

The Peak Performance Center
The pursuit of performance excellence, critical thinking vs. creative thinking.
Creative thinking is a way of looking at problems or situations from a fresh perspective to conceive of something new or original.
Critical thinking is the logical, sequential disciplined process of rationalizing, analyzing, evaluating, and interpreting information to make informed judgments and/or decisions.
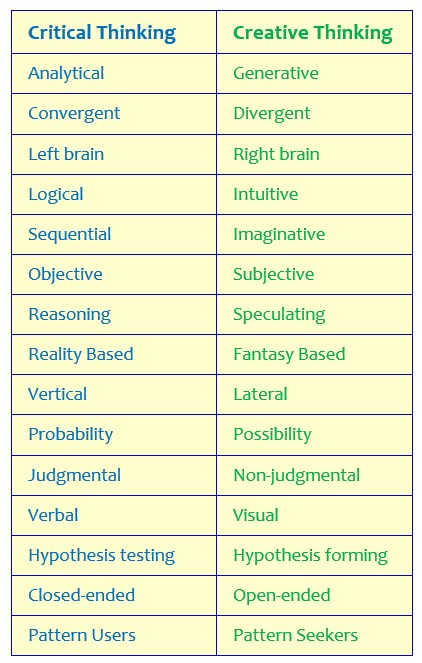
Critical Thinking vs. Creative Thinking – Key Differences
- Creative thinking tries to create something new, while critical thinking seeks to assess worth or validity of something that already exists.
- Creative thinking is generative, while critical thinking is analytical.
- Creative thinking is divergent, while critical thinking is convergent.
- Creative thinking is focused on possibilities, while critical thinking is focused on probability.
- Creative thinking is accomplished by disregarding accepted principles, while critical thinking is accomplished by applying accepted principles.
About Creative Thinking
Creative thinking is a process utilized to generate lists of new, varied and unique ideas or possibilities. Creative thinking brings a fresh perspective and sometimes unconventional solution to solve a problem or address a challenge. When you are thinking creatively, you are focused on exploring ideas, generating possibilities, and/or developing various theories.
Creative thinking can be performed both by an unstructured process such as brainstorming, or by a structured process such as lateral thinking.
Brainstorming is the process for generating unique ideas and solutions through spontaneous and freewheeling group discussion. Participants are encouraged to think aloud and suggest as many ideas as they can, no matter how outlandish it may seem.
Lateral thinking uses a systematic process that leads to logical conclusions. However, it involves changing a standard thinking sequence and arriving at a solution from completely different angles.
No matter what process you chose, the ultimate goal is to generate ideas that are unique, useful and worthy of further elaboration. Often times, critical thinking is performed after creative thinking has generated various possibilities. Critical thinking is used to vet those ideas to determine if they are practical.
Creative Thinking Skills
- Open-mindedness
- Flexibility
- Imagination
- Adaptability
- Risk-taking
- Originality
- Elaboration
- Brainstorming

About Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the process of actively analyzing, interpreting, synthesizing, evaluating information gathered from observation, experience, or communication. It is thinking in a clear, logical, reasoned, and reflective manner to make informed judgments and/or decisions.
Critical thinking involves the ability to:
- remain objective
In general, critical thinking is used to make logical well-formed decisions after analyzing and evaluating information and/or an array of ideas.
On a daily basis, it can be used for a variety of reasons including:
- to form an argument
- to articulate and justify a position or point of view
- to reduce possibilities to convergent toward a single answer
- to vet creative ideas to determine if they are practical
- to judge an assumption
- to solve a problem
- to reach a conclusion
Critical Thinking Skills
- Interpreting
- Integrating
- Contrasting
- Classifying
- Forecasting
- Hypothesizing

Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes
Creative Thinking vs. Critical Thinking
What's the difference.
Creative thinking and critical thinking are two distinct but equally important cognitive processes. Creative thinking involves generating new ideas, concepts, and solutions by exploring various possibilities and thinking outside the box. It encourages imagination, originality, and innovation. On the other hand, critical thinking involves analyzing, evaluating, and questioning ideas, arguments, and information to make informed decisions and judgments. It emphasizes logical reasoning, evidence-based thinking, and the ability to identify biases and fallacies. While creative thinking focuses on generating ideas, critical thinking focuses on evaluating and refining those ideas. Both thinking processes are essential for problem-solving, decision-making, and personal growth.
Further Detail
Introduction.
Creative thinking and critical thinking are two distinct cognitive processes that play crucial roles in problem-solving, decision-making, and innovation. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct attributes that set them apart. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of creative thinking and critical thinking, highlighting their differences and showcasing how they complement each other in various contexts.
Creative Thinking
Creative thinking is a cognitive process that involves generating new ideas, concepts, or solutions by exploring possibilities, making connections, and thinking outside the box. It is characterized by originality, flexibility, and fluency of thought. Creative thinkers often challenge conventional wisdom, embrace ambiguity, and are open to taking risks. They are adept at finding alternative perspectives and exploring multiple solutions to problems.
One of the key attributes of creative thinking is the ability to think divergently. This means being able to generate a wide range of ideas or possibilities, often through brainstorming or free association. Creative thinkers are not limited by constraints and are willing to explore unconventional or unorthodox approaches to problem-solving.
Another important aspect of creative thinking is the ability to make connections between seemingly unrelated concepts or ideas. This skill, known as associative thinking, allows creative thinkers to draw upon a diverse range of knowledge and experiences to generate innovative solutions. They can see patterns, analogies, and relationships that others may overlook.
Furthermore, creative thinking involves the willingness to take risks and embrace failure as a learning opportunity. Creative thinkers understand that not all ideas will be successful, but they are not deterred by setbacks. They view failures as stepping stones towards finding the right solution and are persistent in their pursuit of innovative ideas.
In summary, creative thinking is characterized by divergent thinking, associative thinking, risk-taking, and persistence. It encourages the exploration of new ideas and unconventional approaches to problem-solving.
Critical Thinking
Critical thinking, on the other hand, is a cognitive process that involves analyzing, evaluating, and interpreting information to form reasoned judgments or decisions. It is characterized by logical, systematic, and objective thinking. Critical thinkers are skilled at identifying biases, assumptions, and fallacies in arguments, and they strive to make well-informed and rational decisions based on evidence.
One of the key attributes of critical thinking is the ability to think analytically. Critical thinkers break down complex problems or situations into smaller components, examine the relationships between them, and evaluate the evidence or information available. They are adept at identifying logical inconsistencies or flaws in reasoning, which helps them make sound judgments.
Another important aspect of critical thinking is the ability to evaluate information objectively. Critical thinkers are skeptical and question the validity and reliability of sources. They seek evidence, consider alternative viewpoints, and weigh the strengths and weaknesses of different arguments before forming their own opinions. This attribute is particularly valuable in today's information-rich society, where misinformation and biased narratives are prevalent.
Furthermore, critical thinking involves the ability to think systematically. Critical thinkers follow a logical and structured approach to problem-solving, ensuring that all relevant factors are considered. They are skilled at identifying assumptions, clarifying concepts, and drawing logical conclusions based on the available evidence. This systematic approach helps minimize errors and biases in decision-making.
In summary, critical thinking is characterized by analytical thinking, objective evaluation, skepticism, and systematic reasoning. It emphasizes the importance of evidence-based decision-making and helps individuals navigate complex and information-rich environments.
Complementary Attributes
While creative thinking and critical thinking have distinct attributes, they are not mutually exclusive. In fact, they often complement each other and can be seen as two sides of the same coin.
Creative thinking can benefit from critical thinking by providing a framework for evaluating and refining ideas. Critical thinking helps creative thinkers assess the feasibility, viability, and desirability of their innovative ideas. It allows them to identify potential flaws, consider alternative perspectives, and make informed decisions about which ideas to pursue further.
On the other hand, critical thinking can benefit from creative thinking by expanding the range of possibilities and solutions. Creative thinking encourages critical thinkers to explore unconventional approaches, challenge assumptions, and consider alternative viewpoints. It helps them break free from rigid thinking patterns and discover innovative solutions to complex problems.
Moreover, both creative thinking and critical thinking require open-mindedness and a willingness to embrace ambiguity. They both involve a certain level of discomfort and uncertainty, as individuals venture into uncharted territories of thought. By combining creative and critical thinking, individuals can develop a well-rounded cognitive toolkit that enables them to tackle a wide range of challenges.
Creative thinking and critical thinking are two distinct cognitive processes that bring unique attributes to problem-solving, decision-making, and innovation. Creative thinking emphasizes divergent thinking, associative thinking, risk-taking, and persistence, while critical thinking emphasizes analytical thinking, objective evaluation, skepticism, and systematic reasoning.
While they have their differences, creative thinking and critical thinking are not mutually exclusive. They complement each other and can be seen as two sides of the same coin. Creative thinking benefits from critical thinking by providing a framework for evaluation and refinement, while critical thinking benefits from creative thinking by expanding the range of possibilities and solutions.
By cultivating both creative and critical thinking skills, individuals can enhance their ability to navigate complex problems, make well-informed decisions, and drive innovation in various domains. These cognitive processes are not only valuable in academic and professional settings but also in everyday life, where the ability to think creatively and critically can lead to personal growth and success.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.

Exploring the Difference: Creative Thinking vs. Critical Thinking
Annie Walls
Creative thinking and critical thinking are two distinct cognitive processes that play important roles in problem-solving and decision-making. While creative thinking involves generating innovative ideas and solutions, critical thinking involves analyzing and evaluating information to make reasoned judgments. Both types of thinking have their unique characteristics and benefits. In this article, we will explore the difference between creative thinking and critical thinking, and how they can be applied in various contexts.
Key Takeaways
- Creative thinking involves generating new ideas and solutions.
- Critical thinking involves analyzing and evaluating information to make reasoned judgments.
- Creative thinkers are characterized by their curiosity, open-mindedness, and willingness to take risks.
- Critical thinkers are characterized by their skepticism, logical reasoning, and attention to detail.
- Creative thinking can lead to innovation and breakthroughs.
Understanding Creative Thinking
Defining creative thinking.
Creative thinking is the ability to think outside the box and generate innovative ideas. It involves breaking free from conventional ways of thinking and exploring new possibilities. Creativity is the key element in creative thinking , as it allows individuals to come up with unique and original solutions to problems.
Creative thinking is not limited to artistic endeavors; it can be applied to various aspects of life, including problem-solving, decision-making, and even everyday tasks. It requires an open mind, a willingness to take risks, and the ability to see things from different perspectives.
In order to foster creative thinking, it is important to create an environment that encourages experimentation and exploration. This can be done by providing opportunities for brainstorming, encouraging collaboration, and embracing failure as a learning opportunity.
Here are some techniques that can enhance creative thinking:
- Mind mapping: A visual tool that helps organize thoughts and generate new ideas.
- Divergent thinking: Generating multiple solutions to a problem.
- Analogical thinking: Drawing connections between unrelated concepts.
Tip: Embrace curiosity and embrace the unknown. Be open to new experiences and ideas, and don't be afraid to take risks.
Characteristics of Creative Thinkers
Creative thinkers possess a unique set of characteristics that set them apart from others. They have the ability to think outside the box and come up with innovative solutions to problems. Imagination plays a crucial role in their thought process, allowing them to envision possibilities that others may not see. They are open-minded and willing to explore different perspectives, which helps them generate fresh ideas. Creative thinkers are also comfortable with ambiguity and uncertainty, as they understand that these conditions can lead to breakthroughs. They are not afraid to take risks and are willing to challenge the status quo.
Benefits of Creative Thinking
Creative thinking offers numerous benefits that can enhance various aspects of life. One of the key advantages of creative thinking is the ability to generate innovative ideas and solutions. Creativity allows individuals to think outside the box and come up with unique approaches to problems. This can lead to breakthroughs and advancements in various fields.
Another benefit of creative thinking is its impact on personal growth and self-expression. By engaging in creative activities, individuals can explore their inner thoughts and emotions, allowing for self-discovery and self-reflection. Creative pursuits such as painting, writing, or playing an instrument can serve as outlets for self-expression and can contribute to overall well-being.
In addition, creative thinking can foster collaboration and teamwork. When individuals approach problems with a creative mindset, they are more likely to seek input and ideas from others. This promotes a collaborative environment where diverse perspectives are valued and innovative solutions are developed.
Furthermore, creative thinking can enhance problem-solving skills. By thinking creatively, individuals are able to consider multiple perspectives and explore alternative solutions. This can lead to more effective problem-solving and decision-making processes.
Overall, creative thinking offers a range of benefits, from generating innovative ideas to fostering collaboration and enhancing problem-solving skills.
Techniques for Enhancing Creative Thinking
In order to enhance creative thinking, there are several techniques that can be employed:
- Mind Mapping : This technique involves visually organizing ideas and concepts in a non-linear manner, allowing for connections and associations to be made.
- Brainstorming : This popular technique involves generating a large number of ideas in a short amount of time, without judgment or evaluation.
- Divergent Thinking : This approach encourages exploring multiple possibilities and perspectives, thinking outside the box, and avoiding conventional solutions.
Tip: When using these techniques, it is important to create a supportive and non-judgmental environment that encourages free thinking and idea generation.
By utilizing these techniques, individuals and teams can unlock their creative potential and generate innovative ideas to drive growth and success.
Exploring Critical Thinking

Defining Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is essentially a questioning, challenging approach to knowledge and perceived wisdom. It involves ideas and information from an objective perspective, analyzing and evaluating them to form well-reasoned judgments and decisions. It goes beyond accepting information at face value and encourages a deeper understanding of the subject matter. Critical thinkers are curious, open-minded, and willing to consider different perspectives. They are skilled at identifying biases and assumptions, and they strive to make logical and evidence-based conclusions.
Characteristics of Critical Thinkers
Critical thinkers possess several key characteristics that set them apart:
- Analytical Skills : Critical thinkers are adept at analyzing information and breaking it down into its component parts. They can identify patterns, evaluate evidence, and draw logical conclusions.
- Open-mindedness : Critical thinkers are willing to consider different perspectives and are open to changing their beliefs or opinions based on new evidence or information.
- Skepticism : Critical thinkers approach information with a healthy dose of skepticism. They question assumptions, challenge authority, and seek evidence to support or refute claims.
Tip: Critical thinkers actively engage in critical reflection, constantly questioning their own thinking and seeking to improve their reasoning abilities.
Benefits of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking has numerous benefits that can positively impact various aspects of life. It enhances problem-solving skills, allowing individuals to analyze complex situations and make informed decisions. Analytical thinking is a key component of critical thinking, enabling individuals to break down problems into smaller parts and examine them from different perspectives. This approach helps in identifying potential biases and assumptions, leading to more objective and rational decision-making.
In addition, critical thinking promotes effective communication . By critically evaluating information and arguments, individuals can articulate their thoughts and ideas more clearly and persuasively. They can also identify logical fallacies and inconsistencies in others' arguments, enabling them to engage in meaningful and constructive discussions.
Furthermore, critical thinking fosters creativity and innovation . By questioning assumptions and challenging conventional wisdom, individuals can generate new ideas and approaches. Critical thinkers are more open to exploring alternative solutions and are willing to take risks in order to achieve better outcomes.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Developing critical thinking skills is essential for success in both personal and professional life. It involves the ability to analyze information objectively, evaluate arguments and evidence, and make informed decisions. Here are some strategies that can help enhance your critical thinking skills:
- Ask Questions: One of the key aspects of critical thinking is asking thoughtful and probing questions. This helps you gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter and challenges assumptions.
- Seek Different Perspectives: To develop critical thinking skills, it is important to consider multiple viewpoints and perspectives. This allows you to evaluate arguments from different angles and make well-rounded judgments.
- Practice Problem-Solving: Critical thinking involves problem-solving skills. Engaging in activities that require you to analyze and solve problems can help sharpen your critical thinking abilities.
- Reflect on Your Thinking: Take time to reflect on your own thinking process. Consider the biases, assumptions, and logical fallacies that may be influencing your thoughts and decisions.
- Continuous Learning: Critical thinking is a skill that can be developed and improved over time. Engage in continuous learning, read diverse perspectives, and challenge your own beliefs and assumptions.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily life, you can enhance your critical thinking skills and become a more effective problem solver and decision-maker.
Comparing Creative and Critical Thinking

