MCQtimes.Com

Oral Presentation
The section contains questions and answers on oral presentation roles and parameters, speech preparation, stage fear overcome, notice and minutes, seminars and conferences.
General Presentation Skills MCQs
1. The benefits of arriving early for a presentation include:
2. What's the most important aspect of your presentation slides?
3. True or False? During a presentation, it's best to read the text on your slides so you don't get off track
4. What is a commonly used color in corporate presentations because it's positively associated with conservatism, confidence, dependability, and the male gender.
5. Which of these is a good way to create contrast in your presentation?
6. To be a good presenter, you need to be _________
7. Presentations of an hour or longer are more impactful than a presentation of 20 Minutes.
8. Which type of body language is encouraged when delivering a presentation?
9. If you are presenting slides to a room of people, you should stand so that you are facing the:
10. True or False? Humor can be successfully incorporated into a professional presentation to create a connection with the audience.
11. What is the best plan when preparing for a presentation?
12. What is the best way to practice and review for a presentation?
13. What should be considered before making a presentation?
14. What could be fatal to the success of a presentation?
15. True or False? If you have been given a 60-minute window for your presentation, you should intentionally finish early to allow time for questions.
16. Towards the end of a presentation, what should be the focus?
17. The benefits of Guy Kawasaki's "10/20/30" method include:
18. What would always be a successful enhancement to a business presentation?
19. How can you know what to expect before a presentation?
20. True or false? Comparative design is a great way to find common ground with an audience.
21. True or false? Audience feedback only comes from verbal clues.
22. Maslow's heirarchy of needs helps a speaker conceptualize how to _______ their audience.
23. Providing a handout separate from your slides:
24. Which of the following is NOT a recommended presentation technique?
25. True or False? Reading from slides is an effective way to convey information to the audience.
26. Filler words should be withheld from presentations, including "Umm", "Like" or "Uh"
27. The correct order for handling your content when creating a presentation from scratch is:
28. True or False? You can give the exact same presentation to any room, regardless of who your audience is.
29. The ability to recognize emotions and connect with others, a critical skill for presenters, is known as:
30. True or false? Repetition is never effective when giving a presentation.
31. True or False? The design of your slides does not matter if your content is interesting enough.
32. The quality of your presentation is most directly related to the quality of your:
33. Which statement demonstrates lack of confidence in the subject?
34. What is positive nervousness?
35. According to Seth Godin, each chart in your presentation should:
36. Studies conducted by Dr. Albert Mehrabian showed that the impact of communication is:
37. Finish this statement: A PowerPoint presentation should
38. Experts generally agree that _________ is one of the most effective means of communication.
39. True or false? You should put all the information that you want your audience to understand on your slides.
40. True or False? It is necessary to present all of the related information supporting your argument in a presentation, or else the audience won't believe you.
41. Many experts believe that the best way to plan your presentation and organize your content during brainstorming is:
42. According to Pixar filmmaker and TED speaker Andrew Stanton, the first rule of storytelling is:
43. When using an analagous example, a speaker is using a/an ___________.
44. Which of the following is NOT important for effective communication with an audience?
45. Making a presentation, it's best to be __________
46. Some good transition phrases that humanize you, and so are good to throw into your presentation, might be "To Be Honest" and "You Know" or "Like"
47. "Say what you're going to tell them, tell them, then_______," is a classic presentation format.
48. What is vital in building a good impression on top of the presentation itself?
49. Research has found that most decision-making is based not on logic, but:
50. Which of the following is NOT a commonly accepted type of speech design?
51. Guy Kawasaki's "10/20/30" method refers to which aspects of the presentation, respectively?
52. The method of connecting to an audience through common ground is called ________.
53. Which of the following is NOT an example of a plosive?
54. Which of these is the most accurate analogy for the relationship between you (the presenter) and the audience?
55. According to Edward Tufte, when presenting complex material you should follow what pattern?
56. True or False? Bullet points have been scientifically proven to be more effective than full sentences on slides.
57. True or False? Animations and builds are a surefire way to get your audience engaged.
58. The process of brainstorming as many ideas as possible is known as _______ thinking, and the process of narrowing your focus to the best of those ideas is known as ________ thinking.
59. True or false? It's always best to leave basic printed brochures about your services after a presentation
60. A multimedia presentation is _____
Join our newsletter for the latest updates.

Our Products
© Copyrights 2024 Quizack.com
Oral Presentation MCQs
Welcome to our comprehensive collection of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) on Oral Presentation , a fundamental topic in the field of Professional Communication . Whether you're preparing for competitive exams, honing your problem-solving skills, or simply looking to enhance your abilities in this field, our Oral Presentation MCQs are designed to help you grasp the core concepts and excel in solving problems.
In this section, you'll find a wide range of Oral Presentation mcq questions that explore various aspects of Oral Presentation problems. Each MCQ is crafted to challenge your understanding of Oral Presentation principles, enabling you to refine your problem-solving techniques. Whether you're a student aiming to ace Professional Communication tests, a job seeker preparing for interviews, or someone simply interested in sharpening their skills, our Oral Presentation MCQs are your pathway to success in mastering this essential Professional Communication topic.
Note: Each of the following question comes with multiple answer choices. Select the most appropriate option and test your understanding of Oral Presentation . You can click on an option to test your knowledge before viewing the solution for a MCQ. Happy learning!
So, are you ready to put your Oral Presentation knowledge to the test? Let's get started with our carefully curated MCQs!
Oral Presentation MCQs | Page 2 of 5
Discover more topics under professional communication, language,phonetics and articles, grammar,syntax and clear communication, transformation of sentences, vocabulary and use of abbreviations, letter writing and proposal writing, verbal communication, technical writing, report writing and precis writing, interview skills and group discussion, communication basics, principles of public speaking.
suggestions
perspectives
He must convey precise information.
He must ensure that the information is understood by the audience.
He must inspire the audience to totally accept his point of view.
He must force the audience to totally accept his point of view.
May be True or False
Can't say
Preparation
Abstract words
Short sentences
Good pronunciation
Steady pace
Staring at the floor
Making eye contact
Simple words
Illogical sounds
Eye contact
show over confidence
show under confidence

24 Oral Presentations
Many academic courses require students to present information to their peers and teachers in a classroom setting. This is usually in the form of a short talk, often, but not always, accompanied by visual aids such as a power point. Students often become nervous at the idea of speaking in front of a group.
This chapter is divided under five headings to establish a quick reference guide for oral presentations.

A beginner, who may have little or no experience, should read each section in full.

For the intermediate learner, who has some experience with oral presentations, review the sections you feel you need work on.

