- Click here - to use the wp menu builder

- Privacy Policy
- Refund Policy
- Terms Of Service
- Nursing notes PDF
- Nursing Foundations
- Medical Surgical Nursing
- Maternal Nursing
- Pediatric Nursing
- Behavioural sciences
- BSC NURSING
- GNM NURSING
- MSC NURSING
- PC BSC NURSING
- HPSSB AND HPSSC
- Nursing Assignment

The 10 Importance of Health Education
Importance of Health Education – Health education is important for individuals, families, and communities. It can help people learn about their health, make healthy choices, and reduce their risk of disease. Health education plays a crucial role in improving individual and community well-being. It encompasses the dissemination of knowledge and information to promote healthy lifestyles, prevent diseases, and enhance the overall quality of life. Here are 10 importance of health education.
Table of Contents
What is Health Education and Why is it important?
Health education is the process of providing knowledge and skills to promote good health. It’s important because it empowers individuals to prevent illness, adopt healthy behaviors, and make informed decisions about their well-being. It covers various topics, from disease prevention to mental health awareness, and helps create healthier communities while reducing healthcare costs.
Benefits of Health Education
When you embrace health education, you open the door to a host of benefits. First and foremost, it enhances your understanding of your body and mind. You’ll learn how to identify warning signs, spot the red flags, and take action before issues escalate. Moreover, it’s the secret to a longer, happier life. With the right knowledge, you can reduce the risk of chronic diseases, live with vitality, and enjoy your golden years to the fullest.
Definition of health education
Health education is the process of imparting knowledge and skills related to health and well-being. It aims to empower individuals with the information they need to make informed decisions about their health and adopt positive behaviors that contribute to overall wellness.
Here are 10 importance of health education:
Promotes Disease Prevention
One of the primary objectives of health education is to prevent diseases. By educating people about healthy practices, such as maintaining proper hygiene, exercising regularly, and having a balanced diet , health education can significantly reduce the risk of various illnesses and health conditions.
Empowers Individuals to Make Informed Decisions
Informed decision-making is vital for personal health management. Health education equips individuals with the necessary knowledge to assess health-related choices critically. This empowers them to make informed decisions about medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and preventive measures.
Encourages Healthy Behaviors
Health education inspires the adoption of healthy behaviors. When people are aware of the benefits of good habits like regular exercise, avoiding smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption, they are more likely to embrace these positive changes for a healthier life.
Reduces Healthcare Costs
Preventive measures encouraged through health education can lead to a significant reduction in healthcare costs. By preventing diseases and promoting healthier lifestyles, the burden on healthcare systems decreases, allowing resources to be allocated more efficiently.
Fosters a Healthier Society
A society that prioritizes health education experiences improved overall well-being. It creates a community that supports and encourages healthy choices, leading to a positive and productive environment for everyone.
Addresses Mental Health and Well-being
Health education isn’t limited to physical health; it also encompasses mental health. By promoting awareness about mental health issues and providing support systems, health education contributes to reducing the stigma surrounding mental health and improving overall well-being.
Improves the Quality of Life
When individuals take charge of their health through education and informed decision-making, they experience an enhanced quality of life. Good health positively impacts various aspects of life, including relationships, careers, and overall happiness.
Health Education in Schools and Communities
Schools and communities play a pivotal role in promoting health education . Integrating health education into school curriculums and community programs ensures that individuals receive the necessary information from an early age, establishing a foundation for lifelong healthy habits.
Health Education for a Sustainable Future
Health education is vital for creating a sustainable future. By raising awareness about environmental issues, healthy living, and responsible consumption, health education contributes to a greener, more sustainable planet.
10 importance of health education in schools
Health education in schools plays a crucial role in promoting overall well-being and empowering students to make informed decisions about their health. Here are ten important reasons why health education in schools is essential:
- Promotes Healthy Behavior: Health education equips students with knowledge about nutrition, physical activity, and hygiene, encouraging them to adopt healthy lifestyle choices.
- Disease Prevention: It educates students about common diseases, their causes, and prevention strategies, reducing the risk of illness.
- Sexual Education: Provides essential information about sexual health, safe practices, and contraceptive methods to reduce the risk of unwanted pregnancies and sexually transmitted infections.
- Mental Health Awareness: Helps students recognize signs of mental health issues, reducing stigma, and encouraging seeking help when needed.
- Substance Abuse Prevention: Teaches about the dangers of drug and alcohol abuse, promoting responsible behavior and addiction prevention.
- Healthy Relationships: Educates students about healthy communication, consent, and building positive relationships while preventing abusive behavior.
- Safety Awareness: Teaches safety measures, first aid, and emergency response, ensuring students are prepared for unexpected situations.
- Nutrition and Diet: Provides knowledge about balanced diets, portion control, and food choices, reducing the risk of obesity and related health issues.
- Stress Management: Equips students with coping strategies for stress, anxiety, and emotional challenges, promoting mental resilience.
- Lifelong Skills: Imparts life skills such as decision-making, problem-solving, and critical thinking, which are essential for making informed health choices throughout life.
Aims and objectives of health education
The aims and objectives of health education are to:
- Increase health knowledge: Understand the body, its functioning, and how to maintain good health.
- Encourage healthy behaviors: Adopt a balanced diet, regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Prevent diseases: Learn about specific risk factors and modify your lifestyle accordingly.
- Promote self-care: Equip individuals to manage their health and access necessary healthcare services.
- Empower individuals: Teach patients’ rights and self-advocacy for better health outcomes.
- Create supportive environments: Advocate for policies promoting healthy living, including nutritious food and physical activity.
The Purpose of Health Education in Nursing
Health education is a crucial component of nursing practice. It is the process of providing patients and communities with the knowledge, skills, and support they need to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Health education in nursing plays a number of important roles, including:
- Promoting health and preventing illness. Health education empowers individuals to adopt healthy behaviors, make lifestyle changes, and take preventive measures to avoid illness and disease. By providing information about risk factors and healthy habits, nurses can help people lead healthier lives.
- Enhancing patient understanding. Nurses educate patients about their medical conditions, treatment options, and medications. This helps patients understand their health conditions better, adhere to prescribed treatments, and actively participate in their care.
- Improving self-management. For patients with chronic illnesses, health education equips them with the skills needed to manage their conditions effectively. This may include teaching them about symptom management, monitoring techniques, and when to seek medical help.
- Empowering patients. Health education empowers patients to take charge of their own health. Nurses provide them with knowledge and tools to make informed decisions, enabling them to be active partners in their healthcare journey.
- Supporting healthy lifestyles. Nurses promote healthy habits, such as proper nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep. By educating patients about these lifestyle factors, nurses encourage the prevention of chronic diseases and overall well-being.
- Addressing health disparities. Health education can target specific populations or communities that may face health disparities. By tailoring education to their unique needs, nurses can work towards reducing health inequalities.
- Community health promotion. Nurses engage in health education at the community level to address public health concerns, raise awareness about prevalent health issues, and promote health initiatives that benefit the entire community.
- Facilitating recovery and rehabilitation. Health education supports patients during the recovery and rehabilitation process, helping them understand post-treatment care, medications, and lifestyle adjustments to optimize their recovery outcomes.
Conclusion -Importance of Health Education
In conclusion, health education is an indispensable aspect of our society. By promoting disease prevention, empowering individuals to make informed decisions, and encouraging healthy behaviors, health education significantly improves individual and community well-being. It addresses physical and mental health, reduces healthcare costs, and fosters a healthier and more sustainable future.
FAQs -Importance of Health Education
What is health education.
Health education is the process of imparting knowledge and skills related to health and well-being to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
How does health education promote disease prevention?
Health education disseminates information about healthy practices, which helps in reducing the risk of various diseases and health conditions.
Why is health education crucial in schools and communities?
Integrating health education in schools and communities ensures that individuals receive the necessary information from an early age, establishing a foundation for lifelong healthy habits.
Please note that this article is for informational purposes only and should not substitute professional medical advice.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Recent articles, understanding the duration of stages of labor, disorders of menstruation causes, symptoms, and treatments, top 11 study tips for nursing students, nursing management of premature baby, fundamentals of nursing care, leadership in nursing and its qualities, download nursing notes pdf, reproductive system nursing notes pdf, study material nurse recruitment exam solved paper pdf – ii, pdf note medical surgical nursing, obstetrics & gynaecology pdf notes, human body digestive system bsc nursing notes pdf, psychology note nursing pdf, sensory system and sense organs pdf, human skeletal system nursing, more like this, gifts for nursing home residents, gift ideas for nursing students, crystalloid and colloid: differences and when to use each, how to insert a catheter in a female patient -female catheterization, mental health nursing diagnosis care plan pdf, child pediatric health nursing notes -bsc nursing, mid-wifery pdf notes for nursing students, national health programmes in india pdf, primary health care nursing notes pdf, nursingenotes.com.
- STUDY NOTES
- SUBJECT NOTES
A Digital Platform For Nursing Study Materials
Latest Articles
Most popular.
© Nursingenotes.com | All rights reserved |
The Big Role of Nurses in Health Education Essay
Nurses not only dedicate their time and energy to patients’ care but also for educational purposes. The role of nurses as health educators is critical as they instruct and train care takers both theoretically and practically. Nurses are also responsible for the promotion of quality health care (GlobalHealth, 2020). There are lots of strategies nurses can consider while developing individual care plans and programs for health promotion.
One of the strategies that would be effective is evidence-based practice. This assists nurse educators in making the best decisions about individual care plans, thus training care takers with well-tested and evidence-rich methods. For example, during the pandemic, nurse educators teach other nurses to meet the urgent needs of the virus, facilitating their learning with the newest evidence they had (Walden University). Another strategy is assessment and evaluation that allow nurses to examine existing data critically. Creating care plans should be specific for each case and consider patients’ needs (Berland et al., 2020). Therefore, nurse educators must analyze patients from different perspectives carefully.
When it is done, nurses should explain adequately how to take care of patients by addressing language and cultural aspects. A health educator is required to find a way how to approach a learner, thus making him or her comfortable about the learning process. Additionally, health promotion by educators should proceed to motivate learners to proper care management. When it comes to behavioral objectives, which is a measurable learning outcome, it should be utilized in care plans, as it provides guidance for care at home. Care takers and patients should be ready to learn about care management and interact with educators actively.
Berland, A., Capone, K., Etcher, L., Ewing, H., Keating, S., & Chickering, M. (2020). Open education resources to support the WHO nurse educator core competencies. International Nursing Review , 67(2), 282-287.
Global Health. (2020). The role of nurse educators.
Walden University. (n.d.). Nurse as educator during a public health crisis.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, July 25). The Big Role of Nurses in Health Education. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-big-role-of-nurses-in-health-education/
"The Big Role of Nurses in Health Education." IvyPanda , 25 July 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/the-big-role-of-nurses-in-health-education/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'The Big Role of Nurses in Health Education'. 25 July.
IvyPanda . 2022. "The Big Role of Nurses in Health Education." July 25, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-big-role-of-nurses-in-health-education/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Big Role of Nurses in Health Education." July 25, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-big-role-of-nurses-in-health-education/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Big Role of Nurses in Health Education." July 25, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-big-role-of-nurses-in-health-education/.
- Williams Syndrome Description and Nursing Actions
- The English Influence on Modern Police
- Testing Procedures and Security
- COVID-19 Testing and Social Distancing at Barcelona Concert
- Guidelines and Procedures for Protecting Research Participants
- A Study of Juvenile Type 1 Diabetes in the Northwest of England
- “Experiences of Infant and Child Care...” Article Summary
- Tuskegee Syphilis Experiment and African Americans Hesitancy to Receive COVID-19 Vaccines
Health Education and Health Promotion: Key Concepts and Exemplary Evidence to Support Them
- First Online: 09 October 2018
Cite this chapter

- Hein de Vries 8 ,
- Stef P. J. Kremers 8 &
- Sonia Lippke 9
3111 Accesses
8 Citations
Health is regarded as the result of an interaction between individual and environmental factors. While health education is the process of educating people about health and how they can influence their health, health promotion targets not only people but also their environments. Promoting health behavior can take place at the micro level (the personal level), the meso level (the organizational level, including e.g. families, schools and worksites) and at the macro level (the (inter)national level, including e.g. governments). Health education is one of the methods used in health promotion, with health promotion extending beyond just health education.
Models and theories that focus on understanding health and health behavior are of key importance for health education and health promotion. Different classes of models and theories can be distinguished, such as planning models, behavioral change models, and diffusion models. Within these models different topics and factors are relevant, ranging from health literacy, attitudes, social influences, self-efficacy, planning, and stages of change to evaluation, implementation, stakeholder involvement, and policy changes. Exemplary health promotion settings are schools, worksites, and healthcare, but also the domains that are involved with policy development. Main health promotion methods can involve a variety of different methods and approaches, such as counseling, brochures, eHealth, stakeholder involvement, consensus meetings, community ownership, panel discussions, and policy development. Because health education and health promotion should be theory- and evidence-based, personalized interventions are recommended to take empirical findings and proven theoretical assumptions into account.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Health Promotion Practice

