
Prevention of Soil Pollution: What You Should Know
Looking after the earth’s precious soils is not only vital, but it’s everyone’s responsibility.
Green Coast is supported by its readers. We may earn an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you if you buy through a link on this page . Learn more .

The prevention of soil pollution is vital for human health, food production, and healthy ecosystems. Land contamination is a huge problem globally – an estimated 16% of all soil in China is polluted, and the EPA reports that there are up to 1.3 million sites classified as “contaminated lands” in the USA – so we must take immediate action.
17 actionable ways to prevent soil pollution (and keep it clean)
Human activities are causing various kinds of soil contamination, with major culprits including fertilizers and pesticides used in agriculture, the mining industry, waste disposal , and the improper handling of hazardous chemicals.
This has a range of implications for people and the planet, from risks to human and animal health to threatening our food supply, destroying forests and other habitats, and contributing to climate change.
If you want to learn more about soil pollution, its causes, and its impacts, take a look at our comprehensive guide here .
Thankfully, there are plenty of things we can do to prevent soil pollution on an individual, community, and political level. Let’s start with the big-picture policies and approaches, then look at actionable and easy steps you can take to make a difference.
1. Involve local communities in land and soil management
As with virtually all kinds of conservation, soil management is most effective when it involves governments, companies, and the local community. Protecting our precious land resources demands dedicated efforts and buy-in from all levels of society.
Therefore, it is essential to educate individuals and groups about the importance of soil conservation and what they should do to prevent land pollution . Equally, governments must listen to the voices of the local community and take the time to hear their concerns and ideas about land management.

People often have unique on-the-ground insights that can be invaluable for legislators and help them to create better laws and guidelines. Additionally, communities will be more likely to comply with the rules if they are created with their needs in mind.
2. Improve legislation on soil pollution control and prevention
Unfortunately, there need to be stronger laws in the US and elsewhere to prevent soil pollution. While companies, organizations, and communities are responsible for protecting the natural environment, the best way to ensure that they do this is through strict legislation.
Given the diverse causes of soil pollution, preventing it requires a range of laws and guidelines across various areas and at the state, federal, and international level.
These areas could include:
- Tighter controls on the transport, storage, and use of hazardous substances
- Permanent solutions for safe, long-term storage of nuclear waste
- Restrictions on the use of chemical pesticides and agriculture
- Incentives for organic farmers
- Bans on mining practices that release toxic dust or liquids into the environment
- Encouraging vertical cities to limit urban sprawl
- Laws to avoid food wastage, such as incentivizing companies to donate unneeded food through tax breaks
- A price on carbon to encourage industry to move away from fossil fuels and towards renewables
3. Adopt waste-to-energy practices
Waste-to-energy (WtE) is, in essence, turning trash into power. More specifically, it involves using waste treatment processes to generate energy, whether in the form of electricity, steam, heat, or fuels like diesel.
Industry can adopt WtE to power their facilities and municipalities can use it to run power stations that feed the grid 24 hours a day, just like a normal power plant, but completely clean, with no greenhouse gas emissions.

Many different types of waste can be used as fuel, including municipal solid waste (MSW), semi-solid effluents from industry, liquids such as domestic sewage, and gasses like refinery exhaust fumes.
The most common type of waste used in WtE is MSW, which represents an abundant and continual supply of fuel. Furthermore, it helps to prevent soil pollution by diverting solid waste from landfills, where it could disperse contaminants into the environment.
4. Conduct research on the soil environment quality baseline
In order to protect the health of the soil environment, it’s important to know where we stand. Therefore, one of the key steps in preventing soil pollution is to conduct research to get a clear picture of the current condition and quality of the soil.
Ground quality surveys give us a baseline that we can use to identify changes as early as possible and take the necessary action. This also means conducting regular surveys to monitor the situation and address any issues.
This work could be commissioned by local authorities, non-government organizations, or by establishing community-based monitoring networks of the quality of the soil environment. Strong networks with a suitable data-sharing process will make it easier to develop quick and effective solutions when problems emerge.
5. Implement soil remediation
Prevention is always better than cure, but when soil has been polluted, the responsible party should address this through remediation. If the company or person responsible isn’t willing or able to do so, local authorities should step in to repair the damage.
There are three methods that can be used to resolve soil contamination:
- Thermal remediation: This process uses heat to remove contaminants from the soil and groundwater. As the subsurface heats up, certain organic compounds mobilize, making it easy to remove these particles.
- Bioremediation: As the name suggests, bioremediation uses living organisms such as bacteria and other microbes. The microorganisms digest organic contaminants like solvents, phosphates, and hydrocarbons, converting them into carbon dioxide and water.
- Mycoremediation: This type of remediation uses fungi which remove contaminants like heavy metals by absorbing and metabolizing them.
6. Control mining and industrial pollution
Another essential part of preventing soil pollution is keeping a close eye on major polluters, such as mining, agriculture, and industry. Rather than introducing laws and leaving companies to get on with things, governments need to ensure that they’re following the rules.
This should involve formal monitoring, with detailed plans for supervision built into legislation to ensure key actors are complying with all rules and guidelines.
It could also be a good idea to conduct regular checks of the soil environment to make sure it is not contaminated – this could be done by the company and reported to the government or, better yet, by an independent expert.
Furthermore, as the carrot to this stick approach, governments can offer incentives to companies that implement eco- and soil-friendly practices. There are a wide range of ways to do this: examples include subsidies for organic producers and tax breaks for companies that install solar panels and other renewable energy systems.
7. Be strict when approving new uses of land
Soil pollution prevention is closely linked to how land is approved for new uses. It’s essential that governments carefully consider each application for land use, whether for construction, agriculture, mining, and industry, and weigh it up against possible environmental impacts, including implications for soil health.
Even residential construction can have a range of negative impacts on the soil, so it’s important for authorities to critically assess this use and whether it could lead to soil pollution. Furthermore, before giving approval, authorities should conduct detailed surveys on the current soil condition, and use this to set appropriate guidelines for management and control if the new land use does go ahead.
These surveys will also show if the soil is already contaminated, so that authorities can order a stop to any planned construction or use of the land until the situation is addressed and any risks eliminated.

8. Make companies pay for polluting
It’s not enough to simply have laws and guidelines in place that aim to avoid soil pollution. For these to be effective, there need to be consequences for anyone who breaks the rules.
Furthermore, these consequences should be harsh enough to be a true deterrent to wealthy companies. This could include steep financial penalties and even jail time for activities like illegal dumping, dispersing pollutants into the environment, use of prohibited chemicals, or unauthorized land use.
Another effective approach is having polluters pay the costs of treating and remediating contaminated land. This is a great way to directly hold companies responsible for the damage they cause and discourage repeat offenders, though is most effective if governments retain responsibility for creating plans for remediation and monitoring the results.
9. Promote research and development
Although we know a fair amount about the causes of soil pollution and how we can prevent it, more research is needed. Further research and development will allow us to develop better processes and more effective solutions to not only remediate contaminated soil but also stop it from being damaged in the first place.
This could include research into detecting soil contamination, new soil remediation techniques, and alternatives to pollutants like chemical fertilizers and pesticides, as well as the soil environment more generally and the impacts of soil pollution.

Unfortunately, research dollars are all too often spent on areas of commercial or military priority, rather than concepts and technologies that could benefit the environment.
Governments and companies alike should take a farsighted approach instead, and support research that promotes sustainability . After all, the long-term health of the planet is essential for the economy, human health, and all aspects of life as we know it.
10. Go organic
Conventional agriculture is one of the biggest causes of soil pollution through the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, and insecticides which contaminate the soil with a range of toxic components. Modern farming also typically involves the use of heavy machinery that can damage the earth.
Finally, overgrazing is all too common: in seeking higher and higher profits, producers pack farm too many animals on each piece of grazing land. The large concentration of animals strips the plants and nutrients from the soil, causing permanent damage over the long term.
Organic farming is all about returning to more traditional and eco-friendly practices that are kinder to the soil and the environment in general, as well as being safer for human health.
Organic producers do not use any of the following:
- synthetic fertilizers and pesticides
- genetically modified organisms (GMOs)
- artificial preservatives
- artificial flavors or coloring.
Instead, they rely on natural fertilizers like manure and compost , natural methods to control pests , and keep weeds under control through crop rotation, mulching, tilling, and hand weeding.

Organic farmers also only feed animals only organic food, don’t give them antibiotics or hormones, and keep them in an environment that is suitable to their natural behaviors, instead of being confined in small areas. You can be confident that a product is truly organic if it carries a recognized, independent certification such as USDA , NSF , and GOTS .
Buying sustainable food is one of the best things you can do as a consumer to prevent soil pollution. Not only to you avoid products that directly contribute to ground contamination, but by supporting organic brands you’re sending a message to other producers.
If enough people shop organic, the industry will shift towards organic methods to meet consumer demand. You could even grow your own organic herbs and veggies at home with an Aerogarden or vertical farm .
Buying organic products isn’t just limited to food: there are a range of textiles, personal care products, and cosmetics that contain materials or ingredients that can damage the soil, depending on how they’re produced.
To prevent soil pollution, shop organic when it comes to:
- All foodstuffs, but notably fruits, vegetables, meat, grains, seafood, and animal products
- Cosmetics such as face masks , cleaners, and makeup
- Shampoo, body wash, bubble bath , and other personal care products
- Natural textiles like cotton , wool , bamboo, and hemp (many bamboo and hemp products are organic, but it’s good to check)
- Furniture , rugs , and home décor products made from natural materials such as cane and bamboo
Equally, if you choose to buy wooden furniture or anything else made from wood or tree products, check that it’s sustainably sourced. This ensures you’re not supporting deforestation and that the plantations the wood comes from are handled responsibly to avoid polluting the soil.
11. Dispose of solid waste properly
Solid waste is a major cause of soil pollution. When virtually any type of waste isn’t disposed of correctly, it can disperse pollutants into the environment: as it breaks down, the material may give off harmful gasses, leach toxins into the soil, or particles can wash into waterways.
Even if these contaminants aren’t directly released into the soil, they may make their way there eventually, whether carried by rivers, absorbed through the atmosphere, or traveling through groundwater.
For this reason, it’s important to responsibly dispose of all of your waste, especially potentially-hazardous materials, such as batteries, light bulbs , metal items , propane tanks , and pharmaceuticals.
At a government level, authorities can encourage practices to treat both solid waste and wastewater to avoid it leading to pollution. This includes practices such as neutralizing acidic and alkaline waste, and separating biodegradable trash to break it down in a controlled environment.
12. Slash the waste you produce
Responsibly disposing of your waste is important, but an even better solution is to reduce the amount of waste you produce in the first place. Even when you send it to landfill , regular household waste can produce a range of pollutants that can contaminate the soil and groundwater .
Recycling is a good place to start. In 2018, US households collectively produced nearly 300 million tons of solid waste , of which only 70 million tons were recycled.
Make sure you recycle everything you possibly can and prep it properly first, such as rinsing out bottles and food containers. Failing to do this can mean the entire load of recyclable items are sent to landfill – so check the rules with your local sanitation department.
Many materials are recyclable, including plenty that you probably didn’t realize you could recycle. Check out our guides to recycling things like broken glass , food containers , and aluminum foil to learn how.

Another great approach is to buy zero-waste products, from toilet paper and shampoo to deodorants and toothpaste . These items are free from plastic, from the materials they’re made from to their packaging, instead using materials that can be recycled, composted, or reused.
Additionally, try to repair items as much as possible rather than replacing them: darn that small hole in your socks, sew in a new zipper, or put a patch on your jeans. Take your electronics and home appliances to a licensed repair shop, or have a cobbler resole your shoes or repair your damaged purse.
Finally, you can reduce your waste by taking action at the beginning of the cycle. Buying fewer things will ultimately mean you produce less waste. Carefully consider whether you really need something before you purchase it and develop a capsule wardrobe of eight to 10 pieces per season – we really don’t need so much stuff in our lives!
13. Get composting
Even organic waste can produce contaminants when it decomposes in landfill. On the other hand, when you compost your food scraps and other organic waste, it breaks down with minimal impact, turning into excellent organic fertilizer perfect for nourishing your garden plants.
Organic matter can’t decompose normally in landfill because it doesn’t have enough oxygen, so it rots anaerobically, releasing large amounts of methane. In compost, it breaks down aerobically, as nature intended, releasing smaller amounts of carbon dioxide – although this is also a greenhouse gas, methane’s global warming potential (GWP) is significantly higher .
In this way, composting at home can help avoid pollutants being released from landfills and potentially contaminating the soil. You can compost even if you don’t have a big yard: learn about composting in an apartment here .

While composting is an excellent way to deal with your organic trash, it’s critical to limit the amount of waste you produce in the first place, especially when it comes to food. Wastage represents a staggering 30 to 40% of the US’ food supply .
This means acres and acres of land used to grow unneeded food, potentially polluting the soil in the process. Be careful to only buy as much food as you need, check your fridge and pantry daily and use items that are about to expire, and freeze things that you won’t eat immediately.
14. Minimize chemical use
The modern American household is full of chemicals, from cleaning products and air fresheners to motor oil and laundry detergent.
Simply using these products can pollute the environment: when you spray aerosols, fine particles dissipate into the atmosphere. Similarly, washing cleaning products, body wash, or shampoo down the drain can send a host of toxins and even microplastics into the sewage system.
These particles can eventually make their way into the soil, whether absorbed from the air, groundwater, or through waterways.
In the US, waste-water treatment only removes some chemicals from sewage: around half of all pharmaceuticals and “newly emerging contaminants” remain after treatment to be released into waterways, according to Scientific American .
Instead of using chemical-based cleaners and other household products, opt for alternatives made from natural, non-toxic ingredients. For example, take a look at these chemical-free laundry detergents .
If you can’t avoid using certain chemicals, be sure to handle them carefully and dispose of them responsibly. Never throw hazardous materials or pharmaceuticals in the trash our pour liquids down the drain, instead, contact your local sanitation department and ask how to dispose of them responsibly.
15. Spread the word
Taking a few steps yourself and changing your habits can go a long way to help prevent soil contamination. However, you can multiply your impact exponentially by educating others about the causes and impacts of this type of pollution, as well as what they can do about.
Start by learning all you can about the issue: check out websites like World Soil Information , Science Direct , and the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization , or read books such as Earth Detox , The World We Need , and The Monsanto Papers . There are also some great documentaries and movies that educate and inspire, such as The 11 th Hour, Home , Michael Clayton, and Erin Brockovich.
From there, spread the word among your networks. Talk to your friends and family, share posts on social media (you can start with this one!), and teach your children eco-friendly behaviors.
You could even volunteer with local organizations that educate the community about soil pollution or related issues.

16. Lobby your representatives
Even if you aren’t in a position to implement new legislation or policies, you can use the democratic system to drive change. Get in touch with your elected representatives at all levels – local, state, and federal – and tell them how important soil pollution prevention is to you.
Pressure them to introduce laws that protect the soil environment, as well as mechanisms to ensure that everyone complies with these rules. You can also encourage them to be tougher on companies and groups who cause soil pollution, and to fund research and development that will promote better soil environments.
17. Join campaigns
If you really care about soil pollution, why not get involved? Many groups and organizations are working on protecting the soil environment and associated issues, from groundwater safety to protecting forests and other wilderness areas.
The organizations working on these issues include:
- World Wildlife Fund
- Groundwater Foundation
- The Nature Conservancy
- The Land Institute
- Asia Soil Conservation Network
- African Forest Landscape Restoration Initiative
- Kiss the Ground
There are loads of ways you can get involved in these campaigns, depending on the amount of time and energy you’re able to give. It could be something as simple as signing a petition or sharing a campaign on social media, or you may want to become a volunteer and advocate for the cause.
How to do your part to prevent soil pollution
The prevention of soil pollution is everyone’s responsibility. This is a critical issue that can have a wide range of negative impacts on people, animals, and the environment, from posing a risk to human health to threatening natural habitats and even the global food supply.
Therefore, it’s essential that we take action to remediate already contaminated areas and prevent further pollution, as individuals, companies, and responsible authorities. At a political level, essential actions include introducing legislation to prevent soil pollution and hold polluters accountable, funding research, involving local communities, and improving waste management systems, including incorporating waste-to-energy approaches.
As individuals, living more sustainable lifestyles, from better managing our waste to avoiding chemicals and buying organic products, will go a long way to prevent all kinds of further damage to the environment, including soil pollution. We can also educate others and advocate for change, whether lobbying our politicians, joining campaigns, or both!
For more pointers on how to live an eco-friendly lifestyle, check out our introduction to zero-waste or our post on solar panels to power your home with renewable energy.
Articles you might also like

What Are the Causes and Effects of Land Pollution and How Can We Prevent It?

Depletion of Natural Resources: 11 Natural Resources That Show the Scale of the Problem

Top 3 Causes, Effects, and Solutions of Ozone Layer Depletion

35 Ways to Reduce Air Pollution and Boost Air Quality for All

The Main Causes of Water Pollution and How They Affect Us All

What is Soil Pollution: Causes, Effects, and Prevention

What is Groundwater Pollution, and How Can it be Prevented?

The Most Effective Natural Bee Repellent

How to Help Endangered Species: 16 Ways to Protect Vulnerable Species Anyone Can Do!

