Business growth
Marketing tips

16 case study examples (+ 3 templates to make your own)
I like to think of case studies as a business's version of a resume. It highlights what the business can do, lends credibility to its offer, and contains only the positive bullet points that paint it in the best light possible.
Imagine if the guy running your favorite taco truck followed you home so that he could "really dig into how that burrito changed your life." I see the value in the practice. People naturally prefer a tried-and-true burrito just as they prefer tried-and-true products or services.
To help you showcase your success and flesh out your burrito questionnaire, I've put together some case study examples and key takeaways.
What is a case study?
A case study is an in-depth analysis of how your business, product, or service has helped past clients. It can be a document, a webpage, or a slide deck that showcases measurable, real-life results.
For example, if you're a SaaS company, you can analyze your customers' results after a few months of using your product to measure its effectiveness. You can then turn this analysis into a case study that further proves to potential customers what your product can do and how it can help them overcome their challenges.
It changes the narrative from "I promise that we can do X and Y for you" to "Here's what we've done for businesses like yours, and we can do it for you, too."
16 case study examples
While most case studies follow the same structure, quite a few try to break the mold and create something unique. Some businesses lean heavily on design and presentation, while others pursue a detailed, stat-oriented approach. Some businesses try to mix both.
There's no set formula to follow, but I've found that the best case studies utilize impactful design to engage readers and leverage statistics and case details to drive the point home. A case study typically highlights the companies, the challenges, the solution, and the results. The examples below will help inspire you to do it, too.
1. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Volcanica Coffee and AdRoll

People love a good farm-to-table coffee story, and boy am I one of them. But I've shared this case study with you for more reasons than my love of coffee. I enjoyed this study because it was written as though it was a letter.
In this case study, the founder of Volcanica Coffee talks about the journey from founding the company to personally struggling with learning and applying digital marketing to finding and enlisting AdRoll's services.
It felt more authentic, less about AdRoll showcasing their worth and more like a testimonial from a grateful and appreciative client. After the story, the case study wraps up with successes, milestones, and achievements. Note that quite a few percentages are prominently displayed at the top, providing supporting evidence that backs up an inspiring story.
Takeaway: Highlight your goals and measurable results to draw the reader in and provide concise, easily digestible information.
2. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Taylor Guitars and Airtable

This Airtable case study on Taylor Guitars comes as close as one can to an optimal structure. It features a video that represents the artistic nature of the client, highlighting key achievements and dissecting each element of Airtable's influence.
It also supplements each section with a testimonial or quote from the client, using their insights as a catalyst for the case study's narrative. For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail.
Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail.
3. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} EndeavourX and Figma

My favorite part of Figma's case study is highlighting why EndeavourX chose its solution. You'll notice an entire section on what Figma does for teams and then specifically for EndeavourX.
It also places a heavy emphasis on numbers and stats. The study, as brief as it is, still manages to pack in a lot of compelling statistics about what's possible with Figma.
Takeaway: Showcase the "how" and "why" of your product's differentiators and how they benefit your customers.
4. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} ActiveCampaign and Zapier

Zapier's case study leans heavily on design, using graphics to present statistics and goals in a manner that not only remains consistent with the branding but also actively pushes it forward, drawing users' eyes to the information most important to them.
The graphics, emphasis on branding elements, and cause/effect style tell the story without requiring long, drawn-out copy that risks boring readers. Instead, the cause and effect are concisely portrayed alongside the client company's information for a brief and easily scannable case study.
Takeaway: Lean on design to call attention to the most important elements of your case study, and make sure it stays consistent with your branding.
5. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Ironclad and OpenAI
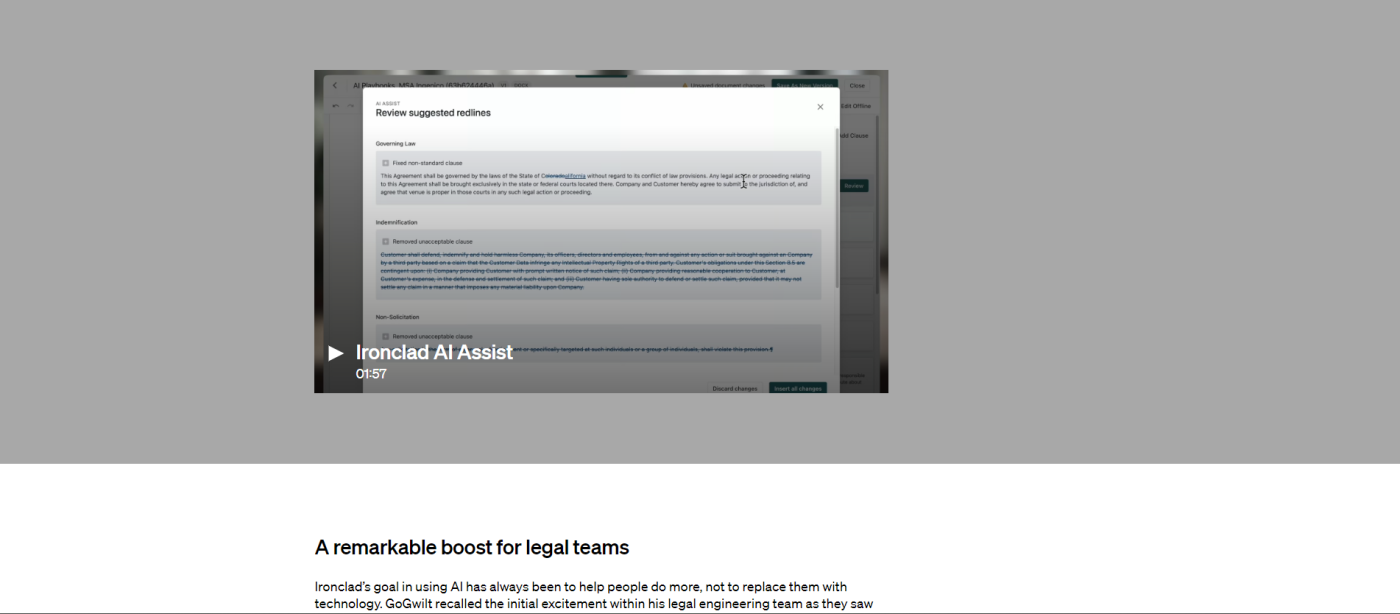
In true OpenAI fashion, this case study is a block of text. There's a distinct lack of imagery, but the study features a narrated video walking readers through the product.
The lack of imagery and color may not be the most inviting, but utilizing video format is commendable. It helps thoroughly communicate how OpenAI supported Ironclad in a way that allows the user to sit back, relax, listen, and be impressed.
Takeaway: Get creative with the media you implement in your case study. Videos can be a very powerful addition when a case study requires more detailed storytelling.
6. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Shopify and GitHub

GitHub's case study on Shopify is a light read. It addresses client pain points and discusses the different aspects its product considers and improves for clients. It touches on workflow issues, internal systems, automation, and security. It does a great job of representing what one company can do with GitHub.
To drive the point home, the case study features colorful quote callouts from the Shopify team, sharing their insights and perspectives on the partnership, the key issues, and how they were addressed.
Takeaway: Leverage quotes to boost the authoritativeness and trustworthiness of your case study.
7 . .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Audible and Contentful

Contentful's case study on Audible features almost every element a case study should. It includes not one but two videos and clearly outlines the challenge, solution, and outcome before diving deeper into what Contentful did for Audible. The language is simple, and the writing is heavy with quotes and personal insights.
This case study is a uniquely original experience. The fact that the companies in question are perhaps two of the most creative brands out there may be the reason. I expected nothing short of a detailed analysis, a compelling story, and video content.
Takeaway: Inject some brand voice into the case study, and create assets that tell the story for you.
8 . .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Zoom and Asana
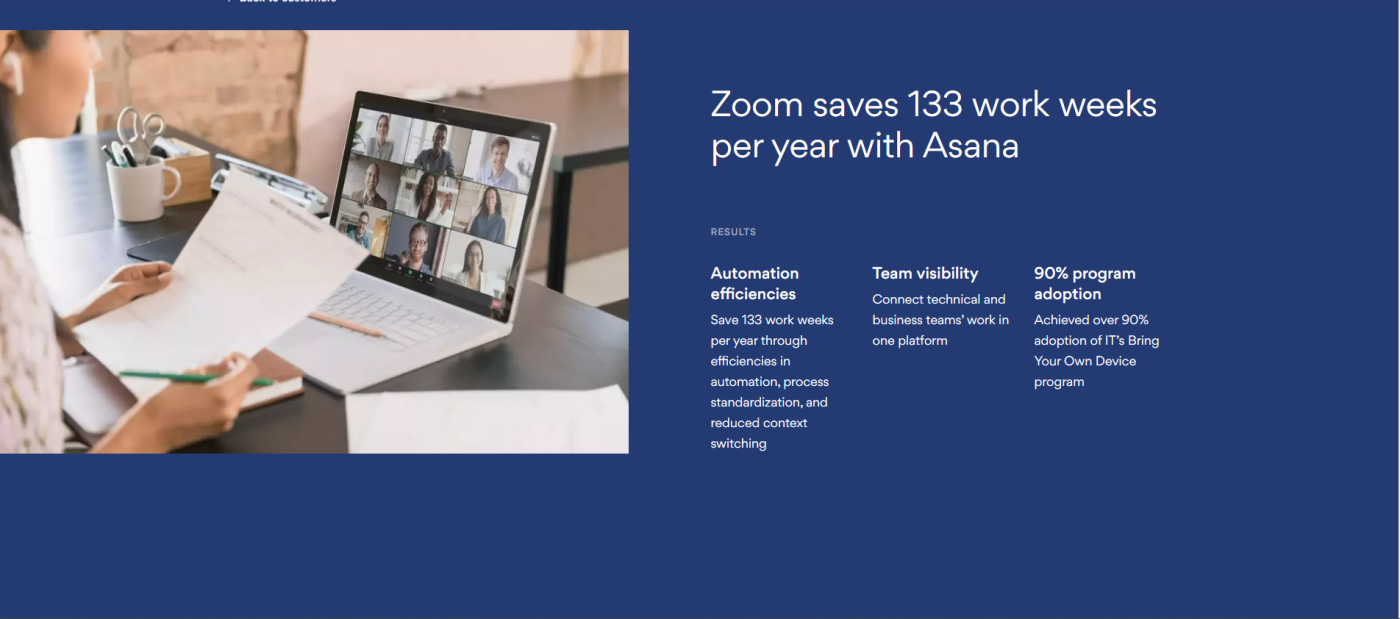
Asana's case study on Zoom is longer than the average piece and features detailed data on Zoom's growth since 2020. Instead of relying on imagery and graphics, it features several quotes and testimonials.
It's designed to be direct, informative, and promotional. At some point, the case study reads more like a feature list. There were a few sections that felt a tad too promotional for my liking, but to each their own burrito.
Takeaway: Maintain a balance between promotional and informative. You want to showcase the high-level goals your product helped achieve without losing the reader.
9 . .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Hickies and Mailchimp

I've always been a fan of Mailchimp's comic-like branding, and this case study does an excellent job of sticking to their tradition of making information easy to understand, casual, and inviting.
It features a short video that briefly covers Hickies as a company and Mailchimp's efforts to serve its needs for customer relationships and education processes. Overall, this case study is a concise overview of the partnership that manages to convey success data and tell a story at the same time. What sets it apart is that it does so in a uniquely colorful and brand-consistent manner.
Takeaway: Be concise to provide as much value in as little text as possible.
10. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} NVIDIA and Workday
The gaming industry is notoriously difficult to recruit for, as it requires a very specific set of skills and experience. This case study focuses on how Workday was able to help fill that recruitment gap for NVIDIA, one of the biggest names in the gaming world.
Though it doesn't feature videos or graphics, this case study stood out to me in how it structures information like "key products used" to give readers insight into which tools helped achieve these results.
Takeaway: If your company offers multiple products or services, outline exactly which ones were involved in your case study, so readers can assess each tool.
11. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} KFC and Contentful
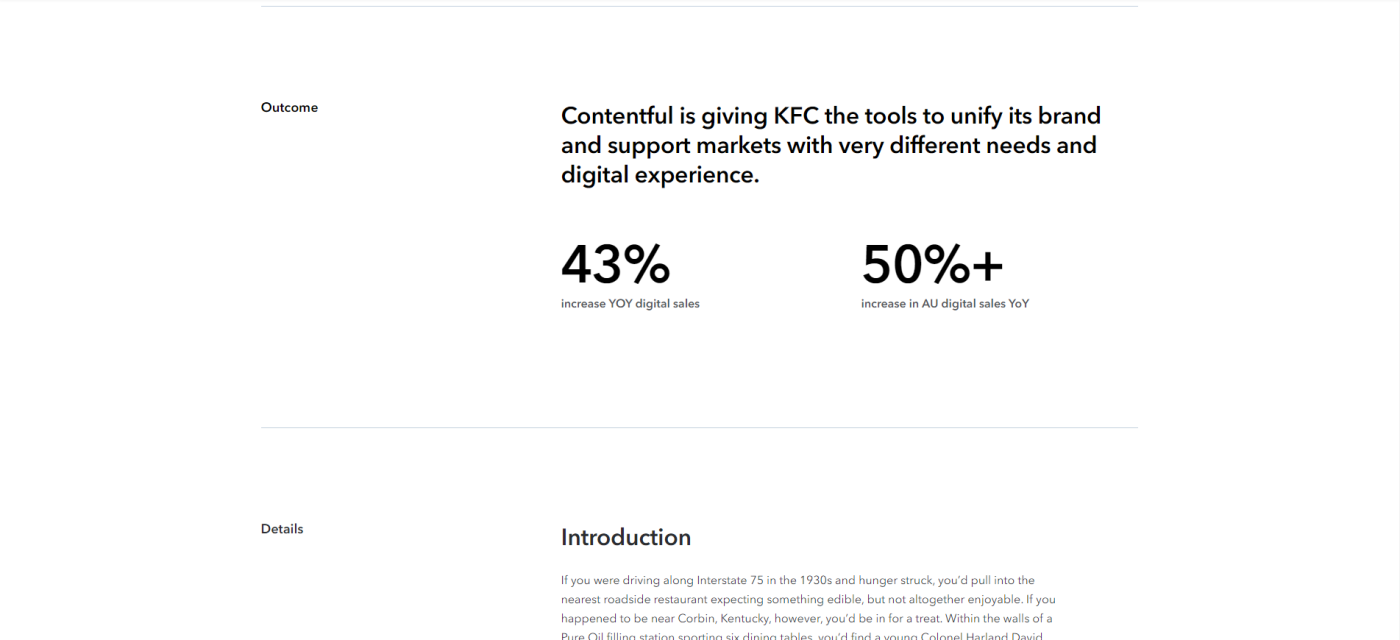
I'm personally not a big KFC fan, but that's only because I refuse to eat out of a bucket. My aversion to the bucket format aside, Contentful follows its consistent case study format in this one, outlining challenges, solutions, and outcomes before diving into the nitty-gritty details of the project.
Say what you will about KFC, but their primary product (chicken) does present a unique opportunity for wordplay like "Continuing to march to the beat of a digital-first drum(stick)" or "Delivering deep-fried goodness to every channel."
Takeaway: Inject humor into your case study if there's room for it and if it fits your brand.
12. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Intuit and Twilio

Twilio does an excellent job of delivering achievements at the very beginning of the case study and going into detail in this two-minute read. While there aren't many graphics, the way quotes from the Intuit team are implemented adds a certain flair to the study and breaks up the sections nicely.
It's simple, concise, and manages to fit a lot of information in easily digestible sections.
Takeaway: Make sure each section is long enough to inform but brief enough to avoid boring readers. Break down information for each section, and don't go into so much detail that you lose the reader halfway through.
13. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Spotify and Salesforce

Salesforce created a video that accurately summarizes the key points of the case study. Beyond that, the page itself is very light on content, and sections are as short as one paragraph.
I especially like how information is broken down into "What you need to know," "Why it matters," and "What the difference looks like." I'm not ashamed of being spoon-fed information. When it's structured so well and so simply, it makes for an entertaining read.
14. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Benchling and Airtable

Benchling is an impressive entity in its own right. Biotech R&D and health care nuances go right over my head. But the research and digging I've been doing in the name of these burritos (case studies) revealed that these products are immensely complex.
And that's precisely why this case study deserves a read—it succeeds at explaining a complex project that readers outside the industry wouldn't know much about.
Takeaway: Simplify complex information, and walk readers through the company's operations and how your business helped streamline them.
15. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Chipotle and Hubble

The concision of this case study is refreshing. It features two sections—the challenge and the solution—all in 316 words. This goes to show that your case study doesn't necessarily need to be a four-figure investment with video shoots and studio time.
Sometimes, the message is simple and short enough to convey in a handful of paragraphs.
Takeaway: Consider what you should include instead of what you can include. Assess the time, resources, and effort you're able and willing to invest in a case study, and choose which elements you want to include from there.
16. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Hudl and Zapier
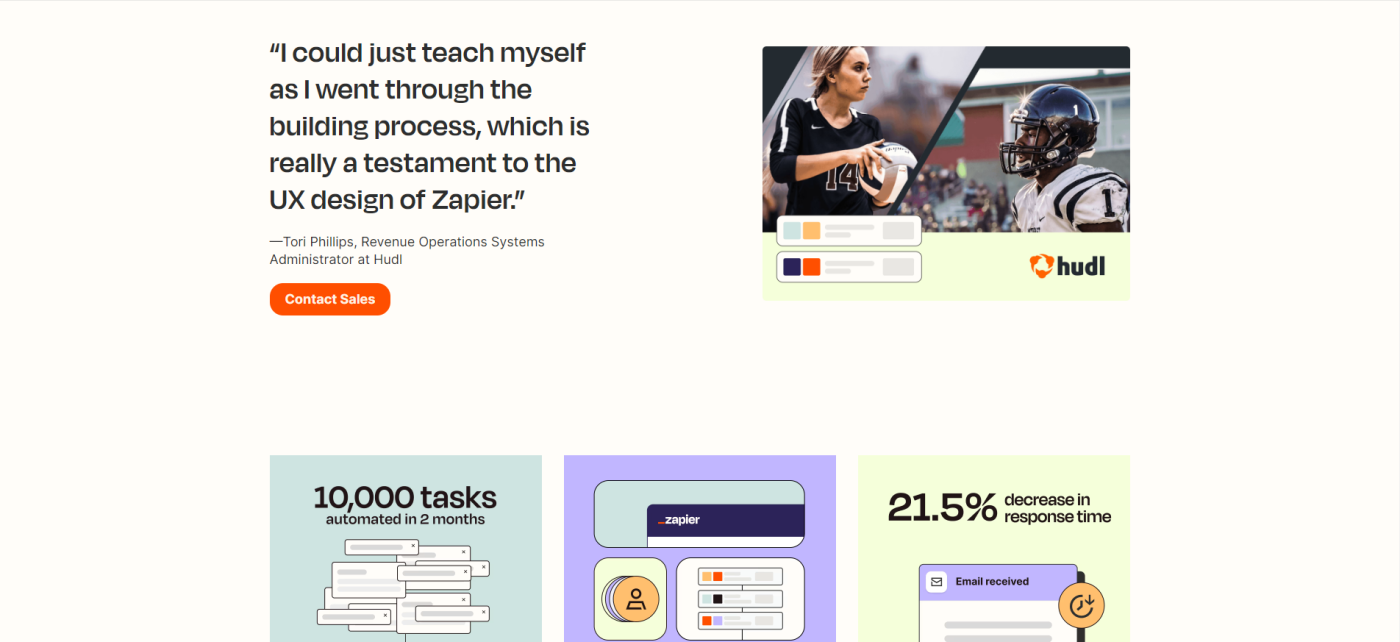
I may be biased, but I'm a big fan of seeing metrics and achievements represented in branded graphics. It can be a jarring experience to navigate a website, then visit a case study page and feel as though you've gone to a completely different website.
The case study is essentially the summary, and the blog article is the detailed analysis that provides context beyond X achievement or Y goal.
Takeaway: Keep your case study concise and informative. Create other resources to provide context under your blog, media or press, and product pages.
3 case study templates
Now that you've had your fill of case studies (if that's possible), I've got just what you need: an infinite number of case studies, which you can create yourself with these case study templates.
Case study template 1

If you've got a quick hit of stats you want to show off, try this template. The opening section gives space for a short summary and three visually appealing stats you can highlight, followed by a headline and body where you can break the case study down more thoroughly. This one's pretty simple, with only sections for solutions and results, but you can easily continue the formatting to add more sections as needed.
Case study template 2

For a case study template with a little more detail, use this one. Opening with a striking cover page for a quick overview, this one goes on to include context, stakeholders, challenges, multiple quote callouts, and quick-hit stats.
Case study template 3

Whether you want a little structural variation or just like a nice dark green, this template has similar components to the last template but is designed to help tell a story. Move from the client overview through a description of your company before getting to the details of how you fixed said company's problems.
Tips for writing a case study
Examples are all well and good, but you don't learn how to make a burrito just by watching tutorials on YouTube without knowing what any of the ingredients are. You could , but it probably wouldn't be all that good.
Have an objective: Define your objective by identifying the challenge, solution, and results. Assess your work with the client and focus on the most prominent wins. You're speaking to multiple businesses and industries through the case study, so make sure you know what you want to say to them.
Focus on persuasive data: Growth percentages and measurable results are your best friends. Extract your most compelling data and highlight it in your case study.
Use eye-grabbing graphics: Branded design goes a long way in accurately representing your brand and retaining readers as they review the study. Leverage unique and eye-catching graphics to keep readers engaged.
Simplify data presentation: Some industries are more complex than others, and sometimes, data can be difficult to understand at a glance. Make sure you present your data in the simplest way possible. Make it concise, informative, and easy to understand.
Use automation to drive results for your case study
A case study example is a source of inspiration you can leverage to determine how to best position your brand's work. Find your unique angle, and refine it over time to help your business stand out. Ask anyone: the best burrito in town doesn't just appear at the number one spot. They find their angle (usually the house sauce) and leverage it to stand out.
Case study FAQ
Got your case study template? Great—it's time to gather the team for an awkward semi-vague data collection task. While you do that, here are some case study quick answers for you to skim through while you contemplate what to call your team meeting.
What is an example of a case study?
An example of a case study is when a software company analyzes its results from a client project and creates a webpage, presentation, or document that focuses on high-level results, challenges, and solutions in an attempt to showcase effectiveness and promote the software.
How do you write a case study?
To write a good case study, you should have an objective, identify persuasive and compelling data, leverage graphics, and simplify data. Case studies typically include an analysis of the challenge, solution, and results of the partnership.
What is the format of a case study?
While case studies don't have a set format, they're often portrayed as reports or essays that inform readers about the partnership and its results.
Related reading:
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Hachem Ramki
Hachem is a writer and digital marketer from Montreal. After graduating with a degree in English, Hachem spent seven years traveling around the world before moving to Canada. When he's not writing, he enjoys Basketball, Dungeons and Dragons, and playing music for friends and family.
- Content marketing
Related articles