The Purpose of an Oral Presentation
Generally, oral presentation is public speaking, either individually or as a group, the aim of which is to provide information, entertain, persuade the audience, or educate. In an academic setting, oral presentations are often assessable tasks with a marking criteria. Therefore, students are being evaluated on their capacity to speak and deliver relevant information within a set timeframe. An oral presentation differs from a speech in that it usually has visual aids and may involve audience interaction; ideas are both shown and explained . A speech, on the other hand, is a formal verbal discourse addressing an audience, without visual aids and audience participation.
Types of Oral Presentations
Individual presentation.
- Breathe and remember that everyone gets nervous when speaking in public. You are in control. You’ve got this!
- Know your content. The number one way to have a smooth presentation is to know what you want to say and how you want to say it. Write it down and rehearse it until you feel relaxed and confident and do not have to rely heavily on notes while speaking.
- Eliminate ‘umms’ and ‘ahhs’ from your oral presentation vocabulary. Speak slowly and clearly and pause when you need to. It is not a contest to see who can race through their presentation the fastest or fit the most content within the time limit. The average person speaks at a rate of 125 words per minute. Therefore, if you are required to speak for 10 minutes, you will need to write and practice 1250 words for speaking. Ensure you time yourself and get it right.
- Ensure you meet the requirements of the marking criteria, including non-verbal communication skills. Make good eye contact with the audience; watch your posture; don’t fidget.
- Know the language requirements. Check if you are permitted to use a more casual, conversational tone and first-person pronouns, or do you need to keep a more formal, academic tone?
Group Presentation
- All of the above applies, however you are working as part of a group. So how should you approach group work?
- Firstly, if you are not assigned to a group by your lecturer/tutor, choose people based on their availability and accessibility. If you cannot meet face-to-face you may schedule online meetings.
- Get to know each other. It’s easier to work with friends than strangers.
- Also consider everyone’s strengths and weaknesses. This will involve a discussion that will often lead to task or role allocations within the group, however, everyone should be carrying an equal level of the workload.
- Some group members may be more focused on getting the script written, with a different section for each team member to say. Others may be more experienced with the presentation software and skilled in editing and refining power point slides so they are appropriate for the presentation. Use one visual aid (one set of power point slides) for the whole group. Take turns presenting information and ideas.
- Be patient and tolerant with each other’s learning style and personality. Do not judge people in your group based on their personal appearance, sexual orientation, gender, age, or cultural background.
- Rehearse as a group, more than once. Keep rehearsing until you have seamless transitions between speakers. Ensure you thank the previous speaker and introduce the one following you. If you are rehearsing online, but have to present in-person, try to schedule some face-to-face time that will allow you to physically practice using the technology and classroom space of the campus.
- For further information on working as a group see:
Working as a group – my.UQ – University of Queensland
Writing Your Presentation
Approach the oral presentation task just as you would any other assignment. Review the available topics, do some background reading and research to ensure you can talk about the topic for the appropriate length of time and in an informed manner. Break the question down as demonstrated in Chapter 17 Breaking Down an Assignment. Where it differs from writing an essay is that the information in the written speech must align with the visual aid. Therefore, with each idea, concept or new information you write, think about how this might be visually displayed through minimal text and the occasional use of images. Proceed to write your ideas in full, but consider that not all information will end up on a power point slide. After all, it is you who are doing the presenting , not the power point. Your presentation skills are being evaluated; this may include a small percentage for the actual visual aid. This is also why it is important that EVERYONE has a turn at speaking during the presentation, as each person receives their own individual grade.
Using Visual Aids
A whole chapter could be written about the visual aids alone, therefore I will simply refer to the key points as noted by my.UQ
To keep your audience engaged and help them to remember what you have to say, you may want to use visual aids, such as slides.
When designing slides for your presentation, make sure:
- any text is brief, grammatically correct and easy to read. Use dot points and space between lines, plus large font size (18-20 point).
- Resist the temptation to use dark slides with a light-coloured font; it is hard on the eyes
- if images and graphs are used to support your main points, they should be non-intrusive on the written work
Images and Graphs
- Your audience will respond better to slides that deliver information quickly – images and graphs are a good way to do this. However, they are not always appropriate or necessary.
When choosing images, it’s important to find images that:
- support your presentation and aren’t just decorative
- are high quality, however, using large HD picture files can make the power point file too large overall for submission via Turnitin
- you have permission to use (Creative Commons license, royalty-free, own images, or purchased)
- suggested sites for free-to-use images: Openclipart – Clipping Culture ; Beautiful Free Images & Pictures | Unsplash ; Pxfuel – Royalty free stock photos free download ; When we share, everyone wins – Creative Commons
This is a general guide. The specific requirements for your course may be different. Make sure you read through any assignment requirements carefully and ask your lecturer or tutor if you’re unsure how to meet them.
Using Visual Aids Effectively
Too often, students make an impressive power point though do not understand how to use it effectively to enhance their presentation.
- Rehearse with the power point.
- Keep the slides synchronized with your presentation; change them at the appropriate time.
- Refer to the information on the slides. Point out details; comment on images; note facts such as data.
- Don’t let the power point just be something happening in the background while you speak.
- Write notes in your script to indicate when to change slides or which slide number the information applies to.
- Pace yourself so you are not spending a disproportionate amount of time on slides at the beginning of the presentation and racing through them at the end.
- Practice, practice, practice.
Nonverbal Communication
It is clear by the name that nonverbal communication are the ways that we communicate without speaking. Many people are already aware of this, however here are a few tips that relate specifically to oral presentations.
Being confident and looking confident are two different things. Fake it until you make it.
- Avoid slouching or leaning – standing up straight instantly gives you an air of confidence.
- Move! When you’re glued to one spot as a presenter, you’re not perceived as either confident or dynamic. Use the available space effectively, though do not exaggerate your natural movements so you look ridiculous.
- If you’re someone who “speaks with their hands”, resist the urge to constantly wave them around. They detract from your message. Occasional gestures are fine.
- Be animated, but don’t fidget. Ask someone to watch you rehearse and identify if you have any nervous, repetitive habits you may be unaware of, for example, constantly touching or ‘finger-combing’ your hair, rubbing your face.
- Avoid ‘voice fidgets’ also. If you needs to cough or clear your throat, do so once then take a drink of water.
- Avoid distractions. No phone turned on. Water available but off to one side.
- Keep your distance. Don’t hover over front-row audience members; this can be intimidating.
- Have a cheerful demeaner. You do not need to grin like a Cheshire cat throughout the presentation, yet your facial expression should be relaxed and welcoming.
- Maintain an engaging TONE in your voice. Sometimes it’s not what you’re saying that is putting your audience to sleep, it’s your monotonous tone. Vary your tone and pace.
- Don’t read your presentation – PRESENT it! Internalize your script so you can speak with confidence and only occasionally refer to your notes if needed.
- Lastly, make good eye contact with your audience members so they know you are talking with them, not at them. You’re having a conversation. Watch the link below for some great speaking tips, including eye contact.
Below is a video of some great tips about public speaking from Amy Wolff at TEDx Portland [1]
- Wolff. A. [The Oregonion]. (2016, April 9). 5 public speaking tips from TEDxPortland speaker coach [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JNOXZumCXNM&ab_channel=TheOregonian ↵
communication of thought by word
Academic Writing Skills Copyright © 2021 by Patricia Williamson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Public Speaking MCQs
Public speaking mcqs topics.
General MCQs
Building Confidence MCQs
Inclusion, Ethics, and Critical Thinking MCQs
Listening Critically MCQs
Analyzing and Adapting to the Audience MCQs
Selecting a Topic and Purpose MCQs
Finding and Evaluating Research MCQs
Integrating Support MCQs
Organizing the Main Points of Speech MCQs
Outlining of Speech MCQs
Beginning and Ending of Speech MCQs
Wording the Speech MCQs
Delivery Modes and Practice of Speech MCQs
Nonverbal Messages Matter MCQs
Presentation Aids of Speech MCQs
Speak to Inform MCQs
Prepare to Persuade MCQs
Persuasion Methods in in Public Speaking MCQs
Planning and Presenting in Small Groups MCQs
Special Occasion Speeches MCQs
Business and Professional Speaking MCQs
Storytelling in Public Speaking MCQs
Speaking Across College Courses MCQs
Presenting Online MCQs
Answering Questions in Public Speaking MCQs
Introduction to Public Speaking MCQs
These Public Speaking multiple-choice questions and their answers will help you strengthen your grip on the subject of Public Speaking. You can prepare for an upcoming exam or job interview with these Public Speaking MCQs. So scroll down and start answering.
1: Which of these should you focus on before a speech?
A. Pronunciation
B. All of these
C. Pace
D. Inflection
2: When public speaking, what is the generally accepted number of points you should focus on?
A. 5
B. 3
C. 10
D. 1
3: It is always appropriate to use hand gestures while speaking
A. False
B. True
4: Which visual cue is critical to engaging your audience?
A. Standing extremely far from your audience
B. Standing or sitting upright, head up and confident
C. Making glaring eye contact
D. Clean, professional attire matching the same dress code as the client
5: True or false? With enough practice and experience, stage fright will disappear entirely.
6: which is not important for effective communication with your audience.
A. motivation
B. memorization
C. attention
D. retention
7: If the microphone is malfunctioning, what should you do?
A. Pause a moment only, then continue in a louder voice if at all possible.
B. Stop and wait for a sound technician to fix it.
C. Make a knowing remark to the audience.
D. Begin shouting from where you left off.
A. True
B. False
10: Which of these should you avoid?
A. Pacing across the stage
B. Getting visibly relaxed and comfortable in front of your audience
C. Backing up your points with stories
D. Using as many words as possible when making your point to prove you know what you are talking about
11: Which of the following is best practice for memorization?
A. Memorize everything, and bring a copy with you just in case.
B. Look at the speech once or twice before delivering it in public.
C. Adequately familiarize yourself with the speech, and refer to your copy as needed.
D. It's more professional and less distracting to memorize everything and leave the printed copy elsewhere.
12: Who should be responsible of knowing how the equipment works?
A. The audience
B. You
C. Technical support
D. You and any technical support
13: True or False? You should stay put whilst you are making a speech.
14: the first step in structuring a speech should be.
A. determining your main points
B. writing out the body of the speech
C. arranging main point in the most effective order
D. writing out the introduction
15: The topic of your speech should be:
A. Of interest to you
B. Something that bores you
C. Of interest to the audience but not you
D. Something that you have never spoken about
16: Who should you practice your speech with?
A. Friends
B. Family
C. Anyone
D. Strangers
17: When should you introduce props to the audience?
A. Never use props
B. All at once in the middle of the speech
C. Throughout the speech, not all at once.
18: True or False? It is better to memorize your speech word for word.
19: before a speech, you should:.
A. Drink milk to calm down
B. Talk on a full stomach
C. Wait a few minutes after being introduced
D. Know the equipment you will be using
20: Which of these is optimal?
A. A concise, clear speech delivered fairly quickly.
B. A lengthy speech delivered at a relaxed pace.
C. A fast, information-packed speech delivered fairly quickly.
D. A concise, clear speech at a relaxed pace.
21: A chronological speech design ________.
A. tells histories alone
B. is only used in a legal setting
C. moves from event to event
D. uses space as a tool
22: Which of these are NOT recommended presentation styles?
A. Reading every word of your presentation from your notes
B. Writing/typing notes with very large font
C. Writing down hints like "pause" or "change slide"
D. Speaking slowly
23: When speaking publicly you should:
A. Speak from the diaphragm to project your voice
B. Always be serious; never tell a joke
C. Read directly from your prepared remarks
D. Speak quickly
E. Speak quietly; the microphone will amplify your voice
24: Which of these are a main goal of the opening segment of your presentation?
A. Break the audience's attention from their preoccupations
C. Give a hint as to the direction of your speech
D. Give the audience a clear reason how they will benefit from listening to you
25: What should you do just before speaking publicly?
A. Take a walk to center yourself and meditate.
B. Take a shot - espresso or vodka.
C. Stay hydrated, keep positive and excited, relax.
D. Pretend there is nothing out of the ordinary; it's a walk in the park.
26: True or False? You should repeat what you said earlier in your speech as a closing to your speech.
27: true/false: if you are shy of direct eye contact, you can increase your confidence when speaking to someone by looking directly at the bridge of their nose (between the eyes), when you are speaking to them., 28: how should your posture be when public speaking.
A. Whatever is most comfortable
B. Slouchy
C. Leaning on something for support
D. Tall and strong
29: To fight anxiety during a speech, you should:
A. Sit down
B. End the speech
C. Focus on your anxiety problems
D. None of these
30: Many great public speakers suffer from nerves.
31: why are diction and enunciation important.
A. For the clarity of your presentation.
B. If your audience is older or hard of hearing.
C. To attract attention to your presentation.
D. To spit on the audience.
32: True or False? It is not okay to use offensive language even if you know your audience.
33: stage fright diminishes with practice and experience., 34: true or false filler words should be withheld from presentations, including "umm", "like" or "uh", 35: how can stage fright be a good thing.
A. It causes you to sweat, keeping you cool.
B. It increases stimulation and is necessary to get you in the 'zone.'
C. If you get very nervous, it is a good indicator that public speaking is not for you.
D. Nerves make you speak faster, so you can communicate more information.
36: Which part of your speech should be the strongest?
A. End
B. Beginning and end
C. Middle
37: What is one thing you want your audience to be able to do after your speech?
A. Remember what you look like
B. Remember where you're from
C. Sum up the take-away message
D. Be able to recite most of your speech
38: True or False? Using visuals is a distraction for the audience.
39: you should have a 'target' audience member in mind when writing and performing your speech., 40: true or false you should focus eye contact on one person., 41: how should you prepare the day before a public speaking engagement.
A. Write the whole speech, sleep or no. It'll be fresher in your mind.
B. Laze around all day, eat junk food, and relax.
C. Eat well, exercise, and get a good night's sleep.
D. Engage in strenous activity and really tire yourself out for the night.
42: What should you do if you can't answer a question?
A. It's better to make up an answer than not answer
B. Try to break it down and subtly shift the topic of the question to something you can answer
C. Say ' That's a good question!', telling them that you honestly don't know the answer and you will try get back to them.
D. Pretend you didn't hear the question and move on.
43: Which of these is the best option to calm down during your speech?
A. Taking a sip of water
B. Taking a deep breath
C. Walking around a bit
D. All of these
44: Which of these are a useful method for becoming a better and more credible public speaker?
A. Fitting more jokes into your presentation
B. Make sure to drink plenty of coffee so you are alert for your presentation
C. Gathering and analyzing information about your audience
D. Speaking more quickly to get your point across quickly
45: What is the best way to improve your public speaking?
A. Watch great speakers and take note.
B. Rehearse things repeatedly while going to sleep.
C. Drink caffeine or take a Xanax before you speak.
D. Practice - at home, in the mirror, with friends, in front of an audience.
46: True or False? You should repeat questions when asked by someone in the audience so that everyone knows what question you are answering.
47: what is the best way to feel confident in public speaking.
A. Knowing your surroundings
B. Talking really fast
C. Not looking up at the audience and focusing on your index cards or the screen
D. Drinking alcohol beforehand
48: How much preparation time should a speech take?
A. Couple of hours
B. Until you feel absolutely confident
C. 1 day
D. 1 week
49: What should you do if you are momentarily overwhelmed, for example, by coughing or emotion?
A. Just leave - it's too much to take.
B. Pause, breath, and take a drink. Then continue.
C. Leave the stage, take a breather, and come right back.
D. Just push through - it's almost over.
50: Faster is better.
List of public speaking mcqs m..., related public speaking mcqs:.
Salesforce CRM MCQs
Twitter Management MCQs
Marketing Methods and Techniques MCQs
Selling Skills MCQs
Help Desk Skills MCQs
Available in:
Latest mcqs:.
Promotion Strategy MCQs
Declarative Memory MCQs
Principles of Marketing MCQs
Social Media Management MCQs

Popular MCQs:
Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions | Contact Us
© copyright 2024 by mcqss.com

The Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild gameplay on the Nintendo Switch

Shadow Tactics: Blades of the Shogun Review

macOS Sierra review: Mac users get a modest update this year

Hands on: Samsung Galaxy A5 2017 review

The Last Guardian Playstation 4 Game review

These Are the 5 Big Tech Stories to Watch in 2017
Trending tags.
- Nintendo Switch
- Playstation 4 Pro
- Mark Zuckerberg