Carbon Cycle Steps: What is the Carbon Cycle and How Does It Work
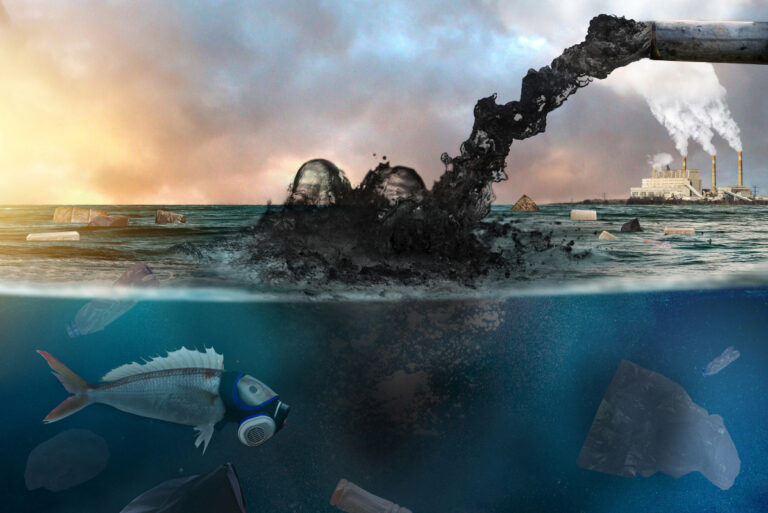
Ocean Dumping: What It is and How It Harms Our Environment
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Soil Pollution Essay

Essay on Soil Pollution
Soil is also called Earth, ground or dirt, which is formed by the accumulation of Organic and Inorganic matter as a bedrock through several years of physical weathering. And, Soil Pollution is the imbalance in the composition of this Organic matter which naturally decomposes and Inorganic matter which may be integrated with harmful chemicals that don’t decompose easily and degrade the quality of the Soil causing Soil Pollution. In this Soil Pollution essay, we will understand the cause and effects of Soil Pollution.
Soil is a thin layer that consists of both Organic and Inorganic components. These materials cover the Earth's rocky surfaces. Also included is the organic part, which is made up of decomposed animal and plant material. While rock bits make up the inorganic portion. This section was created through the chemical and physical weathering of bedrock over a thousand years. Soils that are productive are important for agriculture in order to meet the world's food needs. As a result, the essay on Soil Pollution focuses on the reasons that cause Soil contamination as well as the negative consequences of Soil Pollution.
Short Essay on Soil Pollution
Human-made chemicals are the leading cause of Soil Pollution as it alters the natural Soil Environment. And the ingestion of chemicals is at a big-time high due to industrialization and increase in population. This Soil Pollution essay in English will emphasize on the fact that there are millions of chemicals naturally present in the Soil. But when there is an increase in the concentration of a few harmful chemicals, it becomes a threat to living beings as it leads to serious health hazards.
The main contributors to Soil Pollution are the frequent use of chemical pesticides, fertilizers with higher concentrations of chemicals then decrease the natural fertility of the Earth, uncontrolled disposal of sewage, careless industrial waste spillage like of oils and solid matter from concrete matter used in making buildings and medical waste from hospitals and pharmaceutical labs and poor waste management.
All of the aforementioned causes lead to serious health conditions at all levels of the ecosystem. The plant growth is stunted when grown on such harmful grounds, the humans who are exposed to food yielded from such an environment can experience short term consequences like fatigue, weakness, headache, skin conditions or long term problems like depression, nervous system damage and animals including aquatic life suffers a great deal from this damage as they live on the polluted water seeped from the polluted Soil.
All of this can be resolved when people are consciously reducing the disposal of such harmful wastes into the natural bodies and a proper waste management system is followed.
Long Essay on Soil Pollution
Soil like all other forms of Pollution in nature is a growing sense of dread due to its deadly consequences in all living beings in the Ecosystem. Man-made materials are the leading cause of Soil Pollution. When any matter is present in quantities larger than the needed amount, then that becomes a potent threat. In trying to grow at a greater pace they are harming the Environment. The biggest threat to this problem is the irresponsibility displayed while disposing of any waste as the disposal of chemicals are not naturally present in the Soil so this causes contamination and as the levels increase leads to Pollution. In this essay on Soil Pollution, let’s understand the causes, effects and possible solutions.
What Causes Soil Pollution?
Soil Pollution is characterized as chemicals, salts, poisonous compounds, and radioactive contaminants that stay in the Soil and have negative impacts on animal health and plant growth. Pollution of Soils can occur in a variety of ways. These are the following:
Industrial garbage is dumped on the Earth's surface.
A landfill seeps water.
Underground storage tanks are bursting.
Contaminated water seeps into the ground.
Seepage of solid waste.
Heavy metals, petroleum hydrocarbons, solvents, and insecticides are examples of chemicals.
Soil Pollution Causes
A Soil pollutant is a factor that causes Soil to deteriorate owing to a reduction in the texture, mineral, or quality content of the Soil. This also disrupts the biological equilibrium of Soil-dependent organisms. Furthermore, Soil Pollution has negative consequences for plant growth. Soil contamination is usually produced by man-made applications such as contaminated surface water percolation, pesticides, fuel dumping, oil dumping, and so on.
Other operations include the leaching of pollutants from landfills, the direct dumping of industrial wastes into the Soil, and so on. Solvents, petroleum hydrocarbons, lead, pesticides, and various heavy metals are among the most prevalent compounds implicated. As a result, the occurrence of the phenomenon is highly correlated with the intensities and industrialisation of chemical use.
The following are some of the most common sources of Soil Pollution:
Fertilizer usage is increasing.
Insecticides, herbicides, and pesticides are used indiscriminately.
Solid waste disposal
Deforestation
Effects of Soil Pollution
As we go about our lives, we disregard the devastating effects of Soil Pollution on the Ecosystem and inevitably our health.
When we consume the food grown on such polluted Soil the crop absorbs it and then is passed on to us and leads to fatal diseases overtime.
Soil loses its fertility and stunts the growth of the plants and when they are harvested the contaminated Soil becomes futile as it is no longer useful for further cultivation as such lands become incompetent to support life and are deserted leaving more space to dump such harmful waste this cyclical nature of cause and effect is deadly.
The food that is produced from such lands also lacks good nutrients and thus creates another generation of malnourished children which hinders their natural growth physically and mentally.
The underground Soil water when it meets the natural aquatic bodies, it does a great deal of damage to aquatic life, both plants that grow underwater and animals.
Soil Pollution's Consequences
Some radioactive pollutants from nuclear reactors, explosions, hospitals, science labs, and other sources penetrate deeply into the Soil, where they linger for a long time and pollute the Soil.
False agricultural practices involving advanced agro-technology entail the use of massive volumes of harmful fertilisers such as herbicides, weedicides, insecticides, and other chemicals, which improve Soil fertility while gradually reducing Soil physio-chemical and biological qualities. Other forms of Soil Pollution include municipal rubbish, food processing waste, mining practices, and many others.
Soil Pollution is extremely detrimental to one's health since poisonous substances enter the body through the food chain and disrupt the entire inner body system. Individuals, particularly industrialists, should adopt all effective control measures, including environmental protection regulations, in order to reduce and minimise Soil Pollution. People should encourage the recycling and reuse of solid waste, as well as the planting of as many trees as possible.
Ways to Curb Soil Pollution
The most important step in starting to solve this problem is by creating awareness and informing people about the dire consequences, and how their contribution can do good to the ecosystem and human nature. The possible solutions to these problems are-
No excess use of fertilizers, and other chemicals used. As these are useful only in required quantities and when overdone leads to the damage so one can avoid overuse of the harmful substances containing chemicals.
Encouraging afforestation i.e. the planting of trees as the more trees planted the Erosion of Soil will be less and this will help in retaining the useful chemicals in the Soil and hence increasing the fertility of the Soil as well.
Recycling and reusing of waste materials will help a great deal and lessen the harm to a greater degree.
As the saying goes Prevention is better than cure, it is better to take steps in creating a safer environment instead of regretting later. India being Agricultural Land, we can take steps to organize programs and educate the farmers and other locals to use natural manure, and make them aware of the problems caused by chemicals used.

FAQs on Soil Pollution Essay
1. How can we Control Soil Pollution?
On an individual level, we have to take it upon ourselves to reduce the amount of waste produced due to our regular activities on a daily basis. We should also plant more trees and encourage nearby ones to do the same. The effect is more impactful when individuals take accountability for their duty to give back to nature. Students can learn how to control Soil Pollution and educate their elders for the same.
2. What are the different types of Soil Pollution?
There are two types of Soil Pollution, the one caused by natural disasters like floods which also erodes the Soil, this can be in a specific region or can be widespread. The other one is man-made or called anthropogenic type which is the major cause of the problem. We cannot control the natural one but the man-made one. By taking to certain protocols and following the code of conduct, we will be able to control the Soil Pollution caused by the people.
3. How to curb Soil Pollution?
There are three ways to curb Soil Pollution. One way is to not use excess fertilisers and chemicals on the ground. The fertilisers can cause degradation of the Soil and kill the organic microorganisms that help to promote Soil fertility. The second way is by recycling and reusing man-made products. We should ban plastic and opt for products that can be reused and recycled. Trees should be planted and deforestation should be in control. For every tree cut, there should be twice the plantation.
4. How can chemicals affect biodiversity?
The fertilisers used as chemicals in the Soil can affect crop growth. It kills the macronutrients that are essential and causes toxic effects to the crop. These when taken up by humans or animals can promote biomagnification and increase toxicity at every level in the food chain. Even when we water the crops, the water can contain toxic chemicals and affect aquatic marine life. Hence the chemicals can affect biodiversity to a broad level.
5. Is an Essay on Soil Pollution for Students in English helpful?
Yes, the Essay on Soil Pollution for Students in English is very helpful. Firstly it helps the student to know about Soil Pollution and its prevention. Secondly, students will be able to write a well-composed essay on the topic of Soil Pollution. It is important to get environmental knowledge and write it properly in English medium. Regular practice and learning can help students to compose a good essay on diverse topics. Learn and read to get a better grip on essay writing.

Soil Pollution Essay

Updated November 21, 2023
Introduction to Soil Pollution
“The earth does not belong to us; we belong to the earth.” – Chief Seattle.
The words of Chief Seattle, a Native American leader, echo through time, reminding us of our profound connection to the land we inhabit. However, in an era marked by relentless industrialization and rapid urbanization, the very soil beneath our feet, the foundation of life itself, is under siege. Soil pollution, a silent and insidious enemy, threatens the environment and future generations’ health and well-being. To put this issue in perspective, consider this alarming statistic: every year, an estimated 24 billion tons of fertile soil, equivalent to over 3 tons for every person on the planet, is lost due to pollution and degradation. This silent crisis deserves our immediate attention and concerted action. This essay will explore the causes, effects, and potential solutions to soil pollution, a challenge that demands our commitment to preserving the fragile equilibrium of our shared home – Earth.
Watch our Demo Courses and Videos
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Mobile Apps, Web Development & many more.

Causes of Soil Pollution
Soil pollution results from various human activities and natural processes that introduce harmful substances into the soil, disrupting its composition and compromising its quality. Understanding these causes is crucial in devising effective strategies to combat soil pollution. Here are some of the primary causes:
1. Industrial Activities
Industries are significant contributors to soil pollution. Chemical factories, manufacturing plants, and processing industries often release hazardous chemicals and pollutants directly into the soil or nearby water bodies. These substances include heavy metals, solvents, and toxic byproducts, which can contaminate the soil and disrupt its natural balance.
2. Agricultural Practices
While essential for feeding the growing global population, modern agricultural practices often involve using pesticides, herbicides, and chemical fertilizers. These agrochemicals seep into the soil when used excessively or improperly, leading to contamination. Moreover, monoculture, improper irrigation, and overuse of pesticides can degrade soil quality over time.
3. Improper Waste Disposal
Inadequate disposal of various types of waste, such as household, industrial, and electronic, can introduce harmful substances into the soil. Landfills, if not properly designed and managed, can leak toxic chemicals into the surrounding soil, contaminating it for years. Dumping of hazardous waste illegally exacerbates the issue.
4. Mining and Construction Activities
Mining operations and large-scale construction projects often involve excavation, which exposes underlying soil layers. Chemicals and heavy metals in the soil can be released during these activities, contaminating the surrounding land. Improper handling of mining byproducts, such as tailings, can also lead to soil pollution.
5. Deforestation and Soil Erosion
Deforestation disrupts the natural vegetation cover, leading to soil erosion. When the topsoil, rich in nutrients, is eroded away, the soil lacks fertility. Soil erosion is exacerbated by poor agricultural practices and construction activities, leaving the land barren and susceptible to pollution.
6. Accidental Spills and Leaks
Accidental spills of hazardous substances, such as oil, chemicals, or sewage, can lead to immediate soil pollution. These incidents often occur during transportation or storage of toxic materials and can have severe and lasting effects on the soil and surrounding ecosystems.
7. Atmospheric Deposition
Airborne pollutants, including heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial emissions, can settle onto the soil through precipitation (acid rain) or atmospheric dust. Over time, these pollutants accumulate in the soil, affecting its quality and fertility.
Effects of Soil Pollution
Soil pollution has profound implications beyond just the ground under our feet. It impacts ecosystems, biodiversity, human health, and the economy in various ways. Here are some of the primary effects of soil pollution:
1. Environmental Consequences
- Loss of Biodiversity: Soil pollution disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, leading to a decline in biodiversity. Many plants, animals, and microorganisms depend on healthy soil for survival. When the soil is contaminated, these species suffer; some may even become endangered or extinct.
- Habitat Destruction: Pollution can make certain areas uninhabitable for various organisms, reducing available habitats and contributing to habitat destruction.
- Soil Degradation: Soil pollution depletes the fertility and structure of the soil, making it less suitable for plant growth. This can result in soil degradation and desertification, turning once-arable land into barren wastelands.
2. Human Health Implications
- Contaminated Food Supply: Plants can absorb soil pollutants and enter the food chain. Humans may be exposed to dangerous elements such as heavy metals and organic pollutants when they consume crops cultivated in polluted soil, which can cause cancer, developmental defects, and organ damage.
- Direct Exposure: People can contact contaminated soil directly, especially in high pollution levels. This can result in skin disorders, respiratory issues, and other health problems.
- Water Contamination: When contaminants seep through the soil into underground aquifers, they can contaminate groundwater. This contaminated groundwater could be a source of drinking water, putting human health at risk.
3. Economic Impact
- Agricultural Decline: Soil pollution can significantly reduce agricultural productivity. Crops grown in contaminated soil yield lower quantities and lower-quality produce. This can result in economic losses for farmers and food shortages in impacted areas.
- Property Values: Contaminated soil can reduce property values, making it difficult for landowners to sell or develop their land. It can also lead to increased costs for land remediation and legal liabilities.
- Cleanup Costs: The costs associated with cleaning up polluted soil, especially at industrial and waste disposal sites, can be substantial. Taxpayers or private entities often fund these cleanup efforts.
Case Studies
The following case studies illustrate the diverse nature of soil pollution incidents and the impact they have on ecosystems, communities, and economies:
1. Love Canal, USA (1978)
- Background : Love Canal, located in Niagara Falls, New York, gained international attention when it was discovered that a residential neighborhood had been built on top of a former chemical waste disposal site.
- Cause : The Hooker Chemical Company had disposed of toxic waste in the canal, which led to soil and groundwater contamination.
- Effects : Residents had serious health problems, including birth abnormalities and cancer. The disaster spurred the United States to enact the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA).
2. Bhopal, India (1984)
- Background : The main cause of the Bhopal disaster was the release of methyl isocyanate gas from a Union Carbide pesticide plant.
- Cause : Chemicals released during the gas leak contaminated the soil in and around the plant site.
- Effects : The soil remained polluted with heavy metals and other toxic substances, affecting agricultural productivity and posing ongoing health risks for local communities.
3. Minamata, Japan (1950s-1960s)
- Background : Industrial wastewater containing mercury was discharged into Minamata Bay by the Chisso Corporation.
- Cause : The mercury in the water accumulates in the sediment, contaminating marine life and subsequently affecting the soil in the surrounding areas.
- Effects : Consumption of contaminated fish led to severe health issues, known as Minamata disease, including neurological damage and birth defects.
4. Chernobyl, Ukraine (1986)
- Background : The Chernobyl nuclear disaster released radioactive materials into the environment.
- Cause : The incident led to widespread soil contamination with radioactive isotopes, including cesium-137 and strontium-90.
- Effects : Contaminated soil in the exclusion zone limits agricultural activities and poses ongoing risks to human health.
5. Guanajuato, Mexico (2006)
- Background : Lead-acid battery recycling plants in Guanajuato released lead and other pollutants into the air and soil.
- Cause : Improper disposal and handling of lead-acid batteries led to soil contamination in residential areas.
- Effects : Elevated blood lead levels were found in children, leading to neurological and developmental issues. The incident prompted regulatory actions and cleanup efforts.
Pollutants Contaminating the Soil
Here are some common pollutants that contaminate the soil:
1. Heavy Metals
- Sources : Industrial discharges, mining activities, and improper electronic waste disposal contribute to heavy metal contamination. Common heavy metals include lead, mercury, cadmium, and arsenic.
- Effects : Heavy metals can accumulate in the soil, threatening plant and microbial life. They can also leach into groundwater, leading to potential human exposure and health risks.
2. Pesticides and Herbicides
- Sources : Agricultural practices often involve the excessive use of pesticides and herbicides, which can result in these chemicals entering the soil due to improper application.
- Effects : Pesticides and herbicides can persist in the soil, affecting non-target organisms, disrupting ecosystems, and potentially entering the food chain, posing risks to human health.
3. Industrial Chemicals
- Sources : Industrial activities release many environmental chemicals, including solvents, heavy industrial metals, and organic compounds.
- Effects : Industrial pollutants can contaminate the soil, affecting soil structure and microbial activity. Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) can bioaccumulate in organisms, posing long-term ecological and human health risks.
4. Petroleum Hydrocarbons
- Sources : Oil spills, leaking underground storage tanks, and improper disposal of petroleum products contribute to soil contamination with hydrocarbons.
- Effects : Petroleum hydrocarbons can alter soil structure and hinder microbial activity. In severe cases, they can contaminate groundwater, posing risks to ecosystems and human health.
5. Radioactive Substances
- Sources : Nuclear accidents, industrial activities involving radioactive materials, and improper disposal of radioactive waste contribute to soil contamination with radioactive substances.
- Effects : Radioactive pollutants can persist in the soil for extended periods, leading to long-term environmental and human health risks. Contaminated areas may be restricted for agricultural use.
6. Agricultural Runoff
- Sources : Excess fertilizer use and runoff from agricultural fields can introduce nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus into the soil.
- Effects : While essential for plant growth, excessive nutrients can lead to soil degradation, nutrient imbalances, and water pollution. This phenomenon is often associated with eutrophication in water bodies.
7. Plastic and Microplastics
- Sources : Improper disposal of plastic waste and the breakdown of larger plastic items contribute to soil contamination with microplastics.
- Effects : Microplastics can accumulate in the soil, affecting soil structure and potentially entering the food chain. The long-term effects of microplastic contamination are still being studied.
Solutions to Soil Pollution
Here are some effective strategies to mitigate and prevent soil pollution:
- Sustainable Agricultural Practices: Encourage the adoption of organic farming methods that minimize synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. This promotes soil health and biodiversity. Implement crop rotation and diversification strategies to maintain soil fertility, reduce reliance on chemical inputs, and prevent the buildup of pests and diseases.
- Responsible Waste Management: Promote recycling programs for household, industrial, and electronic waste to prevent the improper disposal of hazardous materials. Improve landfill design and management practices to minimize the leaching of pollutants into the soil. Encourage the use of modern landfill technologies, such as liners and leachate collection systems.
- Contaminated Site Remediation: Utilize biological processes to clean up contaminated soil through bioremediation. Microorganisms can be introduced to break down or neutralize pollutants, restoring soil quality. Use plants to absorb, accumulate, or transform contaminants in the soil through phytoremediation. Certain plant species can extract and retain contaminants, aiding soil remediation.
- Regulation and Enforcement: Implement and enforce stringent regulations on industrial discharges, waste disposal, and the use of agrochemicals. Penalties for non-compliance should act as deterrents to irresponsible practices. Implement effective land-use planning to prevent incompatible activities in areas vulnerable to soil pollution. Establish buffer zones between industrial sites and residential areas.
- Education and Awareness: Raise awareness about the impacts of soil pollution through public awareness campaigns. Inform communities about proper waste disposal, sustainable agriculture, and the importance of soil conservation. Provide training and support for farmers to adopt sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural practices, reducing reliance on harmful chemicals.
- Sustainable Land Management: Planting trees helps prevent soil erosion, enhances soil structure, and contributes to the absorption of pollutants through afforestation and reforestation. Implement erosion control measures such as terracing, cover cropping, and contour plowing to minimize soil erosion and degradation.
- Research and Monitoring: Regularly test soil quality and pollution levels to identify potential issues early through soil testing and monitoring. Implement systems for continuous monitoring, especially in areas with a history of contamination. Invest in research to develop innovative technologies and approaches for soil remediation. Support the development of sustainable alternatives to current agricultural and industrial practices through research and innovation.
Measures Taken by Governments
Governments worldwide have recognized the urgency of addressing soil pollution and have implemented various measures to mitigate its impact. These proactive steps include:
- Environmental Legislation: Governments enact and enforce stringent environmental laws regulating industrial emissions, waste disposal, and agrochemical use to prevent soil pollution at its sources.
- Soil Monitoring Programs: Governments institute soil monitoring programs to assess pollution levels, identify contaminated areas, and implement targeted remediation efforts.
- Sustainable Agriculture Initiatives: Promoting sustainable agricultural practices, governments encourage farmers to adopt organic farming, agroecological methods, and precision farming to minimize the use of chemical inputs.
- Waste Management Regulations: Implementing comprehensive waste management regulations ensures proper disposal of hazardous waste, reducing the risk of soil contamination from landfills and illegal dumping.
- Brownfield Redevelopment Programs: Governments initiate programs to rehabilitate contaminated sites (brownfields), promoting their safe reuse after thorough remediation.
- Research and Innovation Funding: Governments support the development of new technologies for soil remediation and sustainable land management practices by investing in research and innovation.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Governments conduct public awareness campaigns to educate citizens about the impact of soil pollution and promote responsible waste disposal and sustainable lifestyle choices.
- International Collaboration: Participating in international agreements and collaborations, governments work collectively to address cross-border soil pollution issues, sharing best practices and resources.
Soil pollution is a serious threat to the delicate balance of our environment and significantly impacts biodiversity, water quality, and climate resilience. Urgent action is necessary to recognize its pervasive effects on ecosystems and human health. We can protect the vitality of our soil through sustainable agricultural practices, responsible waste management, and strict regulations. Preserving this foundational resource is an environmental necessity and a collective responsibility for a sustainable future.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Soil Pollution Essay” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
- Essay on Summer Vacation
- Water Pollution
- Essay on Pollution
- Essay on Technology

