Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper

Definition and Purpose of Abstracts
An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes:
- an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to read the full paper;
- an abstract prepares readers to follow the detailed information, analyses, and arguments in your full paper;
- and, later, an abstract helps readers remember key points from your paper.
It’s also worth remembering that search engines and bibliographic databases use abstracts, as well as the title, to identify key terms for indexing your published paper. So what you include in your abstract and in your title are crucial for helping other researchers find your paper or article.
If you are writing an abstract for a course paper, your professor may give you specific guidelines for what to include and how to organize your abstract. Similarly, academic journals often have specific requirements for abstracts. So in addition to following the advice on this page, you should be sure to look for and follow any guidelines from the course or journal you’re writing for.
The Contents of an Abstract
Abstracts contain most of the following kinds of information in brief form. The body of your paper will, of course, develop and explain these ideas much more fully. As you will see in the samples below, the proportion of your abstract that you devote to each kind of information—and the sequence of that information—will vary, depending on the nature and genre of the paper that you are summarizing in your abstract. And in some cases, some of this information is implied, rather than stated explicitly. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , which is widely used in the social sciences, gives specific guidelines for what to include in the abstract for different kinds of papers—for empirical studies, literature reviews or meta-analyses, theoretical papers, methodological papers, and case studies.
Here are the typical kinds of information found in most abstracts:
- the context or background information for your research; the general topic under study; the specific topic of your research
- the central questions or statement of the problem your research addresses
- what’s already known about this question, what previous research has done or shown
- the main reason(s) , the exigency, the rationale , the goals for your research—Why is it important to address these questions? Are you, for example, examining a new topic? Why is that topic worth examining? Are you filling a gap in previous research? Applying new methods to take a fresh look at existing ideas or data? Resolving a dispute within the literature in your field? . . .
- your research and/or analytical methods
- your main findings , results , or arguments
- the significance or implications of your findings or arguments.
Your abstract should be intelligible on its own, without a reader’s having to read your entire paper. And in an abstract, you usually do not cite references—most of your abstract will describe what you have studied in your research and what you have found and what you argue in your paper. In the body of your paper, you will cite the specific literature that informs your research.
When to Write Your Abstract
Although you might be tempted to write your abstract first because it will appear as the very first part of your paper, it’s a good idea to wait to write your abstract until after you’ve drafted your full paper, so that you know what you’re summarizing.
What follows are some sample abstracts in published papers or articles, all written by faculty at UW-Madison who come from a variety of disciplines. We have annotated these samples to help you see the work that these authors are doing within their abstracts.
Choosing Verb Tenses within Your Abstract
The social science sample (Sample 1) below uses the present tense to describe general facts and interpretations that have been and are currently true, including the prevailing explanation for the social phenomenon under study. That abstract also uses the present tense to describe the methods, the findings, the arguments, and the implications of the findings from their new research study. The authors use the past tense to describe previous research.
The humanities sample (Sample 2) below uses the past tense to describe completed events in the past (the texts created in the pulp fiction industry in the 1970s and 80s) and uses the present tense to describe what is happening in those texts, to explain the significance or meaning of those texts, and to describe the arguments presented in the article.
The science samples (Samples 3 and 4) below use the past tense to describe what previous research studies have done and the research the authors have conducted, the methods they have followed, and what they have found. In their rationale or justification for their research (what remains to be done), they use the present tense. They also use the present tense to introduce their study (in Sample 3, “Here we report . . .”) and to explain the significance of their study (In Sample 3, This reprogramming . . . “provides a scalable cell source for. . .”).
Sample Abstract 1
From the social sciences.
Reporting new findings about the reasons for increasing economic homogamy among spouses
Gonalons-Pons, Pilar, and Christine R. Schwartz. “Trends in Economic Homogamy: Changes in Assortative Mating or the Division of Labor in Marriage?” Demography , vol. 54, no. 3, 2017, pp. 985-1005.
![abstracts articles research “The growing economic resemblance of spouses has contributed to rising inequality by increasing the number of couples in which there are two high- or two low-earning partners. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the topic under study (the “economic resemblance of spouses”). This sentence also implies the question underlying this research study: what are the various causes—and the interrelationships among them—for this trend?] The dominant explanation for this trend is increased assortative mating. Previous research has primarily relied on cross-sectional data and thus has been unable to disentangle changes in assortative mating from changes in the division of spouses’ paid labor—a potentially key mechanism given the dramatic rise in wives’ labor supply. [Annotation for the previous two sentences: These next two sentences explain what previous research has demonstrated. By pointing out the limitations in the methods that were used in previous studies, they also provide a rationale for new research.] We use data from the Panel Study of Income Dynamics (PSID) to decompose the increase in the correlation between spouses’ earnings and its contribution to inequality between 1970 and 2013 into parts due to (a) changes in assortative mating, and (b) changes in the division of paid labor. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The data, research and analytical methods used in this new study.] Contrary to what has often been assumed, the rise of economic homogamy and its contribution to inequality is largely attributable to changes in the division of paid labor rather than changes in sorting on earnings or earnings potential. Our findings indicate that the rise of economic homogamy cannot be explained by hypotheses centered on meeting and matching opportunities, and they show where in this process inequality is generated and where it is not.” (p. 985) [Annotation for the previous two sentences: The major findings from and implications and significance of this study.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-1.png)
Sample Abstract 2
From the humanities.
Analyzing underground pulp fiction publications in Tanzania, this article makes an argument about the cultural significance of those publications
Emily Callaci. “Street Textuality: Socialism, Masculinity, and Urban Belonging in Tanzania’s Pulp Fiction Publishing Industry, 1975-1985.” Comparative Studies in Society and History , vol. 59, no. 1, 2017, pp. 183-210.
![abstracts articles research “From the mid-1970s through the mid-1980s, a network of young urban migrant men created an underground pulp fiction publishing industry in the city of Dar es Salaam. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the context for this research and announces the topic under study.] As texts that were produced in the underground economy of a city whose trajectory was increasingly charted outside of formalized planning and investment, these novellas reveal more than their narrative content alone. These texts were active components in the urban social worlds of the young men who produced them. They reveal a mode of urbanism otherwise obscured by narratives of decolonization, in which urban belonging was constituted less by national citizenship than by the construction of social networks, economic connections, and the crafting of reputations. This article argues that pulp fiction novellas of socialist era Dar es Salaam are artifacts of emergent forms of male sociability and mobility. In printing fictional stories about urban life on pilfered paper and ink, and distributing their texts through informal channels, these writers not only described urban communities, reputations, and networks, but also actually created them.” (p. 210) [Annotation for the previous sentences: The remaining sentences in this abstract interweave other essential information for an abstract for this article. The implied research questions: What do these texts mean? What is their historical and cultural significance, produced at this time, in this location, by these authors? The argument and the significance of this analysis in microcosm: these texts “reveal a mode or urbanism otherwise obscured . . .”; and “This article argues that pulp fiction novellas. . . .” This section also implies what previous historical research has obscured. And through the details in its argumentative claims, this section of the abstract implies the kinds of methods the author has used to interpret the novellas and the concepts under study (e.g., male sociability and mobility, urban communities, reputations, network. . . ).]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-2.png)
Sample Abstract/Summary 3
From the sciences.
Reporting a new method for reprogramming adult mouse fibroblasts into induced cardiac progenitor cells
Lalit, Pratik A., Max R. Salick, Daryl O. Nelson, Jayne M. Squirrell, Christina M. Shafer, Neel G. Patel, Imaan Saeed, Eric G. Schmuck, Yogananda S. Markandeya, Rachel Wong, Martin R. Lea, Kevin W. Eliceiri, Timothy A. Hacker, Wendy C. Crone, Michael Kyba, Daniel J. Garry, Ron Stewart, James A. Thomson, Karen M. Downs, Gary E. Lyons, and Timothy J. Kamp. “Lineage Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into Proliferative Induced Cardiac Progenitor Cells by Defined Factors.” Cell Stem Cell , vol. 18, 2016, pp. 354-367.
![abstracts articles research “Several studies have reported reprogramming of fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocytes; however, reprogramming into proliferative induced cardiac progenitor cells (iCPCs) remains to be accomplished. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence announces the topic under study, summarizes what’s already known or been accomplished in previous research, and signals the rationale and goals are for the new research and the problem that the new research solves: How can researchers reprogram fibroblasts into iCPCs?] Here we report that a combination of 11 or 5 cardiac factors along with canonical Wnt and JAK/STAT signaling reprogrammed adult mouse cardiac, lung, and tail tip fibroblasts into iCPCs. The iCPCs were cardiac mesoderm-restricted progenitors that could be expanded extensively while maintaining multipo-tency to differentiate into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells in vitro. Moreover, iCPCs injected into the cardiac crescent of mouse embryos differentiated into cardiomyocytes. iCPCs transplanted into the post-myocardial infarction mouse heart improved survival and differentiated into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells. [Annotation for the previous four sentences: The methods the researchers developed to achieve their goal and a description of the results.] Lineage reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs provides a scalable cell source for drug discovery, disease modeling, and cardiac regenerative therapy.” (p. 354) [Annotation for the previous sentence: The significance or implications—for drug discovery, disease modeling, and therapy—of this reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-3.png)
Sample Abstract 4, a Structured Abstract
Reporting results about the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis, from a rigorously controlled study
Note: This journal requires authors to organize their abstract into four specific sections, with strict word limits. Because the headings for this structured abstract are self-explanatory, we have chosen not to add annotations to this sample abstract.
Wald, Ellen R., David Nash, and Jens Eickhoff. “Effectiveness of Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Potassium in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis in Children.” Pediatrics , vol. 124, no. 1, 2009, pp. 9-15.
“OBJECTIVE: The role of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis (ABS) in children is controversial. The purpose of this study was to determine the effectiveness of high-dose amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate in the treatment of children diagnosed with ABS.
METHODS : This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Children 1 to 10 years of age with a clinical presentation compatible with ABS were eligible for participation. Patients were stratified according to age (<6 or ≥6 years) and clinical severity and randomly assigned to receive either amoxicillin (90 mg/kg) with potassium clavulanate (6.4 mg/kg) or placebo. A symptom survey was performed on days 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, and 30. Patients were examined on day 14. Children’s conditions were rated as cured, improved, or failed according to scoring rules.
RESULTS: Two thousand one hundred thirty-five children with respiratory complaints were screened for enrollment; 139 (6.5%) had ABS. Fifty-eight patients were enrolled, and 56 were randomly assigned. The mean age was 6630 months. Fifty (89%) patients presented with persistent symptoms, and 6 (11%) presented with nonpersistent symptoms. In 24 (43%) children, the illness was classified as mild, whereas in the remaining 32 (57%) children it was severe. Of the 28 children who received the antibiotic, 14 (50%) were cured, 4 (14%) were improved, 4(14%) experienced treatment failure, and 6 (21%) withdrew. Of the 28children who received placebo, 4 (14%) were cured, 5 (18%) improved, and 19 (68%) experienced treatment failure. Children receiving the antibiotic were more likely to be cured (50% vs 14%) and less likely to have treatment failure (14% vs 68%) than children receiving the placebo.
CONCLUSIONS : ABS is a common complication of viral upper respiratory infections. Amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate results in significantly more cures and fewer failures than placebo, according to parental report of time to resolution.” (9)
Some Excellent Advice about Writing Abstracts for Basic Science Research Papers, by Professor Adriano Aguzzi from the Institute of Neuropathology at the University of Zurich:

