TypeError: Assignment to Constant Variable in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024 Reading time · 3 min


# TypeError: Assignment to Constant Variable in JavaScript
The "Assignment to constant variable" error occurs when trying to reassign or redeclare a variable declared using the const keyword.
When a variable is declared using const , it cannot be reassigned or redeclared.
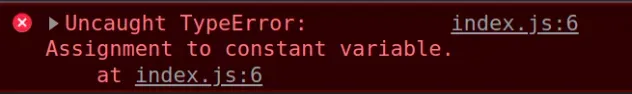
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
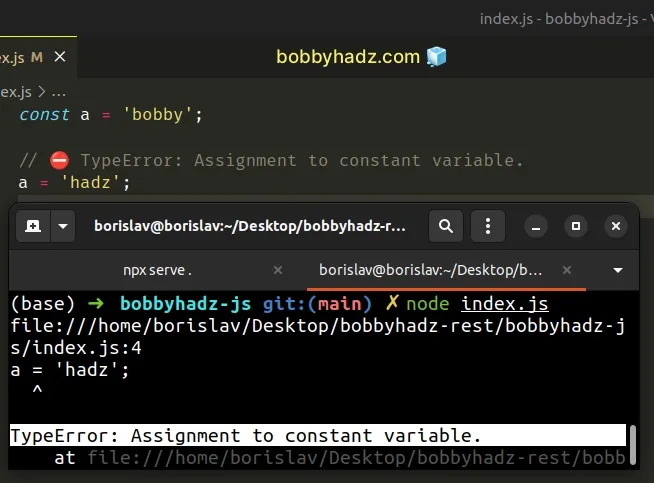
# Declare the variable using let instead of const
To solve the "TypeError: Assignment to constant variable" error, declare the variable using the let keyword instead of using const .
Variables declared using the let keyword can be reassigned.
We used the let keyword to declare the variable in the example.
Variables declared using let can be reassigned, as opposed to variables declared using const .
You can also use the var keyword in a similar way. However, using var in newer projects is discouraged.
# Pick a different name for the variable
Alternatively, you can declare a new variable using the const keyword and use a different name.
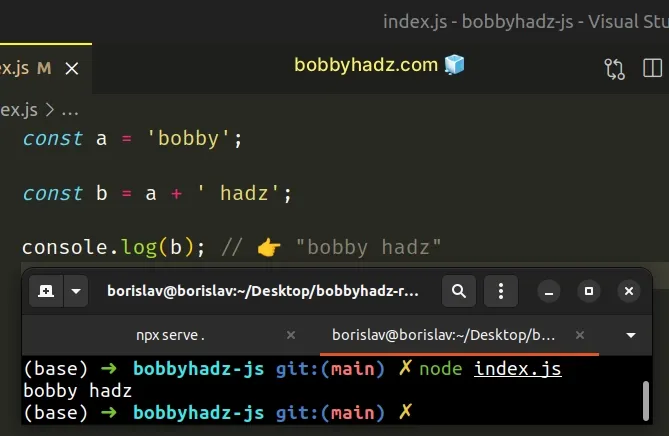
We declared a variable with a different name to resolve the issue.
The two variables no longer clash, so the "assignment to constant" variable error is no longer raised.
# Declaring a const variable with the same name in a different scope
You can also declare a const variable with the same name in a different scope, e.g. in a function or an if block.
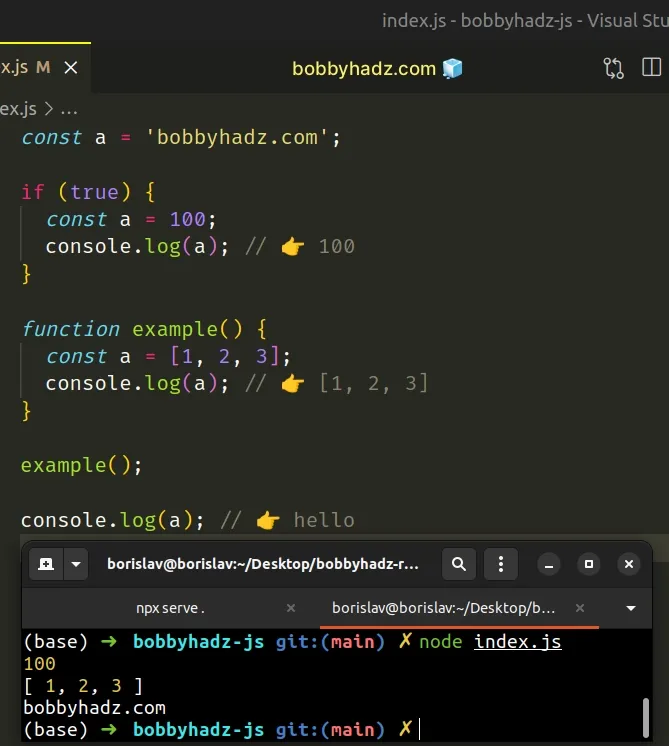
The if statement and the function have different scopes, so we can declare a variable with the same name in all 3 scopes.
However, this prevents us from accessing the variable from the outer scope.
# The const keyword doesn't make objects immutable
Note that the const keyword prevents us from reassigning or redeclaring a variable, but it doesn't make objects or arrays immutable.
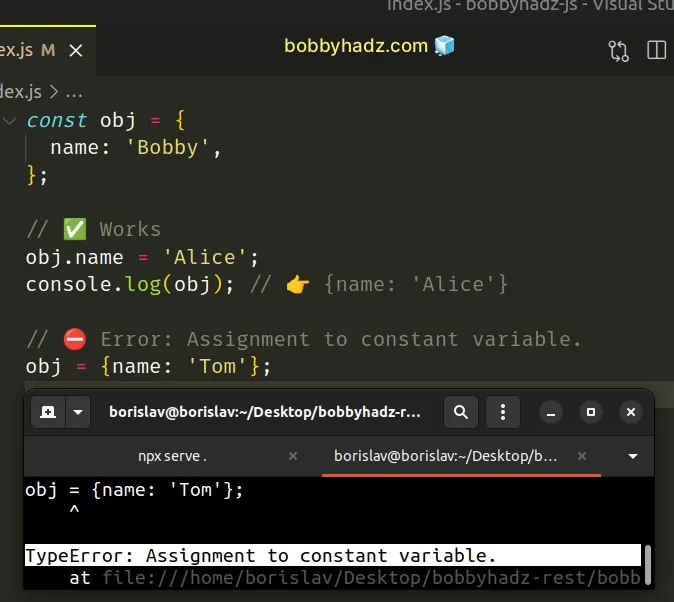
We declared an obj variable using the const keyword. The variable stores an object.
Notice that we are able to directly change the value of the name property even though the variable was declared using const .
The behavior is the same when working with arrays.
Even though we declared the arr variable using the const keyword, we are able to directly change the values of the array elements.
The const keyword prevents us from reassigning the variable, but it doesn't make objects and arrays immutable.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- SyntaxError: Unterminated string constant in JavaScript
- TypeError (intermediate value)(...) is not a function in JS