*Please provide your correct email id. Login details for this Free course will be emailed to you
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Web Development & many more.
Forgot Password?
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the cookie policy. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to our Privacy Policy

Explore 1000+ varieties of Mock tests View more
Submit Next Question
🚀 Limited Time Offer! - 🎁 ENROLL NOW

Polluting our soils is polluting our future
#stopsoilpollution: 6 reasons why soil pollution should not go unnoticed.
It is estimated that 95 percent of our food is directly or indirectly produced on our soils.
Soil is a finite resource, meaning its loss and degradation is not recoverable within a human lifespan. Soils affect the food we eat, the water we drink, the air we breathe, our health and the health of all organisms on the planet. Without healthy soils we wouldn’t be able to grow our food. In fact, it is estimated that 95 percent of our food is directly or indirectly produced on our soils.
Healthy soils are the key to food security and our sustainable future. They help sustain food production, mitigate and adapt to climate change, filter water, improve resilience to floods and droughts and so much more. Yet, an invisible threat is putting soils and all that they offer at risk.
Soil pollution causes a chain reaction. It alters soils’ biodiversity, reduces soil organic matter and soils’ capacity to act as a filter. It also contaminates the water stored in the soil and groundwater, and causes an imbalance of soil nutrients. Among the most common soil pollutants are heavy metals, persistent organic pollutants and emerging pollutants – like pharmaceutical and personal care products.
Soil pollution is devastating to the environment and has consequences for all forms of life that encounter it. Unsustainable agricultural practices that reduce soil organic matter can facilitate the transfer of pollutants into the food chain. For example: polluted soil can release contaminants into the groundwater, which goes on to accumulate in plant tissue, and is then passed to grazing animals, birds, and finally to the humans that eat the plants and animals. Pollutants in soil, groundwater and in the food chain can cause a variety of diseases and excess mortality in humans, from short-term acute effects, such as intoxications or diarrhea to long-term chronic effects, like cancer.
Beyond the impact on the environment, soil pollution also has high economic costs due to the reduction of crop yields and quality. The prevention of soil pollution should be a top priority worldwide. The fact that the vast majority of pollutants are a result of human action means that we are directly responsible for making the necessary changes to ensure a less polluted, more secure future.
Soils need to be recognized and valued for their productive capacities as well as their contribution to food security and the maintenance of key ecosystem services. Here are just a few reasons why soil pollution can’t be underestimated:
1. Soil pollution affects everything. The food we eat, the water we drink, the air we breathe – our health and the health of all the organisms on the planet is dependent on healthy soil. The nutrient content of a plant’s tissues is directly related to the nutrient content of the soil and its ability to exchange nutrients and water with the plant’s roots.
2. Soil pollution is invisible. Today, one third of our soils are moderately or highly degraded due to erosion, loss of soil organic carbon, salinization, compaction, acidification and chemical pollution. It takes about 1 000 years to form 1 cm of top soil, meaning that we won’t be able to produce more soil within our lifetime. What we see is all there is. Yet, soils are facing even more pressure from soil pollution. The current rate of soil degradation threatens the capacity of future generations to meet their most basic needs.
3. Soil pollution affects soils’ capacity to filter. Soils act as a filter and buffer for contaminants. The potential of soil to cope with the strain of pollutants is finite. If soil’s capacity to protect us is exceeded, contaminants will (and do) seep into other parts of the environment – like our food chain.

Left: Benefits of soils go beyond just food production. Did you know most well-known antibiotics, including penicillin, originated from soil microorganisms? Right: Nutritious and good quality food can only be produced if our soils are healthy.
4. Soil pollution affects food security by reducing crop yields and quality. Safe, nutritious and good quality food can only be produced if our soils are healthy. Without healthy soils, we won’t be able to produce enough food to achieve #ZeroHunger.
5. Soil pollution can be a result of poor agricultural practices . Unsustainable agricultural practices reduce soil organic matter, compromising soils’ capacity to degrade organic pollutants. This increases the risk of the pollutants being released into the environment. In many countries, intensive crop production has depleted the soil, jeopardizing our ability to maintain production in these areas in the future. Sustainable agricultural production practices have therefore become imperative for reversing the trend of soil degradation and ensuring current and future global food security.
6. Soil pollution can put our health at risk. A significant proportion of antibiotics, used widely in agriculture and human healthcare, are released into the environment after being excreted from the organism to which they were administered. These antibiotics can seep into our soils and spread throughout the environment. This creates antimicrobial resistant bacteria, which decreases the effectiveness of antibiotics. Each year around 700 000 deaths are attributable to antimicrobial resistant bacteria. By 2050, if not tackled, it will kill more people than cancer, and cost, globally, more than the size of the current global economy.

Soil protection and conservation starts with us.
With a global population that is projected to exceed 9 billion by 2050, our current and future food security hinges on our ability to increase yields and food quality using the soils that we already have available today. Soil pollution negatively impacts us all, and has been identified as one of the main threats to soil functions worldwide.
We need to be aware of the causes of soil pollution so that we can create and implement solutions. Soil protection and conservation starts with us. Making sustainable food choices, properly recycling dangerous materials like batteries , composting at home to reduce the amount of waste that enters landfills or managing antibiotic waste more responsibly, are just a few examples of how we can be part of the solution. On a larger scale, we need to promote sustainable agricultural practices in our communities.
Healthy soil is a precious, non-renewable commodity that is increasingly threatened by destructive human behaviours. We are responsible for the soils that provide us with food, water and air, and we need to take action today to ensure that we have healthy soils for a sustainable and food secure future. Be the solution to soil pollution!
Related links
Learn more:
- Global Symposium on Soil Pollution | #GSOP18
- Publication | Soil pollution: a hidden reality
- Publication | Soil Organic Mapping Cookbook (2nd Edition)
- FAO's work on soils
- Cherishing the ground we walk on
Essay on Soil Pollution
Soil is one of the essential natural resources. It is the basis of food production, and it supports a wide variety of plant and animal life. Soil pollution is the contamination of soil with substances that would not usually be naturally found in a place. It can be caused by many factors, such as fertilisers and pesticides from farms, construction sites that discard dirt, and the improper disposal of household chemicals. BYJU’S essay on soil pollution teaches us the causes, effects and ways to prevent soil pollution.
Besides the factors mentioned above, the substances responsible for soil pollution can come from various sources, such as industrial wastes, sewage disposal, and pesticides. These substances can impact humans and other organisms in the soil to die. They also contaminate water sources. Moreover, soil pollution causes groundwater contamination, making it dangerous for people to drink without boiling first because it could contain germs and chemicals. The chemical substances that result in soil pollution can also cause air pollution . Now, let us learn the reasons for soil pollution by reading the soil pollution introduction essay.
Causes of Soil Pollution
Soil pollution essay in English helps understand its reasons and impact. It can occur from various sources, but the most common sources are agricultural and industrial activities. As the careless use of these chemicals affects soil quality, it will eventually lead to a shortage in food production.
Waste disposal sites or factories near rivers or streams also often cause soil pollution because they release pollutants into the surface and water, which leads to water pollution . Another common cause of soil pollution is dumping trash. This can include anything from household garbage to industrial and medical waste. The toxins in these materials can leach into the soil and contaminate it; this means that any plants grown in that soil will also be tainted. Some chemicals are even known to cause cancer or other diseases. Pollution from toxic waste, such as metal smelting, chemical manufacturing, and oil refining, can also harm soil quality.
Effects of Soil Pollution
After understanding the causes of soil pollution, let us know the adverse effects by reading the soil pollution essay . Harmful substances disposed of in water can leach into the soil and contaminate nearby water sources. One of the negative effects of soil pollution is that it can be challenging to grow plants in areas where the soil is contaminated.
Soil pollution has detrimental effects on our environment, but it is hard to see the accumulation of pollutants and how severe the damage is. Soil can act as a sink that soaks up contaminants such as pesticides and heavy metals. However, soil can take in only a limited amount of these substances, at which point they are no longer absorbed into the ground and start to build up in the atmosphere. This will eventually lead to the contamination of air, water, and food supplies.
How to Prevent Soil Pollution?
Soil pollution is a global issue and is a problem that affects everyone. The most important things to do are to stop using pesticides and herbicides, use organic fertilisers and compost, avoid spreading trash or hazardous materials in the park , and limit chemical fertilisers. Sewage from cities and factory waste can contaminate the soil. One way to reduce this is to use a two-chamber septic tank, which effectively reduces soil pollution.
The effects of soil pollution are a significant concern, and hence, we must learn how to prevent soil pollution by reading BYJU’S how to prevent soil pollution essay.
To conclude, we must join hands in preventing soil pollution for a better future. For more kids learning activities like GK questions and worksheets , visit BYJU’S website.
Frequently Asked Questions on Soil Pollution
Do chemical fertilisers harm the soil.
Yes. Chemical fertilisers harm the soil.
What are the three significant causes of soil pollution?
Three significant causes of soil pollution are careless waste disposal, oil spills and industrial activities.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
What Is Soil Pollution? Environmental Impacts and Mitigation
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/DSC00174-2-6ddfbd1f7dd0404f85aca2b9b30acadd.jpg)
- Western University
- University of Guelph
- Planet Earth
- Climate Crisis
- Recycling & Waste
- Natural Disasters
- Transportation
Causes of Soil Pollution
Environmental impacts, where soil pollution occurs.
Soil pollution refers to the dangerously high concentrations of contaminants in soil. While contaminants such as metals, inorganic ions, salts, and organic compounds naturally occur in soils, these can exceed natural levels and qualify as pollution.
Soil pollution can have far-reaching consequences; it is often detrimental to plant growth, disrupting food chains and entire ecosystems. In turn, it has a direct impact on food security . Here, we'll review the causes of soil pollution, its widespread environmental impacts, and how to improve soil conditions.
As with other types of pollution, the causes of soil pollution often come back to humans.
Industrial Pollutants
Industrial pollutants are among the most common causes of soil pollution. Chemicals are released from industrial facilities in both liquid and solid form. Industrial activities emit large amounts of arsenic fluorides and sulfur dioxide, which raise soil acidity and impact vegetation. Accidental spills and leaks during storage, transport, and usage contribute to soil pollution.
Agricultural Activities
There are several sources of soil pollution in industrial agriculture. Many fertilizers, for example, contain substantial amounts of heavy metals, such as calcium, nitrate, and potassium chloride that can disrupt regular growing seasons. Sewage and other liquid waste from domestic water use, agricultural effluents from animal husbandry, and urban runoff also pollute soils.
Another cause is deforestation; the clearing of trees results in increased soil erosion, which lessens the soil’s ability to support vegetation.
Soil has a finite capacity to cope with pollutants; when this is surpassed, contaminants will impact other parts of the environment, such as the food chain. As a result, soil pollution also affects food security as it reduces crop yields and quality.
Soil pollution contributes to air pollution as it releases volatile compounds into the atmosphere. Furthermore, air pollution created by the burning of fossil fuels can cause acid rain which produces an acidic environment in the soils . This harms micro-organisms, which improve the soil structure by breaking down organic material and helping water flow.
Chemicals within soils can also be leached into groundwater, which can then reach streams, lakes, and oceans. Also, soils with high levels of nitrogen and phosphorus can leach into waterways, causing algal blooms , which decrease the oxygen available for aquatic life. Likewise, soil erosion can lead to pollution and sedimentation in waterways.
Soil pollution can be found all over the world, but particularly in areas in Europe and North America.
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, there are approximately 2.8 million potentially polluted sites in Europe, and 19% need remediation or risk-reduction measures. Actions from industrial, commercial, production, waste disposal, and treatment activities have been the main source of point-source soil pollution in Europe. Mining has been a significant contributor to soil pollution in Cyprus, Slovakia, and North Macedonia.
Although there have been improvements in waste management and legislation has become stricter, recent assessments in countries such as Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, and Turkey, indicate that soil pollution is still a significant problem.
North America
There are thousands of polluted sites in both the U.S. and Canada. There are approximately 23,000 abandoned mines in the state of Colorado alone, which contribute to soil pollution. Additionally, coal combustion from provinces in Canada such as Alberta, Saskatchewan, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia produces coal ash. Also, lakes and rivers in Alberta and Saskatchewan are currently experiencing very high levels of acid pollution which threatens aquatic ecosystems.
To counter soil pollution on the agricultural level, the EPA has recommended that farmers adopt sustainable practices:
- Nutrient management techniques
- Drainage practices that conserve resources
- Year-round ground covering
- Field buffers
- Conservation tillage
- Access to streams for livestock.
Additionally, Congress passed the Pollution Prevention Act , which has led to the creation of programs and strategies that aims to reduce or eliminate pollution at the source.
Strategies that focus on the mining industry include improving the management of mining waste, restoring the landscape, and conserving topsoil. Urban planning and wastewater treatment are also effective in decreasing urban sources of soil pollution, such as sewage.
Ashraf, Muhammad, Maah, Mohd., Yusoff, Ismail. "Soil Contamination, Risk Assessment and Remediation". Environmental Risk Assessment of Soil Contamination, edited by Maria Hernandez-Soriano, IntechOpen, 2014. 10.5772/57287.
FAO and UNEP. 2021. Global assessment of soil pollution: Report. Rome. https://doi.org/10.4060/cb4894en
- What Is Water Pollution? Sources, Environmental Impacts, Mitigation
- The Environmental Impact of Ocean Noise
- 10 Examples of Why the Superfund Program Matters
- What Is Nutrient Pollution? Causes, Impacts, and Mitigation
- How Does Mercury Get in Fish?
- Noise Pollution: Environmental Impact and What You Can Do
- What Is BPA? Definition and Environmental Impact
- 155 Million Pounds of Pesticide Leach Into Aquifers Every Year
- What Are PFAS? Definition, Sources, and Health Risks
- What Is Thermal Pollution? Causes, Impact, and Mitigation
- What Are Fugitive Emissions? Definition and Impact
- How Does BPA Affect Animals and the Environment?
- What Is a Trophic Cascade? Definition and Ecological Impact
- How Plants and Microorganisms Can Clean up the Mess We Make
- The 10 Worst Forms of Pollution
- What Is Air Pollution? Definition, Types, and Environmental Impact
- News, Stories & Speeches
- Get Involved
- Structure and leadership
- Committee of Permanent Representatives
- UN Environment Assembly
- Funding and partnerships
- Policies and strategies
- Evaluation Office
- Secretariats and Conventions

- Asia and the Pacific
- Latin America and the Caribbean
- New York Office
- North America
- Climate action
- Nature action
- Chemicals and pollution action
- Digital Transformations
- Disasters and conflicts
- Environment under review
- Environmental rights and governance
- Extractives
- Fresh Water
- Green economy
- Ocean, seas and coasts
- Resource efficiency
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Youth, education and environment
- Publications & data

Soil pollution a risk to our health and food security
Each year, the world marks World Soil Day on 5 December to raise awareness about the growing challenges in soil management and soil biodiversity loss, and encourage governments, communities and individuals around the world to commit to improving soil health.
“We depend, and will continue to depend, on the ecosystem services provided by soils,” explains United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) soil expert Abdelkader Bensada.
While soil pollution traditionally has not received the same attention as issues like tree-planting, global momentum picked up in 2018, when the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) published a ground-breaking study: Soil Pollution: A Hidden Reality .
The report found that the main anthropogenic sources of soil pollution are the chemicals used in or produced as byproducts of industrial activities; domestic, livestock and municipal wastes (including wastewater); agrochemicals; and petroleum-derived products.
These chemicals are released to the environment accidentally, for example from oil spills or leaching from landfills, or intentionally, through use of fertilizers and pesticides, irrigation with untreated wastewater, or land application of sewage sludge.

The report found that soil pollution has an adverse impact on food security in two ways –it can reduce crop yields due to toxic levels of contaminants, and crops grown in polluted soils are unsafe for consumption by animals and humans. It urged governments to help reverse the damage and encouraged better soil management practices to limit agricultural pollution.
In follow up to the 2018 study, UNEP, the Global Soils Partnership, the Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils, the World Health Organization and the Basel, Rotterdam and Stockholm Conventions Secretariat are working on another report on the extent and future trends of soil pollution, including risks and impacts on health, the environment and food security. Scheduled to be released in February 2021, it builds on another UNEP report - Towards a pollution-free planet .
“Soil pollution can lead to the emergence of new pests and diseases by changing the balance of ecosystems and causing the disappearance of predators or competing species that regulate their biomass. It also contributes to the spreading of antimicrobial resistant bacteria and genes, limiting humanity’s ability to cope with pathogens,” says Bensada.
Pollution can also cause the quality of soil to dwindle over time, making it harder to grow crops. Currently, the degradation of land and soils is affecting at least 3.2 billion people – 40 per cent of the world’s population.
FAO’s Revised World Soil Charter recommends that national governments implement regulations on soil pollution and limit the accumulation of contaminants beyond established levels in order to guarantee human health and wellbeing, a healthy environment and safe food.
Contaminated soil is also a major cause of land degradation – an issue that is at the heart of the United Nations Decade on Ecosystem Restoration 2021-2030 . Led by UNEP, FAO and partners, the initiative is a global call to action to scale up restoration of terrestrial, coastal and marine ecosystems over the next 10 years. This includes promoting sustainable practices to improve soil management.
“Soil has a key role to play in the UN Decade through its ecosystem functions as it affects water regulation, nutrient recycling, food production, climate change and the biodiversity of terrestrial ecosystems,” says Bensada. “Transitioning from soil degradation to practices that restore soil is critical to ensure the food security and wellbeing of generations to come.”
For more information, please contact Abdelkader Bensada: [email protected]
- Fresh water
- Agriculture
- Biodiversity
Further Resources
- Microplastics negatively affect soil fauna but stimulate microbial activity: insights from a field-based microplastic addition experiment
Related Content