12 Linkedin Lead Gen Form examples to inspire your next campaign
12 Linkedin Lead Gen Form examples to...

14 types of email marketing to experiment with
14 types of email marketing to experiment...
8 business anniversary marketing ideas and examples worth celebrating
8 business anniversary marketing ideas and...
A guide to verticalization: What it is, when to try it, and how to get started
A guide to verticalization: What it is, when...
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

Standout Traits for a Great Partner Case Study (With Examples)
It’s no surprise that partner case studies are a wee bit of a struggle to produce. Getting your customers to agree to a case study is one thing; getting your customer and your partner to agree to a case study is a miracle. On top of the fact that the partnerships world is still such a gray area for partner managers everywhere (let alone their leadership), partner case studies in SaaS are a rare sighting in the wild (think: the bat-eared fox. Do you even know what that is? 😝) .
So, think of this roundup as snapshots of the elusive partner case studies that lurk in the depths of the SaaS ecosystem — a co-marketing material still so new that, just maybe, by producing one of your own, you’ll be ahead of the curve already.
Below, we offer some partner case study standout traits, followed by a collection of examples located in (butler voice) the gallery , and a checklist for rolling out your own case study program.
1. Wow your readers by placing the results in the title.
While the rest of your case study should give the reader context, the results are what matter most to your potential buyers and their leadership teams. So, put the results at the top! SugarCRM kicks off its case study with Kyloe Partners and Bullhorn by sharing how they doubled lead-gen campaigns while cutting 60% of their customer’s workload.
Our suggestion: if someone were to ask you “What is the most impressive part of this case study?”, what is the first thing you’d say? That’s your headline.
2. Make the metrics obvious.
If your customer has observed more than one area of growth, that’s awesome. Draw the reader’s eyes right to the numbers. In Facebook’s case study with Zapier and Wicked Good Cupcakes , they placed their metrics in a standalone box that makes the numbers the most important information on the page.
Meanwhile, Acquia’s case study with Third and Grove and King Arthur Baking Company features their results point-blank in a standalone line that reads “Results.” (Say what?)
3. Define the customer’s use case or challenge.
It’s likely that your customers can use your integration for multiple use cases, so be clear about what this particular customer’s use case is from the start. In Microsoft Azure’s case study with Sourced Group and a Canadian bank , they clearly list out the challenge, the solution, and the result in three brief columns.
They also dive deeper into the bank’s challenges with a numbered list.
4. Define the audience or market.
Your customers will want to know how you’ve solved challenges they’re facing internally or that their customers may be facing. Make an easy connection for them by pointing out the specific audience or market the case study applies to.
Greenlight Guru’s case study with Rook Quality Systems explicitly describes how RQS’s clientele of medical professionals informs RQS’s product investments.
5. Get customer quotes.
Tableau’s case study with AWS and ride-hailing app FREE NOW includes quotes from FREE NOW’s Head of Analytics showing how indispensable Tableau has been, in tandem with AWS, for their team’s daily operations.
Tip: Repurpose your customer quotes by including them on your website, in press releases, and even in your outbound sales outreach.
6. Put the results in perspective: Include a timeframe.
Growth metrics don’t mean anything if they’re not tied to a before and after. Include the exact timeframe your analysis fits into.
And yes, Facebook’s case study with Zapier and Wicked Good Cupcakes is, indeed, cupcake-themed!
7. Get partner quotes.
You have quotes from your shared customer, why not also include a quote from your partner? Partner quotes can be especially useful for agencies who want to prove the value of their services to their customers and software vendors.
Cisco’s case study with Matternet and Stratus Information Systems includes quotes from individuals from Stratus Information Systems and Matternet — each of whom found the other to be invaluable while implementing Cisco’s software.
8. Add personal stories.
Including brief personal stories can give extra life to an otherwise data-heavy document (think: the people behind the products and, more specifically, the customer service that makes working with a SaaS company so customer-friendly).
SugarCRM’s case study with Kyloe Partners and Bullhorn shares a meet-cute-ish story detailing how Kyloe Partners’ co-founder and director and Bullhorn’s co-founder met back in the day (Can’t you just see it in a movie?).
9. Show them the people behind the product.
Did I mention a big part of SaaS is that last “S”? It’s all about the service.
Greenlight Guru’s case study with Rook Quality Systems talks about how much RQS values the company because of its relationship with GG employees.
10. Avoid the “wall of text” effect.
Grab your designer (Hi, Nick !), and develop a creative way to organize the benefits or data you’re showcasing in the case study.
Braze’s case study with Segment, Amplitude, and IBM includes a graphic displaying their in-platform activities.
And Acquia’s case study with Third and Grove and King Arthur Baking Company includes the stakeholders, situation, challenge, solution, and results neatly laid out — bringing the good stuff front and center.
11. Create video content.
For an extra special case study, and if your customer’s on board for the extra time commitment, consider creating a video.
ActiveCampaign’s case study with Salesforce and the Museum of Science and Industry, Chicago , includes a video at the top that dives into what the MSI team’s work days look like, the challenges they experience, and how the ActiveCampaign-Salesforce integration has helped them.
If you’re curious, we picked apart ActiveCampaign’s entire co-marketing playbook for getting to #1 in Salesforce’s marketing automation AppExchange .
From ActiveCampaign’s case study with Salesforce and the Museum of Science and Industry, Chicago
Sensyne includes a case study video on their website , existing outside of their official case study with Microsoft and Cognizant , explaining how they’ve deployed patient monitoring capabilities during COVID-19.
From Cognizant’s case study with Microsoft and Sensyne Health (video case study on Sensyne Health’s website)
12. Talk up your partners.
Include context about your partners, and talk them up. This case study should make you and your partner shine!
Tip: Include your partner case studies on the customer success section of your website and your partner page . It’s not just your potential customers reading these case studies, it’s also your potential partners.
Amazon Web Services’ case study with Deluxe Entertainment Services and Capgemini features a description of Deluxe Entertainment Services in a standalone section on the right.
13. Include a CTA.
‘Nuff said.
14. Create ancillary content that promotes your case studies.
Braze’s article in their Perspectives magazine links directly to their case study with Segment , Amplitude , and IBM .
If you’re developing partner case studies for the first time, or if you want to give your existing case studies a second life, check out our partner case study gallery below to gander everything we’ve mentioned thus far in a big picture view .
Partner Case Study Gallery:
And now, a collection of examples to help inspire your own work.
1. Facebook, Zapier, and Wicked Good Cupcakes
Read the case study .
2. Braze, Segment, Amplitude, and IBM
3. greenlight guru and rook quality systems, 4. sugarcrm, kyloe partners, and bullhorn.
Read the case study .
5. WPengine, BCF Agency, and Orangetheory Fitness
6. activecampaign, salesforce, and the museum of science and industry, chicago, 7. microsoft azure, sourced group, and a canadian bank, 8. cisco, matternet, and stratus information systems, 9. aws, deluxe entertainment services, and capgemini , 10. boomi and workiva.
This case study is a little different. In Dell Boomi’s case study with Workiva , they talk about how Workiva’s developers use Boomi to develop integrations for a variety of customers.
11. Tableau Software, AWS, and FREE NOW
12. acquia, third and grove, king arthur baking company, 13. cognizant, microsoft, and sensyne health, your partner case study checklist.
Great, you have the fundamentals. But what now? To rollout successful case studies you’ll need to make a few decisions: Considerations for planning your partner case study strategy:
- Will you develop joint case studies with some of your early adopters before going live with a given integration? (hint: case studies like this can help strengthen your press release and make the case for other customers interested in adopting)
- Which customers do you have the best relationship with, who may be interested in participating in a case study?
- Is it okay to reach out to the above customers, or will it cause friction in their relationship with your sales or marketing team? (e.g. your team has already sent that customer a number of asks in the past month. Enough is enough!)
- Are there specific use cases you’re looking to amplify through the case study? (e.g. an increase in revenue vs. a better leads to opportunities rate)
- Will your case studies be more like a blog post-like or a fact-sheet-like? (note: Braze publishes case studies in their magazine, Perspectives )
- Will you create video case studies in addition to written case studies (like Cognizant’s case study with Microsoft and Sensyne Health )?
- How long will your case studies be? ( ActiveCampaign and Salesforce’s case study with Museum of Science and Industry is quite extensive while Acquia, Third and Grove, and King Arthur Baking Company’s case study spans a single page.
Considerations for distributing your partner case studies:
- Where will your case studies live? Will they be gated with the goal of lead-gen? Or will they be available to the public? (Tip: If you make your case studies publicly available, you may want to consider a “Download PDF” button anyway so readers can pass the case study along to their team, just like Microsoft Azure does)
- Will your case studies exist as standalone, downloadable documents, as dedicated pages on your site, or another format entirely?
- Will you pull quotes or pieces of analysis from your case studies as previews for a case study homepage — or for elsewhere on your site/marketing materials? (You’ll want to let your customer know your plans ahead of time)
- Will you use your case studies in nurture sequences to drive engagement with your leads?
- Will your case studies be part of a bigger campaign with the participating partner ?
What makes a partner case study great? We called out the best attributes and developed a checklist for planning your case study strategy.
You Might Also Like

Your B2B SaaS Partner Page Checklist (with 50 Examples)

5 Signs Your Tech Partner's About to Get Acquired (And How to Prepare for Change)
This is a test comment.
This is a longer test comment to see how this looks if the person decides to ramble a bit. So they're rambling and rambling and then they even lorem ipsum.
Become a Crossbeam Insider
Crossbeam Insider is a not-so-secret club for driving revenue, growing your career, and staying ahead of the market with original research and analysis.
By checking this box you agree to the terms outlined in Crossbeam's Privacy Policy .
Something went wrong.
Thanks for subscribing!
Thanks for subscribing to Crossbeam Insider, where you can enjoy the latest Ecosystem-Led Growth insights, analysis, and best practices all in one place. Plus, keep an eye on your inbox for new stories each week.
Check your email for a magic link to unlock all our exclusive content.
Need help? Email
Magic Link Code Invalid
Please try signing in again.
Edit Profile
Successfully Updated Profile!
How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template
Published: November 30, 2023
Earning the trust of prospective customers can be a struggle. Before you can even begin to expect to earn their business, you need to demonstrate your ability to deliver on what your product or service promises.

Sure, you could say that you're great at X or that you're way ahead of the competition when it comes to Y. But at the end of the day, what you really need to win new business is cold, hard proof.
One of the best ways to prove your worth is through a compelling case study. In fact, HubSpot’s 2020 State of Marketing report found that case studies are so compelling that they are the fifth most commonly used type of content used by marketers.

Below, I'll walk you through what a case study is, how to prepare for writing one, what you need to include in it, and how it can be an effective tactic. To jump to different areas of this post, click on the links below to automatically scroll.
Case Study Definition
Case study templates, how to write a case study.
- How to Format a Case Study
Business Case Study Examples
A case study is a specific challenge a business has faced, and the solution they've chosen to solve it. Case studies can vary greatly in length and focus on several details related to the initial challenge and applied solution, and can be presented in various forms like a video, white paper, blog post, etc.
In professional settings, it's common for a case study to tell the story of a successful business partnership between a vendor and a client. Perhaps the success you're highlighting is in the number of leads your client generated, customers closed, or revenue gained. Any one of these key performance indicators (KPIs) are examples of your company's services in action.
When done correctly, these examples of your work can chronicle the positive impact your business has on existing or previous customers and help you attract new clients.

Free Case Study Templates
Showcase your company's success using these three free case study templates.
- Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Product-Specific Case Study Template
- General Case Study Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Why write a case study?
I know, you’re thinking “ Okay, but why do I need to write one of these? ” The truth is that while case studies are a huge undertaking, they are powerful marketing tools that allow you to demonstrate the value of your product to potential customers using real-world examples. Here are a few reasons why you should write case studies.
1. Explain Complex Topics or Concepts
Case studies give you the space to break down complex concepts, ideas, and strategies and show how they can be applied in a practical way. You can use real-world examples, like an existing client, and use their story to create a compelling narrative that shows how your product solved their issue and how those strategies can be repeated to help other customers get similar successful results.
2. Show Expertise
Case studies are a great way to demonstrate your knowledge and expertise on a given topic or industry. This is where you get the opportunity to show off your problem-solving skills and how you’ve generated successful outcomes for clients you’ve worked with.
3. Build Trust and Credibility
In addition to showing off the attributes above, case studies are an excellent way to build credibility. They’re often filled with data and thoroughly researched, which shows readers you’ve done your homework. They can have confidence in the solutions you’ve presented because they’ve read through as you’ve explained the problem and outlined step-by-step what it took to solve it. All of these elements working together enable you to build trust with potential customers.
4. Create Social Proof
Using existing clients that have seen success working with your brand builds social proof . People are more likely to choose your brand if they know that others have found success working with you. Case studies do just that — putting your success on display for potential customers to see.
All of these attributes work together to help you gain more clients. Plus you can even use quotes from customers featured in these studies and repurpose them in other marketing content. Now that you know more about the benefits of producing a case study, let’s check out how long these documents should be.
How long should a case study be?
The length of a case study will vary depending on the complexity of the project or topic discussed. However, as a general guideline, case studies typically range from 500 to 1,500 words.
Whatever length you choose, it should provide a clear understanding of the challenge, the solution you implemented, and the results achieved. This may be easier said than done, but it's important to strike a balance between providing enough detail to make the case study informative and concise enough to keep the reader's interest.
The primary goal here is to effectively communicate the key points and takeaways of the case study. It’s worth noting that this shouldn’t be a wall of text. Use headings, subheadings, bullet points, charts, and other graphics to break up the content and make it more scannable for readers. We’ve also seen brands incorporate video elements into case studies listed on their site for a more engaging experience.
Ultimately, the length of your case study should be determined by the amount of information necessary to convey the story and its impact without becoming too long. Next, let’s look at some templates to take the guesswork out of creating one.
To help you arm your prospects with information they can trust, we've put together a step-by-step guide on how to create effective case studies for your business with free case study templates for creating your own.
Tell us a little about yourself below to gain access today:
And to give you more options, we’ll highlight some useful templates that serve different needs. But remember, there are endless possibilities when it comes to demonstrating the work your business has done.
1. General Case Study Template

Do you have a specific product or service that you’re trying to sell, but not enough reviews or success stories? This Product Specific case study template will help.
This template relies less on metrics, and more on highlighting the customer’s experience and satisfaction. As you follow the template instructions, you’ll be prompted to speak more about the benefits of the specific product, rather than your team’s process for working with the customer.
4. Bold Social Media Business Case Study Template

You can find templates that represent different niches, industries, or strategies that your business has found success in — like a bold social media business case study template.
In this template, you can tell the story of how your social media marketing strategy has helped you or your client through collaboration or sale of your service. Customize it to reflect the different marketing channels used in your business and show off how well your business has been able to boost traffic, engagement, follows, and more.
5. Lead Generation Business Case Study Template