Borislav Hadzhiev
Web Developer

Copyright © 2024 Borislav Hadzhiev
- Skip to main content
- Select language
- Skip to search
TypeError: invalid assignment to const "x"
Const and immutability, what went wrong.
A constant is a value that cannot be altered by the program during normal execution. It cannot change through re-assignment, and it can't be redeclared. In JavaScript, constants are declared using the const keyword.
Invalid redeclaration
Assigning a value to the same constant name in the same block-scope will throw.
Fixing the error
There are multiple options to fix this error. Check what was intended to be achieved with the constant in question.
If you meant to declare another constant, pick another name and re-name. This constant name is already taken in this scope.
const , let or var ?
Do not use const if you weren't meaning to declare a constant. Maybe you meant to declare a block-scoped variable with let or global variable with var .
Check if you are in the correct scope. Should this constant appear in this scope or was is meant to appear in a function, for example?
The const declaration creates a read-only reference to a value. It does not mean the value it holds is immutable, just that the variable identifier cannot be reassigned. For instance, in case the content is an object, this means the object itself can still be altered. This means that you can't mutate the value stored in a variable:
But you can mutate the properties in a variable:
Document Tags and Contributors
- JavaScript basics
- JavaScript first steps
- JavaScript building blocks
- Introducing JavaScript objects
- Introduction
- Grammar and types
- Control flow and error handling
- Loops and iteration
- Expressions and operators
- Numbers and dates
- Text formatting
- Regular expressions
- Indexed collections
- Keyed collections
- Working with objects
- Details of the object model
- Iterators and generators
- Meta programming
- A re-introduction to JavaScript
- JavaScript data structures
- Equality comparisons and sameness
- Inheritance and the prototype chain
- Strict mode
- JavaScript typed arrays
- Memory Management
- Concurrency model and Event Loop
- References:
- ArrayBuffer
- AsyncFunction
- Float32Array
- Float64Array
- GeneratorFunction
- InternalError
- Intl.Collator
- Intl.DateTimeFormat
- Intl.NumberFormat
- ParallelArray
- ReferenceError
- SIMD.Bool16x8
- SIMD.Bool32x4
- SIMD.Bool64x2
- SIMD.Bool8x16
- SIMD.Float32x4
- SIMD.Float64x2
- SIMD.Int16x8
- SIMD.Int32x4
- SIMD.Int8x16
- SIMD.Uint16x8
- SIMD.Uint32x4
- SIMD.Uint8x16
- SharedArrayBuffer
- StopIteration
- SyntaxError
- Uint16Array
- Uint32Array
- Uint8ClampedArray
- WebAssembly
- decodeURI()
- decodeURIComponent()
- encodeURI()
- encodeURIComponent()
- parseFloat()
- Arithmetic operators
- Array comprehensions
- Assignment operators
- Bitwise operators
- Comma operator
- Comparison operators
- Conditional (ternary) Operator
- Destructuring assignment
- Expression closures
- Generator comprehensions
- Grouping operator
- Legacy generator function expression
- Logical Operators
- Object initializer
- Operator precedence
- Property accessors
- Spread syntax
- async function expression
- class expression
- delete operator
- function expression
- function* expression
- in operator
- new operator
- void operator
- Legacy generator function
- async function
- for each...in
- try...catch
- Arguments object
- Arrow functions
- Default parameters
- Method definitions
- Rest parameters
- constructor
- element loaded from a different domain for which you violated the same-origin policy." href="Property_access_denied.html">Error: Permission denied to access property "x"
- InternalError: too much recursion
- RangeError: argument is not a valid code point
- RangeError: invalid array length
- RangeError: invalid date
- RangeError: precision is out of range
- RangeError: radix must be an integer
- RangeError: repeat count must be less than infinity
- RangeError: repeat count must be non-negative
- ReferenceError: "x" is not defined
- ReferenceError: assignment to undeclared variable "x"
- ReferenceError: deprecated caller or arguments usage
- ReferenceError: invalid assignment left-hand side
- ReferenceError: reference to undefined property "x"
- SyntaxError: "0"-prefixed octal literals and octal escape seq. are deprecated
- SyntaxError: "use strict" not allowed in function with non-simple parameters
- SyntaxError: "x" is a reserved identifier
- SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad parsing
- SyntaxError: Malformed formal parameter
- SyntaxError: Unexpected token
- SyntaxError: Using //@ to indicate sourceURL pragmas is deprecated. Use //# instead
- SyntaxError: a declaration in the head of a for-of loop can't have an initializer
- SyntaxError: applying the 'delete' operator to an unqualified name is deprecated
- SyntaxError: for-in loop head declarations may not have initializers
- SyntaxError: function statement requires a name
- SyntaxError: invalid regular expression flag "x"
- SyntaxError: missing ) after argument list
- SyntaxError: missing ; before statement
- SyntaxError: missing = in const declaration
- SyntaxError: missing ] after element list
- SyntaxError: missing formal parameter
- SyntaxError: missing variable name
- SyntaxError: missing } after property list
- SyntaxError: redeclaration of formal parameter "x"
- SyntaxError: return not in function
- SyntaxError: test for equality (==) mistyped as assignment (=)?
- SyntaxError: unterminated string literal
- TypeError: "x" has no properties
- TypeError: "x" is (not) "y"
- TypeError: "x" is not a constructor
- TypeError: "x" is not a function
- TypeError: "x" is read-only
- TypeError: More arguments needed
- TypeError: can't define property "x": "obj" is not extensible
- TypeError: cyclic object value
- TypeError: invalid Array.prototype.sort argument
- TypeError: invalid arguments
- TypeError: invalid assignment to const "x"
- TypeError: property "x" is non-configurable and can't be deleted
- TypeError: setting a property that has only a getter
- TypeError: variable "x" redeclares argument
- URIError: malformed URI sequence
- Warning: -file- is being assigned a //# sourceMappingURL, but already has one
- Warning: 08/09 is not a legal ECMA-262 octal constant
- Warning: Date.prototype.toLocaleFormat is deprecated
- Warning: JavaScript 1.6's for-each-in loops are deprecated
- Warning: String.x is deprecated; use String.prototype.x instead
- Warning: expression closures are deprecated
- Warning: unreachable code after return statement
- JavaScript technologies overview
- Lexical grammar
- Enumerability and ownership of properties
- Iteration protocols
- Transitioning to strict mode
- Template literals
- Deprecated features
- ECMAScript 2015 support in Mozilla
- ECMAScript 5 support in Mozilla
- ECMAScript Next support in Mozilla
- Firefox JavaScript changelog
- New in JavaScript 1.1
- New in JavaScript 1.2
- New in JavaScript 1.3
- New in JavaScript 1.4
- New in JavaScript 1.5
- New in JavaScript 1.6
- New in JavaScript 1.7
- New in JavaScript 1.8
- New in JavaScript 1.8.1
- New in JavaScript 1.8.5
- Documentation:
- All pages index
- Methods index
- Properties index
- Pages tagged "JavaScript"
- JavaScript doc status
- The MDN project
What's new
JavaScript Error: Assignment to Constant Variable
Last updated on October 3, 2023 at 3:29 PM
Krste Rajchevski
Software Engineer @ Bugpilot
Annoyed by React errors? Bugpilot is the error monitoring platform for React. Catch unexpected errors, troubleshoot, and fix with our AI assistant. Learn more and create an account to start your 14-day free trial.
TypeError: Assignment to constant variable
Have you ever encountered a JavaScript error like "TypeError: Assignment to constant variable"? Don't worry, you're not alone! This error occurs when you try to reassign a value to a variable that has been declared with the const keyword. In this blog post, we'll explore what this error means, why it happens, and how you can solve it.
There are a few common causes for the "TypeError: Assignment to constant variable" error. Let's take a closer look at each one and discuss possible solutions.
Cause 1: Attempting to Change a Constant Variable
In JavaScript, const is used to declare variables that are meant to remain constant and cannot be reassigned. Therefore, if you try to assign a new value to a constant variable, such as:
The above code will throw a "TypeError: Assignment to constant variable" error. The solution is simple: if you need to change the value of a variable, use the let keyword instead of const :
Cause 2: Accidental Re-declaration of a Constant Variable
Another common mistake that leads to this error is accidentally re-declaring a constant variable within the same scope. Consider the following example:
The above code will result in a "TypeError: Assignment to constant variable" error because the variable myConstant has already been declared using const . To fix this issue, choose a different name for the re-declaration or remove the second declaration altogether:
Cause 3: Trying to Update Properties of an Object Declared as Constant
In JavaScript, when we declare an object as a constant using the const keyword, we can still modify the properties of that object. However, we cannot assign a new object to the constant variable itself. Consider the following example:
In the code above, attempting to assign a new object to myObject will result in a "TypeError: Assignment to constant variable" error. However, updating the property of myObject itself, such as myObject.value = 20 , is allowed.
To fix the "TypeError: Assignment to constant variable" error, you need to identify the cause and apply the appropriate solution.
If you are trying to change the value of a variable, make sure it is declared using the let keyword instead of const .
If you accidentally re-declared a constant variable within the same scope, either choose a different name for the re-declaration or remove the second declaration.
If you need to modify the properties of an object declared as a constant, make sure you are not trying to assign a new object to the constant variable itself. Instead, update the properties of the existing object.
By following these solutions, you'll be able to overcome the "TypeError: Assignment to constant variable" error and write error-free JavaScript code.
The "TypeError: Assignment to constant variable" error occurs when you try to reassign a value to a variable declared with const . This error can be solved by understanding the causes and implementing the appropriate solutions. Remember to use let instead of const when you need to change the value of a variable, avoid re-declaring constants within the same scope, and update the properties of an object instead of assigning a new object to a constant variable. With these tips in mind, you'll be well equipped to handle this error and write more robust JavaScript code.
We hope this article has been helpful! If you have any questions or need further assistance, please feel free to leave a comment below. Happy coding!
Was this article helpful?

