Home — Essay Samples — Life — Child — About Child Development Stages

About Child Development Stages
- Categories: Child Children
About this sample

Words: 691 |
Published: Jan 4, 2019
Words: 691 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
- Giving praise for achievement
- Giving children guidance but respecting their choices
- Giving them the chance to meet and spend time with other children and adults
- Providing activities that involve sharing and taking turns
- Giving support and encouragement and the right amount of supervision
- Providing opportunities to share in decisions
- Listening to children and taking them seriously
- Providing opportunities where children take responsibility
- 12-19 years
Works Cited
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Learn the signs. Act early. Milestones. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/spanish/actearly/milestones/index.html
- National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC). (n.d.). Child development: A closer look. Retrieved from https://www.naeyc.org/our-work/families/child-development/closer-look
- Raver, C. C., Blair, C., & Willoughby, M. (2013). Poverty as a predictor of 4-year-olds' executive function: New perspectives on models of differential susceptibility. Developmental Psychology, 49(2), 292-304. doi:10.1037/a0028343
- Stein, A., Woolley, H., Senior, R., & Hertzman, C. (2008). Social inequalities in physical and mental health: Possible mechanisms and pathways. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 49(6), 661-672. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.01934.x
- Zero to Three. (n.d.). Developmental milestones. Retrieved from https://www.zerotothree.org/resources/developmental-milestones
- Kostelnik, M. J., Soderman, A. K., & Whiren, A. P. (2019). Developmentally appropriate curriculum: Best practices in early childhood education (7th ed.). Pearson.
- Berk, L. E. (2020). Child development (10th ed.). Pearson.
- Papalia, D. E., Olds, S. W., & Feldman, R. D. (2019). Human development (13th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education.
- National Scientific Council on the Developing Child. (2014). Excessive stress disrupts the architecture of the developing brain. Working Paper No. 3. Retrieved from https://developingchild.harvard.edu/resources/wp3/
- Pianta, R. C., & Walsh, D. J. (1996). High-risk children in schools: Constructing sustaining relationships. Routledge.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 895 words
2 pages / 994 words
1 pages / 535 words
7 pages / 3092 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Child
To own a Tamagotchi at age nine, you were the coolest person ever. It will dangle from your backpack when you’d go to school and everyone who didn’t have one would envy you and want one, and those who did have one would flaunt [...]
The physical activity of children today is much different than it was even 30 years ago. Then, children had physical chores, free play and back yard games. Today, children are in organized and structured activities. Large [...]
Your kid's talents will uncover themselves. Your job is to pay attention. Having the ability to discovering your kid's talent is often as simple as paying attention to exactly what piques her curiosity and fascination. You do [...]
As long as I can remember music has been one of the greatest influences in how I navigate through the world. My mother has always loved music with all her heart, and I am very grateful that she was able to pass that same love on [...]
First, I would like to give a brief description of the teaching context. This lesson was designed for 16 intermediate to advanced adult ESL learners from different countries with diverse L1 such as Arabic, Chinese, French, [...]
Duffy explores ideas, thoughts and feelings about love in Valentine and Havisham by commenting on societal expectations of the outcomes and portraying love as unstable, dangerous and likely to cause hurt. Firstly, Duffy [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Developmental Psychology 101: Theories, Stages, & Research

You can imagine how vast this field of psychology is if it has to cover the whole of life, from birth through death.
Just like any other area of psychology, it has created exciting debates and given rise to fascinating case studies.
In recent years, developmental psychology has shifted to incorporate positive psychology paradigms to create a holistic lifespan approach. As an example, the knowledge gained from positive psychology can enhance the development of children in education.
In this article, you will learn a lot about different aspects of developmental psychology, including how it first emerged in history and famous theories and models.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free . These science-based exercises explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology, including strengths, values, and self-compassion, and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students, or employees.
This Article Contains:
What is developmental psychology, 4 popular theories, stages, & models, 2 questions and research topics, fascinating case studies & research findings, a look at positive developmental psychology, applying developmental psychology in education, resources from positivepsychology.com, a take-home message.
Human beings change drastically over our lifetime.
The American Psychological Association (2020) defines developmental psychology as the study of physical, mental, and behavioral changes, from conception through old age.
Developmental psychology investigates biological, genetic, neurological, psychosocial, cultural, and environmental factors of human growth (Burman, 2017).
Over the years, developmental psychology has been influenced by numerous theories and models in varied branches of psychology (Burman, 2017).
History of developmental psychology
Developmental psychology first appeared as an area of study in the late 19th century (Baltes, Lindenberger, & Staudinger, 2007). Developmental psychology focused initially on child and adolescent development, and was concerned about children’s minds and learning (Hall, 1883).
There are several key figures in developmental psychology. In 1877, the famous evolutionary biologist Charles Darwin undertook the first study of developmental psychology on innate communication forms. Not long after, physiologist William Preyer (1888) published a book on the abilities of an infant.
The 1900s saw many significant people dominating the developmental psychology field with their detailed theories of development: Sigmund Freud (1923, 1961), Jean Piaget (1928), Erik Erikson (1959), Lev Vygotsky (1978), John Bowlby (1958), and Albert Bandura (1977).
By the 1920s, the scope of developmental psychology had begun to include adult development and the aging process (Thompson, 2016).
In more recent years, it has broadened further to include prenatal development (Brandon et al., 2009). Developmental psychology is now understood to encompass the complete lifespan (Baltes et al., 2007).

Each of these models has contributed to the understanding of the process of human development and growth.
Furthermore, each theory and model focuses on different aspects of development: social, emotional, psychosexual, behavioral, attachment, social learning, and many more.
Here are some of the most popular models of development that have heavily contributed to the field of developmental psychology.
1. Bowlby’s attachment styles
The seminal work of psychologist John Bowlby (1958) showcased his interest in children’s social development. Bowlby (1969, 1973, 1980) developed the most famous theory of social development, known as attachment theory .
Bowlby (1969) hypothesized that the need to form attachments is innate, embedded in all humans for survival and essential for children’s development. This instinctive bond helps ensure that children are cared for by their parent or caregiver (Bowlby, 1969, 1973, 1980).
Bowlby’s original attachment work was developed further by one of his students, Mary Ainsworth. She proposed several attachment styles between the child and the caregiver (Ainsworth & Bell, 1970).
This theory clearly illustrates the importance of attachment styles to a child’s future development. Consistent and stable caregiving results in a secure attachment style (Ainsworth, Blehar, Waters, & Wall, 1978). In contrast, unstable and insecure caregiving results in several negative attachment styles: ambivalent, avoidant, or disorganized (Ainsworth & Bell, 1970; Main & Solomon, 1986).
Bowlby’s theory does not consider peer group influence or how it can shape children’s personality and development (Harris, 1998).
2. Piaget’s stage theory
Jean Piaget was a French psychologist highly interested in child development. He was interested in children’s thinking and how they acquire, construct, and use their knowledge (Piaget, 1951).
Piaget’s (1951) four-stage theory of cognitive development sequences a child’s intellectual development. According to this theory, all children move through these four stages of development in the same order (Simatwa, 2010).
The sensorimotor stage is from birth to two years old. Behaviors are triggered by sensory stimuli and limited to simple motor responses. If an object is removed from the child’s vision, they think it no longer exists (Piaget, 1936).
The pre-operational stage occurs between two and six years old. The child learns language but cannot mentally manipulate information or understand concrete logic (Wadsworth, 1971).
The concrete operational stage takes place from 7 to 11 years old. Children begin to think more logically about factual events. Abstract or hypothetical concepts are still difficult to understand in this stage (Wadsworth, 1971).
In the formal operational stage from 12 years to adulthood, abstract thought and skills arise (Piaget, 1936).
Piaget did not consider other factors that might affect these stages or a child’s progress through them. Biological maturation and interaction with the environment can determine the rate of cognitive development in children (Papalia & Feldman, 2011). Individual differences can also dictate a child’s progress (Berger, 2014).
3. Freud’s psychosexual development theory
One of the most influential developmental theories, which encompassed psychosexual stages of development, was developed by Austrian psychiatrist Sigmund Freud (Fisher & Greenberg, 1996).
Freud concluded that childhood experiences and unconscious desires influence behavior after witnessing his female patients experiencing physical symptoms and distress with no physical cause (Breuer & Freud, 1957).
According to Freud’s psychosexual theory, child development occurs in a series of stages, each focused on different pleasure areas of the body. During each stage, the child encounters conflicts, which play a significant role in development (Silverman, 2017).
Freud’s theory of psychosexual development includes the oral, anal, phallic, latent, and genital stages. His theory suggests that the energy of the libido is focused on these different erogenous zones at each specific stage (Silverman, 2017).
Freud concluded that the successful completion of each stage leads to healthy adult development. He also suggested that a failure to progress through a stage causes fixation and developmental difficulties, such as nail biting (oral fixation) or obsessive tidiness (anal fixation; Silverman, 2017).
Freud considered personality to be formed in childhood as a child passes through these stages. Criticisms of Freud’s theory of psychosexual development include its failure to consider that personality can change and grow over an entire lifetime. Freud believed that early experiences played the most significant role in shaping development (Silverman, 2017).
4. Bandura’s social learning theory
American psychologist Albert Bandura proposed the social learning theory (Bandura, Ross, & Ross, 1961). Bandura did not believe that classical or operant conditioning was enough to explain learned behavior because some behaviors of children are never reinforced (Bandura, 1986). He believed that children observe, imitate, and model the behaviors and reactions of others (Bandura, 1977).
Bandura suggested that observation is critical in learning. Further, the observation does not have to be of a live actor, such as in the Bobo doll experiment (Bandura, 1986). Bandura et al. (1961) considered that learning and modeling can also occur from listening to verbal instructions on behavior performance.
Bandura’s (1977) social theory posits that both environmental and cognitive factors interact to influence development.
Bandura’s developmental theory has been criticized for not considering biological factors or children’s autonomic nervous system responses (Kevin, 1995).
Overview of theories of development – Khan Academy
Developmental psychology has given rise to many debatable questions and research topics. Here are two of the most commonly discussed.
1. Nature vs nurture debate
One of the oldest debates in the field of developmental psychology has been between nature and nurture (Levitt, 2013).
Is human development a result of hereditary factors (genes), or is it influenced by the environment (school, family, relationships, peers, community, culture)?
The polarized position of developmental psychologists of the past has now changed. The nature/nurture question now concerns the relationship between the innateness of an attribute and the environmental effects on that attribute (Nesterak, 2015).
The field of epigenetics describes how behavioral and environmental influences affect the expression of genes (Kubota, Miyake, & Hirasawa, 2012).
Many severe mental health disorders have a hereditary component. Yet, the environment and behavior, such as improved diet, reduced stress, physical activity, and a positive mindset, can determine whether this health condition is ever expressed (Śmigielski, Jagannath, Rössler, Walitza, & Grünblatt, 2020).
When considering classic models of developmental psychology, such as Piaget’s schema theory and Freud’s psychosexual theory, you’ll see that they both perceive development to be set in stone and unchangeable by the environment.
Contemporary developmental psychology theories take a different approach. They stress the importance of multiple levels of organization over the course of human development (Lomas, Hefferon, & Ivtzan, 2016).
2. Theory of mind
Theory of mind allows us to understand that others have different intentions, beliefs, desires, perceptions, behaviors, and emotions (American Psychological Association, 2020).
It was first identified by research by Premack and Woodruff (1978) and considered to be a natural developmental stage of progression for all children. Starting around the ages of four or five, children begin to think about the thoughts and feelings of others. This shows an emergence of the theory of mind (Wellman & Liu, 2004).
However, the ability of all individuals to achieve and maintain this critical skill at the same level is debatable.
Children diagnosed with autism exhibit a deficit in the theory of mind (Baron-Cohen, Leslie, & Frith, 1985).
Individuals with depression (psychotic and non-psychotic) are significantly impaired in theory of mind tasks (Wang, Wang, Chen, Zhu, & Wang, 2008).
People with social anxiety disorder have also been found to show less accuracy in decoding the mental states of others (Washburn, Wilson, Roes, Rnic, & Harkness, 2016).
Further research has shown that the theory of mind changes with aging. This suggests a developmental lifespan process for this concept (Meinhardt-Injac, Daum, & Meinhardt, 2020).

1. Little Albert
The small child who was the focus of the experiments of behavioral psychologists Watson and Rayner (1920) was referred to as ‘Little Albert.’ These experiments were essential landmarks in developmental psychology and showed how an emotionally stable child can be conditioned to develop a phobia.
Albert was exposed to several neutral stimuli including cotton wool, masks, a white rat, rabbit, monkey, and dog. Albert showed no initial fear to these stimuli.
When a loud noise was coupled with the initially neutral stimulus, Albert became very distressed and developed a phobia of the object, which extended to any similar object as well.
This experiment highlights the importance of environmental factors in the development of behaviors in children.
2. David Reimer
At the age of eight months, David Reimer lost his penis in a circumcision operation that went wrong. His worried parents consulted a psychologist, who advised them to raise David as a girl.
David’s young age meant he knew nothing about this. He went through the process of hormonal treatment and gender reassignment. At the age of 14, David found out the truth and wanted to reverse the gender reassignment process to become a boy again. He had always felt like a boy until this time, even though he was socialized and brought up as a girl (Colapinto, 2006).

Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Exercises (PDF)
Enhance wellbeing with these free, science-based exercises that draw on the latest insights from positive psychology.
Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
Contemporary theories of developmental psychology often encompass a holistic approach and a more positive approach to development.
Positive psychology has intersected with developmental disciplines in areas such as parenting, education, youth, and aging (Lomas et al., 2016).
These paradigms can all be grouped together under the umbrella of positive developmental psychology. This fresh approach to development focuses on the wellbeing aspects of development, while systematically bringing them together (Lomas, et al., 2016).
- Positive parenting is the approach to children’s wellbeing by focusing on the role of parents and caregivers (Latham, 1994).
- Positive education looks at flourishing in the context of school (Seligman, Ernst, Gillham, Reivich, & Linkins, 2009).
- Positive youth development is the productive and constructive focus on adolescence and early adulthood to enhance young people’s strengths and promote positive outcomes (Larson, 2000).
- Positive aging , also known as healthy aging, focuses on the positivity of aging as a healthy, normal stage of life (Vaillant, 2004).
Much of the empirical and theoretical work connected to positive developmental psychology has been going on for years, even before the emergence of positive psychology itself (Lomas et al., 2016).
We recommend this related article Applying Positive Psychology in Schools & Education: Your Ultimate Guide for further reading.

In the classroom, developmental psychology considers children’s psychological, emotional, and intellectual characteristics according to their developmental stage.
A report on the top 20 principles of psychology in the classroom, from pre-kindergarten to high school, was published by the American Psychological Association in 2015. The report also advised how teachers can respond to these principles in the classroom setting.
The top 5 principles and teacher responses are outlined in the table below.
There are many valuable resources to help you foster positive development no matter whether you’re working with young children, teenagers, or adults.
To help get you started, check out the following free resources from around our blog.
- Adopt A Growth Mindset This exercise helps clients recognize instances of fixed mindset in their thinking and actions and replace them with thoughts and behaviors more supportive of a growth mindset.
- Childhood Frustrations This worksheet provides a space for clients to document key challenges experienced during childhood, together with their emotional and behavioral responses.
- What I Want to Be This worksheet helps children identify behaviors and emotions they would like to display and select an opportunity in the future to behave in this ideal way.
- 17 Positive Psychology Exercises If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others enhance their wellbeing, this signature collection contains 17 validated positive psychology tools for practitioners. Use them to help others flourish and thrive.
- Developmental Psychology Courses If you are interested in a career in Developmental Psychology , we suggest 15 of the best courses in this article.

