienced ICU nurse meant that she had a preunderstanding of the routines, traditions but not personal relationships of staff which helped them in seeing with an attentive and receptive gaze. 4 , 41 In addition, this meant that actions and interactions were observed and interpreted through a caring science lens which underpinned the study. This approach is founded on the writings made by Katie Eriksson 42 as well as theory of professional growth as a nurse described by Patricia Benner. 43 , 44 The study had a phenomenological-hermeneutical approach, where lived experiences were in focus. 32 This was used as a framework to assess the performed and given care. The insider–outsider perspective in observations and ethnographical studies has been debated. 45 We and other researchers argue that it is not a dichotomous approach 46 rather a movement between these approaches.
When a researcher, in this case, a trained ICU nurse, takes on a non-participant observer role in an ICU setting s/he may witness situations that risk patient safety. This becomes particularly salient in an ICU setting where patients are critically ill, and treatment is connected to fast decisions and technological equipment. This means that the researcher may need to be able to rapidly assess what is witnessed and know when to act. In an editorial, 47 the researchers discuss the phenomenon of “guilty knowledge” which means witnessing situations that might be reported to an authority. Here we argue that although it could be misinterpreted that the observer was a member of the staff, it was also a patient safety issue that the observer could and did interact when needed. Thus, observation is connected not only to seeing but also to having the knowledge and courage to decide when to act. Consequently, it is important for there to be ongoing discussions within research groups about ethical dilemmas that might arise during observation sessions and how to manage these. 4
We found conflicting results between a previous interview study 16 and the observations 1 in relation to the influence of the ICU environment on the caring actions of nurses which confirms the usefulness of unstructured non-participation observation. There is no standardized way to record field notes. 48 The observations in this study were guided by the themes; Time, People, and Context, as described in methodological texts concerning observations and ethnography. 49 , 50 It is important that the researcher takes a rigorous approach in making field notes that involves careful contemporaneous description of what is observed before moving to an interpretation process using both subjective and objective approaches. 4 , 32 , 44 Our field notes focused on the atmosphere and people present in the room, their actions, and interactions. Moreover, notes were made about the technical equipment, sounds, and lighting as these factors influenced the environment as well as the view from the windows into the outside green area. In the study, 1 the observation sessions were followed by an interview with the staff who had been observed. Here, the field notes were used as a tool to enable the sharing of the events in the observation session as well as deepening the conversation between the interviewees and researcher.
Conclusions
In this paper, we have presented our personal reflections about our experiences of conducting unstructured non-participation observations in an area that is often considered as closed to such research due to the vulnerability of critically ill patients. Our recommendations for conducting observation work are grounded in our experiences in hospital high-tech environments, but we also consider them transferable to other contexts.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the participants for their willingness to share their everyday caring practice.
Author Contribution: The authors made a substantial contribution to the design of the paper, and we have all taken part in drafting and reflecting on the content and consequently take public responsibility for the content.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: There is no conflict of interest or funding in relation to the work with this manuscript.
Funding: The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Fredrika Sundberg https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7400-6574

COMMENTS
Observation in qualitative research "is one of the oldest and most fundamental research methods approaches. This approach involves collecting data using one's senses, especially looking and listening in a systematic and meaningful way" (McKechnie, 2008, p. 573).Similarly, Adler and Adler (1994) characterized observations as the "fundamental base of all research methods" in the social ...
The methods of qualitative data collection most commonly used in health research are document study, observations, semi-structured interviews and focus groups [1, 14, 16, 17]. Document study These can include personal and non-personal documents such as archives, annual reports, guidelines, policy documents, diaries or letters.
Observation. Observation is a type of qualitative research method which not only included participant's observation, but also covered ethnography and research work in the field. In the observational research design, multiple study sites are involved. Observational data can be integrated as auxiliary or confirmatory research.
Broadly, research designs are classified into qualitative and quantitative research and mixed methods . The quantitative study design is subdivided into descriptive versus analytical study designs or as observational versus interventional (Figure (Figure1). 1). Descriptive designs occupy the middle and lower parts of the hierarchy of evidence ...
An observational study is used to answer a research question based purely on what the researcher observes. There is no interference or manipulation of the research subjects, and no control and treatment groups. These studies are often qualitative in nature and can be used for both exploratory and explanatory research purposes.
