- Subject guides
- Announcements
Subject guide

International Studies: how to write your thesis
This Subject Guide is designed to support students of International Studies with writing their BA thesis and research papers. This guide focuses on the research process, and suggests effective ways to: 1. find a topic and formulate a good research question; 2. search, find and evaluate literature; 3. search, find and organize primary sources; and 4. organize the research and writing process.
A. Getting Started & Staying Organized
Writing a thesis, or a larger research paper, can often be a challenge. It requires not only research skills, but also organizational skills to break down the process in smaller steps and make a realistic planning.
Sage Research Methods is a tool that helps you develop your research from the first to the last step .
B. Finding a good Topic
Leiden University’s library offers a number of tools to help you find a good research topic: Start your thesis .
Portland State University’s library, too, offers a good tool to help you get started: the DIY Library , and Ohio State University offers a handbook .
Three short videos that can help you get started are: Picking a topic IS research (by NC State); Choosing a Research Paper Topic (by University of Minnesota Libraries); How to Develop a Good Research Topic (by Kansas State Libraries).
C. Formulating a Research Question
The instruction page ‘ How to write a research question ’ of George Mason University’s Writing Center can form a good starting point, as well as this handbook .
You can also watch these short videos to help you get started: Developing a Research Question (by Steely Library); and Research Questions tutorial (by George Washington University Library).
D. Finding & Evaluating literature
Leiden University’s library offers help with finding and evaluating literature for your thesis or research paper.
You can find tutorials on searching for literature ; as well as tutorials on evaluating sources , or use this handbook .
You can also ask for help by asking questions directly to library staff; or by a meeting with a subject librarian .
Two helpful short videos on finding literature include: One perfect source? (by NC State); and Tips & Tricks: Phrase Searching (by NC State).
E. Finding Primary Sources
The library provides access to a large number of digital resources, databases and archives . The Subject Guide for International Studies provides an overview of the various resources.
Four examples of digital primary sources are digital & digitised newspapers ; the Global Encyclopedia of Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, and Queer (LGBTQ) History ; the Economist Intelligence Unit , which provides economic profiles and country reports; and the The Digital National Security Archive , which contains declassified CIA and US government documents.
You can gain an overview of the databases and e-resources offered through the library via this link .
F. Planning your Research Project
Students often struggle with making a realistic time-plan and then sticking with it. The following tools can help:
The Open University’s interactive website Time Management Skills portal helps you to develop your time management skills. See the following links for topics such as: - setting goals , - how to prepare a schedule and -tips for time management .
G. Help & Support
For questions about finding the right literature, you can approach the library, by asking questions directly to library staff; or by requesting a one-on-one meeting with a subject librarian .
For help with writing your thesis or research paper, you can also contact the International Studies Writing Lab .
For help with developing your Study skills & managing your studies (for example help with managing your time or coping with study stress), you can approach the Student Support Services for various workshops and courses .
If you are coping with more serious study-related or mental issues, you contact the study advisers or the university’s student psychologist , or visit the university’s website on well being .
Find a topic, formulate a research question, make a realistic time-plan
As a student you will have to do research assignments, write papers and hand in your final thesis before graduation. In order to succeed in this, you need to choose a good topic, formulate a researchable question, and make a realistic planning.
An effective tool for designing your research process in an effective way, is the SAGE Research Methods website . This website is user-friendly and helps you to break down your research process into smaller blocks. It also provides help with planning your research project.
Tips on how to choose a topic
- Get inspired: Take inspiration from your required readings for a course you like, browse the books in the Wijnhaven Library reading room , explore topics in peer-reviewed international studies journals , or have a look at other theses by former students . Ask yourself: which question has not yet been answered? What information seems to be missing? What can you add to the discussion?
- Brainstorm: Write down possible topic that comes to mind. These tutorials can help you with your brainstorm.
- P ick something you like : If you have little influence over your thesis topic, try and steer your assigned topic in the direction you would like to take it to. This can be a specific discipline (sociology, anthropology, politics, linguistics) era (historical approach) or method (surveys, data sets, newspapers, personal stories etc).
- Make sure you can make it into an academic treatise: A good number of students choose a thesis topic that aligns with their private interests. However, it can be a challenge to turn such topics into an academic treatise, because you may not have enough (1) relevant (2) academic and (3) accessible sources about the topic to base your argument on. Make sure that you choose a topic that you are passionate about, but that also has received scholarly interest, on which there is literature available, as well as other sources. If you start searching for sources in an early stage you can quickly determine whether your topic is in fact viable as a thesis topic or not.
- Mind the size of your topic: it is important to narrow down your topic to a manageable size. Too few sources means you may want to expand your topic a bit. On the other hand, having too many sources on your topic means you need to narrow your topic down further. This is one of the reasons why starting to search for sources early is an important step in pinpointing a research topic that is just the right size for you.
- Use the Sage Project Planner or other tutorials for defining a topic
Tips on how to formulate a good question
- Avoid questions that can be answered with ‘yes’ or ‘no’
- Have a voice: Ideally you already have a hypothesis, idea or point of view through which you can enter this topic. Often times you will adjust your view on the topic the more you learn about it.
- Formulate a ‘problem’ that you need to answer: Think about the big questions, such as ‘why’, ‘how’, ‘when’, and ‘who’. This will give you an open-ended question through which you can explore your topic.
- Avoid ‘Compare A to B and see what happens’ scenarios: There needs to be a formulation of a ‘problem’ and a point of view.
- Use these tutorials or the Sage project planner to develop a researchable question
Tips on how to meet your deadline
- Start with a general overview of the amount of time you have: When is your deadline? When can (and when should) you get started? How many hours can you realistically spend per week on this project?
- Write down the steps you need to take from start to end: Go through this research guide to get an idea of how much time you need for your research. Don’t forget about things that might not be included here, such as spell checks, format checks, printing and binding etc.
- You can use the Sage project planner to make a planning .
- Be realistic: A realistic planning will help you to set goals and avoid stress by impeding deadlines. Underestimating the amount of work needed to write a well-researched, well-written paper is the number one reason students experience a lot of overwhelm from the research process. Therefore, be realistic about the amount of work you can put in in a day.
- Write down your daily top 3: Write down three achievable things you want to have finished by the time you are done for the day and start with the most important thing.
- Don’t forget to take a break: It is important to put away what you wrote for a bit so you can revisit it later. Oftentimes, when you go back to your text at a later point, you see little inconsistencies that you overlooked earlier; or you have new insights to add to your argument.
- Time Management Skills: Planning your research is about much more than just prioritizing and setting goals. It is also about how you deal with distractions, procrastination, and what to do if you fall behind. Time management skills are essential skills not only for now, but also for when you find employment. Read more about Time Management Skills : - setting goals , - how to prepare a schedule and -tips for time management .
Recommended Books
- Yvonne N. Bui - How to Write a Master’s Thesis
- Umberto Eco - Hoe schrijf ik een scriptie
- Umberto Eco - How to write a thesis (e-book)
- Nel Verhoeven – Doing Research: the hows and whys of applied research
- Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research
A. Finding literature is not like a trip to the supermarket
Some students approach the act of gathering information for their research as if they were taking a trip to the supermarket; they expect to be able to find exactly what they need within a certain set amount of time. Unlike a supermarket trip, however, searching for scholarly information is difficult, and you do not always get the results you want. This is mostly due to the fact that it is easy to (1) overestimate the quality and availability of the sources you need, and (2) underestimate the amount of time and skill needed to find these sources amidst the millions of sources out there.
In other words, some students expect to find ‘perfect sources’ for their thesis topic – meaning; academic sources that ‘tick all the right boxes’ of their thesis topic – fully downloadable, and found with little effort with just a few keywords and clicks. In reality, however, the ‘perfect source’ likely does not exist, many sources you need will not be available digitally, it will take quite some time and effort to find these sources, and you will have to pick up some new search skills along the way. This often causes students to experience the ‘search’ and ‘access’ phase as the most frustrating, unsatisfactory experience in the whole research experience.
Frustration, coupled with a lack of time, makes it tempting for students to turn to less trustworthy or relevant sources because they are more familiar (Google), or more easily available (full-text search only). This, however, leads to an unbalanced and incomplete list of sources. It is therefore important to think about how you search; are your expectations realistic? What are your pitfalls when pressed for time or when something does not work out immediately? How can you avoid them?
The good news is that you don’t need to find a ‘perfect source’, and this brief video shows you why : ‘Good research isn’t about finding the perfect article that makes all the connections for you, it’s about finding information that helps you form your ideas, and tying it together yourself to form a cohesive argument.’
If the perfect source already existed, there would not be a reason for you to write your thesis or paper. As a researcher, your assignment is to get to know the literature on a topic, identify what is missing, and add to the existing knowledge with our own writing. Sage Research Methods helps you to approach your research project in exactly this way.
Second, there are many ways the library can help you get access to difficult-to-obtain sources and teach you how to search. Third, if you make a project plan early and manage your time, you should have enough time to search for the sources you need, thus avoiding a lot of stress and frustration.
B. First Step: Background Search
The best way to start your search is getting yourself more acquainted with the topic; you know some things about it, but there is a lot that you do not (yet) know. Background search can help you to identify important facts (dates, events, people, terminology) refine your topic (what aspect about this topic is it that truly interests you?), and give you additional information and tips on where to search (dictionaries, encyclopedias, databases). For your background search you can use Google, Wikipedia, your textbooks, bibliographies and encyclopedias .
At this stage of your research, important tools to start with are Google Scholar , which allows you to search and browse journal articles as well as the bibliographies that you can find in this Subject Guide for International Studies . The bibliographies are curated by a specialized staff and are more complete and systematic.
When doing background research you can start with a couple of keywords. You can use keywords from titles or abstracts. Specific keywords can narrow or broaden the amount of information you will find. Try out different (combinations of) keywords/synonyms to see what kind of information you get and which terms are useful. Learn more in these tutorials about keywords.
You can also use the so-called snowball-method to find literature on your topic: simply browse the bibliography at the end of a book or article that you found convincing to see if it contains other titles related to your topic.
C. Searching in the Library Catalogue
Try out different search terms when you start searching in the catalogue. The catalogue automatically searches for all of the entered search terms in one document unless you use OR. You can use NOT if you want specific words to be excluded. If you don’t know how to spell a word or it can be written in different ways, you can use the symbol # or ? (wom#n finds woman and women). When you have found a relevant item, you can also use the references or citations as new sources. It is not recommended to limit yourself to things only available in Leiden University by selecting ‘Leiden Collections’ instead of ‘All content’ in the search screen. See our catalogue tutorial .
D. Find Literature Elsewhere
Though Leiden University provides access to an extensive collection of literature related to International Studies, many more can be found elsewhere.
Recommended Library Catalogues
- Worldcat : is the biggest world-wide search engine for library holdings. You can use it to search information about books, but also to locate the nearest library (inside or outside the library) that holds a copy. If any book or journal you found is unavailable in Leiden, you can either visit the holding library (which is often free for Dutch University Students) or request the item through (International) Inter Library Loan .
Recommended Online Search Engines
- Google Scholar is Google’s search engine for scientific articles and academic books. It is recommended not to limit your search activities to Google, but it does offer a good starting point.
Recommended Bibliographies
- A great number of specialized, academically curated bibliographies on many topics and fields can be found through the Subject Guide for International Studies .
A. Digital and Paper Sources
Tips for accessing digital sources.
- If you have found a digital source in the catalogue that you wish to access from home you need to login via the library catalogue, using your ULCN credentials, and not via a publisher portal. You can also use the Get Access browser extension .
- If you come across a source in the catalogue that is listed as “Online Access” or “Open Access” but you cannot get access, click the ‘report a problem’ option within the record.
Tips for accessing Paper sources
- You need a valid LU card for access in most buildings.
- Leiden University Libraries consists of several library locations. Depending on your research topic, you may need to access physical books from these different locations.
B. Not available in Leiden?
There are a number of ways in which you can get access to materials that are not available at Leiden University Libraries.
How to get access to materials not available in Leiden
- Look up the book or journal in Worldcat . If you enter your zip code, you can find the library nearest to you that has a copy, such as the Royal Library in the Hague or other University Libraries.
- The Royal Library in the Hague offers a 50% discount for students for a one-year membership. Leiden University Students can apply for a library card free of charge at all Dutch Universities.
- Request the item through Inter Library Loan (ILL ) or through International ILL .
- Ask Leiden University to acquire the item : You can file a request for the library to purchase a book, access to a journal or database. All requests are considered by the relevant subject librarian, and a decision is made depending on collection policy, available budget and price of the item. Please keep in mind that, in case an item is purchased, it can take several weeks for the item to be shipped and processed.
- Contact your subject librarian . If the above measures did not help, reach out to your subject librarian. It is possible that they know different means and methods within their field of expertise to obtain access to the materials you need.
A. Why do I need to evaluate scholarly publications – wasn´t that evaluated already?
Students are required to be critical of all their sources, including the ones you find in the library catalogue, academic databases, and those quoted in other scholarly publications. In today’s world, publishing and sharing information has become accessible to all, which also has made it easier to publish misinformation.
Academic information, at least, has put up a number of hurdles to tackle misinformation and disinformation from spreading, such as peer review . However, aside from the fact that these measures are far from failsafe , journals, books and authors can certainly be biased or prejudiced while working within the academic framework. It is your job as a scholar to be critical of all sources you use – academic or not – and train yourself in recognizing credible sources and using them in a critical fashion.
B. Popular & Scholarly
At the beginning of your student career at Leiden University, you may sometimes miss the difference between scholarly information and popular sources, and why this difference is important.
Media like YouTube videos, blog posts, or magazine articles can be tempting to use in a paper, because they (1) mainly focus on being entertaining instead of being informative, (2) use clear and easy to understand language, and (3) due to algorithms, are likely to confirm your pre-existing worldview and ideas. The goal of a research project, however, is to approach a certain problem in an open way, and embark on a research as an open-ended process. For such a project, usage of scholarly publications is crucial.
One of the main differences between popular sources and scholarly sources is the scientific rigor that lies at the basis of an analysis and argument, and transparent presentation of the used methods and sources. These are part of the scholarly format of peer-reviewed and annotated texts. Illustrative of the importance of this format is the fact that an op-ed written by a professor is categorized as a popular source, while an article in a scientific journal by the same professor is categorized as a scholarly text.
It is especially tricky when opinions of the author are presented as ‘facts’ that seem correct due to being based on cherry-picked data. If you are not yet confident in discerning between scholarly and popular sources, we recommend you follow a couple of tutorials .
C. Evaluating information
It is important you ask yourself a number of questions while reading a source, such as: Who wrote the information, why did they publish it, is there an agenda and when/where was it published? All of this comes before you can think about the text itself. This follows a technique used by professional factcheckers, called lateral reading , where you first consider the container of the text, before you look at the text itself.
The above is useful for information found both in print and online. For information found solely online there is an additional method, called the SIFT method . SIFT stands for Stop, Investigate the Source, Find trusted coverage, Trace claims, quotes, and media back to the original context. In many cases it will take about 30 seconds to quickly check whether for example a news report is true once you have trained yourself in the four moves of SIFT.
Take a look at these tutorials about evaluating information.
A. Reading and searching: two sides of the same coin
The most conventional method of discovering relevant authors and publications for your research is discovering them citations and references of other publications. We therefore recommend to make enough time to read your sources, and then do follow-up searches. When reading ask yourself: which authors are talking about my topic, what do they say, what books/articles did they write, which sources do they cite and how was the research conducted?
You may think that reading all the sources you find in order to do follow up search will take too long. However, in this part of the research process, you are only reading your sources to (1) confirm that they match your information need, (2) double-check that they are academic (3) not too old for your topic of choice, and (4) find references to other scholars and publication about your topic.
Tips on strategic reading
- Scan : Quickly go through a text by reading just the titles of chapters, abstracts of papers, paragraph titles, or the first sentence of a new paragraph, and the conclusion. This will help you determine whether or not you want to read the source more in detail, and which parts you can easily skip.
- Reading and Note making: You will have to read, process and remember information from a lot of different sources. To stay organized, it is important to make efficient notes while reading. Look here for a top five of critical reading techniques and a brief course on critical reading .
- Don’t forget to write down where your information comes from ! If you are not sure where the information comes from when you start writing, you are at risk of plagiarism. Tip: The quickest way to make a short note when you are reading is taking the last name of the author + page. For example: Hall, p. 31. If you use multiple sources by the same author, add the publication year. (Hall, 2005, p. 31)
- For more information see the Critical Reading Techniques .
Rinse and Repeat
At this stage, you have found a good number of sources, read them, took notes, and likely found other publications authors and data that you have not found before. This marks the second round of searching for sources – look up that interesting looking book you found in a citation, find out what else the author of that book wrote, see if you can get it through Leiden University or other means, and... read! By repeating this cycle of read-search-access-read two or three times, you are very likely to find (1) the majority of relevant publications on your topic of choice, (2) the majority of authors writing about your topic of choice, and (3) a good overview of primary sources relating to your topic of choice. Only once you have followed this thorough and deliberate way of locating your sources are you ready to move forward.
B. Refine your topic
This is a good point in your research to revisit your topic and your research question. While reading you may have found that there is much more information available about your topic than you initially thought – or not enough. You may have found that your research question has already been dealt with in length by other scholars, while at the same time, another question that is even more interesting may have come to mind. Perhaps you would like to take your research into a whole different direction after doing some reading and follow up research? When you are refining your topic, allow yourself to be flexible. It is common to modify your topic during the research process.
Take some time to visit the checklist for your topic and research question again, and see if you need to make any chances. If you have already handed in your topic and research question to your supervisor, you should always inform them of any major changes you wish to make. Have a look at this overview of tips for refining your research topic .
In some cases, using primary sources for your research is optional, in other cases it is an obligatory part of your research. Students can use a variety of primary sources for their projects, depending on their topics. Different sources may require different research methodologies.
Central to all primary research projects is, however, that you systematically analyze a well-delineated corpus of sources. The delineation refers both to the source and the time-frame. For example, instead of analyzing how ‘the media’ reported on a topic, choose a specific media outlet (for example one newspaper) or set of media outlets (a well-delineated set of newspaper titles), and research the news reports over a specific time-frame (for example: how did the New York Times report on North Korea’s nuclear weapons program between 2010 and 2020). A similar systematic can be used when analyzing statistical data, CIA reports, the correspondence between Marx and Engels, etc.
Sage Research Methods provides a good overview of the most important primary source research methods , as well as examples and cases.
The library provides access to a large number of digital resources, databases and archives . The Subject Guide for International Studies provides an overview of the various resources.
A. Managing your research project
Once you have found, evaluated, and read all of your literature (for now) it is time to think about what you have read and to organize your findings. This can be a challenging phase in the research project. If you feel overwhelmed by the work you have to do, various actions may help: 1.) break down the project into smaller steps; 2.) make a time plan that enables you to find a good balance between reading, researching, writing, and free time; 3.) break down your thesis or paper into smaller blocks that you can separately work on.
Tools that can help you to break down your project into smaller parts and to manage time-planning are: the Sage project planner ; and the Open University’s Time Management Skills portal. See the following links for topics such as: setting goals , how to prepare a schedule> tips for time management .
For help with developing your study skills & managing your studies (for example help with managing your time or coping with study stress), you can approach the Student Support Services for various workshops and courses .
B. Synthesizing; Interrogating the literature
Your thesis or research paper needs to clearly relate to the existing literature on a topic: you need to show who you (dis)agree with and what you are adding to the existing body of knowledge. This means that you need to identify at least the following three points (1) common themes between sources, (2) points on which the sources/authors (direct or indirect) disagree and (3) gaps in the literature (what is missing?).
This does not mean that you should just give a number of summaries of articles. Instead, it is important to compare and contrast, broaden the argument and give your own thoughts and conclusions. For a more detailed explanation on synthesizing and integrating information, use one of the following sources:
- “Help…I’ve been asked to synthesize!”
- Simply Psychology – how to synthesize written information from multiple sources.
C. Footnotes, Citations and Citation Managers
For your thesis or research paper you are potentially going to refer to a large body of sources. Typing up all the footnotes by hand, and maintaining one consistent reference style is time-consuming. Therefore, it is highly recommended to use an electronic citation manager. Learning how to work with a reference manager is a new skill, but it will save you time in the long run – the more papers you write, the more time you save.
Mendeley, EndNote and Zotero are three of the main refence managers. You can learn more about these programmes on our page about reference managers.
- There are brief introductory videos on Mendeley , Endnote , and Zotero .
There are various citation methods. International Studies theses and papers are to use CMS as their citation style. The most important thing about using a citation style is consistency . Do not mix up the different styles and rules! If you are uncertain which style you should use for your paper or thesis, always consult with your supervisor. See these tutorials and books below that can help you get started with making your own citations below.
Recommended Books:
- Cite Right : a quick guide to citation styles.
- Doing honest work in college: how to prepare citations, avoid plagiarism and achieve real academic success : deals with today’s issues, like citing podcasts or social media posts, using mobile devices during tests, and the pro-s and cos of reference managers.
- Cite them right : the essential referencing guide.
D. Writing the Report
For the actual writing of your thesis or research paper, structure is important in a double sense of the word. First of all, it is important to structure your thesis into smaller parts that you can write in subsequent order. Secondly, it is important to structure your working day and working week in such a way that you can find a productive balance between working on your thesis and doing other things.
Next to the Sage project planner , the website of the Australian National University can help you to design an effective structure for your thesis.
For structuring your working day and working week, you can take cue from the Open University’s Time Management Skills portal. See the following links for topics such as: setting goals , how to prepare a schedule and tips for time management .
Another helpful website is the Thesis Whisperer , which among other offers advice on How to become a literature searching Ninja , and on How to write 1000 words a day (and not go bat shit crazy) .
Library For questions about finding the right literature, you can approach the library, by asking questions directly to library staff; or by requesting a one-on-one meeting with a subject librarian . If you would like to suggest purchase requests, contact the subject librarian for International Studies, Nathaniël Linssen .
Writing Lab For help with writing your thesis or research paper, you can also contact the International Studies Writing Lab .
Workshops on Managing Time and Coping with Study Stress For help with developing your Study skills & managing your studies (for example help with managing your time or coping with study stress), you can approach the Student Support Services for various workshops and courses.
Study-related and Mental Support If you are coping with more serious study-related or mental issues, you contact the study advisers or the university’s student psychologist , or visit the university’s website .
Programs submenu
Regions submenu, topics submenu, the red zone: charting paths to resilience in the climate-conflict nexus, the murky world of deepfakes, the red zone: the crossfire between conflict and climate change, the red zone: adaptation in action: the drc’s solutions for climate resilience.
- Abshire-Inamori Leadership Academy
- Aerospace Security Project
- Africa Program
- Americas Program
- Arleigh A. Burke Chair in Strategy
- Asia Maritime Transparency Initiative
- Asia Program
- Australia Chair
- Brzezinski Chair in Global Security and Geostrategy
- Brzezinski Institute on Geostrategy
- Chair in U.S.-India Policy Studies
- China Power Project
- Chinese Business and Economics
- Defending Democratic Institutions
- Defense-Industrial Initiatives Group
- Defense 360
- Defense Budget Analysis
- Diversity and Leadership in International Affairs Project
- Economics Program
- Emeritus Chair in Strategy
- Energy Security and Climate Change Program
- Europe, Russia, and Eurasia Program
- Freeman Chair in China Studies
- Futures Lab
- Geoeconomic Council of Advisers
- Global Food and Water Security Program
- Global Health Policy Center
- Hess Center for New Frontiers
- Human Rights Initiative
- Humanitarian Agenda
- Intelligence, National Security, and Technology Program
- International Security Program
- Japan Chair
- Kissinger Chair
- Korea Chair
- Langone Chair in American Leadership
- Middle East Program
- Missile Defense Project
- Project on Critical Minerals Security
- Project on Fragility and Mobility
- Project on Nuclear Issues
- Project on Prosperity and Development
- Project on Trade and Technology
- Renewing American Innovation Project
- Scholl Chair in International Business
- Smart Women, Smart Power
- Southeast Asia Program
- Stephenson Ocean Security Project
- Strategic Technologies Program
- Transnational Threats Project
- Wadhwani Center for AI and Advanced Technologies
- All Regions
- Australia, New Zealand & Pacific
- Middle East
- Russia and Eurasia
American Innovation
Civic education, climate change, cybersecurity, defense budget and acquisition, defense and security, energy and sustainability, food security, gender and international security, geopolitics, global health, human rights, humanitarian assistance, intelligence, international development, maritime issues and oceans, missile defense, nuclear issues, transnational threats, water security.
The Center for Strategic & International Studies (CSIS) examines research topics surrounding global studies, international relations, & foreign policy issues.