17 Top-Rated Positive Psychology Exercises for Practitioners
Expand your arsenal and impact with these 17 Positive Psychology Exercises [PDF] , scientifically designed to promote human flourishing, meaning, and wellbeing.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
Earlier developmental psychology models and theories were focused on specific areas, such as attachment, psychosexual, cognitive, and social learning. Although informative, they did not take in differing perspectives and were fixed paradigms.
We’ve now come to understand that development is not fixed. Individual differences take place in development, and the factors that can affect development are many. It is ever changing throughout life.
The modern-day approach to developmental psychology includes sub-fields of positive psychology. It brings these differing disciplines together to form an overarching positive developmental psychology paradigm.
Developmental psychology has helped us gain a considerable understanding of children’s motivations, social and emotional contexts, and their strengths and weaknesses.
This knowledge is essential for educators to create rich learning environments for students to help them develop positively and ultimately flourish to their full potential.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free .
- Ainsworth, M. D. S., & Bell, S. M. (1970). Attachment, exploration, and separation: Illustrated by the behavior of one-year-olds in a strange situation. Child Development , 41 , 49–67.
- Ainsworth, M. D. S., Blehar, M. C., Waters, E., & Wall, S. (1978). Patterns of attachment: A psychological study of the strange situation . Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- American Psychological Association. (2015). Top 20 principles from psychology for PREK-12 teaching and learning: Coalition for psychology in schools and education . Retrieved July 16, 2021, from https://www.apa.org/ed/schools/teaching-learning/top-twenty-principles.pdf
- American Psychological Association. (2020). Developmental psychology. Dictionary of Psychology . Retrieved July 20, 2021, from https://dictionary.apa.org/
- Baltes, P. B., Lindenberger, U., & Staudinger, U. M. (2007). Life span theory in developmental psychology. In R. M. Lerner & W. Damon (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology (pp. 569–564). Elsevier.
- Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory . Prentice Hall.
- Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory . Prentice-Hall.
- Bandura, A. Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. (1961). Transmission of aggression through the imitation of aggressive models. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology , 63 , 575–582.
- Baron-Cohen, S., Leslie, A. M., & Frith, U. (1985). Does the autistic child have a ‘theory of mind’? Cognition , 21 (1), 37–46.
- Berger, K. S. (2014). The developing person through the lifespan (9th ed.). Worth.
- Bowlby, J. (1958). The nature of the child’s tie to his mother. International Journal of Psychoanalysis , 39 , 350–371.
- Bowlby, J. (1969). Attachment and loss: Volume 1: Attachment . Hogarth Press.
- Bowlby, J. (1973). Attachment and loss: Volume 2: Anger and anxiety . Hogarth Press.
- Bowlby, J. (1980). Attachment and loss: Volume 3: Loss, sadness and depression . Hogarth Press.
- Brandon, A. R., Pitts, S., Wayne, H., Denton, C., Stringer, A., & Evans, H. M. (2009). A history of the theory of prenatal attachment. Journal of Prenatal and Perinatal Psychological Health , 23 (4), 201–222.
- Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1957). Studies on hysteria . Basic Books.
- Burman, E. (2017). Deconstructing developmental psychology . Routledge.
- Colapinto, J. (2006). As nature made him: The boy who was raised as a girl . Harper Perennial.
- Darwin, C. (1877). A biographical sketch of an infant. Mind, 2 , 285–294.
- Erikson, E. (1959). Psychological issues . International Universities Press.
- Fisher, S., & Greenberg, R. P. (1996). Freud scientifically reappraised: Testing the theories and therapy . John Wiley & Sons.
- Freud, S. (1961). The ego and the id. In J. Strachey (Ed. & Trans.), The standard edition of the complete psychological works of Sigmund Freud (pp. 3–66). Hogarth Press. (Original work published 1923).
- Hall, G. S. (1883). The contents of children’s minds. The Princeton Review , 1 , 249–272.
- Harris, J. R. (1998). The nurture assumption: Why children turn out the way they do . Free Press.
- Kevin, D. (1995). Developmental social psychology: From infancy to old age . Wiley-Blackwell.
- Kubota, T., Miyake, K., & Hirasawa, T. (2012). Epigenetic understanding of gene-environment interactions in psychiatric disorders: A new concept of clinical genetics. Clinical Epigenetics , 4 (1), 1–8.
- Larson, R. W. (2000). Toward a psychology of positive youth development. American Psychologist , 55 (1), 170–183.
- Latham, G. I. (1994). The power of positive parenting . P&T Ink.
- Levitt, M. (2013). Perceptions of nature, nurture and behaviour. Life Sciences Society and Policy , 9 (1), 1–13.
- Lomas, T., Hefferon, K., & Ivtzan, I. (2016). Positive developmental psychology: A review of literature concerning well-being throughout the lifespan. The Journal of Happiness & Well-Being , 4 (2), 143–164.
- Main, M., & Solomon, J. (1986). Discovery of an insecure-disorganized/disoriented attachment pattern. In T. B. Brazelton & M. W. Yogman (Eds.), Affective development in infancy . Ablex.
- Meinhardt-Injac, B., Daum, M. M., & Meinhardt, G. (2020). Theory of mind development from adolescence to adulthood: Testing the two-component model. British Journal of Developmental Psychology , 38 , 289–303.
- Nesterak, E. (2015, July 10). The end of nature versus nature. Behavioral Scientist. Retrieved July 19, 2021 from https://behavioralscientist.org/the-end-of-nature-versus-nurture/
- Papalia, D. E., & Feldman, R. D. (2011). A child’s world: Infancy through adolescence . McGraw-Hill.
- Piaget, J. (1928). La causalité chez l’enfant. British Journal of Psychology , 18 (3), 276–301.
- Piaget, J. (1936). Origins of intelligence in the child . Routledge & Kegan Paul.
- Piaget, J. (1951). Play, dreams and imitation in Childhood (vol. 25). Routledge.
- Premack, D., & Woodruff, G. (1978). Does the chimpanzee have a theory of mind? Behavioral and Brain Sciences , 1 (4), 515–526.
- Preyer, W. T. (1888). The mind of the child: Observations concerning the mental development of the human being in the first years of life (vol. 7). D. Appleton.
- Seligman, M. E. P., Ernst, R. M., Gillham, J., Reivich, K., & Linkins, M. (2009). Positive education: Positive psychology and classroom interventions. Oxford Review of Education , 35 (3), 293–311.
- Silverman, D. K. (2017). Psychosexual stages of development (Freud). In V. Zeigler-Hill & T. Shackelford (Eds.), Encyclopedia of personality and individual differences . Springer.
- Simatwa, E. M. W. (2010). Piaget’s theory of intellectual development and its implications for instructional management at pre-secondary school level. Educational Research Review 5 , 366–371.
- Śmigielski, L., Jagannath, V., Rössler, W., Walitza, S., & Grünblatt, E. (2020). Epigenetic mechanisms in schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders: A systematic review of empirical human findings. Molecular Psychiatr y, 25 (8), 1718–1748.
- Thompson, D. (2016). Developmental psychology in the 1920s: A period of major transition. The Journal of Genetic Psychology , 177 (6), 244–251.
- Vaillant, G. (2004). Positive aging. In P. A. Linley & S. Joseph (Eds.), Positive psychology in practice (pp. 561–580). John Wiley & Sons.
- Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes . Harvard University Press.
- Wadsworth, B. J. (1971). Piaget’s theory of cognitive development: An introduction for students of psychology and education . McKay.
- Wang, Y. G., Wang, Y. Q., Chen, S. L., Zhu, C. Y., & Wang, K. (2008). Theory of mind disability in major depression with or without psychotic symptoms: a componential view. Psychiatry Research , 161 (2), 153–161.
- Washburn, D., Wilson, G., Roes, M., Rnic, K., & Harkness, K. L. (2016). Theory of mind in social anxiety disorder, depression, and comorbid conditions. Journal of Anxiety Disorders , 37 , 71–77.
- Watson, J. B., & Rayner, R. (1920). Conditioned emotional reactions. Journal of Experimental Psychology , 3 (1), 1–14.
- Wellman, H. M., & Liu, D. (2004). Scaling theory of mind tasks. Child Development , 75 , 759–763.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
This article has enticed me to delve deeper into the subject of Positive Psychology. As a primary school teacher, I believe that positive psychology is a field that is imperative to explore. Take my gratitude from the core of my heart for your excellent work.
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Hierarchy of Needs: A 2024 Take on Maslow’s Findings
One of the most influential theories in human psychology that addresses our quest for wellbeing is Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. While Maslow’s theory of [...]

Emotional Development in Childhood: 3 Theories Explained
We have all witnessed a sweet smile from a baby. That cute little gummy grin that makes us smile in return. Are babies born with [...]

Using Classical Conditioning for Treating Phobias & Disorders
Does the name Pavlov ring a bell? Classical conditioning, a psychological phenomenon first discovered by Ivan Pavlov in the late 19th century, has proven to [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (49)
- Coaching & Application (58)
- Compassion (25)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (23)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (30)
- Positive Communication (20)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (18)
- Positive Parenting (15)
- Positive Psychology (34)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (17)
- Relationships (43)
- Resilience & Coping (37)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)
3 Positive Psychology Tools (PDF)

- Bachelor’s Degrees
- Master’s Degrees
- Doctorate Degrees
- Certificate Programs
- Nursing Degrees
- Cybersecurity
- Human Services
- Science & Mathematics
- Communication
- Liberal Arts
- Social Sciences
- Computer Science
- Admissions Overview
- Tuition and Financial Aid
- Incoming Freshman and Graduate Students
- Transfer Students
- Military Students
- International Students
- Early Access Program
- About Maryville
- Our Faculty
- Our Approach
- Our History
- Accreditation
- Tales of the Brave
- Student Support Overview
- Online Learning Tools
- Infographics
Home / Online Bachelor’s Degree Programs / Online Bachelor’s in Human Development and Family Studies / Bachelor’s in Human Development and Family Studies Resources / Stages of Human Development: What It Is & Why It’s Important
What Is Human Development and Why Is It Important? What Is Human Development and Why Is It Important? What Is Human Development and Why Is It Important?
Take your next brave step.
Receive information about the benefits of our programs, the courses you'll take, and what you need to apply.
Tables of Contents
- Eight Stages of Human Development?
- Theories of Human Development
Human Development vs. Developmental Psychology
What are the genetic factors that affect human growth and development, why do we study human growth and development.
Imagine two children born in the same town and the same year to families with similar socioeconomic statuses. One child grows up to be assertive and confident, while the other grows up to be timid and shy. The study of the stages of human development can help explain the reasons for these differences and much more.
What is human development, exactly? Human development is a branch of psychology with the goal of understanding people — how they develop, grow, and change throughout their lives. This discipline, which can help individuals better understand themselves and their relationships, is broad. As such, it can be used in various professional settings and career paths.

What Are the Eight Stages of Human Development?
If human development is the study of how people change throughout their lives, how and when does this development happen? Many scientists and psychologists have studied various aspects of human development, including ego psychologist Erik Erikson. He examined the impact of social experiences throughout an individual’s life and theorized that psychosocial development happens in eight sequential parts . What are the eight stages of human development?
Stage 1 — Infancy: Trust vs. Mistrust
In the first stage of human development, infants learn to trust based on how well their caregivers meet their basic needs and respond when they cry. If an infant cries out to be fed, the parent can either meet this need by feeding and comforting the infant or not meet this need by ignoring the infant. When their needs are met, infants learn that relying on others is safe; when their needs go unmet, infants grow up to be less trusting.
Stage 2 — Toddlerhood: Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
In addition to autonomy versus shame and doubt, another way to think of the second stage is independence versus dependence. Like in the first stage, toddlers go through this stage responding to their caregivers. If caregivers encourage them to be independent and explore the world on their own, toddlers will grow up with a sense of self-efficacy. If the caregivers hover excessively or encourage dependence, these toddlers grow up with less confidence in their abilities.
For example, if a toddler wants to walk without assistance in a safe area, the caregiver should encourage this autonomy by allowing the independent behavior. If the caregiver insists on holding the toddler’s hand even when it’s not necessary, this attention can lead to doubt later in life.
Stage 3 — Preschool Years: Initiative vs. Guilt
During the preschool years, children learn to assert themselves and speak up when they need something. Some children may state that they’re sad because a friend stole their toy. If this assertiveness is greeted with a positive reaction, they learn that taking initiative is helpful behavior. However, if they’re made to feel guilty or ashamed for their assertiveness, they may grow up to be timid and less likely to take the lead.
Stage 4 — Early School Years: Industry vs. Inferiority
When children begin school, they start to compare themselves with peers. If children feel they’re accomplished in relation to peers, they develop strong self-esteem. If, however, they notice that other children have met milestones that they haven’t, they may struggle with self-esteem. For example, a first grader may notice a consistently worse performance on spelling tests when compared with peers. If this becomes a pattern, it can lead to feelings of inferiority.
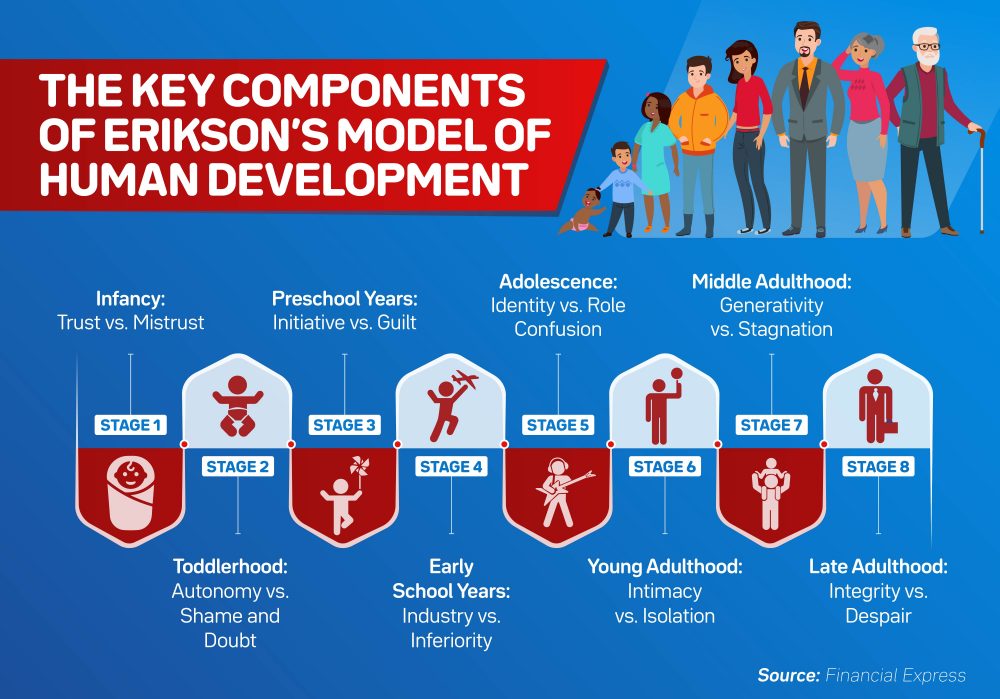
The key components of Erikson’s model of human development include stage one, infancy, trust versus mistrust; stage two, toddlerhood, autonomy versus shame and doubt; stage three, preschool years, initiative versus guilt; stage four, early school years, industry versus inferiority; stage five, adolescence, identity versus role confusion; stage six, young adulthood, intimacy versus isolation; stage seven, middle adulthood, generativity versus stagnation; and stage eight, late adulthood, integrity versus despair.
Back To Top
Stage 5 — Adolescence: Identity vs. Role Confusion
The adolescent stage is where the term “identity crisis” originated, and for good reason. Adolescence is all about developing a sense of self. Adolescents who can clearly identify who they are grow up with stronger goals and self-knowledge than teenagers who struggle to break free of their parents’ or friends’ influences. Adolescents who still deeply depend on their parents for social interaction and guidance may experience more role confusion than teenagers who pursue their own interests.
Stage 6 — Young Adulthood: Intimacy vs. Isolation
In young adulthood, which begins roughly at age 20, people begin to solidify their lifelong bonds; many people enter committed relationships or marriages, while others form lifelong friendships. People who can create and maintain these relationships reap the emotional benefits, while those who struggle to maintain relationships may suffer from isolation. A young adult who develops strong friendships in college may feel more intimacy than one who struggles to form and maintain close friendships.
Stage 7 — Middle Adulthood: Generativity vs. Stagnation
In middle adulthood, people tend to struggle with their contributions to society. They may be busy raising children or pursuing careers. Those who feel that they’re contributing experience generativity, which is the sense of leaving a legacy. On the other hand, those who don’t feel that their work or lives matter may experience feelings of stagnation. For example, a middle-aged adult who’s raising a family and working in a career that presumably helps people may feel more fulfilled than an adult who’s working at a day job that feels meaningless.
Stage 8 — Late Adulthood: Integrity vs. Despair
As adults reach the end of life, they look back on their lives and reflect. Adults who feel fulfilled by their lives, either through a successful family or a meaningful career, reach ego integrity, in which they can face aging and dying with peace. If older adults don’t feel that they’ve lived a good life, they risk falling into despair.
Other Theories of Human Development
Although widely used, Erikson’s psychosocial development theory has been critiqued for focusing too much on childhood. Critics claim that his emphasis makes the model less representative of the growth that people experienced in adulthood. Erikson’s model of the stages of human development is only one theory addressing growth and change throughout life, as many other psychologists have researched their own theories of human development , including the following:
Cognitive Development
Jean Piaget developed the theory of cognitive development. Piaget’s theory is widely used in education programs to prepare teachers to instruct students in developmentally appropriate ways. The theory is based on four stages:
- Sensorimotor — In the sensorimotor stage (birth to 2 years old), children learn object permanence, which is the understanding that people and objects still exist even when they’re out of view.
- Preoperational — In the preoperational stage (2-7 years old), children develop symbolic thought, which is when they begin to progress from concrete to abstract thinking. Children in this stage often have imaginary friends.
- Concrete operational — In the concrete operational stage (7-11 years old), children solidify their abstract thinking and begin to understand cause and effect and logical implications of actions.
- Formal operational — In the formal operational stage (adolescence to adulthood), humans plan for the future, think hypothetically, and assume adult responsibilities.
Moral Development
Lawrence Kohlberg created a theory of human development based on moral development concepts. The theory comprises the following stages:
- Preconventional — In the preconventional stage, people follow rules because they’re afraid of punishment and make choices only with their best interests in mind.
- Conventional — In the conventional stage, people act to avoid society’s judgment and follow rules to maintain the systems and structures that are already in place.
- Postconventional — In the postconventional stage, a genuine concern for the welfare of others and the greater good of society guides people.
Psychosexual Theory
Sigmund Freud popularized the psychosexual theory . The theory comprises five stages:
- Oral — In the oral stage (birth to 1 year old), children learn to suck and swallow and may experience conflict with weaning.
- Anal — In the anal stage (1-3 years old), children learn to withhold or expel feces and may experience conflict with potty training.
- Phallic — In the phallic stage (3-6 years old), children discover that their genitals can give them pleasure.
- Latency — In the latency stage (roughly 6 years old through puberty), they take a break from these physical stages and instead develop mentally and emotionally.
- Genital — In the genital stage (puberty through adulthood), people learn to express themselves sexually.
Ideally, children move through each phase fluidly as their sexual libidos develop, but if they’re stuck in any of the phases, they may develop a fixation that hinders their development.
Behavioral Theory
The behavioral theory focuses solely on a person’s behaviors rather than the feelings that go alongside those behaviors. It suggests that behaviors are conditioned in an environment due to certain stimuli. Behavioral theorists believe that behavior determines feelings, so changing behaviors is important because this will in turn change feelings.
The attachment theory focuses on the deep relationships between people across their lifetime. An important attachment theory finding is that children must develop at least one strong bond in childhood to trust and develop relationships as adults. The attachment theory comprises four stages:
- Asocial or pre-attachment (birth to 6 weeks old)
- Indiscriminate attachment (6 weeks old to 7 months old)
- Specific or discriminate attachment (7-9 months old)
- Multiple attachments (10 months old or later)
Social Learning Theory
The social learning theory builds upon the behavioral theory and postulates that people learn best by observing the behavior of others. They watch how others act, view the consequences, and then make decisions regarding their own behavior accordingly. The four stages in this theory are:
- Reproduction
In the attention stage, people first notice the behavior of others. In the retention stage, they remember the behavior and the resulting consequences. In the reproduction stage, people develop the ability to imitate the behaviors they want to reproduce, and in the motivation stage, they perform these behaviors.
Sociocultural Theory
The sociocultural theory ties human development to the society or culture in which people live. It focuses on the contributions that society as a whole makes to individual human development. For example, children who are raised to play outdoors develop differently from children who are raised to play indoors.
An important part of this theory is the zone of proximal development, which is an area of knowledge and skills slightly more advanced than a child’s current level. The zone of proximal development helps teachers think about and plan instruction, so sociocultural theory plays a large role in preservice teacher training.
Resources: More Information on Theories of Human Development
- BetterHelp, “Behavioral Theory, Behavioral Psychology, or Behaviorism? How Behavior and Personality Intersect ”
- Encyclopedia Britannica, “Lawrence Kohlberg’s Stages of Moral Development”
- Healthline, “What Are Freud’s Psychosexual Stages of Development?”
- PositivePsychology.com, “What Is Attachment Theory? Bowlby’s 4 Stages Explained”
- Psychology Today , Social Learning Theory
- SimplyPsychology, “Lev Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory”
- SimplyPsychology, Theories of Psychology
- Verywell Mind, “The 4 Stages of Cognitive Development”
What are the differences between human development and developmental psychology? These terms are closely related. In fact, the study of developmental psychology is most people’s entry into human development.
Developmental psychology is defined as a scientific approach to explaining growth, change, and consistency throughout a lifetime. It uses various frameworks to understand how people develop and transform throughout their lives. The goals of developmental psychology are to describe, explain, and optimize development to improve people’s lives. In the real world, developmental psychology is used in the study of physical, psychological, emotional, social, personality, and perceptual development.
The study of developmental psychology can lead to careers in several different fields. Developmental psychologists often work in colleges and universities and focus on research and teaching. Others work in healthcare facilities, clinics, assisted living facilities, hospitals, mental health clinics, or homeless shelters. In these applied settings, their focus is more on assessing, evaluating, and treating people. According to June 2020 data from PayScale, developmental psychologists earn an average annual salary of about $68,000 .
One more key element of human growth and development left to explore is genetics . Genetics influences the speed and way in which people develop, though other factors, such as parenting, education, experiences, and socioeconomic factors, are also at play. The multiple genetic factors that affect human growth and development include genetic interactions and sex chromosome abnormalities.
Genetic Interactions
Genes can act in an additive way or sometimes conflict with one another. For example, a child with one tall parent and one short parent may end up between the two of them, at average height. Other times, genes follow a dominant-recessive pattern. If one parent has brown hair and the other has red hair, the red hair gene is the dominant gene if their child has red hair.
Gene-Environment Interactions
Humans’ genetic information is always interacting with the environment, and sometimes this can impact development and growth. For example, if a child in utero is exposed to drugs, the child’s cognitive abilities may be impacted, thus changing the developmental process. In addition, even if a child’s genes would indicate a tall height, if that child experiences poor nutrition as children, it may impact their height.
Sex Chromosome Abnormalities
Sex chromosome abnormalities impact as many as 1 in 500 births. The following syndromes are examples of sex chromosome abnormalities that can impact development:
- Klinefelter syndrome is the presence of an extra X chromosome in males, which can cause physical characteristics such as decreased muscle mass and reduced body hair and may cause learning disabilities.
- Fragile X syndrome is caused by a mutation in the FMR1 gene that makes the X chromosome appear fragile . It can cause intellectual disability, developmental delays, or distinctive physical features such as a long face.
- Turner syndrome happens when one of the X chromosomes is missing or partially missing. It only affects females and results in physical characteristics like short stature and webbed neck.
Down Syndrome
Down syndrome is another common example of how genetics can impact development. This chromosomal disorder may cause some individuals to experience physical or intellectual development differences. Down syndrome occurs at the 21st chromosomal site, in which people with Down syndrome have three chromosomes rather than two.
Those with Down syndrome often have different physical characteristics and may be prone to physical problems like heart defects and hearing problems. Most individuals with Down syndrome have intellectual impairment, but the degree of this impairment varies from person to person.
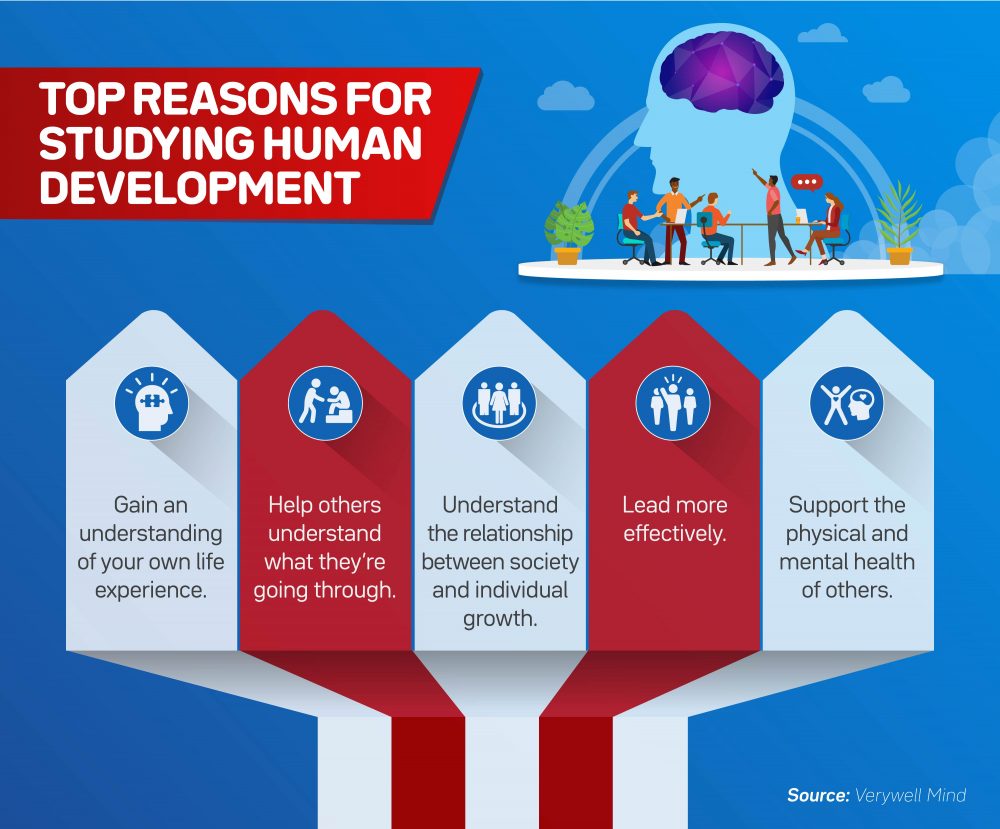
The top reasons for studying human development are to gain an understanding of your own life experience, help others understand what they’re going through, understand the relationship of society and individual growth, lead more effectively, and support the physical and mental health of others.
The study of human growth and development offers a wealth of value for personal and professional growth and understanding. Many reasons exist for why we study human growth and development.
Common benefits include the following:
- To gain a better understanding of one’s own life experiences. This can help people personally reach an understanding of what childhood events shaped their adulthood.
- To gain knowledge of how social context impacts development. This knowledge can be invaluable for professionals like teachers as they gain a deeper understanding of their students.
- To help others understand and contextualize the ups and downs of life. This helps therapists and psychologists better aid their clients in self-discovery.
- To understand how societal change can support growth and development. This understanding helps decision-makers in schools change the educational culture for the better.
- To become a more effective research, teacher, or leader in many different industries. Understanding human development deeply and in context has many professional benefits that can lead to greater insight.
- To support the physical and mental health of individuals throughout their life span. Professionals like doctors, nurses, and therapists must understand human growth and development to better support their clients.
Students may choose to study human growth and development because of its array of applications across many professional fields. For example, students who want to become elementary school teachers may take courses on the stages of human development to understand cognitive development and how children’s brains grow and change.
Human development is a wide-reaching and ever-changing discipline. A knowledge of human development can be invaluable to people personally as they continue to learn and grow throughout their lives and professionally as they learn to apply what they’ve learned to their careers.
Infographic Sources
Financial Express, “The Eight Stages of Human Development”
VeryWell Mind, “5 Reasons to Study Human Development”
Bring us your ambition and we’ll guide you along a personalized path to a quality education that’s designed to change your life.
Erik Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Erikson maintained that personality develops in a predetermined order through eight stages of psychosocial development, from infancy to adulthood. During each stage, the person experiences a psychosocial crisis that could positively or negatively affect personality development.
For Erikson (1958, 1963), these crises are psychosocial because they involve the psychological needs of the individual (i.e., psycho) conflicting with the needs of society (i.e., social).
According to the theory, successful completion of each stage results in a healthy personality and the acquisition of basic virtues. Basic virtues are characteristic strengths that the ego can use to resolve subsequent crises.
Failure to complete a stage can result in a reduced ability to complete further stages and, therefore, a more unhealthy personality and sense of self. These stages, however, can be resolved successfully at a later time.