Heroes of the Storm Global Championship 2017 starts tomorrow, here’s what you need to know

Harnessing the power of VR with Power Rangers and Snapdragon 835

So you want to be a startup investor? Here are things you should know

Shooting More than 40 Years of New York’s Halloween Parade

Why Millennials Need to Save Twice as Much as Boomers Did

Doctors take inspiration from online dating to build organ transplant AI

How couples can solve lighting disagreements for good

Ducati launch: Lorenzo and Dovizioso’s Desmosedici
- Golden Globes
- Game of Thrones
- MotoGP 2017
- Fashion Week
Presentation Skills MCQs with Answers
Presentation Skills MCQs
- .A presentation is a form of oral communication in which person shares factual information with an audience that is__.
a) specific b) small c) large d) mixed
a) specific
- The presenter acts as the:
a) delivery of the information b) medium of the information c) advocate of the information d) supporter of the information
c) advocate of the information
- The three major element of presentation do not include?
a) an audience b) specific content c) a presenter d) visual aids
c) a presenter
- Reading out a presentation is:
a) not allowed b) allowed c) helpful d) dull
a) not allowed
- To select the content of your presentation you should know the audience need.
a) your purpose b) the time limit c) available material
b) the time limit
- When giving a presentation in front of an audience you should do all of the following except for__?
a) speak loud and clear b) provide handout if needed c) dress professionally d) look at your screen not the audience
a) speak loud and clear
- The key of success is__
a) practice b) preparation c) effort d) both a and b
d) both a and b
- A good presenter should take a well__.
a) good physical appearance b) dressing well c) speak louder d)
a) good physical appearance
- To become more affective you need to take control of
a) the material b) the audience c) your behavior d) all of the above
a) the material
- ___of a presentation is the most important part
a) beginning b) middle c) end d) none of these
a) beginning
- In beginning you should give firstly
a) your introduction b) summary of a topic c) asking irrelevant questions d) further information
a) your introduction
- A good technique to get your audience attention
a) a statement made to surprise b) asking rhetorical questions c) asking introduction to the audience d) none of these
b) asking rhetorical questions
- What should you give your objectives to the audience
a) aim b) goals c) purpose d) All of These
d) All of These
- All your information should support your
a) purpose b) ideas c) topic d) merits
- A good presenter should
a) sequencing your idea b) manage the time c) clear all the confusion d) all of these
d) all of these
- Keeping the audience attention
a) emphasizing b) summarize the topic c) used bore words
a) emphasizing
- A conclusion should be
a) short and easy b) lengthy c) difficult words d) specific key points
a) short and easy
- Visual involves the audience
a) motivate b) attention c) reinforce idea d) all of these
- How much of the language is made up of verbal language
a) 7% b) 6% c) 2% d) 15%
- 38% message is communication with non verbal
a) vocal b) verbal c) body movement d) gesture
- Body language is included in communication
a) 55% b) 35% c) 25% d) 45%
- facial expression should be
a) aggressive b) shy c) naturally d) bored
c) naturally
- A speaker looks into the eyes of the audience
a) confident b) impatient c) rude d) impolite
a) confident
- The tone of the speaker should be
a) loud b) clear c) low d) soft
- A speech must advance __
a) dishonesty b) negativity c) truth d) aggressiveness
- Which of these doesn’t enhance listening skills?
a) attention b) frankness c) clear perception d) ignoring
d) ignoring
- Using your whole body to communicate is called what?
a) miming b) sign language c) body language d) gesture
c) body language
- Waving is what type of communication?
a) gesture b) body language c) sign language d) body position
- positive gesture are body sihnals that make you look_
a) relaxed b) hurtful c) nervous d) arrogant
- Communication Skill MCQS
- Communication Barrier MCQs
- Listening Skills MCQs
- Barrier of Listening MCQs
“ presentation skills mcqs with answers pdf”,” technical writing and presentation skills mcqs pdf”,”communication and presentation skills mcqs “,”presentation skills questions and answers pdf “,”test your presentation skills”,”mcqs on oral presentation”,”presentation skills questions and answers”,,”presentation skills questions and answers pdf”,”question paper on presentation skills”,” test your presentation skills “,” mcqs on oral presentation “,”technical writing and presentation skills mcqs pdf”,”presentation skills mcqs with answers pdf”
2nd year Physics Important MCQs with Answer
Formal and informal communication skills mcqs.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Privacy Policy
Copyright @ 2024 All Rights Reserved | Powered By Pkilm4u .
How to Give an Oral Presentation?
- Open Access
- First Online: 24 October 2021
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- Samiran Nundy 4 ,
- Atul Kakar 5 &
- Zulfiqar A. Bhutta 6
28k Accesses
1 Citations
1 Altmetric
An oral presentation is a form of communication, where you impart and then exchange information with your audience. This can be either one-way, a didactic, or two-way called a Socratic or a Dialectic presentation. There are many forms of oral presentation and you should find out where and when you are required to speak [1]. The National Training Laboratory in Maine, USA has suggested a ‘cone’ of learning or learning ‘pyramid’. In this, they have found that the most effective way of learning is through teaching others. Most students remembered only 10% of the material given in books but remembered 90% of the facts they learned when they had to teach others [2] (Fig. 38.1).
The first 30 seconds and the last 30 seconds have the most impact in a presentation. — Patricia Fripp, American author
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others

Strategies for the Preparation and Delivery of Oral Presentation

How to Prepare and Give a Scholarly Oral Presentation

See It, Speak It, Draw It, and Learn to Communicate in Simple Language
An oral presentation is a form of communication, where you impart and then exchange information with your audience. This can be either one-way, a didactic, or two-way called a Socratic or a Dialectic presentation. There are many forms of oral presentation and you should find out where and when you are required to speak [ 1 ]. The National Training Laboratory in Maine, USA has suggested a ‘cone’ of learning or learning ‘pyramid’. In this, they have found that the most effective way of learning is through teaching others. Most students remembered only 10% of the material given in books but remembered 90% of the facts they learned when they had to teach others [ 2 ] (Fig. 38.1 ).
The Lecture is an old way of teaching and by convention called the ‘chalk and talk’ method. The talk needs to be prepared carefully but it is thought to be an ineffective way of imparting knowledge. The flow of ideas and organization of a lecture is an art. It is usually taken by a qualified person. In this, there is passive learning of the attendees as it is a one-way communication. The number of people in a lecture should be around 30 and its duration should be 15–20 minutes. In a lecture during a conference, the number of participants can vary from 50 to 1000.
Symposium —This consists of a series of lectures usually on a single selected topic. Each speaker gives a brief presentation, there is no discussion between the speakers during the presentation and finally the chairman summarizes the talks. People who speak in symposia are experts in the field and all talks are delivered in a single day.
Group discussion or Round table talk —In this, there is a face-to-face discussion between a group of people of usually 6–12 members who sit around a table. The leader initiates the talk and the other members give their opinions. Most round table sessions are fairly structured and require attention to time management and content, with intermittent audience participation.
Workshop— This is a series of lectures in a smaller group. There is an interaction between the members but it is usually at a local level.
Seminar— This is a half to full-day discussion on a particular topic with about 30–40 participants.
Debate— This is an increasingly popular format utilized in larger meetings with two speakers discussing controversy and arguing for either side. This can be through formal presentations or interactive discussions.
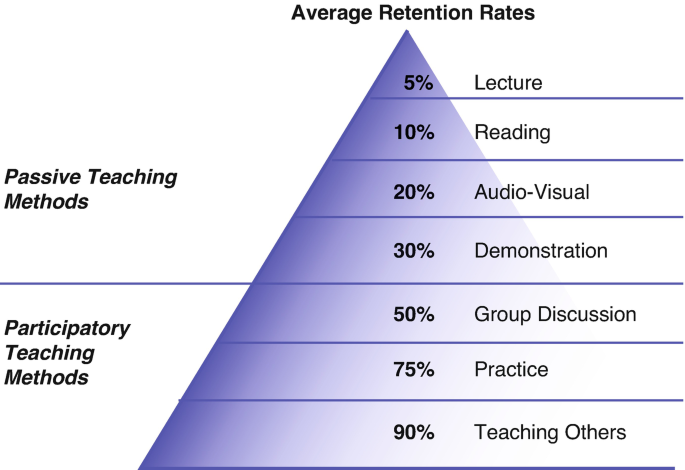
Retention rate of various teaching methods adapted from National Training Laboratories, Bethel, Maine, USA
All these teaching activities can now be virtual and recent circumstances have indicated that this might be the ‘new normal’. Physicians need to be accustomed to this as it may be the way forward for medical education.
2 Does the Success of an Oral Presentation Depend on the Audience?
This is generally true and a presentation works if:
The audience feels the need for the information.
Is enthusiastic.
The subject is applicable to their clinical practice.
Its content is clear and easy to grasp.
There is active audience participation.
Multiple ways of presentation are used, i.e., PowerPoint slides and videos.
3 What Is a Powerful Oral Presentation?
A powerful oral presentation can be summarized with 5 C’s
Contains C rucial information
There is a Clear style of presentation
Confidently delivered
With Concise data
The delivery is Creative and Clever
4 What Are the Steps You Should Take Before an Oral Presentation?
An oral presentation can be divided into:
A Pre-Presentation stage
The Presentation
The Post-presentation stage [ 3 , 4 , 5 ]
In the Pre-Presentation stage:
It is important to check the venue and equipment. It is always better to arrive on time, load the presentation, and recheck it in the preview room to see if the presentation is in order. You should also check with the organizer whether there is double projection, because this requires a lot of coordination and rehearsal.
Check the podium and make a mental picture of how much of the area of the podium and dais you will use during the presentation. Currently, many people follow the TED (Technology, Entertainment, Design) format where there is no podium and they use the entire stage for the talk. For this type of presentation, you should be a seasoned public speaker. Body language is important in this.
Find out about your target audience—general physicians, a mixed group of doctors, a specialty group, or the lay public. However, if it is a speciality lecture the content should cater only to specialists.
You should be appropriately dressed—properly and professionally.
It is always better to email the presentation in case there is a hitch in your pen drive function at the last minute.
Before planning the presentation, go through the programme of the conference as many of the topics in the session might have been covered by someone else. So, those aspects should be omitted from your talk.
The preparation time for your lecture, whether it is 10 min or 30 min long is the same as you need to review all the relevant literature before the presentation. The shorter the talk the more difficult it is to condense and give a powerful performance.
‘Rehearse, rehearse and rehearse’ are the three most important mantras for a flawless delivery.