Our Journals

Latest News
Virtual Events
Stats & Scope
Conferences
Annual Convention Special Programming
Upcoming Conferences
Past Meetings
The International Studies Association
Representing 100 countries, ISA has over 6,500 members worldwide and is the most respected and widely known scholarly association in this field. Endeavoring to create communities of scholars dedicated to international studies, ISA is divided into 7 geographic subdivisions of ISA (Regions), 29 thematic groups (Sections) and 4 Caucuses which provide opportunities to exchange ideas and research with local colleagues and within specific subject areas.
Looking for Something?
Development, publication, how can we help.
- Email Address
- Message (please limit your message to less than 500 words)
Regions, Sections, Caucuses, Committees

ISA is made up of geographic and thematic sub-units (regions and sections), advocacy groups (caucuses), and standing committees to better faciliate interactions and represent the diversity of our membership.
Search ... Academic Freedom Committee (AFC) Active Learning in International Affairs Section (ALIAS) Annual Convention Program Chairs Committee on the James N. Rosenau Post-Doctoral Fellowship Committee on the Status of Engagement with the Global South Committee on the Status of Representation and Diversity Committee on the Status of Women (CSW) Diplomatic Studies Section (DPLST) English School Section (ENGSS) Environmental Studies Section (ESS) Ethnicity, Nationalism, & Migration Studies (ENMISA) Executive Director Evaluation Committee Feminist Theory and Gender Studies Section (FTGS) Finance Committee Foreign Policy Analysis Section (FPA) Global Development Studies Section (GDS) Global Health Studies Section (GHS) Global International Relations Section (GIRS) Global South Caucus (GSCIS) Historical International Relations Section (HIST) Human Rights Section (HR) Intelligence Studies Section (ISS) Interdisciplinary Studies Section (IDSS) International Communication Section (ICOMM) International Education Section (IEDUC) International Ethics Section (IETHICS) International Law Section (ILAW) International Organization Section (IO) International Political Economy Section (IPE) International Political Sociology Section (IPS) International Security Studies Section (ISSS) ISA Asia-Pacific (AP) ISA Canada ISA Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) ISA Midwest ISA Northeast (NE) ISA South ISA West Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, Queer, & Allies Caucus (LGBTQA) Long Range Planning Committee (LRP) Nominating Committee Online Media Caucus (OMC) Peace Studies Section (PEACE) Pedagogy Conference Planning Committee Political Demography and Geography Section (PDG) Post-Communist Systems in International Relations Section (POSTCOMM) Professional Development Committee (PDC) Professional Rights and Responsibilities Committee Publications Committee (Pubs) Religion and International Relations Section (REL) Research Workshop Grants Committee (RWG) Science, Technology and Art in International Relations (STAIR) Scientific Study of International Processes Section (SSIP) South Asia in World Politics (SAWP) Theory Section (THEORY) United Nations - NGO Representative (UN-NGO) Women's Caucus (WCIS)
HOW CAN YOU MAKE A DIFFERENCE?
Site search.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
International Studies
- Most Cited Papers
- Most Downloaded Papers
- Newest Papers
- Save to Library
- Last »
- International Security Follow Following
- International Relations Theory Follow Following
- International Relations Follow Following
- Political Science Follow Following
- Security Studies Follow Following
- Foreign Policy Analysis Follow Following
- Peace and Conflict Studies Follow Following
- Post-Soviet Studies Follow Following
- Russian Foreign Policy Follow Following
- Critical Security Studies Follow Following
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- Academia.edu Publishing
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Search Menu
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- About International Studies Review
- About the International Studies Association
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
High-Impact Articles
International Studies Review provides a window on current trends and research in international studies worldwide. To highlight the impact of the journal, we have organized a collection of some of the most read, most cited, and most discussed articles from recent years. The articles are freely available through December 31, 2021.
Interested in submitting your research to International Studies Review ? Read our author guidelines.
Highly Cited Articles
Things we lost in the fire: how different types of contestation affect the robustness of international norms, forum: complex systems and international governance, the impact of environmental cooperation on peacemaking: definitions, mechanisms, and empirical evidence, most read articles, forum: power and rules in the profession of international studies, embrace ir anxieties (or, morgenthau's approach to power, and the challenge of combining the three domains of ir theorizing), asymmetry, hierarchy, and the ecclesiastes trap, most discussed articles.
Who Publishes Where? Exploring the Geographic Diversity of Global IR Journals
What isn't a norm redefining the conceptual boundaries of “norms” in the human rights literature, the international trade regime and the quest for free digital trade.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1468-2486
- Print ISSN 1521-9488
- Copyright © 2024 International Studies Association
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
What Research Has Been Conducted on Procrastination? Evidence From a Systematical Bibliometric Analysis
Associated data.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/ Supplementary Material , further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Procrastination is generally perceived as a common behavioral tendency, and there are a growing number of literatures to discuss this complex phenomenon. To elucidate the overall perspective and keep abreast of emerging trends in procrastination research, this article presents a bibliometric analysis that investigates the panorama of overviews and intellectual structures of related research on procrastination. Using the Web of Science Database, we collected 1,635 articles published between 1990 and 2020 with a topic search on “procrastination” and created diverse research maps using CiteSpace and VOS viewer. Bibliometric analysis in our research consists of category distribution, keyword co-occurrence networks, main cluster analysis, betweenness centrality analysis, burst detection analysis, and structure variation analysis. We find that most research has focused on students' samples and has discussed the definition, classification, antecedents, consequences and interventions to procrastination, whereas procrastination in diverse contexts and groups remains to be investigated. Regarding the antecedents and consequences, research has mainly been about the relationship between procrastination and personality differences, such as the five-factor model, temperament, character, emotional intelligence, and impulsivity, but functions of external factors such as task characteristics and environmental conditions to procrastination have drawn scant attention. To identify the nature and characteristics of this behavior, randomized controlled trials are usually adopted in designing empirical research. However, the predominant use of self-reported data collection and for a certain point in time rather than longitudinal designs has limited the validation of some conclusions. Notably, there have been novel findings through burst detection analysis and structure variation analysis. Certain research themes have gained extraordinary attention in a short time period, have evolved progressively during the time span from 1990 to 2020, and involve the antecedents of procrastination in a temporal context, theoretical perspectives, research methods, and typical images of procrastinators. And emerging research themes that have been investigated include bedtime procrastination, failure of social media self-control, and clinical interventions. To our knowledge, this is almost the first time to conduct systematically bibliometric analysis on the topic of procrastination and findings can provide an in-depth view of the patterns and trends in procrastination research.
Introduction
Procrastination is commonly conceptualized as an irrational tendency to delay required tasks or assignments despite the negative effects of this postponement on the individuals and organizations (Lay, 1986 ; Steel, 2007 ; Klingsieck, 2013 ). Poets have even written figuratively about procrastination, with such phrases as “ Procrastination is the Thief of Time ,” and “ Procrastination is the Art of Keeping Up with Yesterday ” (Ferrari et al., 1995 ). Literal meanings are retained today in terms of time management. The conceptualizations of procrastination imply inaction, or postponing, delaying, or putting off a decision, in keeping with the Latin origins of the term “pro-,” meaning “forward, forth, or in favor of,” and “-crastinus,” meaning “tomorrow” (Klein, 1971 ). Time delay is just the behavioral reflection, while personality traits, cognitive and motivational process, as well as contextual conditions are in-depth inducements to procrastination. Procrastination can be viewed as purposive and irrational delay so as to miss the deadlines (Akerlof, 1991 ; Schraw et al., 2007 ).
Procrastination is believed to be a self-regulation failure that is associated with a variety of personal and situational determinants (Hen and Goroshit, 2018 ). Specifically, research suggests that task characteristics (e.g., unclear instructions, the timing of rewards and punishment, as well as task aversiveness), personality facets (e.g., the five-factor model, motivation, and cognition), and environmental factors (e.g., temptation, incentives, and accountability) are the main determinants of procrastination (Harris and Sutton, 1983 ; Johnson and Bloom, 1995 ; Green et al., 2000 ; Wypych et al., 2018 ). Procrastination can be an impediment to success, and may influence the individual's mood, and increase the person's anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem (Ferrari, 1991 ; Duru and Balkis, 2017 ). Furthermore, a person with procrastination is prone to poor performance, with lower exam scores, slower job promotions, and poorer health (Sirois, 2004 ; Legood et al., 2018 ; Bolden and Fillauer, 2020 ). Importantly, if policymakers postpone conducting their decision-making until after the proper timing, that procrastination can cause a significant and negative impact on the whole society, such as the cases with the COVID-19 pandemic management in some countries (Miraj, 2020 ).
In practice, procrastination is stable and complex across situations, ranging from students' academic procrastination, to staffs' work procrastination, to individuals' bedtime procrastination, to administrative behavior procrastination when government organizations face multiple tasks in national governance, and even to delayed leadership decision-making in crisis situations in global governance (Nevill, 2009 ; Hubner, 2012 ; Broadbent and Poon, 2015 ; Legood et al., 2018 ). As for science research, procrastination has attracted more and more attention and been studied extensively. Personally, possible explanations for emerging research focuses mainly consist of two aspects. On one hand, procrastination with high prevalence and obvious consequences highlights the importance to explore the complex phenomenon deeply, especially the meteoric rise in availability of information and communications technologies (ICTs) amplifies chronic procrastination, such as problematic social media use, smartphone addictions as well as mobile checking habit intrusion (Ferrari et al., 2007 ; Przepiorka et al., 2021 ; Aalbers et al., 2022 ). On the other hand, more and more basic and milestone research emerges in large numbers, which set the foundation for latecomer' further exploration toward procrastination. In particular, it can't be ignored the efforts of those productive authors in different periods to drive the knowledge development of procrastination.
Procrastination research has experienced tremendous expansion and diversification, but systematic and overview discussion is lacking. Several meta-analyses about procrastination have emerged, but they emphasize more on specific topics (Steel, 2007 ; Sirois et al., 2017 ; Malouff and Schutte, 2019 ). Furthermore, the number of newly published articles is increasing, so it becomes difficult to fully track the relevant domain literature. In order to grasp knowledge development about the fast-moving and complex research field, bibliometric analysis is necessary to construct diagram-based science mapping, so as to provide a comprehensive and intuitive reference for subsequent researchers. Thus, this article emphasizes on the following major research question: what is the intellectual base and structure of procrastination research? How does the emerging direction of procrastination develop? In our research, bibliometric analysis included the annual distribution of literature, distribution of categories, keyword co-occurrence networks, main research clusters, high citation betweenness centrality, and the strongest citation bursts, as well as the recent publications with transformative potential, in order to look back on the early development of procrastination research and look forward to the future transformation of that research. For both scholars and members of the public, this study can comprehensively enhance their understanding of procrastination and can provide overall perspectives for future research.
Data and Methodology
Bibliometric analysis is a quantitative method to investigate intellectual structures of topical field. On the basis of co-citation assumption that if two articles are usually cited together, then there are high associations between those articles, bibliometric analysis can reflect the scientific communicational structures holistically (Garfield, 1979 ; Chen et al., 2012 ). Bibliometric techniques, such as CiteSpace, VOSviewer, HistCite, can generate the science maps based on plenty of literature concerning certain domain. Through the process of charting, mining, analyzing, sorting, and displaying knowledge, science mapping can extract pivotal information from huge complex literature, present knowledge base and intellectual structure of a given field visually, then researchers even general individual can quickly grasp one subject's core structure, development process, frontier field and the whole knowledge framework (Chen, 2017 ; Widziewicz-Rzonca and Tytla, 2020 ). Bibliometric analysis is commonly regarded as a complementary method to traditional structured literature reviews such as narrative analysis and meta-analysis (Fang et al., 2018 ; Jiang et al., 2019 ). Traditional literature analysis tends to labor intensive with subjective preferences, and faces difficulties in analyzing larger body of literature, whereas bibliometric analysis provides a more objective approach for investigating considerable literature's intellectual structure through statistical analysis and interactive visual exploration.
In order to master the characteristics of procrastination research, the study adopted the bibliometric software of CiteSpace and VOSviewer to analyze the literature on procrastination during the time period 1990–2020. The software tool VOSviewer is designed for creating maps of authors, journals, and keyword co-occurrences based on network data (van Eck and Waltman, 2010 ), whereas CiteSpace is applied to conduct co-citation analysis, including centrality betweenness analysis, burst detection, and the emerging trends of research (Chen, 2006 , 2017 ). In our study, we adopted the CiteSpace (5.7.R1) and VOSviewer (1.6.15) software together. Specifically, co-citation analysis mainly depends on CiteSpace software, and co-occurrence analysis is conducted through VOS viewer (Markscheffel and Schroeter, 2021 ).
Though there is one similar bibliometrics analysis toward this topic (Tao et al., 2021 ), related research just focuses on academic procrastination, and mainly conducts co-occurrence analysis using VOSviewer, so as to there is a lack of analysis to core co-citation structures including high betweenness centrality articles, citation burst research and structure variation analysis. To offer insight into the intellectual structure of procrastination research, we further employ CiteSpace — a java application including bibliometric analysis, data mining algorithms and visualization methods developed by Chen — to visualize and elucidate vital trends and pivotal points about knowledge development.
To conduct our bibliometric analysis of procrastination research, we collected bibliographic records from the Web of Science Core Collection as of December 31, 2020. Web of Science is currently the most relevant scientific platform regarding systematic review needs, allowing for a “Topic” query, including searching a topic in the documents' “title”, “abstract”, “author keywords” and “keywords plus” of the documents being reviewed (Yi et al., 2020 ). A topic search strategy is broad enough to be used in science mapping (Olmeda-Gomez et al., 2019 ). Given the aim of the study, records were downloaded if they had the term “procrastination” in the “Topic” field. After restricting the type of publication to “Article” for the years 1900–2020, we had searched 2105 papers about procrastination research.
Figure 1 shows the yearly distribution of 2105 literature during 1900–2020, and it can be classified into three phases. In phase I (1900–1989), the annual number of publications never exceeded 10. In phase II (1990–2010), the annual quantity gradually increased from 11 papers in 1991 to 48 in 2010. The annual number of publications had begun to grow in this period, but remained below 50 papers yearly. In phase III (2011–2020), however, the procrastination research experienced a dramatic growth, with 255 literature in the year 2020. Although procrastination research appeared as early as 1900s, it had a stable total volume until the 1990s, when it developed sustained growth, and that growth became extraordinary during the 2010s. Therefore, this research emphasized centered on 1,635 literature that were published during the time span 1990–2020.

Distribution of publications on the topic of procrastination, 1900-2020.

Panoramic Overview of Procrastination Research
Category distribution.
Procrastination research has been attracting increasing attention from scholars, and it has been successfully integrated into various scientific fields. With the help of CiteSpace software, we present in Figure 2 the timelines of the various disciplines that are involved in procrastination research, and the cumulative numbers of literature that have been published.

Distribution of categories involved in procrastination research.
As Figure 2 shows, the size of node on the horizontal lines represents the quantity of literature published. Node colors denote the range of years of occurrence, and purple outlining is an indication of those articles with prominent betweenness centrality, and red nodes present references with high citation burst (Chen, 2017 ). Besides, the uppermost line shows the timeline of different disciplines, and the numbers on the longitudinal lines describe the distinct categories of procrastination research, of which are arranged vertically in the descending order of cluster's size. Clusters are numbered from 0, i.e Cluster #0 is the largest cluster and Cluster #1 is the second largest one. Specifically, the earlier research about procrastination occurs in the Psychology and Social Science disciplines. Subsequently, research has expanded into Computer Science and Information Systems, Economics, the Neurosciences, the Environmental Sciences, Ethics, Surgery, and general Medicine. As the connections arc in the Figure 2 presents, those categories #0 Psychology and Social Sciences, #1 Computer Science, and #2 Economics interact actively, but the interdisciplinary research about the remaining categories, such as #9 Medicine, #5 Ethics, and #4 Environmental Science, is not active.
Our analysis of the category distribution reveals two aspects of the characteristics about procrastination research. One, related research mostly has its roots in the Psychology and Social Science disciplines, and interdisciplinary research needs to be improved. And Two, the foundational literature dates back to the 1990s, and transformational exploration is currently needed in order to further develop the research on procrastination.
Keyword Co-occurrence Network: Core Contents
Analysis of co-occurring keywords is often used to obtain the content of research fields. Using the VOS viewer, we obtained a total of 5,203 keywords and created a co-occurrence network. As mentioned above, the size of a node represents the number of times that a specific keyword occurs. Several keywords turn up frequently, such as Procrastination, Performance, Academic Procrastination, Motivation, Personality, Self-regulation, Self-control, and Behavior. To create a readable map, the “minimum number of occurrences” is set to 20, and the final network includes 90 high-frequency keywords and five clusters with 2,650 links, as is shown in Figure 3 .

Keywords co-occurrence network for procrastination research.
Among the five clusters depicted in Figure 3 , the blue cluster is mainly related to the definition of procrastination, with keywords such as Procrastination, Delay, Deadlines, Choice, Self-Control, and Implementation Intentions. Procrastination is a complex phenomenon, and previous research has elaborated on the core traits about procrastination from various dimensions. Mainstream views hold that procrastination can be defined as the intentional delay of work because of a self-regulation failure, time-management inefficiency, short-term benefits, a gap between intention and action (Tice and Baumeister, 1997 ; Steel, 2007 ; Pychyl and Flett, 2012 ; Klingsieck, 2013 ), or missing a deadline and causing negative outcomes (Johnson and Bloom, 1995 ; Howell and Watson, 2007 ; Sirois, 2021 ).
The cluster in red in Figure 3 involves procrastination performance in relation to different life-domains, including Academic Achievement, Life Satisfaction, Online Learning, and Technology Uses. Previous research has elaborated on procrastination as being negatively correlated with performance. However, intrinsic motivation, self-regulated learning, and time-management have been shown to relieve the procrastination behavior (Wolters, 2003 ; Howell and Watson, 2007 ; Baker et al., 2019 ).
The green cluster highlights traits associated with procrastination. Related research in that cluster mostly discusses the correlation between the five-factor model (neuroticism, extraversion, openness to experience, agreeableness, conscientiousness) and procrastination (Schouwenburg and Lay, 1995 ). In addition, personality traits including indecisiveness, indecision, and perfectionism have been elaborated upon (Klingsieck, 2013 ; Tibbett and Ferrari, 2019 ). Furthermore, to measure the trait of procrastination itself, various scales have been developed, such as the General Procrastination Scale, Decisional Procrastination Questionnaire, Procrastination at Work Scale, Irrational Procrastination Scale, Adult Inventory of Procrastination Scale and so on (Lay, 1986 ; Ferrari et al., 1995 ; Steel, 2010 ; Metin et al., 2016 ). The validity and reliability of those scales have also been investigated fully.
The cluster presented in yellow depicts studies that focuses on academic procrastination, and especially those that discuss the antecedents of the prevalent behavior, such as Anxiety, Perfectionism, Self-efficacy, Depression, and Stress (Schraw et al., 2007 ; Goroshit, 2018 ). Owing to their accessibility for use as a research sample, a large body of procrastination research has chosen students in an academic setting as the research objects. Researchers have found that academic procrastination is an impediment to academic performance, especially for very young students. Notably, too, female students may perform lower levels of academic procrastination than males do.
The last cluster, presented in purple, relates to chronic procrastination's involvement in health and addiction, for either adults or adolescents. Discussion about chronic procrastination is growing, and interventions can be effective in relieving this behavior.
From the analysis of co-occurrence keywords, we can infer that procrastination research has been developing steadily. The fundamental discussion has become more adequate and persuasive in regard to the definition, the individual differences, and the antecedents of procrastination, and a discussion of how to relieve the behavior has begun.
Main Research Cluster: Core Theme and Hot Topics
Comparing to keyword co-occurrence network analyses, cluster analysis can help us grasp the primary themes in procrastination research. Clusters are based on the assumption that if two references are often cited together, they may be associated in some way (Chen et al., 2012 ; Pan et al., 2019 ). Eventually, related references shape diverse co-citation networks. Clustering is a procedure to classify co-cited references into groups, with references in the same clusters being tightly connected with each other but loosely associated with other clusters (Chen et al., 2010 ).
Based on the references of the top 50 articles with the most citations every year (if the number was less than 50 in a certain year, then all of the articles were combined), the final network contained 982 references and we were able to develop the final cluster landscape. Two procedures are used to label each cluster: (1) retrieval of keywords from the citing articles using the log likelihood ratio, and (2) retrieval of terms contained in the cited articles with latent semantic indexing (Olmeda-Gomez et al., 2019 ). In our research, we adopted the log-likelihood ratio (LLR) method to label the clusters automatically. Given the related structural and time-based values, articles in the co-citation network are assigned to each cluster. Eventually, the network was divided into 23 co-citation clusters.
In addition, two critical parameters, silhouette and modularity, are used to measure whether clusters are available and whether they are well-constructed. Silhouette indicates the homogeneity of clusters, whereas modularity measures whether the network is reasonably divided into independent clusters. The silhouette value ranges from −1 to 1, and the modularity score ranges from 0 to 1. When values of the two metrics are high, the co-citation network is well-constructed (Chen et al., 2010 ; Widziewicz-Rzonca and Tytla, 2020 ). As is shown in Figure 4 , the mean silhouette score of 0.9223 suggested that the homogeneity of these clusters was acceptable, and the modularity score of 0.7822 indicated that the network was reasonably divided.