Stage 1. Trust vs. Mistrust
Trust vs. mistrust is the first stage in Erik Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development. This stage begins at birth continues to approximately 18 months of age. During this stage, the infant is uncertain about the world in which they live, and looks towards their primary caregiver for stability and consistency of care.
Here’s the conflict:
Trust : If the caregiver is reliable, consistent, and nurturing, the child will develop a sense of trust, believing that the world is safe and that people are dependable and affectionate.
This sense of trust allows the child to feel secure even when threatened and extends into their other relationships, maintaining their sense of security amidst potential threats.
Mistrust : Conversely, if the caregiver fails to provide consistent, adequate care and affection, the child may develop a sense of mistrust and insecurity .
This could lead to a belief in an inconsistent and unpredictable world, fostering a sense of mistrust, suspicion, and anxiety.
Under such circumstances, the child may lack confidence in their ability to influence events, viewing the world with apprehension.
Infant Feeding
Feeding is a critical activity during this stage. It’s one of infants’ first and most basic ways to learn whether they can trust the world around them.
It sets the stage for their perspective on the world as being either a safe, dependable place or a place where their needs may not be met.
This consistent, dependable care helps the child feel a sense of security and trust in the caregiver and their environment.
They understand that when they have a need, such as hunger, someone will be there to provide for that need.
These negative experiences can lead to a sense of mistrust in their environment and caregivers.
They may start to believe that their needs may not be met, creating anxiety and insecurity.
Success and Failure In Stage One
Success in this stage will lead to the virtue of hope . By developing a sense of trust, the infant can have hope that as new crises arise, there is a real possibility that other people will be there as a source of support.
Failing to acquire the virtue of hope will lead to the development of fear. This infant will carry the basic sense of mistrust with them to other relationships. It may result in anxiety, heightened insecurities, and an over-feeling mistrust in the world around them.
Consistent with Erikson’s views on the importance of trust, research by Bowlby and Ainsworth has outlined how the quality of the early attachment experience can affect relationships with others in later life.
The balance between trust and mistrust allows the infant to learn that while there may be moments of discomfort or distress, they can rely on their caregiver to provide support.
This helps the infant to build resilience and the ability to cope with stress or adversity in the future.
Stage 2. Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
Autonomy versus shame and doubt is the second stage of Erik Erikson’s stages of psychosocial development. This stage occurs between the ages of 18 months to approximately 3 years. According to Erikson, children at this stage are focused on developing a sense of personal control over physical skills and a sense of independence.
Autonomy : If encouraged and supported in their increased independence, children will become more confident and secure in their ability to survive.
They will feel comfortable making decisions, explore their surroundings more freely, and have a sense of self-control. Achieving this autonomy helps them feel able and capable of leading their lives.
Shame and Doubt : On the other hand, if children are overly controlled or criticized, they may begin to feel ashamed of their autonomy and doubt their abilities.
This can lead to a lack of confidence, fear of trying new things, and a sense of inadequacy about their self-control abilities.
What Happens During This Stage?
The child is developing physically and becoming more mobile, discovering that he or she has many skills and abilities, such as putting on clothes and shoes, playing with toys, etc.
Such skills illustrate the child’s growing sense of independence and autonomy.
For example, during this stage, children begin to assert their independence, by walking away from their mother, picking which toy to play with, and making choices about what they like to wear, to eat, etc.
Toilet Training
This is when children start to exert their independence, taking control over their bodily functions, which can greatly influence their sense of autonomy or shame and doubt.
Autonomy : When parents approach toilet training in a patient, supportive manner, allowing the child to learn at their own pace, the child may feel a sense of accomplishment and autonomy.
They understand they have control over their own bodies and can take responsibility for their actions. This boosts their confidence, instilling a sense of autonomy and a belief in their ability to manage personal tasks.
Shame and Doubt : Conversely, if the process is rushed, if there’s too much pressure, or if parents respond with anger or disappointment to accidents, the child may feel shame and start doubting their abilities.
They may feel bad about their mistakes, and this can lead to feelings of shame, self-doubt, and a lack of confidence in their autonomy.
Success and Failure In Stage Two
Erikson states parents must allow their children to explore the limits of their abilities within an encouraging environment that is tolerant of failure.
Success in this stage will lead to the virtue of will . If children in this stage are encouraged and supported in their increased independence, they become more confident and secure in their own ability to survive in the world.
The infant develops a sense of personal control over physical skills and a sense of independence.
Suppose children are criticized, overly controlled, or not given the opportunity to assert themselves. In that case, they begin to feel inadequate in their ability to survive, and may then become overly dependent upon others, lack self-esteem , and feel a sense of shame or doubt in their abilities.
How Can Parents Encourage a Sense of Control?
Success leads to feelings of autonomy, and failure results in shame and doubt.
Erikson states it is critical that parents allow their children to explore the limits of their abilities within an encouraging environment that is tolerant of failure.
For example, rather than put on a child’s clothes, a supportive parent should have the patience to allow the child to try until they succeed or ask for assistance.
So, the parents need to encourage the child to become more independent while at the same time protecting the child so that constant failure is avoided.
A delicate balance is required from the parent. They must try not to do everything for the child, but if the child fails at a particular task, they must not criticize the child for failures and accidents (particularly when toilet training).
The aim has to be “self-control without a loss of self-esteem” (Gross, 1992).
The balance between autonomy and shame and doubt allows the child to understand that while they can’t always control their environment, they can exercise control over their actions and decisions, thus developing self-confidence and resilience.
Stage 3. Initiative vs. Guilt
Initiative versus guilt is the third stage of Erik Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development. During the initiative versus guilt stage, children assert themselves more frequently through directing play and other social interaction.
Initiative : When caregivers encourage and support children to take the initiative, they can start planning activities, accomplish tasks, and face challenges.
The children will learn to take the initiative and assert control over their environment.
They can begin to think for themselves, formulate plans, and execute them, which helps foster a sense of purpose.
Guilt : If caregivers discourage the pursuit of independent activities or dismiss or criticize their efforts, children may feel guilty about their desires and initiatives.
This could potentially lead to feelings of guilt, self-doubt, and lack of initiative.
These are particularly lively, rapid-developing years in a child’s life. According to Bee (1992), it is a “time of vigor of action and of behaviors that the parents may see as aggressive.”
During this period, the primary feature involves the child regularly interacting with other children at school. Central to this stage is play, as it allows children to explore their interpersonal skills through initiating activities.
The child begins to assert control and power over their environment by planning activities, accomplishing tasks, and facing challenges.
Exploration
Here’s why exploration is important:
Developing Initiative : Exploration allows children to assert their power and control over their environment. Through exploration, children engage with their surroundings, ask questions, and discover new things.
This active engagement allows them to take the initiative and make independent choices, contributing to their autonomy and confidence.
Learning from Mistakes : Exploration also means making mistakes, and these provide crucial learning opportunities. Even if a child’s efforts lead to mistakes or failures, they learn to understand cause and effect and their role in influencing outcomes.
Building Self-Confidence : When caregivers support and encourage a child’s explorations and initiatives, it bolsters their self-confidence. They feel their actions are valuable and significant, which encourages them to take more initiative in the future.
Mitigating Guilt : If caregivers respect the child’s need for exploration and do not overly criticize their mistakes, it helps prevent feelings of guilt. Instead, the child learns it’s okay to try new things and perfectly fine to make mistakes.
Success and Failure In Stage Three
Children begin to plan activities, make up games, and initiate activities with others. If given this opportunity, children develop a sense of initiative and feel secure in their ability to lead others and make decisions. Success at this stage leads to the virtue of purpose .
Conversely, if this tendency is squelched, either through criticism or control, children develop a sense of guilt . The child will often overstep the mark in his forcefulness, and the danger is that the parents will tend to punish the child and restrict his initiative too much.
It is at this stage that the child will begin to ask many questions as his thirst for knowledge grows. If the parents treat the child’s questions as trivial, a nuisance, or embarrassing or other aspects of their behavior as threatening, the child may feel guilty for “being a nuisance”.
Too much guilt can slow the child’s interaction with others and may inhibit their creativity. Some guilt is, of course, necessary; otherwise the child would not know how to exercise self-control or have a conscience.
A healthy balance between initiative and guilt is important.
The balance between initiative and guilt during this stage can help children understand that it’s acceptable to take charge and make their own decisions, but there will also be times when they must follow the rules or guidelines set by others. Successfully navigating this stage develops the virtue of purpose.
How Can Parents Encourage a Sense of Exploration?
In this stage, caregivers must provide a safe and supportive environment that allows children to explore freely. This nurtures their initiative, helps them develop problem-solving skills, and builds confidence and resilience.
By understanding the importance of exploration and providing the right support, caregivers can help children navigate this stage successfully and minimize feelings of guilt.
Stage 4. Industry vs. Inferiority
Erikson’s fourth psychosocial crisis, involving industry (competence) vs. Inferiority occurs during childhood between the ages of five and twelve. In this stage, children start to compare themselves with their peers to gauge their abilities and worth.
Industry : If children are encouraged by parents and teachers to develop skills, they gain a sense of industry—a feeling of competence and belief in their skills.
They start learning to work and cooperate with others and begin to understand that they can use their skills to complete tasks. This leads to a sense of confidence in their ability to achieve goals.
Inferiority : On the other hand, if children receive negative feedback or are not allowed to demonstrate their skills, they may develop a sense of inferiority.
They may start to feel that they aren’t as good as their peers or that their efforts aren’t valued, leading to a lack of self-confidence and a feeling of inadequacy.
The child is coping with new learning and social demands.
Children are at the stage where they will be learning to read and write, to do sums, and to do things on their own. Teachers begin to take an important role in the child’s life as they teach specific skills.
At this stage, the child’s peer group will gain greater significance and become a major source of the child’s self-esteem.
The child now feels the need to win approval by demonstrating specific competencies valued by society and develop a sense of pride in their accomplishments.
This stage typically occurs during the elementary school years, from approximately ages 6 to 11, and the experiences children have in school can significantly influence their development.
Here’s why:
Development of Industry : At school, children are given numerous opportunities to learn, achieve, and demonstrate their competencies. They work on various projects, participate in different activities, and collaborate with their peers.
These experiences allow children to develop a sense of industry, reinforcing their confidence in their abilities to accomplish tasks and contribute effectively.
Social Comparison : School provides a context where children can compare themselves to their peers.
They gauge their abilities and achievements against those of their classmates, which can either help build their sense of industry or lead to feelings of inferiority, depending on their experiences and perceptions.
Feedback and Reinforcement : Teachers play a crucial role during this stage. Their feedback can either reinforce the child’s sense of industry or trigger feelings of inferiority.
Encouraging feedback enhances the child’s belief in their skills, while persistent negative feedback can lead to a sense of inferiority.
Building Life Skills : School also provides opportunities for children to develop crucial life skills, like problem-solving, teamwork, and time management. Successfully acquiring and utilizing these skills promotes a sense of industry.
Dealing with Failure : School is where children may encounter academic difficulties or fail for the first time.
How they learn to cope with these situations— and how teachers and parents guide them through these challenges—can influence whether they develop a sense of industry or inferiority.
Success and Failure In Stage Four
Success leads to the virtue of competence , while failure results in feelings of inferiority .
If children are encouraged and reinforced for their initiative, they begin to feel industrious (competence) and confident in their ability to achieve goals.
If this initiative is not encouraged, if parents or teacher restricts it, then the child begins to feel inferior, doubting his own abilities, and therefore may not reach his or her potential.
If the child cannot develop the specific skill they feel society demands (e.g., being athletic), they may develop a sense of Inferiority.
Some failure may be necessary so that the child can develop some modesty. Again, a balance between competence and modesty is necessary.
The balance between industry and inferiority allows children to recognize their skills and understand that they have the ability to work toward and achieve their goals, even if they face challenges along the way.
How Can Parents & Teachers Encourage a Sense of Exploration?
In this stage, teachers and parents need to provide consistent, constructive feedback and encourage effort, not just achievement.
This approach helps foster a sense of industry, competence, and confidence in children, reducing feelings of inferiority.
Stage 5. Identity vs. Role Confusion
The fifth stage of Erik Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development is identity vs. role confusion, and it occurs during adolescence, from about 12-18 years. During this stage, adolescents search for a sense of self and personal identity, through an intense exploration of personal values, beliefs, and goals.
Identity : If adolescents are supported in their exploration and given the freedom to explore different roles, they are likely to emerge from this stage with a strong sense of self and a feeling of independence and control.
This process involves exploring their interests, values, and goals, which helps them form their own unique identity.
Role Confusion : If adolescents are restricted and not given the space to explore or find the process too overwhelming or distressing, they may experience role confusion.
This could mean being unsure about one’s place in the world, values, and future direction. They may struggle to identify their purpose or path, leading to confusion about their personal identity.
During adolescence, the transition from childhood to adulthood is most important. Children are becoming more independent and looking at the future regarding careers, relationships, families, housing, etc.
The individual wants to belong to a society and fit in.
Teenagers explore who they are as individuals, seek to establish a sense of self, and may experiment with different roles, activities, and behaviors.
According to Erikson, this is important to forming a strong identity and developing a sense of direction in life.
The adolescent mind is essentially a mind or moratorium, a psychosocial stage between childhood and adulthood, between the morality learned by the child and the ethics to be developed by the adult (Erikson, 1963, p. 245).
This is a major stage of development where the child has to learn the roles he will occupy as an adult. During this stage, the adolescent will re-examine his identity and try to find out exactly who he or she is.
Erikson suggests that two identities are involved: the sexual and the occupational.
Social Relationships
Given the importance of social relationships during this stage, it’s crucial for adolescents to have supportive social networks that encourage healthy exploration of identity.
It’s also important for parents, teachers, and mentors to provide guidance as adolescents navigate their social relationships and roles.
Formation of Identity : Social relationships provide a context within which adolescents explore different aspects of their identity.
They try on different roles within their peer groups, allowing them to discover their interests, beliefs, values, and goals. This exploration is key to forming their own unique identity.
Peer Influence : Peer groups often become a significant influence during this stage. Adolescents often start to place more value on the opinions of their friends than their parents.
How an adolescent’s peer group perceives them can impact their sense of self and identity formation.
Social Acceptance and Belonging : Feeling accepted and fitting in with peers can significantly affect an adolescent’s self-esteem and sense of identity.
They are more likely to develop a strong, positive identity if they feel accepted and valued. Feeling excluded or marginalized may lead to role confusion and a struggle with identity formation.
Experiencing Diversity : Interacting with a diverse range of people allows adolescents to broaden their perspectives, challenge their beliefs, and shape their values.
This diversity of experiences can also influence the formation of their identity.
Conflict and Resolution : Social relationships often involve conflict and the need for resolution, providing adolescents with opportunities to explore different roles and behaviors.
Learning to navigate these conflicts aids in the development of their identity and the social skills needed in adulthood.
Success and Failure In Stage Five
According to Bee (1992), what should happen at the end of this stage is “a reintegrated sense of self, of what one wants to do or be, and of one’s appropriate sex role”. During this stage, the body image of the adolescent changes.
Erikson claims adolescents may feel uncomfortable about their bodies until they can adapt and “grow into” the changes. Success in this stage will lead to the virtue of fidelity .
Fidelity involves being able to commit one’s self to others on the basis of accepting others, even when there may be ideological differences.
During this period, they explore possibilities and begin to form their own identity based on the outcome of their explorations.
Adolescents who establish a strong sense of identity can maintain consistent loyalties and values, even amidst societal shifts and changes.
Erikson described 3 forms of identity crisis:
- severe (identity confusion overwhelms personal identity)
- prolonged (realignment of childhood identifications over an extended time)
- aggravated (repeated unsuccessful attempts at resolution)
Failure to establish a sense of identity within society (“I don’t know what I want to be when I grow up”) can lead to role confusion.
However, if adolescents don’t have the support, time, or emotional capacity to explore their identity, they may be left with unresolved identity issues, feeling unsure about their roles and uncertain about their future.
This could potentially lead to a weak sense of self, role confusion, and lack of direction in adulthood.
Role confusion involves the individual not being sure about themselves or their place in society.
In response to role confusion or identity crisis , an adolescent may begin to experiment with different lifestyles (e.g., work, education, or political activities).
Also, pressuring someone into an identity can result in rebellion in the form of establishing a negative identity, and in addition to this feeling of unhappiness.
Stage 6. Intimacy vs. Isolation
Intimacy versus isolation is the sixth stage of Erik Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development. This stage takes place during young adulthood between the ages of approximately 18 to 40 yrs. During this stage, the major conflict centers on forming intimate, loving relationships with other people.
Intimacy : Individuals who successfully navigate this stage are able to form intimate, reciprocal relationships with others.
They can form close bonds and are comfortable with mutual dependency. Intimacy involves the ability to be open and share oneself with others, as well as the willingness to commit to relationships and make personal sacrifices for the sake of these relationships.
Isolation : If individuals struggle to form these close relationships, perhaps due to earlier unresolved identity crises or fear of rejection, they may experience isolation.
Isolation refers to the inability to form meaningful, intimate relationships with others. This could lead to feelings of loneliness, alienation, and exclusion.
Success and Failure In Stage Six
Success leads to strong relationships, while failure results in loneliness and isolation.
Successfully navigating this stage develops the virtue of love . Individuals who develop this virtue have the ability to form deep and committed relationships based on mutual trust and respect.
During this stage, we begin to share ourselves more intimately with others. We explore relationships leading toward longer-term commitments with someone other than a family member.
Successful completion of this stage can result in happy relationships and a sense of commitment, safety, and care within a relationship.
However, if individuals struggle during this stage and are unable to form close relationships, they may feel isolated and alone. This could potentially lead to a sense of disconnection and estrangement in adulthood.
Avoiding intimacy and fearing commitment and relationships can lead to isolation, loneliness, and sometimes depression.
Stage 7. Generativity vs. Stagnation
Generativity versus stagnation is the seventh of eight stages of Erik Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development. This stage takes place during during middle adulthood (ages 40 to 65 yrs). During this stage, individuals focus more on building our lives, primarily through our careers, families, and contributions to society.
Generativity : If individuals feel they are making valuable contributions to the world, for instance, through raising children or contributing to positive changes in society, they will feel a sense of generativity.
Generativity involves concern for others and the desire to contribute to future generations, often through parenting, mentoring, leadership roles, or creative output that adds value to society.
Stagnation : If individuals feel they are not making a positive impact or are not involved in productive or creative tasks, they may experience stagnation.
Stagnation involves feeling unproductive and uninvolved, leading to self-absorption, lack of growth, and feelings of emptiness.
Psychologically, generativity refers to “making your mark” on the world through creating or nurturing things that will outlast an individual.
During middle age, individuals experience a need to create or nurture things that will outlast them, often having mentees or creating positive changes that will benefit other people.
We give back to society by raising our children, being productive at work, and participating in community activities and organizations. We develop a sense of being a part of the bigger picture through generativity.
Work & Parenthood
Both work and parenthood are important in this stage as they provide opportunities for adults to extend their personal and societal influence.
Work : In this stage, individuals often focus heavily on their careers. Meaningful work is a way that adults can feel productive and gain a sense of contributing to the world.
It allows them to feel that they are part of a larger community and that their efforts can benefit future generations. If they feel accomplished and valued in their work, they experience a sense of generativity.
However, if they’re unsatisfied with their career or feel unproductive, they may face feelings of stagnation.
Parenthood : Raising children is another significant aspect of this stage. Adults can derive a sense of generativity from nurturing the next generation, guiding their development, and imparting their values.
Through parenthood, adults can feel they’re making a meaningful contribution to the future.
On the other hand, individuals who choose not to have children or those who cannot have children can also achieve generativity through other nurturing behaviors, such as mentoring or engaging in activities that positively impact the younger generation.
Success and Failure In Stage Seven
If adults can find satisfaction and a sense of contribution through these roles, they are more likely to develop a sense of generativity, leading to feelings of productivity and fulfillment.
Successfully navigating this stage develops the virtue of care . Individuals who develop this virtue feel a sense of contribution to the world, typically through family and work, and feel satisfied that they are making a difference.
Success leads to feelings of usefulness and accomplishment, while failure results in shallow involvement in the world.
We become stagnant and feel unproductive by failing to find a way to contribute. These individuals may feel disconnected or uninvolved with their community and with society as a whole.
This could potentially lead to feelings of restlessness and unproductiveness in later life.
Stage 8. Ego Integrity vs. Despair
Ego integrity versus despair is the eighth and final stage of Erik Erikson’s stage theory of psychosocial development. This stage begins at approximately age 65 and ends at death. It is during this time that we contemplate our accomplishments and can develop integrity if we see ourselves as leading a successful life.
Ego Integrity : If individuals feel they have lived a fulfilling and meaningful life, they will experience ego integrity.
This is characterized by a sense of acceptance of their life as it was, the ability to find coherence and purpose in their experiences, and a sense of wisdom and fulfillment.
Despair : On the other hand, if individuals feel regretful about their past, feel they have made poor decisions, or believe they’ve failed to achieve their life goals, they may experience despair.
Despair involves feelings of regret, bitterness, and disappointment with one’s life, and a fear of impending death.
This stage takes place after age 65 and involves reflecting on one’s life and either moving into feeling satisfied and happy with one’s life or feeling a deep sense of regret.
Erikson described ego integrity as “the acceptance of one’s one and only life cycle as something that had to be” (1950, p. 268) and later as “a sense of coherence and wholeness” (1982, p. 65).
As we grow older (65+ yrs) and become senior citizens, we tend to slow down our productivity and explore life as retired people.
Success and Failure In Stage Eight
Success in this stage will lead to the virtue of wisdom . Wisdom enables a person to look back on their life with a sense of closure and completeness, and also accept death without fear.
Individuals who reflect on their lives and regret not achieving their goals will experience bitterness and despair.
Erik Erikson believed if we see our lives as unproductive, feel guilt about our past, or feel that we did not accomplish our life goals, we become dissatisfied with life and develop despair, often leading to depression and hopelessness.
This could potentially lead to feelings of fear and dread about their mortality.
A continuous state of ego integrity does not characterize wise people, but they experience both ego integrity and despair. Thus, late life is characterized by integrity and despair as alternating states that must be balanced.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Erikson’s Theory
By extending the notion of personality development across the lifespan, Erikson outlines a more realistic perspective of personality development, filling a major gap in Freud’s emphasis on childhood. (McAdams, 2001).
- Based on Erikson’s ideas, psychology has reconceptualized how the later periods of life are viewed. Middle and late adulthood are no longer viewed as irrelevant, because of Erikson, they are now considered active and significant times of personal growth.
- Erikson’s theory has good face validity . Many people find they can relate to his theories about various life cycle stages through their own experiences.
Indeed, Erikson (1964) acknowledges his theory is more a descriptive overview of human social and emotional development that does not adequately explain how or why this development occurs.
For example, Erikson does not explicitly explain how the outcome of one psychosocial stage influences personality at a later stage.
Erikson also does not explain what propels the individual forward into the next stage once a crisis is resolved. His stage model implies strict sequential progression tied to age, but does not address variations in timing or the complexity of human development.
However, Erikson stressed his work was a ‘tool to think with rather than a factual analysis.’ Its purpose then is to provide a framework within which development can be considered rather than testable theory.
The lack of elucidation of the dynamics makes it challenging to test Erikson’s stage progression hypotheses empirically. Contemporary researchers have struggled to operationalize the stages and validate their universal sequence and age ranges.
Erikson based his theory of psychosocial development primarily on observations of middle-class White children and families in the United States and Europe. This Western cultural perspective may limit the universality of the stages he proposed.
The conflicts emphasized in each stage reflect values like independence, autonomy, and productivity, which are deeply ingrained in Western individualistic cultures. However, the theory may not translate well to more collectivistic cultures that value interdependence, social harmony, and shared responsibility.
For example, the autonomy vs. shame and doubt crisis in early childhood may play out differently in cultures where obedience and conformity to elders is prioritized over individual choice. Likewise, the identity crisis of adolescence may be less pronounced in collectivist cultures.
As an illustration, the identity crisis experienced in adolescence often resurfaces as adults transition into retirement (Logan, 1986). Although the context differs, managing similar emotional tensions promotes self-awareness and comprehension of lifelong developmental dynamics.
Applications
Retirees can gain insight into retirement challenges by recognizing the parallels between current struggles and earlier psychosocial conflicts.
Retirees often revisit identity issues faced earlier in life when adjusting to retirement. Although the contexts differ, managing similar emotional tensions can increase self-awareness and understanding of lifelong psychodynamics.
Cultural sensitivity can increase patient self-awareness during counseling. For example, nurses could use the model to help adolescents tackle identity exploration or guide older adults in finding purpose and integrity.
Recent research shows the ongoing relevance of Erikson’s theory across the lifespan. A 2016 study found a correlation between middle-aged adults’ sense of generativity and their cognitive health, emotional resilience, and executive function.
Interprofessional teams could collaborate to create stage-appropriate, strengths-based care plans. For instance, occupational therapists could engage nursery home residents in reminiscence therapy to increase ego integrity.
Specific tools allow clinicians to identify patients’ current psychosocial stage. Nurses might use Erikson’s Psychosocial Stage Inventory (EPSI) to reveal trust, autonomy, purpose, or despair struggles.
With this insight, providers can deliver targeted interventions to resolve conflicts and support developmental advancement. For example, building autonomy after a major health crisis or fostering generativity by teaching parenting skills.
Erikson vs Maslow
How does Maslow’s hierarchy of needs differ from Erikson’s stages of psychosocial development?