5 How to Deliver an Oral Presentation?
Making a presentation is a skilful art, which has to be learned over years. Richard Leech, a medically qualified actor, stated that ‘Lecturing is like Acting, where you have to a tell a tale to the audience but it is more difficult than acting because you have to write the script as well’. You cannot inherit the ability to give a good lecture—it comes with repeated practice and as you lecture more you become more confident of speaking in public.
A presentation has two important components, i.e., its content and style.
The content can be further divided into introductory slides, the main text, and conclusions.
The Introduction is the most powerful part of the presentation. There are various models that have been suggested for an introduction slide.
The expected introduction would be to greet the audience and start reading the slides. However, this approach although considered polite, is benign, boring, and lacks power and passion.
Model 1–2-3 consists of, step 1 to greet the audience, step 2 pause, and step 3 is to make an attention-grabbing statement or relate a story that is linked to the presentation.
The opening few slides should make the audience believe that you are the best person to deliver this lecture and also it has important content for them (WIIFM—What’s in it for me?). In case the chairperson has not introduced you it would be relevant to provide some personal and professional information in the first few slides. Typically, the introduction should take 2–3 minutes or 10–15% of your allotted time. This is also the time you will take to establish a relationship with your audience.
Thus, the introduction slides are:
The first contact with the audience and they set the tone for the rest of the lecture.
An opportunity to grab the audience’s attention.
You can start by asking a question or pose a hypothesis to the audience.
The main body of the talk should be divided into 3–4 subheadings and each subheading should have a learning and take-home message to reduce the monotony and increase (Fig. 38.1 ) the learning. The content of the presentation should also contain the purpose of the talk. Although information repeated is important for learning, unnecessary facts are usually boring. You should use diagrams, charts, cartoons, tables, and photos to decrease the written parts.
You should use varied modes of presentation which may include PowerPoint slides, clips of videos, or discuss real-world scenarios. These make the presentation more interesting.
The Conclusions can take up the last few slides and rather than re-stating the same sentences try to find new and easily understood words.
As for the style of the presentation, it should be bold and exude confidence.
The other qualities are:
Maintain calm—Many people get anxious when it comes to an oral presentation. Mild anxiety increases the androgenic drive which makes the presentation more exciting, however, if you have moderate-to-severe anxiety it may manifest as jitteriness and you may fumble. Sometimes deep breathing exercises can help to allay symptoms of anxiety. Do not take any drugs before the presentation.
Rehearse your presentation. This has two advantages—you can do time management and you can speak with clarity on all the important slides. You should not read out the slide but use it as a point of reference to dilate on the subject. Under all circumstances, DON’T read your slides!
You should not be nervous, shuffle, fidget, and fumble once you are on stage. Even if you are anxious, like a good actor you should not show it.
A boring presentation can be judged by the non-verbal communication during it. The audience will see how many people are sleeping, busy on their cell phones and how many are learning and taking notes.
During the presentation, you should have eye contact with the audience and not with the slides.
6 What Should Be Done in the Post-Presentation Period?
You should invite questions. Do not be afraid to answer questions because you as a presenter have more knowledge about the subject than the audience [ 5 ]. The questions can be answered by saying ‘thank you, it was an intelligent question’. The answer to the question should be brief and should not be the signal to launch a second presentation.
The questions after the lecture can be divided into irrelevant . For which you need to be polite in answering, profound to which you can regret that there is a lack of time and the person can interact with you during the break or might be challenging and requires inputs from the house. You can ask for a show of hands or a debate on such challenging questions.
7 What Should Be the Speed of the Presentation?
The newsreaders on the media speak at 120–130 words per minute. You need to practice this. If you speak very fast the information is not grasped. In the case of an international talk, you need to speak slowly as language and pronunciation may be a problem for the audience [ 6 ].
8 Should You Take Short Pauses During a 30-Minute Talk?
You should not take a pause or stop the presentation as it becomes boring for the audience. There is an attention curve that is maximum in the first few minutes of the lecture and then during the last portion of the lecture (Fig. 38.1 ). However, in case the lecture is lengthy, you can change the tone of your voice or show a visual aid rather than pause. In general, avoid lectures exceeding 30 min and as a general principle, try not to exceed one slide per minute.
9 What Kind of Slides Should There Be?
The background of the slide should be such that the information written is clear; traditionally a light colour with black writing is recommended. There should be no more than 6–8 lines in a slide with not more than 8 words in a line and with proper alignment. No detailed sentences are required while making the slide [ 7 , 8 ]. Examples of good and bad slides are shown in Figs. 38.2 and 38.3 .

Example of good studies

Example of bad studies
10 What Are the Ten Steps Towards a Robust PowerPoint Presentation?
Delivering PowerPoint presentation requires skill in public speaking. Below we summarize the six steps for a power-packed presentation [ 9 ].
Step 1 —Know what are goals of your presentation. Is it to educate the audience on a naïve subject or to update existing knowledge?
Step 2 —Know your audience. It is usually said that one size does not fit all and similarly your audience may be heterogenous and your aim will be to give all of them a basic level of information. Each time there is a new audience your slides should change accordingly.
Step 3 —Prepare an outline of your talk. Each topic can be subdivided into small topics and try to focus on 3–4 subpoints in your presentation.
Step 4 —Build up your subpoints. Work on the ‘pyramidal’ approach to build up your presentation (Fig. 38.4 ).
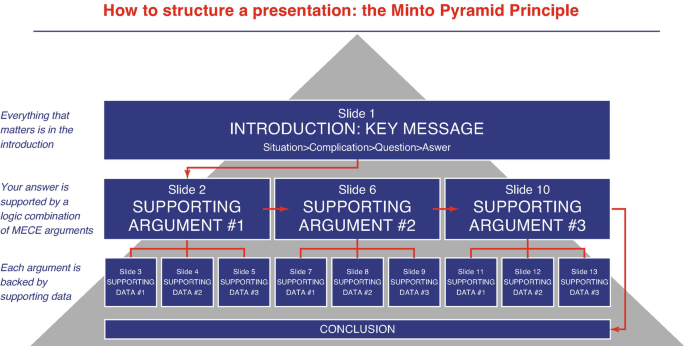
The Minto Pyramid
Step 5 —know the layout, designs, and background available. Few of the layouts and background designs are shown (Fig. 38.5 ).
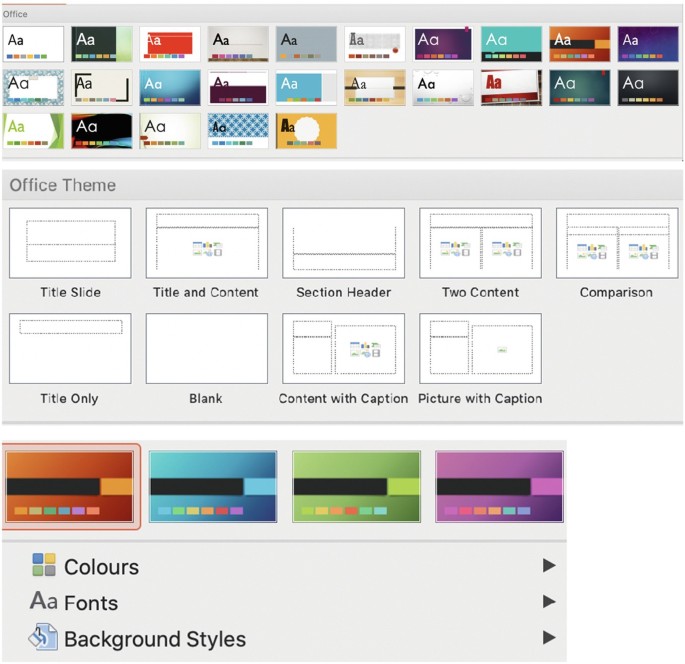
Some designs available
Step 6 —Your PowerPoints slides should be perfect. Use a font which is legible, a background colour which is soothing, and a template which suits your presentation.
Step 7 —Follow the 5/5/5 rule that is not more than five words in line, not more than five lines per slide, and no more than five text slides in a row.
Step 8— Adjust the number of slides according to the time allowed. For a five-minute presentation about 5–6 slides are recommended.
Step 9 —The slide design should match the audience and ambience.
Step 10 —Use graphs, photos, and other visual aids to decrease the monotony.
11 What Is the Conclusion for an Oral Presentation?
Conclude by recapitulating what you have said in your slides. Why did you do this study, How did you do it, what results did you get and what is your ‘take home’ message.
An Oral presentation is a powerful way of communication with the audience. It should be presented clearly and with confidence.
The Stages of an oral presentation include the pre-presentation preparation, podium presentation, and post-presentation period. An Oral presentation is an art that is learnt with time.
The Slides for an oral presentation should follow the 5 × 5 rules.
Conference Monkey Last accessed on 12th May 2020. Available on https://conferencemonkey.org/blog/whats-the-difference-between-a-conference-a-seminar-a-workshop-and-a-symposium-1075915 .
Ken Masters. Edgar Dale’s Pyramid of Learning in medical education: A literature review, Medical Teacher 2013;35:11, e1584–e1593.
Google Scholar
Haber RJ, Lingard LA. Learning oral presentation skills: a rhetorical analysis with pedagogical and professional implications. J Gen Intern Med. 2001;16:308–14.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Bourne PE. Ten simple rules for making good oral presentations. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007;3(4):e77.
Article Google Scholar
Hall GH. How to present at meetings. BMJ; 2001, London.
What’s your speech rate. Last accessed on 12th May 2020. Available on https://www.write-out-loud.com/speech-rate.html .
How to give successful oral presentation. Last accessed on 12th May 2020. Available on https://www.scientificleaders.com/presentations/ .
Top eight rules to make PowerPoint presentation. Last accessed on 12th May 2020. Available on https://www.pharmacoepi.org/pub/?id=76a123f3-c419-8689-f823-a38e28f5fd02 .
How to make & give great PowerPoint presentations (in 5 simple steps). Last accessed on 12th July 2020. Available on https://business.tutsplus.com/tutorials/how-to-make-and-give-great-powerpoint-presentations%2D%2Dcms-28734 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Surgical Gastroenterology and Liver Transplantation, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India
Samiran Nundy
Department of Internal Medicine, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India
Institute for Global Health and Development, The Aga Khan University, South Central Asia, East Africa and United Kingdom, Karachi, Pakistan
Zulfiqar A. Bhutta
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Nundy, S., Kakar, A., Bhutta, Z.A. (2022). How to Give an Oral Presentation?. In: How to Practice Academic Medicine and Publish from Developing Countries?. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5248-6_38
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5248-6_38
Published : 24 October 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-16-5247-9
Online ISBN : 978-981-16-5248-6
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Communication Skills
Lesson 6. ORAL PRESENTATION SKILLS
Current course
22 February - 28 February
1 March - 7 March
8 March - 14 March
15 March - 21 March
22 March - 28 March
29 March - 4 April
5 April - 11 April
12 April - 18 April
19 April - 25 April
26 April - 2 May
Communication and Presentation Skills MCQs – Quiz
Communication and Presentation Skills MCQs This course aims to Make students able to understand, analyze and use English in written and oral communication. Develop student’s personality as a good English speaker, writer and presenter in realistic life. Help student to identify essential components of a presentation. Polish their knowledge, skills and attitudes required to deliver effective academic presentation and communicate clearly. Help students to learn various presentation and communication techniques. Provide techniques to facilitate effective inter-personal and interactive communication. Guide how to build stronger relationships through powerful communication.
Topics to be covered
Introduction + Subject Orientation, Factors affecting communication effectiveness , Verbal-communication Skills , Art of public speaking , Better listening , Effective Reading and Technical writing Quiz , Presentation Skills , Personality development (emphasis on content, style and pronunciation) Study Skills Skimming and scanning, intensive and extensive, speed reading Summary , Precis Writing , Comprehension Paragraph , Paragraph Writing + Use of library and internet , Letter Writing + Application Writing , Essay Writing and its types