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write an Abstract

Expedite peer review, increase search-ability, and set the tone for your study
The abstract is your chance to let your readers know what they can expect from your article. Learn how to write a clear, and concise abstract that will keep your audience reading.
How your abstract impacts editorial evaluation and future readership
After the title , the abstract is the second-most-read part of your article. A good abstract can help to expedite peer review and, if your article is accepted for publication, it’s an important tool for readers to find and evaluate your work. Editors use your abstract when they first assess your article. Prospective reviewers see it when they decide whether to accept an invitation to review. Once published, the abstract gets indexed in PubMed and Google Scholar , as well as library systems and other popular databases. Like the title, your abstract influences keyword search results. Readers will use it to decide whether to read the rest of your article. Other researchers will use it to evaluate your work for inclusion in systematic reviews and meta-analysis. It should be a concise standalone piece that accurately represents your research.
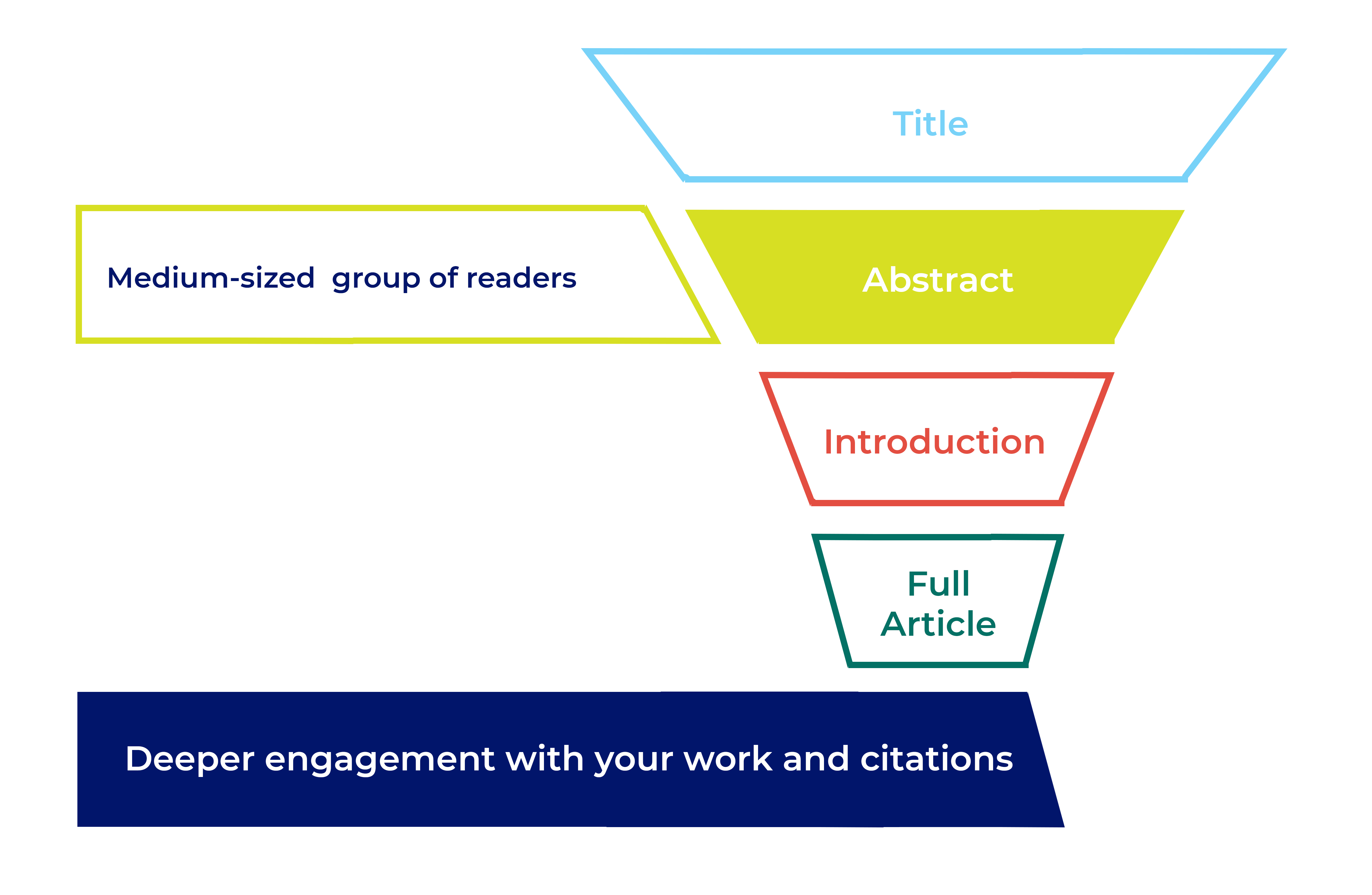
What to include in an abstract
The main challenge you’ll face when writing your abstract is keeping it concise AND fitting in all the information you need. Depending on your subject area the journal may require a structured abstract following specific headings. A structured abstract helps your readers understand your study more easily. If your journal doesn’t require a structured abstract it’s still a good idea to follow a similar format, just present the abstract as one paragraph without headings.
Background or Introduction – What is currently known? Start with a brief, 2 or 3 sentence, introduction to the research area.
Objectives or Aims – What is the study and why did you do it? Clearly state the research question you’re trying to answer.
Methods – What did you do? Explain what you did and how you did it. Include important information about your methods, but avoid the low-level specifics. Some disciplines have specific requirements for abstract methods.
- CONSORT for randomized trials.
- STROBE for observational studies
- PRISMA for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
Results – What did you find? Briefly give the key findings of your study. Include key numeric data (including confidence intervals or p values), where possible.
Conclusions – What did you conclude? Tell the reader why your findings matter, and what this could mean for the ‘bigger picture’ of this area of research.
Writing tips
The main challenge you may find when writing your abstract is keeping it concise AND convering all the information you need to.

- Keep it concise and to the point. Most journals have a maximum word count, so check guidelines before you write the abstract to save time editing it later.
- Write for your audience. Are they specialists in your specific field? Are they cross-disciplinary? Are they non-specialists? If you’re writing for a general audience, or your research could be of interest to the public keep your language as straightforward as possible. If you’re writing in English, do remember that not all of your readers will necessarily be native English speakers.
- Focus on key results, conclusions and take home messages.
- Write your paper first, then create the abstract as a summary.
- Check the journal requirements before you write your abstract, eg. required subheadings.
- Include keywords or phrases to help readers search for your work in indexing databases like PubMed or Google Scholar.
- Double and triple check your abstract for spelling and grammar errors. These kind of errors can give potential reviewers the impression that your research isn’t sound, and can make it easier to find reviewers who accept the invitation to review your manuscript. Your abstract should be a taste of what is to come in the rest of your article.

Don’t
- Sensationalize your research.
- Speculate about where this research might lead in the future.
- Use abbreviations or acronyms (unless absolutely necessary or unless they’re widely known, eg. DNA).
- Repeat yourself unnecessarily, eg. “Methods: We used X technique. Results: Using X technique, we found…”
- Contradict anything in the rest of your manuscript.
- Include content that isn’t also covered in the main manuscript.
- Include citations or references.
Tip: How to edit your work
Editing is challenging, especially if you are acting as both a writer and an editor. Read our guidelines for advice on how to refine your work, including useful tips for setting your intentions, re-review, and consultation with colleagues.
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write an abstract

What is an abstract?
General format of an abstract, the content of an abstract, abstract example, abstract style guides, frequently asked questions about writing an abstract, related articles.
An abstract is a summary of the main contents of a paper.
The abstract is the first glimpse that readers get of the content of a research paper. It can influence the popularity of a paper, as a well-written one will attract readers, and a poorly-written one will drive them away.
➡️ Different types of papers may require distinct abstract styles. Visit our guide on the different types of research papers to learn more.
Tip: Always wait until you’ve written your entire paper before you write the abstract.
Before you actually start writing an abstract, make sure to follow these steps:
- Read other papers : find papers with similar topics, or similar methodologies, simply to have an idea of how others have written their abstracts. Notice which points they decided to include, and how in depth they described them.
- Double check the journal requirements : always make sure to review the journal guidelines to format your paper accordingly. Usually, they also specify abstract's formats.
- Write the abstract after you finish writing the paper : you can only write an abstract once you finish writing the whole paper. This way you can include all important aspects, such as scope, methodology, and conclusion.
➡️ Read more about what is a research methodology?
The general format of an abstract includes the following features:
- Between 150-300 words .
- An independent page , after the title page and before the table of contents.
- Concise summary including the aim of the research, methodology , and conclusion .
- Keywords describing the content.
As mentioned before, an abstract is a text that summarizes the main points of a research. Here is a break down of each element that should be included in an abstract:
- Purpose : every abstract should start by describing the main purpose or aim of the research.
- Methods : as a second point, the methodology carried out should be explained.
- Results : then, a concise summary of the results should be included.
- Conclusion : finally, a short outline of the general outcome of the research should be given.
- Keywords : along with the abstract, specific words and phrases related to the topics discussed in the research should be added. These words are usually around five, but the number can vary depending on the journal's guidelines.
This abstract, taken from ScienceDirect , illustrates the ideal structure of an abstract. It has 155 words, it's concise, and it clearly shows the division of elements necessary to write a successful abstract.
This paper explores the implicit assumption in the growing body of literature that social media usage is fundamentally different in business-to-business (B2B) companies than in the extant business-to-consumer (B2C) literature. Sashi's (2012) customer engagement cycle is utilized to compare organizational practices in relation to social media marketing in B2B, B2C, Mixed B2B/B2C and B2B2C business models. Utilizing 449 responses to an exploratory panel based survey instrument, we clearly identify differences in social media usage and its perceived importance as a communications channel. In particular we identify distinct differences in the relationship between social media importance and the perceived effectiveness of social media marketing across business models. Our results indicate that B2B social media usage is distinct from B2C, Mixed and B2B2C business model approaches. Specifically B2B organizational members perceive social media to have a lower overall effectiveness as a channel and identify it as less important for relationship oriented usage than other business models.
The exact format of an abstract depends on the citation style you implement. Whether it’s a well-known style (like APA, IEEE, etc.) or a journal's style, each format has its own guidelines, so make sure you know which style you are using before writing your abstract.
APA is one of the most commonly used styles to format an abstract. Therefore, we created a guide with exact instructions on how to write an abstract in APA style, and a template to download:
📕 APA abstract page: format and template
Additionally, you will find below an IEEE and ASA abstract guide by Purdue Online Writing Lab :
📗 IEEE General Format - Abstract
📘 ASA Manuscript Formatting - Abstract
No. You should always write an abstract once you finish writing the whole paper. This way you can include all important aspects of the paper, such as scope, methodology, and conclusion.
The length of an abstract depends on the formatting style of the paper. For example, APA style calls for 150 to 250 words. Generally, you need between 150-300 words.
No. An abstract has an independent section after the title page and before the table of contents, and should not be included in the table of contents.
Take a look at APA abstract page: format and template for exact details on how to format an abstract in APA style.
You can access any paper through Google Scholar or any other search engine; pick a paper and read the abstract. Abstracts are always freely available to read.


- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing for Publication: Abstracts
An abstract is "a brief, comprehensive summary of the contents of the paper" (American Psychological Association [APA], 2020, p. 38). This summary is intended to share the topic, argument, and conclusions of a research study or course paper, similar to the text on the back cover of a book. When submitting your work for publication, an abstract is often the first piece of your writing a reviewer will encounter. An abstract may not be required for course papers.
Read on for more tips on making a good first impression with a successful abstract.
An abstract is a single paragraph preceded by the heading " Abstract ," centered and in bold font. The abstract does not begin with an indented line. APA (2020) recommends that abstracts should generally be less than 250 words, though many journals have their own word limits; it is always a good idea to check journal-specific requirements before submitting. The Writing Center's APA templates are great resources for visual examples of abstracts.
Abstracts use the present tense to describe currently applicable results (e.g., "Results indicate...") and the past tense to describe research steps (e.g., "The survey measured..."), and they do not typically include citations.
Key terms are sometimes included at the end of the abstract and should be chosen by considering the words or phrases that a reader might use to search for your article.
An abstract should include information such as
- The problem or central argument of your article
- A brief exposition of research design, methods, and procedures.
- A brief summary of your findings
- A brief summary of the implications of the research on practice and theory
It is also appropriate, depending on the type of article you are writing, to include information such as:
- Participant number and type
- Study eligibility criteria
- Limitations of your study
- Implications of your study's conclusions or areas for additional research
Your abstract should avoid unnecessary wordiness and focus on quickly and concisely summarizing the major points of your work. An abstract is not an introduction; you are not trying to capture the reader's attention with timeliness or to orient the reader to the entire background of your study. When readers finish reading your abstract, they should have a strong sense of your article's purpose, approach, and conclusions. The Walden Office of Research and Doctoral Services has additional tutorial material on abstracts .
Clinical or Empirical Study Abstract Exemplar
In the following abstract, the article's problem is stated in red , the approach and design are in blue , and the results are in green .
End-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients have a high cardiovascular mortality rate. Precise estimates of the prevalence, risk factors and prognosis of different manifestations of cardiac disease are unavailable. In this study a prospective cohort of 433 ESRD patients was followed from the start of ESRD therapy for a mean of 41 months. Baseline clinical assessment and echocardiography were performed on all patients. The major outcome measure was death while on dialysis therapy. Clinical manifestations of cardiovascular disease were highly prevalent at the start of ESRD therapy: 14% had coronary artery disease, 19% angina pectoris, 31% cardiac failure, 7% dysrhythmia and 8% peripheral vascular disease. On echocardiography 15% had systolic dysfunction, 32% left ventricular dilatation and 74% left ventricular hypertrophy. The overall median survival time was 50 months. Age, diabetes mellitus, cardiac failure, peripheral vascular disease and systolic dysfunction independently predicted death in all time frames. Coronary artery disease was associated with a worse prognosis in patients with cardiac failure at baseline. High left ventricular cavity volume and mass index were independently associated with death after two years. The independent associations of the different echocardiographic abnormalities were: systolic dysfunction--older age and coronary artery disease; left ventricular dilatation--male gender, anemia, hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia; left ventricular hypertrophy--older age, female gender, wide arterial pulse pressure, low blood urea and hypoalbuminemia. We conclude that clinical and echocardiographic cardiovascular disease are already present in a very high proportion of patients starting ESRD therapy and are independent mortality factors.
Foley, R. N., Parfrey, P. S., Harnett, J. D., Kent, G. M., Martin, C. J., Murray, D. C., & Barre, P. E. (1995). Clinical and echocardiographic disease in patients starting end-stage renal disease therapy. Kidney International , 47 , 186–192. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1995.22
Literature Review Abstract Exemplar
In the following abstract, the purpose and scope of the literature review are in red , the specific span of topics is in blue , and the implications for further research are in green .
This paper provides a review of research into the relationships between psychological types, as measured by the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI), and managerial attributes, behaviors and effectiveness. The literature review includes an examination of the psychometric properties of the MBTI and the contributions and limitations of research on psychological types. Next, key findings are discussed and used to advance propositions that relate psychological type to diverse topics such as risk tolerance, problem solving, information systems design, conflict management and leadership. We conclude with a research agenda that advocates: (a) the exploration of potential psychometric refinements of the MBTI, (b) more rigorous research designs, and (c) a broadening of the scope of managerial research into type.
Gardner, W. L., & Martinko, M. J. (1996). Using the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator to study managers: A literature review and research agenda. Journal of Management, 22 (1), 45–83. https://doi.org/10.1177/014920639602200103
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Cover Letters
- Next Page: Formatting and Editing
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 3. The Abstract
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
An abstract summarizes, usually in one paragraph of 300 words or less, the major aspects of the entire paper in a prescribed sequence that includes: 1) the overall purpose of the study and the research problem(s) you investigated; 2) the basic design of the study; 3) major findings or trends found as a result of your analysis; and, 4) a brief summary of your interpretations and conclusions.
Writing an Abstract. The Writing Center. Clarion University, 2009; Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper. The Writing Center, University of Wisconsin, Madison; Koltay, Tibor. Abstracts and Abstracting: A Genre and Set of Skills for the Twenty-first Century . Oxford, UK: Chandos Publishing, 2010;
Importance of a Good Abstract
Sometimes your professor will ask you to include an abstract, or general summary of your work, with your research paper. The abstract allows you to elaborate upon each major aspect of the paper and helps readers decide whether they want to read the rest of the paper. Therefore, enough key information [e.g., summary results, observations, trends, etc.] must be included to make the abstract useful to someone who may want to examine your work.
How do you know when you have enough information in your abstract? A simple rule-of-thumb is to imagine that you are another researcher doing a similar study. Then ask yourself: if your abstract was the only part of the paper you could access, would you be happy with the amount of information presented there? Does it tell the whole story about your study? If the answer is "no" then the abstract likely needs to be revised.
Farkas, David K. “A Scheme for Understanding and Writing Summaries.” Technical Communication 67 (August 2020): 45-60; How to Write a Research Abstract. Office of Undergraduate Research. University of Kentucky; Staiger, David L. “What Today’s Students Need to Know about Writing Abstracts.” International Journal of Business Communication January 3 (1966): 29-33; Swales, John M. and Christine B. Feak. Abstracts and the Writing of Abstracts . Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2009.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Types of Abstracts
To begin, you need to determine which type of abstract you should include with your paper. There are four general types.
Critical Abstract A critical abstract provides, in addition to describing main findings and information, a judgment or comment about the study’s validity, reliability, or completeness. The researcher evaluates the paper and often compares it with other works on the same subject. Critical abstracts are generally 400-500 words in length due to the additional interpretive commentary. These types of abstracts are used infrequently.
Descriptive Abstract A descriptive abstract indicates the type of information found in the work. It makes no judgments about the work, nor does it provide results or conclusions of the research. It does incorporate key words found in the text and may include the purpose, methods, and scope of the research. Essentially, the descriptive abstract only describes the work being summarized. Some researchers consider it an outline of the work, rather than a summary. Descriptive abstracts are usually very short, 100 words or less. Informative Abstract The majority of abstracts are informative. While they still do not critique or evaluate a work, they do more than describe it. A good informative abstract acts as a surrogate for the work itself. That is, the researcher presents and explains all the main arguments and the important results and evidence in the paper. An informative abstract includes the information that can be found in a descriptive abstract [purpose, methods, scope] but it also includes the results and conclusions of the research and the recommendations of the author. The length varies according to discipline, but an informative abstract is usually no more than 300 words in length.
Highlight Abstract A highlight abstract is specifically written to attract the reader’s attention to the study. No pretense is made of there being either a balanced or complete picture of the paper and, in fact, incomplete and leading remarks may be used to spark the reader’s interest. In that a highlight abstract cannot stand independent of its associated article, it is not a true abstract and, therefore, rarely used in academic writing.
II. Writing Style
Use the active voice when possible , but note that much of your abstract may require passive sentence constructions. Regardless, write your abstract using concise, but complete, sentences. Get to the point quickly and always use the past tense because you are reporting on a study that has been completed.
Abstracts should be formatted as a single paragraph in a block format and with no paragraph indentations. In most cases, the abstract page immediately follows the title page. Do not number the page. Rules set forth in writing manual vary but, in general, you should center the word "Abstract" at the top of the page with double spacing between the heading and the abstract. The final sentences of an abstract concisely summarize your study’s conclusions, implications, or applications to practice and, if appropriate, can be followed by a statement about the need for additional research revealed from the findings.
Composing Your Abstract
Although it is the first section of your paper, the abstract should be written last since it will summarize the contents of your entire paper. A good strategy to begin composing your abstract is to take whole sentences or key phrases from each section of the paper and put them in a sequence that summarizes the contents. Then revise or add connecting phrases or words to make the narrative flow clearly and smoothly. Note that statistical findings should be reported parenthetically [i.e., written in parentheses].
Before handing in your final paper, check to make sure that the information in the abstract completely agrees with what you have written in the paper. Think of the abstract as a sequential set of complete sentences describing the most crucial information using the fewest necessary words. The abstract SHOULD NOT contain:
- A catchy introductory phrase, provocative quote, or other device to grab the reader's attention,
- Lengthy background or contextual information,
- Redundant phrases, unnecessary adverbs and adjectives, and repetitive information;
- Acronyms or abbreviations,
- References to other literature [say something like, "current research shows that..." or "studies have indicated..."],
- Using ellipticals [i.e., ending with "..."] or incomplete sentences,
- Jargon or terms that may be confusing to the reader,
- Citations to other works, and
- Any sort of image, illustration, figure, or table, or references to them.
Abstract. Writing Center. University of Kansas; Abstract. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Abstracts. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Borko, Harold and Seymour Chatman. "Criteria for Acceptable Abstracts: A Survey of Abstracters' Instructions." American Documentation 14 (April 1963): 149-160; Abstracts. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Hartley, James and Lucy Betts. "Common Weaknesses in Traditional Abstracts in the Social Sciences." Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology 60 (October 2009): 2010-2018; Koltay, Tibor. Abstracts and Abstracting: A Genre and Set of Skills for the Twenty-first Century. Oxford, UK: Chandos Publishing, 2010; Procter, Margaret. The Abstract. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Riordan, Laura. “Mastering the Art of Abstracts.” The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association 115 (January 2015 ): 41-47; Writing Report Abstracts. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing Abstracts. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Koltay, Tibor. Abstracts and Abstracting: A Genre and Set of Skills for the Twenty-First Century . Oxford, UK: 2010; Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper. The Writing Center, University of Wisconsin, Madison.
Writing Tip
Never Cite Just the Abstract!
Citing to just a journal article's abstract does not confirm for the reader that you have conducted a thorough or reliable review of the literature. If the full-text is not available, go to the USC Libraries main page and enter the title of the article [NOT the title of the journal]. If the Libraries have a subscription to the journal, the article should appear with a link to the full-text or to the journal publisher page where you can get the article. If the article does not appear, try searching Google Scholar using the link on the USC Libraries main page. If you still can't find the article after doing this, contact a librarian or you can request it from our free i nterlibrary loan and document delivery service .
- << Previous: Research Process Video Series
- Next: Executive Summary >>
- Last Updated: May 30, 2024 9:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper | Examples
What is a research paper abstract?
Research paper abstracts summarize your study quickly and succinctly to journal editors and researchers and prompt them to read further. But with the ubiquity of online publication databases, writing a compelling abstract is even more important today than it was in the days of bound paper manuscripts.
Abstracts exist to “sell” your work, and they could thus be compared to the “executive summary” of a business resume: an official briefing on what is most important about your research. Or the “gist” of your research. With the majority of academic transactions being conducted online, this means that you have even less time to impress readers–and increased competition in terms of other abstracts out there to read.
The APCI (Academic Publishing and Conferences International) notes that there are 12 questions or “points” considered in the selection process for journals and conferences and stresses the importance of having an abstract that ticks all of these boxes. Because it is often the ONLY chance you have to convince readers to keep reading, it is important that you spend time and energy crafting an abstract that faithfully represents the central parts of your study and captivates your audience.
With that in mind, follow these suggestions when structuring and writing your abstract, and learn how exactly to put these ideas into a solid abstract that will captivate your target readers.
Before Writing Your Abstract
How long should an abstract be.
All abstracts are written with the same essential objective: to give a summary of your study. But there are two basic styles of abstract: descriptive and informative . Here is a brief delineation of the two:
Of the two types of abstracts, informative abstracts are much more common, and they are widely used for submission to journals and conferences. Informative abstracts apply to lengthier and more technical research and are common in the sciences, engineering, and psychology, while descriptive abstracts are more likely used in humanities and social science papers. The best method of determining which abstract type you need to use is to follow the instructions for journal submissions and to read as many other published articles in those journals as possible.
Research Abstract Guidelines and Requirements
As any article about research writing will tell you, authors must always closely follow the specific guidelines and requirements indicated in the Guide for Authors section of their target journal’s website. The same kind of adherence to conventions should be applied to journal publications, for consideration at a conference, and even when completing a class assignment.
Each publisher has particular demands when it comes to formatting and structure. Here are some common questions addressed in the journal guidelines:
- Is there a maximum or minimum word/character length?
- What are the style and formatting requirements?
- What is the appropriate abstract type?
- Are there any specific content or organization rules that apply?
There are of course other rules to consider when composing a research paper abstract. But if you follow the stated rules the first time you submit your manuscript, you can avoid your work being thrown in the “circular file” right off the bat.
Identify Your Target Readership
The main purpose of your abstract is to lead researchers to the full text of your research paper. In scientific journals, abstracts let readers decide whether the research discussed is relevant to their own interests or study. Abstracts also help readers understand your main argument quickly. Consider these questions as you write your abstract:
- Are other academics in your field the main target of your study?
- Will your study perhaps be useful to members of the general public?
- Do your study results include the wider implications presented in the abstract?
Outlining and Writing Your Abstract
What to include in an abstract.
Just as your research paper title should cover as much ground as possible in a few short words, your abstract must cover all parts of your study in order to fully explain your paper and research. Because it must accomplish this task in the space of only a few hundred words, it is important not to include ambiguous references or phrases that will confuse the reader or mislead them about the content and objectives of your research. Follow these dos and don’ts when it comes to what kind of writing to include:
- Avoid acronyms or abbreviations since these will need to be explained in order to make sense to the reader, which takes up valuable abstract space. Instead, explain these terms in the Introduction section of the main text.
- Only use references to people or other works if they are well-known. Otherwise, avoid referencing anything outside of your study in the abstract.
- Never include tables, figures, sources, or long quotations in your abstract; you will have plenty of time to present and refer to these in the body of your paper.
Use keywords in your abstract to focus your topic
A vital search tool is the research paper keywords section, which lists the most relevant terms directly underneath the abstract. Think of these keywords as the “tubes” that readers will seek and enter—via queries on databases and search engines—to ultimately land at their destination, which is your paper. Your abstract keywords should thus be words that are commonly used in searches but should also be highly relevant to your work and found in the text of your abstract. Include 5 to 10 important words or short phrases central to your research in both the abstract and the keywords section.
For example, if you are writing a paper on the prevalence of obesity among lower classes that crosses international boundaries, you should include terms like “obesity,” “prevalence,” “international,” “lower classes,” and “cross-cultural.” These are terms that should net a wide array of people interested in your topic of study. Look at our nine rules for choosing keywords for your research paper if you need more input on this.
Research Paper Abstract Structure
As mentioned above, the abstract (especially the informative abstract) acts as a surrogate or synopsis of your research paper, doing almost as much work as the thousands of words that follow it in the body of the main text. In the hard sciences and most social sciences, the abstract includes the following sections and organizational schema.
Each section is quite compact—only a single sentence or two, although there is room for expansion if one element or statement is particularly interesting or compelling. As the abstract is almost always one long paragraph, the individual sections should naturally merge into one another to create a holistic effect. Use the following as a checklist to ensure that you have included all of the necessary content in your abstract.