- DSA with JS - Self Paced
- JS Tutorial
- JS Exercise
- JS Interview Questions
- JS Operator
- JS Projects
- JS Examples
- JS Free JS Course
- JS A to Z Guide
- JS Formatter
- JavaScript Tutorial
JavaScript Basics
- Introduction to JavaScript
- JavaScript Versions
- How to Add JavaScript in HTML Document?
- JavaScript Statements
- JavaScript Syntax
- JavaScript Output
- JavaScript Comments
JS Variables & Datatypes
- Variables and Datatypes in JavaScript
- Global and Local variables in JavaScript
- JavaScript Let
JavaScript Const
- JavaScript var
JS Operators
- JavaScript Operators
- Operator precedence in JavaScript
- JavaScript Arithmetic Operators
- JavaScript Assignment Operators
- JavaScript Comparison Operators
- JavaScript Logical Operators
- JavaScript Bitwise Operators
- JavaScript Ternary Operator
- JavaScript Comma Operator
- JavaScript Unary Operators
- JavaScript Relational operators
- JavaScript String Operators
- JavaScript Loops
- 7 Loops of JavaScript
- JavaScript For Loop
- JavaScript While Loop
- JavaScript for-in Loop
- JavaScript for...of Loop
- JavaScript do...while Loop
JS Perfomance & Debugging
- JavaScript | Performance
- Debugging in JavaScript
- JavaScript Errors Throw and Try to Catch
- Objects in Javascript
- Introduction to Object Oriented Programming in JavaScript
- JavaScript Objects
- Creating objects in JavaScript (4 Different Ways)
- JavaScript JSON Objects
- JavaScript Object Reference
JS Function
- Functions in JavaScript
- How to write a function in JavaScript ?
- JavaScript Function Call
- Different ways of writing functions in JavaScript
- Difference between Methods and Functions in JavaScript
- Explain the Different Function States in JavaScript
- JavaScript Function Complete Reference
- JavaScript Arrays
- JavaScript Array Methods
- Best-Known JavaScript Array Methods
- What are the Important Array Methods of JavaScript ?
- JavaScript Array Reference
- JavaScript Strings
- JavaScript String Methods
- JavaScript String Reference
- JavaScript Numbers
- How numbers are stored in JavaScript ?
- How to create a Number object using JavaScript ?
- JavaScript Number Reference
- JavaScript Math Object
- What is the use of Math object in JavaScript ?
- JavaScript Math Reference
- JavaScript Map
- What is JavaScript Map and how to use it ?
- JavaScript Map Reference
- Sets in JavaScript
- How are elements ordered in a Set in JavaScript ?
- How to iterate over Set elements in JavaScript ?
- How to sort a set in JavaScript ?
- JavaScript Set Reference
- JavaScript Date
- JavaScript Promise
- JavaScript BigInt
- JavaScript Boolean
- JavaScript Proxy/Handler
- JavaScript WeakMap
- JavaScript WeakSet
- JavaScript Function Generator
- JavaScript JSON
- Arrow functions in JavaScript
- JavaScript this Keyword
- Strict mode in JavaScript
- Introduction to ES6
- JavaScript Hoisting
- Async and Await in JavaScript
JavaScript Exercises
- JavaScript Exercises, Practice Questions and Solutions
The JavaScript const keyword declares variables that cannot be reassigned, preventing their modification. It prohibits redeclaration and provides block scope, introduced in ES2015 (ES6) for defining immutable variables.
Properties:
- Cannot be reassigned.
- It has Block Scope
- It can be assigned to the variable on the declaration line.
- It’s a Primitive value.
- The property of a const object can be changed but it cannot be changed to a reference to the new object
- The values inside the const array can be changed, it can add new items to const arrays but it cannot reference a new array.
- Re-declaring of a const variable inside different block scopes is allowed.
- Cannot be Hoisted.
- Creates only read-only references to value.
Examples of JavaScript Const
Cannot be reassigned.
Example 1: It describes that the const variable cannot be reassigned.
Example 2: It describes the const variable which contains the Block Scope.
Variables must be Assigned
Example: It describes the const variable and assigned it after declaration.
Output:
Cannot be Hoisted
Example: It describes the const variable cannot be Hoisted.
Const in Arrays
Example: It describes that the array values can be modified only reference to the array cannot be changed.
Const in Objects
Example: It describes that the object properties can be modified only reference to the object cannot be changed.
Supported Browsers:
- Google Chrome
- Edge
P.S: To clear your concept of var, const, and let please go through How to declare variables in different ways in JavaScript?
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- javascript-basics
- Web Technologies
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Java Tutorials
- Java Interview questions
- Java 8 Stream
Data structure and algorithm
- Data structure in java
- Data structure interview questions
Spring tutorials
- Spring tutorial
- Spring boot tutorial
- Spring MVC tutorial
- Spring interview questions
- keyboard_arrow_left Previous
[Fixed] TypeError: Assignment to constant variable in JavaScript
Table of Contents
Problem : TypeError: Assignment to constant variable
Rename the variable, change variable type to let or var, check if scope is correct, const and immutability.
TypeError: Assignment to constant variable in JavaScript occurs when we try to reassign value to const variable. If we have declared variable with const , it can’t be reassigned.
Let’s see with the help of simple example.