Communication and Presentation Skills MCQs
1. ____ Is Being Particular And Clear Rather Than Fuzzy And General
A. Concreteness B. Courtesy C. Consideration D. Clarity View Answer A. Concreteness
2. ___ Is To Inform, Influence Or Entertain The Listeners.
A. Leader B. Public Speaking C. Small Group Communication D. Task Oriented Group View Answer B. Public Speaking
3. Have A Strong ____on What You Want To Talk.
A. Perception B. Conviction C. Deception D. Affirmation View Answer B. Conviction
4. In Public Speaking, It’s All About___
A. Speaker B. Message C. Audience D. Feedback View Answer C. Audience
5. A Persuasive Speech Works To Convince People To ___.
A. Listen B. Look C. Accommodate D. Change View Answer D. Change
6. No Matter How Kind You Are, Being Leader You Should Know Your___
A. Humility B. Role C. Limits D. Position View Answer C. Limits
7. Which Of The Following Contribute To The Small Group Climate?
A. Cohesiveness B. Function C. Role D. Emotion View Answer A. Cohesiveness
8. ___gives People What They Want.
A. Avoiding B. Competing C. Collaborating D. Compromising
View Answer D. Compromising
9. ___seeks Win-win Solution To Conflict
A. Avoiding B. Competing C. Collaborating D. Compromising View Answer C. Collaborating
10. ___ Is A Flip Side Of Accommodation
A. Avoiding B. Competing C. Collaborating D. Compromising View Answer B. Competing
Read Also >> Business Communication MCQs
11. A ___conflict Style In Which Parties ___ The Problem At Hand
A. Lose-lose, Attempt B. Lose/win, Avoid C. A&b D. None view Answer Answer: A
12. ___ Shows That There Is No Good Way To Resolve The Issue.
A. Lose/lose B. Avoiding C. Your Way D. A&b view Answer Answer: B
13. The Process Of Accurately Decoding The Message You Share With The Speaker Is__
A. Hearing B. Listening C. Attending D. Understanding view Answer Answer: D
14. The Process Of Getting Physically And Mentally Ready To Listen Is___
A. Hearing B. Listening C. Attending D. Understanding view Answer Answer: C
15. A Physiological Activity That Occurs When Sound Waves Hit Our Eardrums.
A. Hearing B. Listening C. Understanding D. Attending view Answer Answer: A
16. Listening Creates____
A. Audience B. Mindset C. Reality D. A&b view Answer Answer: C
17. To Listen Means To____
A. Understand & Feel B. Perceive & Sense C. A&b D. None view Answer Answer: C
18. The Process Of Receiving, Constructing Meaning From, And Responding To Spoken And/or Nonverbal Messages Is:
A. Hearing B. Listening C. Attending D. Understanding view Answer Answer: B
19. ___of The Time We Are Distracted, Preoccupied Or Forgetful.
A. 20% B. 35% C. 2% D. 75% view Answer Answer: D
20. ____ Of The Time, We Remember What We Hear.
A. 20% B. 35% C. 2% D. 75% view Answer Answer: A
21. We Think At ____ Wpm.
A. 1000-3000 B. 1250-2500 C. 100-300 D. 125-250 view Answer Answer: A
22. We Listen At____ Wpm.
A. 1000-3000 B. 1250-2500 C. 100-300 D. 125-250 view Answer Answer: D
23. Communicating Our Values, Ideas, Beliefs, Opinions, Needs And Wants Freely Is____
A. Assertiveness B. Negotiation C. Decision Making D. None view Answer Answer: A
24. Working With Others To Identify, Define And Solve Problems Is___
A. Assertiveness B. Negotiation C. Decision Making D. None view Answer Answer: D
25. Working With Others To Find A Mutually Agreeable Outcome Is ___
A. Assertiveness B. Negotiation C. Decision Making D. None view Answer Answer: B
26. Paralanguage Is A Type Of___
A. Verbal B. Non-verbal C. Sign D. Semantic view Answer Answer: B
27. Paralanguage Is Almost Similar To ____communication.
A. Verbal B. Non-verbal C. Sign D. Semantic view Answer Answer: A
28. Personal Distance Is From _____
A. 6 To 18 Inches B. 18 Inches To 4 Feet C. 4 Feet To 12 Feet D. 12 Feet To 25 Feet view Answer Answer: B
29. Personal Space Is Your ____- The Space You Place Between Yourself And Others.
A. Bubble B. Bound C. Base D. None view Answer Answer: A
30. In Germany Tapping Your Finger On Your Head Means_____
A. Good Luck B. You Are Crazy C. You Are Insane D. You Are Insane view Answer Answer: B
Read Also >> Data Communication MCQs
31.Scientific Study Of ‘how The Body Speaks Has Been Labeled As_____.
A. Non-verbal B. Semantic C. Kinesics D. None view Answer Answer: C
32. The Usage Of ___can Clarify Even The Toughest Message To Understand
A. Verbal Communication B. Non-verbal Communication C. Perception D. A & C view Answer Answer: B
33. Distrust Of Communication Is____
A. Organizational Barrier B. Semantic Barrier C. Psychological Barrier D. B & C view Answer Answer: C
34. Which Of The Following Are The Barriers In Communication?
A. Assumptions B. Emotions C. Noise D. All view Answer Answer: D
35. Verbal Communication Consists Of_____
A. Speaking B. Reading C. Listening D. All Above view Answer Answer: D
36. ‘verbal’ Is The Latin Adjective Of ___
A. Vocal B. Voice C. Words D. Convey view Answer Answer: C
37. In Verbal Communication, Words Account For Only____.
A. 5% B. 6% C. 7% D. 8% view Answer Answer: C
38. he Result Of Perceptual Process Is____
A. Behavior B. Experience C. Norms D. Values view Answer Answer: A
39. In Perceptual Process _____ Is ______.
A. Stimuli, Output B. Stimuli, Mechanism C. Stimuli, Input D. Stimuli, Experience view Answer Answer: C
40. Perception Is A Process That Operates Constantly Between Us And ____.
A. Listener B. Audience C. Mindset D. Reality view Answer Answer: D
41. There Can Be No Behavior Without ______ And Perception Lies At The Base Of Every Human Action.
A. Experience B. Frame Of Reference C. Perception D. Understanding view Answer Answer: C
42. People Tend To Behave And Act On Certain Things On The Basis Of Their____.
43. _______ Avoids The Language That Manipulates, Discriminate And Exaggerate.
A. Effective Communication B. Communication Ethics C. Perception D. Attribution Error view Answer Answer: B
44. Maintaining The Correct Balance Between Speaking And Listening Is _____
45. There Are ____ Components Of Communication
A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 7 view Answer Answer: C
46. Every Communication Involves _____.
A. Sender& Recipient B. Sender And Message C. None Of Above D. A & B view Answer Answer: D
47. Public Speaking Is A.
A. Showmanship B. Show Business C. Showbiz D. None view Answer Answer: B
48. Students Studying For An Exam Are An Example Of.
A. Assigned Group B. Task-oriented Group C. Emergent Group D. None view Answer Answer: B
49. ____ Communication Makes Immediate Impact
A. Verbal B. Non-verbal C. Intrapersonal D. None
view Answer Answer: A
50. _____ Is A Cognitive And Psychological Process
A. Intrapersonal Skills B. Perception C. Norms D. Deception view Answer Answer: B
51. A structured meeting between you and an employer: A. Presentation B. Interview C. Demonstration D. None View Answer Answer: B
52. Effective presentation involves ____key components A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 5 View Answer Answer: C
53. It involves finding the purpose, occasion, and environment in which the presentation is made. A. The situation B. The audience C. The speaker D. The presentation View Answer Answer: A
54. Public speaking is a. A. Showmanship B. Show business C. Showbiz D. None View Answer Answer: B
55. There are ____ components of effective presentation. A. 3 B. 4 C. 5 D. 6 View Answer Answer: A
56. Audience’s knowledge about the topic involves in. A. Planning Phase B. Preparation Phase C. Delivery Phase D. A & C View Answer Answer: A
57. According to the suggested model for presentation “The View” contains. A. Introduction B. Body of your talk C. Your summary D. None View Answer Answer: B
58. Building rapport involves: A. Don’t mingle B. Don’t shake hands C. Both A & B D. None View Answer Answer: D
59. Cover the subject of your presentation in ____ order. A. Chronological B. Logical C. Descending D. A & C View Answer Answer: B
60. Good speakers ____ their voice to draw the attention of the audience, and ____it to make a point A. Raise, lower B. Lower, raise C. Raise, neutral D. Neutral, raise View Answer Answer: A
61. Modulate your tone to avoid ____. A. Autonomy B. Monotony C. A & B D. None View Answer Answer: B
62. Vary your voice, to maintain audience’s interest is A. Tone B. Pace C. Volume D. None View Answer Answer: B
63. Keep the presentation ___ enough to create interest and ___ enough to cover the subject. A. Long, short B. Short, Long C. Long, long D. Short, short View Answer Answer: B
64. While presenting in dark room – use ____font on dark background A. Light B. Dark C. Bold D. Italic View Answer Answer: A
65. While presenting in light room – use ____font on light background A. Light B. Dark C. Bold D. Italic View Answer Answer: B
66. If ____ does not add value, don’t use it. A. Colors B. Content C. Pace D. None View Answer Answer: B
67. While designing your presentation, do not use more than __ lines on any page and not more than __ words per line A. 5, 7 B 7, 5 C. 7, 7 D. 6, 7 View Answer Answer: C
68. Student union advisory board is an example of A. Assigned group B. Task-oriented group C. Emergent group D. None View Answer Answer: A
69. Group of friend who meet at college is an example of. A. Assigned group B. Task-oriented group C. Emergent group D. None View Answer Answer: C
70. Students studying for an exam are an example of. A. Assigned group B. Task-oriented group C. Emergent group D. None View Answer Answer: B
71. Family is an example of A. Assigned group B. Task-oriented group C. Emergent group D. None View Answer Answer: D
72. Generally there are ___ of small group communication A. 3 B. 4 C. 5 D. 6 View Answer Answer: B
73. The role that is developed spontaneously within a group is A. Formal B. Behavioral C. Informal D. B & C View Answer Answer: D
74. Roles in small group are defined by___ A. Ethics B. Behaviors C. Norms D. N one View Answer Answer: B
75. Behaviors that focus on interpersonal relationships among group members are A. Task Functions B. Self-centered functions C. A&B D. None View Answer Answer: D
76. Behaviors directly relevant to the group’s purpose are: A. Maintenance Functions B. Self-centered functions C. A&B D. None View Answer Answer: D
77. Behaviors that serve the needs of individual at the expense of the group are A. Task Functions B. Self-centered functions C. A&B D. None View Answer Answer: B
78. ____ is to conveys all the facts and figures required A. Conciseness B. Completeness C. Correctness D. Clarity View Answer Answer: B
79. ____ enhances the meaning of message. A. Conciseness B. Completeness C. Correctness D. Clarity View Answer Answer: D
80. _____ highlights the main message. A. Conciseness B. Completeness C. Correctness D. Clarity View Answer Answer: A
81. ____ is stepping into the shoes of others A. Concreteness B. Courtesy C. Consideration D. Clarity View Answer Answer: C
82. _____communication addressed to an extremely large audience, mediated by visual and/or audio means A. Public B. Mass C. Computer-mediated D. Organizational View Answer Answer: B
83. ____ is communication that proceeds through questions and answers. A. Small Group B. Organizational C. Interviewing D. Computer-mediated View Answer Answer: C
84. _____is the process by which an individual gives meaning to the environment A. Intrapersonal skills B. Perception C. Norms D. Deception View Answer Answer: B
85. _____ is a cognitive and psychological process A. Intrapersonal skills B. Perception C. Norms D. Deception View Answer Answer: B
86. Objects, Events and people are A. Perceptual inputs B. Perceptual outputs C. Perceptual mechanism D. A & C View Answer Answer: A
87. Attitudes, Opinions, Feelings & Values are A. Perceptual inputs B. Perceptual outputs C. Perceptual mechanism D. A & C View Answer Answer: B
88. Factor that effects the situation of perception is A. Expectation B, Novelty C. Experience D. None View Answer Answer: D
89. Factor that affects the target of perception is A. Expectation B, Time C. Experience D. None View Answer Answer: D
90. Factor that affects the perceiver, A. Work Setting B, Time C. Experience D. None View Answer Answer: D
91. In ______, individual shows different behaviors in different situations. A. Distinctiveness B. Consensus C. Consistency D. Stereotype View Answer Answer: A
92. In ____, response is the same as others to same situation. A. A. Distinctiveness B. Consensus C. Consistency D. Stereotype View Answer Answer: B
93. In____, individual responds in the same way over time. A. A. Distinctiveness B. Consensus C. Consistency D. Stereotype View Answer Answer: C
94. _____is the tendency to perceive another person or judging someone on the basis of one’s perception of the group, class or category to which that person belongs. A. A. Distinctiveness B. Consensus C. Consistency D. Stereotype View Answer Answer: D
95. “Horns effect” is opposite to ____where a person is degraded because of single negative trait. A. Contrast Effect B. Halo Effect C. A&B D. None View Answer Answer: B
96. In _______, we blame people first, not the situation. A. Selective Perception B. Self-Serving Bias C. Fundamental attribution Error D. A & B View Answer Answer: C
97. Profiling is a form of_____. A. Self-Serving Bias B. Contrast effect C. Stereotype D. None View Answer Answer: C
98. ____ Communication makes immediate impact A. Verbal B. Non-Verbal C. Intrapersonal D. None View Answer Answer: A
99. Premature evaluation is _____ in communication. A. Organizational barrier B. Semantic barrier C. Psychological barrier D. B & C View Answer Answer: C
100. Non-verbal communication counts for___ in communication. A. 35% B. 45% C. 55% D.18% View Answer Answer: C
Share this:
Related posts.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser .
T4Tutorials.com
Types of oral presentation.
Whether you are at your job or in your academic career, you have to give a presentation. So, you must know the types of presentations so that you can prepare yourself for the best. There are four types of oral presentation. Each type is used in different forms of communication.
In a manuscript, the speech or presentation is in the written form that the speaker reads word for word. We can say that manuscript involves speaking from the text. The manuscript is useful when the presentation you are going to deliver is complex, critical, some official statement, or has technical information. In any of these cases, there is no space for a single error. It must be accurate and exact. The manuscript also helps you to prevent grammatical, technical, or pronunciation mistakes.