Landscape view of co-citation network of procrastination research.
In our research, we summed the largest nine clusters. As is shown in Table 1 , the silhouette value for all clusters was higher than 0.8, suggesting the references in each cluster were highly homogeneous. The labels of these clusters were controlled trial, avoidant procrastination, conscientiousness procrastination, smoking cessation, explaining lack, academic achievement, procrastinatory media use, career indecision, and goal orientation.
Summary of the nine largest clusters in procrastination research.
In Table 1 , the year in the far-right column indicated the average year when the reference was cited. Ranking the clusters by the mean cited year, we can follow the development of research themes. During the 1990s, research themes focused on discussions about the antecedents of procrastination. For example, Lay ( 1988 ) discussed that the self-regulation model cannot explain procrastination fully, and errors in estimations of the time taken to complete a task may be attributed to procrastination. Procrastinators were thought to tend to lack conscientiousness and goal orientation as well as to be motivated by neurotic avoidance (Ferrari et al., 1995 ; Elliot and Harackiewicz, 1996 ). Besides, procrastination was prevalent throughout our lifespan, and empirical research on procrastination conducted through controlled trials had considered various settings or scenarios, such as academic procrastination, smoking cessation, career indecision, and in the most recent years, media use (Klassen et al., 2008 ; Germeijs and Verschueren, 2011 ; Du et al., 2019 ). Because procrastination was negatively associated with performance, life satisfaction, health and well-being, research on procrastination avoidance and intervention, including strengths-based training and cognitive behavioral therapy had attracted the most attention from scholars (van Eerde, 2003 ; Balkis and Duru, 2016 ; Visser et al., 2017 ).
Intellectual Structure of Procrastination Research
Co-citation analysis and clustering analysis form the cornerstone for bibliometric investigation (Olmeda-Gomez et al., 2019 ), especially for the microscopic intellectual structures of the science, such as betweenness centrality, burst detection, and structural variation analysis (Pan et al., 2019 ). Based on the cited references network during the period of 1990–2020, we generated a landscape visualization of intellectual structures about procrastination research. The section consists of three parts: (1) Betweenness Centrality Analysis captures the bridge nodes, which represents the landmark and pivotal literature of a scientific field (Freeman, 1978 ). (2) Burst Detection Analysis is used to detect the emergent and sharp increases of interest in a research field (Kleinberg, 2003 ), which is a useful method for easily tracing the development of research focus and research fronts. (3) Structural Variation Analysis (SVA) is an optional measurement to identify whether newly published articles have the potential to transform the citation network in the latest years. Newly published articles initially have fewer citations and may be overlooked. To overcome the limitation, structural variation analysis often employs zero-inflated negative binomial (ZINB) and negative binomial (NB) models to detect these transformative and potential literature (Chen, 2013 ).
Betweenness Centrality Analysis
Literature with high betweenness centrality tends to represent groundbreaking and landmark research. On the basis of our co-citation network on procrastination research for the period 1990–2020, we chose the top 10 articles to explore (see Supplementary Material for details). Related research mainly focuses on three areas.
Definition and Classification of Procrastination
Procrastination is described as the postponement of completion of a task or the failure to meet deadlines, even though the individual would meet adverse outcomes and feel uncomfortable as a result (Johnson and Bloom, 1995 ). Extracting from authoritative procrastination scales, Diaz-Morales et al. ( 2006 ) proposed a four-factor model of procrastination: dilatory behaviors, indecision, lack of punctuality, and lack of planning. Procrastination is commonly considered to be a pattern of self-regulation failure or self-defeating behavior (Tice and Baumeister, 1997 ; Sirois and Pychyl, 2013 ).
The most popular classification is the trinity of procrastination: decisional, arousal, and avoidant procrastination (Ferrari, 1992 ). Using the General Behavioral Procrastination Scale and Adult Inventory of Procrastination Scale, Ferrari et al. ( 2007 ) measured the difference between arousal and avoidant procrastination, and they elaborated that those two patterns of procrastination showed similarity and commonality across cultural values and norms. However, by conducting a meta-analytic review and factor analyses, Steel ( 2010 ) found that evidence for supporting the tripartite model of procrastination may not be sufficient. Research has reached a consensus about the basic definition of procrastination, but how to classify procrastination needs further discussion.
Procrastination Behavior in a Temporal Context
Procrastination is related to time management in its influence on one's behavior. Non-procrastinators or active procrastinators have better time control and purposive use of time (Corkin et al., 2011 ). However, time management is an obstacle to procrastinators. From the temporal disjunction between present and future selves, Sirois and Pychyl ( 2013 ) pointed out that procrastinators tended to give priority to short-term mood repair in the present, even though their future self would pay for the inaction. Similarly, in a longitudinal study Tice and Baumeister ( 1997 ) pointed out that maladjustment about benefits-costs in participants' timeframe shaped their procrastination. When a deadline is far off, procrastination can bring short-term benefits, such as less stress suffering and better health, whereas early benefits are often outweighed by possible long-term costs, including poor performance, low self-esteem, and anxiety. These viewpoints confirm that procrastination is a form of self-regulation failure, and that it involves the regulation of mood and emotion, as well as benefit-cost tradeoffs.
Causes of and Interventions for Procrastination
Procrastination shows significant stability among persons across time and situations. Predictors of procrastination include personality traits, task characteristics, external environments, and demographics (Steel, 2007 ). However, typically, empirical research has mostly focused on the relationship between the five-factor model and procrastination behavior. Johnson and Bloom ( 1995 ) systematically discussed five factors of personality to variance in academic procrastination. Research also had found that facets of conscientiousness and neuroticism were factors that explained most procrastination. In alignment with these findings above, Schouwenburg and Lay ( 1995 ) elaborated that procrastination was largely related to a lack of conscientiousness, which was associated with six facets: competence, order, dutifulness, achievement-striving, self-discipline, and deliberation. Meanwhile, impulsiveness (a facet of neuroticism) has some association with procrastination, owing to genetic influences (Gustavson et al., 2014 ). These discussions have established a basis for research about personality traits and procrastination (Flett et al., 2012 ; Kim et al., 2017 ).
To relieve procrastination, time management (TM) strategies and clinical methods are applied in practice. Glick and Orsillo ( 2015 ) compared the effectiveness of those interventions and found that acceptance-based behavior therapies (ABBTs) were more effective for chronic procrastinators. Regarding academic procrastination, Balkis ( 2013 ) discussed the role of rational beliefs in mediating procrastination, life satisfaction, and performance. However, there is no “Gold Standard” intervention for procrastination. How to manage this complex behavior needs further investigation.
Burst Detection Analysis
A citation burst indicates that one reference has gained extraordinary attention from the scientific community in a short period of time, and thus it can help us to detect and identify emergent research in a specialty (Kleinberg, 2003 ). A citation burst contains two dimensions: the burst strength and the burst status duration. Articles with high strength values can be considered to be especially relevant to the research theme (Widziewicz-Rzonca and Tytla, 2020 ). Burst status duration is labeled by the red segment lines in Figure 5 , which presents active citations' beginning year and ending year during the period 1990-2020. As can be seen in Figure 5 , we ranked the top 20 references (see Supplementary Material for details) with the strongest citation bursts, from the oldest to the most recent.

Top 20 references with the strongest citation bursts.
To systematically investigate the active areas of procrastination research in different time periods, we divided the study's overall timespan into three time periods. During the period 1990 through 1999, there were six references with high citation bursts, with two of them by Ferrari and a third by Ferrari, Johnson, and McCown. Subsequently, in 2000 through 2009, there were eight reference bursts, and the meta-analysis and theoretical review by Steel ( 2007 ) had the highest citation burst among those 20 references. From the period 2010 through 2020, six references showed high citation bursts.
Period I (1990–1999): Preliminary Understanding of Procrastination's Antecedents
How one defines procrastination is important to interventions. During the early period of procrastination research, scholars paid significant attention to define procrastination and discuss its antecedents. Time delay in completing tasks constitutes the vital dimension that distinguishes procrastination behavior, and that distinction has set the foundation for future exploration of the behavior. Lay ( 1988 ) found that errors in estimations of time led to procrastination, then identified two types of procrastinators: pessimistic procrastinators and optimistic ones, according to whether one is optimistic or pessimistic about judgments of time. In addition, the timeframe or constraint scenario influences one's behavioral choices. Procrastinators tend to weigh short-term benefits over long-term costs (Tice and Baumeister, 1997 ).
However, time delay is just a behavioral representation, and personality traits may be in-depth inducements to procrastination behavior (Ferrari, 1991 ; Ferrari et al., 1995 ). Schouwenburg and Lay ( 1995 ) empirically studied and elaborated upon the relationship between the five-factor model and procrastination facing a sample of students, and their findings showed consistency with research by Ferrari ( 1991 ) which demonstrated that the trait facets of lacking conscientiousness and of neurotic avoidance were associated with procrastination. In addition, Ferrari ( 1992 ) evaluated two popular scales to measure procrastination: the General Procrastination (GP) scale and the Adult Inventory for Procrastination (AIP) scale. Regarding the measurement of procrastination, a variety of scales have been constructed to further enhance the development of procrastination research.
Period II (2000–2009): Investigation of Cognitive and Motivational Facets and Emergence of Various Research Methods
During period II, procrastination research with high citation bursts focused largely on two dimensions: behavioral antecedences and empirical methods. On one hand, discussions about cognitive and motivational antecedents spring up. A series of studies find that cognitive and motivational beliefs, including goal orientation, perceived self-efficacy, self-handicapping, and self-regulated learning strategies, are strongly related to procrastination (Wolters, 2003 ; Howell and Watson, 2007 ; Klassen et al., 2008 ). Specifically, Howell and Watson ( 2007 ) examined the achievement goal framework with two variables, achievement goal orientation and learning strategies usage, in which four types of goal orientation can be derived by the performance vs. mastery dimension and the approach vs. avoidance dimension. Their research found that procrastination was attributed to a mastery-avoidance orientation, whereas it was adversely related to a mastery-approach orientation. Moreover, Chu and Choi ( 2005 ) identified two types of procrastinators, active procrastinators versus passive procrastinators, in terms of the individual's time usage and perception, self-efficacy beliefs, motivational orientation, stress-coping strategies, and final outcomes. This classification of procrastinators has aroused a hot discussion about procrastination research (Zohar et al., 2019 ; Perdomo and Feliciano-Garcia, 2020 ). Cognitive and motivational antecedents are complementary to personality traits, and the antecedents and traits together reveal the complex phenomenon.
In addition, there are various research methods being applied in the research, such as meta-analyses and grounded theory. Having the strongest citation burst in period II, research that was based on a meta-analysis of procrastination by Steel ( 2007 ) elaborated on temporal motivation theory (TMT). Temporal motivational theory provides an innovative foothold for understanding self-regulation failure, using four critical indicators: expectancy, value, sensitivity to delay, and delay itself. Similarly, van Eerde ( 2003 ) conducted a meta-analysis to examine the relationship between procrastination and personality traits, and proposed that procrastination was negatively related to conscientiousness and self-efficacy, but was also actively associated with self-handicapping. Procrastinators commonly set deadlines, but research has found that external deadlines may be more effective than self-imposed ones (Ariely and Wertenbroch, 2002 ). Furthermore, Schraw et al. ( 2007 ) constructed a paradigm model through grounded theory to analyze the phenomenon of academic procrastination, looking at context and situational conditions, antecedents, phenomena, coping strategies, and consequences. These diverse research methods are enhancing our comprehensive and systematical understanding of procrastination.
Period III (2010–2020): Diverse Focuses on Procrastination Research
After nearly two decades of progressive developments, procrastination research has entered a steady track with diverse current bursts, on topics such as type distinction, theoretical perspective, temporal context, and the typical image of procrastinators. Steel ( 2010 ) revisited the trinity of procrastination — arousal procrastinators, avoidant procrastinators, and decisional procrastinators — and using the Pure Procrastination Scale (PPS) and the Irrational Procrastination Scale (IPS), he found that there was no distinct difference among the three types. Regarding research settings, a body of literature has focused on academic procrastination in-depth, and that literature has experienced a significant citation burst (Kim and Seo, 2015 ; Steel and Klingsieck, 2016 ). For example, academic procrastination is associated more highly with performance for secondary school students than for other age groups.
Notably, theoretical discussions and empirical research have been advancing synchronously. Klingsieck ( 2013 ) investigated systematic characteristics of procrastination research and concluded that theoretical perspectives to explain the phenomenon, whereas Steel and Ferrari ( 2013 ) portrayed the “typical procrastinator” using the variables of sex, age, marital status, education, community location, and nationality. Looking beyond the use of time control or time perception to define procrastination, Sirois and Pychyl ( 2013 ) compared the current self and the future self, then proposed that procrastination results from short-term mood repair and emotion regulation with the consequences being borne by the future self. In line with the part of introduction, in the last 10 years, research on procrastination has flourished and knowledge about this complex phenomenon has been emerging and expanding.
Structure Variation Analysis
Structure variation analysis (SVA) can predict the literature that will have potential transformative power in the future. Proposed by Chen ( 2012 ), structure variation analysis includes three primary metrics — the modularity change rate, cluster linkage, and centrality divergence — to monitor and discern the potential of newly published articles in specific domains. The modularity change rate measures the changes in and interconnectivity of the overall structure when newly published articles are introduced into the intellectual network. Cluster linkage focuses on these differences in linkages before and after a new between-cluster link is added by an article, whereas centrality divergence measures the structural variations in the divergence of betweenness centrality that a newly published article causes (Chen, 2012 ; Hou et al., 2020 ). The values of these metrics are higher, and the newly published articles are expected to have more potential to transform the intellectual base (Hou et al., 2020 ). Specifically, cluster linkage is a direct measure of intellectual potential and structural change (Chen, 2012 ). Therefore, we adopted cluster linkage as an indicator by which to recognize and predict the valuable ideas in newly published procrastination research. These top 20 articles with high transformative potential that were published during the period 2016-2020 were listed (see Supplementary Material for details). Research contents primarily consist of four dimensions.
Further Investigations Into Academic Procrastination
Although procrastination research has drawn mostly on samples of students, innovative research contents and methods have been emerging that enhance our understanding of academic procrastination. In the past five years, different language versions of scales have been measured and validated (Garzon Umerenkova and Gil-Flores, 2017a , b ; Svartdal, 2017 ; Guilera et al., 2018 ), and novel research areas and contents have arisen, such as how gender difference influences academic procrastination, what are the effective means of intervention, and what are the associations among academic procrastination, person-environment fit, and academic achievement (Balkis and Duru, 2016 ; Garzon Umerenkova and Gil-Flores, 2017a , b ; Goroshit, 2018 ). Interestingly, research has found that females perform academic procrastination less often and gain better academic achievements than males do (Balkis and Duru, 2017 ; Perdomo and Feliciano-Garcia, 2020 ).
In addition, academic procrastination is viewed as a fluid process. Considering the behavior holistically, three different aspects of task engagement have been discussed: initiation, completion, and pursuit. Vangsness and Young ( 2020 ) proposed the metaphors of “turtles” (steady workers), “task ninjas” (precrastinators), and “time wasters” (procrastinators) to elaborate vividly on task completion strategies when working toward deadlines. Individual differences and task characteristics can influence one's choices of a task-completion strategy. To understand the fluid and multifaceted phenomenon of procrastination, longitudinal research has been appearing. Wessel et al. ( 2019 ) observed behavioral delay longitudinally through tracking an undergraduate assignment over two weeks to reveal how passive and active procrastination each affected assignment completion.
Relationships Between Procrastination and Diverse Personality Traits
In addition to the relationship between procrastination and the five-factor model, other personality traits, such as temperament, character, emotional intelligence, impulsivity, and motivation, have been investigated in connection with procrastination. Because the five-factor model is not effective for distinguishing the earlier developing temperamental tendencies and the later developing character traits, Zohar et al. ( 2019 ) discussed how temperament and character influence procrastination in terms of active and passive procrastinators, and revealed that a dependable temperament profile and well-developed character predicted active procrastination.
Procrastination is commonly defined as a self-regulation failure that includes emotion and behavior. Emotional intelligence (EI) is an indicator with which to monitor one's feelings, thinking, and actions, and hot discussions about its relationship with procrastination have sprung up recently. Sheybani et al. ( 2017 ) elaborated on how the relationship between emotional intelligence and the five-factor model influence decisional procrastination on the basis of a students' sample. As a complement to the research above, Wypych et al. ( 2018 ) explored the roles of impulsivity, motivation, and emotion regulation in procrastination through path analysis. Motivation and impulsivity reflecting a lack of value, along with delay discounting and lack of perseverance, are predicators of procrastination, whereas emotion regulation, especially for suppression of procrastination, has only appeared to be significant in student and other low-age groups. How personality traits influence procrastination remains controversial, and further research is expected.
Procrastination in Different Life-Domains and Settings
Newly published research is paying more attention to procrastination in different sample groups across the entire life span. Not being limited to student samples, discussions about procrastination in groups such as teachers, educated adults, and workers have been emerging. With regard to different life domains, the self-oriented domains including health and leisure time, tend to procrastinate, whereas parenting is low in procrastination among highly educated adults. Although the achievement-oriented life domains of career, education, and finances are found with moderate frequency in conjunction with procrastination, these three domains together with health affect life the most (Hen and Goroshit, 2018 ). Similarly, Tibbett and Ferrari ( 2019 ) investigated the main regret domains facing cross-cultural samples, so as to determine which factors increased the likelihood of identifying oneself as a procrastinator. Their research found that forms of earning potential, such as education, finances, and career, led participants to more easily label themselves as procrastinators. Procrastination can lead to regret, and this research adopted reverse thinking to discuss the antecedents of procrastination.
In addition to academic procrastination, research about the behavior in diverse-context settings has begun to draw scholars' attention. Nauts et al. ( 2019 ) used a qualitative study to investigate why people delay their bedtime, and the study identified three forms of bedtime procrastination: deliberate procrastination, mindless procrastination, and strategic delay. Then, those researchers proposed coached interventions involving time management, priority-setting skills, and reminders according to the characteristics of the bedtime procrastination. Interestingly, novel forms of procrastination have been arising in the attention-shortage situations of the age of the internet, such as social media self-control failure (SMSCF). Du et al. ( 2019 ) found that habitual checking, ubiquity, and notifications were determinants for self-control failures due to social media use, and that finding provided insight into how to better use ICTs in a media-pervasive environment. Moreover, even beyond those life-related-context settings, procrastination in the workplace has been further explored. Hen ( 2018 ) emphasized the factor of professional role ambiguity underlying procrastination. Classification of procrastination context is important for the effectiveness of intervention and provides us with a better understanding of this multifaceted behavior.
Interventions to Procrastination
Overcoming procrastination is a necessary topic for discussion. Procrastination is prevalent and stable across situations, and it is commonly averse to one's performance and general well-being. Various types of interventions are used, such as time management, self-management, and cognitive behavioral therapy. To examine the effectiveness of those interventions, scholars have used longitudinal studies or field experimental designs to investigate these methods of intervention for procrastination. Rozental et al. ( 2017 ) examined the efficacy of internet-based cognitive behavior therapy (ICBT) to relieve procrastination, from the perspective of clinical trials. Through a one-year follow-up in a randomized controlled trial, researchers found that ICBT could be beneficial to relieve severe, chronic procrastination. Taking the temporal context into consideration, Visser et al. ( 2017 ) discussed a strengths-based approach — one element of the cognitive behavioral approach — that showed greater usefulness for students at an early stage of their studies than it did at later ages. Overall, research on the effectiveness of intervention for procrastination is relatively scarce.
Discussion and Conclusion
Discussion on procrastination research.
This article provides a systematic bibliometric analysis of procrastination research over the past 30 years. The study identifies the category distribution, co-occurrence keywords, main research clusters, and intellectual structures, with the help of CiteSpace and VOS viewer. As is shown in Figure 6 , the primary focuses for research themes have been on the definition and classification of procrastination, the relationships between procrastination and personality traits, the influences brought by procrastination, and how to better intervene in this complex phenomenon.

Bibliometric analysis and science map of the literature on procrastination.
Those contents have built the bases for procrastination research, but determining how those bases are constructed is important to the development of future research. Therefore, this article primarily discusses three aspects of intellectual structure of procrastination research: betweenness centrality, burst detection, and structural variation analysis. From the betweenness centrality analysis, three research themes are identifiable and can be generally summarized as: definition and classification of procrastination, procrastination behavior in a temporal context, and causes and interventions for procrastination.
However, procrastination research themes have evolved significantly across the time period from 1990–2020. Through burst detection analysis, we are able to infer that research has paid extraordinary attention to diverse themes at different times. In the initial stage, research is mainly about the antecedents of procrastination from the perspectives of time-management, self-regulation failure, and the five-factor model, which pays more attention to the behavior itself, such as delays in time. Subsequently, further discussions have focused on how cognitive and motivational facets such as goal orientation, perceived self-efficacy, self-handicapping, as well as self-regulated learning strategies influence procrastination. In the most recent 10 years, research has paid significant attention to expanding diverse themes, such as theoretical perspectives, typical images of procrastinators, and procrastination behavior in diverse temporal contexts. Research about procrastination has been gaining more and more attention from scholars and practitioners.
To explore newly published articles and their transformative potential, we conduct structural variation analysis. Beyond traditional research involving academic procrastination, emerging research themes consist of diverse research settings across life-domains, such as bedtime procrastination, social media self-control failure, procrastination in the workplace, and procrastination comparisons between self-oriented and achievement-oriented domains. Furthermore, novel interventions from the perspective of clinical and cognitive orientations to procrastination have been emerging in response to further investigation of procrastination's antecedents, such as internet-based cognitive behavior therapy (ICBT) and the strengths-based approach.
Conclusions and Limitations
In summary, research on procrastination has gained increasing attention during 1990 to 2020. Specifically in Figure 7 , research themes have involved in the definition, classification, antecedents, consequences, interventions, and diverse forms of procrastination across different life-domains and contexts. Furthermore, empirical research has been conducted to understand this complex and multifaceted behavior, including how best to design controlled trial experiments, how to collect and analyze the data, and so on.