Related Sustainable Development Goals

© 2024 UNEP Terms of Use Privacy Report Project Concern Report Scam Contact Us

Essay on Soil Pollution 500+ Words
Soil pollution may not always be visible, but it’s a pressing issue that affects our environment, food, and health. In this essay, we will explore the hidden dangers of soil pollution and why we should all be concerned about it.
Defining Soil Pollution
Soil pollution occurs when harmful chemicals, pollutants, or contaminants find their way into the earth’s soil. These substances can come from various sources, including industrial activities, agriculture, and improper waste disposal. It’s a widespread problem that impacts both rural and urban areas.
The Consequences for Earth
Soil pollution poses a significant threat to our planet. It can harm the delicate balance of ecosystems, disrupt food chains, and reduce biodiversity. Healthy soil is essential for plants, animals, and even humans to thrive.
Food for Thought
One of the most critical impacts of soil pollution is on our food. When pollutants seep into the soil, they can be absorbed by the plants we eat. This means that the food on our plates may contain harmful chemicals. This poses a risk to our health and well-being.
The Human Health Connection
Soil pollution isn’t just an environmental problem; it’s also a public health concern. When we consume polluted food, we expose ourselves to toxins that can lead to various health issues, including cancer, respiratory problems, and developmental disorders.
The Hidden Costs
Soil pollution comes with a hefty price tag. It leads to increased healthcare costs, reduced crop yields, and damage to infrastructure. Addressing soil pollution is not just a moral duty but also an economic necessity.
The Slow Road to Recovery
Once soil is polluted, it can take years, decades, or even centuries to clean up. This means that the effects of soil pollution can be long-lasting and difficult to reverse. Prevention is often the best approach.
Voices of Experts
According to soil scientists and environmental experts, sustainable farming practices and responsible waste management are key to reducing soil pollution. They also emphasize the importance of raising awareness about this issue.
Taking Action
It’s not too late to make a difference. We can all contribute to combating soil pollution by reducing our use of harmful chemicals, supporting sustainable agriculture, and advocating for stricter regulations on industrial pollution.
Conclusion of Essay on Soil Pollution
In conclusion, soil pollution is a silent threat that affects us all. It harms our environment, endangers our health, and burdens our economies. However, by understanding the issue, listening to experts, and taking action in our daily lives, we can work together to prevent further soil pollution and protect the precious earth beneath our feet. Let us remember that a healthy planet starts with healthy soil, and it’s our responsibility to ensure its well-being for generations to come.
Also Check: The Essay on Essay: All you need to know
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades
Soil Pollution Essay | Essay on Soil Pollution for Students and Children in English
February 13, 2024 by Prasanna
Soil Pollution Essay: Soil is an essential component of our nature. There are many reasons as to why and how soil gets polluted. And this soil pollution has become one of the major crises for the ecosystem and humankind because it causes an imbalance in nature. Soil pollution both directly and indirectly concerns and affects us. Therefore we must understand the causes and effects of soil pollution to reduce it.
To help students write an essay on ‘Soil Pollution,’ we will provide them with long and short essay samples. Along with this, we will also give ten pointers about the topic that will work as guidance for framing the essay.
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more.
Long and Short Essays on Soil Pollution for Students and Kids in English
We are providing a long essay of 400-500 words and a short essay of 100-200 words on the topic of Soil Pollution.
Long Essay on Soil Pollution 500 words in English
Soil Pollution essay will be helpful as a reference for students of class 7, 8, 9, and 10.
Soil is the uppermost dry layer of the Earth made up of organic and inorganic materials. The importance of soil is to sustain terrestrial life on this planet, and it is also the component where the sources of life like water and sunlight air come together. Soil pollution can be declared to be the presence of toxic chemicals that pollute the soil, to high concentrations, to risk the ecosystem and human health. Several factors cause soil pollution and many adverse effects that are resulted in it.
There are two types of soil pollution, one nature’s doing or other human-made (anthropogenic soil pollution). The causes of soil pollution include: Chemicals and heavy metal solvents are some toxic elements that cause soil pollution.
When saline water gets mixed with the soil, sometimes it destroys the good qualities of the land during Tsunami and other natural calamities. Acid rain is one of the primary causes of soil pollution and one of the biggest concerns in environmental issues. Excess use of fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides, etc. in agriculture has resulted in a lot of soil pollution.
With time and because of corrosion, accidents like seepage through a landfill, rupture of underground storage tanks, or mixing of contaminated water into the soil can result in polluting the soil. Industrial wastes, nuclear wastes (radioactive wastes), etc. are also some primary reasons for soil pollution.
Due to deforestation, soil erosion takes place, which turns the area into a wasteland. Industrial accidents like the oil spill, acid or chemical spills, etc. are also hazardous and can cause soil pollution. Effects of soil pollution are the ones that negatively impact our environment and change the excellent natural qualities of the soil and cause harm to the life cycle of every living being on the planet.
Some effects of soil pollution to name are: The toxicities of the soil can reduce the productivity quality of it, and this affects the healthy growth of crops and plants. If plants are not grown in the amount or condition they should, it also affects the food cycle for humans and other animals.
If the productivity of the soil decreases due to soil pollution, then the economy is also affected by it. Soil pollution can also cause water pollution by contaminating the drinkable water. Hence, soil pollution also concerns human health. If soil erosion increases, then accidents like landslides and floods can happen. The soil is responsible for the health and development of humankind; hence it is our responsibility to keep it safe and pure and avoid conditions that can cause soil pollution.

Short Essay on Soil Pollution 150 words in English
Soil Pollution essay will be beneficial for students of classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. It will help them understand the structure of writing a short essay on ‘Soil Pollution.’
Soil is a vital element of this planet, and it is directly connected to our survival. The pollution of this precious element has now turned into a global problem and not the only country’s concern. Soil pollution can be defined as the increase of persistent toxic elements in the soil like the presence of chemicals, salts, disease-causing agents, radioactive wastes, or anything that changes the soil’s quality and causes an adverse effect in the growth of the plant and on human health.
Soil pollution can be reduced by proper regulated waste dumping and by avoiding littering, reduced use and throwing of toxic material, recycling of waste materials, decreasing the use of toxic fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides, and instead opting for organic products, stop deforestation by growing more plants (reforestation). It is our role as students to understand the importance of preserving the purity in soil and saving it from contamination by educating others on the matter through the spreading of awareness. we will soonly update Soil Pollution essay in Hindi, Kannada, Punjabi and Telugu.
10 Lines on Soil Pollution Essay in English
- Soil is the outermost layer of the Earth’s surface, which is the foundation of essential environmental functions.
- Drinkable underground water is also possible because the soil layer acts as a filter and a source of essential nutrients to that water.
- Soil also plays a significant role in regulating the Earth’s temperature to make it livable.
- A soil pollutant is an agent that degenerates the quality, composition, mineral quantity of the soil.
- There are two ways by which soil can get polluted: Natural and Anthropogenic.
- Soil contamination or soil pollution should concern us because when the toxic elements of the soil enter the human body because of food-chain, it can cause harm to the inner body-system.
- Corrupt agricultural practices ruin the excellent qualities of the soil in that particular area.
- Contaminants that cause soil pollution are metals, inorganic ions, and salts, including sulfates, phosphates, nitrates, carbonates, etc. Organic compounds like lipid, fatty acids, alcohols, proteins, hydrocarbons, etc.
- Anthropogenic or man-caused soil pollution can be controlled with enough effort by making changes in our industrial processes and some daily activities.
- Soil pollution is an environmental issue that concerns every aspect of life.

FAQ’s on Soil Pollution Essay
Question 1. How does soil pollution cause harm to human health?
Answer: Soils are essential and connected to human health in many ways, such as being the base for growing plants. The land is also a significant source of nutrients, and they act as a natural filter to remove contamination from the drinkable water. Similarly, soil pollution also can leave an adverse effect on human health as contaminated soil contains heavy metals, toxic chemicals, pathogens, etc. that negatively impact human health by entering the body through food directly or indirectly. Soil pollution can cause neuromuscular blockade, nausea, depression, headaches, eye irritation, fatigue, and skin rash.
Question 2. What are the significant causes of soil pollution?
Answer: With the ever-evolving and developing science, industrialization also advances. However, the blessings of manufacturing come with the boon of pollution like industrial or by-product wastes.
Question 3. How does soil pollution affect us other than causing adverse effects on health?
Answer: Other than our health, soil pollution causes harm to the nutrients in the soil by decreasing its fertility. This results in the damage of crop production and eventually affects our economy.
Question 4. How can the necessary household activities cause soil pollution?
Answer: Littering is one of the most fundamental reasons for soil to get polluted. Other than this, excessive urbanization and cutting of trees cause soil erosion. The sewage channel or underground storage, if not done right then it can cause soil pollution. Similarly, if detergent used soap water is dumped on a particular soil, it can harm the soil quality.
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education

Essay on Soil Pollution
Soil pollution refers to the mixture of toxic and harmful substances in the soil.
Soil is one of the important natural resources that are the basis of human survival on this Earth. People are not only dependent on soil for food but they have another connection with it. The soil contains the blood of our brave soldiers and also the hard work of our farmers. People love and give special importance to the soil. But today, the scenario is changed completely and the world is facing the major concern of soil pollution. On seeing the importance of soil and the need to protect it, we will discuss soil pollution in detail.
Short and Long Soil Pollution Essay in English
Here, I’m presenting long and short essays on Soil Pollution in 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, and 500 words. This topic is useful for students of classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12 to write effective essays, paragraphs, or speeches in English.
Soil Pollution Essay 10 Lines (100 – 150 Words)
1) Soil is an important natural resource necessary for human survival.
2) The mixing of toxic substances into the soil is referred to as soil pollution.
3) Soil pollution is harmful to nature as well as to all living organisms.
4) It can be caused due to natural means or due to human interventions.
5) Soil pollution can lead to harmful diseases in humans.
6) It also affects the fertility and quality of the soil.
7) Chemicals from industries and agriculture are the major source of soil pollution.
8) It can be controlled by minimizing chemical fertilizers.
9) Industries should treat chemicals before disposing of them in the soil.
10) Preventing soil pollution will help to live happily on Earth.
Short Essay on Soil Pollution (250 – 300 Words)
One of the most vital components of the nature is soil. At the moment, soil pollution is the main cause of harm to our environment. When plenty of toxic substances are mixed into the soil, it becomes toxic resulting in soil pollution. A soil pollutant is anything that hurts the soil’s quality, texture, or mineral content, or that affects the balance of the living things in the soil.
Soil pollution harms all living organisms in one or another way. It turns soil acidic which is most unfriendly for most microorganisms. However, it affects human health majorly. Soil pollution is caused by dumping pesticides, Herbicides, insecticides, fuel, oil, and other things in the soil. The use of fertilizers to increase soil fertility is harmful to the soil. Solid waste disposal and deforestation are some other causes of soil pollution. Loss of nutrients in the soil is often linked to soil degradation.
Soil pollution is a problem because it hurts not only the crops but also the whole ecosystem. Before putting industrial waste in the soil, it must be made less dangerous. Government should make strict rules for industries. People should be made aware of the hazards of soil pollution. Farmers should use bio-fertilizers instead of chemical fertilizers. Things like plastics and other non-biodegradable substances should be prohibited. Planting more trees will result in minimizing soil erosion and preventing soil pollution.
As the saying goes, “Prevention is better than Cure”, it’s better to take steps to make the world a safer place than to wish you had. Therefore, we should play our part to control soil pollution and make Earth a safer and better place to live.
Long Essay on Soil Pollution (500 Words)
Introduction
Soil is an essential part of our surroundings. It covers the rocky parts of the Earth’s surface and is mainly made up of organic and inorganic substances. Soil pollution is now one of the biggest problems faced by the entire humanity. It is where many small animals live, where plants grow, and where people grow a wide range of crops to keep the cycle of life going.
What is Soil Pollution?
Soil pollution is any unwanted change in the physical, chemical, or biological properties of the soil that affects its fertility and usefulness. It is a big problem for the environment and has long-term effects on people’s health. Soil pollution makes it impossible for plants to grow the way they should. Some contaminants are made by nature, but most are caused by industrialization and human activities.
Causes of Soil Pollution
There are many things that can pollute the soil, but farming and manufacturing are the most common ones. The discharge of wastes and chemicals from industries into the soil without treating them pollutes the soil. Farmers use fertilizers to grow crops but they seep down the soil making it poisonous.
Putting trash in the ground is another common way to pollute the soil. This can be anything from the garbage of homes to waste from factories and hospitals. The poisons in these things can seep into the ground and pollute it.
Effects of Soil Pollution
Soil Pollution is very dangerous to the health of people and other living things. When we eat food grown in polluted soil, the crop absorbs the chemicals, which are then passed on to us and can cause severe life-taking diseases. As an effect of soil pollution, the soil becomes useless and it is no longer used to grow crops. When water from the soil seeps below the ground and gets into natural water bodies, it does a lot of damage to the animals and plants that live there. It can also be responsible for causing soil erosion. Acid rain is made worse in part by dirty soil.
How to Control Soil Pollution?
People can control soil pollution in many ways. The most important thing to solve this problem is to make people aware of the consequences of soil pollution. Industrialists should follow all effective control measures, such as environmental protection laws, to cut down and limit soil pollution. Farmers should stop using excessive pesticides and herbicides and instead can switch to organic fertilizers and compost. People should encourage recycling and reusing solid waste, as well as planting as many trees as possible.
Soil pollution is a worldwide problem that everyone has to deal with. Studies have shown that soil pollution is getting worse in both cities and rural areas at a very scary rate. We can’t let soil’s beauty go away by making it dirty. Therefore, it is high time to apply efforts and save soil from pollution.
I hope the above provided essay on Soil Pollution will be helpful in understanding the effect, causes, and prevention of this type of pollution.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions on Soil Pollution
Ans. Loamy soil is considered best for farming.
Ans. Alluvial soil is mostly found in India.
Ans. Cancer, skin disease, respiratory disease, nervous system damage, etc are some diseases caused by soil pollution
Ans. No, the soil is a non-renewal resource as it takes long years to form.
Related Posts
Essay on digital india, cashless india essay, essay on child is father of the man, essay on causes, effects and prevention of corona virus, essay on dr. sarvepalli radhakrishnan, durga puja essay, essay on summer vacation, essay on my plans for summer vacation, essay on holiday.
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Advanced Cutoff
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Advanced Answer Key
- JEE Advanced Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams

Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2024
- CAT 2024 College Predictor
- TS ICET 2024 Results
- AP ICET Counselling 2024
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Result 2024
- NEET Asnwer Key 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET DU Cut off 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET DU CSAS Portal 2024
- CUET Response Sheet 2024
- CUET Result 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET PG Counselling 2024
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Soil Pollution Essay
Soil is an important part of the resources that Mother Nature provides. The stability of life is unimaginable without the presence of soil; from infrastructure to agriculture, we are totally dependent on soil. But because of some of our actions, the soil we depend on is getting polluted. Here are some essays on the topic ‘soil pollution’.

100 Words Essay On Soil Pollution
One of the vital natural resources that form the cornerstone of human existence on this planet is soil. It provides us with almost everything: the house we live in, the metals we use, minerals, and even those scenic beauties that everybody loves.
But today, this important resource of ours is getting polluted due to some of our actions. Soil pollution is the leading cause of harm to our environment. Overuse of pesticides and herbicides and the release of chemical waste by industries should be immediately banned to prevent soil pollution. Every person, on an individual level, must take responsibility for protecting this important resource.
200 Words Essay On Soil Pollution
The soil is one of the most significant natural resources. It serves as the foundation for food production and provides a variety of habitats for both plants and animals. The relationship between people and the soil goes beyond just their need for food. However, for personal gain, we have allowed improper actions to lead to contamination. Today, soil pollution is the leading cause of disturbance in our lifestyle and our environment.
We have polluted it with chemicals and other unnatural substances, such as the use of urea and other chemicals in agriculture and industries such as tanning and dyeing, which release chemical residue into open water sources and later settle down and pollute the soil. As a result, the quality of the food and water we consume has suffered.
The government should impose strict regulations on various industries. It is important to educate people about the dangers of soil pollution. Biofertilizers should be used by farmers in place of chemical fertilisers. Plastic and other non-biodegradable materials should be banned. In order to reduce soil erosion and stop soil pollution, more trees should be planted.
It's better to take action to make the world a safer place than to wish for it. As a result, we must do our part to reduce soil pollution and make the planet a better and safer place to live.
500 Words Essay On Soil Pollution
It is a well-known fact that the soil is important for us in every way; we depend on it for food, and it provides grazing fields for animals. It is the substratum of every monument that humanity has ever built. Although, because of some of our actions, this important resource of ours is getting polluted, which is harmful not only for us but will also affect other lifeforms.
Soil is a thin layer made up of organic as well as inorganic materials. Earth's rocky surfaces are covered in these substances. There is also the organic component, which comes from the decomposed remains of plants and animals whereas rock fragments make up the inorganic component. Over the course of a thousand years, bedrock underwent chemical and physical weathering, resulting in the formation of this section. In order to provide the world with the necessary food, productive soils are important for agriculture.
Soil is essential for healthy plant growth, human nutrition, and water filtration. A landscape supported by healthy soil is more resistant to the effects of drought, flood, or fire. Soil stores more carbon than all of the world's forests combined, and soil helps to regulate global climate. We cannot survive without healthy soils.
Soil Pollution And Why Is It A Problem
Soil pollution is the process by which toxic chemicals and other pollutants contaminate the soil in high concentrations, affecting the ecosystem. The soil's top layer is disturbed by metals, ions, salts, and organic compounds created by microbial activity and organism decomposition. This slowly seeps into groundwater and then into bodies of water. Pesticides and insecticides used on crops, as well as large-scale radioactive production by humans, pollute the soil.
Humans and other living things are extremely vulnerable to the health effects of soil pollution. When we consume food that was grown in contaminated soil, the crop absorbs the chemicals, which are then ingested by us and can have a serious negative impact on our health. Because of soil pollution, crops can no longer be grown on the soil because it is no longer useful. The plants and animals that inhabit natural water bodies suffer significant harm when soil-derived water seeps through the surface and enters them. It can also be responsible for causing soil erosion. Dirty soil contributes to the worsening of acid rain.
The most crucial action we can take is to stop using pesticides and herbicides in favour of compost and organic fertilisers, refrain from throwing trash or hazardous materials in parks, and use fewer chemical fertilisers. Plastic products should be banned, and anyone found in violation must pay a hefty fine. Before disseminating chemicals into the environment, industries must refine their releases. In order to improve soil quality and stop soil erosion, reforestation is a useful strategy. In order to accomplish that, we must plant as many trees as we can.
Being a country with a sizable amount of agricultural land, we can take action to organise programmes that inform farmers and other locals about the benefits of using natural manure and the harm caused by the use of chemicals.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in

Essay on Soil Pollution for Children and Students

Table of Contents
Soil pollution is caused by a number of factors; however, most of them are human induced. In simple words soil pollution refers to the contamination of the soil when some unwanted external compound gets mixed with it. This compound could be in the form of soluble chemicals or non bio degradable compounds like plastic. Chemical fertilizers and pesticides used in farming are some of the causes of soil pollution. Harmful chemicals get mixed with the soil and make it infertile. Also, waste from the urban areas, if not disposed of properly, reaches the soil and pollutes it. There are several other factors causing soil pollution such as acid rain, industrial accidents, road debris, nuclear waste etc.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
Also Check: Pollution Essay
Long and Short Essay on Soil Pollution in English
We have provided below short and long essay on soil pollution in English for your knowledge and information.
The essays have been written in simple yet effective English to let you know about the causes, effects and meaning of soil pollution.
After reading the essays you will know what soil pollution is, what causes soil pollution, what could be done to prevent soil pollution etc.
These soil pollution essay will be extremely helpful to you in your school and college assignment and speech giving and debate, essay writing competitions.
Essay on Soil Pollution 100 Words
Soil is the natural resource on the earth which directly supports the life of plants and indirectly of animals since the origin of life on the earth. It is very important complex substance available everywhere on the earth. Productive soil is a soil useful to grow crops. As a human being, we need to keep our land safe and secure and away from all the impurities. However, it is not possible because of the technological advancement.
Soil is getting polluted through the toxic substances released by the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides, industrial wastes, etc which are badly affecting the fertility of land. Soil pollution depletes the soil nutrients because of the availability of heavy concentration of undesirable foreign elements into soil through chemicalization.
Also Check: Air Pollution Essay

Essay on Soil Pollution 150 Words
Polluted soil is the low quality soil by various actions of man and natural processes which makes soil unfit for the crop production. Increasing human population and advancement of the human lives is causing soil pollution to a great extent. Main cause of the soil pollution are excessive soil erosion, forest fires, use of chemical fertilizers to improve crop production, pesticides (insecticides and herbicides), biocides (malathion, D.D.T., dieldrin, endrin, aldrin, lindane) to get control over insects, urban and industrial wastes, leaching, drought, untreated industrial water irrigation, water logging, over irrigation, deforestation, etc. It is increasing day by day at a faster rate in the rural and urban areas of the country.
According to the statistics, it is noted that consumption of chemical fertilizers by the farmers has been increased by 5.5 million tons from 1980-81 and by 18.07 million tons from 1999-2000 in order to increase crop production. Such toxic chemicals enter the human body through food chain and harm by causing physical deformities, neural tube defect in the new born babies.
Essay on Soil Pollution 200 Words
Soil pollution is the polluted soil because of the presence of toxic chemicals (also called pollutants or contaminants) in very high concentration to the soil of fertile land. Some of the contaminants occur naturally however most of them are due to the industrialization and human activities. Soil pollutants are generally of two types called as organic and inorganic whether released naturally and man-made. The main reasons of soil pollution are human activities including accidental leaks, spills, manufacturing processes, dumping, etc. Human released toxic chemicals are increasing the overall soil toxicity level.
Also Check: Soil Pollution Slogans
All the soil contaminants get mixed to the fertile land and causes variety of health disorders directly or indirectly such as respiratory illness, bronchitis, asthma, cancer, etc. Kids are more prone to the polluted soil than the adults as they play into it and gets attacked by many diseases especially respiratory disorders. Increasing human population need more grains thus in order to fulfill this requirement people use highly concentrated fertilizers to improve the crop production which ultimately affects health through the food chain. Soil pollution is the gradual process of soil poisoning of the toxic soil contaminants.
Essay on Soil Pollution 250 Words
Soil pollution is the contamination of the soil of fertile land which is gradually increasing day by day mainly because of the use of fertilizers and industrialization. Soil pollution has become a major challenge to the whole human fraternity in modern time. Soil is the most important natural resource highly required to maintain the healthy life here. It is the home for many small animals, it is the life of plants and used by the human beings to produce variety of crops to continue life cycle here. However, increasing human population increases the need of crops production and other technological resources to live life comfortably. There are many highly effective fertilizers available in the market proving their best to improve crop production however getting more toxic and polluting the whole fertile soil when sprinkled over crops.
Varieties of other pesticides (like insecticides, fungicides, etc) are also getting used by the farmers to save their crops from the insects and fungus. Such type of pesticides are also very toxic and spreading their side effects to the environment by polluting the land and air. Other ways of soil pollution are acidification, agrochemical pollution, salinization, and contamination by metalliferous wastes. Acidification is a common natural cause associated with long term leaching and microbial respiration which gradually decomposes the organic materials of soil (like humic and fulvic acids) which again stimulates leaching. Use of inorganic fertilizers on the fertile lands has increased the level of soil pollution by decreasing the soil fertility at a faster rate.
Also Check: Speech on Soil Pollution