Theory and Fundamentals of Health Promotion for Children and Adolescents
Aarts, H., Paulussen, T., & Schaalma, H. (1997). Physical exercise habit: On the conceptualization and formation of habitual health behaviours. Health Education Research, 12 (3), 363.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Abraham, C., & Michie, S. (2008). A taxonomy of behavior change techniques used in interventions. Health Psychology, 27 (3), 379–387.
Abraham, C., & Sheeran, P. (2003). Acting on intentions: The role of anticipated regret. The British Journal of Social Psychology, 42 (Pt 4), 495–511.
Abraham, C., & Sheeran, P. (2005). The Health Belief Model. In M. Conner & P. Norman (Eds.), Predicting health behaviour (pp. 28–80). Berkshire: Open University Press.
Google Scholar
Abroms, L. C., & Maibach, E. W. (2008). The effectiveness of mass communication to change public behavior. Annual Review of Public Health, 29 , 219–234.
Adams, J., & White, M. (2003). Are activity promotion interventions based on the transtheoretical model effective? A critical review. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 37 (2), 106–114.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ajzen, I. (1988). Attitudes, personality, and behavior . Chicago: Dorsey Press.
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50 (2), 179–211.
Article Google Scholar
Ajzen, I., & Fishbein, M. (1980). Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior . Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Aldana, S. G., Merrill, R. M., Price, K., Hardy, A., & Hager, R. (2005). Financial impact of a comprehensive multisite workplace health promotion program. Preventive Medicine, 40 (2), 131–137.
Alderman, M. H., & Schoenbaum, E. E. (1975). Detection and treatment of hypertension at the work site. The New England Journal of Medicine, 293 (2), 65–68.
Armitage, C. J. (2009). Is there utility in the transtheoretical model? British Journal of Health Psychology, 14 (2), 195–210.
Armitage, C. J. (2004). Evidence that implementation intentions reduce dietary fat intake: A randomized trial. Health Psychology, 23 (3), 319.
Armitage, C. J., & Conner, M. (2001). Efficacy of the theory of planned behaviour: A meta-analytic review. The British Journal of Social Psychology, 40 (Pt 4), 471–499.
Armstrong, N., & Powell, J. (2008). Preliminary test of an Internet-based diabetes self-management tool. Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare, 14 (3), 114–116.
Asch, S. E. (1956). Studies of independence and conformity: I. A minority of one against a unanimous majority. Psychological Monographs, 70 (9), 1.
Ashford, S., Edmunds, J., & French, D. P. (2010). What is the best way to change self-efficacy to promote lifestyle and recreational physical activity? A systematic review with meta-analysis. British Journal of Health Psychology, 15 (Pt 2), 265–288.
Ausems, M., Mesters, I., van Breukelen, G., & De Vries, H. (2004). Effects of in-school and tailored out-of-school smoking prevention among Dutch vocational school students. Health Education Research, 19 (1), 51–63.
Austin, J. T., & Vancouver, J. B. (1996). Goal constructs in psychology: Structure, process, and content. Psychological Bulletin, 120 (3), 338.
Aveyard, P., Massey, L., Parsons, A., Manaseki, S., & Griffin, C. (2009). The effect of Transtheoretical Model based interventions on smoking cessation. Social science and medicine, 68 (3), 397–403.
Babbin, S. F., Harrington, M., Burditt, C., Redding, C., Paiva, A., Meier, K., Oatley, K., McGee, H., & Velicer, W. F. (2011). Prevention of alcohol use in middle school students: Psychometric assessment of the decisional balance inventory. Addictive Behaviors, 36 (5), 543–546.
Bagozzi, R. P. (1992). The self-regulation of attitudes, intentions, and behavior. Social Psychology Quarterly, 55 (2), 178.
Bagozzi, R. P., & Dholakia, U. (1999). Goal setting and goal striving in consumer behavior. Journal of Marketing, 63 , 19–32.
Baker, D. W., Parker, R. M., Williams, M. V., & Clark, W. S. (1998). Health literacy and the risk of hospital admission. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 13 (12), 791–798.
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory . New York: General Learning Press.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory . Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Bandura, A. (1989). Human agency in social cognitive theory. American Psychologist, 44 (9), 1175–1184.
Bandura, A. (1993). Perceived self-efficacy in cognitive development and functioning. Educational Psychologist, 28 (2), 117–148.
Bandura, A. (1997). Editorial. American Journal of Health Promotion, 12 (1), 8–10.
Bargh, J. A. (2005). Bypassing the will: Toward demystifying the nonconscious control of social behavior. In R. R. Hassin, J. S. Uleman, & J. A. Bargh (Eds.), The new unconscious (pp. 37–58). New York: Oxford University Press.
Bartholomew, L. K., Parcel, G. S., Kok, G., & Gottlieb, N. H. (2001). Intervention-mapping: Designing theory and evidence-based health promotion programs . Mountain View: Mayfield.
Bartholomew, L. K., Parcel, G. S., Kok, G., Gottlieb, N. H., & Fernández, M. E. (2011). Planning health promotion: An intervention mapping approach (3rd ed.). San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Bentz, C. J., Bruce Bayley, K., Bonin, K. E., Fleming, L., Hollis, J. F., Hunt, J. S., LeBlanc, B., McAfee, T., Payne, N., & Siemienczuk, J. (2007). Provider feedback to improve 5A’s tobacco cessation in primary care: A cluster randomized clinical trial. Nicotine & Tobacco Research, 9 (3), 341–349.
Berkman, L. F., & Syme, S. L. (1979). Social networks, host resistance, and mortality: A nine-year follow-up study of Alameda County residents. American Journal of Epidemiology, 109 (2), 186–204.
Beyer, J. M., & Trice, H. M. (1978). Implementing change: Alcoholism policies in work organization . New York: Free Press.
Blissmer, B., & McAuley, E. (2002). Testing the requirements of stages of physical activity among adults: The comparative effectiveness of stage-matched, mismatched, standard care, and control interventions. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 24 (3), 181–189.
Bodenheimer, T., Lorig, K., Holman, H., & Grumbach, K. (2002). Patient self-management of chronic disease in primary care. JAMA, 288 (19), 2469–2475.
Boer, H., & Seydel, E. R. (1996). Protection motivation theory. In M. Conner & P. Norman (Eds.), Predicting health behavior (pp. 95–120). Buckingham: Open University Press.
Bolman, C., Arwert, T. G., & Vollink, T. (2011). Adherence to prophylactic asthma medication: Habit strength and cognitions. Heart & Lung, 40 (1), 63–75.
Bonfadelli, H. (2002). Medieninhaltsforschung: Grundlagen, Methoden, Anwendungen . Konstanz: UVK.
Borland, R., Balmford, J., Segan, C., Livingston, P., & Owen, N. (2003). The effectiveness of personalized smoking cessation strategies for callers to a Quitline service. Addiction, 98 (6), 837–846.
Botvin, G. J., Eng, A., & Williams, C. L. (1980). Preventing the onset of cigarette smoking through life skills training. Preventive Medicine, 9 (1), 135–143.
Botvin, G. J., & Griffin, K. W. (2004). Life skills training: Empirical findings and future directions. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 25 (2), 211.
Bracht, N. (1990). Community organization principles in health promotion: A five-stage model. In N. Bracht & L. Kingsbury (Eds.), Health promotion at the community level . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Bracht, N. (1999). Health promotion at the community level: New advances . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Brewer, N. T., Weinstein, N. D., Cuite, C. L., & Herrington, J. E. (2004). Risk perceptions and their relation to risk behavior. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 27 (2), 125.
Brewer, N. T., Brewer, N. T., & Fazekas, K. I. (2007). Predictors of HPV vaccine acceptability: A theory-informed, systematic review. Preventive Medicine: An International Journal Devoted to Practice and Theory, 45 (2–3), 107.
Brinn, M. P., Carson, K. V., Esterman, A. J., Chang, A. B., & Smith, B. J. (2010). Mass media interventions for preventing smoking in young people. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 11 , CD001006.
Britt, E., Hudson, S. M., & Blampied, N. M. (2004). Motivational interviewing in health settings: A review. Patient Education and Counseling, 53 (2), 147–155.
Brodie, M., Flournoy, R. E., Altman, D. E., Blendon, R. J., Benson, J. M., & Rosenbaum, M. D. (2000). Health information, the Internet, and the digital divide. Health Affairs (Millwood), 19 (6), 255–265.
Brouwer, W., Oenema, A., Raat, H., Crutzen, R., de Nooijer, J., de Vries, N. K., & Brug, J. (2010). Characteristics of visitors and revisitors to an Internet-delivered computer-tailored lifestyle intervention implemented for use by the general public. Health Education Research, 25 (4), 585–595.
Brown, T., & Summerbell, C. (2009). Systematic review of school-based interventions that focus on changing dietary intake and physical activity levels to prevent childhood obesity: An update to the obesity guidance produced by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Obesity Reviews, 10 (1), 110–141.
Brug, J., Lechner, L., & De Vries, H. (1995). Psychosocial determinants of fruit and vegetable consumption. Appetite, 25 (3), 285.
Brug, J., Steenhuis, I., van Assema, P., & de Vries, H. (1996). The impact of a computer-tailored nutrition intervention. Preventive Medicine, 25 (3), 236–242.
Brug, J., Steenhuis, I. H. M., Van Assema, P., Glanz, K., & De Vries, H. (1999). The impact of two computer tailored nutrition education interventions. Health Education Research, 14 , 249–256.
Brug, J., Conner, M., Harré, N., Kremers, S., McKellar, S., & Whitelaw, S. (2005). The transtheoretical model and stages of change: A critique. Observations by five commentators on the paper by Adams, J., & White, M. (2004). Why don’t stage-based activity promotion interventions work? Health Education Research, 20 (2), 244.
Bruvold, W. H. (1993). A meta-analysis of adolescent smoking prevention programs. American Journal of Public Health, 83 (6), 872.
Bryan, A., Fisher, J. D., & Fisher, W. A. (2002). Tests of the mediational role of preparatory safer sexual behavior in the context of the theory of planned behavior. Health Psychology, 21 (1), 71–80.
Campbell, M. K., Demark-Wahnefried, W., Symons, M., Kalsbeek, W. D., Dodds, J., Cowan, A., Jackson, B., Motsinger, B., Hoben, K., Lashley, J., Demissie, S., & McClelland, J. W. (1999). Fruit and vegetable consumption and prevention of cancer: The Black Churches United for Better Health project. American Journal of Public Health, 89 (9), 1390–1396.
Chaiken, S., Liberman, A., & Eagly, A. H. (1989). Heuristic and systematic information processing within and beyond the persuasion context. In J. S. Uleman & J. A. Bargh (Eds.), Unintended thought . New York: The Guilford Press.
Charles, C., Whelan, T., & Gafni, A. (1999). What do we mean by partnership in making decisions about treatment? BMJ, 319 (7212), 780–782.
Chinn, M. D., & Fairlie, R. W. (2007). The determinants of the global digital divide: A cross-country analysis of computer and internet penetration. Oxford Economic Papers, 16 , f-44.
Cohen, S., & Wills, T. A. (1985). Stress, social support, and the buffering hypothesis. Psychological Bulletin, 98 (2), 310.
Collins, J. L. (1982, March). Self-efficacy and ability in achievement behavior. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New York.
Conner, M., & Norman, P. (2005). Predicting health behaviour: Research and practice with social cognition models . Maidenhead: Open University Press.
Conner, M., & Armitage, C. J. (1998). Extending the theory of planned behavior: A review and avenues for further research. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 28 (15), 1429.
Conner, M., Godin, G., Sheeran, P., & Germain, M. (2013). Some feelings are more important: Cognitive attitudes, affective attitudes, anticipated affect, and blood donation. Health Psychology, 32 (3), 264.
Coster, S., & Norman, I. (2009). Cochrane reviews of educational and self-management interventions to guide nursing practice: A review. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 46 (4), 508–528.
Cramer, J. A. (2004). A systematic review of adherence with medications for diabetes. Diabetes Care, 27 (5), 1218–1224.
Cranney, M., Warren, E., Barton, S., Gardner, K., & Walley, T. (2001). Why do GPs not implement evidence-based guidelines? A descriptive study. Family Practice, 18 (4), 359–363.
Cutrona, S. L., Choudhry, N. K., Stedman, M., Servi, A., Liberman, J. N., Brennan, T., Fischer, M. A., Alan Brookhart, M., & Shrank, W. H. (2010). Physician effectiveness in interventions to improve cardiovascular medication adherence: A systematic review. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 25 (10), 1090–1096.
de Bruijn, G. J., Kremers, S. P., De Vries, H., Van Mechelen, W., & Brug, J. (2007). Associations of social-environmental and individual-level factors with adolescent soft drink consumption: Results from the SMILE study. Health Education Research, 22 (2), 227–237.
de Meij, J. S., Chinapaw, M. J., Kremers, S. P., Jurg, M. E., & Van Mechelen, W. (2010). Promoting physical activity in children: The stepwise development of the primary school-based JUMP-in intervention applying the RE-AIM evaluation framework. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 44 (12), 879–887.
de Nooijer, J., Lechner, L., & de Vries, H. (2002). Early detection of cancer: Knowledge and behavior among Dutch adults. Cancer Detection and Prevention, 26 (5), 362–369.
de Vet, E., de Nooijer, J., de Vries, N. K., & Brug, J. (2008a). Testing the transtheoretical model for fruit intake: Comparing web-based tailored stage-matched and stage-mismatched feedback. Health Education Research, 23 (2), 218–227.
de Vet, E., De Nooijer, J., De Vries, N. K., & Brug, J. (2008b). Do the transtheoretical processes of change predict transitions in stages of change for fruit intake? Health Education & Behavior, 35 (5), 603–618.
de Vet, E., Gebhardt, W. A., Sinnige, J., Van Puffelen, A., Van Lettow, B., & de Wit, J. B. (2011). Implementation intentions for buying, carrying, discussing and using condoms: The role of the quality of plans. Health Education Research, 26 (3), 443–455.
de Vries, H., & Backbier, E. (1994). Self-efficacy as an important determinant of quitting among pregnant women who smoke: The phi-pattern. Preventive Medicine, 23 (2), 167–174.
de Vries, H., & Brug, J. (1999). Computer-tailored interventions motivating people to adopt health promoting behaviours: Introduction to a new approach. Patient Education and Counseling, 36 (2), 99–105.
de Vries, H., & van Dillen, S. (2002). Prevention of Lyme disease in Dutch children: Analysis of determinants of tick inspection by parents. Preventive Medicine, 35 (2), 160–165.
de Vries, H., & van Dillen, S. (2007). I PLAN: Planning the prevention of Lyme disease, a health promotion approach. In P. van Nitch (Ed.), Research on Lyme disease . New York: Nova Science.
de Vries, H., Dijkstra, M., & Kuhlman, P. (1988). Self-efficacy: The third factor besides attitude and subjective norm as a predictor of behavioural intentions. Health Education Research, 3 (3), 273.
de Vries, H., Backbier, E., Kok, G., & Dijkstra, M. (1995). The impact of social influences in the context of attitude, self-efficacy, intention and previous behavior as predictors of smoking onset. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 25 , 237–257.
de Vries, H., Mudde, A. N., Dijkstra, A., & Willemsen, M. C. (1998). Differential beliefs, perceived social influences, and self-efficacy expectations among smokers in various motivational phases. Preventive Medicine, 27 (5 Pt 1), 681–689.
de Vries, H., Mudde, A., Leijs, I., Charlton, A., Vartiainen, E., Buijs, G., Clemente, M. P., Storm, H., González Navarro, A., Nebot, M., Prins, T., & Kremers, S. (2003). The European Smoking Prevention Framework Approach (EFSA): An example of integral prevention. Health Education Research, 18 (5), 611–626.
de Vries, H., Lezwijn, J., Hol, M., & Honing, C. (2005). Skin cancer prevention: Behaviour and motives of Dutch adolescents. European Journal of Cancer Prevention, 14 (1), 39–50.
de Vries, H., Candel, M., Engels, R., & Mercken, L. (2006). Challenges to the peer influence paradigm: Results for 12–13 year olds from six European countries from the European Smoking Prevention Framework Approach study. Tobacco Control, 15 (2), 83–89.
de Vries, H., van’t Riet, J., Panday, S., & Reubsaet, A. (2007). Access point analysis in smoking and nonsmoking adolescents: Findings from the European Smoking Prevention Framework Approach study. European Journal of Cancer Prevention, 16 (3), 257–265.
de Vries, H., Kremers, S., Smeets, T., & Reubsaet, A. (2008a). Clustering of diet, physical activity and smoking and a general willingness to change. Psychology & Health, 23 (3), 265.
de Vries, H., van’t Riet, J., Spigt, M., Metsemakers, J., van den Akker, M., Vermunt, J. K., & Kremers, S. (2008b). Clusters of lifestyle behaviors: Results from the Dutch SMILE study. Preventive Medicine, 46 (3), 203–208.
de Vries, H., Kremers, S. P. J., Smeets, T., Brug, J., & Eijmael, K. (2008c). The effectiveness of tailored feedback and action plans in an intervention addressing multiple health behaviors. American Journal of Health Promotion, 22 (6), 417–425.
Dean, A. J., Walters, J., & Hall, A. (2010). A systematic review of interventions to enhance medication adherence in children and adolescents with chronic illness. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 95 (9), 717–723.
Della Mea, V. (2001). What is e-Health (2): The death of telemedicine? Journal of Medical Internet Research, 3 (2), e22.
Dempsey, A. R., Johnson, S. S., & Westhoff, C. L. (2011). Predicting oral contraceptive continuation using the transtheoretical model of health behavior change. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 43 (1), 23–29.
Dictionary, O. E. (2010). “Mass media, n.”, Oxford University Press.
Dijk, F., & de Vries, H. (2009). Smoke alert: A computer-tailored smoking-cessation intervention for Dutch adolescents. Documentation of a FCHE workshop held in Berlin, 18–19 September 2008. Research and Practice of Health Promotion, 14 , 34–46.
Dijkstra, A. (2005). Working mechanisms of computer-tailored health education: Evidence from smoking cessation. Health Education Research, 20 (5), 527–539.
Dijkstra, A., & De Vries, H. (1999). The development of computer-generated tailored interventions. Patient Education and Counseling, 36 (2), 193–203.
Dijkstra, A., & De Vries, H. (2000). Subtypes of precontemplating smokers defined by different long-term plans to change their smoking behavior. Health Education Research, 15 (4), 423–434.
Dijkstra, A., Bakker, M., & De Vries, H. (1997). Subtypes within a sample of precontemplating smokers: A preliminary extension of the stages of change. Addictive Behaviors, 22 (3), 327–337.
Dijkstra, A., De Vries, H., Roijackers, J., & van Breukelen, G. (1998). Tailored interventions to communicate stage-matched information to smokers in different motivational stages. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 66 (3), 549–557.
Dijkstra, A., Conijn, B., & De Vries, H. (2006). A match–mismatch test of a stage model of behaviour change in tobacco smoking. Addiction, 101 (7), 1035–1043.
DiMatteo, M. R. (2004). Social support and patient adherence to medical treatment: A meta-analysis. Health Psychology, 23 (2), 207–218.
Dlamini, S., Taylor, M., Mkhize, N., Huver, R., Sathiparsad, R., de Vries, H., Naidoo, K., & Jinabhai, C. (2009). Gender factors associated with sexual abstinent behaviour of rural South African high school going youth in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Health Education Research, 24 (3), 450–460.
Dunton, G. F., Lagloire, R., & Robertson, T. (2009). Using the RE-AIM framework to evaluate the statewide dissemination of a school-based physical activity and nutrition curriculum: “Exercise Your Options”. American Journal of Health Promotion, 23 (4), 229–232.
Dusenbury, L., Brannigan, R., Falco, M., & Hansen, W. B. (2003). A review of research on fidelity of implementation: Implications for drug abuse prevention in school settings. Health Education Research, 18 (2), 237–256.
Epstein, S. (1994). Integration of the cognitive and the psychodynamic unconscious. The American Psychologist, 49 (8), 709–724.
Etter, J. F. (2009). Comparing computer-tailored, internet-based smoking cessation counseling reports with generic, untailored reports: A randomized trial. Journal of Health Communication, 14 (7), 646–657.
Evans, R. I. (1976). Smoking in children: Developing a social psychological strategy of deterrence. Preventive Medicine, 5 (1), 122–127.
Evans-Whipp, T., Beyers, J. M., Lloyd, S., Lafazia, A. N., Toumbourou, J. W., Arthur, M. W., & Catalano, R. F. (2004). A review of school drug policies and their impact on youth substance use. Health Promotion International, 19 (2), 227.
Eysenbach, G. (2005). The law of attrition. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 7 (1), e11.
Faggiano, F., Vigna-Taglianti, F. D., Versino, E., Zambon, A., Borraccino, A., & Lemma, P. (2008). School-based prevention for illicit drugs use: A systematic review. Preventive Medicine, 46 (5), 385–396.
Farquhar, J. W., Fortmann, S. P., Flora, J. A., Taylor, C. B., Haskell, W. L., Williams, P. T., Maccoby, N., & Wood, P. D. (1990). Effects of communitywide education on cardiovascular disease risk factors. The Stanford Five-City Project. JAMA, 264 (3), 359–365.
Fazio, R. H. (1990). Multiple processes by which attitudes guide behaviour: The MODE model as an integrative framework. In M. P. Zanna (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology (pp. 75–109). San Diego: Academic Press.
Feifer, C., Ornstein, S. M., Jenkins, R. G., Wessell, A., Corley, S. T., Nemeth, L. S., Roylance, L., Nietert, P. J., & Liszka, H. (2006). The logic behind a multimethod intervention to improve adherence to clinical practice guidelines in a nationwide network of primary care practices. Evaluation & the Health Professions, 29 (1), 65–88.
Festinger, L. (1954). A theory of social comparison processes. Human Relations, 7 , 117.
Fishbein, M., & Ajzen, I. (1975). Belief, attitude, intention, and behavior: An introduction to theory and research . Reading: Addison-Wesley.
Fishbein, M., & Ajzen, I. (2010). Predicting and changing behavior: The reasoned action approach . New York: Taylor & Francis Group.
Fletcher, A., Bonell, C., & Hargreaves, J. (2008). School effects on young people’s drug use: A systematic review of intervention and observational studies. The Journal of Adolescent Health, 42 (3), 209–220.
Fleuren, M., Wiefferink, K., & Paulussen, T. (2004). Determinants of innovation within health care organizations: Literature review and Delphi study. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 16 (2), 107–123.
Floyd, D. L., Prentice-Dunn, S., & Rogers, R. W. (2000). A meta-analysis of research on protection motivation theory. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 30 (2), 407–429.
Fox, M. P. (2009). A systematic review of the literature reporting on studies that examined the impact of interactive, computer-based patient education programs. Patient Education and Counseling, 77 (1), 6–13.
Fransen, G. A. J., Mesters, I., Janssen, M. J. R., Knottnerus, J. A., & Muris, J. W. M. (2009). Which patient-related factors determine self-perceived patient adherence to prescribed dyspepsia medication? Health Education Research, 24 (5), 788–798.
Gaglio, B., Shoup, J. A., & Glasgow, R. E. (2013). The RE-AIM framework: A systematic review of use over time. American Journal of Public Health, 103 (6), e38–e46.
Gagne, C., & Godin, G. (2000). The theory of planned behavior: Some measurement issues concerning belief-based variables. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 30 (10), 2173–2193.
Glanz, K., Rimer, B. K., & Viswanath, K. (2008). Health behavior and health education: Theory, research, and practice . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Glasgow, R. E., Vogt, T. M., & Boles, S. M. (1999). Evaluating the public health impact of health promotion interventions: The RE-AIM framework. American Journal of Public Health, 89 (9), 1322–1327.
Glasgow, R. E., Lichtenstein, E., & Marcus, A. C. (2003). Why don’t we see more translation of health promotion research to practice? Rethinking the efficacy-to-effectiveness transition. American Journal of Public Health, 93 (8), 1261–1267.
Glynn, T. J. (1989). Essential elements of school-based smoking prevention programs. The Journal of School Health, 59 (5), 181–188.
Godin, G., & Conner, M. (2008). Intention-behavior relationship based on epidemiologic indices: An application to physical activity. American Journal of Health Promotion, 22 (3), 180–182.
Godin, G., & Kok, G. (1996). The theory of planned behavior: A review of its applications to health-related behaviors. American Journal of Health Promotion, 11 (2), 87–98.
Goebbels, A. F., Goebbels, A. F. G., Nicholson, J. M., Walsh, K., & De Vries, H. (2008). Teachers’ reporting of suspected child abuse and neglect: Behaviour and determinants. Health Education Research, 23 (6), 941–951.
Goetzel, R. Z., & Ozminkowski, R. J. (2008). The health and cost benefits of work site health-promotion programs. Annual Review of Public Health, 29 , 303–323.
Gollwitzer, P. M. (1990). Action phases and mind-sets. In E. T. Higgins & R. M. Sorrentino (Eds.), Handbook of motivation and cognition: Foundations of social behavior (Vol. 2, pp. 53–92). New York: Guilford Press.
Gollwitzer, P. M. (1999). Implementation intentions: Strong effects of simple plans. American Psychologist, 54 (7), 493.
Gollwitzer, P. M., & Sheeran, P. (2006). Implementation intentions and goal achievement: A Meta-analysis of effects and processes. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 38 , 69–119.
Grant, R. W., Wald, J. S., Poon, E. G., Schnipper, J. L., Gandhi, T. K., Volk, L. A., & Middleton, B. (2006). Design and implementation of a web-based patient portal linked to an ambulatory care electronic health record: Patient gateway for diabetes collaborative care. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics, 8 (5), 576–586.
Green, L. W. (1980). Health education planning: A diagnostic approach . Palo Alto: Mayfield.
Green, L. W., & Kreuter, M. W. (1991). Health promotion planning: An educational and environmental approach . Mountain View: Mayfield.
Green, L. W., & Kreuter, M. (1999). Health promotion planning: An educational and ecological approach . Mountain View: Mayfield.
Green, L. W., & Kreuter, M. W. (2005). Health program planning: An educational and ecological approach . New York: McGraw-Hill.
Grilli, R., Ramsay, C., & Minozzi, S. (2002). Mass media interventions: Effects on health services utilisation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 1 , CD000389.
Groeneveld, I. F., Proper, K. I., Van der Beek, A. J., & Van Mechelen, W. (2010). Sustained body weight reduction by an individual-based lifestyle intervention for workers in the construction industry at risk for cardiovascular disease: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Preventive Medicine, 51 (3-4), 240–246.
Grol, R., & Jones, R. (2000). Twenty years of implementation research. Family Practice, 17 (Suppl 1), S32–S35.
Grube, J. W., Morgan, M., & McGree, S. T. (1986). Attitudes and normative beliefs as predictors of smoking intentions and behaviours: A test of three models. The British Journal of Social Psychology, 25 (Pt 2), 81–93.
Hagger, M. S., Lonsdale, A. J., Hein, V., Koka, A., Lintunen, T., Pasi, H., Lindwall, M., Rudolfsson, L., & Chatzisarantis, N. L. D. (2011). Predicting alcohol consumption and binge drinking in company employees: An application of planned behaviour and self-determination theories. British Journal of Health Psychology, 17 (2), 379–407.
Hall, K. L., & Rossi, J. S. (2008). Meta-analytic examination of the strong and weak principles across 48 health behaviors. Preventive Medicine, 46 (3), 266–274.
Hallfors, D., & Godette, D. (2002). Will the ‘principles of effectiveness’ improve prevention practice? Early findings from a diffusion study. Health Education Research, 17 (4), 461–470.
Handley, M., MacGregor, K., Schillinger, D., Sharifi, C., Wong, S., & Bodenheimer, T. (2006). Using action plans to help primary care patients adopt healthy behaviors: A descriptive study. Journal of American Board of Family Medicine, 19 (3), 224–231.
Hansen, W. B. (1992). School-based substance abuse prevention: A review of the state of the art in curriculum, 1980–1990. Health Education Research, 7 (3), 403–430.
Harakeh, Z., Scholte, R. H., Vermulst, A. A., de Vries, H., & Engels, R. C. (2004). Parental factors and adolescents’ smoking behavior: An extension of the theory of planned behavior. Preventive Medicine, 39 (5), 951–961.
Harden, A., Peersman, G., Oliver, S., Mauthner, M., & Oakley, A. (1999). A systematic review of the effectiveness of health promotion interventions in the workplace. Occupational Medicine (London), 49 (8), 540–548.
Harting, J., Rutten, G. M., Rutten, S. T., & Kremers, S. P. (2009). A qualitative application of the diffusion of innovations theory to examine determinants of guideline adherence among physical therapists. Physical Therapy, 89 (3), 221–232.
Hawkins, R. P., Kreuter, M., Resnicow, K., Fishbein, M., & Dijkstra, A. (2008). Understanding tailoring in communicating about health. Health Education Research, 23 (3), 454–466.
US Department of Health and Human Services. (1991). Healthy people 2000: National health promotion and disease prevention objectives and healthy schools. Journal of School Health, 61 (7), 298–328.
Heckhausen, H. (1991). Motivation and action . New York: Springer.
Book Google Scholar
Helmink, J. H., Meis, J. J., de Weerdt, I., Visser, F. N., de Vries, N. K., & Kremers, S. P. (2010). Development and implementation of a lifestyle intervention to promote physical activity and healthy diet in the Dutch general practice setting: The BeweegKuur programme. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 7 , 49.
Henderson, V. (1966). The nature of nursing . New York: Macmillan.
Hendriksen, E. S., Pettifor, A., Lee, S. J., Coates, T. J., & Rees, H. V. (2007). Predictors of condom use among young adults in South Africa: The Reproductive Health and HIV Research Unit National Youth Survey. American Journal of Public Health, 97 (7), 1241–1248.
Herzog, T. A., & Blagg, C. O. (2007). Are most precontemplators contemplating smoking cessation? Assessing the validity of the stages of change. Health Psychology, 26 (2), 222.
Hettema, J., Steele, J., & Miller, W. R. (2005). Motivational interviewing. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 1 , 91–111.
Hochbaum, G. M. (1971). Measurement of effectiveness of health education activites. International Journal of Health Education, 2 , 54–59.
Hoffman, D. L., & Novak, T. P. (1998). Bridging the racial divide on the Internet. Science, 280 , 390–391.
Hofmann, W., Friese, M., & Wiers, R. W. (2008). Impulsive versus reflective influences on health behavior: A theoretical framework and empirical review. Health Psychology Review, 2 , 111–137.
Holm, K., Kremers, S. P., & de Vries, H. (2003). Why do Danish adolescents take up smoking? European Journal of Public Health, 13 (1), 67–74.
Horowitz, S. M. (2003). Applying the transtheoretical model to pregnancy and STD prevention: A review of the literature. American Journal of Health Promotion, 17 (5), 304–328.
Hoving, E. F., Mudde, A. N., & de Vries, H. (2006). Smoking and the O pattern; predictors of transitions through the stages of change. Health Education Research, 21 (3), 305–314.
Hovland, C. I., Janis, I. L., & Kelley, H. H. (1953). Communication and persuasion: Psychological studies of opinion change . New Haven: Yale UP.
Huver, R. M. E., Engels, R. C. M. E., & de Vries, H. (2006). Are anti-smoking parenting practices related to adolescent smoking cognitions and behavior? Health Education Research, 21 (1), 66–77.
Huver, R. M., Engels, R. C. M. E., Vermulst, A. A., & de Vries, H. (2007). Is parenting style a context for smoking-specific parenting practices? Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 89 (2-3), 116–125.
Hyman, H. H., & Sheatsley, P. B. (1947). Some reasons why information campaigns fail. Public Opinion Quarterly, 11 , 412–423.
Ito, K. E., & Brown, J. D. (2010). To friend or not to friend: Using new media for adolescent health promotion. North Carolina Medical Journal, 71 (4), 367–372.
PubMed Google Scholar
Jackson, C., Lawton, R., Knapp, P., Raynor, D. K., Conner, M., Lowe, C., & Closs, S. J. (2005). Beyond intention: Do specific plans increase health behaviours in patients in primary care? A study of fruit and vegetable consumption. Social Science & Medicine, 60 (10), 2383.
James, S., Reddy, P., Ruiter, R. A., McCauley, A., & Borne, B. V. D. (2006). The impact of an HIV and AIDS life skills program on secondary school students in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. AIDS Educ Prev, 18 (4), 281–294.
Janis, I. L., & Mann, L. (1977). Decision making: A psychological analysis of conflict, choice, and commitment . New York: Free Press.
Janssen, E., van Osch, L., de Vries, H., & Lechner, L. (2011). Measuring risk perceptions of skin cancer: Reliability and validity of different operationalizations. British Journal of Health Psychology, 16 (Pt 1), 92–112.
Janssen, E., van Osch, L., Lechner, L., Candel, M., & de Vries, H. (2012). Thinking versus feeling: Differentiating between cognitive and affective components of perceived cancer risk. Psychology & Health, 27 (7), 767–783.
Janssen, E., van Osch, L., de Vries, H., & Lechner, L. (2013). Examining direct and indirect pathways to health behaviour: The influence of cognitive and affective probability beliefs. Psychology & Health, 28 (5), 546–560.
Janz, N. K., & Becker, M. H. (1984). The Health Belief Model: A decade later. Health Education Quarterly, 11 (1), 1–47.
Johnson, C. E., Mues, K. E., Mayne, S. L., & Kiblawi, A. N. (2008). Cervical cancer screening among immigrants and ethnic minorities: A systematic review using the Health Belief Model. Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease, 12 (3), 232–241.
Joosten, E. A., DeFuentes-Merillas, L., De Weert, G. H., Sensky, T., Van Der Staak, C. P. F., & de Jong, C. A. (2008). Systematic review of the effects of shared decision-making on patient satisfaction, treatment adherence and health status. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, 77 (4), 219–226.
Jurg, M. E., Kremers, S. P., Candel, M. J., Van der Wal, M. F., & Meij, J. S. D. (2006). A controlled trial of a school-based environmental intervention to improve physical activity in Dutch children: JUMP-in, kids in motion. Health Promotion International, 21 (4), 320.
Kamarck, T. W., Manuck, S. B., & Jennings, J. R. (1990). Social support reduces cardiovascular reactivity to psychological challenge: A laboratory model. Psychosomatic Medicine, 52 (1), 42.
Kemp, R., Kirov, G., Everitt, B., Hayward, P., & David, A. (1998). Randomised controlled trial of compliance therapy. 18-month follow-up. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 172 , 413–419.
King, E. S., Rimer, B. K., Seay, J., Balshem, A., & Engstrom, P. F. (1994). Promoting mammography use through progressive interventions: Is it effective? American Journal of Public Health, 84 (1), 104–106.
Kirby, D. B., Laris, B. A., & Rolleri, L. A. (2007). Sex and HIV education programs: Their impact on sexual behaviors of young people throughout the world. The Journal of Adolescent Health, 40 (3), 206–217.
Knai, C., Pomerleau, J., Lock, K., & McKee, M. (2006). Getting children to eat more fruit and vegetables: A systematic review. Preventive Medicine: An International Journal Devoted to Practice and Theory, 42 (2), 85.
Kok, G., Lo, S. H., Peters, G. J. Y., & Ruiter, R. A. (2011). Changing energy-related behavior: An intervention mapping approach. Energy Policy, 39 , 5280–5286.
Kolbe, L. J. (1985). Why school health education? An empirical point of view. Health Education, 16 (2), 116–120.
Kremers, S. P. (2010). Theory and practice in the study of influences on energy balance-related behaviors. Patient Education and Counseling, 79 (3), 291–298.
Kremers, S. P., & Brug, J. (2008). Habit strength of physical activity and sedentary behavior among children and adolescents. Pediatric Exercise Science, 20 (1), 5–14. Discussion 14-7.
Kremers, S. P. J., Mudde, A. N., & de Vries, H. (2001). Subtypes within the precontemplation stage of adolescent smoking acquisition. Addictive Behaviors, 26 (2), 237.
Kremers, S. P., De Bruijn, G. J., Visscher, T. L., Van Mechelen, W., De Vries, N. K., & Brug, J. (2006). Environmental influences on energy balance-related behaviors: A dual-process view. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 3 , 9.
Kreuter, M. W., & Strecher, V. J. (1996). Do tailored behavior change messages enhance the effectiveness of health risk appraisal? Results from a randomized trial. Health Education Research, 11 (1), 97–105.
Kreuter, M. W., Farrell, D. W., Olevitch, L. R., & Brennan, L. K. (2000). Tailoring health messages: Customizing communication with computer technology . Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Kroeze, W., Werkman, A., & Brug, J. (2006). A systematic review of randomized trials on the effectiveness of computer-tailored education on physical activity and dietary behaviors. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 31 (3), 205–223.
Kruger, S. (1991). The patient educator role in nursing. Applied Nursing Research, 4 (1), 19–24.
Kwak, L., Kremers, S. P., van Baak, M. A., & Brug, J. (2007). Formation of implementation intentions promotes stair use. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 32 (3), 254.