Different Approaches to Problem Solving
When it comes to problem solving, creative thinking and critical thinking take different approaches. Creative thinkers often rely on their imagination and intuition to generate unique and innovative solutions. They think outside the box and are not afraid to take risks. On the other hand, critical thinkers approach problem solving in a more analytical and logical manner. They carefully analyze the problem, gather information, and evaluate different options before making a decision.
Role of Imagination and Logic
The role of imagination and logic in creative and critical thinking is crucial. Imagination allows us to think outside the box, explore new possibilities, and come up with innovative ideas. It is the fuel that ignites creativity and helps us see beyond the obvious. On the other hand, logic provides the framework for organizing and analyzing information, making rational decisions, and solving problems systematically. It helps us evaluate the feasibility and effectiveness of our ideas.
When it comes to problem-solving, a balance between imagination and logic is essential. While imagination helps generate unique and unconventional solutions, logic ensures that these solutions are practical and viable. By combining the two, we can approach problems with a structured yet imaginative mindset, finding innovative solutions and making connections that others may overlook.
In summary, imagination and logic are two sides of the same coin when it comes to creative and critical thinking. They complement each other and work together to enhance our ability to think creatively and critically.
Balancing Intuition and Analysis
When it comes to problem-solving, finding the right balance between intuition and analysis is crucial. Intuition allows us to tap into our subconscious knowledge and make quick decisions based on gut feelings. On the other hand, analysis involves a systematic and logical approach to gather and evaluate information. Both intuition and analysis have their strengths and weaknesses, and leveraging both can lead to more effective problem-solving.
To strike a balance between intuition and analysis, consider the following:
- Trust your instincts: Pay attention to your gut feelings and initial reactions, as they can provide valuable insights.
- Gather and evaluate data: Take the time to gather relevant information and analyze it objectively.
- Seek different perspectives: Engage with others who have different viewpoints to challenge your assumptions and broaden your thinking.
Tip: Remember that finding the right balance between intuition and analysis is a dynamic process. It requires practice and reflection to develop a nuanced approach to problem-solving.
Collaboration and Individuality in Thinking
Collaboration and individuality are two key aspects of thinking that play a crucial role in both creative and critical thinking. While collaboration allows for the exchange of ideas and perspectives, individuality brings unique insights and approaches to the table. Collaboration fosters a sense of teamwork and encourages diverse thinking, which can lead to innovative solutions. On the other hand, individuality allows individuals to think independently and bring their own creativity and expertise to the problem-solving process.
In order to effectively balance collaboration and individuality in thinking, it is important to create an environment that values both. This can be achieved by promoting open communication and active listening, where team members feel comfortable sharing their ideas and opinions. Additionally, providing opportunities for individual reflection and brainstorming can help stimulate creativity and encourage unique perspectives.
To further enhance collaboration and individuality in thinking, organizations can implement strategies such as group brainstorming sessions , where team members can collectively generate ideas and build upon each other's thoughts. This encourages collaboration while also allowing individuals to contribute their own unique insights. Another strategy is to assign individual tasks within a larger project, giving team members the opportunity to work independently and bring their own creative solutions to the table.
In summary, collaboration and individuality are both essential components of thinking that contribute to creative and critical thinking processes. By fostering a balance between collaboration and individuality, organizations can harness the power of teamwork and individual creativity to drive innovation and problem-solving.
In the article section of my website, I would like to discuss the topic of 'Comparing Creative and Critical Thinking'. Creative thinking and critical thinking are two essential cognitive skills that play a significant role in problem-solving, decision-making, and innovation. While creative thinking involves generating new ideas, thinking outside the box, and exploring different perspectives , critical thinking focuses on analyzing, evaluating, and questioning information to make informed judgments. Both types of thinking are crucial in today's fast-paced and complex world. By understanding the differences and similarities between creative and critical thinking, individuals can enhance their problem-solving abilities and foster a culture of innovation. If you want to learn more about the power of creative thinking and how it can transform your business, visit th website, Creativity Keynote Speaker James Taylor - Inspiring Creative Minds .
In conclusion, both creative thinking and critical thinking are essential skills that complement each other in problem-solving and decision-making. While creative thinking allows for innovative ideas and out-of-the-box solutions, critical thinking provides the necessary analysis and evaluation to ensure the feasibility and effectiveness of those ideas. Flexibility is a key aspect of creative thinking, enabling individuals to adapt and explore different perspectives, while accuracy is a fundamental element of critical thinking, ensuring logical reasoning and evidence-based conclusions. By harnessing the power of both creative and critical thinking, individuals can enhance their problem-solving abilities and make well-informed decisions in various aspects of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between creative thinking and critical thinking.
Creative thinking involves generating new ideas, possibilities, and solutions, while critical thinking involves analyzing, evaluating, and making reasoned judgments.
Can someone be both a creative thinker and a critical thinker?
Yes, individuals can possess both creative and critical thinking skills. They can use creative thinking to generate ideas and critical thinking to evaluate and refine those ideas.
Which is more important, creative thinking or critical thinking?
Both creative thinking and critical thinking are important and complement each other. Creative thinking generates new ideas, while critical thinking helps evaluate and implement those ideas effectively.
How can I enhance my creative thinking skills?
You can enhance your creative thinking skills by engaging in activities that stimulate your imagination, such as brainstorming, mind mapping, and exploring new perspectives.
What are some techniques for developing critical thinking skills?
Techniques for developing critical thinking skills include analyzing arguments, evaluating evidence, questioning assumptions, and considering different perspectives.
Is creative thinking limited to artistic pursuits?
No, creative thinking is not limited to artistic pursuits. It can be applied to various fields and industries, including problem-solving in science, business, technology, and more.

Popular Posts
Meilleur conférencier principal en teambuilding.
Les conférences virtuelles et les sommets peuvent être des moyens très efficaces pour inspirer, informer
Meilleur conférencier principal sur le bien-être
Les conférences sur le bien-être et la santé mentale sont essentielles pour promouvoir un environnement
Meilleur conférencier principal en communication
Les conférences virtuelles, les réunions et les sommets peuvent être un moyen très efficace d’inspirer,
Meilleur Conférencier en Stratégie
Les conférenciers en stratégie jouent un rôle crucial dans l’inspiration et la motivation des entreprises
Meilleur Conférencier Culturel
En tant que conférencier de keynote sur la culture, il est essentiel d’avoir un partenaire
Meilleur conférencier principal dans le domaine des soins de santé
Les conférenciers principaux en santé et bien-être jouent un rôle crucial dans l’industrie de la
James is a top motivational keynote speaker who is booked as a creativity and innovation keynote speaker, AI speaker , sustainability speaker and leadership speaker . Recent destinations include: Dubai , Abu Dhabi , Orlando , Las Vegas , keynote speaker London , Barcelona , Bangkok , Miami , Berlin , Riyadh , New York , Zurich , motivational speaker Paris , Singapore and San Francisco
Latest News
- 415.800.3059
- [email protected]
- Media Interviews
- Meeting Planners
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
FIND ME ON SOCIAL
© 2024 James Taylor DBA P3 Music Ltd.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Part Two: You are the President and CEO of You
Thinking Critically and Creatively
Dr. andrew robert baker.
Critical and creative thinking skills are perhaps the most fundamental skills involved in making judgments and solving problems. They are some of the most important skills I have ever developed. I use them everyday and continue to work to improve them both.
The ability to think critically about a matter—to analyze a question, situation, or problem down to its most basic parts—is what helps us evaluate the accuracy and truthfulness of statements, claims, and information we read and hear. It is the sharp knife that, when honed, separates fact from fiction, honesty from lies, and the accurate from the misleading. We all use this skill to one degree or another almost every day. For example, we use critical thinking every day as we consider the latest consumer products and why one particular product is the best among its peers. Is it a quality product because a celebrity endorses it? Because a lot of other people may have used it? Because it is made by one company versus another? Or perhaps because it is made in one country or another? These are questions representative of critical thinking.
The academic setting demands more of us in terms of critical thinking than everyday life. It demands that we evaluate information and analyze a myriad of issues. It is the environment where our critical thinking skills can be the difference between success and failure. In this environment we must consider information in an analytical, critical manner. We must ask questions—What is the source of this information? Is this source an expert one and what makes it so? Are there multiple perspectives to consider on an issue? Do multiple sources agree or disagree on an issue? Does quality research substantiate information or opinion? Do I have any personal biases that may affect my consideration of this information? It is only through purposeful, frequent, intentional questioning such as this that we can sharpen our critical thinking skills and improve as students, learners, and researchers. Developing my critical thinking skills over a twenty year period as a student in higher education enabled me to complete a quantitative dissertation, including analyzing research and completing statistical analysis, and earning my Ph.D. in 2014.
While critical thinking analyzes information and roots out the true nature and facets of problems, it is creative thinking that drives progress forward when it comes to solving these problems. Exceptional creative thinkers are people that invent new solutions to existing problems that do not rely on past or current solutions. They are the ones who invent solution C when everyone else is still arguing between A and B. Creative thinking skills involve using strategies to clear the mind so that our thoughts and ideas can transcend the current limitations of a problem and allow us to see beyond barriers that prevent new solutions from being found.
Brainstorming is the simplest example of intentional creative thinking that most people have tried at least once. With the quick generation of many ideas at once we can block-out our brain’s natural tendency to limit our solution-generating abilities so we can access and combine many possible solutions/thoughts and invent new ones. It is sort of like sprinting through a race’s finish line only to find there is new track on the other side and we can keep going, if we choose. As with critical thinking, higher education both demands creative thinking from us and is the perfect place to practice and develop the skill. Everything from word problems in a math class, to opinion or persuasive speeches and papers, call upon our creative thinking skills to generate new solutions and perspectives in response to our professor’s demands. Creative thinking skills ask questions such as—What if? Why not? What else is out there? Can I combine perspectives/solutions? What is something no one else has brought-up? What is being forgotten/ignored? What about ______? It is the opening of doors and options that follows problem-identification.
Consider an assignment that required you to compare two different authors on the topic of education and select and defend one as better. Now add to this scenario that your professor clearly prefers one author over the other. While critical thinking can get you as far as identifying the similarities and differences between these authors and evaluating their merits, it is creative thinking that you must use if you wish to challenge your professor’s opinion and invent new perspectives on the authors that have not previously been considered.
So, what can we do to develop our critical and creative thinking skills? Although many students may dislike it, group work is an excellent way to develop our thinking skills. Many times I have heard from students their disdain for working in groups based on scheduling, varied levels of commitment to the group or project, and personality conflicts too, of course. True—it’s not always easy, but that is why it is so effective. When we work collaboratively on a project or problem we bring many brains to bear on a subject. These different brains will naturally develop varied ways of solving or explaining problems and examining information. To the observant individual we see that this places us in a constant state of back and forth critical/creative thinking modes.
For example, in group work we are simultaneously analyzing information and generating solutions on our own, while challenging other’s analyses/ideas and responding to challenges to our own analyses/ideas. This is part of why students tend to avoid group work—it challenges us as thinkers and forces us to analyze others while defending ourselves, which is not something we are used to or comfortable with as most of our educational experiences involve solo work. Your professors know this—that’s why we assign it—to help you grow as students, learners, and thinkers!
Foundations of Academic Success: Words of Wisdom Copyright © 2015 by Thomas Priester is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Please log in to save materials. Log in
- Austin Community College
- Effective Learning Strategies
- Student Success
- https-www-oercommons-org-courseware-module-25864-s
- https://www.oercommons.org/courseware/module/25864/student/206121
Chapter 7: Critical and Creative Thinking

Learning Framework: Effective Strategies for College Success
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Define critical thinking
- Describe the role that logic plays in critical thinking
- Describe how critical thinking skills can be used to evaluate information
- Apply the CRAAP test to evaluate sources of information
- Identify strategies for developing yourself as a critical thinker
- Identify applications in education and one's career where creative thinking is relevant and beneficial
- Explore key elements and stages in the creative process
- Apply specific skills for stimulating creative perspectives and innovative options
- Integrate critical and creative thinking in the process of problem-solving
Critical and Creative Thinking
Critical Thinking
As a college student, you are tasked with engaging and expanding your thinking skills. One of the most important of these skills is critical thinking because it relates to nearly all tasks, situations, topics, careers, environments, challenges, and opportunities. It is a “domain-general” thinking skill, not one that is specific to a particular subject area.
What Is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is clear, reasonable, reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do (Robert Ennis.) It means asking probing questions like “How do we know?” or “Is this true in every case or just in this instance?” It involves being skeptical and challenging assumptions rather than simply memorizing facts or blindly accepting what you hear or read.
Imagine, for example, that you’re reading a history textbook. You wonder who wrote it and why, because you detect certain biases in the writing. You find that the author has a limited scope of research focused only on a particular group within a population. In this case, your critical thinking reveals that there are “other sides to the story.”
Who are critical thinkers, and what characteristics do they have in common? Critical thinkers are usually curious and reflective people. They like to explore and probe new areas and seek knowledge, clarification, and new solutions. They ask pertinent questions, evaluate statements and arguments, and they distinguish between facts and opinion. They are also willing to examine their own beliefs, possessing a manner of humility that allows them to admit lack of knowledge or understanding when needed. They are open to changing their mind. Perhaps most of all, they actively enjoy learning, and seeking new knowledge is a lifelong pursuit. This may well be you!
No matter where you are on the road to being a critical thinker, you can always more fully develop and finely tune your skills. Doing so will help you develop more balanced arguments, express yourself clearly, read critically, and glean important information efficiently. Critical thinking skills will help you in any profession or any circumstance of life, from science to art to business to teaching. With critical thinking, you become a clearer thinker and problem solver.
The following video, from Lawrence Bland, presents the major concepts and benefits of critical thinking.
Critical Thinking and Logic
Critical thinking is fundamentally a process of questioning information and data and then reflecting on and assessing what you discover to arrive at a reasonable conclusion. You may question the information you read in a textbook, or you may question what a politician or a professor or a classmate says.
You can also question a commonly held belief or a new idea. It is equally important (and even more challenging) to question your own thinking and beliefs! With critical thinking, anything and everything is subject to question and examination for the purpose of logically constructing reasoned perspectives.
What Is Logic?
The word logic comes from the Ancient Greek logike , referring to the science or art of reasoning. Using logic, a person evaluates arguments and reasoning and strives to distinguish between good and bad reasoning, or between truth and falsehood. Using logic, you can evaluate the ideas and claims of others, make good decisions, and form sound beliefs about the world.
Questions of Logic in Critical Thinking
Let’s use a simple example of applying logic to a critical-thinking situation. In this hypothetical scenario, a man has a Ph.D. in political science, and he works as a professor at a local college. His wife works at the college, too. They have three young children in the local school system, and their family is well known in the community. The man is now running for political office. Are his credentials and experience sufficient for entering public office? Will he be effective in the political office? Some voters might believe that his personal life and current job, on the surface, suggest he will do well in the position, and they will vote for him. In truth, the characteristics described don’t guarantee that the man will do a good job. The information is somewhat irrelevant. What else might you want to know? How about whether the man had already held a political office and done a good job? In this case, we want to think critically about how much information is adequate in order to make a decision based on logic instead of assumptions.
The following questions, presented in Figure 1, below, are ones you may apply to formulate a logical, reasoned perspective in the above scenario or any other situation:
- What’s happening? Gather the basic information and begin to think of questions.
- Why is it important? Ask yourself why it’s significant and whether or not you agree.
- What don’t I see? Is there anything important missing?
- How do I know? Ask yourself where the information came from and how it was constructed.
- Who is saying it? What’s the position of the speaker and what is influencing them?
- What else? What if? What other ideas exist and are there other possibilities?