Essay on Soil Pollution 300 Words
Soil pollution is the contamination of the fertile soil which reduces the productivity of soil because of various toxic pollutants. Toxic pollutants are very dangerous and adversely affect the physical, chemical and biological properties of the soil. Variety of pollutants such as pesticides, insecticides, fertilizers, chemicals, radioactive wastes, organic manure, discarded food, clothes, plastics, paper, leather goods, bottles, tins-cans, carcasses, etc gets mixed to the soil and cause soil pollution. Other released chemicals by various means like iron, mercury, lead, copper, cadmium, aluminium, zinc, industrial wastes, cyanides, acids, alkalies etc are the toxic chemicals causes soil pollution. Acid rain is a natural cause also affects soil fertility directly.
Earlier, the soil were very much fertile without the use of any fertilizers but now-a-days all the farmers have started using very strong fertilizers in order to increase crop production because of high demand of food by the increasing population. Improper, unnecessary and continuous use of variety of strong organic or inorganic insecticides (DDT, benzene hexa chloride, aldrin, etc), herbicides, fungicides, pesticides, etc in order to secure crops from insects, pests, fungus, etc are gradually toxifying the soil. All types of such chemicals have very dangerous effects directly on the plants growth (inhibits growth, reduces production and reduces size of fruit) and indirectly on the human health. Such chemicals slowly get absorbed by the soil and then plants which ultimately reaches to the animals and human beings body through the food chains.
Other radioactive wastes from the sources like mining and nuclear processes reach to the soil through water and affects the soil and ultimately to the plants, animals (through grazing) and human (through food, milk, meat etc). Eating such type of food causes growth retardation and abnormal growth of the animals and human. Increasing industrialization in the modern world creates huge heap of wastes on daily basis which directly or indirectly gets mixed to the soil and contaminate it.
Also Check: Noise Pollution Essay
Essay on Soil Pollution 400 Words
Soil pollution is the contamination of fresh and fertile soil which adversely affects the health of crops, plants, animals, human beings and other organisms living in it. Addition of variety of unwanted substances and toxic chemicals from many sources to the soil in the odd proportion causes whole land pollution. Once the pollutants gets mixed to the soil remains in direct contact with soil for long period of time. Increasing industrialization and increasing consumption of various effective fertilizers in the fertile land is continuously changing the soil composition and complexion of earth strata which is very dangerous indication to the future of life on the earth.
All the fertile land on the earth is getting heavily polluted gradually day by day through the mixing of toxic materials released by the industries and domestic circles. Major sources of the soil pollution are industrial wastes, urban wastes, chemical pollutants, metallic pollutants, biological agents, radioactive pollutants, wrong agricultural practices, etc. Industrial wastes released by the industrial processes contain organic, inorganic and non-biodegradable materials which have ability to change physiochemical and biological characteristics of the soil. It totally disturbs the level of texture and mineral, bacterial and fungal colonies of the soil.
Urban wastes are solid wastes include commercial and domestic wastes which make a huge heap on the soil and contribute to the soil pollution. Chemical pollutants and metallic pollutants are the industrial wastes from the textile, soap, dyes, synthetic, detergents, metal, and drugs industries which are dumping their hazardous wastes continuously in the soil and water. It directly affects the living organisms of the soil and reduces fertility level of soil. Biological agents (such as bacteria, algae, fungi, protozoan and microorganisms like nematodes, millipedes, earthworms, snail, etc) also disturb the physio chemical and biological atmosphere of soil and cause soil pollution.
Some radioactive pollutants from the sources like nuclear reactors, explosions, hospitals, scientific laboratories, etc go very deep to the soil, remain there for long time and cause soil pollution. Wrong agricultural practices using advance agro-technology means use of huge quantities of toxic fertilizers including herbicides, weedicides, pesticides, etc enhances soil fertility however gradually declines the physio-chemical and biological property of the soil.
Other sources of the soil pollution are municipal garbage heap, food processing wastes, mining practices, and many more. Soil pollution is very hazardous to the health because toxic chemicals enter to the body through food chain and disturbs whole internal body system. In order to reduce and restrict the soil pollution, all the effective control measures including environment protection laws should be followed by the people especially industrialist. Recycling and reuse of the solid wastes and maximum possible tree plantation should be promoted among people.
More Informative Resources on Pollution
Essay on Soil Pollution FAQs
What is soil pollution short note.
Soil pollution happens when harmful substances contaminate the soil, affecting its quality and harming plants, animals, and humans.
What is the short line of soil pollution?
Soil pollution occurs when harmful chemicals or waste spoil the earth's natural balance, making it unfit for healthy growth.
How is soil polluted Class 10?
Soil gets polluted by chemicals from pesticides, industrial waste, improper disposal of garbage, and oil spills, harming its fertility and health.
What is pollution causes and effects?
Pollution is caused by human activities releasing harmful substances into the environment, leading to various detrimental effects on nature, animals, and human health.
What are 10 ways to reduce pollution?
Use public transport, recycle and reuse, conserve energy, plant trees, limit plastic use, proper waste disposal, reduce water wastage, use eco-friendly products, support clean energy, spread awareness.
What is the problem of pollution?
Pollution disrupts the natural balance of the environment, harming ecosystems, endangering wildlife, and impacting human health.
What are the 5 effects of air pollution?
Breathing problems, increased health risks, environmental damage, reduced visibility, climate change.
Related content
Talk to our academic expert!
Language --- English Hindi Marathi Tamil Telugu Malayalam
Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Editorial article, editorial: soil pollution, risk assessment and remediation.