Latham, G. P., & Locke, E. A. (2006). Enhancing the benefits and overcoming the pitfalls of goal setting. Organizational Dynamics, 35 (4), 332–340.
Lazarus, R. S. (1966). Psychological stress and the coping process . New York: McGraw-Hill.
Leung, L. (2008). Internet embeddedness: Links with online health information seeking, expectancy value/quality of health information websites, and Internet usage patterns. Cyberpsychology & Behavior, 11 (5), 565–569.
Leventhal, H. (1970). Findings and theory in the study of fear communications. In L. Berkowitz (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology . New York: Academic Press.
Leventhal, H., & Cameron, L. (1987). Behavioral theories and the problem of compliance. Patient Education and Counseling, 10 (2), 117.
Leventhal, H., Nerenz, D. R., & Steele, D. J. (1984). Illness representation and coping with health threats . In A. Baum, S. E. Taylor, & J. E. Singer (Eds.), Handbook of psychology and health (pp. 219–252). Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Lewis, B. A., Williams, D. M., Neighbors, C. J., Jakicic, J. M., & Marcus, B. H. (2010). Cost analysis of Internet vs. print interventions for physical activity promotion. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 11 (3), 246–249.
Lippke, S., & Plotnikoff, R. C. (2012). Testing two principles of the health action process approach in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Health Psychology .
Lippke, S., & Ziegelmann, J. P. (2008). Theory-based health behavior change: Developing, testing, and applying theories for evidence-based interventions. Applied Psychology, 57 (4), 698–716.
Lippke, S., Ziegelmann, J. P., & Schwarzer, R. (2004). Initiation and maintenance of physical exercise: Stage-specific effects of a planning intervention. Research in Sports Medicine, 12 (3), 221.
Lippke, S., Ziegelmann, J. P., & Schwarzer, R. (2005). Stage-specific adoption and maintenance of physical activity: Testing a three-stage model. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 6 , 585–603.
Lippke, S., Schwarzer, R., Ziegelmann, J. P., Scholz, U., & Schüz, B. (2010). Testing stage-specific effects of a stage-matched intervention: A randomized controlled trial targeting physical exercise and its predictors. Health Education & Behavior, 37 (4), 533–546.
Liu, L. L., & Park, D. C. (2004). Aging and medical adherence: The use of automatic processes to achieve effortful things. Psychology and Aging, 19 (2), 318–325.
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (2002). Building a practically useful theory of goal setting and task motivation. A 35-year odyssey. The American Psychologist, 57 (9), 705–717.
Lotrean, L. M., Dijk, F., Mesters, I., Ionut, C., & De Vries, H. (2010). Evaluation of a peer-led smoking prevention programme for Romanian adolescents. Health Education Research, 25 (5), 803.
Luszczynska, A., & Schwarzer, R. (2003). Planning and self-efficacy in the adoption and maintenance of breast self-examination: A longitudinal study on self-regulatory cognitions. Psychology & Health, 18 (1), 93–108.
MacGregor, K., Handley, M., Wong, S., Sharifi, C., Gjeltema, K., Schillinger, D., & Bodenheimer, T. (2006). Behavior-change action plans in primary care: A feasibility study of clinicians. The Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine, 19 , 215–223.
Marks, R., Allegrante, J. P., & Lorig, K. (2005). A review and synthesis of research evidence for self-efficacy-enhancing interventions for reducing chronic disability: Implications for health education practice (part II). Health Promotion Practice, 6 (2), 148–156.
Marlatt, G. A., & George, W. H. (1984). Relapse prevention: Introduction and overview of the model. British Journal of Addiction, 79 (3), 261–273.
Marshall, S. J., & Biddle, S. J. (2001). The transtheoretical model of behavior change: A meta-analysis of applications to physical activity and exercise. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 23 (4), 229–246.
Martinez, M. (2008). High attrition rates in e-learning: Challenges, predictors, and solutions (p. 15). Santa Rosa: The E-Learning Developers’ Journal.
Mays, D., Streisand, R., Walker, L. R., Prokhorov, A. V., & Tercyak, K. P. (2012). Cigarette smoking among adolescents with type 1 diabetes: Strategies for behavioral prevention and intervention. Journal of Diabetes and its Complications, 26 (2), 148–153.
McGuire, W. J. (1985). Attitudes and attitude change. In G. Lindzey & E. Aronson (Eds.), Handbook of social psychology (Vol. II). New York: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
McKenzie, J. F., & Smeltzer, J. L. (2001). Planning, implementing and evaluating health promotion programs . Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
McLean, S. M., Burton, M., Bradley, L., & Littlewood, C. (2010). Interventions for enhancing adherence with physiotherapy: A systematic review. Manual Therapy, 15 (6), 514–521.
McLeroy, K. R., Bibeau, D., Steckler, A., & Glanz, K. (1988). An ecological perspective on health promotion programs. Health Education Quarterly, 15 (4), 351–377.
Mercken, L., Snijders, T. A., Steglich, C., & de Vries, H. (2009). Dynamics of adolescent friendship networks and smoking behavior: Social network analyses in six European countries. Social Science & Medicine, 69 (10), 1506.
Mercken, L., Candel, M., Van Osch, L., & De Vries, H. (2010). No smoke without fire: The impact of future friends on adolescent smoking behaviour. British Journal of Health Psychology, 16 (Pt 1), 170–188.
Milgram, S. (1963). Behavioral study of obedience. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 67 , 371–378.
Miller, W. R., & Rollnick, S. (2002). Motivational interviewing: Preparing people to change (2nd ed.). New York: Guilford Press.
Milne, S., Sheeran, P., & Orbell, S. (2000). Prediction and intervention in health-related behavior: A meta-analytic review of protection motivation theory. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 30 (1), 106.
Milne, S., Orbell, S., & Sheeran, P. (2002). Combining motivational and volitional interventions to promote exercise participation: Protection motivation theory and implementation intentions. British Journal of Health Psychology, 7 (Pt 2), 163–184.
Montaño, D. E., & Kasprzyk, D. (2008). Theory of reasoned action, theory of planned behavior and the integrated behavioral model. In K. Glanz, B. K. Rimer, & K. Viswanath (Eds.), Health behavior and health education (4th ed.). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Moritz, S. E., Feltz, D. L., Fahrbach, K. R., & Mack, D. E. (2000). The relation of self-efficacy measures to sport performance: A meta-analytic review. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport, 71 (3), 280–294.
Morrison, V., & Bennett, P. (2008). An introduction to health psychology (2nd ed.). London: Pearson Publishing.
Mulvaney, S. A., Rothman, R. L., Wallston, K. A., Lybarger, C., & Dietrich, M. S. (2010). An internet-based program to improve self-management in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 33 (3), 602–604.
Newman, I. M., Martin, G. L., & Ang, J. (1982). The role of attitudes and social norms in adolescent cigarette smoking. The New Zealand Medical Journal, 95 (715), 618–621.
Ni Mhurchu, C., Aston, L. M., & Jebb, S. A. (2010). Effects of worksite health promotion interventions on employee diets: A systematic review. BMC Public Health, 10 (62), 1.
Nichols, J., Schutte, N. S., Brown, R. F., Dennis, C. L., & Price, I. (2009). The impact of a self-efficacy intervention on short-term breast-feeding outcomes. Health Education & Behavior, 36 (2), 250–258.
Nigg, C. R., Albright, C., Williams, R., Nichols, C., Renda, G., Stevens, V. J., & Vogt, T. M. (2010). Are physical activity and nutrition indicators of the checklist of health promotion environments at worksites (CHEW) associated with employee obesity among hotel workers? Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 52 (Suppl. 1), S4–S7.
Noar, S. M., & Harrington, N. G. (2012). eHealth applications . New York: Routledge.
Noar, S. M., Benac, C. N., & Harris, M. S. (2007). Does tailoring matter? Meta-analytic review of tailored print health behavior change interventions. Psychological Bulletin, 133 (4), 673–693.
Noar, S. M., Black, H. G., & Pierce, L. B. (2009). Efficacy of computer technology-based HIV prevention interventions: A meta-analysis. AIDS, 23 (1), 107.
Noar, S. M., Webb, E. M., Van Stee, S. K., Redding, C. A., Feist-Price, S., Crosby, R., & Troutman, A. (2011). Using computer technology for HIV prevention among African-Americans: Development of a tailored information program for safer sex (TIPSS). Health Education Research, 26 (3), 393–406.
Norman, G. J., Velicer, W. F., Fava, J. L., & Prochaska, J. O. (2000). Cluster subtypes within stage of change in a representative sample of smokers. Addictive Behaviors, 25 (2), 183.
Norman, P., Boer, H., & Seydel, E. R. (2005). Protection motivation theory. In M. Conner & P. Norman (Eds.), Predicting health behavior (pp. 81–126). London: Open University Press.
Norris, S. L., Engelgau, M. M., & Narayan, K. V. (2001). Effectiveness of self-management training in type 2 diabetes a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care, 24 (3), 561–587.
Norris, S. L., Lau, J., Smith, S. J., Schmid, C. H., & Engelgau, M. M. (2002). Self-management education for adults with type 2 diabetes a meta-analysis of the effect on glycemic control. Diabetes Care, 25 (7), 1159–1171.
O’Leary, A. (1985). Self-efficacy and health. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 23 (4), 437.
Oei, T. P., & Burrow, T. (2000). Alcohol expectancy and drinking refusal self-efficacy: A test of specificity theory. Addictive Behaviors, 25 (4), 499–507.
Oenema, A., Brug, J., & Lechner, L. (2001). Web-based tailored nutrition education: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Health Education Research, 16 (6), 647–660.
Oostveen, T., Knibbe, R., & de Vries, H. (1996). Social influences on young adults’ alcohol consumption: Norms, modeling, pressure, socializing, and conformity. Addictive Behaviors, 21 (2), 187–197.
Orbell, S., & Sheeran, P. (1998). ‘Inclined abstainers’: A problem for predicting health-related behaviour. The British Journal of Social Psychology, 37 (Pt 2), 151–165.
Panday, S., Reddy, S. P., Ruiter, R. A., Bergström, E., & de Vries, H. (2005). Determinants of smoking cessation among adolescents in South Africa. Health Education Research, 20 (5), 586–599.
Parcel, G. S., Eriksen, M. P., Lovato, C. Y., Gottlieb, N. H., Brink, S. G., & Green, L. W. (1989). The diffusion of school-based tobacco-use prevention programs: Project description and baseline data. Health Education Research, 4 (1), 111.
Parker, R. M., & Jacobson, T. A. (2000). The role of health literacy in narrowing the treatment gap for hypercholesterolemia. The American Journal of Managed Care, 6 (12), 1340–1342.
Pelletier, K. R. (2009). A review and analysis of the clinical and cost-effectiveness studies of comprehensive health promotion and disease management programs at the worksite: Update VII 2004–2008. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 51 (7), 822–837.
Perry, C. L., Kelder, S. H., & Klepp, K. I. (1994). Community-wide cardiovascular disease prevention in young people: Long-term outcomes of the class of 1989 study. European Journal of Public Health, 4 (3), 188–194.
Perry, C. L., Williams, C. L., Veblen-Mortenson, S., Toomey, T. L., Komro, K. A., Anstine, P. S., McGovern, P. G., Finnegan, J. R., Forster, J. L., Wagenaar, A. C., & Wolfson, M. (1996). Project Northland: Outcomes of a communitywide alcohol use prevention program during early adolescence. American Journal of Public Health, 86 (7), 956–965.
Peters, L. W., Wiefferink, C. H., Hoekstra, F., Buijs, G. J., ten Dam, G. T., & Paulussen, T. G. (2009). A review of similarities between domain-specific determinants of four health behaviors among adolescents. Health Education Research, 24 (2), 198–223.
Peterson, A. V., Jr., Kealey, K. A., Mann, S. L., Marek, P. M., & Sarason, I. G. (2000). Hutchinson Smoking Prevention Project: Long-term randomized trial in school-based tobacco use prevention – Results on smoking. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 92 (24), 1979–1991.
Petty, R. E., & Cacioppo, J. T. (1986). Communication and persuasion, central and peripheral routes to attitude change . New York: Springer.
Pinto, A. M., Heinberg, L. J., Coughlin, J. W., Fava, J. L., & Guarda, A. S. (2008). The Eating Disorder Recovery Self-Efficacy Questionnaire (EDRSQ): Change with treatment and prediction of outcome. Eating Behaviors, 9 (2), 143.
Plotnikoff, R. C., Lippke, S., Courneya, K. S., Birkett, N., & Sigal, R. J. (2008). Physical activity and social cognitive theory: A test in a population sample of adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Applied Psychology, 57 (4), 628–643.
Plotnikoff, R. C., Lippke, S., Johnson, S. T., & Courneya, K. S. (2010a). Physical activity and stages of change: A longitudinal test in types 1 and 2 diabetes samples. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 40 (2), 138–149.
Plotnikoff, R. C., Lippke, S., Trinh, L., Courneya, K. S., Birkett, N., & Sigal, R. J. (2010b). Protection motivation theory and the prediction of physical activity among adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes in a large population sample. British Journal of Health Psychology, 15 (Pt 3), 643–661.
Pomp, S., Lippke, S., Fleig, L., & Schwarzer, R. (2010). Synergistic effects of intention and depression on action control: Longitudinal predictors of exercise after rehabilitation. Mental Health and Physical Activity, 2 , 78–84.
Presson, C. C., Chassin, L., Sherman, S. J., Olshavsky, R., Bensenberg, M., & Corty, E. (1984). Predictors of adolescents’ intentions to smoke: Age, sex, race, and regional differences. The International Journal of the Addictions, 19 (5), 503–519.
Elders, M. J. (1994). Preventing tobacco use among young people. A report of the Surgeon General. Executive summary. MMWR – Recommendations and Reports, 43 (RR-4), 1–10.
Price, V., & Zaller, J. (1993). Who gets the news? Alternative measures of news reception and their implications for research. Public Opinion Quarterly, 57 (2), 133.
Prochaska, J. O., & DiClemente, C. C. (1983). Stages and processes of self-change of smoking: Toward an integrative model of change. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 51 (3), 390–395.
Prochaska, J. O., & Velicer, W. F. (1997). The transtheoretical model of health behavior change. American Journal of Health Promotion, 12 (1), 38–48.
Prochaska, J. O., Velicer, W. F., Rossi, J. S., Goldstein, M. G., Marcus, B. H., Rakowski, W., Fiore, C., Harlow, L. L., Redding, C. A., Rosenbloom, D., & Rossi, S. R. (1994). Stages of change and decisional balance for 12 problem behaviors. Health Psychology, 13 (1), 39–46.
Prochaska, J. O., Velicer, W. F., Redding, C., Rossi, J. S., Goldstein, M., DePue, J., Greene, G. W., Rossi, S. R., Sun, X., & Fava, J. L. (2005). Stage-based expert systems to guide a population of primary care patients to quit smoking, eat healthier, prevent skin cancer, and receive regular mammograms. Preventive Medicine, 41 (2), 406–416.
Prochaska, J. J., Spring, B., & Nigg, C. R. (2008). Multiple health behavior change research: An introduction and overview. Preventive Medicine, 46 (3), 181–188.
Puska, P. M., Puska, P. M. J., Barrueco, M., Roussos, C., Hider, A., & Hogue, S. (2005). The participation of health professionals in a smoking-cessation programme positively influences the smoking cessation advice given to patients. International Journal of Clinical Practice, 59 (4), 447–452.
Quinlan, K. B., & McCaul, K. D. (2000). Matched and mismatched interventions with young adult smokers: Testing a stage theory. Health Psychology, 19 (2), 165.
Rahimi, B., Timpka, T., Vimarlund, V., Uppugunduri, S., & Svensson, M. (2009). Organization-wide adoption of computerized provider order entry systems: A study based on diffusion of innovations theory. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 9 (1), 52.
Rakowski, W., Ehrich, B., Goldstein, M. G., Rimer, B. K., Pearlman, D. N., Clark, M. A., Velicer, W. F., & Woolverton III, H. (1998). Increasing mammography among women aged 40–74 by use of a stage-matched, tailored intervention. Preventive Medicine, 27 (5 Pt 1), 748–756.
Renner, B., Kwon, S., Yang, B.-H., Paik, K.-C., Kim, S. H., Roh, S., Song, J., & Schwarzer, R. (2008). Social-cognitive predictors of dietary behaviors in South Korean men and women. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 15 (1), 4–13.
Resnicow, K., & Vaughan, R. (2006). A chaotic view of behavior change: A quantum leap for health promotion. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 3 , 25.
Resnicow, K., DiIorio, C., Soet, J. E., Borrelli, B., Hecht, J., & Ernst, D. (2002). Motivational interviewing in health promotion: It sounds like something is changing. Health Psychology, 21 (5), 444.
Rigotti, N. A., Munafo, M. R., & Stead, L. F. (2008). Smoking cessation interventions for hospitalized smokers: A systematic review. Archives of Internal Medicine, 168 (18), 1950–1960.
Riper, H., Kramer, J., Smit, F., Conijn, B., Schippers, G., & Cuijpers, P. (2008). Web-based self-help for problem drinkers: A pragmatic randomized trial. Addiction, 103 (2), 218.
Rivis, A., & Sheeran, P. (2003). Descriptive norms as an additional predictor in the theory of planned behaviour: A meta-analysis. Current Psychology: Developmental, Learning, Personality, Social, 22 , 218–233.
Rogers, R. W. (1975). A protection motivation theory of fear appeals and attitude change. Journal of Psychology: Interdisciplinary and Applied, 91 (1), 93.
Rogers, R. W. (1983). Cognitive and physiological processes in fear appeals and attitude change: A revised theory of protection motivation. In J. T. Cacioppo & R. E. Petty (Eds.), Social psychophysiology . New York: Guilford Press.
Rogers, R. W. (2003). Diffusion of innovations (5th ed.). New York: Free Press.
Rohrbach, L. A., Grana, R., Sussman, S., & Valente, T. W. (2006). Type II translation: Transporting prevention interventions from research to real-world settings. Evaluation & the Health Professions, 29 (3), 302–333.
Rosenstock, I. (1974). Historical origins of the Health Belief Model. Health Education Monographs, 2 (4), 336.
Rosseel, J. P., Hilberink, S. R., Jacobs, J. E., Maassen, I. M., Plasschaert, A. J. M., & Grol, R. P. T. M. (2010). Are oral health complaints related to smoking cessation intentions? Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology, 38 (5), 470–478.
Ruiter, R. A., Kessels, L. T., Jansma, B. M., & Brug, J. (2006). Increased attention for computer-tailored health communications: An event-related potential study. Health Psychology, 25 (3), 300–306.
Rutter, D. R., Steadman, L., & Quine, L. (2006). An implementation intentions intervention to increase uptake of mammography. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 32 (2), 127–134.
Salpeter, S. R., Buckley, N. S., Ormiston, T. M., & Salpeter, E. E. (2006). Meta-analysis: Effect of long-acting beta-agonists on severe asthma exacerbations and asthma-related deaths. Annals of Internal Medicine, 144 (12), 904–912.
Sarafino, E. P. (1994). Health psychology: Biopsychosocial interactions (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Sarkar, U., Karter, A. J., Liu, J. Y., Adler, N. E., Nguyen, R., López, A., & Schillinger, D. (2011). Social disparities in internet patient portal use in diabetes: Evidence that the digital divide extends beyond access. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 18 (3), 318–321.
Say, R. E., & Thomson, R. (2003). The importance of patient preferences in treatment decisions – Challenges for doctors. BMJ, 327 (7414), 542–545.
Schaalma, H., Kok, G., & Peters, L. (1993). Determinants of consistent condom use by adolescents: The impact of experience of sexual intercourse. Health Education Research, 8 (2), 255.
Schoenmakers, T., Wiers, R. W., & Field, M. (2008). Effects of a low dose of alcohol on cognitive biases and craving in heavy drinkers. Psychopharmacology, 197 (1), 169–178.
Schwarzer, R. (Ed.). (1992). Self-efficacy: Thought control of action . Washington, DC: Hemisphere.
Schwarzer, R. (2008a). Modeling health behavior change: The Health Action Process Approach (HAPA) . Available from: http://www.hapa-model.de/
Schwarzer, R. (2008b). Modeling health behavior change: How to predict and modify the adoption and maintenance of health behaviors. Applied Psychology. An International Review, 57 (1), 1.
Schwarzer, R., Schüz, B., Ziegelmann, J. P., Lippke, S., Luszczynska, A., & Scholz, U. (2007). Adoption and maintenance of four health behaviors: Theory-guided longitudinal studies on dental flossing, seat belt use, dietary behavior, and physical activity. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 33 (2), 156.
Schwarzer, R., Luszczynska, A., Ziegelmann, J. P., Scholz, U., & Lippke, S. (2008). Social-cognitive predictors of physical exercise adherence: Three longitudinal studies in rehabilitation. Health Psychology, 27 (Suppl. 1), S54.
Schwarzer, R., Lippke, S., & Luszczynska, A. (2011). Mechanisms of health behavior change in persons with chronic illness or disability: The Health Action Process Approach (HAPA). Rehabilitation Psychology, 56 (3), 161.
Segaar, D., Willemsen, M. C., Bolman, C., & De Vries, H. (2007a). Nurse adherence to a minimal-contact smoking cessation intervention on cardiac wards. Research in Nursing & Health, 30 (4), 429–444.
Segaar, D., Bolman, C., Willemsen, M. C., & De Vries, H. (2007b). Identifying determinants of protocol adoption by midwives: A comprehensive approach. Health Education Research, 22 (1), 14–26.
Senge, P. (1990). The fifth discipline: The art and practice of the learning organization . New York: Currency Doubleday.
Sheeran, P., & Orbell, S. (2000). Using implementation intentions to increase attendance for cervical cancer screening. Health Psychology, 19 (3), 283–289.
Sheeran, P., Webb, T. L., & Gollwitzer, P. M. (2005). The interplay between goal intentions and implementation intentions. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 31 (1), 87–98.
Sherif, M. (1935). A study of some social factors in perception. Archives of Psychology, 187 .
Simonds, S. K. (1978). Health education: Facing issues of policy, ethics, and social justice. Health Education Monographs, 6 (Suppl. 1), 18–27.
Skår, S., Sniehotta, F. F., Molloy, G. J., Prestwich, A., & Araujo-Soares, V. (2011). Do brief online planning interventions increase physical activity amongst university students? A randomised controlled trial. Psychology & Health, 26 (4), 399–417.
Skinner, C. S., Sykes, R. K., Monsees, B. S., Andriole, D. A., Arfken, C. L., & Fisher, E. B. (1998). Learn, share, and live: Breast cancer education for older, urban minority women. Health Education & Behavior, 25 (1), 60–78.
Slovic, P. (1987). Perception of risk. Science, 236 (4799), 280–285.
Slovic, P., & Peters, E. (2006). Risk perception and affect. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 15 (6), 322–325.
Smeets, T., Brug, J., & de Vries, H. (2008). Effects of tailoring health messages on physical activity. Health Education Research, 23 (3), 402–413.
Smerecnik, C., Quaak, M., van Schayck, C. P., van Schooten, F. J., & de Vries, H. (2011). Are smokers interested in genetic testing for smoking addiction? A socio-cognitive approach. Psychology & Health, 26 (8), 1099–1112.
Sniehotta, F. F. (2009). Towards a theory of intentional behaviour change: Plans, planning, and self-regulation. British Journal of Health Psychology, 14 (2), 261.
Sniehotta, F. F., Scholz, U., Schwarzer, R., Fuhrmann, B., Kiwus, U., & Völler, H. (2005). Long-term effects of two psychological interventions on physical exercise and self-regulation following coronary rehabilitation. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 12 (4), 244–255.
Sniehotta, F. F., Scholz, U., & Schwarzer, R. (2006). Action plans and coping plans for physical exercise: A longitudinal intervention study in cardiac rehabilitation. British Journal of Health Psychology, 11 (Pt 1), 23–37.
Snyder, L. B., Hamilton, M. A., Mitchell, E. W., Kiwanuka-Tondo, J., Fleming-Milici, F., & Proctor, D. (2004). A meta-analysis of the effect of mediated health communication campaigns on behavior change in the United States. Journal of Health Communication, 9 (Suppl. 1), 71–96.
Soler, R. E., Leeks, K. D., Razi, S., Hopkins, D. P., Griffith, M., Aten, A., Chattopadhyay, S. K., Smith, S. C., Habarta, N., & Goetzel, R. Z. (2010). A systematic review of selected interventions for worksite health promotion. The assessment of health risks with feedback. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 38 (2 Suppl), S237–S262.
Stock, J., & Cervone, D. (1990). Proximal goal-setting and self-regulatory processes. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 14 (5), 483–498.
Strack, F., & Deutsch, R. (2004). Reflective and impulsive determinants of social behavior. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 8 (3), 220.
Strecher, V. J. (1999). Computer-tailored smoking cessation materials: A review and discussion. Patient Education and Counseling, 36 (2), 107–117.
Strecher, V. J., & Rosenstock, I. M. (1997). The Health Belief Model. In A. Baum et al. (Eds.), Cambridge handbook of psychology, health and medicine . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Strecher, V. J., McEvoy DeVellis, B., Becker, M. H., & Rosenstock, I. M. (1986). The role of self-efficacy in achieving health behavior change. Health Education Quarterly, 13 (1), 73–92.
Strecher, V. J., Kreuter, M., Den Boer, D. J., Kobrin, S., Hospers, H. J., & Skinner, C. S. (1994). The effects of computer-tailored smoking cessation messages in family practice settings. The Journal of Family Practice, 39 (3), 262–270.
Strecher, V. J., Shiffman, S., & West, R. (2005). Randomized controlled trial of a web-based computer-tailored smoking cessation program as a supplement to nicotine patch therapy. Addiction, 100 (5), 682–688.
Strecher, V. J., McClure, J. B., Alexander, G. L., Chakraborty, B., Nair, V. N., Konkel, J. M., Greene, S. M., Collins, L. M., Carlier, C. C., & Wiese, C. J. (2008). Web-based smoking-cessation programs: Results of a randomized trial. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 34 (5), 373–381.
Suissa, S., & Ernst, P. (2001). Inhaled corticosteroids: Impact on asthma morbidity and mortality. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 107 (6), 937–944.
Sutton, S. (2000). Interpreting cross-sectional data on stages of change. Psychology and Health, 15 (2), 163–171.
Swinburn, B., Egger, G., & Raza, F. (1999). Dissecting obesogenic environments: The development and application of a framework for identifying and prioritizing environmental interventions for obesity. Preventive Medicine, 29 (6 Pt 1), 563–570.
Taylor, S. E., Falke, R. L., Shoptaw, S. J., & Lichtman, R. R. (1986). Social support, support groups, and the cancer patient. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 54 (5), 608–615.
Te Poel, F., Bolman, C., Reubsaet, A., & de Vries, H. (2009). Efficacy of a single computer-tailored e-mail for smoking cessation: Results after 6 months. Health Education Research, 24 (6), 930–940.
Thomas, R. (2002). School-based programmes for preventing smoking. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 4 , CD001293.
Thomas, R., & Perera, R. (2013). School-based programmes for preventing smoking. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 4 , CD001293.
Thurstone, L. L. (1931). Measurement of social attitudes. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 26 , 249–269.
Tichenor, P. J., Donohue, G. A., & Olien, C. N. (1970). Mass media flow and differential growth in knowledge. Public Opinion Quarterly, 34 .
Tu, H. T., & Cohen, G. R. (2008). Striking jump in consumers seeking health care information. Tracking Report, 20 , 1–8.
Turner, J. C. (1991). Social influence . Belmont: Wadsworth Publishing.
Tyler-Smith, K. (2006). Early attrition among first time eLearners: A review of factors that contribute to drop-out, withdrawal and non-completion rates of adult learners undertaking eLearning programmes. Journal of Online Learning and Teaching, 2 , 73–85.
Uchino, B. N. (2006). Social support and health: A review of physiological processes potentially underlying links to disease outcomes. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 29 (4), 377.
USDHHS. (1980). Promoting health/preventing disease: Objectives for the nation . Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office.
USDHHS. (1990). The health benefits of smoking cessation. A report of the Surgeon General’s Office on Smoking and Health . Rockville: U.S. Govt. Printing Office.
Valente, T. W. (2002). Evaluating health promotion programs . New York: Oxford University Press.
van der Velde, F. W., Hooykaas, C., & van der Pligt, J. (1996). Conditional versus unconditional risk estimates in models of AIDS-related risk behaviour. Psychology & Health, 12 (1), 87.
van Keulen, H. M., Mesters, I., Ausems, M., Van Breukelen, G., Campbell, M., Resnicow, K., Brug, J., & De Vries, H. (2011). Tailored print communication and telephone motivational interviewing are equally successful in improving multiple lifestyle behaviors in a randomized controlled trial. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 41 (1), 104–118.
van Osch, L., Reubsaet, A., Lechner, L., & de Vries, H. (2008a). The formation of specific action plans can enhance sun protection behavior in motivated parents. Preventive Medicine, 47 (1), 127–132.
van Osch, L., Reubsaet, A., Lechner, L., Candel, M., Mercken, L., & De Vries, H. (2008b). Predicting parental sunscreen use: Disentangling the role of action planning in the intention-behavior relationship. Psychology and Health, 23 (7), 829–846.
van Osch, L., Lechner, L., Reubsaet, A., & De Vries, H. (2010). From theory to practice: An explorative study into the instrumentality and specificity of implementation intentions. Psychology & Health, 25 (3), 351–364.
van Stralen, M. M., Kok, G., de Vries, H., Mudde, A. N., Bolman, C., & Lechner, L. (2008). The Active plus protocol: Systematic development of two theory-and evidence-based tailored physical activity interventions for the over-fifties. BMC Public Health, 8 (1), 399.
Vartiainen, E., Puska, P., Koskela, K., Nissinen, A., & Toumilehto, J. (1986). Ten-year results of a community-based anti-smoking program (as part of the North Karelia Project in Finland). Health Education Research, 1 (3), 175–184.
Vassallo, M., Saba, A., Arvola, A., Dean, M., Messina, F., Winkelmann, M., Claupein, E., Lähteenmäki, L., & Shepherd, R. (2009). Willingness to use functional breads. Applying the Health Belief Model across four European countries. Appetite, 52 (2), 452.
Velicer, W. F., Diclemente, C. C., Rossi, J. S., & Prochaska, J. O. (1990). Relapse situations and self-efficacy: An integrative model. Addictive Behaviors, 15 (3), 271–283.
Velicer, W. F., Prochaska, J. O., Bellis, J. M., DiClemente, C. C., Rossi, J. S., Fava, J. L., & Steiger, J. H. (1993). An expert system intervention for smoking cessation. Addictive Behaviors, 18 (3), 269–290.
Velicer, W. F., Prochaska, J. O., & Redding, C. A. (2006). Tailored communications for smoking cessation: Past successes and future directions. Drug and Alcohol Review, 25 (1), 49–57.
Vernon, S. W. (1999). Risk perception and risk communication for cancer screening behaviors: A review. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. Monographs, 25 , 101–119.
Verplanken, B., & Faes, S. (1999). Good intentions, bad habits, and effects of forming implementation intentions on healthy eating. European Journal of Social Psychology, 29 (5-6), 591.
Vries, H. D., & Mudde, A. N. (1998). Predicting stage transitions for smoking cessation applying the attitude-social influence-efficacy model. Psychology and Health, 13 (2), 369–385.
Wagner, T. H., Bundorf, M. K., Singer, S. J., & Baker, L. C. (2005). Free internet access, the digital divide, and health information. Medical Care, 43 (4), 415–420.
Webb, T. L., & Sheeran, P. (2006). Does changing behavioral intentions engender behavior change? A meta-analysis of the experimental evidence. Psychological Bulletin, 132 (2), 249–268.
Webb, T. L., Joseph, J., Yardley, L., & Michie, S. (2010). Using the internet to promote health behavior change: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of theoretical basis, use of behavior change techniques, and mode of delivery on efficacy. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 12 (1), e4.
Weinstein, N. D. (1988). The precaution adoption process. Health Psychology, 7 (4), 355–386.
Weinstein, N. D., & Sandman, P. M. (1992). A model of the precaution adoption process: Evidence from home radon testing. Health Psychology, 11 (3), 170–180.
Weinstein, N. D., Lyon, J. E., Sandman, P. M., & Cuite, C. L. (1998). Experimental evidence for stages of health behavior change: The precaution adoption process model applied to home radon testing. Health Psychology, 17 (5), 445.
WHO. (1978). Declaration of Alma-Ata . International conference on Primary Health Care, Alma-Ata, USSR, 6–12 September. Geneva: WHO.
WHO. (1985). Prerequisites for health. In WHO Regional Office of Europe (Ed.), Targets for all: Targets in support of the European regional strategy for health for all . Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office of Europe.
WHO. (1986). Ottawa charter of health promotion . In Health promotion I , Ottawa.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2000). Healthy people 2010: Understanding and improving health (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office.
WHO. (2013). In J. M. Pelikan, I. Kickbusch, F. Apfel, & A. D. Tsouros (Eds.), Health literacy; solid facts .
WHO, [WHO definition of Health]. (1946). Preamble to the Constitution of the World Health Organization as adopted by the International Health Conference , New York, 19–22 June 1946; signed on 22 July 1946 by the representatives of 61 States (Official Records of the World Health Organization, no. 2, p. 100) and entered into force on 7 April 1948.
Wielm, A. G. (2004). Digital Nation: Towards an inclusive information society (pp. 133–134). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Wiers, R. W., Bartholow, B. D., van den Wildenberg, E., Thush, C., Engels, R. C. M. E., Sher, K. J., Grenard, J., Ames, S. L., & Stacy, A. W. (2007). Automatic and controlled processes and the development of addictive behaviors in adolescents: A review and a model. Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior, 86 (2), 263–283.
Wiers, R. W., Rinck, M., Kordts, R., Houben, K., & Strack, F. (2009). Retraining automatic action-tendencies to approach alcohol in hazardous drinkers. Addiction, 105 (2), 279–287.
Wilde, M. H., & Garvin, S. (2007). A concept analysis of self-monitoring. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 57 (3), 339–350.
Wilson, M. G., Holman, P. B., & Hammock, A. (1996). A comprehensive review of the effects of worksite health promotion on health-related outcomes. American Journal of Health Promotion, 10 (6), 429–435.
Winett, L. B., & Wallack, L. (1996). Advancing public health goals through the mass media. Journal of Health Communication, 1 (2), 173–196.
Ziegelmann, J. P., Lippke, S., & Schwarzer, R. (2006). Adoption and maintenance of physical activity: Planning interventions in young, middle-aged, and older adults. Psychology & Health, 21 (2), 145–163.
Ziegelmann, J. P., Luszczynska, A., Lippke, S., & Schwarzer, R. (2007). Are goal intentions or implementation intentions better predictors of health behavior? A longitudinal study in orthopedic rehabilitation. Rehabilitation Psychology, 52 (1), 97.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Health Promotion, Maastricht University, Maastricht, The Netherlands
Hein de Vries & Stef P. J. Kremers
Department of Psychology and Methods, Bremen International Graduate School of Social Sciences, Jacobs University Bremen, Bremen, Germany
Sonia Lippke
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hein de Vries .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Health Behavior, Gillings School of Global Public Health, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA
Edwin B. Fisher
Psychological Sciences, University of California, Merced, Merced, CA, USA
Linda D. Cameron
Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences and Department of Internal Medicine, The University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, USA
Alan J. Christensen
Department of Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy, University of Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland
Ulrike Ehlert
School of Public Health, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing, China
Melbourne School of Population and Global Health, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia
Brian Oldenburg
Departments of Medical Psychology, Academic Medical Center (AMC) and VU University Medical Center (VUMC), Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Frank J. Snoek
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Science+Business Media LLC
About this chapter
de Vries, H., Kremers, S.P.J., Lippke, S. (2018). Health Education and Health Promotion: Key Concepts and Exemplary Evidence to Support Them. In: Fisher, E., et al. Principles and Concepts of Behavioral Medicine. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-93826-4_17
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-93826-4_17
Published : 09 October 2018
Publisher Name : Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN : 978-0-387-93825-7
Online ISBN : 978-0-387-93826-4
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Behavioral Science and Psychology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.4: Relevance of Scholarly Writing to the Nursing Profession
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 16483