Solution : TypeError: Assignment to constant variable
If you are supposed to declare another constant, just declare another name.
If you are supposed to change the variable value, then it shouldn’t be declared as constant.
Change type to either let or var.
You can check if scope is correct as you can have different const in differnt scopes such as function.
This is valid declaration as scope for country1 is different.
const declaration creates read only reference. It means that you can not reassign it. It does not mean that you can not change values in the object.
Let’s see with help of simple example:
But, you can change the content of country object as below:
That’s all about how to fix TypeError: Assignment to constant variable in javascript.
Was this post helpful?
Related posts:.
- jQuery before() and insertBefore() example
- jQuery append and append to example
- Round to 2 decimal places in JavaScript
- Convert Seconds to Hours Minutes Seconds in Javascript
- [Solved] TypeError: toLowerCase is not a function in JavaScript
- TypeError: toUpperCase is not a function in JavaScript
- Remove First Character from String in JavaScript
- Get Filename from Path in JavaScript
- Write Array to CSV in JavaScript
Get String Between Two Characters in JavaScript
[Fixed] Syntaxerror: invalid shorthand property initializer in Javascript
Convert epoch time to Date in Javascript

Follow Author
Related Posts

Table of ContentsUsing substring() MethodUsing slice() MethodUsing split() MethodUsing substr() Method 💡TL;DR Use the substring() method to get String between two characters in JavaScript. [crayon-6656809eb21c9272710862/] [crayon-6656809eb21d2927738692/] Here, we got String between , and ! in above example. Using substring() Method Use the substring() method to extract a substring that is between two specific characters from […]