1) Identify your purpose and motivation
So your research is about rabies in Brazilian squirrels. Why is this important? You should start your abstract by explaining why people should care about this study—why is it significant to your field and perhaps to the wider world? And what is the exact purpose of your study; what are you trying to achieve? Start by answering the following questions:
- What made you decide to do this study or project?
- Why is this study important to your field or to the lay reader?
- Why should someone read your entire article?
In summary, the first section of your abstract should include the importance of the research and its impact on related research fields or on the wider scientific domain.
2) Explain the research problem you are addressing
Stating the research problem that your study addresses is the corollary to why your specific study is important and necessary. For instance, even if the issue of “rabies in Brazilian squirrels” is important, what is the problem—the “missing piece of the puzzle”—that your study helps resolve?
You can combine the problem with the motivation section, but from a perspective of organization and clarity, it is best to separate the two. Here are some precise questions to address:
- What is your research trying to better understand or what problem is it trying to solve?
- What is the scope of your study—does it try to explain something general or specific?
- What is your central claim or argument?
3) Discuss your research approach
Your specific study approach is detailed in the Methods and Materials section . You have already established the importance of the research, your motivation for studying this issue, and the specific problem your paper addresses. Now you need to discuss how you solved or made progress on this problem—how you conducted your research. If your study includes your own work or that of your team, describe that here. If in your paper you reviewed the work of others, explain this here. Did you use analytic models? A simulation? A double-blind study? A case study? You are basically showing the reader the internal engine of your research machine and how it functioned in the study. Be sure to:
- Detail your research—include methods/type of the study, your variables, and the extent of the work
- Briefly present evidence to support your claim
- Highlight your most important sources
4) Briefly summarize your results
Here you will give an overview of the outcome of your study. Avoid using too many vague qualitative terms (e.g, “very,” “small,” or “tremendous”) and try to use at least some quantitative terms (i.e., percentages, figures, numbers). Save your qualitative language for the conclusion statement. Answer questions like these:
- What did your study yield in concrete terms (e.g., trends, figures, correlation between phenomena)?
- How did your results compare to your hypothesis? Was the study successful?
- Where there any highly unexpected outcomes or were they all largely predicted?
5) State your conclusion
In the last section of your abstract, you will give a statement about the implications and limitations of the study . Be sure to connect this statement closely to your results and not the area of study in general. Are the results of this study going to shake up the scientific world? Will they impact how people see “Brazilian squirrels”? Or are the implications minor? Try not to boast about your study or present its impact as too far-reaching, as researchers and journals will tend to be skeptical of bold claims in scientific papers. Answer one of these questions:
- What are the exact effects of these results on my field? On the wider world?
- What other kind of study would yield further solutions to problems?
- What other information is needed to expand knowledge in this area?
After Completing the First Draft of Your Abstract
Revise your abstract.
The abstract, like any piece of academic writing, should be revised before being considered complete. Check it for grammatical and spelling errors and make sure it is formatted properly.
Get feedback from a peer
Getting a fresh set of eyes to review your abstract is a great way to find out whether you’ve summarized your research well. Find a reader who understands research papers but is not an expert in this field or is not affiliated with your study. Ask your reader to summarize what your study is about (including all key points of each section). This should tell you if you have communicated your key points clearly.
In addition to research peers, consider consulting with a professor or even a specialist or generalist writing center consultant about your abstract. Use any resource that helps you see your work from another perspective.
Consider getting professional editing and proofreading
While peer feedback is quite important to ensure the effectiveness of your abstract content, it may be a good idea to find an academic editor to fix mistakes in grammar, spelling, mechanics, style, or formatting. The presence of basic errors in the abstract may not affect your content, but it might dissuade someone from reading your entire study. Wordvice provides English editing services that both correct objective errors and enhance the readability and impact of your work.
Additional Abstract Rules and Guidelines
Write your abstract after completing your paper.
Although the abstract goes at the beginning of your manuscript, it does not merely introduce your research topic (that is the job of the title), but rather summarizes your entire paper. Writing the abstract last will ensure that it is complete and consistent with the findings and statements in your paper.
Keep your content in the correct order
Both questions and answers should be organized in a standard and familiar way to make the content easier for readers to absorb. Ideally, it should mimic the overall format of your essay and the classic “introduction,” “body,” and “conclusion” form, even if the parts are not neatly divided as such.
Write the abstract from scratch
Because the abstract is a self-contained piece of writing viewed separately from the body of the paper, you should write it separately as well. Never copy and paste direct quotes from the paper and avoid paraphrasing sentences in the paper. Using new vocabulary and phrases will keep your abstract interesting and free of redundancies while conserving space.
Don’t include too many details in the abstract
Again, the density of your abstract makes it incompatible with including specific points other than possibly names or locations. You can make references to terms, but do not explain or define them in the abstract. Try to strike a balance between being specific to your study and presenting a relatively broad overview of your work.
Wordvice Resources
If you think your abstract is fine now but you need input on abstract writing or require English editing services (including paper editing ), then head over to the Wordvice academic resources page, where you will find many more articles, for example on writing the Results , Methods , and Discussion sections of your manuscript, on choosing a title for your paper , or on how to finalize your journal submission with a strong cover letter .
How to Write an Abstract?
- Open Access
- First Online: 24 October 2021
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- Samiran Nundy 4 ,
- Atul Kakar 5 &
- Zulfiqar A. Bhutta 6
58k Accesses
5 Altmetric
An abstract is a crisp, short, powerful, and self-contained summary of a research manuscript used to help the reader swiftly determine the paper’s purpose. Although the abstract is the first paragraph of the manuscript it should be written last when all the other sections have been addressed.
Research is formalized curiosity. It is poking and prying with a purpose. — Zora Neale Hurston, American Author, Anthropologist and Filmmaker (1891–1960)
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others