- Lapum et al.
- Ryerson University (Daphne Cockwell School of Nursing) via Ryerson University Library
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Scholarly writing is a form of communication and a necessary skill that is important to the nurse’s role as a clinician, professional, a leader, a scholar, an educator, and an advocate. As a student, developing skills in scholarly writing will help prepare you for your nursing role.
Types of scholarly writing that you may be involved in as a nurse are:
- Social awareness and advocacy campaigns in which you share knowledge and bring awareness to an issue or a new policy.
- Educating and influencing people and communities. The power of writing provides a means for nurses to state their position and influence others. Nurses are involved in crafting policy ideas to influence stakeholders and government bodies on public health issues.
- Best practice guidelines, standards of practice, and policies and procedures to inform nursing practice.
- Research grants and manuscripts for publication.
- Reflective practice, which is a professional expectation for nurses to demonstrate their commitment to life-long learning and continuing competence by reflecting on their practice (College of Nurses of Ontario, 2018).
Nurses may engage in scholarly writing in ways that differ from other disciplines . For example:
- As noted above, nurses engage in many forms of scholarly writing, so you should be prepared to tailor the style of writing to your audience and your objectives.
- In nursing and other health-related fields, you must incorporate evidence to support your statements.
- It is important that you draw from scholarly sources, such as peer-reviewed journals, as opposed to magazines or books.
- You need to be clear and concise, with a logical flow in your writing from point A to B.
- Scholarly writing allows you develop your capacity as a communicator, a skill that transcends domains of professional and personal life.
College of Nurses of Ontario (2018, October). QA Program. Retrieved from https://www.cno.org/en/myqa/
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- Themed Collections
- Editor's Choice
- Ilona Kickbusch Award
- Supplements
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Online
- Open Access Option
- Self-Archiving Policy
- About Health Promotion International
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
Introduction, authors' contributions, acknowledgements.
- < Previous
Nurses' roles in health promotion practice: an integrative review
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Virpi Kemppainen, Kerttu Tossavainen, Hannele Turunen, Nurses' roles in health promotion practice: an integrative review, Health Promotion International , Volume 28, Issue 4, December 2013, Pages 490–501, https://doi.org/10.1093/heapro/das034
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Nurses play an important role in promoting public health. Traditionally, the focus of health promotion by nurses has been on disease prevention and changing the behaviour of individuals with respect to their health. However, their role as promoters of health is more complex, since they have multi-disciplinary knowledge and experience of health promotion in their nursing practice. This paper presents an integrative review aimed at examining the findings of existing research studies (1998–2011) of health promotion practice by nurses. Systematic computer searches were conducted of the Cochrane databases, Cinahl, PubMed, Web of Science, PsycINFO and Scopus databases, covering the period January 1998 to December 2011. Data were analysed and the results are presented using the concept map method of Novak and Gowin. The review found information on the theoretical basis of health promotion practice by nurses, the range of their expertise, health promotion competencies and the organizational culture associated with health promotion practice. Nurses consider health promotion important but a number of obstacles associated with organizational culture prevent effective delivery.
The role of nurses has included clinical nursing practices, consultation, follow-up treatment, patient education and illness prevention. This has improved the availability of health-care services, reduced symptoms of chronic diseases, increased cost-effectiveness and enhanced customers' experiences of health-care services ( Strömberg et al ., 2003 ; Griffiths et al ., 2007 ). In addition, health promotion by nurses can lead to many positive health outcomes including adherence, quality of life, patients' knowledge of their illness and self-management ( Bosch-Capblanc et al ., 2009 ; Keleher et al ., 2009 ). However, because of the broad field of health promotion, more research is needed to examine the role of health promotion in nursing ( Whitehead, 2011 ).
The concept of health promotion was developed to emphasize the community-based practice of health promotion, community participation and health promotion practice based on social and health policies ( Baisch, 2009 ). However, empirical studies indicate that nurses have adopted an individualistic approach and a behaviour-changing perspective, and it seems that the development of the health promotion concept has not influenced practical health promotion practices by nurses ( Casey, 2007a ; Irvine, 2007 ). On the other hand, there has been much discussion about how to include health promotion in nursing programmes and how to redirect nurse education from being disease-orientated towards a health promotion ideology ( Rush, 1997 ; Whitehead, 2003 ; Mcilfatrick, 2004 ).
The aim of this integrative review was to collate the findings of past research studies (1998–2011) of nurses' health promotion activities. The research questions addressed were: (i) What type of health promotion provides the theoretical basis for nurses' health promotion practice? (ii) What type of health promotion expertise do nurses have? (iii) What type of professional knowledge and skills do nurses undertaking health promotion exhibit? (iv) What factors contribute to nurses' ability to carry out health promotion?
An integrative review was chosen because it allowed the inclusion of studies with diverse methodologies (for example, qualitative and quantitative research) in the same review ( Cooper, 1989 ; Whittemore, 2005 ; Whittemore and Knafl, 2005 ). Integrative reviews have the potential to generate a comprehensive understanding, based on separate research findings, of problems related to health care ( Kirkevold, 1997 ; Whittemore and Knafl, 2005 ). The integrative review was split into the following phases: problem identification, literature search, data evaluation, data analysis and presentation of the results ( Whittemore and Knafl, 2005 ).
Search method
Several different databases were searched to identify relevant published material. Systematic searches of the Cochrane databases, Cinahl, PubMed, Web of Science, PsycINFO and Scopus databases were undertaken using the search string ‘nurs* AND professional competence* OR clinical competence* OR professional skill* OR professional knowledg* OR clinical skill* OR clinical knowledg* AND health promotion OR preventive health care OR preventive healthcare’. The searches were limited to studies published during the period 1998–2011 because, prior to 1998, nurses' health promotion practice was mainly linked to health education.
Search result
The original search identified 1141 references: 119 in the Cochrane databases; 227 in Cinah, 345 in PubMed, 128 in the Web of Science, 100 in PsycINFO and 222 in Scopus. After duplicate papers were excluded one researcher (V.K.) read the titles and abstracts of the remaining 412 research papers. No specific evaluation criteria are employed when conducting an integrative review using diverse empirical sources; one approach is to evaluate methodological quality and informational value ( Whittemore and Knafl, 2005 ). All three researchers (V.K., K.T. and H.T.) defined the inclusion criteria together. Studies were included in the integrative review if they met the following criteria: the language had to be English, Swedish or Finnish, as translators for other languages were not available and the papers had to be published in peer-reviewed journals and describe nurses' health promotion roles, knowledge or skills and/or factors that contributed to nurses' ability to implement health promotion in nursing delivered through hospital or primary health-care services. The main exclusion criteria were: the published works were editorials, opinions, discussions or textbooks, or they described health promotion programmes, competencies other than health promotion or nursing curricula, or if the group studied included patients. The included studies were tabulated in chronological order under the following headings: citation, aim of the paper, methodology, size of the sample, measured variables, method of analysis, major results, concepts used as the basis of the study and limitations. Studies included in this review are available in Supplementary data, Table S1 .
Data analysis
Conducting an integrative review that analyses various types of research paper is a major challenge ( Whittemore and Knafl, 2005 ). In this review, the concept map method was adopted for both data analysis and presentation of the results. The use of concept mapping promotes conceptual understanding and provides a strategy for analysing and organizing information and identifying, graphically displaying and linking concepts. The concept map method was applied according to the recommendations of Novak and Gowin [( Novak and Gowin, 1984 ), p. 15–40] and Novak ( Novak, 1993 , 2002 , 2005 ). According to Novak ( Novak, 1993 , 2002 , 2005 ) the process of concept mapping involves six phases: (i) Identify a key question that focuses on a problem, issue or knowledge central to the purpose of the concept map. (ii) Identify concepts through the key question. (iii) Start to construct the concept map by placing the key concepts at the top of the hierarchy. After that, select defining concepts and arrange hierarchially below of the key concepts. (iv) Combine the concepts by cross-links or links between concepts in different segments or domains of the concept map. (v) Give the cross-links a name of a word or two. (vi) To concepts can be added specific examples of events or objectives that clarify the meaning of the concept.
All three researchers (V.K., K.T. and H.T.) were involved in the concept mapping process. The process proceeded as follows: first, one researcher (V.K.) read studies that met the inclusion criteria and the concepts were identified through the four research questions upon which the review is based. Second, one researcher (V.K.) began to construct four concept maps hierarchically. This was achieved by putting the key concepts on the top of the left side of a page then listing definitions of the concepts down the middle of each page. Other researchers (K.T. and H.T.) verified the first and the second phases of the concept mapping process. Third, one researcher (V.K.) continued the construction of each concept map by combining main concepts and definition concepts using links that were then named. Other researchers (K.T. and H.T.) critically evaluated the concept maps thus produced. Fourth, one researcher (V.K.) selected examples of the main concepts and these were listed on the right side of each page for clarification.
In the end 40 research papers, were included in our integrative review. The research papers were methodologically very diverse: 16 of them included qualitative approaches; 14 were different types of reviews; 8 were quantitative; 1 used concept analysis and 1 was a mixed-method study. Twelve empirical studies were conducted in hospitals and fourteen in primary health-care settings. Eleven studies were published in the period 1998–2004, twenty-two between 2005 and 2009 six between 2010 and 2011.
What type of health promotion provides the theoretical basis for nurses' health promotion practice?
The theoretical basis underlying nurses' health promotion activities was identified in 25 of the research papers ( Benson and Latter, 1998 ; McDonald, 1998 ; Robinson and Hill, 1998 ; Sheilds and Lindsey, 1998 ; Burge and Fair, 2003 ; Hopia et al ., 2004 ; Whitehead, 2004 , 2006a , b , c , 2009 , 2011 ; Berg et al ., 2005 ; Runciman et al ., 2006 ; Casey, 2007a , b ; Folke et al ., 2007 ; Irvine, 2007 ; Piper, 2008 ; Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008 ; Chambres and Thompson, 2009 ; Fagerström, 2009 ; Richard et al ., 2010 ; Samarasinghe et al ., 2010 ; Povlsen and Borup, 2011 ). According to these papers the theoretical basis of health promotion reflects the type of practical actions undertaken by nurses to promote the health of patients, families and communities. The research suggests that nurses work from either a holistic and patient-oriented theoretical basis or take a chronic diseases and medical-oriented approach. These theoretical foundations were considered to represent the main concepts of health promotion orientation and public health orientation in this review (Figure 1 ).
Concepts and examples of the theoretical basis of nurses' health promotion activities.
Health promotion orientation
The most common factor influencing the concept of health promotion orientation was individual perspective ( Robinson and Hill, 1998 ; Hopia et al ., 2004 ; Runciman et al ., 2006 ; Casey, 2007a ; Chambres and Thompson, 2009 ; Samarasinghe et al ., 2010 ; Povlsen and Borup, 2011 ). When nurses' health promotion activities were guided by individual perspective nurses' exhibited a holistic approach in their health promotion practice, they concentrated on activities such as helping individuals or families to make health decisions or supporting people in their engagement with health promotion activities ( Hopia et al ., 2004 ; Irvine, 2007 ; Chambres and Thompson, 2009 ; Samarasinghe et al ., 2010 ; Povlsen and Borup, 2011 ). Nurses' strategies for health promotion included giving information to patients and providing health education ( Casey, 2007a ). However, patient participation was mainly limited to personal aspects of care, such as letting patients decide on a menu, when to get out of bed and what clothes they wanted to wear ( Casey, 2007a ).
The second common defining concept of health promotion orientation was empowerment, which was related to collaboration with individuals, groups and communities ( McDonald, 1998 ; Berg et al., 2005 ; Whitehead, 2006a ; Irvine, 2007 ; Piper, 2008 ; Richard et al ., 2010 ; Samarasinghe et al ., 2010 ). Such orientation was described in these studies in terms of nurse–patient communication and patient, group and community participation. Although these studies found empowerment to be one of the most important theoretical bases for health promotion activities by nurses, empowerment was not embedded in nurses' health promotion activities ( Irvine, 2007 ).
The third common defining concept of health promotion orientation was social and health policy ( Benson and Latter, 1998 ; Whitehead, 2004 , 2006a , b , 2009 , 2011 ). These studies suggested that nurses' health promotion activities should be based on the recommendations in, for example, the World Health Organization's (WHO) charters and declarations and directives and guidance from professional and governmental organizations. However, the studies examined found that nurses were not familiar with social and health policy documents and that they did not apply them to their nursing practice ( Benson and Latter, 1998 ; Whitehead, 2011 ).
The last defining concept of health promotion orientation was community orientation ( Sheilds and Lindsey, 1998 ; Whitehead, 2004 ; Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008 ). These papers revealed that nurses had knowledge of community-orientated health promotion: they were expected to use health surveillance strategies, work collaboratively with other professionals and groups and respect and interact with different cultures. In addition a health promotion orientation appeared to result in nurses working more closely with members of communities, for example, being involved in voluntary work and implementation of protective and preventive health measures.
Public health orientation
Public health-orientated chronic disease prevention and treatment has traditionally been the theoretical basis of nurses' health promotion activities ( Burge and Fair, 2003 ; Berg et al ., 2005 ; Whitehead, 2006c ; Folke et al ., 2007 ; Casey, 2007b ; Irvine, 2007 ; Chambres and Thompson, 2009 ; Fagerström, 2009 ; Richard et al. , 2010 ). The first defining concept of public health orientation was disease prevention ( Berg et al ., 2005 ; Whitehead, 2006c , Folke et al ., 2007 ; Irvine, 2007 ; Fagerström, 2009 ; Richard et al. , 2010 ). According to these studies, this occurred in health promotion when the focus was on diagnosis, physical health and the relief of the physical symptoms of disease. The second defining concept of public health orientation was the authoritative approach ( Burge and Fair, 2003 ; Casey, 2007b ; Irvine, 2007 ; Chambres and Thompson, 2009 ). This approach emphasizes the need for nurses to give information to patients. In addition, the authoritative approach suggests that health promotion activities should aim to change patients' behaviour ( Irvine, 2007 ; Chambres and Thompson, 2009 ).
What type of health promotion expertise do nurses have?
The expertise of nurses with respect to health promotion was described in 16 research papers ( Robinson and Hill, 1998 ; Whitehead, 2001 , 2006b , 2007 , 2009 , 2011 ; Hopia et al ., 2004 ; Cross, 2005 ; Jerden et al ., 2006 ; Runciman et al ., 2006 ; Kelley and Abraham, 2007 ; Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008 ; Fagerström, 2009 ; Parker et al ., 2009 ; Goodman et al ., 2011 ; Whitehead, 2011 ). According to these papers nurses implemented a range of types of health promotion activity and applied different health promotion expertise across a wide range of nursing contexts. Depending on the context nurses are able to make use of a variety of types of expertise in health promotion. Nurses can be classified into: general health promoters, patient-focused health promoters and project management health promoters (Figure 2 ).
Concepts and examples of the types of nurses' expertise as health promoters.
General health promoters
Health promotion by nurses is associated with common universal principles of nursing. The most common health promotion intervention used by nurses is health education ( Robinson and Hill, 1998 ; Whitehead, 2001 , 2007 , 2011 ; Runciman et al ., 2006 ; Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008 ; Parker et al ., 2009 ). General health promoters are expected to have knowledge of health promotion, effective health promotion actions, national health and social care policies and to have the ability to apply these to their nursing practice ( Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008 ; Whitehead, 2009 ).
Patient-focused health promoters
There is growing recognition that different patient groups, such as the elderly or families with chronic diseases, have different health promotion needs. In promoting the health of these different groups, nurses can be regarded as patient-focused health promoters ( Hopia et al ., 2004 ; Cross, 2005 ; Jerden et al ., 2006 ; Kelley and Abraham, 2007 ; Goodman et al ., 2011 ). These studies revealed that when health promotion for patient groups who need high levels of care and treatment is required, nurses must have the ability to include health promotion activities in their daily nursing practice.
Managers of health promotion projects
Nurses should be able to plan, implement and evaluate health promotion interventions and projects ( Runciman et al ., 2006 ; Whitehead, 2006b ; Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008 ; Fagerström, 2009 ). Projects can facilitate the development of health promotion in nursing practice ( Runciman et al ., 2006 ). Thus, managers of health promotion projects should have advanced clinical skills and take the responsibility in supervising and leading research and development actions in nursing as well as having the ability to co-ordinate educational and developmental interventions in health-care units and communities ( Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008 ; Fagerström, 2009 ).
What type of professional knowledge and skills do nurses undertaking health promotion exhibit?
Nurses' knowledge of health promotion and their relevant practical skills were described in 18 research papers ( McDonald, 1998 ; Nacion et al. , 2000 ; Burge and Fair, 2003 ; Whitehead, 2003 ; Hopia et al ., 2004 ; Reeve et al ., 2004 ; Spear, 2004 ; Cross, 2005 ; Irvine, 2005 , 2007 ; Rush et al ., 2005 ; Jerden et al ., 2006 ; Casey, 2007b ; Kelley and Abraham, 2007 ; Piper, 2008 ; Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008 ; Wilhelmsson and Lindberg, 2009 ; Goodman et al ., 2011 ). These studies suggested that nurses' health promotion activities consisted of a variety of competencies. We classified these into multidisciplinary knowledge, skill-related competence, competence with respect to attitudes and personal characteristics (Figure 3 ).
Concepts and examples of nurses' health promotion competencies.
Multidisciplinary knowledge
Nurses' health promotion activities were often based on a broad and multidisciplinary knowledge ( Nacion et al ., 2000 ; Burge and Fair, 2003 ; Spear, 2004 ; Irvine, 2005 ; Casey, 2007b ; Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008 ; Whitehead, 2009 ). This included a knowledge of: health in different age groups; epidemiology and disease processes and health promotion theories. In addition, nurses need to have the ability to apply this knowledge to their health promotion activities ( Burge and Fair, 2003 ; Spear, 2004 ; Irvine, 2005 ; Runciman et al ., 2006 ; Piper, 2008 ; Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008 ). Nurses were also expected to be aware of economic, social and cultural issues, social and health policies and their influence on lifestyle and health behaviour ( Burge and Fair, 2003 ; Irvine, 2005 ).
Skill-related competence
Nurses must possess a variety of health promotion skills; of these, communication skills were considered to be the most important ( McDonald, 1998 ; Nacion et al. , 2000 ; Burge and Fair, 2003 ; Hopia et al ., 2004 ; Irvine, 2005 ; Jerden et al ., 2006 ; Casey, 2007b ). Nurses play a particularly important role when they encourage patients and their families to participate in decision-making related to treatment or to discuss and express their feelings about situations associated with serious illness ( Hopia et al ., 2004 ). Skill-related competence also includes the ability to support behavioural changes in patients and the skill to respond to patients' attitudes and beliefs ( Burge and Fair, 2003 ). In addition, skill-related competence involves teamwork, time management, information gathering and interpretation and the ability to search for information from different data sources ( Irvine, 2005 ; Jerden et al ., 2006 ).
Competence with respect to attitudes
Competence with respect to attitudes emerged as a positive feature of health promotion ( Whitehead, 2003 ; Reeve et al ., 2004 ; Spear, 2004 ; Cross, 2005 ; Irvine, 2005 , 2007 ; Kelley and Abraham, 2007 ; Piper, 2008 ; Wilhelmsson and Lindberg, 2009 ). Effective health promotion practice requires nurses to adopt a proactive stance and act as an advocate. An affirmative and egalitarian attitude towards patients and their families, as well as the desire to promote their health and well-being, are important attitudes with respect to health promotion activities ( Irvine, 2005 , 2007 ; Wilhelmsson and Lindberg, 2009 ). In addition, nurses who have personal experience, for example, of having had a baby, have a more positive attitude towards promoting the health of patients in the same situation ( Spear, 2004 ).
Personal characteristics
Traditionally, nurses were perceived to be healthy role models, engaging in healthy activities, not smoking and maintaining an ideal weight Burge and Fair, (2003) ; Reeve et al. , 2004 ; Rush et al ., 2005 ). In addition, personal confidence and flexibility are personal characteristics that nurses working in health promotion are expected to possess ( Burge and Fair, 2003 ; Rush et al ., 2005 ).
What factors contribute to nurses' ability to carry out health promotion?
Thirteen research papers identified features which contributed to nurses' health promotion activities ( Robinson and Hill, 1998 ; Reeve et al ., 2004 ; Jerden et al. , 2006 ; Runciman et al ., 2006 ; Whitehead, 2006b , 2009 , 2011 ; Casey, 2007a , b ; Kelley and Abraham, 2007 ; Wilhelmsson and Lindberg, 2009 ; Beaudet et al ., 2011 ; Goodman et al ., 2011 ). All of the features related to cultural aspects of the organization in which nurses work. We considered that these could be classified as either supportive or discouraging (Figure 4 ).
Concepts and examples of organizational culture associated with health promotion activities.
First, organizational culture consisted of three supportive aspects: hospital managers, culture of health and education. The hospital managers were responsible for whether health promotion was a strategically planned and whether it was considered to be of great importance ( Whitehead, 2006b , 2009 ). In addition, the hospital managers were key individuals in ensuring that health promotion activities did not conflict with other work priorities ( Jerden et al ., 2006 ; Casey, 2007a ; Beaudet et al ., 2011 ). Hospital managers also have an important role in cultivating a culture of health in the work community, for instance by prohibiting smoking during working time ( Casey, 2007a ). Education enhanced nurses' health promotion skills and health promotion projects were catalysts for health promotion in nursing practice ( Goodman et al ., 2011 ). Organizational culture included three discouraging factors. The major one was a lack of resources, including a lack of time, equipment (e.g. computers) and health education material ( Robinson and Hill, 1998 ; Reeve et al ., 2004 ; Runciman et al ., 2006 ; Casey, 2007b ; Kelley and Abraham, 2007 ; Wilhelmsson and Lindberg, 2009 ; Beaudet et al ., 2011 ). In addition, nurses may lack skills to implement health promotion in their working place ( Goodman et al ., 2011 ). Recent studies have also revealed that health promotion activities are still unclear to nurses ( Beaudet et al ., 2011 ; Whitehead, 2011 ).
Several authors have identified a need to clarify the concept of health promotion in nursing ( Goodman et al ., 2011 ; Whitehead, 2011 ). We found the concept map method useful to enhance conceptual understanding of this complex nursing phenomenon. This integrative review was intended to identify the findings of nursing-specific studies of health promotion activities published in the period 1998–2011. We identified 40 relevant English research papers. Most of these studies were published between 2005 and 2009. Combining qualitative and quantitative studies is complex and can introduce bias and error ( Whittemore and Knafl, 2005 ). The data examined herein originated from methodologically diverse research. Therefore, we should be cautious of generalizing our findings. Most of the studies were qualitative, but a broad range of health promotion activities undertaken by nurses was described. The concept map method was used to analyse the data; the results of this review are reported both as text and concept maps. Concept maps are rarely used as a data analysis tool and therefore we employed researcher triangulation (V.K., K.T. and H.T.) during the research process; this enhanced our understanding and increased scientific rigour ( Jones and Bugge, 2006 ).
We found that health promotion and public health orientation have guided nurses' health promotion activities (e.g. McDonald, 1998 ; Whitehead, 2009 ; Richard et al ., 2010 ; Povlsen and Borup, 2011 ). It was surprising that, even though there has been much public debate and research has emphasized that health policies should guide nurses' health promotion activities worldwide, health policies have little impact on nursing practice (e.g. Benson and Latter, 1998 ; Irvine, 2007 ; Whitehead, 2011 ). Nurses have a variety of types of expertise, some working as general health promoters, some as patient-focused health promoters and some as managers of health promotion projects (e.g. Whitehead, 2008 ; Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008 ; Fagerström, 2009 ; Goodman et al ., 2011 ). The management of health promotion projects is particularly important, although only three studies ( Whitehead, 2006b ; Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008 ; Fagerström, 2009 ) described the type of expertise possessed by such managers. We found that there has been great interest in nurses' health promotion competencies (e.g. Irvine, 2005 , 2007 ; Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008 ; Wilhelmsson and Lindberg, 2009 ). A number of studies found that nurses' health promotion activities were based on multidisciplinary knowledge (e.g. Burge and Fair, 2003 ; Irvine, 2005 ; Whitehead, 2009 ). Interestingly, knowing about the trends that will influence the population's health in the future, such as multiculturalism, new technologies and ecological changes, were not identified as nurses' health promotion competencies. Unexpectedly for us the competencies associated with attitudes were not emphasized as one of the most important competencies even though nurses should be advocates of good health. We also found that nurses' individual health-related beliefs and lifestyles are important personal characteristics in health promotion and that nurses are expected to be healthy role models (e.g. Burge and Fair, 2003 ; Reeve et al. , 2004 ; Rush et al. , 2005 ). Nurses are aware of the importance of health promotion, but organizational culture with respect to health promotion can either support or discourage them from implementing it (e.g. Reeve et al ., 2004 ; Casey, 2007a , b ; Goodman et al ., 2011 ; Whitehead, 2011 ). Managers in health-care organizations should appreciate the value of health promotion activities and ensure adequate resources for their implementation (e.g. Casey, 2007b ; Beaudet et al ., 2011 ).
According to much of the health promotion research, it appears that nurses have not yet demonstrated a clear and obvious political role in implementing health promotion activities. Instead, nurses can be considered general health promoters, with their health promotion activities based on sound knowledge and giving information to patients. Nursing is an appropriate profession in which to implement health promotion, but several barriers associated with organizational culture have a marked effect on delivery. Therefore, more research is needed to determine how to support nurses in implementing health promotion in their roles in a variety of health-care services.
V.K. was responsible for the computer-based data searches and the data analysis via the concept map method. K.T. and H.T. verified that the data searches were made properly. K.T. and H.T. verified that the concept mapping process proceeded properly and made critical appraisals in every phase of the research process. V.K. was responsible for the drafting of the manuscript. K.T. and H.T. made critical revisions to the paper for important intellectual contents, conceptualization, support in theorizing the findings and provided material support. K.T. and H.T. supervised the study.
This research received a specific grant from The Finnish Foundation for Nurse Education and The Finnish Nurses Association.
Virpi Kemppainen would like to acknowledge the support from the University of Eastern Finland, Department of Nursing Science.
Google Scholar
Google Preview
Supplementary data
Email alerts, citing articles via.
- Recommend to Your Librarian
- Journals Career Network
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1460-2245
- Print ISSN 0957-4824
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