Erikson vs Freud
Freud (1905) proposed a five-stage model of psychosexual development spanning infancy to puberty, focused on the maturation of sexual drives. While groundbreaking, Freud’s theory had limitations Erikson (1958, 1963) aimed to overcome.
- Erikson expanded the timeline through the full lifespan, while Freud focused only on the first few years of life. This more holistic perspective reflected the ongoing social challenges confronted into adulthood and old age.
- Whereas Freud highlighted biological, pleasure-seeking drives, Erikson incorporated the influence of social relationships, culture, and identity formation on personality growth. This broader psychosocial view enhanced realism.
- Erikson focused on the ego’s growth rather than the primacy of the id. He saw personality developing through negotiation of social conflicts rather than only frustration/gratification of innate drives.
- Erikson organized the stages around psychosocial crises tied to ego maturation rather than psychosexual erogenous zones. This reformulation felt more relevant to personal experiences many could identify with.
- Finally, Erikson emphasized healthy progression through the stages rather than psychopathology stemming from fixation. He took a strengths-based perspective focused on human potential.
Summary Table
Like Freud and many others, Erik Erikson maintained that personality develops in a predetermined order, and builds upon each previous stage. This is called the epigenetic principle.
Erikson’s eight stages of psychosocial development include:
Bee, H. L. (1992). The developing child . London: HarperCollins.
Brown, C., & Lowis, M. J. (2003). Psychosocial development in the elderly: An investigation into Erikson’s ninth stage. Journal of Aging Studies, 17 (4), 415–426.
Erikson, E. H. (1950). Childhood and society . New York: Norton.
Erickson, E. H. (1958). Young man Luther: A study in psychoanalysis and history . New York: Norton.
Erikson, E. H. (1963). Youth: Change and challenge . New York: Basic books.
Erikson, E. H. (1964). Insight and responsibility . New York: Norton.
Erikson, E. H. (1968). Identity: Youth and crisis . New York: Norton.
Erikson E. H . (1982). The life cycle completed . New York: W.W. Norton & Company.
Erikson, E. H. (1959). Psychological issues . New York, NY: International University Press
Fadjukoff, P., Pulkkinen, L., & Kokko, K. (2016). Identity formation in adulthood: A longitudinal study from age 27 to 50. Identity , 16 (1), 8-23.
Freud, S. (1905). Three essays on the theory of sexuality. Standard Edition 7 : 123- 246.
Freud, S. (1923). The ego and the id . SE, 19: 1-66.
Gross, R. D., & Humphreys, P. (1992). Psychology: The science of mind and behavior . London: Hodder & Stoughton.
Logan , R.D . ( 1986 ). A reconceptualization of Erikson’s theory: The repetition of existential and instrumental themes. Human Development, 29 , 125 – 136.
Malone, J. C., Liu, S. R., Vaillant, G. E., Rentz, D. M., & Waldinger, R. J. (2016). Midlife Eriksonian psychosocial development: Setting the stage for late-life cognitive and emotional health. Developmental Psychology , 52 (3), 496.
McAdams, D. P. (2001). The psychology of life stories . Review of General Psychology , 5(2), 100.
McCrae, R. R., & Costa Jr, P. T. (1997). Personality trait structure as a human universal . American Psychologist, 52(5) , 509.
Meeus, W., van de Schoot, R., Keijsers, L., & Branje, S. (2012). Identity statuses as developmental trajectories: A five-wave longitudinal study in early-to-middle and middle-to-late adolescents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence , 41 , 1008-1021.
Osborne, J. W. (2009). Commentary on retirement, identity, and Erikson’s developmental stage model. Canadian Journal on Aging/La Revue canadienne du vieillissement , 28 (4), 295-301.
Rosenthal, D. A., Gurney, R. M., & Moore, S. M. (1981). From trust on intimacy: A new inventory for examining Erikson’s stages of psychosocial development. Journal of Youth and Adolescence , 10 (6), 525-537.
Sica, L. S., Aleni Sestito, L., Syed, M., & McLean, K. (2018). I became adult when… Pathways of identity resolution and adulthood transition in Italian freshmen’s narratives. Identity , 18 (3), 159-177.
Vogel-Scibilia, S. E., McNulty, K. C., Baxter, B., Miller, S., Dine, M., & Frese, F. J. (2009). The recovery process utilizing Erikson’s stages of human development. Community Mental Health Journal , 45 , 405-414.
What is Erikson’s main theory?
Erikson said that we all want to be good at certain things in our lives. According to psychosocial theory, we go through eight developmental stages as we grow up, from being a baby to an old person. In each stage, we have a challenge to overcome.
If we do well in these challenges, we feel confident, our personality grows healthily, and we feel competent. But if we don’t do well, we might feel like we’re not good enough, leading to feelings of inadequacy.
What is an example of Erikson’s psychosocial theory?
Throughout primary school (ages 6-12), children encounter the challenge of balancing industry and inferiority. During this period, they start comparing themselves to their classmates to evaluate their own standing.
As a result, they may either cultivate a feeling of pride and achievement in their academics, sports, social engagements, and family life or experience a sense of inadequacy if they fall short.
Parents and educators can implement various strategies and techniques to support children in fostering a sense of competence and self-confidence.
Related Articles