Writing the Abstract

Abstract and Keywords

Additional Commentaries
1 what is an abstract.
An abstract is usually a standalone document that informs the reader about the details of the manuscript to follow. It is like a trailer to a movie, if the trailer is good, it stimulates the audience to watch the movie. The abstract should be written from scratch and not ‘cut –and-pasted’ [ 1 ].
2 What is the History of the Abstract?
An abstract, in the form of a single paragraph, was first published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal in 1960 with the idea that the readers may not have enough time to go through the whole paper, and the first abstract with a defined structure was published in 1991 [ 2 ]. The idea sold and now most original articles and reviews are required to have a structured abstract. The abstract attracts the reader to read the full manuscript [ 3 ].
3 What are the Qualities of a Good Abstract?
The quality of information in an abstract can be summarized by four ‘C’s. It should be:
C: Condensed
C: Critical
4 What are the Types of Abstract?
Before writing the abstract, you need to check with the journal website about which type of abstract it requires, with its length and style in the ‘Instructions to Authors’ section.
The abstract types can be divided into:
Descriptive: Usually written for psychology, social science, and humanities papers. It is about 50–100 words long. No conclusions can be drawn from this abstract as it describes the major points in the paper.
Informative: The majority of abstracts for science-related manuscripts are informative and are surrogates for the research done. They are single paragraphs that provide the reader an overview of the research paper and are about 100–150 words in length. Conclusions can be drawn from the abstracts and in the recommendations written in the last line.
Critical: This type of abstract is lengthy and about 400–500 words. In this, the authors’ own research is discussed for reliability, judgement, and validation. A comparison is also made with similar studies done earlier.
Highlighting: This is rarely used in scientific writing. The style of the abstract is to attract more readers. It is not a balanced or complete overview of the article with which it is published.
Structured: A structured abstract contains information under subheadings like background, aims, material and methods, results, conclusion, and recommendations (Fig. 15.1 ). Most leading journals now carry these.
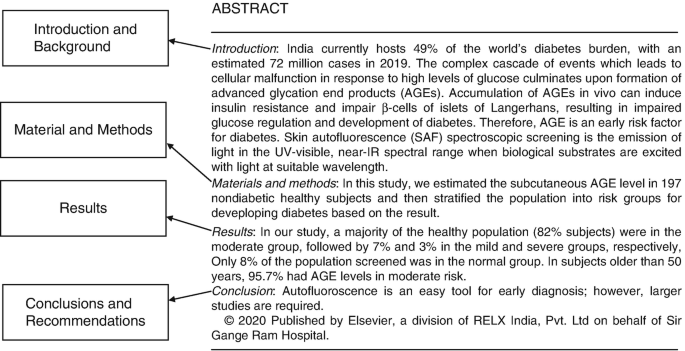
Example of a structured abstract (with permission editor CMRP)
5 What is the Purpose of an Abstract?
An abstract is written to educate the reader about the study that follows and provide an overview of the science behind it. If written well it also attracts more readers to the article. It also helps the article getting indexed. The fate of a paper both before and after publication often depends upon its abstract. Most readers decide if a paper is worth reading on the basis of the abstract. Additionally, the selection of papers in systematic reviews is often dependent upon the abstract.
6 What are the Steps of Writing an Abstract?
An abstract should be written last after all the other sections of an article have been addressed. A poor abstract may turn off the reader and they may cause indexing errors as well. The abstract should state the purpose of the study, the methodology used, and summarize the results and important conclusions. It is usually written in the IMRAD format and is called a structured abstract [ 4 , 5 ].
I: The introduction in the opening line should state the problem you are addressing.
M: Methodology—what method was chosen to finish the experiment?
R: Results—state the important findings of your study.
D: Discussion—discuss why your study is important.
Mention the following information:
Important results with the statistical information ( p values, confidence intervals, standard/mean deviation).
Arrange all information in a chronological order.
Do not repeat any information.
The last line should state the recommendations from your study.
The abstract should be written in the past tense.
7 What are the Things to Be Avoided While Writing an Abstract?
Cut and paste information from the main text
Hold back important information
Use abbreviations
Tables or Figures
Generalized statements
Arguments about the study

8 What are Key Words?
These are important words that are repeated throughout the manuscript and which help in the indexing of a paper. Depending upon the journal 3–10 key words may be required which are indexed with the help of MESH (Medical Subject Heading).
9 How is an Abstract Written for a Conference Different from a Journal Paper?
The basic concept for writing abstracts is the same. However, in a conference abstract occasionally a table or figure is allowed. A word limit is important in both of them. Many of the abstracts which are presented in conferences are never published in fact one study found that only 27% of the abstracts presented in conferences were published in the next five years [ 6 ].
Table 15.1 gives a template for writing an abstract.
10 What are the Important Recommendations of the International Committees of Medical Journal of Editors?
The recommendations are [ 7 ]:
An abstract is required for original articles, metanalysis, and systematic reviews.
A structured abstract is preferred.
The abstract should mention the purpose of the scientific study, how the procedure was carried out, the analysis used, and principal conclusion.
Clinical trials should be reported according to the CONSORT guidelines.
The trials should also mention the funding and the trial number.
The abstract should be accurate as many readers have access only to the abstract.
11 Conclusions
An Abstract should be written last after all the other sections of the manuscript have been completed and with due care and attention to the details.
It should be structured and written in the IMRAD format.
For many readers, the abstract attracts them to go through the complete content of the article.
The abstract is usually followed by key words that help to index the paper.
Andrade C. How to write a good abstract for a scientific paper or conference presentation? Indian J Psychiatry. 2011;53:172–5.
Article Google Scholar
Squires BP. Structured abstracts of original research and review articles. CMAJ. 1990;143:619–22.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Pierson DJ. How to write an abstract that will be accepted for presentation at a national meeting. Respir Care. 2004 Oct;49:1206–12.
PubMed Google Scholar
Tenenbein M. The abstract and the academic clinician. Pediatr Emerg Care. 1995;11:40–2.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Bahadoran Z, Mirmiran P, Kashfi K, Ghasemi A. The principles of biomedical scientific writing: abstract and keywords. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2020;18:e100159.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Grover S, Dalton N. Abstract to publication rate: do all the papers presented in conferences see the light of being a full publication? Indian J Psychiatry. 2020;62:73–9.
Preparing a manuscript for submission to a medical journal. Available on http://www.icmje.org/recommendations/browse/manuscript-preparation/preparing-for-submission.html . Accessed 10 May 2020.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Surgical Gastroenterology and Liver Transplantation, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India
Samiran Nundy
Department of Internal Medicine, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India
Institute for Global Health and Development, The Aga Khan University, South Central Asia, East Africa and United Kingdom, Karachi, Pakistan
Zulfiqar A. Bhutta
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Nundy, S., Kakar, A., Bhutta, Z.A. (2022). How to Write an Abstract?. In: How to Practice Academic Medicine and Publish from Developing Countries?. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5248-6_15
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5248-6_15
Published : 24 October 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-16-5247-9
Online ISBN : 978-981-16-5248-6
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Psychiatry
- v.53(2); Apr-Jun 2011
How to write a good abstract for a scientific paper or conference presentation
Chittaranjan andrade.
Department of Psychopharmacology, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Abstracts of scientific papers are sometimes poorly written, often lack important information, and occasionally convey a biased picture. This paper provides detailed suggestions, with examples, for writing the background, methods, results, and conclusions sections of a good abstract. The primary target of this paper is the young researcher; however, authors with all levels of experience may find useful ideas in the paper.
INTRODUCTION
This paper is the third in a series on manuscript writing skills, published in the Indian Journal of Psychiatry . Earlier articles offered suggestions on how to write a good case report,[ 1 ] and how to read, write, or review a paper on randomized controlled trials.[ 2 , 3 ] The present paper examines how authors may write a good abstract when preparing their manuscript for a scientific journal or conference presentation. Although the primary target of this paper is the young researcher, it is likely that authors with all levels of experience will find at least a few ideas that may be useful in their future efforts.
The abstract of a paper is the only part of the paper that is published in conference proceedings. The abstract is the only part of the paper that a potential referee sees when he is invited by an editor to review a manuscript. The abstract is the only part of the paper that readers see when they search through electronic databases such as PubMed. Finally, most readers will acknowledge, with a chuckle, that when they leaf through the hard copy of a journal, they look at only the titles of the contained papers. If a title interests them, they glance through the abstract of that paper. Only a dedicated reader will peruse the contents of the paper, and then, most often only the introduction and discussion sections. Only a reader with a very specific interest in the subject of the paper, and a need to understand it thoroughly, will read the entire paper.
Thus, for the vast majority of readers, the paper does not exist beyond its abstract. For the referees, and the few readers who wish to read beyond the abstract, the abstract sets the tone for the rest of the paper. It is therefore the duty of the author to ensure that the abstract is properly representative of the entire paper. For this, the abstract must have some general qualities. These are listed in Table 1 .
General qualities of a good abstract

SECTIONS OF AN ABSTRACT
Although some journals still publish abstracts that are written as free-flowing paragraphs, most journals require abstracts to conform to a formal structure within a word count of, usually, 200–250 words. The usual sections defined in a structured abstract are the Background, Methods, Results, and Conclusions; other headings with similar meanings may be used (eg, Introduction in place of Background or Findings in place of Results). Some journals include additional sections, such as Objectives (between Background and Methods) and Limitations (at the end of the abstract). In the rest of this paper, issues related to the contents of each section will be examined in turn.
This section should be the shortest part of the abstract and should very briefly outline the following information:
- What is already known about the subject, related to the paper in question
- What is not known about the subject and hence what the study intended to examine (or what the paper seeks to present)
In most cases, the background can be framed in just 2–3 sentences, with each sentence describing a different aspect of the information referred to above; sometimes, even a single sentence may suffice. The purpose of the background, as the word itself indicates, is to provide the reader with a background to the study, and hence to smoothly lead into a description of the methods employed in the investigation.
Some authors publish papers the abstracts of which contain a lengthy background section. There are some situations, perhaps, where this may be justified. In most cases, however, a longer background section means that less space remains for the presentation of the results. This is unfortunate because the reader is interested in the paper because of its findings, and not because of its background.
A wide variety of acceptably composed backgrounds is provided in Table 2 ; most of these have been adapted from actual papers.[ 4 – 9 ] Readers may wish to compare the content in Table 2 with the original abstracts to see how the adaptations possibly improve on the originals. Note that, in the interest of brevity, unnecessary content is avoided. For instance, in Example 1 there is no need to state “The antidepressant efficacy of desvenlafaxine (DV), a dual-acting antidepressant drug , has been established…” (the unnecessary content is italicized).
Examples of the background section of an abstract

The methods section is usually the second-longest section in the abstract. It should contain enough information to enable the reader to understand what was done, and how. Table 3 lists important questions to which the methods section should provide brief answers.
Questions regarding which information should ideally be available in the methods section of an abstract

Carelessly written methods sections lack information about important issues such as sample size, numbers of patients in different groups, doses of medications, and duration of the study. Readers have only to flip through the pages of a randomly selected journal to realize how common such carelessness is.
Table 4 presents examples of the contents of accept-ably written methods sections, modified from actual publications.[ 10 , 11 ] Readers are invited to take special note of the first sentence of each example in Table 4 ; each is packed with detail, illustrating how to convey the maximum quantity of information with maximum economy of word count.
Examples of the methods section of an abstract

The results section is the most important part of the abstract and nothing should compromise its range and quality. This is because readers who peruse an abstract do so to learn about the findings of the study. The results section should therefore be the longest part of the abstract and should contain as much detail about the findings as the journal word count permits. For example, it is bad writing to state “Response rates differed significantly between diabetic and nondiabetic patients.” A better sentence is “The response rate was higher in nondiabetic than in diabetic patients (49% vs 30%, respectively; P <0.01).”
Important information that the results should present is indicated in Table 5 . Examples of acceptably written abstracts are presented in Table 6 ; one of these has been modified from an actual publication.[ 11 ] Note that the first example is rather narrative in style, whereas the second example is packed with data.
Information that the results section of the abstract should ideally present