It’s important to note that not every case study has to be the product of a sale or customer story, sometimes they can be informative lessons that your own business has experienced. A great example of this is the Lead Generation Business case study template.
If you’re looking to share operational successes regarding how your team has improved processes or content, you should include the stories of different team members involved, how the solution was found, and how it has made a difference in the work your business does.
Now that we’ve discussed different templates and ideas for how to use them, let’s break down how to create your own case study with one.
- Get started with case study templates.
- Determine the case study's objective.
- Establish a case study medium.
- Find the right case study candidate.
- Contact your candidate for permission to write about them.
- Ensure you have all the resources you need to proceed once you get a response.
- Download a case study email template.
- Define the process you want to follow with the client.
- Ensure you're asking the right questions.
- Layout your case study format.
- Publish and promote your case study.
1. Get started with case study templates.
Telling your customer's story is a delicate process — you need to highlight their success while naturally incorporating your business into their story.
If you're just getting started with case studies, we recommend you download HubSpot's Case Study Templates we mentioned before to kickstart the process.
2. Determine the case study's objective.
All business case studies are designed to demonstrate the value of your services, but they can focus on several different client objectives.
Your first step when writing a case study is to determine the objective or goal of the subject you're featuring. In other words, what will the client have succeeded in doing by the end of the piece?
The client objective you focus on will depend on what you want to prove to your future customers as a result of publishing this case study.
Your case study can focus on one of the following client objectives:
- Complying with government regulation
- Lowering business costs
- Becoming profitable
- Generating more leads
- Closing on more customers
- Generating more revenue
- Expanding into a new market
- Becoming more sustainable or energy-efficient
3. Establish a case study medium.
Next, you'll determine the medium in which you'll create the case study. In other words, how will you tell this story?
Case studies don't have to be simple, written one-pagers. Using different media in your case study can allow you to promote your final piece on different channels. For example, while a written case study might just live on your website and get featured in a Facebook post, you can post an infographic case study on Pinterest and a video case study on your YouTube channel.
Here are some different case study mediums to consider:
Written Case Study
Consider writing this case study in the form of an ebook and converting it to a downloadable PDF. Then, gate the PDF behind a landing page and form for readers to fill out before downloading the piece, allowing this case study to generate leads for your business.
Video Case Study
Plan on meeting with the client and shooting an interview. Seeing the subject, in person, talk about the service you provided them can go a long way in the eyes of your potential customers.
Infographic Case Study
Use the long, vertical format of an infographic to tell your success story from top to bottom. As you progress down the infographic, emphasize major KPIs using bigger text and charts that show the successes your client has had since working with you.
Podcast Case Study
Podcasts are a platform for you to have a candid conversation with your client. This type of case study can sound more real and human to your audience — they'll know the partnership between you and your client was a genuine success.
4. Find the right case study candidate.
Writing about your previous projects requires more than picking a client and telling a story. You need permission, quotes, and a plan. To start, here are a few things to look for in potential candidates.
Product Knowledge
It helps to select a customer who's well-versed in the logistics of your product or service. That way, he or she can better speak to the value of what you offer in a way that makes sense for future customers.
Remarkable Results
Clients that have seen the best results are going to make the strongest case studies. If their own businesses have seen an exemplary ROI from your product or service, they're more likely to convey the enthusiasm that you want prospects to feel, too.
One part of this step is to choose clients who have experienced unexpected success from your product or service. When you've provided non-traditional customers — in industries that you don't usually work with, for example — with positive results, it can help to remove doubts from prospects.
Recognizable Names
While small companies can have powerful stories, bigger or more notable brands tend to lend credibility to your own. In fact, 89% of consumers say they'll buy from a brand they already recognize over a competitor, especially if they already follow them on social media.
Customers that came to you after working with a competitor help highlight your competitive advantage and might even sway decisions in your favor.
5. Contact your candidate for permission to write about them.
To get the case study candidate involved, you have to set the stage for clear and open communication. That means outlining expectations and a timeline right away — not having those is one of the biggest culprits in delayed case study creation.
Most importantly at this point, however, is getting your subject's approval. When first reaching out to your case study candidate, provide them with the case study's objective and format — both of which you will have come up with in the first two steps above.
To get this initial permission from your subject, put yourself in their shoes — what would they want out of this case study? Although you're writing this for your own company's benefit, your subject is far more interested in the benefit it has for them.
Benefits to Offer Your Case Study Candidate
Here are four potential benefits you can promise your case study candidate to gain their approval.
Brand Exposure
Explain to your subject to whom this case study will be exposed, and how this exposure can help increase their brand awareness both in and beyond their own industry. In the B2B sector, brand awareness can be hard to collect outside one's own market, making case studies particularly useful to a client looking to expand their name's reach.
Employee Exposure
Allow your subject to provide quotes with credits back to specific employees. When this is an option for them, their brand isn't the only thing expanding its reach — their employees can get their name out there, too. This presents your subject with networking and career development opportunities they might not have otherwise.
Product Discount
This is a more tangible incentive you can offer your case study candidate, especially if they're a current customer of yours. If they agree to be your subject, offer them a product discount — or a free trial of another product — as a thank-you for their help creating your case study.
Backlinks and Website Traffic
Here's a benefit that is sure to resonate with your subject's marketing team: If you publish your case study on your website, and your study links back to your subject's website — known as a "backlink" — this small gesture can give them website traffic from visitors who click through to your subject's website.
Additionally, a backlink from you increases your subject's page authority in the eyes of Google. This helps them rank more highly in search engine results and collect traffic from readers who are already looking for information about their industry.
6. Ensure you have all the resources you need to proceed once you get a response.
So you know what you’re going to offer your candidate, it’s time that you prepare the resources needed for if and when they agree to participate, like a case study release form and success story letter.
Let's break those two down.
Case Study Release Form
This document can vary, depending on factors like the size of your business, the nature of your work, and what you intend to do with the case studies once they are completed. That said, you should typically aim to include the following in the Case Study Release Form:
- A clear explanation of why you are creating this case study and how it will be used.
- A statement defining the information and potentially trademarked information you expect to include about the company — things like names, logos, job titles, and pictures.
- An explanation of what you expect from the participant, beyond the completion of the case study. For example, is this customer willing to act as a reference or share feedback, and do you have permission to pass contact information along for these purposes?
- A note about compensation.
Success Story Letter
As noted in the sample email, this document serves as an outline for the entire case study process. Other than a brief explanation of how the customer will benefit from case study participation, you'll want to be sure to define the following steps in the Success Story Letter.
7. Download a case study email template.
While you gathered your resources, your candidate has gotten time to read over the proposal. When your candidate approves of your case study, it's time to send them a release form.
A case study release form tells you what you'll need from your chosen subject, like permission to use any brand names and share the project information publicly. Kick-off this process with an email that runs through exactly what they can expect from you, as well as what you need from them. To give you an idea of what that might look like, check out this sample email:
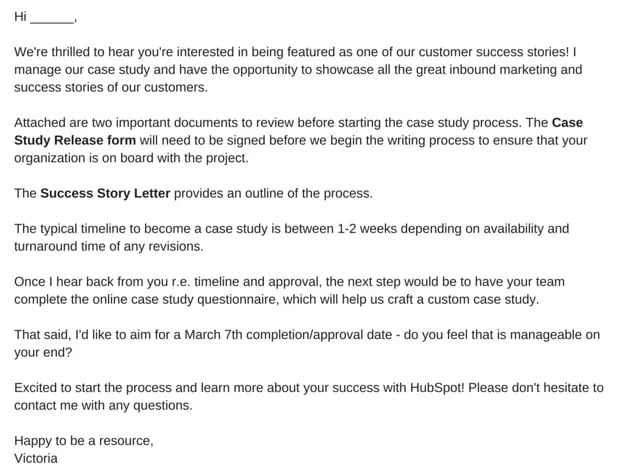
8. Define the process you want to follow with the client.
Before you can begin the case study, you have to have a clear outline of the case study process with your client. An example of an effective outline would include the following information.
The Acceptance
First, you'll need to receive internal approval from the company's marketing team. Once approved, the Release Form should be signed and returned to you. It's also a good time to determine a timeline that meets the needs and capabilities of both teams.
The Questionnaire
To ensure that you have a productive interview — which is one of the best ways to collect information for the case study — you'll want to ask the participant to complete a questionnaire before this conversation. That will provide your team with the necessary foundation to organize the interview, and get the most out of it.
The Interview
Once the questionnaire is completed, someone on your team should reach out to the participant to schedule a 30- to 60-minute interview, which should include a series of custom questions related to the customer's experience with your product or service.
The Draft Review
After the case study is composed, you'll want to send a draft to the customer, allowing an opportunity to give you feedback and edits.
The Final Approval
Once any necessary edits are completed, send a revised copy of the case study to the customer for final approval.
Once the case study goes live — on your website or elsewhere — it's best to contact the customer with a link to the page where the case study lives. Don't be afraid to ask your participants to share these links with their own networks, as it not only demonstrates your ability to deliver positive results and impressive growth, as well.
9. Ensure you're asking the right questions.
Before you execute the questionnaire and actual interview, make sure you're setting yourself up for success. A strong case study results from being prepared to ask the right questions. What do those look like? Here are a few examples to get you started:
- What are your goals?
- What challenges were you experiencing before purchasing our product or service?
- What made our product or service stand out against our competitors?
- What did your decision-making process look like?
- How have you benefited from using our product or service? (Where applicable, always ask for data.)
Keep in mind that the questionnaire is designed to help you gain insights into what sort of strong, success-focused questions to ask during the actual interview. And once you get to that stage, we recommend that you follow the "Golden Rule of Interviewing." Sounds fancy, right? It's actually quite simple — ask open-ended questions.
If you're looking to craft a compelling story, "yes" or "no" answers won't provide the details you need. Focus on questions that invite elaboration, such as, "Can you describe ...?" or, "Tell me about ..."
In terms of the interview structure, we recommend categorizing the questions and flowing them into six specific sections that will mirror a successful case study format. Combined, they'll allow you to gather enough information to put together a rich, comprehensive study.
Open with the customer's business.
The goal of this section is to generate a better understanding of the company's current challenges and goals, and how they fit into the landscape of their industry. Sample questions might include:
- How long have you been in business?
- How many employees do you have?
- What are some of the objectives of your department at this time?
Cite a problem or pain point.
To tell a compelling story, you need context. That helps match the customer's need with your solution. Sample questions might include:
- What challenges and objectives led you to look for a solution?
- What might have happened if you did not identify a solution?
- Did you explore other solutions before this that did not work out? If so, what happened?
Discuss the decision process.
Exploring how the customer decided to work with you helps to guide potential customers through their own decision-making processes. Sample questions might include:
- How did you hear about our product or service?
- Who was involved in the selection process?
- What was most important to you when evaluating your options?
Explain how a solution was implemented.
The focus here should be placed on the customer's experience during the onboarding process. Sample questions might include:
- How long did it take to get up and running?
- Did that meet your expectations?
- Who was involved in the process?
Explain how the solution works.
The goal of this section is to better understand how the customer is using your product or service. Sample questions might include:
- Is there a particular aspect of the product or service that you rely on most?
- Who is using the product or service?
End with the results.
In this section, you want to uncover impressive measurable outcomes — the more numbers, the better. Sample questions might include:
- How is the product or service helping you save time and increase productivity?
- In what ways does that enhance your competitive advantage?
- How much have you increased metrics X, Y, and Z?
10. Lay out your case study format.
When it comes time to take all of the information you've collected and actually turn it into something, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. Where should you start? What should you include? What's the best way to structure it?
To help you get a handle on this step, it's important to first understand that there is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to the ways you can present a case study. They can be very visual, which you'll see in some of the examples we've included below, and can sometimes be communicated mostly through video or photos, with a bit of accompanying text.
Here are the sections we suggest, which we'll cover in more detail down below:
- Title: Keep it short. Develop a succinct but interesting project name you can give the work you did with your subject.
- Subtitle: Use this copy to briefly elaborate on the accomplishment. What was done? The case study itself will explain how you got there.
- Executive Summary : A 2-4 sentence summary of the entire story. You'll want to follow it with 2-3 bullet points that display metrics showcasing success.
- About the Subject: An introduction to the person or company you served, which can be pulled from a LinkedIn Business profile or client website.
- Challenges and Objectives: A 2-3 paragraph description of the customer's challenges, before using your product or service. This section should also include the goals or objectives the customer set out to achieve.
- How Product/Service Helped: A 2-3 paragraph section that describes how your product or service provided a solution to their problem.
- Results: A 2-3 paragraph testimonial that proves how your product or service specifically benefited the person or company and helped achieve its goals. Include numbers to quantify your contributions.
- Supporting Visuals or Quotes: Pick one or two powerful quotes that you would feature at the bottom of the sections above, as well as a visual that supports the story you are telling.
- Future Plans: Everyone likes an epilogue. Comment on what's ahead for your case study subject, whether or not those plans involve you.
- Call to Action (CTA): Not every case study needs a CTA, but putting a passive one at the end of your case study can encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
When laying out your case study, focus on conveying the information you've gathered in the most clear and concise way possible. Make it easy to scan and comprehend, and be sure to provide an attractive call-to-action at the bottom — that should provide readers an opportunity to learn more about your product or service.
11. Publish and promote your case study.
Once you've completed your case study, it's time to publish and promote it. Some case study formats have pretty obvious promotional outlets — a video case study can go on YouTube, just as an infographic case study can go on Pinterest.
But there are still other ways to publish and promote your case study. Here are a couple of ideas:
Lead Gen in a Blog Post
As stated earlier in this article, written case studies make terrific lead-generators if you convert them into a downloadable format, like a PDF. To generate leads from your case study, consider writing a blog post that tells an abbreviated story of your client's success and asking readers to fill out a form with their name and email address if they'd like to read the rest in your PDF.
Then, promote this blog post on social media, through a Facebook post or a tweet.
Published as a Page on Your Website
As a growing business, you might need to display your case study out in the open to gain the trust of your target audience.
Rather than gating it behind a landing page, publish your case study to its own page on your website, and direct people here from your homepage with a "Case Studies" or "Testimonials" button along your homepage's top navigation bar.
Format for a Case Study
The traditional case study format includes the following parts: a title and subtitle, a client profile, a summary of the customer’s challenges and objectives, an account of how your solution helped, and a description of the results. You might also want to include supporting visuals and quotes, future plans, and calls-to-action.

Image Source
The title is one of the most important parts of your case study. It should draw readers in while succinctly describing the potential benefits of working with your company. To that end, your title should:
- State the name of your custome r. Right away, the reader must learn which company used your products and services. This is especially important if your customer has a recognizable brand. If you work with individuals and not companies, you may omit the name and go with professional titles: “A Marketer…”, “A CFO…”, and so forth.
- State which product your customer used . Even if you only offer one product or service, or if your company name is the same as your product name, you should still include the name of your solution. That way, readers who are not familiar with your business can become aware of what you sell.
- Allude to the results achieved . You don’t necessarily need to provide hard numbers, but the title needs to represent the benefits, quickly. That way, if a reader doesn’t stay to read, they can walk away with the most essential information: Your product works.
The example above, “Crunch Fitness Increases Leads and Signups With HubSpot,” achieves all three — without being wordy. Keeping your title short and sweet is also essential.
2. Subtitle

Your subtitle is another essential part of your case study — don’t skip it, even if you think you’ve done the work with the title. In this section, include a brief summary of the challenges your customer was facing before they began to use your products and services. Then, drive the point home by reiterating the benefits your customer experienced by working with you.
The above example reads:
“Crunch Fitness was franchising rapidly when COVID-19 forced fitness clubs around the world to close their doors. But the company stayed agile by using HubSpot to increase leads and free trial signups.”
We like that the case study team expressed the urgency of the problem — opening more locations in the midst of a pandemic — and placed the focus on the customer’s ability to stay agile.
3. Executive Summary

The executive summary should provide a snapshot of your customer, their challenges, and the benefits they enjoyed from working with you. Think it’s too much? Think again — the purpose of the case study is to emphasize, again and again, how well your product works.
The good news is that depending on your design, the executive summary can be mixed with the subtitle or with the “About the Company” section. Many times, this section doesn’t need an explicit “Executive Summary” subheading. You do need, however, to provide a convenient snapshot for readers to scan.
In the above example, ADP included information about its customer in a scannable bullet-point format, then provided two sections: “Business Challenge” and “How ADP Helped.” We love how simple and easy the format is to follow for those who are unfamiliar with ADP or its typical customer.
4. About the Company

Readers need to know and understand who your customer is. This is important for several reasons: It helps your reader potentially relate to your customer, it defines your ideal client profile (which is essential to deter poor-fit prospects who might have reached out without knowing they were a poor fit), and it gives your customer an indirect boon by subtly promoting their products and services.
Feel free to keep this section as simple as possible. You can simply copy and paste information from the company’s LinkedIn, use a quote directly from your customer, or take a more creative storytelling approach.
In the above example, HubSpot included one paragraph of description for Crunch Fitness and a few bullet points. Below, ADP tells the story of its customer using an engaging, personable technique that effectively draws readers in.

5. Challenges and Objectives

The challenges and objectives section of your case study is the place to lay out, in detail, the difficulties your customer faced prior to working with you — and what they hoped to achieve when they enlisted your help.
In this section, you can be as brief or as descriptive as you’d like, but remember: Stress the urgency of the situation. Don’t understate how much your customer needed your solution (but don’t exaggerate and lie, either). Provide contextual information as necessary. For instance, the pandemic and societal factors may have contributed to the urgency of the need.
Take the above example from design consultancy IDEO:
“Educational opportunities for adults have become difficult to access in the United States, just when they’re needed most. To counter this trend, IDEO helped the city of South Bend and the Drucker Institute launch Bendable, a community-powered platform that connects people with opportunities to learn with and from each other.”
We love how IDEO mentions the difficulties the United States faces at large, the efforts its customer is taking to address these issues, and the steps IDEO took to help.
6. How Product/Service Helped
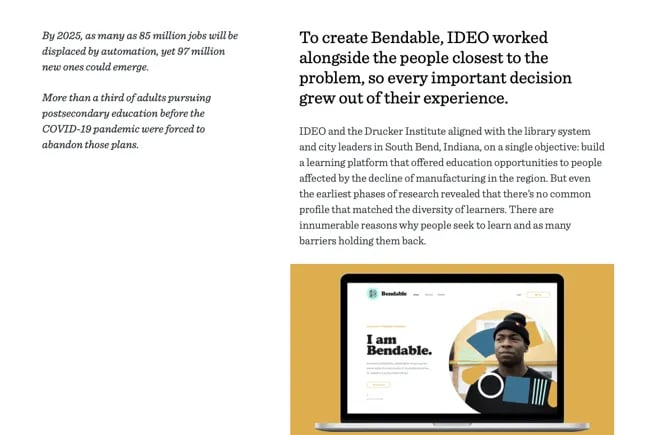
This is where you get your product or service to shine. Cover the specific benefits that your customer enjoyed and the features they gleaned the most use out of. You can also go into detail about how you worked with and for your customer. Maybe you met several times before choosing the right solution, or you consulted with external agencies to create the best package for them.
Whatever the case may be, try to illustrate how easy and pain-free it is to work with the representatives at your company. After all, potential customers aren’t looking to just purchase a product. They’re looking for a dependable provider that will strive to exceed their expectations.
In the above example, IDEO describes how it partnered with research institutes and spoke with learners to create Bendable, a free educational platform. We love how it shows its proactivity and thoroughness. It makes potential customers feel that IDEO might do something similar for them.

The results are essential, and the best part is that you don’t need to write the entirety of the case study before sharing them. Like HubSpot, IDEO, and ADP, you can include the results right below the subtitle or executive summary. Use data and numbers to substantiate the success of your efforts, but if you don’t have numbers, you can provide quotes from your customers.
We can’t overstate the importance of the results. In fact, if you wanted to create a short case study, you could include your title, challenge, solution (how your product helped), and result.
8. Supporting Visuals or Quotes

Let your customer speak for themselves by including quotes from the representatives who directly interfaced with your company.
Visuals can also help, even if they’re stock images. On one side, they can help you convey your customer’s industry, and on the other, they can indirectly convey your successes. For instance, a picture of a happy professional — even if they’re not your customer — will communicate that your product can lead to a happy client.
In this example from IDEO, we see a man standing in a boat. IDEO’s customer is neither the man pictured nor the manufacturer of the boat, but rather Conservation International, an environmental organization. This imagery provides a visually pleasing pattern interrupt to the page, while still conveying what the case study is about.
9. Future Plans
This is optional, but including future plans can help you close on a more positive, personable note than if you were to simply include a quote or the results. In this space, you can show that your product will remain in your customer’s tech stack for years to come, or that your services will continue to be instrumental to your customer’s success.
Alternatively, if you work only on time-bound projects, you can allude to the positive impact your customer will continue to see, even after years of the end of the contract.
10. Call to Action (CTA)
Not every case study needs a CTA, but we’d still encourage it. Putting one at the end of your case study will encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
It will also make it easier for them to reach out, if they’re ready to start immediately. You don’t want to lose business just because they have to scroll all the way back up to reach out to your team.
To help you visualize this case study outline, check out the case study template below, which can also be downloaded here .
You drove the results, made the connection, set the expectations, used the questionnaire to conduct a successful interview, and boiled down your findings into a compelling story. And after all of that, you're left with a little piece of sales enabling gold — a case study.
To show you what a well-executed final product looks like, have a look at some of these marketing case study examples.
1. "Shopify Uses HubSpot CRM to Transform High Volume Sales Organization," by HubSpot
What's interesting about this case study is the way it leads with the customer. This reflects a major HubSpot value, which is to always solve for the customer first. The copy leads with a brief description of why Shopify uses HubSpot and is accompanied by a short video and some basic statistics on the company.
Notice that this case study uses mixed media. Yes, there is a short video, but it's elaborated upon in the additional text on the page. So, while case studies can use one or the other, don't be afraid to combine written copy with visuals to emphasize the project's success.
2. "New England Journal of Medicine," by Corey McPherson Nash
When branding and design studio Corey McPherson Nash showcases its work, it makes sense for it to be visual — after all, that's what they do. So in building the case study for the studio's work on the New England Journal of Medicine's integrated advertising campaign — a project that included the goal of promoting the client's digital presence — Corey McPherson Nash showed its audience what it did, rather than purely telling it.
Notice that the case study does include some light written copy — which includes the major points we've suggested — but lets the visuals do the talking, allowing users to really absorb the studio's services.
3. "Designing the Future of Urban Farming," by IDEO
Here's a design company that knows how to lead with simplicity in its case studies. As soon as the visitor arrives at the page, he or she is greeted with a big, bold photo, and two very simple columns of text — "The Challenge" and "The Outcome."
Immediately, IDEO has communicated two of the case study's major pillars. And while that's great — the company created a solution for vertical farming startup INFARM's challenge — it doesn't stop there. As the user scrolls down, those pillars are elaborated upon with comprehensive (but not overwhelming) copy that outlines what that process looked like, replete with quotes and additional visuals.
4. "Secure Wi-Fi Wins Big for Tournament," by WatchGuard
Then, there are the cases when visuals can tell almost the entire story — when executed correctly. Network security provider WatchGuard can do that through this video, which tells the story of how its services enhanced the attendee and vendor experience at the Windmill Ultimate Frisbee tournament.
5. Rock and Roll Hall of Fame Boosts Social Media Engagement and Brand Awareness with HubSpot
In the case study above , HubSpot uses photos, videos, screenshots, and helpful stats to tell the story of how the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame used the bot, CRM, and social media tools to gain brand awareness.
6. Small Desk Plant Business Ups Sales by 30% With Trello
This case study from Trello is straightforward and easy to understand. It begins by explaining the background of the company that decided to use it, what its goals were, and how it planned to use Trello to help them.
It then goes on to discuss how the software was implemented and what tasks and teams benefited from it. Towards the end, it explains the sales results that came from implementing the software and includes quotes from decision-makers at the company that implemented it.
7. Facebook's Mercedes Benz Success Story
Facebook's Success Stories page hosts a number of well-designed and easy-to-understand case studies that visually and editorially get to the bottom line quickly.
Each study begins with key stats that draw the reader in. Then it's organized by highlighting a problem or goal in the introduction, the process the company took to reach its goals, and the results. Then, in the end, Facebook notes the tools used in the case study.
Showcasing Your Work
You work hard at what you do. Now, it's time to show it to the world — and, perhaps more important, to potential customers. Before you show off the projects that make you the proudest, we hope you follow these important steps that will help you effectively communicate that work and leave all parties feeling good about it.
Editor's Note: This blog post was originally published in February 2017 but was updated for comprehensiveness and freshness in July 2021.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![case study partnership examples 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/most%20popular%20types%20of%20content.jpg)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]
![case study partnership examples How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]

28 Case Study Examples Every Marketer Should See
![case study partnership examples What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

Partnership Marketing: Definition, Case Studies & Impact
With partnership marketing , two or more companies team up to create marketing campaigns that help them grow organically with a mutual agreement, thus making it possible to reach shared business goals. Partnership marketing leverages the time and resources of partners that help them expand their market.
Table of Contents
Why and when partnership marketing makes sense
Partnership marketing can be a great way to grow a business in several circumstances. As financial resources might be scarce and a company wants to grow more organically, partnership marketing can help in forming long-term relationships to expand overnight the market of your company.
In short, partnership marketing can be the most effective organic growth strategy as an alternative to other paid channels.
The Pinterest Shopify’s app case study
Announcing our new channel partnership with our friends at @Pinterest ! Get @Shopify products in front of 350m+ Pinners for free with shoppable Pins and shop profile tabs, plus buy shopping ads all from one app. 📍 https://t.co/IHmw7xN8yi — Satish Kanwar (@skanwar) May 7, 2020
The Pinterest app on Shopify is a great example of how partnerships can be used as a win-win-win.
Both companies (Shopify and Pinterest) can gain from the partnership. And as effect also its main partners (e-commerce websites on Shopify, users on Pinterest).
Indeed, Shopify makes it even easier for its e-commerce websites to directly post their product listing on Pinterest, thus expanding each of its products.
At the same time, Pinterest benefits by gaining more active users and by enabling more curated images on the platform, which makes it more valuable for Pinterest users. And in turn, the company would be able to sell more advertising.
As specified on the Pinterest blog:
The Pinterest app on Shopify includes a suite of shopping features like tag installation, catalog ingestion, automatic daily updating of products, and an ads buying interface.

As further explained on the Pinterest blog:
By uploading their catalog feed, merchants make it possible for people to discover and save their products and buy directly from their website. People come to Pinterest with an intent to plan and purchase.


In a well-executed Partnership Marketing agreement, everyone wins
As we saw, partnership marketing can be a great way to organically growt a business while simultaneously expanding its boundaries, as partners can draw from each other’s markets to add more value to their existing audience.
A well-executed partnership marketing plan then adds value for everyone!
The Pinterest-Shopify Partnership Two Years Later
It’s always interesting to look at how partnerships evolve.
Building effective partnerships is not a simple task.
So how did eventually go the partnership between Pinterest and Shopify?
After two years after its launch, the partnership expanded across many other countries.
As of June 2022, Pinterest and Shopify expanded the discoverability feature to 29 markets and 450+ million users!
Key Highlights
- Partnership Marketing Overview : Partnership marketing involves collaboration between two or more companies to create marketing campaigns that leverage each other’s resources and reach to achieve shared business goals. It’s a strategy for organic growth and expanding markets.
- Benefits and Scenarios : Partnership marketing is effective in situations where a company wants to grow organically with limited financial resources. It forms long-term relationships and allows businesses to tap into each other’s markets, providing an alternative to paid advertising channels.
- Pinterest Shopify App Case Study : The partnership between Pinterest and Shopify is highlighted as an example of successful partnership marketing . Both companies benefit, as do their primary users (e-commerce websites on Shopify and users on Pinterest). The app allows Shopify sellers to easily showcase products on Pinterest, expanding their reach, while Pinterest gains more active users and valuable content.
- Shopify’s Pinterest App : The Pinterest app on Shopify facilitates shopping features, including product tagging, catalog integration, daily updates of products, and an ad buying interface. Merchants uploading their catalog feed can benefit from Pinterest’s user intent to plan and purchase.
- Win-Win-Win Situation : Partnership marketing , when executed well, benefits all parties involved. Partners can tap into each other’s markets, adding value to their audiences and expanding their boundaries, resulting in mutual growth.
- Pinterest-Shopify Partnership’s Progress : The partnership between Pinterest and Shopify evolved positively. After two years, it expanded to many other countries and markets, reaching over 450 million users in 29 markets by June 2022.
Other Case Studies
Related visual stories.
Shopify Business Model

Shopify Cost Structure

Shopify Profitability

Shopify Revenue

Shopify Merchants

Shopify Competitors

Visual Marketing Glossary
Account-Based Marketing

AARRR Funnel

Affinity Marketing

Ambush Marketing

Affiliate Marketing

Bullseye Framework

- Brand Building

Brand Dilution

Brand Essence Wheel

- Brand Equity

Brand Positioning

Business Storytelling

Content Marketing

Customer Lifetime Value

- Customer Segmentation

Developer Marketing

Digital Marketing Channels

Field Marketing

Funnel Marketing

Go-To-Market Strategy

Greenwashing

Grassroots Marketing

Growth Marketing

Guerrilla Marketing

Hunger Marketing

Integrated Communication

Inbound Marketing

Integrated Marketing

Marketing Mix

Marketing Myopia

Marketing Personas

Meme Marketing

Microtargeting

Multi-Channel Marketing

Multi-Level Marketing

Net Promoter Score

Neuromarketing

Newsjacking

Niche Marketing

Push vs. Pull Marketing

Real-Time Marketing

Relationship Marketing

Reverse Marketing

Remarketing

Sensory Marketing

Services Marketing

Sustainable Marketing

Word-of-Mouth Marketing

360 Marketing

- Market Segmentation
- Brand Awareness
- Types of Business Models You Need to Know
- Business Strategy: Definition, Examples, And Case Studies
- Marketing Strategy: Definition, Types, And Examples
- Platform Business Models In A Nutshell
- Network Effects In A Nutshell
- Gross Margin In A Nutshell
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- 70+ Business Models
- Airbnb Business Model
- Amazon Business Model
- Apple Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Facebook [Meta] Business Model
- Microsoft Business Model
- Netflix Business Model
- Uber Business Model
Jump to navigation

Cochrane Training
Case studies in partnerships.