Problem-Solving with Critical Thinking
For most people, a typical day is filled with critical thinking and problem-solving challenges. In fact, critical thinking and problem-solving go hand-in-hand. They both refer to using knowledge, facts, and data to solve problems effectively. But with problem-solving, you are specifically identifying, selecting, and defending your solution. Below are some examples of using critical thinking to problem-solve:
- Your roommate was upset and said some unkind words to you, which put a crimp in the relationship. You try to see through the angry behaviors to determine how you might best support the roommate and help bring the relationship back to a comfortable spot.
- Your campus club has been languishing due to a lack of participation and funds. The new club president, though, is a marketing major and has identified some strategies to interest students in joining and supporting the club. Implementation is forthcoming.
- Your final art class project challenges you to conceptualize form in new ways. On the last day of class when students present their projects, you describe the techniques you used to fulfill the assignment. You explain why and how you selected that approach.
- Your math teacher sees that the class is not quite grasping a concept. They use clever questioning to dispel anxiety and guide you to a new understanding of the concept.
You have a job interview for a position that you feel you are only partially qualified for, although you really want the job and are excited about the prospects. You analyze how you will explain your skills and experiences in a way to show that you are a good match for the prospective employer.
- You are doing well in college, and most of your college and living expenses are covered. But there are some gaps between what you want and what you feel you can afford. You analyze your income, savings, and budget to better calculate what you will need to stay in college and maintain your desired level of spending.
Evaluating Information with Critical Thinking
Evaluating information can be one of the most complex tasks you will be faced with in college. But if you utilize the following four strategies, you will be well on your way to success:
- Read for understanding
- Examine arguments
- Clarify thinking
- Cultivate “habits of mind”
Read for Understanding
When you read, take notes or mark the text to track your thinking about what you are reading. As you make connections and ask questions in response to what you read, you monitor your comprehension and enhance your long-term understanding of the material. You will want to mark important arguments and key facts. Indicate where you agree and disagree or have further questions. You don’t necessarily need to read every word, but make sure you understand the concepts or the intentions behind what is written. See the chapter on Active Reading Strategies for additional tips.
Examine Arguments
When you examine arguments or claims that an author, speaker, or other source is making, your goal is to identify and examine the hard facts. You can use the spectrum of authority strategy for this purpose. The spectrum of authority strategy assists you in identifying the “hot” end of an argument—feelings, beliefs, cultural influences, and societal influences—and the “cold” end of an argument—scientific influences. The most compelling arguments balance elements from both ends of the spectrum. The following video explains this strategy in further detail:
Clarify Thinking
When you use critical thinking to evaluate information, you need to clarify your thinking to yourself and likely to others. Doing this well is mainly a process of asking and answering probing questions, such as the logic questions discussed earlier. Design your questions to fit your needs, but be sure to cover adequate ground. What is the purpose? What question are we trying to answer? What point of view is being expressed? What assumptions are we or others making? What are the facts and data we know, and how do we know them? What are the concepts we’re working with? What are the conclusions, and do they make sense? What are the implications?
Cultivate “Habits of Mind”
“Habits of mind” are the personal commitments, values, and standards you have about the principle of good thinking. Consider your intellectual commitments, values, and standards. Do you approach problems with an open mind, a respect for truth, and an inquiring attitude? Some good habits to have when thinking critically are being receptive to having your opinions changed, having respect for others, being independent and not accepting something is true until you’ve had the time to examine the available evidence, being fair-minded, having respect for a reason, having an inquiring mind, not making assumptions, and always, especially, questioning your own conclusions—in other words, developing an intellectual work ethic. Try to work these qualities into your daily life.
In 2010, a textbook being used in fourth-grade classrooms in Virginia became big news for all the wrong reasons. The book, Our Virginia by Joy Masoff, had caught the attention of a parent who was helping her child do her homework, according to an article in The Washington Post . Carol Sheriff was a historian for the College of William and Mary and as she worked with her daughter, she began to notice some glaring historical errors, not the least of which was a passage that described how thousands of African Americans fought for the South during the Civil War.
Further investigation into the book revealed that, although the author had written textbooks on a variety of subjects, she was not a trained historian. The research she had done to write Our Virginia, and in particular the information she included about Black Confederate soldiers, was done through the Internet and included sources created by groups like the Sons of Confederate Veterans, an organization that promotes views of history that de-emphasize the role of slavery in the Civil War.
How did a book with errors like these come to be used as part of the curriculum and who was at fault? Was it Masoff for using untrustworthy sources for her research? Was it the editors who allowed the book to be published with these errors intact? Was it the school board for approving the book without more closely reviewing its accuracy?
There are a number of issues at play in the case of Our Virginia , but there’s no question that evaluating sources is an important part of the research process and doesn’t just apply to Internet sources. Using inaccurate, irrelevant, or poorly researched sources can affect the quality of your own work. Being able to understand and apply the concepts that follow is crucial to becoming a more savvy user and creator of information.
When you begin evaluating sources, what should you consider? The CRAAP test is a series of common evaluative elements you can use to evaluate the C urrency, R elevance, A uthority, A ccuracy, and P urpose of your sources. The CRAAP test was developed by librarians at California State University at Chico and it gives you a good, overall set of elements to look for when evaluating a resource. Let’s consider what each of these evaluative elements means.
One of the most important and interesting steps to take as you begin researching a subject is selecting the resources that will help you build your thesis and support your assertions. Certain topics require you to pay special attention to how current your resource is—because they are time sensitive, because they have evolved so much over the years, or because new research comes out on the topic so frequently. When evaluating the currency of an article, consider the following:
- When was the item written, and how frequently does the publication come out?
- Is there evidence of newly added or updated information in the item?
- If the information is dated, is it still suitable for your topic?
- How frequently does information change about your topic?
Understanding what resources are most applicable to your subject and why they are applicable can help you focus and refine your thesis. Many topics are broad and searching for information on them produces a wide range of resources. Narrowing your topic and focusing on resources specific to your needs can help reduce the piles of information and help you focus in on what is truly important to read and reference. When determining relevance consider the following:
- Does the item contain information relevant to your argument or thesis?
- Read the article’s introduction, thesis, and conclusion.
- Scan main headings and identify article keywords.
- For book resources, start with the index or table of contents—how wide a scope does the item have? Will you use part or all of this resource?
- Does the information presented support or refute your ideas?
- If the information refutes your ideas, how will this change your argument?
- Does the material provide you with current information?
- What is the material’s intended audience?
Understanding more about your information’s source helps you determine when, how, and where to use that information. Is your author an expert on the subject? Do they have some personal stake in the argument they are making? What is the author or information producer’s background? When determining the authority of your source, consider the following:
- What are the author’s credentials?
- What is the author’s level of education, experience, and/or occupation?
- What qualifies the author to write about this topic?
- What affiliations does the author have? Could these affiliations affect their position?
- What organization or body published the information? Is it authoritative? Does it have an explicit position or bias?
Determining where information comes from, if the evidence supports the information, and if the information has been reviewed or refereed can help you decide how and whether to use a source. When determining the accuracy of a source, consider the following:
- Is the source well-documented? Does it include footnotes, citations, or a bibliography?
- Is information in the source presented as fact, opinion, or propaganda? Are biases clear?
- Can you verify information from the references cited in the source?
- Is the information written clearly and free of typographical and grammatical mistakes? Does the source look to be edited before publication? A clean, well-presented paper does not always indicate accuracy, but usually at least means more eyes have been on the information.
Knowing why the information was created is a key to evaluation. Understanding the reason or purpose of the information, if the information has clear intentions, or if the information is fact, opinion, or propaganda will help you decide how and why to use information:
- Is the author’s purpose to inform, sell, persuade, or entertain?
- Does the source have an obvious bias or prejudice?
- Is the article presented from multiple points of view?
- Does the author omit important facts or data that might disprove their argument?
- Is the author’s language informal, joking, emotional, or impassioned?
- Is the information clearly supported by evidence?
When you feel overwhelmed by the information you are finding, the CRAAP test can help you determine which information is the most useful to your research topic. How you respond to what you find out using the CRAAP test will depend on your topic. Maybe you want to use two overtly biased resources to inform an overview of typical arguments in a particular field. Perhaps your topic is historical and currency means the past hundred years rather than the past one or two years. Use the CRAAP test, be knowledgeable about your topic, and you will be on your way to evaluating information efficiently and well!
Next, visit the ACC Library’s Website for a tutorial and quiz on using the CRAAP test to evaluate sources.
Developing Yourself As a Critical Thinker