- 1 Institute of Environmental Processes and Pollution Control, School of Environmental and Civil Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, China
- 2 Key Laboratory of Soil Contamination Bioremediation of Zhejiang Province, Zhejiang A & F University, Hangzhou, China
- 3 Key Laboratory of Agro-Forestry Environmental Processes and Ecological Regulation of Hainan Province, College of Ecology and Environment, Hainan University, Haikou, China
- 4 School of Chemistry, Environmental & Life Sciences, University of the Bahamas, Nassau, Bahamas
Editorial on the Research Topic Soil pollution, risk assessment and remediation
Soil pollution is a global issue that poses serious threats to human and ecosystem health ( Singh and Singh, 2020 ). Soils are crucial in providing numerous ecosystem services essential for sustaining life on Earth. However, the alarming reality is that we have been witnessing a rapid loss of the quality of our soils and the invaluable benefits they offer ( Jie et al., 2002 ). For example, it has been estimated that 16.1% of soils are contaminated in China, as reported by the Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection ( MEP, 2014 ). Similar findings have been reported in the United States, where an estimated 294,000 sites require cleanup ( USEPA, 2004 ), and in the United Kingdom, where it is estimated that 2% of the land area of England and Wales is contaminated ( Environment Agency, 2009 ). These figures highlight the widespread nature of soil contamination and the urgent need for action to address this critical problem.
Anthropogenic activities are the primary source of soil contaminants. Both organic and inorganic pollutants can enter the soil matrix through various pathways, including the application of fertilizers and pesticides, improper disposal of wastewater, pharmaceuticals, plastics, and the burning of fossil fuels ( Peña, 2022 ; Gautam et al., 2023 ). Once these pollutants have infiltrated the soil matrix, remediation becomes extremely challenging and costly. Moreover, they can pose significant health risks through the food chain. For instance, studies have demonstrated that heavy metals such as arsenic and cadmium reduce crop yields and severely impede crop quality and food security ( Djahed et al., 2018 ; Yuan et al., 2021 ). Additionally, these organic and inorganic pollutants have been linked to serious illnesses in humans. Trace toxic metals like arsenic, lead, and cadmium have been associated with various types of cancers, while organic substances like polychlorinated biphenyls, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, insecticides, and herbicides have been linked to various human diseases ( Rahman et al., 2015 ).
To date, numerous studies have been conducted to address the soil pollution crisis by developing feasible risk assessment and remediation methods. Researchers have explored both biological and non-biological approaches to tackle this problem. The methods can be categorized as physical, chemical, and biological. Physical methods involve the physical removal, washing, encapsulation, and electrokinetic extraction contaminates in soil ( Liu et al., 2018 ). Chemical methods include soil precipitation and solidification to immobilize and reduce pollutants bioavailability ( Jiang et al., 2023 ). On the other hand, biological methods utilize plants and microorganisms to remove or transform pollutants into less toxic species. Among these approaches, biological methods are considered the most promising due to their ability to mitigate pollutants without generating secondary contaminants and their relative cost-effectiveness compared to physical methods ( Gustave et al., 2022 ). Moreover, other techniques, such as the use of bioreporters, have focused on accurately assessing the risk posed by these contaminants ( Zhang et al., 2022 ; Zhang et al., 2023 ).
Despite the significant amount of work that has been done on soil pollutant risk assessment and remediation, there is still a pressing need for further research in this field. Many existing methods are still in their infancy stages, and only a few have been implemented in real-world field settings. Additionally, there is a crucial requirement for more investigation into the risk assessment of soil and crop contamination resulting from these polluted soils. Recognizing this pressing need, a special focus was placed on this Research Topic, aiming to gather the latest studies that describe results pertaining to various areas, including but not limited to 1) Whole-cell bioreporter and biotic ligand model technology, 2) Bioavailability-based soil pollution risk assessment, 3) Utilization of biochar for soil remediation, 4) Investigation of biogeochemical behaviors of heavy metal(loid)s in soils, 5) Study of degradation, transformation, and immobilization of emerging organic pollutants in soils, and 6) Assessment of the impact of organic and/or inorganic soil amendments on the fate and transport of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils.
A total of nine articles made significant contributions to the Research Topic, consisting of seven Original Research papers, one Brief Research Report, and one Review article. Xu et al. conducted a field study to investigate the effects of biochar and biochar-based fertilizers on soil properties, cadmium availability, and translocation in rice plants grown in cadmium-contaminated rice paddies. Similarly, Antonangelo et al. explored the potential of switchgrass and poultry litter biochar to immobilize and restrict the accumulation of heavy metals in ryegrass. Zhang et al. examined the use of various types of biochar, applied at low rates in the field, to mitigate cadmium contamination in Brassica campestris L. He et al. assessed the prevalence and risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in top soils across China. Similarly, Maurin et al. presented a standardized extraction and analysis method to detect organic pollutants using samples from France. Dong et al. reported on the aggregation of organic amendments on bauxite residue particles and the associated mechanisms. Duan et al. focused on the effects of Paenibacillus sabinae and Leptolyngbya sp. RBD05 on the nutrient and chemical properties of saline-alkali soil. Lastly, Watson and Gustave assessed the potential risks associated with arsenic exposure from consuming market rice in The Bahamas, while Song et al. provided a review on the use of microalgae for wastewater remediation, soil improvement, and enhancement of crop quality.
Collectively, these studies greatly contribute to our understanding of soil pollution, its effects, and potential remediation strategies. Notably, the studies conducted by Xu et al. , Zhang et al. , and Antonangelo et al. provide valuable insights into the latest use of soil amendment, such as biochar, for effectively remediating cadmium and other trace toxic heavy metals. This is particularly crucial considering cadmium’s ranking as the foremost heavy metal contaminant in Chinese soils ( Zhao et al., 2015 ). Furthermore, the review by Song et al. and the studies by Duan et al. and Dong et al. shed further light on how microorganisms can play a vital role in bioremediation, establishing it as the most promising method. Additionally, other articles within this Research Topic present innovative standardized approaches for detecting organic pollutants, addressing a challenging issue that obstructs the accurate assessment of organic pollutants in soils. Lastly, the paper by Watson and Gustave unveils the extent of arsenic contamination in the market rice available in the Bahamas, a Small Island Developing State. While these articles have made significant contributions to our understanding of the subject, it is crucial to emphasize that substantial further research is required to tackle the pressing issue of soil pollution, mitigate associated human and ecological risks, and pave the way for effective solutions.
Author contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
Acknowledgments
We would like to extend our heartfelt appreciation to the numerous reviewers who generously volunteered their time to assist the authors in enhancing their manuscripts.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Djahed, B., Taghavi, M., Farzadkia, M., Norzaee, S., and Miri, M. (2018). Stochastic exposure and health risk assessment of rice contamination to the heavy metals in the market of Iranshahr, Iran. Food Chem. Toxicol. 115, 405–412. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2018.03.040
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Environment Agency (2009). Reporting the evidence: Dealing with contaminated land in England and Wales: A review of progress from 2000–2007 with Part 2A of the environmental protection act . Bristol, UK .
Google Scholar
Gautam, K., Sharma, P., Dwivedi, S., Singh, A., Gaur, V. K., Varjani, S., et al. (2023). A review on control and abatement of soil pollution by heavy metals: Emphasis on artificial intelligence in recovery of contaminated soil. Environ. Res. 115592, 115592. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2023.115592
Gustave, W., Yuan, Z., Liu, F., and Chen, Z. (2021). Mechanisms and challenges of microbial fuel cells for soil heavy metal (loid) s remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 756, 143865. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143865
Jiang, M., He, L., Niazi, N. K., Wang, H., Gustave, W., Vithanage, M., et al. (2023). Nanobiochar for the remediation of contaminated soil and water: Challenges and opportunities. Biochar 5 (1), 2. doi:10.1007/s42773-022-00201-x
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Jie, C., Jing, Z. C., Man, Z. T., and Zi, T. G. (2002). Soil degradation: A global problem endangering sustainable development. J. Geogr. Scie. 12, 243–252. doi:10.1007/bf02837480
Liu, L., Li, W., Song, W., and Guo, M. (2018). Remediation techniques for heavy metal-contaminated soils: Principles and applicability. Sci. Total Environ. 633, 206–219. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.161
Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP) (2014). National soil contamination survey report . Beijing, China: Ministry of Environmental Protection . Available at: http://www.mep.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/qt/201404/t20140417_270670 .
Peña, A. (2022). A comprehensive review of recent research concerning the role of low molecular weight organic acids on the fate of organic pollutants in soil. J. Hazard. Mat. 434, 128875. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128875
Rahman, M. M., Dong, Z., and Naidu, R. (2015). Concentrations of arsenic and other elements in groundwater of Bangladesh and West Bengal, India: Potential cancer risk. Chemosphere 139, 54–64. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.05.051
Singh, S. P., and Singh, M. K. (2020). “Soil pollution and human health,” in Plant responses to soil pollution . Editors P. Singh, S. K. Singh, and S. M. Prasad (Singapore: Springer ).
US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (2004). Cleaning up the nation’s waste sites: Markets and technology trends , Washington, DC
Yuan, H., Wan, Q., Huang, Y., Chen, Z., He, X., Gustave, W., et al. (2021). Warming facilitates microbial reduction and release of arsenic in flooded paddy soil and arsenic accumulation in rice grains. J. Hazard. Mat. 408, 124913. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124913
Zhang, X., Jiang, M., He, L., Niazi, N. K., Vithanage, M., Li, B., et al. (2023). Pandemic COVID-19 ends but soil pollution increases: Impacts and a new approach for risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 890, 164070. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164070
Zhang, X., Li, B., Schillereff, D. N., Chiverrell, R. C., Tefsen, B., and Wells, M. (2022). Whole-cell biosensors for determination of bioavailable pollutants in soils and sediments: Theory and practice. Sci. Total Environ. 811, 152178. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152178
Zhao, F. J., Ma, Y., Zhu, Y. G., Tang, Z., and McGrath, S. P. (2015). Soil contamination in China: Current status and mitigation strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49 (2), 750–759. doi:10.1021/es5047099
Keywords: soil contamination, bioavailability, biogeochemistry, environmental toxicity, biochar
Citation: Zhang X, He L, Yang X and Gustave W (2023) Editorial: Soil pollution, risk assessment and remediation. Front. Environ. Sci. 11:1252139. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2023.1252139
Received: 04 July 2023; Accepted: 07 July 2023; Published: 18 July 2023.
Edited and reviewed by:
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, He, Yang and Gustave. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Williamson Gustave, [email protected]
This article is part of the Research Topic
Soil Pollution, Risk Assessment and Remediation
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment. These harmful materials are called pollutants.
Biology, Ecology, Health, Earth Science, Geography
Loading ...
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment . These harmful materials are called pollutants . Pollutants can be natural, such as volcanic ash . They can also be created by human activity, such as trash or runoff produced by factories. Pollutants damage the quality of air, water, and land. Many things that are useful to people produce pollution. Cars spew pollutants from their exhaust pipes. Burning coal to create electricity pollutes the air. Industries and homes generate garbage and sewage that can pollute the land and water. Pesticides —chemical poisons used to kill weeds and insects— seep into waterways and harm wildlife . All living things—from one-celled microbes to blue whales—depend on Earth ’s supply of air and water. When these resources are polluted, all forms of life are threatened. Pollution is a global problem. Although urban areas are usually more polluted than the countryside, pollution can spread to remote places where no people live. For example, pesticides and other chemicals have been found in the Antarctic ice sheet . In the middle of the northern Pacific Ocean, a huge collection of microscopic plastic particles forms what is known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch . Air and water currents carry pollution. Ocean currents and migrating fish carry marine pollutants far and wide. Winds can pick up radioactive material accidentally released from a nuclear reactor and scatter it around the world. Smoke from a factory in one country drifts into another country. In the past, visitors to Big Bend National Park in the U.S. state of Texas could see 290 kilometers (180 miles) across the vast landscape . Now, coal-burning power plants in Texas and the neighboring state of Chihuahua, Mexico have spewed so much pollution into the air that visitors to Big Bend can sometimes see only 50 kilometers (30 miles). The three major types of pollution are air pollution , water pollution , and land pollution . Air Pollution Sometimes, air pollution is visible . A person can see dark smoke pour from the exhaust pipes of large trucks or factories, for example. More often, however, air pollution is invisible . Polluted air can be dangerous, even if the pollutants are invisible. It can make people’s eyes burn and make them have difficulty breathing. It can also increase the risk of lung cancer . Sometimes, air pollution kills quickly. In 1984, an accident at a pesticide plant in Bhopal, India, released a deadly gas into the air. At least 8,000 people died within days. Hundreds of thou sands more were permanently injured. Natural disasters can also cause air pollution to increase quickly. When volcanoes erupt , they eject volcanic ash and gases into the atmosphere . Volcanic ash can discolor the sky for months. After the eruption of the Indonesian volcano of Krakatoa in 1883, ash darkened the sky around the world. The dimmer sky caused fewer crops to be harvested as far away as Europe and North America. For years, meteorologists tracked what was known as the “equatorial smoke stream .” In fact, this smoke stream was a jet stream , a wind high in Earth’s atmosphere that Krakatoa’s air pollution made visible. Volcanic gases , such as sulfur dioxide , can kill nearby residents and make the soil infertile for years. Mount Vesuvius, a volcano in Italy, famously erupted in 79, killing hundreds of residents of the nearby towns of Pompeii and Herculaneum. Most victims of Vesuvius were not killed by lava or landslides caused by the eruption. They were choked, or asphyxiated , by deadly volcanic gases. In 1986, a toxic cloud developed over Lake Nyos, Cameroon. Lake Nyos sits in the crater of a volcano. Though the volcano did not erupt, it did eject volcanic gases into the lake. The heated gases passed through the water of the lake and collected as a cloud that descended the slopes of the volcano and into nearby valleys . As the toxic cloud moved across the landscape, it killed birds and other organisms in their natural habitat . This air pollution also killed thousands of cattle and as many as 1,700 people. Most air pollution is not natural, however. It comes from burning fossil fuels —coal, oil , and natural gas . When gasoline is burned to power cars and trucks, it produces carbon monoxide , a colorless, odorless gas. The gas is harmful in high concentrations , or amounts. City traffic produces highly concentrated carbon monoxide. Cars and factories produce other common pollutants, including nitrogen oxide , sulfur dioxide, and hydrocarbons . These chemicals react with sunlight to produce smog , a thick fog or haze of air pollution. The smog is so thick in Linfen, China, that people can seldom see the sun. Smog can be brown or grayish blue, depending on which pollutants are in it. Smog makes breathing difficult, especially for children and older adults. Some cities that suffer from extreme smog issue air pollution warnings. The government of Hong Kong, for example, will warn people not to go outside or engage in strenuous physical activity (such as running or swimming) when smog is very thick.
When air pollutants such as nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide mix with moisture, they change into acids . They then fall back to earth as acid rain . Wind often carries acid rain far from the pollution source. Pollutants produced by factories and power plants in Spain can fall as acid rain in Norway. Acid rain can kill all the trees in a forest . It can also devastate lakes, streams, and other waterways. When lakes become acidic, fish can’t survive . In Sweden, acid rain created thousands of “ dead lakes ,” where fish no longer live. Acid rain also wears away marble and other kinds of stone . It has erased the words on gravestones and damaged many historic buildings and monuments . The Taj Mahal , in Agra, India, was once gleaming white. Years of exposure to acid rain has left it pale. Governments have tried to prevent acid rain by limiting the amount of pollutants released into the air. In Europe and North America, they have had some success, but acid rain remains a major problem in the developing world , especially Asia. Greenhouse gases are another source of air pollution. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane occur naturally in the atmosphere. In fact, they are necessary for life on Earth. They absorb sunlight reflected from Earth, preventing it from escaping into space. By trapping heat in the atmosphere, they keep Earth warm enough for people to live. This is called the greenhouse effect . But human activities such as burning fossil fuels and destroying forests have increased the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This has increased the greenhouse effect, and average temperatures across the globe are rising. The decade that began in the year 2000 was the warmest on record. This increase in worldwide average temperatures, caused in part by human activity, is called global warming . Global warming is causing ice sheets and glaciers to melt. The melting ice is causing sea levels to rise at a rate of two millimeters (0.09 inches) per year. The rising seas will eventually flood low-lying coastal regions . Entire nations, such as the islands of Maldives, are threatened by this climate change . Global warming also contributes to the phenomenon of ocean acidification . Ocean acidification is the process of ocean waters absorbing more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Fewer organisms can survive in warmer, less salty waters. The ocean food web is threatened as plants and animals such as coral fail to adapt to more acidic oceans. Scientists have predicted that global warming will cause an increase in severe storms . It will also cause more droughts in some regions and more flooding in others. The change in average temperatures is already shrinking some habitats, the regions where plants and animals naturally live. Polar bears hunt seals from sea ice in the Arctic. The melting ice is forcing polar bears to travel farther to find food , and their numbers are shrinking. People and governments can respond quickly and effectively to reduce air pollution. Chemicals called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are a dangerous form of air pollution that governments worked to reduce in the 1980s and 1990s. CFCs are found in gases that cool refrigerators, in foam products, and in aerosol cans . CFCs damage the ozone layer , a region in Earth’s upper atmosphere. The ozone layer protects Earth by absorbing much of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation . When people are exposed to more ultraviolet radiation, they are more likely to develop skin cancer, eye diseases, and other illnesses. In the 1980s, scientists noticed that the ozone layer over Antarctica was thinning. This is often called the “ ozone hole .” No one lives permanently in Antarctica. But Australia, the home of more than 22 million people, lies at the edge of the hole. In the 1990s, the Australian government began an effort to warn people of the dangers of too much sun. Many countries, including the United States, now severely limit the production of CFCs. Water Pollution Some polluted water looks muddy, smells bad, and has garbage floating in it. Some polluted water looks clean, but is filled with harmful chemicals you can’t see or smell. Polluted water is unsafe for drinking and swimming. Some people who drink polluted water are exposed to hazardous chemicals that may make them sick years later. Others consume bacteria and other tiny aquatic organisms that cause disease. The United Nations estimates that 4,000 children die every day from drinking dirty water. Sometimes, polluted water harms people indirectly. They get sick because the fish that live in polluted water are unsafe to eat. They have too many pollutants in their flesh. There are some natural sources of water pollution. Oil and natural gas, for example, can leak into oceans and lakes from natural underground sources. These sites are called petroleum seeps . The world’s largest petroleum seep is the Coal Oil Point Seep, off the coast of the U.S. state of California. The Coal Oil Point Seep releases so much oil that tar balls wash up on nearby beaches . Tar balls are small, sticky pieces of pollution that eventually decompose in the ocean.
Human activity also contributes to water pollution. Chemicals and oils from factories are sometimes dumped or seep into waterways. These chemicals are called runoff. Chemicals in runoff can create a toxic environment for aquatic life. Runoff can also help create a fertile environment for cyanobacteria , also called blue-green algae . Cyanobacteria reproduce rapidly, creating a harmful algal bloom (HAB) . Harmful algal blooms prevent organisms such as plants and fish from living in the ocean. They are associated with “ dead zones ” in the world’s lakes and rivers, places where little life exists below surface water. Mining and drilling can also contribute to water pollution. Acid mine drainage (AMD) is a major contributor to pollution of rivers and streams near coal mines . Acid helps miners remove coal from the surrounding rocks . The acid is washed into streams and rivers, where it reacts with rocks and sand. It releases chemical sulfur from the rocks and sand, creating a river rich in sulfuric acid . Sulfuric acid is toxic to plants, fish, and other aquatic organisms. Sulfuric acid is also toxic to people, making rivers polluted by AMD dangerous sources of water for drinking and hygiene . Oil spills are another source of water pollution. In April 2010, the Deepwater Horizon oil rig exploded in the Gulf of Mexico, causing oil to gush from the ocean floor. In the following months, hundreds of millions of gallons of oil spewed into the gulf waters. The spill produced large plumes of oil under the sea and an oil slick on the surface as large as 24,000 square kilometers (9,100 square miles). The oil slick coated wetlands in the U.S. states of Louisiana and Mississippi, killing marsh plants and aquatic organisms such as crabs and fish. Birds, such as pelicans , became coated in oil and were unable to fly or access food. More than two million animals died as a result of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Buried chemical waste can also pollute water supplies. For many years, people disposed of chemical wastes carelessly, not realizing its dangers. In the 1970s, people living in the Love Canal area in Niagara Falls, New York, suffered from extremely high rates of cancer and birth defects . It was discovered that a chemical waste dump had poisoned the area’s water. In 1978, 800 families living in Love Canal had to a bandon their homes. If not disposed of properly, radioactive waste from nuclear power plants can escape into the environment. Radioactive waste can harm living things and pollute the water. Sewage that has not been properly treated is a common source of water pollution. Many cities around the world have poor sewage systems and sewage treatment plants. Delhi, the capital of India, is home to more than 21 million people. More than half the sewage and other waste produced in the city are dumped into the Yamuna River. This pollution makes the river dangerous to use as a source of water for drinking or hygiene. It also reduces the river’s fishery , resulting in less food for the local community. A major source of water pollution is fertilizer used in agriculture . Fertilizer is material added to soil to make plants grow larger and faster. Fertilizers usually contain large amounts of the elements nitrogen and phosphorus , which help plants grow. Rainwater washes fertilizer into streams and lakes. There, the nitrogen and phosphorus cause cyanobacteria to form harmful algal blooms. Rain washes other pollutants into streams and lakes. It picks up animal waste from cattle ranches. Cars drip oil onto the street, and rain carries it into storm drains , which lead to waterways such as rivers and seas. Rain sometimes washes chemical pesticides off of plants and into streams. Pesticides can also seep into groundwater , the water beneath the surface of the Earth. Heat can pollute water. Power plants, for example, produce a huge amount of heat. Power plants are often located on rivers so they can use the water as a coolant . Cool water circulates through the plant, absorbing heat. The heated water is then returned to the river. Aquatic creatures are sensitive to changes in temperature. Some fish, for example, can only live in cold water. Warmer river temperatures prevent fish eggs from hatching. Warmer river water also contributes to harmful algal blooms. Another type of water pollution is simple garbage. The Citarum River in Indonesia, for example, has so much garbage floating in it that you cannot see the water. Floating trash makes the river difficult to fish in. Aquatic animals such as fish and turtles mistake trash, such as plastic bags, for food. Plastic bags and twine can kill many ocean creatures. Chemical pollutants in trash can also pollute the water, making it toxic for fish and people who use the river as a source of drinking water. The fish that are caught in a polluted river often have high levels of chemical toxins in their flesh. People absorb these toxins as they eat the fish. Garbage also fouls the ocean. Many plastic bottles and other pieces of trash are thrown overboard from boats. The wind blows trash out to sea. Ocean currents carry plastics and other floating trash to certain places on the globe, where it cannot escape. The largest of these areas, called the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, is in a remote part of the Pacific Ocean. According to some estimates, this garbage patch is the size of Texas. The trash is a threat to fish and seabirds, which mistake the plastic for food. Many of the plastics are covered with chemical pollutants. Land Pollution Many of the same pollutants that foul the water also harm the land. Mining sometimes leaves the soil contaminated with dangerous chemicals. Pesticides and fertilizers from agricultural fields are blown by the wind. They can harm plants, animals, and sometimes people. Some fruits and vegetables absorb the pesticides that help them grow. When people consume the fruits and vegetables, the pesticides enter their bodies. Some pesticides can cause cancer and other diseases. A pesticide called DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) was once commonly used to kill insects, especially mosquitoes. In many parts of the world, mosquitoes carry a disease called malaria , which kills a million people every year. Swiss chemist Paul Hermann Muller was awarded the Nobel Prize for his understanding of how DDT can control insects and other pests. DDT is responsible for reducing malaria in places such as Taiwan and Sri Lanka. In 1962, American biologist Rachel Carson wrote a book called Silent Spring , which discussed the dangers of DDT. She argued that it could contribute to cancer in humans. She also explained how it was destroying bird eggs, which caused the number of bald eagles, brown pelicans, and ospreys to drop. In 1972, the United States banned the use of DDT. Many other countries also banned it. But DDT didn’t disappear entirely. Today, many governments support the use of DDT because it remains the most effective way to combat malaria. Trash is another form of land pollution. Around the world, paper, cans, glass jars, plastic products, and junked cars and appliances mar the landscape. Litter makes it difficult for plants and other producers in the food web to create nutrients . Animals can die if they mistakenly eat plastic. Garbage often contains dangerous pollutants such as oils, chemicals, and ink. These pollutants can leech into the soil and harm plants, animals, and people. Inefficient garbage collection systems contribute to land pollution. Often, the garbage is picked up and brought to a dump, or landfill . Garbage is buried in landfills. Sometimes, communities produce so much garbage that their landfills are filling up. They are running out of places to dump their trash. A massive landfill near Quezon City, Philippines, was the site of a land pollution tragedy in 2000. Hundreds of people lived on the slopes of the Quezon City landfill. These people made their living from recycling and selling items found in the landfill. However, the landfill was not secure. Heavy rains caused a trash landslide, killing 218 people. Sometimes, landfills are not completely sealed off from the land around them. Pollutants from the landfill leak into the earth in which they are buried. Plants that grow in the earth may be contaminated, and the herbivores that eat the plants also become contaminated. So do the predators that consume the herbivores. This process, where a chemical builds up in each level of the food web, is called bioaccumulation . Pollutants leaked from landfills also leak into local groundwater supplies. There, the aquatic food web (from microscopic algae to fish to predators such as sharks or eagles) can suffer from bioaccumulation of toxic chemicals. Some communities do not have adequate garbage collection systems, and trash lines the side of roads. In other places, garbage washes up on beaches. Kamilo Beach, in the U.S. state of Hawai'i, is littered with plastic bags and bottles carried in by the tide . The trash is dangerous to ocean life and reduces economic activity in the area. Tourism is Hawai'i’s largest industry . Polluted beaches discourage tourists from investing in the area’s hotels, restaurants, and recreational activities. Some cities incinerate , or burn, their garbage. Incinerating trash gets rid of it, but it can release dangerous heavy metals and chemicals into the air. So while trash incinerators can help with the problem of land pollution, they sometimes add to the problem of air pollution. Reducing Pollution Around the world, people and governments are making efforts to combat pollution. Recycling, for instance, is becoming more common. In recycling, trash is processed so its useful materials can be used again. Glass, aluminum cans, and many types of plastic can be melted and reused . Paper can be broken down and turned into new paper. Recycling reduces the amount of garbage that ends up in landfills, incinerators, and waterways. Austria and Switzerland have the highest recycling rates. These nations recycle between 50 and 60 percent of their garbage. The United States recycles about 30 percent of its garbage. Governments can combat pollution by passing laws that limit the amount and types of chemicals factories and agribusinesses are allowed to use. The smoke from coal-burning power plants can be filtered. People and businesses that illegally dump pollutants into the land, water, and air can be fined for millions of dollars. Some government programs, such as the Superfund program in the United States, can force polluters to clean up the sites they polluted. International agreements can also reduce pollution. The Kyoto Protocol , a United Nations agreement to limit the emission of greenhouse gases, has been signed by 191 countries. The United States, the world’s second-largest producer of greenhouse gases, did not sign the agreement. Other countries, such as China, the world’s largest producer of greenhouse gases, have not met their goals. Still, many gains have been made. In 1969, the Cuyahoga River, in the U.S. state of Ohio, was so clogged with oil and trash that it caught on fire. The fire helped spur the Clean Water Act of 1972. This law limited what pollutants could be released into water and set standards for how clean water should be. Today, the Cuyahoga River is much cleaner. Fish have returned to regions of the river where they once could not survive. But even as some rivers are becoming cleaner, others are becoming more polluted. As countries around the world become wealthier, some forms of pollution increase. Countries with growing economies usually need more power plants, which produce more pollutants. Reducing pollution requires environmental, political, and economic leadership. Developed nations must work to reduce and recycle their materials, while developing nations must work to strengthen their economies without destroying the environment. Developed and developing countries must work together toward the common goal of protecting the environment for future use.
How Long Does It Last? Different materials decompose at different rates. How long does it take for these common types of trash to break down?
- Paper: 2-4 weeks
- Orange peel: 6 months
- Milk carton: 5 years
- Plastic bag: 15 years
- Tin can: 100 years
- Plastic bottle: 450 years
- Glass bottle: 500 years
- Styrofoam: Never
Indoor Air Pollution The air inside your house can be polluted. Air and carpet cleaners, insect sprays, and cigarettes are all sources of indoor air pollution.
Light Pollution Light pollution is the excess amount of light in the night sky. Light pollution, also called photopollution, is almost always found in urban areas. Light pollution can disrupt ecosystems by confusing the distinction between night and day. Nocturnal animals, those that are active at night, may venture out during the day, while diurnal animals, which are active during daylight hours, may remain active well into the night. Feeding and sleep patterns may be confused. Light pollution also indicates an excess use of energy. The dark-sky movement is a campaign by people to reduce light pollution. This would reduce energy use, allow ecosystems to function more normally, and allow scientists and stargazers to observe the atmosphere.
Noise Pollution Noise pollution is the constant presence of loud, disruptive noises in an area. Usually, noise pollution is caused by construction or nearby transportation facilities, such as airports. Noise pollution is unpleasant, and can be dangerous. Some songbirds, such as robins, are unable to communicate or find food in the presence of heavy noise pollution. The sound waves produced by some noise pollutants can disrupt the sonar used by marine animals to communicate or locate food.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Illustrators
Educator reviewer, last updated.
March 6, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

Children play on the shore of Manila Bay in the Philippines, which is polluted by plastic waste.
- ENVIRONMENT
The world's plastic pollution crisis, explained
Much of the planet is swimming in discarded plastic, which is harming animal and possibly human health. Can it be cleaned up?
Plastic pollution has become one of the most pressing environmental issues , as rapidly increasing production of disposable plastic products overwhelms the world’s ability to deal with them. Plastic pollution is most visible in developing Asian and African nations, where garbage collection systems are often inefficient or nonexistent. But the developed world, especially in countries with low recycling rates , also has trouble properly collecting discarded plastics. Plastic trash has become so ubiquitous it has prompted efforts to write a global treaty negotiated by the United Nations.
Why was plastic invented?
Plastics made from fossil fuels are just over a century old. Production and development of thousands of new plastic products accelerated after World War II, so transforming the modern age that life without plastics would be unrecognizable today. In plastic, inventors found a light, durable material that can be used in everything from transportation to medicine.
Plastics revolutionized medicine with life-saving devices, made space travel possible, lightened cars and jets—saving fuel and pollution—and saved lives with helmets, incubators, and equipment for clean drinking water.
The conveniences plastics offer, however, led to a throw-away culture that reveals the material’s dark side: today, single-use plastics account for 40 percent of the plastic produced every year. Many of these products, such as plastic bags and food wrappers, have a lifespan of mere minutes to hours, yet they may persist in the environment for hundreds of years.
Plastics by the numbers
Some key facts:
- Half of all plastics ever manufactured have been made in the last 20 years.
- Production increased exponentially, from 2.3 million tons in 1950 to 448 million tons by 2015. Production is expected to double by 2050.
- Every year, about eight million tons of plastic waste escapes into the oceans from coastal nations. That’s the equivalent of setting five garbage bags full of trash on every foot of coastline around the world.
- Plastics often contain additives making them stronger, more flexible, and durable. But many of these additives can extend the life of products if they become litter, with some estimates ranging to at least 400 years to break down.
How plastics move around the world
Most of the plastic trash in the oceans, Earth’s last sink, flows from land. Trash is also carried to sea by major rivers , which act as conveyor belts, picking up more and more trash as they move downstream. Once at sea, much of the plastic trash remains in coastal waters. But once caught up in ocean currents, it can be transported around the world.
On Henderson Island , an uninhabited atoll in the Pitcairn Group isolated halfway between Chile and New Zealand, scientists found plastic items from Russia, the United States, Europe, South America, Japan, and China. They were carried to the South Pacific by the South Pacific gyre, a circular ocean current.
Microplastics—a new health threat
Once at sea, sunlight, wind, and wave action break down plastic waste into small particles, often less than one-fifth of an inch across. These so-called microplastics are spread throughout the water column and have been found in every corner of the globe, from Mount Everest, the highest peak, to the Mariana Trench , the deepest trough.
You May Also Like

The world’s nations agree to fix the plastic waste crisis

How a dramatic win in plastic waste case may curb ocean pollution

The Haunting Art of Plastic Pollution
Microplastics are breaking down further into smaller and smaller pieces. Plastic microfibers, meanwhile, have been found in municipal drinking water systems and drifting through the air.
It's no surprise then that scientists have found microplastics in people. The tiny particles are in our blood, lungs, and even in feces . Exactly how much microplastics might be harming human health is a question scientists are urgently trying to answer. ( Learn more. )
Harm to wildlife
Millions of animals are killed by plastics every year, from birds to fish to other marine organisms. Nearly 700 species, including endangered ones, are known to have been affected by plastics. Nearly every species of seabird eats plastics.
Most of the deaths to animals are caused by entanglement or starvation. Seals, whales , turtles, and other animals are strangled by abandoned fishing gear or discarded six-pack rings . Microplastics have been found in more than 100 aquatic species, including fish, shrimp, and mussels destined for our dinner plates. In many cases, these tiny bits pass through the digestive system and are expelled without consequence. But plastics have also been found to have blocked digestive tracts or pierced organs, causing death. Stomachs so packed with plastics reduce the urge to eat, causing starvation.
Plastics have been consumed by land-based animals, including elephants, hyenas, zebras, tigers, camels, cattle, and other large mammals, in some cases causing death .
Tests have also confirmed liver and cell damage and disruptions to reproductive systems, prompting some species, such as oysters, to produce fewer eggs. New research shows that larval fish are eating nanofibers in the first days of life, raising new questions about the effects of plastics on fish populations.
Stopping plastic pollution
Once in the ocean, it is difficult—if not impossible—to retrieve plastic waste. Mechanical systems, such as Mr. Trash Wheel , a litter interceptor in Maryland’s Baltimore Harbor, can be effective at picking up large pieces of plastic, such as foam cups and food containers, from inland waters. But once plastics break down into microplastics and drift throughout the water column in the open ocean, they are virtually impossible to recover.
The solution is to prevent plastic waste from entering rivers and seas in the first place, many scientists and conservationists—including the National Geographic Society —say. This could be accomplished with improved waste management systems and recycling , better product design that takes into account the short life of disposable packaging, and a reduction in manufacturing of unnecessary single-use plastics.
Related Topics
- WATER POLLUTION
- TOXIC WASTE

We Made Plastic. We Depend on It. Now We’re Drowning in It.