Brief conclusions on procrastination research.
From the perspective of knowledge development, related research about procrastination has experienced tremendous expansion in the last 30 years. There are three notable features to describe the evolutionary process.
First, research focuses are moving from broader topics to more specific issues. Prior research mostly explored the definition and antecedents of procrastination, as well as the relationship between personality traits and procrastination. Besides, earlier procrastination research almost drew on students' setting. Based on previous research above, innovative research starts to shed light on procrastination in situation-specific domains, such as work procrastination, bedtime procrastination, as well as the interaction between problematic new media use and procrastination (Hen, 2018 ; Nauts et al., 2019 ; Przepiorka et al., 2021 ). With the evolvement of research aimed at distinct contexts, more details and core contents about procrastination have been elaborated. For example, procrastination in workplace may have association with professional role ambiguity, abusive supervision, workplace ostracism and task characteristics (Hen, 2018 ; He et al., 2021 ; Levin and Lipshits-Braziler, 2021 ). In particular, owing to the use of information and communication technology (ICTs), there currently are ample temptations to distract our attention, and those distractions can exacerbate the severity of procrastination (Du et al., 2019 ; Hong et al., 2021 ). Therefore, how to identify those different forms of procrastination, and then to reduce their adverse outcomes, will be important to discuss.
Second, antecedents and consequences of procrastination are further explored over time. On one hand, how procrastination occurs arises hot discussions from diverse dimensions including time management, personality traits, contextual characteristics, motivational and cognitive factors successively. Interestingly, investigations about neural evidences under procrastination have been emerging, such as the underlying mechanism of hippocampal-striatal and amygdala-insula to procrastination (Zhang et al., 2021 ). Those antecedents can be divided into internal factors and external factors. Internal factors including character traits and cognitive maladjustments have been elucidated fully, but scant discussion has occurred about how external factors, such as task characteristics, peers' situations, and environmental conditions, influence procrastination (Harris and Sutton, 1983 ; He et al., 2021 ). On the other hand, high prevalence of procrastination necessitates the importance to identify the negative consequences including direct and indirect. Prior research paid more attention to direct consequences, such as low performance, poor productivity, stress and illness, but the indirect consequences that can be brought about by procrastination remain to be unclear. For example, “second-hand” procrastination vividly describes the “spillover effect” of procrastination, which is exemplified by another employee often working harder in order to compensate for the lost productivity of a procrastinating coworker (Pychyl and Flett, 2012 ). Although such phenomena are common, adverse outcomes are less well investigated. Combining the contexts and groups involved, targeted discussions about the external antecedents and indirect consequences of procrastination are expected.
Third, empirical research toward procrastination emphasizes more on validity. When it comes to previous research, longitudinal studies are often of small numbers. However, procrastination is dynamic, so when most studies focus on procrastination of students' sample during just one semester or several weeks, can limit the overall viewpoints about procrastination and the effectiveness of conclusions. With the development of research, more and more longitudinal explorations are springing up to discuss long-term effects of procrastination through behavioral observation studies and so on. Besides, how to design the research and collect data evolves gradually. Self-reported was the dominant method to collect data in prior research, and measurements of procrastination usually depended on different scales. However, self-reported data are often distorted by personal processes and may not reflect the actual situation, even to overestimate the level of procrastination (Kim and Seo, 2015 ; Goroshit, 2018 ). Hence, innovative studies start to conduct field experimental designs to get observed information through randomized controlled trials. For the following research, how to combine self-reported data and observed data organically should be investigated and refined.
This bibliometric analysis to procrastination is expected to provide overall perspective for future research. However, certain limitations merit mentioning here. Owing to the limited number of pages allowed, it is difficult to clarify the related articles in detail, so discussion tends to be heuristic. Furthermore, the data for this research comes from the Web of Science database, and applying the same strategy to a different database might have yielded different results. In the future, we will conduct a systematic analysis using diverse databases to detect pivotal articles on procrastination research.
Data Availability Statement
Author contributions.
BY proposed the research question and conducted the research design. XZ analyzed the data and wrote primary manuscript. On the base of that work mentioned above, two authors discussed and adjusted the final manuscript together.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.809044/full#supplementary-material
- Aalbers G., vanden Abeele M. M., Hendrickson A. T., de Marez L., Keijsers L. (2022). Caught in the moment: are there person-specific associations between momentary procrastination and passively measured smartphone use? Mobile Media Commun . 10 , 115–135. 10.1177/2050157921993896 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Akerlof G. A.. (1991). Procrastination and obedience . Am. Econ. Rev. 81 , 1–19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ariely D., Wertenbroch K. (2002). Procrastination, deadlines, and performance: self-control by precommitment . Psychol. Sci . 13 , 219–224. 10.1111/1467-9280.00441 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baker R., Evans B., Li Q., Cung B. (2019). Does inducing students to schedule lecture watching in online classes improve their academic performance? An experimental analysis of a time management intervention . Res. Higher Educ. 60 , 521–552. 10.1007/s11162-018-9521-3 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Balkis M.. (2013). Academic procrastination, academic life satisfaction and academic achievement: the mediation role of rational beliefs about studying . J. Cogn. Behav. Psychother. 13 , 57–74. [ Google Scholar ]
- Balkis M., Duru E. (2017). Gender differences in the relationship between academic procrastination, satisfaction with academic life and academic performance . Electr. J. Res. Educ. Psychol. 15 , 105–125. 10.25115/ejrep.41.16042 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Balkis M., Duru E. (2016). The analysis of relationships among person-environment fit, academic satisfaction, procrastination and academic achievement . Univ. J. Educ. 39 , 119–129. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bolden J., Fillauer J. P. (2020). “Tomorrow is the busiest day of the week”: executive functions mediate the relation between procrastination and attention problems . J. Am.College Health . 68 , 854–863. 10.1080/07448481.2019.1626399 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Broadbent J., Poon W. L. (2015). Self-regulated learning strategies & academic achievement in online higher education learning environments: a systematic review . Inter Higher Educ. 27 , 1–13. 10.1016/j.iheduc.2015.04.007 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C.. (2006). CiteSpace II: detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature . J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 57 , 359–377. 10.1002/asi.20317 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C.. (2012). Predictive effects of structural variation on citation counts . J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol . 63 , 431–449. 10.1002/asi.21694 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C.. (2013). Hindsight, insight, and foresight: a multi-level structural variation approach to the study of a scientific field . Technol. Analy. Strat. Manage . 25 , 619–640. 10.1080/09537325.2013.801949 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C.. (2017). Science mapping: a systematic review of the literature . J. Data Inf. Sci. 2 , 1–40. 10.1515/jdis-2017-0006 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C. M., Hu Z. G., Liu S. B., Tseng H. (2012). Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace . Expert Opin. Biol. Therapy. 12 , 593–608. 10.1517/14712598.2012.674507 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C. M., Ibekwe-SanJuan F., Hou J. (2010). The structure and dynamics of co-citation clusters: a multiple-perspective co-citation analysis . J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol . 61 , 1386–1409. 10.1002/asi.21309 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chu A. H. C., Choi J. N. (2005). Rethinking procrastination: positive effects of “active” procrastination behavior on attitudes and performance . J. Soc. Psychol . 145 , 245–264. 10.3200/SOCP.145.3.245-264 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Corkin D. M., Yu S. L., Lindt S. F. (2011). Comparing active delay and procrastination from a self-regulated learning perspective . Learn. Indiv. Differ. 21 , 602–606. 10.1016/j.lindif.2011.07.005 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Diaz-Morales J. F., Ferrari J. R., Diaz K., Argumedo D. (2006). Factorial structure of three procrastination scales with a Spanish adult population . Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 22 , 132–137. 10.1027/1015-5759.22.2.132 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Du J., Kerkhof P., van Koningsbruggen G. M. (2019). Predictors of social media self-control failure: immediate gratifications, habitual checking, ubiquity, and notifications . Cyber Psychol. Behav. Soc. Network. 22 , 477–485. 10.1089/cyber.2018.0730 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Duru E., Balkis M. (2017). Procrastination, self-esteem, academic performance, and well-being: a moderated mediation model . International J. Educ. Psychol . 6 , 97–119. 10.17583/ijep.2017.2584 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elliot A. J., Harackiewicz J. M. (1996). Approach and avoidance achievement goals and intrinsic motivation: a mediational analysis . J. Personal. Soc. Psychol . 70 , 461–475. 10.1037/0022-3514.70.3.461 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fang Y., Yin J., Wu B. (2018). Climate change and tourism: a scientometric analysis using CiteSpace . J. Sustain. Tour . 26 , 108–126. 10.1080/09669582.2017.1329310 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ferrari J. R.. (1991). Compulsive procrastination: some self-reported characteristics . Psychol. Reports. 68 , 455–458. 10.2466/pr0.1991.68.2.455 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ferrari J. R.. (1992). Psychometric validation of two Procrastination inventories for adults: arousal and avoidance measures . J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 14 , 97–110. 10.1007/BF00965170 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ferrari J. R., Diaz-Morales J. F., O'Callaghan J., Diaz K., Argumedo D. (2007). Frequent behavioral delay tendencies by adults - International prevalence rates of chronic procrastination . J. Cross-Cultural Psychol . 38 , 458–464. 10.1177/0022022107302314 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ferrari J. R., Johnson J. L., McCown W. G. (1995). Procrastination and Task Avoidance: Theory, Research, and Treatment . US: Springer US. 10.1007/978-1-4899-0227-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Flett G. L., Stainton M., Hewitt P. L., Sherry S. B., Lay C. (2012). Procrastination automatic thoughts as a personality construct: an analysis of the procrastinatory cognitions inventory . J. Rational-Emot. Cogn. Behav. Therapy. 30 , 223–236. 10.1007/s10942-012-0150-z [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Freeman L.. (1978). Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification . Soc. Netw. 1 , 215–239. 10.1016/0378-8733(78)90021-7 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garfield E.. (1979). Is citation analysis a legitimate evaluation tool . Scientometrics . 1 , 359–375. 10.1007/BF02019306 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garzon Umerenkova A., Gil-Flores J. (2017a). Psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the test procrastination assessment scale-students (PASS) . Rev. Iberoamericana De Diagnostico Y Evaluacion-E Avaliacao Psicol. 1 , 149–163. 10.21865/RIDEP43_149 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garzon Umerenkova A., Gil-Flores J. (2017b). Academic procrastination in non-traditional college students . Electronic J. Res. Educ. Psychol . 15 , 510–531. 10.14204/ejrep.43.16134 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Germeijs V., Verschueren K. (2011). Indecisiveness and big five personality factors: relationship and specificity . Person. Indiv. Differ. 50 , 1023–1028. 10.1016/j.paid.2011.01.017 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Glick D. M., Orsillo S. M. (2015). An investigation of the efficacy of acceptance-based behavioral therapy for academic procrastination . J. Experim. Psychol. General. 144 , 400–409. 10.1037/xge0000050 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Goroshit M.. (2018). Academic procrastination and academic performance: an initial basis for intervention . J. Prevent Intervent. Commun. 46 , 131–142. 10.1080/10852352.2016.1198157 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Green M. C., Visser P. S., Tetlock P. E. (2000). Coping with accountability cross-pressures: low-effort evasive tactics and high-effort quests for complex compromises . Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 26 , 1380–1391. 10.1177/0146167200263006 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Guilera G., Barrios M., Penelo E., Morin C., Steel P., Gomez-Benito J. (2018). Validation of the Spanish version of the irrational procrastination scale (IPS) . PLoS ONE. 13 , 1–11. 10.1371/journal.pone.0190806 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gustavson D. E., Miyake A., Hewitt J. K., Friedman N. P. (2014). Genetic relations among procrastination, impulsivity, and goal-management ability: implications for the evolutionary origin of procrastination . Psychol. Sci. 25 , 1178–1188. 10.1177/0956797614526260 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harris N. N., Sutton R. I. (1983). Task procrastination in organizations: a framework for research . Human Relat. 36 , 987–995. 10.1177/001872678303601102 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- He Q., Wu M., Wu W., Fu J. (2021). The effect of abusive supervision on employees' work procrastination behavior . Frontiers in Psychol . 12 , 596704. 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.596704 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hen M.. (2018). Causes for procrastination in a unique educational workplace . J. Prevent. Inter. Commun. 46 , 215–227. 10.1080/10852352.2018.1470144 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hen M., Goroshit M. (2018). General and life-domain procrastination in highly educated adults in Israel . Front. Psychol . 9 , 1173. 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01173 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hong W., Liu R. D., Ding Y., Jiang S. Y., Yang X. T., Sheng X. T. (2021). Academic procrastination precedes problematic mobile phone use in Chinese adolescents: a longitudinal mediation model of distraction cognitions . Addic. Behav. 121 , 106993. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2021.106993 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hou J. H., Yang X. C., Chen C. M. (2020). Measuring researchers' potential scholarly impact with structural variations: four types of researchers in information science (1979-2018) . PLoS ONE. 15 , e0234347. 10.1371/journal.pone.0234347 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Howell A. J., Watson D. C. (2007). Procrastination: associations with achievement goal orientation and learning strategies . Personal. Indiv. Differ. 43 , 167–178. 10.1016/j.paid.2006.11.017 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hubner K.. (2012). German crisis management and leadership-from ignorance to procrastination to action . Asia Eur. J. 9 , 159–177. 10.1007/s10308-012-0313-7 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jiang Y., Ritchie B. W., Benckendorff P. (2019). Bibliometric visualization: an application in tourism crisis and disaster management research . Curr. Issues Tour . 22 , 1925–1957. 10.1080/13683500.2017.1408574 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson J. L., Bloom A. M. (1995). An analysis of the contribution of the five factors of personality to variance in academic procrastination . Personal. Indiv. Differ. 18 , 127–133. 10.1016/0191-8869(94)00109-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim K. R., Seo E. H. (2015). The relationship between procrastination and academic performance: a meta-analysis . Personal. Indiv. Differ. 82 , 26–33. 10.1016/j.paid.2015.02.038 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim S., Fernandez S., Terrier L. (2017). Procrastination, personality traits, and academic performance: when active and passive procrastination tell a different story . Personal. Indiv. Differ. 108 , 154–157. 10.1016/j.paid.2016.12.021 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Klassen R. M., Krawchuk L. L., Rajani S. (2008). Academic procrastination of undergraduates: low self-efficacy to self-regulate predicts higher levels of procrastination . Contemp. Educ.Psychol . 33 , 915–931. 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2007.07.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Klein E.. (1971). A comprehensive etymological dictionary of the Hebrew language for readers of English . Tyndale House Publishers. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kleinberg J.. (2003). Bursty and hierarchical structure in streams . Data Mining Knowl. Disc. 7 , 373–397. 10.1023/A:1024940629314 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Klingsieck K. B.. (2013). Procrastination: when good things don't come to those who wait . Eur. Psychol . 18 , 24–34. 10.1027/1016-9040/a000138 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lay C.. (1986). At last, my research article on procrastination . J. Res. Personal . 20 , 474–495. 10.1016/0092-6566(86)90127-3 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lay C.. (1988). The relation of procrastination and optimism to judgments of time to complete an essay and anticipation of setbacks . J. Soc. Behav. Personal. 3 , 201–214. [ Google Scholar ]
- Legood A., Lee A., Schwarz G., Newman A. (2018). From self-defeating to other defeating: examining the effects of leader procrastination on follower work outcomes . J. Occup. Organiz. Psychol . 91 , 430–439. 10.1111/joop.12205 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Levin N., Lipshits-Braziler Y. (2021). Facets of adaptability in career decision-making . Int. J. Educ. Vocat. Guidance . 6 , 1–12. 10.1007/s10775-021-09489-w [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Malouff J. M., Schutte N. S. (2019). The efficacy of interventions aimed at reducing procrastination: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials . J. Counsel. Develop. 97 , 117–127. 10.1002/jcad.12243 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Markscheffel B., Schroeter F. (2021). Comparison of two science mapping tools based on software technical evaluation and bibliometric case studies . Collnet J. Scientometr. Inf. Manage . 15 , 365–396. 10.1080/09737766.2021.1960220 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Metin U. B., Tanis T. W., Peeters M. C. W. (2016). Measuring procrastination at work and its associated workplace aspects . Personal. Indiv. Differ . 101 , 254–263. 10.1016/j.paid.2016.06.006 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miraj S. A.. (2020). Coronavirus disease 2019: the public health challenge and our preparedness . Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Commun. 13 , 361–364. 10.21786/bbrc/13.2/1 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nauts S., Kamphorst B. A., Stut W., De Ridder D. T. D., Anderson J. H. (2019). The explanations people give for going to bed late: a qualitative study of the varieties of bedtime procrastination . Behav. Sleep Med. 17 , 753–762. 10.1080/15402002.2018.1491850 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nevill C. J.. (2009). Managing cumulative impacts: groundwater reform in the Murray-Darling basin, Australia . Water Res. Manage. 23 , 2605–2631. 10.1007/s11269-009-9399-0 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Olmeda-Gomez C., Roma-Mateo C., Ovalle-Perandones M. A. (2019). Overview of trends in global epigenetic research (2009-2017) . Scientometrics. 119 , 1545–1574. 10.1007/s11192-019-03095-y [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pan W. W., Jian L. R., Liu T. (2019). Grey system theory trends from 1991 to 2018: a bibliometric analysis and visualization . Scientometrics. 121 , 1407–1434. 10.1007/s11192-019-03256-z [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Perdomo A. S., Feliciano-Garcia L. (2020). The influence of active procrastination: a profile on educational sciences students' academic achievement . Bordon-Rev. De Pedagogia. 72 , 157–170. 10.13042/Bordon.2020.73642 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Przepiorka A., Blachnio A., Cudo A. (2021). Procrastination and problematic new media use: the mediating role of future anxiety . Current Psychol . 5 , 1–10. 10.1007/s12144-021-01773-w [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pychyl T. A., Flett G. L. (2012). Procrastination and self-regulatory failure: an introduction to the special issue . J. Rational-Emotive Cogn. Behav. Therapy. 30 , 203–212. 10.1007/s10942-012-0149-5 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rozental A., Forsell E., Svensson A., Andersson G., Carlbring P. (2017). Overcoming procrastination: one-year follow-up and predictors of change in a randomized controlled trial of Internet-based cognitive behavior therapy . Cogn. Behav.Therapy. 46 , 177–195. 10.1080/16506073.2016.1236287 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schouwenburg H. C., Lay C. H. (1995). Trait procrastination and the Big-five factors of personality . Personal. Indiv. Differ. 18 , 481–490. 10.1016/0191-8869(94)00176-S [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schraw G., Wadkins T., Olafson L. (2007). Doing the things we do: a grounded theory of academic procrastination . J. Educ.Psychol . 99 , 12–25. 10.1037/0022-0663.99.1.12 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheybani F., Gharraee B., Bakhshizadeh M., Tamanaeefar S. (2017). Decisional procrastination: prevalence among students and relationship with emotional intelligence and big five-factor model of personality . Int. J. Life Sci. Pharma Res. 7 , 26–32. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sirois F., Pychyl T. (2013). Procrastination and the priority of short-term mood regulation: consequences for future self . Soc. Personal. Psychol. Compass. 7 , 115–127. 10.1111/spc3.12011 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sirois F. M.. (2004). Procrastination and intentions to perform health behaviors: the role of self-efficacy and the consideration of future consequences . Personal. Indiv. Differ. 37 , 115–128. 10.1016/j.paid.2003.08.005 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sirois F. M.. (2021). Trait procrastination undermines outcome and efficacy expectancies for achieving health-related possible selves . Curr. Psychol . 40 , 3840–3847. 10.1007/s12144-019-00338-2 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sirois F. M., Molnar D. S., Hirsch J. K. (2017). A meta-analytic and conceptual update on the associations between procrastination and multidimensional perfectionism . Eur. J. Personal. 31 , 137–159. 10.1002/per.2098 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Steel P.. (2007). The nature of procrastination: a meta-analytic and theoretical review of quintessential self-regulatory failure . Psychol.Bull. 133 , 65–94. 10.1037/0033-2909.133.1.65 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Steel P.. (2010). Arousal, avoidant and decisional procrastinators: do they exist? Personal. Indiv. Differ. 48 , 926–934. 10.1016/j.paid.2010.02.025 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Steel P., Ferrari J. (2013). Sex, education and procrastination: an epidemiological study of procrastinators' characteristics from a global sample . Eur. J. Personal. 27 , 51–58. 10.1002/per.1851 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Steel P., Klingsieck K. B. (2016). Academic procrastination: psychological antecedents revisited . Austral. Psychol . 51 , 36–46. 10.1111/ap.12173 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Svartdal F.. (2017). Measuring procrastination: psychometric properties of the Norwegian versions of the irrational procrastination scale (IPS) and the pure procrastination scale (PPS) . Scand. J. Educ. Res . 61 , 18–30. 10.1080/00313831.2015.1066439 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tao X., Hanif H., Ahmed H. H., Ebrahim N. A. (2021). Bibliometric analysis and visualization of academic procrastination . Front. Psychol . 12 , 722332. 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.722332 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tibbett T., Ferrari J. (2019). Return to the origin: what creates a procrastination identity? Curr. Issues Personal. Psychol . 7 , 1–7. 10.5114/cipp.2018.75648 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tice D. M., Baumeister R. F. (1997). Longitudinal study of procrastination, performance, stress, and health: the costs and benefits of dawdling . Psychol. Sci. 8 , 454–458. 10.1111/j.1467-9280.1997.tb00460.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Eck N. J., Waltman L. (2010). Software survey: VOS viewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping . Scientometrics. 84 , 523–538. 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Eerde W.. (2003). A meta-analytically derived nomological network of procrastination . Personal. Indiv. Differ. 35 , 1401–1418. 10.1016/S0191-8869(02)00358-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vangsness L., Young M. E. (2020). Turtle, task ninja, or time waster? Who cares? traditional task-completion strategies are overrated . Psychol. Sci. 31 , 306–315. 10.1177/0956797619901267 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Visser L., Schoonenboom J., Korthagen F. A. J. (2017). A field experimental design of a strengths-based training to overcome academic procrastination: short- and long-term effect . Front. Psychol . 8 , 1949. 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01949 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wessel J., Bradley G. L., Hood M. (2019). Comparing effects of active and passive procrastination: a field study of behavioral delay . Personal. Indiv. Differ. 139 , 152–157. 10.1016/j.paid.2018.11.020 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Widziewicz-Rzonca K., Tytla M. (2020). First systematic review on PM-bound water: exploring the existing knowledge domain using the CiteSpace software . Scientometrics. 124 , 1945–2008. 10.1007/s11192-020-03547-w [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wolters C. A.. (2003). Understanding procrastination from a self-regulated learning perspective . J. Educ.Psychol . 95 , 179–187. 10.1037/0022-0663.95.1.179 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wypych M., Matuszewski J., Dragan W. Ł. (2018). Roles of impulsivity, motivation, and emotion regulation in procrastination – path analysis and comparison between students and non-students . Front. Psychol . 9 , 891. 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00891 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yi Y. T., Luo J. S., Wubbenhorst M. (2020). Research on political instability, uncertainty and risk during 1953-2019: a scientometric review . Scientometrics. 123 , 1051–1076. 10.1007/s11192-020-03416-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang S. M., Verguts T., Zhang C. Y., Feng P., Chen Q., Feng T. Y. (2021). Outcome value and task aversiveness impact task procrastination through separate neural pathways . Cerebral Cortex . 31 , 3846–3855. 10.1093/cercor/bhab053 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zohar A. H., Shimone L. P., Hen M. (2019). Active and passive procrastination in terms of temperament and character . Peerj. 7 , e6988. 10.7717/peerj.6988 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Technical Support
- Find My Rep
You are here
International Studies
Preview this book
- Description
- Aims and Scope
- Editorial Board
- Abstracting / Indexing
- Submission Guidelines
International Studies is a peer-reviewed journal that is committed to exploring and understanding Indian foreign policy, the theory and practice of non-alignment and the developmental and security problems of Third World countries.
This scholarly journal publishes original research articles on a wide range of issues and problems of contemporary relevance in the broad field of international studies. The journal provides insights in international politics and organization, international economics, defence and strategic studies, political geography and international law. This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) .
Electronic Access :
International Studies is available electronically on SAGE Journals Online at http://journals.sagepub.com/home/ISQ
International Studies, a peer reviewed scholarly journal, publishes original theoretical and empirical research articles of contemporary relevance in the field of International Relations, Area Studies and allied subjects. This scholarly journal encourages exploration and critical evaluation of new ideas in the field. It is a quarterly journal of the School of International Studies, Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi, but the views contained therein are those of the individual authors and not necessarily those of the University.
- Indian Citation Index (ICI)
- Pro-Quest-RSP
- ProQuest-Illustrata
- ProQuest: International Bibliography of the Social Sciences (IBSS)
- UGC-CARE (GROUP I)
This Journal is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics
International Studies is hosted on Sage Peer Review, a web-based online submission and peer review system. Please read the Manuscript Submission Guidelines below, and then visit https://peerreview.sagepub.com/isq to login and submit your article online. Remember you can log in to the submission site at any time to check on the progress of your paper through the peer review process.
Only manuscripts of sufficient quality that meet the aims and scope of International Studies will be reviewed.
There are no fees payable to submit or publish in this Journal. Open Access options are available - see section 3.3 below.
As part of the submission process you will be required to warrant that you are submitting your original work, that you have the rights in the work, and that you have obtained and can supply all necessary permissions for the reproduction of any copyright works not owned by you, that you are submitting the work for first publication in the Journal and that it is not being considered for publication elsewhere and has not already been published elsewhere. Please see our guidelines on prior publication and note that International Studies will consider submissions of papers that have been posted on preprint servers; please alert the Editorial Office when submitting (contact details are at the end of these guidelines) and include the DOI for the preprint in the designated field in the manuscript submission system. Authors should not post an updated version of their paper on the preprint server while it is being peer reviewed for possible publication in the Journal. If the article is accepted for publication, the author may re-use their work according to the Journal's author archiving policy.
If your paper is accepted, you must include a link on your preprint to the final version of your paper.
If you have any questions about publishing with Sage, please visit the Sage Journal Solutions Portal
1. What do we publish?
1.1 Aims & Scope 1.2 Article types 1.3 Writing your paper
2. Editorial policies
2.1 Peer review policy 2.2 Authorship 2.3 Acknowledgements 2.4 Funding 2.5 Declaration of conflicting interests 2.6 Research data
3. Publishing Policies
3.1 Publication ethics 3.2 Contributor’s publishing agreement 3.3 Open access and author archiving
4. Preparing your manuscript
4.1 Formatting 4.2 Artwork, figures and other graphics 4.3 Supplemental material 4.4 Reference style
5. Submitting your manuscript
5.1 ORCID 5.2 Information required for completing your submission 5.3 Permissions
6. On acceptance and publication
6.1 Sage Production 6.2 Online First publication 6.3 Access to your published article 6.4 Promoting your article
7. Further information
1.1 Aims & Scope
Before submitting your manuscript to International Studies , please ensure you have read the Aims & Scope [link to A&S].
1.2 Article types
This scholarly journal publishes original research articles on a wide range of issues and problems of contemporary relevance in the broad field of international studies. The journal provides insights in international politics and organization, international economics, defence and strategic studies, political geography and international law. Area studies research papers having global relevance are also published. Alternative approaches and perspectives from the global south are encouraged.
1.3 Writing your paper
The Sage Author Gateway has some general advice on how to get published , plus links to further resources.
1.3.1 Make your article discoverable For information and guidance on how to make your article more discoverable, visit our Gateway page on How to Help Readers Find Your Article Online
Return to Top
2.1 Peer review policy
International Studies adheres to a rigorous double-anonymize reviewing policy in which the identity of both the reviewer and author are always concealed from both parties.
International Studies is committed to delivering high quality, fast peer-review for your paper, and as such has partnered with Publons. Publons is a third party service that seeks to track, verify and give credit for peer review. Reviewers for International Studies can opt in to Publons in order to claim their reviews or have them automatically verified and added to their reviewer profile. Reviewers claiming credit for their review will be associated with the relevant journal, but the article name, reviewer’s decision and the content of their review is not published on the site. For more information visit the Publons website.
The Editor or members of the Editorial Board may occasionally submit their own manuscripts for possible publication in the Journal. In these cases, the peer review process will be managed by alternative members of the Board and the submitting Editor/Board member will have no involvement in the decision-making process.
2.2 Authorship
All parties who have made a substantive contribution to the article should be listed as authors. Principal authorship, authorship order, and other publication credits should be based on the relative scientific or professional contributions of the individuals involved, regardless of their status. A student is usually listed as principal author on any multiple-authored publication that substantially derives from the student’s dissertation or thesis.
Please note that AI chatbots, for example ChatGPT, should not be listed as authors. For more information see the policy on Use of ChatGPT and generative AI tools .
If the named authors for a manuscript change at any point between submission and acceptance , an Authorship Change Form must be completed and digitally signed by all authors (including any added or removed) . An addition of an author is only permitted following feedback raised during peer review. Completed forms can be uploaded at Revision Submission stage or emailed to the Journal Editorial Office contact (listed on the journal’s manuscript submission guidelines). All requests will be moderated by the Editor and/or Sage staff.
Important: Changes to the author by-line by adding or deleting authors are NOT permitted following acceptance of a paper .
2.3 Acknowledgements
All contributors who do not meet the criteria for authorship should be listed in an Acknowledgements section. Examples of those who might be acknowledged include a person who provided purely technical help, or a department chair who provided only general support.
Please supply any personal acknowledgements separately to the main text to facilitate anonymous peer review.
2.3.1 Writing assistance Individuals who provided writing assistance, e.g. from a specialist communications company, do not qualify as authors and so should be included in the Acknowledgements section. Authors must disclose any writing assistance – including the individual’s name, company and level of input – and identify the entity that paid for this assistance. It is not necessary to disclose use of language polishing services.
2.4 Funding
International Studies requires all authors to acknowledge their funding in a consistent fashion under a separate heading. Please visit the Funding Acknowledgements page on the Sage Journal Author Gateway to confirm the format of the acknowledgment text in the event of funding, or state that: This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
2.5 Declaration of conflicting interests
International Studies encourages authors to include a declaration of any conflicting interests and recommends you review the good practice guidelines on the Sage Journal Author Gateway
2.6 Research data
The journal is committed to facilitating openness, transparency and reproducibility of research, and has the following research data sharing policy. For more information, including FAQs please visit the Sage Research Data policy pages .
Subject to appropriate ethical and legal considerations, authors are encouraged to:
- share your research data in a relevant public data repository
- include a data availability statement linking to your data. If it is not possible to share your data, we encourage you to consider using the statement to explain why it cannot be shared.
- cite this data in your research
3.1 Publication ethics
Sage is committed to upholding the integrity of the academic record. We encourage authors to refer to the Committee on Publication Ethics’ International Standards for Authors and view the Publication Ethics page on the Sage Author Gateway
3.1.1 Plagiarism International Studies and Sage take issues of copyright infringement, plagiarism or other breaches of best practice in publication very seriously. We seek to protect the rights of our authors and we always investigate claims of plagiarism or misuse of published articles. Equally, we seek to protect the reputation of the Journal against malpractice. Submitted articles may be checked with duplication-checking software. Where an article, for example, is found to have plagiarized other work or included third-party copyright material without permission or with insufficient acknowledgement, or where the authorship of the article is contested, we reserve the right to take action including, but not limited to: publishing an erratum or corrigendum (correction); retracting the article; taking up the matter with the head of department or dean of the author's institution and/or relevant academic bodies or societies; or taking appropriate legal action.
3.1.2 Prior publication If material has been previously published it is not generally acceptable for publication in a Sage journal. However, there are certain circumstances where previously published material can be considered for publication. Please refer to the guidance on the Sage Author Gateway or if in doubt, contact the Editor at the address given below.
3.2 Contributor’s publishing agreement
Before publication, Sage requires the author as the rights holder to sign a Journal Contributor’s Publishing Agreement. Sage’s Journal Contributor’s Publishing Agreement is an exclusive licence agreement which means that the author retains copyright in the work but grants Sage the sole and exclusive right and licence to publish for the full legal term of copyright. Exceptions may exist where an assignment of copyright is required or preferred by a proprietor other than Sage. In this case copyright in the work will be assigned from the author to the society. For more information please visit the Sage Author Gateway
3.3 Open access and author archiving
International Studies offers optional open access publishing via the Sage Choice programme and Open Access agreements, where authors can publish open access either discounted or free of charge depending on the agreement with Sage. Find out if your institution is participating by visiting Open Access Agreements at Sage . For more information on Open Access publishing options at Sage please visit Sage Open Access . For information on funding body compliance, and depositing your article in repositories, please visit Sage’s Author Archiving and Re-Use Guidelines and Publishing Policies .
4. Preparing your manuscript for submission
4.1 Formatting
The preferred format for your manuscript is Word. LaTeX files are also accepted. A LaTex template is available on the Manuscript Submission Guidelines page of our Author Gateway.
Although there is no word limit, the authors are advised to submit articles between 5000 and 10,000 words; and book reviews between 1200 and 1800 words. Sharp commentaries of about 3000 words on current themes are also accepted.
The manuscript must include the following:
- Title of the paper, name of author, author’s affiliation and institutional address with pin code, email id and abstract of not more than 200 words. In case there are two or more authors, then corresponding author’s name and postal address details must be clearly specified.
- The contributors should provide 4–6 keywords for online searchability.
- All articles must be accompanied by 4–6 keywords and an abstract of 150–200 words. Notes should be numbered serially and presented at the end of the article. Notes must contain more than a mere reference.
- British spellings throughout (‘labour’ not ‘labor’, ‘centre’ not ‘center’); universal ‘z’ in ‘-ize’ and ‘-ization’ words.
- Use single quotes throughout. Double quotes only to be used within single quotes. Spellings of words in quotations should not be changed. Quotations of 45 words or more should be separated from the text and indented with one space with a line space above and below.
- Use ‘19th century’, ‘1980s’. Spell out numbers from one to nine, 10 and above to remain in figures. However, for exact measurements, use only figures (3 km, 9 percent, not %). Use thousands and millions, not lakhs and crores. Avoid saying ‘recently’ but rather give the year.
4.2 Artwork, figures and other graphics
For guidance on the preparation of illustrations, pictures and graphs in electronic format, please visit Sage’s Manuscript Submission Guidelines
- Figures, including maps, graphs and drawings, should not be larger than page size. They should be numbered and arranged as per their references in the text. All photographs and scanned images should have a resolution of minimum 300 dpi and 1,500 pixels and their format should be TIFF or JPEG.
- Due permissions should be taken for copyright protected photographs/images. Even for photographs/images available in the public domain, it should be clearly ascertained whether or not their reproduction requires permission for purposes of publishing (which is a profit-making endeavour).
- All photographs/scanned images should be provided separately in a folder along with the main article.
Please Note: All figures and tables should be cited in the text and should have the source (a specific URL, a reference or, if it is author’s own work, ‘The Author’) mentioned irrespective of whether or not they require permissions
Figures supplied in colour will appear in colour online regardless of whether or not these illustrations are reproduced in colour in the printed version. For specifically requested colour reproduction in print, you will receive information regarding the costs from Sage after receipt of your accepted article.
4.3 Supplemental material
This Journal is able to host additional materials online (e.g. datasets, podcasts, videos, images etc) alongside the full-text of the article. For more information please refer to our guidelines on submitting supplemental files
4.4 Reference style
International Studies adheres to the APA reference style. View the APA guidelines to ensure your manuscript conforms to this reference style.
There is no limit on the number of references allowed.
International Studies is hosted on Sage Peer Review, a web based online submission and peer review system. Please read the manuscript submission guidelines, and then visit https://peerreview.sagepub.com/isq to login and submit your article online.
IMPORTANT: Please check whether you already have an account in the system before trying to create a new one. If you have reviewed or authored for the journal in the past year it is likely that you will have had an account created.
As part of our commitment to ensuring an ethical, transparent and fair peer review process Sage is a supporting member of ORCID, the Open Researcher and Contributor ID . ORCID provides a unique and persistent digital identifier that distinguishes researchers from every other researcher, even those who share the same name, and, through integration in key research workflows such as manuscript and grant submission, supports automated linkages between researchers and their professional activities, ensuring that their work is recognized.
The collection of ORCID IDs from corresponding authors is now part of the submission process of this Journal. If you already have an ORCID ID you will be asked to associate that to your submission during the online submission process. We also strongly encourage all co-authors to link their ORCID ID to their accounts in our online peer review platforms. It takes seconds to do: click the link when prompted, sign into your ORCID account and our systems are automatically updated. Your ORCID ID will become part of your accepted publication’s metadata, making your work attributable to you and only you. Your ORCID ID is published with your article so that fellow researchers reading your work can link to your ORCID profile and from there link to your other publications.
If you do not already have an ORCID ID please follow this link to create one or visit our ORCID homepage to learn more.
5.2 Information required for completing your submission
You will be asked to provide contact details and academic affiliations for all co-authors via the submission system and identify who is to be the corresponding author. These details must match what appears on your manuscript. The affiliation listed in the manuscript should be the institution where the research was conducted. If an author has moved to a new institution since completing the research, the new affiliation can be included in a manuscript note at the end of the paper. At this stage please ensure you have included all the required statements and declarations and uploaded any additional supplementary files (including reporting guidelines where relevant).
5.3 Permissions
Please also ensure that you have obtained any necessary permission from copyright holders for reproducing any illustrations, tables, figures or lengthy quotations previously published elsewhere. For further information including guidance on fair dealing for criticism and review, please see the Copyright and Permissions page on the Sage Author Gateway
6.1 Sage Production
Your Sage Production Editor will keep you informed as to your article’s progress throughout the production process. Proofs will be made available to the corresponding author via email, and corrections should be made directly or notified to us promptly. Authors are reminded to check their proofs carefully to confirm that all author information, including names, affiliations, sequence and contact details are correct, and that Funding and Conflict of Interest statements, if any, are accurate.
6.2 Online First publication
Online First allows final articles (completed and approved articles awaiting assignment to a future issue) to be published online prior to their inclusion in a journal issue, which significantly reduces the lead time between submission and publication. Visit the Sage Journals help page for more details, including how to cite Online First articles.
6.3 Access to your published article
Sage provides authors with online access to their final article.
6.4 Promoting your article
Publication is not the end of the process! You can help disseminate your paper and ensure it is as widely read and cited as possible. The Sage Author Gateway has numerous resources to help you promote your work. Visit the Promote Your Article page on the Gateway for tips and advice.
Manuscripts and all editorial correspondence should be addressed to the journal administrator at https://peerreview.sagepub.com/isq
- Read Online
- Sample Issues
- Current Issue
- Email Alert
- Permissions
- Foreign rights
- Reprints and sponsorship
- Advertising
Individual Subscription, Print Only
Institutional Subscription, E-access
Institutional Subscription & Backfile Lease, E-access Plus Backfile (All Online Content)
Institutional Subscription, Print Only
Institutional Subscription, Combined (Print & E-access)
Institutional Subscription & Backfile Lease, Combined Plus Backfile (Current Volume Print & All Online Content)
Institutional Backfile Purchase, E-access (Content through 1998)
Individual, Single Print Issue
Institutional, Single Print Issue
To order single issues of this journal, please contact SAGE Customer Services at 1-800-818-7243 / 1-805-583-9774 with details of the volume and issue you would like to purchase.