But the drawback of this type of presentation is that the concentration of the speaker remains on the paper and text and he can’t make eye contact with the audience. So, as a result, he is unable to capture the attention of his audience.
- Memorization
This type is suitable for those presenters who are beginners or fear to come on stage and face the audience. They get nervous and forget what they want to present. So, they memorize what they are going to present. But you should be careful while delivering it. It must look natural and spontaneous. The flow of your words and ideas should not be mechanical and speedy. One of the pros of this type is that you can maintain eye contact with the public. The drawback is that during the presentation if you forget what you memorized, you will feel embarrassed in front of the audience.
Impromptu is the spur-of-the-moment that you have to present without any preparation. It often happens when at the end, you are asked to give your remarks by sharing your opinion or thoughts with the audience. At this moment, the best way is to focus on the main point, share your opinion concisely, and wind it up with the best conclusion. Your conclusion must be connected to the main idea or your opening remarks. For the best impromptu, you must have vast knowledge, a lot of practice, long experience, and presentations. An ordinary or new speaker can’t perform impromptu excellently.
- Extemporaneous
Unlike impromptu, extemporaneous allows great flexibility to the speaker. Extemporaneous is considered one of the best methods of presentation. In this type, the presentation is not written out completely. Rather the speaker prepares his presentation in the form of an outline or notes and practices it many times. During the presentation, he has a glance at the outline or notes to read the key points and elaborate them in front of the audience. He speaks in a conversational tone and natural manner. In Extemporaneous, he can maintain eye contact with his audience and grab their attention as well. For a good Extemporaneous, you must command the key points so that you can explain them appropriately. The speaker can include references to the surroundings, news, or previous speeches.
Related Posts:
- Speech about Oral Communication [1,2,3,5 Minutes]
- Housing Society Management System project PPT Presentation Download
- Information Retrieval topics for presentation
- Machine Learning topics for presentation
- Computer graphics topics for presentation
- HCI Human Computer Interaction topics for presentation
Presentation Skills MCQs 4
Uploaded by: AamirKhanMohmand
Description
1. .A presentation is a form of oral communication in which person shares factual information with an audience that is__. a) specific b) small c) large d) mixed
a) specific
2. The presenter acts as the: a) delivery of the information b) medium of the information c) advocate of the information d) supporter of the information
c) advocate of the information
3. The three major element of presentation do not include? a) an audience b) specific content c) a presenter d) visual aids
c) a presenter
4. Reading out a presentation is: a) not allowed b) allowed c) helpful d) dull
a) not allowed 5. To select the content of your presentation you should know the audience need. a) your purpose b) the time limit c) available material
b) the time limit
6. When giving a presentation in front of an audience you should do all of the following except for__? a) speak loud and clear b) provide handout if needed c) dress professionally d) look at your screen not the audience
a) speak loud and clear
7. The key of success is__ a) practice b) preparation c) effort d) both a and b
d) both a and b
8. A good presenter should take a well__. a) good physical appearance b) dressing well c) speak louder d)
a) good physical appearance 9. To become more affective you need to take control of a) the material b) the audience c) your behavior d) all of the above
a) the material
10. ___of a presentation is the most important part a) beginning b) middle c) end d) none of these
a) beginning
11. In beginning you should give firstly a) your introduction b) summary of a topic c) asking irrelevant questions d) further information
a) your introduction
12. A good technique to get your audience attention a) a statement made to surprise b) asking rhetorical questions c) asking introduction to the audience d) none of these
b) asking rhetorical questions 13. What should you give your objectives to the audience a) aim b) goals c) purpose d) All of These
d) All of These
14. All your information should support your a) purpose b) ideas c) topic d) merits
15. A good presenter should a) sequencing your idea b) manage the time c) clear all the confusion d) all of these
d) all of these
16. Keeping the audience attention a) emphasizing b) summarize the topic c) used bore words
a) emphasizing 17. A conclusion should be a) short and easy b) lengthy c) difficult words d) specific key points
a) short and easy
18. Visual involves the audience a) motivate b) attention c) reinforce idea d) all of these
19. How much of the language is made up of verbal language a) 7% b) 6% c) 2% d) 15%
20. 38% message is communication with non verbal a) vocal b) verbal c) body movement d) gesture
a) vocal 21. Body language is included in communication a) 55% b) 35% c) 25% d) 45%
22. facial expression should be a) aggressive b) shy c) naturally d) bored
c) naturally
23. A speaker looks into the eyes of the audience a) confident b) impatient c) rude d) impolite
a) confident
24. The tone of the speaker should be a) loud b) clear c) low d) soft
b) clear 25. A speech must advance __ a) dishonesty b) negativity c) truth d) aggressiveness
26. Which of these doesn’t enhance listening skills? a) attention b) frankness c) clear perception d) ignoring
d) ignoring
27. Using your whole body to communicate is called what? a) miming b) sign language c) body language d) gesture
c) body language
28. Waving is what type of communication? a) gesture b) body language c) sign language d) body position
a) gesture 29. positive gesture are body sihnals that make you look_ a) relaxed b) hurtful c) nervous d) arrogant
a) relaxed 1. A presentation is a kind of verbal communication in which a person shares fact-based information to an audience that is____1. Specific2. Small3. Big4. Diverse Answer: 1. specific
2. The presenter works as the1. Offering of the2. Knowledge3. Mean of the knowledge4. An advocate of the knowledge5. Provider of the knowledge Answer: 4. An Advocate of the knowledge
Check out: Reading Short Story MCQs 3. The 3 main components of the presentation do not include?1. Topic2. Precise data3. A presenter4. Visual assistance Answer: 3. A presenter
4. Just reading out a presentation from slides is:1. Appreciated2. Good3. Important4. Not appreciated Answer: 4. Not appreciated 5. To choose the content of the presentation one must understand1. Need of the audience2. The time limit3. Both 1 & 24. Available material Answer: 3. Both 1 & 2
6. You should do all of the following except ________ while delivering a presentation in front of your audience?1. Introduce yourself2. Introduce your topic3. Dress professionally4. Look at the slides, not your audience Answer: 4. Look at the slides, not your audience
7. The key to perfection is__1. Practice2. Hard work3. Both of above4. None of these Answer: 3. Both of above
8. A great presenter must have1. Professional2. Attitude3. Well dressed4. Speak clearly5. All of above Answer: 5. All of above
9. To become more effective one should take control of1. Material of presentation2. The gathering3. Attitude4. None of these Answer: 1. Material of presentation 10. The _________ of a presentation is the most crucial part1. Beginning2. Punch line3. Final part4. None of above Answer: 1. Beginning
11 You should start your presentation with ____?1. Your introduction2. Introduction to your topic3. Asking questions4. Background knowledge Answer: 1. Your introduction
12. ________ is an effective way to catch your audience’s attention1. A proverb2. Asking interesting questions3. A loud voice4. All of above Answer: 4. All of above
13. You should introduce your ________ to your audience1. Objective2. Purposes3. View4. All of above Answer: 4. All of above
14. All your data must support your1. Objective2. Ideas3. Subject4. Characters Answer: 1. Objective 15. A great presenter must1. Sequence the2. Thoughts3. Use time effectively4. Grab the attention of the audience 5. All of above Answer: 5. All of above
16. A good technique to grab the audience’s attention is1. Loud voice2. Coughing3. Break an appropriate joke4. All of above Answer: 3. Break an appropriate joke
17. A Ending of the presentation should be1. Short2. Long3. Precise4. None of above Answer: 3. Precise
18. Visual improves the audience’s1. Anger2. Attention3. Strengthen the approach4. All of above Answer: 2. Attention
19. How much of the language is formed up of verbal language1. 7%2. 10%3. 34%4. 89% Answer: 1. 7% 20. __________ is a non-verbal communication1. Vocal2. Body movement3. Gesture4. Both 2 & 3 Answer: 1. Vocal
21. ________ Body language is included in the communication1. 40%2. 26%3. 29%4. 10% Answer: 1. 40%
22. Facial expression must be ______?1. Dynamic2. No3. Natural4. Dull Answer: 3. Natural
23. A/an _____ presenter always looks into the eyes of the listeners?1. Confident2. Anxious3. Rude4. Ill-mannered Answer: 1. Confident
24. The Voice of the presenter must be________?1. Powerful2. Clear3. Soft4. All of above Answer: 4. All of above 25. A presentation must be__1. Honest2. Positive3. True4. None of these Answer: 1. Honest
26. Which of the following doesn’t improve the listening and attention of your audience?1. Respects2. Openness3. Clear thought4. Overlooking Answer: 4. Overlooking
27. The technique to use your whole body to win the attention of the audience is called_______?1. Acting2. Brick language3. Body language4. Pose Answer: 3. Body language
28. What type of communication waving is?1. Gesture2. Body language3. Brick language4. Pose Answer: 1. Gesture
29. Positive gestures are body signals that make you look______?1. Comfortable2. Bad3. Worried4. Self-important Answer: 1. Comfortable 1. What does we use for presentations? (a) Power point (b) Word (c) Office (d) Documents Answer (a) Power point2. What features should our presentation have? (a) Impressive and effective (b) Inefficient (c) Incompetent (d) Ordinary Answer (a) Impressive and effective3. In presentation which things are play equal role? (a) Content and voice (b) Text and font (c) Time and size (d) Sort and indent Answer (a) Content and voice4. In presentation what is we use to create a simple design template? (a) Slide master (b) Outlook (c) OneNote (d) Drive Answer (a) Slide master 5. In the following above which is the content of presentation? (a) Bulleted list (b) Text and images (c) 2-column (d) These all Answer (d) These all6. What should be used in presentation with the audience in mind? (a) Language and techniques (b) Font (c) Symbols (d) Styles Answer (a) Language and techniques7. What should we use for effective presentation? (a) Limited words and key phrases (b) Images (c) Layouts (d) Styles Answer (a) Limited words and key phrases8. How can we deliver the right message to our target audience effectively? (a) With Researched, planned and prepared professionally (b) Casual (c) Superficiality (d) Unprepared Answer (a) With Researched, planned and prepared professionally 9. How our points land as practiced with our live audience? (a) With rehearsal and timed practice (b) Researched (c) Planned (d) Prepared Answer (a) With rehearsal and timed practice10. Which thing will enhance readability in presentation? (a) Empty space on the slide (b) Background of the slide (c) Font size (d) Style of font Answer (a) Empty space on the slide11. Which text is the best for the background in presentation? (a) Light text on dark background (b) Dark text on light background (c) Colorful font (d) Black and white style Answer (a) Light text on dark background12. Which background can reduce the readability of text? (a) Patterned background (b) Vinyl (c) Foil (d) Flock Answer (a) Patterned background 13. Which features seems impressive at first but get old quickly? (a) Flashy transitions such as text fly-ins (b) Toned-down (c) Restrained (d) Modest Answer (a) Flashy transitions such as text fly-ins14. Which special effects can negative impact on the credibility of text? (a) Animation and sounds (b) Font and style (c) Language and content (d) Layouts Answer (a) Animation and sounds15. Which thing maintains its impact and resolution when projected on a larger screen? (a) Image (b) Layouts (c) Styles (d) Clip arts Answer (a) Image16. What is a good rule of thumb during presentation? (a) One slide per minute (b) Five slides per minute (c) One slide in few seconds (d) Avail max time Answer (a) One slide per minute 17. What we learn presentation in a non-linear presentation? (a) Learn to navigation (b) Cruise (c) Skipper (d) Neglect Answer (a) Learn to navigation18. Through what power point allows the presenter to jump ahead or back without having to page? (a) Interim slides (b) Permanent slides (c) Unlimited slides (d) Perpetual slides Answer (a) Interim slides19. What will not be shown by animation or other special effects? (a) Transparencies and handouts (b) Obscurity (c) Ambiguity (d) Cunning Answer (a) Transparencies and handouts20. Which thing we should use for run our presentation? (a) Hard disk (b) Floppy disk (c) Compact disk (d) Digital versatile disk Answer (a) Hard disk 21. Which thing may slow down our presentation? (a) USB (b) Flash drive (c) Hard disk (d) Compact disk Answer (a) USB22. In presentation which font style is not used? (a) Italics (b) Bold (c) Underline (d) Outline Answer (a) Italics23. Which audio should be avoided in presentation? (a) Unlicensed music (b) Folk music (c) Swing (d) Plainsong Answer (a) Unlicensed music24. At the end of the presentation which thing will we done? (a) Record and rehearse the timing (b) Planning (c) Checkout (d) Present Answer (a) Record and rehearse the timing 25. In dialogue box which feature we find to saw our slides? (a) Slide show (b) Print (c) Animation (d) Shuffle Answer (a) Slide