Return Boolean from Function in JavaScript
Table of ContentsUsing the Boolean() FunctionUse the Boolean() Function with Truthy/Falsy ValuesUsing Comparison OperatorUse ==/=== Operator to Get Boolean Using Booleans as ObjectsUse ==/=== Operator to Compare Two Boolean Objects Using the Boolean() Function To get a Boolean from a function in JavaScript: Create a function which returns a Boolean value. Use the Boolean() function […]
Create Array from 1 to 100 in JavaScript
Table of ContentsUse for LoopUse Array.from() with Array.keys()Use Array.from() with Array ConstructorUse Array.from() with length PropertyUse Array.from() with fill() MethodUse ... Operator Use for Loop To create the array from 1 to 100 in JavaScript: Use a for loop that will iterate over a variable whose value starts from 1 and ends at 100 while […]
Get Index of Max Value in Array in JavaScript
Table of ContentsUsing indexOf() with Math.max() MethodUsing for loopUsing reduce() FunctionUsing _.indexOf() with _.max() MethodUsing sort() with indexOf() Method Using indexOf() with Math.max() Method To get an index of the max value in a JavaScript array: Use the Math.max() function to find the maximum number from the given numbers. Here, we passed an array and […]
Update Key with New Value in JavaScript
Table of ContentsUsing Bracket NotationUpdate Single Key with New ValueUpdate Multiple Keys with New ValuesUsing Dot NotationUpdate Single Key with New ValueUpdate Multiple Keys with New ValuesUsing forEach() MethodUpdate All Keys with New ValuesUsing map() MethodUpdate All Keys with New Values Using Bracket Notation We can use bracket notation to update the key with the […]
Format Phone Number in JavaScript
Table of ContentsUsing match() MethodFormat Without Country CodeFormat with Country Code Using match() Method We use the match() method to format a phone number in JavaScript. Format Without Country Code To format the phone number without country code: Use the replace() method with a regular expression /\D/g to remove non-numeric elements from the phone number. […]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
What went wrong?
A constant is a value that cannot be altered by the program during normal execution. It cannot change through re-assignment, and it can't be redeclared. In JavaScript, constants are declared using the const keyword.
Invalid redeclaration
Assigning a value to the same constant name in the same block-scope will throw.
Fixing the error
There are multiple options to fix this error. Check what was intended to be achieved with the constant in question.
If you meant to declare another constant, pick another name and re-name. This constant name is already taken in this scope.
const , let or var ?
Do not use const if you weren't meaning to declare a constant. Maybe you meant to declare a block-scoped variable with let or global variable with var .
Check if you are in the correct scope. Should this constant appear in this scope or was it meant to appear in a function, for example?
const and immutability
The const declaration creates a read-only reference to a value. It does not mean the value it holds is immutable, just that the variable identifier cannot be reassigned. For instance, in case the content is an object, this means the object itself can still be altered. This means that you can't mutate the value stored in a variable:
But you can mutate the properties in a variable:
Document Tags and Contributors
- JavaScript basics
- JavaScript first steps
- JavaScript building blocks
- Introducing JavaScript objects
- Introduction
- Grammar and types
- Control flow and error handling
- Loops and iteration
- Expressions and operators
- Numbers and dates
- Text formatting
- Regular expressions
- Indexed collections
- Keyed collections
- Working with objects
- Details of the object model
- Using promises
- Iterators and generators
- Meta programming
- Client-side web APIs
- A re-introduction to JavaScript
- JavaScript data structures
- Equality comparisons and sameness
- Inheritance and the prototype chain
- Strict mode
- JavaScript typed arrays
- Memory Management
- Concurrency model and Event Loop
- References:
- ArrayBuffer
- AsyncFunction
- Float32Array
- Float64Array
- GeneratorFunction
- InternalError
- Intl.Collator
- Intl.DateTimeFormat
- Intl.ListFormat
- Intl.NumberFormat
- Intl.PluralRules
- Intl.RelativeTimeFormat
- ReferenceError
- SharedArrayBuffer
- SyntaxError
- Uint16Array
- Uint32Array
- Uint8ClampedArray
- WebAssembly
- decodeURI()
- decodeURIComponent()
- encodeURI()
- encodeURIComponent()
- parseFloat()
- Arithmetic operators
- Array comprehensions
- Assignment operators
- Bitwise operators
- Comma operator
- Comparison operators
- Conditional (ternary) operator
- Destructuring assignment
- Expression closures
- Generator comprehensions
- Grouping operator
- Legacy generator function expression
- Logical operators
- Object initializer
- Operator precedence
- (currently at stage 1) allows the creation of chained function calls in a readable manner. Basically, the pipeline operator provides syntactic sugar on a function call with a single argument allowing you to write">Pipeline operator
- Property accessors
- Spread syntax
- async function expression
- class expression
- delete operator
- function expression
- function* expression
- in operator
- new operator
- void operator
- Legacy generator function
- async function
- for await...of
- for each...in
- function declaration
- import.meta
- try...catch
- Arrow functions
- Default parameters
- Method definitions
- Rest parameters
- The arguments object
- constructor
- element loaded from a different domain for which you violated the same-origin policy.">Error: Permission denied to access property "x"
- InternalError: too much recursion
- RangeError: argument is not a valid code point
- RangeError: invalid array length
- RangeError: invalid date
- RangeError: precision is out of range
- RangeError: radix must be an integer
- RangeError: repeat count must be less than infinity
- RangeError: repeat count must be non-negative
- ReferenceError: "x" is not defined