Child Psychology
Vygotsky vs. Piaget: A Paradigm Shift

Interactional Synchrony

Internal Working Models of Attachment

Freudian Psychology
Attachment Theory and Psychoanalysis

Soft Determinism In Psychology

Branches of Psychology
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Understanding Developmental Psychology
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Daniel B. Block, MD, is an award-winning, board-certified psychiatrist who operates a private practice in Pennsylvania.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/block-8924ca72ff94426d940e8f7e639e3942.jpg)
- Seeking Treatment
Frequently Asked Questions
Change is inevitable. As humans, we constantly grow throughout our lifespans, from conception to death. The field of developmental psychology explores the behavioral, emotional, physical, and cognitive changes that happen as people age.
Psychologists strive to understand and explain how and why people change throughout life. While many of these changes are normal and expected, they can still pose challenges that people sometimes need extra assistance to manage.
The principles of normative development help professionals spot potential problems and provide early intervention for better outcomes. Developmental psychologists can work with people of all ages to address roadblocks and support growth, although some choose to specialize in a specific age group such as childhood, adulthood, or old age.
What Is Developmental Psychology?
Developmental psychology is the branch of psychology that focuses on how people grow and change over the course of a lifetime.
Those who specialize in this field are not just concerned with the physical changes that occur as people grow; they also look at the social, emotional, and cognitive development that occurs throughout life.
Some of the many issues developmental psychologists assist with include:
- Cognitive development during childhood and throughout life
- Developmental challenges and learning disabilities
- Emotional development
- Language acquisition
- Moral reasoning
- Motor skill development
- Personality development
- Self-awareness and self-concept
- Social and cultural influences on child development
These professionals spend a great deal of time investigating and observing how these processes occur under normal circumstances, but they are also interested in learning about things that can disrupt developmental processes.
By better understanding how and why people change and grow, developmental psychologists help people live up to their full potential. Understanding the course of normal human development and recognizing potential problems early on can prevent difficulties with depression, low self-esteem, frustration, and low achievement in school.
Developmental Psychology Theories
Developmental psychologists often utilize a number of theories to think about different aspects of human development. For example, a psychologist assessing intellectual development in a child might consider Piaget's theory of cognitive development , which outlined the key stages that children go through as they learn.
A psychologist working with a child might also want to consider how the child's relationships with caregivers influences his or her behaviors, and so turn to Bowlby's theory of attachment .
Psychologists are also interested in looking at how social relationships influence the development of both children and adults. Erikson's theory of psychosocial development and Vygotsky's theory of sociocultural development are two popular theoretical frameworks that address the social influences on the developmental process.
Each approach tends to stress different aspects of development such as mental, social, or parental influences on how children grow and progress .
When to See a Developmental Psychologist
While development tends to follow a fairly predictable pattern, there are times when things might go off course. Parents often focus on what are known as developmental milestones, which represent abilities that most children tend to display by a certain point in development. These typically focus on one of four different areas:
- Physical milestones
- Cognitive milestones
- Social/emotional milestones
- Communication milestones
For example, walking is one physical milestone that most children achieve sometime between the ages of 9 and 15 months. If a child is not walking or attempting to walk by 16 to 18 months, parents might consider consulting with their family physician to determine if a developmental issue might be present.
While all children develop at different rates, when a child fails to meet certain milestones by a certain age, there may be cause for concern.
By being aware of these milestones, parents can seek assistance, and healthcare professionals can offer interventions that can help kids overcome developmental delays.
These professionals often evaluate children to determine if a developmental delay might be present, or they might work with elderly patients who are facing health concerns associated with old age such as cognitive declines, physical struggles, emotional difficulties, or degenerative brain disorders.
Developmental psychologists can provide support to individuals at all points of life who may be facing developmental issues or problems related to aging.
Developmental Psychology Stages
As you might imagine, developmental psychologists often break down development according to various phases of life. Each of these periods of development represents a time when different milestones are typically achieved.
People may face particular challenges at each point, and developmental psychologists can often help people who might be struggling with problems to get back on track.
Prenatal Development
The prenatal period is of interest to developmental psychologists who seek to understand how the earliest influences on development can impact later growth during childhood. Psychologists may look at how primary reflexes emerge before birth, how fetuses respond to stimuli in the womb, and the sensations and perceptions that fetuses are capable of detecting prior to birth.
Developmental psychologists may also look at potential problems such as Down syndrome, maternal drug use, and inherited diseases that might have an impact on the course of future development.
Early Childhood Development
The period from infancy through early childhood is a time of remarkable growth and change. Developmental psychologists look at things such as the physical, cognitive, and emotional growth that takes place during this critical period of development.
In addition to providing interventions for potential developmental problems at this point, psychologists are also focused on helping kids achieve their full potential . Parents and healthcare experts are often on the lookout to ensure that kids are growing properly, receiving adequate nutrition, and achieving cognitive milestones appropriate for their age.
Middle Childhood Development
This period of development is marked by both physical maturation and the increased importance of social influences as children make their way through elementary school.
Kids begin to make their mark on the world as they form friendships, gain competency through schoolwork, and continue to build their unique sense of self. Parents may seek the assistance of a developmental psychologist to help kids deal with potential problems that might arise at this age including social, emotional, and mental health issues.
Adolescent Development
The teenage years are often the subject of considerable interest as children experience the psychological turmoil and transition that often accompanies this period of development. Psychologists such as Erik Erikson were especially interested in looking at how navigating this period leads to identity formation .
At this age, kids often test limits and explore new identities as they explore the question of who they are and who they want to be. Developmental psychologists can help support teens as they deal with some of the challenging issues unique to the adolescent period including puberty, emotional turmoil, and social pressure.
Early Adult Development
This period of life is often marked by forming and maintaining relationships. Critical milestones during early adulthood may include forming bonds, intimacy, close friendships, and starting a family.
Those who can build and sustain such relationships tend to experience connectedness and social support while those who struggle with such relationships may be left feeling alienated and lonely .
People facing such issues might seek the assistance of a developmental psychologist in order to build healthier relationships and combat emotional difficulties.
Middle Adult Development
This stage of life tends to center on developing a sense of purpose and contributing to society. Erikson described this as the conflict between generativity and stagnation .
Those who engage in the world, contribute things that will outlast them, and leave a mark on the next generation emerge with a sense of purpose. Activities such as careers, families, group memberships, and community involvement are all things that can contribute to this feeling of generativity.
Older Adult Development
The senior years are often viewed as a period of poor health, yet many older adults are capable of remaining active and busy well into their 80s and 90s. Increased health concerns mark this period of development, and some individuals may experience mental declines related to dementia.
Theorist Erik Erikson also viewed the elder years as a time of reflection back on life . Those who are able to look back and see a life well-lived emerge with a sense of wisdom and readiness to face the end of their lives, while those who look back with regret may be left with feelings of bitterness and despair.
Developmental psychologists may work with elderly patients to help them cope with issues related to the aging process.
Diagnosing Developmental Issues
To determine if a developmental problem is present, a psychologist or other highly trained professional may administer either a developmental screening or evaluation.
For children, such an evaluation typically involves interviews with parents and other caregivers to learn about behaviors they may have observed, a review of a child's medical history, and standardized testing to measure functioning in terms of communication, social/emotional skills, physical/motor development, and cognitive skills.
If a problem is found to be present, the patient may then be referred to a specialist such as a speech-language pathologist, physical therapist, or occupational therapist.
A Word From Verywell
Receiving a diagnosis of a developmental issue can often feel both confusing and frightening, particularly when it is your child who is affected. Once you or your loved one has received a diagnosis of a developmental issue, spend some time learning as much as you can about the diagnosis and available treatments.
Prepare a list of questions and concerns you may have and discuss these issues with your doctor, developmental psychologist, and other healthcare professionals who may be part of the treatment team. By taking an active role in the process, you will feel better informed and equipped to tackle the next steps in the treatment process.
The three major developmental psychology issues are focused on physical development, cognitive development, and emotional development.
The seven major stages of development are:
- Infant development
- Toddler development
- Preschool development
- Middle childhood development
- Adolescent development
- Early adult development
- Older adult development
The principles of developmental psychology outlined by Paul Baltes suggest that development is (1) lifelong, (2) multidimensional, (3) multidirectional, (4) involves gains and losses, (5) plastic, and that developmental psychology is (6) multidisciplinary.
Four developmental issues that psychologists explore are focused on the relative contributions of:
- Nature vs. nurture : Is development primarily influenced by genetics or environmental factors?
- Early vs. later experience : Do early childhood events matter more than events that happen later in life?
- Continuity vs discontinuity : Is developmental change a gradual process or do changes happen suddenly and follow a specific course?
- Abnormal behavior vs. individual differences : What represents abnormal development and what can be considered individual variations in development?
Keenan T, Evans S. An Introduction to Child Development . 2nd ed. SAGE; 2009.
- Erikson EH. (1963).Childhood and Society. (2nd ed.). New York: Norton.
- Erikson EH. (1968).Identity: Youth and Crisis. New York: Norton.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Piaget’s Preoperational Stage: Child Development and Cognitive Growth
This essay about Jean Piaget’s preoperational stage explores children’s cognitive development from ages 2 to 7, focusing on their burgeoning symbolic thought, egocentrism, lack of conservation, animism, and centration. It delves into Piaget’s experiments and criticisms of his theory while highlighting its enduring influence on education. Understanding this stage aids parents and educators in supporting children’s cognitive growth through imaginative play and problem-solving activities, fostering empathy and patience. In summary, Piaget’s preoperational stage illuminates a crucial period of cognitive evolution, emphasizing both its creative potential and cognitive limitations in children’s intellectual journey.
How it works
The illustrious Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget is celebrated for his groundbreaking contributions to cognitive development, propounding a theory that has profoundly influenced the comprehension of children’s intellectual maturation. The second phase of his conceptual framework, denoted as the preoperational stage, offers invaluable insights into the cognitive landscape of individuals aged approximately 2 to 7 years. This developmental juncture is distinguished by the nascent capacity of children to wield symbols and engage in imaginative play, albeit juxtaposed with limitations in logical reasoning and perspective-taking.
Through an exploration of the preoperational stage, we glean profound insights into the intricate tapestry of children’s cognitive evolution and its ramifications for their apprehension of the surrounding milieu.
A seminal characteristic of the preoperational stage is the onset of symbolic thought. During this epoch, children acquire the ability to employ language and other symbolic constructs to denote objects and concepts, facilitating their immersion in make-believe scenarios and narrative construction. This developmental milestone assumes paramount significance in their cognitive trajectory, laying the groundwork for future endeavors in problem-solving and abstract ratiocination. For instance, a child might ingeniously repurpose a banana as an ersatz telephone or fashion a cardboard carton into an interstellar vessel. Through such flights of fancy, children embark on a voyage of self-discovery, navigating diverse roles and scenarios that afford them a kaleidoscopic vista of the world, albeit within the confines of their developmental purview.
However, the preoperational stage is also marked by cognitive constraints of considerable import. Foremost among these is egocentrism, a phenomenon wherein children grapple with the concept that others may harbor perspectives distinct from their own. Piaget’s seminal “three mountains task” exemplifies this cognitive quirk, wherein children were tasked with delineating the vista from a doll’s vantage point. Predominantly, children in this stage evinced a proclivity for describing the scene solely from their own standpoint, thereby laying bare the contours of their egocentric cogitation. It is imperative to discern that egocentrism does not connote narcissism but rather underscores a normative developmental phase wherein children are yet to discern the dichotomy between their subjective viewpoint and the plurality of perspectives inherent in social interaction.
Another salient feature of the preoperational stage is the absence of conservation, denoting the inability to apprehend that certain attributes of an object remain invariant despite alterations in form or appearance. In Piaget’s seminal experiment, children were confronted with two identical vessels brimming with equidistant quantities of liquid. Subsequent to transferring the contents of one receptacle into a taller, more slender vessel, a substantial cohort of children erroneously surmised that the elongated vessel harbored a greater volume of liquid, attesting to their incipient grasp of the concept of conservation.
Animism represents yet another hallmark of this developmental epoch, wherein children ascribe animate attributes to inanimate objects. They may posit that the moon tails them during the nocturnal hours or opine that a stuffed bear experiences despondency when forsaken. Such flights of fancy exemplify children’s proclivity for melding the realms of fantasy and reality, thereby fashioning a syncretic worldview that transcends conventional boundaries.
Centration, denoting the proclivity to fixate on a singular aspect of a scenario while disregarding ancillary factors, also looms large in this developmental vista. For instance, when tasked with comparing two arrays of coins, children may gravitate towards quantifying the number of coins rather than evaluating their spatial disposition, thereby precipitating erroneous conclusions regarding quantity. This predilection for singular focus underscores the incipient nature of children’s cognitive faculties, which are still in the nascent stages of acquiring the ability to grapple with multifarious variables concurrently.
Whilst Piaget’s theoretical framework has exerted a profound influence, it is not impervious to criticism. Some scholars contend that Piaget may have underestimated children’s cognitive acumen, positing that egocentrism and other hallmark features may exhibit diminished prominence under varied circumstances. Nonetheless, Piaget’s construct remains a bedrock for comprehending cognitive development and continues to undergird contemporary educational methodologies.
A nuanced understanding of the preoperational stage furnishes parents, educators, and caregivers with a heightened appreciation for the idiosyncratic modes of cognition inherent in children. Fostering an environment conducive to imaginative play and affording children ample opportunities to grapple with problem-solving endeavors can catalyze their cognitive evolution during this formative juncture. Moreover, cognizance of the cognitive constraints endemic to this developmental phase can engender forbearance and empathy in adults guiding children through the nascent stages of their intellectual odyssey.
In summation, Piaget’s preoperational stage unveils a captivating epoch of cognitive development characterized by burgeoning creativity and symbolic ratiocination, interspersed with impediments in logical ratiocination and perspective-taking. By discerning the salient features of this developmental phase, we can proffer invaluable support for children’s cognitive progression, shepherding them towards the threshold of more advanced stages of cognitive acumen.
Remember, this exposition serves as a springboard for further contemplation and inquiry. For bespoke elucidation and scholarly validation, consider availing yourself of the services of professionals at EduBirdie.
Cite this page
Piaget’s Preoperational Stage: Child Development and Cognitive Growth. (2024, May 12). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/piagets-preoperational-stage-child-development-and-cognitive-growth/
"Piaget’s Preoperational Stage: Child Development and Cognitive Growth." PapersOwl.com , 12 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/piagets-preoperational-stage-child-development-and-cognitive-growth/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Piaget’s Preoperational Stage: Child Development and Cognitive Growth . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/piagets-preoperational-stage-child-development-and-cognitive-growth/ [Accessed: 18 May. 2024]
"Piaget’s Preoperational Stage: Child Development and Cognitive Growth." PapersOwl.com, May 12, 2024. Accessed May 18, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/piagets-preoperational-stage-child-development-and-cognitive-growth/
"Piaget’s Preoperational Stage: Child Development and Cognitive Growth," PapersOwl.com , 12-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/piagets-preoperational-stage-child-development-and-cognitive-growth/. [Accessed: 18-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Piaget’s Preoperational Stage: Child Development and Cognitive Growth . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/piagets-preoperational-stage-child-development-and-cognitive-growth/ [Accessed: 18-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