Critical thinking is a fundamental skill for college students, but it should also be a lifelong pursuit. Below are additional strategies to develop yourself as a critical thinker in college and in everyday life:
- Reflect and practice : Always reflect on what you’ve learned. Is it true all the time? How did you arrive at your conclusions?
- Use wasted time : It’s certainly important to make time for relaxing, but if you find you are indulging in too much of a good thing, think about using your time more constructively. Determine when you do your best thinking and try to learn something new during that part of the day.
- Redefine the way you see things : It can be very uninteresting to always think the same way. Challenge yourself to see familiar things in new ways. Put yourself in someone else’s shoes and consider things from a different angle or perspective. If you’re trying to solve a problem, list all your concerns: what you need in order to solve it, who can help, what some possible barriers might be, etc. It’s often possible to reframe a problem as an opportunity. Try to find a solution where there seems to be none.
- Analyze the influences on your thinking and in your life : Why do you think or feel the way you do? Analyze your influences. Think about who in your life influences you. Do you feel or react a certain way because of social convention, or because you believe it is what is expected of you? Try to break out of any molds that may be constricting you.
- Express yourself : Critical thinking also involves being able to express yourself clearly. Most important in expressing yourself clearly is stating one point at a time. You might be inclined to argue every thought, but you might have greater impact if you focus just on your main arguments. This will help others to follow your thinking clearly. For more abstract ideas, assume that your audience may not understand. Provide examples, analogies, or metaphors where you can.
- Enhance your wellness : It’s easier to think critically when you take care of your mental and physical health. Try taking activity breaks throughout the day to reach 30 to 60 minutes of physical activity each day. Scheduling physical activity into your day can help lower stress and increase mental alertness. Also, do your most difficult work when you have the most energy . Think about the time of day you are most effective and have the most energy. Plan to do your most difficult work during these times. And be sure to reach out for help i f you feel you need assistance with your mental or physical health (see Maintaining Your Mental (and Physical) Health for more information).
Complete ACTIVITY 1: REFLECT ON CRITICAL THINKING at the end of the chapter to deepen your understanding of critical thinking in action.
Creative thinking.
Creative thinking is an invaluable skill for college students because it helps you look at problems and situations from a fresh perspective. Creative thinking is a way to develop novel or unorthodox solutions that do not depend wholly on past or current solutions. It’s a way of employing strategies to clear your mind so that your thoughts and ideas can transcend what appears to be the limitations of a problem. Creative thinking is a way of moving beyond barriers and it can be understood as a skill —as opposed to an inborn talent or natural “gift”—that can be taught as well as learned.
However, the ability to think and act in creative ways is a natural ability that we all exhibited as children. The curiosity, wonder, imagination, playfulness, and persistence in obtaining new skills are what transformed us into the powerful learners that we became well before we entered school. As a creative thinker now, you are curious, optimistic, and imaginative. You see problems as interesting opportunities, and you challenge assumptions and suspend judgment. You don’t give up easily. You work hard. Is this you? Even if you don’t yet see yourself as a competent creative thinker or problem-solver yet, you can learn solid skills and techniques to help you become one.
Creative Thinking in Education
College is a great ground for enhancing creative thinking skills. The following are some examples of college activities that can stimulate creative thinking. Are any familiar to you? What are some aspects of your own college experience that require you to think creatively?
- Design sample exam questions to test your knowledge as you study for a final.
- Devise a social media strategy for a club on campus.
- Propose an education plan for a major you are designing for yourself.
- Prepare a speech that you will give in a debate in your course.
- Arrange audience seats in your classroom to maximize attention during your presentation.
- Participate in a brainstorming session with your classmates on how you will collaborate on a group project.
- Draft a script for a video production that will be shown to several college administrators.
- Compose a set of requests and recommendations for a campus office to improve its services for students.
- Develop a marketing pitch for a mock business you are developing.
- Develop a plan to reduce energy consumption in your home, apartment, or dorm.
How to Stimulate Creative Thinking
The following video, How to Stimulate the Creative Process , identifies six strategies to stimulate your creative thinking.
- Sleep on it . Over the years, researchers have found that the REM sleep cycle boosts our creativity and problem-solving abilities, providing us with innovative ideas or answers to vexing dilemmas when we awaken. Keep a pen and paper by the bed so you can write down your nocturnal insights if they wake you up.
- Go for a run or hit the gym . Studies indicate that exercise stimulates creative thinking, and the brainpower boost lasts for a few hours.
- Allow your mind to wander a few times every day. Far from being a waste of time, daydreaming has been found to be an essential part of generating new ideas. If you’re stuck on a problem or creatively blocked, think about something else for a while.
- Keep learning . Studying something far removed from your area of expertise is especially effective in helping you think in new ways.
- Put yourself in nerve-racking situations once in a while to fire up your brain. Fear and frustration can trigger innovative thinking.
- Keep a notebook with you, or create a file for ideas on your smartphone or laptop, so you always have a place to record fleeting thoughts. They’re sometimes the best ideas of all.
The following video, Where Good Ideas Come From by Steven Johnson, reinforces the idea that time allows creativity to flourish.
Watch this supplemental video by PBS Digital Studies: How To Be Creative | Off Book | PBS Digital Studio for a more in-depth look on how to become a “powerful creative person.”
Below is an article by Professor Tobin Quereau, called In Search of Creativity . Perhaps the article can help you think about some simple principles that can enhance your own creative thinking.
In Search of Creativity Tobin Quereau As I was searching through my files the other day for materials on creativity, I ran across some crumpled, yellowed notes which had no clear identification as to their source. Though I cannot remember exactly where they came from, I pass them along to you as an example of the absurd lengths to which some authors will go to get people’s attention. The notes contained five principles or practices with accompanying commentary which supposedly enhance creativity. I reprint them here as I found them and leave you to make your own judgment on the matter.... 1. Do It Poorly! One has to start somewhere and hardly anyone I know starts perfectly at anything. As a result, hardly anyone seems to start very much at all. Often times the quest for excellence quashes any attempt at writing, thinking, doing, saying, etc., since we all start rather poorly in the beginning. Therefore, I advocate more mediocrity as a means to success. Whatever you want, need, or have to do, start doing it! (Apologies to Nike, but this was written long before they stole the concept....) Do it poorly at first with pleasure, take a look or listen to what you’ve done, and then do it again. If you can turn out four good, honest, poor quality examples, the fifth time you should have enough information and experience to turn out something others will admire. And if you do the first four tries in private, only you need to know how you got there. 2. Waste Time! Don’t spend it all doing things. Give yourself time and permission to daydream, mull over, muse about your task or goal without leaping into unending action. “But what,” you say, “if I find myself musing more about the grocery shopping than the gross receipts?” Fine, just see what relationships you can come up with between groceries and gross receipts. (How about increasing the volume and lowering mark-ups? Or providing comfortable seating in the local superstore so that people can relax while shopping and thus have more energy with which to spend their money??) Whatever you do, just pay attention to what comes and get it down in writing somewhere somehow before it goes again. No need to waste ideas.... 3. Be Messy! (Not hard for some of us.) Don’t go for clarity before confusion has had time to teach you something new. In fact, I advocate starting with a large sheet of blank paper–anything up to 2 feet by 4 feet in size–and then filling it up as quickly and randomly as possible with everything that is, might be, or ought to be related to the task at hand. Then start drawing arrows, underlining, scratching through, highlighting, etc., to make a real mess that no one but you can decipher. (If you can’t figure it out either, that’s O.K., too–it doesn’t have to make sense in the beginning.) Then go back to Principle #1 and start doing something. 4. Make Mistakes! Search out your stumbling blocks. Celebrate your errors. Rejoice in your “wrongs” for in them lie riches. Consider your faux pas as feedback not failure and you’ll learn (and possibly even earn!) a lot more. Be like a research scientist and get something publishable out of whatever the data indicates. As one creative consultant, Sidney X. Shore, suggests, always ask, “What’s Good About It?” Some of our most precious inventions have resulted from clumsy hands and creative insight. 5. Forget Everything You Have Learned! (Except, perhaps, these principles!) Give yourself a chance to be a neophyte, return to innocence, start with “beginner’s mind”. In the Zen tradition of Japan, there is a saying in support of this approach because in the beginner’s mind all things are possible, in the expert’s mind only one or two. What would a five-year-old do with your task, goal, project, or problem? Take a risk and be naive again. Many major advances in math and science have come from young, wet-behind-the-ears upstarts who don’t know enough to get stuck like everyone else. Even Picasso worked hard at forgetting how to draw.... But I must stop! There was more to this unusual manuscript, but it would be a poor idea to prolong this further. As a responsible author, I don’t want to waste any more of your time on such ramblings. You know as well as I that such ideas would quickly make a mess of things. I am sure that the original author, whoever that was, has by now repudiated these mistaken notions which could be quite dangerous in the hands of untrained beginners. I even recall a reference to these principles being advocated for groups and teams as well as for individual practice—if you can imagine such a thing! It is a pity that the author or authors did not have more to offer, however, “In Search of Creativity” could have made a catchy title for a book....
Problem Solving with Creative Thinking
Creative problem-solving is a type of problem-solving that involves searching for new and novel solutions to problems. It’s a way to think “outside of the box.” Unlike critical thinking, which scrutinizes assumptions and uses reasoning, creative thinking is about generating alternative ideas— practices and solutions that are unique and effective. It’s about facing sometimes muddy and unclear problems and seeing how things can be done differently.
Complete ACTIVITY 2: ASSESS YOUR CREATIVE-PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS at the end of the chapter to see what skills you currently have and which new ones you can develop further.
As you continue to develop your creative thinking skills, be alert to perceptions about creative thinking that could slow down progress. Remember that creative thinking and problem-solving are ways to transcend the limitations of a problem and see past barriers.
Critical and creative thinking complement each other when it comes to problem-solving. The process of alternatively focusing and expanding your thinking can generate more creative, innovative, and effective outcomes. The following words, by Dr. Andrew Robert Baker, are excerpted from his “Thinking Critically and Creatively ” essay. Dr. Baker illuminates some of the many ways that college students will be exposed to critical and creative thinking and how it can enrich their learning experiences.
THINKING CRITICALLY AND CREATIVELY Critical thinking skills are perhaps the most fundamental skills involved in making judgments and solving problems. You use them every day, and you can continue improving them. The ability to think critically about a matter—to analyze a question, situation, or problem down to its most basic parts—is what helps us evaluate the accuracy and truthfulness of statements, claims, and information we read and hear. It is the sharp knife that, when honed, separates fact from fiction, honesty from lies, and the accurate from the misleading. We all use this skill to one degree or another almost every day. For example, we use critical thinking every day as we consider the latest consumer products and why one particular product is the best among its peers. Is it a quality product because a celebrity endorses it? Because a lot of other people may have used it? Because it is made by one company versus another? Or perhaps because it is made in one country or another? These are questions representative of critical thinking. The academic setting demands more of us in terms of critical thinking than everyday life. It demands that we evaluate information and analyze myriad issues. It is the environment where our critical thinking skills can be the difference between success and failure. In this environment we must consider information in an analytical, critical manner. We must ask questions—What is the source of this information? Is this source an expert one and what makes it so? Are there multiple perspectives to consider on an issue? Do multiple sources agree or disagree on an issue? Does quality research substantiate information or opinion? Do I have any personal biases that may affect my consideration of this information? It is only through purposeful, frequent, intentional questioning such as this that we can sharpen our critical thinking skills and improve as students, learners and researchers. While critical thinking analyzes information and roots out the true nature and facets of problems, it is creative thinking that drives progress forward when it comes to solving these problems. Exceptional creative thinkers are people that invent new solutions to existing problems that do not rely on past or current solutions. They are the ones who invent solution C when everyone else is still arguing between A and B. Creative thinking skills involve using strategies to clear the mind so that our thoughts and ideas can transcend the current limitations of a problem and allow us to see beyond barriers that prevent new solutions from being found. Brainstorming is the simplest example of intentional creative thinking that most people have tried at least once. With the quick generation of many ideas at once, we can block-out our brain’s natural tendency to limit our solution-generating abilities so we can access and combine many possible solutions/thoughts and invent new ones. It is sort of like sprinting through a race’s finish line only to find there is new track on the other side and we can keep going, if we choose. As with critical thinking, higher education both demands creative thinking from us and is the perfect place to practice and develop the skill. Everything from word problems in a math class, to opinion or persuasive speeches and papers, call upon our creative thinking skills to generate new solutions and perspectives in response to our professor’s demands. Creative thinking skills ask questions such as—What if? Why not? What else is out there? Can I combine perspectives/solutions? What is something no one else has brought-up? What is being forgotten/ignored? What about ______? It is the opening of doors and options that follows problem-identification. Consider an assignment that required you to compare two different authors on the topic of education and select and defend one as better. Now add to this scenario that your professor clearly prefers one author over the other. While critical thinking can get you as far as identifying the similarities and differences between these authors and evaluating their merits, it is creative thinking that you must use if you wish to challenge your professor’s opinion and invent new perspectives on the authors that have not previously been considered. So, what can we do to develop our critical and creative thinking skills? Although many students may dislike it, group work is an excellent way to develop our thinking skills. Many times I have heard from students their disdain for working in groups based on scheduling, varied levels of commitment to the group or project, and personality conflicts too, of course. True—it’s not always easy, but that is why it is so effective. When we work collaboratively on a project or problem we bring many brains to bear on a subject. These different brains will naturally develop varied ways of solving or explaining problems and examining information. To the observant individual we see that this places us in a constant state of back and forth critical/creative thinking modes. For example, in group work we are simultaneously analyzing information and generating solutions on our own, while challenging other’s analyses/ideas and responding to challenges to our own analyses/ideas. This is part of why students tend to avoid group work—it challenges us as thinkers and forces us to analyze others while defending ourselves, which is not something we are used to or comfortable with as most of our educational experiences involve solo work. Your professors know this—that’s why we assign it—to help you grow as students, learners, and thinkers! —Dr. Andrew Robert Baker, Foundations of Academic Success: Words of Wisdom
Problem-Solving Action Checklist
Problem-solving can be an efficient and rewarding process, especially if you are organized and mindful of critical steps and strategies. Remember to assume the attributes of a good critical thinker: if you are curious, reflective, knowledge-seeking, open to change, probing, organized, and ethical, your challenge or problem will be less of a hurdle, and you’ll be in a good position to find intelligent solutions. The steps outlined in this checklist will help you adhere to these qualities in your approach to any problem:
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Critical thinking is logical and reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do.
- Critical thinking involves questioning and evaluating information.
- Evaluating information is a complex, but essential, process. You can use the CRAAP test to help determine if sources and information are reliable.
- Creative thinking is both a natural aspect of childhood and a re-learnable skill as an adult.
- Creative thinking is as essential a skill as critical thinking and integrating them can contribute to innovative and rewarding experiences in life.
- Critical and creative thinking both contribute to our ability to solve problems in a variety of contexts.
- You can take specific actions to develop and strengthen your critical and creative thinking skills.
ACTIVITY 1: REFLECT ON CRITICAL THINKING
- Apply critical thinking strategies to your life
Directions:
- Think about someone you consider to be a critical thinker (friend, professor, historical figure, etc). What qualities does he/she have?
- Review some of the critical thinking strategies discussed on this page. Pick one strategy that makes sense to you. How can you apply this critical thinking technique to your academic work?
- Habits of mind are attitudes and beliefs that influence how you approach the world (i.e., inquiring attitude, open mind, respect for truth, etc). What is one habit of mind you would like to actively develop over the next year? How will you develop a daily practice to cultivate this habit?
- Write your responses in journal form, and submit according to your instructor’s guidelines.

ACTIVITY 2: ASSESS YOUR CREATIVE PROBLEM-SOLVING SKILLS
- Access Psychology Today ’s Creative Problem-Solving Test at the Psychology Today Web site.
- Read the introductory text, which explains how creativity is linked to fundamental qualities of thinking, such as flexibility and tolerance of ambiguity.
- Then advance to the questions by clicking on the “Take The Test” button. The test has 20 questions and will take roughly 10 minutes.
- After finishing the test, you will receive a Snapshot Report with an introduction, a graph, and a personalized interpretation for one of your test scores.
Complete any further steps by following your instructor’s directions.
LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS
CC LICENSED CONTENT, ORIGINAL
- Critical and Creative Thinking Authored by : Laura Lucas, Tobin Quereau, and Heather Syrett. Provided by : Austin Community College. License : CC BY-NC-SA-4.0
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SPECIFIC ATTRIBUTION
- Chapter cover image. Authored by : Hans-Peter Gauster. Provided by : Unsplash. Located at : https://unsplash.com/photos/3y1zF4hIPCg . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- Creative Thinking Skills in College Success. Authored by : Linda Bruce. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/collegesuccess-lumen/chapter/creative-thinking-skills/ . License : CC BY 4.0
- Critical Thinking in Educational Psychology. Authored by : Kelvin Seifert and Rosemary Sutton. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/educationalpsychology/chapter/critical-thinking/ . License : CC BY 4.0
- Critical Thinking Skills in College Success. Authored by : Linda Bruce. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/collegesuccess-lumen/chapter/critical-thinking-skills/ . License : CC BY 4.0
- Critical Thinking 101: Spectrum of Authority. Provided by: UCB Learn. Located at : https://youtu.be/9G5xooMN2_c . License : CC BY 4.0
- Evaluate: Assessing Your Research Process and Findings in Information Literacy. Authored by : Bernnard, Bobish, Hecker, Holden, Hosier, Jacobsen, Loney, Bullis. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/informationliteracy/chapter/evaluate-assessing-your-research-process-and-findings/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA-4.0
- Image. Authored by : Mari Helin-Tuominen. Provided by : Unsplash. Located at : https://unsplash.com/photos/ilSnKT1IMxE . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED CONTENT
Where Good Ideas Come From. Authored by : Steven Johnson. Provided by: Riverhead Books. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NugRZGDbPFU . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
How to Stimulate the Creative Process. Provided by : Howcast. Located at : https://youtu.be/kPC8e-Jk5uw . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
Version History
Creativity and Critical Thinking
- First Online: 31 January 2022
Cite this chapter