Cultural Relativity and Acceptance of Embryonic Stem Cell Research
Article sidebar.

Main Article Content
There is a debate about the ethical implications of using human embryos in stem cell research, which can be influenced by cultural, moral, and social values. This paper argues for an adaptable framework to accommodate diverse cultural and religious perspectives. By using an adaptive ethics model, research protections can reflect various populations and foster growth in stem cell research possibilities.
INTRODUCTION
Stem cell research combines biology, medicine, and technology, promising to alter health care and the understanding of human development. Yet, ethical contention exists because of individuals’ perceptions of using human embryos based on their various cultural, moral, and social values. While these disagreements concerning policy, use, and general acceptance have prompted the development of an international ethics policy, such a uniform approach can overlook the nuanced ethical landscapes between cultures. With diverse viewpoints in public health, a single global policy, especially one reflecting Western ethics or the ethics prevalent in high-income countries, is impractical. This paper argues for a culturally sensitive, adaptable framework for the use of embryonic stem cells. Stem cell policy should accommodate varying ethical viewpoints and promote an effective global dialogue. With an extension of an ethics model that can adapt to various cultures, we recommend localized guidelines that reflect the moral views of the people those guidelines serve.
Stem cells, characterized by their unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, enable the repair or replacement of damaged tissues. Two primary types of stem cells are somatic stem cells (adult stem cells) and embryonic stem cells. Adult stem cells exist in developed tissues and maintain the body’s repair processes. [1] Embryonic stem cells (ESC) are remarkably pluripotent or versatile, making them valuable in research. [2] However, the use of ESCs has sparked ethics debates. Considering the potential of embryonic stem cells, research guidelines are essential. The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) provides international stem cell research guidelines. They call for “public conversations touching on the scientific significance as well as the societal and ethical issues raised by ESC research.” [3] The ISSCR also publishes updates about culturing human embryos 14 days post fertilization, suggesting local policies and regulations should continue to evolve as ESC research develops. [4] Like the ISSCR, which calls for local law and policy to adapt to developing stem cell research given cultural acceptance, this paper highlights the importance of local social factors such as religion and culture.
I. Global Cultural Perspective of Embryonic Stem Cells
Views on ESCs vary throughout the world. Some countries readily embrace stem cell research and therapies, while others have stricter regulations due to ethical concerns surrounding embryonic stem cells and when an embryo becomes entitled to moral consideration. The philosophical issue of when the “someone” begins to be a human after fertilization, in the morally relevant sense, [5] impacts when an embryo becomes not just worthy of protection but morally entitled to it. The process of creating embryonic stem cell lines involves the destruction of the embryos for research. [6] Consequently, global engagement in ESC research depends on social-cultural acceptability.
a. US and Rights-Based Cultures
In the United States, attitudes toward stem cell therapies are diverse. The ethics and social approaches, which value individualism, [7] trigger debates regarding the destruction of human embryos, creating a complex regulatory environment. For example, the 1996 Dickey-Wicker Amendment prohibited federal funding for the creation of embryos for research and the destruction of embryos for “more than allowed for research on fetuses in utero.” [8] Following suit, in 2001, the Bush Administration heavily restricted stem cell lines for research. However, the Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005 was proposed to help develop ESC research but was ultimately vetoed. [9] Under the Obama administration, in 2009, an executive order lifted restrictions allowing for more development in this field. [10] The flux of research capacity and funding parallels the different cultural perceptions of human dignity of the embryo and how it is socially presented within the country’s research culture. [11]
b. Ubuntu and Collective Cultures
African bioethics differs from Western individualism because of the different traditions and values. African traditions, as described by individuals from South Africa and supported by some studies in other African countries, including Ghana and Kenya, follow the African moral philosophies of Ubuntu or Botho and Ukama , which “advocates for a form of wholeness that comes through one’s relationship and connectedness with other people in the society,” [12] making autonomy a socially collective concept. In this context, for the community to act autonomously, individuals would come together to decide what is best for the collective. Thus, stem cell research would require examining the value of the research to society as a whole and the use of the embryos as a collective societal resource. If society views the source as part of the collective whole, and opposes using stem cells, compromising the cultural values to pursue research may cause social detachment and stunt research growth. [13] Based on local culture and moral philosophy, the permissibility of stem cell research depends on how embryo, stem cell, and cell line therapies relate to the community as a whole. Ubuntu is the expression of humanness, with the person’s identity drawn from the “’I am because we are’” value. [14] The decision in a collectivistic culture becomes one born of cultural context, and individual decisions give deference to others in the society.
Consent differs in cultures where thought and moral philosophy are based on a collective paradigm. So, applying Western bioethical concepts is unrealistic. For one, Africa is a diverse continent with many countries with different belief systems, access to health care, and reliance on traditional or Western medicines. Where traditional medicine is the primary treatment, the “’restrictive focus on biomedically-related bioethics’” [is] problematic in African contexts because it neglects bioethical issues raised by traditional systems.” [15] No single approach applies in all areas or contexts. Rather than evaluating the permissibility of ESC research according to Western concepts such as the four principles approach, different ethics approaches should prevail.
Another consideration is the socio-economic standing of countries. In parts of South Africa, researchers have not focused heavily on contributing to the stem cell discourse, either because it is not considered health care or a health science priority or because resources are unavailable. [16] Each country’s priorities differ given different social, political, and economic factors. In South Africa, for instance, areas such as maternal mortality, non-communicable diseases, telemedicine, and the strength of health systems need improvement and require more focus [17] Stem cell research could benefit the population, but it also could divert resources from basic medical care. Researchers in South Africa adhere to the National Health Act and Medicines Control Act in South Africa and international guidelines; however, the Act is not strictly enforced, and there is no clear legislation for research conduct or ethical guidelines. [18]
Some parts of Africa condemn stem cell research. For example, 98.2 percent of the Tunisian population is Muslim. [19] Tunisia does not permit stem cell research because of moral conflict with a Fatwa. Religion heavily saturates the regulation and direction of research. [20] Stem cell use became permissible for reproductive purposes only recently, with tight restrictions preventing cells from being used in any research other than procedures concerning ART/IVF. Their use is conditioned on consent, and available only to married couples. [21] The community's receptiveness to stem cell research depends on including communitarian African ethics.
c. Asia
Some Asian countries also have a collective model of ethics and decision making. [22] In China, the ethics model promotes a sincere respect for life or human dignity, [23] based on protective medicine. This model, influenced by Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), [24] recognizes Qi as the vital energy delivered via the meridians of the body; it connects illness to body systems, the body’s entire constitution, and the universe for a holistic bond of nature, health, and quality of life. [25] Following a protective ethics model, and traditional customs of wholeness, investment in stem cell research is heavily desired for its applications in regenerative therapies, disease modeling, and protective medicines. In a survey of medical students and healthcare practitioners, 30.8 percent considered stem cell research morally unacceptable while 63.5 percent accepted medical research using human embryonic stem cells. Of these individuals, 89.9 percent supported increased funding for stem cell research. [26] The scientific community might not reflect the overall population. From 1997 to 2019, China spent a total of $576 million (USD) on stem cell research at 8,050 stem cell programs, increased published presence from 0.6 percent to 14.01 percent of total global stem cell publications as of 2014, and made significant strides in cell-based therapies for various medical conditions. [27] However, while China has made substantial investments in stem cell research and achieved notable progress in clinical applications, concerns linger regarding ethical oversight and transparency. [28] For example, the China Biosecurity Law, promoted by the National Health Commission and China Hospital Association, attempted to mitigate risks by introducing an institutional review board (IRB) in the regulatory bodies. 5800 IRBs registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry since 2021. [29] However, issues still need to be addressed in implementing effective IRB review and approval procedures.
The substantial government funding and focus on scientific advancement have sometimes overshadowed considerations of regional cultures, ethnic minorities, and individual perspectives, particularly evident during the one-child policy era. As government policy adapts to promote public stability, such as the change from the one-child to the two-child policy, [30] research ethics should also adapt to ensure respect for the values of its represented peoples.
Japan is also relatively supportive of stem cell research and therapies. Japan has a more transparent regulatory framework, allowing for faster approval of regenerative medicine products, which has led to several advanced clinical trials and therapies. [31] South Korea is also actively engaged in stem cell research and has a history of breakthroughs in cloning and embryonic stem cells. [32] However, the field is controversial, and there are issues of scientific integrity. For example, the Korean FDA fast-tracked products for approval, [33] and in another instance, the oocyte source was unclear and possibly violated ethical standards. [34] Trust is important in research, as it builds collaborative foundations between colleagues, trial participant comfort, open-mindedness for complicated and sensitive discussions, and supports regulatory procedures for stakeholders. There is a need to respect the culture’s interest, engagement, and for research and clinical trials to be transparent and have ethical oversight to promote global research discourse and trust.
d. Middle East
Countries in the Middle East have varying degrees of acceptance of or restrictions to policies related to using embryonic stem cells due to cultural and religious influences. Saudi Arabia has made significant contributions to stem cell research, and conducts research based on international guidelines for ethical conduct and under strict adherence to guidelines in accordance with Islamic principles. Specifically, the Saudi government and people require ESC research to adhere to Sharia law. In addition to umbilical and placental stem cells, [35] Saudi Arabia permits the use of embryonic stem cells as long as they come from miscarriages, therapeutic abortions permissible by Sharia law, or are left over from in vitro fertilization and donated to research. [36] Laws and ethical guidelines for stem cell research allow the development of research institutions such as the King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, which has a cord blood bank and a stem cell registry with nearly 10,000 donors. [37] Such volume and acceptance are due to the ethical ‘permissibility’ of the donor sources, which do not conflict with religious pillars. However, some researchers err on the side of caution, choosing not to use embryos or fetal tissue as they feel it is unethical to do so. [38]
Jordan has a positive research ethics culture. [39] However, there is a significant issue of lack of trust in researchers, with 45.23 percent (38.66 percent agreeing and 6.57 percent strongly agreeing) of Jordanians holding a low level of trust in researchers, compared to 81.34 percent of Jordanians agreeing that they feel safe to participate in a research trial. [40] Safety testifies to the feeling of confidence that adequate measures are in place to protect participants from harm, whereas trust in researchers could represent the confidence in researchers to act in the participants’ best interests, adhere to ethical guidelines, provide accurate information, and respect participants’ rights and dignity. One method to improve trust would be to address communication issues relevant to ESC. Legislation surrounding stem cell research has adopted specific language, especially concerning clarification “between ‘stem cells’ and ‘embryonic stem cells’” in translation. [41] Furthermore, legislation “mandates the creation of a national committee… laying out specific regulations for stem-cell banking in accordance with international standards.” [42] This broad regulation opens the door for future global engagement and maintains transparency. However, these regulations may also constrain the influence of research direction, pace, and accessibility of research outcomes.
e. Europe
In the European Union (EU), ethics is also principle-based, but the principles of autonomy, dignity, integrity, and vulnerability are interconnected. [43] As such, the opportunity for cohesion and concessions between individuals’ thoughts and ideals allows for a more adaptable ethics model due to the flexible principles that relate to the human experience The EU has put forth a framework in its Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being allowing member states to take different approaches. Each European state applies these principles to its specific conventions, leading to or reflecting different acceptance levels of stem cell research. [44]
For example, in Germany, Lebenzusammenhang , or the coherence of life, references integrity in the unity of human culture. Namely, the personal sphere “should not be subject to external intervention.” [45] Stem cell interventions could affect this concept of bodily completeness, leading to heavy restrictions. Under the Grundgesetz, human dignity and the right to life with physical integrity are paramount. [46] The Embryo Protection Act of 1991 made producing cell lines illegal. Cell lines can be imported if approved by the Central Ethics Commission for Stem Cell Research only if they were derived before May 2007. [47] Stem cell research respects the integrity of life for the embryo with heavy specifications and intense oversight. This is vastly different in Finland, where the regulatory bodies find research more permissible in IVF excess, but only up to 14 days after fertilization. [48] Spain’s approach differs still, with a comprehensive regulatory framework. [49] Thus, research regulation can be culture-specific due to variations in applied principles. Diverse cultures call for various approaches to ethical permissibility. [50] Only an adaptive-deliberative model can address the cultural constructions of self and achieve positive, culturally sensitive stem cell research practices. [51]
II. Religious Perspectives on ESC
Embryonic stem cell sources are the main consideration within religious contexts. While individuals may not regard their own religious texts as authoritative or factual, religion can shape their foundations or perspectives.
The Qur'an states:
“And indeed We created man from a quintessence of clay. Then We placed within him a small quantity of nutfa (sperm to fertilize) in a safe place. Then We have fashioned the nutfa into an ‘alaqa (clinging clot or cell cluster), then We developed the ‘alaqa into mudgha (a lump of flesh), and We made mudgha into bones, and clothed the bones with flesh, then We brought it into being as a new creation. So Blessed is Allah, the Best of Creators.” [52]
Many scholars of Islam estimate the time of soul installment, marked by the angel breathing in the soul to bring the individual into creation, as 120 days from conception. [53] Personhood begins at this point, and the value of life would prohibit research or experimentation that could harm the individual. If the fetus is more than 120 days old, the time ensoulment is interpreted to occur according to Islamic law, abortion is no longer permissible. [54] There are a few opposing opinions about early embryos in Islamic traditions. According to some Islamic theologians, there is no ensoulment of the early embryo, which is the source of stem cells for ESC research. [55]
In Buddhism, the stance on stem cell research is not settled. The main tenets, the prohibition against harming or destroying others (ahimsa) and the pursuit of knowledge (prajña) and compassion (karuna), leave Buddhist scholars and communities divided. [56] Some scholars argue stem cell research is in accordance with the Buddhist tenet of seeking knowledge and ending human suffering. Others feel it violates the principle of not harming others. Finding the balance between these two points relies on the karmic burden of Buddhist morality. In trying to prevent ahimsa towards the embryo, Buddhist scholars suggest that to comply with Buddhist tenets, research cannot be done as the embryo has personhood at the moment of conception and would reincarnate immediately, harming the individual's ability to build their karmic burden. [57] On the other hand, the Bodhisattvas, those considered to be on the path to enlightenment or Nirvana, have given organs and flesh to others to help alleviate grieving and to benefit all. [58] Acceptance varies on applied beliefs and interpretations.
Catholicism does not support embryonic stem cell research, as it entails creation or destruction of human embryos. This destruction conflicts with the belief in the sanctity of life. For example, in the Old Testament, Genesis describes humanity as being created in God’s image and multiplying on the Earth, referencing the sacred rights to human conception and the purpose of development and life. In the Ten Commandments, the tenet that one should not kill has numerous interpretations where killing could mean murder or shedding of the sanctity of life, demonstrating the high value of human personhood. In other books, the theological conception of when life begins is interpreted as in utero, [59] highlighting the inviolability of life and its formation in vivo to make a religious point for accepting such research as relatively limited, if at all. [60] The Vatican has released ethical directives to help apply a theological basis to modern-day conflicts. The Magisterium of the Church states that “unless there is a moral certainty of not causing harm,” experimentation on fetuses, fertilized cells, stem cells, or embryos constitutes a crime. [61] Such procedures would not respect the human person who exists at these stages, according to Catholicism. Damages to the embryo are considered gravely immoral and illicit. [62] Although the Catholic Church officially opposes abortion, surveys demonstrate that many Catholic people hold pro-choice views, whether due to the context of conception, stage of pregnancy, threat to the mother’s life, or for other reasons, demonstrating that practicing members can also accept some but not all tenets. [63]
Some major Jewish denominations, such as the Reform, Conservative, and Reconstructionist movements, are open to supporting ESC use or research as long as it is for saving a life. [64] Within Judaism, the Talmud, or study, gives personhood to the child at birth and emphasizes that life does not begin at conception: [65]
“If she is found pregnant, until the fortieth day it is mere fluid,” [66]
Whereas most religions prioritize the status of human embryos, the Halakah (Jewish religious law) states that to save one life, most other religious laws can be ignored because it is in pursuit of preservation. [67] Stem cell research is accepted due to application of these religious laws.
We recognize that all religions contain subsets and sects. The variety of environmental and cultural differences within religious groups requires further analysis to respect the flexibility of religious thoughts and practices. We make no presumptions that all cultures require notions of autonomy or morality as under the common morality theory , which asserts a set of universal moral norms that all individuals share provides moral reasoning and guides ethical decisions. [68] We only wish to show that the interaction with morality varies between cultures and countries.
III. A Flexible Ethical Approach
The plurality of different moral approaches described above demonstrates that there can be no universally acceptable uniform law for ESC on a global scale. Instead of developing one standard, flexible ethical applications must be continued. We recommend local guidelines that incorporate important cultural and ethical priorities.
While the Declaration of Helsinki is more relevant to people in clinical trials receiving ESC products, in keeping with the tradition of protections for research subjects, consent of the donor is an ethical requirement for ESC donation in many jurisdictions including the US, Canada, and Europe. [69] The Declaration of Helsinki provides a reference point for regulatory standards and could potentially be used as a universal baseline for obtaining consent prior to gamete or embryo donation.
For instance, in Columbia University’s egg donor program for stem cell research, donors followed standard screening protocols and “underwent counseling sessions that included information as to the purpose of oocyte donation for research, what the oocytes would be used for, the risks and benefits of donation, and process of oocyte stimulation” to ensure transparency for consent. [70] The program helped advance stem cell research and provided clear and safe research methods with paid participants. Though paid participation or covering costs of incidental expenses may not be socially acceptable in every culture or context, [71] and creating embryos for ESC research is illegal in many jurisdictions, Columbia’s program was effective because of the clear and honest communications with donors, IRBs, and related stakeholders. This example demonstrates that cultural acceptance of scientific research and of the idea that an egg or embryo does not have personhood is likely behind societal acceptance of donating eggs for ESC research. As noted, many countries do not permit the creation of embryos for research.
Proper communication and education regarding the process and purpose of stem cell research may bolster comprehension and garner more acceptance. “Given the sensitive subject material, a complete consent process can support voluntary participation through trust, understanding, and ethical norms from the cultures and morals participants value. This can be hard for researchers entering countries of different socioeconomic stability, with different languages and different societal values. [72]
An adequate moral foundation in medical ethics is derived from the cultural and religious basis that informs knowledge and actions. [73] Understanding local cultural and religious values and their impact on research could help researchers develop humility and promote inclusion.
IV. Concerns
Some may argue that if researchers all adhere to one ethics standard, protection will be satisfied across all borders, and the global public will trust researchers. However, defining what needs to be protected and how to define such research standards is very specific to the people to which standards are applied. We suggest that applying one uniform guide cannot accurately protect each individual because we all possess our own perceptions and interpretations of social values. [74] Therefore, the issue of not adjusting to the moral pluralism between peoples in applying one standard of ethics can be resolved by building out ethics models that can be adapted to different cultures and religions.
Other concerns include medical tourism, which may promote health inequities. [75] Some countries may develop and approve products derived from ESC research before others, compromising research ethics or drug approval processes. There are also concerns about the sale of unauthorized stem cell treatments, for example, those without FDA approval in the United States. Countries with robust research infrastructures may be tempted to attract medical tourists, and some customers will have false hopes based on aggressive publicity of unproven treatments. [76]
For example, in China, stem cell clinics can market to foreign clients who are not protected under the regulatory regimes. Companies employ a marketing strategy of “ethically friendly” therapies. Specifically, in the case of Beike, China’s leading stem cell tourism company and sprouting network, ethical oversight of administrators or health bureaus at one site has “the unintended consequence of shifting questionable activities to another node in Beike's diffuse network.” [77] In contrast, Jordan is aware of stem cell research’s potential abuse and its own status as a “health-care hub.” Jordan’s expanded regulations include preserving the interests of individuals in clinical trials and banning private companies from ESC research to preserve transparency and the integrity of research practices. [78]