In a first, microplastic particles have been linked to heart disease

One Stanley bottle helps the environment. But a whole collection?

‘Forever chemicals’ are hiding in your kitchen. Here’s where—and what you can do

We got rid of BPA in some products—but are the substitutes any safer?
- Environment
- Paid Content
- Photography
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Assessing spatiotemporal risks of nonpoint source pollution via soil erosion: a coastal case in the Yellow River Delta, China
- Wang, Youxiao
- Huang, Chong
- Liu, Gaohuan
- Zhao, Zhonghe
- Sun, Yingjun
Nonpoint source pollution (NPSP) has always been the dominant threat to regional waters. Based on empirical models of the revised universal soil loss equation and the phosphorus index, an NPSP risk assessment model denoted as SL-NPSRI was developed. The surface soil pollutant loss was estimated by simulating the rain-runoff topographic process, and the influence of path attenuation was quantified. A case study in the Yellow River Delta and corresponding field surveys of soil pollutants and water quality showed that the established model can be applied to evaluate the spatial heterogeneity of NPSP. NPSP usually occurs during high-intensity rainfall periods and in larger estuaries. Summer rainfall increased pollutant transport into the sea from late July to mid-August and caused estuarine dilution. Higher NPSP risks often correspond to coastal areas with lower vegetation coverage, higher soil erodibility, and higher soil pollutant concentrations. Agricultural NPSP originating from cropland significantly increase the pollutant fluxes. Therefore, area-specific land use management and vegetation coverage improvement, and temporal-specific strategies can be explored for NPSP control during source-transport hydrological processes. This research provides a novel insight for coastal NPSP simulations by comprehensively analyzing the soil erosion process and its associated pollutant loss effects, which can be useful for targeted spatiotemporal solutions.
- Yellow River Delta;
- Soil erosion;
- Rainfall influence;
- Total nitrogen;
- Total phosphorus;
- Nonpoint source pollution
Soil Pollution
What causes Soil Pollution? Human activities are the primary cause of soil pollution and land degradation. By the end of this topic, you will know how different forms of human activities are responsible for the majority of different types of soil pollution.
Suggested Videos

What is Soil Pollution
Soil Pollution has gradually become a major challenge that we need to overcome for establishing a healthy environment . Weathering of the earth’s crusts by different processes leads to the formation of soil that accumulates over the centuries. The soil is the home for a large part of bacterial biodiversity and other microscopic and macroscopic living organisms .

Example of Soil Pollution (Source: Wikipedia)
However, let us consider our very own country India. Indian economy is largely dependent on agriculture. Thus, we Indians give very high priority to the development of agriculture , fisheries, and livestock. Therefore, for surplus production, it is very important to protect crops from any type of damage that occurs due to insects, weeds, rodents and other crop diseases.
So, how do we protect crops? The very obvious answer is pesticides and herbicides. However, do you know these pesticides and herbicides is a leading cause of soil pollution? Therefore, it is very important to judiciously use pesticides because it contains lots of different harmful chemicals. Therefore, to improve soil and prevent soil pollution it is important to limit the use of pesticides and herbicides.
Causes of Soil Erosion here.
Types of Soil Pollutants
- Heavy metals (such as lead and mercury, at excessively high amounts) in the soil can make it very poisonous to humans.
- PAHs (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) are a class of organic chemicals where only carbon and hydrogen atoms are present.
- Coke (coal) production, automobile emissions, cigarette smoke, and shale oil extraction are all sources of PAHs in the soil.
- Industrial Waste Soil contamination can come from the dumping of industrial waste into soils.
- Pesticides are chemicals (or chemical mixes) that are used to kill or prevent pests from reproducing.
However, unintended pesticide dispersion into the environment (often referred to as “pesticide drift”) raises a number of environmental issues, including water and soil degradation.
Definition of Soil Pollution
Soil pollution refers to anything that causes contamination of soil and degrades the soil quality. It occurs when the pollutants causing the pollution reduce the quality of the soil and convert the soil inhabitable for microorganisms and macro organisms living in the soil.
Soil contamination or soil pollution can occur either because of human activities or because of natural processes. However, mostly it is due to human activities. The soil contamination can occur due to the presence of chemicals such as pesticides, herbicides, ammonia , petroleum hydrocarbons , lead, nitrate, mercury, naphthalene, etc in an excess amount.

The primary cause of soil pollution is a lack of awareness in general people. Thus, due to many different human activities such as overuse of pesticides the soil will lose its fertility. Moreover, the presence of excess chemicals will increase the alkalinity or acidity of soil thus degrading the soil quality. This will in turn cause soil erosion . This soil erosion refers to soil pollution.
Causes of Soil Pollution
Soil pollution can be natural or due to human activity. However, it mostly boils down to the activities of the human that causes the majority of soil pollution such as heavy industries, or pesticides in agriculture.
Before World War II , the chemical nicotine chemical present in the tobacco plants was used as the pest controlling substance in agricultural practices. However, DDT was found to be extremely useful for malaria control and as pest control of many insects during World War II. Therefore, it was used for controlling many diseases.
Hence, post-war, people started using it as pest control in agriculture for killing rodents , weeds, insects, etc and avoiding the damages due to these pests. However, everyone gradually the adverse effects of this chemical which led to the ban of this chemical in many parts of the world including India.
Moreover, pests became resistance to DDT due to the chemicals regular use. Hence this led to the introduction of other harmful chemicals such as Aldrin and Dieldrin. Pesticides are synthetic toxic chemicals that definitely kill different types of pests and insects causing damage to agriculture but it has many ecological repercussions.
They are generally insoluble in water and non-biodegradable. Therefore, these chemicals will not gradually decompose and keep on accumulating in the soil. Therefore, the concentration of these chemicals will increase when the transfer of these chemicals take place from lower to higher trophic level via the food chain . Hence, it will cause many metabolic and physiological disorders in humans.

Chlorinated Organic toxins
The harmful effect of DDT and other chemicals led to the introduction of less persistent organic and more-biodegradable substance such as carbamates and organophosphates. However, these chemicals act as harmful toxins for nerves , hence they are more dangerous to humans. It led to pesticides related to the death of field workers in some agricultural fields.
Learn about the Causes and Effects of Water Pollution here.
Slowly, the industries began production of herbicides like sodium arsenite (Na 3 AsO 3 ), sodium chlorate (NaClO 3 ), etc. Herbicides can decompose in a span of few months. However, even they affect the environment and are not environmental friendly. Even though they are not as harmful as organo-chlorides but most of the herbicides are toxic. They are known to cause birth defects.
Furthermore, research suggests that spraying herbicides causes more insect attack and diseases of plants in comparison to manual weeding. One thing to note here is all the above factors occupy just a small portion of the causes. Majority of the causes is related to manufacturing activities in chemical and industrial processes that are released in nature or environment.
Inorganic Fertilizers
Excessive use of inorganic nitrogen fertilizers leads to acidification of soil and contaminate the agricultural soil. Also known as agrochemical pollution.
Industrial Pollution
The incorrect way of chemical waste disposal from different types of industries can cause contamination of soil. Human activities like this have led to acidification of soil and contamination due to the disposal of industrial waste , heavy metals, toxic chemicals, dumping oil and fuel, etc.
Inferior Irrigation Practices
Poor irrigation methods increase the soil salinity. Moreover, excess watering, improper maintenance of canals and irrigation channels, lack of crop rotation and intensive farming gradually decreases the quality of soil over time and cause degradation of land.
Solid Waste
Disposal of plastics, cans, and other solid waste falls into the category of soil pollution. Disposal of electrical goods such as batteries causes an adverse effect on the soil due to the presence of harmful chemicals . For instance, lithium present in batteries can cause leaching of soil.
Urban Activities
Lack of proper waste disposal, regular constructions can cause excessive damage to the soil due to lack of proper drainage and surface run-off. These waste disposed of by humans contain chemical waste from residential areas. Moreover leaking of sewerage system can also affect soil quality and cause soil pollution by changing the chemical composition of the soil.
Download Soil Pollution Cheat Sheet PDF

Effects of Soil Pollution
Soil pollution is not only the problem in India but it is a global problem. It causes harmful effect on the soil and the environment at large. Contamination of soil will decrease the agricultural output of a land. Major soil pollution after effects are:
Inferior Crop Quality
It can decrease the quality of the crop. Regular use of chemical fertilizers, inorganic fertilizers, pesticides will decrease the fertility of the soil at a rapid rate and alter the structure of the soil. This will lead to decrease in soil quality and poor quality of crops. Over the time the soil will become less productive due to the accumulation of toxic chemicals in large quantity.
Harmful Effect on Human Health
It will increase the exposure to toxic and harmful chemicals thus increasing health threats to people living nearby and on the degraded land. Living, working or playing in the contaminated soil can lead to respiratory diseases, skin diseases , and other diseases. Moreover, it can cause other health problems.
Water Sources Contamination
The surface run-off after raining will carry the polluted soil and enter into different water resource. Thus, it can cause underground water contamination thereby causing water pollution. This water after contamination is not fit for human as well as animal use due to the presence of toxic chemicals.
Negative Impact on Ecosystem and Biodiversity
Soil pollution can cause an imbalance of the ecosystem of the soil. The soil is an important habitat and is the house of different type of microorganisms , animals, reptiles, mammals, birds, and insects. Thus, soil pollution can negatively impact the lives of the living organisms and can result in the gradual death of many organisms. It can cause health threats to animals grazing in the contaminated soil or microorganisms residing in the soil.
Therefore, human activities are responsible for the majority of the soil pollution. We as humans buy things that are harmful and not necessary, use agricultural chemicals (fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, etc.), drop waste here and there. Without being aware we harm our own environment.
Therefore, it is very important to educate people around you the importance of environment if they are not aware. Prevention of soil erosion will help to cease soil pollution. Thus, it is our small steps and activities that can help us to achieve a healthier planet for us. Therefore, it is essential for industries, individuals and businesses to understand the importance of soil and prevent soil pollution and stop the devastation caused to plant and animal life.
The solution to reduce the soil pollution
- Use of correct farming techniques
- Recycling of Waste before disposal, Recycle and Reuse Products
- Use of organic fertilizers instead of chemical fertilizers and pesticides
- Community education and awareness, Get the Locals Involved
- Proper maintenance of sewage system, Proper disposal method of household and industrial waste
- Reforestation and Afforestation Should be Promoted
- Planting new trees and plants is afforestation. We live because plants live. If the plants die, all living things will also die. Thus, whenever trees are cut down new trees should be planted. Planting trees in hilly areas are most effective for conservation.
How are people exposed to soil contaminants?
Contaminants in the soil can be present in all three periods (solid, liquid, and gaseous). As a result, these pollutants can enter the human body through a variety of routes, including direct skin contact or inhalation of contaminated soil dust.
Solved Examples for You
Question: List down some preventive measures of soil pollution?
- Recycling of Waste before disposal
- Proper disposal method of household and industrial waste
- Community education and awareness
- Proper maintenance of sewage system
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Environmental Chemistry
- Fire Extinguisher
- Precipitation
- Ozone Layer
- Conservation of Water
- Air Pollution
One response to “Urea”
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Environmental Factor
Your online source for niehs news, papers of the month.
Extramural By Adeline Lopez
Interaction of toxic metals in the digestive system revealed
NIEHS-funded researchers revealed how arsenic and cadmium may interact inside the human body, potentially altering their toxicity. The two metals frequently occur together in contaminated soil, but little is known about how combined exposure may affect health.
Using an simulated gastrointestinal (GI) tract in the lab, the team measured arsenic and cadmium bioaccessiblity, which is the amount of arsenic or cadmium that could be released during digestion and absorbed into the bloodstream. They exposed the artificial GI tract to cadmium only, arsenic only, or to a mixture of both metals. They also explored the effects of ferrihydrite, an iron mineral commonly found in dust, and pepsin, an enzyme responsible for protein digestion, to better replicate conditions inside the human body.
The team reported that cadmium bioaccessibility increased when arsenic was present. Arsenic bioaccessibility decreased with the addition of cadmium, but the arsenic present was transformed into a more toxic form. Both metals formed complexes with ferrihydrite, which promoted the release of cadmium but inhibited the release of arsenic. Pepsin formed soluble complexes with both metals, increasing their bioaccessibility.
According to the authors, these findings highlight the importance of understanding how exposure to contaminant mixtures affects their potential toxicity and may inform more protective regulatory strategies for soil and dust when cadmium and arsenic are both present.
Citation : Bai B, Kong S, Root RA, Liu R, Wei X, Cai D, Chen Y, Chen J, Yi Z, Chorover J. 2024. Release mechanism and interactions of cadmium and arsenic co-contaminated ferrihydrite by simulated in-vitro digestion assays . J Hazard Mater 467:133633.
Prenatal exposure to glyphosate linked to neurodevelopmental delays
An NIEHS-funded study found that glyphosate exposure during pregnancy may alter early brain development in children. According to the authors, this is one of the first studies to examine the relationship between exposure to the common herbicide before birth and neurodevelopment in young children.
The scientists studied 143 mother-baby pairs from Puerto Rico. To assess exposure, they collected urine samples from the mothers during pregnancy and measured levels of glyphosate and a common breakdown product of the herbicide. Then, they evaluated the children’s brain development at 6, 12, and 24 months using the Battelle Developmental Inventory. This test measures how well babies communicate, move, learn, and socialize. Using statistical models, they assessed potential links between the levels of glyphosate and the breakdown product in the mothers’ urine and their children’s performance on the test.
Children of mothers with higher glyphosate exposure scored lower in communication skills at 12 and 24 months. At 24 months, children with higher prenatal glyphosate exposure also scored lower in other areas, such as the ability to adapt to and understand new situations, attention, and memory.
These findings suggest that exposure to glyphosate during pregnancy may affect early neurodevelopment, with more pronounced delays by the time children reach 24 months, according to the authors. Because glyphosate is widely used, they noted that more research is needed to fully understand potential impacts on children’s neurodevelopment as they grow older.
Citation : Jenkins HM, Meeker JD, Zimmerman E, Cathey A, Fernandez J, Montañez GH, Park S, Pabón ZR, Vélez Vega CM, Cordero JF, Alshawabkeh A, Watkins DJ. 2024. Gestational glyphosate exposure and early childhood neurodevelopment in a Puerto Rico birth cohort . Environ Res 246:118114.
Maternal air pollution exposure, telomere length, and child sex interact to affect birthweight
NIEHS-funded researchers discovered that the length of a mother’s telomeres and the sex of her child complicate the effects of prenatal air pollution exposure on birthweight. Telomeres are regions of repetitive DNA sequences at the end of chromosomes that shorten with age. Several factors, including stress and exposure to environmental contaminants, can accelerate telomere shortening and biological aging.
The researchers explored whether premature aging of the placenta, reflected by telomere length, modifies the relationship between air pollution exposure and birthweight. Abnormal birthweight is associated with higher risk for health problems later in life. They looked at data from 306 mothers and their babies who participated in an urban health study in the Northeast U.S. Using mathematical models, the team assessed the effects of air pollution exposure during pregnancy and placental telomere length at delivery on birthweight while accounting for the length of the pregnancy and the baby’s sex.
Results differed by exposure window, air pollutant, sex, and placental telomere length. For boys, exposure to fine particulate matter during the third trimester was associated with lower birthweight if their mothers had longer telomeres. In contrast, exposure to ozone during the first trimester or nitrogen dioxide in the third trimester was associated with higher birthweight if mothers had shorter telomeres. For girls, exposure to a mix of pollutants during the second trimester was associated with lower birthweight if their mothers had longer placental telomeres.
According to the authors, the results suggest that exploring the complex relationships between exposure timing, air pollutant exposure, placental telomere length, and a baby’s sex may help researchers identify women at higher risk for adverse birth outcomes, informing targeted interventions.
Citation : Zhang X, Colicino E, Cowell W, Enlow MB, Kloog I, Coull BA, Schwartz JD, Wright RO, Wright RJ. 2024. Prenatal exposure to air pollution and BWGA Z-score: Modifying effects of placenta leukocyte telomere length and infant sex . Environ Res 246:117986.
Sorbent materials decrease movement and toxicity of PFAS in soil
A strategy developed by NIEHS-funded scientists may trap PFAS in soil and prevent the chemicals from spreading to plants or water. Immobilizing the chemicals in soil is one remediation strategy to reduce human exposure.
The scientists evaluated the ability of six different sorbent materials, made up of activated carbon or specialized clays, to trap four PFAS chemicals in soil. They measured how much PFAS solution leaked out of soil — a proxy for how much could be absorbed by plants or animals, called bioavailability — when each sorbent was added. They also explored how changes in PFAS bioavailability translated to toxicity by exposing worms and aquatic plants to soil or water following extraction.
Overall, adding any of the sorbent materials reduced PFAS bioavailability in soil by 58-97%. Activated carbon was the most effective at trapping PFAS, reducing the bioavailable amount by 73-97%, depending on the amount of sorbent used. Their method was effective in trapping PFAS for up to 21 days, even when the soil samples were exposed to different conditions, including simulations of acid rain, fresh water, and brackish water. Mirroring the reduced bioavailability of PFAS, the team reported a dose-dependent decrease in toxicity to plants and worms in the presence of any of the six individual sorbents — some modified clays promoted plant growth due to added nutrients.
According to the authors, adding a combination of activated carbon and modified clays is a practical approach to help reduce the spread of PFAS in soils while protecting surrounding plants and animals.
Citation : Wang M, Rivenbark KJ, Nikkhah H, Beykal B, Phillips TD. 2024. In vitro and in vivo remediation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances by processed and amended clays and activated carbon in soil . Appl Soil Ecol 196:105285.
(Adeline Lopez is a science writer for MDB Inc., a contractor for the NIEHS Division of Extramural Research and Training.)
Read the current Superfund Research Program Research Brief . New issues are published on the first Wednesday of every month.
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
Harmful Risk of Bioaerosol Pollution at Major Indoor Sites of a Summer Campus in Guilin City
Reviewer 1 Report
The authors investigated the harmful risk of indoor bioaerosols from some areas on the campus. They found that the total number of bacteria (mostly microbes) detected in the classroom during no lesson in the morning (33% of samples) and in the canteen during meal time (55% of samples) was greater than the World Health Organization's recommended value (1000 CFU/m 3 ). The study shows data on controlling indoor bioaerosol pollution. This study is within the scope of the journal and the necessary topic, but I recommend posing the following questions and comments to enhance the manuscript's quality:
1- In the title of the study, the word “indoor” is repeated twice; please revise.
2- More papers should be evaluated, and the literature review section should be improved to highlight the novelty of the study.
3- Give more information about the material and devices used in the study.
4- It is better to add table 1 to the “material and methods” section.
5- The subtitle “3.5. Figure and Tables” is unnecessary. It is better to distribute the figures according to the paper’s structure.
6- Explain “DOOP, CAOP, CAUP, etc.” term in the first used paragraph. Prepare and add the nomenclature table.
7- There is no comment for Fig. 6. Explain each figure and table in the manuscript.
8- In line 265, there is a comment for Fig. 7c. However, comments should be added for other graphs (Fig. 7a, b, d, e, f).
9- In Fig. 6, add a, b, c, and d for the different charts.
10- Enhance the conclusions part, highlighting the novel findings.
The manuscript's English language quality is sufficient for understanding, yet the authors should review it to eliminate grammar mistakes and typos before publishing.
Author Response
Reviewer 2 Report
In the reviewed article Authors describe the results of research concerning microbial quality of indoor air and bioaerosols from the canteen, classroom, and dormitory on a university campus in Guilin, China. The reviewed manuscript is well-written, relevant for the field and presented in a well-structured manner. The cited references are mostly recent publications (67% within the last 5 years) and they are relevant to the subject of the article. The figures and tables are prepared appropriately, they properly show the data and are easy to interpret and understand. I must admit, I find the results obtained by the Authors in classrooms very important - obviously open windows and air exchange between indoor and outdoor air have much bigger effect on the number of microorganisms in air than expected. Most literature data indicate that humans are the biggest and the most important 'microbial source' for the air, which was not confirmed here.
However, chapter 2 (Materials and methods) requires some improvement:
1. How many samples were really taken? Summer months seems to indicate that there were three analyses, each taking three days, but in line 69 there is information “particulate matter sampling was conducted on one day in July”. It is very hard to draw any conclusions based on analysis made only one day.
2. Were the windows open in classrooms all day or only during the classes?
3. In lines 88-90 authors state “ Quartz filter membranes (80 mm diameter, 0.3 μm pore size) were used to collect samples of bioaerosol particulate matter, which were stored in a refrigerator at -20℃ after collection and analyzed for microbial community characterization on the particulate matter by high-throughput sequencing.” What sequencing method was used? How were the sample prepared? How was it analysed (methods, programmes)?
4. Also, please check the article for the proper formatting (Latin names should be in italics; please see lines 186-211, abstract etc.).
Dear Editor, Dear reviewers
This is a revised response to manuscript ID: atmosphere-3031635 . We express our gratitude for the professional review work conducted on our article. In response to your insightful suggestions, we have implemented extensive revisions to our initial draft. The detailed corrections are outlined below. We sincerely appreciate the efforts of the editor and all reviewers for providing valuable feedback that has significantly enhanced the quality of our manuscript.
Reviewer comments are presented in italicized font, and specific concerns have been numbered. Our responses are provided in normal font, with changes/additions to the manuscript highlighted in blue text.
Respond to Reviewer #2’s comments
- How many samples were really taken? Summer months seems to indicate that there were three analyses, each taking three days, but in line 69 there is information “particulate matter sampling was conducted on one day in July”. It is very hard to draw any conclusions based on analysis made only one day.
Response: First of all, the comments you made are still very informative and I would like to express my deep gratitude, but I am also sorry that the particulate samples for our bioaerosol community composition analysis were collected in one day, on the other hand, we collected and performed the community analysis on different six particle size range particulates separately, and the three sites for two periods contained 36 samples that were collected by the glass fiber filter membrane. The number of samples in each group was six, and our conclusions are all based on the analysis of six samples in each group, and the conclusions have credibility. We really hope you can understand.
- Were the windows open in classrooms all day or only during the classes?
Response: Thank you for raising this issue, which we have corrected and explained in the manuscript as follows.
Lines 166-168: the windows and doors of the classrooms are open throughout the day and the fans are turned on to assist in the ventilation of the classrooms during class hours.
- In lines 88-90 authors state “ Quartz filter membranes (80 mm diameter, 0.3 μm pore size) were used to collect samples of bioaerosol particulate matter, which were stored in a refrigerator at -20 ℃ after collection and analyzed for microbial community characterization on the particulate matter by high-throughput sequencing.” What sequencing method was used? How were the sample prepared? How was it analysed (methods, programmes)?
Response: Thanks to your comments, we added specific processes and methods regarding high-throughput sequencing as described below:
Line 115-133: Sequencing Methods:
(1) Sample DNA purification. Sample gDNA purification was performed using the Zymo Research BIOMICS DNA Microprep Kit (Cat# D4301). gDNA integrity was detected using 0.8 % agarose electrophoresis, followed by nucleic acid concentration detection (PicoGreen dye method) using a Tecan F200.
(2) PCR amplification. According to the sequenced region, specific primers with index sequences were synthesized to amplify the 16S rDNA V4 region of the samples, and the amplification primer sequences were as follows: Primer5'-3': 515F (5'-GTGYCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA-3') and 806R (5'- GGAC-TACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3')
(3) PCR product detection, purification and quantification. PCR products were mixed with a 6-fold sampling buffer, followed by electrophoretic detection of the tar-get fragments using a 2 % agarose gel. Samples that passed the assay were taken for recovery of the destination bands, and the recovery was performed using Zymoclean Gel Recovery Kit (D4008); quantification was performed using Qubit@ 2.0 Fluorometer (Thermo Scientific); and finally, equimolar amounts were mixed.
(4) Library construction. Library construction was performed using NEBNext Ul-tra II DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (NEB#E7645L) from NEW ENGLAND Bi-oLabs.
(5) High-throughput sequencing. PE250 sequencing was used, and the sequencing kit was Hiseq Rapid SBS Kit v2 (FC-402-4023 500 Cycle) for Illumina.
- Also, please check the article for the proper formatting (Latin names should be in italics; please see lines 186-211, abstract etc.).
Response: Thanks to your suggestion, we have corrected the names of bacteria at the genus and species level in the manuscript to italics in accordance with the International Code of Bacterial Nomenclature.
We tried our best to improve the manuscript and made some changes marked in blue in the revised manuscript which will not influence the paper's framework. We appreciate for Editors/Reviewers’ warm work earnestly, and hope the correction will meet with approval. Once again, thank you very much for your comments and suggestions.
The manuscript can be accepted with its revised version.
Thank you for sending me the revised version of your manuscript and for the very detailed explanations to my comments. All my comments were replied in a very professional manner. I have no further comments.
Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Liao, L.; Qin, A.; Mo, S.; Fan, Y. Harmful Risk of Bioaerosol Pollution at Major Indoor Sites of a Summer Campus in Guilin City. Atmosphere 2024 , 15 , 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060696
Zhang X, Xu W, Liao L, Qin A, Mo S, Fan Y. Harmful Risk of Bioaerosol Pollution at Major Indoor Sites of a Summer Campus in Guilin City. Atmosphere . 2024; 15(6):696. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060696
Zhang, Xibiao, Wei Xu, Lei Liao, Aimiao Qin, Shengpeng Mo, and Yinming Fan. 2024. "Harmful Risk of Bioaerosol Pollution at Major Indoor Sites of a Summer Campus in Guilin City" Atmosphere 15, no. 6: 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060696
Article Metrics
Further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals
Stay informed every day of the week
Sign up for Mississippi Today's daily and weekly newsletters.
- The Today The latest headlines delivered weekdays at 7:30 a.m.
- The Report A weekly roundup of Mississippi Today stories delivered Saturdays at 7:30 a.m.
- Marshall's Mississippi Commentary and exclusive cartoons from Marshall Ramsey delivered Sundays at noon
- Legislative Guide Legislative updates from Mississippi Today's politics team delivered Mondays at noon