Here you will find a series of case studies of partnerships in action within a range of Cochrane Groups. These talk about the background to the partnership, its development, the benefit to both sides and tips for Groups.
If you have examples of partnership work that you would like to share, please contact Cochrane KT Department .
Cancer Review Group Network identifies potential stakeholders across the network in a mapping exercise

Cochrane Airways and a UK based charity, Asthma UK
Cochrane oral health and their global alliance of partners, cochrane rehabilitation and various national societies of rehabilitation medicine, cochrane rehabilitation and the international society of physical and rehabilitation medicine, cochrane child health and trekk (translating emergency knowledge for kids).
Partner(s): TREKK, a Canadian organisation committed to improving emergency care for children and families across Canada. Partnership activities: identification of high quality evidence and development of KT tools for healthcare practitioners and parents, made available through the TREKK website. Type of partnership agreement: formal Date: 2018 Read more
Further examples
Here you can find links to a range of further examples of partnerships taking place across Cochrane.
Partnership for priority setting
- Neuro-Oncology Group Priority Setting Partnership
- Developing a research agenda for ENT, Hearing and Balance Care
Partnership for review dissemination
- BMJ partners with Cochrane Clinical Answers to boost knowledge at the point of care
- Cochrane UK partnership with Mediwikis
- Cochrane Airways working with Sense about Science
Partnership for guideline development
- Cochrane Eyes and Vision partnering with American Academy of Ophthalmology
- South African Guidelines Excellence project
- Cochrane Incontinence: working with guideline developers
Partnership for consumer engagement
- Consumers United for Evidence-Based Healthcare (CUE)
- PartecipaSalute : Involving patients, citizens and their association in research
- Consumer/patient engagement Cochrane Child Health
Improving the management of complex business partnerships
Partnerships never go out of style. Companies regularly seek partners with complementary capabilities to gain access to new markets and channels, share intellectual property or infrastructure, or reduce risk. The more complex the business environment becomes—for instance, as new technologies emerge or as innovation cycles get faster—the more such relationships make sense. And the better companies get at managing individual relationships, the more likely it is that they will become “partners of choice” and able to build entire portfolios of practical and value-creating partnerships.
Of course, the perennial problems associated with managing business partnerships don’t go away either—particularly as companies increasingly strike relationships with partners in different sectors and geographies. The last time we polled executives on their perceived risks for strategic partnerships, 1 Observations collected in McKinsey’s 2015 survey of more than 1,250 executives. Sixty-eight percent said they expect their organizations to increase the number of joint ventures or large partnerships they participate in over the next five years. A separate, follow-up survey in 2018 showed that 73 percent of participants expect their companies to increase the number of large partnerships they engage in. the main ones were: partners’ disagreements on the central objectives for the relationship, poor communication practices among partners, poor governance processes, and, when market or other circumstances change, partners’ inability to identify and quickly make the changes needed for the relationship to succeed (exhibit).
In our work helping executive teams set up and navigate complex partnerships, we have witnessed firsthand how these problems crop up, and we have observed the different ways companies deal with them . The reality is: successful partnerships don’t just happen. Strong partners set a clear foundation for business relationships and nurture them. They emphasize accountability within and across partner companies, and they use metrics to gauge success. And they are willing to change things up if needed. Focusing on these priorities can help partnerships thrive and create more value than they would otherwise.
Establish a clear foundation
It seems obvious that partner companies would strive to find common ground from the start—particularly in the case of large joint ventures in which each side has a big financial stake, or in partnerships in which there are extreme differences in cultures, communications, and expectations.
Yet, in a rush to complete the deal, discussions about common goals often get overlooked. This is especially true in strategic alliances within an industry, where everyone assumes that because they are operating in the same sector they are already on the same page. By skipping this step, companies increase the stress and tension placed on the partnership and reduce the odds of its success. For instance, the day-to-day operators end up receiving confusing guidance or conflicting priorities from partner organizations.
Would you like to learn more about our Strategy & Corporate Finance Practice ?
How can the partners combat it? The individuals expected to lead day-to-day operations of the partnership, whether business-unit executives or alliance managers, should be part of negotiations at the outset. This happens less often than you think because business-development teams and lawyers are typically charged with hammering out the terms of the deal—the objectives, scope, and governance structure—while the operations piece often gets sorted out after the fact.
Transparency during negotiations is the only way to ensure that everyone understands the partners’ goals (whether their primary focus is on improving operations or launching a new strategy) and that everyone is using the same measures of success. Even more important, transparency encourages trust and collaboration among partners, which is especially important when you consider the number of executives across the organizations who will likely rotate in and out of leadership roles during the life of the relationship.
Inevitably, points of tension will emerge. For instance, companies often disagree on financial flows or decision rights. But we have seen partners articulate such differences during the negotiation period, find agreement on priorities, and reset timelines and milestones. They defused much of the tension up front, so when new wrinkles—such as market shifts and changes in partners’ strategies—did emerge, the companies were more easily able to avoid costly setbacks and delays in the business activities they were pursuing together.
Nurture the relationship
Even business relationships that start off solidly can erode, given individual biases and common communication and collaboration issues. There are several measures partners can take to avoid these traps.
Connect socially
If executives in the partner organizations actively look for opportunities to understand one another, good collaboration and communication at the operations level are likely to follow. Given time and geographic constraints, it can be hard for them to do so, but as one energy-sector executive who has negotiated and managed dozens of partnerships noted, “It’s important to spend as much time as you can on their turf.” He says about 30 to 40 percent of partnership meetings are about business; the rest of the time is spent building friendships and trust.
Keep everyone in the loop
Skipping the step of keeping everyone informed can create unnecessary confusion and rework for partner organizations. That is what happened in the case of an industrial joint venture: the first partner in the joint venture included a key business-unit leader in all venture-related discussions. The second partner apprised a key business-unit leader about major developments, but this individual did not actually join the discussions until late in the joint-venture negotiation. At that point, as he learned more about the agreement, he flagged several issues, including inconsistencies in the partners’ access to vendors and related data. He immediately recognized these issues because they directly affected operations in his division. Because he hadn’t been included in early discussions, however, the partners wasted time designing an operating model for the joint venture that would likely not work for one of them. They had to go back to the drawing board.
Recognize each other’s capabilities, cultures, and motivations
Partners come together to take advantage of complementary geographies, corresponding sales and marketing strengths, or compatibilities in other functional areas. But it is important to understand which partner is best at what . This process must start before the deal is completed—but cannot stop at signing. In the case of one consumer-goods joint venture, for instance, the two partner organizations felt confident in their plan to combine the manufacturing strength of one company with the sales and marketing strengths of the other. During their discussions on how to handle financial reporting, however, it became clear that the partner with sales and marketing strengths had a spike in forecasting, budgeting, and reporting expertise. The product team for the first partner had originally expected to manage these finance tasks, but both partner teams ultimately agreed that the second partner should take them on. In this way, they were able to enhance the joint venture’s ongoing operations and ensure its viability.
Equally important is understanding each partner’s motivation behind the deal. This is a common point of focus during early negotiations; it should continue to be discussed as part of day-to-day operations—particularly if there are secondary motivators, such as access to suppliers or transfer of capabilities, that are important to each partner. Within one energy-sector partnership, for instance, the nonoperating partner was keen to understand how its local workforce would receive training over the course of the partnership. This company wanted to enhance the skills of the local workforce to create more opportunities for long-term employment in the region. The operating partner incorporated training and skill-evaluation metrics in the venture’s quarterly updates, thus improving the companies’ communication on the topic and explicitly acknowledging the importance of this point to its partner.
Invest in tools, processes, and personnel
Bringing different business cultures together can be challenging, given partners’ varying communication styles and expectations. The good news is that there are a range of tools—among them, financial models, key performance indicators, playbooks, and portfolio reviews—companies can use to help bridge any gaps. And not all these interventions are technology dependent. Some companies simply standardize the format of partnership meetings and agendas so that teams know what to expect. Others follow stringent reporting requirements.
Another good move is to convene an alliance-management team. This group tracks and reviews the partnership’s progress against defined metrics and helps to spot potential areas of concern—ideally with enough time to change course. Such teams take different forms. One pharmaceutical company with dozens of commercial and research partnerships has a nine-member alliance-management team charged mostly with monitoring and flagging potential issues for business-unit leaders, so it consists of primarily junior members and one senior leader who interacts directly with partners. An energy company with four large-scale joint ventures has taken a different approach: its alliance-management team comprises four people, but each is an experienced business leader who can serve as a resource for the respective joint-venture-leadership teams.
Sometimes partnerships need a structural shake-up—and not just as an act of last resort.
How companies structure these teams depends on concrete factors—the number and complexity of the partnerships, for instance—as well as intangibles like executive support for alliances and joint ventures and the experiences and capabilities of the individuals who would make up the alliance-management team.
Emphasize accountability and metrics
Good governance is the linchpin for successful partnerships; as such, it is critical that senior executives from the partner organizations remain involved in oversight of the partnership. At the very least, each partner should assign a senior line executive from the company to be “deal sponsor”—someone who can keep operations leaders and alliance managers focused on priorities, advocate for resources when needed, and generally create an environment in which everyone can act with more confidence and coordination.
Additionally, the partners must define “success” for their operations teams: What metrics will they use to determine whether they have hit their goals, and how will they track them? Some companies have built responsibility matrices; others have used detailed process maps or project stage gates to clarify expectations, timelines, and critical performance measures. When partnerships are initially formed, it is usually the business-development teams that are responsible for building the case for the deal and identifying the value that may be created for both sides. As the partnership evolves, the operations teams must take over this task, but they will need ongoing guidance from senior leaders in the partner organizations.
Build a dynamic partnership
Sometimes partnerships need a structural shake-up—and not just as an act of last resort. For instance, it might be less critical to revisit the structure of a partnership in which both sides are focused on joint commercialization of complementary products than it would be for a partnership focused on the joint development of a set of new technologies. But there are some basic rules of thumb for considering changes in partnership structure.
Partner organizations must acknowledge that the scope of the relationship is likely to shift over time. This will be the case whether the partners are in a single- or multiasset venture, expect that services will be shared, anticipate expansion, or have any geographic, regulatory, or structural complexities. Accepting the inevitable will encourage partners to plan more carefully at the outset. For example, during negotiations, the partners in a pharmaceutical partnership determined that they had different views on future demand for drugs in development. This wasn’t a deal breaker, however. Instead, the partners designated a formula by which financial flows would be evaluated at specific intervals to address any changes in expected performance. This allowed the partners to adjust the partnership based on changes in market demand or the emergence of new products. All changes could be incorporated fairly into the financial splits of the partnership.

Avoiding blind spots in your next joint venture
Partners should also consider the potential for restructuring during the negotiation process—ideally framing the potential endgame for the relationship. What market shifts might occur, how might that affect both sides’ interests and incentives, and what mechanisms would allow for orderly restructuring? When one oil and gas joint venture began struggling, the joint-venture leader realized he was being pulled in opposing directions by the two partner companies because of the companies’ conflicting incentives. “It made the alliance completely unstable,” he told us. He brought the partners back to the negotiation table to determine how to reconcile these conflicting incentives, restructure their agreement, and continue the relationship, thus avoiding deep resentment and frustration on both sides of the deal.
Such dialogues about the partnership’s future, while potentially stressful, should be conducted regularly—at least annually.
The implementation of these four principles requires some forethought and care. Every relationship comes with its own idiosyncrasies, after all, depending on industry, geography, previous experience, and strategy. Managing relationships outside of developed markets, for instance, can present additional challenges involving local cultures, integration norms, and regulatory complexities. Even in these emerging-market deals, however, the principles can serve as effective prerequisites for initiating discussions about how to change long-standing practices and mind-sets.
An emphasis on clarity, proactive management, accountability, and agility can not only extend the life span of a partnership or joint venture but also help companies build the capability to establish more of them—and, in the process, create outsize value and productivity in their organizations.
Ruth De Backer is a partner in McKinsey’s New York office, where Eileen Kelly Rinaudo is a senior expert.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Joint ventures on the rise

M&A as competitive advantage

Partnership Marketing: The Ultimate Guide for 2024
Partnership marketing is a broad term for several collaborative marketing techniques, including affiliate marketing, influencer marketing, loyalty marketing, cross-promotion, joint product developments, and more!
All these techniques are incredibly effective if you have the right partners, and choose the right type of partnership marketing, for your objectives.
But which partnership marketing strategy is the right one for your brand? And how do you find the right partners to collaborate with?
How do you implement your partnership marketing strategy and manage all your partners?
It can be challenging to answer these questions, especially when there are so many different types of partnership marketing, and so many different techniques to use.
Today, we’re covering everything you need to know about partnership marketing and how to make it work for you!
In this guide, we go over what partnership marketing is, the different types of partnership marketing, the benefits, and how to find and choose the best partners.
We also review some of the best partnership marketing software and look at some real-life partnership marketing examples.
To demonstrate just how successful partner marketing can be, we have a case study provided by the award-winning experts at Acceleration Partners , a leading, global, partnership marketing agency!
Let’s get right into it!
Skip to What You Need
What is Partnership Marketing?
Partnership marketing (sometimes called partner marketing) is collaboration between parties that benefits both entities and helps them achieve their business and marketing objectives. These objectives range from increased brand awareness, recognition and credibility, to lead generation, sales and business growth.
There are many types of partnership marketing (more on those below) and partnerships can be between two brands or between an individual and a brand, or even two individuals.
Some of the most well known marketing partnerships include affiliate partners who promote a brand on their own platforms in exchange for a commission on the sales or actions they generate, and influencers who promote a brand on their channel in exchange for payment or a sample product that they can unbox, test and review – creating valuable content for their channel.
The main goal or objective of partnership marketing is for two entities to join forces in a strategic marketing collaboration that benefits them both and helps them reach their respective objectives.
DEFINITION: WHAT IS PARTNERSHIP MARKETING?
Partnership marketing (sometimes called partner marketing) can be defined as a strategic marketing collaboration between parties that benefits both entities and helps them achieve their business and marketing objectives. These objectives range from increased brand awareness, recognition and credibility to content creation, lead generation, sales and business growth.
Partnership Marketing vs Business Partnerships – What is the Difference?
Business partnerships are usually formal, legal agreements between parties. For example, when two law firms merge or one company partners with another to provide a combined service or product. These types of partnerships involve a lot of red tape, think contracts, taxes, registrations, levels of liability etc. and are usually permanent or long-term agreements.
Partnership marketing, on the other hand, can be much less formal and may not involve any kind of legal agreements, tax complications or even an exchange of money. While we call it partnership marketing, and there are formalized types of partnership marketing, it is often a much looser agreement, or collaboration between parties.
The aim is to achieve marketing objectives that can be difficult to quantify, for example, a collaboration may lead to improved brand awareness, credibility and trust, but these benefits may not have any immediate impact on revenue.
This is why many marketing partnerships are measured in terms of actions taken or impressions, rather than a sales commission that relies on an immediate impact on sales.
In some cases, like when two influencers collaborate to jointly create new content, there is no exchange of money, no agreement and the collaboration may be a spontaneous, once-off event with no paperwork or agreement at all.

What Are the Main Types of Partnership Marketing?
There is a range of different types of partnership marketing approaches to choose from. According to Acceleration Partners , it is vital to choose the right type of partnership (and the right partners) to be successful.
Let’s take a quick look at some of the most popular strategies:
- Affiliate Marketing: a mutually-beneficial strategy that involves collaboration with a publisher, such as a blogger or an influencer, who will advertise and promote your product or service to their respective audience.
- Influencer Marketing: when an influencer or industry expert markets the brand’s product/service to their followers in exchange for a fee or free products/perks or upgrades. Influencers also benefit from creating content for the brand, as it forms part of their channel’s content and adds value for their followers.
- Loyalty Marketing: when a brand offers incentives to its customers to buy more frequently or spend more with a formalized program to earn points and receive benefits like discounts or a free product after x purchases.
- Distribution Partnership Marketing: when a certain brand will bundle up another brand’s products or services with their own products or services, as a package deal, and the brands then benefit from reaching each other’s distribution networks.
- Referral Marketing: referral programs are similar to affiliate and loyalty marketing, where a brand partners with people who will refer people to the brand in exchange for an incentive, reward, or commission.
- Cross-Promotion Marketing: when partners promote each other to their particular audiences through a joint marketing campaign that promotes the other’s product/service.
- Sponsorships: when a brand publicly sponsors the second party in exchange for visibility and views. Sponsors can sponsor events, public figures like athletes or musicians, or content creators, their channels, or individual pieces of content like a specific YouTube video by a popular creator.
- Product Placements: when a clearly branded product is used in a TV show or movie and the scene places emphasis on the product or brand, ensuring that viewers see it being used by a beloved character in the show.
- Co-branding: when two brands come together to create a co-branded product or upgrade, like the Apple Watch Nike Edition.
- Content Marketing: when a brand has their product placed in content like blogs, videos, and social media posts to promote their products in a natural and relevant way.
- Licensing: when a brand allows another brand to make and market a product under its branding. For example, Netflix and Ben & Jerry’s “Netflix and Chill’d” ice-cream edition.
How to Choose the Right Partnership Marketing Partners
When you decide to give partnership marketing a go, take your time and find the right strategic partners – it will make all the difference to your experience, and the success of your partnership marketing!
According to Acceleration Partners, choosing the best strategic partners for your partnerships is essential. Look for partners that are complementary to your brand in terms of both their products/service s and their values . Aim to create relationships that will last, with partners that share your business and ethical values, as well as being a good fit for your products and your audience.
Your partners will reflect on you, and you will reflect on them, so do your homework and choose them wisely!
Not everyone will make a great partner. But even if the people you connect with aren’t right choice for your partnership marketing, looking for partners can still be a productive exercise. Expanding your existing network and making new contacts that are relevant to your brand and marketing may lead to other valuable opportunities.

Now let’s take you through some of the key steps of selecting the right marketing partner:
- Define Your Marketing Objectives
Before you start searching for a partner, make sure that you have clearly articulated what your brand wants to achieve through your potential business partnership .
Your objectives will inform the type of partnership marketing that will be the most beneficial for you. Choosing the right type of partner and right type of partnership collaboration will make a huge difference to the results you’re able to achieve.
Once you have set up your partnership, you can assess whether the relationship is meeting these objectives and how you can improve things or change things as needed.
Find a Company With Common Ground
This common ground must include a very similar audience to your company. This is very important, as this could lead to future problems if this is not clearly defined from the start. In essence, their target audience must be in the same sector and industry as your target audience.
Additional common ground includes having similar values to your company. This will ensure that you both can build on a similar foundation.
It is also worth offering products or services that are complementary to one another.
You can find potential partners for your partnership marketing through:
- Google search
- Social media searches and industry related hashtags
- Online forums in your niche
- Business directories
- Tradeshows and conventions
- Networking events online and in person
- Affiliate and influencer platforms and marketplaces
Once you have selected some potential partners, research them before you reach out so that you can weed out any partners that will obviously be a poor fit. Once you have narrowed it down, find out who the right person to speak to is and reach out to them directly.
From there, focus on building a relationship that is mutually beneficial and be clear about the value you can offer them, as well as what you want in return.
Here are the next steps to follow, and what to consider when you’re choosing a partnership marketing partner, in more detail:
Research, Research and More Research
And, you guessed it, more research! When it comes to finding a great partner, this is when research counts a great deal. Whatever a potential partner does in the future, will reflect either positively on negatively on your brand, so this is an important decision for you to make.
Start by reading up on all the reviews you can find of the companies that spark your interest. Then be sure to ask for references. Try to get an opinion from an outside third party on what they think of the partner you are planning to approach.
And finally, ask to see their buyer persona. It will also be an advantage if you have your own to provide to potential partners.
- Identify Any Potential Conflicts of Interest
Once you have found a company with more common ground than other companies, it is good to start identifying if there are any potential conflicts that may arise. For starters, avoid a brand that will result in direct competition to your brand.
You will also need to determine who would own particular leads? And how would the profits be shared? Make sure that all these matters are ironed out early on.
Define Fair Expectations, an Even Workload Spread and a Clear Agreement
Make sure that you both clearly articulate the responsibilities for each partner and what the expected outcomes are for each of those responsibilities.
It’s no good being ‘wishy-washy’ when it comes to responsibilities, and each partner must receive an equal share. This means that both parties must input the same amount of time and resources to get their jobs done.
Partnerships of all kinds work best when there is a clear agreement between parties, that sets out who is responsible for what, timeframes, contingences for unexpected delays or roadblocks along the way, as well as what happens of either party fails to deliver what they’re responsible for, and how assets like contact lists, leads etc. will be handled when the partnership ends.
- Play to Your Specific Strengths
While it is good to have an equal share of responsibilities, it is not necessary to split them right down the middle.
Simply make sure that each partner is able to use their particular expertise or strengths in the relationship. Both of you will be specialists in certain areas, so make sure you focus on those strengths unique to you.
- Develop a Feedback Loop
It’s important that a space is created where feedback can be provided. So ensure that you and your various stakeholders gather together on a regular basis to talk over how things are going.
It will also be good to give each stakeholder a turn to chair the meeting. Basically everyone needs to feel heard.
Define How Results Will Be Tracked and Measured
It’s important to identify and track your progress against your objectives as closely and accurately as possible. Decide which metrics will be measured, and how, ahead of time so that there can be no disagreement or dispute of the results down the line.
Make sure that your goals are measurable and that you define how long you will track progress, and how often you will evaluate your progress.
- Create that Personal Touch and Focus on Building a Relationship
While it is about business, it’s also about a personal relationship. Take the time to get to know your partners – who are they, what are their likes and dislikes? Their values? What’s their pet’s name?
This might sound odd, but it’s always worth having that personal connection when it comes to business. This might just be the glue that holds it all together!
SUMMARY: HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT PARTNERS FOR PARTNERSHIP MARKETING
- Find a Company with Common Ground
- Do a Lot of Research
- Define Fair Expectations, an Even Workload Spread and a Clear Agreement
1 Partnership Marketing Case Study
Partnership marketing involves two entities working together so that they both benefit from the collaboration.
The purpose of marketing partnerships is to build brand awareness for both entities, increase sales/engagement and provide their target audience/s with additional value by joining forces.
Let’s take a look at a partnership marketing case study (and then some partnership marketing examples from brands you know) to see just how successful it can be:
Case Study: Reebok Loyalty Affiliate Campaign Results in 161% (YoY) Revenue Increase
Despite an initial rise, fitness, and lifestyle apparel brand Reebok saw a marked drop in orders during the Covid-19 pandemic. To combat this and gain new customers, Reebok turned to Acceleration Partners , a leading partnership marketing agency.
Their objectives were to:
- Gain new customer revenue through a targeted campaign with a loyalty affiliate;
- Increase average order value (AOV) from new customers; and
- Engage previous customers to bolster lifetime value and brand loyalty.
Acceleration Partners developed a strategic two-week campaign with Cartera, a leading loyalty program provider that works strategically with banks and airlines.
Choosing Cartera and the type of partners they work with was a crucial component of the campaign, which proved to be incredibly successful.
With Cartera, Reebok was able to join forces with a major U.S. airline. The carefully targeted campaign included a limited-time bonus, where qualifying purchases of at least $100 with Reebok gave consumers 500 bonus points, which were applied as bonus miles for the airline.
Promoting the campaign included homepage placements on the airline’s homepage and a newsletter from Cartera announcing the Reebok bonus offer to all airline loyalty members.
While the campaign targeted just one airline, it created a halo effect that resulted in a 38% increase in revenue from other programs on Cartera.
Acceleration Partner’s approach revolved around strategically identifying a valuable media placement opportunity, precise audience targeting, and choosing the best loyalty affiliate partner for the campaign.
Each of these elements was carefully considered, and the solutions strategically selected, which lead to impressive results from just a two-week campaign:
- 161% increase in revenue YoY from Cartera
- 329% increase in clicks YoY from Cartera
- 143% increase in new customer revenue YoY from Cartera
- 49% increase in AOV YoY from Cartera
These results took Reebok back to, and surpassed their pre-pandemic order volume and revenue.
4 Successful Partnership Marketing Examples
As you can see from the case study above, partnership marketing done right can rapid drive growth and provide a significant bump in revenue, as well as set you up for long-term success with dynamic on-going partnerships.
The best marketing partnerships are between brands that share an audience in terms of their audience’s values and desires, as well as demographics.
Here are some partnership marketing examples from popular brands you know (and maybe love) that really leveraged their shared audiences’ values and passions:
1. BMW and Louis Vuitton
The marketing partnership between BMW and Louis Vuitton is a great example of brand giants coming together for a joint purpose. Both of their types of customers travel frequently and strive for exclusivity, luxury and comfort, so what better way to target their audience than co-branding their retail products?