The social priorities of the community are also a concern. The ISSCR explicitly states that guidelines “should be periodically revised to accommodate scientific advances, new challenges, and evolving social priorities.” [79] The adaptable ethics model extends this consideration further by addressing whether research is warranted given the varying degrees of socioeconomic conditions, political stability, and healthcare accessibilities and limitations. An ethical approach would require discussion about resource allocation and appropriate distribution of funds. [80]
While some religions emphasize the sanctity of life from conception, which may lead to public opposition to ESC research, others encourage ESC research due to its potential for healing and alleviating human pain. Many countries have special regulations that balance local views on embryonic personhood, the benefits of research as individual or societal goods, and the protection of human research subjects. To foster understanding and constructive dialogue, global policy frameworks should prioritize the protection of universal human rights, transparency, and informed consent. In addition to these foundational global policies, we recommend tailoring local guidelines to reflect the diverse cultural and religious perspectives of the populations they govern. Ethics models should be adapted to local populations to effectively establish research protections, growth, and possibilities of stem cell research.
For example, in countries with strong beliefs in the moral sanctity of embryos or heavy religious restrictions, an adaptive model can allow for discussion instead of immediate rejection. In countries with limited individual rights and voice in science policy, an adaptive model ensures cultural, moral, and religious views are taken into consideration, thereby building social inclusion. While this ethical consideration by the government may not give a complete voice to every individual, it will help balance policies and maintain the diverse perspectives of those it affects. Embracing an adaptive ethics model of ESC research promotes open-minded dialogue and respect for the importance of human belief and tradition. By actively engaging with cultural and religious values, researchers can better handle disagreements and promote ethical research practices that benefit each society.
This brief exploration of the religious and cultural differences that impact ESC research reveals the nuances of relative ethics and highlights a need for local policymakers to apply a more intense adaptive model.
[1] Poliwoda, S., Noor, N., Downs, E., Schaaf, A., Cantwell, A., Ganti, L., Kaye, A. D., Mosel, L. I., Carroll, C. B., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2022). Stem cells: a comprehensive review of origins and emerging clinical roles in medical practice. Orthopedic reviews , 14 (3), 37498. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.37498
[2] Poliwoda, S., Noor, N., Downs, E., Schaaf, A., Cantwell, A., Ganti, L., Kaye, A. D., Mosel, L. I., Carroll, C. B., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2022). Stem cells: a comprehensive review of origins and emerging clinical roles in medical practice. Orthopedic reviews , 14 (3), 37498. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.37498
[3] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2023). Laboratory-based human embryonic stem cell research, embryo research, and related research activities . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/blog-post-title-one-ed2td-6fcdk ; Kimmelman, J., Hyun, I., Benvenisty, N. et al. Policy: Global standards for stem-cell research. Nature 533 , 311–313 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/533311a
[4] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2023). Laboratory-based human embryonic stem cell research, embryo research, and related research activities . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/blog-post-title-one-ed2td-6fcdk
[5] Concerning the moral philosophies of stem cell research, our paper does not posit a personal moral stance nor delve into the “when” of human life begins. To read further about the philosophical debate, consider the following sources:
Sandel M. J. (2004). Embryo ethics--the moral logic of stem-cell research. The New England journal of medicine , 351 (3), 207–209. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp048145 ; George, R. P., & Lee, P. (2020, September 26). Acorns and Embryos . The New Atlantis. https://www.thenewatlantis.com/publications/acorns-and-embryos ; Sagan, A., & Singer, P. (2007). The moral status of stem cells. Metaphilosophy , 38 (2/3), 264–284. http://www.jstor.org/stable/24439776 ; McHugh P. R. (2004). Zygote and "clonote"--the ethical use of embryonic stem cells. The New England journal of medicine , 351 (3), 209–211. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp048147 ; Kurjak, A., & Tripalo, A. (2004). The facts and doubts about beginning of the human life and personality. Bosnian journal of basic medical sciences , 4 (1), 5–14. https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2004.3453
[6] Vazin, T., & Freed, W. J. (2010). Human embryonic stem cells: derivation, culture, and differentiation: a review. Restorative neurology and neuroscience , 28 (4), 589–603. https://doi.org/10.3233/RNN-2010-0543
[7] Socially, at its core, the Western approach to ethics is widely principle-based, autonomy being one of the key factors to ensure a fundamental respect for persons within research. For information regarding autonomy in research, see: Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, & National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research (1978). The Belmont Report. Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research.; For a more in-depth review of autonomy within the US, see: Beauchamp, T. L., & Childress, J. F. (1994). Principles of Biomedical Ethics . Oxford University Press.
[8] Sherley v. Sebelius , 644 F.3d 388 (D.C. Cir. 2011), citing 45 C.F.R. 46.204(b) and [42 U.S.C. § 289g(b)]. https://www.cadc.uscourts.gov/internet/opinions.nsf/6c690438a9b43dd685257a64004ebf99/$file/11-5241-1391178.pdf
[9] Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005, H. R. 810, 109 th Cong. (2001). https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/109/hr810/text ; Bush, G. W. (2006, July 19). Message to the House of Representatives . National Archives and Records Administration. https://georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov/news/releases/2006/07/20060719-5.html
[10] National Archives and Records Administration. (2009, March 9). Executive order 13505 -- removing barriers to responsible scientific research involving human stem cells . National Archives and Records Administration. https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/removing-barriers-responsible-scientific-research-involving-human-stem-cells
[11] Hurlbut, W. B. (2006). Science, Religion, and the Politics of Stem Cells. Social Research , 73 (3), 819–834. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40971854
[12] Akpa-Inyang, Francis & Chima, Sylvester. (2021). South African traditional values and beliefs regarding informed consent and limitations of the principle of respect for autonomy in African communities: a cross-cultural qualitative study. BMC Medical Ethics . 22. 10.1186/s12910-021-00678-4.
[13] Source for further reading: Tangwa G. B. (2007). Moral status of embryonic stem cells: perspective of an African villager. Bioethics , 21(8), 449–457. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8519.2007.00582.x , see also Mnisi, F. M. (2020). An African analysis based on ethics of Ubuntu - are human embryonic stem cell patents morally justifiable? African Insight , 49 (4).
[14] Jecker, N. S., & Atuire, C. (2021). Bioethics in Africa: A contextually enlightened analysis of three cases. Developing World Bioethics , 22 (2), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12324
[15] Jecker, N. S., & Atuire, C. (2021). Bioethics in Africa: A contextually enlightened analysis of three cases. Developing World Bioethics, 22(2), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12324
[16] Jackson, C.S., Pepper, M.S. Opportunities and barriers to establishing a cell therapy programme in South Africa. Stem Cell Res Ther 4 , 54 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt204 ; Pew Research Center. (2014, May 1). Public health a major priority in African nations . Pew Research Center’s Global Attitudes Project. https://www.pewresearch.org/global/2014/05/01/public-health-a-major-priority-in-african-nations/
[17] Department of Health Republic of South Africa. (2021). Health Research Priorities (revised) for South Africa 2021-2024 . National Health Research Strategy. https://www.health.gov.za/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/National-Health-Research-Priorities-2021-2024.pdf
[18] Oosthuizen, H. (2013). Legal and Ethical Issues in Stem Cell Research in South Africa. In: Beran, R. (eds) Legal and Forensic Medicine. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32338-6_80 , see also: Gaobotse G (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[19] United States Bureau of Citizenship and Immigration Services. (1998). Tunisia: Information on the status of Christian conversions in Tunisia . UNHCR Web Archive. https://webarchive.archive.unhcr.org/20230522142618/https://www.refworld.org/docid/3df0be9a2.html
[20] Gaobotse, G. (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[21] Kooli, C. Review of assisted reproduction techniques, laws, and regulations in Muslim countries. Middle East Fertil Soc J 24 , 8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43043-019-0011-0 ; Gaobotse, G. (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[22] Pang M. C. (1999). Protective truthfulness: the Chinese way of safeguarding patients in informed treatment decisions. Journal of medical ethics , 25(3), 247–253. https://doi.org/10.1136/jme.25.3.247
[23] Wang, L., Wang, F., & Zhang, W. (2021). Bioethics in China’s biosecurity law: Forms, effects, and unsettled issues. Journal of law and the biosciences , 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsab019 https://academic.oup.com/jlb/article/8/1/lsab019/6299199
[24] Wang, Y., Xue, Y., & Guo, H. D. (2022). Intervention effects of traditional Chinese medicine on stem cell therapy of myocardial infarction. Frontiers in pharmacology , 13 , 1013740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1013740
[25] Li, X.-T., & Zhao, J. (2012). Chapter 4: An Approach to the Nature of Qi in TCM- Qi and Bioenergy. In Recent Advances in Theories and Practice of Chinese Medicine (p. 79). InTech.
[26] Luo, D., Xu, Z., Wang, Z., & Ran, W. (2021). China's Stem Cell Research and Knowledge Levels of Medical Practitioners and Students. Stem cells international , 2021 , 6667743. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6667743
[27] Luo, D., Xu, Z., Wang, Z., & Ran, W. (2021). China's Stem Cell Research and Knowledge Levels of Medical Practitioners and Students. Stem cells international , 2021 , 6667743. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6667743
[28] Zhang, J. Y. (2017). Lost in translation? accountability and governance of Clinical Stem Cell Research in China. Regenerative Medicine , 12 (6), 647–656. https://doi.org/10.2217/rme-2017-0035
[29] Wang, L., Wang, F., & Zhang, W. (2021). Bioethics in China’s biosecurity law: Forms, effects, and unsettled issues. Journal of law and the biosciences , 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsab019 https://academic.oup.com/jlb/article/8/1/lsab019/6299199
[30] Chen, H., Wei, T., Wang, H. et al. Association of China’s two-child policy with changes in number of births and birth defects rate, 2008–2017. BMC Public Health 22 , 434 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-12839-0
[31] Azuma, K. Regulatory Landscape of Regenerative Medicine in Japan. Curr Stem Cell Rep 1 , 118–128 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40778-015-0012-6
[32] Harris, R. (2005, May 19). Researchers Report Advance in Stem Cell Production . NPR. https://www.npr.org/2005/05/19/4658967/researchers-report-advance-in-stem-cell-production
[33] Park, S. (2012). South Korea steps up stem-cell work. Nature . https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2012.10565
[34] Resnik, D. B., Shamoo, A. E., & Krimsky, S. (2006). Fraudulent human embryonic stem cell research in South Korea: lessons learned. Accountability in research , 13 (1), 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/08989620600634193 .
[35] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics, 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
[36] Association for the Advancement of Blood and Biotherapies. https://www.aabb.org/regulatory-and-advocacy/regulatory-affairs/regulatory-for-cellular-therapies/international-competent-authorities/saudi-arabia
[37] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: Interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics , 21 (1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
[38] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: Interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics , 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
Culturally, autonomy practices follow a relational autonomy approach based on a paternalistic deontological health care model. The adherence to strict international research policies and religious pillars within the regulatory environment is a great foundation for research ethics. However, there is a need to develop locally targeted ethics approaches for research (as called for in Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics, 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6), this decision-making approach may help advise a research decision model. For more on the clinical cultural autonomy approaches, see: Alabdullah, Y. Y., Alzaid, E., Alsaad, S., Alamri, T., Alolayan, S. W., Bah, S., & Aljoudi, A. S. (2022). Autonomy and paternalism in Shared decision‐making in a Saudi Arabian tertiary hospital: A cross‐sectional study. Developing World Bioethics , 23 (3), 260–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12355 ; Bukhari, A. A. (2017). Universal Principles of Bioethics and Patient Rights in Saudi Arabia (Doctoral dissertation, Duquesne University). https://dsc.duq.edu/etd/124; Ladha, S., Nakshawani, S. A., Alzaidy, A., & Tarab, B. (2023, October 26). Islam and Bioethics: What We All Need to Know . Columbia University School of Professional Studies. https://sps.columbia.edu/events/islam-and-bioethics-what-we-all-need-know
[39] Ababneh, M. A., Al-Azzam, S. I., Alzoubi, K., Rababa’h, A., & Al Demour, S. (2021). Understanding and attitudes of the Jordanian public about clinical research ethics. Research Ethics , 17 (2), 228-241. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016120966779
[40] Ababneh, M. A., Al-Azzam, S. I., Alzoubi, K., Rababa’h, A., & Al Demour, S. (2021). Understanding and attitudes of the Jordanian public about clinical research ethics. Research Ethics , 17 (2), 228-241. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016120966779
[41] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[42] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[43] The EU’s definition of autonomy relates to the capacity for creating ideas, moral insight, decisions, and actions without constraint, personal responsibility, and informed consent. However, the EU views autonomy as not completely able to protect individuals and depends on other principles, such as dignity, which “expresses the intrinsic worth and fundamental equality of all human beings.” Rendtorff, J.D., Kemp, P. (2019). Four Ethical Principles in European Bioethics and Biolaw: Autonomy, Dignity, Integrity and Vulnerability. In: Valdés, E., Lecaros, J. (eds) Biolaw and Policy in the Twenty-First Century. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 78. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05903-3_3
[44] Council of Europe. Convention for the protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being with regard to the Application of Biology and Medicine: Convention on Human Rights and Biomedicine (ETS No. 164) https://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/full-list?module=treaty-detail&treatynum=164 (forbidding the creation of embryos for research purposes only, and suggests embryos in vitro have protections.); Also see Drabiak-Syed B. K. (2013). New President, New Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research Policy: Comparative International Perspectives and Embryonic Stem Cell Research Laws in France. Biotechnology Law Report , 32 (6), 349–356. https://doi.org/10.1089/blr.2013.9865
[45] Rendtorff, J.D., Kemp, P. (2019). Four Ethical Principles in European Bioethics and Biolaw: Autonomy, Dignity, Integrity and Vulnerability. In: Valdés, E., Lecaros, J. (eds) Biolaw and Policy in the Twenty-First Century. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 78. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05903-3_3
[46] Tomuschat, C., Currie, D. P., Kommers, D. P., & Kerr, R. (Trans.). (1949, May 23). Basic law for the Federal Republic of Germany. https://www.btg-bestellservice.de/pdf/80201000.pdf
[47] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Germany . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-germany
[48] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Finland . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-finland
[49] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Spain . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-spain
[50] Some sources to consider regarding ethics models or regulatory oversights of other cultures not covered:
Kara MA. Applicability of the principle of respect for autonomy: the perspective of Turkey. J Med Ethics. 2007 Nov;33(11):627-30. doi: 10.1136/jme.2006.017400. PMID: 17971462; PMCID: PMC2598110.
Ugarte, O. N., & Acioly, M. A. (2014). The principle of autonomy in Brazil: one needs to discuss it ... Revista do Colegio Brasileiro de Cirurgioes , 41 (5), 374–377. https://doi.org/10.1590/0100-69912014005013
Bharadwaj, A., & Glasner, P. E. (2012). Local cells, global science: The rise of embryonic stem cell research in India . Routledge.
For further research on specific European countries regarding ethical and regulatory framework, we recommend this database: Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Europe . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-europe
[51] Klitzman, R. (2006). Complications of culture in obtaining informed consent. The American Journal of Bioethics, 6(1), 20–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15265160500394671 see also: Ekmekci, P. E., & Arda, B. (2017). Interculturalism and Informed Consent: Respecting Cultural Differences without Breaching Human Rights. Cultura (Iasi, Romania) , 14 (2), 159–172.; For why trust is important in research, see also: Gray, B., Hilder, J., Macdonald, L., Tester, R., Dowell, A., & Stubbe, M. (2017). Are research ethics guidelines culturally competent? Research Ethics , 13 (1), 23-41. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016116650235
[52] The Qur'an (M. Khattab, Trans.). (1965). Al-Mu’minun, 23: 12-14. https://quran.com/23
[53] Lenfest, Y. (2017, December 8). Islam and the beginning of human life . Bill of Health. https://blog.petrieflom.law.harvard.edu/2017/12/08/islam-and-the-beginning-of-human-life/
[54] Aksoy, S. (2005). Making regulations and drawing up legislation in Islamic countries under conditions of uncertainty, with special reference to embryonic stem cell research. Journal of Medical Ethics , 31: 399-403.; see also: Mahmoud, Azza. "Islamic Bioethics: National Regulations and Guidelines of Human Stem Cell Research in the Muslim World." Master's thesis, Chapman University, 2022. https://doi.org/10.36837/ chapman.000386
[55] Rashid, R. (2022). When does Ensoulment occur in the Human Foetus. Journal of the British Islamic Medical Association , 12 (4). ISSN 2634 8071. https://www.jbima.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/2-Ethics-3_-Ensoulment_Rafaqat.pdf.
[56] Sivaraman, M. & Noor, S. (2017). Ethics of embryonic stem cell research according to Buddhist, Hindu, Catholic, and Islamic religions: perspective from Malaysia. Asian Biomedicine,8(1) 43-52. https://doi.org/10.5372/1905-7415.0801.260
[57] Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[58] Lecso, P. A. (1991). The Bodhisattva Ideal and Organ Transplantation. Journal of Religion and Health , 30 (1), 35–41. http://www.jstor.org/stable/27510629 ; Bodhisattva, S. (n.d.). The Key of Becoming a Bodhisattva . A Guide to the Bodhisattva Way of Life. http://www.buddhism.org/Sutras/2/BodhisattvaWay.htm
[59] There is no explicit religious reference to when life begins or how to conduct research that interacts with the concept of life. However, these are relevant verses pertaining to how the fetus is viewed. (( King James Bible . (1999). Oxford University Press. (original work published 1769))
Jerimiah 1: 5 “Before I formed thee in the belly I knew thee; and before thou camest forth out of the womb I sanctified thee…”
In prophet Jerimiah’s insight, God set him apart as a person known before childbirth, a theme carried within the Psalm of David.
Psalm 139: 13-14 “…Thou hast covered me in my mother's womb. I will praise thee; for I am fearfully and wonderfully made…”
These verses demonstrate David’s respect for God as an entity that would know of all man’s thoughts and doings even before birth.
[60] It should be noted that abortion is not supported as well.
[61] The Vatican. (1987, February 22). Instruction on Respect for Human Life in Its Origin and on the Dignity of Procreation Replies to Certain Questions of the Day . Congregation For the Doctrine of the Faith. https://www.vatican.va/roman_curia/congregations/cfaith/documents/rc_con_cfaith_doc_19870222_respect-for-human-life_en.html
[62] The Vatican. (2000, August 25). Declaration On the Production and the Scientific and Therapeutic Use of Human Embryonic Stem Cells . Pontifical Academy for Life. https://www.vatican.va/roman_curia/pontifical_academies/acdlife/documents/rc_pa_acdlife_doc_20000824_cellule-staminali_en.html ; Ohara, N. (2003). Ethical Consideration of Experimentation Using Living Human Embryos: The Catholic Church’s Position on Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research and Human Cloning. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology . Retrieved from https://article.imrpress.com/journal/CEOG/30/2-3/pii/2003018/77-81.pdf.
[63] Smith, G. A. (2022, May 23). Like Americans overall, Catholics vary in their abortion views, with regular mass attenders most opposed . Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2022/05/23/like-americans-overall-catholics-vary-in-their-abortion-views-with-regular-mass-attenders-most-opposed/
[64] Rosner, F., & Reichman, E. (2002). Embryonic stem cell research in Jewish law. Journal of halacha and contemporary society , (43), 49–68.; Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[65] Schenker J. G. (2008). The beginning of human life: status of embryo. Perspectives in Halakha (Jewish Religious Law). Journal of assisted reproduction and genetics , 25 (6), 271–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-008-9221-6
[66] Ruttenberg, D. (2020, May 5). The Torah of Abortion Justice (annotated source sheet) . Sefaria. https://www.sefaria.org/sheets/234926.7?lang=bi&with=all&lang2=en
[67] Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[68] Gert, B. (2007). Common morality: Deciding what to do . Oxford Univ. Press.
[69] World Medical Association (2013). World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA , 310(20), 2191–2194. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.281053 Declaration of Helsinki – WMA – The World Medical Association .; see also: National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research. (1979). The Belmont report: Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research . U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.hhs.gov/ohrp/regulations-and-policy/belmont-report/read-the-belmont-report/index.html
[70] Zakarin Safier, L., Gumer, A., Kline, M., Egli, D., & Sauer, M. V. (2018). Compensating human subjects providing oocytes for stem cell research: 9-year experience and outcomes. Journal of assisted reproduction and genetics , 35 (7), 1219–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-018-1171-z https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6063839/ see also: Riordan, N. H., & Paz Rodríguez, J. (2021). Addressing concerns regarding associated costs, transparency, and integrity of research in recent stem cell trial. Stem Cells Translational Medicine , 10 (12), 1715–1716. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.21-0234
[71] Klitzman, R., & Sauer, M. V. (2009). Payment of egg donors in stem cell research in the USA. Reproductive biomedicine online , 18 (5), 603–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1472-6483(10)60002-8
[72] Krosin, M. T., Klitzman, R., Levin, B., Cheng, J., & Ranney, M. L. (2006). Problems in comprehension of informed consent in rural and peri-urban Mali, West Africa. Clinical trials (London, England) , 3 (3), 306–313. https://doi.org/10.1191/1740774506cn150oa
[73] Veatch, Robert M. Hippocratic, Religious, and Secular Medical Ethics: The Points of Conflict . Georgetown University Press, 2012.
[74] Msoroka, M. S., & Amundsen, D. (2018). One size fits not quite all: Universal research ethics with diversity. Research Ethics , 14 (3), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016117739939
[75] Pirzada, N. (2022). The Expansion of Turkey’s Medical Tourism Industry. Voices in Bioethics , 8 . https://doi.org/10.52214/vib.v8i.9894
[76] Stem Cell Tourism: False Hope for Real Money . Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI). (2023). https://hsci.harvard.edu/stem-cell-tourism , See also: Bissassar, M. (2017). Transnational Stem Cell Tourism: An ethical analysis. Voices in Bioethics , 3 . https://doi.org/10.7916/vib.v3i.6027
[77] Song, P. (2011) The proliferation of stem cell therapies in post-Mao China: problematizing ethical regulation, New Genetics and Society , 30:2, 141-153, DOI: 10.1080/14636778.2011.574375
[78] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[79] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2024). Standards in stem cell research . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/5-standards-in-stem-cell-research
[80] Benjamin, R. (2013). People’s science bodies and rights on the Stem Cell Frontier . Stanford University Press.
Mifrah Hayath
SM Candidate Harvard Medical School, MS Biotechnology Johns Hopkins University
Olivia Bowers
MS Bioethics Columbia University (Disclosure: affiliated with Voices in Bioethics)
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
Highly-Cited Papers on Fracture Non-union – A Bibliometric Analysis of the Global Literature (1990–2023)
- Review Article
- Published: 13 May 2024
Cite this article