show26. A presentation is a form of oral communication in which person shares factual information with an audience that is. (a) specific (b) small (c) large (d) mixed Answer (a) specific27. The presenter acts as the: (a) delivery of the information (b) medium of the information (c) advocate of the information (d) supporter of the information Answer (c) advocate of the information28. The three major element of presentation do not include. (a) an audience (b) specific content (c) a presenter (d) visual aids Answer (c) a presenter 29. Reading out a presentation is: (a) not allowed (b) allowed (c) helpful (d) dull Answer (a) not allowed30. To select the content of your presentation you should know the audience need. (a) your purpose (b) the time limit (c) available material Answer (b) the time limit31. When giving a presentation in front of an audience you should do all of the following except for. (a) speak loud and clear (b) provide handout if needed (c) dress professionally (d) look at your screen not the audience Answer (a) speak loud and clear32. The key of success is. (a) practice (b) preparation (c) effort (d) both a and b Answer (d) both a and b 33. A good presenter should take a well. (a) good physical appearance (b) dressing well (c) speak louder Answer (a) good physical appearance34. To become more affective you need to take control of. (a) the material (b) the audience (c) your behavior (d) all of the above Answer (a) the material35. ___of a presentation is the most important part. (a) beginning (b) middle (c) end (d) none of these Answer (a) beginning36. In beginning you should give firstly. (a) your introduction (b) summary of a topic (c) asking irrelevant questions (d) further information Answer (a) your introduction37. A good technique to get your audience attention. (a) a statement made to surprise (b) asking rhetorical questions (c) asking introduction to the audience (d) none of these Answer (b) asking rhetorical questions 38. What should you give your objectives to the audience. (a) aim (b) goals (c) purpose (d) both a, b & c Answer (d) both a, b & c39. All your information should support your: (a) purpose (b) ideas (c) topic (d) merits Answer (a) purpose40. A good presenter should. (a) sequencing your idea (b) manage the time (c) clear all the confusion (d) all of these Answer (d) all of these41. Illustrate your presentation topic with: (a) real life example (b) experimental example (c) fake stories (d) none of these Answer (a) real life example 42. Keeping the audience attention. (a) emphasizing (b) summarize the topic (c) used bore words Answer (a) emphasizing43. A conclusion should be : (a) short & easy (b) lengthy (c) difficult words (d) specific key points Answer (a) short & easy44. Visual involves the audience : (a) motivate (b) attention (c) reinforce idea (d) all of these Answer (d) all of these45. How much of the language is made up of verbal language. (a) 7% (b)6% (c)2% (d) 15% Answer (a) 7%46. 38% message is communication with non verbal. (a) vocal (b) verbal (c) body movement (d) gesture Answer (a) vocal 47. Body language is included in communication. (a) 55% (b)35% (c)25% (d) 45% Answer (a) 55%48. facial expression should be. (a) aggressive (b) shy (c) naturally (d) bored Answer (c) naturally49. A speaker looks into the eyes of the audience. (a) confident (b) impatient (c) rude (d) impolite Answer (a) confident50. The tone of the speaker should be: (a) loud (b) clear (c) low (d) soft Answer (b) clear 51. A speech must advance ___. (a) dishonesty (b) negativity (c) truth (d) aggressiveness Answer (c) truth52. Which of these doesn't enhance listening skills? (a) attention (b) frankness (c) clear perception (d) ignoring Answer (d) ignoring53. Using your whole body to communicate is called what? (a) miming (b) sign language (c) body language (d) gesture Answer (c) body language54. Waving is what type of communication? (a) gesture (b) body language (c) sign language (d) body position Answer (a) gesture 55. positive gesture are body sihnals that make you look. (a) relaxed (b) hurtful (C) nervous (d) arrogant Answer (a) relaxed Basic presentation skills MCQ This is a sample Multiple Choice Questions for the basic understanding of presentationskills.1. Communication is a non stop______________.(A) paper (B) process (C) programme (D) plan2. Communication is a part of ________ skills.(A) soft (B) hard (C) rough (D) short3. The _______________ is the person who transmits the message.(A) receiver (B) driver (C) sender (D) cleaner4._____________ is the person who notices and decodes and attaches some meaning to amessage. (A) receiver (B) driver (C) sender (D) cleaner5. Message is any signal that triggers the response of a _________(A) receiver (B) driver (C) sender (D) cleaner6. The response to a sender’s message is called _________(A) food bank (B) feedback (C) food (D) back 7. ___________ context refers to the relationship between the sender and the receiver (A) social (B) physical (C) cultural (D) chronological8. ___________ context refers to the similarity of backgrounds between the sender and thereceiver.(A) physical (B) social (C) chronological (D) cultural9. _________ refers to all these factors that disrupt the communication.(A) nonsense (B) noise (C) nowhere (D) nobody 10.Environmental barriers are the same as ______ noise.A) physiological (B) psychological (C) physical (D) sociological 11. Our dress code is an example of _____________ communication.(A) verbal (B) nonverbal (C) written (D) spoken 12.Communication strengthens _______ & ______________ relationship is anorganization.(A) employer-father (B) employer-employer (C) mother-employer (D) mother-child 13._______________ communication includes tone of voice body language, facialexpressions etc.(A) non verbal (B) verbal (C) letter (D) notice 14.When there is similarity of background between the sender and the receives such asage, language nationality, religion, gender then this is called _____________ context. (A) social (B) cultural (C) physical (D) dynamic 15.Letter, e-mail telephone are examples of __________(A) message (B) feedback (C) channel (D) encoding 16.Understanding __________different parts of speech forms the base of leaning grammar(A) Five (B) Eight (C) Six (D) Seven17.It is of paramount importance that one need to construct a __________sentence in theday to day affairs(A) Wrong (B) Correct (C) Incorrect (D) Night18.A__________may be defined as the name of a person place or thing (A) Verb (B) Noun (C) Pronoun (D) Adverb19.According to hoben “communication is the _____ nituchange of thought or idea.(A) Visual (B) Audio (C) Verbal (D) Written20.The person who transmits the message is called the ____(A) Sender (B) Gives (C) Taker (D) Receiver 21.Proper nouns always begin with ________letters(A) Running (B) Capital (C) Small (D) Numerical22.______________nouns require capitalization only if they start the sentence or are part ofa title(A) Common (B) Proper (C) Abstract (D) Collective23.Once the message is encoded in a desired format it is transferred through a mediumcalled ______(A) Channel (B) Medium (C) Media (D) Way 24.The nouns which cannot be felt, seen or heard are called __________(A) Common (B) Proper (C) Abstract (D) Collective 25.The information which is transferred to the receiver has to be interpreted this process iscalled _____(A) Encoding (B) Decoding (C) Opening (D) Closing 26.All communication events have a _________.(A) Resource (B) Source (C) Start (D) End 27.Personifications of strength and violence are considered as ________ gender. (A) masculine (B) Feminine (C) common (D) Neuter 28.The message may be misinterpreted because of _____(A) Barriers (B) Distortions (C) Distractions (D) Noise 29.The environment in which the transmitter or receiver are should be ____(A) Complex (B) Competent (C) Complete (D) Compatible 30.A noun that dandies neither a male or a female is ___________gender (A) Masculine (B) Feminine (C) Common (D) Neuter 31.Countries when referred to by names are also considered _____________(A) Masculine (B) Feminine (C) Common (D) Neuter 32.The Christian sign of the ____ is a gesture pertaining to religion and spirituality.(A) Plus (B) Minus (C) Division (D) Cross33.In oral communication there is a possibility of immediate _________(A) Reaction (B) Response (C) Refection (D) Reset 34.In oral communication the speaker can observe the listener’s _______ to what is beingelated. (A) Reaction (B) Response (C) Rejection (D) Reset35.Nouns that end in “Y” but have a constant before “Y” form their plural by dropping “Y”and adding ___(A) ves (B) es (C) s (D) ies 36.White talking to friends you do not pay attention to the skills of _____ Communication.(A) Written (B) Oral (C) audio (D) visual37.In oral presentation outside your organisation you must first give the audience a ______of your organization.(A) Flash back (B) Background (C) Front view (D) Forword view38. ‘A’ and ‘an’ are the ___________–articles (A) Definite (B) Indefinite (C) Particular (D) Specified39.The _______ are used to present using overhead projectors.(A) Acetate film transparent sheet (B) Paper sheets (C) Polythene sheet (D) Butter paper 40.Any word that adds more meaning to the noun is called an __________(A) Adverb (B) Verb (C) Adjective (D) Noun 41.A__________indicates the action done by the subject(A) Verb (B) Adverb (C) Noun (D) Pronoun 42.A___________is a word which connects words phrases , clauses or sentences(A) Preposition (B) Conjunction (C) Interjection (D) Verb 43.During presentation using an OHP. One can read information line by line using anopaque sheet to cover the transparency with a view to minimize distraction. This technologyis called _________ (A) Positive disclosure (B) Zero disclosure (C) Negative disclosure (D) Progressive disclosure 44.Another thing that you have to avoid is adding to OHP’s with a ________ during a talk.(A) Chalk (B) Pencil (C) Pen (D) Marker 45.It is important to consider proper _____ room where you are giving your presentation.(A) Darkness (B) lighting (C) Lightning (D) ventilation46._____ Listening means learning through conversation(A) Evaluative (B) Appreciative (C) Dialogic (D) Empathetic 47.In _____ Listening the difference between the sounds is identified(A) Discriminative (B) Comprehension (C) Dialogic (D) Empathetic48.The ___________is an exclamation mark(A) ? (B) . (C) , (D) ! 49.Evaluative listening is also called _____(A) Therapeutic (B) Evaluative (C) Dialogic (D) Impathetic50.The___________is the action or description that occur in the sentence (A) Predicate (B) Subject (C) Object (D) Complement 51.The _____________speech is also called as reported speech(A) Direct (B) Indirect (C) Indefinite (D) Definite52.A positive statement (in a question tag) takes a ___________tag(A) Negative (B) Positive (C) Question (D) Answer 53.Hearing is only an important component of ____(A) Hearing (B) Listening (C) Talking (D) Speaking 54.In _____ Listening the main intention is to seek certain information which will beappreciated(A) Empathetic (B) Appreciative (C) Evaluative (D) Dialogic 55._____ Is an aggressive behavior and will most likely bring a negative response from thespeaker.(A) Interrupting (B) Yawning (C) Slapping (D) Dancing 56.It is important to choose the right environment because it will help the listener focus &avoid ____(A) Attrition (B) Distractions (C) Disturbances (D) Noise57.Semantic market are the links between two ____(A) Words (B) Phrases (C) Clauses (D) Sentences 58._____ Customer not only returns to your organization for a second time but also tellsabout his satisfaction others.(A) Unsatisfied (B) Impatient (C) Satisfied (D) Patient 59.Always ____ the customer for calling(A) Slap (B) Reprimand (C) Thank (D) Never thank 60.The technique of ____ should be mastered to handle displeased customers.(A) BLAST (B) BLSAT (C) BALST (D) None61.In __________verb the action passes from the subject an object(A) Transitive (B) Un transitive (C) Modal (D)Main 62.__________refers to the time of action(A) Tense (B) Transitive (C) Intransitive (D) Main verb 63.Reading comprehension means understanding a ____ text. (A) Oral (B) Written (C) Usual (D) Audio 64.Reading is a __________________ process.(A) Encoding (B) Listening (C) Decoding (D) Talking
65.While making a slide, the number of words should be limited to a maximum of _______per slide.(A) 8 (B) 9 (C) 10 (D) 11 66.A group of related words that contain both a subject and predicate and that functions aspart of a sentence is(A) Sentence (B) Phrase (C) Clause (D) Compound 67.When we read shorter texts like research papers for specific detailed information weread slowly & with a lot of concentration ,this is called ____ reading. (A) Intensive (B) Extensive (C) Detailed (D Short 68.Most of our day-to-day reading it done _____(A) Loudly (B) Extensively (C) Intensively (D) Silently69._____ is to relate the content to that previous and future learning of the subject(A) Review (B) Reading (C) Recalling (D) All 70.______ Is nothing but checking whether we have followed the earlier stages promptlyand efficiently(A) Review (B) Reading (C) Recalling (D) All71.Different types of letters used for printing are called _______.(A) Fonts (B) Fronts (C) Both (D) None72._______ is a technique that involves changing a text-matter so that it is similar to themain source.(A) Note – taking (B) Paraphrasing (C) Summarizing (D) Precs writer 73.Effective paraphrasing avoids the risk of ______(A) Changing (B) Noting (C) Copying (D) Plagiarism 74.____ Means linking words and phrases together so that the whole text is clear andreadable.(A) Cohesion (B) Joining (C) Conjunctions (D) Junctions75.In the structure of the business letter what comes first.(A) Reference (B) Date (C) Salutation (D) Heading76.In the writing of an apology letter, concentrate on (A) Problem (B) Compensation (C) Rectification of problem (D) Words 77.is the vital part of the letter which to as good as wishing the person.(A) Salutation (B) Enclosure (C) Subject (D) Reference78.People cannot interact with each other without ____(A) Communication (B) Transport (C) Voice (D) Loudspeaker 79.The language of the report should be _____(A) Formality (B) Formal (C) Casual (D) Loose80.A circular or notice may be issued by only _____ designated for the purpose (A) Peon (B) Clerk (C) Typist (D) Officer
Report "Presentation Skills MCQs 4"