Online Students
For All Online Programs
International Students
On Campus, need or have Visa
Campus Students
For All Campus Programs
The Importance of Health Education

Understanding the Numbers When reviewing job growth and salary information, it’s important to remember that actual numbers can vary due to many different factors — like years of experience in the role, industry of employment, geographic location, worker skill and economic conditions. Cited projections do not guarantee actual salary or job growth.
When it comes to building a healthy community, the importance of health education cannot be overlooked. Community health workers collaborate with all stakeholders in a community — from its citizens to its government, education and medical officials — to improve health and wellness and ensure equal access to healthcare.
First, What is Health Education?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), health education is a tool to improve a population's general health and wellness through promoting knowledge and healthy practices ( WHO PDF source ).
Although the subject is often taught in school settings, students aren't the only ones who need to know about health. In fact, all age groups and demographics can benefit from health education.
Why is Health Education Important?
Community health education looks at the health of a community as a whole, seeking to identify health issues and trends within a population and work with stakeholders to find solutions to these concerns.
The importance of health education impacts many areas of wellness within a community, including:
- Chronic disease awareness and prevention
- Injury and violence prevention
- Maternal and infant health
- Mental and behavioral health
- Nutrition, exercise and obesity prevention
- Tobacco use and substance abuse

Community health educators work with public health departments, schools, government offices and even local nonprofits to design educational programs and other resources to address a community’s specific needs.
“As public health professionals, with aid of community leaders, we strive to ensure community wellness as it pertains to health education,” said Dr. Tanyi Obenson .
Obenson is a public health clinical faculty member at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU) who holds a PhD in Public Health. “A healthier community is a better community,” he said.
How Does Health Education Impact a Community?
Health education can impact communities by addressing relevant issues and concerns at a local level. For example:
Healthcare Disparities

In addition to providing educational resources and programming to a community, public health educators also work to ensure all members of a community have equal access to wellness resources and healthcare services.
“When considering care access and delivery within communities, health equity and social justice are one in the same,” said Dr. Natalie Rahming , an adjunct healthcare faculty member at SNHU with almost two decades of experience working in the healthcare field. “The social determinants of health classify the various ways in which an individual’s identity characteristics and social positions are woven into a fabric of discrimination.”
According to Rahming, common health disparities include:
- Gender health disparities
- Racial or ethnic health disparities
- Rural and urban health disparities
- Socioeconomic health disparities
Rahming said racism and other disparities have manifested into unequal distribution of care across distinct groups over many generations.
“A community health worker seeks to abolish or ameliorate health inequity from a social lens, whereas other health care workers approach it at an individual perspective,” she said. “Both are critical for healthcare advancement.”
Community Health Education and Government Policy
The importance of health education also extends into policy and legislation development at a local, state and national level, informing and influencing key decisions that impact community health.
From campaigns and legislation to enforce seat belt use and prevent smoking to programs that boost the awareness and prevention of diabetes, public health workers provide research and guidance to inform policy development.

“The collaboration of community leaders is essential to form a shared commitment and results-oriented approach to improving the health of our most vulnerable populations,” she said.
The Economic Importance of Health Education
Health education can also boost a community’s economy by reducing healthcare spending and lost productivity due to preventable illness.
Obesity and tobacco use, for example, cost the United States billions of dollars each year in healthcare costs and lost productivity.
According to the National Collaborative on Childhood Obesity (NCCOR), the annual loss in economic productivity due to obesity and related issues is expected to total as much as $580 billion by 2030 ( NCCOR PDF source ). The total economic cost of tobacco use costs the United States more than $300 billion each year, including $156 billion in lost productivity , according to the CDC.
Programs designed to help community members combat expensive health issues not only boost individuals’ health but also provide a strong return on investment for communities.
According to the CDC, states with strong tobacco control programs see a $55 return on every $1 investment , mostly from avoiding costs to treat smoking-related illness. The national cost of offering the National Diabetes Prevention Program is about $500 per participant , significantly lower than the $9,600 spent on diabetes care per type 2 diabetes patient each year.
Find Your Program
How to become a community healthcare worker.
A community healthcare worker's goal is to help others, starting with education.
To begin your career in community healthcare, you'll typically need a minimum of a high school diploma or associate degree . The work done within public health and community healthcare differs from other healthcare fields and impacts communities in different ways requiring different training and understanding of healthcare.
“Unlike individual healthcare delivery, public health investigates the systems and trends that impact behaviors and outcomes within a community collectively," said Rahming. “This research facilitates the identification of needs and provision of tools to promote disease prevention, individual empowerment, and improved wellness that enhances the quality of life for all."
Earning your bachelor's degree in public health or community health could help you advance your career and better understand your work. On top of your classroom education, many community health care workers are required to complete on-the-job training. According to BLS, training often covers communication, outreach, and information based upon your specific community health focus.

Public Health Education: A Growing Field
As the health, social and economic impacts of community health education continue to grow, so does the field of public health and health promotion.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the role of health education specialist is projected to grow by 7% through 2032, faster than the average for all occupations.*
BLS said that health education specialists usually need a bachelor's degree but that some health education specialist jobs require you to have a master's degree, too.
Earning your Master of Public Health (MPH) degree could be a proactive way to expand your knowledge and prepare for a career in the public health education field. Whether you want to be a health education specialist or an epidemiologist, there are a variety of things you can do with your MPH . You can also focus your MPH studies on specific areas, such as global health, by adding a concentration to your degree.
When considering MPH programs, look for one accredited by the Council on Education for Public Health ( CEPH ), such as SNHU's. CEPH is an independent agency recognized by the U.S. Department of Education, and their accreditation means that the program has met the standards.
In an accredited MPH program, you can gain the skills you need to lead illness and disease prevention efforts, build community wellness programs and advocate for public health policy.
Whether you decide to pursue an MPH or community health education degree, the public health education field has a wide variety of settings where you may work. According to BLS, these settings include:
- Government organizations and public health departments
- Hospitals and healthcare facilities
- Nonprofit organizations
- Private businesses and employee wellness programs
- Schools and colleges

“I believe that more and more communities are seeing benefits from wellness-related initiatives and receiving positive marks about them,” Gifford said. “Hence, community leaders are seeing this as not just a business-driven necessity, but also something that impacts the well being and quality of life of their citizens.”
Discover more about SNHU’s bachelor's in community health : Find out what courses you'll take, skills you’ll learn and how to request information about the program.
*Cited job growth projections may not reflect local and/or short-term economic or job conditions and do not guarantee actual job growth. Actual salaries and/or earning potential may be the result of a combination of factors including, but not limited to: years of experience, industry of employment, geographic location, and worker skill.
Danielle Gagnon is a freelance writer focused on higher education. She started her career working as an education reporter for a daily newspaper in New Hampshire, where she reported on local schools and education policy. Gagnon served as the communications manager for a private school in Boston, MA before later starting her freelance writing career. Today, she continues to share her passion for education as a writer for Southern New Hampshire University. Connect with her on LinkedIn .
Explore more content like this article

What is Post-Graduation Depression and How to Overcome It
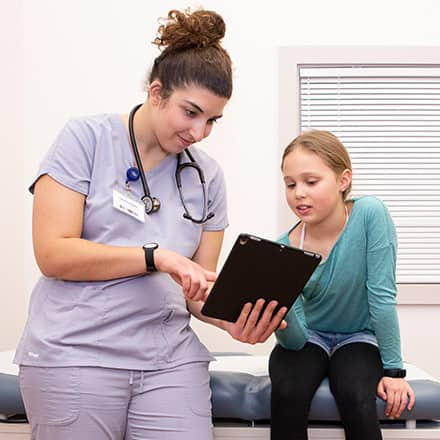

What is a Nurse Practitioner? A Valuable Healthcare Provider
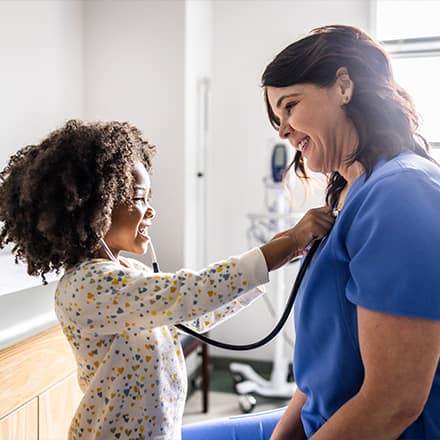

Nursing's Alphabet Soup: Nursing Acronyms Explained
About southern new hampshire university.