- Peter Ellerton 6 &
- Robert Kelly 7
1101 Accesses
1 Citations
The twenty-first century has seen a rapid growth of curriculum initiatives that consider the development of cross-curriculum competencies as a core issue, and significant for every discipline area. Both because of such cross-curriculum developments and because of the nature of STEM itself, the integration of the particular core competencies of ‘creativity’ and ‘critical thinking’ across the STEM disciplines has also grown rapidly in educational importance. Creativity and critical thinking in education are best viewed from the perspectives of both learner development and teacher expertise, with the attributes specific to each concept appropriately seen as increasing in sophistication or complexity over time. A broad examination of each of the two concepts and their interrelatedness, and the consequent implications for educational practice concerned with developing them, creates a lens through which to view the application of creativity and critical thinking across the complexity and diversity of the STEM disciplines and their integrated forms.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Altan, S., Lane, J. F., & Dottin, E. (2017). Using habits of mind, intelligent behaviors, and educational theories to create a conceptual framework for developing effective teaching dispositions. Journal of Teacher Education, 70 (2), 169–183. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022487117736024 .
Article Google Scholar
Amabile, T. (2012). The componential theory of creativity . Boston: Harvard Business School.
Google Scholar
Amabile, T., & Pratt, M. (2017). The dynamic componential model of creativity and innovation in organizations: Making progress, making meaning. Research in Organizational Behavior, 37 , 157–183.
Annas, J. (1995). Virtue as a skill. International Journal of Philosophical Studies, 3 (2), 227–243. https://doi.org/10.1080/09672559508570812 .
Bailin, S., & Battersby, M. (2016). Fostering the virtues of inquiry. An International Review of Philosophy, 35 (2), 367–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11245-015-9307-6 .
Bowers, S. (2019). Irish teenager wins Google science award for microplastics project . Retrieved from https://www.irishtimes.com/news/science/irish-teenager-wins-google-science-award-for-microplastics-project-1.3971256
Dewey, J. (1938). Logic: The theory of inquiry . New York.
Dottin, E. (2009). Professional judgment and dispositions in teacher education. Teaching and Teacher Education, 25 , 83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2008.06.005
Ellerton, P. (2015). Metacognition and critical thinking: Some pedagogical imperatives. In M. Davies & R. Barnett (Eds.), The Palgrave handbook of critical thinking in higher education (pp. 409–426). https://doi.org/10.1057/9781137378057_25 .
Facione, P. A. (1990). Critical thinking: A statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. Research findings and recommendations . Retrieved from http://www.eric.ed.gov/ERICWebPortal/detail?accno=ED315423
Gloor, P. (2017). Swarm leadership and the collective mind . Bingley, UK: Emerald.
Book Google Scholar
Gotz, I. (1981). On defining creativity. Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism, 39 , 297–301.
Guilford, J. (1959). Traits of creativity. In H. Anderson (Ed.), Creativity and its cultivation (pp. 142–161). New York: Harper.
IDEO . (2012). Design thinking toolkit for educators (2nd ed.). Retrieved from https://designthinkingforeducators.com
Kallick, B., & Costa, A. L. (2008). Learning and leading with habits of mind: 16 essential characteristics for success. Association for Supervision & Curriculum Development . http://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/uql/detail.action?docID=410671
Kelly, R. (2012). Educating for creativity: A global conversation . Edmonton: Brush Education.
Kelly, R. (2016). Creative development: Transforming education through design thinking, innovation and invention . Edmonton: Brush Education.
Kelly, R. (2020). Collaborative creativity: Educating for creative development, innovation and entrepreneurship . Edmonton: Brush Education.
Lipman, M. (2003). Thinking in education (2nd ed.). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University.
Lubart, T. I. (2000). Models of creative process: Past, present and future. Creativity Research Journal, 13 (3–4), 295–308.
Mead, G. H. (1910). The psychology of social consciousness implied in instruction. Science, 31 (801), 688–693.
Mulnix, J. W. (2010). Thinking critically about critical thinking. Educational Philosophy and Theory, 44 (5), 464–479. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-5812.2010.00673.x .
OECD. (2018a). Teaching, assessing and learning creative and critical thinking skills in education . Retrieved from http://www.oecd.org/education/ceri/assessingprogressionincreativeandcriticalthinkingskillsineducation.htm
OECD. (2018b). Fostering and assessing students’ critical and creative thinking skills in higher education . Retrieved from https://www.oecd.org/education/ceri/Fostering-and-assessing-students-creative-and-critical-thinking-skills-in-higher-education.pdf
Osborn, A. (1963). Applied imagination . New York: Charles Schribner.
Partnership for 21st Century Learning (P21). (2018). Retrieved from http://www.p21.org/members-states/partner-states
Paul, R., & Elder, L. (2008). The miniature guide to critical thinking: Concepts and tools / by Richard Paul and Linda Elder (5th ed.). Dillon Beach, CA: Foundation for Critical Thinking.
Piirto, J. (2004). Understanding creativity . Scottsdale: Great Potential.
Plucker, J., Beghetto, R., & Dow, G. (2004). Why isn’t creativity more important to educational psychologists? Potentials, pitfalls, and future directions in creativity research. Educational Psychologist, 39 , 83–96.
Sawyer, R. K. (2012). Explaining creativity: The science of innovation . New York: Oxford University.
Scriven, M., & Paul, R. (2011, November 23). Defining critical thinking . Retrieved from http://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/defining-critical-thinking/766
United Nations. (2019). United Nations sustainable development goals . Retrieved from https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/
Siegel, H. (1989). Epistemology, critical thinking, and critical thinking pedagogy. Argumentation, 3 (2), 127–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00128144 .
Siegel, H. (2017). Education’s epistemology: Rationality, diversity, and critical thinking . https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780190682675.003.0007 .
Sperber, D., & Mercier, H. (2012). Reason as a social competence. In H. Landemore & J. Elster (Eds.), Collective wisdom—Principles and mechanisms (pp. 368–392). New York: Cambridge University.
Chapter Google Scholar
The Association of American Colleges and Universities. (2013). It takes more than a major: Employer priorities for college learning and student success . Retrieved from https://www.aacu.org/sites/default/files/files/LEAP/2013_EmployerSurvey.pdf
Topping, K. J., & Trickey, S. (2007). Impact of philosophical enquiry on school students’ interactive behaviour. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 2 (2), 73–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2007.03.001 .
Van Gelder, T., Bissett, M., & Cumming, G. (2004). Cultivating expertise in informal reasoning. Canadian Journal of Experimental Psychology/Revue Canadienne de Psychologie Expérimentale, 58 (2), 142–152. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0085794 .
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes . Cambridge\London: Harvard University.
Waks, L. J. (2014). Education 2.0: The learning web revolution and the transformation of the school . Boulder: Paradigm.
Wallas, G. (1926). The art of thought . New York: Harcourt Brace.
Willingham, D. T. (2008). Critical thinking: Why is it so hard to teach? Arts Education Policy Review, 109 , 21–32. https://doi.org/10.3200/AEPR.109.4.21-32 .
Willingham, D.T. (2019). How to teach critical thinking . Retrieved from https://education.nsw.gov.au/media/exar/How-to-teach-critical-thinking-Willingham.pdf
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, University of Queensland, Brisbane, QLD, Australia
Peter Ellerton
Faculty of Arts, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada
Robert Kelly
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Robert Kelly .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Monash University, Clayton, VIC, Australia
Amanda Berry
University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand
Cathy Buntting
Deborah Corrigan
Richard Gunstone
Alister Jones
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Ellerton, P., Kelly, R. (2021). Creativity and Critical Thinking. In: Berry, A., Buntting, C., Corrigan, D., Gunstone, R., Jones, A. (eds) Education in the 21st Century. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85300-6_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85300-6_2
Published : 31 January 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-85299-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-85300-6
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
Critical thinking vs Creative thinking

Both critical thinking and creative thinking are used for solving problems , only in different ways. For critical thinking, the process is structured and methodical. For creative thinking, the process is fluid and somewhat experimental. Both thinking strategies are useful, with neither being innately superior to the other and in some unexpected ways even being linked. Now without further ado, let us explore the various components of critical thinking and creative thinking.
The Intersection of Critical Thinking & Creative Thinking
Critical thinking:
Critical thinking as we understand it can be traced all the way back to Ancient Greece in the thoughts of Socrates as recorded by Plato. Critical thinking can be summarized as the careful analysis of facts in order to form judgments. With critical, being derived from the word critic, to think critically is to critique the process of thinking itself. In layman’s terms, this means to develop an efficient and ordered system of both written and oral discourse. There are different subsets of critical thinking, which broadly speaking are; unbiased, skeptical, and rational. Let’s break down these different sections individually.
The unbiased system attempts to remove all possible biases from thinking. Everybody has some form of bias or another. Perhaps a personal bias that one has towards someone or something. Or be it a more ethnocentric bias that prevents an individual from being able to see past the beliefs instilled in them by their culture. The unbiased analysis aims to view things from an objective instead of a subjective stand-point.
The skeptical system is one that encourages both doubt and constant questioning. That includes careful examination of both longstanding beliefs and dogmas. As far as skeptics are concerned nothing is beyond the realms of inquisition. If evidence is not available to support beliefs, then they should not be accepted.
The rationality system is based on obtaining rationality, which can be defined as one being agreeable to reason. What is reason? In philosophical terms, reason is the ability to make sense of the world around us through the application of logic. Logic is a key tenet of the three systems and the cornerstone of critical thinking.
Logic is the systematic study of premises and the arguments that they form and is judged based on their validity (whether the statements make sense and lead to the conclusion) and their truth value (whether or not statements are true or false). There are three primary types of logical reasoning; deductive, inductive, and abductive. Deductive reasoning leads to certain conclusions, inductive reasoning leads to probable conclusions, and abductive reasoning is a quick and practical approach to logic.
When examining deductive arguments, we begin by not looking at the truth value of the premises, but if they lead to the conclusion in a coherent manner. If they do not then the argument is deemed invalid and unsound. If the argument is deemed valid we then examine the truth value of the premises. If true, then the argument is sound, if they are not true then the argument is still valid but unsound.
For inductive arguments, a very similar approach is taken to deductive arguments. First, we begin by examining the validity of the premises. If they are invalid the argument is weak and by extension uncogent. If the premises are valid, the argument is strong and we then examine their truth value. If false then the argument while strong is uncogent, if true however the argument is both strong and cogent.
Abductive arguments are drawn from the heuristic technique. The heuristic technique entails non-optimal problem-solving solutions, but are none the less sufficient for immediate decisions and approximations. Abductive reasoning includes such tactics as making an educated guess, following the general rule of thumb, or simple trial and error.
Creative thinking:
Creativity itself is the process where something truly new, but also valuable is formed. Be it a new idea, invention, or piece of art. Unlike logical thinking, there is no stringent set of rules or guidelines for how to undergo creative thinking. The process itself isn’t even entirely understood and there is much speculation and theorizing as to how creative thinking works, with no theory currently set in stone. This makes it a little more challenging to explain how to become a creative thinker. In attempting to do so we will go over some general principles of creative thinking and theories that may explain it.
One of the most obvious traits of creative thinkers is that they are open-minded individuals. Basically, they are willing to at least consider new ideas that other people would either never have thought of or would outright refuse due to a close-minded nature. Being open-minded doesn’t mean automatically accepting every new idea that comes your way. It just means having the willingness to unbiasedly look at things from a new perspective.
In a sense being open-minded can be viewed as somewhat pragmatic as it allows people to examine, chose, and combine different aspects of various ideas to make something both new and useful. Creative thinking also enhances communications as through being open to new experiences a person is better able to talk and work with those with different beliefs than oneself.
Creative thinking has been hypothesized by some scientists as being a part of the evolutionary process. Some scientists think that by thinking of things in abstract terms we were better able to come up with new and innovative solutions in changing environments. Various scientists and academics have attempted to map out the process of creative thinking, one popular theory being largely developed by the psychologist J.P Guilford. Guilford helped develop the theory of divergent thinking.
Divergent thinking is the process some think is responsible for producing creativity and this is done by examining many possible solutions. Divergent thinking is more spontaneous and doesn’t occur in a linear manner. With divergent thinking a great many possible activities are explored over a short period of time, often with unexpected yet original connections being made. Common activities to help engage in divergent thinking are to create a list of questions, taking the time to think and meditate on ideas, artistic endeavors such as writing and drawing are also encouraged.
You may also like

Masterclass vs Skillshare: An In-Depth Comparison for Lifelong Learners
In the burgeoning market of online learning, MasterClass and SkillShare have emerged as two leading platforms, each offering a distinct approach to […]

What Is Drone Mentality?
Drone mentality is a pattern of going through the motions, paying little to no attention to what’s going on around you. Think […]

Thinking Vs. Critical Thinking: What’s the Difference?
Thinking and critical thinking do not sound that different in nature. After all, they both include the verb thinking, and therefore, imply […]

How to Demonstrate Critical Thinking
We live in the Information age—barraged by news and other content, and surrounded by information sources such as online archives, ebooks, webinars, […]

Key Difference
Know the Differences & Comparisons

Difference Between Creative Thinking and Critical Thinking
Table of Contents
Introduction
As our world becomes more complex and quickly changing, the ability to think both critically and creatively is increasingly prized.
Both creative thinking and critical thinking play crucial roles in problem-solving, decision making, and innovation – though they should be understood separately with different approaches from each one bringing something unique to the table.
Creative thinking encompasses brainstorming novel ideas, exploring possibilities and thinking out of the box. It fosters imagination and intuition while building connections between seemingly disparate concepts.
On the other hand, critical thinking involves evaluating information, challenging assumptions and applying logical reasoning in assessing validity of arguments or evidence presented against one.
Understanding the differences between creative thinking and critical thinking is vital for unlocking their full cognitive potential.
By investigating their respective characteristics, processes, and outcomes we can gain a more in-depth knowledge of both types of thinking as well as their roles and how they complement one another.
This content outline seeks to clearly differentiate creative thinking and critical thinking by outlining their unique features, approaches, and applications.
By understanding their differences as well as examining how they may work together in various situations, we can foster more holistic thinking skill sets while improving problem-solving capabilities in various contexts.
Definition of creative thinking
Creative thinking refers to the cognitive process of coming up with novel and original ideas or solutions by exploring various perspectives, making connections between seemingly disparate elements, and thinking beyond conventional boundaries.
Divergent thinking plays a central role in creative thinking by providing multiple possibilities and exploring various approaches; creative thinking often relies on imagination, intuition, and risk-taking; it involves divergent thinking as well.
Creative thinking relies on flexible mindsets openness to new experiences as well as transcendence from established norms and patterns in its pursuit.
Creativity plays an essential part in problem-solving, innovation as well as the creation of artistic, scientific, technological breakthroughs.

Definition of critical thinking
Critical thinking refers to the mental process of analyzing, evaluating, and interpreting information or situations logically and objectively.
Skillful reasoning involves being able to assess evidence objectively, identify logical fallacies, and apply reasoning skills in order to form rational judgements or conclusions.
Critical thinking involves critically analyzing assumptions, biases and arguments to ascertain the validity and reliability of information.
Critical thinking emphasizes evidence-based reasoning, logical consistency and being able to recognize and evaluate different perspectives or arguments in order to effectively solve problems, make informed decisions and form informed opinions across various domains – be they academic institutions, professional settings or daily life.