Essay on Developmental Stages In Adolescence
Students are often asked to write an essay on Developmental Stages In Adolescence in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Developmental Stages In Adolescence
Introduction to adolescence.
Adolescence is the time when kids grow into adults. This period, from age 13 to 19, is full of changes. Young people’s bodies and minds develop quickly. They learn to handle new feelings, make more choices, and build their own identities.
Physical Growth
During adolescence, bodies change fast. This is called puberty. Boys and girls grow taller, and their bodies start to look more like adult men and women. These changes can be exciting, but sometimes confusing or even stressful.
Emotional Changes
Adolescents start to feel emotions more intensely. They might feel very happy or very sad quickly. Making friends becomes very important. They also start to seek more privacy and might want to spend more time alone.
Thinking Skills
Adolescents begin to think more deeply. They start to question things and think about their future. This is when they develop their own opinions and start to understand more complex ideas. Their school work might get harder as they study more advanced topics.
Seeking Independence
As adolescents grow, they want to make their own choices. They might argue with parents as they try to be more independent. It’s normal for them to want to spend more time with friends and less with family.
Adolescence is a key time of growth. Understanding these stages helps adults support teenagers better. For adolescents, knowing what’s happening to them can make this journey less scary.
250 Words Essay on Developmental Stages In Adolescence
Understanding adolescence.
Adolescence is the time when kids grow into young adults. This period is full of changes and can be broken down into different stages. Each stage has its own set of changes that happen to a person’s body and mind.
Early Adolescence (Ages 10-13)
In early adolescence, children start to look different as their bodies begin to change. Boys and girls both grow taller and start to look more like grown-ups. They might feel awkward or shy about these changes. It’s also a time when they want to fit in with friends more and might start to pull away from their parents a bit.
Middle Adolescence (Ages 14-17)
During middle adolescence, teens become more independent. They make more choices on their own and start to think about the future, like what jobs they might want. Friendships become very important, and they might experience their first crush or relationship. It’s also a time for big feelings, and sometimes teens might feel happy one minute and sad the next.
Late Adolescence (Ages 18-21)
In late adolescence, young adults are almost ready to be on their own. They finish school, start working, or go to college. They learn to take care of themselves, like cooking and managing money. It’s also when they make important decisions about their lives and who they want to be.
Adolescence is a special time filled with growth and learning. Each stage is important and helps kids become the adults they are meant to be. It’s a journey full of ups and downs, but with support and understanding, teens can navigate through it successfully.
500 Words Essay on Developmental Stages In Adolescence
Adolescence is a time of big changes. It is the period in a person’s life when they are no longer a child but not yet an adult. This stage usually starts around the age of 10 and lasts until about 19 or 20. During this time, young people go through many different kinds of growth. They grow physically, their feelings and thinking change, and they learn how to become more independent.
One of the first things people notice about adolescents is how quickly they grow taller. This rapid growth is called a “growth spurt.” Along with getting taller, their bodies change in other ways, too. Boys may notice their voices getting deeper, and girls begin to develop more of a womanly shape. These changes can be exciting, but they can also be confusing and uncomfortable. It is a normal part of becoming older, and everyone goes through it.
Adolescents also start to feel different emotions more strongly. They might feel very happy one moment and sad the next. These mood swings are because their brains are still developing, and they are trying to handle all the new experiences they are having. Making friends and fitting in with a group becomes very important. It’s also a time when they start to figure out who they are and what they believe in.
Thinking and Learning
As adolescents grow, their brains become better at thinking about complex ideas. They start to question things and think about the future. School work gets harder, and they learn to solve more difficult problems. This is also when they start to think more about what is right and what is wrong, and they develop their own sense of morals.
One of the biggest parts of adolescence is becoming more independent from parents and other adults. Adolescents might want to spend more time with their friends or alone in their room. They start to make decisions for themselves and learn from their own mistakes. This is an important step in becoming an adult.
Adolescence can be a confusing and exciting time. Young people are growing in so many ways. They are getting taller and their bodies are changing. Their feelings can be all over the place, and they start to think about more serious things. They also work on becoming their own person, separate from their parents. It’s important for adults to support them through these changes and help them grow into happy and healthy adults. Remember, everyone goes through these stages, so if you are an adolescent, you are not alone.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Mathematics For Control
- Essay on Math In Our Daily Life
- Essay on Mass Tourism
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Child Development Stages, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 609
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Childhood development is important to study, as it reveals the main steps of personality formation and socialization. Early childhood experiences and gender socialization patterns influence the personal values and preferences of the individual. According to my observation and experience, traumatic events during childhood and the quality of child care will impact career choices, as well as future socialization.
In adolescence, individuals usually need to face choices and will develop their own path. In early adolescence (10-14 years), individuals will expand their social circle outside of their family and choose peers based on their preferences. Friendships are becoming extremely important, as they help define one’s personality. The trust of authority figures disappears as later teenagers become more independent in thinking and initiating change. By late adolescence, a well defined image of self-identity will develop, and people become able to compromise and decide based on an independent analysis of facts.
In adulthood, people usually choose a path. They select an attractive profession, enter the world of work and family life. Many choose partners based on past experiences and well defined ideas of what they imagine the future to be like. Responsibilities take over individuals’ lives, and instead of searching for ways, they start pursuing their personal goals. This is the time when many will identify their mission in life, and surround themselves with people who are like them.
Reaching old age is a challenging period for many. It is full of reflection on the past, and the assessment of achievements. One would feel left out, and when children grow up and move away, older people often feel the need to find a hobby or interest after retiring. Many will catch up with things they did not have time for while they were working and taking care of their family.
Briefly describe how Freud, Erickson, and Piaget developed their theories
Freud’s theory was closely related to biological maturity stages. According to the theorist, the five stages of child development are oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital. Freud also stated that three parts of personality impact development: id, ego, and superego.
Erickson, just like Freud, considered development to be an individual journey, however, stated that there is no conflict among the different layers of ego. Further, the author states that each stage of development has a conflict that the individual has to resolve.
Piaget, unlike the above two authors, viewed development from the cognitive perspective. The older the child gets, the more complex cognitive functions it is able to develop. The stages are based on different cognitive development phases.
Explain why there is much criticism about race, ethnicity, gender, and social and economic status when it comes to human growth and development theories.
According to Vygotsky, a child’s development cannot be viewed as a standalone process, and is always influenced by the environment. Bronfenbrenner, however, went further than that, and stated that the system of social and family relationships impacts children’s cognitive and emotional development. Therefore, it is important to examine the impact of race, gender, and socialization in general.
Choose two theories, each from a different area (e.g., psychoanalytic, cognitive, and behavioral or social cognitive theories). Briefly describe their main features, explain their major similarities and differences.
The cognitive development theory developed by Piaget is based on the assumption that children go through various cognitive phases, and educators need to develop programs to provide a stimulating environment. The stages of cognitive development are sensory-motor, pre-operational, concrete operations, and formal operation.
As a contrast, Vygotsky’s social development theory emphasized not only the importance of development stages, but also the influence of peer and family relationships on social, cognitive, and emotional development.
Santrock, J. (11/2012). Life-Span Development, 14th Edition. [VitalSource Bookshelf Online]. Retrieved from https://digitalbookshelf.southuniversity.edu/#/books/0077733908/
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases, Essay Example
Post Life Span Development, Essay Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371
Development Stage: Early Adulthood
Introduction.
Early adulthood is one of the age-related stages of life, considering people in the age of twenty to forty. The phase is characterized by the individuals transiting from late adolescence who are determined to have a well-defined identity and lead a responsible life. They engage in various developmental tasks, including establishing personality, achievement of autonomy, and becoming a part of a community. This essay describes the social, emotional, physical, and cognitive development of people in early adulthood, as well as the theories and personal experiences related to the stage.
Social and Emotional Development in Early Adulthood
The social and emotional changes in this phase of life involve intimacy and establishing one’s identity. Men and women develop the thoughts and feelings of committing to an intimate partner. Their self-esteem becomes positive because of being loved and affectionate to others (Overstreet, 2019). They develop flexible and self-regulatory emotional coping strategies and skills to resolve conflicts. Peer influence and incidences of conflicts with parents decline significantly (Overstreet, 2019). Further, people commit to social groups and have positive feelings about their membership, and integrate spiritual or religious beliefs into their identity. Indeed, social and emotional changes in early adulthood facilitate the formation and maintenance of relationships.
Physical and Cognitive Development in Early Adulthood
In early adulthood, physiological development is characterized by various aspects, such as enhanced motor performance, increased reproductive capacity, and better health and fitness. People at this stage have increased strength and the ability to act and move their body muscles. Additionally, their reproductive capacity peaks, with men and women becoming more sexually responsive, which leads to a healthy life minimizing their risks for illnesses (Overstreet, 2019). However, they have lower immune systems and engage in substance abuse behaviors, which may contribute to psychological problems and other health conditions. Cognitive development involves the way persons aged twenty to forty years think and make decisions. Thoughts become more practical, realistic, and individualistic, with the necessity or prior experience influencing the decision-making process. Thinking also becomes more flexible and balanced, allowing people to integrate salient aspects of opposing perspectives. Undeniably, the physical and cognitive changes in early adulthood enhance the way individuals at this state approach things.
Trends and Theories
Major trends in early adulthood are related to dating, marriage, and cohabiting. Courting has become more diversified and flexible, particularly because of social media. Most young adults live together and engage in a romantic relationship, even when they are not married, and delay assuming adult roles and responsibilities. The concepts which explain early adulthood include Erikson’s theory, which compares intimacy and isolation, and Levinson’s theory, dividing the stage into four phases (17-22, 22-28, 28-33, and 33-40 years) (Overstreet, 2019). The two theories help understand the changes which happen in early adulthood. Indeed, the treads and theories explain important factors which characterize early adulthood.
Personal Experience and the Benefits of Early Adulthood’s Knowledge
My experience at this stage is positive because I have developed social skills, which facilitate effective forming and maintaining of relationships. Friends’ opinions have an insignificant influence on my decision-making process. Additionally, I have become more practical and developed a desire to commit to an intimate relationship and become a part of certain social groups. The acquired knowledge will help provide evidence-based services to the patients at this life-developmental stage. For instance, it will facilitate a better understanding of the causes of mental disorders, such as stress and depression, and provide appropriate interventions. Notably, the individuals at this phase of life are prone to psychological illnesses because of failed relationships, exams, or unsuccessful job-hunting.
To sum up, early adulthood is one of the developmental stages characterized by persons aged between twenty and forty years. Social and emotional changes in this phase allow people to form and sustain relationships. Physical and cognitive growth are at their peak at this stage. People have increased motor ability and reproductive capacity, and their thoughts become practical and realistic. The knowledge about early adulthood will facilitate the provision of evidence-based nursing services.
Overstreet, L. (2019). Human development life span . Western Washington University.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, May 16). Development Stage: Early Adulthood. https://studycorgi.com/development-stage-early-adulthood/
"Development Stage: Early Adulthood." StudyCorgi , 16 May 2022, studycorgi.com/development-stage-early-adulthood/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'Development Stage: Early Adulthood'. 16 May.
1. StudyCorgi . "Development Stage: Early Adulthood." May 16, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/development-stage-early-adulthood/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Development Stage: Early Adulthood." May 16, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/development-stage-early-adulthood/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "Development Stage: Early Adulthood." May 16, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/development-stage-early-adulthood/.
This paper, “Development Stage: Early Adulthood”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: November 11, 2023 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Membership sale! Use promo code JOIN35 and save $7 (reg. $42). Sign up today! See if you qualify to join TDF.
- Discount Ticket Programs 01
- What's On Stage 02
- Accessibility Services 03
- School and Community Programs 04
- For The Makers 05
- Support TDF 06
Show Finder
An online theatre magazine
Read about NYC's best theatre and dance productions and watch video interviews with innovative artists
Translate Page

The cast of Hell's Kitchen on Broadway. Photo by Marc J. Franklin.
How Choreographer Camille A. Brown Channels Her NYC Youth in 'Hell's Kitchen'

The Tony nominee on why she hopes this Alicia Keys musical will inspire a love of theatre in the next generation
Right now on Broadway, there's no show more authentically New York than Hell's Kitchen . A longtime labor of love for Grammy-winning R&B star Alicia Keys, the Tony-nominated musical is loosely inspired by her own coming of age in 1990s NYC and centers on Ali (Tony nominee Maleah Joi Moon), a talented and headstrong 17 year old who finds a passion for piano and forbidden love—much to the dismay of her single mom (Tony nominee Shoshana Bean). Featuring Keys' hits as well as a few new songs, it throbs with the vitality of the Big Apple—a diverse city of young dreamers. That's why TDF is thrilled to be partnering with Hell's Kitchen and the New York City Public Schools Arts Office to present a Graduation Gift of free TDF Memberships to all students graduating from NYC public and charter high schools this spring. As the next generation of theatregoers, they will get access to deeply discounted tickets to help them build a lifelong relationship with the performing arts. Seniors who sign up can also enter a drawing to win free tickets to a special performance of Hell's Kitchen on Wednesday, June 26 at 7:30 p.m. preceded by a celebration at TDF's TKTS Booth in Times Square.
It's fitting that Hell's Kitchen is our Graduation Gift show since some of the key folks involved are NYC public school alums. Keys went to the Professional Performing Arts School in her home neighborhood of Hell's Kitchen at the same time choreographer Camille A. Brown attended the Fiorello H. LaGuardia High School of Music & Art and Performing Arts at Lincoln Center. Although the two didn't meet until they started collaborating on Hell's Kitchen , which premiered at The Public Theater last fall and transferred to Broadway in March, they both have vivid memories of growing up in the city.
"Being from New York, it's an amazing feeling to contribute to a show about New York," says Brown, who earned her fourth Tony nomination for her exhilarating choreography for Hell's Kitchen . "I started taking the subway when I was 13 years old because I lived in Queens and went to LaGuardia High School. Walking in the streets, I noticed how diverse New York City was. To bring that diversity to the stage—so many different personalities and energies—and to be able to pour that into the dancers' bodies feels good. I'm representing my hometown in my hometown."
While Brown started her career in dance and earned accolades for her powerful, politically charged pieces with her namesake company , theatre was a longtime goal. "I've always been interested in musical theatre," she says. "My mom introduced me to it when I was a little girl. I was four when she started taking me to Broadway. I remember seeing Black and Blue ; Jelly's Last Jam ; Bring in 'Da Noise, Bring in 'Da Funk ; Damn Yankees ; Sarafina! —I could go on and on. I took something away from every show. So I've always wanted to do theatre because it has a special place in my heart because of my mom."
Brown likes to say that she "speaks things into existence." As a Black woman in an industry long dominated by white men, that perseverance was necessary. A little over a decade ago, she started choreographing on Broadway (the Blair Underwood A Streetcar Named Desire , Once on This Island ) and beyond ( Bella: An American Tall Tale , This Ain't No Disco , Toni Stone ). Interestingly, her first three Tony nominations were for her work on plays with movement: Choir Boy and the lauded Broadway revival of for colored girls… , which she directed and choreographed, earning nods for both. Hell's Kitchen is the first time she's being nominated for a musical.
"This is my fifth show for Broadway but the first time that I've had a dance ensemble, so that's really exciting," Brown says. Creating choreography for Keys' "iconic songs" such as "Fallin,'" "Girl on Fire" and "Empire State of Mind" has been a welcome challenge. "They fall into the story in really beautiful and clever ways, and my job is to find movement to help push that story forward," she says. "I'm using social dance to set the time and place. But the dancers also represent the emotions surrounding Ali"—all those complicated feelings of adolescence: love, longing, anger, titillation, pain.
The dancers come through as individuals, yet collectively they conjure the spirit of the city: the teens flirting on the corner, the musicians banging on their buckets, the ladies gossiping on the street, the workers running to their jobs. "New York City is constantly moving and shifting and progressing, and that's what the show is doing, too," Brown explains.
Hell's Kitchen is one of multiple projects Brown has been working on. Earlier this month, her staging of Fire Shut Up in My Bones for The Metropolitan Opera wrapped up its run, and in August, her dance company will travel to Jacob's Pillow in Massachusetts to perform the world premiere of I AM , inspired by an episode of the HBO series Lovecraft Country .
Although her schedule is jam-packed, she hopes to be in the Shubert Theatre the evening of June 26 so she can experience Hell's Kitchen with a house full of enthusiastic, newly minted NYC public school graduates.
Asked what she wants those students to take away from the show, she quotes the lyrics of 'Empire State of Mind.' "'In New York, concrete jungle where dreams are made of, there's nothing you can't do.' I want them to realize that all dreams are possible, whether they're in the arts or not. I hope they see a reflection of themselves, and also see how important the arts are to the character of Ali and to the world. I love sharing theatre with kids because they show you how they're feeling. They laugh, they respond. It's visceral and it's real. I can only imagine how much fun this particular performance is going to be. To feel that New York energy—there's nothing like being in a room with other New Yorkers."
Know a NYC public or charter school senior who's graduating this spring? Send them this link with info about TDF's Graduation Gift and Hell's Kitchen ticket drawing.
If you would like to support TDF's Graduation Gift, please make a donation to our Education Programs .
Hell's Kitchen is also frequently available at our TKTS Discount Booths .
TDF MEMBERS: Go here to browse our latest discounts for dance, theatre and concerts.
Raven Snook is the Editor of TDF Stages. Follow her on Facebook at @ Raven.Snook . Follow TDF on Facebook at @TDFNYC .