These two created a four-piece luggage collection, retailing for $20 000, which was designed to fit perfectly into the trunk of the BMW i8. This is a great example of an innovative marketing partnership that leveraged their shared audiences values and desires to cross-promote their core product offerings to a shared audience.
2. AirBnb & Flipboard
I bet most of you have heard of Airbnb, but not as many will know about the social network aggregator, Flipboard. In this partnership marketing example , these two got together to create new content and in turn promoted each other to each of their (overlapping) audiences.

Thanks to their collaboration with Airbnb, Flipboard was able to greatly increase their number of users and Airbnb was able to generate valuable brand awareness, engagement and marketing content.
3. H&M and Balmain
Over the years the Swedish retailer H&M have been known to collaborate with a number of different luxury fashion designers. Perhaps the best example is when they partnered with the Balmain clothing collection in 2015.
This collaborative clothing collection was launched onto the H&M website and their brick and mortar stores, which had queues that could be seen far and wide.
Every year H&M collaborates with these types of designer brands, allowing their customers to pay for designer clothing items at a fraction of the price. Now that’s a win win partnership!
By collaborating with a highly desirable designer/brand, H&M was able drive a massive sales by using the desirability of Balmain products from consumers who would not normally be able to afford or access such a high-end brand.
Balmain benefitted from a huge amount of awareness and buzz around their brand that reached H&M’s huge audience of people who value high-fashion brands.
4. Red Bull and GoPro
Back in 2012, when the novelty of GoPro was a really big deal, they partnered with Red Bull to support Australian skydiving legend, Felix Baumgartner. Here the two brands collaborated to capture his record-breaking jump from a 24 mile high balloon.
GoPro: Red Bull Stratos – The Full Story :
This turned out to be quite the enthralling take, captured on GoPro, and both brands received a great deal of exposure through this partnership.
These partnership marketing examples demonstrate how brands can join forces and generate huge value in terms of brand awareness, engagement, anticipation/buzz, content marketing, user generated content AND sales!
9 Great Partnership Marketing Benefits

There are many significant benefits to partnership marketing and here are some of them:
1. Branching into New Markets
Partnering with another brand that has a presence in a particular region, area or niche, will enable you to reach a new market, that you wouldn’t have been able to reach before.
This opens up new opportunities for growth and greater productivity for your brand.
You can also sit back and enjoy the benefits of a customer base that will more easily trust your brand, due to the trust they already have for your partner.
You will be marketing to an audience that will already be interested in the kinds of things you offer. This can maximize your marketing efforts, with the least amount of input.
2. Providing Fresh Perspectives
By working with a marketing partner, you will be exposing yourself and your team to some different and new outlooks on marketing.
Perhaps there are a few gaps that you might have missed that need improvement? Or maybe there’s something completely out of the ordinary that you hadn’t thought of before?
The great advantage of partner marketing is that each partner can use it as an opportunity to learn from each other and to gather wisdom from each other’s strengths and weaknesses.
3. More Cost-effective than Traditional Marketing Channels
It’s worth keeping in mind that the industry is moving closer to a pay-per-performance model, and away from a pay-per-ad and impression model.
So in the case of partnership marketing, it will now be easier to measure your ROI based on how a particular post performs, as opposed to measuring social media metrics, such as likes, shares and comments etc. This will be more relevant to the affiliate partnership marketing strategy.
For some partner strategies a swap can also be included, which can save costs and benefit both partners.
Partnership marketing also requires less financial risk on your part, as only a small fee or commission will be required. This will be more relevant to the affiliate type of partnership marketing.
4. Provides You with a Support System
It is comforting from time to time to know that you are not alone in the marketing game!
When you succeed, your partner succeeds with you and this just highlights how mutually beneficial this type of marketing relationship is.
The true benefit comes when you find a partner who is open and communicates clearly with you from the start.
5. Targeting Customers at the Ideal Time
Through cross-promotion, you are more likely to be noticed when a customer makes a purchase from your partner and stumbles across your brand at the same time.
The timing couldn’t have been more perfect!
For example, when driving with Uber you can tune into Spotify and listen to songs through them while driving. And when booking flights, you might also notice a hotel ad popping up and recommendation a stay with them near your destination.
The opportunities are endless!
6. Delivering Added Value to Your Brand
When partnering with a trusted brand, you will be adding greater value to your existing brand.
Whether it’s through developing new content, making necessary improvements or doing a content swap, customers are more likely to take notice and to become more attracted to your brand.
It can only be beneficial when you open up new avenues of interest and strive to enrich your brand even more than before.
7. Building Your Brand Identity
Partnerships open up the opportunity of brand association.
For smaller brands, partnering with a larger brand means they will be able to reach a much wider audience. On the flip side, a larger brand can benefit by reaching a more specific, niche audience, by partnering with a smaller brand.
It’s through these types of partnerships, that customers might begin to associate better with your brand, if they see you partnering with a unique or more popular brand.
8. Providing Unique and Innovative Solutions
Partnership marketing is a great way for two complementary products/services to join forces and provide an innovative new solution. By drawing on each other’s strengths they can provide a more comprehensive product/service, or package, which often leads to the development of an entirely new solution.
9. Growth and Increased Revenue
We have talked a lot about the more indirect benefits of partnership marketing but biggest benefit (like all other forms of marketing) is increased revenue and growth.
Strategically harnessing the power of partnerships and collaborations allows you to reach more people in your target audience, generate leads, and close sales. All while giving you all the less direct benefits, like brand awareness and improved trust, AND costing you very little!
SUMMARY: THE BENEFITS OF PARTNERSHIP MARKETING ARE:
- Branching into New Markets
- Providing Fresh Perspectives
- More Cost-effective than Traditional Marketing Channels
- Provides You with a Support System
- Targeting Customers at the Ideal Time
- Delivering Added Value to Your Brand
- Building Your Brand Identity
- Providing New and Innovative Solutions
- Growth and Increased Revenue
3 Top Partner Marketing Software to Use
What is partnership management software?
Partnership management software is used to track sales and affiliates through a variety of channels, as well as streamline communication between partners. It also allows you to see an overview of your partners and their performance so you can continually optimize your marketing and improve your partnerships.
Essentially, it gives you everything you need for simple and effective partnership relationship management (PRM), which includes all the activities and strategies used to manage your partners and your partnership marketing as a whole.
Partnership management platforms , on the other hand, are online platforms and marketplaces where you can search and connect with potential partners. These are especially useful for finding affiliates and influencers to partner with.
There are a huge number of partnership management software tools out there!
It can be daunting and time consuming to sift through all the options to find the best ones, which is precisely why we have selected three of the best partnership marketing software to review here:
1. Tapfiliate
Tapfiliate is a customizable, cloud-based Affiliate Tracking Software that allows you to develop and track your affiliate marketing campaigns. You can successfully automate a number of tasks, such as tracking, managing commissions and marketing across different levels.
You will also be happy to know that Tapfiliate can be integrated with over 30 different e-commerce and digital marketing platforms. It is also very easy to implement for those who are not familiar with management software.
- Simple to set up and manage
- Very responsive customer service
- Can be easily integrated with different platforms
- 14 day free trial available
- Can only support a limited number of languages
- A bit pricey
- A free version of the software is not available
Pricing: Starting at 89$/month
P2P Score: 4.7/5
Website: tapfiliate.com
2. Post Affiliate Pro
Post Affiliate Pro is one of the pioneers in affiliate software, used by many e-commerce websites and online stores. This great software allows you to easily manage and engage with your affiliate partners . You can also monitor a number of tasks, such as commission payouts, affiliate automation and different online payment options.
In addition, you will have access to over 170 major Content Management Systems (CMS), such as Stripe and PayPal, with WordPress and Shopify also included.
- Provides a great affiliate tracking system
- User-friendly for managing affiliates
- Flexible and customizable user interface
- Allows for detailed reports and data analysis
- Responsive and engaging customer service
- Supports a number of different languages
- A bit on the pricey side
Pricing: Starting at 97$/month up to 477$/month
Website: postaffiliatepro.com
3. LeadDyno

LeadDyno is a user-friendly affiliate management platform that provides great support for running successful affiliate marketing campaigns. The system is easily integrated with third-party websites and platforms, which is a huge plus when needing a smooth workflow.
Other huge attractions include email automation, conversion tracking, payout management and detailed reporting functions.
- Provides a long 30 day trial for users
- Very simple to sign up and use features
- Easy for influencers to use
- Easy to integrate with social media platforms and e-commerce stores
- Poor customer service
Pricing: Starting at 49$/month up to 79$/month
P2P Score: 4.5/5
Website: leaddyno.com
Final Thoughts on Partnership Marketing – Where to From Here?
Partnership marketing includes a large number of different marketing channels and strategies. Done right, it can lead to massive growth and increased revenue for your business, as well as improved brand awareness, recognition, trust and credibility.
Finding the right partners, and choosing the right type of partnership marketing for your objectives is critical for success.
Start by finding a partner with the same brand positioning – such as having a similar type of audience and then check whether their values match up to yours.
Then reach out and start the conversation with brands that stand out to you the most. If nothing comes of it today or tomorrow, either way, you would have met some other brands in a similar industry, and you would have made some great, new connections.
Using an agency can help you get off on the right foot and establish your partnership marketing strategies and programs.
Agencies are not always an option, but if you’re looking for experts to help you with partner marketing, check out Acceleration Partners – a specialist, innovative and an award-winning partner marketing agency, that always gets it right.
Ready to find your ideal marketing partners? Check out our expert marketing guides on affiliate marketing, loyalty marketing, influencer marketing and more!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is partnership marketing.
Partnership marketing is a collaborative relationship that is formed between two or more parties, in which they help each other to reach their unique marketing and business objectives. Take a look at our comprehensive guide on how to set up a successful partnership marketing strategy for your business.
What are the main partnership marketing types?
There are many types of partnership marketing strategies, but the common types include affiliate marketing, distribution partnership, influencer marketing, sponsorships, and cross promotion. For a complete understanding on how each of these function, go and check out our full partnership marketing article.
What are the best partnership marketing software tools?
The best tools to help manage and monitor a partnership marketing program, are Tapfiliate, Post Affiliate Pro and LeadDyno. If you're interested in seeing what makes these so great and how to effectively use them, go and see our complete partnership marketing article.
What is an example of partnership marketing?
There are many examples of partnership marketing that we see and participate in every day, such as influencer marketing, content marketing, and loyalty marketing. One well-known partnership marketing example is when BMW and Louis Vuitton collaborated to create and promote an LV luggage set that was designed to fit perfectly into the trunk of a popular BMW model. Check out the full guide for more examples of partnership marketing and a detailed partnership marketing case study.
What is a partner marketing platform?
Partnership marketing platforms are online platforms and marketplaces where you can search, find and connect with potential partners for your partnership marketing. They are most frequently used to find affiliates and influencers. Check out the full guide to learn more and find out what the difference is between a partnership marketing platform and partnership marketing software.
Streamline Marketing: What is Partnership Parketing
BluLeadz: Partnership Marketing Types and Benefits
Business2Community: Main Types of Partnership Marketing
Woodpecker: How Does Cross-promotion Work
Cobloom: How to Choose the Right Partner
BluLeadz: Great Examples of Co-marketing
Suggested Articles

Affiliate Marketing Marketing Guides
10 Affiliate Marketing Trends in 2024: Best Programs & Channels to Skyrocket Revenue [Guide]
Affiliate marketing trends show it has become a key component of successful digital marketing and is...
Affiliate Marketing Marketing Agencies
13 Best Affiliate Tracking Software to Maximize ROI in 2024 [Full Review]
Using the right affiliate tracking software is crucial for your affiliate marketing program! Trac...

Affiliate Marketing Marketing Tools
PPC System: How it works and the 5 Best PPC Systems in 2024 [Detailed Review]
Organic traffic doesn't always cut it! Business owners (like you) often look for ways to accelerate ...
- Building Referral Program
- Building Employee Advocacy Program
- Building Ambassador Program
- Building Loyalty Program
- Building Affiliate Program
- Choosing Digital Marketing Agency
Solutions Review
- Affiliate Management
- Brand Ambassador Management
- Customer Loyalty
- Cold Emailing
- Referral Marketing
- Influencer Marketing

Master Affiliate Management to Boost Sales
Enroll now in our free 6-lesson email course

We created P2P to provide free resources to brands that believe in the power of peers to promote their service or products.
- Affiliate Disclaimer
- Privacy Policy
- Affiliate Program
- Ambassador Program
- Customer Loyalty Program
- Employee Advocacy Program
- Referral Program
© 2019 P2P Marketing All Rights Reserved.
Why Attend?
- Live Online
- 1,00,000+ people attended since 2009
- Rs 1999 FREE
- Certificate of Participation
- An exclusive Surprise

[Case Study]: 5 Examples of SUCCESSFUL Co-branding Partnerships
Table of Contents
![[Case Study]: 5 Examples of SUCCESSFUL Co-branding Partnerships 1 co branding dsim e1512045825590](https://dsim.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/co-branding-dsim-e1512045825590.jpg)
Strategic partnerships between brands can be a mutually beneficial relationship. It is basically the alliance of two totally different companies that get together to form and sell a new product telling of their uniqueness.
Brand collaboration will boost audience , reach new markets, and gain greater distribution and eventually revenue.
In this case study, you’ll see brand collaboration examples that fit the bill and represent a win-win for brands and consumers.
Why Co-branding?
“Double Marketing Budget and Half the Cost”
Co-branding opportunities allow you to launch a brand new product and divide the expenses together with your partner.
With this, you’ll gain visibility, and reach a new audience. When two brands come together to form a co-branding partnership , they automatically are given the opportunity to gain the interest of each other’s market.
It can help your startup in establishing credibility . The consumers who are already in love with one brand will automatically trust the newly introduced product.
Benefits of Co-branding
- Create financial benefits
- Provide customers with greater value
- Improve on a property’s overall image
- Strengthen an operation’s competitive position
- Create operational advantages
5 Examples of Co-branding Partnerships
1) gopro + red bull.
Red Bull and GoPro have a best co-branding partnership example. Both brands not just sell products- energy drinks and portable cameras respectively- but a lifestyle. Both have established themselves as lifestyle brands — in particular, a lifestyle that’s action-packed, adventurous, fearless, and usually pretty extreme.
Both brands are made for each other, not only because they represent the same values for their customers but also because they both associated themselves with outdoor lifestyle and action sports.
“GoPro camera technology is allowing us to complement the programming by delivering new athlete perspectives that have never been seen before,”- Sean Eggert, Red Bull’s director of sports marketing
The collaboration allows exclusive GoPro content to enhance both companies’ growth.
2) Levis + Google
Levi’s teamed up with Google to enter the wearable technology market. Codenamed Project Jacquard, the Levi’s Commuter-Jacquard by Google partnership manufactured a touch-and-gesture interactive denim jacket designed to prevent cyclists having to reach for their phones while riding.
By lightly selecting or swiping a sleeve on their jacket, cyclists can access a map or change a song on Spotify, for example, without give in their safety on the road.
3) Spotify + Uber
It is another genius partnership. The ability to enter a hired car welcomed by your favorite playlist offers added value, meaningful competitive advantage and exclusivity for Uber cars.
For Spotify, it offers a reason for users to upgrade to the premium level and a unique point of difference that Pandora, iTunes or YouTube don’t have.
The partnership means one more additional benefit for Uber to differentiate itself from taxis and for Spotify to give its subscribers one more avenue to use its product, it’s simple and brilliant.
4) Google + Luxottica
The Google and Luxottica partnership has been an excellent one. Google glasses speak to technology but not fashion and Luxottica’s brands speak to fashion and not tech.
The partnership will result in attractive Google glasses that could be purchased based on looks alone, and the cutting edge technology can give Luxottica brands a reason for purchase that explains a premium price.
Luxottica’s glasses are progressively being undercut on price by retailers such as Costco, TJ Maxx and Warby Parker.
5) Snapchat + Square’s Snapcash
For Square, it adds significant incremental revenue and a further boost to its cutting-edge, hip brand image through the association with Snapchat.
Brands are looking to partnerships that improve their brand descriptions and boost awareness in a cost-effective and united, combining two brand budgets and marketing channels.
For partnerships to work, they must be win/win for all players. The target audiences , brand price/value insights, and level of performance must be well matched.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
30 Social Bookmarking Sites to Boost SEO & Drive Traffic
8 Digital Marketing Tips Your Competitors Probably Don’t Know
13 CTA Stats to Quantify Its POWER for BRANDS
DSIM Reviews – See What DSIM’s Awesome Trainees Say about DSIM
[CASE STUDY]: How M.A.C Cosmetics became the world’s leading Makeup Company?
5 Google Penalty Checker tools To Save You

How Dell generated USD 6.5 M in sales using Twitter alone?
Case study: how jabong became most valuable among rocket internet’s e-commerce portfolio.