- Raju Vaishya ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9577-9533 1 ,
- Brij Mohan Gupta ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0685-8342 2 ,
- Ghouse Modin N. Mamdapur ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4155-1987 3 ,
- Abhishek Vaish ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7347-0917 4 ,
- Janki Sharan Bhadani ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3329-8355 5 &
- John Mukhopadhaya ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9185-6274 6
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The growing interest in this field of fracture nonunion has been informally acknowledged through published studies. A bibliometric analysis was conducted to objectively outline the patterns in published clinical research concerning nonunion fractures by utilizing highly cited papers (HCPs).
Through a predetermined search strategy, we gathered literature on the clinical management of nonunion fractures from the Scopus database and utilized bibliometrics to examine the publication dates, countries, institutions, journals, authors, HCPs, and research focal points. Statistical analysis and visualization were conducted using MS Excel and VOSviewer software.
From 1990 to 2023, a total of 168 HCPs in the field of fracture nonunion were identified. They received an average of 167.68 citations per paper (CPP). Among them, 4.08% received external funding, while 17.26% were involved in international collaboration. The United States (49.4% share) was the most productive country and France had the highest citation impact. P.V. Gianoudis had the highest productivity with 13 publications and P. Hernigou had the highest citation impact. The Mayo Clinic was the most productive organization and Hopital Henri Mondor achieved the highest citation impact. The most productive journal was Clinical Orthopedics & Related Research, and the Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery, American Volume had the highest average citation impact.
This contemporary bibliometric study illustrates the research features and developments of nonunion fractures. Through the use of VOSviewer, key countries, organizations, and authors could be identified, providing researchers with essential information to pinpoint current and future areas of interest in fracture nonunion.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
A historical review and bibliometric analysis of research on fracture nonunion in the last three decades
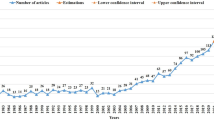
Open Fractures from Gustilo and Anderson to the Present: A Bibliometric Analysis with Global Productivity and Research Trends
Fifty top-cited fracture articles from china: a systematic review and bibliometric analysis, data availability.
The data for this paper is available in the public domain.
Cunningham, B. P., Brazina, S., Morshed, S., & Miclau, T. (2017). Fracture healing: A review of clinical, imaging and laboratory diagnostic options. Injury, 48 (Suppl 1), S69–S75.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Calori, G. M., Albisetti, W., Agus, A., Iori, S., & Tagliabue, L. (2007). Risk factors contributing to fracture nonunions. Injury, 38 (Suppl 2), S11–S18.
Fong, K., Truong, V., Foote, C. J., Petrisor, B., Williams, D., Ristevski, B., Sprague, S., & Bhandari, M. (2013). Predictors of nonunion and reoperation in patients with fractures of the tibia: An observational study. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 14 , 103.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Brinker, M. R., O’Connor, D. P., Monla, Y. T., & Earthman, T. P. (2007). Metabolic and endocrine abnormalities in patients with nonunions. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, 21 (8), 557–570.
JD Thomas JL Kehoe 2024 Bone Nonunion. [Updated 2023 Mar 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554385/
Bell, A., Templeman, D., & Weinlein, J. C. (2016). Nonunion of the femur and tibia: An update. Orthopedic Clinics of North America, 47 (2), 365–375.
Hak, D. J., Fitzpatrick, D., Bishop, J. A., Marsh, J. L., Tilp, S., Schnettler, R., Simpson, H., & Alt, V. (2014). Delayed union and nonunions: Epidemiology, clinical issues, and financial aspects. Injury, 45 (Suppl 2), S3-7.
Rupp, M., Biehl, C., Budak, M., Thormann, U., Heiss, C., & Alt, V. (2018). Diaphyseal long bone nonunions – types, aetiology, economics, and treatment recommendations. International Orthopaedics, 42 (2), 247–258.
Dailey, H. L., Wu, K. A., Wu, P. S., McQueen, M. M., & Court-Brown, C. M. (2018). Tibial fracture nonunion and time to healing after reamed intramedullary nailing: Risk factors based on a single-center review of 1003 patients. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, 32 (7), e263–e269.
Stewart, S. K. (2019). Fracture nonunion: A review of clinical challenges and future research needs. Malays Orthop J., 13 (2), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1907.001
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Giannoudis, P. V., Chloros, G. D., & Ho, Y. S. (2021). A historical review and bibliometric analysis of research on fracture nonunion in the last three decades. International Orthopaedics, 45 (7), 1663–1676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-021-05020-6
Lucio-Arias, D., & Leydesdorff, L. (2009). An indicator of research front activity: Measuring intellectual organization as uncertainty reduction in document sets. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 60 (12), 2488–2498. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.21199
Article Google Scholar
R Vaishya BM Gupta M Kappi A Vaish 2023 Fracture research from India between 1989 to 2022: A scientometric study . Iberoamerican Journal of Science Measurement and Communication [Internet]. 8 [cited 2024 Apr. 2];3(1). Available from: https://ijsmc.pro-metrics.org/index.php/i/article/view/35
Vaishya, R., Gupta, B. M., Kappi, M. K., & Vaish, A. (2023). A scientometric analysis of the most highlycited publications on fracture research from india: 1989–2022. Ann Natl Acad Med Sci (India), 59 , 209–218.
Walter, N., Orbenes, N., Rupp, M., & Alt, V. (2022). The state of research in fracture-related infection—a bibliometric analysis. Medicina, 58 (9), 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58091170
Elshohna, M., & Tsouklidis, N. (2022). Top 50 cited bone graft orthopedic papers. Cureus, 14 (3), e23419. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.23419
Li, J., Zhao, Y., et al. (2023). Research hotspots and trends of bone xenograft in clinical procedures: A bibliometric and visual analysis of the past decade. Bioengineering, 10 (8), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080929
Lin, H., Wang, X., Huang, M., et al. (2020). Research hotspots and trends of bone defects based on web of science: A bibliometric analysis. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 15 , 463. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-01973-3
Huang, X., Liu, X., Shang, Y., Qiao, F., & Chen, G. (2020). Current trends in research on bone regeneration: A bibliometric analysis. BioMed Research International, 2020 , 8787394. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8787394
Zhang, X., Li, Q., Wang, Z., et al. (2022). Bone regeneration materials and their application over 20 years: A bibliometric study and systematic review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol., 10 , 921092. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.921092
Deng, Z., Luo, F., Lin, Y., et al. (2022). Research trends of mesenchymal stem cells application in orthopedics: A bibliometric analysis of the past 2 decades. Frontiers in Public Health, 10 , 1021818. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.1021818
Jindal, R., Dhillon, M., Mittal, N., Aggarwal, A., Malhotra, A., & Garg, S. K. (2021). Gaps in the care of open fractures: An indian scenario. Indian J Orthop., 56 (2), 280–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-021-00476-5
Tissingh, E. K., Marais, L., Loro, A., Bose, D., Paner, N. T., Ferguson, J., Morgensten, M., & McNally, M. (2022). Management of fracture-related infection in low resource settings: How applicable are the current consensus guidelines? EFORT Open Rev., 7 (6), 422–432. https://doi.org/10.1530/EOR-22-0031
Vaishya, R., Gupta, B. M., Misra, A., Mamdapur, G. M. N., Walke, R., & Vaish, A. (2023). Top 100 highly cited papers from India on COVID-19 research: A bibliometric analysis of the core literature. Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews, 17 (11), 102898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2023.102898
Article CAS Google Scholar
Vaishya, R., Gupta, B. M., Mamdapur, G. M. N., Vaish, A., & Migliorini, F. (2023). Scientometric analysis of highly cited papers on avascular necrosis of the femoral head from 1991 to 2022. Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, 24 (1), 27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10195-023-00709-3
Vaishya, R., Gupta, B. M., Misra, A., Mamdapurj, G. M., & Vaish, A. (2022). Global research in sarcopenia: High-cited papers, research institutions, funding agencies and collaborations, 1993–2022. Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews, 16 (11), 102654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102654
Yang, J., Zhang, X., Liang, W., Chen, G., Ma, Y., Zhou, Y., Fen, R., & Jiang, K. (2022). Efficacy of adjuvant treatment for fracture nonunion/delayed union: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 23 (1), 481. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-022-05407-5
Ding, Z. C., Lin, Y. K., Gan, Y. K., & Tang, T. T. (2018). Molecular pathogenesis of fracture nonunion. J Orthop Translat., 14 , 45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jot.2018.05.002
Dimitriou, R., Carr, I. M., West, R. M., Markham, A. F., & Giannoudis, P. V. (2011). Genetic predisposition to fracture nonunion: A case-control study of a preliminary single nucleotide polymorphisms analysis of the BMP pathway. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 12 , 44. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-12-44
Schlickewei, C. W., Kleinertz, H., Thiesen, D. M., Mader, K., Priemel, M., Frosch, K. H., & Keller, J. (2019). Current and future concepts for the treatment of impaired fracture healing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20 (22), 5805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225805
Szwed-Georgiou, A., Płociński, P., Kupikowska-Stobba, B., Urbaniak, M. M., Rusek-Wala, P., Szustakiewicz, K., et al. (2023). Bioactive materials for bone regeneration: Biomolecules and delivery systems. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 9 (9), 5222–5254. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c00609
Zhu, L., Liu, Y., Wang, A., Zhu, Z., Li, Y., Zhu, C., et al. (2022). Application of BMP in Bone Tissue Engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 10 , 810880. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.810880
Ma, Q., Miri, Z., Haugen, H. J., Moghanian, A., & Loca, D. (2023). Significance of mechanical loading in bone fracture healing, bone regeneration, and vascularization. J Tissue Eng., 14 , 20417314231172572. https://doi.org/10.1177/20417314231172573
Ghiasi, M. S., Chen, J., Vaziri, A., Rodriguez, E. K., & Nazarian, A. (2017). Bone fracture healing in mechanobiological modeling: A review of principles and methods. Bone Rep., 6 , 87–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bonr.2017.03.002
Marmor, M. T., Grimm, B., Hanflik, A. M., Richter, P. H., Sivananthan, S., Yarboro, S. R., & Braun, B. J. (2022). Use of wearable technology to measure activity in orthopaedic trauma patients: A systematic review. Indian J Orthop., 56 (7), 1112–1122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-022-00629-0
Kumar, Y., Koul, A., Singla, R., & Ijaz, M. F. (2023). Artificial intelligence in disease diagnosis: A systematic literature review, synthesizing framework and future research agenda. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 14 (7), 8459–8486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03612-z
Griffin, X. L., Parsons, N., Costa, M. L., & Metcalfe, D. (2014). Ultrasound and shockwave therapy for acute fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Systematic Review, 2014 (6), CD008579. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD008579.
Sansone, V., Ravier, D., Pascale, V., Applefield, R., Del Fabbro, M., & Martinelli, N. (2022). Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in the treatment of nonunion in long bones: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11 (7), 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071977
Download references
No funding in any form was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Orthopaedics and Joint Replacement Surgery, Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, Sarita Vihar, New Delhi, 110076, India
Raju Vaishya
Retired Scientist, CSIR-NISTADS, Pusa, New Delhi, 110012, India
Brij Mohan Gupta
Department of Library and Information Science, Yenepoya (Deemed to Be University), Deralakatte, Mangalore, 575018, Karnataka, India
Ghouse Modin N. Mamdapur
Department of Orthopaedics, Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi, 110076, India
Abhishek Vaish
Department of Orthopaedics, Paras HMRI Hospital, Patna, India
Janki Sharan Bhadani
Department of Orthopaedics Paras, HMRI Hospital, Patna, India
John Mukhopadhaya
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
RV: Conceptualization, Literature Search and Analysis, Manuscript writing, editing and final approval. BMG: Conceptualization, Data Curation and Analysis, Literature Search, Manuscript writing, editing and final approval. GMNM: Data Curation and Analysis, Literature Search, Manuscript writing, editing and final approval. AV: Literature Search and Analysis, Manuscript writing, editing and final approval. JSB: Literature Search and Analysis, Manuscript writing, editing and final approval. JM: Literature Search and Analysis, Manuscript writing, editing and final approval.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Raju Vaishya .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The paper is a review article so no ethical approval is required.
Informed consent
For this type of study informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 418 KB)
Rights and permissions.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Vaishya, R., Gupta, B.M., Mamdapur, G.M.N. et al. Highly-Cited Papers on Fracture Non-union – A Bibliometric Analysis of the Global Literature (1990–2023). JOIO (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-024-01176-6
Download citation
Received : 04 April 2024
Accepted : 30 April 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-024-01176-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bibliometrics
- Epidemiology
- Highly cited papers
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Global Site
Breadcrumb navigation
Internship experience interview report: akira nakashima.
April 2, 2024
Evolving From an Internship to Joint Research Between NEC and University Laboratories

Researcher, Secure System Platform Research Laboratories Akira Nakashima
Nakashima joined NEC after completing his master's degree in 2023. He has been involved in cryptography research since his students days and is currently conducting research in the data security field with a focus on secure computation.
Participating in an internship for his studies with no thought of finding a job
I first learned about the NEC internship through an announcement on a university mailing list around May during the first year of my master's degree. The announcement was framed as a research internship opportunity for students in homomorphic encryption, which is my major. So, I thought that I might learn something since that is my major, and I applied for the internship. At the time, I wasn't even thinking about finding a job, so to be honest, I only applied for the sake of my own research. In particular, NEC has many researchers who are internationally active in the cryptography field. I recall that when I consulted with my academic adviser, he told me, "I think that you can learn a lot at NEC's research laboratory" and recommended that I participate in the internship. At the time, I was living in Kyushu and participated remotely in the internship. However, that was in the summer of 2021, right when the Tokyo Olympics were being held. It was a time when the number of people infected with COVID-19 was increasing. Initially, I planned to visit the research laboratory at the beginning and end of my internship, but in light of the situation at that time, I shifted to a fully remote arrangement with my PC being delivered and returned by home delivery service. The employment interviews and presentation of the employment offer were also held online, so I only set foot inside NEC after I joined the company. That being said, during the internship period NEC provided a mentor, established online opportunities to consult and report on my progress once every two days, and I was connected via chat at all times, so I did not feel like I was being left alone. NEC also established time for one-on-one chats with the team members during the internship period. Of course, I am no longer working only remotely but also reporting to the office to work face to face. In fact, it seems many of the students who interned this year were working in-house. I think that is a more stimulating environment.
Feeling enjoyment and a sense of purpose during his first full-scale implementation

The overall theme of the internship is presented during the recruiting process, but the specific details of the work are determined in consultation with your supervisor and mentor in light of the situation where you are assigned as well as your own interests and skills. In my case, I mainly focused on the implementation of cryptography. In addition, I also investigated encryption methods, held seminar-format study sessions, and conducted improvement studies. In the study sessions, I summarized the encryption method algorithms and other information that I investigated on slides, gave a presentation to the team members, received suggestions, and engaged in a question and answer session to jointly think about ways to improve the algorithms. This led to a lively discussion and created a very stimulating forum. During the implementation, I worked on the development of homomorphic encryption (encryption method which can perform computation with data in an encrypted form). I had never really carried out a full-scale implementation at university, so it was a really fresh experience for me. When trying to implement cryptography in a practical way, there are various aspects that you must pay attention to. For example, when generating a random number, you cannot use the kind of algorithm that is implemented in a game, etc. because you have to use something which is properly secured. I majored in mathematics during my undergraduate days and was a novice when I started doing cryptography for real with my master's degree, so I had not even mastered such basic rules and only learned about them when a team member pointed them out to me. In addition, the pursuit of practical speed also became an important point. Naturally, the goal in corporate research is to tie it to productization and business. The discussion unfolds such that one might say, "If you are going to use it for this solution, then this encryption method is probably better" or conversely, "This method is unsuited to this authentication, so we should do it a different way." This kind of discussion which places social implementation as the goal was very stimulating. I was able to come to the realization that technologies that I thought up or implemented could benefit society and people, which was a lot of fun. Of course, that feeling remains unchanged to this day.