The State of Development Journals 2024: Quality, Acceptance Rates, Review Times, and What’s New
David mckenzie.

This is the eighth in my annual series of efforts to put together data on development economics journals that is not otherwise publicly available or easy to access (see 2017 , 2018 , 2019 , 2020 , 2021 , 2022 , 2023 for the previous editions). I once again thank all the journal editors and editorial staff who graciously shared their statistics with me.
Journal Quality
The most well-known metric of journal quality is its impact factor . The standard impact factor is the mean number of citations in the last year of papers published in the journal in the past 2 years, while the 5-year is the mean number of cites in the last year of papers published in the last 5. As noted in previous years, the distribution of citations are highly skewed, and while the mean number of citations differs across journals, there is substantial overlap in the distributions – most of the variation in citations is within, rather than across journals. We continue to see growth in these impact factors at many journals. The big news this year is that they have decided that you really don’t need three decimal places any more in the impact factors. I compliment these stats with RePec’s journal rankings which take into account article downloads and abstract views in addition to citations.

Table 3 then shows two additional metrics, taken from Scimago , which uses information from the Scopus database. The first is the SJR (SCImago Journal Rank), which is a prestige-weighted citation metric – which works like Google PageRank, giving more weight to citations in sources with a relatively high SJR. I’ve included some of the top general journals in economics for comparison. Scimago also provides an H-index which is the number of papers published by a journal in any year that were cited at least h times in the reference year – so this captures how many papers continue to be influential but as a result, favors more established journals, and ones that publish more articles, that have a larger body of articles to draw upon.

How many submissions are received, and what are the chances of getting accepted?
Table 4 shows the number of submissions received each year. See previous years posts for statistics before 2019. The total submissions in the 11 journals tracked is almost 10,000 papers (note I received no data from the Review of Development Economics this year so have excluded it). Total submissions in these journals are up 7.7% over last year, although not quite at the 2020 peak.

At most journals the number of submissions has either leveled off or fallen since a peak in 2020-21. World Development had the largest 2020 peak when they had a special call for a variety of short papers on COVID-19, but perhaps the combination of people sending off lots of papers during the pandemic and then being a little slower to start new projects has halted the rapid growth somewhat.
· The newish World Development Perspectives already received 532 submissions last year, more than many long established development journals.
· The Review of Development Economics has seen very rapid growth in submissions. I only started collecting stats for it last year, but the editors note that in 2015 they received about 450 submissions, and this has now grown to more than 1,500 last year.
Table 5 shows the total number of papers published in each journal. 782 papers were published in 2023, so that’s a lot of development research (even though less than 1 in 10 of the submitted papers and down slightly on the 811 papers published in 2022). I’ve noted in previous years that some of the journals have been able to flexibly increase the number of articles published as their submission numbers have risen, reducing publication lags as well.

The ratio of the number of papers published to those submitted is approximately the acceptance rate. Of course papers are often published in a different year from when they are submitted, and so journals calculate acceptance rates by trying to match up the timing. Each journal does this in somewhat different ways. Hence Economia-Lacea reports a 0% acceptance rate for 2023 since none of the papers submitted in 2023 have yet been accepted, although some are still under review. Table 6 shows the acceptance rates at different journals as reported by these journals. Of course the number and quality of submissions varies across journals, and so comparing acceptance rates across journals does not tell you what the chances are of your particular paper getting accepted is at these different journals.

How long does it take papers to get refereed?
In addition to wanting to publish in a high quality outlet, and having a decent chance of publication, authors also care a lot about how efficient the process is. Table 7 provides data on the review process (see the previous years’ posts for historic data). The first column shows the desk rejection rate, which averages 73%. Column 2 uses the desk rejection rates and acceptance rates to estimate the acceptance rate conditional on you making it past the desk rejection stage. On average, about one in three papers that gets sent to referees gets accepted, with this varying from 12% to 63% across journals.
The remaining columns give some numbers on how long it takes to get a first-round decision. The statistics “Unconditional on going to referees” includes all the desk rejections, which typically don’t take that many days. The average conditional on going to referees is in the 3-5 month range. The last two columns then show that at most journals, almost all papers have a decision within 6 months – so in my opinion, you should feel free to send an enquiry if your paper takes longer than that.

Do revisions typically get sent back to the referees or handled by the editor?
Another factor that can make a big difference in how long it takes to publish a paper is whether editors send revised papers back to referees, or instead reads the response letter and revision themselves and just makes a decision on this basis. This is something that the AER and AEJ Applied have been trying to do more and more, with only 25% of revisions at the AEJ Applied going back to referees. In my own editing at WBE, I send fewer than 5% of revisions back to referees. This year I asked the different journals what their approaches were. Many do not systematically track this, but offered some approximations:
· Journal of Development Economics: approximately 60% of revisions go back to referees, although 0% for the short papers (see below)
· Development Policy Review: only 10% of revisions go back to referees.
· Journal of Development Effectiveness: 7.7% were sent back to referees
· Journal of Development Studies: not tracked, but less than 20% go back to referees
· Journal of African Economies: 52% are sent back to referees
· Economia: 70% go back to referees.
· EDCC: does not track this, but first revisions are usually sent back to referees.
· World Development, World Development Perspectives, WBRO, and WBER do not track this, and results may vary a lot by editor.
Updates on the JDE Short Paper and Registered Report Tracks
The Journal of Development Economics has two other categories of papers that differ from other development journals:
· The short paper format has proved popular. There were 148 submissions in 2023 (about 8% of total submissions), and 21 short papers were accepted. These papers follow the model of AER Insights, ReStat, etc in which papers are either conditionally accepted or rejected, and so any revisions are minor and are not sent back to referees.
· The JDE registered reports had 19 stage 1 acceptances in 2023, and 1 stage 2 acceptance, reflecting a lag from COVID when there were not many new submissions. They have a website jdepreresults.org which tracks the stage 1 and stage 2 registered reports, but some of the data was lost when transitioning the website, so if you have a registered report accepted that is not listed there, please let the journal know.
Other Development Journal News
Finally, I asked the journals if they had any other major news or changes to report. Here are what they wanted to share:
· At EDCC, Prashant Bharadwaj has replaced Marcel Fafchamps as editor. Thanks to Marcel for 10 years at the helm. The journal is one of the few development journals with a submission fee ($50), but offers a fee waiver to referees who have submitted a timely report in the year prior to submission.
· Other editorial changes are Ganeshan Wignaraja replacing Colin Kirkpatrick as co-editor at Development Policy Review, and Marie Gardner and Ashu Handa taking over from Manny Jimenez at the Journal of Development Effectiveness.
· The Journal of Development Effectiveness notes they are implementing a set of actions to raise awareness about transparency, ethics and equity in research, and to address power imbalances among HIC-L&MIC research teams. The editors note they are particularly concerned with research involving primary data collection in an L&MIC where there is no author from an institution in that country. For articles submitted to JDEff that fall into this category, they will require the authors to complete a short author reflexivity statement that will be published along with the article. The statement will explain the contribution of each author per Taylor & Francis authorship criteria, which are consistent with the criteria established by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Authors will be asked to explain why there is no contributing author from the study location, specifically, whether any team member based in the study location made a ’significant contribution to conception, study design, execution or acquisition of data,’ and if so, why they were not subsequently invited to review the manuscript and take responsibility for its contents. And for work involving randomized controlled trials or interviews with vulnerable groups, authors will also be asked to answer a set of questions about research ethics. Final manuscript acceptance and publication in JDEff will be based on the scientific quality of the work as well as an assessment of whether the work was conducted in an equitable, inclusive and ethical manner.
Finally, thanks again to all the editors for all the time and effort they devote to improving the quality and visibility of development research. As you can see, they have a lot to deal with!

Lead Economist, Development Research Group, World Bank
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added

The families risking everything to keep Ukraine’s trains running – photo essay
Dutch photographer Jelle Krings has been documenting the workers of the Ukrainian railway since the war began. Here, he revisits the families that have kept a war-torn country moving, often to great personal sacrifice
- Words and pictures by Jelle Krings
I n the early hours of 24 February 2022, when Russian bombs and rockets struck Ukrainian cities and infrastructure throughout the country, railway workers boarded trains heading east. Determined to get as many people as possible to safety , they would end up evacuating millions to Ukraine’s borders in the west.
Ukraine’s new railway chief Yevhen Liashchenko was in the team that guided the network through the first stages of the war. He says his people acted not because they were instructed to but because “they didn’t know any other way”. There was no time for bureaucracy, “decisions were made by the people on the ground, and they love the railway, not as a business but as a family”.
It takes more than 230,000 people to keep the trains running in Ukraine.

The railway station in Lyman, Donbas, destroyed by shelling

Yevhen Liashchenko, chief executive of Ukrainian railways, has been leading Ukraine’s 230,000 railway workers through the war
Together they run a vast railway network of more than 15,000 miles (24,000km) of track, one that has been invaluable for Ukraine’s ability to withstand the invasion. Despite continual bombing, the network has largely remained operational. Damage to the tracks is swiftly repaired, and shell-hit critical infrastructure is promptly restored.
Over two years, we followed families and workers living by the tracks near the frontlines to find out how the war and the struggle to keep the trains running is shaping their lives.
The Neschcheryakovas
Nadiya Neschcheryakova works as an attendant at a railway crossing in Bucha, about 10 miles from Kyiv. She works in shifts, sharing her post with her mother and two other women. On the morning of the invasion, the sound of explosions pierced the sky above the thick pine forests surrounding her home. She went to work anyway. A few days later, her post at the railway crossing was occupied by Russian troops. Her home in the next village along the track was now at the frontline of the war.

Nadiya Neschcheryakova operates her railway crossing in Bucha, near Kyiv . A freight train passes transporting materials such as wood for possible use in Ukraine’s defensive efforts along the frontline

Remnants of the Neschcheryakovas’ family house, destroyed by shelling, lie in the yard at Spartak, Kyiv oblast

Nadiya Neschcheryakova with her husband, Yuriy, their daughter Kateryna and grandson Andriy. Yuriy built a new house after their home was destroyed by shelling early in the war
With her husband, daughter and grandson, Nadiya managed to flee to the west where they stayed for a month waiting for the Russian withdrawal from Kyiv. When they returned home, they found their home had been reduced to rubble.
The Petrovs
When the city of Kherson was liberated after nine months of Russian occupation in November 2022, Oleksandr Petrov was sent on a mission to repair the tracks leading to the city. When he set out in a van with a team of repairmen in the morning, he knew the risks: the fields along the tracks were heavily mined in an attempt to slow the Ukrainian advance.

Railway workers wash their wounds after driving over a mine in the Kherson region, 13 November 2022. They were carrying out repair works just days after Kherson was liberated. Oleksandr Petrov lost a leg in the incident

Oleksandr shows his prosthetic leg to workers in a railway repair team in Voznesensk, Mykolaiv oblast. Since his injury, Oleksandr has been given a desk job

Oleksandr Petrov at his parents’ house in Voznesensk. Family members spend a day at the cemetery to maintain their relatives’ graves and pay their respects
Russian troops were expected to start shelling the city once they’d had a chance to regroup on the other side of the Dnipro River. The civilians left in the city would have to be evacuated by train, so Oleksandr went anyway. Later that day, Oleksandr lost his leg after they drove over a Russian anti-vehicle mine.
The Lyman community
When Ukrainian troops recaptured the railway hub of Lyman from Russian troops in November 2022, it had been under Russian occupation for six months. Since then, it has been on the frontline of the war in Ukraine’s Donbas region. Yet, a small community of railway families continues to live in the basements of their battered apartment buildings on the outskirts of the city.

The Rosokha family mourn the death of Nina Rosokha, who was killed by a Russian artillery strike on Lyman. Nina had worked in a railway service department, her husband was a train driver for 36 years. During the funeral, sounds of fighting could be heard in the nearby Kreminna forest

A forest on the outskirts of Lyman smoulders after shelling. Firefighters do not go into the forests for fear of mines

Fedya, 13, plays his accordion outside the apartment building where he lives with his mother and grandmother, both of whom work for the railway. Evelyna, 12, with one of her cats
The families in the community stay underground most of the time. The frontline is too close for the air raid alert system to be effective, and artillery and missiles can strike at any moment. The community have paid a heavy price in the war . Railway worker Nina Rosokha was killed on her way to the post office in a Russian artillery strike on a market. During another attack, Lyubov Surzhan’s top-floor apartment was obliterated. A piece of shrapnel skimmed Fedya’s head during a strike on a nearby railway depot. Yet the railway is their home and, despite the danger, they don’t want to leave.
The Mykolaychuks
The Mykolaychuk brothers live in an apartment building in the centre of Podilsk. Both are fifth generation locomotive drivers. Before the invasion, their jobs were mostly local, transporting grain from the region to the port of Odesa. Now, they go farther east towards the frontlines of the war, driving evacuation trains and weapons transports.

Alla Valeriyivna Mykolaychuk in Podilsk with her daughter and niece, both aged one
They don’t get paid if they don’t work, and jobs have become less frequent since the war. With money hard to come by, they have had to sell their family car to make ends meet.
The Tereshchenkos
Olha Tereshchenko survived a Russian attack on a convoy of civilians fleeing the then occupied city of Kupiansk. Her husband and five-year-old son were killed. Consumed with grief, she now works at a railway office in Kharkiv and gets support from her fellow workers there. Urns containing the ashes of her husband and son still sit on a shelf in a nearby crematorium. She hopes to bury them near their home in Kupiansk one day, when the frontline is further away.

Olha Tereshchenko in Saltivka, the area of Kharkiv where she now lives

Olha’s husband and son, photographed as a baby, were killed in a Russian attack on a civilian convoy. Olha is overcome when she visits their remains in a nearby crematorium: she hopes one day to bury her husband and son near their home in Kupiansk
- Rights and freedom
- Rail transport
Most viewed
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Implement AI — Responsibly
- Michael Wade
- Tomoko Yokoi

Four ways nontechnical leaders can foster a culture that values ethical AI.
Researchers engaged with organizations across a variety of industries, each at a different stage of implementing responsible AI. They determined that, although data engineers and data scientists typically take on most responsibility from conception to production of AI development lifecycles, non-technical leaders can play a key role in ensuring the integration of responsible AI. They identified four key moves — translate, integrate, calibrate, and proliferate — that leaders can make to ensure that responsible AI practices are fully integrated into broader operational standards.
When the EU Parliament approved the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Act in early 2024, Deutsche Telekom, a leading German telecommunications provider, felt confident and prepared. Since establishing its responsible AI principles in 2018, the company had worked to embed these principles into the development cycle of its AI-based products and services. “We anticipated that AI regulations were on the horizon and encouraged our development teams to integrate the principles into their operations upfront to avoid disruptive adjustments later on. Responsible AI has now become part of our operations,” explained Maike Scholz, Group Compliance and Business Ethics at Deutsche Telekom.
- Michael Wade is a professor of innovation and strategy and the director of IMD Business School’s Global Center for Digital Business Transformation. He is a coauthor of ALIEN Thinking: The Unconventional Path to Breakthrough Ideas (PublicAffairs, 2021).
Partner Center
Lateral Partner Integration Requires Business Development Plan