View all MCQs in
No comments yet
Related MCQs
- Which is NOT one of the three purposes for giving oral presentations?
- Good strategies for planning oral presentations include all of the following EXCEPT
- Which of the following purposes of an oral presentation is specific in nature?
- ---------- presentations include talks, seminars, proposals, workshops, conferences, and meetings the presenter or presenters share their expertise, and information is exchanged.
- A summary of your educational and academic backgrounds as well as teaching and research experience, publications, presentations, awards, honours and affiliations.
- All of the following would be examples of persuasive presentations EXCEPT
- An oral message is preferable to a written one when one of the goals is to
- Which of the following are examples of oral communication?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This set of Professional Communication Multiple Choice Questions & Answers (MCQs) focuses on "Parameters and Role of Oral Presentation". 1. Which of these is the most important tool of communication? a) Body language b) Gestures c) Language d) Posture View Answer
Presentation Skills MCQs will test your knowledge. Our Free Presentation Skills multiple-choice questions and answers are in quiz format, so test your skill in an easy and fun way. ... D. Asking the right amount and types of questions. Check Answer. 49: Research has found that most decision-making is based not on logic, but: A. Emotion. B ...
simple and active form of sentences. To select the content of your presentation, you should know: the audience's needs. In presentation design, maximum time is given to the: main body. Initially, a presentation is a form of: one-way communication. QUIZ Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.
Salique Hussain 122. ALiMallaH 76. Shuaib Uddin 64. Rabail Lashari 54. Arshad Memon 36. SHEHZAD ALI KHOSO 29. Abdul Rahim Chandio 14. Syed Ali Akbar Bokhari 6. MCQs on Professional Communication - Oral Presentation - Multiple Choice Questions, Solved Answer, Trivia, Test, Quiz, Notes, PDF - MCQtimes.Com.
50-50! Q10. Which of these can be used to break the monotony in a speech? a. b. d. 50-50! Multiple choice questions on Professional Communication topic Oral Presentation. Practice these MCQ questions and answers for preparation of various competitive and entrance exams.
the public. preparing an oral presentation consists of 5 steps. 1.analyze the speaking situation. 2.organize and develop the presentation. 3.prepare the presentation. 4.choose effective language. 5.rehearse the presentation. Follow these five guidelines when introducing a presentation (1 of 2) introduce yourself.
The correct order for handling your content when creating a presentation from scratch is: 28. True or False? You can give the exact same presentation to any room, regardless of who your audience is. 29. The ability to recognize emotions and connect with others, a critical skill for presenters, is known as: 30.
In this section, you'll find a wide range of Oral Presentation mcq questions that explore various aspects of Oral Presentation problems. Each MCQ is crafted to challenge your understanding of Oral Presentation principles, enabling you to refine your problem-solving techniques. Whether you're a student aiming to ace Professional Communication tests, a job seeker preparing for interviews, or ...
Test your knowledge of Chapter 10: Presentations by answering the following multiple-. choice questions. You can find the answers to each question at the end of this document. 1. Effective presentations require: a. good presentation skills and especially the ability to present material. dramatically. b.
The Purpose of an Oral Presentation. Generally, oral presentation is public speaking, either individually or as a group, the aim of which is to provide information, entertain, persuade the audience, or educate. In an academic setting, oral presentations are often assessable tasks with a marking criteria. Therefore, students are being evaluated ...
This set of Professional Communication Multiple Choice Questions & Answers (MCQs) focuses on "Non-verbal Communication". ... Parameters and Role of Oral Presentation ; Professional Communication Questions & Answers - List of Abbreviations ; ... Forms of Technical Writing.
Presentation Aids of Speech MCQs. Speak to Inform MCQs. Prepare to Persuade MCQs. Persuasion Methods in in Public Speaking MCQs. ... These Public Speaking multiple-choice questions and their answers will help you strengthen your grip on the subject of Public Speaking. You can prepare for an upcoming exam or job interview with these Public ...
Presentation Skills MCQs.A presentation is a form of oral communication in which person shares factual information with an audience that is__. a) specific b) small c) large d) mixed . Answer. a) specific. The presenter acts as the: a) delivery of the information b) medium of the information
The document contains 29 multiple choice questions about presentation skills. Some key points covered include: - A presentation involves verbally sharing factual information with a specific audience. The presenter acts as an advocate for the information. - Effective presentations involve selecting content based on audience needs, practicing delivery, using visual aids to reinforce ideas, and ...
An oral presentation is a form of communication, where you impart and then exchange information with your audience. This can be either one-way, a didactic, or two-way called a Socratic or a Dialectic presentation. There are many forms of oral presentation and you...
6.1 Introduction. An individual has to interact with other members of the society throughout the life; and, herein lies the importance of possession of communication skills. These communication skills may range from oral to listening; writing to reading and note-taking. The details of oral presentation skills have been discussed in this lesson.
Oral Presentation Mcqs - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
This set of Professional Communication Multiple Choice Questions & Answers (MCQs) focuses on "Proper Use of Body Language". 1. A ______ speaker looks into the eyes of the audience. a) confident. b) impatient. c) rude. d) impolite. View Answer. 2.
Communication and Presentation Skills MCQs This course aims to Make students able to understand, analyze and use English in written and oral communication. Develop student's personality as a good English speaker, writer and presenter in realistic life. Help student to identify essential components of a presentation. Polish their knowledge, skills and attitudes required to deliver effective ...
There are four types of oral presentation. Each type is used in different forms of communication. In a manuscript, the speech or presentation is in the written form that the speaker reads word for word. We can say that manuscript involves speaking from the text. The manuscript is useful when the presentation you are going to deliver is complex ...
Answer» D. sender, message, channel, receiver, feedback. discuss. 62. "Communication is a process involving the selection, production and transmission of signs in such a way as to help a receiver perceive a meaning similar to that in the mind of the communicator.". This definition of communication was given by:
Presentation Skills MCQs with Answers. 1. .A presentation is a form of oral communication in which person shares factual information with an audience that is__. a) specific b) small c) large d) mixed. Answer. a) specific. 2.
----- presentations include talks, seminars, proposals, workshops, conferences, and meetings the presenter or presenters share their expertise, and information is exchanged. A summary of your educational and academic backgrounds as well as teaching and research experience, publications, presentations, awards, honours and affiliations.