- ReferenceError: assignment to undeclared variable "x"
- ReferenceError: can't access lexical declaration`X' before initialization
- ReferenceError: deprecated caller or arguments usage
- ReferenceError: invalid assignment left-hand side
- ReferenceError: reference to undefined property "x"
- SyntaxError: "0"-prefixed octal literals and octal escape seq. are deprecated
- SyntaxError: "use strict" not allowed in function with non-simple parameters
- SyntaxError: "x" is a reserved identifier
- SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad parsing
- SyntaxError: Malformed formal parameter
- SyntaxError: Unexpected token
- SyntaxError: Using //@ to indicate sourceURL pragmas is deprecated. Use //# instead
- SyntaxError: a declaration in the head of a for-of loop can't have an initializer
- SyntaxError: applying the 'delete' operator to an unqualified name is deprecated
- SyntaxError: for-in loop head declarations may not have initializers
- SyntaxError: function statement requires a name
- SyntaxError: identifier starts immediately after numeric literal
- SyntaxError: illegal character
- SyntaxError: invalid regular expression flag "x"
- SyntaxError: missing ) after argument list
- SyntaxError: missing ) after condition
- SyntaxError: missing : after property id
- SyntaxError: missing ; before statement
- SyntaxError: missing = in const declaration
- SyntaxError: missing ] after element list
- SyntaxError: missing formal parameter
- SyntaxError: missing name after . operator
- SyntaxError: missing variable name
- SyntaxError: missing } after function body
- SyntaxError: missing } after property list
- SyntaxError: redeclaration of formal parameter "x"
- SyntaxError: return not in function
- SyntaxError: test for equality (==) mistyped as assignment (=)?
- SyntaxError: unterminated string literal
- TypeError: "x" has no properties
- TypeError: "x" is (not) "y"
- TypeError: "x" is not a constructor
- TypeError: "x" is not a function
- TypeError: "x" is not a non-null object
- TypeError: "x" is read-only
- TypeError: 'x' is not iterable
- TypeError: More arguments needed
- TypeError: Reduce of empty array with no initial value
- TypeError: can't access dead object
- TypeError: can't access property "x" of "y"
- TypeError: can't define property "x": "obj" is not extensible
- TypeError: can't delete non-configurable array element
- TypeError: can't redefine non-configurable property "x"
- TypeError: cannot use 'in' operator to search for 'x' in 'y'
- TypeError: cyclic object value
- TypeError: invalid 'instanceof' operand 'x'
- TypeError: invalid Array.prototype.sort argument
- TypeError: invalid arguments
- TypeError: property "x" is non-configurable and can't be deleted
- TypeError: setting getter-only property "x"
- TypeError: variable "x" redeclares argument
- URIError: malformed URI sequence
- Warning: -file- is being assigned a //# sourceMappingURL, but already has one
- Warning: 08/09 is not a legal ECMA-262 octal constant
- Warning: Date.prototype.toLocaleFormat is deprecated
- Warning: JavaScript 1.6's for-each-in loops are deprecated
- Warning: String.x is deprecated; use String.prototype.x instead
- Warning: expression closures are deprecated
- Warning: unreachable code after return statement
- X.prototype.y called on incompatible type
- JavaScript technologies overview
- Lexical grammar
- Enumerability and ownership of properties
- Iteration protocols
- Transitioning to strict mode
- Template literals
- Deprecated features
- ECMAScript 2015 support in Mozilla
- ECMAScript 5 support in Mozilla
- ECMAScript Next support in Mozilla
- Firefox JavaScript changelog
- New in JavaScript 1.1
- New in JavaScript 1.2
- New in JavaScript 1.3
- New in JavaScript 1.4
- New in JavaScript 1.5
- New in JavaScript 1.6
- New in JavaScript 1.7
- New in JavaScript 1.8
- New in JavaScript 1.8.1
- New in JavaScript 1.8.5
- Documentation:
- All pages index
- Methods index
- Properties index
- Pages tagged "JavaScript"
- JavaScript doc status
- The MDN project
Learn the best of web development
Get the latest and greatest from MDN delivered straight to your inbox.
Thanks! Please check your inbox to confirm your subscription.
If you haven’t previously confirmed a subscription to a Mozilla-related newsletter you may have to do so. Please check your inbox or your spam filter for an email from us.
Constants are block-scoped, much like variables declared using the let keyword. The value of a constant can't be changed through reassignment, and it can't be redeclared.
The constant's name, which can be any legal identifier .
The constant's value. This can be any legal expression , including a function expression.
The Destructuring Assignment syntax can also be used to declare variables.
Description
This declaration creates a constant whose scope can be either global or local to the block in which it is declared. Global constants do not become properties of the window object, unlike var variables.
An initializer for a constant is required. You must specify its value in the same statement in which it's declared. (This makes sense, given that it can't be changed later.)
The const creates a read-only reference to a value. It does not mean the value it holds is immutable—just that the variable identifier cannot be reassigned. For instance, in the case where the content is an object, this means the object's contents (e.g., its properties) can be altered.
All the considerations about the " temporal dead zone " apply to both let and const .
A constant cannot share its name with a function or a variable in the same scope.
Basic const usage
Constants can be declared with uppercase or lowercase, but a common convention is to use all-uppercase letters.
Block scoping
It's important to note the nature of block scoping.
const needs to be initialized
Const in objects and arrays.
const also works on objects and arrays.
Specifications
Browser compatibility.
- Constants in the JavaScript Guide
© 2005–2021 MDN contributors. Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License v2.5 or later. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Statements/const