Examples of the results section of an abstract

CONCLUSIONS
This section should contain the most important take-home message of the study, expressed in a few precisely worded sentences. Usually, the finding highlighted here relates to the primary outcome measure; however, other important or unexpected findings should also be mentioned. It is also customary, but not essential, for the authors to express an opinion about the theoretical or practical implications of the findings, or the importance of their findings for the field. Thus, the conclusions may contain three elements:
- The primary take-home message
- The additional findings of importance
- The perspective
Despite its necessary brevity, this section has the most impact on the average reader because readers generally trust authors and take their assertions at face value. For this reason, the conclusions should also be scrupulously honest; and authors should not claim more than their data demonstrate. Hypothetical examples of the conclusions section of an abstract are presented in Table 7 .
Examples of the conclusions section of an abstract

MISCELLANEOUS OBSERVATIONS
Citation of references anywhere within an abstract is almost invariably inappropriate. Other examples of unnecessary content in an abstract are listed in Table 8 .
Examples of unnecessary content in a abstract

It goes without saying that whatever is present in the abstract must also be present in the text. Likewise, whatever errors should not be made in the text should not appear in the abstract (eg, mistaking association for causality).
As already mentioned, the abstract is the only part of the paper that the vast majority of readers see. Therefore, it is critically important for authors to ensure that their enthusiasm or bias does not deceive the reader; unjustified speculations could be even more harmful. Misleading readers could harm the cause of science and have an adverse impact on patient care.[ 12 ] A recent study,[ 13 ] for example, concluded that venlafaxine use during the second trimester of pregnancy may increase the risk of neonates born small for gestational age. However, nowhere in the abstract did the authors mention that these conclusions were based on just 5 cases and 12 controls out of the total sample of 126 cases and 806 controls. There were several other serious limitations that rendered the authors’ conclusions tentative, at best; yet, nowhere in the abstract were these other limitations expressed.
As a parting note: Most journals provide clear instructions to authors on the formatting and contents of different parts of the manuscript. These instructions often include details on what the sections of an abstract should contain. Authors should tailor their abstracts to the specific requirements of the journal to which they plan to submit their manuscript. It could also be an excellent idea to model the abstract of the paper, sentence for sentence, on the abstract of an important paper on a similar subject and with similar methodology, published in the same journal for which the manuscript is slated.
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.