An introduction to Nakashima's daily schedule during his internship
Evolving from research conducted during his internship to co-authoring research papers presented at top international conferences.
In my case, the research activities into cryptography that I worked on during my internship continued even after the internship period ended. The university research laboratory entered into a full-scale collaboration with NEC to conduct joint research. As a result, a research paper summarizing this work was successfully published by ESORICS '23, a top cryptography related international conference, and I was able to list my name as a co-author. (Note 1) My senior colleagues are heading to the conference site to give an oral presentation. In this way, it is not unusual for research conducted during an NEC internship to lead to presentations at an academic conference. This year as well, results produced by students during their internship period were presented at an academic conference in Japan with the students' names listed as co-authors. Moreover, even if the research content does not tie into results in academia, what you learn in the internship will nourish your own research. I myself was able to acquire knowledge about cryptographic technology through my NEC internship, which I believe helped me to grow. In fact, the research paper that I presented during the second year of my master's degree won a research paper award at the SCIS conference in Japan. (Note 2) The award ceremony was held in January of this year. I believe that the NEC internship was a good opportunity to broaden and deepen the scope of my own research. After finishing my internship, I discovered that the recruiting process had started and immediately applied. For my interview, I created materials and gave a presentation on "what I would like to achieve after joining NEC." The selection process advanced very quickly, and they extended an offer, so I decided to directly join NEC. The internship was a lot of fun, and the team members were all very kind and nice, so I considered myself lucky to be able to join NEC. There are many NEC researchers that I hold in high regard. There are some who have been active in academia as researchers and produced results for many years while others excel at coordinating with others and promoting co-creation as business people. I am very grateful to be able to work in such an extremely inspiring workplace.

- ※ The information posted on this website is the information at the time of publication.
- Find My Rep
You are here
International Studies
Preview this book
- Description
- Aims and Scope
- Editorial Board
- Abstracting / Indexing
- Submission Guidelines
International Studies is a peer-reviewed journal that is committed to exploring and understanding Indian foreign policy, the theory and practice of non-alignment and the developmental and security problems of Third World countries.
This scholarly journal publishes original research articles on a wide range of issues and problems of contemporary relevance in the broad field of international studies. The journal provides insights in international politics and organization, international economics, defence and strategic studies, political geography and international law. This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) .
Electronic Access :
International Studies is available electronically on SAGE Journals Online at http://journals.sagepub.com/home/ISQ
International Studies, a peer reviewed scholarly journal, publishes original theoretical and empirical research articles of contemporary relevance in the field of International Relations, Area Studies and allied subjects. This scholarly journal encourages exploration and critical evaluation of new ideas in the field. It is a quarterly journal of the School of International Studies, Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi, but the views contained therein are those of the individual authors and not necessarily those of the University.
- Indian Citation Index (ICI)
- Pro-Quest-RSP
- ProQuest-Illustrata
- ProQuest: International Bibliography of the Social Sciences (IBSS)
- UGC-CARE (GROUP I)
This Journal is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics
International Studies is hosted on Sage Peer Review, a web-based online submission and peer review system. Please read the Manuscript Submission Guidelines below, and then visit https://peerreview.sagepub.com/isq to login and submit your article online. Remember you can log in to the submission site at any time to check on the progress of your paper through the peer review process.
Only manuscripts of sufficient quality that meet the aims and scope of International Studies will be reviewed.
There are no fees payable to submit or publish in this Journal. Open Access options are available - see section 3.3 below.
As part of the submission process you will be required to warrant that you are submitting your original work, that you have the rights in the work, and that you have obtained and can supply all necessary permissions for the reproduction of any copyright works not owned by you, that you are submitting the work for first publication in the Journal and that it is not being considered for publication elsewhere and has not already been published elsewhere. Please see our guidelines on prior publication and note that International Studies will consider submissions of papers that have been posted on preprint servers; please alert the Editorial Office when submitting (contact details are at the end of these guidelines) and include the DOI for the preprint in the designated field in the manuscript submission system. Authors should not post an updated version of their paper on the preprint server while it is being peer reviewed for possible publication in the Journal. If the article is accepted for publication, the author may re-use their work according to the Journal's author archiving policy.
If your paper is accepted, you must include a link on your preprint to the final version of your paper.
If you have any questions about publishing with Sage, please visit the Sage Journal Solutions Portal
1. What do we publish?
1.1 Aims & Scope 1.2 Article types 1.3 Writing your paper
2. Editorial policies
2.1 Peer review policy 2.2 Authorship 2.3 Acknowledgements 2.4 Funding 2.5 Declaration of conflicting interests 2.6 Research data
3. Publishing Policies
3.1 Publication ethics 3.2 Contributor’s publishing agreement 3.3 Open access and author archiving
4. Preparing your manuscript
4.1 Formatting 4.2 Artwork, figures and other graphics 4.3 Supplemental material 4.4 Reference style
5. Submitting your manuscript
5.1 ORCID 5.2 Information required for completing your submission 5.3 Permissions
6. On acceptance and publication
6.1 Sage Production 6.2 Online First publication 6.3 Access to your published article 6.4 Promoting your article
7. Further information
1.1 Aims & Scope
Before submitting your manuscript to International Studies , please ensure you have read the Aims & Scope [link to A&S].
1.2 Article types
This scholarly journal publishes original research articles on a wide range of issues and problems of contemporary relevance in the broad field of international studies. The journal provides insights in international politics and organization, international economics, defence and strategic studies, political geography and international law. Area studies research papers having global relevance are also published. Alternative approaches and perspectives from the global south are encouraged.
1.3 Writing your paper
The Sage Author Gateway has some general advice on how to get published , plus links to further resources.
1.3.1 Make your article discoverable For information and guidance on how to make your article more discoverable, visit our Gateway page on How to Help Readers Find Your Article Online
Return to Top
2.1 Peer review policy
International Studies adheres to a rigorous double-anonymize reviewing policy in which the identity of both the reviewer and author are always concealed from both parties.
International Studies is committed to delivering high quality, fast peer-review for your paper, and as such has partnered with Publons. Publons is a third party service that seeks to track, verify and give credit for peer review. Reviewers for International Studies can opt in to Publons in order to claim their reviews or have them automatically verified and added to their reviewer profile. Reviewers claiming credit for their review will be associated with the relevant journal, but the article name, reviewer’s decision and the content of their review is not published on the site. For more information visit the Publons website.
The Editor or members of the Editorial Board may occasionally submit their own manuscripts for possible publication in the Journal. In these cases, the peer review process will be managed by alternative members of the Board and the submitting Editor/Board member will have no involvement in the decision-making process.
2.2 Authorship
All parties who have made a substantive contribution to the article should be listed as authors. Principal authorship, authorship order, and other publication credits should be based on the relative scientific or professional contributions of the individuals involved, regardless of their status. A student is usually listed as principal author on any multiple-authored publication that substantially derives from the student’s dissertation or thesis.
Please note that AI chatbots, for example ChatGPT, should not be listed as authors. For more information see the policy on Use of ChatGPT and generative AI tools .
If the named authors for a manuscript change at any point between submission and acceptance , an Authorship Change Form must be completed and digitally signed by all authors (including any added or removed) . An addition of an author is only permitted following feedback raised during peer review. Completed forms can be uploaded at Revision Submission stage or emailed to the Journal Editorial Office contact (listed on the journal’s manuscript submission guidelines). All requests will be moderated by the Editor and/or Sage staff.
Important: Changes to the author by-line by adding or deleting authors are NOT permitted following acceptance of a paper .
2.3 Acknowledgements
All contributors who do not meet the criteria for authorship should be listed in an Acknowledgements section. Examples of those who might be acknowledged include a person who provided purely technical help, or a department chair who provided only general support.
Please supply any personal acknowledgements separately to the main text to facilitate anonymous peer review.
2.3.1 Writing assistance Individuals who provided writing assistance, e.g. from a specialist communications company, do not qualify as authors and so should be included in the Acknowledgements section. Authors must disclose any writing assistance – including the individual’s name, company and level of input – and identify the entity that paid for this assistance. It is not necessary to disclose use of language polishing services.
2.4 Funding
International Studies requires all authors to acknowledge their funding in a consistent fashion under a separate heading. Please visit the Funding Acknowledgements page on the Sage Journal Author Gateway to confirm the format of the acknowledgment text in the event of funding, or state that: This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
2.5 Declaration of conflicting interests
International Studies encourages authors to include a declaration of any conflicting interests and recommends you review the good practice guidelines on the Sage Journal Author Gateway
2.6 Research data
The journal is committed to facilitating openness, transparency and reproducibility of research, and has the following research data sharing policy. For more information, including FAQs please visit the Sage Research Data policy pages .
Subject to appropriate ethical and legal considerations, authors are encouraged to:
- share your research data in a relevant public data repository
- include a data availability statement linking to your data. If it is not possible to share your data, we encourage you to consider using the statement to explain why it cannot be shared.
- cite this data in your research
3.1 Publication ethics
Sage is committed to upholding the integrity of the academic record. We encourage authors to refer to the Committee on Publication Ethics’ International Standards for Authors and view the Publication Ethics page on the Sage Author Gateway
3.1.1 Plagiarism International Studies and Sage take issues of copyright infringement, plagiarism or other breaches of best practice in publication very seriously. We seek to protect the rights of our authors and we always investigate claims of plagiarism or misuse of published articles. Equally, we seek to protect the reputation of the Journal against malpractice. Submitted articles may be checked with duplication-checking software. Where an article, for example, is found to have plagiarized other work or included third-party copyright material without permission or with insufficient acknowledgement, or where the authorship of the article is contested, we reserve the right to take action including, but not limited to: publishing an erratum or corrigendum (correction); retracting the article; taking up the matter with the head of department or dean of the author's institution and/or relevant academic bodies or societies; or taking appropriate legal action.
3.1.2 Prior publication If material has been previously published it is not generally acceptable for publication in a Sage journal. However, there are certain circumstances where previously published material can be considered for publication. Please refer to the guidance on the Sage Author Gateway or if in doubt, contact the Editor at the address given below.
3.2 Contributor’s publishing agreement
Before publication, Sage requires the author as the rights holder to sign a Journal Contributor’s Publishing Agreement. Sage’s Journal Contributor’s Publishing Agreement is an exclusive licence agreement which means that the author retains copyright in the work but grants Sage the sole and exclusive right and licence to publish for the full legal term of copyright. Exceptions may exist where an assignment of copyright is required or preferred by a proprietor other than Sage. In this case copyright in the work will be assigned from the author to the society. For more information please visit the Sage Author Gateway
3.3 Open access and author archiving
International Studies offers optional open access publishing via the Sage Choice programme and Open Access agreements, where authors can publish open access either discounted or free of charge depending on the agreement with Sage. Find out if your institution is participating by visiting Open Access Agreements at Sage . For more information on Open Access publishing options at Sage please visit Sage Open Access . For information on funding body compliance, and depositing your article in repositories, please visit Sage’s Author Archiving and Re-Use Guidelines and Publishing Policies .
4. Preparing your manuscript for submission
4.1 Formatting
The preferred format for your manuscript is Word. LaTeX files are also accepted. A LaTex template is available on the Manuscript Submission Guidelines page of our Author Gateway.
Although there is no word limit, the authors are advised to submit articles between 5000 and 10,000 words; and book reviews between 1200 and 1800 words. Sharp commentaries of about 3000 words on current themes are also accepted.
The manuscript must include the following:
- Title of the paper, name of author, author’s affiliation and institutional address with pin code, email id and abstract of not more than 200 words. In case there are two or more authors, then corresponding author’s name and postal address details must be clearly specified.
- The contributors should provide 4–6 keywords for online searchability.
- All articles must be accompanied by 4–6 keywords and an abstract of 150–200 words. Notes should be numbered serially and presented at the end of the article. Notes must contain more than a mere reference.
- British spellings throughout (‘labour’ not ‘labor’, ‘centre’ not ‘center’); universal ‘z’ in ‘-ize’ and ‘-ization’ words.
- Use single quotes throughout. Double quotes only to be used within single quotes. Spellings of words in quotations should not be changed. Quotations of 45 words or more should be separated from the text and indented with one space with a line space above and below.
- Use ‘19th century’, ‘1980s’. Spell out numbers from one to nine, 10 and above to remain in figures. However, for exact measurements, use only figures (3 km, 9 percent, not %). Use thousands and millions, not lakhs and crores. Avoid saying ‘recently’ but rather give the year.
4.2 Artwork, figures and other graphics
For guidance on the preparation of illustrations, pictures and graphs in electronic format, please visit Sage’s Manuscript Submission Guidelines
- Figures, including maps, graphs and drawings, should not be larger than page size. They should be numbered and arranged as per their references in the text. All photographs and scanned images should have a resolution of minimum 300 dpi and 1,500 pixels and their format should be TIFF or JPEG.
- Due permissions should be taken for copyright protected photographs/images. Even for photographs/images available in the public domain, it should be clearly ascertained whether or not their reproduction requires permission for purposes of publishing (which is a profit-making endeavour).
- All photographs/scanned images should be provided separately in a folder along with the main article.
Please Note: All figures and tables should be cited in the text and should have the source (a specific URL, a reference or, if it is author’s own work, ‘The Author’) mentioned irrespective of whether or not they require permissions
Figures supplied in colour will appear in colour online regardless of whether or not these illustrations are reproduced in colour in the printed version. For specifically requested colour reproduction in print, you will receive information regarding the costs from Sage after receipt of your accepted article.
4.3 Supplemental material
This Journal is able to host additional materials online (e.g. datasets, podcasts, videos, images etc) alongside the full-text of the article. For more information please refer to our guidelines on submitting supplemental files
4.4 Reference style
International Studies adheres to the APA reference style. View the APA guidelines to ensure your manuscript conforms to this reference style.
There is no limit on the number of references allowed.
International Studies is hosted on Sage Peer Review, a web based online submission and peer review system. Please read the manuscript submission guidelines, and then visit https://peerreview.sagepub.com/isq to login and submit your article online.
IMPORTANT: Please check whether you already have an account in the system before trying to create a new one. If you have reviewed or authored for the journal in the past year it is likely that you will have had an account created.
As part of our commitment to ensuring an ethical, transparent and fair peer review process Sage is a supporting member of ORCID, the Open Researcher and Contributor ID . ORCID provides a unique and persistent digital identifier that distinguishes researchers from every other researcher, even those who share the same name, and, through integration in key research workflows such as manuscript and grant submission, supports automated linkages between researchers and their professional activities, ensuring that their work is recognized.
The collection of ORCID IDs from corresponding authors is now part of the submission process of this Journal. If you already have an ORCID ID you will be asked to associate that to your submission during the online submission process. We also strongly encourage all co-authors to link their ORCID ID to their accounts in our online peer review platforms. It takes seconds to do: click the link when prompted, sign into your ORCID account and our systems are automatically updated. Your ORCID ID will become part of your accepted publication’s metadata, making your work attributable to you and only you. Your ORCID ID is published with your article so that fellow researchers reading your work can link to your ORCID profile and from there link to your other publications.
If you do not already have an ORCID ID please follow this link to create one or visit our ORCID homepage to learn more.
5.2 Information required for completing your submission
You will be asked to provide contact details and academic affiliations for all co-authors via the submission system and identify who is to be the corresponding author. These details must match what appears on your manuscript. The affiliation listed in the manuscript should be the institution where the research was conducted. If an author has moved to a new institution since completing the research, the new affiliation can be included in a manuscript note at the end of the paper. At this stage please ensure you have included all the required statements and declarations and uploaded any additional supplementary files (including reporting guidelines where relevant).
5.3 Permissions
Please also ensure that you have obtained any necessary permission from copyright holders for reproducing any illustrations, tables, figures or lengthy quotations previously published elsewhere. For further information including guidance on fair dealing for criticism and review, please see the Copyright and Permissions page on the Sage Author Gateway
6.1 Sage Production
Your Sage Production Editor will keep you informed as to your article’s progress throughout the production process. Proofs will be made available to the corresponding author via email, and corrections should be made directly or notified to us promptly. Authors are reminded to check their proofs carefully to confirm that all author information, including names, affiliations, sequence and contact details are correct, and that Funding and Conflict of Interest statements, if any, are accurate.
6.2 Online First publication
Online First allows final articles (completed and approved articles awaiting assignment to a future issue) to be published online prior to their inclusion in a journal issue, which significantly reduces the lead time between submission and publication. Visit the Sage Journals help page for more details, including how to cite Online First articles.
6.3 Access to your published article
Sage provides authors with online access to their final article.
6.4 Promoting your article
Publication is not the end of the process! You can help disseminate your paper and ensure it is as widely read and cited as possible. The Sage Author Gateway has numerous resources to help you promote your work. Visit the Promote Your Article page on the Gateway for tips and advice.
Manuscripts and all editorial correspondence should be addressed to the journal administrator at https://peerreview.sagepub.com/isq
- Read Online
- Sample Issues
- Current Issue
- Email Alert
- Permissions
- Foreign rights
- Reprints and sponsorship
- Advertising
Subscription Information
South Asia includes Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka and the Maldives
To subscribe to this journal or to purchase single/back issues, please contact Customer Service - Journals: [email protected] +91 (11) 4063 9222 extn 406
To purchase bundled content, backfiles or any other electronic products, please contact: [email protected]
For exciting offers and deals, write to: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The International Studies Review ( ISR) is a journal of the International Studies Association. It provides a window on current trends and research in international studies worldwide. Find out more. The ISR Podcast is the official podcast of International Studies Review, the flagship review journal of the International Studies Association.
International Studies, a peer reviewed scholarly journal, publishes original theoretical and empirical research articles of contemporary relevance in the field of International Relations, Area Studies and allied subjects. This scholarly journal encourages … | View full journal description. This journal is a member of the Committee on ...
About the journal. International Studies Quarterly ( ISQ) is the flagship journal of the International Studies Association. It seeks to publish leading scholarship that engages with significant theoretical, empirical, and normative subjects in international studies. Find out more. Words, Images, Enemies: Securitization and International Politics.
Review of International Studies (RIS) publishes high-quality research that makes significant contributions to conversations about global politics, broadly defined. We encourage submissions that are attentive to historical and contemporary dynamics of global politics and their effects. We welcome theoretically informed, empirically rich, and ...
An official journal of the International Studies Association. Publishes papers on policy research and commentary, pedagogical analyses, visions of the Discipline, and pieces of interest to the international studies profession.
International Studies: how to write your thesis. This Subject Guide is designed to support students of International Studies with writing their BA thesis and research papers. This guide focuses on the research process, and suggests effective ways to: 1. find a topic and formulate a good research question; 2. search, find and evaluate literature ...
The journal provides insights in international politics and organization, international economics, defence and strategic studies, political geography and international law. Area studies research papers having global relevance are also published. Alternative approaches and perspectives from the global south are encouraged. 1.3 Writing your paper
ISA Publications. ISA proudly publishes seven journals (FPA, GSQ, JoGSS, IPS, ISP, ISQ, and ISR), co-sponsors an eighth (II), and partners with Oxford University Press to publish the Encyclopedia of International Studies (OREIS). Our latest publication, Global Studies Quarterly, is ISA's newest open access peer-reviewed journal.
Center for Strategic and International Studies 1616 Rhode Island Avenue, NW Washington, DC 20036. Tel: 202.887.0200 Fax: 202.775.3199
The Components of a Research Paper 228 Writing Up Your Research: Getting Started 237 Writing Tips and Strategies 238 Writing Up Your Research: Wrapping Up 240 ... Edinburgh (2005) and a BA in International Studies from the University of Mississippi. Previously, Dr Lamont was Assistant Professor of International Relations at the University of ...
International collaborative research involves cross-country teams that share research interests, conduct research, and promote research results to advance knowledge and promote positive shifts in practice. A rigorous cross-national study can bring many benefits to a particular research field, including more significant impact and broader ...
Global higher education studies, and research on international mobility in higher education, have each emerged out of the more extensive and intensive cross-border activity of the last three decades. ... Four explicitly reference the 'glonacal' paper by Marginson and Rhoades (Citation 2002) which theorises a geo-spatiality both multiple and ...
The International Studies Association. Representing 100 countries, ISA has over 6,500 members worldwide and is the most respected and widely known scholarly association in this field. Endeavoring to create communities of scholars dedicated to international studies, ISA is divided into 7 geographic subdivisions of ISA (Regions), 29 thematic ...
This paper profiles Saudi Arabia in terms of its government and political administration, economics, traditions, and other factors important for its business climate. While Saudi Arabia's economy is based on oil and oil-related products,... more. Download. by Andrew Bertsch. International Studies.
International Studies Review provides a window on current trends and research in international studies worldwide. To highlight the impact of the journal, we have organized a collection of some of the most read, most cited, and most discussed articles from recent years. The articles are freely available through December 31, 2021.
As the discipline of International Studies is highly unique in the sense that it lends itself to many perspectives (historical, anthropological, political, etc.), the writing assignment topics and prompts require careful planning. ... Research papers. Research papers require a significant amount of time outside of writing the paper to do ...
In educational research, important studies have highlighted how international students grapple with new learning environments and how they manage the challenges associated with living abroad (Arkoudis & Tran, 2007, 2010; Baas, 2014). These studies are effective for showing the diversity of the international students, the various factors which ...
Data transparency is fundamental to scholarly research. Beugelsdijk, van Witteloostuijn, and Meyer (2020: 887) define data transparency in quantitative empirical studies, including hypothesis-testing studies, "as comprised of an easy-to-follow explanation of the way in which data are generated or collected and also of the procedures used to reach conclusions."
The International Journal of Educational Research publishes research papers in the field of Education. Papers published in IJER address themes of major interest to researchers, practitioners, and policy makers working in different international contexts. Work must be of a quality and context that …. View full aims & scope.
The annual output of all other journals was, on average, less than five articles in almost all years from 1990 through 2022 except the years 2012 for Journal of Studies in International Education (N = 6), 2022 for Frontiers in Psychology (N = 10), and nearly all years for International Journal of Intercultural Relations which retook the top ...
Data and Methodology. Bibliometric analysis is a quantitative method to investigate intellectual structures of topical field. On the basis of co-citation assumption that if two articles are usually cited together, then there are high associations between those articles, bibliometric analysis can reflect the scientific communicational structures holistically (Garfield, 1979; Chen et al., 2012).
Background and aim: Research on international students conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic has persistently highlighted the vulnerabilities and challenges that they experienced when staying in the host country to continue with their studies. The findings from such research can inevitably create a negative image of international students and their ability to respond to challenges during ...
The journal provides insights in international politics and organization, international economics, defence and strategic studies, political geography and international law. Area studies research papers having global relevance are also published. Alternative approaches and perspectives from the global south are encouraged. 1.3 Writing your paper
The International Journal of Consumer Studies is a leading international consumer research journal. ... and Methodology (TCCM) framework, we systematically analyzed 79 identified papers using the Scientific Procedures and Rationales for Systematic Literature Reviews (SPAR-4-SLR) protocol. The findings highlight the multifaceted factors shaping ...
Research on the international entrepreneurial behavior of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) originating from Africa has been receiving growing scholarly attention. Despite a proliferation of studies on the subject, the literature has hitherto remained fragmented, theoretically limited, and empirically inconclusive, thereby leaving important topics underexplored. This paper seeks to ...
Voices in Bioethics is currently seeking submissions on philosophical and practical topics, both current and timeless. Papers addressing access to healthcare, the bioethical implications of recent Supreme Court rulings, environmental ethics, data privacy, cybersecurity, law and bioethics, economics and bioethics, reproductive ethics, research ethics, and pediatric bioethics are sought.
International Journal of Cultural Studies is a fully peer-reviewed journal and a leading venue for scholarship committed to rethinking cultural practices, processes, texts and infrastructures beyond traditional national frameworks and regional biases. Established to revitalize cultural studies against the dangers of parochialism and intellectual ossification, the journal interrogates what ...
Objective The growing interest in this field of fracture nonunion has been informally acknowledged through published studies. A bibliometric analysis was conducted to objectively outline the patterns in published clinical research concerning nonunion fractures by utilizing highly cited papers (HCPs). Methods Through a predetermined search strategy, we gathered literature on the clinical ...
The university research laboratory entered into a full-scale collaboration with NEC to conduct joint research. As a result, a research paper summarizing this work was successfully published by ESORICS '23, a top cryptography related international conference, and I was able to list my name as a co-author.
The journal provides insights in international politics and organization, international economics, defence and strategic studies, political geography and international law. Area studies research papers having global relevance are also published. Alternative approaches and perspectives from the global south are encouraged. 1.3 Writing your paper