DEV Community
Posted on Feb 27, 2019
Here is how I change the value of const keyword in Javascript
Every Javascript developer knows that var and let is reassignable but const cannot be reassigned or redeclared again.
But there is a little secret about const , let's look at some code.
As expected, we are unable to reassign val to another number. How about string?
Still no. How about the array and object?
Javascript: Nope nope nope you can't do that nope... But what if we do this:
What?! Let's continue and play around a bit...
OMG what just happened?
From MDN Web Docs, it describes:
The const declaration creates a read-only reference to a value. It does not mean the value it holds is immutable, just that the variable identifier cannot be reassigned . For instance, in the case where the content is an object, this means the object's contents (e.g., its properties) can be altered.
Who is the variable identifier/constant here? arrVariable , not the array itself.
MDN said variable identifier/constant cannot be reassigned, which means arrVariable cannot be reassigned . But what about the array? It doesn't have any effect, of course, it is still mutable.
const tells the reader that your variable cannot be reassigned, which is why it is highly recommended to use. It prevents us to create some unnecessary bugs and improve code readability.
Similar to object:
So next time if someone asks you about our friend const , you know what to say.
Still nope, anyway...
Top comments (1)
Templates let you quickly answer FAQs or store snippets for re-use.
- Location Sialkot, Pakistan
- Work Mahrukh at Student
- Joined Jan 9, 2020
Good one. enjoyed it
Are you sure you want to hide this comment? It will become hidden in your post, but will still be visible via the comment's permalink .
Hide child comments as well
For further actions, you may consider blocking this person and/or reporting abuse

Streamlining React: Utilizing React Query for Scalability
Cristafovici Dan - May 6

All About NPM (Node Package Manager)
Olibhia Ghosh - May 25

New Component Variations 🚀
Wind UI - May 10

Best sites to practice your programming logic 💻
Miguel - May 26

We're a place where coders share, stay up-to-date and grow their careers.
关于“TypeError: Assignment to constant variable”的问题解决方案

在项目开发过程中,在使用变量声明时,如果不注意,可能会造成类型错误 比如:
Uncaught (in promise) TypeError: Assignment to constant variable. 未捕获的类型错误:赋值给常量变量。
我们使用 const 定义了变量且存在初始值。 后面又给这个变量赋值,所以报错了。
ES6 标准引入了新的关键字 const 来定义常量, const 与 let 都具有块级作用域:
- 使用 const 定义的常量,不能修改它的值,且定义的常量必须赋初值;
- let 定义的是变量,可以进行变量赋值操作,且不需要赋初值。
这个错误就是因为我们修改了常量而引起的错误,虽然某些浏览器不报错,但是无效果!
将 const 改为 let 进行声明。

“相关推荐”对你有帮助么?

请填写红包祝福语或标题

1.余额是钱包充值的虚拟货币,按照1:1的比例进行支付金额的抵扣。 2.余额无法直接购买下载,可以购买VIP、付费专栏及课程。


javascript エラー「Uncaught TypeError: Assignment to constant variable.」の原因
- 作成日 2020.10.21
- 更新日 2022.08.04

chromeでエラー「Uncaught TypeError: Assignment to constant variable.」が発生する原因と解決方法を記述をしてます。
- 5.1. オブジェクトの値を操作
- OS windows10 pro 64bit
- Apache 2.4.43
- ブラウザ chrome 103.0.5060.114
chrome103にて、以下のエラーが発生
発生したコード ※ その他の発生パターンは後述してます。
firefox102の場合は以下となります。
IE11の場合は以下となります。
constで、定数にしたものに値を代入しようとしたため
値を代入するのであれば、「let」 か 「var」を使用します。
もしくは別の定数を用意して、そこに代入します。
どうしても同じ変数名にしたい場合は、関数などを使用してスコープを変更します。
オブジェクトの値を操作
オブジェクトに、値を再割り当てすると同じエラーが発生します。
こちらも「let」か「var」を使用することが解決します。
ちなみに、配列は操作可能です。
「const」を使用して「if」文に「=」が足らない場合も発生します。
「==」か「===」を使用すれば解決します。
C# listBoxの値を全て削除する 2020.10.21