SNHU is a nonprofit, accredited university with a mission to make high-quality education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Founded in 1932, and online since 1995, we’ve helped countless students reach their goals with flexible, career-focused programs . Our 300-acre campus in Manchester, NH is home to over 3,000 students, and we serve over 135,000 students online. Visit our about SNHU page to learn more about our mission, accreditations, leadership team, national recognitions and awards.
- Login / Register

‘Nearly a week has passed already since International Nurses Day 2024’
STEVE FORD, EDITOR
- You are here: Nurse educators
Nurses as educators: creating teaching moments in practice
27 January, 2020
Identifying teachable moments in clinical practice is an effective way to increase workplace learning with all nurses playing a role, not just nurse educators. This article comes with a handout for a journal club discussion
Effective workplace teaching is increasingly important in healthcare, with all staff being potential educators. The introduction of new roles and the need to create capacity for increased numbers of students can make it difficult to create a good learning experience. Despite the richness of clinical practice as a learning environment, creating capacity for teaching can be challenging. This article explores the possibilities for identifying and creating teachable moments in busy clinical environments and suggests a developmental model for incorporating these learning opportunities. Teachable moments linked directly to optimal patient care can potentially influence and shape a positive learning culture in clinical environments.
Citation: Reynolds L et al (2020) Nurses as educators: creating teachable moments in practice. Nursing Times [online]; 116: 2, 25-28.
Authors: Lisa Reynolds is senior lecturer; Julie Attenborough is associate dean – director of undergraduate studies, both at School of Health Sciences, City, University of London; Jenny Halse is head of nurse education and Florence Nightingale Scholar, King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
- This article has been double-blind peer reviewed
- Scroll down to read the article or download a print-friendly PDF here (if the PDF fails to fully download please try again using a different browser)
- Download the Nursing Times Journal Club handout here to distribute with the article before your journal club meeting
Introduction
New nursing roles and apprenticeship routes, such as nursing associates and nurse degree apprenticeships, have increased the focus on work-based learning (Halse et al, 2018). This is set to be a growing area for nurse education because of the need to increase student capacity and expand the nursing workforce to meet rising demand.
The global shortage of nurses and the acute shortage in the NHS (NHS, 2019), requires immediate action including increasing nurse recruitment through traditional university routes and expanding new roles and apprenticeship routes. Each approach requires clinical workplaces to increase their teaching capacity while supporting the existing workforce to provide first-class care. Educating the workforce of tomorrow while caring for the patients of today is a challenge faced by healthcare globally. To achieve this, we propose integrating these two activities rather than treating them as separate entities.
Greater focus on the workplace as a learning environment and on the relationship between learners and their supervisors/assessors is required throughout care systems. Every nurse, midwife and nursing associate – not just those in educator roles – must see themselves as an educator. Educating others is a key principle of the Nursing and Midwifery Council’s Code (NMC, 2018), and learning opportunities need to be clearly identified by care providers, and fully exploited and valued by all.
Despite the richness of clinical practice as a learning environment, achieving and maintaining a focus on work-based learning can be challenging in busy and complex settings where patient care is the priority. However, with preparation and by embedding education and learning throughout the workplace, learning can take place in even the most-pressurised settings (Attenborough et al, 2019). The duty to support and educate students is embedded in the Code and the creation of the practice supervisor role aligns learning with care delivery. It also gives nursing and midwifery education the opportunity to engage other health professionals, although there is evidence that some nurses consider it an additional task (Attenborough et al, 2019).
This article explores how exploiting teachable moments (T-moments), or brief opportunities for learning, can be an effective way of aligning care delivery and education in the workplace, and proposes a developmental model for incorporating these learning opportunities. This follows Benner et al’s (2010) call to arms for a new approach to nurse education that moves away from decontextualised knowledge and the separation of the classroom and clinical teaching to situated learning and integration in all settings.
Learning is a combination of knowledge acquisition and its application in practice (Fuller and Unwin, 2003). In this article we explore the opportunities for work-based learning, and how to harness this opportunistically and proactively, to make T-moments an integral part of learning in practice.
T-moments are well established in school settings, where teachers identify spontaneous opportunities to explore problems and situations as they happen, with the aim of guiding learning at the student’s own pace (Lewis, 2019). They have also been conceptualised as an opportunity for learning that may be co-created through communication, often through reflective discussion and challenging assumptions (Lawson and Flocke, 2009). This approach views learning as developmental, with T-moments or brief learning opportunities building in practice on previous developmental tasks to enable the success of future learning (Ward et al, 2000). To protect learners’ self-esteem and allow them to take risks for learning to occur, supervisors must consider their maturity or readiness for learning when identifying or co-creating T-moments.
The use of T-moments in the health setting has been established in the context of patient education by harnessing key events to influence the health behaviours of service users (Lawson and Flocke, 2009). Practice supervisors may also apply T-moments in partnership with patients and carers to explore key moments in care provision and develop learners’ understanding of service users’ experiences. In this way, learners may develop skills and attributes for effective partnership working, as well as enhancing their nursing practice by developing their understanding of patients’ illness experiences and perspectives (Benner et al, 2010). A Health Education England model of delivering bite-sized teaching in the clinical environment has also had some success. For more information about bite-sized teaching , see Thompson et al (2020, p29) .
T-moments may be used to create learning opportunities by exploring conflict situations or lack of congruity between expectations and real life. For student nurses, this may be when:
- Entering a new setting;
- Joining a team;
- Confronting the theory-practice gap.
Recognising challenging situations as T-moments, and offering students time to explore their reactions through supervision or coaching in the moment, opens up space for learning and can prevent learners from acting in a confrontational or defensive manner. In this way, students can learn from their experience and adapt to the organisational culture, rather than simply being informed by it and reframing their understanding of it. This can be exposing for students and clinical teams, so support is needed to create a safe space for open communication and learning, where failure or naivety can be embraced as an opportunity for learning (Ekebergh et al, 2004).
The success of contextualised teaching, or supported learning moments, depends in part on the supervisor and requires investment in developing skilled supervisors. Constructivist educational theories operate on the premise that learning is a socially active process, in which participation and engagement with others is essential (Dudley-Marling 2012).
Supervisor role
Given that opportunistic T-moments can arise from highly charged, emotive and challenging situations, supervisors need to develop effective and trusting relationships with their learners. To be truly effective, they must try to put themselves in the position of the learner to create the conditions needed for learning to take place.
Learning may be considered a social, cultural process that happens through interactions in human relationships (Dudley-Marling, 2012), thereby in concert with others – and, in the case of T-moments, collaboratively. Supervisors may need to flag up T-moments so learners can recognise them for what they are and fully engage in the process. This may require supervisors to be explicit in their interactions with learners, rather than assuming they will automatically make the link to a learning opportunity, to break away from the perception that learning only takes place in a classroom or behind a desk. It could be as obvious as physically signalling to learners that this is a learning moment or by taking a few minutes to explain what the learning possibilities are in a given situation. Framing learning within the care context, from the patient’s perspective, assists this process (Ekebergh et al, 2004).
By signposting T-moments, and making learning from practice explicit, supervisors will support learners to develop a sense of salience, so they recognise what is important in clinical situations and develop towards effective clinical reasoning (Benner et al, 2010).
T-moments in practice
In the model presented here, T-Moments are part of a conscious process in which learners are supported to recognise learning opportunities and capitalise on this with their supervisors. Through reflection, the learning is embedded and provides the foundation for future experiential learning in the practice setting (Fig 1).

T-moments or brief learning opportunities, while largely opportunistic, can also be routine and proactively structured. A supervisor may plan an activity with a learner or try to signpost and shape the learning inherent in routine events, such as ward rounds.
Opportunistic T-moments
Many T-moments or brief learning opportunities are opportunistic, occurring during interactions and activities in clinical practice. Practice supervisors need to be able to recognise and draw on such learning opportunities to create developmental T-moments for students. This can be done in collaboration with clinical teams, bringing education to the forefront of practice.
The examples in Box 1 highlight the potential of T-moments to:
- Impart knowledge and awareness to students, staff and patients;
- Help educators grow and develop;
- Influence organisational learning through a snowballing effect.
Box 1. Opportunistic T-moments
- A midwife visits a woman three days post partum with a student midwife she is supervising. The woman is exhausted, tearful and says she feels unable to cope. The midwife involves the student in appreciating the woman’s situation and lived experience, and recognising the difference between ‘baby blues’, postnatal depression and puerperal psychosis, as explained to the mother
- A mental health nurse recognises that substance misuse is masking a mental illness in one of her patients. She works with a student to build trust, and help the service user and the student appreciate how the two things are connected
- A learning disability nurse supports a client to access contraception at a family planning clinic run by a registered nurse and midwife, and to educate staff about the sexual and relationship needs experienced by a person with learning disabilities
- A practice nurse running an asthma clinic sees a child with low oxygen saturation; he uses the exacerbation of breathing difficulties to teach the child’s family how to use an inhaler more effectively and the importance of preventative treatment, while talking to the child about a famous footballer who has asthma
- A learning disability nurse works with a student to access a social club for a client. This teaches the student that inclusive facilities for people with learning disabilities are rare, and raises awareness of the stigma and isolation that many of them face
- During a consultant-led multidisciplinary ward round, a consultant identifies a moment in which to discuss a patient’s condition and course of treatment. This could also enable interprofessional education, with the physiotherapist or nutritionist sharing their expertise and treatment plans
They show the need to include T-moments in wider strategies for supervisors and educators in practice, including identifying learning that has taken place and allowing time for reflection to maximise all opportunistic T-moments.
Drawing on real-life challenges
Nurses work in pressurised environments supporting patients with complex needs. Often, resources are limited, vacancy rates high and, increasingly, staff are working at the edge of their scope of practice. The impact of this on the learning environment and the high levels of stress experienced by nurses – evident in the 2018 NHS Staff Survey – need to be considered when introducing T-moments. A systematic review found student nurses had medium-to-high stress levels – greater than in other students – partly due to the clinical component of the programme (Labrague et al, 2017). Sources of student stress identified in the study are outlined in Box 2.
Box 2. Sources of stress among nursing students
- Fear of the unknown
- New clinical environments
- Taking care of patients
- Lack of professional knowledge/nursing skills
- Fear of failure/clinical incompetence/making mistakes
- Unfamiliarity with patients’ medical history
- Unfamiliarity with patients’ diagnoses and treatments
- Giving medication to children
- Lack of control in relationships with patients
Source: Labrague et al (2017)
Each of these areas may be exploited as a T-moment by exploring conflict situations, emotional reactions and lack of congruence between learners’ self-perceptions and how they themselves are received. The expectations students may have about clinical practice and how they will be supported may contrast with their experience of reality – this can cause stress.
Delivering education in practice settings where learners are experiencing moderate-to-severe stress is a huge barrier to learning. Acknowledging learners’ stress and a lack of congruence with expectations can help create a safe space to fully exploit T-moments, rather than focusing on bridging a theory-practice gap. Techniques such as self-disclosure and storytelling may also make students less fearful about clinical practice and more able to recognise learning opportunities in challenging situations (Attenborough and Abbott, 2018).
Proactive T-moments
Supervisors in practice may also identify opportunities to plan for T-moments to occur during day-to-day activities and scheduled events, such as routine admissions or clinical reviews. Planning considerations include how to:
- Engage the multidisciplinary team;
- Involve service users and carers in the teaching;
- Create a safe, comfortable learning environment.
Observation
A supervisor can identify opportunities for learners to observe scheduled events. Observations may focus on specific areas with learning and development supported by creating an observation guide or including a task for the learner. Observation notes can be used for reflection and further learning.
Integration
Incorporating education into existing structures ensures it is integrated into current work, instead of being treated as an additional activity, requiring additional resources. For example, learning may be included as standard on routine meeting agendas, and identifying learning opportunities can be incorporated into the structure of huddles in the clinical setting for the benefit of the team as well as learners. In this way, potential T-moments can be harnessed and learning embedded more fully within a team or organisation.
Schwartz Rounds
Organising and delivering Schwartz Rounds may require extra time and financial commitment, but where they are established students should be encouraged to attend as there is evidence of deep learning (Barker et al, 2016; Cornwell et al, 2014). Schwartz Rounds bring patients and their experience into learning in the clinical setting. They create a safe, supportive environment that allows participants to explore aspects of multidisciplinary team working and care by reflecting on the emotional impact of the work.
Often Schwartz Rounds highlight a lack of congruence between theory and practice, or provoke an emotional reaction; these may be further explored to support learners’ development. The rounds also encourage a more-collaborative approach to care and allow emotional reactions to be heard, reducing clinicians’ stress. This can create a positive environment that encourages a collective approach to learning. Learning is also possible from adverse events or by focusing discussions on patient care, such as starting the meeting with a patient story.
Bite-sized teaching
HEE’s bite-sized teaching focuses on embracing every possible teaching moment and delivering high-impact tutorials in the work environment. Defined as “high-impact learning”, such teaching encourages staff to become involved in an informal way, without needing expensive equipment or IT facilities. It is accessible and finely tuned to the needs of particular clinical areas and delivered across disciplines.
Maximising T-moments
Supervisors can use a range of approaches to maximise T-moments, including:
- Coaching in situ/in the moment and observing rather than instructing, drawing on established coaching models such as OSCAR (Outcome, Situation, Choices, Actions, Review), in which learners shape their own learning (Ashworth, 2018). Examples are Collaborative Learning in Practice (CLiP) (Clarke et al, 2018) and practice learning at Northampton (PL@N) (Ashworth, 2018);
- Focusing conversation on established clinical tools and models, such as SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) to focus learning (Leonard et al, 2004);
- Encouraging the learner to think aloud during an activity;
- Reversing roles, so the learner leads an activity or teaches the supervisor;
- Supporting the learner through a structured debrief after an event;
- Signposting T-moments and learning opportunities;
- Embracing new technology and the opportunities for learning, including its impact on learners’ perceptions of their role and future career (Basheer et al, 2018);
- Actively seeking time to speak with patients to understand how living with an illness affects their lives.
There is great potential in the workplace to draw on T-moments and brief learning opportunities to enhance the experience of learners and the wider organisation. T-moments are an opportunity to raise the status of work-based learning in the clinical environment and ensure that the work of supporting learning is shared between all team members in care settings.
Identifying and recording T-moments challenges assumptions that teaching only happens in a classroom, or when linked to an academic programme, and raises the value of all learning in the practice setting. Embedding education in care provision and developing the conditions needed for effective learning may bring benefits across an organisation (Basheer et al, 2018).
Work-based learning puts greater emphasis on positive team working and addressing unhealthy practices; this can include horizontal violence – hostile, aggressive and often psychologically and socially harmful behaviour conducted by nurses towards each other (Darbyshire et al, 2019). Bullying was highlighted in the 2018 NHS Staff Survey results; these will be used to inform initiatives to enhance productivity and improve staff retention.
The increase in work-based learning in response to changes in the NHS workforce means T-moments are more important than ever. Creating a culture of learning in healthcare is the responsibility of every practitioner. They can use T-moments to link learning to patients’ needs, and ensure staff have the right skills and knowledge to deliver first-class care.
- New roles in healthcare, along with new apprenticeship routes, have resulted in a greater focus on workplace learning
- The role of all nurses as educators is embedded in new regulations for practice learning and the Nursing and Midwifery Council’s code of conduct
- Identifying teachable moments enables learning to take place in the practice setting
- Teachable moments can be both opportunistic and planned
- Educators in practice need to work in partnership with learners to recognise and maximise the benefits of teachable moments
Related files
200129 nurses as educators – creating teachable moments in practice, journal club handoutfeb 2020 t-moments.
- Add to Bookmarks
Related articles
Have your say.
Sign in or Register a new account to join the discussion.
The Importance of Nursing Education
Introduction.
In the context of present-day developments, the demand for health care services of high quality is increasing. In this regard, the significance of nurses cannot be underestimated, as they spent the greatest amount of time delivering medical services to patients. In addition, there are considerable problems with the accessibility of medical care among the broad categories of the Unites States population (Institute of Medicine (US), 2011). The necessity to expand the role of health care providers is also widely discussed (Institute of Medicine (US), 2011). The Institute of Medicine (2011) has published the report Future of Nursing: Leading Change, Advancing Health , which is aimed to address the aforementioned issues. According to it, it is essential to improve the quality of nursing education and encourage continuing it on an obligatory basis in order to resolve the current problems in the long run.
Job Options Based on Educational Level
In the modern world, there is a significant demand for nurses, and it tends to increase from year to year. There is a variety of options to start the career path. Currently, I am receiving a bachelor’s degree in nursing, which opens a range of job options in the market after finishing it. For instance, it is possible to obtain a position of a registered nurse ( Types of nursing specialties, n. d.). In case of receiving Registered Nursing License, employment opportunities of a cardiac nurse, critical care nurse, ER nurse, geriatric nurse, and a perioperative nurse ( Types of nursing specialties, n. d.). In addition, after obtaining this academic degree allows to occupy leadership and managerial positions.
Furthermore, it is possible to be employed as a certified registered nurse anesthetist, clinical nurse specialist, family nurse practitioner, mental health nurse, nurse educator, and nurse practitioner. However, the outline professions imply more in-depth training, and it is essential to receive a Master’s degree in order to apply for them. In some cases, it is required to finish a Doctoral program, and a Registered Nursing License is obligatory for all these positions.
Goals for Professional Education
The IOM report recommends the nurse to have a comprehensive education and training in their field. In addition, it insists on higher levels of education and seamless academic progression (Institute of Medicine (US), 2011). This advice defines my education plan to some extent. It is evident that as a future nurse, I have a variety of fields to establish my career. My first goal, which I am currently pursuing, is receiving a Bachelor’s Degree, which allows me to work in a variety of nursing fields. In addition, it makes my candidature more competitive in the current market.
Moreover, I am determined to continue my training and finish a doctoral program in the near six years. I am convinced that this option will make me a more qualified professional in my sphere. In addition, I am willing to try myself in administrative and managerial duties. For this reason, I consider it essential to accompany my professional education with a Master’s degree in business. I am planning to combine this program with my major one. From my perspective, these educational options are highly likely to provide me with vital knowledge, skills, and competencies in order to become a qualified and competent specialist in the future.
Competitiveness in the Job Market
Today, the higher level of education a nurse receives the more competitive worker it becomes. Hospitals are interested in employing professionals, who have completed bachelor program, and Linda Aiken, Leadership Professor of Nursing, admits this tendency (Childers, n. d.). She claims: “While there is a strong preference in all healthcare settings for nurses to have a bachelor’s degree, many hospitals in particular prefer to hire nurses who have a BSN” (as cited in Childers, n. d., para. 3). Conducting several experiments, Lind Aiken revealed the impact of educational level on patient outcomes and mortality rate. This explains the fact that employers are highly likely to prefer workers with finished a Bachelor’s degree. Therefore, completing this program will definitely make me more competitive in the market of nurses.
In addition, a Doctoral degree will help me achieve the highest credential in my professional sphere. The major benefit of this program regards its focus on practice, and consequently, it will guarantee high quality of my performance. A Master’s degree in business will be attractive for the potential employers as well, as I will be capable of occupying managerial and administrative positions ( Why nurses should get their MBA, n. d.). Therefore, these education paths will significantly increase my competitiveness in the job market. The Code also includes the positions of beneficence and nonmaleficence.
Continuing Nursing Education and Competency, Attitudes, and Knowledge
The fact that continuing nursing education has a positive impact on competencies, attitudes, and knowledge is undeniable in the context of present-day developments. Today, the field of health care is actively developing, and therefore, there is a necessity to update the knowledge and obtain new skills on a regular basis. Furthermore, this approach allows to match the requirements of the ANA Scope and Standards for Practice and Code of Ethics. It promotes “carrying out nursing responsibilities in a manner consistent with quality in nursing care and the ethical obligations of the profession” (Gains, 2020, para. 1). It is evident that it is impossible to perform these requirements without comprehensive training. A lack of education equals a lack of relevant knowledge and competencies, which increases the risk of harming the health of a patient. Thus, there is a direct connection between nursing education and the outcomes of clients.
Mandatory Continuing Education in Nursing
Continuing the reflections on nursing education presented in the previous paragraph, I should mention that I believe in the necessity for mandatory continuing education in nursing. As it has been already mentioned, it has a significant impact on treatment outcomes. Seamless academic progression and regular updating of the qualification allows to deliver medical devices of high quality and provide patient-centered care, which is the priority these days. In addition, according to the IOM report, it will be beneficial for making medicine easier to access in the long run (Institute of Medicine (US), 2011). However, I am convinced that not only nurses, but also employers should be interested in supplying mandatory continuing education. The latter should provide the workers with a possibility to achieve higher degrees and training for improving the skills and updating knowledge. Furthermore, they should support nurses in their determination for education by supplying additional holidays for academic purposes. Thus, this approach will guarantee positive results, and the state healthcare systems will be significantly improved, as well as the health condition of the population.
Childers, L. (n. d.). Higher nursing degrees can give RNs a competitive edge . Nurse.com. Web.
Gains, K. (2020). What is Nursing Code of Ethics?. Nurse.org . Web.
Institute of Medicine (US). (2011). The future of nursing: Leading change, advancing health . Web.
Types of nursing specialties: 20 fast-growing nursing fields (n. d.). Gwynedd Mercy University. Web.
Why nurses should get their MBA. (n. d.). Herzing University. Web.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, August 29). The Importance of Nursing Education. https://studycorgi.com/the-importance-of-nursing-education/
"The Importance of Nursing Education." StudyCorgi , 29 Aug. 2022, studycorgi.com/the-importance-of-nursing-education/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'The Importance of Nursing Education'. 29 August.
1. StudyCorgi . "The Importance of Nursing Education." August 29, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/the-importance-of-nursing-education/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "The Importance of Nursing Education." August 29, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/the-importance-of-nursing-education/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "The Importance of Nursing Education." August 29, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/the-importance-of-nursing-education/.
This paper, “The Importance of Nursing Education”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: November 11, 2023 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
- Jump to Cookie Consent
Help us improve your website experience! Take a brief survey >>
Visit the COVID Information Center >>

- MyChart Login
- Find a Location
Healthy Driven Blogs
Why nurses are the heart of healthcare.
If you’ve never been cared for by a nurse, you likely will be eventually.
Nurses are the foundation of healthcare. They play a vital role in providing care, comfort and compassion for their patients and patients’ families.
Despite their caring demeanor, nurses would rather not see you in the hospital. Preventive healthcare is their priority for patients — getting regular checkups and keeping health concerns from developing into a serious condition is key to avoiding the hospital, not to mention the intensive care unit.
"One of the biggest things is preventative healthcare," says Marguerite Manseau, RN , at Edward Hospital. “If your baseline overall health that has accumulated over 40 plus years is not good, a lot of the conditions people develop that land them in the hospital are not as easy to cure."
Many chronic conditions can be prevented by living a healthier lifestyle.
Also, stay on top of warning signs. "Listen to your body. If something doesn't feel right, get it checked out," says Marijana Vidovic, RN , at Elmhurst Hospital.
What it means to be a nurse
Being a nurse isn’t always easy. Nurses work hard. During the pandemic, and even before, nurses have experienced burnout. They emotionally invest in their patients and patients’ families, which can be exhausting during tough times. It’s even contributed to a national nurse shortage.
There are also times nurses need a thick skin. They can face heartbreaking situations, and it can be a stressful job. But nurses are realistic. Knowing what to expect and having the support of a team helps them get through stressful times.
"Having a level head is sometimes difficult. We're human and have emotions," Manseau says. "There are days you leave work and you're just so physically tired from not just how much physical work you've done but how much mental work. That accumulates over time.
"Being bombarded by anything and everything for 12 hours means nurses need to find healthy channels to get support and blow off steam so we avoid compassion fatigue."
Staying in the moment and maintaining perspective helps, the nurses say. Connection with the nursing team is also crucial for mental well-being, as nursing coworkers understand what each other is facing and can offer vital support.
The rewards
Becoming a nurse starts with nursing school. A good foundation in nursing school helps nurses understand and think critically about their duties.
Technology is involved in every aspect of a nurse’s day. From electronic records to the pharmacy and bedside technology, nurses need to know how it all works.
Nurses don’t just provide clinical care and medication, they provide emotional support for their patients and the patient’s family members, which is particularly important in the hospital where it helps to have a human connection during what is often a scary time.
Nurses work together and help coordinate care from physicians, physical therapists and others to do what's best for each patient. Working with the team is a rewarding part of the job, says Vidovic. Watching a patient walk out of the hospital after a lengthy hospitalization or being on a ventilator is also an amazing reward, they say.
Nurses are needed now more than ever
Nurses are in high demand, as the American healthcare industry faces a shortage of nurses. And it’s not just bedside nurses — there is so much you can do as a nurse beyond working in a hospital. You can become a teacher; you can become an APN. You can always expand your skills — specialize, do clinicals or teach. That's the beauty of a nursing degree.
"Really, if you think about your daily life, there's probably a nurse involved in some capacity at every step,” Manseau says. “Elementary school, there’s a nurse. You can work in an operating room. You can work at the bedside. You can teach. If you have a specific interest in something, you can find a program to get certified in it.”
Nurses are an unstoppable force. Providing care, comfort and compassion is all in a day’s work. In this Health 360 with Dr. G podcast episode, “Shout out to nurses: Heroes in healthcare,” host Mark Gomez, MD, and his guests discuss nurse life and the future of nursing. Listen to the podcast.
Edward-Elmhurst Health is hiring nurses! Learn more about nursing and search for nursing opportunities.
You may be interested in

Preparing for the “Big Game”

5 signs of a healthy relationship

Winter blues? How to boost your mood
If you have reached this screen, your current device or browser is unable to access the full Edward-Elmhurst Health Web site.
To see the full site, please upgrade your browser to the most recent version of Safari, Chrome, Firefox or Internet Explorer. If you cannot upgrade your browser, you can remain on this site.
This website uses cookies that measure website usage and help us give you the best experience. By continuing to use this website, you consent to this website’s use of these cookies and you accept and agree to our Privacy Statement and Terms of Use .
Essay on Health Education for Students and Children
500 words essay on health education.
We all know that health education has become very important nowadays. It refers to a career where people are taught about healthcare . Professionals teach people how to maintain and restore their health. In other words, health does not merely refer to physical but also mental, social and sexual health. Health education aims to enhance health literacy and develop skills in people which will help them maintain good health.