When a lateral is hired into a new firm, following the tone set during the recruiting process is essential. The firm needs to ensure the lateral is set up for success on day one. Openness, honesty, and transparency are key.
A 12-month marketing and business development plan should be created as a roadmap for integrating new lateral hires and partnering them with a business development liaison. The assigned liaison should host regular check-in calls and serve as the lateral’s initial point of contact for all client development activities.
Setting the Stage
An introductory call between the lateral and their assigned BD liaison should take place prior to their start date or within the first two weeks. This should be the first in a series of integration meetings that take place during the lateral’s first year.
The goal of the meeting is to help the lateral understand the resources of the firm, services the marketing and BD department provides (i.e., requests for proposals, pitches, collateral, conference/speaking engagement prep, awards & rankings, bio updates, etc.) and to answer firm questions that may not have been addressed during the recruiting process.
The lateral and liaison should discuss any immediate client needs/opportunities, expectations, what support the lateral needs, and alert clients about the move.
The lateral should walk away from the meeting feeling confident, comfortable, and with a clear path forward.
Read more: Lateral Partner Recruiting Must Focus on Honesty and Clear Data
Introduction and Implementation
The BD liaison must also obtain a fulsome knowledge of the lateral’s practice, portable book of business, client targets, and preferred marketing styles. They should ascertain the partner’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as business goals and objectives.
The liaison needs to know why the lateral was hired—their niche expertise, specific client needs, and regional presence—to help identify cross-sell opportunities, make appropriate introductions to targeted attorneys within the firm, and plug the lateral into pre-existing client and industry teams. Prioritization should be placed on client-facing activities and the lawyer’s strengths.
The new partner’s BD liaison should have the same information as the legal recruiting team, which includes the lateral’s resume, partner questionnaire, offer letter, and revenue goals. Armed with these resources, the business development liaison is positioned as a part of the firm’s long time revenue strategy for the lateral partner, versus as a document producer.
Positioning the BD liaison as a key to the lateral’s success at the onset will encourage the partner to engage them in a meaningful way with strategy, innovation, and revenue generating activities for a sustaining practice. This allows the partner to focus on delivering quality legal services, while the BD liaison can focus on collaboratively growing their book of business.
Having a thoughtful, written integration plan is imperative. A written process ensures not only accountability, but gives each lateral the same onboarding experience regardless of which practice group or industry team they sit in.
During each meeting, the liaison should probe the lateral on topics such as satisfaction with the firm, sense of being valued, client growth opportunities, bandwidth and utilization, and cross-selling successes or frustrations. Regular status updates should be provided to firm leadership and other stakeholders. If the lateral flags an issue or perceived roadblock, the liaison should dig deeper to understand the root cause, and work with leadership to course correct.
It’s critical that firms not overpromise and underdeliver. For example, a lateral may have been hired to inherit a portfolio that fell through, or perhaps market fluctuations prohibited the opening of a new office that the lateral was intended to join. It’s important to keep the lateral’s business development liaison informed of these developments so they can monitor follow-though, manage expectations, and help pivot if necessary.
The firm should be clear about their commitments. Conversely, expectations for new partners’ client development and relationship building activities, for example, should also be addressed directly.
The most successful laterals are engaged and actively participate in regular integration calls. Holding 90-day reviews that include members of the recruiting team and practice group or department leaders can provide an opportunity for the partner to be heard as well as to receive direct feedback.
Integration Process
Avoid letting new lateral partners fall between the cracks, especially if they’re rainmakers or inexperienced business developers, by having a continuity plan that includes the written integration process. The BD liaisons shouldn’t work in silos.
Find a collaboration tool that works for the team’s communication style and commit to using it. Keep detailed records and have a plan of continued support should the assigned BD liaison leave the firm, or if there is significant recent or impending change happening within the firm, such as a merger or acquisition.
Recruiting and integration don’t cease when a merger is on the horizon, and the potential for new laterals to get lost in transition during a major change increases. Firms must adapt their recruiting and integration strategies not only to speak to the newly merged firm’s emerging cultural differentiators but also to how laterals will be supported in a fluid environment.
This article does not necessarily reflect the opinion of Bloomberg Industry Group, Inc., the publisher of Bloomberg Law and Bloomberg Tax, or its owners.
Author Information
Brian J. Carrozza is director of client development at Goulston & Storrs.
Courtney C. Hudson is business development manager at Baker, Donelson, Bearman, Caldwell & Berkowitz.
Megan K. Senese is co-founder and principal at stage, a women-owned business development and legal marketing firm.
Write for Us: Author Guidelines
To contact the editors responsible for this story: Jada Chin at [email protected] ; Jessie Kokrda Kamens at [email protected]
Learn more about Bloomberg Law or Log In to keep reading:
Learn about bloomberg law.
AI-powered legal analytics, workflow tools and premium legal & business news.
Already a subscriber?
Log in to keep reading or access research tools.
The Days of My Life: Personal Development Essay
Introduction: purpose, goals, and methods, in search for my own self: from early childhood to these days, conclusion: personal development in retrospect, reference list.
Taking a retrospect at one’s own development is a good way to analyze the current behavioral patterns and define the issues that may possibly jeopardize building relationships with the people around. In the given research, I am going to take a look at my won cognitive development through the lens of various cognitive development theories (CDTs) and check the effects of various internal and external factors on my life. Thus, I will learn not only to apply the theories that I have learned to practice but also to define the aspects that I will have to work on later.
The journey starts in early childhood
Naturally, browsing through my early childhood memories is quite complicated, seeing how I remember quite little about the given stage of my life. However, there were some choice moments that I clearly remember as the pivoting points of my development. For example, I can still recall some of the games that my mother used to play with me to develop my ability to think logically and be able to communicate.
Piaget’s theory at its best
Perhaps, one of the best ways to demonstrate a child’s development of cognitive and analytical skills, Piaget’s theory can be easily applied to my childhood memories. As an infant, I played with a teddy bear. Being a single parent, my mother had to leave me in daycare, yet I protested against being alone. To calm me down, my mother suggested that I draw a portrait of my teddy bear, which I did. Therefore, my ability to cognize the world through object permanence (tactile functions) transformed into symbolic thinking (transfer of the tactile experience into visual one).
Erikson: at the sixth stage
My childhood development can also be seen through the prism of Erikson’s stages of cognitive development. An alternative to Piaget’s and Vygotsky’s theories, it also has the right to exist, which my childhood experience has confirmed. I developed trust in my mother at the stage of infancy. It should be noted that the link between trust and breastfeeding, which Erikson provided, seems quite inconsistent, since in my case, mother-child relationships were very strong, even though my mother gave up breastfeeding when I was six weeks and started using bottle feeding. Like other children, I started fighting for my autonomy when I was around three; with little experience of raising children, my mother did not encourage my attempts at being independent properly and scolded me down when I failed, which resulted in enhancing my shame and doubt.
Vygotsky: the world around me
My childhood impressions, however, can also be analyzed from the point of view provided by Vygotsky. For instance, in my early childhood, I refused to share my toys with my playmates. The given phenomenon, in fact, can be explained with the help of Vygotsky’s theory. Noticing my greediness, my mother started giving me examples of generosity. For example, she tried to have me around when lending money, books, etc., to her friends and giving her things to charity. Thus, my mother performed the function of a scaffold, teaching me the basic principles of sharing.
Psychodynamic theory: new discoveries
Motivated both consciously and unconsciously, in accordance with the principles of psychodynamic theory, I learned new skills from interacting with the environment around me and the emotions that I had in the process. Sometimes these experiences were useful, like the pride that I felt after being praised for reading a very long word without mistakes at school. However, some of the emotions blocked my enthusiasm as a learner for quite along. For example, even now, I shiver a bit when I need to strike a match because of the burn that I got at five when playing with my mother’s lighter when she could not see me.
Growing pains: teenage angst
Much like any other teenager, I had to face a number of problems in order to accept the new patterns of relationships and to learn new communication skills. Apart from the way in which society works, I also had to learn how to be accepted and, at the same time, remain an individual. To describe the stages that I had to pass in the course of this transformation, Sternberg’s theory should be used.
Sternberg’s theory: from conventional to creative intelligence
I must admit that, as a child, I did not socialize with the rest of the children much; as a result, growing into a teenager, I was socially awkward most of the time. What I knew about people and society, I learned mostly from books and soon discovered that there was a huge gap between novels and reality. At this point, my development could be viewed through the lens of Sternberg’s theory.
Practical sub theory in action: acquiring communication skills
In the fifth grade, I started working on my communication skills. The process of skills acquisition was rather complicated, even though I had some experience in communication. In accordance with Sternberg’s theory (Bussey & Bandura, 1999, p. 677), I had to learn the basics of conventional communication principles before choosing the communication patterns that suited me best.
Experimental sub theory in action: training communication skills
After learning new skills, I tried them on the people around me in an attempt at winning them over. In some cases, my attempts were successful – I managed to find a sidekick when I enrolled in an art class. However, in a number of instances, these attempts led nowhere, which made me work harder on my social skills.
Gender issues and Chodorow’s theory: defining the differences
However, intelligence development and the skill of thinking outside of the box were not the only issues that I had to learn in the process of growing up. As I had stressed previously, at the age of 11, my knowledge of the social and physiological differences between boys and girls made me flock with girls of my age. However, at the age of 14, I started feeling that building relationships with boys are also an important part of my cognitive experience.
I remember dating boys at 15–17 and being romantically involved; however, it was all a part of growing up and cognizing the world and people around me, which was the key reason why these relationships never went anywhere. Perhaps, being relatively short, these experiences did not lead me to succumb to “women’s universal subordination that is based on a social, rather than a biological, explanation” (Ryle, 2012, p. 135), as Chodorow put it.
The world, through the lens of a young adult
Triarchic theory is still powerful: new experiences.
After I gave birth to my daughter, I discovered a whole new world of new experiences. Not all of them were positive – some included such problems as fighting fears when my daughter got sick, etc. However, by learning to be a mother, I realized that I have a plethora of both practical and artistic skills to learn. Therefore, Sternberg’s theory of learning to handle new tasks is still powerful. For example, while I used to be quite awkward when teaching my daughter to talk, I now feel experienced enough to develop sets of exercises for her creative learning.
Horney and Freud’s legacy: gender theories
As I have stressed above, I have been having issues in communication with the opposite sex. The given issues must have been stemming from my childhood experience. Being a child of a single mother, I could not observe the interactions between a man and a woman and, therefore, had to discover the specifics of gender relationships on my own. As Freud specifies, the so-called scripts, i.e., patterns of relationships, are learned in late childhood (Ryle, 2012, p. 135); in my case, these scripts did not include a male counterpart, which was the key stumbling block in my relationships with my male friends. As a result, I seem to have developed what Horney defined as a masculinity complex, which makes my gender relationships even more complicated (Paris, 2003, p. 22).
Divorce and the associated threats: Jung
I have to admit that at some point in my development, I had to face a serious crisis. In contrast to my expectations, my family life left much to be desired in terms of relationships with my husband. The problems that I encountered could be traced back to my Electra complex, as Jung (Borovečki-Jakovljev & Matacic, 2005, p. 351) defined it. Being raised by a single parent, I had little to no examples of interactions between a husband and a wife, which meant that I had to create my own interactional patterns.
Evaluating my experience, I must admit that I have a number of issues to confront. While my development did not differ much from the development of other children, such factors as being raised by a single parent and failing at claiming my independence in early childhood have affected my character and, therefore, shape my current behavioral patterns.
What needs to be addressed
As Jung’s theory allowed defining, I will have to work on learning to build relationships with men. Without a particular pattern learned from early childhood, the given task is extremely complicated. However, the situation that I face at present also has a positive side to it – I do not have the inherently wrong male-female relationship pattern based on the example set by my parents.
Future developmental prospects
Despite the fact that I already have a number of behavioral patterns cemented in my brain, changes in the environment that I live in, particularly new influences and interactions with new people mat possibly change the way I build relationships with people around me. By using the theories listed above to analyze my behavioral patterns, I will be capable of shaping my attitude towards other people and be open to new experiences.
Borovečki-Jakovljev, S. & Matacic, S. (2005). The Oedipus complex in contemporary psychoanalysis. Collegium Antropologicum 29 (1), pp. 351–360.
Bussey, K., & Bandura, A. (1999). Social cognitive theory of gender development and differentiation. Psychological Review, 106 (6), pp. 676-713.
Paris, B. J. (2003). Horney & humanistic psychoanalysis. In Frager, R. & Fadiman, J. (Eds.), Personality and personal growth (pp. 1–29). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Ryle, R. (2012). How do we learn Gender? Questioning Gender (pp. 119–165). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, March 22). The Days of My Life: Personal Development. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-days-of-my-life-personal-development/
"The Days of My Life: Personal Development." IvyPanda , 22 Mar. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/the-days-of-my-life-personal-development/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'The Days of My Life: Personal Development'. 22 March.
IvyPanda . 2021. "The Days of My Life: Personal Development." March 22, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-days-of-my-life-personal-development/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Days of My Life: Personal Development." March 22, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-days-of-my-life-personal-development/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Days of My Life: Personal Development." March 22, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-days-of-my-life-personal-development/.
- Retrospect Into the Glo-Bus Experience
- Developmental Psychology Theories of Piaget and Vygotsky
- Jean Piaget and Lev Vygotsky: Theories Comparison
- Rebecca’s Literacy Development: Non-Cognitive Aspects
- Parenting Strategies for Early Childhood Development
- Individual Presentation and Plan: Developing Self-Awareness
- Developing Self-Awareness: Individual Plan
- Secure Attachment in Psychological Theories

COMMENTS
About Child Development Stages. The main stages of child and young person development From birth through to adulthood children continually grow, develop, and learn. A child's development can be measured through social, emotional, intellectual, physical and language developmental milestones. Say no to plagiarism.
Piaget's (1951) four-stage theory of cognitive development sequences a child's intellectual development. According to this theory, all children move through these four stages of development in the same order (Simatwa, 2010). The sensorimotor stage is from birth to two years old. Behaviors are triggered by sensory stimuli and limited to ...
Piaget divided children's cognitive development into four stages; each of the stages represents a new way of thinking and understanding the world. He called them (1) sensorimotor intelligence, (2) preoperational thinking, (3) concrete operational thinking, and (4) formal operational thinking. Each stage is correlated with an age period of ...
Stage 5: Identity vs. Confusion . The fifth psychosocial stage takes place during the often turbulent teenage years. This stage plays an essential role in developing a sense of personal identity which will continue to influence behavior and development for the rest of a person's life.
Introduction. Erikson's theory of development describes eight stages which occur at a certain time of life (from infancy to old age) and are associated with specific developmental crises and tasks (Erikson, Erikson, & Kivnick, 1986; Malone, Liu, Vaillant, Rentz, & Waldinger, 2016). Erikson viewed the ability to meet these tasks and resolve ...
The theory comprises five stages: Oral — In the oral stage (birth to 1 year old), children learn to suck and swallow and may experience conflict with weaning. Anal — In the anal stage (1-3 years old), children learn to withhold or expel feces and may experience conflict with potty training.
Erikson's theory outlines 8 stages of psychosocial development from infancy to late adulthood. At each stage, individuals face a conflict between two opposing states that shapes personality. Successfully resolving the conflicts leads to virtues like hope, will, purpose, and integrity. Failure leads to outcomes like mistrust, guilt, role confusion, and despair.
Some of the many issues developmental psychologists assist with include: Cognitive development during childhood and throughout life. Developmental challenges and learning disabilities. Emotional development. Language acquisition. Moral reasoning. Motor skill development. Personality development.
First child (age 4 years): Relative stage - Initiative v Guilt (Erikson) By the age of 4 years, a child has already passed the stages of 'Trust v Mistrust' and 'Autonomy v Doubt'. This means that the infancy and early childhood periods are over and the child is entering into the play age. As the name of the stage (Initiative v Guilt ...
This paper aims at evaluating major issues pertinent to child development in one of the developmental phases from birth up to 12 years. During this period, an individual develops key skills that not only shape outcomes in later life but almost irreversibly shapes ones personality. Of the eight stages identified by Erickson, four of them account ...
Child development describes how children grow and change. Experts divide developmental stages into five periods from birth to 18 years old. At each stage, healthcare providers expect children to meet certain developmental milestones. Identifying and knowing the cause of any delays can help provide appropriate supports.
Childrens cognitive developmental stages (outline) I. Introduction - Piaget Stages of Development - Childrens cognitive development can depend on II. Piaget stages of development - Sensorimotor. Birth through ages 18-24 months a. Reflexive Stage (0-2 months) At this stage of development, infants between the ages of 0 and 2 months develop the ...
This essay about Jean Piaget's preoperational stage explores children's cognitive development from ages 2 to 7, focusing on their burgeoning symbolic thought, egocentrism, lack of conservation, animism, and centration. It delves into Piaget's experiments and criticisms of his theory while highlighting its enduring influence on education.
500 Words Essay on Developmental Stages In Adolescence Understanding Adolescence. Adolescence is a time of big changes. It is the period in a person's life when they are no longer a child but not yet an adult. This stage usually starts around the age of 10 and lasts until about 19 or 20. During this time, young people go through many ...
Briefly describe how Freud, Erickson, and Piaget developed their theories. Freud's theory was closely related to biological maturity stages. According to the theorist, the five stages of child development are oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital. Freud also stated that three parts of personality impact development: id, ego, and superego.
Cite this essay. Download. Humans go through the different steps throughout their life; they will change and develop. These development changes can be organized into 4 sections: physical, intellectual, emotional and social. Throughout my work I will be showing the differences between each life stage.
Conclusion. To sum up, early adulthood is one of the developmental stages characterized by persons aged between twenty and forty years. Social and emotional changes in this phase allow people to form and sustain relationships. Physical and cognitive growth are at their peak at this stage. People have increased motor ability and reproductive ...
To understand human growth and development properly, all these features are carefully put into consideration. Major stages of development include infancy/childhood, puberty/adolescence and adult hood. This paper carefully looks the adolescence stage (Papalia and Fieldman, 2003).
Write an essay on the developmental stage and school readiness of the grade R learner (5-6 Years). ... Introduction • Physical development • Cognitive development • Emotional development • Social development • Conclusion Focus on the milestones and include criteria and behavior that will enable a teacher to identify problems a child ...
Adolescence is a period of significant development that begins with the onset of puberty1 and ends in the mid-20s. Consider how different a person is at the age of 12 from the person he or she is at age 24. The trajectory between those two ages involves a profound amount of change in all domains of development—biological, cognitive, psychosocial, and emotional. Personal relationships and ...
The Tony nominee on why she hopes this Alicia Keys musical will inspire a love of theatre in the next generation---Right now on Broadway, there's no show more authentically New York than Hell's Kitchen.A longtime labor of love for Grammy-winning R&B star Alicia Keys, the Tony-nominated musical is loosely inspired by her own coming of age in 1990s NYC and centers on Ali (Tony nominee Maleah Joi ...
The Journal of Development Economics has two other categories of papers that differ from other development journals: · The short paper format has proved popular. There were 148 submissions in 2023 (about 8% of total submissions), and 21 short papers were accepted. ... · The JDE registered reports had 19 stage 1 acceptances in 2023, and 1 ...
Dutch photographer and multimedia journalist Jelle Krings revisits the families that have kept a war-torn country moving, despite the Russian onslaught and in the face of great personal sacrifice
The global economy has been resilient and appears headed for a soft landing. Inflation continues to recede and risks have become more balanced globally. Nonetheless, medium-term growth prospects remain at the lowest level in decades and a smooth completion of the disinflation process should not be taken for granted. While the outlook for low-income developing countries (LIDCs) is improving ...
According to the IDC, enterprise spending on generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) could reach $143 billion in 2027, up from $16 billion in 2023. The world's largest companies are expected to ...
Summary. Researchers engaged with organizations across a variety of industries, each at a different stage of implementing responsible AI. They determined that, although data engineers and data ...
A 12-month marketing and business development plan should be created as a roadmap for integrating new lateral hires and partnering them with a business development liaison. The assigned liaison should host regular check-in calls and serve as the lateral's initial point of contact for all client development activities. Setting the Stage
Piaget's theory at its best. Perhaps, one of the best ways to demonstrate a child's development of cognitive and analytical skills, Piaget's theory can be easily applied to my childhood memories. As an infant, I played with a teddy bear. Being a single parent, my mother had to leave me in daycare, yet I protested against being alone.