Introduction. Although there are many possible forms of data collection in the qualitative researcher's toolkit, the two predominant forms are interviewing and observing. This chapter and the following chapter explore observational data collection. While most observers also include interviewing, many interviewers do not also include observation.
Qualitative observation is a type of observational study, often used in conjunction with other types of research through triangulation. It is often used in fields like social sciences, education, healthcare, marketing, and design. This type of study is especially well suited for gaining rich and detailed insights into complex and/or subjective ...
Qualitative research methods. Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods.These are some of the most common qualitative methods: Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes. Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations. Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among ...
There are three main categories: Participant observation. Researcher becomes a participant in the culture or context being observed. Direct Observation. Researcher strives to be as unobtrusive as possible so as not to bias the observations; must remain detached. Technology can be useful (i.e. video, audio recording). Indirect Observation.
Naturalistic Observation | Definition, Guide, & Examples. Published on February 10, 2022 by Pritha Bhandari.Revised on June 22, 2023. Naturalistic observation is a qualitative research method where you record the behaviors of your research subjects in real world settings. You avoid interfering with or influencing any variables in a naturalistic observation.
The term "observational methods" seems to be a source of some confusion in medical research circles. Qualitative observational studies are very different from the category of observational studies (non-experimental research designs) used in epidemiology, nor are they like the clinical observation of a patient.
A way to gather data by watching people, events, or noting physical characteristics in their natural setting. Observations can be overt (subjects know they are being observed) or covert (do not know they are being watched). Participant Observation. Researcher becomes a participant in the culture or context being observed.
Health research study designs benefit from observations of behaviors and contexts. •. Direct observation methods have a long history in the social sciences. •. Social science approaches should be adapted for health researchers' unique needs. •. Health research observations should be feasible, well-defined and piloted.
2.1 Introduction. Observation is one of the most important research methods in social sci-. ences and at the same time one of the most diverse. e term includes. several types, techniques, and ...
Observation is one way for researchers to seek to understand and interpret situations based on the social and cultural meanings of those involved. In the field of education, observation can be a meaningful tool for understanding the experiences of teachers, students, caregivers, and administrators. Rigorous qualitative research is long-term ...
The term observational research is used to refer to several different types of non-experimental studies in which behavior is systematically observed and recorded. The goal of observational research is to describe a variable or set of variables. More generally, the goal is to obtain a snapshot of specific characteristics of an individual, group ...
This paper explores the validity of qualitative observational research methods, specifically participant observation. Through an exploration of the relevant literature and a critical review of a ...
Participant observation is a type of observational study. Like most observational studies, these are primarily qualitative in nature, used to conduct both explanatory research and exploratory research. Participant observation is also often used in conjunction with other types of research, like interviews and surveys.
Peshkin's in-depth research represents a qualitative study that uses observations and unstructured interviews, without any assumptions or hypotheses. He utilizes descriptive or non-quantifiable data on Bethany Baptist Academy specifically, without attempting to generalize the findings to other Christian schools. 4. Understanding buyers' trends
While formative research may employ many qualitative methods, focus group discussions and in-depth interviews are the most common. ... The observation study is based on a small purposive sample, the survey on a population-based representative sample; the data were collected in different years and at different times of year. But the wide gap ...
The purpose of this single instrumental case study was to understand how a virtual coaching program provides opportunities for self-directed learning during the implementation of evidence-based practices for adults at Navigator Coaching. The theory guiding this study was Deci and Ryan's self-determination theory as conceptualizations of self-directed learning described in the literature ...
In qualitative research, trustworthiness is determined by credibility, dependability, conformability and transferability. Establishing credibility involved the primary researcher spending a considerable amount of time at the study site to get a feel for the environment, receiving ongoing feedback from peers during peer debriefing, and applying ...
Qualitative synthesis and quantitative meta-analysis identified D-dimer, location of insertion, type of catheter, number of lumens, catheter indwelling time, and central line-associated ...
Building component reuse (BCR) is a critical means to reach sustainability goals in the construction industry through decreasing resource consumption, waste generation, and associated emissions. However, little is known about how BCR in circular construction can create economic value and opportunities for value creation and capture. Therefore, a qualitative multiple case study was conducted of ...
In an earlier study in the research program, nurses described how they felt that they provided nursing care with a more caring attitude in the refurbished ICU room. 16 Thus, a subsequent study was designed to examine this reported change in caring attitude in more depth including observation. 1 The focus for the observations was to capture the ...