Importance of Health Education
Health education is very essential for enhancing the condition of the overall health of different communities and people. It will also help in improving the health of the whole nation. You can also say that the economy of a country is directly proportional to health education. In other words, it means that the higher the life expectancy the better will be the standard of living.
Health education is given to people by professionals in the field known as health educators. They are qualified and certified enough to talk about these issues. Furthermore, they undergo training related to health and hygiene for educating people.
Similarly, health education is very important as it improves the health conditions of the people. It does so by teaching them ways on how to remain healthy and prevent diseases. Moreover, it also makes them responsible enough as a whole community.
The developing nations especially are in dire need of health education. It not only conveys basic knowledge about health but also shapes their habits and way of living. Most importantly, it not only focuses on physical health but also addresses other issues like mental illnesses, sexual well-being and more.
Methods to Improve Health Education
Although health education is very important, we often see how it is not given the importance it deserves. The poor condition of the prevalent health education in many countries is proof of this statement. We need to improve the state of public health education in the world, especially in developing countries.
As the developing countries have many remote areas, the necessary help does not reach there. We must emphasis more on conveying this education to such people. The villagers especially must be made aware of health education and what role it plays in our lives. We can organize these programs which will attract more audience like fares or markets, which already has a gathering.
Moreover, as most of the audience will be illiterate we can make use of visuals like plays, folk shows and more to convey the message in a clear manner. Subsequently, we must also make the most of the opportunity we get at hospitals. The patients coming in to get checked must be made conscious of their health conditions and also be properly educated on these matters.
Similarly, we must target schools and inculcate healthy habits amongst children from an early age. This way, students can spread this knowledge better to their homes and amongst their friends. Therefore, we must enhance the state of health education in the world to help people become healthier and maintain their vitality and dynamism.
FAQs on Health Education
Q.1 Why is Health Education important?
A.1 Health education is very important as it improves the health standards of the country. It further helps in preventing diseases and making people more aware of their health conditions. Most importantly, it not only focuses on physical health but also mental health and others.
Q.2 How can we improve health education?
A.2 We can improve health education by making the people of remote areas more aware. One can organize programs, camps, plays, folk shows and more plus teach it properly at schools too.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Military & Veterans
- Transfer Students
- Education Partnerships
- COVID-19 Info
- 844-PURDUE-G
- Student Login
- Request Info
- Bachelor of Science
- Master of Science
- Associate of Applied Science
- Graduate Certificate
- Master of Business Administration
- ExcelTrack Master of Business Administration
- ExcelTrack Bachelor of Science
- Postbaccalaureate Certificate
- Certificate
- Associate of Applied Science (For Military Students)
- Programs and Courses
- Master of Public Administration
- Doctor of Education
- Postgraduate Certificate
- Bachelor of Science in Psychology
- Master of Health Care Administration
- Master of Health Informatics
- Doctor of Health Science
- Associate of Applied of Science (For Military Students)
- Associate of Science (For Military Students)
- Master of Public Health
- Executive Juris Doctor
- Juris Doctor
- Dual Master's Degrees
- ExcelTrack Master of Science
- Master of Science (DNP Path)
- Bachelor of Science (RN-to-BSN)
- ExcelTrack Bachelor of Science (RN-to-BSN)
- Associate of Science
- Doctor of Nursing Practice
- Master of Professional Studies
The average Purdue Global military student is awarded 54% of the credits needed for an associate's and 45% of the credits needed for a bachelor's.
- General Education Mobile (GEM) Program
- AAS in Health Science
- AS in Health Science
- BS in Organizational Management
- BS in Professional Studies
- AAS in Criminal Justice
- AAS in Small Group Management
- AAS Small Group Management
- Master's Degrees
- Bachelor's Degrees
- Associate's Degrees
- Certificate Programs
- Noncredit Courses
- Tuition and Financial Aid Overview
- Financial Aid Process
- Financial Aid Awards
- Financial Aid Resources
- Financial Aid Frequently Asked Questions
- Financial Aid Information Guide
- Tuition and Savings
- Aviation Degree Tuition and Fees
- Professional Studies Tuition and Fees
- Single Courses and Micro-Credentials
- Time and Tuition Calculator
- Net Price Calculator
- Military Benefits and Tuition Assistance
- Military Educational Resources
- Military Tuition Reductions
- Military Spouses
- Student Loans
- Student Grants
- Outside Scholarships
- Loan Management
- Financial Literacy Tools
- Academic Calendar
- General Requirements
- Technology Requirements
- Work and Life Experience Credit
- DREAMers Education Initiative
- Student Identity
- Student Experience
- Online Experience
- Student Life
- Alumni Engagement
- International Students
- Academic Support
- All Purdue Online Degrees
- Career Services
- COVID-19 FAQs
- Student Accessibility Services
- Student Resources
- Transcript Request
- About Purdue Global
- Accreditation
- Approach to Learning
- Career Opportunities
- Diversity Initiatives
- Purdue Global Commitment
- Cybersecurity Center
- Chancellor's Corner
- Purdue Global Moves
- Leadership and Board
- Facts and Statistics
- Researcher Request Intake Form
Most Commonly Searched:
- All Degree Programs
- Communication
- Criminal Justice
- Fire Science
- Health Sciences
- Human Services
- Information Technology
- Legal Studies
- Professional Studies
- Psychology and ABA
- Public Policy
- Military and Veterans
- Tuition and Fee Finder
- Financial Aid FAQs
- Military Benefits and Aid
- Admissions Overview
- Student Experience Overview
- Academic Support Overview
- The Importance of Community Health Nurses
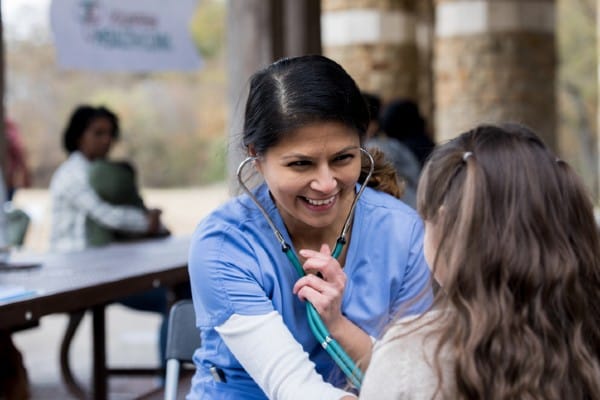

The Importance of Community Health Nursing
Community health nurses are a vital link in the health and welfare of neighborhoods. These registered nurses focus on improving the lives of diverse communities of infants, children, adolescents, and adults through education, prevention, and treatment.
“They assist with equalizing health care in diverse populations, so that care is more equitable, affordable, and well-coordinated,” says Sheila Rucki , faculty member in the Purdue Global School of Nursing.
“Community health nurses look at the broader needs of a population, not just an individual,” says Jessica Gordon , associate dean. “The agenda is health promotion, disease prevention, and recognizing the needs of the community.”
Learn more about the role of community health nurses, what their future looks like, and how to become one.
What Is a Community Health Nurse?
Community health nurses start by building trust and relationships with individuals and local leaders. They also develop a strong understanding of people’s backgrounds, experiences, and the social factors that influence health, with the goal of practicing cultural humility with empathetic care.
Many members of the community who take advantage of these services might not otherwise have access to private physicians or testing services, among other medical necessities.
“Ethnically diverse and culturally diverse populations are the most underserved,” Rucki says. “Those are the individual groups that benefit most from this kind of health care."
Community health nurses often participate in mobile clinics to help underserved populations, she says.
“The homeless are hard to reach because they are mobile,” Rucki says. “They benefit greatly from the care provided by community-focused providers, particularly nurses.”
What Do Community Health Nurses Do and Where Do They Work?
Community health nurses work in a variety of settings from community-based centers to government agencies to shelters to vaccine distribution sites. They build coalitions, craft policies, educate the public, manage public health programs, and more.
Services Provided by Community Health Nurses
The American Public Health Association lists 10 essential public health services provided by community nurses and other front-line professionals:
- Assess and monitor population health
- Investigate, diagnose, and address health hazards and root causes
- Communicate effectively to inform and educate
- Strengthen, support, and mobilize communities and partnerships
- Create, champion, and implement policies, plans, and laws
- Utilize legal and regulatory actions
- Enable equitable access
- Build a diverse and skilled workforce
- Improve and innovate through evaluation, research, and quality improvement
- Build and maintain a strong organizational infrastructure for public health
“Community health nurses are this incredible file cabinet of resources. They can point people in the right direction for what they need at that time,” Gordon says. “They're dealing with the community, but they provide education on where the community can get the help they need for individualized attention.”
For example, if a community has a high diabetes rate, one of the focuses for that area might be diabetes prevention education.
“Every single community health nurse works based on the population and the needs of that population specifically,” Gordon says.
Other health issues that could affect a community include:
- Substance abuse
- Teen pregnancy
Where Community Health Nurses Are Needed
Community health nurses, like other registered nurses, often work in local hospitals, trauma centers, and clinics. Many work in locations more focused on underserved communities, such as:
- Aid organizations, such as Doctors Without Borders or the Red Cross, providing disaster relief along with other daily local needs
- Community health centers, treating and educating around such topics as family planning, sexual health, and other preventative care
- Correctional facilities, working to limit the spread of communicable disease, along with running educational programs for inmates and staff
- Government agencies, helping with health policy development and implementation to create change on a large scale
- Homeless shelters, focusing on preventative care through screenings and assessments, and helping people find social service assistance
- Schools, providing education about illness prevention and good health habits, along with managing existing health problems and intervening in cases of abuse or neglect
“A lot of the community-based care centers are in parts of town or areas of the country or state where access to care might be limited or not affordable,” Rucki says. “Being based directly in the community provides access opportunities that might otherwise not be available to diverse populations.”
What Does the Future Look Like for Community Health Nurses?
Community health nurses have a bright future, but some serious challenges remain ahead.
“We’re seeing an increased need because what we thought was the traditional way of delivering care is really no longer applicable,” Rucki says. “Community-based care is becoming the primary way for many people today.”
What Job Growth Looks Like
The national nursing shortage, which has been exacerbated by the pandemic, will continue to fuel a 9% job growth rate through 2030, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics . The agency projects employers to add 276,800 RN positions from 2020–2030.*
Because of these growing needs, becoming a community health nurse has some advantages:
- Creating strong partnerships between nurses and clients and/or community population
- Enjoying collaborative nursing care working with clients in a nonhospital setting
- Having a variety of work settings
- Helping vulnerable communities
- Providing holistic and more individualized care
- Working a convenient schedule with little to no holiday or weekend hours
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, community health worker programs particularly need nurses trained in preventing and controlling infectious diseases, to deliver home-based care to low-income people.
What Challenges Remain Ahead
The National Institutes of Health indicate that public nurses face many challenges aside from the day-to-day demands of practice, including:
- Concerns for personal safety
- Frequent overtime
- Inadequate staffing levels
- Limited management support and supervision
- On-call duties
- Professional isolation
- Restricted opportunities for career development
However, Gordon says a greater challenge facing community nurses is resistance.
“This can happen whether you're in acute care or community health, but you often see a population as a whole resisting care,” she says. “It can be incredibly frustrating when you've provided quality education and care. But you persevere. The challenge is not being rejected, it's how you overcome it.”
“It may take time to build trust in populations,” Rucki says. “Once you build trust and build that ongoing relationship, you're more likely to see change, behavior changes in people’s health care practices.”
Who Would Make a Good Community Health Nurse?
You need certain qualities and qualifications if you’re interested in becoming an effective community health nurse.
The Qualifications You Need
At a minimum, you must earn an associate or bachelor’s degree in nursing and pass the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN). † Some may wish to complete a two-year master's degree program in nursing. Employers often prefer community health nurses who have one to two years of nursing experience.
“Because this is such an education-heavy job, there's a strong preference toward those with a bachelor's degree,” Gordon says.
Community health nurses also are strongly encouraged to have ties to the areas in which they wish to work. Participating in volunteer programs both before and after becoming a community health nurse is highly recommended.
Community health nurses should also consider certification. One exam, the Advanced Public Health Nurse certification exam, is being phased out.
“However, there are opportunities in interprofessional groups to demonstrate excellence and receive certifications,” Rucki says.
Currently, there is no certification specific to public health nursing at the generalist level. However, nurses with a bachelor’s degree and at least five years of public health experience can obtain the Certification in Public Health (CPH). Visit the National Board of Public Health Examiners for more information on the CPH.
The Qualities You Need
A panel convened by the National Institutes of Health agreed that a successful nurse needs such qualities as being analytical, communicative, cooperative, coordinating, disseminating knowledge, empathic, evidence driven, innovative, and introspective.
Community health nurses should also be connected to their community, open-minded to those different from them, sensitive to different opinions, and objective in their view of the communities they serve.
“An essential component to these roles is a passion for serving the communities that are around them,” Gordon says. “These nurses have a connection and they understand the populations. They want to see them thrive and do better.”
“What's really so rewarding for nurses is this long-term engagement with a population,” Rucki says. “In an acute care setting, you're engaged with the patient and family for a short period of time. But in the community, they're your patients for life. You see families grow and care for them over a number of years.
“That ability to connect and learn and know about the individuals that make up your community is so rewarding for nurses.”
How Purdue Global Can Help You Become a Community Health Nurse
“Community-based nurses are very strong force for change in a community,” Rucki says. Gordon says this theme is woven throughout all programs at Purdue Global.
Purdue Global’s online nursing programs can help you start on the road to becoming a community health nurse. ‡ Reach out for more information today .
About the Author
Purdue Global
Earn a degree you're proud of and employers respect at Purdue Global, Purdue's online university for working adults. Accredited and online, Purdue Global gives you the flexibility and support you need to come back and move your career forward. Choose from 175+ programs, all backed by the power of Purdue.
- General Education
- Legal Studies & Public Policy
- Online Learning
Your Path to Success Begins Here
Learn more about online programs at Purdue Global and download our program guide.
Connect with an Advisor to explore program requirements, curriculum, credit for prior learning process, and financial aid options.
* Job Growth Projections: National long-term projections may not reflect local and/or short-term economic or job conditions, and do not guarantee actual growth.
† NCLEX Exam : Graduates must meet state licensing and certification requirements and pass the NCLEX-RN exam to become a registered nurse or the NCLEX-PN to become a licensed practical nurse. The University cannot guarantee students will be eligible to sit for or pass exams. NCLEX is a registered trademark of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc. Licensure-track programs may limit enrollment to students in certain states. Refer to Purdue Global’s State Licensure and Certifications page for state-specific licensure.
‡ Employment and Career Advancement: Purdue Global does not guarantee employment placement or career advancement. Actual outcomes vary by geographic area, previous work experience and opportunities for employment.
This website is intended for healthcare professionals

- { $refs.search.focus(); })" aria-controls="searchpanel" :aria-expanded="open" class="hidden lg:inline-flex justify-end text-gray-800 hover:text-primary py-2 px-4 lg:px-0 items-center text-base font-medium"> Search
Search menu
Academic essays part 1: the importance of academic writing.
John Fowler
Educational Consultant, explores how to survive your nursing career
View articles
John Fowler, Educational Consultant, explores academic writing

How confident are you in your ability to write academic essays? If you are a student nurse in your first year of training then your answer will depend largely on your previous success, or not, in GCSEs, A levels and the equivalent. If you entered nursing via an alternative route that had less emphasis on traditional academic preparation, then your confidence in writing an essay that draws on referenced literature will probably be much reduced. Even if you were quite strong at school or college work, you may find the transition to self-directed degree study quite difficult. If you are a qualified nurse with a pre-registration diploma or degree, returning to university study to complete a post-registration master's degree, you may still have reservations about your ability to re-engage with academic writing. If you are confident of your ability to communicate nursing theory and its application to clinical care, then this series of articles is probably not for you! However, my experience of teaching nurses, from first-year students to specialist nurses undertaking PhDs, is that very few are confident in their academic writing skills.
Academic ability versus academic writing
For most nurses who struggle with academic skills, it is usually not their innate academic ability that is the problem, but the lack of specific skills required to research the question and then communicate valid findings in a reliable way. For student nurses, this is about understanding where the body of nursing knowledge lies, be that the literature, protocols or clinical practice, how to access it and then communicate those findings. For the experienced nurse undertaking a post-registration degree, it is about dusting off library skills, getting to grips with different IT, exploring the knowledge base relevant to, but outside, pure nursing, understanding the relevance and use of clinical experience and, finally, mastering the skills of writing a long essay that communicates knowledge, experience and innovative ideas.
What ‘sister says’
When I trained as a nurse, it was in pre-university and pre-diploma or degree days; the ward sister or the medical consultant was the source of knowledge. Students quickly learned to develop their nursing skills according to what ‘sister says’: ward sisters and ward routines were the source of knowledge and authority. As nursing research and evidence-based protocols developed and began to inform nursing practice in the 1980s, the source of knowledge moved away from this and included ‘what the literature says’. Nurse training was underpinned at diploma level, validated by a university system that stressed the importance of referencing published materials as the source of authority. As the scientific base and the wealth of nursing-related literature increased over the next 20 years, student nurses were required not just to refer to the literature, but to demonstrate their discussion and critical review of a body of knowledge based on valid and robust evidence; this was reflected in the move to make nursing an all-graduate profession in the early 2010s. In what ways has this transition from ‘sister says’ to the ‘literature says’ changed the way we inform our practice?
Has our ability to apply knowledge to clinical practice changed?
To inform clinical practice and develop clinical expertise, a nurse needs to take various aspects of evidence, evaluate its appropriateness and then apply it to a specific patient or clinical situation. This was true when I was a student nurse and the source of knowledge was the ward sister. It is equally true today when the source of knowledge is more literature-based. What has changed is the origin of the knowledge. In my student days it was probably 85% ward sister and 15% text books. Today it is more like 40% clinical staff and 60% evidenced-based literature. To inform clinical practice, we need to assess the validity and reliability of the knowledge, both clinical- and literature-based, evaluate it and then apply it to clinical care. The difficulty that nursing has over the pure biological science healthcare professions, such as pharmacy and medical sciences, is that a significant proportion of nursing practice draws from the social sciences concerned with feelings and interactions. When a patient is in pain, we know we can draw upon the science of pharmacology and pain administration protocols, but it is only our observation of experienced staff and our own experiential learning that guides us as to when to hold a hand, sit by the bedside or ask about the patient's worries regarding family or pets. Communicating this interaction of hard biological science, evidence-based protocols and the application of softer caring skills is a difficult, yet important, part of academic writing for the nurse. How do we write an essay that justifies the possible benefits of holding a patient's hand, when there are no randomised controlled trials to support its application?
This forthcoming series will explore all the practicalities of planning an essay, managing the literature, developing structure and content, but it will not lose sight of this important principle of incorporating holistic clinical nursing care into academic writing.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Wiley Open Access Collection