Magnum Proofreading Services
- Jake Magnum
- Jan 2, 2021
Writing an Abstract for a Research Paper: Guidelines, Examples, and Templates
There are six steps to writing a standard abstract. (1) Begin with a broad statement about your topic. Then, (2) state the problem or knowledge gap related to this topic that your study explores. After that, (3) describe what specific aspect of this problem you investigated, and (4) briefly explain how you went about doing this. After that, (5) describe the most meaningful outcome(s) of your study. Finally, (6) close your abstract by explaining the broad implication(s) of your findings.
In this article, I present step-by-step guidelines for writing an abstract for an academic paper. These guidelines are fo llowed by an example of a full abstract that follows these guidelines and a few fill-in-the-blank templates that you can use to write your own abstract.
Guidelines for Writing an Abstract
The basic structure of an abstract is illustrated below.
A standard abstract starts with a very general statement and becomes more specific with each sentence that follows until once again making a broad statement about the study’s implications at the end. Altogether, a standard abstract has six functions, which are described in detail below.
Start by making a broad statement about your topic.
The first sentence of your abstract should briefly describe a problem that is of interest to your readers. When writing this first sentence, you should think about who comprises your target audience and use terms that will appeal to this audience. If your opening sentence is too broad, it might lose the attention of potential readers because they will not know if your study is relevant to them.
Too broad : Maintaining an ideal workplace environment has a positive effect on employees.
The sentence above is so broad that it will not grab the reader’s attention. While it gives the reader some idea of the area of study, it doesn’t provide any details about the author’s topic within their research area. This can be fixed by inserting some keywords related to the topic (these are underlined in the revised example below).
Improved : Keeping the workplace environment at an ideal temperature positively affects the overall health of employees.
The revised sentence is much better, as it expresses two points about the research topic—namely, (i) what aspect of workplace environment was studied, (ii) what aspect of employees was observed. The mention of these aspects of the research will draw the attention of readers who are interested in them.
Describe the general problem that your paper addresses.
After describing your topic in the first sentence, you can then explain what aspect of this topic has motivated your research. Often, authors use this part of the abstract to describe the research gap that they identified and aimed to fill. These types of sentences are often characterized by the use of words such as “however,” “although,” “despite,” and so on.
However, a comprehensive understanding of how different workplace bullying experiences are associated with absenteeism is currently lacking.
The above example is typical of a sentence describing the problem that a study intends to tackle. The author has noticed that there is a gap in the research, and they briefly explain this gap here.
Although it has been established that quantity and quality of sleep can affect different types of task performance and personal health, the interactions between sleep habits and workplace behaviors have received very little attention.
The example above illustrates a case in which the author has accomplished two tasks with one sentence. The first part of the sentence (up until the comma) mentions the general topic that the research fits into, while the second part (after the comma) describes the general problem that the research addresses.
Express the specific problem investigated in your paper.
After describing the general problem that motivated your research, the next sentence should express the specific aspect of the problem that you investigated. Sentences of this type are often indicated by the use of phrases like “the purpose of this research is to,” “this paper is intended to,” or “this work aims to.”
Uninformative : However, a comprehensive understanding of how different workplace bullying experiences are associated with absenteeism is currently lacking. The present article aimed to provide new insights into the relationship between workplace bullying and absenteeism .
The second sentence in the above example is a mere rewording of the first sentence. As such, it adds nothing to the abstract. The second sentence should be more specific than the preceding one.
Improved : However, a comprehensive understanding of how different workplace bullying experiences are associated with absenteeism is currently lacking. The present article aimed to define various subtypes of workplace bullying and determine which subtypes tend to lead to absenteeism .
The second sentence of this passage is much more informative than in the previous example. This sentence lets the reader know exactly what they can expect from the full research article.
Explain how you attempted to resolve your study’s specific problem.
In this part of your abstract, you should attempt to describe your study’s methodology in one or two sentences. As such, you must be sure to include only the most important information about your method. At the same time, you must also be careful not to be too vague.
Too vague : We conducted multiple tests to examine changes in various factors related to well-being.
This description of the methodology is too vague. Instead of merely mentioning “tests” and “factors,” the author should note which specific tests were run and which factors were assessed.
Improved : Using data from BHIP completers, we conducted multiple one-way multivariate analyses of variance and follow-up univariate t-tests to examine changes in physical and mental health, stress, energy levels, social satisfaction, self-efficacy, and quality of life.
This sentence is very well-written. It packs a lot of specific information about the method into a single sentence. Also, it does not describe more details than are needed for an abstract.
Briefly tell the reader what you found by carrying out your study.
This is the most important part of the abstract—the other sentences in the abstract are there to explain why this one is relevant. When writing this sentence, imagine that someone has asked you, “What did you find in your research?” and that you need to answer them in one or two sentences.
Too vague : Consistently poor sleepers had more health risks and medical conditions than consistently optimal sleepers.
This sentence is okay, but it would be helpful to let the reader know which health risks and medical conditions were related to poor sleeping habits.
Improved : Consistently poor sleepers were more likely than consistently optimal sleepers to suffer from chronic abdominal pain, and they were at a higher risk for diabetes and heart disease.
This sentence is better, as the specific health conditions are named.
Finally, describe the major implication(s) of your study.
Most abstracts end with a short sentence that explains the main takeaway(s) that you want your audience to gain from reading your paper. Often, this sentence is addressed to people in power (e.g., employers, policymakers), and it recommends a course of action that such people should take based on the results.
Too broad : Employers may wish to make use of strategies that increase employee health.
This sentence is too broad to be useful. It does not give employers a starting point to implement a change.
Improved : Employers may wish to incorporate sleep education initiatives as part of their overall health and wellness strategies.
This sentence is better than the original, as it provides employers with a starting point—specifically, it invites employers to look up information on sleep education programs.
Abstract Example
The abstract produced here is from a paper published in Electronic Commerce Research and Applications . I have made slight alterations to the abstract so that this example fits the guidelines given in this article.
(1) Gamification can strengthen enjoyment and productivity in the workplace. (2) Despite this, research on gamification in the work context is still limited. (3) In this study, we investigated the effect of gamification on the workplace enjoyment and productivity of employees by comparing employees with leadership responsibilities to those without leadership responsibilities. (4) Work-related tasks were gamified using the habit-tracking game Habitica, and data from 114 employees were gathered using an online survey. (5) The results illustrated that employees without leadership responsibilities used work gamification as a trigger for self-motivation, whereas employees with leadership responsibilities used it to improve their health. (6) Work gamification positively affected work enjoyment for both types of employees and positively affected productivity for employees with leadership responsibilities. (7) Our results underline the importance of taking work-related variables into account when researching work gamification.
In Sentence (1), the author makes a broad statement about their topic. Notice how the nouns used (“gamification,” “enjoyment,” “productivity”) are quite general while still indicating the focus of the paper. The author uses Sentence (2) to very briefly state the problem that the research will address.
In Sentence (3), the author explains what specific aspects of the problem mentioned in Sentence (2) will be explored in the present work. Notice that the mention of leadership responsibilities makes Sentence (3) more specific than Sentence (2). Sentence (4) gets even more specific, naming the specific tools used to gather data and the number of participants.
Sentences (5) and (6) are similar, with each sentence describing one of the study’s main findings. Then, suddenly, the scope of the abstract becomes quite broad again in Sentence (7), which mentions “work-related variables” instead of a specific variable and “researching” instead of a specific kind of research.
Abstract Templates
Copy and paste any of the paragraphs below into a word processor. Then insert the appropriate information to produce an abstract for your research paper.
Template #1
Researchers have established that [Make a broad statement about your area of research.] . However, [Describe the knowledge gap that your paper addresses.] . The goal of this paper is to [Describe the purpose of your paper.] . The achieve this goal, we [Briefly explain your methodology.] . We found that [Indicate the main finding(s) of your study; you may need two sentences to do this.] . [Provide a broad implication of your results.] .
Template #2
It is well-understood that [Make a broad statement about your area of research.] . Despite this, [Describe the knowledge gap that your paper addresses.] . The current research aims to [Describe the purpose of your paper.] . To accomplish this, we [Briefly explain your methodology.] . It was discovered that [Indicate the main finding(s) of your study; you may need two sentences to do this.] . [Provide a broad implication of your results.] .
Template #3
Extensive research indicates that [Make a broad statement about your area of research.] . Nevertheless, [Describe the knowledge gap that your paper addresses.] . The present work is intended to [Describe the purpose of your paper.] . To this end, we [Briefly explain your methodology.] . The results revealed that [Indicate the main finding(s) of your study; you may need two sentences to do this.] . [Provide a broad implication of your results.] .
- How to Write an Abstract
Related Posts
How to Write a Research Paper in English: A Guide for Non-native Speakers
How to Write an Abstract Quickly
Using the Present Tense and Past Tense When Writing an Abstract
Well explained! I have given you a credit
- Interlibrary Loan and Scan & Deliver
- Course Reserves
- Purchase Request
- Collection Development & Maintenance
- Current Negotiations
- Ask a Librarian
- Instructor Support
- Library How-To
- Research Guides
- Research Support
- Study Rooms
- Research Rooms
- Partner Spaces
- Loanable Equipment
- Print, Scan, Copy
- 3D Printers
- Poster Printing
- OSULP Leadership
- Strategic Plan
Scholarly Articles: How can I tell?
- Journal Information
- Literature Review
- Author and affiliation
- Introduction
- Specialized Vocabulary
- Methodology
- Research sponsors
- Peer-review
An abstract is a summary of the main article. An abstract will include information about why the research study was done, what the methodology was and something about the findings of the author(s). The abstract is always at the beginning of the article and will either be labeled "abstract" or will be set apart from the rest of the article by a different font or margins.
The abstract should tell you what the research study is about, how the research was done (methodology), who the research sample was, what the authors found and why this is important to the field.
- << Previous: Author and affiliation
- Next: Introduction >>
- Last Updated: Apr 15, 2024 3:26 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.oregonstate.edu/ScholarlyArticle
Contact Info
121 The Valley Library Corvallis OR 97331–4501
Phone: 541-737-3331
Services for Persons with Disabilities
In the Valley Library
- Oregon State University Press
- Special Collections and Archives Research Center
- Undergrad Research & Writing Studio
- Graduate Student Commons
- Tutoring Services
- Northwest Art Collection
Digital Projects
- Oregon Explorer
- Oregon Digital
- ScholarsArchive@OSU
- Digital Publishing Initiatives
- Atlas of the Pacific Northwest
- Marilyn Potts Guin Library
- Cascades Campus Library
- McDowell Library of Vet Medicine
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Advance Articles
- Collections
- Focus Collections
- Teaching Tools in Plant Biology
- Browse by cover
- High-Impact Research
- Author Guidelines
- Quick and Simple Author Support
- Focus Issues Call for Papers
- Submission Site
- Open Access Options
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Why Publish with Us?
- About The Plant Cell
- About The American Society of Plant Biologists
- Editorial Board
- Advertising & Corporate Services
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
The calcium-dependent protein kinase cpk16 regulates hypoxia-induced ros production by phosphorylating the nadph oxidase rbohd in arabidopsis.
Wei-Wei Yu and Qin-Fang Chen contributed equally to this work.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Wei-Wei Yu, Qin-Fang Chen, Ke Liao, De-Mian Zhou, Yi-Cong Yang, Miao He, Lu-Jun Yu, De-Ying Guo, Shi Xiao, Ruo-Han Xie, Ying Zhou, The calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK16 regulates hypoxia-induced ROS production by phosphorylating the NADPH oxidase RBOHD in Arabidopsis, The Plant Cell , 2024;, koae153, https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koae153
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production is a key event in modulating plant responses to hypoxia and post-hypoxia reoxygenation. However, the molecular mechanism by which hypoxia-associated ROS homeostasis is controlled remains largely unknown. Here, we showed that the calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK16 regulates plant hypoxia tolerance by phosphorylating the plasma membrane–anchored NADPH oxidase RESPIRATORY BURST OXIDASE HOMOLOG D (RBOHD) to regulate ROS production in Arabidopsis ( Arabidopsis thaliana ). In response to hypoxia or reoxygenation, CPK16 was activated through phosphorylation of its Ser274 residue. The cpk16 knockout mutant displayed enhanced hypoxia tolerance, whereas CPK16- overexpressing ( CPK16- OE) lines showed increased sensitivity to hypoxic stress. In agreement with these observations, hypoxia and reoxygenation both induced ROS accumulation in the rosettes of CPK16- OEs more strongly than in rosettes of the cpk16-1 mutant or the wild type. Moreover, CPK16 interacted with and phosphorylated the N terminus of RBOHD at four serine residues (Ser133, Ser148, Ser163, and Ser347) that were necessary for hypoxia- and reoxygenation-induced ROS accumulation. Furthermore, the hypoxia-tolerant phenotype of cpk16-1 was fully abolished in the cpk16 rbohd double mutant. Thus, we have uncovered a regulatory mechanism by which the CPK16–RBOHD module shapes ROS production during hypoxia and reoxygenation in Arabidopsis.
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to Your Librarian
- Advertising & Corporate Services
- Awards & Funding
- Plant Science Today
- Plant Biology Meeting
- Meeting Management Services
- Plant Science Research Weekly
- Taproot: A Plantae Podcast
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1532-298X
- Print ISSN 1040-4651
- Copyright © 2024 American Society of Plant Biologists
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Download PDF
- CME & MOC
- Share X Facebook Email LinkedIn
- Permissions
Accounting for Competing Risks in Clinical Research
- 1 Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES), Toronto, Ontario, Canada
- 2 Institute of Health Policy, Management and Evaluation, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
- 3 Sunnybrook Research Institute, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
- 4 NHS Blood and Transplant, Bristol, United Kingdom
- 5 Department of Biomedical Data Sciences, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, the Netherlands
- Original Investigation Metformin or Sulfonylurea Use in Kidney Disease Christianne L. Roumie, MD, MPH; Jonathan Chipman, PhD; Jea Young Min, PharmD, MPH, PhD; Amber J. Hackstadt, PhD; Adriana M. Hung, MD, MPH; Robert A. Greevy Jr, PhD; Carlos G. Grijalva, MD, MPH; Tom Elasy, MD, MPH; Marie R. Griffin, MD, MPH JAMA
Survival analyses are statistical methods for the analysis of time-to-event outcomes. 1 An example is time from study entry to death. A competing risk is an event whose occurrence precludes the occurrence of the primary event of interest. In a study whose outcome is time to death due to cardiovascular causes, for instance, death due to a noncardiovascular cause is a competing risk. Conventional statistical methods for the analysis of survival data typically aim to estimate the probability of the event of interest over time or the effect of a risk factor or treatment on that probability or on the intensity with which events occur. These methods require modification in the presence of competing risks. A key feature of survival analysis is the ability to properly account for censoring, which occurs when the outcome event is not observed before the end of the study participant’s follow-up period.
Read More About
Austin PC , Ibrahim M , Putter H. Accounting for Competing Risks in Clinical Research. JAMA. Published online May 29, 2024. doi:10.1001/jama.2024.4970
Manage citations:
© 2024
Artificial Intelligence Resource Center
Cardiology in JAMA : Read the Latest
Browse and subscribe to JAMA Network podcasts!
Others Also Liked
Select your interests.
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts
Physical Review Research
- Collections
- Editorial Team
- Open Access
Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 – A large hybridization-gap variant of Ce 3 Bi 4 Pt 3
D. m. kirschbaum, x. yan, m. waas, r. svagera, a. prokofiev, b. stöger, g. giester, p. rogl, d.-g. oprea, c. felser, r. valentí, m. g. vergniory, j. custers, s. paschen, and d. a. zocco, phys. rev. research 6 , 023242 – published 4 june 2024.
- No Citing Articles
The family of cubic noncentrosymmetric 3-4-3 compounds has become a fertile ground for the discovery of novel correlated metallic and insulating phases. Here, we report the synthesis of a new heavy fermion compound, Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 . It is an isoelectronic analog of the prototypical Kondo insulator Ce 3 Bi 4 Pt 3 and of the recently discovered Weyl-Kondo semimetal Ce 3 Bi 4 Pd 3 . In contrast to the volume-preserving Pt-Pd substitution, structural and chemical analyses reveal a positive chemical pressure effect in Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 relative to its heavier counterparts. Based on the results of electrical resistivity, Hall effect, magnetic susceptibility, and specific heat measurements, we identify an energy gap of 65–70 meV, about eight times larger than that in Ce 3 Bi 4 Pt 3 and about 45 times larger than that of the Kondo-insulating background hosting the Weyl nodes in Ce 3 Bi 4 Pd 3 . We show that this gap as well as other physical properties do not evolve monotonically with increasing atomic number, i.e., in the sequence Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 − Ce 3 Bi 4 Pd 3 − Ce 3 Bi 4 Pt 3 , but instead with increasing partial electronic density of states of the d orbitals at the Fermi energy. This work opens the possibility to investigate the conditions under which topological states develop in this series of strongly correlated 3-4-3 materials.
- Received 26 January 2024
- Accepted 23 April 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.6.023242
Published by the American Physical Society under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. Further distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the published article's title, journal citation, and DOI.
Published by the American Physical Society
Physics Subject Headings (PhySH)
- Physical Systems
Authors & Affiliations
- 1 Institute of Solid State Physics, Vienna University of Technology, 1040 Vienna, Austria
- 2 X-ray Center, Vienna University of Technology, 1040 Vienna, Austria
- 3 Institute of Mineralogy and Crystallography, University of Vienna, 1090 Vienna, Austria
- 4 Institute of Materials Chemistry, University of Vienna, 1090 Vienna, Austria
- 5 Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, 01187 Dresden, Germany
- 6 Institute for Theoretical Physics, Goethe University Frankfurt, 60438 Frankfurt a.M., Germany
- 7 Donostia International Physics Center, 20018 Donostia/San Sebastián, Spain
- 8 Department of Condensed Matter Physics, Charles University, 121 16 Prague, Czech Republic
- * Corresponding author: [email protected]
- † Corresponding author: [email protected]
Article Text
Vol. 6, Iss. 2 — June - August 2024
Subject Areas
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Strongly Correlated Materials