CASE STUDY: How Yatra.com became the leading online travel portal in India?
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What Successful Public-Private Partnerships Do
- Elyse Maltin

They build trust beyond the confines of the contract.
Despite spending $2.5 trillion a year on roads, railways, ports, water, and other public infrastructure projects, countries around the world are still falling far short of what they need to invest, according to one estimate. Thus, it’s no surprise that there is renewed interest in public-private partnership (P3) projects, where businesses supplement public investment in return for reaping rewards such as tolls and fees. But many P3 projects go off the rails. For example, a European Union review of nine such projects launched between 2000 and 2014 found seven were late and over budget. A U.S. interstate highway project near Indianapolis was found to be 51% over budget and two years past the proposed completion date. These highly publicized travails not only make P3 projects a public nuisance (or more), they create big political hurdles to overcome the next time a much-needed infrastructure project requires outside funding. But over the last three years, we conducted research interviews with 72 leaders from organizations that design, build, finance, provide legal advice, manage projects and advise North American P3 projects. when we examined what led to productive working relationship over the life of these projects, we found they had three things in common: a commitment to a strong partnership beyond the terms of the contract; built-in mechanisms to share perspectives about the project (especially problems and concerns); and effective ways to rebound from failures to deliver.
Despite spending $2.5 trillion a year on roads, railways, ports, water, and other public infrastructure projects, countries around the world are still falling far short of what they need to invest, according to one estimate . Thus, it’s no surprise that there is renewed interest in public-private partnership (P3) projects, where businesses supplement public investment in return for reaping rewards such as tolls and fees. The White House, for one, suggests using private investments to fund most of its proposed $1.5 trillion in U.S. infrastructure spending.
- EM Elyse Maltin is an associate consultant at JMW Consultants Inc. , a Stamford, Conn.-based management consulting firm.
Partner Center

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Partnership Case Study
Niagara adapts case study: an interview with dr. jessica blythe, what qualities or ingredients are most important for collaboration to succeed.
Inclusion, trust, and mutual respect are critical for successful interdisciplinary collaboration (Blythe & Cvitanovic, 2020). Research is showing that these feelings are essential for building effective interdisciplinary research teams and organizations (Ledford et al., 2015). Critically, qualities of trust and respect are vital for nurturing innovative solutions (Blythe et al., 2017). In general, people do not feel safe sharing innovative ideas unless they are among trusted colleagues.
Strong leadership is another essential quality of successful collaboration. This quality can be closely linked to the first. For example, in reflecting on more than a decade of collaborative water research, Brown et al. (2015) attribute successful collaboration to leaders who nurtured empathy and respect between team members. Female leaders may be particularly well suited to fostering collaborative environments built on inclusion, trust, and mutual respect. For example, Nielsen et al. (2018) recently found that gender diversity can drive scientific discovery. They attribute the boost in innovation to the cognitive diversity associated with gender balanced teams. They describe cognitive diversity as the varied ways in which women frame problems, which can drive creative solutions for complex challenges (Nielsen et al., 2018).
Finally, clear and shared goals are essential for successful collaboration. Joint framing of the purpose and objectives of a partnerships enables a successful process (Lang et al. 2012). This phase can consist of the co-identification and description of the real-world problem, the joint formulation of research objectives, the co-design of a conceptual and/or methodological frameworks, and the building of a collaborative research team (Lang et al., 2012).
What qualities or ingredients cause collaboration to go horribly wrong?
Managing expectations is very important. Without clear and shared expectations or expected outcomes, partnerships may be set up for disappointment. You can mitigate these risks by transparent about all aspects of the partnership. For example, clear memorandums of understanding (MOUs) can be a useful tool to manage expectations. Before beginning a partnership, conducting a survey with partnerships about expectations can be another useful way to understand what each partner is hoping to achieve. Plummer et al. (2021) identify four essential inputs for partnerships: financial resources, human resources, motivations for partnership, and transparency. These attributes are a useful touch point for avoiding miscommunications or conflict associated with poorly managed expectations.
Building Sustainable Communities: Collaboration Copyright © 2022 by Ryan Plummer; Amanda Smits; Samantha Witkowski; Bridget McGlynn; Derek Armitage; Ella-Kari Muhl; and Jodi Johnston is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Welcome to CM Murray LLP. This site uses cookies, read our policy here .
3 of the Must-Know Partnership Law Cases of 2021
In this alert, we summarise three of the most notable and interesting Partnership and LLP law cases heard by the UK courts in 2021, with some practical commentary on how these cases might affect LLPs and partnerships, and their members and partners.
1. Dixon Coles and Gill (a firm) v Right Reverend, Nicholas Baines, Bishop of Leeds and another [2021] EWCA Civ 1097
Summary of case
The Court of Appeal held that innocent partners in a firm of solicitors are not always liable to former clients of the firm for losses caused by the acts of a fraudulent partner.
One of three individuals carrying on a solicitor’s partnership, Partner C, had been misappropriating funds from the firm’s client account for many years. Partners A and B were entirely innocent and unaware of the misappropriation. Approximately three years after discovery of the fraudulent conduct, proceedings were issued against all three partners by a former client of the firm, on the basis that they were trustees of the funds that the client had paid into the client account of the firm and which Partner C had misappropriated. Specifically, the former client relied upon sections 10 (liability of the firm for wrongs) , 11 (misapplication of money or property received for or in custody of the firm) and 12 (liability for wrongs joint and several) of the Partnership Act 1890.
Partners A and B sought to defend claims in relation to certain losses on the basis that claims had been commenced after expiry of the relevant limitation period. The key issue related to whether the innocent partners could rely on sections 21 (1) and (3) of the Limitation Act 1980 (“LA”), which provide as follows:
(1) No period of limitation prescribed by this Act shall apply to an action by a beneficiary under a trust, being an action –
(a) in respect of any fraud or fraudulent breach of trust to which the trustee was a party or privy; or
(b) to recover from the trustee trust property or the proceeds of trust property in the possession of the trustee, or previously received by him and converted to his use.
(3) Subject to the proceedings provisions of this section, an action by a beneficiary to recover trust property or in respect of any breach of trust, not being an action for which a period of limitation is prescribed by any other provision of this Act, shall not be brought after the expiration of six years from the date on which the right of action accrued.
The partners argued that they were not “party or privy” to Partner C’s misconduct. The Court of Appeal agreed that the innocent partners were not “party or privy to” the misconduct, and that they could therefore rely on section 21 of the LA as a defence to claims against them in respect of monies appropriated by Partner C more than six years before the commencement of litigation.
Practical takeaways
The Court of Appeal’s decision will offer some reassurance to innocent partners facing claims from former clients because of a fellow partner’s misconduct, to which they are not party or privy. It should also serve as a useful reminder to those advising on claims to be brought against individual partners of a partnership that a delay in issuing proceedings may enable innocent partners to avoid liability to a certain extent by relying on relevant provisions of the LA.
2. Re Bell Pottinger LLP, Secretary of State for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy v Geoghegan and others [2021] EWHC 672 (Ch)
The High Court held that members of an LLP, who were not members of the LLP’s management committee, could potentially be liable to face disqualification proceedings under the Company Directors Disqualification Act 1986 (“CDDA”).
The Secretary of State for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (“Secretary of State”) sought disqualification orders against three members of former PR Agency, Bell Pottinger LLP (“Bell Pottinger”), which went into liquidation in September 2019, on the ground that they were not fit to be concerned with the management of a company or an LLP. Only one of the members had been a member of Bell Pottinger’s management committee. The other two members tried to argue that the CDDA did not apply to them as they were not members of the management committee and were not involved in its management.
It was held that Parliament intended to “ cast a wide net ” and, therefore, that potential liability to face disqualification proceedings was not limited to members on the management board or at a level equivalent to a director in a company. The Court also confirmed that the conduct relied upon for disqualification could be anything done in their capacity as an LLP member.
Some may view this as a harsh decision, given the potential exposure to disqualification faced by members of an LLP who do not sit on the management committee of an LLP and are not otherwise concerned or authorised to deal with the management of the LLP. However, it serves as a reminder that those who take up positions as members of an LLP and who benefit from limited personal liability for loss and damage caused to third parties by the LLP, should reasonably be expected to be held to high standards of behaviour.
3. Tribe v Elborne Mitchell LLP [2021] EWHC 1863 (Ch)
The High Court held that, when deciding how to allocate profits to members of an LLP under the terms of an LLP Deed, management need to act rationally.
The partner concerned claimed that he was not awarded a fair profit share in his last two years at the firm after more than 25 years of service. The court agreed that the principles developed in Braganza v BP Shipping Ltd Braganza v BP Shipping Ltd [2015] UKSC 17, concerning the exercise of discretionary powers, applied to the senior partner’s decision to make recommendations as to allocations among the partners. This meant that, in making his recommendations, the senior partner had been duty-bound not to “ take into account irrelevant matters or ignore relevant ones ”. His recommendations could not be “ outside the range of reasonable proposals that might be made in the circumstances ”. Indeed, in this case, the court found that the profit allocation had been within the range of proposals that it was reasonable for the senior partner to make.
The High Court’s decision confirms that members of an LLP, particularly those exercising management powers, will be held to a particular standard when allocating profits and cannot act capriciously or irrationally in the decision-making process. However, it also shows that following a reasonable and explicable process should make it difficult to challenge any ultimate decision as to profit allocation. Those exercising discretionary powers in making recommendations and/or decisions regarding the allocation of profit (or indeed other discretionary decision making regarding LLP members such as, for example, equity partner promotions or partner suspension or exits), would be well advised to consider the basis of previous decisions and clearly document the basis of their current decision and rationale, setting out a non-exhaustive list of the range of relevant matters to be taken into account and irrelevant factors to be ignored in the exercise of their discretionary powers.
If you have any questions arising from this alert, or require specific legal advice in relation to similar issues, please contact Zulon Begum or Clare Murray (Partners), who specialise in partnership issues for partnerships, LLPs, partners and LLP members. Please click here to see the overview of our market-leading Contentious and Non-Contentious Partnership Practice.
CM Murray LLP is Ranked Band 1 and Tier 1 for Partnership Law by Chambers and Partners UK and Legal 500 UK , and is recognised as “one of the legal world’s strongest offerings in this area.”
If you would like to stay up to date with the latest Partnership law news and updates from CM Murray, subscribe here .
RELATED CONTENT