Comparison Table of Creative Thinking and Critical Thinking
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between creative thinking and critical thinking:
While creative thinking and critical thinking have distinct focuses and approaches, they are not mutually exclusive. In fact, they can complement and enhance each other.
By integrating creative thinking into critical thinking processes, new and innovative solutions can be explored, and by applying critical thinking to creative ideas, their feasibility and effectiveness can be evaluated.
Understanding the differences and connections between creative thinking and critical thinking provides individuals with a broader thinking toolkit, enabling them to approach problems and challenges from multiple angles and make more informed decisions.
Creative thinking focuses on generating new ideas and possibilities
Creative thinking primarily centers on developing novel ideas and possibilities. To do this effectively, creative thinkers often break away from conventional patterns of thought by opening themselves up to different perspectives and engaging in divergent thinking, which involves coming up with multiple ideas or solutions for any given situation.
Divergent thinking allows creative thinkers to expand the range of possible options available while considering unconventional or innovative approaches.
Creative thinking involves the willingness to explore unfamiliar territories, question assumptions and push the limits of what is considered possible.
This type of thinking encourages imagination, brainstorming and free association of ideas in order to generate fresh insights and unique solutions – the goal being originality, novelty and creativity in problem-solving decisions as well as art, literature, design or innovation projects.
Creative thinking unleashes new possibilities by sparking creative thought processes that produce fresh concepts.
Creative thinking paves the way for exploration and innovation, helping individuals to find unconventional solutions, uncover groundbreaking discoveries, and produce lasting impacts.
Critical thinking focuses on analyzing and evaluating information
Critical thinking involves the analysis and evaluation of information. This involves thoroughly scrutinizing evidence, arguments or situations to ascertain their validity, reliability and logical coherence before reaching informed judgments or decisions based on objective reasoning. Critical thinkers strive to use objective and rational analyses in making well-informed judgements or decisions.
Critical thinking requires individuals to engage in an active process of questioning assumptions, identifying biases, assessing arguments or evidence critically and attempting to comprehend its underlying reasoning – whether logical, supported by evidence, or susceptible to fallacies.
Critical thinking involves applying logic, evidence evaluation and systematic analysis in an organized fashion to make informed decisions, avoid misinformation or manipulation and gain a more nuanced understanding of complex issues.
Critically evaluating information allows individuals to make more informed decisions by recognizing patterns, drawing inferences and recognizing logical inconsistencies – this skill involves skills such as data analysis, pattern recognition and inferencing; critically analyzing it provides opportunities for more informed decisions that avoid misinform or manipulation and increases understanding more nuanced understanding of complex issues by critically analyzing it!
Critical thinking has many applications in academia, professional settings and everyday life. It allows individuals to evaluate the credibility of sources, identify flaws in arguments and navigate complex or ambiguous situations with an analytical mindset.
Complementary Relationship Between Creative and Critical Thinking
Creativity and critical thinking do not contradict each other; in fact, they form a complementary relationship that can enhance problem-solving and decision-making processes. Creative thinking generates new ideas while critical thinking provides an analytical framework to evaluate and refine those concepts. Here are some ways creative and critical thinking can work together:
Idea Generation and Evaluation: Creative thinking fosters an array of concepts, while critical thinking enables evaluation and selection of those most likely to bear fruit. Critical thinking allows objective evaluation, identification of any flaws or potential defects, consideration of practicality and feasibility and ultimately determines success or failure of projects.
Problem Identification and Analysis: Creative thinking allows us to quickly recognize problems or challenges by approaching them from different angles and considering multiple viewpoints, while critical thinking allows for an in-depth examination of its underlying causes and possible solutions.
Innovative Solutions and Refinement: Creative thinking fosters original and novel solutions, while critical analysis assesses them on viability, potential shortcomings and practical constraints to make sure they align.
Decision-Making: Creative thinking can provide a variety of options; critical thinking helps evaluate their advantages and disadvantages. Critical thinking allows a systematic consideration of evidence, logic reasoning, potential consequences and other forms of evidence resulting in more informed and effective decision-making processes.
Adaptation and Improvement: Creative thinking allows for flexibility and adaptation in response to changing circumstances or feedback, while critical thinking helps identify areas for improvement, recognize potential pitfalls, and refine ideas or strategies based on evidence or feedback.
Individuals can achieve more comprehensive and effective problem-solving, innovation, and decision making by integrating creative and critical thinking. This combination encourages exploration while still remaining analytical; ultimately producing more robust outcomes.
Importance of integrating both types of thinking
Integrating both creative and critical thinking skills is of critical importance for various reasons:
Holistic Problem-Solving: By integrating creative and critical thinking, individuals can approach problems from various angles. Creative thinking generates fresh concepts, while critical analysis provides tools to evaluate and refine these new ideas. By taking this holistic approach to problem-solving, individuals increase the odds of finding effective and well-rounded solutions.
Critical Thinking Improves Decision-Making: Critical thinking allows individuals to assess the feasibility, reliability and coherence of ideas generated through creative thinking, thus aiding individuals in making more informed and evidence-based decisions while considering both imaginative possibilities as well as real world realities.
Adaptability and Innovation: Creative thinking promotes flexibility, adaptability and thinking beyond established norms; critical thinking adds structure for evaluating creative ideas against viability and effectiveness criteria. Combining both types of thinking enables innovative forward-looking approaches while remaining grounded by rationality and evidence.
Overcoming Challenges: Meeting obstacles and complex problems requires both creative and critical thinking skills, with creative thought producing innovative perspectives and solutions while critical analysis evaluates each option’s merits and drawbacks. Combining both types of thinking allows individuals to tackle problems more effectively while developing comprehensive strategies.
Transdisciplinary Thinking: Many complex real-world problems and projects necessitate multidisciplinary or transdisciplinary approaches, where creative and critical thinking come together seamlessly to bring diverse fields, perspectives and methodologies together into a synthesis that fosters holistic understanding while also producing innovative and well-informed solutions. By merging creative and critical thinking approaches in such environments individuals are better able to draw from multiple fields, perspectives and methodologies in order to solve them successfully.
Lifelong Learning: Integrating creative and critical thinking fosters an attitude of curiosity, open-mindedness and continuous learning. Both forms of thinking involve actively engaging with information while questioning assumptions and exploring possibilities – these combined abilities equip individuals with valuable tools for lifelong education in an ever-evolving world.
By integrating creative and critical thinking, individuals can leverage both approaches for enhanced problem-solving, decision making, and creative endeavors.
Examples of how creative and critical thinking can work together
Absolutely! Below are a few examples of how creative and critical thinking work hand-in-hand:
Product Design: Creativity can lead to groundbreaking ideas for product designs, while critical analysis identifies any feasible, market demand or manufacturing challenges associated with each idea. By employing both aspects of thinking together, designers can produce products which fulfill both functional and creative criteria.
Scientific Research: Creative and critical thinking both play important roles in scientific inquiry. Creative thought can generate hypotheses and explore novel avenues of inquiry while critical thought ensures the research design is rigorous and data analysis valid. Integrating both types of thinking allows scientists to make groundbreaking discoveries while maintaining scientific integrity of their work.
Marketing Campaigns: Creative thinking provides imaginative and eye-catching marketing concepts, while critical analysis evaluates target audiences, market trends and potential effects of each concept. By combining creative with critical thinking, marketers can develop campaigns that not only catch attention but also resonate with target audiences to deliver desired outcomes.
Problem Solving in Business: Creative and critical thinking work together to generate many potential solutions to business issues, while creative thinkers generate numerous creative potential solutions while critical thinkers evaluate risks, costs and impacts of each solution.
By employing both types of thinking together, business professionals can come up with novel yet cost-effective strategies aligned with organizational goals.
Literary Analysis: Creative thinking allows for imaginative interpretations and exploration of themes and symbols within literature, while critical thinking assesses textual evidence, evaluates coherence of arguments, and considers author intent. When used together, literary scholars can produce sophisticated analyses of literary works that integrate creative and critical thought effectively.
Entrepreneurship: Creative thinking helps entrepreneurs identify new business opportunities and innovative business models, while critical analysis examines market potential, competitive landscape analysis and financial viability for each idea. By employing both forms of thinking to formulate successful ventures they can create sustainable and long-term ventures.
In these instances, the integration of creative and critical thinking leads to more robust and effective results. It allows innovative ideas to be evaluated, refined, and implemented logically and thoughtfully; ultimately resulting in solutions that are both innovative and pragmatic.
Creative and critical thinking are Complementary approaches to Problem-solving, decision-making and Innovation.
Creative thinking entails Brainstorming for new ideas while Exploring Possibilities; critical thinking uses objective evaluation of information to evaluate it logically and critically.
Integrating both types of thinking allows individuals to maximize both approaches and produce more comprehensive and effective results.
Creative thinking encourages innovation, broadens perspectives and fosters out-of-the-box thinking; critical thinking provides evidence-based analysis which verifies those ideas.
Integrating Creative and critical Thinking skills is crucial for both Personal and Professional growth, Adaptability, Informed decision-making, and the establishment of an environment of continuous learning and innovation.
Together these forms of thinking help individuals meet challenges with resilience, flexibility and balance that leads to improved problem-solving abilities, innovation and eventual success.
As part of your journey, embrace both creative thinking and critical thinking equally to unlock your full potential, broaden your horizons and lead you towards greater achievements in every area of life.
Recap of the key differences between creative thinking and critical thinking
Here’s an overview of the differences between creative thinking and critical thinking:
Creative Thinking: Engaging in creative thinking involves brainstorming new ideas, possibilities and solutions; emphasizing exploration, intuition and imagination; employing divergent thinking techniques in order to generate multiple solutions simultaneously; leading to innovative and original concepts.
Critical Thinking is used across artistic, scientific, and technological endeavors and emphasizes analysis, logic, and objectivity to assess information critically. Critical Thinking develops skills such as fluency, flexibility and originality of thinking that lead to positive results in any endeavor.
Eventually this leads to Critical Thinking being applied by experts in an academic environment for analysis purposes – typically this means writing essays for examination in exams! Utilizes convergent thinking to identify and select the optimal solutions, leading to informed decision-making and problem solving.
Also used for problem-solving, decision-making, and critical evaluation of information. Develops analytical, logical and evaluative skills. Though creative thinking and critical thinking may have different approaches and purposes, both types are equally essential in terms of effective problem-solving and decision making.
By integrating both types of thinking, individuals are better able to approach challenges from various angles, generate innovative ideas while critically assessing them for successful outcomes.
Importance of developing both types of thinking skills
Strengthening both creative thinking and critical thinking abilities is of great significance, for several reasons:
Comprehensive Problem Solving: Cultivating both types of thinking allows individuals to approach problems from multiple angles. Creative thinking helps generate innovative solutions while critical thinking provides analytical tools for evaluating and refining those ideas.
Combined together, this holistic approach enhances problem-solving abilities while increasing chances of finding effective and comprehensive solutions.
Adaptability and Resilience: In an ever-evolving world, being adaptable and creative are two vital skills. Creative thinking promotes flexibility, adaptability, and thinking outside established norms; critical thinking equips individuals with skills for evaluating creative ideas critically.
By cultivating both types of thinking simultaneously, individuals can more successfully navigate complex or changing situations with resilience and creativity.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Innovation and entrepreneurialism require creative thinking skills for success. Individuals who cultivate these abilities are better able to generate new ideas, identify opportunities, and think outside the box when developing products, services or solutions with innovative features or capabilities.
Meanwhile, critical thinking helps evaluate market potential and risks associated with such ideas – all essential elements for innovation and entrepreneurialism success.
Critical Thinking Skills Are Essential to Informed Decision-Making: Critical thinking skills are integral in making informed and effective decisions. Cultivating them allows individuals to evaluate evidence, consider opposing viewpoints and evaluate logical coherence of arguments; creative thinking adds variety and imagination that enables informed decisions with both practical and innovative potential in mind.
Personal and Professional Growth: Fostering creative and critical thinking abilities is central to personal and professional growth. Creative thinking develops imagination, open-mindedness and the capacity for forward-thinking; while critical thinking expands analytical, logical and evaluative capabilities.
Both skills can be utilized across various domains as transferrable assets that aid problem-solving, innovative thinking and lifelong learning.
As previously discussed, developing both creative thinking and critical thinking abilities is fundamental for effective problem-solving, adaptability, innovation, informed decision-making and personal growth.
By honing both forms of thinking simultaneously, individuals can approach challenges with an adaptive and balanced mindset for greater success and satisfaction across various aspects of life.
Encouragement for readers to embrace and cultivate both thinking approaches
As readers, I urge all to embrace and develop both creative thinking and critical thinking approaches. Doing so can open up new possibilities, enhance problem-solving abilities, and lead to greater success across various areas of life.
Here’s why both approaches should be explored:
Expand Your Perspectives: Embracing both creative and critical thinking will enable you to look at problems and opportunities from different angles. Creative thinking offers fresh approaches and imaginative solutions; critical analysis provides objective evaluation. By adopting both approaches simultaneously, your perspective broadens considerably while you gain greater insight into complex issues.
Creativity Fuels Innovation and Growth: Creativity is essential to innovation, driving both personal and professional success. By challenging conventional thinking patterns and considering unique solutions for issues that arise.
Critical Thinking serves to validate those unique concepts by making sure they’re practical, viable and well-reasoned; cultivating both ways of thinking will allow you to foster innovation while propelling you toward continuous development and success.
Enhance Problem-Solving Capabilities: Integrating creative and critical thinking creates an invaluable problem-solving arsenal. Creative thinking helps generate ideas, while critical thinking evaluates and refines them using evidence and logic – this combination gives you a powerful set of tools for taking on challenges effectively and finding lasting solutions.
Navigating Change with Resilience: In an ever-evolving world, adaptability is of the utmost importance. Creative thinking teaches you the ability to accept change with open arms, adapt with the times, and seize new opportunities with flexibility and curiosity.
Critical thinking complements this by making sure decisions are grounded in evidence and sound reasoning; together these approaches help you navigate uncertainties with grace and welcome change with resilience.
Making Informed Decisions: Critical thinking helps you assess information objectively, evaluate arguments fairly and make well-informed decisions. Creative thinking opens up more options and possibilities.
By combining both approaches together, you become a more thoughtful decision-maker who considers both innovative ideas as well as practical concerns when making choices.
Never stop working towards improving both creative and critical thinking abilities; it is a journey worth embarking upon. So nurture your curiosity, practice brainstorming sessions, seek diverse viewpoints, sharpen analytical abilities, embrace discomfort when exploring new ideas or challenging assumptions, cultivating both forms of thinking can unlock full cognitive potential while positioning you for success in an ever-evolving world.
Harness the power of creative and critical thinking together and allow them to drive you toward greater creativity, innovation, and success.
Related Posts