Mississippi Today
Pulitzer Prize-winning Nonprofit News
Ex-employees sue Water Valley facility over TCE pollution

Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
A group of north Mississippians have filed a negligence lawsuit in federal court claiming that pollution their former employer released into the air, groundwater and soil near the Water Valley facility where they worked inflicted them with long-term symptoms such as cancer and Parkinson’s disease.
Plaintiffs Odester Andrews, Excell Vance, Josephine Martin, Eddie Foster, Billy Harris, Joan Berryhill, Patricia Camp, and Clayfers Walton all used to work at the carburetor manufacturer, now owned by North Carolina company EnPro Industries, Inc.
“It’s well known that this is a dangerous chemical, and yet we were exposed to dangerous levels, and they polluted the land and drinking water with it,” Vance, 69, said. “The harm that they caused to my life, my family, and this community is unspeakable.”
The lawsuit filed Tuesday says the business, at the time owned by Coltec Industries, used a “vapor degreaser” it bought from another company, Detrex Corp., to clean debris and oil from car parts. The degreaser contained a toxic chemical called trichloroethylene, or TCE, the complaint says, a substance the Environmental Protection Agency is now working to ban.

TCE has been around for decades, and is mostly used in degreasers, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, but is also an ingredient in “adhesives, paint removers, typewriter correction fluids, and spot removers.” TCE is a known carcinogen, the CDC says , and the National Cancer Institute specifically links prolonged exposure to TCE with kidney cancer.
The complaint lists EnPro, Detrex, and Italmatch Chemicals — an Italian company that bought Detrex in 2017 — as defendants. Mississippi Today reached out to EnPro for comment but did not hear back.
Coltec used the degreaser containing TCE from 1972 to 1986, according to state enforcement records. All except one of the eight plaintiffs worked at the facility during that time. The other plaintiff, Andrews, was exposed to TCE either through drinking water or from breathing vapors at the facility, the lawsuit claims. Seven of the plaintiffs have some form of cancer, and other diagnoses among the group include Parkinson’s disease and kidney disease.
Coltec, the lawsuit claims, did not have a plan for disposing its TCE waste. The complaint details an incident where Coltec told an employee to dump TCE waste in a ditch behind the facility and, the next day, an employee told their supervisor that they saw about 20 dead turtles in the same ditch. The lawsuit also claims the company told employees to spray TCE in the parking lot to kill weeds.
In 1988, Coltec and the Mississippi Department of Environmental Quality sampled two water wells, one the company used and the other a “domestic” well near the facility, MDEQ records show. The samples revealed TCE levels above 5 parts per billion, or ppb, the limit set by the Environmental Protection Agency. Two years later, MDEQ ordered the company to investigate the extent of and then remediate its pollution of TCE into the nearby groundwater.
But for years the harmful chemical remained present in the nearby air and groundwater. Testing from 2017 at monitoring wells near the facility shows TCE levels as high as 13,200 ppb in the groundwater, shattering the EPA limit. Around the same time, TCE levels in the air inside the facility also surpassed the EPA action level, the Clarion Ledger reported .
Also in 2017, then-Attorney General Jim Hood filed a lawsuit against the company seeking repayment of cleanup costs incurred by the state. The two sides reached a settlement in 2020.
Last October, the EPA proposed banning the use of TCE in manufacturing. The agency said it’s suggesting an exemption to the ban for “battery separators” because they’re critical to the economy and don’t yet have a substitute for TCE.
Data from National Cancer Institute, which was cited in the lawsuit, show that Yalobusha County, where Water Valley is, has seen the biggest rise in cancer diagnoses over the last five years of any county in the state.
Republish This Story
Republish our articles for free, online or in print, under a Creative Commons license.
Republish this article

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License .
- Look for the "Republish This Story" button underneath each story. To republish online, simply click the button, copy the html code and paste into your Content Management System (CMS).
- Editorial cartoons and photo essays are not included under the Creative Commons license and therefore do not have the "Republish This Story" button option. To learn more about our cartoon syndication services, click here .
- You can’t edit our stories, except to reflect relative changes in time, location and editorial style.
- You can’t sell or syndicate our stories.
- Any web site our stories appear on must include a contact for your organization.
- If you share our stories on social media, please tag us in your posts using @MSTODAYnews on Facebook and @MSTODAYnews on Twitter.
- You have to credit Mississippi Today. We prefer “Author Name, Mississippi Today” in the byline. If you’re not able to add the byline, please include a line at the top of the story that reads: “This story was originally published by Mississippi Today” and include our website, mississippitoday.org .
- You cannot republish our editorial cartoons, photographs, illustrations or graphics without specific permission (contact our managing editor Michael Guidry for more information). To learn more about our cartoon syndication services, click here .
- Our stories may appear on pages with ads, but not ads specifically sold against our stories.
- You can only publish select stories individually — not as a collection.
by Alex Rozier, Mississippi Today June 5, 2024
This <a target="_blank" href="https://mississippitoday.org/2024/06/05/ex-employees-sue-water-valley-facility-over-tce-pollution/">article</a> first appeared on <a target="_blank" href="https://mississippitoday.org">Mississippi Today</a> and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.<img src="https://i0.wp.com/mississippitoday.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/MT_icon-logo-favicon-1.png?fit=134%2C150&ssl=1" style="width:1em;height:1em;margin-left:10px;"><img id="republication-tracker-tool-source" src="https://mississippitoday.org/?republication-pixel=true&post=1119134&ga4=G-VSX4B701MS" style="width:1px;height:1px;">
Alex Rozier
Alex Rozier, from New York City, is Mississippi Today’s data and environment reporter. His work has appeared in the Boston Globe, Open Secrets, and on NBC.com. In 2019, Alex was a grantee through the Pulitzer Center’s Connected Coastlines program, which supported his coverage around the impact of climate change on Mississippi fisheries.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
17 actionable ways to prevent soil pollution (and keep it clean) 1. Involve local communities in land and soil management. 2. Improve legislation on soil pollution control and prevention. 3. Adopt waste-to-energy practices. 4. Conduct research on the soil environment quality baseline.
500+ Words Essay on Soil Pollution. Soil is a thin layer made up of organic as well as inorganic materials. These materials cover the rocky surfaces of Earth. Also, the organic portion, which is derived from the decayed remains of animals and plants. While the inorganic portion is made up of rock fragments.
Yes, the Essay on Soil Pollution for Students in English is very helpful. Firstly it helps the student to know about Soil Pollution and its prevention. Secondly, students will be able to write a well-composed essay on the topic of Soil Pollution. It is important to get environmental knowledge and write it properly in English medium.
Here are some of the primary effects of soil pollution: 1. Environmental Consequences. Loss of Biodiversity: Soil pollution disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, leading to a decline in biodiversity. Many plants, animals, and microorganisms depend on healthy soil for survival.
Intensive Farming. Intensive farming can lead to soil pollution in a number of ways. First, the overuse of agrochemicals such as pesticides and herbicides can contaminate the soil. Second, the over-grazing of livestock can strip away vegetation, leaving the soil exposed to erosion.
The prevention of soil pollution should be a top priority worldwide. The fact that the vast majority of pollutants are a result of human action means that we are directly responsible for making the necessary changes to ensure a less polluted, more secure future. ... Soil pollution affects soils' capacity to filter. Soils act as a filter and ...
Soil pollution is a global issue and is a problem that affects everyone. The most important things to do are to stop using pesticides and herbicides, use organic fertilisers and compost, avoid spreading trash or hazardous materials in the park, and limit chemical fertilisers. Sewage from cities and factory waste can contaminate the soil.
Mitigation. Soil pollution refers to the dangerously high concentrations of contaminants in soil. While contaminants such as metals, inorganic ions, salts, and organic compounds naturally occur in ...
The report found that soil pollution has an adverse impact on food security in two ways -it can reduce crop yields due to toxic levels of contaminants, and crops grown in polluted soils are unsafe for consumption by animals and humans. It urged governments to help reverse the damage and encouraged better soil management practices to limit ...
Soil filters the water we drink, grows the food we eat, and captures the carbon dioxide that causes climate change. Soil is the largest carbon sink after the ocean and holds more carbon than all ...
Addressing soil pollution is not just a moral duty but also an economic necessity. The Slow Road to Recovery. Once soil is polluted, it can take years, decades, or even centuries to clean up. This means that the effects of soil pollution can be long-lasting and difficult to reverse. Prevention is often the best approach. Voices of Experts
Soil Pollution essay will be helpful as a reference for students of class 7, 8, 9, and 10. Soil is the uppermost dry layer of the Earth made up of organic and inorganic materials. The importance of soil is to sustain terrestrial life on this planet, and it is also the component where the sources of life like water and sunlight air come together.
Soil Pollution Essay 10 Lines (100 - 150 Words) 1) Soil is an important natural resource necessary for human survival. 2) The mixing of toxic substances into the soil is referred to as soil pollution. 3) Soil pollution is harmful to nature as well as to all living organisms. 4) It can be caused due to natural means or due to human ...
500 Words Essay On Soil Pollution. It is a well-known fact that the soil is important for us in every way; we depend on it for food, and it provides grazing fields for animals. ... Prevention. The most crucial action we can take is to stop using pesticides and herbicides in favour of compost and organic fertilisers, refrain from throwing trash ...
Essay on Soil Pollution 400 Words. Soil pollution is the contamination of fresh and fertile soil which adversely affects the health of crops, plants, animals, human beings and other organisms living in it. Addition of variety of unwanted substances and toxic chemicals from many sources to the soil in the odd proportion causes whole land pollution.
500+ Words Essay on Land Pollution. The various human activities and also natural factors are the various causes of land pollution. Besides, some of the causes of land pollution are the use of pesticides, agricultural and industrial waste, deforestation, growing urbanization, acid rains, and mining activities.Furthermore, these activities not only cause damage to the soil but also the reason ...
Soil contamination leads to health. risks due to direct and indirect contact with. contaminated soil. Soil pollution ca uses. huge disturbances in the ecological. balance and the health of the ...
Soil influences human health in a variety of ways, with human health being linked to the health of the soil. Historically, emphasis has been placed on the negative impacts that soils have on human health, including exposures to toxins and pathogenic organisms or the problems created by growing crops in nutrient-deficient soils.
Soil pollution is a global issue that poses serious threats to human and ecosystem health (Singh and Singh, 2020). Soils are crucial in providing numerous ecosystem services essential for sustaining life on Earth. However, the alarming reality is that we have been witnessing a rapid loss of the quality of our soils and the invaluable benefits they offer (Jie et al., 2002). For example, it has ...
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment. These harmful materials are called pollutants. Pollutants can be natural, such as volcanic ash. They can also be created by human activity, such as trash or runoff produced by factories. Pollutants damage the quality of air, water, and land.
Soil is able to accumulate and purify pollutants, which protects water, but it also releases and transmits pollutants into waters by leaching and migration, causing water pollution. Thus, soil is a potential source and transmission passage of pollution for water bodies. Therefore, soil pollution prevention and control play an important role in ...
Some key facts: Half of all plastics ever manufactured have been made in the last 20 years. Production increased exponentially, from 2.3 million tons in 1950 to 448 million tons by 2015 ...
Increased level of carbon dioxide will lead to global warming. Further, the water is polluted in the name of industrial development, religious practices and more will cause a shortage of drinking water. Without water, human life is not possible. Moreover, the way waste is dumped on the land eventually ends up in the soil and turns toxic.
Nonpoint source pollution (NPSP) has always been the dominant threat to regional waters. Based on empirical models of the revised universal soil loss equation and the phosphorus index, an NPSP risk assessment model denoted as SL-NPSRI was developed. The surface soil pollutant loss was estimated by simulating the rain-runoff topographic process, and the influence of path attenuation was quantified.
Effects of Soil Pollution. Soil pollution is not only the problem in India but it is a global problem. It causes harmful effect on the soil and the environment at large. Contamination of soil will decrease the agricultural output of a land. Major soil pollution after effects are: Inferior Crop Quality. It can decrease the quality of the crop.
Prenatal exposure to air pollution and BWGA Z-score: Modifying effects of placenta leukocyte telomere length and infant sex. Environ Res 246:117986. Sorbent materials decrease movement and toxicity of PFAS in soil. A strategy developed by NIEHS-funded scientists may trap PFAS in soil and prevent the chemicals from spreading to plants or water.
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. ... This study aims to provide basic data for risk assessment and prevention of indoor bioaerosol hazards on campus and try to provide new ideas for analyzing and studying bioaerosols. */3- Give more information about the material and ...
A group of north Mississippians have filed a negligence lawsuit in federal court claiming that pollution their former employer released into the air, groundwater and soil near the Water Valley facility where they worked inflicted them with long-term symptoms such as cancer and Parkinson's disease.. Plaintiffs Odester Andrews, Excell Vance, Josephine Martin, Eddie Foster, Billy Harris, Joan ...