- < Previous
Home > Faculty Scholarship > Books > 30

Cases on the Law of Partnership
Floyd R. Mechem , University of Michigan Law School Follow
Download Full Text (60.4 MB)
Download Table of Contents (3.0 MB)
Download Table of Cases (2.7 MB)
Download I: What is a Partnership (21.6 MB)
Download II: For What Purpose Organized (14.8 MB)
Download III: Who May Be Partners (18.4 MB)
Download IV: What Contracts and Acts Create Partnership (11.7 MB)
Download V: Nature of Partner's Interest in Property (30.8 MB)
Download VI: The Firm Name and Good Will (4.6 MB)
Download VII: Rights and Duties of Partners Toward Each Other (29.0 MB)
Download VIII: Actions Between Partners (35.2 MB)
Download IX: Powers of Partners (5.0 MB)
Download X: Who is Liable for the Acts of a Partner (29.5 MB)
Download XI: Of the Nature and Extent of a Partner's Liability (10.9 MB)
Download XII: Of Dissolution and Notice (35.3 MB)
Download XIII: Of the Consequences of Dissolution (5.9 MB)
Download XIV: Agreements Between Partners at Dissolution Respecting Payment of Debts (10.4 MB)
Download XV: Application of Assets to Claims of Creditors (63.4 MB)
Download XVI: Distribution of Assets Between Partners (7.5 MB)
Download Index (10.1 MB)
Description
A casebook with selected cases to aid the teaching of partnership law. First edition. Missing front matter.
Publication Date
Callaghan & Company
Partnerships, Property, Property interests, Firms, Liability, Dissolution, Notice, Debts, Claims, Assets, Limited partnerships
- Disciplines
Business Organizations Law | Legal Education
Recommended Citation
Mechem, Floyd R. Cases on the Law of Partnership . Chicago: Callaghan & Company, 1896.
Since February 04, 2016
Included in
Business Organizations Law Commons , Legal Education Commons
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Collections
Submissions
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
- Open access
- Published: 15 May 2024
Learning together for better health using an evidence-based Learning Health System framework: a case study in stroke
- Helena Teede 1 , 2 na1 ,
- Dominique A. Cadilhac 3 , 4 na1 ,
- Tara Purvis 3 ,
- Monique F. Kilkenny 3 , 4 ,
- Bruce C.V. Campbell 4 , 5 , 6 ,
- Coralie English 7 ,
- Alison Johnson 2 ,
- Emily Callander 1 ,
- Rohan S. Grimley 8 , 9 ,
- Christopher Levi 10 ,
- Sandy Middleton 11 , 12 ,
- Kelvin Hill 13 &
- Joanne Enticott ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4480-5690 1
BMC Medicine volume 22 , Article number: 198 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
228 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
In the context of expanding digital health tools, the health system is ready for Learning Health System (LHS) models. These models, with proper governance and stakeholder engagement, enable the integration of digital infrastructure to provide feedback to all relevant parties including clinicians and consumers on performance against best practice standards, as well as fostering innovation and aligning healthcare with patient needs. The LHS literature primarily includes opinion or consensus-based frameworks and lacks validation or evidence of benefit. Our aim was to outline a rigorously codesigned, evidence-based LHS framework and present a national case study of an LHS-aligned national stroke program that has delivered clinical benefit.
Current core components of a LHS involve capturing evidence from communities and stakeholders (quadrant 1), integrating evidence from research findings (quadrant 2), leveraging evidence from data and practice (quadrant 3), and generating evidence from implementation (quadrant 4) for iterative system-level improvement. The Australian Stroke program was selected as the case study as it provides an exemplar of how an iterative LHS works in practice at a national level encompassing and integrating evidence from all four LHS quadrants. Using this case study, we demonstrate how to apply evidence-based processes to healthcare improvement and embed real-world research for optimising healthcare improvement. We emphasize the transition from research as an endpoint, to research as an enabler and a solution for impact in healthcare improvement.
Conclusions
The Australian Stroke program has nationally improved stroke care since 2007, showcasing the value of integrated LHS-aligned approaches for tangible impact on outcomes. This LHS case study is a practical example for other health conditions and settings to follow suit.
Peer Review reports
Internationally, health systems are facing a crisis, driven by an ageing population, increasing complexity, multi-morbidity, rapidly advancing health technology and rising costs that threaten sustainability and mandate transformation and improvement [ 1 , 2 ]. Although research has generated solutions to healthcare challenges, and the advent of big data and digital health holds great promise, entrenched siloes and poor integration of knowledge generation, knowledge implementation and healthcare delivery between stakeholders, curtails momentum towards, and consistent attainment of, evidence-and value-based care [ 3 ]. This is compounded by the short supply of research and innovation leadership within the healthcare sector, and poorly integrated and often inaccessible health data systems, which have crippled the potential to deliver on digital-driven innovation [ 4 ]. Current approaches to healthcare improvement are also often isolated with limited sustainability, scale-up and impact [ 5 ].
Evidence suggests that integration and partnership across academic and healthcare delivery stakeholders are key to progress, including those with lived experience and their families (referred to here as consumers and community), diverse disciplines (both research and clinical), policy makers and funders. Utilization of evidence from research and evidence from practice including data from routine care, supported by implementation research, are key to sustainably embedding improvement and optimising health care and outcomes. A strategy to achieve this integration is through the Learning Health System (LHS) (Fig. 1 ) [ 2 , 6 , 7 , 8 ]. Although there are numerous publications on LHS approaches [ 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ], many focus on research perspectives and data, most do not demonstrate tangible healthcare improvement or better health outcomes. [ 6 ]
Monash Learning Health System: The Learn Together for Better Health Framework developed by Monash Partners and Monash University (from Enticott et al. 2021 [ 7 ]). Four evidence quadrants: Q1 (orange) is evidence from stakeholders; Q2 (green) is evidence from research; Q3 (light blue) is evidence from data; and, Q4 (dark blue) is evidence from implementation and healthcare improvement
In developed nations, it has been estimated that 60% of care provided aligns with the evidence base, 30% is low value and 10% is potentially harmful [ 13 ]. In some areas, clinical advances have been rapid and research and evidence have paved the way for dramatic improvement in outcomes, mandating rapid implementation of evidence into healthcare (e.g. polio and COVID-19 vaccines). However, healthcare improvement is challenging and slow [ 5 ]. Health systems are highly complex in their design, networks and interacting components, and change is difficult to enact, sustain and scale up. [ 3 ] New effective strategies are needed to meet community needs and deliver evidence-based and value-based care, which reorients care from serving the provider, services and system, towards serving community needs, based on evidence and quality. It goes beyond cost to encompass patient and provider experience, quality care and outcomes, efficiency and sustainability [ 2 , 6 ].
The costs of stroke care are expected to rise rapidly in the next decades, unless improvements in stroke care to reduce the disabling effects of strokes can be successfully developed and implemented [ 14 ]. Here, we briefly describe the Monash LHS framework (Fig. 1 ) [ 2 , 6 , 7 ] and outline an exemplar case in order to demonstrate how to apply evidence-based processes to healthcare improvement and embed real-world research for optimising healthcare. The Australian LHS exemplar in stroke care has driven nationwide improvement in stroke care since 2007.
An evidence-based Learning Health System framework
In Australia, members of this author group (HT, AJ, JE) have rigorously co-developed an evidence-based LHS framework, known simply as the Monash LHS [ 7 ]. The Monash LHS was designed to support sustainable, iterative and continuous robust benefit of improved clinical outcomes. It was created with national engagement in order to be applicable to Australian settings. Through this rigorous approach, core LHS principles and components have been established (Fig. 1 ). Evidence shows that people/workforce, culture, standards, governance and resources were all key to an effective LHS [ 2 , 6 ]. Culture is vital including trust, transparency, partnership and co-design. Key processes include legally compliant data sharing, linkage and governance, resources, and infrastructure [ 4 ]. The Monash LHS integrates disparate and often siloed stakeholders, infrastructure and expertise to ‘Learn Together for Better Health’ [ 7 ] (Fig. 1 ). This integrates (i) evidence from community and stakeholders including priority areas and outcomes; (ii) evidence from research and guidelines; (iii) evidence from practice (from data) with advanced analytics and benchmarking; and (iv) evidence from implementation science and health economics. Importantly, it starts with the problem and priorities of key stakeholders including the community, health professionals and services and creates an iterative learning system to address these. The following case study was chosen as it is an exemplar of how a Monash LHS-aligned national stroke program has delivered clinical benefit.
Australian Stroke Learning Health System
Internationally, the application of LHS approaches in stroke has resulted in improved stroke care and outcomes [ 12 ]. For example, in Canada a sustained decrease in 30-day in-hospital mortality has been found commensurate with an increase in resources to establish the multifactorial stroke system intervention for stroke treatment and prevention [ 15 ]. Arguably, with rapid advances in evidence and in the context of an ageing population with high cost and care burden and substantive impacts on quality of life, stroke is an area with a need for rapid research translation into evidence-based and value-based healthcare improvement. However, a recent systematic review found that the existing literature had few comprehensive examples of LHS adoption [ 12 ]. Although healthcare improvement systems and approaches were described, less is known about patient-clinician and stakeholder engagement, governance and culture, or embedding of data informatics into everyday practice to inform and drive improvement [ 12 ]. For example, in a recent review of quality improvement collaborations, it was found that although clinical processes in stroke care are improved, their short-term nature means there is uncertainty about sustainability and impacts on patient outcomes [ 16 ]. Table 1 provides the main features of the Australian Stroke LHS based on the four core domains and eight elements of the Learning Together for Better Health Framework described in Fig. 1 . The features are further expanded on in the following sections.
Evidence from stakeholders (LHS quadrant 1, Fig. 1 )
Engagement, partners and priorities.
Within the stroke field, there have been various support mechanisms to facilitate an LHS approach including partnership and broad stakeholder engagement that includes clinical networks and policy makers from different jurisdictions. Since 2008, the Australian Stroke Coalition has been co-led by the Stroke Foundation, a charitable consumer advocacy organisation, and Stroke Society of Australasia a professional society with membership covering academics and multidisciplinary clinician networks, that are collectively working to improve stroke care ( https://australianstrokecoalition.org.au/ ). Surveys, focus groups and workshops have been used for identifying priorities from stakeholders. Recent agreed priorities have been to improve stroke care and strengthen the voice for stroke care at a national ( https://strokefoundation.org.au/ ) and international level ( https://www.world-stroke.org/news-and-blog/news/world-stroke-organization-tackle-gaps-in-access-to-quality-stroke-care ), as well as reduce duplication amongst stakeholders. This activity is built on a foundation and culture of research and innovation embedded within the stroke ‘community of practice’. Consumers, as people with lived experience of stroke are important members of the Australian Stroke Coalition, as well as representatives from different clinical colleges. Consumers also provide critical input to a range of LHS activities via the Stroke Foundation Consumer Council, Stroke Living Guidelines committees, and the Australian Stroke Clinical Registry (AuSCR) Steering Committee (described below).
Evidence from research (LHS quadrant 2, Fig. 1 )
Advancement of the evidence for stroke interventions and synthesis into clinical guidelines.
To implement best practice, it is crucial to distil the large volume of scientific and trial literature into actionable recommendations for clinicians to use in practice [ 24 ]. The first Australian clinical guidelines for acute stroke were produced in 2003 following the increasing evidence emerging for prevention interventions (e.g. carotid endarterectomy, blood pressure lowering), acute medical treatments (intravenous thrombolysis, aspirin within 48 h of ischemic stroke), and optimised hospital management (care in dedicated stroke units by a specialised and coordinated multidisciplinary team) [ 25 ]. Importantly, a number of the innovations were developed, researched and proven effective by key opinion leaders embedded in the Australian stroke care community. In 2005, the clinical guidelines for Stroke Rehabilitation and Recovery [ 26 ] were produced, with subsequent merged guidelines periodically updated. However, the traditional process of periodic guideline updates is challenging for end users when new research can render recommendations redundant and this lack of currency erodes stakeholder trust [ 27 ]. In response to this challenge the Stroke Foundation and Cochrane Australia entered a pioneering project to produce the first electronic ‘living’ guidelines globally [ 20 ]. Major shifts in the evidence for reperfusion therapies (e.g. extended time-window intravenous thrombolysis and endovascular clot retrieval), among other advances, were able to be converted into new recommendations, approved by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council within a few months of publication. Feedback on this process confirmed the increased use and trust in the guidelines by clinicians. The process informed other living guidelines programs, including the successful COVID-19 clinical guidelines [ 28 ].
However, best practice clinical guideline recommendations are necessary but insufficient for healthcare improvement and nesting these within an LHS with stakeholder partnership, enables implementation via a range of proven methods, including audit and feedback strategies [ 29 ].
Evidence from data and practice (LHS quadrant 3, Fig. 1 )
Data systems and benchmarking : revealing the disparities in care between health services. A national system for standardized stroke data collection was established as the National Stroke Audit program in 2007 by the Stroke Foundation [ 30 ] following various state-level programs (e.g. New South Wales Audit) [ 31 ] to identify evidence-practice gaps and prioritise improvement efforts to increase access to stroke units and other acute treatments [ 32 ]. The Audit program alternates each year between acute (commencing in 2007) and rehabilitation in-patient services (commencing in 2008). The Audit program provides a ‘deep dive’ on the majority of recommendations in the clinical guidelines whereby participating hospitals provide audits of up to 40 consecutive patient medical records and respond to a survey about organizational resources to manage stroke. In 2009, the AuSCR was established to provide information on patients managed in acute hospitals based on a small subset of quality processes of care linked to benchmarked reports of performance (Fig. 2 ) [ 33 ]. In this way, the continuous collection of high-priority processes of stroke care could be regularly collected and reviewed to guide improvement to care [ 34 ]. Plus clinical quality registry programs within Australia have shown a meaningful return on investment attributed to enhanced survival, improvements in quality of life and avoided costs of treatment or hospital stay [ 35 ].
Example performance report from the Australian Stroke Clinical Registry: average door-to-needle time in providing intravenous thrombolysis by different hospitals in 2021 [ 36 ]. Each bar in the figure represents a single hospital
The Australian Stroke Coalition endorsed the creation of an integrated technological solution for collecting data through a single portal for multiple programs in 2013. In 2015, the Stroke Foundation, AuSCR consortium, and other relevant groups cooperated to design an integrated data management platform (the Australian Stroke Data Tool) to reduce duplication of effort for hospital staff in the collection of overlapping variables in the same patients [ 19 ]. Importantly, a national data dictionary then provided the common data definitions to facilitate standardized data capture. Another important feature of AuSCR is the collection of patient-reported outcome surveys between 90 and 180 days after stroke, and annual linkage with national death records to ascertain survival status [ 33 ]. To support a LHS approach, hospitals that participate in AuSCR have access to a range of real-time performance reports. In efforts to minimize the burden of data collection in the AuSCR, interoperability approaches to import data directly from hospital or state-level managed stroke databases have been established (Fig. 3 ); however, the application has been variable and 41% of hospitals still manually enter all their data.
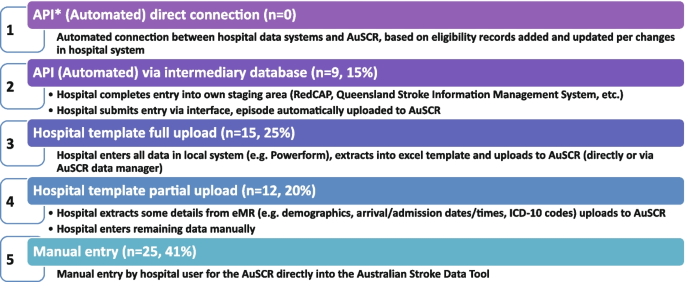
Current status of automated data importing solutions in the Australian Stroke Clinical Registry, 2022, with ‘ n ’ representing the number of hospitals. AuSCR, Australian Stroke Clinical Registry; AuSDaT, Australian Stroke Data Tool; API, Application Programming Interface; ICD, International Classification of Diseases; RedCAP, Research Electronic Data Capture; eMR, electronic medical records
For acute stroke care, the Australian Commission on Quality and Safety in Health Care facilitated the co-design (clinicians, academics, consumers) and publication of the national Acute Stroke Clinical Care Standard in 2015 [ 17 ], and subsequent review [ 18 ]. The indicator set for the Acute Stroke Standard then informed the expansion of the minimum dataset for AuSCR so that hospitals could routinely track their performance. The national Audit program enabled hospitals not involved in the AuSCR to assess their performance every two years against the Acute Stroke Standard. Complementing these efforts, the Stroke Foundation, working with the sector, developed the Acute and Rehabilitation Stroke Services Frameworks to outline the principles, essential elements, models of care and staffing recommendations for stroke services ( https://informme.org.au/guidelines/national-stroke-services-frameworks ). The Frameworks are intended to guide where stroke services should be developed, and monitor their uptake with the organizational survey component of the Audit program.
Evidence from implementation and healthcare improvement (LHS quadrant 4, Fig. 1 )
Research to better utilize and augment data from registries through linkage [ 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 ] and to ensure presentation of hospital or service level data are understood by clinicians has ensured advancement in the field for the Australian Stroke LHS [ 41 ]. Importantly, greater insights into whole patient journeys, before and after a stroke, can now enable exploration of value-based care. The LHS and stroke data platform have enabled focused and time-limited projects to create a better understanding of the quality of care in acute or rehabilitation settings [ 22 , 42 , 43 ]. Within stroke, all the elements of an LHS culminate into the ready availability of benchmarked performance data and support for implementation of strategies to address gaps in care.
Implementation research to grow the evidence base for effective improvement interventions has also been a key pillar in the Australian context. These include multi-component implementation interventions to achieve behaviour change for particular aspects of stroke care, [ 22 , 23 , 44 , 45 ] and real-world approaches to augmenting access to hyperacute interventions in stroke through the use of technology and telehealth [ 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 ]. The evidence from these studies feeds into the living guidelines program and the data collection systems, such as the Audit program or AuSCR, which are then amended to ensure data aligns to recommended care. For example, the use of ‘hyperacute aspirin within the first 48 h of ischemic stroke’ was modified to be ‘hyperacute antiplatelet…’ to incorporate new evidence that other medications or combinations are appropriate to use. Additionally, new datasets have been developed to align with evidence such as the Fever, Sugar, and Swallow variables [ 42 ]. Evidence on improvements in access to best practice care from the acute Audit program [ 50 ] and AuSCR is emerging [ 36 ]. For example, between 2007 and 2017, the odds of receiving intravenous thrombolysis after ischemic stroke increased by 16% 9OR 1.06 95% CI 1.13–1.18) and being managed in a stroke unit by 18% (OR 1.18 95% CI 1.17–1.20). Over this period, the median length of hospital stay for all patients decreased from 6.3 days in 2007 to 5.0 days in 2017 [ 51 ]. When considering the number of additional patients who would receive treatment in 2017 in comparison to 2007 it was estimated that without this additional treatment, over 17,000 healthy years of life would be lost in 2017 (17,786 disability-adjusted life years) [ 51 ]. There is evidence on the cost-effectiveness of different system-focussed strategies to augment treatment access for acute ischemic stroke (e.g. Victorian Stroke Telemedicine program [ 52 ] and Melbourne Mobile Stroke Unit ambulance [ 53 ]). Reciprocally, evidence from the national Rehabilitation Audit, where the LHS approach has been less complete or embedded, has shown fewer areas of healthcare improvement over time [ 51 , 54 ].
Within the field of stroke in Australia, there is indirect evidence that the collective efforts that align to establishing the components of a LHS have had an impact. Overall, the age-standardised rate of stroke events has reduced by 27% between 2001 and 2020, from 169 to 124 events per 100,000 population. Substantial declines in mortality rates have been reported since 1980. Commensurate with national clinical guidelines being updated in 2007 and the first National Stroke Audit being undertaken in 2007, the mortality rates for men (37.4 deaths per 100,000) and women (36.1 deaths per 100,0000 has declined to 23.8 and 23.9 per 100,000, respectively in 2021 [ 55 ].
Underpinning the LHS with the integration of the four quadrants of evidence from stakeholders, research and guidelines, practice and implementation, and core LHS principles have been addressed. Leadership and governance have been important, and programs have been established to augment workforce training and capacity building in best practice professional development. Medical practitioners are able to undertake courses and mentoring through the Australasian Stroke Academy ( http://www.strokeacademy.com.au/ ) while nurses (and other health professionals) can access teaching modules in stroke care from the Acute Stroke Nurses Education Network ( https://asnen.org/ ). The Association of Neurovascular Clinicians offers distance-accessible education and certification to develop stroke expertise for interdisciplinary professionals, including advanced stroke co-ordinator certification ( www.anvc.org ). Consumer initiative interventions are also used in the design of the AuSCR Public Summary Annual reports (available at https://auscr.com.au/about/annual-reports/ ) and consumer-related resources related to the Living Guidelines ( https://enableme.org.au/resources ).
The important success factors and lessons from stroke as a national exemplar LHS in Australia include leadership, culture, workforce and resources integrated with (1) established and broad partnerships across the academic-clinical sector divide and stakeholder engagement; (2) the living guidelines program; (3) national data infrastructure, including a national data dictionary that provides the common data framework to support standardized data capture; (4) various implementation strategies including benchmarking and feedback as well as engagement strategies targeting different levels of the health system; and (5) implementation and improvement research to advance stroke systems of care and reduce unwarranted variation in practice (Fig. 1 ). Priority opportunities now include the advancement of interoperability with electronic medical records as an area all clinical quality registry’s programs needs to be addressed, as well as providing more dynamic and interactive data dashboards tailored to the need of clinicians and health service executives.
There is a clear mandate to optimise healthcare improvement with big data offering major opportunities for change. However, we have lacked the approaches to capture evidence from the community and stakeholders, to integrate evidence from research, to capture and leverage data or evidence from practice and to generate and build on evidence from implementation using iterative system-level improvement. The LHS provides this opportunity and is shown to deliver impact. Here, we have outlined the process applied to generate an evidence-based LHS and provide a leading exemplar in stroke care. This highlights the value of moving from single-focus isolated approaches/initiatives to healthcare improvement and the benefit of integration to deliver demonstrable outcomes for our funders and key stakeholders — our community. This work provides insight into strategies that can both apply evidence-based processes to healthcare improvement as well as implementing evidence-based practices into care, moving beyond research as an endpoint, to research as an enabler, underpinning delivery of better healthcare.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable
Abbreviations
Australian Stroke Clinical Registry
Confidence interval
- Learning Health System
World Health Organization. Delivering quality health services . OECD Publishing; 2018.
Enticott J, Braaf S, Johnson A, Jones A, Teede HJ. Leaders’ perspectives on learning health systems: A qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20:1087.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Melder A, Robinson T, McLoughlin I, Iedema R, Teede H. An overview of healthcare improvement: Unpacking the complexity for clinicians and managers in a learning health system. Intern Med J. 2020;50:1174–84.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Alberto IRI, Alberto NRI, Ghosh AK, Jain B, Jayakumar S, Martinez-Martin N, et al. The impact of commercial health datasets on medical research and health-care algorithms. Lancet Digit Health. 2023;5:e288–94.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Dixon-Woods M. How to improve healthcare improvement—an essay by Mary Dixon-Woods. BMJ. 2019;367: l5514.
Enticott J, Johnson A, Teede H. Learning health systems using data to drive healthcare improvement and impact: A systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21:200.
Enticott JC, Melder A, Johnson A, Jones A, Shaw T, Keech W, et al. A learning health system framework to operationalize health data to improve quality care: An Australian perspective. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:730021.
Dammery G, Ellis LA, Churruca K, Mahadeva J, Lopez F, Carrigan A, et al. The journey to a learning health system in primary care: A qualitative case study utilising an embedded research approach. BMC Prim Care. 2023;24:22.
Foley T, Horwitz L, Zahran R. The learning healthcare project: Realising the potential of learning health systems. 2021. Available from https://learninghealthcareproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/LHS2021report.pdf . Accessed Jan 2024.
Institute of Medicine. Best care at lower cost: The path to continuously learning health care in America. Washington: The National Academies Press; 2013.
Google Scholar
Zurynski Y, Smith CL, Vedovi A, Ellis LA, Knaggs G, Meulenbroeks I, et al. Mapping the learning health system: A scoping review of current evidence - a white paper. 2020:63
Cadilhac DA, Bravata DM, Bettger J, Mikulik R, Norrving B, Uvere E, et al. Stroke learning health systems: A topical narrative review with case examples. Stroke. 2023;54:1148–59.
Braithwaite J, Glasziou P, Westbrook J. The three numbers you need to know about healthcare: The 60–30-10 challenge. BMC Med. 2020;18:1–8.
Article Google Scholar
King D, Wittenberg R, Patel A, Quayyum Z, Berdunov V, Knapp M. The future incidence, prevalence and costs of stroke in the UK. Age Ageing. 2020;49:277–82.
Ganesh A, Lindsay P, Fang J, Kapral MK, Cote R, Joiner I, et al. Integrated systems of stroke care and reduction in 30-day mortality: A retrospective analysis. Neurology. 2016;86:898–904.
Lowther HJ, Harrison J, Hill JE, Gaskins NJ, Lazo KC, Clegg AJ, et al. The effectiveness of quality improvement collaboratives in improving stroke care and the facilitators and barriers to their implementation: A systematic review. Implement Sci. 2021;16:16.
Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. Acute stroke clinical care standard. 2015. Available from https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/our-work/clinical-care-standards/acute-stroke-clinical-care-standard . Accessed Jan 2024.
Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. Acute stroke clinical care standard. Sydney: ACSQHC; 2019. Available from https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/publications-and-resources/resource-library/acute-stroke-clinical-care-standard-evidence-sources . Accessed Jan 2024.
Ryan O, Ghuliani J, Grabsch B, Hill K, G CC, Breen S, et al. Development, implementation, and evaluation of the Australian Stroke Data Tool (AuSDaT): Comprehensive data capturing for multiple uses. Health Inf Manag. 2022:18333583221117184.
English C, Bayley M, Hill K, Langhorne P, Molag M, Ranta A, et al. Bringing stroke clinical guidelines to life. Int J Stroke. 2019;14:337–9.
English C, Hill K, Cadilhac DA, Hackett ML, Lannin NA, Middleton S, et al. Living clinical guidelines for stroke: Updates, challenges and opportunities. Med J Aust. 2022;216:510–4.
Cadilhac DA, Grimley R, Kilkenny MF, Andrew NE, Lannin NA, Hill K, et al. Multicenter, prospective, controlled, before-and-after, quality improvement study (Stroke123) of acute stroke care. Stroke. 2019;50:1525–30.
Cadilhac DA, Marion V, Andrew NE, Breen SJ, Grabsch B, Purvis T, et al. A stepped-wedge cluster-randomized trial to improve adherence to evidence-based practices for acute stroke management. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2022.
Elliott J, Lawrence R, Minx JC, Oladapo OT, Ravaud P, Jeppesen BT, et al. Decision makers need constantly updated evidence synthesis. Nature. 2021;600:383–5.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
National Stroke Foundation. National guidelines for acute stroke management. Melbourne: National Stroke Foundation; 2003.
National Stroke Foundation. Clinical guidelines for stroke rehabilitation and recovery. Melbourne: National Stroke Foundation; 2005.
Phan TG, Thrift A, Cadilhac D, Srikanth V. A plea for the use of systematic review methodology when writing guidelines and timely publication of guidelines. Intern Med J . 2012;42:1369–1371; author reply 1371–1362
Tendal B, Vogel JP, McDonald S, Norris S, Cumpston M, White H, et al. Weekly updates of national living evidence-based guidelines: Methods for the Australian living guidelines for care of people with COVID-19. J Clin Epidemiol. 2021;131:11–21.
Grimshaw JM, Eccles MP, Lavis JN, Hill SJ, Squires JE. Knowledge translation of research findings. Implement Sci. 2012;7:50.
Harris D, Cadilhac D, Hankey GJ, Hillier S, Kilkenny M, Lalor E. National stroke audit: The Australian experience. Clin Audit. 2010;2:25–31.
Cadilhac DA, Purvis T, Kilkenny MF, Longworth M, Mohr K, Pollack M, et al. Evaluation of rural stroke services: Does implementation of coordinators and pathways improve care in rural hospitals? Stroke. 2013;44:2848–53.
Cadilhac DA, Moss KM, Price CJ, Lannin NA, Lim JY, Anderson CS. Pathways to enhancing the quality of stroke care through national data monitoring systems for hospitals. Med J Aust. 2013;199:650–1.
Cadilhac DA, Lannin NA, Anderson CS, Levi CR, Faux S, Price C, et al. Protocol and pilot data for establishing the Australian Stroke Clinical Registry. Int J Stroke. 2010;5:217–26.
Ivers N, Jamtvedt G, Flottorp S, Young J, Odgaard-Jensen J, French S, et al. Audit and feedback: Effects on professional practice and healthcare outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev . 2012
Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. Economic evaluation of clinical quality registries. Final report. . 2016:79
Cadilhac DA, Dalli LL, Morrison J, Lester M, Paice K, Moss K, et al. The Australian Stroke Clinical Registry annual report 2021. Melbourne; 2022. Available from https://auscr.com.au/about/annual-reports/ . Accessed 6 May 2024.
Kilkenny MF, Kim J, Andrew NE, Sundararajan V, Thrift AG, Katzenellenbogen JM, et al. Maximising data value and avoiding data waste: A validation study in stroke research. Med J Aust. 2019;210:27–31.
Eliakundu AL, Smith K, Kilkenny MF, Kim J, Bagot KL, Andrew E, et al. Linking data from the Australian Stroke Clinical Registry with ambulance and emergency administrative data in Victoria. Inquiry. 2022;59:469580221102200.
PubMed Google Scholar
Andrew NE, Kim J, Cadilhac DA, Sundararajan V, Thrift AG, Churilov L, et al. Protocol for evaluation of enhanced models of primary care in the management of stroke and other chronic disease (PRECISE): A data linkage healthcare evaluation study. Int J Popul Data Sci. 2019;4:1097.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mosalski S, Shiner CT, Lannin NA, Cadilhac DA, Faux SG, Kim J, et al. Increased relative functional gain and improved stroke outcomes: A linked registry study of the impact of rehabilitation. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021;30: 106015.
Ryan OF, Hancock SL, Marion V, Kelly P, Kilkenny MF, Clissold B, et al. Feedback of aggregate patient-reported outcomes (PROs) data to clinicians and hospital end users: Findings from an Australian codesign workshop process. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e055999.
Grimley RS, Rosbergen IC, Gustafsson L, Horton E, Green T, Cadigan G, et al. Dose and setting of rehabilitation received after stroke in Queensland, Australia: A prospective cohort study. Clin Rehabil. 2020;34:812–23.
Purvis T, Middleton S, Craig LE, Kilkenny MF, Dale S, Hill K, et al. Inclusion of a care bundle for fever, hyperglycaemia and swallow management in a national audit for acute stroke: Evidence of upscale and spread. Implement Sci. 2019;14:87.
Middleton S, McElduff P, Ward J, Grimshaw JM, Dale S, D’Este C, et al. Implementation of evidence-based treatment protocols to manage fever, hyperglycaemia, and swallowing dysfunction in acute stroke (QASC): A cluster randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2011;378:1699–706.
Middleton S, Dale S, Cheung NW, Cadilhac DA, Grimshaw JM, Levi C, et al. Nurse-initiated acute stroke care in emergency departments. Stroke. 2019:STROKEAHA118020701.
Hood RJ, Maltby S, Keynes A, Kluge MG, Nalivaiko E, Ryan A, et al. Development and pilot implementation of TACTICS VR: A virtual reality-based stroke management workflow training application and training framework. Front Neurol. 2021;12:665808.
Bladin CF, Kim J, Bagot KL, Vu M, Moloczij N, Denisenko S, et al. Improving acute stroke care in regional hospitals: Clinical evaluation of the Victorian Stroke Telemedicine program. Med J Aust. 2020;212:371–7.
Bladin CF, Bagot KL, Vu M, Kim J, Bernard S, Smith K, et al. Real-world, feasibility study to investigate the use of a multidisciplinary app (Pulsara) to improve prehospital communication and timelines for acute stroke/STEMI care. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e052332.
Zhao H, Coote S, Easton D, Langenberg F, Stephenson M, Smith K, et al. Melbourne mobile stroke unit and reperfusion therapy: Greater clinical impact of thrombectomy than thrombolysis. Stroke. 2020;51:922–30.
Purvis T, Cadilhac DA, Hill K, Reyneke M, Olaiya MT, Dalli LL, et al. Twenty years of monitoring acute stroke care in Australia from the national stroke audit program (1999–2019): Achievements and areas of future focus. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2023.
Cadilhac DA, Purvis T, Reyneke M, Dalli LL, Kim J, Kilkenny MF. Evaluation of the national stroke audit program: 20-year report. Melbourne; 2019.
Kim J, Tan E, Gao L, Moodie M, Dewey HM, Bagot KL, et al. Cost-effectiveness of the Victorian Stroke Telemedicine program. Aust Health Rev. 2022;46:294–301.
Kim J, Easton D, Zhao H, Coote S, Sookram G, Smith K, et al. Economic evaluation of the Melbourne mobile stroke unit. Int J Stroke. 2021;16:466–75.
Stroke Foundation. National stroke audit – rehabilitation services report 2020. Melbourne; 2020.
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Heart, stroke and vascular disease: Australian facts. 2023. Webpage https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/heart-stroke-vascular-diseases/hsvd-facts/contents/about (accessed Jan 2024).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The following authors hold National Health and Medical Research Council Research Fellowships: HT (#2009326), DAC (#1154273), SM (#1196352), MFK Future Leader Research Fellowship (National Heart Foundation #105737). The Funders of this work did not have any direct role in the design of the study, its execution, analyses, interpretation of the data, or decision to submit results for publication.
Author information
Helena Teede and Dominique A. Cadilhac contributed equally.
Authors and Affiliations
Monash Centre for Health Research and Implementation, 43-51 Kanooka Grove, Clayton, VIC, Australia
Helena Teede, Emily Callander & Joanne Enticott
Monash Partners Academic Health Science Centre, 43-51 Kanooka Grove, Clayton, VIC, Australia
Helena Teede & Alison Johnson
Stroke and Ageing Research, Department of Medicine, School of Clinical Sciences at Monash Health, Monash University, Level 2 Monash University Research, Victorian Heart Hospital, 631 Blackburn Rd, Clayton, VIC, Australia
Dominique A. Cadilhac, Tara Purvis & Monique F. Kilkenny
Stroke Theme, The Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health, University of Melbourne, Heidelberg, VIC, Australia
Dominique A. Cadilhac, Monique F. Kilkenny & Bruce C.V. Campbell
Department of Neurology, Melbourne Brain Centre, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Parkville, VIC, Australia
Bruce C.V. Campbell
Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Dentistry and Health Sciences, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
School of Health Sciences, Heart and Stroke Program, University of Newcastle, Hunter Medical Research Institute, University Drive, Callaghan, NSW, Australia
Coralie English
School of Medicine and Dentistry, Griffith University, Birtinya, QLD, Australia
Rohan S. Grimley
Clinical Excellence Division, Queensland Health, Brisbane, Australia
John Hunter Hospital, Hunter New England Local Health District and University of Newcastle, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Christopher Levi
School of Nursing, Midwifery and Paramedicine, Australian Catholic University, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Sandy Middleton
Nursing Research Institute, St Vincent’s Health Network Sydney and and Australian Catholic University, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Stroke Foundation, Level 7, 461 Bourke St, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
Kelvin Hill
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
HT: conception, design and initial draft, developed the theoretical formalism for learning health system framework, approved the submitted version. DAC: conception, design and initial draft, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. TP: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, approved the submitted version. MFK: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. BC: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. CE: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. AJ: conception, design and initial draft, developed the theoretical formalism for learning health system framework, approved the submitted version. EC: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, approved the submitted version. RSG: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. CL: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. SM: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. KH: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. JE: conception, design and initial draft, developed the theoretical formalism for learning health system framework, approved the submitted version. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ Twitter handles
@HelenaTeede
@DominiqueCad
@Coralie_English
@EmilyCallander
@EnticottJo
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Helena Teede or Dominique A. Cadilhac .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests, additional information, publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Teede, H., Cadilhac, D.A., Purvis, T. et al. Learning together for better health using an evidence-based Learning Health System framework: a case study in stroke. BMC Med 22 , 198 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-024-03416-w
Download citation
Received : 23 July 2023
Accepted : 30 April 2024
Published : 15 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-024-03416-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Evidence-based medicine
- Person-centred care
- Models of care
- Healthcare improvement
BMC Medicine
ISSN: 1741-7015
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
In the tech world and beyond, new 5G applications are being discovered every day. From driverless cars to smarter cities, farms, and even shopping experiences, the latest standard in wireless networks is poised to transform the way we interact with information, devices and each other. What better time to take a closer look at how humans are putting 5G to use to transform their world.
What is 5G?
5G (fifth-generation mobile technology is the newest standard for cellular networks. Like its predecessors, 3G, 4G and 4G LTE, 5G technology uses radio waves for data transmission. However, due to significant improvements in latency, throughput and bandwidth, 5G is capable of faster download and upload speeds than previous networks.
Since its release in 2019, 5G broadband technology has been hailed as a breakthrough technology with significant implications for both consumers and businesses. Primarily, this is due to its ability to handle large volumes of data that is generated by complex devices that use its networks.
As mobile technology has expanded over the years, the number of data users generate every day has increased exponentially. Currently, other transformational technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT ) and machine learning (ML) require faster speeds to function than 3G and 4G networks offer. Enter 5G, with its lightning-fast data transfer capabilities that allow newer technologies to function in the way they were designed to.
Here are some of the biggest differences between 5G and previous wireless networks.
- Physical footprint : The transmitters that are used in 5G technology are smaller than in predecessors’ networks, allowing for discrete placement in out-of-the-way places. Furthermore, “cells”—geographical areas that all wireless networks require for connectivity—in 5G networks are smaller and require less power to run than in previous generations.
- Error rates : 5G’s adaptive Modulation and Coding Scheme (MCS), a schematic that wifi devices use to transmit data, is more powerful than ones in 3G and 4G networks. This makes 5G’s Block Error Rate (BER)—a metric of error frequency—much lower.
- Bandwidth : By using a broader spectrum of radio frequencies than previous wireless networks, 5G networks can transmit on a wider range of bandwidths. This increases the number of devices that they can support at any given time.
- Lower latency : 5G’s low latency , a measurement of the time it takes data to travel from one location to another, is a significant upgrade over previous generations. This means that routine activities like downloading a file or working in the cloud is going to be faster with a 5G connection than a connection on a different network.
Like all wireless networks, 5G networks are separated into geographical areas that are known as cells. Within each cell, wireless devices—such as smartphones, PCs, and IoT devices—connect to the internet via radio waves that are transmitted between an antenna and a base station. The technology that underpins 5G is essentially the same as in 3G and 4G networks. But due to its lower latency, 5G networks are capable of delivering faster download speeds—in some cases as high as 10 gigabits per second (Gbps).
As more and more devices are built for 5G speeds, demand for 5G connectivity is growing. Today, many popular Internet Service Providers (ISPs), such as Verizon, Google and AT&T, offer 5G networks to homes and businesses. According to Statista, more than 200 million homes and businesses have already purchased it with that number expected to at least double by 2028 (link resides outside ibm.com).
Let’s take a look at three areas of technological improvement that have made 5G so unique.
New telecom specifications
The 5G NR (New Radio) standard for cellular networks defines a new radio access technology (RAT) specification for all 5G mobile networks. The 5G rollout began in 2018 with a global initiative known as the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3FPP). The initiative defined a new set of standards to steer the design of devices and applications for use on 5G networks.
The initiative was a success, and 5G networks grew swiftly in the ensuing years. Today, 45% of networks worldwide are 5G compatible, with that number forecasted to rise to 85% by the end of the decade according to a recent report by Ericsson (link resides outside ibm.com).
Independent virtual networks (network slicing)
On 5G networks, network operators can offer multiple independent virtual networks (in addition to public ones) on the same infrastructure. Unlike previous wireless networks, this new capability allows users to do more things remotely with greater security than ever before. For example, on a 5G network, enterprises can create use cases or business models and assign them their own independent virtual network. This dramatically improves the user experience for their employees by adding greater customizability and security.
Private networks
In addition to network slicing, creating a 5G private network can also enhance personalization and security features over those available on previous generations of wireless networks. Global businesses seeking more control and mobility for their employees increasingly turn to private 5G network architectures rather than public networks they’ve used in the past.
Now that we better understand how 5G technology works, let’s take a closer look at some of the exciting applications it’s enabling.
Autonomous vehicles
From taxi cabs to drones and beyond, 5G technology underpins most of the next-generation capabilities in autonomous vehicles. Until the 5G cellular standard came along, fully autonomous vehicles were a bit of a pipe dream due to the data transmission limitations of 3G and 4G technology. Now, 5G’s lightning-fast connection speeds have made transport systems for cars, trains and more, faster than previous generations, transforming the way systems and devices connect, communicate and collaborate.
Smart factories
5G, along with AI and ML, is poised to help factories become not only smarter but more automated, efficient, and resilient. Today, many mundane but necessary tasks that are associated with equipment repair and optimization are being turned over to machines thanks to 5G connectivity paired with AI and ML capabilities. This is one area where 5G is expected to be highly disruptive, impacting everything from fuel economy to the design of equipment lifecycles and how goods arrive at our homes.
For example, on a busy factory floor, drones and cameras that are connected to smart devices that use the IoT can help locate and transport something more efficiently than in the past and prevent theft. Not only is this better for the environment and consumers, but it also frees up employees to dedicate their time and energy to tasks that are more suited to their skill sets.
Smart cities
The idea of a hyper-connected urban environment that uses 5G network speeds to spur innovation in areas like law enforcement, waste disposal and disaster mitigation is fast becoming a reality. Some cities already use 5G-enabled sensors to track traffic patterns in real time and adjust signals, helping guide the flow of traffic, minimize congestion, and improve air quality.
In another example, 5G power grids monitor supply and demand across heavily populated areas and deploy AI and ML applications to “learn” what times energy is in high or low demand. This process has been shown to significantly impact energy conservation and waste, potentially reducing carbon emissions and helping cities reach sustainability goals.
Smart healthcare
Hospitals, doctors, and the healthcare industry as a whole already benefit from the speed and reliability of 5G networks every day. One example is the area of remote surgery that uses robotics and a high-definition live stream that is connected to the internet via a 5G network. Another is the field of mobile health, where 5G gives medical workers in the field quick access to patient data and medical history. This enables them to make smarter decisions, faster, and potentially save lives.
Lastly, as we saw during the pandemic, contact tracing and the mapping of outbreaks are critical to keeping populations safe. 5G’s ability to deliver of volumes of data swiftly and securely allows experts to make more informed decisions that have ramifications for everyone.
5G paired with new technological capabilities won’t just result in the automation of employee tasks, it will dramatically improve them and the overall employee experience . Take virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), for example. VR (digital environments that shut out the real world) and AR (digital content that augments the real world) are already used by stockroom employees, transportation drivers and many others. These employees rely on wearables that are connected to a 5G network capable of high-speed data transfer rates that improve several key capabilities, including the following:
- Live views : 5G connectivity provides live, real-time views of equipment, events, and even people. One way in which this feature is being used in professional sports is to allow broadcasters to remotely call a sporting event from outside the stadium where the event is taking place.
- Digital overlays : IoT applications in a warehouse or industrial setting allow workers that are equipped with smart glasses (or even just a smartphone) to obtain real-time insights from an application. This includes repair instructions or the name and location of a spare part.
- Drone inspections : Right now, one of the leading causes of employee injury is inspection of equipment or project sites in remote and potentially dangerous areas. Drones, which are connected via 5G networks, can safely monitor equipment and project sites and even take readings from hard-to-reach gauges.
Edge computing , a computing framework that allows computations to be done closer to data sources, is fast becoming the standard for enterprises. According to this Gartner white paper (link resides outside ibm.com), by 2025, 75% of enterprise data will be processed at the edge (compared to only 10% today). This shift saves businesses time and money and enables better control over large volumes of data. It would be impossible without the new speed standards that are generated by 5G technology.
Ultra-reliable edge computing and 5G enable the enterprise to achieve faster transmission speeds, increased control and greater security over massive volumes of data. Together, these twin technologies will help reduce latency while increasing speed, reliability and bandwidth, resulting in faster, more comprehensive data analysis and insights for businesses everywhere.
5G solutions with IBM Cloud Satellite
5G presents significant opportunities for the enterprise, but first, you need a platform that can handle its speed. IBM Cloud Satellite® lets you deploy and run apps consistently across on-premises, edge computing and public cloud environments on a 5G network. And it’s all enabled by secure and auditable communications within the IBM Cloud®.
Get the latest tech insights and expert thought leadership in your inbox.
Get our newsletters and topic updates that deliver the latest thought leadership and insights on emerging trends.
An official website of the United States government, Department of Justice.
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Drug-Impaired Driving: The Contribution of Emerging and Undertested Drugs
Impaired driving is often associated with alcohol use and frequently leads to accidents, injuries, and fatalities. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, one person was killed every 39 minutes in an alcohol-related crash in 2021. [1] But alcohol is not the only concern; the use of illicit drugs, legalized drugs such as cannabis, and the abuse of prescription medications may also impair a driver’s abilities. In 2022, an estimated 13.6 million people drove under the influence of illicit drugs during the prior year. [2]
In 2007, the National Safety Council (NSC) introduced testing scope and cutoff standardization for impaired driving cases and traffic fatalities to improve testing consistency. Since 2013, it has recommended that forensic toxicology labs regularly test blood for 35 of the most often encountered drugs and metabolites. Referred to as Tier I drugs ( Figure 1 ), they are now included as a testing standard in many forensic toxicology labs. [3] Furthermore, these compounds can be detected and confirmed with commonly used analytical instrumentation.
Figure 1. List of Tier I and Tier II drugs. Tier II drugs can be both individually named drugs and classes of drugs (e.g., atypical antipsychotics).
NSC also created a second drug category with significant impairment potential, termed Tier II drugs. These drugs include emerging novel psychoactive substances, prescription drugs, and traditional drugs of abuse with limited or regional prevalence, many of which require advanced instrumentation for detection. Most laboratories test for Tier I drugs, but only test for select Tier II drugs when they are regionally relevant. Therefore, the frequency and the types of Tier II substances contributing to drug-impaired driving cases and fatal crashes is not well understood.
NIJ-funded researchers from the Center for Forensic Science Research and Education examined blood samples from over 2,500 driving under the influence of drugs (DUID) cases. The goal was to create a detailed picture of both Tier I and Tier II drugs that contribute to impaired driving cases and compare results to the NSC’s recommended testing scopes. Researchers also analyzed drug presence at various blood alcohol concentrations to assess the operational impact of different testing thresholds and stop limit testing.
What is Stop Limit Testing?
If a sample meets or exceeds a pre-determined blood alcohol concentration threshold, some labs will not perform any additional drug tests. This cutoff is most commonly either 0.08% or 0.10%. [4] The legal blood alcohol limit in the U.S. across every state is 0.08%. Labs that adhere to this practice will not detect other drugs that may cause or contribute to driving impairment.
This stop limit testing can interfere with a comprehensive understanding of drug involvement in impaired driving. Why do so many labs use it?
- Toxicology labs have limited budgets and resources.
- Driving impairment can be explained by the blood alcohol concentration alone.
- A lack of enhanced penalties for drug use means there is no need to measure beyond the blood alcohol level.
- Agencies that use the laboratories’ services have requested this limit.
National Safety Council Recommendations Are Supported
Researchers estimated the frequency with which drugs contribute to the national DUID problem by testing 2,514 cases using a scope of 850 therapeutic, abused, and emerging drugs. They examined deidentified blood samples randomly selected from a pool of suspected impaired driving cases. The samples were collected from NMS Labs in Horsham, Pennsylvania, between 2017 –2020.
Of the 2,514 suspected DUID cases examined:
- The overall drug positivity (Tier I or Tier II drugs) was 79%, nearly double the 40% positive for alcohol ( Figure 2 ).
- A smaller portion of cases (23%) tested positive for both drugs and alcohol.
- Only 17% of the cases were positive for alcohol alone.
- Naturally occurring cannabinoids experienced a statistically significant increase in positivity over the four years.
Figure 2. The frequency of cases with (a) no drugs or ethanol detected (4%), (b) ethanol detected (40%), (c) drugs and ethanol detected (23%), and (d) drugs detected (79%).
Alcohol use in combination with drugs spanning multiple categories was common, as was multiple drugs used in combination. THC (the primary psychoactive component of marijuana) was most often found with ethanol (n=359), and it was frequently found with amphetamine/methamphetamine (n=146).
Samples with a blood alcohol content of 0.08% or higher that were also positive for either Tier I or Tier II drugs occurred 19% of the time (n=478). Cases with blood alcohol content of 0.10% (the cutoff used most frequently by toxicology labs) were also positive for Tier I or Tier II drugs 17.3% of the time (n=434). This suggests that laboratories employing stop limit testing may miss many drug-positive cases.
“Limiting testing based on alcohol results precludes information of drug involvement in several cases and leads to underreporting of drug contributions to impaired driving,” said Mandi Moore, one of the researchers involved in the study.
The research supported NSC’s recommendations for Tier I and Tier II testing. Tier I drugs were found in 73% of suspected impaired driving cases while only 3% contained just Tier II drugs. This suggests that Tier I testing captures the vast majority of drug-involved DUID cases. However, some Tier II drugs (diphenhydramine, gabapentin, hydroxyzine, and two novel psychoactive substances) were found as often or more often than some Tier I drugs, potentially indicating their increased prevalence and a need to re-examine guidelines.
Study Limitations
The cases used in this analysis were exclusively from Pennsylvania. Therefore, they provide a geographically limited snapshot rather than a comprehensive characterization for the entire U.S. population. However, the sample size of over 2,500 cases was “suitable to meet the research goals outlined” by the researchers.
Because Tier II and novel psychoactive substances were found in relatively low frequencies, the researchers did not develop or validate additional confirmatory methods as they had previously planned.
Filling in the Big Picture Details
This work increases awareness of drugs that labs are less likely to test for and labs’ role in addressing the DUID problem. It also demonstrates how frequently DUID cases involve drugs other than alcohol. Although stop limit testing can be justified, data on both alcohol and drug use creates the clearest picture of DUID contributing factors. Current estimates of drug frequency in DUID cases are likely to be inaccurate and actual usage is likely to be higher than previously believed due to stop limit testing. Equipping labs with sufficient resources could encourage labs to eliminate stop limit testing.
About This Article
The work described in this article was supported by NIJ award number 2020-DQ-BX-0009 , awarded to the Frederic Rieders Family Renaissance Foundation.
This article is based on the grantee report “ Assessment of the Contribution to Drug Impaired Driving from Emerging and Undertested Drugs ” (pdf, 26 pages), by Amanda L.A. Mohr and Barry Logan, The Center for Forensic Science Research and Education (CFSRE) at the Frederic Rieders Family Renaissance Foundation.
[1] NHTSA.gov, accessed January 29,2024, https://www.nhtsa.gov/risky-driving .
[2] Select Illicit Drugs include the use of marijuana, cocaine (including crack), heroin, hallucinogens, inhalants, or methamphetamine. For more information, see "Table 8.35A" in 2022 NSDUH Detailed Tables, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt42728/NSDUHDetailedTabs2022/NSDUHDetailedTabs2022/NSDUHDetTabsSect8pe2022.htm#tab8.35a .
[3] ANSO/ASB Standard 120.
[4] Amanda D’Orazio, Amada Mohr, and Barry Logan, “Updates for Recommendations for Drug Testing in DUID & Traffic Fatality Investigations, Toxicology Laboratory Survey,” Willow Grove, PA: The Center for Forensic Science Research & Education at the Frederic Rieders Family Foundation, June 28, 2020, https://www.cfsre.org/images/content/research/toxicology/Survey_Report_Final.pdf .
Cite this Article
Read more about:, related publications.
- Assessment of the Contribution to Drug Impaired Driving from Emerging and Undertested Drugs
Related Awards
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to footer
Products and Services
Contact cisco.
To get global contact information, please make your selections in the drop-down menus.
Country/region and language
Get in touch
Please reach out to sales for general inquiries or to chat with a live agent.
Sales inquiries
1 800 553 6387 , press 1
Order and billing
1 800 553 6387 , press 2-1
Monday to Friday 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. Eastern Time Chat is available to you 24/7.
Find technical support for products and licensing, access to support case manager, and chat with support assistant. Technical support is available 24/7.
Enterprise and service providers
1 800 553 2447 (U.S. and Canada)
Small business
1 866 606 1866 (U.S. and Canada)
Training and certifications
1 800 553 6387 , press 4
Explore support
Explore certification support
Cisco partners
Become a partner, locate a partner, get updates, and partner support.
Explore Cisco partners
Get partner support
Find a Cisco office
Find offices around the world.
Locate offices
Corporate headquarters
300 East Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134
Legal mailing address
Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, California 95134