Authentic thinking vs. critical thinking: a side-by-side comparison
Introduction.
In today’s complex and rapidly changing world, the ability to think critically and authentically is essential for effective problem-solving and decision-making. Both authentic thinking and critical thinking play vital roles in helping individuals navigate through various challenges and make well-informed choices. While these two thinking styles share certain similarities, they also possess distinct features that set them apart.
Authentic thinking is based on genuine reflection and a deep understanding of oneself and the situation at hand. It involves thinking independently and creatively, considering multiple perspectives, and seeking solutions that align with one’s values and beliefs. Authentic thinking allows individuals to approach problems and decisions with authenticity, integrity, and a strong sense of personal identity.
On the other hand, critical thinking is a disciplined and objective approach to evaluating information, arguments, and evidence. It involves analyzing, questioning, and challenging assumptions, biases, and logical inconsistencies. Critical thinkers rely on logic, evidence, and rationality to assess situations, identify problems, and develop effective solutions.
Both authentic thinking and critical thinking are vital in problem-solving and decision-making processes. They equip individuals with the skills and mindset necessary to navigate through complex issues, weigh options, and arrive at well-reasoned and informed choices. By nurturing these thinking styles, individuals can enhance their ability to address challenges, overcome obstacles, and achieve desired outcomes.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the characteristics, benefits, differences, and similarities of authentic thinking and critical thinking. We will explore how these thinking styles contribute to effective problem-solving and decision-making. Additionally, we will provide real-life examples of how these types of thinking can be applied, highlighting the outcomes and benefits of employing these approaches in various scenarios.
Understanding Authentic Thinking
Authentic thinking is a cognitive process that involves generating original ideas, perspectives, and solutions based on personal experiences, beliefs, and values. It encourages individuals to think independently and critically, challenging traditional norms and assumptions. Authentic thinking is characterized by creativity, individuality, and a focus on personal meaning and purpose.
Characteristics of Authentic Thinking
Creativity : Authentic thinking encourages individuals to think outside the box and come up with innovative ideas. It is about finding new and unique perspectives and solutions that may not conform to traditional approaches.
Individuality : Authentic thinking acknowledges the value of diverse thoughts and perspectives. It emphasizes the importance of individual beliefs and experiences in shaping one’s thinking, rather than simply conforming to societal norms or predetermined frameworks.
Critical Reflection : Authentic thinking involves a deep and critical examination of one’s own beliefs, biases, and assumptions. It requires individuals to reflect on the underlying reasons behind their thoughts and consider alternative viewpoints.
Personal Meaning and Purpose : Authentic thinking is driven by a sense of personal meaning and purpose. It involves aligning one’s thoughts and actions with one’s values and goals, allowing individuals to pursue what is important to them on a deeper level.
Examples of Situations Requiring Authentic Thinking
Workplace Innovation : In a rapidly changing business environment, authentic thinking is crucial for generating innovative ideas that can help organizations stay competitive. It allows employees to challenge traditional ways of doing things and propose creative solutions.
Personal Growth and Self-Reflection : Authentic thinking can be applied to personal development, as it encourages individuals to critically examine their beliefs, values, and goals. It allows them to explore their own passions and interests, leading to a more fulfilling and purpose-driven life.
Problem-Solving in Relationships : Authentic thinking plays a vital role in resolving conflicts and improving relationships. By considering different perspectives, empathizing with others, and challenging assumptions, individuals can find solutions that respect both their own needs and the needs of others involved.
Benefits of Authentic Thinking
Innovation : Authentic thinking fosters creativity and helps individuals come up with original and innovative ideas. It encourages experimentation and risk-taking, leading to breakthrough solutions.
Personal Growth : Authentic thinking allows individuals to explore their own beliefs, values, and goals on a deeper level. It promotes personal growth and self-awareness, contributing to a more fulfilling and meaningful life.
Improved Decision-Making : Authentic thinking enables individuals to make decisions based on their own values and instincts, rather than simply conforming to external expectations. This leads to more confident and authentic decision-making.
Enhanced Problem-Solving : Authentic thinking encourages individuals to approach problems from different angles, considering diverse perspectives. This broadens the range of potential solutions and improves the overall problem-solving process.
In conclusion, authentic thinking is a cognitive process that promotes independent and creative thinking. It emphasizes personal meaning and purpose and encourages individuals to challenge traditional norms and assumptions. By developing authentic thinking skills, individuals can enhance their decision-making and problem-solving abilities in various aspects of life.
Understanding Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a cognitive process that involves analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to form reasoned judgments and make informed decisions. It is a disciplined approach to thinking that is focused on questioning assumptions, reasoning logically, and evaluating evidence objectively.
Characteristics of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is characterized by several key attributes:
Questioning Assumptions : Critical thinkers have a natural inclination to challenge assumptions and question the validity of information or beliefs. They don’t take things at face value and seek to understand the underlying reasons and evidence.
Logical Reasoning : Critical thinkers are skilled in using logic and reason to analyze problems and arguments. They are able to identify logical fallacies, inconsistencies, and flaws in reasoning.
Evidence-Based Evaluation : Critical thinkers rely on evidence and data to evaluate claims and make informed judgments. They seek to gather relevant information and assess its credibility and relevance before drawing conclusions.
Open-Mindedness : Critical thinkers are open to considering different perspectives and alternative viewpoints. They are willing to change their beliefs and opinions if presented with compelling evidence or logical arguments.
Problem-Solving Skills : Critical thinkers excel at problem-solving by breaking complex issues into smaller, manageable parts, and systematically analyzing each component. They are creative in generating multiple solutions and considering the potential consequences of each.
Examples of Situations Where Critical Thinking is Needed
Critical thinking is essential in various aspects of life, including:
Professional Life : In the workplace, critical thinking skills are valued by employers as it helps employees make sound decisions based on evidence and logical reasoning. For example, a manager may need to critically evaluate different proposals before selecting the best one for a project.
Academic Settings : Critical thinking is necessary for students to think independently, assess information critically, and evaluate theories or arguments. It enables them to develop their own opinions and contribute intelligently to class discussions.
Everyday Life : Critical thinking is crucial in everyday situations where we need to make decisions based on limited information. For instance, deciding which health insurance policy to choose or evaluating the credibility of a news article before sharing it on social media.
Benefits of Critical Thinking
Developing critical thinking skills offers numerous advantages:
Effective Problem-Solving : Critical thinkers are more effective problem-solvers as they can break down complex problems, analyze the components, and develop innovative solutions.
Enhanced Decision-Making : Critical thinkers are better equipped to make informed decisions by evaluating alternatives, considering potential consequences, and weighing evidence objectively.
Reduced Bias : Critical thinking helps individuals recognize and challenge their own biases, allowing for more objective and fair evaluations of situations or arguments.
Improved Communication : Critical thinkers can articulate their thoughts and viewpoints more clearly and coherently. They can effectively present and defend their ideas while engaging in respectful and productive discussions.
Innovation and Creativity : Critical thinking encourages individuals to think outside the box, explore new ideas, and develop innovative solutions to problems.
In summary, critical thinking is a valuable cognitive skill that enables individuals to analyze and evaluate information critically, make informed judgments, and solve problems effectively. By developing and applying critical thinking skills, individuals can navigate complex situations and make informed decisions in various aspects of life.
Differences between Authentic Thinking and Critical Thinking
Authentic thinking.
Authentic thinking is a type of thinking that emphasizes creativity, originality, and personal connection. It involves the generation of ideas that are unique to an individual’s experiences, perspectives, and values. Authentic thinking encourages individuals to express their true selves, think outside the box, and explore new possibilities.
Distinctive Features of Authentic Thinking:
Self-Expression: Authentic thinking encourages individuals to express their thoughts, opinions, and emotions freely. It values personal experiences and individual perspectives as valuable contributions to problem-solving and decision-making.
Creativity: Authentic thinking fosters creative thinking by encouraging individuals to think innovatively and come up with new ideas and solutions. It is characterized by thinking beyond conventional boundaries and exploring unique approaches to problem-solving.
Personal Connection: Authentic thinking emphasizes the importance of personal connection to the subject matter. It encourages individuals to relate their own experiences, values, and beliefs to the problem at hand, leading to a deeper understanding and more meaningful solutions.
Individualized Approach: Authentic thinking recognizes that each individual has their own unique way of thinking and problem-solving. It values diverse perspectives and encourages individuals to bring their authentic selves to the thinking process.
Critical Thinking
Critical thinking, on the other hand, is a type of thinking that focuses on logical reasoning, analysis, and evaluation. It involves systematically examining and questioning information, arguments, and assumptions to arrive at well-informed conclusions. Critical thinking is widely considered a fundamental skill for problem-solving and decision-making.
Distinctive Features of Critical Thinking:
Rationality: Critical thinking is rooted in rationality and logic. It involves carefully analyzing and evaluating information, arguments, and evidence to assess their validity and coherence. It is driven by a commitment to objective and fair-minded thinking.
Analysis and Evaluation: Critical thinking involves breaking down complex issues into smaller components and evaluating them based on their merits. It requires individuals to think critically about the strengths and weaknesses of different perspectives and arguments before arriving at a conclusion.
Objectivity: Critical thinking requires individuals to set aside personal biases and prejudices and approach problems and decisions with an objective mindset. It emphasizes the importance of basing conclusions on evidence and logical reasoning rather than emotions or personal preferences.
Systematic Approach: Critical thinking follows a systematic process of gathering information, evaluating evidence, and drawing well-reasoned conclusions. It involves asking probing questions, considering alternative viewpoints, and weighing the pros and cons before making a decision.
While both authentic thinking and critical thinking are valuable approaches to problem-solving and decision-making, they have distinct characteristics and emphases. Authentic thinking prioritizes self-expression, creativity, and personal connection, while critical thinking focuses on rationality, analysis, and objectivity. Understanding the differences between these two thinking styles can help individuals develop a well-rounded approach to thinking and enhance their problem-solving abilities.
Similarities between Authentic Thinking and Critical Thinking
1. engagement with complex problems.
Both authentic thinking and critical thinking involve engaging with complex problems to gain a deeper understanding. In both types of thinking, individuals are encouraged to explore different perspectives, analyze multiple sources of information, and evaluate various solutions. By engaging with complex problems, individuals develop their ability to think critically and authentically.
2. Open-mindedness and Objectivity
Both authentic thinking and critical thinking require individuals to approach problems with an open mind and maintain objectivity. In authentic thinking, individuals are encouraged to suspend judgment and examine multiple viewpoints before forming their own opinions. Similarly, critical thinking encourages individuals to question assumptions, consider different perspectives, and evaluate evidence objectively. By maintaining open-mindedness and objectivity, individuals can arrive at well-informed and unbiased conclusions.
3. Analytical Thinking
Both authentic thinking and critical thinking involve analytical thinking skills. In authentic thinking, individuals analyze the authenticity and relevance of information, sources, and perspectives. Similarly, critical thinking requires individuals to analyze arguments, evaluate evidence, and identify logical inconsistencies. By developing analytical thinking skills, individuals can effectively evaluate and solve problems.
4. Reflection and Self-awareness
Both authentic thinking and critical thinking emphasize the importance of reflection and self-awareness. Authentic thinking encourages individuals to reflect on their own beliefs, values, and biases, and how they may influence their interpretations of situations. Critical thinking also involves self-reflection to identify personal biases and assumptions that may impact decision-making. By cultivating self-awareness and reflection, individuals can enhance their thinking processes and make more informed decisions.
5. Application to Real-world Situations
Both authentic thinking and critical thinking are applicable to real-world situations. They provide individuals with the skills and mindset necessary to analyze complex problems, consider alternative solutions, and make informed decisions. Both types of thinking are essential in professional contexts such as problem-solving, decision-making, and effective communication. By applying authentic and critical thinking, individuals can navigate real-world challenges with confidence and competence.
6. Continuous Learning and Growth
Both authentic thinking and critical thinking promote continuous learning and growth. They encourage individuals to seek out new information, expand their knowledge, and challenge their existing beliefs. Authentic thinking emphasizes the importance of lifelong learning for personal and professional growth. Critical thinking cultivates a curiosity for knowledge and a willingness to question assumptions. By embracing continuous learning and growth, individuals can adapt to changing circumstances and develop innovative solutions to complex problems.
In summary, while there are distinct differences between authentic thinking and critical thinking, they also share several similarities. Both types of thinking involve engaging with complex problems, maintaining open-mindedness and objectivity, employing analytical thinking, reflecting and practicing self-awareness, applying to real-world situations, and fostering continuous learning and growth. By recognizing these similarities and integrating both types of thinking, individuals can enhance their problem-solving and decision-making skills for greater success in today’s complex world.
Applying Authentic Thinking and Critical Thinking
Real-life examples of applying authentic thinking.
Authentic Thinking in the Workplace
- In a team meeting, an employee suggests taking a different approach to solve a problem by involving multiple stakeholders in the decision-making process. This authentic thinking helps to gather diverse perspectives and foster collaboration, leading to more innovative and effective solutions.
Authentic Thinking in Education
- A teacher encourages students to explore real-world issues and connect their learning to practical applications. By incorporating authentic thinking into the curriculum, students develop problem-solving skills, critical reasoning abilities, and a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Real-Life Examples of Applying Critical Thinking
Critical Thinking in Healthcare
- A nurse encounters a patient with ambiguous symptoms. Instead of making assumptions or jumping to conclusions, the nurse utilizes critical thinking by carefully assessing the patient’s condition, gathering additional information, consulting with other healthcare professionals, and considering various possible diagnoses before making an informed decision.
Critical Thinking in Business
- A manager is faced with a challenging decision regarding budget cuts in the organization. Instead of relying on instinct and personal biases, the manager applies critical thinking by analyzing financial data, considering the short-term and long-term consequences, evaluating alternative options, and seeking input from relevant stakeholders before making a well-informed and rational decision.
Outcomes and Benefits of Applying Authentic Thinking and Critical Thinking
- By applying authentic thinking, individuals and organizations can foster creativity, innovation, and collaboration, leading to more effective problem-solving and decision-making processes.
- Authentic thinking allows individuals to appreciate diverse perspectives, embrace uncertainty, and think beyond the status quo, resulting in more robust and adaptable solutions.
- Critical thinking enables individuals to analyze information critically, evaluate different viewpoints, identify biases and assumptions, and make well-reasoned judgments, leading to better decision-making and problem-solving outcomes.
- The application of critical thinking skills nurtures individuals’ ability to adapt to change, learn from failures, and continuously improve their decision-making processes.
- By emphasizing both authentic thinking and critical thinking, individuals can enhance their overall cognitive abilities, become more open-minded, and develop a deeper understanding of complex issues.
In conclusion, the application of both authentic thinking and critical thinking is crucial in various areas of life, including the workplace, education, healthcare, and business. By actively practicing and honing these thinking skills, individuals can navigate the complexities of the modern world more effectively, making informed decisions and generating innovative solutions. It is essential for individuals to recognize the distinctive features and benefits of both authentic thinking and critical thinking, as they complement each other and contribute to holistic problem-solving and decision-making processes.
In conclusion, authentic thinking and critical thinking are two distinct but complementary approaches to problem-solving and decision-making.
Authentic thinking involves seeking and understanding the truth, being open to new ideas and perspectives, and recognizing the value of personal experiences and emotions. It encourages individuals to think deeply, reflect on their own beliefs and biases, and develop a genuine understanding of complex issues. Authentic thinking is particularly important in situations that require empathy, creativity, and the ability to navigate through ambiguity.
On the other hand, critical thinking involves analyzing and evaluating information, questioning assumptions and biases, and making reasoned judgments based on evidence and logic. Critical thinking enables individuals to identify and challenge flawed arguments, weigh different perspectives, and make informed decisions. It plays a crucial role in situations that require objectivity, analytical thinking, and problem-solving.
While there are differences between authentic thinking and critical thinking, they share common elements and can be seen as complementary approaches. Both require intellectual curiosity, open-mindedness, and the willingness to challenge assumptions. They emphasize the importance of evidence, reasoning, and sound judgment. By combining the strengths of both types of thinking, individuals can develop a well-rounded approach to problem-solving and decision-making.
Applying authentic thinking and critical thinking in real-life situations can lead to positive outcomes and numerous benefits. Authentic thinking allows individuals to better understand others, build meaningful relationships, and foster an inclusive and empathetic community. It encourages innovative ideas, diverse perspectives, and creative solutions to complex problems. Critical thinking, on the other hand, helps individuals avoid logical fallacies, make sound decisions, and navigate through challenging situations. It promotes intellectual growth, enables effective problem-solving, and contributes to personal and professional success.
In today’s complex world, authentic thinking and critical thinking are invaluable skills that individuals need to develop. By cultivating these skills, individuals can enhance their ability to solve problems and make decisions that are well-informed, unbiased, and ethically sound. Authentic thinking and critical thinking empower individuals to navigate through the vast amount of information available, navigate through complexities, and contribute to positive change in their communities and beyond. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals to embrace both types of thinking and continually strive to improve their skills in order to thrive in an ever-changing world.
Thinking bigger: solutions for overcoming self-doubt
The power of storytelling in cultivating authentic thinking, unleash the power of your mind with these words, insightful interviews with top thinkers in their fields.