SQL server2017 サーバー移行時にメンテナンスプランが実行エラーになる 2020.10.21

COMMENTS
Remember, const is appropriate for values that remain constant during execution, while let is more suitable for mutable variables. as an example I am giving an code. const pi = 3.14; // This variable cannot be reassigned a new value // To fix the error, use 'let' if you need to change the value let counter = 0; counter = 1; // This is valid ...
For instance, in case the content is an object, this means the object itself can still be altered. This means that you can't mutate the value stored in a variable: js. const obj = { foo: "bar" }; obj = { foo: "baz" }; // TypeError: invalid assignment to const `obj'. But you can mutate the properties in a variable:
To solve the "TypeError: Assignment to constant variable" error, declare the variable using the let keyword instead of using const. Variables declared using the let keyword can be reassigned. The code for this article is available on GitHub. We used the let keyword to declare the variable in the example. Variables declared using let can be ...
Maybe what you are looking for is Object.assign(resObj, { whatyouwant: value} ) This way you do not reassign resObj reference (which cannot be reassigned since resObj is const), but just change its properties. Reference at MDN website. Edit: moreover, instead of res.send(respObj) you should write res.send(resObj), it's just a typo
The const declaration creates a read-only reference to a value. It does not mean the value it holds is immutable, just that the variable identifier cannot be reassigned. For instance, in case the content is an object, this means the object itself can still be altered. This means that you can't mutate the value stored in a variable: const obj ...
Uncaught TypeError: Assignment to constant variable. So far so good. Let's say we want to give an id to the toast status: ... constant. The Solution..s Object.freeze: From MDN: The Object.freeze() method freezes an object. A frozen object can no longer be changed; freezing an object prevents new properties from being added to it, existing ...
In JavaScript, const is used to declare variables that are meant to remain constant and cannot be reassigned. Therefore, if you try to assign a new value to a constant variable, such as: 1 const myConstant = 10; 2 myConstant = 20; // Error: Assignment to constant variable 3. The above code will throw a "TypeError: Assignment to constant ...
This JavaScript exception invalid assignment to const occurs if a user tries to change a constant value. Const declarations in JavaScript can not be re-assigned or re-declared. Const declarations in JavaScript can not be re-assigned or re-declared.
In this tutorial we will see how to solve the error Uncaught TypeError: Assignment to constant variable in javascript
This JavaScript exception invalid assignment to const occurs if a user tries to change a constant value. Const declarations in JavaScript can not be re-assigned or re-declared. Message: TypeError: invalid assignment to const "x" (Firefox) TypeError: Assignment to constant variable. (Chrome) TypeError: Assignment to const (Edge) TypeError: Redeclara
Problem : TypeError: Assignment to constant variable. TypeError: Assignment to constant variable in JavaScript occurs when we try to reassign value to const variable. If we have declared variable with const, it can't be reassigned. Let's see with the help of simple example. Typeerror:assignment to constant variable. 1.
The const declaration creates a read-only reference to a value. It does not mean the value it holds is immutable, just that the variable identifier cannot be reassigned. For instance, in case the content is an object, this means the object itself can still be altered. This means that you can't mutate the value stored in a variable: const obj ...
const Constants are block-scoped, much like variables declared using the let keyword. The value of a constant can't be changed through reassignment, and it can't be redeclared. Syntax const name1 = value1 [, name2 = value2 [, ... [, nameN = valueN]]]; nameN The constant's name, which can be any legal identifier. valueN The constant's value. This can be any legal expression, including a ...
OMG what just happened? From MDN Web Docs, it describes: The const declaration creates a read-only reference to a value. It does not mean the value it holds is immutable, just that the variable identifier cannot be reassigned.For instance, in the case where the content is an object, this means the object's contents (e.g., its properties) can be altered.
Uncaught TypeError: Assignment to constant variableIf you're a JavaScript developer, you've probably seen this error more than you care to admit. This one oc...
Uncaught (in promise) TypeError: Assignment to constant variable. 未捕获的类型错误:赋值给常量变量。 原因. 我们使用 const 定义了变量且存在初始值。 后面又给这个变量赋值,所以报错了。 ES6 标准引入了新的关键字 const 来定义常量,const 与 let 都具有块级作用域:
たとえば、コンテンツがオブジェクトである場合、オブジェクト自体はまだ変更可能であることを意味します。. つまり、変数に格納されている値を変更することはできないということです。. js. const obj = { foo: "bar" }; obj = { foo: "baz" }; // TypeError: invalid assignment ...
Uncaught (in promise) TypeError: Assignment to constant variable in JavaScript File [duplicate] Ask Question Asked 3 years, 1 month ago. ... TypeError: Assignment to constant variable. at letsscan1.js:12. javascript; tensorflow; Share. Improve this question. Follow asked Mar 22, 2021 at 12:51. Yeezus123 Yeezus123. 11 6 6 bronze badges. 1.
Uncaught TypeError: Assignment to constant variable. 発生したコード. ※ その他の発生パターンは後述してます。. const num = 0; num = 7; console.log(num); firefox102の場合は以下となります。. Uncaught TypeError: invalid assignment to const 'num'. IE11の場合は以下となります。.
What I see is that you assigned the variable apartments as an array and declared it as a constant. Then, you tried to reassign the variable to an object. When you assign the variable as a const array and try to change it to an object, you are actually changing the reference to the variable, which is not allowed using const.. const apartments = []; apartments = { link: getLink, descr ...