Authorization Required
Other options.
- Buy Article »
- Find an Institution with the Article »
Download & Share
(a) Photo of a single crystal of Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 with indicated crystallographic directions obtained from Laue diffraction. Typical sample length is 1.5 mm. (b) Laue XRD pattern (white spots). The center of the image corresponds to the [-2-1-1] crystallographic direction. (c) Sketch of the unit cell. The polyhedron emphasizes the close environment of a Ce atom. (d) Room-temperature powder XRD pattern of Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 (black dots). Vertical bars indicate the positions of the expected diffraction peaks. The difference (blue line) between the measured data and the refinement (red line) shows no signs of impurity phases. (e) Lattice parameter a across the Ce 3 Bi 4 X 3 series ( X = Ni , Pd, Pt). Intermediate Pd-Pt values (white diamonds) taken from Ref. [ 8 ]. The gray shaded line is a guide to the eye.
EDX spectrum corresponding to one point measurement of a polished Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 crystal (inset, top right). Inset: Backscattered SEM images of as-grown (bottom left) and polished (top right) Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 samples. The lighter spots visible on the surface of the as-grown crystal correspond to Pb, and are absent in the polished sample.
(a) Electrical resistivity ρ of Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 as a function of temperature T in zero magnetic field, with the electrical current applied along the crystallographic [111] direction. (b) Temperature-dependent Hall coefficient R H . The shaded gray line is a guide to the eye. (c), (d) Arrhenius plots of the resistivity (normalized to 300 K) and Hall coefficient data. The red solid lines are linear fits to the data above 100 K.
(a) Temperature dependence of the magnetic susceptibility χ of Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 , measured with B = 1 T. (b) Inverse magnetic susceptibility χ − 1 ( T ) . The paramagnetic Weiss temperate Θ and the effective magnetic moment μ eff were determined from a Curie-Weiss fit for T > T max χ (red line). (c) Magnetization M vs B at 2 K (black), 10 K (blue), 100 K (green), and 300 K (red). The curves show up and down B sweeps, with no signs of magnetic hysteresis detected. For all cases, B was applied parallel to the crystallographic [11-2] direction.
Specific heat C vs T of Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 measured between 2 K and 300 K. The red dashed line is a fit with the Debye model plus an additional Schottky-like electronic contribution derived for Kondo insulators (see main text). The inset shows the low temperature C / T vs T 2 and the fit. The Sommerfeld coefficient ( γ ) is then determined by shifting the fitting line by γ = 6.92 mJ / mol Ce K 2 to match the measured data (blue line).
(a) Electrical resistance R ( T ) normalized to its room temperature value R (300 K) and (b) magnetic susceptibility χ ( T ) of the Ce 3 Bi 4 X 3 series, with X = Ni (black dots), Pd (blue line), Pt (red line), and of a partially substituted Ni-Pd single crystal (19% Ni, white triangles). The data for Ce 3 Bi 4 Pd 3 and Ce 3 Bi 4 Pt 3 were taken from Refs. [ 8 ] and [ 10 ].
Comparison of characteristic parameters for the Ce 3 Bi 4 X 3 series ( X = Ni, Pd, Pt). Shaded grey areas are guides to the eyes. (a) i R R R values (from Fig. 6 ) and temperature scales T K , Δ / k B , and T max χ . For Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 , T max χ is taken from Fig. 4 , T K is calculated from T max χ (see Sec. 3 ), and Δ / k B is obtained from the fits in Figs. 3 . Values for the Pd and Pt compounds taken from Ref. [ 8 ]. (b) Kondo energy gap Δ / k B as a function of the d -electron density of states ( d DOS) at the Fermi level (from DFT calculations, see Figs. 10 and 11 in Appendix D).
Crystal structure of Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 , with atoms displayed as ellipsoids representing their anisotropic atomic displacement parameters (ADPs). Derived from the refinement (including Ni deficiency in the structure) of single crystal XRD data corresponding to a highly stoichiometric sample (see Table 2 ).
(a) Lattice parameter a vs Ni content of Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 obtained from room-temperature powder XRD and EDX measurements, respectively, of selected samples from different growth batches (labeled by numbers). Data in the gray-shaded area correspond to the most stoichiometric samples (close to three Ni atoms per formula unit), with an average value of a = 9.7715 ( 9 ) Å. (b) Magnetic susceptibility χ vs T of Ce 3 Bi 4 Ni 3 single crystals from different batches ( B ∥ [11-2] = 1 T). Broad maxima at T max χ are marked with arrows. (c) T max χ (left scale) and susceptibility magnitude at T max χ (right scale) obtained from (b) vs lattice parameter from (a).
Electronic structure of Ce 3 Bi 4 X 3 ( X = Ni, Pd, Pt), with the 4 f orbitals of Ce treated as corelike. The experimentally determined structure data were used as input. The Fermi energy ɛ F is set to zero.
Total and d -electron density of states ( d DOS) of Ce 3 Bi 4 X 3 ( X = Ni, Pd, Pt), obtained from the band structure calculations displayed in Fig. 10 . The Fermi energy is set to zero (vertical line).
Sign up to receive regular email alerts from Physical Review Research
Reuse & Permissions
It is not necessary to obtain permission to reuse this article or its components as it is available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided attribution to the author(s) and the published article's title, journal citation, and DOI are maintained. Please note that some figures may have been included with permission from other third parties. It is your responsibility to obtain the proper permission from the rights holder directly for these figures.
- Forgot your username/password?
- Create an account
Article Lookup
Paste a citation or doi, enter a citation.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes: an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to….
An abstract is a short summary of a longer work (such as a thesis, dissertation or research paper). The abstract concisely reports the aims and outcomes of your research, so that readers know exactly what your paper is about. ... You probably already read lots of journal article abstracts while conducting your literature review—try using them ...
Write your paper first, then create the abstract as a summary. Check the journal requirements before you write your abstract, eg. required subheadings. Include keywords or phrases to help readers search for your work in indexing databases like PubMed or Google Scholar. Double and triple check your abstract for spelling and grammar errors.
Abstracts also include the key terms found in the longer work and the purpose and methods of the research. Authors abstract various longer works, including book proposals, dissertations, and online journal articles. There are two main types of abstracts: descriptive and informative. A descriptive abstract briefly describes the longer work ...
An informative abstract is a comprehensive outline of the research. There are times when people rely on the abstract as an information source. And the reason is why it is crucial to provide entire data of particular research. A well-written, informative abstract could be a good substitute for the remainder of the paper on its own.
Developing such a skill takes practice. Here is an exercise to help you develop this skill. Pick a scientific article in your field. Read the paper with the abstract covered. Then try to write an abstract based on your reading. Compare your abstract to the author's. Repeat until you feel confident.
Set page margins to 1 inch (2.54 cm). Write "Abstract" (bold and centered) at the top of the page. Place the contents of your abstract on the next line. Do not indent the first line. Double-space the text. Use a legible font like Times New Roman (12 pt.). Limit the length to 250 words.
An abstract should be a stand-alone summary of a research project. 1 Although abstracts are most used to provide an overview of a research project, they may also be used to summarize an implementation project related to practice, policy, or education in nursing. The abstract may be a precursor to a scientific manuscript, chapter, thesis, or ...
Keywords: along with the abstract, specific words and phrases related to the topics discussed in the research should be added. These words are usually around five, but the number can vary depending on the journal's guidelines. Abstract example. This abstract, taken from ScienceDirect, illustrates the ideal structure of an abstract. It has 155 ...
An abstract is "a brief, comprehensive summary of the contents of the paper" (American Psychological Association [APA], 2020, p. 38). This summary is intended to share the topic, argument, and conclusions of a research study or course paper, similar to the text on the back cover of a book. When submitting your work for publication, an abstract ...
An abstract summarizes, usually in one paragraph of 300 words or less, the major aspects of the entire paper in a prescribed sequence that includes: 1) the overall purpose of the study and the research problem(s) you investigated; 2) the basic design of the study; 3) major findings or trends found as a result of your analysis; and, 4) a brief summary of your interpretations and conclusions.
Introduction. This article deals with drafting a suitable "title" and an appropriate "abstract" for an original research paper. Because the "title" and the "abstract" are the "initial impressions" or the "face" of a research article, they need to be drafted correctly, accurately, carefully, meticulously, and consume time and energy.[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] Often, these ...
Abstracts tell the reader what is in an article. Doesn't analyze or make conclusions. It must accurately state the contents. Encourages the reader to read the original article. Research abstracts should include the objective and scope of the investigation, the methods used in the research, the primary results and the main conclusions as stated ...
Abstracts are usually a student's first point of contact with professional scientific research. Although reading a whole article can be daunting, reading an abstract is much simpler and the benefits to your learning are direct. Here are some ways reading abstracts helps you learn: Finding sources quickly. Gaining knowledge.
Include 5 to 10 important words or short phrases central to your research in both the abstract and the keywords section. For example, if you are writing a paper on the prevalence of obesity among lower classes that crosses international boundaries, you should include terms like "obesity," "prevalence," "international," "lower ...
Abstract. An abstract is a crisp, short, powerful, and self-contained summary of a research manuscript used to help the reader swiftly determine the paper's purpose. Although the abstract is the first paragraph of the manuscript it should be written last when all the other sections have been addressed. Research is formalized curiosity.
INTRODUCTION. This paper is the third in a series on manuscript writing skills, published in the Indian Journal of Psychiatry.Earlier articles offered suggestions on how to write a good case report,[] and how to read, write, or review a paper on randomized controlled trials.[2,3] The present paper examines how authors may write a good abstract when preparing their manuscript for a scientific ...
Journal editors are busy professionals who read hundreds of abstracts annually to screen papers for preliminary consideration. Although some editors contend that "[a] bad abstract won't by itself cause journal editors to reject a scholarly article, but it does incline them toward an initial negative answer," 5 unless it is a slow day in the editorial office, I would anticipate the latter ...
There are six steps to writing a standard abstract. (1) Begin with a broad statement about your topic. Then, (2) state the problem or knowledge gap related to this topic that your study explores. After that, (3) describe what specific aspect of this problem you investigated, and (4) briefly explain how you went about doing this.
Informative Abstract Example 1. Emotional intelligence (EQ) has been correlated with leadership effectiveness in organizations. Using a mixed-methods approach, this study assesses the importance of emotional intelligence on academic performance at the high school level. The Emotional Intelligence rating scale was used, as well as semi ...
An abstract is a summary of the main article. An abstract will include information about why the research study was done, what the methodology was and something about the findings of the author (s). The abstract is always at the beginning of the article and will either be labeled "abstract" or will be set apart from the rest of the article by a ...
Research has shown that articles which have graphical abstracts are beneficial both in terms of views of the article as well as increased activity on social media. In particular, the average annual use of an article is doubled when compared with those without a visual abstract opens in new tab/window .
Key Points. Question Does infarct size modify the safety and efficacy of early vs late initiation of direct oral anticoagulation (DOAC) after ischemic stroke in people with atrial fibrillation?. Findings In this post hoc analysis of 1962 participants from the Early Versus Later Anticoagulation for Stroke With Atrial Fibrillation (ELAN) randomized clinical trial, the odds of the primary outcome ...
Figure 2. An example of a quantum circuit obtained by decomposing a time-evolution operator [including state initialization as described in Eq. ()].This particular circuit was used for the final data point (at t = 20 ℏ / v) for the k = 0.5 case in the results presented below in Fig. 3.The circuit features two qubits (the system qubit and the ancilla) as well as a two-bit classical register ...
Abstract. The intersection of precision medicine and artificial intelligence (AI) holds profound implications for cancer treatment, with the potential to significantly advance our understanding of drug responses based on the intricate architecture of tumor cells. A recent study by Park and colleagues titled "A Deep Learning Model of Tumor Cell Architecture Elucidates Response and Resistance ...
Compared to a typical tokamak coil set, only a single simple type of stellarator coil has to be added which leads to a compact, volume- and transport-preserving magnetic field, with an added rotational transform that reaches levels thought to enhance stability. Received 12 January 2024. Accepted 6 May 2024.
Abstract. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production is a key event in modulating plant responses to hypoxia and post-hypoxia reoxygenation. However, the molecular mechanism by which hypoxia-associated ROS homeostasis is controlled remains largely unknown.
The format of your abstract will depend on the work being abstracted. An abstract of a scientific research paper will contain elements not found in an abstract of a literature article, and vice versa. However, all abstracts share several mandatory components, and there are also some optional parts that you can decide to include or not.
Survival analyses are statistical methods for the analysis of time-to-event outcomes. 1 An example is time from study entry to death. A competing risk is an event whose occurrence precludes the occurrence of the primary event of interest.
Reuse & Permissions. It is not necessary to obtain permission to reuse this article or its components as it is available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided attribution to the author(s) and the published article's title, journal citation, and DOI are maintained.