Creativity and the Brain: How to Be a Creative Thinker
What do we know from research on brain activity involved in creative thought.
Posted April 30, 2024 | Reviewed by Michelle Quirk
- The book "The Creative Act" argues that creativity is a skill we can all use daily.
- Creativity is complex and involves multiple brain regions.
- Research shows that there are several ways to improve our creative thinking.
This post is part 2 of a series.
In my previous post, I wrote that, after being inspired by Rick Rubin’s book, The Creative Act: A Way of Being, I decided to find out what is going on in the human brain that results in creativity. It turned out to be a very complex and complicated subject. That is mainly because it is difficult to clearly define creativity, and there are many different kinds of creative processes, such as visual art, music, creative thinking , etc.
Coming from the field of cognitive processes, I decided that I would concentrate on research related to brain activity involved in creative thought processes. Most of the time, cognitive creativity involves testing the person’s divergent thinking (generating possible solutions to the problem) or convergent thinking (finding a single, correct solution to the problem).
The review of research papers indicated that creative thinking (convergent and divergent thinking) requires the coordination of multiple brain regions, mainly the executive control network (simply speaking involves planning, organizing, problem-solving, and decision-making ), default mode network (areas of the brain that are activated when we are letting our minds wander at rest), and salience network (a network that is involved in the awareness of the feelings associated with rewards). But, obviously, other parts of the brain are also involved, and this depends on the specific goal/outcome that we want to achieve.
I also promised my readers that I would try to find answers to the question of how to be a creative thinker. There are many suggestions on the internet, but let’s see what the research says.
_4.jpg?itok=56gQnN6I)
You can learn how to meditate and practice it daily.
It may come as a surprise to many people, but the majority of the research papers in that area point to the daily practice of meditation as a way to improve creative thinking. It is not a surprise to me because I am a believer in meditation and do it daily. I also encourage all my patients to try to do it daily.
In a Chinese study (Ding, X. et al. 2014), 40 Chinese undergraduate students were assigned to three groups, a meditation group (30 minutes daily for 7 days), a relaxation training group, and a control group. Creativity performance was assessed by the Torrance Test of Creative Thinking (TTCT). The results indicated that the subjects in the meditation group improved their creativity performance on the divergent thinking tasks.
Research studies on meditation also indicate that it helps improve attention/ concentration skills and emotional regulation and reduces stress and anxiety , so it looks like a good daily habit to start.
You can read aloud and do arithmetic calculations.
In a Taiwan study (Lin, WL. et al. 2018), 50 junior high students were divided into a training group or a control group. The training group was reading aloud and performing arithmetic calculations for 20 sessions. The control group played the game Tetris (a puzzle video game). The results indicated that the participants in the training group outperformed the control group in thinking and creative abilities.
You can do neurofeedback.
Neurofeedback is a computer-guided, noninvasive brain-function training based on electroencephalography (EEG) feedback. Neurofeedback is also called neurotherapy, neurobiofeedback, or EEG biofeedback, and it helps control involuntary processes such as muscle tension and heart rate. Usually, the person is responding to a computer display of her/his own electrical activity of the brain, but it may also simply be a sound stimulation. The most important factor is that neurofeedback focuses on helping a person train himself/herself to regulate brain functions.
In an Italian study (Agnoli, S. et al. 2018), 80 female students from the University of Bologna got three neurofeedback training sessions. The researchers also measured the participants’ lifetime creative achievement by using the Creative Activity and Accomplishment Checklist. The results were measured with the divergent thinking tasks (producing original and effective ideas). The results indicated an increase in both originality and fluency. The increase was particularly evident in participants with an initial low creative achievement level.
This is good news for people who believe that they are not that creative. You may get better with neurofeedback training sessions. Artists and athletes do this nowadays to enhance their performance.
You can do overinclusive thinking training.
Overinclusive thinking can be described as increased generalization and/or considering concepts that most people consider unrelated to certain categories, which provides an increased number of options. In a Taiwan study (Chiu, F.C. 2015), the researcher examined the effect of overinclusive thinking on creativity. Four experiments were designed, and the subjects were undergraduate students who were randomly assigned to an overinclusive thinking training group or a control group. The training group did better on the overinclusive thinking that is related to creativity. The fluency and originality performance were higher than in the control group and the insight problem-solving was also better than in the control group.

So, if you would like to be a creative thinker, you can try some of the ideas described above. Good luck on the road to creativity!
Rick Rubin. The Creative Act: A Way of Being . Penguin Press, NY 2023.
Ding, X. et al. “Improving creativity performance by short-term meditation” Behavioral and Brain Functions. Vol. 10, 2014.
Lin, WL. et al. “ Improving junior high students’ thinking and creative abilities with an executive function training program” Thinking Skills and Creativity . Vol. 29, Sept. 2018.
Agnoli, S. et al. “Enhancing creative cognition with a rapid right-parietal neurofeedback procedure.” Neuropsychologia, Vol. 118, Part A Sept. 2018.
Chiu, F.C. “ Improving your creative potential without awareness: Overinclusive thinking training.” Thinking Skills and Creativity . Vol 15. March 2015.

Barbara Koltuska-Haskin, Ph.D., is a neuropsychologist in Albuquerque, New Mexico and the author of How My Brain Works.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Critical and Creative
Sunday, december 2, 2012, differences and similarities.

5 comments:

Thank you this is very helpful
💙💙💙love this
Thanks, it really helps
Thanks ☺️
Nurturing Critical and Creative Thinking w/ Erik Francis The Optimalist Podcast
- Self-Improvement
In this week’s episode, Erik Francis joins us to explore the pivotal role of critical and creative thinking in modern education. Embracing technology, notably AI, is a key theme, urging educators to leverage tools like ChatGPT to foster inquiry-based learning. Despite systemic challenges within traditional schooling, Erik, a seasoned advocate for innovative education, emphasizes the importance of resilience and motivation in navigating career paths. Our discussion highlighted the transformative potential of AI in generating thought-provoking questions, alongside the need for customized instruction tailored to diverse student needs. We underscored the synergy between technological advancement and human ingenuity, while lamenting the decline of deep, long-form engagement amidst social media's superficial allure. Join us as we unravel the intricacies of education's future, rooted in the belief that nurturing critical and creative thinking is essential for empowering learners in an ever-evolving world. Key reflection: How might you integrate technology, such as AI tools, to cultivate a culture of inquiry-based learning and foster critical and creative thinking in your school? Chapters: (0:01:41) Embracing AI in Education (0:08:32) Finding a Different Path in Education (0:10:36) Motivation and Management in the Face of Challenges (0:14:07) Teaching and Testing with Depth of Knowledge (DOK) Levels (0:16:12) Assessing student progress towards proficiency and overcoming obstacles (0:17:57) Justifying and verifying with evidence to reach DOK-3 (0:23:50) The Power of Technology as an Instructional Tool (0:26:05) Embracing Technology for Productive Learning (0:30:44) The Power of Language in Pixar Cartoons (0:33:05) Finding Purpose in Simon Sinek's Start With Why ------ Links Mentioned: Maverik Education Erik on Twitter DOK Book Find us & join us: Follow Sara Candela on Twitter at @Scandela9 Rate & Subscribe to The Optimalist Podcast on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, your favorite podcast player - or on Substack - to get each episode as soon as it’s released. The Optimalist Podcast is brought to you by Swivl. At Swivl, we understand that the biggest challenge in education is the rate of change. Policy revisions, technological advancements (accelerated by AI), evolving job markets, and ongoing research constantly identifying new best practices are only some of the factors affecting the rate of change in education. To learn how Swivl can help you be more reflective, engaged, and adaptable - including Mirror, our newest tool for complete transformation - visit swivl.com. You can also follow us on Twitter. We are SO EXCITED to introduce Mirror by Swivl - a new tool made to recognize the potential of reflection in classrooms. We built Mirror to thrive with AI, reflect easier, and partner with teachers. I think Mirror is where you and your students are going to meet your potential self. Click here to sign up to try Mirror for FREE as part of our unique demo program starting right now. Follow Swivl on Twitter at @Swivl Follow Swivl on Instagram at @goswivl Credits: Music: “Goodnight, Shapeshifter” by MusicForNothing, used under Creative Commons BY-ND 3.0. Audio Editing & Production: Tim Belmont (@tbelmontedu)
- Episode Website
- More Episodes

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical Thinking vs. Creative Thinking . Creative thinking is a way of looking at problems or situations from a fresh perspective to conceive of something new or original. Critical thinking is the logical, sequential disciplined process of rationalizing, analyzing, evaluating, and interpreting information to make informed judgments and/or ...
It emphasizes logical reasoning, evidence-based thinking, and the ability to identify biases and fallacies. While creative thinking focuses on generating ideas, critical thinking focuses on evaluating and refining those ideas. Both thinking processes are essential for problem-solving, decision-making, and personal growth.
While creative thinking involves generating new ideas, thinking outside the box, and exploring different perspectives, critical thinking focuses on analyzing, evaluating, and questioning information to make informed judgments. Both types of thinking are crucial in today's fast-paced and complex world. By understanding the differences and ...
Similarities between Creative Thinking and Critical Thinking are listed below. Also i'd love to hear your opinions, examples, and thoughts about further topics I can explore.
Critical and creative thinking skills are perhaps the most fundamental skills involved in making judgments and solving problems. They are some of the most important skills I have ever developed. I use them everyday and continue to work to improve them both. The ability to think critically about a matter—to analyze a question, situation, or ...
through intricacies. Purposeful thinking requires both critical and creative thinking. Both are intimately connected to figuring things out. There is a natural marriage between them. Indeed, all truly excellent thinking combines these two dimensions. Whenever our thinking excels, it excels because we succeed in designing or
An introduction to critical thinking and creativity : think more, think better / Joe Y.F. Lau. p. cm. Includes bibliographical references and index. ISBN 978--470-19509-3 (pbk.) 1. Critical thinking. 2. Creative ability. I. Title. B809.2.L38 2011 153.4'2—dc22 2010048204 Printed in the United States of America. 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
As with critical thinking, higher education both demands creative thinking from us and is the perfect place to practice and develop the skill. Everything from word problems in a math class, to opinion or persuasive speeches and papers, call upon our creative thinking skills to generate new solutions and perspectives in response to our professor ...
Discusses the relationship between creative thinking and critical thinking as 2 aspects of cognition, with special emphasis on the implications for the education of adults who can think critically and creatively. Critical thinking and creative thinking are described as complementary and similar but not identical processes. The similarities and differences between these 2 concepts are described ...
Creativity is a process that demands critical analysis and evaluation and shares with critical thinking the need for (to revisit Guilford) fluency, flexibility and originality of thought, the ability and dispositions to reinterpretation and challenge old ideas and to move forward in the face of ambiguity.
Similarly, Qiang et al. [22] investigated the association between creativity and critical thinking in a large sample of high school students (n = 1.153) and discovered a positive relationship (r ...
For critical thinking, the process is structured and methodical. For creative thinking, the process is fluid and somewhat experimental. Both thinking strategies are useful, with neither being innately superior to the other and in some unexpected ways even being linked. Now without further ado, let us explore the various components of critical ...
Creative thinking. Creativity is the ability to make or do something new that is also useful or valued by others (Gardner, 1993). The "something" can be an object (like an essay or painting), a skill (like playing an instrument), or an action (like using a familiar tool in a new way). To be creative, the object, skill, or action cannot simply ...
Critical thinking includes a complex combination of skills. According to Paul and Elder (2006) of the Foundation for Critical Thinking, the standards are: accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, logic, significance and fairness. Critical thinkers display the following characteristics: They are by nature skeptical.
Creative thought can generate hypotheses and explore novel avenues of inquiry while critical thought ensures the research design is rigorous and data analysis valid. Integrating both types of thinking allows scientists to make groundbreaking discoveries while maintaining scientific integrity of their work.
Therefore, we have analyzed the association between creative and critical thinking to determine whether their components are independent or associated with each other. A sample of 291 undergraduate students from Brazil (41.2%) and Spain (58.8%), with ages ranging from 17 to 56 years ( M = 21.35, SD = 5.61), from both genders (84% women ...
In summary, while there are distinct differences between authentic thinking and critical thinking, they also share several similarities. Both types of thinking involve engaging with complex problems, maintaining open-mindedness and objectivity, employing analytical thinking, reflecting and practicing self-awareness, applying to real-world ...
processes of critical and creative thinking, suggesting the interconnectivity of the two. Also in 1987, Joan Boykoff Baron and Raymond S. Nickerson published an even more extensive ... In outlining the similarities between critical thinking and the scientific process, Schafersman highlighted the debt owed by modern ...
Creative thinking is the mental process of bringing something new into existence through imagination. It involves the input of facts and sensory stimuli, interpolation, and critical reflection to imagine something that does not exist (Crockett, 2011). It can also be thinking about something in a new or different way (Doyle, 2022).
The book "The Creative Act" argues that creativity is a skill we can all use daily. Creativity is complex and involves multiple brain regions. Research shows that there are several ways to improve ...
1. Creative problem solving usually resolves in something considered new or unusual as a solution. 2. Critical thinking does not necessary result into a definite solution. 3. Critical thinking sometimes is implemented so that multiple, many solutions are created. Similarities: 1. Both require elevated processes of thinking and a choice/ability ...
As per the ' Journal of Gifted Education and Creativity', creative thinking is related to both problem solving and critical thinking. The Journal also explains three dimensions of creative thinking namely, 'synthesizing', 'articulation', and 'imagination'. It further highlights the general characteristics of this thinking ability.
Critical Thinking versus Problem Solving. Many people lump critical thinking and problem-solving together into one basket, and while there are similarities, there are also distinct differences. Critical thinking utilizes analysis, reflection, evaluation, interpretation, and inference to synthesize information that is obtained through reading ...
between creative thinking and critical thinking disposition scores of students ( r = .24, p < .0 1). This correlation indicates that critical thinking positively affects creative thinking in low ...
In this week's episode, Erik Francis joins us to explore the pivotal role of critical and creative thinking in modern education. Embracing technology, notably AI, is a key theme, urging educators to leverage tools like ChatGPT to foster inquiry-based learning. Despite systemic challenges within trad…