The meaning of reflection for understanding caring and becoming a caring nurse
Turid anita jaastad.
1 Department of Caring Science, Faculty of Education and Welfare Studies, Åbo Akademi University, Vaasa Finland
2 Department of Caring and Ethics, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Stavanger, Stavanger Norway
Venke Ueland
Camilla koskinen.
Reflection is essential for students to learn and understand caring, their formation as human and caring beings, and their ability to meet patients in a caring way. Consequently, to facilitate nurse students’ development into professionals, learning support is needed where the focus is on understanding caring and becoming caring nurses.
Aim and research questions
The exploratory study aim is to gain knowledge of the meaning of reflection in first‐term nursing education, and how reflection grounded in caring theory can deepen the students’ understanding of caring and their professional formation of becoming a caring nurse.
Data consisted of individual written reflections and were collected from 64 nursing students from Norway, who had completed their instruction in caring theories and participated in four reflection groups where they reflected on caring and becoming a caring nurse. A thematic analysis was used.
The results are based on the three main themes, Reflection provides an understanding of caring by developing a language for caring; Reflection provides an understanding of seeing the person behind the illness; and Reflection contributes to increased self‐understanding and awareness of oneself as a caring nurse.
Conclusions
Instruction in caring theories and participation in reflection groups, with reflection grounded in caring theory, has a key function in facilitating students’ development of a language for caring in nursing and appropriation of caring theory. The appropriation of caring theory provides a foundation for the nurse students to see themselves within a broader perspective and is important for mutual support in the professional formation of becoming a caring nurse. The expected outcome of such integration is a nursing curriculum that progressively supports the development of nursing students professionally and personally in the formation of becoming a caring nurses.
INTRODUCTION
The starting point for this study is the challenge in nursing education to create fruitful conditions for nurse students’ learning and reflective processes that strengthen their understanding of caring and their professional formation to become caring nurses [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]. Essential to the process of becoming a caring nurse is the appropriation of a caring attitude where the nurse students, through their actions and attitudes, alleviate human suffering and meet the patient with dignity and compassion [ 5 , 6 ]. The current study is rooted in caring science education with a belief in students’ ability to develop and form in learning. This implies a holistic formation and molding, educating caregivers with a caritative ethical attitude and professional competence [ 7 ].
Caring is widely described by nursing and caring theorists as an important topic and a core mission, and as an ethical value for nursing professions [ 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Suárez‐Baquero et al. [ 11 ] highlight that in the art of caring is embedded the core disciplinary nursing knowledge. An interesting starting point is whether a human being by nature is caring or if caring can be learned and trained. According to Eriksson [ 12 ], human beings are inherently caring, while for Olshansky [ 13 ] and Boykin & Schoenhofer [ 14 ], caring is not necessarily an innate trait in nurses, but more a process and an outcome that occurs over time and involves mastering caring behaviour. Several studies support the idea that caring can be learned and emphasise that the core aim of nursing education is to develop nursing students’ caring competencies [ 15 , 16 , 17 ]. Among many recommendations, nursing education is suggested to focus on strengthening the caring identity of students, enabling them to match their idealistic caring vision with that agreed upon by the nursing profession [ 18 , 19 , 20 ]. Other recommendations are to facilitate the students’ reflection on their experience of caring in personal life and clinical reality [ 21 ]. According to Hörberg [ 22 ], true caring is not possible without carers adopting a caring attitude to gain insight into the patient's lifeworld and thus an opportunity to understand the patient's lived experiences and life situation. A wealth of literature demonstrates that the students’ awareness of the reflective process within themselves, reflection interacting with caring science theory, can integrate and improve the ability to care for suffering human beings [ 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ]. Sandvik et al. [ 29 ] similarly indicates that through active and continuous reflection, caring science theory can live and become lasting.
As reviewed above, previous research shows that the use of caring science theory as part of the reflective process is seen as essential for students’ learning and understanding of caring, their formation as humane and caring beings, and their ability to meet the patient in a caring way. Hence, we find that reflection related to caring theory and students’ unfolding understanding of caring has not been fully explored.
Although reflection is considered a significant component of nursing education and practice [ 30 ], the literature does not provide a consensual definition of or model for it [ 31 ]. This study is grounded in both phenomenological and hermeneutic views on learning and reflection. Within the phenomenological tradition of caring science didactics, the platform for learning and reflection is the life‐world [ 32 ]. According to the phenomenology of Edmund Husserl, the life‐world is related to a natural attitude and involves a type of approach to our everyday activities [ 33 ]. The natural attitude characterises activity which humans are completely directed towards, immersed in, absorbed by, or of being in the moment. In everyday activities, humans do not consciously analyze but take for granted what they experience or what they are absorbed by, as existing the way they perceive it. Consequently, a person's natural attitude is basically unreflective. All meaning has its origin in the life‐world which is the prerequisite for all cultivation of knowledge. The life‐world can, according to Husserl be examined and conceptualised through reflection. Through reflection, phenomena of the world will be brought to awareness and so made available for analysis, instead of being taken for granted. In this way phenomena in the lifeworld might be conceptualised and articulated, which is the basis of the learning process [ 34 , 35 ]. Through a holistic approach to the connection between learning and caring, and based on a life‐world perspective, earlier research within caring science didactics has shown that reflection and the interaction between caring and learning can improve both caring and learning in caring contexts [ 36 ].
From a hermeneutical perspective of caring science didactics and according to Gadamer [ 37 ], learning is related to an individual's understanding process. Understanding always occurs as a fusion of contemporary and historical horizons. The contemporary horizon is always constituted from the past. It is always possible, according to Gadamer, to open and broaden the contemporary horizon, and even necessary for the development of new understanding [ 37 ]. From that point of view, reflection arises in the encounter between experience and pre‐understanding. The reflective activity leads to a new understanding and Gadamer describes this phenomenon as a ‘horizon fusion’ [ 38 ]. Reflection is connected to the processes of understanding and becoming. Understanding and becoming are ongoing processes of appropriation, thus transforming students both professionally and personally. Through appropriation, a new understanding is incorporated into oneself that alters oneself, thus changing one`s thought and action, doing and being [ 2 ], and the appropriated caring science theory provides authority and courage to practice nursing care [ 29 ].
The exploratory study aim is to gain knowledge of the meaning of reflection in first‐term nursing education, and how reflection grounded in caring theory can deepen the students’ understanding of caring and their professional formation of becoming a caring nurse. The research question is: How does reflection ground in caring theories deepen nurse students understanding of caring and of themselves as caring nurses?
Setting and participants
The study was carried out in 2019 at a Norwegian university. All 330 students in the first‐term undergraduate nursing program were invited to participate in the study: 64 agreed to participate, 48 females and 6 males. The sampling and data collection took place before clinical practice.
Reflection seminars focusing on Kari Martinsen's [ 10 ], and Katie Eriksson's [ 12 ] theories about caring that are implemented in the undergraduate nursing program in the first term. The students met four times in groups consisting of 10‒12 students in each group. The caring concepts used in the actual education were inter alia, caring communion, caring relationship, natural caring, compassion, kindness, and the fundamental idea to alleviate suffering and promote health and life.
Data collection
Individually written self‐reflections were used for the data collection [ 39 ] and provided the empirical data material for this study. After the four reflection seminars participants were asked to write individual self‐reflection related to the following questions: What has reflection meant to you? What new insights has reflection contributed to in relation to caring and about yourself as a caring nurse? The reflection questions were open and related to the students’ thinking and understanding of caring after the first term of their nursing education. The purpose was not to investigate what the students had learned about caring and caring theory but to gain knowledge about the students’ own reflections in relation to themselves in becoming caring nurses. The material consists of 44 typed pages. The written reflections were not lengthy but had rich units of meaning. The students used their own words and they reflected on their own experiences and understanding of caring and nursing. An example of a student reflection:
The theory has helped to concretise and understand the concept of care. Knowing in more detail what is included in the concept from a theoretical perspective provides a more holistic understanding. This will help to reflect more effectively on the topic later. To remember and use something in daily life as a nurse, one must first have understood it properly. Linking theory to reflection in plenary as we have now done has been a great help in understanding caring. Caring is extremely important in a nursing situation and being able to put into words the theory and things I will experience in practice will be useful.
The reflection notes were analyzed with thematic analysis in six steps according to Braun and Clarke [ 40 ]. All authors read the reflection notes, and a first analysis was performed. This formed the basis for the preliminary analysis that was conducted by one of the authors (TAJ) Then, all authors convened to discuss the patterns until a unanimous interpretation was agreed upon. To improve trustworthiness and enable readers to follow the research process, the authors strived to describe it as clearly as possible. The first step was to become acquainted with the data. Each note was read several times and notes about ideas were taken. The second step was initial coding. In this step, interesting features among participants’ statements were coded thoroughly and in accordance with the whole data. In this way, relevant data appeared. The third step was to look for themes. In this step, similar codes put together resulted in initial themes. The fourth step was reviewing these themes. In this step, the coordination between codes, related initial themes, and the entire data set was confirmed. In this way, a thematic map was generated. The fifth step was the definition and naming of extracted themes. In this step, the entire process of analyzing was reviewed to refine the characteristics of each code and the story which the whole analyzing process tells. The sixth and last step was reporting, we returned to the research question, and the results were described using themes and sub‐themes, and quotes from the interviews were used to strengthen the credibility of the themes and enable readers to evaluate the transferability of the findings [ 40 ]. Based on the research questions and thematic analysis, three themes and nine sub‐themes are highlighted as follows (See Table Table1. 1 . Overview of findings).
Overview of findings
Ethical approval
This study, conducted in 2019, conformed to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki (World Medical Association Declaration, 2005) and permission to recruit the participant was sought in relation to the Norwegian Centre for Research Data (NSD). Permission was granted by the management of the university. The informants gave written permission for their participation in the study. The research participants were informed of the aims and purposes of the research and collaboration was voluntary and anonymous. They were also informed of the right to refuse to cooperate [ 41 ] and that the collaboration in the research is nonbinding and does not affect the final assessment of the study. The participants had an opportunity to withdraw at any time without any explanation. The reflection notes were sent as a word document by e‐mail and given a code. Names and code lists were stored in paper form in a locked drawer in a locked office, separate from the reflection notes. E‐mails with reflection note attachments were deleted.
Individually written reflections were an appropriate approach to this topic to promote knowledge of how reflection grounded in caring theory deepens the students’ understanding of caring and of themselves in becoming caring nurses. We chose to invite all students. There is always a risk that the students who volunteer may have a special interest and positive view of the topic, and we were aware that the text has been shaped by the students writing something that they know will be read by the researcher.
The description of the results is based on the three main themes, Reflection provides an understanding of caring by developing a language for caring ; Reflection provides an understanding of seeing the person behind the illness ; and Reflection contributes to increased self ‐ understanding and awareness of oneself as a caring nurse .
Reflection provides an understanding of caring by developing a language for caring
The results show that reflection provides a deeper understanding of caring as a basis for nursing and for becoming a caring nurse. This discovery provides new insights and a deeper understanding of the importance of caring in nursing. I have become more aware that this is perhaps the biggest role of being a nurse . Reflection on themes of caring theory opens for the students to recognise that caring in nursing is based not only on a natural caring attitude toward other people but that caring in nursing also requires that the nurse students learn to change both their being and action. Caring is something all people can provide , but as a nurse we need some more professional knowledge . In the reflection, they discover that caring theory can be a resource in their own learning process towards ethical thinking and formation to become a caring nurse. Caring for someone you know comes automatically for most people but caring for a stranger does not necessarily come by itself . For some it must be learned , and then the theory of caring will be very useful . Thus, the caring theory comes alive and inspires learning and professional and personal formation to becoming a caring nurse.
Reflection facilitates the understanding and concretisation of caring theory. Through reflecting with others, the concept of caring and caring theory become more concrete and understandable. Reflection has made it easier to understand heavy theoretical concepts and questions , and use them in practical examples so that it has become easier to understand . The students discovered that words and concepts can have a deeper meaning and significance. In the reflection, the students help each other to concretise the caring theory, and manage in a new way, both to understand how they can take care of the patient in a caring way, and how important caring is for patients and relatives.
Reflection provides a language for communicating caring. All the students have their own understanding of the concept of caring, but it is difficult for them to describe the content of the concept in their own words. In dialogue with fellow students, they gain access to their already implied understanding, and the language opens for them to be able to understand and describe caring in other and new ways. Now I can better put my thoughts into words , and I have a better opportunity to communicate about this . In the meeting between one's own and others’ thoughts a new understanding is formed, and the dedication of caring theory makes it easier to articulate and verbalise caring in nursing.
Reflection provides an understanding of seeing and meeting the person behind the illness
Reflection provides a deeper understanding of the patient's perspective. In the reflection, the students become more aware of how human beings may experience becoming patients. Through reflection, students develop a deeper understanding of the patient's vulnerability and uniqueness. I have thoughts about being a patient , that you are then in a very vulnerable situation… and that everyone's story is unique . They also develop a deeper understanding of human vulnerability and interdependence with other people. In the reflection, the students gain a deeper awareness that their own vulnerability can be a strength for understanding the patient's vulnerability. I have gained a better understanding that as a nurse it is important to be vulnerable , to be able to show compassion in the best possible way . When the students intertwine the caring theory with their own past experiences and pre‐understanding the caring theory becomes more personal.
Reflection provides an understanding of the importance of viewing the patient as a complex whole human being. The students discover the significance of developing an open and responsive approach to the patient, where they show respect and humility for the patient's life‐world. I have learned a lot of new things , how to meet the patient , and how to treat the patient as a person , and not just the disease or diagnosis the patient is admitted for . In the reflection, the humanistic views of human beings and the main values that define professional nursing become clearer, and the students gain a deeper insight into caring as meeting the patient as a unique and whole person. In the reflection, the students share and listen to each other's stories, and in this interaction, the students understand the patient's life‐world in a new and deeper way. By moving between the students’ understanding of caring theory and their own and others’ experiences, the students gain new perspectives on how to be caring. The caring theory has shown me how important it is to do things with caring . It is almost impossible to do things without using caring . Caring goes into everything , and it is important that you use it no matter what you do as a nurse and who you talk to . Thus, the caring theory has a possibility to change nurse students as human beings, and alter their thinking, actions, doing, and being.
Reflection contributes to increased self‐understanding and awareness of oneself as a caring nurse
Reflection allows nurse students to get to know themselves better. Through reflection together with others the students share their feelings, thoughts and in this inner process the students become aware of their own understanding and opinions. During and after the reflection groups , we get to think about philosophical questions to which there is not necessarily a definitive answer . But it requires that we must go into ourselves to ponder , and thus become better acquainted with ourselves and our opinions . By sharing experiences and opinions, they become more aware of who they are and what influences their perception of other people and situations. At the same time, they become more aware of how they affect other people with their personalities. By sharing experiences and views with other fellow students , we can expand our insight and create awareness within ourselves , in meetings with patients and relatives . Reflection gives an increased awareness for assessing oneself. In the reflection, the students take an "outside look" at themselves and try to look at themselves as others see and experience them. By seeing themselves in this way, they become more reflective and aware of themselves. There may have been things that were inside me before , but now I am much more reflective and aware of the choices I make , the way I speak , and the way I act . In reflection, students obtain new ideas about how they want to become caring nurses, and how to develop their caring attitude. They received many new thoughts on how to behave as a caring nurse. You need to be aware of yourself , have good self ‐ awareness , and think about what you say and do . This understanding makes them more self‐aware, and they become better able to assess the quality of their caring behaviors. I think it will be easier to think and reflect on what I do well and what can be improved in practice after we have discussed the concept of caring in the reflection . Thus, the reflection grounded in caring theory facilitated the understanding of self, both professionally and personally.
Reflection offers new thoughts about one's desire to meet the patient in a caring way. Reflection initiates an inner process of change, where the students become more aware of how they treat and relate to other people. The reflection groups have made me more aware of how I am towards patients and other people when I encounter them in different situations in everyday life . As well as how to act in different situations . By reflecting on who they are and how they appear in meeting other people, they discover who they are and who they want to become and develop reflective abilities that they can use as a tool in the learning process of becoming the caring nurse they want to become. I think this reflection is incredibly useful in the job of becoming the best possible nurse , and the best version of oneself , that one can become .
The results show that students participating in reflection groups and reflection grounded in caring theory is a valuable method for the nursing student's appropriation of caring theory. The appropriation of caring theory provides a starting point for their professional and personal formation to becoming a caring nurse. This is in line with Ekebergh's [ 35 , 36 , 42 ] and Lindberg et al.’s [ 26 ] statement that didactics that enable embodied reflection from a life‐world perspective in combination with caring science theory, and didactics that create relationships that enable shared learning can strengthen the students’ learning process so that they can gain a deeper understanding of caring and caring science.
The students described that the caring theory was unknown and difficult to understand. Yet, they demonstrated a willingness to challenge their previous understanding, and together with their fellow students, the caring theory was reflected on and intertwined with earlier knowledge. The students expressed that the encounter with the caring theory, challenged their previous understanding, and in their reflection, they realise and understood something new about caring and themselves in terms of becoming a caring nurse. By developing a language for caring in nursing, the students moved from struggling to understand to an understanding in which the caring concepts are embodied. This is in accordance with Lindström [ 43 ], who argues that when the caring theory is incorporated into previous understanding, it becomes part of one's own personal bearing, and the students’ previous understanding and level of development evolve to a deepened understanding and personal growth. This can be compared with the process of the professional development of a professional identity [ 44 ].
According to the students, through the movement towards a deeper understanding of caring and caring theory they become aware of their ethical stance. Ethos is an important foundation for becoming and formation [ 7 ]. Ethics and ethos represent a bearing, that is, a stance, and are regarded as the caregiver`s innermost core. This leads to a deepening of understanding that one's own caring attitude influences one's thinking, actions, and being. Through the embodied reflection in the relationship with the other, students became more aware that their professional caring identity is important for being able to face patients’ suffering and appeals for help. These findings agree with Hörberg [ 22 ] showing that true caring is not possible without incorporating a caring attitude and constantly reflecting on the care given and how it is received by patients. Through the dedication of caring theory, the students take a new step forward towards forming a caring identity, and a new base to stand on and undergo formation. This movement could be described as a hermeneutical spiral consisting of interconnected loops taking the students further and deeper into their process of understanding caring and professional formation to becoming a caring nurse, which is also described by Sandvik et al [ 2 ] and show that formation is a molding process where understanding requires formation, while in turn, formation is a prerequisite for understanding and appropriation. This leads to the formation and is the result of an ongoing internal process, where the appropriating of caring science theory provides a foundation for professional identities and ethical awareness [ 29 ].
The findings show that the effect of students’ appropriating of caring theory is about creating an understanding of themselves. Through the appropriating of the caring theory, the students learn about themselves, their own knowledge and experiences, and perceptions of the responses of others. According to the students, they used their own and each other's past experiences and pre‐understanding, also described by Knutsson et al. [ 45 ] as the natural stance, as a starting point to create a deeper understanding of caring and of themselves as caring nurses. These findings resonate with Sandvik et al. [ 2 , 46 ] and Ekebergh [ 32 ] showing that reflection sets students’ inner processes in motion. Students explained that, through the reflection process, they became more open‐minded, wondering, and questioning in their meetings with fellow students’ reflections on the caring theory. From a phenomenological point of view, there is a great potential in learning together as we need others to know ourselves and vice versa [ 47 ] However, it can be difficult for students to challenge their natural attitude and the unreflective attitude. We found that students were open and honest about their own prejudices and vulnerabilities. According to the students, reflection with others facilitates the student's self‐reflection, and through self‐reflection, the students become aware of their own values and views on existence and life. This can be compared with Bengtsson [ 48 ] and Ekebergh [ 32 ], who reveal that in the theoretical context of nursing education, a conscious and active self‐reflection enables students to discover themselves in the light of theoretical caring science knowledge. Simultaneously, through appropriation, the caring theory becomes a ground for developing self‐awareness and self‐understanding, and a starting point for growth, both professional and personal.
CONCLUSION AND IMPLICATIONS
This study provides further understanding of how participation in reflection groups where the reflection is grounded in caring theory, provides a foundation for the nurse students to see themselves within a broader perspective and how significant mutual support is for students’ professional formation and becoming a caring nurse. The study shows that when the students understand and internalise caring theory, the caring theory can be translated into a clinical situation and integrated into their way of knowing, acting, and being. Consequently, the appropriated caring theory provides an important starting point for their formation and becoming a professional caring nurse. The result shows how instruction in caring theories, participation in reflection groups, and reflecting on key concepts from caring theories have a key function in facilitating students’ development of a language for caring in nursing, provides wider understanding for human beings as a patient, and increased self‐understanding for oneself as a human being and caregiver.
Professional nursing care and caring are highly dependent on teaching and learning transactions starting from the academic setting and the theoretical standpoints. The better students understand the connection between caring as theory and practice based on teaching and reflection, the more the appropriated knowledge and attitudes will be transferred to clinical practice environments. The expected outcome of the integration of theory and practice in the nursing curriculum thereby adopt to progressively supports the development of nursing students both personally and professionally in their formation of becoming caring nurses.
METHODOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS AND STUDY LIMITATIONS
The study had a qualitative design employing a thematic analysis [ 40 ] which was assessed as suitable for the character of the research subject. Individually written self‐reflection was performed at one university in Norway involving 64 undergraduate nursing students in their first term. The number of participants can be valued as quite small, but after reading the material we found that the quality was sufficiently large and varied to obtain information power to develop new knowledge, referring to the aim of the study [ 49 ]. That the participants came from the same university can be seen as a strength, although they had received the same instruction in caring theory and participated in the same reflection groups. The reflection groups were led by numerous teachers which can be seen as a weakness. Still, this can be a strength in producing more nuanced and richer data. The material consists of 44 typed pages, which may be considered a weakness, but they were rich in content. The written self‐reflections have been shaped by the participants writing something that they know will be read by the researcher, which may be considered a weakness, but because the purpose was not to investigate what the students had learned about caring and caring theory, but to gain knowledge about the students’ own reflections in relation to themselves in becoming caring nurses, this can be seen as a strength in producing more nuanced and richer data.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
The first author has been responsible for the research design, data collection, data analysis, and writing of the article. The second and third author has acted as supervisors and participated in the analysis and completion of the article.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors would like to thank the teachers who led the reflection groups and the students who participated in the study.
Jaastad TA, Ueland V, Koskinen C. The meaning of reflection for understanding caring and becoming a caring nurse . Scand J Caring Sci . 2022; 36 :1180–1188. 10.1111/scs.13080 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship and/or publication of this article

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Patient education materials help educate the patients on their health conditions, improves their health literacy, and enhances and promotes informed decision-making based on the most current and updated medical and clinical evidence as well as patient preference [ 2 ]. Aims. The aim of this study was to develop updated patient education ...
The Purpose of Health Education in Nursing. Health education is a crucial component of nursing practice. It is the process of providing patients and communities with the knowledge, skills, and support they need to make informed decisions about their health and well-being. Health education in nursing plays a number of important roles, including:
Throughout the coming decade, it will be essential for nursing education to evolve rapidly in order to prepare nurses who can meet the challenges articulated in this report with respect to addressing social determinants of health (SDOH), improving population health, and promoting health equity. Nurses will need to be educated to care for a population that is both aging, with declining mental ...
Health education is an important, yet challenging and time-consuming, nursing intervention. It is one of the most important tools school nurses have in teaching students, families, and staff about health. To be effective health educators, nurses need skills in planning and implementing attractive and effective programs to students.
Today's new nurses need more than skills. They must have the ability to assess knowledge and be competent in evidence-based practice and research, health policy and system improvement. They should embrace collaboration and multi-disciplinary teamwork and excel in critical thinking and decision-making. It's a tall order for nursing education ...
The role of nurses as health educators is critical as they instruct and train care takers both theoretically and practically. Nurses are also responsible for the promotion of quality health care (GlobalHealth, 2020). There are lots of strategies nurses can consider while developing individual care plans and programs for health promotion.
reviews health education theories and definitions, identifies the components of evidence-based health education and outlines the abilities necessary to engage in effective practice. Much has been written over the years about the relationship and overlap between health education, health promotion and other concepts, such as health literacy.
An important concept in health education is health behavior. Health behavior often refers to an action taken by a person to reach and/or maintain good health and to prevent illness. ... in contexts of hospitals or clinical settings. Historically, educating patients has been considered a key feature of nursing (Henderson, 1966). Nurses, for ...
Health education is distinct because of its focus on educating individuals in order to promote behaviour change; however, health promotion is much broader than that and encompasses many more types ...
Scholarly writing is a form of communication and a necessary skill that is important to the nurse's role as a clinician, professional, a leader, a scholar, an educator, and an advocate. As a student, developing skills in scholarly writing will help prepare you for your nursing role. Social awareness and advocacy campaigns in which you share ...
In the context of escalating health care costs and shocking future cost projections, the potential for improved health outcomes through patient education and self-management programs is immense. In the early 1990s, it was estimated that 50% of the annual mortality toll in the US was premature. Tobacco use, poor diet, a lack of physical exercise ...
General health promoters. Health promotion by nurses is associated with common universal principles of nursing. The most common health promotion intervention used by nurses is health education (Robinson and Hill, 1998; Whitehead, 2001, 2007, 2011; Runciman et al., 2006; Witt and Puntel de Almeida, 2008; Parker et al., 2009).General health promoters are expected to have knowledge of health ...
The Importance of Health Education. Health education plays a pivotal role in improving community well-being by promoting knowledge and healthy practices across all age groups, addressing a wide range of health issues from chronic diseases to mental health and influencing policy and economic outcomes. Danielle Gagnon. Mar 21, 2024.
Identifying teachable moments in clinical practice is an effective way to increase workplace learning with all nurses playing a role, not just nurse educators. This article comes with a handout for a journal club discussion. Abstract. Effective workplace teaching is increasingly important in healthcare, with all staff being potential educators.
The fact that continuing nursing education has a positive impact on competencies, attitudes, and knowledge is undeniable in the context of present-day developments. Today, the field of health care is actively developing, and therefore, there is a necessity to update the knowledge and obtain new skills on a regular basis.
To further uncover the importance of the nursing role in health promotion, Whitehead explored the current position of nursing concerning its practice, associated concept, ... while the relationship between nurses being aware of the importance of providing health education (HE) to patients with HP practice produced five statistically significant ...
Nurses are the foundation of healthcare. They play a vital role in providing care, comfort and compassion for their patients and patients' families. Despite their caring demeanor, nurses would rather not see you in the hospital. Preventive healthcare is their priority for patients — getting regular checkups and keeping health concerns from ...
500 Words Essay on Health Education. We all know that health education has become very important nowadays. It refers to a career where people are taught about healthcare. Professionals teach people how to maintain and restore their health. In other words, health does not merely refer to physical but also mental, social and sexual health.
The Importance of Community Health Nursing. Community health nurses are a vital link in the health and welfare of neighborhoods. These registered nurses focus on improving the lives of diverse communities of infants, children, adolescents, and adults through education, prevention, and treatment. "They assist with equalizing health care in ...
If you entered nursing via an alternative route that had less emphasis on traditional academic preparation, then your confidence in writing an essay that draws on referenced literature will probably be much reduced. Even if you were quite strong at school or college work, you may find the transition to self-directed degree study quite difficult.
INTRODUCTION. The starting point for this study is the challenge in nursing education to create fruitful conditions for nurse students' learning and reflective processes that strengthen their understanding of caring and their professional formation to become caring nurses [1, 2, 3, 4].Essential to the process of becoming a caring nurse is the appropriation of a caring attitude where the ...
Importance Of Health Education Essay. Health education is an essential foundation to have an efficient and effective individuals, families and communities that aim to bridge the gap between the knowledge and health practices wherein humans must invest on their health to perform duties and responsibilities at work or mediocre.