Complete the form below or log in and the form will autofill. One of our sales specialists will call you within 15 minutes or on a date or time you request. Specialists are available Monday through Friday, 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. Eastern Time. We are currently experiencing delays in response times. If you require an immediate sales response – please call us 1 800-553-6387. Otherwise, a sales advisor will call you as soon as possible. * Required
Want to use a different email? Sign out * Required

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail. Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail. 3. EndeavourX and Figma.
January 7, 2021. It's no surprise that partner case studies are a wee bit of a struggle to produce.Getting your customers to agree to a case study is one thing; getting your customer and your partner to agree to a case study is a miracle. On top of the fact that the partnerships world is still such a gray area for partner managers everywhere (let alone their leadership), partner case studies ...
We've put together 15 real-life case study examples to inspire you. These examples cover a variety of industries and formats, plus templates to inspire you. ... As a result of their partnership, Immi's community grew to more than 400 dedicated members, generating over $200,000 in total affiliate sales.
Why the Apple Co-branding Campaign Works. It's a genius co-branding move that helps both parties give a better experience to customers — and with the popularity of fitness tracking technology, Nike is ahead of the curve by making it easy for athletes to track while they play. 17. Bonne Belle & Dr. Pepper.
Options include PDF documents, web pages, blog posts, slides, videos, or podcasts. To make your case study easy to read, understand, and remember, you should use a catchy title that summarizes the ...
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: ... By showcasing successful partnerships, you make it easier for prospects to place trust in your offerings. This effect is particularly notable when the featured customer holds a reputable status.
These case studies underscore the transformative impact of strategic partnerships on businesses of all sizes. By aligning complementary strengths and resources, companies can unlock new ...
This type of case study can sound more real and human to your audience — they'll know the partnership between you and your client was a genuine success. 4. Find the right case study candidate. ... Business Case Study Examples. You drove the results, made the connection, set the expectations, used the questionnaire to conduct a successful ...
Below I'll provide three partnership case studies of partnerships that paint a picture of the way these three factors influence partnership success, without placing much attention on smart goals. ... For example, if a business takes special care to promote environmentally friendly practices, it would do well to partner with businesses with a ...
Strategic partnerships have led other businesses to great success. Small but quickly growing retailing company Quirky, for example, partnered with manufacturing conglomerate General Electric in a five-year, $30 million deal to release app-enabled household products under the co-branded product line WINK. Due to the partnership, co-branded ...
Pinterest Shopify App Case Study: The partnership between Pinterest and Shopify is highlighted as an example of successful partnership marketing. Both companies benefit, as do their primary users (e-commerce websites on Shopify and users on Pinterest).
Case studies in partnerships. Here you will find a series of case studies of partnerships in action within a range of Cochrane Groups. These talk about the background to the partnership, its development, the benefit to both sides and tips for Groups. If you have examples of partnership work that you would like to share, please contact Cochrane ...
This article explores the various facets of building successful sports partnerships through seven key sections, each illustrated with real-world case studies. 1. Identifying the Right Partners ...
Managing strategic partnerships | McKinsey. Partnerships never go out of style. Companies regularly seek partners with complementary capabilities to gain access to new markets and channels, share intellectual property or infrastructure, or reduce risk. The more complex the business environment becomes—for instance, as new technologies emerge ...
The five case studies listed below are well-written, well-designed, and incorporate a time-tested structure. 1. Lane Terralever and Pinnacle at Promontory. This case study example from Lane Terralever incorporates images to support the content and effectively uses subheadings to make the piece scannable. 2.
One well-known partnership marketing example is when BMW and Louis Vuitton collaborated to create and promote an LV luggage set that was designed to fit perfectly into the trunk of a popular BMW model. Check out the full guide for more examples of partnership marketing and a detailed partnership marketing case study.
5) Snapchat + Square's Snapcash. It is also an intellect partnership. Square adds the credibility of secure money transfers and also a young, hip, complementary brand image for the target audience of this service. For Square, it adds significant incremental revenue and a further boost to its cutting-edge, hip brand image through the ...
Despite spending $2.5 trillion a year on roads, railways, ports, water, and other public infrastructure projects, countries around the world are still falling far short of what they need to invest ...
Partnership Case Study Niagara Adapts Case Study: An Interview with Dr. Jessica Blythe ... You can mitigate these risks by transparent about all aspects of the partnership. For example, clear memorandums of understanding (MOUs) can be a useful tool to manage expectations. Before beginning a partnership, conducting a survey with partnerships ...
This study used data collected for a broader case study that we reported in detail elsewhere (Fynn et al., 2021). We conducted thematic content analysis ( Hsieh and Shannon, 2005 ) of data from semi-structured interviews to identify partnerships, and themes related to stakeholders' experiences and perceptions of those partnerships, the ...
This research is a case study that included 50 partnership businesses (SME-small and medium enterprises) in the District Pulwama, Kashmir valley, India. The information relevant to the aim of ...
In this alert, we summarise three of the most notable and interesting Partnership and LLP law cases heard by the UK courts in 2021, with some practical commentary on how these cases might affect LLPs and partnerships, and their members and partners. 1. Dixon Coles and Gill (a firm) v Right Reverend, Nicholas Baines, Bishop of Leeds and another ...
Download Table of Cases (2.7 MB) Download I: What is a Partnership (21.6 MB) Download II: For What Purpose Organized (14.8 MB) Download III: Who May Be Partners (18.4 MB) Download IV: What Contracts and Acts Create Partnership (11.7 MB) Download V: Nature of Partner's Interest in Property (30.8 MB) Download VI: The Firm Name and Good Will (4.6 MB)
This LHS case study is a practical example for other health conditions and settings to follow suit. Skip to main content. Advertisement. Search. Explore journals ... established and broad partnerships across the academic-clinical sector divide and stakeholder engagement; (2) the living guidelines program; (3) national data infrastructure, ...
The 5G rollout began in 2018 with a global initiative known as the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3FPP). The initiative defined a new set of standards to steer the design of devices and applications for use on 5G networks. ... For example, on a 5G network, enterprises can create use cases or business models and assign them their own ...
Study Limitations. The cases used in this analysis were exclusively from Pennsylvania. Therefore, they provide a geographically limited snapshot rather than a comprehensive characterization for the entire U.S. population. However, the sample size of over 2,500 cases was "suitable to meet the research goals outlined" by the researchers.
Find technical support for products and licensing, access to support case manager, and chat with support assistant. Technical support is available 24/7. Enterprise and service providers. 1 800 553 2447 (U.S. and Canada) Small business. 1 866 606 1866 (U.S. and Canada) Training and certifications. 1 800 553 6387, press 4. Explore support